├── .gitattributes
├── .gitignore
├── .spyproject
└── config
│ ├── backups
│ ├── codestyle.ini.bak
│ ├── encoding.ini.bak
│ ├── vcs.ini.bak
│ └── workspace.ini.bak
│ ├── codestyle.ini
│ ├── defaults
│ ├── defaults-codestyle-0.2.0.ini
│ ├── defaults-encoding-0.2.0.ini
│ ├── defaults-vcs-0.2.0.ini
│ └── defaults-workspace-0.2.0.ini
│ ├── encoding.ini
│ ├── vcs.ini
│ └── workspace.ini
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── SECURITY.md
├── examples
├── svdd_example_KPCA.py
├── svdd_example_PSO.py
├── svdd_example_confusion_matrix.py
├── svdd_example_cross_validation.py
├── svdd_example_grid_search.py
├── svdd_example_hybrid_data.py
├── svdd_example_kernel.py
└── svdd_example_unlabeled_data.py
├── requirements.txt
└── src
├── BaseSVDD.py
└── __pycache__
├── BananaDataset.cpython-38.pyc
├── BaseSVDD.cpython-38.pyc
└── testmodel.cpython-38.pyc
/.gitattributes:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Auto detect text files and perform LF normalization
2 | * text=auto
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Created by https://www.toptal.com/developers/gitignore/api/python
2 | # Edit at https://www.toptal.com/developers/gitignore?templates=python
3 |
4 | ### Python ###
5 | # Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
6 | __pycache__/
7 | *.py[cod]
8 | *$py.class
9 |
10 | # C extensions
11 | *.so
12 |
13 | # Distribution / packaging
14 | .Python
15 | build/
16 | develop-eggs/
17 | dist/
18 | downloads/
19 | eggs/
20 | .eggs/
21 | lib/
22 | lib64/
23 | parts/
24 | sdist/
25 | var/
26 | wheels/
27 | share/python-wheels/
28 | *.egg-info/
29 | .installed.cfg
30 | *.egg
31 | MANIFEST
32 |
33 | # PyInstaller
34 | # Usually these files are written by a python script from a template
35 | # before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it.
36 | *.manifest
37 | *.spec
38 |
39 | # Installer logs
40 | pip-log.txt
41 | pip-delete-this-directory.txt
42 |
43 | # Unit test / coverage reports
44 | htmlcov/
45 | .tox/
46 | .nox/
47 | .coverage
48 | .coverage.*
49 | .cache
50 | nosetests.xml
51 | coverage.xml
52 | *.cover
53 | *.py,cover
54 | .hypothesis/
55 | .pytest_cache/
56 | cover/
57 |
58 | # Translations
59 | *.mo
60 | *.pot
61 |
62 | # Django stuff:
63 | *.log
64 | local_settings.py
65 | db.sqlite3
66 | db.sqlite3-journal
67 |
68 | # Flask stuff:
69 | instance/
70 | .webassets-cache
71 |
72 | # Scrapy stuff:
73 | .scrapy
74 |
75 | # Sphinx documentation
76 | docs/_build/
77 |
78 | # PyBuilder
79 | .pybuilder/
80 | target/
81 |
82 | # Jupyter Notebook
83 | .ipynb_checkpoints
84 |
85 | # IPython
86 | profile_default/
87 | ipython_config.py
88 |
89 | # pyenv
90 | # For a library or package, you might want to ignore these files since the code is
91 | # intended to run in multiple environments; otherwise, check them in:
92 | # .python-version
93 |
94 | # pipenv
95 | # According to pypa/pipenv#598, it is recommended to include Pipfile.lock in version control.
96 | # However, in case of collaboration, if having platform-specific dependencies or dependencies
97 | # having no cross-platform support, pipenv may install dependencies that don't work, or not
98 | # install all needed dependencies.
99 | #Pipfile.lock
100 |
101 | # poetry
102 | # Similar to Pipfile.lock, it is generally recommended to include poetry.lock in version control.
103 | # This is especially recommended for binary packages to ensure reproducibility, and is more
104 | # commonly ignored for libraries.
105 | # https://python-poetry.org/docs/basic-usage/#commit-your-poetrylock-file-to-version-control
106 | #poetry.lock
107 |
108 | # pdm
109 | # Similar to Pipfile.lock, it is generally recommended to include pdm.lock in version control.
110 | #pdm.lock
111 | # pdm stores project-wide configurations in .pdm.toml, but it is recommended to not include it
112 | # in version control.
113 | # https://pdm.fming.dev/#use-with-ide
114 | .pdm.toml
115 |
116 | # PEP 582; used by e.g. github.com/David-OConnor/pyflow and github.com/pdm-project/pdm
117 | __pypackages__/
118 |
119 | # Celery stuff
120 | celerybeat-schedule
121 | celerybeat.pid
122 |
123 | # SageMath parsed files
124 | *.sage.py
125 |
126 | # Environments
127 | .env
128 | .venv
129 | env/
130 | venv/
131 | ENV/
132 | env.bak/
133 | venv.bak/
134 |
135 | # Spyder project settings
136 | .spyderproject
137 | .spyproject
138 |
139 | # Rope project settings
140 | .ropeproject
141 |
142 | # mkdocs documentation
143 | /site
144 |
145 | # mypy
146 | .mypy_cache/
147 | .dmypy.json
148 | dmypy.json
149 |
150 | # Pyre type checker
151 | .pyre/
152 |
153 | # pytype static type analyzer
154 | .pytype/
155 |
156 | # Cython debug symbols
157 | cython_debug/
158 |
159 | # PyCharm
160 | # JetBrains specific template is maintained in a separate JetBrains.gitignore that can
161 | # be found at https://github.com/github/gitignore/blob/main/Global/JetBrains.gitignore
