├── .gitignore
├── .readthedocs.yml
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── docs
├── Makefile
├── conf.py
├── environment.yml
├── firelight.rst
├── firelight.utils.rst
├── firelight.visualizers.rst
├── index.rst
├── introduction.rst
├── list_of_visualizers.rst
├── make.bat
└── requirements.txt
├── examples
├── README.rst
├── example_visualization.png
├── understanding
│ ├── README.rst
│ └── specfunction_example.py
└── usage
│ ├── README.rst
│ ├── example_config_0.yml
│ └── realistic_example.py
├── firelight
├── __init__.py
├── config_parsing.py
├── inferno_callback.py
├── utils
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── dim_utils.py
│ └── io_utils.py
└── visualizers
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── base.py
│ ├── colorization.py
│ ├── container_visualizers.py
│ └── visualizers.py
├── requirements.txt
└── setup.py
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | __pycache__
2 | firelight.egg-info
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.readthedocs.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # .readthedocs.yml
2 | # Read the Docs configuration file
3 | # See https://docs.readthedocs.io/en/stable/config-file/v2.html for details
4 |
5 | # Required
6 | version: 2
7 |
8 | # Build documentation in the docs/ directory with Sphinx
9 | sphinx:
10 | configuration: docs/conf.py
11 |
12 | # Optionally build your docs in additional formats such as PDF and ePub
13 | formats: all
14 |
15 | # conda:
16 | # environment: docs/environment.yml
17 |
18 | # Optionally set the version of Python and requirements required to build your docs
19 | python:
20 | version: 3.7
21 | install:
22 | - requirements: docs/requirements.txt
23 | - method: setuptools
24 | path: .
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Apache License
2 | Version 2.0, January 2004
3 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/
4 |
5 | TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR USE, REPRODUCTION, AND DISTRIBUTION
6 |
7 | 1. Definitions.
8 |
9 | "License" shall mean the terms and conditions for use, reproduction,
10 | and distribution as defined by Sections 1 through 9 of this document.
11 |
12 | "Licensor" shall mean the copyright owner or entity authorized by
13 | the copyright owner that is granting the License.
14 |
15 | "Legal Entity" shall mean the union of the acting entity and all
16 | other entities that control, are controlled by, or are under common
17 | control with that entity. For the purposes of this definition,
18 | "control" means (i) the power, direct or indirect, to cause the
19 | direction or management of such entity, whether by contract or
20 | otherwise, or (ii) ownership of fifty percent (50%) or more of the
21 | outstanding shares, or (iii) beneficial ownership of such entity.
22 |
23 | "You" (or "Your") shall mean an individual or Legal Entity
24 | exercising permissions granted by this License.
25 |
26 | "Source" form shall mean the preferred form for making modifications,
27 | including but not limited to software source code, documentation
28 | source, and configuration files.
29 |
30 | "Object" form shall mean any form resulting from mechanical
31 | transformation or translation of a Source form, including but
32 | not limited to compiled object code, generated documentation,
33 | and conversions to other media types.
34 |
35 | "Work" shall mean the work of authorship, whether in Source or
36 | Object form, made available under the License, as indicated by a
37 | copyright notice that is included in or attached to the work
38 | (an example is provided in the Appendix below).
39 |
40 | "Derivative Works" shall mean any work, whether in Source or Object
41 | form, that is based on (or derived from) the Work and for which the
42 | editorial revisions, annotations, elaborations, or other modifications
43 | represent, as a whole, an original work of authorship. For the purposes
44 | of this License, Derivative Works shall not include works that remain
45 | separable from, or merely link (or bind by name) to the interfaces of,
46 | the Work and Derivative Works thereof.
47 |
48 | "Contribution" shall mean any work of authorship, including
49 | the original version of the Work and any modifications or additions
50 | to that Work or Derivative Works thereof, that is intentionally
51 | submitted to Licensor for inclusion in the Work by the copyright owner
52 | or by an individual or Legal Entity authorized to submit on behalf of
53 | the copyright owner. For the purposes of this definition, "submitted"
54 | means any form of electronic, verbal, or written communication sent
55 | to the Licensor or its representatives, including but not limited to
56 | communication on electronic mailing lists, source code control systems,
57 | and issue tracking systems that are managed by, or on behalf of, the
58 | Licensor for the purpose of discussing and improving the Work, but
59 | excluding communication that is conspicuously marked or otherwise
60 | designated in writing by the copyright owner as "Not a Contribution."
61 |
62 | "Contributor" shall mean Licensor and any individual or Legal Entity
63 | on behalf of whom a Contribution has been received by Licensor and
64 | subsequently incorporated within the Work.
65 |
66 | 2. Grant of Copyright License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
67 | this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
68 | worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
69 | copyright license to reproduce, prepare Derivative Works of,
70 | publicly display, publicly perform, sublicense, and distribute the
71 | Work and such Derivative Works in Source or Object form.
72 |
73 | 3. Grant of Patent License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
74 | this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
75 | worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
76 | (except as stated in this section) patent license to make, have made,
77 | use, offer to sell, sell, import, and otherwise transfer the Work,
78 | where such license applies only to those patent claims licensable
79 | by such Contributor that are necessarily infringed by their
80 | Contribution(s) alone or by combination of their Contribution(s)
81 | with the Work to which such Contribution(s) was submitted. If You
82 | institute patent litigation against any entity (including a
83 | cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that the Work
84 | or a Contribution incorporated within the Work constitutes direct
85 | or contributory patent infringement, then any patent licenses
86 | granted to You under this License for that Work shall terminate
87 | as of the date such litigation is filed.
88 |
89 | 4. Redistribution. You may reproduce and distribute copies of the
90 | Work or Derivative Works thereof in any medium, with or without
91 | modifications, and in Source or Object form, provided that You
92 | meet the following conditions:
93 |
94 | (a) You must give any other recipients of the Work or
95 | Derivative Works a copy of this License; and
96 |
97 | (b) You must cause any modified files to carry prominent notices
98 | stating that You changed the files; and
99 |
100 | (c) You must retain, in the Source form of any Derivative Works
101 | that You distribute, all copyright, patent, trademark, and
102 | attribution notices from the Source form of the Work,
103 | excluding those notices that do not pertain to any part of
104 | the Derivative Works; and
105 |
106 | (d) If the Work includes a "NOTICE" text file as part of its
107 | distribution, then any Derivative Works that You distribute must
108 | include a readable copy of the attribution notices contained
109 | within such NOTICE file, excluding those notices that do not
110 | pertain to any part of the Derivative Works, in at least one
111 | of the following places: within a NOTICE text file distributed
112 | as part of the Derivative Works; within the Source form or
113 | documentation, if provided along with the Derivative Works; or,
114 | within a display generated by the Derivative Works, if and
115 | wherever such third-party notices normally appear. The contents
116 | of the NOTICE file are for informational purposes only and
117 | do not modify the License. You may add Your own attribution
118 | notices within Derivative Works that You distribute, alongside
119 | or as an addendum to the NOTICE text from the Work, provided
120 | that such additional attribution notices cannot be construed
121 | as modifying the License.
122 |
123 | You may add Your own copyright statement to Your modifications and
124 | may provide additional or different license terms and conditions
125 | for use, reproduction, or distribution of Your modifications, or
126 | for any such Derivative Works as a whole, provided Your use,
127 | reproduction, and distribution of the Work otherwise complies with
128 | the conditions stated in this License.
129 |
130 | 5. Submission of Contributions. Unless You explicitly state otherwise,
131 | any Contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the Work
132 | by You to the Licensor shall be under the terms and conditions of
133 | this License, without any additional terms or conditions.
134 | Notwithstanding the above, nothing herein shall supersede or modify
135 | the terms of any separate license agreement you may have executed
136 | with Licensor regarding such Contributions.
137 |
138 | 6. Trademarks. This License does not grant permission to use the trade
139 | names, trademarks, service marks, or product names of the Licensor,
140 | except as required for reasonable and customary use in describing the
141 | origin of the Work and reproducing the content of the NOTICE file.
142 |
143 | 7. Disclaimer of Warranty. Unless required by applicable law or
144 | agreed to in writing, Licensor provides the Work (and each
145 | Contributor provides its Contributions) on an "AS IS" BASIS,
146 | WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or
147 | implied, including, without limitation, any warranties or conditions
148 | of TITLE, NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, or FITNESS FOR A
149 | PARTICULAR PURPOSE. You are solely responsible for determining the
150 | appropriateness of using or redistributing the Work and assume any
151 | risks associated with Your exercise of permissions under this License.
152 |
153 | 8. Limitation of Liability. In no event and under no legal theory,
154 | whether in tort (including negligence), contract, or otherwise,
155 | unless required by applicable law (such as deliberate and grossly
156 | negligent acts) or agreed to in writing, shall any Contributor be
157 | liable to You for damages, including any direct, indirect, special,
158 | incidental, or consequential damages of any character arising as a
159 | result of this License or out of the use or inability to use the
160 | Work (including but not limited to damages for loss of goodwill,
161 | work stoppage, computer failure or malfunction, or any and all
162 | other commercial damages or losses), even if such Contributor
163 | has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
164 |
165 | 9. Accepting Warranty or Additional Liability. While redistributing
166 | the Work or Derivative Works thereof, You may choose to offer,
167 | and charge a fee for, acceptance of support, warranty, indemnity,
168 | or other liability obligations and/or rights consistent with this
169 | License. However, in accepting such obligations, You may act only
170 | on Your own behalf and on Your sole responsibility, not on behalf
171 | of any other Contributor, and only if You agree to indemnify,
172 | defend, and hold each Contributor harmless for any liability
173 | incurred by, or claims asserted against, such Contributor by reason
174 | of your accepting any such warranty or additional liability.
175 |
176 | END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
177 |
178 | APPENDIX: How to apply the Apache License to your work.
179 |
180 | To apply the Apache License to your work, attach the following
181 | boilerplate notice, with the fields enclosed by brackets "[]"
182 | replaced with your own identifying information. (Don't include
183 | the brackets!) The text should be enclosed in the appropriate
184 | comment syntax for the file format. We also recommend that a
185 | file or class name and description of purpose be included on the
186 | same "printed page" as the copyright notice for easier
187 | identification within third-party archives.
188 |
189 | Copyright [yyyy] [name of copyright owner]
190 |
191 | Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
192 | you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
193 | You may obtain a copy of the License at
194 |
195 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
196 |
197 | Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
198 | distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
199 | WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
200 | See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
201 | limitations under the License.
202 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Firelight
2 |
3 | [](https://firelight.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
4 | [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/firelight)
5 | [](https://badge.fury.io/py/firelight)
6 |
7 | Firelight is a visualization library for pytorch.
8 | Its core object is a **visualizer**, which can be called passing some states (such as `inputs`, `target`,
9 | `prediction`) returning a visualization of the data. What exactly that visualization shows, is specified in a yaml
10 | configuration file.
11 |
12 | Why you will like firelight initially:
13 | - Neat image grids, lining up inputs, targets and predictions,
14 | - Colorful images: Automatic scaling for RGB, matplotlib colormaps for grayscale data, randomly colored label images,
15 | - Many available visualizers.
16 |
17 | Why you will keep using firelight:
18 | - Everything in one config file,
19 | - Easily write your own visualizers,
20 | - Generality in dimensions: All visualizers usable with data of arbitrary dimension.
21 |
22 | ## Installation
23 |
24 | ### From source (to get the most recent version)
25 | On python 3.6+:
26 |
27 | ```bash
28 | # Clone the repository
29 | git clone https://github.com/inferno-pytorch/firelight
30 | cd firelight/
31 | # Install
32 | python setup.py install
33 | ```
34 | ### Using conda
35 |
36 | Firelight is available on conda-forge for python > 3.6 and all operating systems:
37 | ```bash
38 | conda install -c pytorch -c conda-forge firelight
39 | ```
40 |
41 | ### Using pip
42 |
43 | In an environment with [scikit-learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/install.html) installed:
44 | ```bash
45 | pip install firelight
46 | ```
47 |
48 | ## Example
49 |
50 | - Run the example `firelight/examples/example_data.py`
51 |
52 | Config file `example_config_0.yml`:
53 |
54 | ```yaml
55 | RowVisualizer: # stack the outputs of child visualizers as rows of an image grid
56 | input_mapping:
57 | global: [B: ':3', D: '0:9:3'] # Show only 3 samples in each batch ('B'), and some slices along depth ('D').
58 | prediction: [C: '0'] # Show only the first channel of the prediction
59 |
60 | pad_value: [0.2, 0.6, 1.0] # RGB color of separating lines
61 | pad_width: {B: 6, H: 0, W: 0, rest: 3} # Padding for batch ('B'), height ('H'), width ('W') and other dimensions.
62 |
63 | visualizers:
64 | # First row: Ground truth
65 | - IdentityVisualizer:
66 | input: 'target' # show the target
67 |
68 | # Second row: Raw input
69 | - IdentityVisualizer:
70 | input: ['input', C: '0'] # Show the first channel ('C') of the input.
71 | cmap: viridis # Name of a matplotlib colormap.
72 |
73 | # Third row: Prediction with segmentation boarders on top.
74 | - OverlayVisualizer:
75 | visualizers:
76 | - CrackedEdgeVisualizer: # Show borders of target segmentation
77 | input: 'target'
78 | width: 2
79 | opacity: 0.7 # Make output only partially opaque.
80 | - IdentityVisualizer: # prediction
81 | input: 'prediction'
82 | cmap: Spectral
83 |
84 | # Fourth row: Foreground probability, calculated by sigmoid on prediction
85 | - IdentityVisualizer:
86 | input_mapping: # the input to the visualizer can also be specified as a dict under the key 'input mapping'.
87 | tensor: ['prediction', pre: 'sigmoid'] # Apply sigmoid function from torch.nn.functional before visualize.
88 | value_range: [0, 1] # Scale such that 0 is white and 1 is black. If not specified, whole range is used.
89 |
90 | # Fifth row: Visualize where norm of prediction is smaller than 2
91 | - ThresholdVisualizer:
92 | input_mapping:
93 | tensor:
94 | NormVisualizer: # Use the output of NormVisualizer as the input to ThresholdVisualizer
95 | input: 'prediction'
96 | colorize: False
97 | threshold: 2
98 | mode: 'smaller'
99 | ```
100 |
101 | Python code:
102 |
103 | ```python
104 | from firelight import get_visualizer
105 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
106 |
107 | # Load the visualizer, passing the path to the config file. This happens only once, at the start of training.
108 | visualizer = get_visualizer('./configs/example_config_0.yml')
109 |
110 | # Get an example state dictionary, containing the input, target, prediction
111 | states = get_example_states()
112 |
113 | # Call the visualizer
114 | image_grid = visualizer(**states)
115 |
116 | # Log your image however you want
117 | plt.imsave('visualizations/example_visualization.jpg', image_grid.numpy())
118 | ```
119 |
120 | Resulting visualization:
121 |
122 | 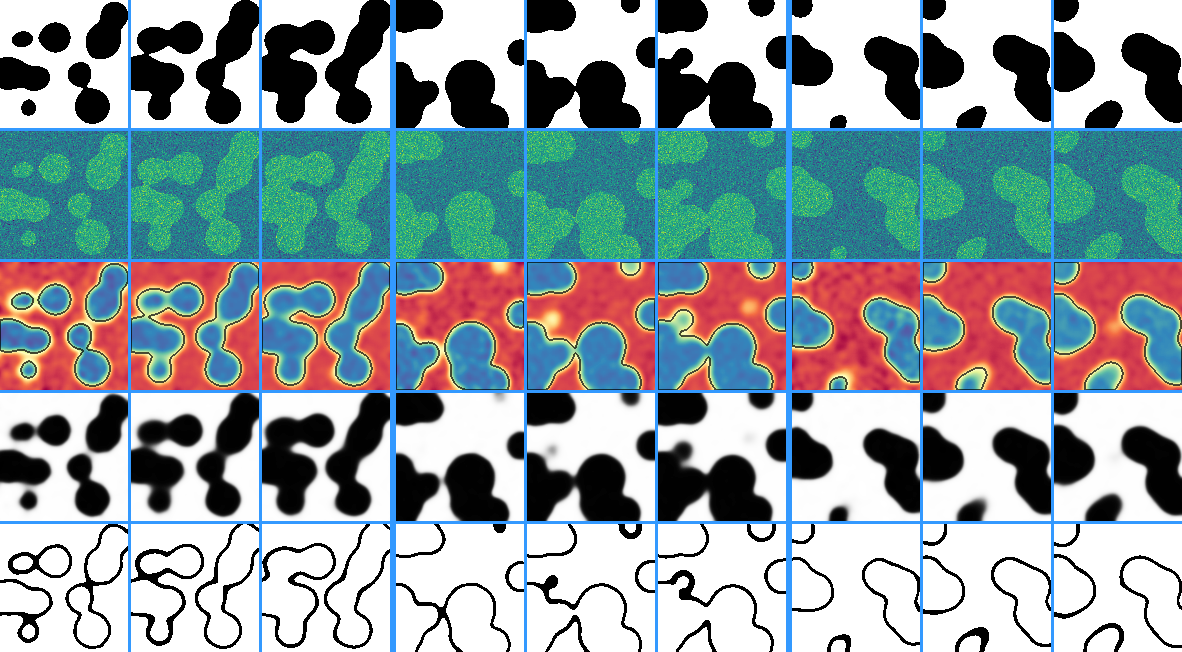
123 |
124 | Many more visualizers are available. Have a look at [visualizers.py](/firelight/visualizers/visualizers.py ) and [container_visualizers.py](/firelight/visualizers/container_visualizers.py) or, for a more condensed list, the imports in [config_parsing.py](/firelight/config_parsing.py).
125 |
126 | ### With Inferno
127 | Firelight can be easily combined with a `TensorboardLogger` from [inferno](https://github.com/inferno-pytorch/inferno).
128 | Simply add an extra line at the start of your config specifying under which tag the visualizations should be logged, and
129 | add a callback to your trainer with `get_visualization_callback` in `firelight/inferno_callback.py`
130 |
131 | Config:
132 | ```yaml
133 | fancy_visualization: # This will be the tag in tensorboard
134 | RowVisualizer:
135 | ...
136 | ```
137 | Python:
138 | ```python
139 | from inferno.trainers.basic import Trainer
140 | from inferno.trainers.callbacks.logging.tensorboard import TensorboardLogger
141 | from firelight.inferno_callback import get_visualization_callback
142 |
143 | # Build trainer and logger
144 | trainer = Trainer(...)
145 | logger = TensorboardLogger(...)
146 | trainer.build_logger(logger, log_directory='path/to/logdir')
147 |
148 | # Register the visualization callback
149 | trainer.register_callback(
150 | get_visualization_callback(
151 | config='path/to/visualization/config'
152 | )
153 | )
154 | ```
155 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Makefile:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Minimal makefile for Sphinx documentation
2 | #
3 |
4 | # You can set these variables from the command line, and also
5 | # from the environment for the first two.
6 | SPHINXOPTS ?=
7 | SPHINXBUILD ?= sphinx-build
8 | SOURCEDIR = .
9 | BUILDDIR = _build
10 |
11 | # Put it first so that "make" without argument is like "make help".
12 | help:
13 | @$(SPHINXBUILD) -M help "$(SOURCEDIR)" "$(BUILDDIR)" $(SPHINXOPTS) $(O)
14 |
15 | clean:
16 | rm -rf $(BUILDDIR)/*
17 | rm -rf auto_examples/
18 |
19 | .PHONY: help Makefile
20 |
21 | # Catch-all target: route all unknown targets to Sphinx using the new
22 | # "make mode" option. $(O) is meant as a shortcut for $(SPHINXOPTS).
23 | %: Makefile
24 | @$(SPHINXBUILD) -M $@ "$(SOURCEDIR)" "$(BUILDDIR)" $(SPHINXOPTS) $(O)
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/conf.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Configuration file for the Sphinx documentation builder.
2 | #
3 | # This file only contains a selection of the most common options. For a full
4 | # list see the documentation:
5 | # https://www.sphinx-doc.org/en/master/usage/configuration.html
6 |
7 | # -- Path setup --------------------------------------------------------------
8 |
9 | # If extensions (or modules to document with autodoc) are in another directory,
10 | # add these directories to sys.path here. If the directory is relative to the
11 | # documentation root, use os.path.abspath to make it absolute, like shown here.
12 | #
13 | import os
14 | import sys
15 | sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath('../'))
16 | sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath('../firelight/'))
17 |
18 | master_doc = 'index'
19 |
20 | # -- Project information -----------------------------------------------------
21 |
22 | project = 'firelight'
23 | copyright = '2019, Roman Remme'
24 | author = 'Roman Remme'
25 |
26 | # The full version, including alpha/beta/rc tags
27 | release = '0.1.0'
28 |
29 |
30 | # -- General configuration ---------------------------------------------------
31 |
32 | # Add any Sphinx extension module names here, as strings. They can be
33 | # extensions coming with Sphinx (named 'sphinx.ext.*') or your custom
34 | # ones.
