├── .env.template
├── requirements.txt
├── assets
├── image-2.png
├── image-4.png
└── image-5.png
├── environment.yml
├── single_agent_example.py
├── multi_agent_example.py
├── .gitignore
├── README.md
└── agent.py
/.env.template:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | OPENAI_API_KEY="Add your OPENAI key here"
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/requirements.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | python-dotenv==1.0.1
2 | openai==1.55.1
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/assets/image-2.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/hexo-ai/agent-from-scratch/HEAD/assets/image-2.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/assets/image-4.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/hexo-ai/agent-from-scratch/HEAD/assets/image-4.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/assets/image-5.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/hexo-ai/agent-from-scratch/HEAD/assets/image-5.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/environment.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: agent-from-scratch
2 | channels:
3 | - defaults
4 | dependencies:
5 | - python=3.11
6 | - pip=23.2.1
7 | - packaging
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/single_agent_example.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from dotenv import load_dotenv
2 | _ = load_dotenv()
3 |
4 | import json
5 | from agent import pretty_print_messages, Agent, Swarm
6 |
7 |
8 | def get_weather(location, time="now"):
9 | return json.dumps({"location": location, "temperature": "65", "time": time})
10 |
11 |
12 | def send_email(recipient, subject, body):
13 | return f"Sent! email to {recipient} with the subject: {subject} and body: {body}"
14 |
15 |
16 | weather_agent = Agent(
17 | name="Weather Agent",
18 | instructions="You are a helpful agent for giving information on weather.",
19 | functions=[get_weather, send_email],
20 | )
21 |
22 | client = Swarm()
23 | print("Starting Single Agent - Weather Agent")
24 | print('Ask me how is the weather today in Brussels?')
25 |
26 | messages = []
27 | agent = weather_agent
28 |
29 | while True:
30 | user_input = input("\033[90mUser\033[0m: ")
31 | messages.append({"role": "user", "content": user_input})
32 |
33 | response = client.run(agent=agent, messages=messages)
34 | pretty_print_messages(response.messages)
35 |
36 | messages.extend(response.messages)
37 | agent = response.agent
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multi_agent_example.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from dotenv import load_dotenv
2 | _ = load_dotenv()
3 |
4 | from agent import Agent, Swarm
5 |
6 | # Initialize Swarm with telemetry
7 | client = Swarm()
8 |
9 | def process_refund(item_id, reason="NOT SPECIFIED"):
10 | """Refund an item. Refund an item. Make sure you have the item_id of the form item_... Ask for user confirmation before processing the refund."""
11 | print(f"[mock] Refunding item {item_id} because {reason}...")
12 | return "Success!"
13 |
14 | def apply_discount():
15 | """Apply a discount to the user's cart."""
16 | print("[mock] Applying discount...")
17 | return "Applied discount of 11%"
18 |
19 |
20 | triage_agent = Agent(
21 | name="Triage Agent",
22 | instructions="""Determine which agent is best suited to handle the user's request, and transfer the conversation to that agent.
23 | - For purchases, pricing, discounts and product inquiries -> Sales Agent
24 | - For refunds, returns and complaints -> Refunds Agent
25 | Never handle requests directly - always transfer to the appropriate specialist.""",
26 | )
27 | sales_agent = Agent(
28 | name="Sales Agent",
29 | instructions="Be super enthusiastic about selling bees.",
30 | )
31 | refunds_agent = Agent(
32 | name="Refunds Agent",
33 | instructions="Help the user with a refund. If the reason is that it was too expensive, offer the user a refund code. If they insist, then process the refund.",
34 | functions=[process_refund, apply_discount],
35 | )
36 |
37 |
38 | def transfer_back_to_triage():
39 | """Call this function if a user is asking about a topic that is not handled by the current agent."""
40 | return triage_agent
41 |
42 |
43 | def transfer_to_sales():
44 | return sales_agent
45 |
46 |
47 | def transfer_to_refunds():
48 | return refunds_agent
49 |
50 |
51 | triage_agent.functions = [transfer_to_sales, transfer_to_refunds]
52 | sales_agent.functions.append(transfer_back_to_triage)
53 | refunds_agent.functions.append(transfer_back_to_triage)
54 |
55 | print("Starting Multiple Agents - Triage Agent, Refunds Agent and Bee Sales Agent")
56 |
57 | messages = []
58 | agent = triage_agent
59 |
60 | while True:
61 | user_input = input("\033[90mUser\033[0m: ")
62 | messages.append({"role": "user", "content": user_input})
63 |
64 | response = client.run(agent=agent, messages=messages)
65 |
66 | for message in response.messages:
67 | if message["role"] == "assistant" and message.get("content"):
68 | print(f"\033[94m{message['sender']}\033[0m: {message['content']}")
69 | elif message["role"] == "tool":
70 | tool_name = message.get("tool_name", "")
71 | if tool_name in ["process_refund", "apply_discount"]:
72 | print(f"\033[93mSystem\033[0m: {message['content']}")
73 |
74 | messages.extend(response.messages)
75 | agent = response.agent
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
2 | __pycache__/
3 | *.py[cod]
4 | *$py.class
5 |
6 | # C extensions
7 | *.so
8 |
9 | # Distribution / packaging
10 | .Python
11 | build/
12 | develop-eggs/
13 | dist/
14 | downloads/
15 | eggs/
16 | .eggs/
17 | lib/
18 | lib64/
19 | parts/
20 | sdist/
21 | var/
22 | wheels/
23 | share/python-wheels/
24 | *.egg-info/
25 | .installed.cfg
26 | *.egg
27 | MANIFEST
28 |
29 | # PyInstaller
30 | # Usually these files are written by a python script from a template
31 | # before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it.
32 | *.manifest
33 | *.spec
34 |
35 | # Installer logs
36 | pip-log.txt
37 | pip-delete-this-directory.txt
38 |
39 | # Unit test / coverage reports
40 | htmlcov/
41 | .tox/
42 | .nox/
43 | .coverage
44 | .coverage.*
45 | .cache
46 | nosetests.xml
47 | coverage.xml
48 | *.cover
49 | *.py,cover
50 | .hypothesis/
51 | .pytest_cache/
52 | cover/
53 |
54 | # Translations
55 | *.mo
56 | *.pot
57 |
58 | # Django stuff:
59 | *.log
60 | local_settings.py
61 | db.sqlite3
62 | db.sqlite3-journal
63 |
64 | # Flask stuff:
65 | instance/
66 | .webassets-cache
67 |
68 | # Scrapy stuff:
69 | .scrapy
70 |
71 | # Sphinx documentation
72 | docs/_build/
73 |
74 | # PyBuilder
75 | .pybuilder/
76 | target/
77 |
78 | # Jupyter Notebook
79 | .ipynb_checkpoints
80 |
81 | # IPython
82 | profile_default/
83 | ipython_config.py
84 |
85 | # pyenv
86 | # For a library or package, you might want to ignore these files since the code is
87 | # intended to run in multiple environments; otherwise, check them in:
88 | # .python-version
89 |
90 | # pipenv
91 | # According to pypa/pipenv#598, it is recommended to include Pipfile.lock in version control.