162 | # and can be added to the global gitignore or merged into this file. For a more nuclear
163 | # option (not recommended) you can uncomment the following to ignore the entire idea folder.
164 | #.idea/
165 |
166 | ### Python Patch ###
167 | # Poetry local configuration file - https://python-poetry.org/docs/configuration/#local-configuration
168 | poetry.toml
169 |
170 | # ruff
171 | .ruff_cache/
172 |
173 | # LSP config files
174 | pyrightconfig.json
175 |
176 | # End of https://www.toptal.com/developers/gitignore/api/python
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.spyproject/config/backups/codestyle.ini.bak:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [codestyle]
2 | indentation = True
3 | edge_line = True
4 | edge_line_columns = 79
5 |
6 | [main]
7 | version = 0.2.0
8 |
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.spyproject/config/backups/encoding.ini.bak:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [encoding]
2 | text_encoding = utf-8
3 |
4 | [main]
5 | version = 0.2.0
6 |
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.spyproject/config/backups/vcs.ini.bak:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [vcs]
2 | use_version_control = False
3 | version_control_system =
4 |
5 | [main]
6 | version = 0.2.0
7 |
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.spyproject/config/backups/workspace.ini.bak:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [workspace]
2 | restore_data_on_startup = True
3 | save_data_on_exit = True
4 | save_history = True
5 | save_non_project_files = False
6 |
7 | [main]
8 | version = 0.2.0
9 | recent_files = ['src\\BaseSVDD.py']
10 |
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.spyproject/config/codestyle.ini:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [codestyle]
2 | indentation = True
3 | edge_line = True
4 | edge_line_columns = 79
5 |
6 | [main]
7 | version = 0.2.0
8 |
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.spyproject/config/defaults/defaults-codestyle-0.2.0.ini:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [codestyle]
2 | indentation = True
3 | edge_line = True
4 | edge_line_columns = 79
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.spyproject/config/defaults/defaults-encoding-0.2.0.ini:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [encoding]
2 | text_encoding = utf-8
3 |
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.spyproject/config/defaults/defaults-vcs-0.2.0.ini:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [vcs]
2 | use_version_control = False
3 | version_control_system =
4 |
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.spyproject/config/defaults/defaults-workspace-0.2.0.ini:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [workspace]
2 | restore_data_on_startup = True
3 | save_data_on_exit = True
4 | save_history = True
5 | save_non_project_files = False
6 |
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.spyproject/config/encoding.ini:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [encoding]
2 | text_encoding = utf-8
3 |
4 | [main]
5 | version = 0.2.0
6 |
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.spyproject/config/vcs.ini:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [vcs]
2 | use_version_control = False
3 | version_control_system =
4 |
5 | [main]
6 | version = 0.2.0
7 |
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.spyproject/config/workspace.ini:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [workspace]
2 | restore_data_on_startup = True
3 | save_data_on_exit = True
4 | save_history = True
5 | save_non_project_files = False
6 |
7 | [main]
8 | version = 0.2.0
9 | recent_files = []
10 |
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2021 Kepeng Qiu
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 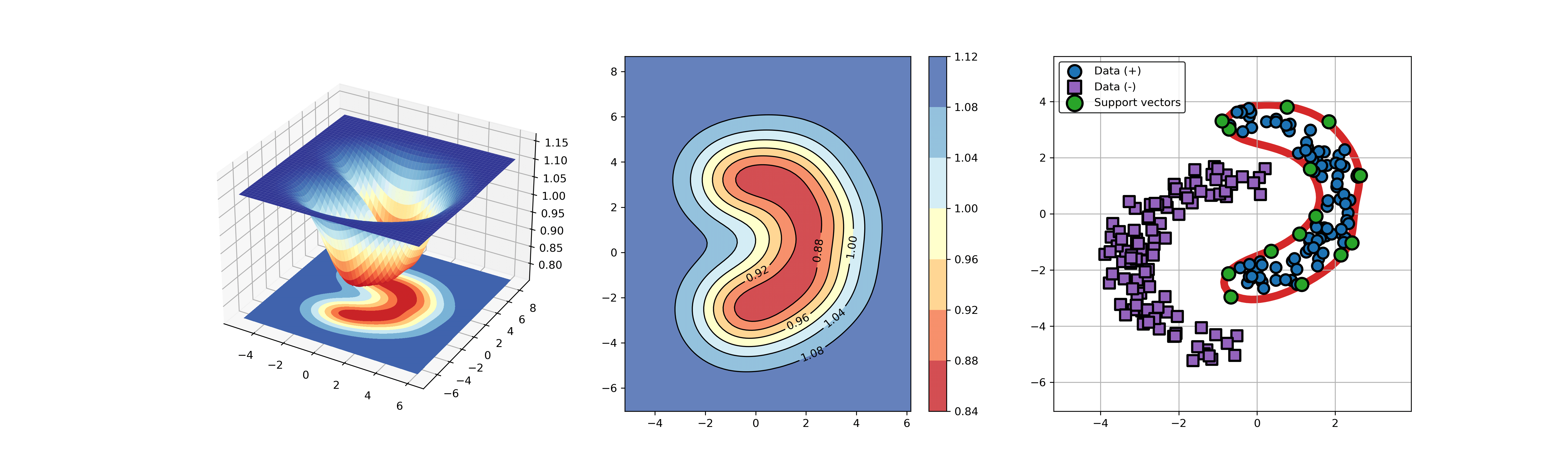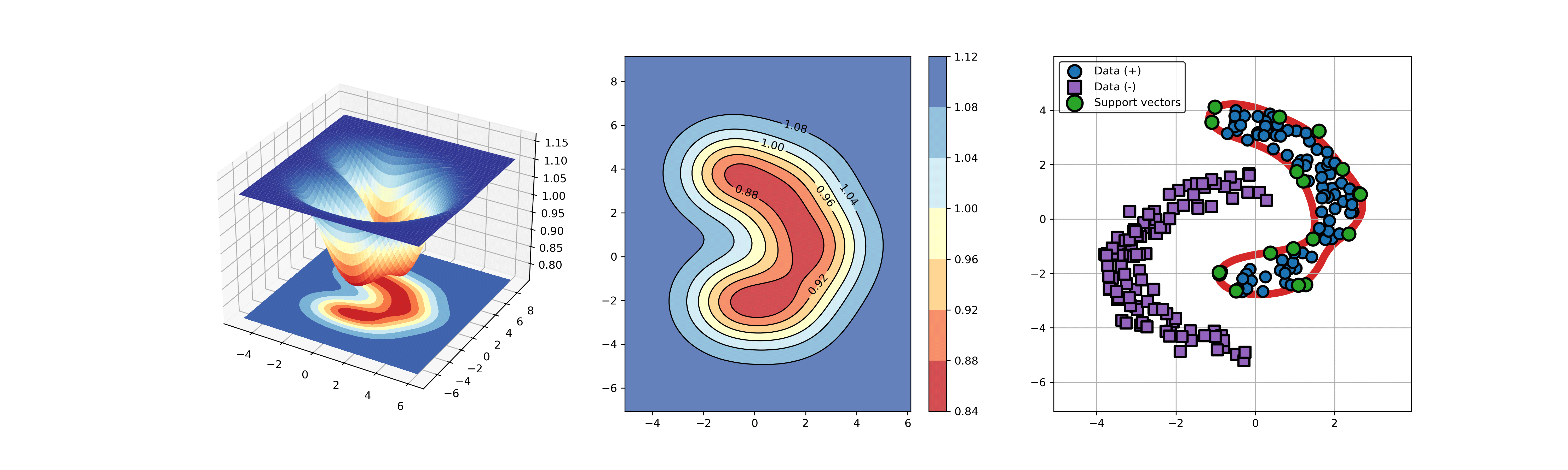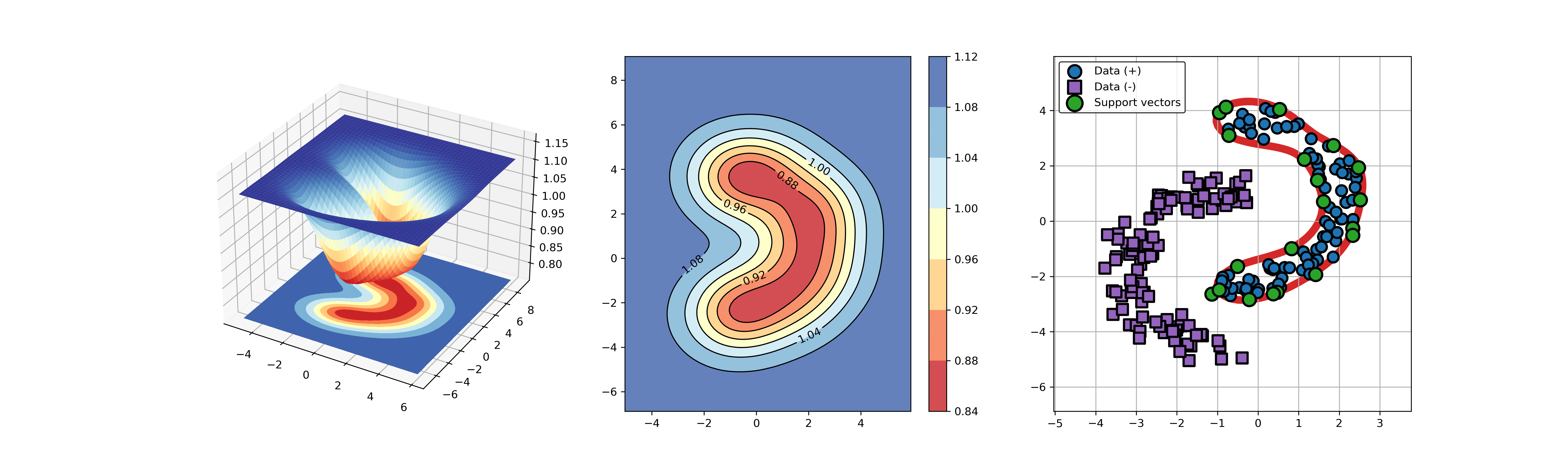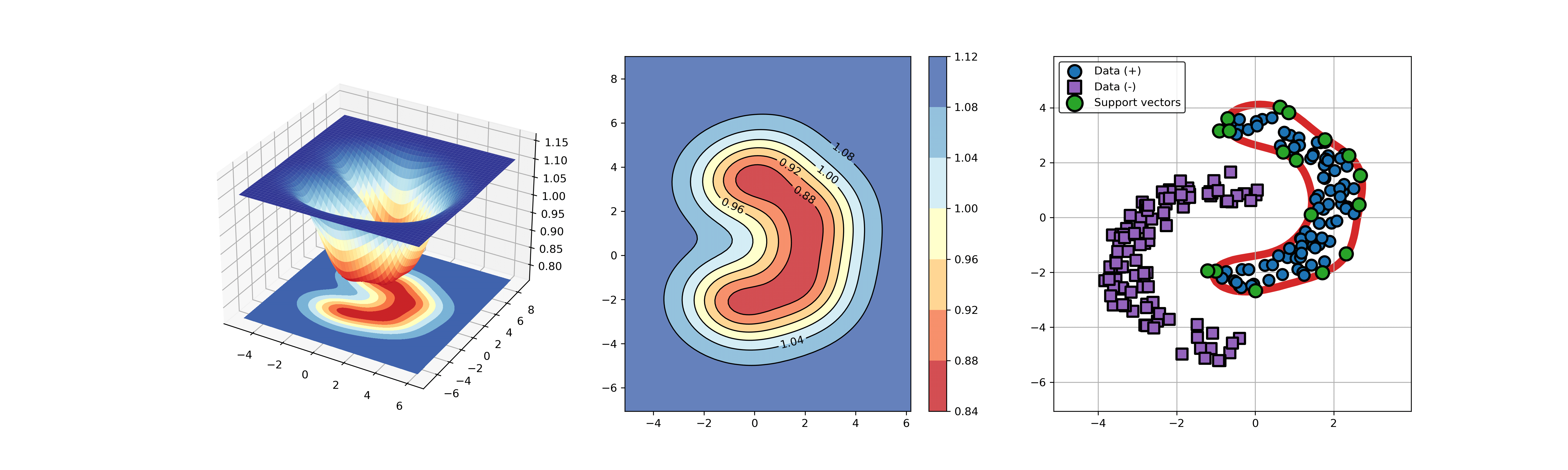 3 |
3 |
4 |
5 | Support Vector Data Description (SVDD)
6 |
7 | Python code for abnormal detection or fault detection using Support Vector Data Description (SVDD)
8 | Version 1.1, 11-NOV-2021
9 | Email: iqiukp@outlook.com
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |

14 |

15 |

16 |

17 |

18 |

19 |
22 |
23 | ## Main features
24 |
25 | - SVDD BaseEstimator based on sklearn.base for one-class or binary classification
26 | - Multiple kinds of kernel functions (linear, gaussian, polynomial, sigmoid)
27 | - Visualization of decision boundaries for 2D data
28 |
29 | ## Requirements
30 |
31 | - cvxopt
32 | - matplotlib
33 | - numpy
34 | - scikit_learn
35 | - scikit-opt (optional, only used for parameter optimization)
36 |
37 | ## Notices
38 |
39 | - The label must be 1 for positive sample or -1 for negative sample.