35 | extensions = [
36 | 'sphinx.ext.autodoc',
37 | 'sphinx.ext.napoleon',
38 | 'sphinx.ext.intersphinx',
39 | 'sphinx.ext.doctest',
40 | 'sphinx.ext.viewcode',
41 | 'sphinx.ext.graphviz',
42 | 'sphinx.ext.inheritance_diagram',
43 | #'sphinx.ext.autosummary',
44 | 'sphinx_gallery.gen_gallery',
45 | 'sphinx_paramlinks',
46 | 'autodocsumm',
47 | 'sphinx_automodapi.automodapi',
48 | ]
49 |
50 | # autodoc_default_options = {
51 | # 'autosummary': True,
52 | # }
53 |
54 | napoleon_include_init_with_doc = True
55 | napoleon_include_special_with_doc = True
56 | napoleon_use_rtype = False
57 | #autosummary_generate = True
58 |
59 | # interphinx configuration
60 | intersphinx_mapping = {
61 | 'numpy': ('http://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/', None),
62 | 'python': ('https://docs.python.org/', None),
63 | 'torch': ('https://pytorch.org/docs/master/', None),
64 | 'sklearn': ('http://scikit-learn.org/stable',
65 | (None, './_intersphinx/sklearn-objects.inv')),
66 | 'inferno': ('http://inferno-pytorch.readthedocs.io/en/latest/', None)
67 | }
68 |
69 | # paths for sphinx gallery
70 | from sphinx_gallery.sorting import ExplicitOrder
71 | sphinx_gallery_conf = {
72 | 'examples_dir': '../examples',
73 | 'gallery_dirs': 'auto_examples',
74 | 'filename_pattern': '/*.py',
75 | 'reference_url': {
76 | # The module you locally document uses None
77 | 'sphinx_gallery': None,
78 | },
79 | 'subsection_order': ExplicitOrder(['../examples/usage',
80 | '../examples/understanding']),
81 | # binder will does not work with readthedocs, see https://github.com/sphinx-gallery/sphinx-gallery/pull/505.
82 | # 'binder': {
83 | # # Required keys
84 | # 'org': 'https://github.com',
85 | # 'repo': 'firelight',
86 | # 'branch': 'docs', # Can be any branch, tag, or commit hash. Use a branch that hosts your docs.
87 | # 'binderhub_url': 'https://mybinder.org', # Any URL of a binderhub deployment. Must be full URL (e.g. https://mybinder.org).
88 | # 'dependencies': 'requirements.txt',
89 | # # Optional keys
90 | # # 'filepath_prefix': 'docs/', # A prefix to prepend to any filepaths in Binder links.
91 | # 'notebooks_dir': 'binder', # Jupyter notebooks for Binder will be copied to this directory (relative to built documentation root).
92 | # 'use_jupyter_lab': False # Whether Binder links should start Jupyter Lab instead of the Jupyter Notebook interface.
93 | # }
94 | }
95 |
96 | doctest_global_setup = """
97 | import torch
98 | from firelight.utils.dim_utils import *
99 | from firelight.config_parsing import *
100 |
101 | from firelight.visualizers.base import *
102 | from firelight.visualizers.visualizers import *
103 | from firelight.visualizers.container_visualizers import *
104 | """
105 |
106 | # Add any paths that contain templates here, relative to this directory.
107 | templates_path = ['_templates']
108 |
109 | # List of patterns, relative to source directory, that match files and
110 | # directories to ignore when looking for source files.
111 | # This pattern also affects html_static_path and html_extra_path.
112 | exclude_patterns = []
113 |
114 |
115 | from unittest.mock import MagicMock
116 |
117 | class Mock(MagicMock):
118 | @classmethod
119 | def __getattr__(cls, name):
120 | return MagicMock()
121 |
122 | MOCK_MODULES = [
123 | 'inferno.trainers.callbacks.base',
124 | 'inferno.trainers.callbacks.logging.tensorboard',
125 | ]
126 | sys.modules.update((mod_name, Mock()) for mod_name in MOCK_MODULES)
127 |
128 | # -- Options for HTML output -------------------------------------------------
129 |
130 | # The theme to use for HTML and HTML Help pages. See the documentation for
131 | # a list of builtin themes.
132 | #
133 | html_theme = 'sphinx_rtd_theme'
134 |
135 | # Add any paths that contain custom static files (such as style sheets) here,
136 | # relative to this directory. They are copied after the builtin static files,
137 | # so a file named "default.css" will overwrite the builtin "default.css".
138 | html_static_path = ['_static']
139 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/environment.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | channels:
2 | - conda-forge
3 | - defaults
4 | dependencies:
5 | - inferno=v0.4.0
6 | - python=3.7.0
7 | - pip:
8 | - sphinx==2.2.0
9 | - sphinx-gallery==0.4.0
10 | - sphinx-rtd-theme==0.4.3
11 |
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/firelight.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | firelight package
2 | =================
3 |
4 | .. toctree::
5 | firelight.visualizers
6 | firelight.utils
7 |
8 | firelight.config\_parsing module
9 | --------------------------------
10 |
11 | .. automodule:: firelight.config_parsing
12 | :members:
13 | :undoc-members:
14 | :show-inheritance:
15 |
16 | firelight.inferno\_callback module
17 | ----------------------------------
18 |
19 | .. automodule:: firelight.inferno_callback
20 | :members:
21 | :undoc-members:
22 | :show-inheritance:
23 |
24 | ..
25 | Module contents
26 | ---------------
27 |
28 | .. automodule:: firelight
29 | :members:
30 | :undoc-members:
31 | :show-inheritance:
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/firelight.utils.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | firelight.utils package
2 | =======================
3 |
4 | ..
5 | Submodules
6 | ----------
7 |
8 | firelight.utils.dim\_utils module
9 | ---------------------------------
10 |
11 | .. automodule:: firelight.utils.dim_utils
12 | :members:
13 | :undoc-members:
14 | :show-inheritance:
15 |
16 | firelight.utils.io\_utils module
17 | --------------------------------
18 |
19 | .. automodule:: firelight.utils.io_utils
20 | :members:
21 | :undoc-members:
22 | :show-inheritance:
23 |
24 |
25 | ..
26 | Module contents
27 | ---------------
28 |
29 | .. automodule:: firelight.utils
30 | :members:
31 | :undoc-members:
32 | :show-inheritance:
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/firelight.visualizers.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | firelight.visualizers package
2 | =============================
3 |
4 | firelight.visualizers.base module
5 | ---------------------------------
6 |
7 | .. automodule:: firelight.visualizers.base
8 | :members:
9 | :undoc-members:
10 | :show-inheritance:
11 |
12 | firelight.visualizers.colorization module
13 | -----------------------------------------
14 |
15 | .. automodule:: firelight.visualizers.colorization
16 | :members:
17 | :undoc-members:
18 | :show-inheritance:
19 |
20 | firelight.visualizers.container\_visualizers module
21 | ---------------------------------------------------
22 |
23 | .. automodule:: firelight.visualizers.container_visualizers
24 | :members:
25 | :undoc-members:
26 | :show-inheritance:
27 |
28 | firelight.visualizers.visualizers module
29 | ----------------------------------------
30 |
31 | .. automodule:: firelight.visualizers.visualizers
32 | :members:
33 | :undoc-members:
34 | :show-inheritance:
35 |
36 | ..
37 | Module contents
38 | ---------------
39 |
40 | .. automodule:: firelight.visualizers
41 | :members:
42 | :undoc-members:
43 | :show-inheritance:
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/index.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. firelight documentation master file, created by
2 | sphinx-quickstart on Tue Oct 29 13:16:38 2019.
3 | You can adapt this file completely to your liking, but it should at least
4 | contain the root `toctree` directive.
5 |
6 | Welcome to firelight's documentation!
7 | =====================================
8 |
9 | .. toctree::
10 | :maxdepth: 3
11 | :caption: Contents:
12 |
13 | introduction
14 | list_of_visualizers
15 | auto_examples/index
16 | firelight
17 |
18 |
19 | Indices and tables
20 | ==================
21 |
22 | * :ref:`genindex`
23 | * :ref:`modindex`
24 | * :ref:`search`
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/introduction.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Introduction
2 | ============
3 |
4 | Firelight is a package for the visualization of `pytorch `_ tensors as images.
5 | It uses a flexible way of handling tensor shapes, which allows visualization of data
6 | of arbitrary dimensionality (See :mod:`firelight.utils.dim_utils` for details).
7 |
8 | This documentation is work in progress, as is the package itself.
9 |
10 | For now, have a look at the `Examples `_,
11 | check out the currently available `visualizers `_
12 | or read the `docstrings `_.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/list_of_visualizers.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | List of Visualizers
2 | -------------------
3 |
4 | .. currentmodule:: firelight.visualizers.base
5 |
6 | The following non-container visualizers are currently available.
7 | They all derive from :class:`BaseVisualizer`.
8 |
9 | ..
10 | inheritance-diagram:: firelight.visualizers.visualizers
11 | :top-classes: firelight.visualizers.base.BaseVisualizer
12 | :parts: 1
13 |
14 | ..
15 | inheritance-diagram:: firelight.visualizers.container_visualizers
16 | :top-classes: firelight.visualizers.base.ContainerVisualizer
17 | :parts: 1
18 |
19 | .. automodsumm:: firelight.visualizers.visualizers
20 | :classes-only:
21 | :skip: PCA, TSNE, BaseVisualizer
22 |
23 | .. currentmodule:: firelight.visualizers.base
24 |
25 | These are the available visualizers combining multiple visualizations.
26 | Their base class is the :class:`ContainerVisualizer`.
27 |
28 | .. automodsumm:: firelight.visualizers.container_visualizers
29 | :classes-only:
30 | :skip: ContainerVisualizer
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/make.bat:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | @ECHO OFF
2 |
3 | pushd %~dp0
4 |
5 | REM Command file for Sphinx documentation
6 |
7 | if "%SPHINXBUILD%" == "" (
8 | set SPHINXBUILD=sphinx-build
9 | )
10 | set SOURCEDIR=.
11 | set BUILDDIR=_build
12 |
13 | if "%1" == "" goto help
14 |
15 | %SPHINXBUILD% >NUL 2>NUL
16 | if errorlevel 9009 (
17 | echo.
18 | echo.The 'sphinx-build' command was not found. Make sure you have Sphinx
19 | echo.installed, then set the SPHINXBUILD environment variable to point
20 | echo.to the full path of the 'sphinx-build' executable. Alternatively you
21 | echo.may add the Sphinx directory to PATH.
22 | echo.
23 | echo.If you don't have Sphinx installed, grab it from
24 | echo.http://sphinx-doc.org/
25 | exit /b 1
26 | )
27 |
28 | %SPHINXBUILD% -M %1 %SOURCEDIR% %BUILDDIR% %SPHINXOPTS% %O%
29 | goto end
30 |
31 | :help
32 | %SPHINXBUILD% -M help %SOURCEDIR% %BUILDDIR% %SPHINXOPTS% %O%
33 |
34 | :end
35 | popd
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/requirements.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | sphinx==2.2.0
2 | sphinx-rtd-theme==0.4.3
3 | sphinx-gallery==0.4.0
4 | sphinx-paramlinks==0.3.7
5 | autodocsumm==0.1.11
6 | sphinx-automodapi==0.12
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/README.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Examples
2 | ========
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/example_visualization.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/inferno-pytorch/firelight/796328f93494248e6a4cf238ea36ac4eeb7fc9b8/examples/example_visualization.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/understanding/README.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Understanding Firelight
2 | -----------------------
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/understanding/specfunction_example.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | SpecFunction Example
3 | ====================
4 |
5 | An example demonstrating the functionality of the :class:`SpecFunction` class.
6 | """
7 |
8 | import torch
9 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
10 | from firelight.utils.dim_utils import SpecFunction
11 |
12 | ##############################################################################
13 | # Let us define a function that takes in two arrays and masks one with the
14 | # other:
15 | #
16 |
17 |
18 | class MaskArray(SpecFunction):
19 | def __init__(self, **super_kwargs):
20 | super(MaskArray, self).__init__(
21 | in_specs={'mask': 'B', 'array': 'BC'},
22 | out_spec='BC',
23 | **super_kwargs
24 | )
25 |
26 | def internal(self, mask, array, value=0.0):
27 | # The shapes are
28 | # mask: (B)
29 | # array: (B, C)
30 | # as specified in the init.
31 |
32 | result = array.clone()
33 | result[mask == 0] = value
34 |
35 | # the result has shape (B, C), as specified in the init.
36 | return result
37 |
38 |
39 | ##############################################################################
40 | # We can now apply the function on inputs of arbitrary shape, such as images.
41 | # The reshaping involved gets taken care of automatically:
42 | #
43 |
44 | W, H = 20, 10
45 | inputs = {
46 | 'array': (torch.rand(H, W, 3), 'HWC'),
47 | 'mask': (torch.randn(H, W) > 0, 'HW'),
48 | 'value': 0,
49 | 'out_spec': 'HWC',
50 | }
51 |
52 | maskArrays = MaskArray()
53 | result = maskArrays(**inputs)
54 | print('output shape:', result.shape)
55 |
56 | plt.imshow(result)
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/usage/README.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Using Firelight
2 | ---------------
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/usage/example_config_0.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | RowVisualizer: # stack the outputs of child visualizers as rows of an image grid
2 | input_mapping:
3 | global: [B: ':3', D: '0:9:3'] # Show only 3 samples in each batch ('B'), and some slices along depth ('D').
4 | prediction: [C: '0'] # Show only the first channel of the prediction
5 |
6 | pad_value: [0.2, 0.6, 1.0] # RGB color of separating lines
7 | pad_width: {B: 6, H: 0, W: 0, rest: 3} # Padding for batch ('B'), height ('H'), width ('W') and other dimensions.
8 |
9 | visualizers:
10 | # First row: Ground truth
11 | - IdentityVisualizer:
12 | input: 'target' # show the target
13 |
14 | # Second row: Raw input
15 | - IdentityVisualizer:
16 | input: ['input', C: '0'] # Show the first channel ('C') of the input.
17 | cmap: viridis # Name of a matplotlib colormap.
18 |
19 | # Third row: Prediction with segmentation boarders on top.
20 | - OverlayVisualizer:
21 | visualizers:
22 | - CrackedEdgeVisualizer: # Show borders of target segmentation
23 | input_mapping:
24 | segmentation: 'target'
25 | width: 2
26 | opacity: 0.7 # Make output only partially opaque.
27 | - IdentityVisualizer: # prediction
28 | input_mapping:
29 | tensor: 'prediction'
30 | cmap: Spectral
31 |
32 | # Fourth row: Foreground probability, calculated by sigmoid on prediction
33 | - IdentityVisualizer:
34 | input_mapping: # the input to the visualizer can also be specified as a dict under the key 'input mapping'.
35 | tensor: ['prediction', pre: 'sigmoid'] # Apply sigmoid function from torch.nn.functional before visualize.
36 | value_range: [0, 1] # Scale such that 0 is white and 1 is black. If not specified, whole range is used.
37 |
38 | # Fifth row: Visualize where norm of prediction is smaller than 2
39 | - ThresholdVisualizer:
40 | input_mapping:
41 | tensor:
42 | NormVisualizer: # Use the output of NormVisualizer as the input to ThresholdVisualizer
43 | input: 'prediction'
44 | colorize: False
45 | threshold: 2
46 | mode: 'smaller'
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/usage/realistic_example.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Realistic Example
3 | =================
4 |
5 | A close-to-real-world example of how to use firelight.
6 | """
7 |
8 | ##############################################################################
9 | # First of all, let us get some mock data to visualize.
10 | # We generate the following tensors:
11 | #
12 | # - :code:`input` of shape :math:`(B, D, H, W)`, some noisy raw data,
13 | # - :code:`target` of shape :math:`(B, D, H, W)`, the ground truth foreground
14 | # background segmentation,
15 | # - :code:`prediction` of shape :math:`(B, D, H, W)`, the predicted foreground
16 | # probability,
17 | # - :code:`embedding` of shape :math:`(B, D, C, H, W)`, a tensor with an
18 | # additional channel dimension, as for example intermediate activations of a
19 | # neural network.
20 | #
21 |
22 | import numpy as np
23 | import torch
24 | from skimage.data import binary_blobs
25 | from skimage.filters import gaussian
26 |
27 |
28 | def get_example_states():
29 | # generate some toy foreground/background segmentation
30 | batchsize = 5 # we will only visualize 3 of the 5samples
31 | size = 64
32 | target = np.stack([binary_blobs(length=size, n_dim=3, blob_size_fraction=0.25, volume_fraction=0.5, seed=i)
33 | for i in range(batchsize)], axis=0).astype(np.float32)
34 |
35 | # generate toy raw data as noisy target
36 | sigma = 0.5
37 | input = target + np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=sigma, size=target.shape)
38 |
39 | # compute mock prediction as gaussian smoothing of input data
40 | prediction = np.stack([gaussian(sample, sigma=3, truncate=2.0) for sample in input], axis=0)
41 | prediction = 10 * (prediction - 0.5)
42 |
43 | # compute mock embedding (if you need an image with channels for testing)
44 | embedding = np.random.randn(prediction.shape[0], 16, *(prediction.shape[1:]))
45 |
46 | # put input, target, prediction in dictionary, convert to torch.Tensor, add dimensionality labels ('specs')
47 | state_dict = {
48 | 'input': (torch.Tensor(input).float(), 'BDHW'), # Dimensions are B, D, H, W = Batch, Depth, Height, Width
49 | 'target': (torch.Tensor(target).float(), 'BDHW'),
50 | 'prediction': (torch.Tensor(prediction).float(), 'BDHW'),
51 | 'embedding': (torch.Tensor(embedding).float(), 'BCDHW'),
52 | }
53 | return state_dict
54 |
55 |
56 | # Get the example state dictionary, containing the input, target, prediction.
57 | states = get_example_states()
58 |
59 | for name, (tensor, spec) in states.items():
60 | print(f'{name}: shape {tensor.shape}, spec {spec}')
61 |
62 | ##############################################################################
63 | # The best way to construct a complex visualizer to show all the tensors in a
64 | # structured manner is to use a configuration file.
65 | #
66 | # We will use the following one:
67 | #
68 | # .. literalinclude:: ../../../examples/usage/example_config_0.yml
69 | # :language: yaml
70 | #
71 | # Lets load the file and construct the visualizer using :code:`get_visualizer`:
72 |
73 | from firelight import get_visualizer
74 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
75 |
76 | # Load the visualizer, passing the path to the config file. This happens only once, at the start of training.
77 | visualizer = get_visualizer('example_config_0.yml')
78 |
79 | ##############################################################################
80 | # Now we can finally apply it on out mock tensors to get the visualization
81 |
82 | # Call the visualizer.
83 | image_grid = visualizer(**states)
84 |
85 | # Log your image however you want.
86 | plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
87 | plt.imshow(image_grid.numpy())
88 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/firelight/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .config_parsing import get_visualizer
2 |
3 | __version__ = '0.2.1'
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/firelight/config_parsing.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .visualizers.base import BaseVisualizer, ContainerVisualizer
2 | from .utils.io_utils import yaml2dict
3 | from pydoc import locate
4 | import logging
5 | import sys
6 |
7 | # List of available visualizers (without container visualizers)
8 | from .visualizers.visualizers import \
9 | IdentityVisualizer, \
10 | PcaVisualizer, \
11 | MaskedPcaVisualizer, \
12 | TsneVisualizer, \
13 | UmapVisualizer, \
14 | SegmentationVisualizer, \
15 | InputVisualizer, \
16 | TargetVisualizer, \
17 | PredictionVisualizer, \
18 | MSEVisualizer, \
19 | RGBVisualizer, \
20 | MaskVisualizer, \
21 | ThresholdVisualizer, \
22 | ImageVisualizer, \
23 | NormVisualizer, \
24 | DiagonalSplitVisualizer, \
25 | CrackedEdgeVisualizer, \
26 | UpsamplingVisualizer, \
27 | SemanticVisualizer, \
28 | DifferenceVisualizer
29 |
30 | # List of available container visualizers (visualizers acting on outputs of child visualizers)
31 | from .visualizers.container_visualizers import \
32 | ImageGridVisualizer, \
33 | RowVisualizer, \
34 | ColumnVisualizer, \
35 | OverlayVisualizer, \
36 | RiffleVisualizer, \
37 | StackVisualizer, \
38 | AverageVisualizer
39 |
40 |
41 | # set up logging
42 | logging.basicConfig(format='[+][%(asctime)-15s][VISUALIZATION]'
43 | ' %(message)s',
44 | stream=sys.stdout,
45 | level=logging.INFO)
46 | parsing_logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
47 |
48 |
49 | def get_single_key_value_pair(d):
50 | """
51 | Returns the key and value of a one element dictionary, checking that it actually has only one element
52 |
53 | Parameters
54 | ----------
55 | d : dict
56 |
57 | Returns
58 | -------
59 | tuple
60 |
61 | """
62 | assert isinstance(d, dict), f'{d}'
63 | assert len(d) == 1, f'{d}'
64 | return list(d.keys())[0], list(d.values())[0]
65 |
66 |
67 | def get_visualizer_class(name):
68 | """
69 | Parses the class of a visualizer from a String. If the name is not found in globals(), tries to import it.