92 | # However, in case of collaboration, if having platform-specific dependencies or dependencies
93 | # having no cross-platform support, pipenv may install dependencies that don't work, or not
94 | # install all needed dependencies.
95 | #Pipfile.lock
96 |
97 | # poetry
98 | # Similar to Pipfile.lock, it is generally recommended to include poetry.lock in version control.
99 | # This is especially recommended for binary packages to ensure reproducibility, and is more
100 | # commonly ignored for libraries.
101 | # https://python-poetry.org/docs/basic-usage/#commit-your-poetrylock-file-to-version-control
102 | #poetry.lock
103 |
104 | # pdm
105 | # Similar to Pipfile.lock, it is generally recommended to include pdm.lock in version control.
106 | #pdm.lock
107 | # pdm stores project-wide configurations in .pdm.toml, but it is recommended to not include it
108 | # in version control.
109 | # https://pdm.fming.dev/latest/usage/project/#working-with-version-control
110 | .pdm.toml
111 | .pdm-python
112 | .pdm-build/
113 |
114 | # PEP 582; used by e.g. github.com/David-OConnor/pyflow and github.com/pdm-project/pdm
115 | __pypackages__/
116 |
117 | # Celery stuff
118 | celerybeat-schedule
119 | celerybeat.pid
120 |
121 | # SageMath parsed files
122 | *.sage.py
123 |
124 | # Environments
125 | .env
126 | .venv
127 | env/
128 | venv/
129 | ENV/
130 | env.bak/
131 | venv.bak/
132 |
133 | # Spyder project settings
134 | .spyderproject
135 | .spyproject
136 |
137 | # Rope project settings
138 | .ropeproject
139 |
140 | # mkdocs documentation
141 | /site
142 |
143 | # mypy
144 | .mypy_cache/
145 | .dmypy.json
146 | dmypy.json
147 |
148 | # Pyre type checker
149 | .pyre/
150 |
151 | # pytype static type analyzer
152 | .pytype/
153 |
154 | # Cython debug symbols
155 | cython_debug/
156 |
157 | # PyCharm
158 | # JetBrains specific template is maintained in a separate JetBrains.gitignore that can
159 | # be found at https://github.com/github/gitignore/blob/main/Global/JetBrains.gitignore
160 | # and can be added to the global gitignore or merged into this file. For a more nuclear
161 | # option (not recommended) you can uncomment the following to ignore the entire idea folder.
162 | #.idea/
163 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Agent from scratch
2 | agent-from-scratch is a Python-based repository for developers and researchers to understand the fundamentals of single and multi-agent systems without going through more dense and sophisticated Agent frameworks such as Langgraph and Autogen. In fact, agent-from-sctach is not even a framework, it is single script repository which you can simply download and meddle with it to understand how agents work.
3 |
4 | It is a fork of OpenAI's Swarm, which is already straightforward. However, agent-from-scratch is even simpler, making it easier to quickly start and understand single and multi-agent systems.
5 |
6 | # Walkthrough video
7 | [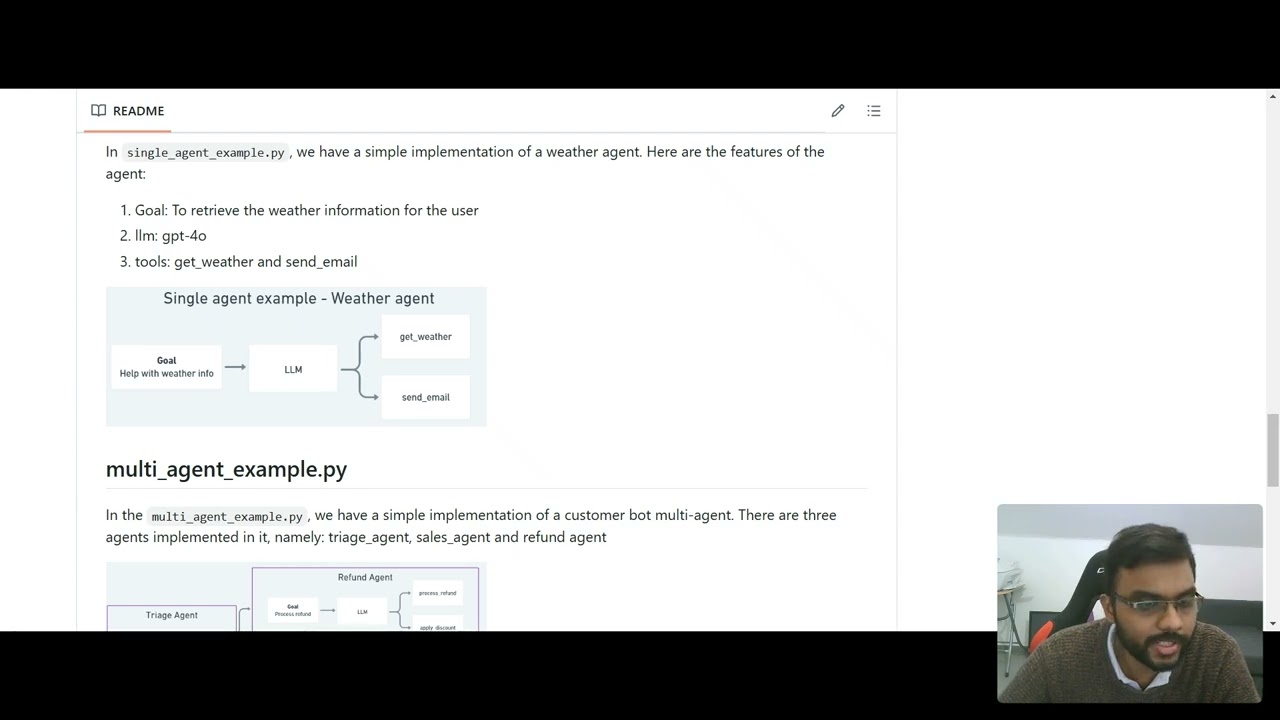](https://youtu.be/gA6T6i8qK-I)
8 |
9 | # Whom is this for?
10 | It is for software developers and ML Engineers who would like to understand what are agents and how are they built. This is not a Agent framework. This is simply a python script
11 |
12 | # What can you do with this?
13 | There is a single script called `agent.py` in this. It is a very easy read. One can read it and understand what Agents are and how they are built. Once you understand you can either fork this repository or just copy paste the `agent.py` script and start building your own agents.
14 |
15 | # Getting started
16 | 1. Clone or fork the repository: `git clone https://github.com/hexo-ai/agent-from-scratch.git`
17 | 2. To set up the conda environment, run the following command: `conda env create -f environment.yml`. Alternatively, you can use a virtual environment.
18 | 3. Create a `.env` file by copying the structure from `.env.template`.
19 | 4. Add your environment variables to the `.env` file.
20 | 5. Activate the conda environment using `conda activate agent-from-scratch` or your virtual environment.
21 | 6. Install the requirements using `pip install -r requirements.txt`.
22 | 7. To run the single agent example, execute `python single_agent_example.py`. This script implements a weather agent with capabilities to send emails.
23 | 8. To run the multi-agent example, execute `python multi_agent_example.py`. This script implements sales and refund agents with capabilities to apply discounts and process refunds.