40 | - Detailed applications please see the examples.
41 | - This code is for reference only.
42 |
43 | ## Examples
44 |
45 | ### 01. svdd_example_unlabeled_data.py
46 |
47 | An example for SVDD model fitting using unlabeled data.
48 |
49 |
50 | 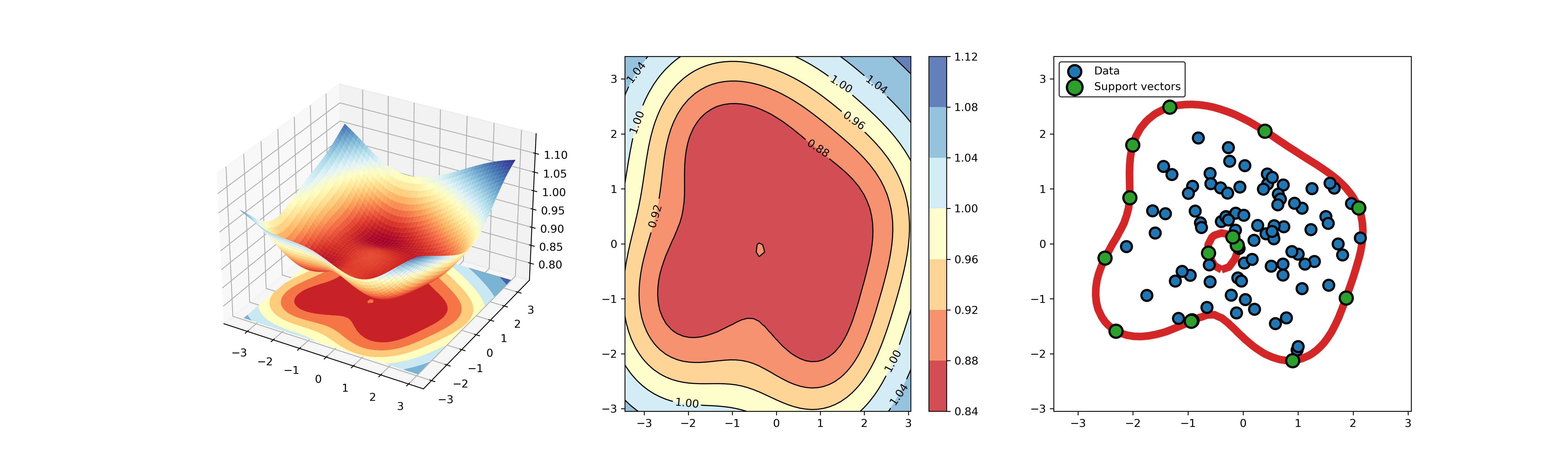 51 |
51 | 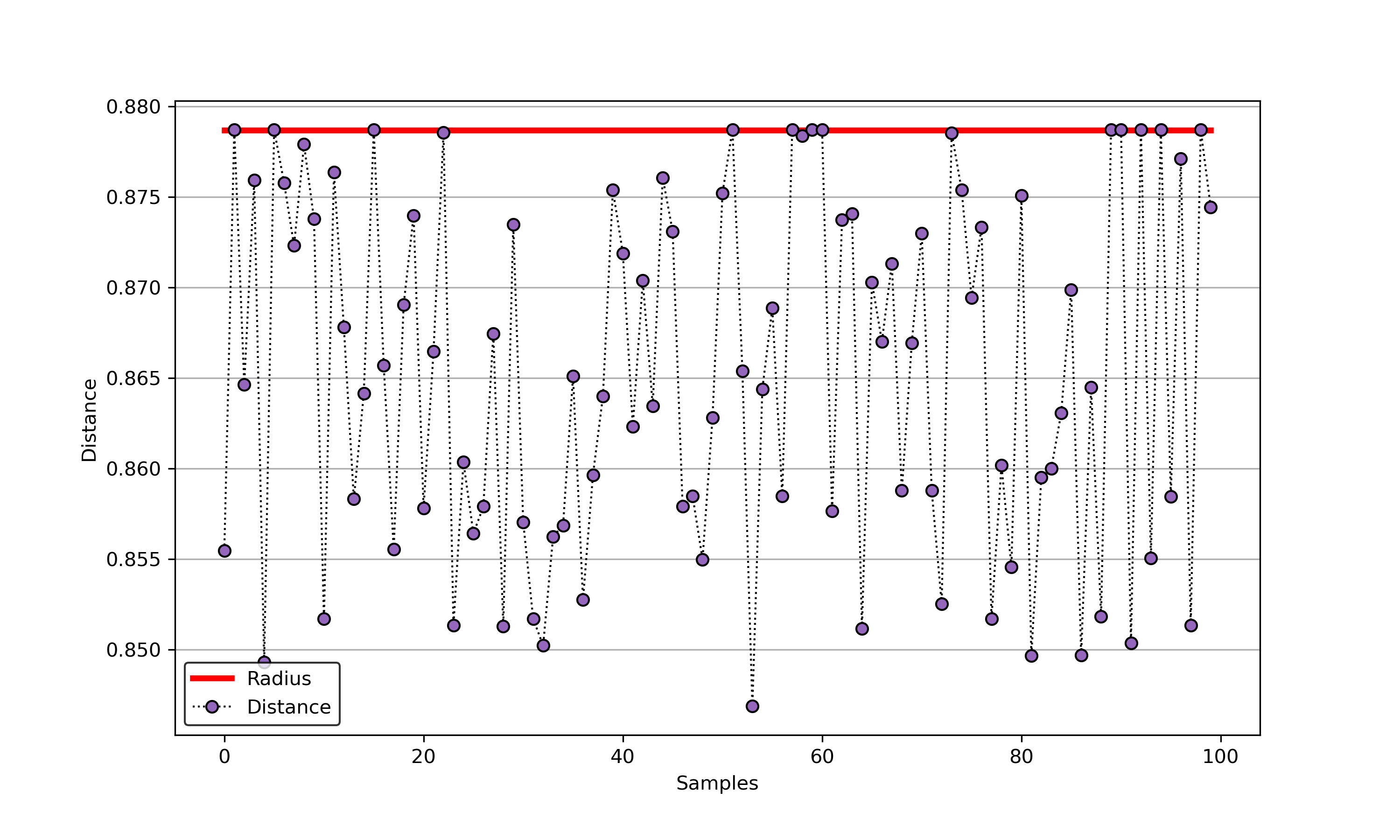 52 |
52 |
53 |
54 | ### 02. svdd_example_hybrid_data.py
55 |
56 | An example for SVDD model fitting with negataive samples.
57 |
58 | ```Python
59 | import sys
60 | sys.path.append("..")