70 |
71 | Parameters
72 | ----------
73 | name : str
74 | Name of a visualization class imported above, or dotted path to one (e.g. your custom visualizer in a different
75 | library).
76 |
77 | Returns
78 | -------
79 | type or None
80 |
81 | """
82 | if name in globals(): # visualizer is imported above
83 | return globals().get(name)
84 | else: # dotted path is given
85 | visualizer = locate(name)
86 | assert visualizer is not None, f'Could not find visualizer "{name}".'
87 | assert issubclass(visualizer, BaseVisualizer), f'"{visualizer}" is no visualizer'
88 |
89 |
90 | def get_visualizer(config, indentation=0):
91 | """
92 | Parses a yaml configuration file to construct a visualizer.
93 |
94 | Parameters
95 | ----------
96 | config : str or dict or BaseVisualizer
97 | Either path to yaml configuration file or dictionary (as constructed by loading such a file).
98 | If already visualizer, it is just returned.
99 | indentation : int, optional
100 | How far logging messages arising here should be indented.
101 | Returns
102 | -------
103 | BaseVisualizer
104 |
105 | """
106 | if isinstance(config, BaseVisualizer): # nothing to do here
107 | return config
108 | # parse config to dict (does nothing if already dict)
109 | config = yaml2dict(config)
110 | # name (or dotted path) and kwargs of visualizer have to be specified as key and value of one element dictionary
111 | name, kwargs = get_single_key_value_pair(config)
112 | # get the visualizer class from its name
113 | visualizer = get_visualizer_class(name)
114 | parsing_logger.info(f'Parsing {" "*indentation}{visualizer.__name__}')
115 | if issubclass(visualizer, ContainerVisualizer): # container visualizer: parse sub-visualizers first
116 | child_visualizer_config = kwargs['visualizers']
117 | assert isinstance(child_visualizer_config, (list, dict)), \
118 | f'{child_visualizer_config}, {type(child_visualizer_config)}'
119 | if isinstance(child_visualizer_config, dict): # if dict, convert do list
120 | child_visualizer_config = [{key: value} for key, value in child_visualizer_config.items()]
121 | child_visualizers = []
122 | for c in child_visualizer_config:
123 | v = get_visualizer(c, indentation + 1)
124 | assert isinstance(v, BaseVisualizer), f'Could not parse visualizer: {c}'
125 | child_visualizers.append(v)
126 | kwargs['visualizers'] = child_visualizers
127 |
128 | # TODO: add example with nested visualizers
129 | def parse_if_visualizer(config):
130 | if not (isinstance(config, dict) and len(config) == 1):
131 | return None
132 | # check if the key is the name of a visualizer
133 | try:
134 | get_visualizer_class(iter(config.items()).__next__()[0])
135 | except AssertionError:
136 | return None
137 | # parse the visualizer
138 | return get_visualizer(config, indentation+1)
139 |
140 | # check if any input in 'input_mapping' should be parsed as visualizer
141 | input_mapping = kwargs.get('input_mapping', {})
142 | for map_to, map_from in input_mapping.items():
143 | nested_visualizer = parse_if_visualizer(map_from)
144 | if nested_visualizer is not None:
145 | input_mapping[map_to] = nested_visualizer
146 |
147 | # check if 'input' should be parsed as visualizer
148 | if kwargs.get('input') is not None:
149 | nested_visualizer = parse_if_visualizer(kwargs.get('input'))
150 | if nested_visualizer is not None:
151 | kwargs['input'] = nested_visualizer
152 |
153 | return visualizer(**kwargs)
154 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/firelight/inferno_callback.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from inferno.trainers.callbacks.base import Callback
2 | from inferno.trainers.callbacks.logging.tensorboard import TensorboardLogger
3 | from .utils.io_utils import yaml2dict
4 | from .config_parsing import get_visualizer
5 | import torch
6 | import logging
7 | import sys
8 |
9 | # Set up logger
10 | logging.basicConfig(format='[+][%(asctime)-15s][VISUALIZATION]'
11 | ' %(message)s',
12 | stream=sys.stdout,
13 | level=logging.INFO)
14 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
15 |
16 |
17 | def _remove_alpha(tensor, background_brightness=1):
18 | return torch.ones_like(tensor[..., :3]) * background_brightness * (1-tensor[..., 3:4]) + \
19 | tensor[..., :3] * tensor[..., 3:4]
20 |
21 |
22 | class VisualizationCallback(Callback):
23 | # Autodoc does not pick up VisualizationCallback, since Callback is mocked.
24 |
25 | VISUALIZATION_PHASES = ['training', 'validation']
26 | TRAINER_STATE_PREFIXES = ('training', 'validation')
27 |
28 | def __init__(self, logging_config, log_during='all'):
29 | super(VisualizationCallback, self).__init__()
30 | assert isinstance(logging_config, dict)
31 | self.logging_config = logging_config # dictionary containing the visualizers as values with their names as keys
32 |
33 | # parse phases during which to log the individual visualizers
34 | for i, name in enumerate(logging_config):
35 | phases = logging_config[name].get('log_during', log_during)
36 | if isinstance(phases, str):
37 | if phases == 'all':
38 | phases = self.VISUALIZATION_PHASES
39 | else:
40 | phases = [phases]
41 | assert isinstance(phases, (list, tuple)), f'{phases}, {type(phases)}'
42 | assert all(phase in self.VISUALIZATION_PHASES for phase in phases), \
43 | f'Some phase not recognized: {phases}. Valid phases: {self.VISUALIZATION_PHASES}'
44 | logging_config[name]['log_during'] = phases
45 |
46 | # parameters specifying logging iterations
47 | # self.logged_last = {'train': None, 'val': None}
48 |
49 | def get_trainer_states(self):
50 | current_pre = self.TRAINER_STATE_PREFIXES[0 if self.trainer.model.training else 1]
51 | ignore_pre = self.TRAINER_STATE_PREFIXES[1 if self.trainer.model.training else 0]
52 | result = {}
53 | for key in self.trainer._state:
54 | if key.startswith(ignore_pre):
55 | continue
56 | state = self.trainer.get_state(key)
57 | if key.startswith(current_pre):
58 | key = '_'.join(key.split('_')[1:]) # remove current prefix
59 | if isinstance(state, torch.Tensor):
60 | state = state.cpu().detach().clone().float() # logging is done on the cpu, all tensors are floats
61 | if isinstance(state, (tuple, list)) and all([isinstance(t, torch.Tensor) for t in state]):
62 | state = list(t.cpu().detach().clone().float() for t in state)
63 |
64 | result[key] = state
65 | return result
66 |
67 | def do_logging(self, phase, **_):
68 | assert isinstance(self.trainer.logger, TensorboardLogger)
69 | writer = self.trainer.logger.writer
70 | pre = 'training' if self.trainer.model.training else 'validation'
71 | for name, config in self.logging_config.items():
72 | if phase not in config['log_during']: # skip visualizer if logging not requested for this phase
73 | continue
74 | visualizer = config['visualizer']
75 | logger.info(f'Logging now: {name}')
76 | image = _remove_alpha(visualizer(**self.get_trainer_states())).permute(2, 0, 1) # to [Color, Height, Width]
77 | writer.add_image(tag=pre+'_'+name, img_tensor=image, global_step=self.trainer.iteration_count)
78 | logger.info(f'Logging finished')
79 |
80 | def end_of_training_iteration(self, **_):
81 | last_match_value = self.trainer.logger.log_images_every._last_match_value
82 | log_now = self.trainer.logger.log_images_every.match(
83 | iteration_count=self.trainer.iteration_count,
84 | epoch_count=self.trainer.epoch_count,
85 | persistent=False)
86 | self.trainer.logger.log_images_every._last_match_value = last_match_value
87 | if log_now:
88 | self.do_logging('training')
89 |
90 | def end_of_validation_run(self, **_):
91 | self.do_logging('validation')
92 |
93 |
94 | def get_visualization_callback(config):
95 | """
96 | Gets an :mod:`inferno` callback for logging of firelight visualizations.
97 |
98 | Uses the :class:`inferno.trainers.basic.Trainer` state dictionary as input for the visualizers.
99 |
100 | The logging frequency is taken from the trainer's
101 | :class:`inferno.trainers.callbacks.logging.tensorboard.TensorboardLogger`.
102 |
103 |
104 |
105 | Parameters
106 | ----------
107 | config : str or dict
108 | If :obj:`str`, will be converted to :obj:`dict` using `pyyaml
109 | `_.
110 |
111 | If :obj:`dict`, the keys are the tags under which the visualizations
112 | will be saved in Tensorboard, while the values are the configuration
113 | dictionaries to get the visualizers producing these visualizations,
114 | using :func:`firelight.config_parsing.get_visualizer`.
115 |
116 | Returns
117 | -------
118 | :class:`inferno.trainers.callbacks.base.Callback`
119 |
120 | Examples
121 | --------
122 | The structure of a configuration file could look like this:
123 |
124 | .. code:: yaml
125 |
126 | # visualize model predictions
127 | predictions:
128 | RowVisualizer:
129 | ...
130 |
131 | # visualize something else
132 | fancy_visualization:
133 | RowVisualizer:
134 | ...
135 |
136 | This configuration would produce images that are saved under the tags :code:`predictions` and
137 | :code:`fancy_visualization` in Tensorboard.
138 |
139 | """
140 | config = yaml2dict(config)
141 | logging_config = {}
142 | default_phases = config.pop('log_during', 'all')
143 | for name, kwargs in config.items():
144 | log_during = kwargs.pop('log_during', default_phases)
145 | visualizer = get_visualizer(kwargs)
146 | logging_config[name] = dict(visualizer=visualizer, log_during=log_during)
147 | callback = VisualizationCallback(logging_config)
148 | return callback
149 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/firelight/utils/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/inferno-pytorch/firelight/796328f93494248e6a4cf238ea36ac4eeb7fc9b8/firelight/utils/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/firelight/utils/dim_utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import torch
3 | from copy import copy
4 | from collections import OrderedDict
5 |
6 | # in this library, 'spec' always stands for a list of dimension names.
7 | # eg. ['B', 'C', 'H', 'W'] standing for [Batch, Channel, Height, Width]
8 |
9 |
10 | def join_specs(*specs):
11 | """
12 | Returns a list of dimension names which includes each dimension in any of the supplied specs exactly once, ordered
13 | by their occurrence in specs.
14 |
15 | Parameters
16 | ----------
17 | specs : list
18 | List of lists of dimension names to be joined
19 |
20 | Returns
21 | -------
22 | list
23 |
24 | Examples
25 | --------
26 |
27 | >>> join_specs(['B', 'C'], ['B', 'H', 'W'])
28 | ['B', 'C', 'H', 'W']
29 | >>> join_specs(['B', 'C'], ['H', 'B', 'W'])
30 | ['B', 'C', 'H', 'W']
31 |
32 | """
33 | if len(specs) != 2:
34 | return join_specs(specs[0], join_specs(*specs[1:]))
35 | spec1, spec2 = specs
36 | result = copy(spec1)
37 | for d in spec2:
38 | if d not in result:
39 | result.append(d)
40 | return result
41 |
42 |
43 | def extend_dim(tensor, in_spec, out_spec, return_spec=False):
44 | """
45 | Adds extra (length 1) dimensions to the input tensor such that it has all the dimensions present in out_spec.
46 |
47 | Parameters
48 | ----------
49 | tensor : torch.Tensor
50 | in_spec : list
51 | spec of the input tensor
52 | out_spec : list
53 | spec of the output tensor
54 | return_spec : bool, optional
55 | Weather the output should consist of a tuple containing the output tensor and the resulting spec, or only the
56 | former.
57 |
58 | Returns
59 | -------
60 | torch.Tensor or tuple
61 |
62 | Examples
63 | --------
64 |
65 | >>> tensor, out_spec = extend_dim(
66 | ... torch.empty(2, 3),
67 | ... ['A', 'B'], ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'],
68 | ... return_spec=True
69 | ... )
70 | >>> print(tensor.shape)
71 | torch.Size([2, 3, 1, 1])
72 | >>> print(out_spec)
73 | ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']
74 |
75 | """
76 | assert all(d in out_spec for d in in_spec)
77 | i = 0
78 | for d in out_spec:
79 | if d not in in_spec:
80 | tensor = tensor.unsqueeze(i)
81 | i += 1
82 | if return_spec:
83 | new_spec = out_spec + [d for d in in_spec if d not in out_spec]
84 | return tensor, new_spec
85 | else:
86 | return tensor
87 |
88 |
89 | def moving_permutation(length, origin, goal):
90 | """
91 | Returns a permutation moving the element at position origin to the position goal (in the format requested by
92 | torch.Tensor.permute)
93 |
94 | Parameters
95 | ----------
96 | length : int
97 | length of the sequence to be permuted
98 | origin : int
99 | position of the element to be moved
100 | goal : int
101 | position the element should end up after the permutation
102 |
103 | Returns
104 | -------
105 | :obj:`list` of :obj:`int`
106 |
107 | Examples
108 | --------
109 |
110 | >>> moving_permutation(length=5, origin=1, goal=3)
111 | [0, 2, 3, 1, 4]
112 | >>> moving_permutation(length=5, origin=3, goal=1)
113 | [0, 3, 1, 2, 4]
114 |
115 | """
116 | result = []
117 | for i in range(length):
118 | if i == goal:
119 | result.append(origin)
120 | elif (i < goal and i < origin) or (i > goal and i > origin):
121 | result.append(i)
122 | elif goal < i <= origin:
123 | result.append(i-1)
124 | elif origin <= i < goal:
125 | result.append(i+1)
126 | else:
127 | assert False
128 | return result
129 |
130 |
131 | def collapse_dim(tensor, to_collapse, collapse_into=None, spec=None, return_spec=False):
132 | """
133 | Reshapes the input tensor, collapsing one dimension into another. This is achieved by
134 |
135 | - first permuting the tensors dimensions such that the dimension to collapse is next to the one to collapse it into,
136 | - reshaping the tensor, making one dimension out of the to affected.
137 |
138 | Parameters
139 | ----------
140 | tensor : torch.Tensor
141 | to_collapse : int or str
142 | Dimension to be collapsed.
143 | collapse_into : int or str, optional
144 | Dimension into which the other will be collapsed.
145 | spec : list, optional
146 | Name of dimensions of input tensor. If not specified, will be taken to be range(len(tensor.shape())).
147 | return_spec : bool, optional
148 | Weather the output should consist of a tuple containing the output tensor and the resulting spec, or only the
149 | former.
150 |
151 | Returns
152 | -------
153 | torch.Tensor or tuple
154 |
155 | Examples
156 | --------
157 |
158 | >>> tensor = torch.Tensor([[1, 2, 3], [10, 20, 30]]).long()
159 | >>> collapse_dim(tensor, to_collapse=1, collapse_into=0)
160 | tensor([ 1, 2, 3, 10, 20, 30])
161 | >>> collapse_dim(tensor, to_collapse=0, collapse_into=1)
162 | tensor([ 1, 10, 2, 20, 3, 30])
163 |
164 | """
165 | spec = list(range(len(tensor.shape))) if spec is None else spec
166 | assert to_collapse in spec, f'{to_collapse}, {spec}'
167 | i_from = spec.index(to_collapse)
168 | if collapse_into is None:
169 | i_delete = i_from
170 | assert tensor.shape[i_delete] == 1, f'{to_collapse}, {tensor.shape[i_delete]}'
171 | tensor = tensor.squeeze(i_delete)
172 | else:
173 | assert collapse_into in spec, f'{collapse_into}, {spec}'
174 | i_to = spec.index(collapse_into)
175 | if i_to != i_from:
176 | i_to = i_to + 1 if i_from > i_to else i_to
177 | tensor = tensor.permute(moving_permutation(len(spec), i_from, i_to))
178 | new_shape = tensor.shape[:i_to-1] + (tensor.shape[i_to-1] * tensor.shape[i_to],) + tensor.shape[i_to+1:]
179 | tensor = tensor.contiguous().view(new_shape)
180 | else:
181 | i_from = -1 # suppress deletion of spec later
182 | if return_spec:
183 | new_spec = [spec[i] for i in range(len(spec)) if i is not i_from]
184 | return tensor, new_spec
185 | else:
186 | return tensor
187 |
188 |
189 | def convert_dim(tensor, in_spec, out_spec=None, collapsing_rules=None, uncollapsing_rules=None,
190 | return_spec=False, return_inverse_kwargs=False):
191 | """
192 | Convert the dimensionality of tensor from in_spec to out_spec.
193 |
194 | Parameters
195 | ----------
196 | tensor : torch.Tensor
197 | in_spec : list
198 | Name of dimensions of the input tensor.
199 | out_spec : list, optional
200 | Name of dimensions that the output tensor will have.
201 | collapsing_rules : :obj:`list` of :obj:`tuple`, optional
202 | List of two element tuples. The first dimension in a tuple will be collapsed into the second (dimensions given
203 | by name).
204 | uncollapsing_rules : :obj:`list` of :obj:`tuple`, optional
205 | List of three element tuples. The first element of each specifies the dimension to 'uncollapse' (=split into
206 | two). The second element specifies the size of the added dimension, and the third its name.
207 | return_spec : bool, optional
208 | Weather the output should consist of a tuple containing the output tensor and the resulting spec, or only the
209 | former.
210 | return_inverse_kwargs : bool, optional
211 | If true, a dictionary containing arguments to reverse the conversion (with this function) are added to the
212 | output tuple.
213 |
214 | Returns
215 | -------
216 | torch.Tensor or tuple
217 |
218 | Examples
219 | --------
220 |
221 | >>> tensor = torch.Tensor([[1, 2, 3], [10, 20, 30]]).long()
222 | >>> convert_dim(tensor, ['A', 'B'], ['B', 'A']) # doctest: +NORMALIZE_WHITESPACE
223 | tensor([[ 1, 10],
224 | [ 2, 20],
225 | [ 3, 30]])
226 | >>> convert_dim(tensor, ['A', 'B'], collapsing_rules=[('A', 'B')]) # doctest: +NORMALIZE_WHITESPACE
227 | tensor([ 1, 10, 2, 20, 3, 30])
228 | >>> convert_dim(tensor, ['A', 'B'], collapsing_rules=[('B', 'A')]) # doctest: +NORMALIZE_WHITESPACE
229 | tensor([ 1, 2, 3, 10, 20, 30])
230 | >>> convert_dim(tensor.flatten(), ['A'], ['A', 'B'], uncollapsing_rules=[('A', 3, 'B')]) # doctest: +NORMALIZE_WHITESPACE
231 | tensor([[ 1, 2, 3],
232 | [10, 20, 30]])
233 |
234 | """
235 | assert len(tensor.shape) == len(in_spec), f'{tensor.shape}, {in_spec}'
236 |
237 | to_collapse = [] if collapsing_rules is None else [rule[0] for rule in collapsing_rules]
238 | collapse_into = [] if collapsing_rules is None else [rule[1] for rule in collapsing_rules]
239 | uncollapsed_dims = []
240 |
241 | temp_spec = copy(in_spec)
242 | # uncollapse as specified
243 | if uncollapsing_rules is not None:
244 | for rule in uncollapsing_rules:
245 | if isinstance(rule, tuple):
246 | rule = {
247 | 'to_uncollapse': rule[0],
248 | 'uncollapsed_length': rule[1],
249 | 'uncollapse_into': rule[2]
250 | }
251 | uncollapsed_dims.append(rule['uncollapse_into'])
252 | tensor, temp_spec = uncollapse_dim(tensor, spec=temp_spec, **rule, return_spec=True)
253 |
254 | # construct out_spec if not given
255 | if out_spec is None:
256 | # print([d for d in in_spec if d not in to_collapse], collapse_into, uncollapsed_dims)
257 | out_spec = join_specs([d for d in in_spec if d not in to_collapse], collapse_into, uncollapsed_dims)
258 |
259 | # bring tensor's spec in same order as out_spec, with dims not present in out_spec at the end
260 | joined_spec = join_specs(out_spec, in_spec)
261 | order = list(np.argsort([joined_spec.index(d) for d in temp_spec]))
262 | tensor = tensor.permute(order)
263 | temp_spec = [temp_spec[i] for i in order]
264 |
265 | # unsqueeze to match out_spec
266 | tensor = extend_dim(tensor, temp_spec, joined_spec)
267 | temp_spec = joined_spec
268 |
269 | # apply dimension collapsing rules
270 | inverse_uncollapsing_rules = [] # needed if inverse is requested
271 | if collapsing_rules is not None:
272 | # if default to collapse into is specified, add appropriate rules at the end
273 | if 'rest' in to_collapse:
274 | ind = to_collapse.index('rest')
275 | collapse_rest_into = collapsing_rules.pop(ind)[1]
276 | for d in temp_spec:
277 | if d not in out_spec:
278 | collapsing_rules.append((d, collapse_rest_into))
279 | # do collapsing
280 | for rule in collapsing_rules:
281 | if rule[0] in temp_spec:
282 | inverse_uncollapsing_rules.append({
283 | 'to_uncollapse': rule[1],
284 | 'uncollapsed_length': tensor.shape[temp_spec.index(rule[0])],
285 | 'uncollapse_into': rule[0]
286 | })
287 | # print(f'{tensor.shape}, {temp_spec}, {out_spec}')
288 | tensor, temp_spec = collapse_dim(tensor, spec=temp_spec, to_collapse=rule[0], collapse_into=rule[1],
289 | return_spec=True)
290 |
291 | # drop trivial dims not in out_spec
292 | for d in reversed(temp_spec):
293 | if d not in out_spec:
294 | tensor, temp_spec = collapse_dim(tensor, to_collapse=d, spec=temp_spec, return_spec=True)
295 |
296 | assert all(d in out_spec for d in temp_spec), \
297 | f'{temp_spec}, {out_spec}: please provide appropriate collapsing rules'
298 | tensor = extend_dim(tensor, temp_spec, out_spec)
299 |
300 | result = [tensor]
301 | if return_spec:
302 | result.append(temp_spec)
303 | if return_inverse_kwargs:
304 | inverse_kwargs = {
305 | 'in_spec': out_spec,
306 | 'out_spec': in_spec,
307 | 'uncollapsing_rules': inverse_uncollapsing_rules[::-1]
308 | }
309 | result.append(inverse_kwargs)
310 | if len(result) == 1:
311 | return result[0]
312 | else:
313 | return result
314 |
315 |
316 | def uncollapse_dim(tensor, to_uncollapse, uncollapsed_length, uncollapse_into=None, spec=None, return_spec=False):
317 | """
318 | Splits a dimension in the input tensor into two, adding a dimension of specified length.