24 |
25 | # Content
26 | ## agent.py
27 | This is the singular script which constructs an Agent. An agent is nothing more nothing lesser than an LLM which can call tools/functions and go in loops to accomplish a goal. Here is an architecture of an Agent.
28 |
29 |  30 |
31 | A User can assign a goal to an agent. An Agent consists of an LLM and the LLM is capable to calling a bunch of tools. The LLM takes up the goal and uses whichever tool, whenever necessary in order to accomplish the goal.
32 |
33 | 1. In `agent.py`, you will see a class called `Agent` which can take up a goal (variable named instructions), an LLM (variable named model) and a bunch of tools (variable named functions).
34 | 2. It has another class called `Swarm` which contains the logic on how the LLM can calls the tools and accomplish the given goal.
35 |
36 | ```python
37 | class Swarm:
38 | def __init__():
39 | # Implements logic of how llm and tool calling works together
40 |
41 | def get_chat_completion():
42 | # Implements LLM completion
43 |
44 | def handle_tool_calls():
45 | # Implements tool calling
46 |
47 | def handle_function_result():
48 | # processes the tool outptu
49 |
50 | def run():
51 | # runs the whole logic of goal -> llm -> tools -> output -> feedback from environment
52 | ```
53 |
54 | We have included two examples in this repository: namely, `single_agent_example.py` and `multi_agent_example.py`.
55 |
56 |
57 | ## single_agent_example.py
58 | In `single_agent_example.py`, we have a simple implementation of a weather agent. Here are the features of the agent:
59 | 1. Goal: To retrieve the weather information for the user
60 | 2. llm: gpt-4o
61 | 3. tools: get_weather and send_email
62 |
63 |
30 |
31 | A User can assign a goal to an agent. An Agent consists of an LLM and the LLM is capable to calling a bunch of tools. The LLM takes up the goal and uses whichever tool, whenever necessary in order to accomplish the goal.
32 |
33 | 1. In `agent.py`, you will see a class called `Agent` which can take up a goal (variable named instructions), an LLM (variable named model) and a bunch of tools (variable named functions).
34 | 2. It has another class called `Swarm` which contains the logic on how the LLM can calls the tools and accomplish the given goal.
35 |
36 | ```python
37 | class Swarm:
38 | def __init__():
39 | # Implements logic of how llm and tool calling works together
40 |
41 | def get_chat_completion():
42 | # Implements LLM completion
43 |
44 | def handle_tool_calls():
45 | # Implements tool calling
46 |
47 | def handle_function_result():
48 | # processes the tool outptu
49 |
50 | def run():
51 | # runs the whole logic of goal -> llm -> tools -> output -> feedback from environment
52 | ```
53 |
54 | We have included two examples in this repository: namely, `single_agent_example.py` and `multi_agent_example.py`.
55 |
56 |
57 | ## single_agent_example.py
58 | In `single_agent_example.py`, we have a simple implementation of a weather agent. Here are the features of the agent:
59 | 1. Goal: To retrieve the weather information for the user
60 | 2. llm: gpt-4o
61 | 3. tools: get_weather and send_email
62 |
63 |  64 |
65 |
66 | ## multi_agent_example.py
67 | In the `multi_agent_example.py`, we have a simple implementation of a customer bot multi-agent. There are three agents implemented in it, namely: triage_agent, sales_agent and refund agent
68 |
69 |
64 |
65 |
66 | ## multi_agent_example.py
67 | In the `multi_agent_example.py`, we have a simple implementation of a customer bot multi-agent. There are three agents implemented in it, namely: triage_agent, sales_agent and refund agent
68 |
69 |  70 |
71 | ### triage_agent
72 | 1. Goal: Route the user request to the correct agent
73 | 2. llm: gpt-4o
74 | 3. tools: sales_agent, refund_agent
75 |
76 | ### sales_agent
77 | 1. Goal: To sell a product
78 | 2. llm: gpt-4o
79 | 3. tools: triage_agent
80 |
81 | ### refund_agent
82 | 1. Goal: To process a refund
83 | 2. llm: gpt-4o
84 | 3. tools: process_refund, apply_discount
85 |
86 | # Going deeper
87 | 1. [Planning and Reasoning with LLMs](https://hexoai.notion.site/Planning-and-Reasoning-with-LLMs-09ed06fe3a3b45f494760d606c4f285b?pvs=74)
88 | 2. [Cognitive Architectures for Language Agents](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.02427v3)
89 |
90 | # Contributing
91 | Please feel free to fork this repository and create PRs. We are eager to get PRs on the following:
92 | 1. Additional working examples of Agents
93 | 2. Tracing and Logging of the Agents
94 | 3. Feedback and learning from experiences
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/agent.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import json
2 | import copy
3 | import inspect
4 |
5 | from openai import OpenAI
6 | from pydantic import BaseModel
7 | from typing_extensions import Literal
8 | from typing import Union, Callable, List, Optional
9 |
10 |
11 | def pretty_print_messages(messages) -> None:
12 | for message in messages:
13 | if message["role"] != "assistant":
14 | continue
15 |
16 | # print agent name in blue
17 | print(f"\033[94m{message['sender']}\033[0m:", end=" ")
18 |
19 | # print response, if any
20 | if message["content"]:
21 | print(message["content"])
22 |
23 | # print tool calls in purple, if any
24 | tool_calls = message.get("tool_calls") or []
25 | if len(tool_calls) > 1:
26 | print()
27 | for tool_call in tool_calls:
28 | f = tool_call["function"]
29 | name, args = f["name"], f["arguments"]
30 | arg_str = json.dumps(json.loads(args)).replace(":", "=")
31 | print(f"\033[95m{name}\033[0m({arg_str[1:-1]})")
32 |
33 | def function_to_json(func) -> dict:
34 | """
35 | Sample Input:
36 | def add_two_numbers(a: int, b: int) -> int:
37 | # Adds two numbers together
38 | return a + b
39 |
40 | Sample Output:
41 | {
42 | 'type': 'function',
43 | 'function': {
44 | 'name': 'add_two_numbers',
45 | 'description': 'Adds two numbers together',
46 | 'parameters': {
47 | 'type': 'object',
48 | 'properties': {
49 | 'a': {'type': 'integer'},
50 | 'b': {'type': 'integer'}
51 | },
52 | 'required': ['a', 'b']
53 | }
54 | }
55 | }
56 | """
57 | type_map = {
58 | str: "string",
59 | int: "integer",
60 | float: "number",
61 | bool: "boolean",
62 | list: "array",
63 | dict: "object",
64 | type(None): "null",
65 | }
66 |
67 | try:
68 | signature = inspect.signature(func)
69 | except ValueError as e:
70 | raise ValueError(
71 | f"Failed to get signature for function {func.__name__}: {str(e)}"
72 | )
73 |
74 | parameters = {}
75 | for param in signature.parameters.values():
76 | try:
77 | param_type = type_map.get(param.annotation, "string")
78 | except KeyError as e:
79 | raise KeyError(
80 | f"Unknown type annotation {param.annotation} for parameter {param.name}: {str(e)}"
81 | )
82 | parameters[param.name] = {"type": param_type}
83 |
84 | required = [
85 | param.name
86 | for param in signature.parameters.values()
87 | if param.default == inspect._empty
88 | ]
89 |
90 | return {
91 | "type": "function",
92 | "function": {
93 | "name": func.__name__,
94 | "description": func.__doc__ or "",
95 | "parameters": {
96 | "type": "object",
97 | "properties": parameters,
98 | "required": required,
99 | },
100 | },
101 | }
102 |
103 | AgentFunction = Callable[[], Union[str, "Agent", dict]]
104 |
105 | class Agent(BaseModel):
106 | # Just a simple class. Doesn't contain any methods out of the box
107 | name: str = "Agent"
108 | model: str = "gpt-4o"
109 | instructions: Union[str, Callable[[], str]] = "You are a helpful agent."