61 | from sklearn.datasets import load_wine
62 | from src.BaseSVDD import BaseSVDD, BananaDataset
63 |
64 | # Banana-shaped dataset generation and partitioning
65 | X, y = BananaDataset.generate(number=100, display='on')
66 | X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = BananaDataset.split(X, y, ratio=0.3)
67 |
68 | #
69 | svdd = BaseSVDD(C=0.9, gamma=0.3, kernel='rbf', display='on')
70 |
71 | #
72 | svdd.fit(X_train, y_train)
73 |
74 | #
75 | svdd.plot_boundary(X_train, y_train)
76 |
77 | #
78 | y_test_predict = svdd.predict(X_test, y_test)
79 |
80 | #
81 | radius = svdd.radius
82 | distance = svdd.get_distance(X_test)
83 | svdd.plot_distance(radius, distance)
84 | ```
85 |
86 |
87 | 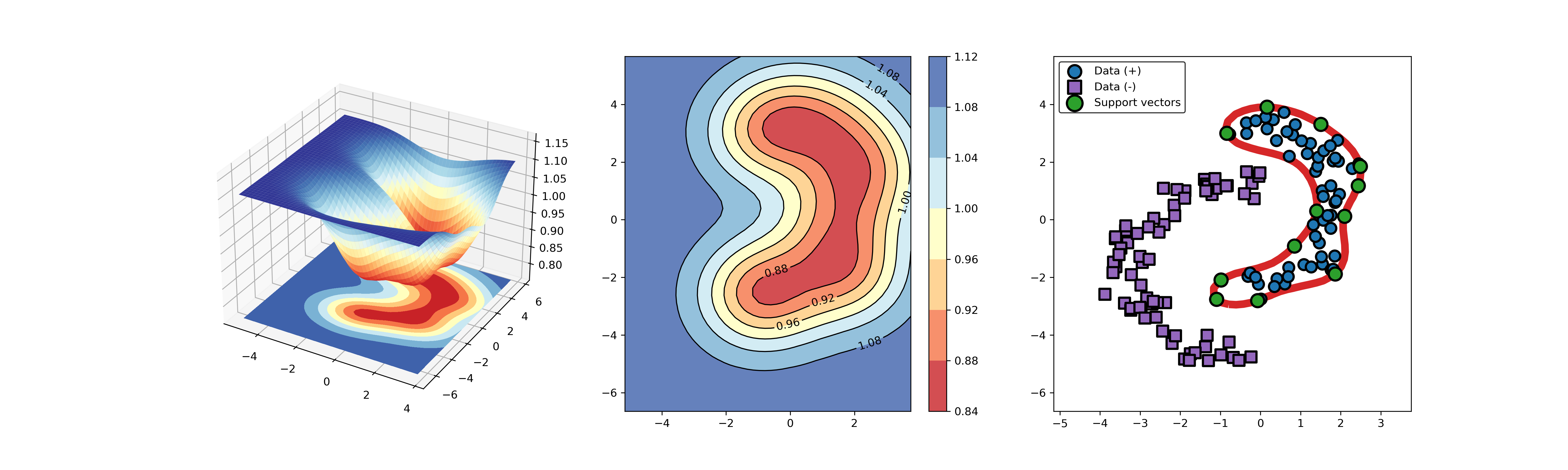 88 |
88 | 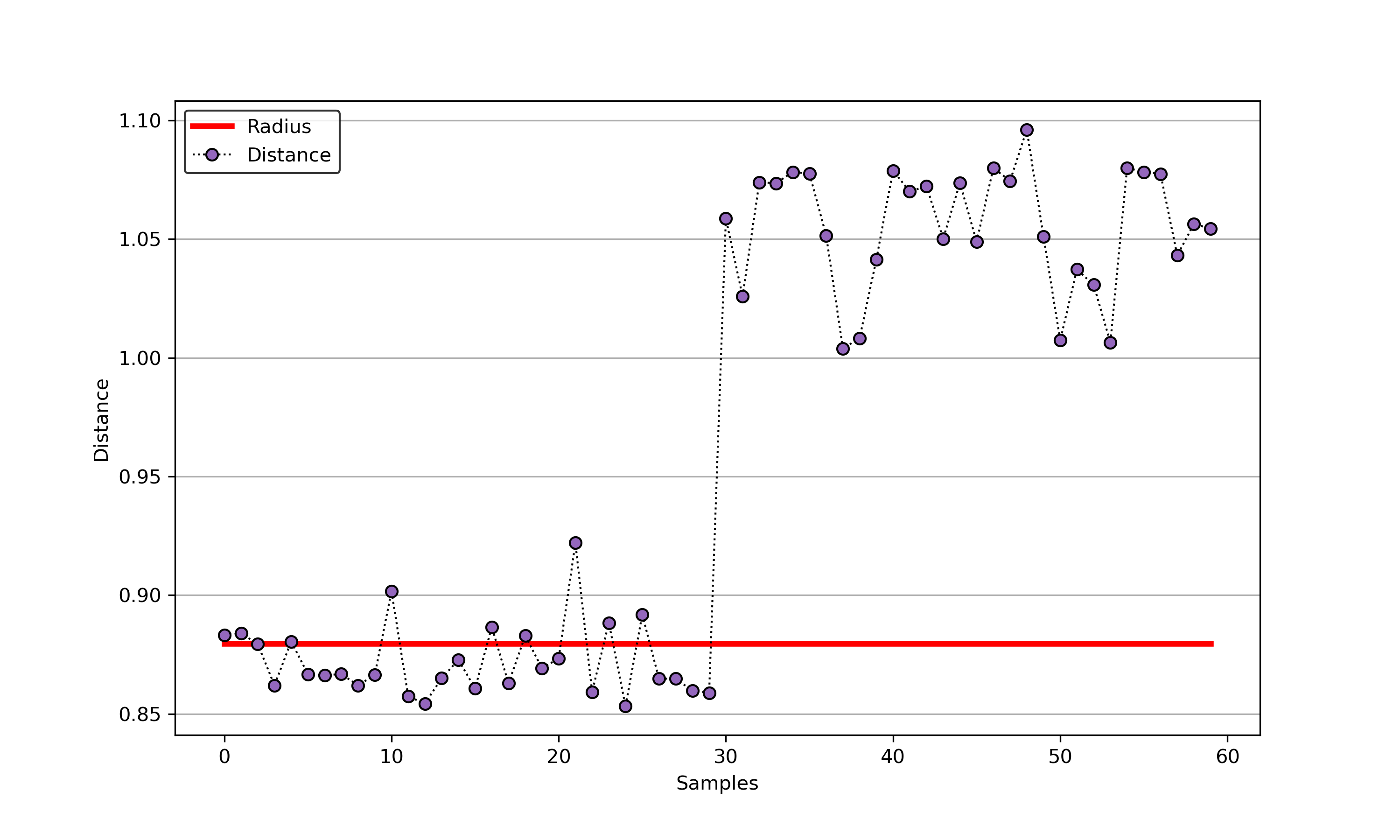 89 |
89 |
90 |
91 | ### 03. svdd_example_kernel.py
92 |
93 | An example for SVDD model fitting using different kernels.
94 |
95 | ```Python
96 | import sys
97 | sys.path.append("..")
98 | from src.BaseSVDD import BaseSVDD, BananaDataset
99 |
100 | # Banana-shaped dataset generation and partitioning
101 | X, y = BananaDataset.generate(number=100, display='on')
102 | X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = BananaDataset.split(X, y, ratio=0.3)
103 |
104 | # kernel list
105 | kernelList = {"1": BaseSVDD(C=0.9, kernel='rbf', gamma=0.3, display='on'),
106 | "2": BaseSVDD(C=0.9, kernel='poly',degree=2, display='on'),
107 | "3": BaseSVDD(C=0.9, kernel='linear', display='on')
108 | }
109 |
110 | #
111 | for i in range(len(kernelList)):
112 | svdd = kernelList.get(str(i+1))
113 | svdd.fit(X_train, y_train)
114 | svdd.plot_boundary(X_train, y_train)
115 | ```
116 |
117 |
118 |  119 |
119 | 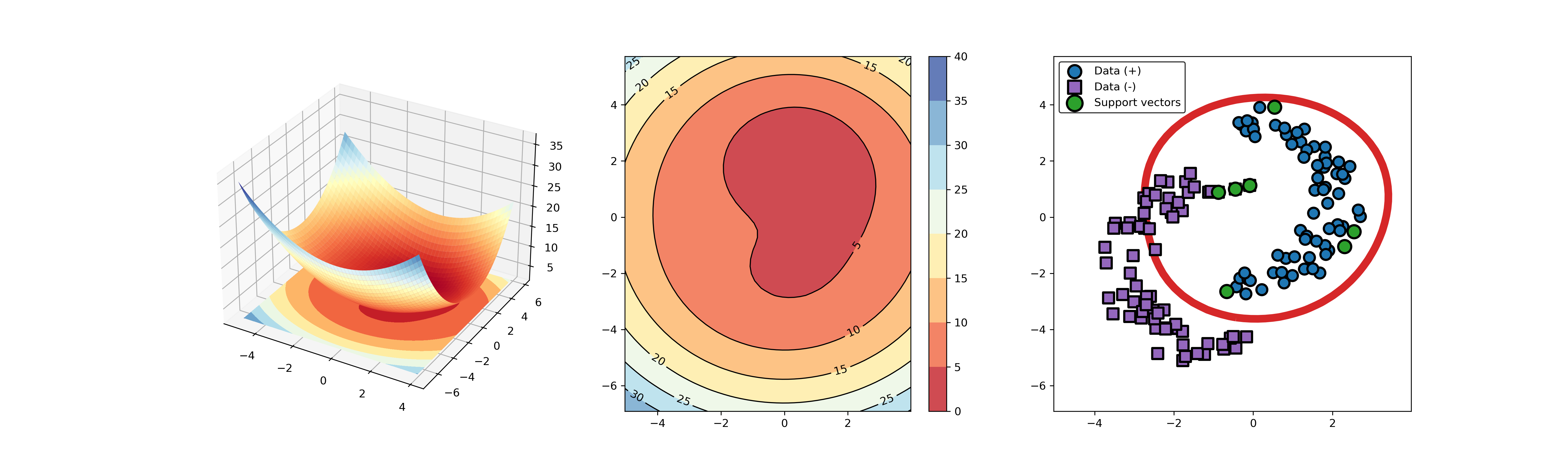 120 |
120 | 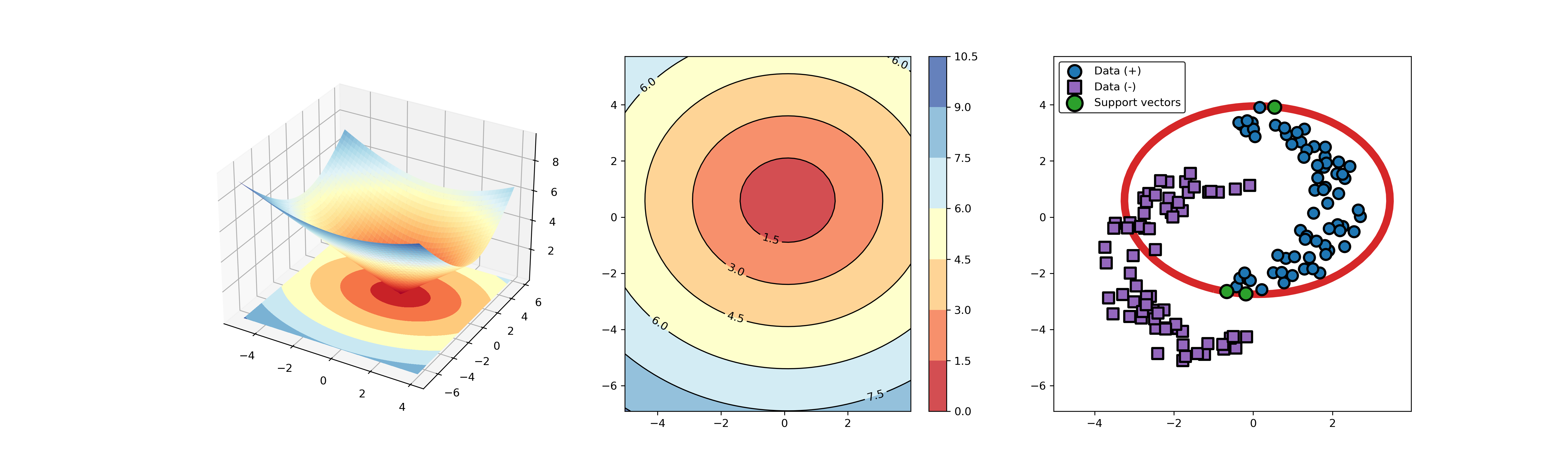 121 |
121 |
122 |
123 |
124 | ### 04. svdd_example_KPCA.py
125 |
126 | An example for SVDD model fitting using nonlinear principal component.