319 |
320 | Parameters
321 | ----------
322 | tensor : torch.Tensor
323 | to_uncollapse : str or int
324 | Dimension to be split.
325 | uncollapsed_length : int
326 | Length of the new dimension.
327 | uncollapse_into : str or int, optional
328 | Name of the new dimension.
329 | spec : list, optional
330 | Names or the dimensions of the input tensor
331 | return_spec : bool, optional
332 | Weather the output should consist of a tuple containing the output tensor and the resulting spec, or only the
333 | former.
334 |
335 | Returns
336 | -------
337 | torch.Tensor or tuple
338 |
339 | Examples
340 | --------
341 |
342 | >>> tensor = torch.Tensor([1, 2, 3, 10, 20, 30]).long()
343 | >>> uncollapse_dim(tensor, 0, 3, 1) # doctest: +NORMALIZE_WHITESPACE
344 | tensor([[ 1, 2, 3],
345 | [10, 20, 30]])
346 | """
347 | # puts the new dimension directly behind the old one
348 | spec = list(range(len(tensor.shape))) if spec is None else spec
349 | assert to_uncollapse in spec, f'{to_uncollapse}, {spec}'
350 | assert uncollapse_into not in spec, f'{uncollapse_into}, {spec}'
351 | assert isinstance(tensor, torch.Tensor), f'unexpected type: {type(tensor)}'
352 | i_from = spec.index(to_uncollapse)
353 | assert tensor.shape[i_from] % uncollapsed_length == 0, f'{tensor.shape[i_from]}, {uncollapsed_length}'
354 | new_shape = tensor.shape[:i_from] + \
355 | (tensor.shape[i_from]//uncollapsed_length, uncollapsed_length) + \
356 | tensor.shape[i_from + 1:]
357 | tensor = tensor.contiguous().view(new_shape)
358 | if return_spec:
359 | assert uncollapse_into is not None
360 | new_spec = copy(spec)
361 | new_spec.insert(i_from + 1, uncollapse_into)
362 | return tensor, new_spec
363 | else:
364 | return tensor
365 |
366 |
367 | def add_dim(tensor, length=1, new_dim=None, spec=None, return_spec=False):
368 | """
369 | Adds a single dimension of specified length (achieved by repeating the tensor) to the input tensor.
370 |
371 | Parameters
372 | ----------
373 | tensor : torch.Tensor
374 | length : int
375 | Length of the new dimension.
376 | new_dim : str, optional
377 | Name of the new dimension
378 | spec : list, optional
379 | Names of dimensions of the input tensor
380 | return_spec : bool, optional
381 | If true, a dictionary containing arguments to reverse the conversion (with this function) are added to the
382 | output tuple.
383 |
384 | Returns
385 | -------
386 | torch.Tensor or tuple
387 |
388 | """
389 | tensor = tensor[None].repeat([length] + [1] * len(tensor.shape))
390 | if return_spec:
391 | return tensor, [new_dim] + spec
392 | else:
393 | return tensor
394 |
395 |
396 | def equalize_specs(tensor_spec_pairs):
397 | """
398 | Manipulates a list of tensors such that their dimension names (including order of dimensions) match up.
399 |
400 | Parameters
401 | ----------
402 | tensor_spec_pairs : :obj:`list` of :obj:`tuple`
403 | List of two element tuples, each consisting of a tensor and a spec (=list of names of dimensions).
404 |
405 | Returns
406 | -------
407 | torch.Tensor
408 |
409 | """
410 | specs = [p[1] for p in tensor_spec_pairs]
411 | unified_spec = list(np.unique(np.concatenate(specs)))
412 | result = []
413 | for i, (tensor, spec) in enumerate(tensor_spec_pairs):
414 | result.append(convert_dim(tensor, spec, unified_spec, return_spec=True))
415 | return result
416 |
417 |
418 | def equalize_shapes(tensor_spec_pairs):
419 | """
420 | Manipulates a list of tensors such that their shapes end up equal.
421 |
422 | Axes that are not present in all tensors will be added as a trivial dimension to all tensors that do not have them.
423 |
424 | If shapes do not match along a certain axis, the tensors with the smaller shape will be repeated along that axis.
425 | Hence, the maximum length along each axis present in the list of tensors must be divisible by the lengths of all
426 | other input tensors along that axis.
427 |
428 | Parameters
429 | ----------
430 | tensor_spec_pairs : :obj:`list` of :obj:`tuple`
431 | List of two element tuples, each consisting of a tensor and a spec (=list of names of dimensions).
432 |
433 | Returns
434 | -------
435 | torch.Tensor
436 |
437 | """
438 | tensor_spec_pairs = equalize_specs(tensor_spec_pairs)
439 | unified_shape = np.max(np.array([list(p[0].shape) for p in tensor_spec_pairs]), axis=0)
440 | result = []
441 | for i, (tensor, spec) in enumerate(tensor_spec_pairs):
442 | old_shape = tensor.shape
443 | assert all(new_length % old_length == 0 for new_length, old_length in zip(unified_shape, old_shape)), \
444 | f'Shapes not compatible: {unified_shape}, {old_shape} (spec: {spec})'
445 | repeats = [new_length // old_length for new_length, old_length in zip(unified_shape, old_shape)]
446 | result.append((tensor.repeat(repeats), spec))
447 | return result
448 |
449 |
450 | class SpecFunction:
451 | """
452 | Class that wraps a function, specified in the method :meth:`internal`, to be applicable to tensors with of almost
453 | arbitrary dimensionality. This is achieved by applying the following steps when the function is called:
454 |
455 | - The inputs are reshaped and their dimensions are permuted to match their respective order of dimensions
456 | specified in in_specs. Dimensions present in inputs but not requested by in_specs are collapsed in the
457 | batch dimension, labeled 'B' (per default, see collapse_into). Dimensions not present in the inputs but
458 | requested by in_specs are added (with length 1).
459 |
460 | - If the batch dimension 'B' is present in the in_specs, 'internal' is applied on the inputs, returning
461 | a tensor with dimensions as specified in out_spec.
462 | If 'B' is not present in the in_specs, this dimension is iterated over and each slice is individually
463 | passed through 'internal'. The individual outputs are then stacked, recovering the 'B' dimension.
464 |
465 | - Finally, the output is reshaped. The dimensions previously collapsed into 'B' are uncollapsed, and
466 | dimensions added in the first step are removed.
467 |
468 | Parameters
469 | ----------
470 | in_specs : dict, optional
471 | Dictionary specifying how the dimensionality and order of dimensions of input arguments of :meth:`internal`
472 | should be adjusted.
473 |
474 | - Keys: Names of input arguments (as in signature of :meth:`internal`)
475 |
476 | - Values: List of dimension names. The tensor supplied to internal under the name of the corresponding key
477 | will have this order of dimensions.
478 |
479 | out_spec : list, optional
480 | List of dimension names of the output of :meth:`internal`
481 | collapse_into : list, optional
482 | If given, the default behaviour of collapsing any extra given dimensions of states into the batch dimension
483 | 'B' is overridden. Each entry of collapse_into must be a two element tuple, with the first element being the
484 | dimension to collapse, the second one being the dimension to collapse it into (prior to passing the tensor
485 | to :meth:`internal` ).
486 | suppress_spec_adjustment : bool, optional
487 | Argument to completely suppress the adjustment of dimensionalities in call(), for example if it is taken
488 | care of in call() of derived class (see firelight.visualizers.base.ConatainerVisualizer)
489 |
490 | """
491 | def __init__(self, in_specs=None, out_spec=None, collapse_into=None, suppress_spec_adjustment=True):
492 | if in_specs is None or out_spec is None:
493 | assert in_specs is None and out_spec is None, 'You probably want to supply both in_specs and an out_spec'
494 | assert suppress_spec_adjustment is True, 'You probably want to supply both in_specs and an out_spec'
495 | self.suppress_spec_adjustment = True
496 | else:
497 | self.suppress_spec_adjustment = False
498 | self.internal_in_specs = {key: list(value) for key, value in in_specs.items()}
499 | self.internal_out_spec = list(out_spec)
500 | assert (all('B' in spec for spec in self.internal_in_specs.values())) or \
501 | (all('B' not in spec for spec in self.internal_in_specs.values())), \
502 | f'"B" has to be in all or none of the internal specs: {self.internal_in_specs}'
503 | if all('B' not in spec for spec in self.internal_in_specs.values()):
504 | self.parallel = False
505 | self.internal_in_specs_with_B = {key: ['B'] + self.internal_in_specs[key] for key in in_specs}
506 | else:
507 | self.parallel = True
508 | self.internal_in_specs_with_B = self.internal_in_specs
509 |
510 | self.collapse_into = {'rest': 'B'} if collapse_into is None else collapse_into
511 |
512 | def __call__(self, *args, out_spec=None, return_spec=False, **kwargs):
513 | """
514 | Apply the wrapped function to a set of input arguments. Tensors will be reshaped as specified at initialization.
515 |
516 | Parameters
517 | ----------
518 | args : list
519 | List of positional input arguments to the wrapped function. They will be passed to :meth:`internal` without
520 | any processing.
521 | out_spec : list, optional
522 | List of dimension names of the output.
523 | return_spec : bool, optional
524 | Weather the output should consist of a tuple containing the output tensor and the resulting spec, or only the
525 | former.
526 | **kwargs
527 | Keyword arguments that will be passed to :meth:`internal`.
528 | The ones with names present in :paramref:`SpecFunction.in_specs` will be reshaped as required.
529 |
530 | Returns
531 | -------
532 | torch.Tensor or tuple
533 |
534 | """
535 | if self.suppress_spec_adjustment: # just do internal if requested
536 | return self.internal(*args, out_spec=out_spec, return_spec=return_spec, **kwargs)
537 |
538 | given_spec_kwargs = [kw for kw in self.internal_in_specs if kw in kwargs]
539 |
540 | # determine the extra specs in the input. they will be put in the 'B' spec.
541 | extra_given_in_specs = OrderedDict()
542 | for kw in given_spec_kwargs: # loop over given argument names that support dynamic specs
543 | assert len(kwargs[kw]) == 2, f'{kwargs[kw]}' # has to be a pair of (arg, spec)
544 | arg, spec = kwargs[kw]
545 | kwargs[kw] = (arg, list(spec)) # make spec list, in case it is given as string
546 | # assert all(d in spec for d in extra_given_in_specs), \
547 | # f'if extra specs are given, all input args need to have them: {kw}, {extra_given_in_specs}, {spec}'
548 | extra_given_in_specs.update({d: arg.shape[spec.index(d)] for d in spec
549 | if (d not in self.internal_in_specs[kw] and d not in extra_given_in_specs)})
550 |
551 | # print('extra specs', extra_given_in_specs)
552 |
553 | # add and repeat extra dimensions not present in some of the inputs
554 | for kw in given_spec_kwargs:
555 | arg, spec = kwargs[kw]
556 | for d in extra_given_in_specs:
557 | if d not in spec:
558 | length = extra_given_in_specs[d]
559 | arg, spec = add_dim(arg, length=length, new_dim=d, spec=spec, return_spec=True)
560 | kwargs[kw] = arg, spec
561 |
562 | # remove specs from extra given specs that are present in internal_in_specs
563 | # TODO: right now, this is unnecessary. allow for partially missing dims in the input_specs!
564 | for d in extra_given_in_specs:
565 | if not all(d not in spec for spec in self.internal_in_specs.values()):
566 | extra_given_in_specs.pop(d)
567 | assert d not in self.internal_out_spec, \
568 | f'spec {d} is an internal_out_spec, cannot be an extra given spec'
569 |
570 | #if 'B' in extra_given_in_specs:
571 | # del extra_given_in_specs['B']
572 |
573 | collapsing_rules = [(d, self.collapse_into.get(d, self.collapse_into.get('rest')))
574 | for d in extra_given_in_specs]
575 | for kw in self.internal_in_specs:
576 | assert kw in kwargs, \
577 | f"Missing key '{kw}'. Provided keys were {kwargs.keys()} in SpecFunction of class {type(self)}"
578 | arg, spec = kwargs[kw]
579 | # make it so 'B' is present
580 | if 'B' not in spec:
581 | arg, spec = extend_dim(arg, spec, ['B'] + spec, return_spec=True)
582 | # collapse the extra dimensions of the input
583 | arg = convert_dim(arg, spec, self.internal_in_specs_with_B[kw], collapsing_rules)
584 | kwargs[kw] = arg # finally update kwargs dictionary
585 |
586 | if self.parallel:
587 | result = self.internal(*args, **kwargs)
588 | spec = self.internal_out_spec
589 | else:
590 | n_batch = kwargs[list(self.internal_in_specs.keys())[0]].shape[0] if len(self.internal_in_specs) > 0 else 1
591 | result = torch.stack(
592 | [self.internal(*args, **{kw: kwargs[kw] if kw not in self.internal_in_specs else kwargs[kw][i]
593 | for kw in kwargs})
594 | for i in range(n_batch)], dim=0)
595 | spec = ['B'] + self.internal_out_spec
596 |
597 | assert isinstance(result, torch.Tensor), f'unexpected type: {type(result)}'
598 |
599 | # uncollapse the previously collapsed dims
600 | dims_to_uncollapse = list(extra_given_in_specs.keys())
601 | for i in reversed(range(len(extra_given_in_specs))):
602 | d = dims_to_uncollapse[i]
603 | if d == 'B' and (d in self.internal_out_spec or not self.parallel): # skip if function 'consumes' parallel dimension
604 | continue
605 |
606 | length = extra_given_in_specs[d]
607 | result, spec = uncollapse_dim(
608 | result,
609 | to_uncollapse=self.collapse_into.get(d, self.collapse_into.get('rest')),
610 | uncollapsed_length=length,
611 | uncollapse_into=d,
612 | spec=spec,
613 | return_spec=True
614 | )
615 |
616 | # finally, convert to out_spec, if specified
617 | if out_spec is not None:
618 | out_spec = list(out_spec)
619 | result, spec = convert_dim(result, in_spec=spec, out_spec=out_spec, return_spec=True)
620 | if return_spec:
621 | return result, spec
622 | else:
623 | return result
624 |
625 | def internal(self, *args, **kwargs):
626 | """
627 | Function that is being wrapped.
628 | """
629 | pass
630 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/firelight/utils/io_utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import yaml
2 |
3 |
4 | def yaml2dict(path):
5 | """
6 | Read a yaml file.
7 |
8 | Parameters
9 | ----------
10 | path : str or dict
11 | Path to the file. If :class:`dict`, will be returned as is.
12 |
13 | Returns
14 | -------
15 | dict
16 |
17 | """
18 | if isinstance(path, dict):
19 | # Forgivable mistake that path is a dict already
20 | return path
21 | with open(path, 'r') as f:
22 | readict = yaml.load(f)
23 | return readict
24 |
25 |
26 | def shape_to_str(shape):
27 | return '(' + ','.join([str(s) for s in shape]) + ')'
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/firelight/visualizers/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/inferno-pytorch/firelight/796328f93494248e6a4cf238ea36ac4eeb7fc9b8/firelight/visualizers/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/firelight/visualizers/base.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | from ..utils.dim_utils import SpecFunction, convert_dim, equalize_shapes
3 | from .colorization import Colorize
4 | from copy import copy
5 | import torch.nn.functional as F
6 | import logging
7 | import sys
8 | from pydoc import locate
9 |
10 | # Set up logger
11 | logging.basicConfig(format='[+][%(asctime)-15s][VISUALIZATION]'
12 | ' %(message)s',
13 | stream=sys.stdout,
14 | level=logging.INFO)
15 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
16 |
17 |
18 | def get_single_key_value_pair(d):
19 | """
20 | Get the key and value of a length one dictionary.
21 |
22 | Parameters
23 | ----------
24 | d : dict
25 | Single element dictionary to split into key and value.
26 |
27 | Returns
28 | -------
29 | tuple
30 | of length 2, containing the key and value
31 |
32 | Examples
33 | --------
34 |
35 | >>> d = dict(key='value')
36 | >>> get_single_key_value_pair(d)
37 | ('key', 'value')
38 |
39 | """
40 | assert isinstance(d, dict), f'{d}'
41 | assert len(d) == 1, f'{d}'
42 | return list(d.items())[0]
43 |
44 |
45 | def list_of_dicts_to_dict(list_of_dicts):
46 | """
47 | Convert a list of one element dictionaries to one dictionary.
48 |
49 | Parameters
50 | ----------
51 | list_of_dicts : :obj:`list` of :obj:`dict`
52 | List of one element dictionaries to merge.
53 |
54 | Returns
55 | -------
56 | dict
57 |
58 | Examples
59 | --------
60 | >>> list_of_dicts_to_dict([{'a': 1}, {'b': 2}])
61 | {'a': 1, 'b': 2}
62 | """
63 |
64 | result = dict()
65 | for d in list_of_dicts:
66 | key, value = get_single_key_value_pair(d)
67 | result[key] = value
68 | return result
69 |
70 |
71 | def parse_slice(slice_string):
72 | """
73 | Parse a slice given as a string.
74 |
75 | Parameters
76 | ----------
77 | slice_string : str
78 | String describing the slice. Format as in fancy indexing: 'start:stop:end'.
79 |
80 | Returns
81 | -------
82 | slice
83 |
84 | Examples
85 | --------
86 |
87 | Everything supported in fancy indexing works here, too:
88 |
89 | >>> parse_slice('5')
90 | slice(5, 6, None)
91 | >>> parse_slice(':5')
92 | slice(None, 5, None)
93 | >>> parse_slice('5:')
94 | slice(5, None, None)
95 | >>> parse_slice('2:5')
96 | slice(2, 5, None)
97 | >>> parse_slice('2:5:3')
98 | slice(2, 5, 3)
99 | >>> parse_slice('::3')
100 | slice(None, None, 3)
101 |
102 | """
103 | # Remove whitespace
104 | slice_string.replace(' ', '')
105 | indices = slice_string.split(':')
106 | if len(indices) == 1:
107 | start, stop, step = indices[0], int(indices[0]) + 1, None
108 | elif len(indices) == 2:
109 | start, stop, step = indices[0], indices[1], None
110 | elif len(indices) == 3:
111 | start, stop, step = indices
112 | else:
113 | raise RuntimeError
114 | # Convert to ints
115 | start = int(start) if start != '' else None
116 | stop = int(stop) if stop != '' else None
117 | step = int(step) if step is not None and step != '' else None
118 | # Build slice
119 | return slice(start, stop, step)
120 |
121 |
122 | def parse_named_slicing(slicing, spec):
123 | """
124 | Parse a slicing as a list of slice objects.
125 |
126 | Parameters
127 | ----------
128 | slicing : str or list or dict
129 | Specifies the slicing that is to be applied. Depending on the type:
130 |
131 | - :obj:`str`: slice strings joined by ','. In this case, spec will be ignored. (e.g. :code:`'0, 1:4'`)
132 | - :obj:`list`: has to be list of one element dictionaries, that will be converted to one dict
133 | with :func:`list_of_dicts_to_dict`
134 | - :obj:`dict`: keys are dimension names, values corresponding slices (as strings)
135 | (e.g. :code:`{'B': '0', 'C': '1:4'}`)
136 |
137 | spec : list
138 | List of names of dimensions of the tensor that is to be sliced.