110 | functions: List[AgentFunction] = []
111 | tool_choice: str = None
112 | parallel_tool_calls: bool = True
113 |
114 | class Response(BaseModel):
115 | # Response is used to encapsulate the entire conversation output
116 | messages: List = []
117 | agent: Optional[Agent] = None
118 |
119 | class Function(BaseModel):
120 | arguments: str
121 | name: str
122 |
123 | class ChatCompletionMessageToolCall(BaseModel):
124 | id: str # The ID of the tool call
125 | function: Function # The function that the model called
126 | type: Literal["function"] # The type of the tool. Currently, only `function` is supported
127 |
128 | class Result(BaseModel):
129 | # Result is used to encapsulate the return value of a single function/tool call
130 | value: str = "" # The result value as a string.
131 | agent: Optional[Agent] = None # The agent instance, if applicable.
132 |
133 |
134 | class Swarm:
135 | # Implements the core logic of orchestrating a single/multi-agent system
136 | def __init__(
137 | self,
138 | client=None,
139 | ):
140 | if not client:
141 | client = OpenAI()
142 | self.client = client
143 |
144 | def get_chat_completion(
145 | self,
146 | agent: Agent,
147 | history: List,
148 | model_override: str
149 | ):
150 | messages = [{"role": "system", "content": agent.instructions}] + history
151 | tools = [function_to_json(f) for f in agent.functions]
152 |
153 | create_params = {
154 | "model": model_override or agent.model,
155 | "messages": messages,
156 | "tools": tools or None,
157 | "tool_choice": agent.tool_choice,
158 | }
159 |
160 | if tools:
161 | create_params["parallel_tool_calls"] = agent.parallel_tool_calls
162 |
163 | return self.client.chat.completions.create(**create_params)
164 |
165 | def handle_function_result(self, result) -> Result:
166 | match result:
167 | case Result() as result:
168 | return result
169 | case Agent() as agent:
170 | return Result(
171 | value=json.dumps({"assistant": agent.name}),
172 | agent=agent
173 | )
174 | case _:
175 | try:
176 | return Result(value=str(result))
177 | except Exception as e:
178 | raise TypeError(e)
179 |
180 | def handle_tool_calls(
181 | self,
182 | tool_calls: List[ChatCompletionMessageToolCall],
183 | functions: List[AgentFunction]
184 | ) -> Response:
185 | function_map = {f.__name__: f for f in functions}
186 | partial_response = Response(messages=[], agent=None)
187 | for tool_call in tool_calls:
188 | name = tool_call.function.name
189 | # handle missing tool case, skip to next tool
190 | if name not in function_map:
191 | partial_response.messages.append(
192 | {
193 | "role": "tool",
194 | "tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
195 | "tool_name": name,
196 | "content": f"Error: Tool {name} not found.",
197 | }
198 | )
199 | continue
200 | args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
201 | raw_result = function_map[name](**args)
202 | print(f'Called function {name} with args: {args} and obtained result: {raw_result}')
203 | print('#############################################')
204 | result: Result = self.handle_function_result(raw_result)
205 | partial_response.messages.append(
206 | {
207 | "role": "tool",
208 | "tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
209 | "tool_name": name,
210 | "content": result.value,
211 | }
212 | )
213 | if result.agent:
214 | partial_response.agent = result.agent
215 |
216 | return partial_response
217 |
218 | def run(
219 | self,
220 | agent: Agent,
221 | messages: List,
222 | model_override: str = None,
223 | max_turns: int = float("inf"),
224 | execute_tools: bool = True,
225 | ) -> Response:
226 | active_agent = agent
227 | history = copy.deepcopy(messages)
228 | init_len = len(messages)
229 |
230 | print('#############################################')
231 | print(f'history: {history}')
232 | print('#############################################')
233 | while len(history) - init_len < max_turns and active_agent:
234 | completion = self.get_chat_completion(
235 | agent=active_agent,
236 | history=history,
237 | model_override=model_override
238 | )
239 | message = completion.choices[0].message
240 | message.sender = active_agent.name
241 | print(f'Active agent: {active_agent.name}')
242 | print(f"message: {message}")
243 | print('#############################################')
244 |
245 |
246 | history.append(json.loads(message.model_dump_json()))
247 |
248 | if not message.tool_calls or not execute_tools:
249 | print('No tool calls hence breaking')
250 | print('#############################################')
251 | break
252 |
253 | partial_response = self.handle_tool_calls(message.tool_calls, active_agent.functions)
254 | history.extend(partial_response.messages)
255 |
256 | if partial_response.agent:
257 | active_agent = partial_response.agent
258 | message.sender = active_agent.name
259 | return Response(
260 | messages=history[init_len:],
261 | agent=active_agent,
262 | )
263 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
70 |
71 | ### triage_agent
72 | 1. Goal: Route the user request to the correct agent
73 | 2. llm: gpt-4o
74 | 3. tools: sales_agent, refund_agent
75 |
76 | ### sales_agent
77 | 1. Goal: To sell a product
78 | 2. llm: gpt-4o
79 | 3. tools: triage_agent
80 |
81 | ### refund_agent
82 | 1. Goal: To process a refund
83 | 2. llm: gpt-4o
84 | 3. tools: process_refund, apply_discount
85 |
86 | # Going deeper
87 | 1. [Planning and Reasoning with LLMs](https://hexoai.notion.site/Planning-and-Reasoning-with-LLMs-09ed06fe3a3b45f494760d606c4f285b?pvs=74)
88 | 2. [Cognitive Architectures for Language Agents](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.02427v3)
89 |
90 | # Contributing
91 | Please feel free to fork this repository and create PRs. We are eager to get PRs on the following:
92 | 1. Additional working examples of Agents
93 | 2. Tracing and Logging of the Agents
94 | 3. Feedback and learning from experiences
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/agent.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import json
2 | import copy
3 | import inspect
4 |
5 | from openai import OpenAI
6 | from pydantic import BaseModel
7 | from typing_extensions import Literal
8 | from typing import Union, Callable, List, Optional
9 |
10 |
11 | def pretty_print_messages(messages) -> None:
12 | for message in messages:
13 | if message["role"] != "assistant":
14 | continue
15 |
16 | # print agent name in blue
17 | print(f"\033[94m{message['sender']}\033[0m:", end=" ")
18 |
19 | # print response, if any
20 | if message["content"]:
21 | print(message["content"])
22 |
23 | # print tool calls in purple, if any
24 | tool_calls = message.get("tool_calls") or []
25 | if len(tool_calls) > 1:
26 | print()
27 | for tool_call in tool_calls:
28 | f = tool_call["function"]
29 | name, args = f["name"], f["arguments"]
30 | arg_str = json.dumps(json.loads(args)).replace(":", "=")
31 | print(f"\033[95m{name}\033[0m({arg_str[1:-1]})")
32 |
33 | def function_to_json(func) -> dict:
34 | """
35 | Sample Input:
36 | def add_two_numbers(a: int, b: int) -> int:
37 | # Adds two numbers together
38 | return a + b
39 |
40 | Sample Output:
41 | {
42 | 'type': 'function',
43 | 'function': {
44 | 'name': 'add_two_numbers',
45 | 'description': 'Adds two numbers together',
46 | 'parameters': {
47 | 'type': 'object',
48 | 'properties': {
49 | 'a': {'type': 'integer'},
50 | 'b': {'type': 'integer'}
51 | },
52 | 'required': ['a', 'b']
53 | }
54 | }
55 | }
56 | """
57 | type_map = {
58 | str: "string",
59 | int: "integer",
60 | float: "number",
61 | bool: "boolean",
62 | list: "array",
63 | dict: "object",
64 | type(None): "null",
65 | }
66 |
67 | try:
68 | signature = inspect.signature(func)
69 | except ValueError as e:
70 | raise ValueError(
71 | f"Failed to get signature for function {func.__name__}: {str(e)}"
72 | )
73 |
74 | parameters = {}
75 | for param in signature.parameters.values():
76 | try:
77 | param_type = type_map.get(param.annotation, "string")
78 | except KeyError as e:
79 | raise KeyError(
80 | f"Unknown type annotation {param.annotation} for parameter {param.name}: {str(e)}"
81 | )
82 | parameters[param.name] = {"type": param_type}
83 |
84 | required = [
85 | param.name
86 | for param in signature.parameters.values()
87 | if param.default == inspect._empty
88 | ]
89 |
90 | return {
91 | "type": "function",
92 | "function": {
93 | "name": func.__name__,
94 | "description": func.__doc__ or "",
95 | "parameters": {
96 | "type": "object",
97 | "properties": parameters,
98 | "required": required,
99 | },
100 | },
101 | }
102 |
103 | AgentFunction = Callable[[], Union[str, "Agent", dict]]
104 |
105 | class Agent(BaseModel):
106 | # Just a simple class. Doesn't contain any methods out of the box
107 | name: str = "Agent"
108 | model: str = "gpt-4o"
109 | instructions: Union[str, Callable[[], str]] = "You are a helpful agent."
110 | functions: List[AgentFunction] = []
111 | tool_choice: str = None
112 | parallel_tool_calls: bool = True
113 |
114 | class Response(BaseModel):
115 | # Response is used to encapsulate the entire conversation output
116 | messages: List = []
117 | agent: Optional[Agent] = None
118 |
119 | class Function(BaseModel):
120 | arguments: str
121 | name: str
122 |
123 | class ChatCompletionMessageToolCall(BaseModel):
124 | id: str # The ID of the tool call
125 | function: Function # The function that the model called
126 | type: Literal["function"] # The type of the tool. Currently, only `function` is supported
127 |
128 | class Result(BaseModel):
129 | # Result is used to encapsulate the return value of a single function/tool call
130 | value: str = "" # The result value as a string.
131 | agent: Optional[Agent] = None # The agent instance, if applicable.
132 |
133 |
134 | class Swarm:
135 | # Implements the core logic of orchestrating a single/multi-agent system
136 | def __init__(
137 | self,
138 | client=None,
139 | ):
140 | if not client:
141 | client = OpenAI()
142 | self.client = client
143 |
144 | def get_chat_completion(
145 | self,
146 | agent: Agent,
147 | history: List,
148 | model_override: str
149 | ):
150 | messages = [{"role": "system", "content": agent.instructions}] + history
151 | tools = [function_to_json(f) for f in agent.functions]
152 |
153 | create_params = {
154 | "model": model_override or agent.model,
155 | "messages": messages,
156 | "tools": tools or None,
157 | "tool_choice": agent.tool_choice,
158 | }
159 |
160 | if tools:
161 | create_params["parallel_tool_calls"] = agent.parallel_tool_calls
162 |
163 | return self.client.chat.completions.create(**create_params)
164 |
165 | def handle_function_result(self, result) -> Result:
166 | match result:
167 | case Result() as result:
168 | return result
169 | case Agent() as agent:
170 | return Result(
171 | value=json.dumps({"assistant": agent.name}),
172 | agent=agent
173 | )
174 | case _:
175 | try:
176 | return Result(value=str(result))
177 | except Exception as e:
178 | raise TypeError(e)
179 |
180 | def handle_tool_calls(
181 | self,
182 | tool_calls: List[ChatCompletionMessageToolCall],
183 | functions: List[AgentFunction]
184 | ) -> Response:
185 | function_map = {f.__name__: f for f in functions}
186 | partial_response = Response(messages=[], agent=None)
187 | for tool_call in tool_calls:
188 | name = tool_call.function.name
189 | # handle missing tool case, skip to next tool
190 | if name not in function_map:
191 | partial_response.messages.append(
192 | {
193 | "role": "tool",
194 | "tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
195 | "tool_name": name,
196 | "content": f"Error: Tool {name} not found.",
197 | }
198 | )
199 | continue
200 | args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
201 | raw_result = function_map[name](**args)
202 | print(f'Called function {name} with args: {args} and obtained result: {raw_result}')
203 | print('#############################################')
204 | result: Result = self.handle_function_result(raw_result)
205 | partial_response.messages.append(
206 | {
207 | "role": "tool",
208 | "tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
209 | "tool_name": name,
210 | "content": result.value,
211 | }
212 | )
213 | if result.agent:
214 | partial_response.agent = result.agent
215 |
216 | return partial_response
217 |
218 | def run(
219 | self,
220 | agent: Agent,
221 | messages: List,
222 | model_override: str = None,
223 | max_turns: int = float("inf"),
224 | execute_tools: bool = True,
225 | ) -> Response:
226 | active_agent = agent
227 | history = copy.deepcopy(messages)
228 | init_len = len(messages)
229 |
230 | print('#############################################')
231 | print(f'history: {history}')
232 | print('#############################################')
233 | while len(history) - init_len < max_turns and active_agent:
234 | completion = self.get_chat_completion(
235 | agent=active_agent,
236 | history=history,
237 | model_override=model_override
238 | )
239 | message = completion.choices[0].message
240 | message.sender = active_agent.name
241 | print(f'Active agent: {active_agent.name}')
242 | print(f"message: {message}")
243 | print('#############################################')
244 |
245 |
246 | history.append(json.loads(message.model_dump_json()))
247 |
248 | if not message.tool_calls or not execute_tools:
249 | print('No tool calls hence breaking')
250 | print('#############################################')
251 | break
252 |
253 | partial_response = self.handle_tool_calls(message.tool_calls, active_agent.functions)
254 | history.extend(partial_response.messages)
255 |
256 | if partial_response.agent:
257 | active_agent = partial_response.agent
258 | message.sender = active_agent.name
259 | return Response(
260 | messages=history[init_len:],
261 | agent=active_agent,
262 | )
263 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 30 |
31 | A User can assign a goal to an agent. An Agent consists of an LLM and the LLM is capable to calling a bunch of tools. The LLM takes up the goal and uses whichever tool, whenever necessary in order to accomplish the goal.