127 |
128 | The KPCA algorithm is used to reduce the dimension of the original data.
129 |
130 | ```Python
131 | import sys
132 | sys.path.append("..")
133 | import numpy as np
134 | from src.BaseSVDD import BaseSVDD
135 | from sklearn.decomposition import KernelPCA
136 |
137 |
138 | # create 100 points with 5 dimensions
139 | X = np.r_[np.random.randn(50, 5) + 1, np.random.randn(50, 5)]
140 | y = np.append(np.ones((50, 1), dtype=np.int64),
141 | -np.ones((50, 1), dtype=np.int64),
142 | axis=0)
143 |
144 | # number of the dimensionality
145 | kpca = KernelPCA(n_components=2, kernel="rbf", gamma=0.1, fit_inverse_transform=True)
146 | X_kpca = kpca.fit_transform(X)
147 |
148 | # fit the SVDD model
149 | svdd = BaseSVDD(C=0.9, gamma=10, kernel='rbf', display='on')
150 |
151 | # fit and predict
152 | svdd.fit(X_kpca, y)
153 | y_test_predict = svdd.predict(X_kpca, y)
154 |
155 | # plot the distance curve
156 | radius = svdd.radius
157 | distance = svdd.get_distance(X_kpca)
158 | svdd.plot_distance(radius, distance)
159 |
160 | # plot the boundary
161 | svdd.plot_boundary(X_kpca, y)
162 | ```
163 |
164 |
165 | 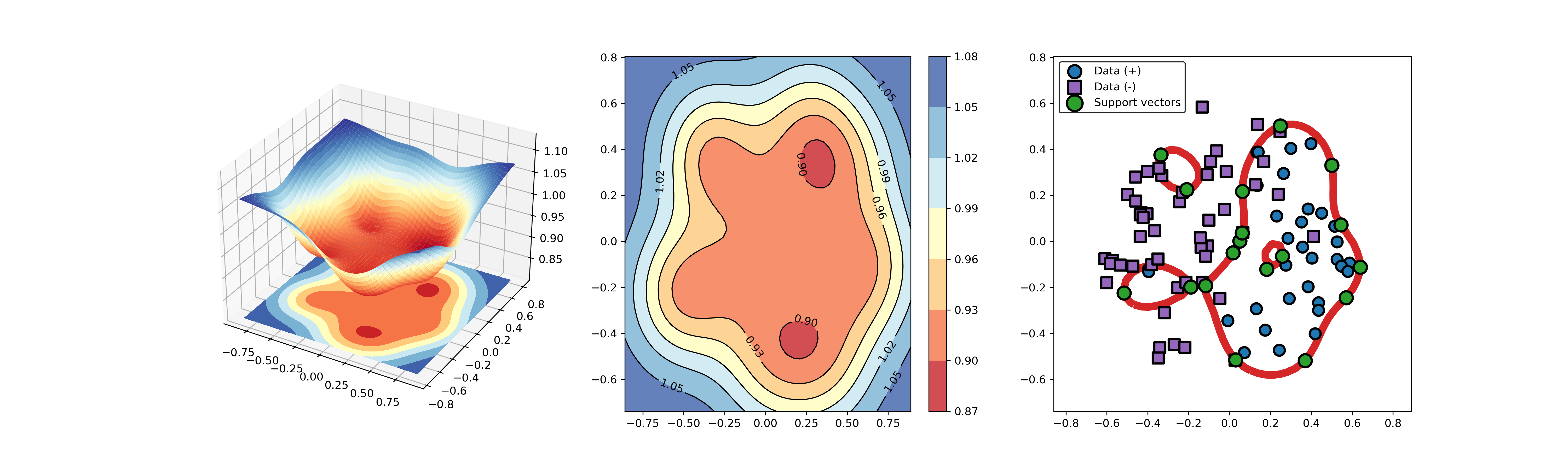 166 |
166 | 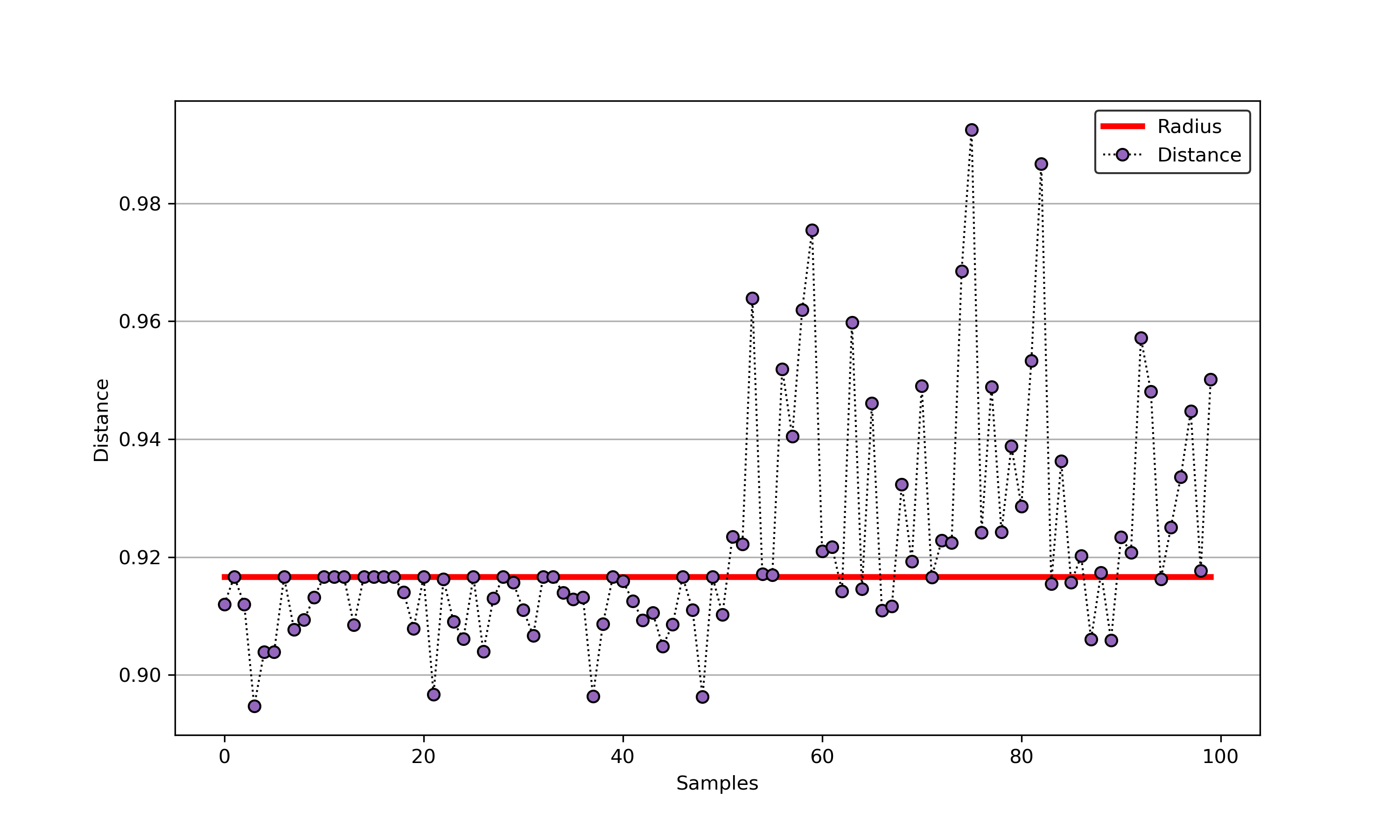 167 |
167 |
168 |
169 | ### 05. svdd_example_PSO.py
170 |
171 | An example for parameter optimization using PSO.
172 |
173 | "scikit-opt" is required in this example.
174 |
175 | https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt
176 |
177 |
178 | ```Python
179 | import sys
180 | sys.path.append("..")