139 |
140 | Returns
141 | -------
142 | list
143 | List of slice objects
144 |
145 | Examples
146 | --------
147 |
148 | Three ways to encode the same slicing:
149 |
150 | >>> parse_named_slicing(':5, :, 1', ['A', 'B', 'C'])
151 | [slice(None, 5, None), slice(None, None, None), slice(1, 2, None)]
152 | >>> parse_named_slicing({'A': ':5', 'C': '1'}, ['A', 'B', 'C'])
153 | [slice(None, 5, None), slice(None, None, None), slice(1, 2, None)]
154 | >>> parse_named_slicing([{'A': ':5'}, {'C': '1'}], ['A', 'B', 'C'])
155 | [slice(None, 5, None), slice(None, None, None), slice(1, 2, None)]
156 |
157 | """
158 | if slicing is None:
159 | return slicing
160 | elif isinstance(slicing, str): # No dimension names given, assume this is the whole slicing as one string
161 | # Remove whitespace
162 | slicing = slicing.replace(' ', '')
163 | # Parse slices
164 | slices = [parse_slice(s) for s in slicing.split(',')]
165 | assert len(slices) <= len(spec)
166 | return list(slices)
167 | elif isinstance(slicing, list):
168 | # if slicing is list, assume it is list of one element dictionaries (something like [B:0, C: '0:3'] in config)
169 | slicing = list_of_dicts_to_dict(slicing)
170 |
171 | assert isinstance(slicing, dict)
172 | # Build slice objects
173 | slices = []
174 | for d in spec:
175 | if d not in slicing:
176 | slices.append(slice(None, None, None))
177 | else:
178 | slices.append(parse_slice(str(slicing[d])))
179 | # Done.
180 | return slices
181 |
182 |
183 | def parse_pre_func(pre_info):
184 | """
185 | Parse the pre-processing function for an input to a visualizer
186 | (as given by the 'pre' key in the input_mapping).
187 |
188 | Parameters
189 | ----------
190 | pre_info: list, dict or str
191 | Depending on the type:
192 |
193 | - :obj:`str`: Name of function in torch, torch.nn.functional, or dotted path to function.
194 | - :obj:`list`: List of functions to be applied in succession. Each will be parsed by this function.
195 | - :obj:`dict`: Has to have length one. The key is the name of a function (see :obj:`str` above),
196 | the value specifies additional arguments supplied to that function (apart from the tensor that will be
197 | transformed). Either positional arguments can be specified as a list, or keyword arguments as a dictionary.
198 |
199 | Examples:
200 |
201 | - :code:`pre_info = 'sigmoid'`
202 | - :code:`pre_info = {'softmax': [1]}}`
203 | - :code:`pre_info = {'softmax': {dim: 0}}}`
204 |
205 | Returns
206 | -------
207 | Callable
208 | The parsed pre-processing function.
209 |
210 | """
211 | if isinstance(pre_info, list):
212 | # parse as concatenation
213 | funcs = [parse_pre_func(info) for info in pre_info]
214 |
215 | def pre_func(x):
216 | for f in funcs:
217 | x = f(x)
218 | return x
219 |
220 | return pre_func
221 | elif isinstance(pre_info, dict):
222 | pre_name, arg_info = get_single_key_value_pair(pre_info)
223 | elif isinstance(pre_info, str):
224 | pre_name = pre_info
225 | arg_info = []
226 | else:
227 | assert False, f'{pre_info}'
228 |
229 | if isinstance(arg_info, dict):
230 | kwargs = arg_info
231 | args = []
232 | elif isinstance(arg_info, list):
233 | kwargs = {}
234 | args = arg_info
235 |
236 | # Parse the function name
237 | pre_func_without_args = getattr(torch, pre_name, None)
238 | if pre_func_without_args is None: # not found in torch
239 | pre_func_without_args = getattr(torch.nn.functional, pre_name, None)
240 | if pre_func_without_args is None: # not found in torch or torch.nn.functional
241 | pre_func_without_args = locate(pre_name)
242 | assert callable(pre_func_without_args), f'Could not find the function {pre_name}'
243 |
244 | def pre_func(x):
245 | return pre_func_without_args(x, *args, **kwargs)
246 |
247 | return pre_func
248 |
249 |
250 | # Default ways to label the dimensions depending on dimensionality # TODO: make this easy to find
251 | DEFAULT_SPECS = {
252 | 3: list('BHW'), # 3D: Batch, Height, Width
253 | 4: list('BCHW'), # 4D: Batch, Channel, Height, Width
254 | 5: list('BCDHW'), # 5D: Batch, Channel, Depth, Height, Width
255 | 6: list('BCTDHW') # 6D: Batch, Channel, Time, Depth, Height, Width
256 | }
257 | """dict: The default ways to label the dimensions depending on dimensionality.
258 |
259 | - 3 Axes : :math:`(B, H, W)`
260 | - 4 Axes : :math:`(B, C, H, W)`
261 | - 5 Axes : :math:`(B, C, D, H, W)`
262 | - 6 Axes : :math:`(B, C, T, D, H, W)`
263 |
264 | """
265 |
266 |
267 | def apply_slice_mapping(mapping, states, include_old_states=True):
268 | """
269 | Add/Replace tensors in the dictionary 'states' as specified with the dictionary 'mapping'. Each key in mapping
270 | corresponds to a state in the resulting dictionary, and each value describes:
271 |
272 | - from which tensors in `states` this state is grabbed (e.g. :code:`['prediction']`)
273 | - if a list of tensors is grabbed: which list index should be used (e.g :code:`'[index': 0]`)
274 | - what slice of the grabbed tensor should be used (e.g :code:`['B': '0', 'C': '0:3']`).
275 | For details see :func:`parse_named_slicing`.
276 | - what function in torch.nn.functional should be applied to the tensor after the slicing
277 | (e.g. :code:`['pre': 'sigmoid']`).
278 | See :func:`parse_pre_func` for details.
279 |
280 | These arguments can be specified in one dictionary or a list of length one dictionaries.
281 |
282 | Parameters
283 | ----------
284 | mapping: dict
285 | Dictionary describing the mapping of states
286 | states: dict
287 | Dictionary of states to be mapped. Values must be either tensors, or tuples of the form (tensor, spec).
288 | include_old_states: bool
289 | Whether or not to include states in the ouput dictionary, on which no operations were performed.
290 |
291 | Returns
292 | -------
293 | dict
294 | Dictionary of mapped states
295 |
296 | """
297 | mapping = copy(mapping)
298 | # assumes states are tuples of (tensor, spec) if included in mapping
299 | assert isinstance(states, dict)
300 | if include_old_states:
301 | result = copy(states)
302 | else:
303 | result = dict()
304 | if mapping is None:
305 | return result
306 |
307 | global_slice_info = mapping.pop('global', {})
308 | if isinstance(global_slice_info, list):
309 | global_slice_info = list_of_dicts_to_dict(global_slice_info)
310 | # add all non-scalar tensors to state mapping if global is specified
311 | for state_name in states:
312 | if state_name not in mapping:
313 | state = states[state_name]
314 | if isinstance(state, tuple):
315 | state = state[0]
316 | if isinstance(state, list) and len(state) > 0: # as e.g. inputs in inferno
317 | state = state[0]
318 | if not isinstance(state, torch.Tensor):
319 | continue
320 | if not len(state.shape) > 0:
321 | continue
322 | mapping[state_name] = {}
323 |
324 | for map_to in mapping:
325 | map_from_info = mapping[map_to]
326 |
327 | # mapping specified not in terms of input tensor, but another visualizer
328 | if isinstance(map_from_info, BaseVisualizer):
329 | visualizer = map_from_info
330 | result[map_to] = visualizer(return_spec=True, **copy(states))
331 | continue
332 |
333 | if isinstance(map_from_info, str):
334 | map_from_key = map_from_info
335 | map_from_info = {}
336 | elif isinstance(map_from_info, (list, dict)):
337 | if isinstance(map_from_info, list) and isinstance(map_from_info[0], str):
338 | map_from_key = map_from_info[0]
339 | map_from_info = map_from_info[1:]
340 | else:
341 | map_from_key = map_to
342 | if isinstance(map_from_info, list):
343 | map_from_info = list_of_dicts_to_dict(map_from_info)
344 |
345 | # add the global slicing
346 | temp = copy(global_slice_info)
347 | temp.update(map_from_info)
348 | map_from_info = temp
349 |
350 | if map_from_key not in states: # needed for container visualizers and 'visualization0'..
351 | continue
352 |
353 | # figure out state
354 | state_info = states[map_from_key] # either (state, spec) or state
355 | state = state_info[0] if isinstance(state_info, tuple) else state_info
356 | if not isinstance(state, (tuple, torch.Tensor)) and isinstance(state, list):
357 | index = map_from_info.pop('index', None)
358 | if index is not None: # allow for index to be left unspecified
359 | index = int(index)
360 | state = state[index]
361 | assert isinstance(state, torch.Tensor), f'{map_from_key}, {type(state)}'
362 | if 'pre' in map_from_info:
363 | pre_func = parse_pre_func(map_from_info.pop('pre'))
364 | else:
365 | pre_func = None
366 | # figure out spec
367 | if 'spec' in map_from_info:
368 | spec = list(map_from_info.pop('spec'))
369 | else:
370 | if isinstance(state_info, tuple):
371 | spec = state_info[1]
372 | else:
373 | dimensionality = len(state.shape) if isinstance(state, torch.Tensor) else len(state[0].shape)
374 | assert dimensionality in DEFAULT_SPECS, f'{map_from_key}, {dimensionality}'
375 | spec = DEFAULT_SPECS[dimensionality]
376 | # get the slices
377 | map_from_slices = parse_named_slicing(map_from_info, spec)
378 | # finally map the state
379 | if isinstance(state, torch.Tensor):
380 | assert len(state.shape) == len(spec), f'{state.shape}, {spec} ({map_from_key})'
381 | state = state[map_from_slices].clone()
382 | elif isinstance(state, list):
383 | assert all(len(s.shape) == len(spec) for s in state), f'{[s.shape for s in state]}, {spec} ({map_from_key})'
384 | state = [s[map_from_slices] for s in state]
385 | else:
386 | assert False, f'state has to be list or tensor: {map_from_key}, {type(state)}'
387 |
388 | if pre_func is None:
389 | result[map_to] = (state, spec)
390 | else:
391 | result[map_to] = (pre_func(state), spec)
392 | return result
393 |
394 |
395 | class BaseVisualizer(SpecFunction):
396 | """
397 | Base class for all visualizers.
398 | If you want to use outputs of other visualizers, derive from ContainerVisualizer instead.
399 |
400 | Parameters
401 | ----------
402 | input: list or None
403 | If the visualizer has one input only, this can be used to specify which state to pass (in the format of a
404 | value in input_mapping).
405 | input_mapping : dict or list
406 | Dictionary specifying slicing and renaming of states for visualization (see :func:`apply_slice_mapping`).
407 | colorize : bool
408 | If False, the addition/rescaling of a 'Color' dimension to RGBA in [0,1] is suppressed.
409 | cmap : str or callable
410 | If string, specifies the name of the matplotlib `colormap
411 | `_
412 | to be used for colorization.
413 |
414 | If callable, must be a mapping from a [Batch x Pixels] to [Batch x Pixels x Color] :class:`numpy.ndarray` used
415 | for colorization.
416 | background_label : int or float
417 | If specified, pixels with this value (after :meth:`visualize`) will be colored with :paramref:`background_color`.
418 | background_color : float or list
419 | Specifies the color for the background_label. Will be interpreted as grey-value if float, and RGB or RGBA if
420 | list of length 3 or 4 respectively.
421 | opacity : float
422 | Opacity of visualization, see colorization.py.
423 | colorize_jointly : list of str
424 | A list containing names of dimensions. Sets of data points separated only in these dimensions will be scaled
425 | equally at colorization (such that they lie in [0, 1]). Not used if 'value_range' is specified.
426 |
427 | Default: :code:`['W', 'H', 'D']` (standing for Width, Height, Depth)
428 |
429 | Examples:
430 |
431 | - :code:`color_jointly = ['W', 'H']` : Scale each image separately
432 | - :code:`color_jointly = ['B', 'W', 'H']` : Scale images corresponding to different samples in the batch
433 | equally, such that their intensities are comparable
434 |
435 | value_range : List
436 | If specified, the automatic scaling for colorization is overridden. Has to have 2 elements.
437 | The interval [value_range[0], value_range[1]] will be mapped to [0, 1] by a linear transformation.
438 |
439 | Examples:
440 |
441 | - If your network has the sigmoid function as a final layer, the data does not need to be scaled
442 | further. Hence :code:`value_range = [0, 1]` should be specified.
443 | - If your network produces outputs normalized between -1 and 1, you could set :code:`value_range = [-1, 1]`.
444 |
445 | verbose : bool
446 | If true, information about the state dict will be printed during visualization.
447 | **super_kwargs:
448 | Arguments passed to the constructor of SpecFunction, above all the dimension names of inputs and output of
449 | visualize()
450 | """
451 | def __init__(self, input=None, input_mapping=None, colorize=True,
452 | cmap=None, background_label=None, background_color=None, opacity=1.0, colorize_jointly=None,
453 | value_range=None, verbose=False, scaling_options=None,
454 | **super_kwargs):
455 |
456 | in_specs = super_kwargs.get('in_specs')
457 | super(BaseVisualizer, self).__init__(**super_kwargs)
458 |
459 | # always have the requested states in input mapping, to make sure their shape is inferred (from DEFAULT_SPECS)
460 | # if not specified.
461 | in_specs = {} if in_specs is None else in_specs
462 | self.input_mapping = {name: name for name in in_specs}
463 | # if 'input' is specified, map it to the first and only name in in_specs
464 | if input is not None:
465 | assert len(in_specs) == 1, \
466 | f"Cannot use 'input' in Visualizer with multiple in_specs. Please pass input mapping containing " \
467 | f"{list(in_specs.keys())} to {type(self).__name__}."
468 | name = get_single_key_value_pair(in_specs)[0]
469 | self.input_mapping[name] = input
470 | # finally set the input_mapping as specified in 'input_mapping'
471 | if input_mapping is not None:
472 | if input is not None:
473 | assert list(in_specs.keys())[0] not in input_mapping, \
474 | f"State specified in both 'input' and 'input_mapping' Please choose one."
475 | self.input_mapping.update(input_mapping)
476 | self.colorize = colorize
477 | self.colorization_func = Colorize(cmap=cmap, background_color=background_color,
478 | background_label=background_label, opacity=opacity,
479 | value_range=value_range, colorize_jointly=colorize_jointly,
480 | scaling_options=scaling_options)
481 | self.verbose = verbose
482 |
483 | def __call__(self, return_spec=False, **states):
484 | """
485 | Visualizes the data specified in the state dictionary, following these steps:
486 |
487 | - Apply the input mapping (using :func:`apply_input_mapping`),
488 | - Reshape the states needed for visualization as specified by in_specs at initialization. Extra dimensions
489 | are 'put into' the batch dimension, missing dimensions are added (This is handled in the base class,
490 | :class:`firelight.utils.dim_utils.SpecFunction`)
491 | - Apply :meth:`visualize`,
492 | - Reshape the result, with manipulations applied on the input in reverse,
493 | - If not disabled by setting :code:`colorize=False`, colorize the result,
494 | leading to RGBA output with values in :math:`[0, 1]`.
495 |
496 | Parameters
497 | ----------
498 | return_spec: bool
499 | If true, a list containing the dimension names of the output is returned additionally
500 | states: dict
501 | Dictionary including the states to be visualized.
502 |
503 | Returns
504 | -------
505 | result: torch.Tensor or (torch.Tensor, list)
506 | Either only the resulting visualization, or a tuple of the visualization and the corresponding spec
507 | (depending on the value of :code:`return_spec`).
508 |
509 | """
510 | logger.info(f'Calling {self.__class__.__name__}.')
511 |
512 | if self.verbose:
513 | print()
514 | print(f'states passed to {type(self)}:')
515 | for name, state in states.items():
516 | print(name)
517 | if isinstance(state, tuple):
518 | print(state[1])
519 | if hasattr(state[0], 'shape'):
520 | print(state[0].shape)
521 | elif isinstance(state[0], list):
522 | for s in state[0]:
523 | print(s.shape)
524 | else:
525 | print(type(state))
526 |
527 | # map input keywords and apply slicing
528 | states = apply_slice_mapping(self.input_mapping, states)
529 |
530 | if self.verbose:
531 | print()
532 | print(f'states after slice mapping:')
533 | for name, state in states.items():
534 | print(name)
535 | if isinstance(state, tuple):
536 | print(state[1])
537 | if hasattr(state[0], 'shape'):
538 | print(state[0].shape)
539 | elif isinstance(state[0], list):
540 | for s in state[0]:
541 | print(s.shape)
542 | else:
543 | print(type(state))
544 |
545 | # apply visualize
546 | result, spec = super(BaseVisualizer, self).__call__(**states, return_spec=True)
547 |
548 | # color the result, if not suppressed
549 | result = result.float()
550 | if self.colorize:
551 | if self.verbose:
552 | print('colorizing now:', type(self))
553 | print('result before colorization:', result.shape)
554 | out_spec = spec if 'Color' in spec else spec + ['Color']
555 | result, spec = self.colorization_func(tensor=(result, spec), out_spec=out_spec, return_spec=True)
556 | if self.verbose:
557 | print('result:', result.shape)
558 | if return_spec:
559 | return result, spec
560 | else:
561 | return result
562 |
563 | def internal(self, *args, **kwargs):
564 | # essentially rename internal to visualize
565 | return self.visualize(*args, **kwargs)
566 |
567 | def visualize(self, **states):
568 | """
569 | Main visualization function that all subclasses have to implement.
570 |
571 | Parameters
572 | ----------
573 | states : dict
574 | Dictionary containing states used for visualization. The states in in_specs (specified at initialization)
575 | will have dimensionality and order of dimensions as specified there.
576 |
577 | Returns
578 | -------
579 | torch.Tensor
580 | """
581 | pass
582 |
583 |
584 | class ContainerVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
585 | """
586 | Base Class for visualizers combining the outputs of other visualizers.
587 |
588 | Parameters
589 | ----------
590 | visualizers : List of BaseVisualizer
591 | Child visualizers whose outputs are to be combined.
592 | in_spec : List of str
593 | List of dimension names. The outputs of all the child visualizers will be brought in this shape to be
594 | combined (in combine()).
595 | out_spec : List of str
596 | List of dimension names of the output of combine().
597 | extra_in_specs : dict
598 | Dictionary containing lists of dimension names for inputs of combine that are directly taken from the state
599 | dictionary and are not the output of a child visualizer.
600 | input_mapping : dict
601 | Dictionary specifying slicing and renaming of states for visualization (see :func:`apply_slice_mapping`).
602 | equalize_visualization_shapes : bool
603 | If true (as per default), the shapes of the outputs of child visualizers will be equalized by repeating
604 | along dimensions with shape mismatches. Only works if the maximum size of each dimension is divisible by the
605 | sizes of all the child visualizations in that dimension.
606 | colorize : bool
607 | If False, the addition/rescaling of a 'Color' dimension to RGBA in [0,1] is suppressed.
608 | **super_kwargs :
609 | Dictionary specifying other arguments of BaseVisualizer.
610 |
611 | """
612 | def __init__(self, visualizers, in_spec, out_spec, extra_in_specs=None, input_mapping=None,
613 | equalize_visualization_shapes=True,
614 | colorize=False, **super_kwargs):
615 | self.in_spec = in_spec
616 | self.visualizers = visualizers
617 | self.n_visualizers = len(visualizers)
618 | self.visualizer_kwarg_names = ['visualized_' + str(i) for i in range(self.n_visualizers)]
619 | if in_spec is None:
620 | in_specs = None
621 | else:
622 | in_specs = dict() if extra_in_specs is None else extra_in_specs
623 | in_specs.update({self.visualizer_kwarg_names[i]: in_spec for i in range(self.n_visualizers)})
624 | super(ContainerVisualizer, self).__init__(
625 | input_mapping={},
626 | in_specs=in_specs,
627 | out_spec=out_spec,
628 | colorize=colorize,
629 | **super_kwargs
630 | )
631 | self.container_input_mapping = input_mapping
632 | self.equalize_visualization_shapes = equalize_visualization_shapes
633 |
634 | def __call__(self, return_spec=False, **states):
635 | """
636 | Like call in BaseVisualizer, but computes visualizations for all child visualizers first, which will be passed
637 | to combine() (equivalent of visualize for BaseVisualizer).
638 |
639 | Parameters
640 | ----------
641 | return_spec: bool
642 | If true, a list containing the dimension names of the output is returned additionally
643 | states: dict
644 | Dictionary including the states to be visualized.
645 |
646 | Returns
647 | -------
648 | torch.Tensor or (torch.Tensor, list), depending on the value of :obj:`return_spec`.