32 |
33 | 1. In `agent.py`, you will see a class called `Agent` which can take up a goal (variable named instructions), an LLM (variable named model) and a bunch of tools (variable named functions).
34 | 2. It has another class called `Swarm` which contains the logic on how the LLM can calls the tools and accomplish the given goal.
35 |
36 | ```python
37 | class Swarm:
38 | def __init__():
39 | # Implements logic of how llm and tool calling works together
40 |
41 | def get_chat_completion():
42 | # Implements LLM completion
43 |
44 | def handle_tool_calls():
45 | # Implements tool calling
46 |
47 | def handle_function_result():
48 | # processes the tool outptu
49 |
50 | def run():
51 | # runs the whole logic of goal -> llm -> tools -> output -> feedback from environment
52 | ```
53 |
54 | We have included two examples in this repository: namely, `single_agent_example.py` and `multi_agent_example.py`.
55 |
56 |
57 | ## single_agent_example.py
58 | In `single_agent_example.py`, we have a simple implementation of a weather agent. Here are the features of the agent:
59 | 1. Goal: To retrieve the weather information for the user
60 | 2. llm: gpt-4o
61 | 3. tools: get_weather and send_email
62 |
63 |
30 |
31 | A User can assign a goal to an agent. An Agent consists of an LLM and the LLM is capable to calling a bunch of tools. The LLM takes up the goal and uses whichever tool, whenever necessary in order to accomplish the goal.
32 |
33 | 1. In `agent.py`, you will see a class called `Agent` which can take up a goal (variable named instructions), an LLM (variable named model) and a bunch of tools (variable named functions).
34 | 2. It has another class called `Swarm` which contains the logic on how the LLM can calls the tools and accomplish the given goal.
35 |
36 | ```python
37 | class Swarm:
38 | def __init__():
39 | # Implements logic of how llm and tool calling works together
40 |
41 | def get_chat_completion():
42 | # Implements LLM completion
43 |
44 | def handle_tool_calls():
45 | # Implements tool calling
46 |
47 | def handle_function_result():
48 | # processes the tool outptu
49 |
50 | def run():
51 | # runs the whole logic of goal -> llm -> tools -> output -> feedback from environment
52 | ```
53 |
54 | We have included two examples in this repository: namely, `single_agent_example.py` and `multi_agent_example.py`.
55 |
56 |
57 | ## single_agent_example.py
58 | In `single_agent_example.py`, we have a simple implementation of a weather agent. Here are the features of the agent:
59 | 1. Goal: To retrieve the weather information for the user
60 | 2. llm: gpt-4o
61 | 3. tools: get_weather and send_email
62 |
63 |  64 |
65 |
66 | ## multi_agent_example.py
67 | In the `multi_agent_example.py`, we have a simple implementation of a customer bot multi-agent. There are three agents implemented in it, namely: triage_agent, sales_agent and refund agent
68 |
69 |
64 |
65 |
66 | ## multi_agent_example.py
67 | In the `multi_agent_example.py`, we have a simple implementation of a customer bot multi-agent. There are three agents implemented in it, namely: triage_agent, sales_agent and refund agent
68 |
69 |  70 |
71 | ### triage_agent
72 | 1. Goal: Route the user request to the correct agent
73 | 2. llm: gpt-4o
74 | 3. tools: sales_agent, refund_agent
75 |
76 | ### sales_agent
77 | 1. Goal: To sell a product
78 | 2. llm: gpt-4o
79 | 3. tools: triage_agent
80 |
81 | ### refund_agent
82 | 1. Goal: To process a refund
83 | 2. llm: gpt-4o
84 | 3. tools: process_refund, apply_discount
85 |
86 | # Going deeper
87 | 1. [Planning and Reasoning with LLMs](https://hexoai.notion.site/Planning-and-Reasoning-with-LLMs-09ed06fe3a3b45f494760d606c4f285b?pvs=74)
88 | 2. [Cognitive Architectures for Language Agents](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.02427v3)
89 |
90 | # Contributing
91 | Please feel free to fork this repository and create PRs. We are eager to get PRs on the following:
92 | 1. Additional working examples of Agents
93 | 2. Tracing and Logging of the Agents
94 | 3. Feedback and learning from experiences
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/agent.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import json
2 | import copy
3 | import inspect
4 |
5 | from openai import OpenAI
6 | from pydantic import BaseModel
7 | from typing_extensions import Literal
8 | from typing import Union, Callable, List, Optional
9 |
10 |
11 | def pretty_print_messages(messages) -> None:
12 | for message in messages:
13 | if message["role"] != "assistant":
14 | continue
15 |
16 | # print agent name in blue
17 | print(f"\033[94m{message['sender']}\033[0m:", end=" ")
18 |
19 | # print response, if any
20 | if message["content"]:
21 | print(message["content"])
22 |
23 | # print tool calls in purple, if any
24 | tool_calls = message.get("tool_calls") or []
25 | if len(tool_calls) > 1:
26 | print()
27 | for tool_call in tool_calls:
28 | f = tool_call["function"]
29 | name, args = f["name"], f["arguments"]
30 | arg_str = json.dumps(json.loads(args)).replace(":", "=")
31 | print(f"\033[95m{name}\033[0m({arg_str[1:-1]})")
32 |
33 | def function_to_json(func) -> dict:
34 | """
35 | Sample Input:
36 | def add_two_numbers(a: int, b: int) -> int:
37 | # Adds two numbers together
38 | return a + b
39 |
40 | Sample Output:
41 | {
42 | 'type': 'function',
43 | 'function': {
44 | 'name': 'add_two_numbers',
45 | 'description': 'Adds two numbers together',
46 | 'parameters': {
47 | 'type': 'object',
48 | 'properties': {
49 | 'a': {'type': 'integer'},
50 | 'b': {'type': 'integer'}
51 | },
52 | 'required': ['a', 'b']
53 | }
54 | }
55 | }
56 | """
57 | type_map = {
58 | str: "string",
59 | int: "integer",
60 | float: "number",
61 | bool: "boolean",
62 | list: "array",
63 | dict: "object",
64 | type(None): "null",
65 | }
66 |
67 | try:
68 | signature = inspect.signature(func)
69 | except ValueError as e:
70 | raise ValueError(
71 | f"Failed to get signature for function {func.__name__}: {str(e)}"
72 | )
73 |
74 | parameters = {}
75 | for param in signature.parameters.values():
76 | try:
77 | param_type = type_map.get(param.annotation, "string")
78 | except KeyError as e:
79 | raise KeyError(
80 | f"Unknown type annotation {param.annotation} for parameter {param.name}: {str(e)}"
81 | )
82 | parameters[param.name] = {"type": param_type}
83 |
84 | required = [
85 | param.name
86 | for param in signature.parameters.values()
87 | if param.default == inspect._empty
88 | ]
89 |
90 | return {
91 | "type": "function",
92 | "function": {
93 | "name": func.__name__,
94 | "description": func.__doc__ or "",
95 | "parameters": {
96 | "type": "object",
97 | "properties": parameters,
98 | "required": required,
99 | },
100 | },
101 | }
102 |
103 | AgentFunction = Callable[[], Union[str, "Agent", dict]]
104 |
105 | class Agent(BaseModel):
106 | # Just a simple class. Doesn't contain any methods out of the box
107 | name: str = "Agent"
108 | model: str = "gpt-4o"
109 | instructions: Union[str, Callable[[], str]] = "You are a helpful agent."