181 | from src.BaseSVDD import BaseSVDD, BananaDataset
182 | from sko.PSO import PSO
183 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
184 |
185 |
186 | # Banana-shaped dataset generation and partitioning
187 | X, y = BananaDataset.generate(number=100, display='off')
188 | X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = BananaDataset.split(X, y, ratio=0.3)
189 |
190 | # objective function
191 | def objective_func(x):
192 | x1, x2 = x
193 | svdd = BaseSVDD(C=x1, gamma=x2, kernel='rbf', display='off')
194 | y = 1-svdd.fit(X_train, y_train).accuracy
195 | return y
196 |
197 | # Do PSO
198 | pso = PSO(func=objective_func, n_dim=2, pop=10, max_iter=20,
199 | lb=[0.01, 0.01], ub=[1, 3], w=0.8, c1=0.5, c2=0.5)
200 | pso.run()
201 |
202 | print('best_x is', pso.gbest_x)
203 | print('best_y is', pso.gbest_y)
204 |
205 | # plot the result
206 | fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
207 | ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
208 | ax.plot(pso.gbest_y_hist)
209 | ax.yaxis.grid()
210 | plt.show()
211 | ```
212 |
213 |
214 | 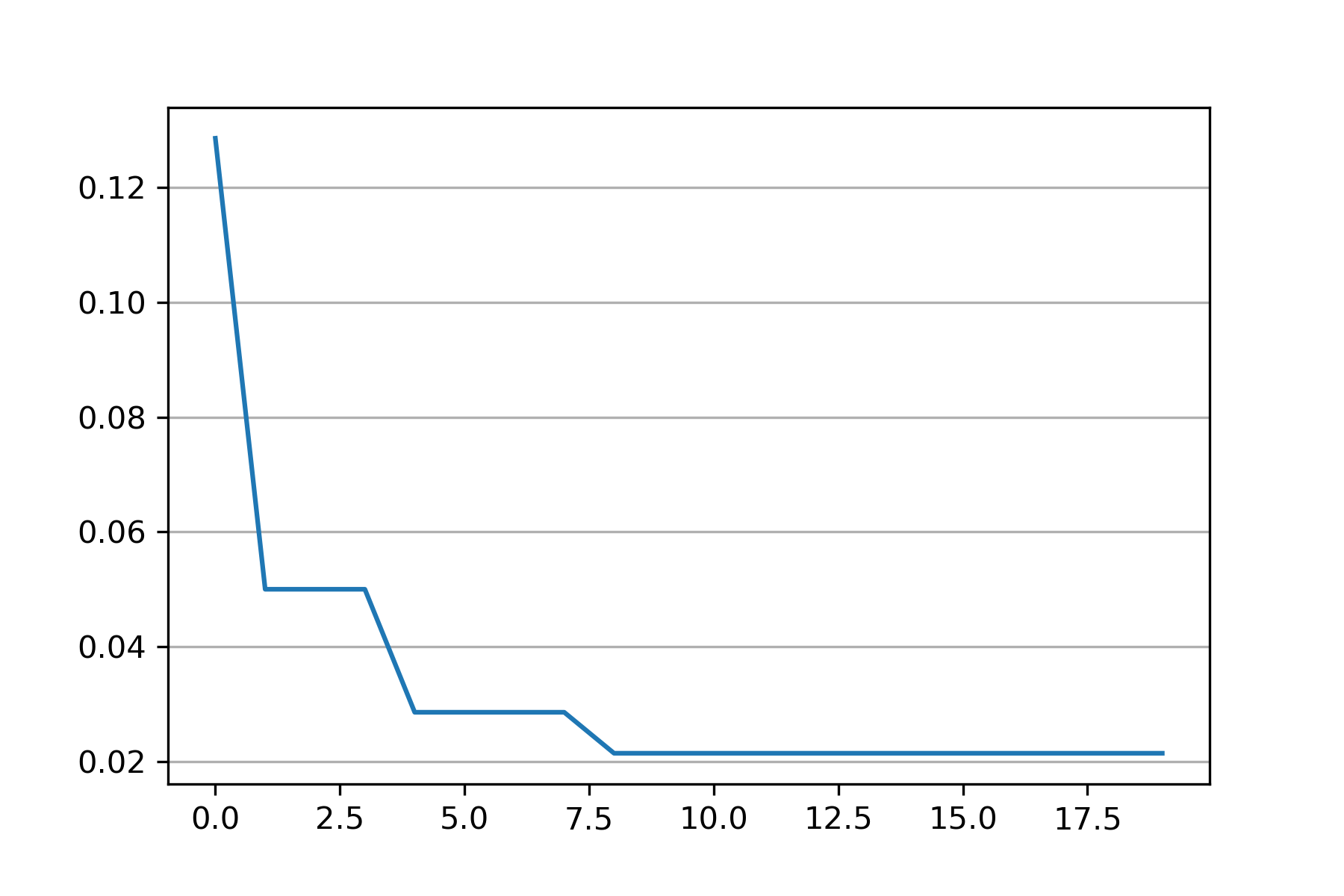 215 |
215 |
216 |
217 | ### 06. svdd_example_confusion_matrix.py
218 |
219 | An example for drawing the confusion matrix and ROC curve.
220 |
221 |
222 | 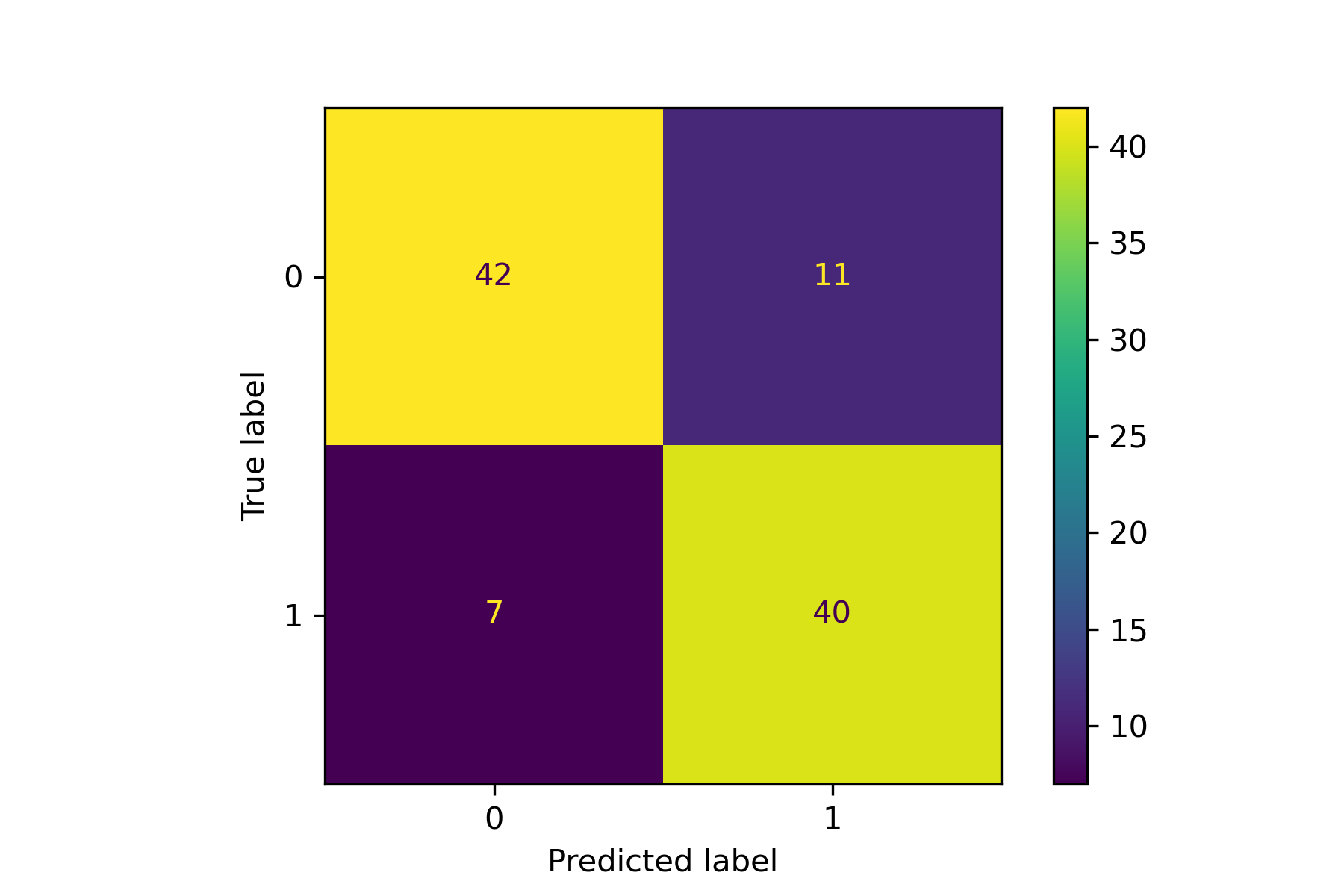 223 |
223 | 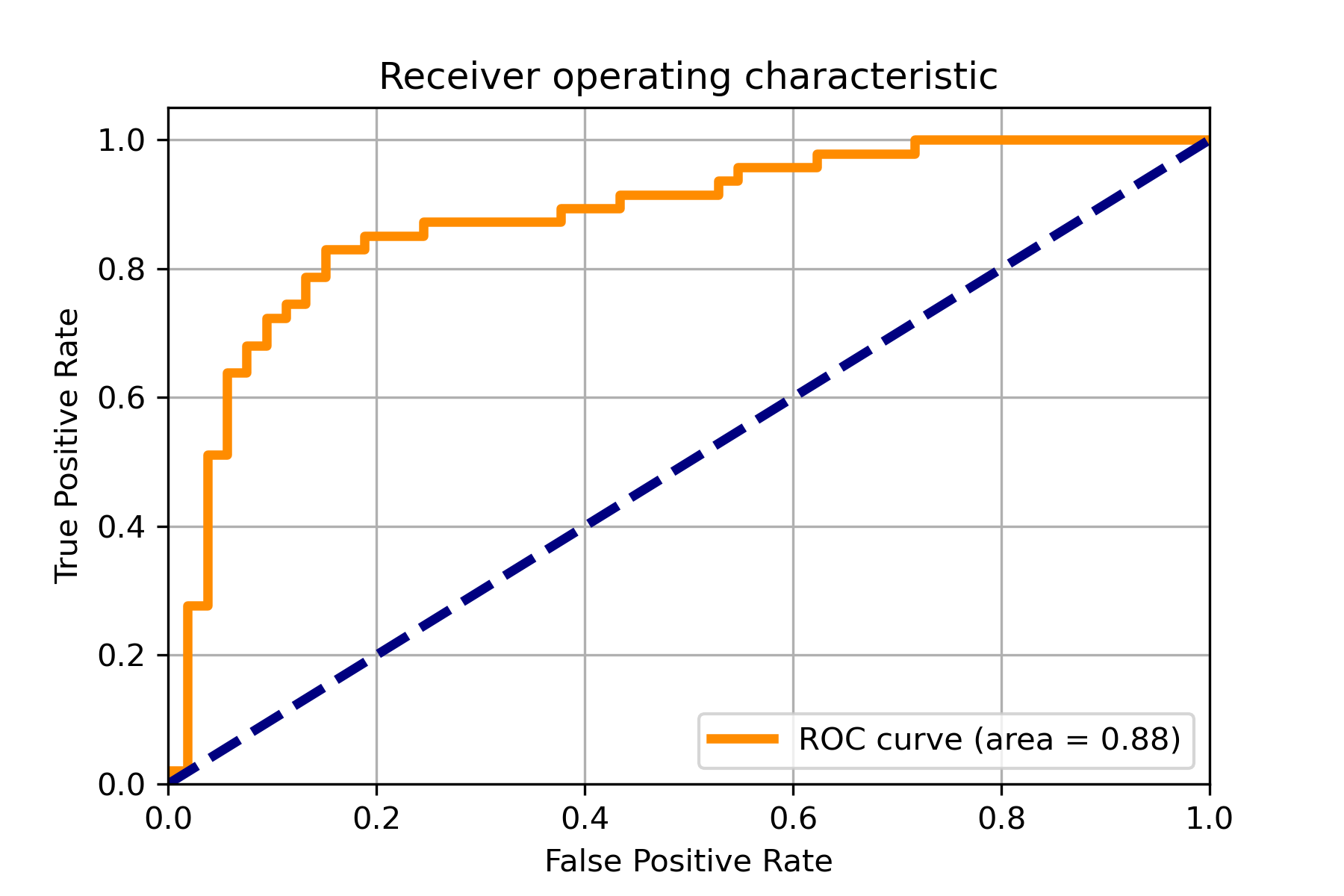 224 |
224 |
225 |
226 | ### 07. svdd_example_cross_validation.py
227 |
228 | An example for cross validation.
229 |
230 | ```Python
231 | import sys
232 | sys.path.append("..")
233 | from src.BaseSVDD import BaseSVDD, BananaDataset
234 | from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
235 |
236 |
237 | # Banana-shaped dataset generation and partitioning
238 | X, y = BananaDataset.generate(number=100, display='on')
239 | X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = BananaDataset.split(X, y, ratio=0.3)
240 |
241 | #
242 | svdd = BaseSVDD(C=0.9, gamma=0.3, kernel='rbf', display='on')
243 |
244 |
245 | # cross validation (k-fold)
246 | k = 5
247 | scores = cross_val_score(svdd, X_train, y_train, cv=k, scoring='accuracy')
248 |
249 | #
250 | print("Cross validation scores:")
251 | for scores_ in scores:
252 | print(scores_)
253 |
254 | print("Mean cross validation score: {:4f}".format(scores.mean()))
255 | ```
256 | Results
257 | ```
258 | Cross validation scores:
259 | 0.5714285714285714
260 | 0.75
261 | 0.9642857142857143
262 | 1.0
263 | 1.0
264 | Mean cross validation score: 0.857143
265 | ```
266 |
267 | ### 08. svdd_example_grid_search.py
268 |
269 | An example for parameter selection using grid search.
270 |
271 | ```Python
272 | import sys
273 | sys.path.append("..")
274 | from sklearn.datasets import load_wine
275 | from src.BaseSVDD import BaseSVDD, BananaDataset
276 | from sklearn.model_selection import KFold, LeaveOneOut, ShuffleSplit
277 | from sklearn.model_selection import learning_curve, GridSearchCV
278 |
279 | # Banana-shaped dataset generation and partitioning
280 | X, y = BananaDataset.generate(number=100, display='off')
281 | X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = BananaDataset.split(X, y, ratio=0.3)