649 |
650 | """
651 | states = copy(states)
652 | # map input keywords and apply slicing
653 | states = apply_slice_mapping(self.container_input_mapping, states)
654 | # apply visualizers and update state dict
655 | in_states = states.copy()
656 | visualizations = []
657 | for i in range(self.n_visualizers):
658 | visualizations.append(self.visualizers[i](**in_states, return_spec=True))
659 | if self.equalize_visualization_shapes:
660 | # add dimensions and reapeat them to make shapes of all visualizations match
661 | visualizations = equalize_shapes(tensor_spec_pairs=visualizations)
662 | for i, v in enumerate(visualizations):
663 | states[self.visualizer_kwarg_names[i]] = visualizations[i]
664 | return super(ContainerVisualizer, self).__call__(**states, return_spec=return_spec)
665 |
666 | def internal(self, **states):
667 | visualizations = []
668 | for name in self.visualizer_kwarg_names:
669 | visualizations.append(states[name])
670 | return self.combine(*visualizations, **states)
671 |
672 | def combine(self, *visualizations, **extra_states):
673 | """
674 | Main visualization function that all subclasses have to implement.
675 |
676 | Parameters
677 | ----------
678 | visualizations : :obj:`list` of :obj:`torch.Tensor`
679 | List containing the visualizations from the child visualizers. Their dimensionality and order of dimensions
680 | will be as specified in in_spec at initialization.
681 | extra_states : dict
682 | Dictionary containing extra states (not outputs of child visualizers) used for visualization. The states in
683 | :obj:`extra_in_specs` (specified at initialization) will have dimensionality and order of dimensions as
684 | specified there.
685 |
686 | Returns
687 | -------
688 | torch.Tensor
689 |
690 | """
691 | raise NotImplementedError
692 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/firelight/visualizers/colorization.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from ..utils.dim_utils import SpecFunction, convert_dim
2 | import matplotlib.cm as cm
3 | import matplotlib.colors as colors
4 | from matplotlib.pyplot import get_cmap
5 | import torch
6 | import numpy as np
7 |
8 |
9 | def hsv_to_rgb(h, s, v): # TODO: remove colorsys dependency
10 | """
11 | Converts a color from HSV to RGB
12 |
13 | Parameters
14 | ----------
15 | h : float
16 | s : float
17 | v : float
18 |
19 | Returns
20 | -------
21 | numpy.ndarray
22 | The converted color in RGB space.
23 | """
24 | i = np.floor(h*6.0)
25 | f = h * 6 - i
26 | p = v * (1 - s)
27 | q = v * (1 - s * f)
28 | t = v * (1 - s * (1 - f))
29 | i = i % 6
30 |
31 | if i == 0:
32 | rgb = (v, t, p)
33 | elif i == 1:
34 | rgb = (q, v, p)
35 | elif i == 2:
36 | rgb = (p, v, t)
37 | elif i == 3:
38 | rgb = (p, q, v)
39 | elif i == 4:
40 | rgb = (t, p, v)
41 | else:
42 | rgb = (v, p, q)
43 |
44 | return np.array(rgb, dtype=np.float32)
45 |
46 |
47 | def get_distinct_colors(n, min_sat=.5, min_val=.5):
48 | """
49 | Generates a list of distinct colors, evenly separated in HSV space.
50 |
51 | Parameters
52 | ----------
53 | n : int
54 | Number of colors to generate.
55 | min_sat : float
56 | Minimum saturation.
57 | min_val : float
58 | Minimum brightness.
59 |
60 | Returns
61 | -------
62 | numpy.ndarray
63 | Array of shape (n, 3) containing the generated colors.
64 |
65 | """
66 | huePartition = 1.0 / (n + 1)
67 | hues = np.arange(0, n) * huePartition
68 | saturations = np.random.rand(n) * (1-min_sat) + min_sat
69 | values = np.random.rand(n) * (1-min_val) + min_val
70 | return np.stack([hsv_to_rgb(h, s, v) for h, s, v in zip(hues, saturations, values)], axis=0)
71 |
72 |
73 | def colorize_segmentation(seg, ignore_label=None, ignore_color=(0, 0, 0)):
74 | """
75 | Randomly colorize a segmentation with a set of distinct colors.
76 |
77 | Parameters
78 | ----------
79 | seg : numpy.ndarray
80 | Segmentation to be colorized. Can have any shape, but data type must be discrete.
81 | ignore_label : int
82 | Label of segment to be colored with ignore_color.
83 | ignore_color : tuple
84 | RGB color of segment labeled with ignore_label.
85 |
86 | Returns
87 | -------
88 | numpy.ndarray
89 | The randompy colored segmentation. The RGB channels are in the last axis.
90 | """
91 | assert isinstance(seg, np.ndarray)
92 | assert seg.dtype.kind in ('u', 'i')
93 | if ignore_label is not None:
94 | ignore_ind = seg == ignore_label
95 | seg = seg - np.min(seg)
96 | colors = get_distinct_colors(np.max(seg) + 1)
97 | np.random.shuffle(colors)
98 | result = colors[seg]
99 | if ignore_label is not None:
100 | result[ignore_ind] = ignore_color
101 | return result
102 |
103 |
104 | def from_matplotlib_cmap(cmap):
105 | """
106 | Converts the name of a matplotlib colormap to a colormap function that can be applied to a :class:`numpy.ndarray`.
107 |
108 | Parameters
109 | ----------
110 | cmap : str
111 | Name of the matplotlib colormap
112 |
113 | Returns
114 | -------
115 | callable
116 | A function that maps greyscale arrays to RGBA.
117 |
118 | """
119 | if isinstance(cmap, str):
120 | cmap = get_cmap(cmap)
121 | cNorm = colors.Normalize(vmin=0, vmax=1)
122 | scalarMap = cm.ScalarMappable(norm=cNorm, cmap=cmap)
123 | return scalarMap.to_rgba
124 |
125 |
126 | def add_alpha(img):
127 | """
128 | Adds a totally opaque alpha channel to a tensor, whose last axis corresponds to RGB color.
129 |
130 | Parameters
131 | ----------
132 | img : torch.Tensor
133 | The RGB image.
134 |
135 | Returns
136 | -------
137 | torch.Tensor
138 | The resulting RGBA image.
139 |
140 | """
141 | alpha_shape = list(img.shape)
142 | alpha_shape[-1] = 1
143 | return torch.cat([img, torch.ones(alpha_shape, dtype=img.dtype)], dim=-1)
144 |
145 |
146 | class ScaleTensor(SpecFunction):
147 | """
148 |
149 | Parameters
150 | ----------
151 | invert: bool
152 | Whether the input should be multiplied with -1.
153 | value_range : [float, float] or None, optional
154 | If specified, tensor will be scaled by a linear map that maps :code:`value_range[0]` will be mapped to 0,
155 | and :code:`value_range[1]` will be to 1.
156 | scale_robust: bool, optional
157 | Whether outliers in the input should be ignored in the scaling.
158 |
159 | Has no effect if :obj:`value_range` is specified.
160 | quantiles : (float, float), optional
161 | Values under the first and above the second quantile are considered outliers for robust scaling.
162 |
163 | Ignored if :obj:`scale_robust` is False or :obj:`value_range` is specified.
164 | keep_centered : bool, optional
165 | Whether the scaling should be symmetric in the sense that (if the scaling function is :math:`f`):
166 |
167 | .. math::
168 | f(-x) = 0.5 - f(x)
169 |
170 | This can be useful in combination with `diverging colormaps
171 | `_.
172 |
173 | """
174 | def __init__(self, invert=False, value_range=None, scale_robust=False, quantiles=(0.05, 0.95), keep_centered=False,
175 | cmap_center_zoom=None):
176 | super(ScaleTensor, self).__init__(
177 | in_specs={'tensor': ['Pixels']},
178 | out_spec=['Pixels']
179 | )
180 | # TODO: decouple quantlies from scale axis (allow e.g. 0.1 -> 0.05)
181 | self.invert = invert
182 | self.value_range = value_range
183 | self.scale_robust = scale_robust
184 | self.quantiles = quantiles
185 | self.keep_centered = keep_centered
186 | assert (keep_centered and not scale_robust) or not cmap_center_zoom, \
187 | f'cmap_center_zoom is only supported for keep_centered=True and scale_robust=False'
188 | self.cmap_center_zoom = cmap_center_zoom
189 | self.eps = 1e-12
190 |
191 | def quantile_scale(self, tensor, quantiles=None, return_params=False):
192 | """
193 | Scale tensor linearly, such that the :code:`quantiles[i]`-quantile ends up on :code:`quantiles[i]`.
194 | """
195 | quantiles = self.quantiles if quantiles is None else quantiles
196 | q_min = np.percentile(tensor.numpy(), 100 * self.quantiles[0])
197 | q_max = np.percentile(tensor.numpy(), 100 * self.quantiles[1])
198 | scale = (quantiles[1] - quantiles[0]) / max(q_max - q_min, self.eps)
199 | offset = quantiles[0] - q_min * scale
200 | # scaled tensor is tensor * scale + offset
201 | if return_params:
202 | return scale, offset
203 | else:
204 | return tensor * scale + offset
205 |
206 | def scale_tails(self, tensor):
207 | """
208 | Scale the tails (the elements below :code:`self.quantiles[0]` and the ones above :code:`self.quantiles[1]`)
209 | linearly to make all values lie in :math:`[0, 1]`.
210 | """
211 | t_min, t_max = torch.min(tensor), torch.max(tensor)
212 | if t_min < 0:
213 | ind = tensor < self.quantiles[0]
214 | tensor[ind] -= t_min
215 | tensor[ind] *= self.quantiles[0] / max(self.quantiles[0] - t_min, self.eps)
216 | if t_max > 1:
217 | ind = tensor > self.quantiles[1]
218 | tensor[ind] -= self.quantiles[1]
219 | tensor[ind] *= (1 - self.quantiles[1]) / max(t_max - self.quantiles[1], self.eps)
220 | tensor[ind] += self.quantiles[1]
221 | return tensor
222 |
223 | def internal(self, tensor):
224 | """
225 | Scales the input tensor to the interval :math:`[0, 1]`.
226 | """
227 | if self.invert:
228 | tensor *= -1
229 | if not self.keep_centered:
230 | if self.value_range is not None or not self.scale_robust:
231 | # just scale to [0, 1], nothing fancy
232 | value_range = (torch.min(tensor), torch.max(tensor)) if self.value_range is None else self.value_range
233 | tensor -= value_range[0]
234 | tensor /= max(value_range[1] - value_range[0], self.eps)
235 | else:
236 | quantiles = list(self.quantiles)
237 | tensor = self.quantile_scale(tensor, quantiles=quantiles)
238 | # if less than the whole range is used, do so
239 | rescale = False
240 | if torch.min(tensor) > 0:
241 | quantiles[0] = 0
242 | rescale = True
243 | if torch.max(tensor) < 1:
244 | quantiles[1] = 0
245 | rescale = True
246 | if rescale:
247 | tensor = self.quantile_scale(tensor, quantiles=quantiles)
248 | # if the tails lie outside the range, rescale them
249 | tensor = self.scale_tails(tensor)
250 |
251 | else:
252 | if self.value_range is not None or not self.scale_robust:
253 | value_range = (torch.min(tensor), torch.max(tensor)) if self.value_range is None else self.value_range
254 |
255 | # center the value range
256 | limit = np.max(np.abs(value_range))
257 | if self.cmap_center_zoom is not None:
258 | limit /= self.cmap_center_zoom
259 | value_range = (-limit, limit)
260 |
261 | tensor -= value_range[0]
262 | tensor /= max(value_range[1] - value_range[0], self.eps)
263 | else:
264 | quantile = self.quantiles[0] if isinstance(self.quantiles, (tuple, list)) else self.quantiles
265 | symmetrized_tensor = torch.cat([tensor, -tensor])
266 | scale, offset = self.quantile_scale(symmetrized_tensor, (quantile, 1-quantile), return_params=True)
267 | tensor = tensor * scale + offset
268 | tensor = self.scale_tails(tensor)
269 | tensor = tensor.clamp(0, 1)
270 | return tensor
271 |
272 |
273 | class Colorize(SpecFunction):
274 | """
275 | Constructs a function used for the colorization / color normalization of tensors. The output tensor has a
276 | length 4 RGBA output dimension labeled 'Color'.
277 |
278 | If the input tensor is continuous, a color dimension will be added if not present already.
279 | Then, it will be scaled to :math:`[0, 1]`.
280 | How exactly the scaling is performed can be influenced by the parameters below.
281 |
282 | If the tensor consists of only ones and zeros, the ones will become black and the zeros transparent white.
283 |
284 | If the input tensor is discrete including values different to zero and one,
285 | it is assumed to be a segmentation and randomly colorized.
286 |
287 | Parameters
288 | ----------
289 | background_label : int or tuple, optional
290 | Value of input tensor that will be colored with background color.
291 | background_color : int or tuple, optional
292 | Color that will be assigned to regions of the input having the value background_label.
293 | opacity : float, optional
294 | .. currentmodule:: firelight.visualizers.container_visualizers
295 |
296 | Multiplier that will be applied to alpha channel. Useful to blend images with :class:`OverlayVisualizer`.
297 | value_range : tuple, optional
298 | Range the input data will lie in (e.g. :math:`[-1, 1]` for l2-normalized vectors). This range will be mapped
299 | linearly to the unit interval :math:`[0, 1]`.
300 | If not specified, the output data will be scaled to use the full range :math:`[0, 1]`.
301 | cmap : str or callable or None, optional
302 | If str, has to be the name of a matplotlib `colormap
303 | `_,
304 | to be used to color grayscale data.
305 |
306 | If callable, has to be function that adds a RGBA color dimension at the end, to an input :class:`numpy.ndarray`
307 | with values between 0 and 1.
308 |
309 | If None, the output will be grayscale with the intensity in the opacity channel.
310 | colorize_jointly : list, optional
311 | List of the names of dimensions that should be colored jointly. Default: :code:`['W', 'H', 'D']`.
312 |
313 | Data points separated only in these dimensions will be scaled equally. See :class:`StackVisualizer` for an
314 | example usage.
315 |
316 | """
317 | def __init__(self, background_label=None, background_color=None, opacity=1.0, value_range=None, cmap=None,
318 | colorize_jointly=None, scaling_options=None):
319 | colorize_jointly = ('W', 'H', 'D') if colorize_jointly is None else list(colorize_jointly)
320 | collapse_into = {'rest': 'B'}
321 | collapse_into.update({d: 'Pixels' for d in colorize_jointly})
322 | super(Colorize, self).__init__(in_specs={'tensor': ['B', 'Pixels', 'Color']},
323 | out_spec=['B', 'Pixels', 'Color'],
324 | collapse_into=collapse_into)
325 | self.cmap = from_matplotlib_cmap(cmap) if isinstance(cmap, str) else cmap
326 | self.background_label = background_label
327 | self.background_color = (0, 0, 0, 0) if background_color is None else tuple(background_color)
328 | if len(self.background_color) == 3:
329 | self.background_color += (1,)
330 | assert len(self.background_color) == 4, f'{len(self.background_color)}'
331 | self.opacity = opacity
332 |
333 | scaling_options = dict() if scaling_options is None else scaling_options
334 | if value_range is not None:
335 | scaling_options['value_range'] = value_range
336 | self.scale_tensor = ScaleTensor(**scaling_options)
337 |
338 | def add_alpha(self, img):
339 | return add_alpha(img)
340 |
341 | def normalize_colors(self, tensor):
342 | """Scale each color channel individually to use the whole extend of :math:`[0, 1]`. Uses :class:`ScaleTensor`.
343 | """
344 | tensor = tensor.permute(2, 0, 1)
345 | # TODO: vectorize
346 | # shape Color, Batch, Pixel
347 | for i in range(min(tensor.shape[0], 3)): # do not scale alpha channel
348 | for j in range(tensor.shape[1]):
349 | tensor[i, j] = self.scale_tensor(tensor=(tensor[i, j], ['Pixels']))
350 | tensor = tensor.permute(1, 2, 0)
351 | return tensor
352 |
353 | def internal(self, tensor):
354 | """If not present, add a color channel to tensor. Scale the colors using :meth:`Colorize.normalize_colors`.
355 | """
356 | if self.background_label is not None:
357 | bg_mask = tensor == self.background_label
358 | bg_mask = bg_mask[..., 0]
359 | else:
360 | bg_mask = None
361 |
362 | # add color if there is none
363 | if tensor.shape[-1] == 1: # no color yet
364 | # if continuous, normalize colors
365 | if (tensor % 1 != 0).any():
366 | tensor = self.normalize_colors(tensor)
367 |
368 | # if a colormap is specified, apply it
369 | if self.cmap is not None:
370 | dtype = tensor.dtype
371 | tensor = self.cmap(tensor.numpy()[..., 0])[..., :3] # TODO: Why truncate alpha channel?
372 | tensor = torch.tensor(tensor, dtype=dtype)
373 | # if continuous and no cmap, use grayscale
374 | elif (tensor % 1 != 0).any() or (torch.min(tensor) == 0 and torch.max(tensor) == 1):
375 | # if tensor is continuous or greyscale, default to greyscale with intensity in alpha channel
376 | tensor = torch.cat([torch.zeros_like(tensor.repeat(1, 1, 3)), tensor], dim=-1)
377 |
378 | else: # tensor is discrete with not all values in {0, 1}, hence color the segments randomly
379 | tensor = torch.Tensor(colorize_segmentation(tensor[..., 0].numpy().astype(np.int32)))
380 | elif tensor.shape[-1] in [3, 4]:
381 | assert self.cmap is None, f'Tensor already has Color dimension, cannot use cmap'
382 | tensor = self.normalize_colors(tensor)
383 | else:
384 | assert False, f'{tensor.shape}'
385 |
386 | # add alpha channel
387 | if tensor.shape[-1] == 3:
388 | tensor = self.add_alpha(tensor)
389 | assert tensor.shape[-1] == 4
390 | tensor[..., -1] *= self.opacity # multiply alpha channel with opacity
391 |
392 | if bg_mask is not None and torch.sum(bg_mask) > 0:
393 | assert tensor.shape[-1] == len(self.background_color)
394 | tensor[bg_mask.byte()] = torch.Tensor(np.array(self.background_color)).type_as(tensor)
395 |
396 | return tensor
397 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/firelight/visualizers/container_visualizers.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .base import ContainerVisualizer
2 | from ..utils.dim_utils import convert_dim
3 | from ..utils.io_utils import shape_to_str
4 | import torch
5 | import torch.nn.functional as F
6 | from texttable import Texttable
7 |
8 |
9 | def _to_rgba(color):
10 | """
11 | Converts a color to RGBA.
12 |
13 | Parameters
14 | ----------
15 | color : int, float or list
16 | If numeric, is interpreted as gray-value between 0 and 1. If list, has to have length 3 or 4 and is interpreted
17 | as RGB / RGBA depending on length (again, with values in [0, 1]).
18 |
19 | Returns
20 | -------
21 | list
22 |
23 | """
24 | if isinstance(color, (int, float)): # color given as brightness
25 | result = [color, color, color, 1]
26 | elif isinstance(color, list):
27 | if len(color) == 3: # color given as RGB
28 | result = color + [1]
29 | elif len(color) == 4:
30 | result = color.copy()
31 | else:
32 | assert False, f'len({color}) = {len(color)} has to be in [3, 4]'
33 | else:
34 | assert False, f'color specification not understood: {color}'
35 | return result
36 |
37 |
38 | def _padded_concatenate(tensors, dim, pad_width, pad_value):
39 | """
40 | Concatenate tensors along specified dimension, adding padding between them.
41 |
42 | Parameters
43 | ----------
44 | tensors : list of torch.Tensor
45 | Tensors to be concatenated.
46 | dim : int
47 | Dimension along witch to concatenate.
48 | pad_width : int
49 | Width of the padding along concatenation dimension.
50 | pad_value : numeric or list like
51 | Value to fill the padding tensor with. Can be list, e.g. RGBA for tensors with color as last dimension.
52 |
53 | Returns
54 | -------
55 | torch.Tensor
56 |
57 | """
58 | tensors = list(tensors)
59 | device = tensors[0].device
60 | if pad_width != 0:
61 | pad_shape = list(tensors[0].shape)
62 | pad_shape[dim] = pad_width
63 | if isinstance(pad_value, list):
64 | pad_value = torch.Tensor(pad_value).to(device).type_as(tensors[0])
65 | pad_tensor = torch.ones(pad_shape).to(device) * pad_value
66 | [tensors.insert(i, pad_tensor) for i in range(len(tensors)-1, 0, -1)]
67 | return torch.cat(tensors, dim=dim)
68 |
69 |
70 | class ImageGridVisualizer(ContainerVisualizer):
71 | """
72 | Visualizer that arranges outputs of child visualizers in a grid of images.
73 |
74 | Parameters
75 | ----------
76 | row_specs: list
77 | List of dimension names. These dimensions of the outputs of child visualizers will be put
78 | into the height dimension of the resulting image, according to the order in the list.
79 |
80 | In other words, data points only separated in dimensions at the beginning of this list will be right next to
81 | each other, while data points separated in dimensions towards the back will be further away from each other
82 | in the output image.