110 | functions: List[AgentFunction] = []
111 | tool_choice: str = None
112 | parallel_tool_calls: bool = True
113 |
114 | class Response(BaseModel):
115 | # Response is used to encapsulate the entire conversation output
116 | messages: List = []
117 | agent: Optional[Agent] = None
118 |
119 | class Function(BaseModel):
120 | arguments: str
121 | name: str
122 |
123 | class ChatCompletionMessageToolCall(BaseModel):
124 | id: str # The ID of the tool call
125 | function: Function # The function that the model called
126 | type: Literal["function"] # The type of the tool. Currently, only `function` is supported
127 |
128 | class Result(BaseModel):
129 | # Result is used to encapsulate the return value of a single function/tool call
130 | value: str = "" # The result value as a string.
131 | agent: Optional[Agent] = None # The agent instance, if applicable.
132 |
133 |
134 | class Swarm:
135 | # Implements the core logic of orchestrating a single/multi-agent system
136 | def __init__(
137 | self,
138 | client=None,
139 | ):
140 | if not client:
141 | client = OpenAI()
142 | self.client = client
143 |
144 | def get_chat_completion(
145 | self,
146 | agent: Agent,
147 | history: List,
148 | model_override: str
149 | ):
150 | messages = [{"role": "system", "content": agent.instructions}] + history
151 | tools = [function_to_json(f) for f in agent.functions]
152 |
153 | create_params = {
154 | "model": model_override or agent.model,
155 | "messages": messages,
156 | "tools": tools or None,
157 | "tool_choice": agent.tool_choice,
158 | }
159 |
160 | if tools:
161 | create_params["parallel_tool_calls"] = agent.parallel_tool_calls
162 |
163 | return self.client.chat.completions.create(**create_params)
164 |
165 | def handle_function_result(self, result) -> Result:
166 | match result:
167 | case Result() as result:
168 | return result
169 | case Agent() as agent:
170 | return Result(
171 | value=json.dumps({"assistant": agent.name}),
172 | agent=agent
173 | )
174 | case _:
175 | try:
176 | return Result(value=str(result))
177 | except Exception as e:
178 | raise TypeError(e)
179 |
180 | def handle_tool_calls(
181 | self,
182 | tool_calls: List[ChatCompletionMessageToolCall],
183 | functions: List[AgentFunction]
184 | ) -> Response:
185 | function_map = {f.__name__: f for f in functions}
186 | partial_response = Response(messages=[], agent=None)
187 | for tool_call in tool_calls:
188 | name = tool_call.function.name
189 | # handle missing tool case, skip to next tool
190 | if name not in function_map:
191 | partial_response.messages.append(
192 | {
193 | "role": "tool",
194 | "tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
195 | "tool_name": name,
196 | "content": f"Error: Tool {name} not found.",
197 | }
198 | )
199 | continue
200 | args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
201 | raw_result = function_map[name](**args)
202 | print(f'Called function {name} with args: {args} and obtained result: {raw_result}')
203 | print('#############################################')
204 | result: Result = self.handle_function_result(raw_result)
205 | partial_response.messages.append(
206 | {
207 | "role": "tool",
208 | "tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
209 | "tool_name": name,
210 | "content": result.value,
211 | }
212 | )
213 | if result.agent:
214 | partial_response.agent = result.agent
215 |
216 | return partial_response
217 |
218 | def run(
219 | self,
220 | agent: Agent,
221 | messages: List,
222 | model_override: str = None,
223 | max_turns: int = float("inf"),
224 | execute_tools: bool = True,
225 | ) -> Response:
226 | active_agent = agent
227 | history = copy.deepcopy(messages)
228 | init_len = len(messages)
229 |
230 | print('#############################################')
231 | print(f'history: {history}')
232 | print('#############################################')
233 | while len(history) - init_len < max_turns and active_agent:
234 | completion = self.get_chat_completion(
235 | agent=active_agent,
236 | history=history,
237 | model_override=model_override
238 | )
239 | message = completion.choices[0].message
240 | message.sender = active_agent.name
241 | print(f'Active agent: {active_agent.name}')
242 | print(f"message: {message}")
243 | print('#############################################')
244 |
245 |
246 | history.append(json.loads(message.model_dump_json()))
247 |
248 | if not message.tool_calls or not execute_tools:
249 | print('No tool calls hence breaking')
250 | print('#############################################')
251 | break
252 |
253 | partial_response = self.handle_tool_calls(message.tool_calls, active_agent.functions)
254 | history.extend(partial_response.messages)
255 |
256 | if partial_response.agent:
257 | active_agent = partial_response.agent
258 | message.sender = active_agent.name
259 | return Response(
260 | messages=history[init_len:],
261 | agent=active_agent,
262 | )
263 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
70 |
71 | ### triage_agent
72 | 1. Goal: Route the user request to the correct agent
73 | 2. llm: gpt-4o
74 | 3. tools: sales_agent, refund_agent
75 |
76 | ### sales_agent
77 | 1. Goal: To sell a product
78 | 2. llm: gpt-4o
79 | 3. tools: triage_agent
80 |
81 | ### refund_agent
82 | 1. Goal: To process a refund
83 | 2. llm: gpt-4o
84 | 3. tools: process_refund, apply_discount
85 |
86 | # Going deeper
87 | 1. [Planning and Reasoning with LLMs](https://hexoai.notion.site/Planning-and-Reasoning-with-LLMs-09ed06fe3a3b45f494760d606c4f285b?pvs=74)
88 | 2. [Cognitive Architectures for Language Agents](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.02427v3)
89 |
90 | # Contributing
91 | Please feel free to fork this repository and create PRs. We are eager to get PRs on the following:
92 | 1. Additional working examples of Agents
93 | 2. Tracing and Logging of the Agents
94 | 3. Feedback and learning from experiences
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/agent.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import json
2 | import copy
3 | import inspect
4 |
5 | from openai import OpenAI
6 | from pydantic import BaseModel
7 | from typing_extensions import Literal
8 | from typing import Union, Callable, List, Optional
9 |
10 |
11 | def pretty_print_messages(messages) -> None:
12 | for message in messages:
13 | if message["role"] != "assistant":
14 | continue
15 |
16 | # print agent name in blue
17 | print(f"\033[94m{message['sender']}\033[0m:", end=" ")
18 |
19 | # print response, if any
20 | if message["content"]:
21 | print(message["content"])
22 |
23 | # print tool calls in purple, if any
24 | tool_calls = message.get("tool_calls") or []
25 | if len(tool_calls) > 1:
26 | print()
27 | for tool_call in tool_calls:
28 | f = tool_call["function"]
29 | name, args = f["name"], f["arguments"]
30 | arg_str = json.dumps(json.loads(args)).replace(":", "=")
31 | print(f"\033[95m{name}\033[0m({arg_str[1:-1]})")