282 |
283 | param_grid = [
284 | {"kernel": ["rbf"], "gamma": [0.1, 0.2, 0.5], "C": [0.1, 0.5, 1]},
285 | {"kernel": ["linear"], "C": [0.1, 0.5, 1]},
286 | {"kernel": ["poly"], "C": [0.1, 0.5, 1], "degree": [2, 3, 4, 5]},
287 | ]
288 |
289 | svdd = GridSearchCV(BaseSVDD(display='off'), param_grid, cv=5, scoring="accuracy")
290 | svdd.fit(X_train, y_train)
291 | print("best parameters:")
292 | print(svdd.best_params_)
293 | print("\n")
294 |
295 | #
296 | best_model = svdd.best_estimator_
297 | means = svdd.cv_results_["mean_test_score"]
298 | stds = svdd.cv_results_["std_test_score"]
299 |
300 | for mean, std, params in zip(means, stds, svdd.cv_results_["params"]):
301 | print("%0.3f (+/-%0.03f) for %r" % (mean, std * 2, params))
302 | print()
303 |
304 | ```
305 | Results
306 | ```Python
307 | best parameters:
308 | {'C': 0.5, 'gamma': 0.1, 'kernel': 'rbf'}
309 |
310 |
311 | 0.921 (+/-0.159) for {'C': 0.1, 'gamma': 0.1, 'kernel': 'rbf'}
312 | 0.893 (+/-0.192) for {'C': 0.1, 'gamma': 0.2, 'kernel': 'rbf'}
313 | 0.857 (+/-0.296) for {'C': 0.1, 'gamma': 0.5, 'kernel': 'rbf'}
314 | 0.950 (+/-0.086) for {'C': 0.5, 'gamma': 0.1, 'kernel': 'rbf'}
315 | 0.921 (+/-0.131) for {'C': 0.5, 'gamma': 0.2, 'kernel': 'rbf'}
316 | 0.864 (+/-0.273) for {'C': 0.5, 'gamma': 0.5, 'kernel': 'rbf'}
317 | 0.950 (+/-0.086) for {'C': 1, 'gamma': 0.1, 'kernel': 'rbf'}
318 | 0.921 (+/-0.131) for {'C': 1, 'gamma': 0.2, 'kernel': 'rbf'}
319 | 0.864 (+/-0.273) for {'C': 1, 'gamma': 0.5, 'kernel': 'rbf'}
320 | 0.807 (+/-0.246) for {'C': 0.1, 'kernel': 'linear'}
321 | 0.821 (+/-0.278) for {'C': 0.5, 'kernel': 'linear'}
322 | 0.793 (+/-0.273) for {'C': 1, 'kernel': 'linear'}
323 | 0.879 (+/-0.184) for {'C': 0.1, 'degree': 2, 'kernel': 'poly'}
324 | 0.836 (+/-0.305) for {'C': 0.1, 'degree': 3, 'kernel': 'poly'}
325 | 0.771 (+/-0.416) for {'C': 0.1, 'degree': 4, 'kernel': 'poly'}
326 | 0.757 (+/-0.448) for {'C': 0.1, 'degree': 5, 'kernel': 'poly'}
327 | 0.871 (+/-0.224) for {'C': 0.5, 'degree': 2, 'kernel': 'poly'}
328 | 0.814 (+/-0.311) for {'C': 0.5, 'degree': 3, 'kernel': 'poly'}
329 | 0.800 (+/-0.390) for {'C': 0.5, 'degree': 4, 'kernel': 'poly'}
330 | 0.764 (+/-0.432) for {'C': 0.5, 'degree': 5, 'kernel': 'poly'}
331 | 0.871 (+/-0.224) for {'C': 1, 'degree': 2, 'kernel': 'poly'}
332 | 0.850 (+/-0.294) for {'C': 1, 'degree': 3, 'kernel': 'poly'}
333 | 0.800 (+/-0.390) for {'C': 1, 'degree': 4, 'kernel': 'poly'}
334 | 0.771 (+/-0.416) for {'C': 1, 'degree': 5, 'kernel': 'poly'}
335 | ```
336 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/SECURITY.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Security Policy
2 |
3 | ## Supported Versions
4 |
5 | Use this section to tell people about which versions of your project are
6 | currently being supported with security updates.
7 |
8 | | Version | Supported |
9 | | ------- | ------------------ |
10 | | 5.1.x | :white_check_mark: |
11 | | 5.0.x | :x: |
12 | | 4.0.x | :white_check_mark: |
13 | | < 4.0 | :x: |
14 |
15 | ## Reporting a Vulnerability
16 |
17 | Use this section to tell people how to report a vulnerability.