83 |
84 | A special dimension name is 'V' (for visualizers).
85 | It stands for the dimension differentiating between the child visualizers.
86 |
87 | **Example**:
88 | Given the tensor :code:`[[1, 2 , 3 ], [10, 20, 30]]` with shape (2, 3)
89 | and dimension names :code:`['A', 'B']`, this is the order of the rows, depending on the specified row_specs
90 | (suppose :code:`column_specs = []`):
91 |
92 | - If :code:`row_specs = ['B', 'A']`, the output will be :code:`[1, 2, 3, 10, 20, 30]`
93 | - If :code:`row_specs = ['A', 'B']`, the output will be :code:`[1, 10, 2, 20, 3, 30]`
94 |
95 | column_specs : list
96 | As row_specs but for columns of resulting image. Each dimension of child visualizations has to either
97 | occur in row_specs or column_specs. The intersection of row_specs and column specs has to be empty.
98 | pad_width : int or dict
99 | Determines the width of padding when concatenating images. Depending on type:
100 |
101 | - int: Padding will have this width for concatenations along all dimensions, apart from H and W (no
102 | padding between adjacent pixels in image)
103 | - dict: Keys are dimension names, values the padding width when concatenating along them. Special key
104 | 'rest' determines default value if given (otherwise no padding is used as default).
105 |
106 | pad_value : int or dict
107 | Determines the color of padding when concatenating images. Colors can be given as floats (gray values) or
108 | list of RGB / RGBA values. If dict, interpreted as pad_width
109 | upsampling_factor : int
110 | The whole resulting image grid will be upsampled by this factor. Useful when visualizing small images in
111 | tensorboard, but can lead to unnecessarily big file sizes.
112 | *super_args : list
113 | **super_kwargs : dict
114 |
115 | """
116 | def __init__(self, row_specs=('H', 'C', 'V'), column_specs=('W', 'D', 'T', 'B'),
117 | pad_width=1, pad_value=.5, upsampling_factor=1, *super_args, **super_kwargs):
118 | super(ImageGridVisualizer, self).__init__(
119 | in_spec=None, out_spec=None,
120 | suppress_spec_adjustment=True,
121 | equalize_visualization_shapes=False,
122 | *super_args, **super_kwargs)
123 | assert all([d not in column_specs for d in row_specs]), 'every spec has to go either in rows or colums'
124 |
125 | # determine if the individual visualizers should be stacked as rows or columns
126 | if 'V' in row_specs:
127 | assert row_specs[-1] == 'V'
128 | row_specs = row_specs[:-1]
129 | self.visualizer_stacking = 'rows'
130 | elif 'V' in column_specs:
131 | assert column_specs[-1] == 'V'
132 | column_specs = column_specs[:-1]
133 | self.visualizer_stacking = 'columns'
134 | else:
135 | self.visualizer_stacking = 'rows'
136 |
137 | self.n_row_dims = len(row_specs)
138 | self.n_col_dims = len(column_specs)
139 | self.row_specs = row_specs
140 | self.column_specs = column_specs
141 | self.initial_spec = list(row_specs) + list(column_specs) + ['out_height', 'out_width', 'Color']
142 |
143 | self.pad_value = pad_value
144 | self.pad_width = pad_width
145 |
146 | self.upsampling_factor = upsampling_factor
147 |
148 | def get_pad_kwargs(self, spec):
149 | # helper function to manage padding widths and values
150 | result = dict()
151 | hw = ('H', 'W')
152 | if isinstance(self.pad_width, dict):
153 | result['pad_width'] = self.pad_width.get(spec, self.pad_width.get('rest', 0))
154 | else:
155 | result['pad_width'] = self.pad_width if spec not in hw else 0
156 |
157 | if isinstance(self.pad_value, dict):
158 | result['pad_value'] = self.pad_value.get(spec, self.pad_value.get('rest', .5))
159 | else:
160 | result['pad_value'] = self.pad_value if spec not in hw else 0
161 | result['pad_value'] = _to_rgba(result['pad_value'])
162 |
163 | return result
164 |
165 | def visualization_to_image(self, visualization, spec, return_debug_info=True):
166 | # converts a high dimensional visualization to a 2D image, as specified by self.row_dims and self.column_dims.
167 |
168 | # this function should not be overridden for regular container visualizers, but is here, as the specs have to be
169 | # known in the main visualization function. 'combine()' is never called, internal is used directly
170 |
171 | debug_info = {} # store information that will be useful if concatenation fails later on
172 |
173 | collapsing_rules = [(d, 'B') for d in spec if d not in self.initial_spec] # everything unknown goes into batch
174 |
175 | # first, add all axes to visualization that are not present (by converting its spec to self.initial_spec)
176 | visualization, spec = convert_dim(visualization, in_spec=spec, out_spec=self.initial_spec,
177 | collapsing_rules=collapsing_rules, return_spec=True)
178 |
179 | debug_info['shape_before_concatenation'] = visualization.shape
180 |
181 | assert visualization.shape[-1] == 4, \
182 | f'Got color dimension of {visualization.shape[-4]} != 4. ' \
183 | f'All visualizers used in ImageGridVisualizer must return RGBA ' \
184 | f'(which is the case if colorization is not disabled).'
185 |
186 | # collapse the rows in the 'out_width' dimension, it is at position -2
187 | for _ in range(self.n_row_dims):
188 | visualization = _padded_concatenate(visualization, dim=-3, **self.get_pad_kwargs(spec[0]))
189 | spec = spec[1:]
190 |
191 | # collapse the columns in the 'out_height' dimension, it is at position -3
192 | for _ in range(self.n_col_dims):
193 | visualization = _padded_concatenate(visualization, dim=-2, **self.get_pad_kwargs(spec[0]))
194 | spec = spec[1:]
195 |
196 | debug_info['shape_after_concatenation'] = visualization.shape
197 |
198 | return visualization if not return_debug_info else visualization, debug_info
199 |
200 | def internal(self, *args, return_spec=False, **states):
201 | images = []
202 | debug_infos = []
203 | for name in self.visualizer_kwarg_names:
204 | image, debug_info = self.visualization_to_image(*states[name])
205 | images.append(image)
206 | debug_infos.append(debug_info)
207 |
208 | try:
209 | if self.visualizer_stacking == 'rows':
210 | result = _padded_concatenate(images, dim=-3, **self.get_pad_kwargs('V'))
211 | else:
212 | result = _padded_concatenate(images, dim=-2, **self.get_pad_kwargs('V'))
213 | except RuntimeError as e:
214 | table = Texttable()
215 | error_string = 'Shape Mismatch:\n'
216 | error_string += 'Shapes returned by child-visualizers: \n'
217 |
218 | table.add_rows([
219 | ['Visualizer Class',
220 | f'row_specs:\n{shape_to_str(self.row_specs)}',
221 | f'column_specs:\n{shape_to_str(self.column_specs)}', 'resulting\nimage shape'],
222 | *[[type(visualizer).__name__,
223 | shape_to_str(shape_before[:self.n_row_dims]),
224 | shape_to_str(shape_before[self.n_row_dims:-3]),
225 | shape_to_str(shape_after)]
226 | for visualizer, (shape_before, shape_after) in zip(
227 | self.visualizers,
228 | [(info['shape_before_concatenation'], info['shape_after_concatenation']) for info in debug_infos]
229 | )]
230 | ])
231 | error_string += table.draw() + ''
232 | if self.visualizer_stacking == 'rows':
233 | error_string += '\nThe column_specs should match, as you want to stack the visualizers as rows'
234 | else:
235 | error_string += '\nThe row_specs should match, as you want to stack the visualizers as columns'
236 |
237 | assert False, error_string
238 |
239 | if self.upsampling_factor is not 1:
240 | result = F.interpolate(
241 | result.permute(2, 0, 1)[None],
242 | scale_factor=self.upsampling_factor,
243 | mode='nearest')
244 | result = result[0].permute(1, 2, 0)
245 |
246 | if return_spec:
247 | return result, ['H', 'W', 'Color']
248 | else:
249 | return result
250 |
251 |
252 | class RowVisualizer(ImageGridVisualizer):
253 | """
254 | Visualizer that arranges outputs of child visualizers in a grid of images, with different child visualizations
255 | stacked vertically.
256 | For more options, see ImageGridVisualizer
257 |
258 | Parameters
259 | ----------
260 | *super_args :
261 | **super_kwargs :
262 |
263 | """
264 | def __init__(self, *super_args, **super_kwargs):
265 | super(RowVisualizer, self).__init__(
266 | row_specs=('H', 'S', 'C', 'V'),
267 | column_specs=('W', 'D', 'T', 'B'),
268 | *super_args, **super_kwargs)
269 |
270 |
271 | class ColumnVisualizer(ImageGridVisualizer):
272 | """
273 | Visualizer that arranges outputs of child visualizers in a grid of images, with different child visualizations
274 | stacked horizontally (side by side).
275 | For more options, see ImageGridVisualizer
276 |
277 | Parameters
278 | ----------
279 | *super_args :
280 | **super_kwargs :
281 |
282 | """
283 | def __init__(self, *super_args, **super_kwargs):
284 | super(ColumnVisualizer, self).__init__(
285 | row_specs=('H', 'D', 'T', 'B'),
286 | column_specs=('W', 'S', 'C', 'V'),
287 | *super_args, **super_kwargs)
288 |
289 |
290 | class OverlayVisualizer(ContainerVisualizer):
291 | """
292 | Visualizer that overlays the outputs of its child visualizers on top of each other, using transparency based on
293 | the alpha channel. The output of the first child visualizer will be on the top, the last on the bottom.
294 |
295 | Parameters
296 | ----------
297 | *super_args :
298 | **super_kwargs :
299 |
300 | """
301 | def __init__(self, *super_args, **super_kwargs):
302 | super(OverlayVisualizer, self).__init__(
303 | in_spec=['Color', 'B'],
304 | out_spec=['Color', 'B'],
305 | *super_args, **super_kwargs
306 | )
307 |
308 | def combine(self, *visualizations, **_):
309 | result = visualizations[-1]
310 | for overlay in reversed(visualizations[:-1]):
311 | a = (overlay[3] + result[3] * (1 - overlay[3]))[None]
312 | rgb = overlay[:3] * overlay[3][None] + result[:3] * result[3][None] * (1 - overlay[3][None])
313 | rgb /= a
314 | result = torch.cat([rgb, a], dim=0)
315 | return result
316 |
317 |
318 | class AverageVisualizer(ContainerVisualizer):
319 | """
320 | Visualizer that averages the outputs of its child visualizers on top of each other,
321 | using the alpha channel as weights .
322 |
323 | Parameters
324 | ----------
325 | *super_args :
326 | **super_kwargs :
327 |
328 | """
329 | def __init__(self, *super_args, **super_kwargs):
330 | super(AverageVisualizer, self).__init__(
331 | in_spec=['Color', 'B'],
332 | out_spec=['Color', 'B'],
333 | *super_args, **super_kwargs
334 | )
335 |
336 | def combine(self, *visualizations, **_):
337 | result = torch.ones_like(visualizations[0]) # alpha = 1
338 | visualizations = torch.stack(visualizations, dim=1)
339 | weights = visualizations[3] / visualizations[3].sum(0, keepdim=True).clamp(min=1e-6)
340 | result[:3] = (visualizations[:3] * weights[None]).sum(1)
341 | return result
342 |
343 |
344 | class RiffleVisualizer(ContainerVisualizer):
345 | """
346 | Riffles the outputs of its child visualizers along specified dimension.
347 |
348 | For a way to also scale target and prediction equally, have a look at StackVisualizer (if the range of
349 | values is known, you can also just use value_range: [a, b] for the child visualizers
350 |
351 | Parameters
352 | ----------
353 | riffle_dim : str
354 | Name of dimension which is to be riffled
355 | *super_args :
356 | **super_kwargs :
357 |
358 | Examples
359 | --------
360 | Riffle the channels of a multidimensional target and prediction, such that corresponding images are closer
361 | spatially. A possible configuration file would look like this::
362 |
363 | RiffleVisualizer:
364 | riffle_dim: 'C'
365 | visualizers:
366 | - ImageVisualizer:
367 | input_mapping:
368 | image: 'target'
369 | - ImageVisualizer:
370 | input_mapping:
371 | image: 'prediction'
372 |
373 | """
374 | def __init__(self, riffle_dim='C', *super_args, **super_kwargs):
375 | super(RiffleVisualizer, self).__init__(
376 | in_spec=[riffle_dim, 'B'],
377 | out_spec=[riffle_dim, 'B'],
378 | *super_args, **super_kwargs
379 | )
380 |
381 | def combine(self, *visualizations, **_):
382 | assert len(visualizations) > 0
383 | assert all(v.shape == visualizations[0].shape for v in visualizations[1:]), \
384 | f'Not all input visualizations have the same shape: {[v.shape for v in visualizations]}'
385 | result = torch.stack(visualizations, dim=1)
386 | result = result.contiguous().view(-1, visualizations[0].shape[1])
387 | return result
388 |
389 |
390 | class StackVisualizer(ContainerVisualizer):
391 | """
392 | Stacks the outputs of its child visualizers along specified dimension.
393 |
394 | Parameters
395 | ----------
396 | stack_dim : str
397 | Name of new dimension along which the child visualizations will be stacked. None of the child visualizations
398 | should have this dimension.
399 | *super_args :
400 | **super_kwargs :
401 |
402 | Example
403 | -------
404 | Stack a multidimensional target and prediction along an extra dimension, e.g. 'TP'. In order to make target
405 | and prediction images comparable, disable colorization in the child visualizers and colorize only in the
406 | StackVisualizer, jointly coloring along 'TP', thus scaling target and prediction images by the same factors.
407 | The config would look like this::
408 |
409 | StackVisualizer:
410 | stack_dim: 'TP'
411 | colorize: True
412 | color_jointly: ['H', 'W', 'TP'] # plus other dimensions you want to scale equally, e.g. D = depth
413 | visualizers:
414 | - ImageVisualizer:
415 | input_mapping:
416 | image: 'target'
417 | colorize = False
418 | - ImageVisualizer:
419 | input_mapping:
420 | image: 'target'
421 | colorize = True
422 |
423 | """
424 | def __init__(self, stack_dim='S', *super_args, **super_kwargs):
425 | super(StackVisualizer, self).__init__(
426 | in_spec=[stack_dim, 'B'],
427 | out_spec=[stack_dim, 'B'],
428 | *super_args, **super_kwargs
429 | )
430 |
431 | def combine(self, *visualizations, **_):
432 | assert len(visualizations) > 0
433 | assert all(v.shape[1:] == visualizations[0].shape[1:] for v in visualizations[1:]), \
434 | f'Not all input visualizations have the same shape, apart from at dimension 0: ' \
435 | f'{[v.shape for v in visualizations]}'
436 | result = torch.cat(visualizations, dim=0)
437 | return result
438 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/firelight/visualizers/visualizers.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .base import BaseVisualizer
2 | import torch
3 | import numpy as np
4 | from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
5 | from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
6 | from torch.nn.functional import pad
7 | try:
8 | import umap
9 | umap_available = True
10 | except ImportError:
11 | umap_available = False
12 |
13 |
14 | class IdentityVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
15 | """
16 | Visualizer that returns the tensor passed to it. Useful to visualize each channel of a tensor as a separate image.
17 | """
18 | def __init__(self, **super_kwargs):
19 | super(IdentityVisualizer, self).__init__(
20 | in_specs={'tensor': 'B'},
21 | out_spec='B',
22 | **super_kwargs
23 | )
24 |
25 | def visualize(self, tensor, **_):
26 | """"""
27 | return tensor
28 |
29 |
30 | class ImageVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
31 | """
32 | Same as :class:`IdentityVisualizer`, but acting on 'image'.
33 | """
34 | def __init__(self, **super_kwargs):
35 | super(ImageVisualizer, self).__init__(
36 | in_specs={'image': 'B'},
37 | out_spec='B',
38 | **super_kwargs
39 | )
40 |
41 | def visualize(self, image, **_):
42 | """"""
43 | return image
44 |
45 |
46 | class InputVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
47 | """
48 | Same as :class:`IdentityVisualizer`, but acting on 'input'.
49 | """
50 | def __init__(self, **super_kwargs):
51 | super(InputVisualizer, self).__init__(
52 | in_specs={'input': 'B'},
53 | out_spec='B',
54 | **super_kwargs
55 | )
56 |
57 | def visualize(self, input, **_):
58 | """"""
59 | return input
60 |
61 |
62 | class TargetVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
63 | """
64 | Same as :class:`IdentityVisualizer`, but acting on 'target'.
65 | """
66 | def __init__(self, **super_kwargs):
67 | super(TargetVisualizer, self).__init__(
68 | in_specs={'target': 'B'},
69 | out_spec='B',
70 | **super_kwargs
71 | )
72 |
73 | def visualize(self, target, **_):
74 | """"""
75 | return target
76 |
77 |
78 | class PredictionVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
79 | """
80 | Same as :class:`IdentityVisualizer`, but acting on 'prediction'.
81 | """
82 | def __init__(self, **super_kwargs):
83 | super(PredictionVisualizer, self).__init__(
84 | in_specs={'prediction': 'B'},
85 | out_spec='B',
86 | **super_kwargs
87 | )
88 |
89 | def visualize(self, prediction, **_):
90 | """"""
91 | return prediction
92 |
93 |
94 | class DifferenceVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
95 | """
96 | Visualizer that returns the difference minuend - subtrahend between the tensors passed to it.
97 | """
98 | def __init__(self, **super_kwargs):
99 | super(DifferenceVisualizer, self).__init__(
100 | in_specs={'minuend': 'B', 'subtrahend': 'B'},
101 | out_spec='B',
102 | **super_kwargs
103 | )
104 |
105 | def visualize(self, minuend, subtrahend, **_):
106 | """"""
107 | return minuend - subtrahend
108 |
109 |
110 | class MSEVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
111 | """
112 | Visualize the Mean Squared Error (MSE) between two tensors (e.g. prediction and target).
113 | """
114 | def __init__(self, **super_kwargs):
115 | super(MSEVisualizer, self).__init__(
116 | in_specs={'prediction': 'B', 'target': 'B'},
117 | out_spec='B',
118 | **super_kwargs
119 | )
120 |
121 | def visualize(self, prediction, target, **_):
122 | """"""
123 | return (prediction - target)**2
124 |
125 |
126 | class SegmentationVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
127 | """
128 | Same as :class:`IdentityVisualizer`, but acting on 'segmentation'.
129 | """
130 | def __init__(self, **super_kwargs):
131 | super(SegmentationVisualizer, self).__init__(
132 | in_specs={'segmentation': 'B'},
133 | out_spec='B',
134 | **super_kwargs
135 | )
136 |
137 | def visualize(self, segmentation, **_):
138 | """"""
139 | return segmentation
140 |
141 |
142 | class RGBVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
143 | """
144 | Visualize the input tensor as RGB images. If the input has n * 3 channels, n color images will be returned.
145 | """
146 | def __init__(self, **super_kwargs):
147 | super(RGBVisualizer, self).__init__(
148 | in_specs={'tensor': ['B', 'C']},
149 | out_spec=['B', 'C', 'Color'],
150 | **super_kwargs
151 | )
152 |
153 | def visualize(self, tensor, **_):
154 | """"""
155 | n_channels = tensor.shape[1]
156 | assert n_channels % 3 == 0, f'the number of channels {tensor.shape[1]} has to be divisible by 3'
157 | tensor = tensor.contiguous().view(tensor.shape[0], n_channels // 3, 3)
158 | return tensor
159 |
160 |
161 | class MaskVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
162 | """
163 | Returns a mask that is 1 where the input image equals the mask label passed at initialization, and 0 elsewhere
164 |
165 | Parameters
166 | ----------
167 | mask_label : float
168 | Label to be used for the construction of the mask
169 | **super_kwargs
170 |
171 | """
172 | def __init__(self, mask_label, **super_kwargs):
173 | super_kwargs['value_range'] = super_kwargs.get('value_range', [0, 1])
174 | super(MaskVisualizer, self).__init__(
175 | in_specs={'tensor': ['B']},
176 | out_spec=['B'],
177 | **super_kwargs
178 | )
179 | self.mask_label = mask_label
180 |
181 | def visualize(self, tensor, **states):
182 | """"""
183 | return (tensor == self.mask_label).float()
184 |
185 |
186 | class ThresholdVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
187 | """
188 | Returns a mask resulting from thresholding the input tensor.
189 |
190 | Parameters
191 | ----------
192 | threshold : int or float
193 | mode : str, optional
194 | one of the :attr:`ThresholdVisualizer.MODES`, specifying how to threshold.