32 |
33 | def function_to_json(func) -> dict:
34 | """
35 | Sample Input:
36 | def add_two_numbers(a: int, b: int) -> int:
37 | # Adds two numbers together
38 | return a + b
39 |
40 | Sample Output:
41 | {
42 | 'type': 'function',
43 | 'function': {
44 | 'name': 'add_two_numbers',
45 | 'description': 'Adds two numbers together',
46 | 'parameters': {
47 | 'type': 'object',
48 | 'properties': {
49 | 'a': {'type': 'integer'},
50 | 'b': {'type': 'integer'}
51 | },
52 | 'required': ['a', 'b']
53 | }
54 | }
55 | }
56 | """
57 | type_map = {
58 | str: "string",
59 | int: "integer",
60 | float: "number",
61 | bool: "boolean",
62 | list: "array",
63 | dict: "object",
64 | type(None): "null",
65 | }
66 |
67 | try:
68 | signature = inspect.signature(func)
69 | except ValueError as e:
70 | raise ValueError(
71 | f"Failed to get signature for function {func.__name__}: {str(e)}"
72 | )
73 |
74 | parameters = {}
75 | for param in signature.parameters.values():
76 | try:
77 | param_type = type_map.get(param.annotation, "string")
78 | except KeyError as e:
79 | raise KeyError(
80 | f"Unknown type annotation {param.annotation} for parameter {param.name}: {str(e)}"
81 | )
82 | parameters[param.name] = {"type": param_type}
83 |
84 | required = [
85 | param.name
86 | for param in signature.parameters.values()
87 | if param.default == inspect._empty
88 | ]
89 |
90 | return {
91 | "type": "function",
92 | "function": {
93 | "name": func.__name__,
94 | "description": func.__doc__ or "",
95 | "parameters": {
96 | "type": "object",
97 | "properties": parameters,
98 | "required": required,
99 | },
100 | },
101 | }
102 |
103 | AgentFunction = Callable[[], Union[str, "Agent", dict]]
104 |
105 | class Agent(BaseModel):
106 | # Just a simple class. Doesn't contain any methods out of the box
107 | name: str = "Agent"
108 | model: str = "gpt-4o"
109 | instructions: Union[str, Callable[[], str]] = "You are a helpful agent."
110 | functions: List[AgentFunction] = []
111 | tool_choice: str = None
112 | parallel_tool_calls: bool = True
113 |
114 | class Response(BaseModel):
115 | # Response is used to encapsulate the entire conversation output
116 | messages: List = []
117 | agent: Optional[Agent] = None
118 |
119 | class Function(BaseModel):
120 | arguments: str
121 | name: str
122 |
123 | class ChatCompletionMessageToolCall(BaseModel):
124 | id: str # The ID of the tool call
125 | function: Function # The function that the model called
126 | type: Literal["function"] # The type of the tool. Currently, only `function` is supported
127 |
128 | class Result(BaseModel):
129 | # Result is used to encapsulate the return value of a single function/tool call
130 | value: str = "" # The result value as a string.
131 | agent: Optional[Agent] = None # The agent instance, if applicable.
132 |
133 |
134 | class Swarm:
135 | # Implements the core logic of orchestrating a single/multi-agent system
136 | def __init__(
137 | self,
138 | client=None,
139 | ):
140 | if not client:
141 | client = OpenAI()
142 | self.client = client
143 |
144 | def get_chat_completion(
145 | self,
146 | agent: Agent,
147 | history: List,
148 | model_override: str
149 | ):
150 | messages = [{"role": "system", "content": agent.instructions}] + history
151 | tools = [function_to_json(f) for f in agent.functions]
152 |
153 | create_params = {
154 | "model": model_override or agent.model,
155 | "messages": messages,
156 | "tools": tools or None,
157 | "tool_choice": agent.tool_choice,
158 | }
159 |
160 | if tools:
161 | create_params["parallel_tool_calls"] = agent.parallel_tool_calls
162 |
163 | return self.client.chat.completions.create(**create_params)
164 |
165 | def handle_function_result(self, result) -> Result:
166 | match result:
167 | case Result() as result:
168 | return result
169 | case Agent() as agent:
170 | return Result(
171 | value=json.dumps({"assistant": agent.name}),
172 | agent=agent
173 | )
174 | case _:
175 | try:
176 | return Result(value=str(result))
177 | except Exception as e:
178 | raise TypeError(e)
179 |
180 | def handle_tool_calls(
181 | self,
182 | tool_calls: List[ChatCompletionMessageToolCall],
183 | functions: List[AgentFunction]
184 | ) -> Response:
185 | function_map = {f.__name__: f for f in functions}
186 | partial_response = Response(messages=[], agent=None)
187 | for tool_call in tool_calls:
188 | name = tool_call.function.name
189 | # handle missing tool case, skip to next tool
190 | if name not in function_map:
191 | partial_response.messages.append(
192 | {
193 | "role": "tool",
194 | "tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
195 | "tool_name": name,
196 | "content": f"Error: Tool {name} not found.",
197 | }
198 | )
199 | continue
200 | args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
201 | raw_result = function_map[name](**args)
202 | print(f'Called function {name} with args: {args} and obtained result: {raw_result}')
203 | print('#############################################')
204 | result: Result = self.handle_function_result(raw_result)
205 | partial_response.messages.append(
206 | {
207 | "role": "tool",
208 | "tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
209 | "tool_name": name,
210 | "content": result.value,
211 | }
212 | )
213 | if result.agent:
214 | partial_response.agent = result.agent
215 |
216 | return partial_response
217 |
218 | def run(
219 | self,
220 | agent: Agent,
221 | messages: List,
222 | model_override: str = None,
223 | max_turns: int = float("inf"),
224 | execute_tools: bool = True,
225 | ) -> Response:
226 | active_agent = agent
227 | history = copy.deepcopy(messages)
228 | init_len = len(messages)
229 |
230 | print('#############################################')
231 | print(f'history: {history}')
232 | print('#############################################')
233 | while len(history) - init_len < max_turns and active_agent:
234 | completion = self.get_chat_completion(
235 | agent=active_agent,
236 | history=history,
237 | model_override=model_override
238 | )
239 | message = completion.choices[0].message
240 | message.sender = active_agent.name
241 | print(f'Active agent: {active_agent.name}')
242 | print(f"message: {message}")
243 | print('#############################################')
244 |
245 |
246 | history.append(json.loads(message.model_dump_json()))
247 |
248 | if not message.tool_calls or not execute_tools:
249 | print('No tool calls hence breaking')
250 | print('#############################################')
251 | break
252 |
253 | partial_response = self.handle_tool_calls(message.tool_calls, active_agent.functions)
254 | history.extend(partial_response.messages)
255 |
256 | if partial_response.agent:
257 | active_agent = partial_response.agent
258 | message.sender = active_agent.name
259 | return Response(
260 | messages=history[init_len:],
261 | agent=active_agent,
262 | )
263 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------