195 | super_kwargs
196 | """
197 |
198 | MODES = ['greater', 'smaller', 'greater_equal', 'smaller_equal']
199 |
200 | def __init__(self, threshold, mode='greater_equal', **super_kwargs):
201 | super_kwargs['value_range'] = super_kwargs.get('value_range', [0, 1])
202 | super(ThresholdVisualizer, self).__init__(
203 | in_specs={'tensor': ['B']},
204 | out_spec=['B'],
205 | **super_kwargs
206 | )
207 | self.threshold = threshold
208 | assert mode in ThresholdVisualizer.MODES, f'Mode {mode} not supported. Use one of {ThresholdVisualizer.MODES}'
209 | self.mode = mode
210 |
211 | def visualize(self, tensor, **_):
212 | """"""
213 | if self.mode == 'greater':
214 | result = tensor > self.threshold
215 | elif self.mode == 'smaller':
216 | result = tensor < self.threshold
217 | elif self.mode == 'greater_equal':
218 | result = tensor >= self.threshold
219 | elif self.mode == 'smaller_equal':
220 | result = tensor <= self.threshold
221 | else:
222 | raise NotImplementedError
223 | return result.float()
224 |
225 |
226 | def pca(embedding, output_dimensions=3, reference=None, center_data=False):
227 | """
228 | Principal component analysis wrapping :class:`sklearn.decomposition.PCA`.
229 | Dimension 1 of the input embedding is reduced
230 |
231 | Parameters
232 | ----------
233 | embedding : torch.Tensor
234 | Embedding whose dimensions will be reduced.
235 | output_dimensions : int, optional
236 | Number of dimension to reduce to.
237 | reference : torch.Tensor, optional
238 | Optional tensor that will be used to train PCA on.
239 | center_data : bool, optional
240 | Whether to subtract the mean before PCA.
241 |
242 | Returns
243 | -------
244 | torch.Tensor
245 | """
246 | # embedding shape: first two dimensions correspond to batchsize and embedding(==channel) dim,
247 | # so shape should be (B, C, H, W) or (B, C, D, H, W).
248 | _pca = PCA(n_components=output_dimensions)
249 | # reshape embedding
250 | output_shape = list(embedding.shape)
251 | output_shape[1] = output_dimensions
252 | flat_embedding = embedding.cpu().numpy().reshape(embedding.shape[0], embedding.shape[1], -1)
253 | flat_embedding = flat_embedding.transpose((0, 2, 1))
254 | if reference is not None:
255 | # assert reference.shape[:2] == embedding.shape[:2]
256 | flat_reference = reference.cpu().numpy().reshape(reference.shape[0], reference.shape[1], -1)\
257 | .transpose((0, 2, 1))
258 | else:
259 | flat_reference = flat_embedding
260 |
261 | if center_data:
262 | means = np.mean(flat_reference, axis=0, keepdims=True)
263 | flat_reference -= means
264 | flat_embedding -= means
265 |
266 | pca_output = []
267 | for flat_reference, flat_image in zip(flat_reference, flat_embedding):
268 | # fit PCA to array of shape (n_samples, n_features)..
269 | _pca.fit(flat_reference)
270 | # ..and apply to input data
271 | pca_output.append(_pca.transform(flat_image))
272 |
273 | return torch.stack([torch.from_numpy(x.T) for x in pca_output]).reshape(output_shape)
274 |
275 |
276 | # TODO: make PcaVisualizer take one embedding to fit and one to transform
277 | class PcaVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
278 | """
279 | PCA Visualization of high dimensional embedding tensor. An arbitrary number of channels is reduced
280 | to a multiple of 3 which are interpreted as sets RGB images.
281 |
282 | Parameters
283 | ----------
284 | n_components : int, optional
285 | Number of components to use. Must be divisible by 3.
286 | joint_specs: :obj:`tuple` of :obj:`str`, optional
287 | Entries only separated along these axis are treated jointly.
288 |
289 | Defaults to spatial dimensions.
290 |
291 | Use e.g. :code:`('B', 'H', 'W')` to run PCA jointly on all images of the batch.
292 | #TODO: make this example work. Right now, all dimensions except 'B' work.
293 | **super_kwargs
294 |
295 | """
296 | def __init__(self, n_components=3, joint_specs=('D', 'H', 'W'), **super_kwargs):
297 | super(PcaVisualizer, self).__init__(
298 | in_specs={'embedding': ['B', 'C'] + list(joint_specs)},
299 | out_spec=['B', 'C', 'Color'] + list(joint_specs),
300 | **super_kwargs)
301 |
302 | assert n_components % 3 == 0, f'{n_components} is not divisible by 3.'
303 | self.n_images = n_components // 3
304 |
305 | def visualize(self, embedding, **_):
306 | """"""
307 | # if there are not enough channels, add some zeros
308 | if embedding.shape[1] < 3 * self.n_images:
309 | expanded_embedding = torch.zeros(embedding.shape[0], 3 * self.n_images, *embedding.shape[2:])\
310 | .float().to(embedding.device)
311 | expanded_embedding[:, :embedding.shape[1]] = embedding
312 | embedding = expanded_embedding
313 | result = pca(embedding, output_dimensions=3 * self.n_images)
314 | result = result.contiguous().view((result.shape[0], self.n_images, 3) + result.shape[2:])
315 | return result
316 |
317 |
318 | class MaskedPcaVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
319 | """
320 | Version of PcaVisualizer that allows for an ignore mask. Data points which are labeled with :code:`ignore_label` in
321 | the segmentation are ignored in the PCA analysis.
322 |
323 | Parameters
324 | ----------
325 | ignore_label : int or float, optional
326 | Data points with this label in the segmentation are ignored.
327 | n_components : int, optional
328 | Number of components for PCA. Has to be divisible by 3, such that a whole number of RGB images can be
329 | returned.
330 | background_label : float, optional
331 | As in BaseVisualizer, here used by default to color the ignored region.
332 | **super_kwargs
333 |
334 | """
335 | def __init__(self, ignore_label=None, n_components=3, background_label=0, **super_kwargs):
336 | super(MaskedPcaVisualizer, self).__init__(
337 | in_specs={'embedding': 'BCDHW', 'segmentation': 'BCDHW'},
338 | out_spec=['B', 'C', 'Color', 'D', 'H', 'W'],
339 | background_label=background_label,
340 | **super_kwargs)
341 | self.ignore_label = ignore_label
342 | assert n_components % 3 == 0, f'{n_components} is not divisible by 3.'
343 | self.n_images = n_components // 3
344 |
345 | def visualize(self, embedding, segmentation, **_):
346 | """"""
347 | # if there are not enough channels, add some zeros
348 | if embedding.shape[1] < 3 * self.n_images:
349 | expanded_embedding = torch.zeros(embedding.shape[0], 3 * self.n_images, *embedding.shape[2:])\
350 | .float().to(embedding.device)
351 | expanded_embedding[:, :embedding.shape[1]] = embedding
352 | embedding = expanded_embedding
353 |
354 | if self.ignore_label is None:
355 | mask = torch.ones((embedding.shape[0],) + embedding.shape[2:])
356 | else:
357 | mask = segmentation != self.ignore_label
358 | if len(mask.shape) == len(embedding.shape):
359 | assert mask.shape[1] == 1, f'{mask.shape}'
360 | mask = mask[:, 0]
361 | mask = mask.bool()
362 |
363 | masked = [embedding[i, :, m] for i, m in enumerate(mask)]
364 | masked = [None if d.nelement() < self.n_images * 3 else pca(d[None], 3 * self.n_images, center_data=True)[0]
365 | for d in masked]
366 | output_shape = list(embedding.shape)
367 | output_shape[1] = 3 * self.n_images
368 | result = torch.zeros(output_shape)
369 | for i, m in enumerate(mask):
370 | if masked[i] is not None:
371 | result[i, :, m] = masked[i]
372 | result = result.contiguous().view((result.shape[0], self.n_images, 3) + result.shape[2:])
373 | return result
374 |
375 |
376 | class TsneVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
377 | """
378 | tSNE Visualization of high dimensional embedding tensor. An arbitrary number of channels is reduced
379 | to a multiple of 3 which are interpreted as sets RGB images.
380 |
381 | Parameters
382 | ----------
383 | n_components : int, optional
384 | Number of components to use. Must be divisible by 3.
385 | joint_dims: :obj:`tuple` of :obj:`str`, optional
386 | Entries only separated along these axis are treated jointly.
387 |
388 | Defaults to spatial dimensions.
389 | **super_kwargs
390 |
391 | """
392 | def __init__(self, joint_dims=None, n_components=3, **super_kwargs):
393 | joint_dims = ['D', 'H', 'W'] if joint_dims is None else joint_dims
394 | assert 'C' not in joint_dims
395 | super(TsneVisualizer, self).__init__(
396 | in_specs={'embedding': joint_dims + ['C']},
397 | out_spec=joint_dims + ['C', 'Color'],
398 | **super_kwargs
399 | )
400 | assert n_components % 3 == 0, f'{n_components} is not divisible by 3.'
401 | self.n_images = n_components // 3
402 |
403 | def visualize(self, embedding, **_):
404 | """"""
405 | shape = embedding.shape
406 | # bring embedding into shape (n_samples, n_features) as requested by TSNE
407 | embedding = embedding.contiguous().view(-1, shape[-1])
408 |
409 | result = TSNE(n_components=self.n_images * 3).fit_transform(embedding.cpu().numpy())
410 | result = torch.Tensor(result).float().to(embedding.device)
411 | # revert flattening, add color dimension
412 | result = result.contiguous().view(*shape[:-1], self.n_images, 3)
413 | return result
414 |
415 |
416 | class UmapVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
417 | """
418 | UMAP Visualization of high dimensional embedding tensor. An arbitrary number of channels is reduced
419 | to 3 which are interpreted as RGB.
420 |
421 | For a detailed discussion of parameters, see https://umap-learn.readthedocs.io/en/latest/parameters.html.
422 |
423 | Parameters
424 | ----------
425 | joint_dims: :obj:`tuple` of :obj:`str`, optional
426 | Entries only separated along these axis are treated jointly.
427 |
428 | Defaults to spatial dimensions.
429 | n_components : int, optional
430 | Number of components to use. Must be divisible by 3.
431 | n_neighbors: int, optional
432 | controls how many neighbors are considered for distance
433 | estimation on the manifold. Low number focuses on local
434 | distance, large numbers more on global structure, default 15.
435 | min_dist: float, optional
436 | minimum distance of points after dimension reduction, default 0.1.
437 |
438 | **super_kwargs
439 |
440 | """
441 | def __init__(self, joint_dims=None, n_components=3, n_neighbors=15, min_dist=0.1, **super_kwargs):
442 | assert umap_available, "You tried to use the UmapVisualizer without having UMAP installed."
443 | joint_dims = ['D', 'H', 'W'] if joint_dims is None else joint_dims
444 | assert 'C' not in joint_dims
445 | super(UmapVisualizer, self).__init__(
446 | in_specs={'embedding': joint_dims + ['C']},
447 | out_spec=joint_dims + ['C', 'Color'],
448 | **super_kwargs
449 | )
450 |
451 | self.min_dist = min_dist
452 | self.n_neighbors = n_neighbors
453 |
454 | assert n_components % 3 == 0, f'{n_components} is not divisible by 3.'
455 | self.n_images = n_components // 3
456 |
457 | def visualize(self, embedding, **_):
458 | """"""
459 | shape = embedding.shape
460 | # bring embedding into shape (n_samples, n_features) as requested by TSNE
461 | embedding = embedding.contiguous().view(-1, shape[-1])
462 |
463 | result = umap.UMAP(n_components=self.n_images * 3,
464 | min_dist=self.min_dist,
465 | n_neighbors=self.n_neighbors).fit_transform(embedding.cpu().numpy())
466 | result = torch.Tensor(result).float().to(embedding.device)
467 | # revert flattening, add color dimension
468 | result = result.contiguous().view(*shape[:-1], self.n_images, 3)
469 | return result
470 |
471 |
472 | class NormVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
473 | """
474 | Visualize the norm of a tensor, along a given direction (by default over the channels).
475 |
476 | Parameters
477 | ----------
478 | order : int, optional
479 | Order of the norm (Default is 2, euclidean norm).
480 | dim : str, optional
481 | Name of the dimension in which the norm is computed.
482 | **super_kwargs
483 |
484 | """
485 | def __init__(self, order=2, dim='C', **super_kwargs):
486 | super(NormVisualizer, self).__init__(
487 | in_specs={'tensor': ['B'] + [dim]},
488 | out_spec='B',
489 | **super_kwargs
490 | )
491 | self.order = order
492 |
493 | def visualize(self, tensor, **_):
494 | """"""
495 | return tensor.norm(p=self.order, dim=1)
496 |
497 |
498 | class DiagonalSplitVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
499 | """
500 | Combine two input images, displaying one above and one below the diagonal.
501 |
502 | Parameters
503 | ----------
504 | offset : int, optional
505 | The diagonal along which the image will be split is shifted by offset.
506 | **super_kwargs
507 |
508 | """
509 | def __init__(self, offset=0, **super_kwargs):
510 | super(DiagonalSplitVisualizer, self).__init__(
511 | in_specs={'upper_right_image': ['B', 'H', 'W'],
512 | 'lower_left_image': ['B', 'H', 'W']},
513 | out_spec=['B', 'H', 'W'],
514 | **super_kwargs
515 | )
516 | self.offset = offset
517 |
518 | def visualize(self, upper_right_image, lower_left_image, **_):
519 | """"""
520 | # upper_right and lower_left are tensors with shape (B, H, W)
521 |
522 | image_shape = upper_right_image.shape[1:]
523 |
524 | # construct upper triangular mask
525 | upper_right_mask = torch.ones(image_shape).triu(self.offset).float()
526 |
527 | upper_right_image = upper_right_image.float()
528 | lower_left_image = lower_left_image.float()
529 | return upper_right_image * upper_right_mask + lower_left_image * (1 - upper_right_mask)
530 |
531 |
532 | class CrackedEdgeVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
533 | """
534 | Visualize the boundaries of a segmentation.
535 |
536 | Parameters
537 | ----------
538 | width : int, optional
539 | width of the boundary in every direction
540 | connective_dims : tuple, optional
541 | Tuple of axis names. Edges in those axes will be shown.
542 |
543 | E.g. use :code:`('D', 'H', 'W')` to visualize edges in 3D.
544 |
545 | **super_kwargs
546 |
547 | """
548 | def __init__(self, width=1, connective_dims=('H', 'W'), **super_kwargs):
549 | super_kwargs['value_range'] = super_kwargs.get('value_range', [0, 1])
550 | self.connective_dims = list(connective_dims)
551 | super(CrackedEdgeVisualizer, self).__init__(
552 | in_specs={'segmentation': ['B'] + self.connective_dims},
553 | out_spec=['B'] + self.connective_dims,
554 | **super_kwargs
555 | )
556 | self.width = width
557 | self.pad_slice_tuples = self.make_pad_slice_tuples()
558 |
559 | def make_pad_slice_tuples(self):
560 | def make_tuple(offset):
561 | padding0 = [int(offset[i//2] if i % 2 == 0 else 0)
562 | for i in reversed(range(2 * len(offset)))]
563 | padding1 = [int(offset[(i-1)//2] if i % 2 == 1 else 0)
564 | for i in reversed(range(2 * len(offset)))]
565 | slicing = [slice(None), ] + [(slice(None) if off == 0 else slice((off)//2, -off//2))
566 | for off in offset]
567 | return tuple(padding0), tuple(padding1), tuple(slicing)
568 |
569 | offsets = np.eye(len(self.connective_dims)).astype(np.int32) * self.width
570 | return [make_tuple(list(offset)) for offset in offsets]
571 |
572 | def visualize(self, segmentation, **_):
573 | """"""
574 | directional_boundaries = []
575 |
576 | for padding0, padding1, slicing in self.pad_slice_tuples:
577 | # e.g. pad0 = (0, 0, 3, 0), pad1=(0, 0, 0, 3), slice = [..., 2:-1, :]
578 | padded0 = pad(segmentation, padding0)
579 | padded1 = pad(segmentation, padding1)
580 | directional_boundaries.append((padded0 != padded1)[slicing])
581 | return torch.stack(directional_boundaries, dim=0).max(dim=0)[0].float()
582 |
583 |
584 | def _upsample_axis(tensor, axis, factor):
585 | shape = tensor.shape
586 | tensor = tensor.unsqueeze(axis + 1)
587 | tensor = tensor.expand(shape[:axis+1] + (factor,) + shape[axis+1:])
588 | tensor = tensor.reshape(shape[:axis] + (shape[axis] * factor,) + shape[axis+1:])
589 | return tensor
590 |
591 |
592 | class UpsamplingVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
593 | """
594 | Upsample a tensor along a list of axis (specified via specs) to a specified shape, by a list of specified
595 | factors or the shape of a reference tensor (given as an optional argument to visualize).
596 |
597 | Parameters
598 | ----------
599 | specs : list of str
600 | Specs of the axes to upsample along.
601 | shape : None or int or list, optional
602 | Shape after upsampling.
603 | factors: None or int or list, optional
604 | Factors to upsample by.
605 | **super_kwargs
606 |
607 | """
608 | def __init__(self, specs, shape=None, factors=None, **super_kwargs):
609 | self.specs = list(specs)
610 | self.out_shape = [shape] * len(specs) if isinstance(shape, int) else shape
611 | self.factors = [factors] * len(specs) if isinstance(factors, int) else shape
612 | assert self.out_shape is None or self.factors is None, \
613 | f'Pleas specify at most one of shape and factors'
614 | self.from_reference = self.out_shape is None and self.factors is None
615 | super(UpsamplingVisualizer, self).__init__(
616 | in_specs={
617 | 'tensor': ['B'] + self.specs,
618 | 'reference': ['B'] + self.specs
619 | },
620 | out_spec=['B'] + self.specs,
621 | **super_kwargs
622 | )
623 |
624 | def visualize(self, tensor, reference=None, **_):
625 | """"""
626 | if self.from_reference:
627 | assert reference is not None, \
628 | f'Please supply a reference when neither upsampled shape nor upsampling factors are specified at init.'
629 | out_shape = reference.shape[1:]
630 | else:
631 | if self.out_shape is not None:
632 | out_shape = self.out_shape
633 | else:
634 | out_shape = [s * f for s, f in zip(tensor.shape[1:], self.factors)]
635 | out_shape = np.array(out_shape)
636 | in_shape = np.array(tensor.shape[1:])
637 | assert all(out_shape % in_shape == 0), f'Cannot upsample from {in_shape} to {out_shape}.'
638 | factors = (out_shape / in_shape).astype(int)
639 | for i, factor in enumerate(factors):
640 | tensor = _upsample_axis(tensor, i+1, factor)
641 | return tensor
642 |
643 |
644 | class SemanticVisualizer(BaseVisualizer):
645 | """
646 | Maps certain values in input data to specified colors
647 |
648 | Parameters
649 | ----------
650 | color_dict : dict
651 | super_kwargs
652 | """
653 |
654 | def __init__(self, color_dict, **super_kwargs):
655 | super_kwargs['value_range'] = super_kwargs.get('value_range', [0, 1])
656 | super(SemanticVisualizer, self).__init__(
657 | in_specs={'tensor': ['B']},
658 | out_spec=['B', 'Color'],
659 | **super_kwargs
660 | )
661 | # add alpha if not present, convert to tensor
662 | for value, color in color_dict.items():
663 | if len(color) == 3:
664 | color_dict[value] = [*color, 1]
665 | color_dict = {int(value): torch.tensor(color).float()
666 | for value, color in color_dict.items()}
667 | self.default_color = color_dict.pop('rest', torch.zeros(4))
668 | self.color_dict = color_dict
669 |
670 | def visualize(self, tensor, **_):
671 | """"""
672 | result = tensor.new_empty((len(tensor), 4), dtype=torch.float)
673 | result[:] = self.default_color
674 | for value, color in self.color_dict.items():
675 | result[tensor == value] = color
676 | return result
677 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/requirements.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | pyyaml>=3.12x
2 | matplotlib
3 | numpy
4 | scikit-learn
5 | scikit-image
6 | torch>=1.0
7 | texttable
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | firelight - A visualization library for PyTorch tensors.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import setuptools
6 | import os
7 |
8 | def read_file(filename):
9 | with open(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), filename)) as f:
10 | return f.read()
11 |
12 | setuptools.setup(
13 | name="firelight",
14 | author="Roman Remme",
15 | author_email="roman.remme@iwr.uni-heidelberg.de",
16 | description="A visualization library for PyTorch tensors.",
17 | long_description=read_file('README.md'),
18 | long_description_content_type='text/markdown',
19 | url='https://github.com/inferno-pytorch/firelight',
20 | version="0.2.1",
21 | install_requires=[
22 | "pyyaml>=3.12",
23 | "matplotlib",
24 | "numpy",
25 | "scikit-learn",
26 | "scikit-image",
27 | "torch",
28 | "texttable",
29 | ],
30 | extras_requires={
31 | 'umap': ['umap-learn>=0.3.8'],
32 | },
33 | license="Apache Software License 2.0",
34 | packages=setuptools.find_packages(),
35 | classifiers=[
36 | "Intended Audience :: Science/Research",
37 | "Programming Language :: Python :: 3",
38 | "License :: OSI Approved :: Apache Software License",
39 | ]
40 | )
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------