18 |
19 | Tell them where to go, how often they can expect to get an update on a
20 | reported vulnerability, what to expect if the vulnerability is accepted or
21 | declined, etc.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/svdd_example_KPCA.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 | """
3 |
4 | An example for SVDD model fitting using nonlinear principal component.
5 |
6 | The KPCA algorithm is used to reduce the dimension of the original data.
7 |
8 | """
9 |
10 | import sys
11 | sys.path.append("..")
12 | import numpy as np
13 | from src.BaseSVDD import BaseSVDD
14 | from sklearn.decomposition import KernelPCA
15 |
16 |
17 | # create 100 points with 5 dimensions
18 | X = np.r_[np.random.randn(50, 5) + 1, np.random.randn(50, 5)]
19 | y = np.append(np.ones((50, 1), dtype=np.int64),
20 | -np.ones((50, 1), dtype=np.int64),
21 | axis=0)
22 |
23 | # number of the dimensionality
24 | kpca = KernelPCA(n_components=2, kernel="rbf", gamma=0.1, fit_inverse_transform=True)
25 | X_kpca = kpca.fit_transform(X)
26 |
27 | # fit the SVDD model
28 | svdd = BaseSVDD(C=0.9, gamma=10, kernel='rbf', display='on')
29 |
30 | # fit and predict
31 | svdd.fit(X_kpca, y)
32 | y_test_predict = svdd.predict(X_kpca, y)
33 |
34 | # plot the distance curve
35 | radius = svdd.radius
36 | distance = svdd.get_distance(X_kpca)
37 | svdd.plot_distance(radius, distance)
38 |
39 | # plot the boundary
40 | svdd.plot_boundary(X_kpca, y)
41 |
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/svdd_example_PSO.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 | """
3 |
4 | An example for parameter optimization using PSO.
5 |
6 | "scikit-opt" is required in this examples.
7 |
8 | https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt
9 |
10 | """
11 |
12 | import sys
13 | sys.path.append("..")
14 | from src.BaseSVDD import BaseSVDD, BananaDataset
15 | from sko.PSO import PSO
16 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
17 |
18 |
19 | # Banana-shaped dataset generation and partitioning
20 | X, y = BananaDataset.generate(number=100, display='off')
21 | X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = BananaDataset.split(X, y, ratio=0.3)
22 |
23 | # objective function
24 | def objective_func(x):
25 | x1, x2 = x
26 | svdd = BaseSVDD(C=x1, gamma=x2, kernel='rbf', display='off')
27 | y = 1-svdd.fit(X_train, y_train).accuracy
28 | return y
29 |
30 | # Do PSO
31 | pso = PSO(func=objective_func, n_dim=2, pop=10, max_iter=20,
32 | lb=[0.01, 0.01], ub=[1, 3], w=0.8, c1=0.5, c2=0.5)
33 | pso.run()
34 |
35 | print('best_x is', pso.gbest_x)
36 | print('best_y is', pso.gbest_y)
37 |
38 | # plot the result
39 | fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
40 | ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
41 | ax.plot(pso.gbest_y_hist)
42 | ax.yaxis.grid()
43 | plt.show()
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/svdd_example_confusion_matrix.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 | """
3 | An example for drawing the confusion matrix and ROC curve
4 |
5 | """
6 | import sys
7 | sys.path.append("..")
8 | import numpy as np
9 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
10 | from src.BaseSVDD import BaseSVDD
11 | from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
12 | from sklearn.metrics import ConfusionMatrixDisplay
13 | from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc
14 | from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
15 |
16 | # generate data
17 | n = 100
18 | dim = 5
19 | X = np.r_[np.random.randn(n, dim) + 1, np.random.randn(n, dim)]
20 | y = np.append(np.ones((n, 1), dtype=np.int64),
21 | -np.ones((n, 1), dtype=np.int64),
22 | axis=0)
23 |
24 | X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.5, random_state=0)
25 |
26 | # SVDD model
27 | svdd = BaseSVDD(C=0.9, gamma=0.1, kernel='rbf', display='on')
28 | svdd.fit(X_train, y_train)
29 | y_test_predict = svdd.predict(X_test, y_test)
30 |
31 | # plot the distance curve
32 | radius = svdd.radius
33 | distance = svdd.get_distance(X_test)
34 | svdd.plot_distance(radius, distance)
35 |
36 | # confusion matrix and ROC curve
37 | cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_test_predict)
38 | cm_display = ConfusionMatrixDisplay(cm).plot()
39 | y_score = svdd.decision_function(X_test)
40 |
41 | fpr, tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_test, y_score)
42 | roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr)
43 |
44 | plt.figure()
45 | plt.plot(fpr, tpr, color="darkorange", lw=3, label="ROC curve (area = %0.2f)" % roc_auc)
46 | plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color="navy", lw=3, linestyle="--")
47 | plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
48 | plt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])
49 | plt.xlabel("False Positive Rate")
50 | plt.ylabel("True Positive Rate")
51 | plt.title("Receiver operating characteristic")
52 | plt.legend(loc="lower right")
53 | plt.grid()
54 | plt.show()
55 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/svdd_example_cross_validation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 | """
3 | An example for cross validation
4 |
5 | """
6 | import sys
7 | sys.path.append("..")
8 | from src.BaseSVDD import BaseSVDD, BananaDataset
9 | from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
10 |
11 |
12 | # Banana-shaped dataset generation and partitioning
13 | X, y = BananaDataset.generate(number=100, display='on')
14 | X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = BananaDataset.split(X, y, ratio=0.3)
15 |
16 | #
17 | svdd = BaseSVDD(C=0.9, gamma=0.3, kernel='rbf', display='on')
18 |
19 |
20 | # cross validation (k-fold)
21 | k = 5
22 | scores = cross_val_score(svdd, X_train, y_train, cv=k, scoring='accuracy')
23 |
24 | #
25 | print("Cross validation scores:")
26 | for scores_ in scores:
27 | print(scores_)
28 |
29 | print("Mean cross validation score: {:4f}".format(scores.mean()))
30 |
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/svdd_example_grid_search.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 | """
3 |
4 | An example for parameter selection using grid search
5 |
6 | """
7 | import sys
8 | sys.path.append("..")
9 | from sklearn.datasets import load_wine
10 | from src.BaseSVDD import BaseSVDD, BananaDataset
11 | from sklearn.model_selection import KFold, LeaveOneOut, ShuffleSplit
12 | from sklearn.model_selection import learning_curve, GridSearchCV
13 |
14 | # Banana-shaped dataset generation and partitioning
15 | X, y = BananaDataset.generate(number=100, display='off')
16 | X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = BananaDataset.split(X, y, ratio=0.3)
17 |
18 | param_grid = [
19 | {"kernel": ["rbf"], "gamma": [0.1, 0.2, 0.5], "C": [0.1, 0.5, 1]},
20 | {"kernel": ["linear"], "C": [0.1, 0.5, 1]},
21 | {"kernel": ["poly"], "C": [0.1, 0.5, 1], "degree": [2, 3, 4, 5]},
22 | ]
23 |
24 | svdd = GridSearchCV(BaseSVDD(display='off'), param_grid, cv=5, scoring="accuracy")
25 | svdd.fit(X_train, y_train)
26 | print("best parameters:")
27 | print(svdd.best_params_)
28 | print("\n")
29 |
30 | #
31 | best_model = svdd.best_estimator_
32 | means = svdd.cv_results_["mean_test_score"]
33 | stds = svdd.cv_results_["std_test_score"]
34 |
35 | for mean, std, params in zip(means, stds, svdd.cv_results_["params"]):
36 | print("%0.3f (+/-%0.03f) for %r" % (mean, std * 2, params))
37 | print()
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/svdd_example_hybrid_data.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 | """
3 |
4 | An example for SVDD model fitting with negataive samples
5 |
6 | """
7 | import sys
8 | sys.path.append("..")
9 | from sklearn.datasets import load_wine
10 | from src.BaseSVDD import BaseSVDD, BananaDataset
11 |
12 | # Banana-shaped dataset generation and partitioning
13 | X, y = BananaDataset.generate(number=100, display='on')
14 | X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = BananaDataset.split(X, y, ratio=0.3)
15 |
16 | #
17 | svdd = BaseSVDD(C=0.9, gamma=0.3, kernel='rbf', display='on')
18 |
19 | #
20 | svdd.fit(X_train, y_train)
21 |
22 | #
23 | svdd.plot_boundary(X_train, y_train)
24 |
25 | #
26 | y_test_predict = svdd.predict(X_test, y_test)
27 |
28 | #
29 | radius = svdd.radius
30 | distance = svdd.get_distance(X_test)
31 | svdd.plot_distance(radius, distance)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/svdd_example_kernel.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 | """
3 |
4 | An example for SVDD model fitting using different kernels
5 |
6 | """
7 | import sys
8 | sys.path.append("..")
9 | from src.BaseSVDD import BaseSVDD, BananaDataset
10 |
11 | # Banana-shaped dataset generation and partitioning
12 | X, y = BananaDataset.generate(number=100, display='on')
13 | X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = BananaDataset.split(X, y, ratio=0.3)
14 |
15 | # kernel list
16 | kernelList = {"1": BaseSVDD(C=0.9, kernel='rbf', gamma=0.3, display='on'),
17 | "2": BaseSVDD(C=0.9, kernel='poly',degree=2, display='on'),
18 | "3": BaseSVDD(C=0.9, kernel='linear', display='on')
19 | }
20 |
21 | #
22 | for i in range(len(kernelList)):
23 | svdd = kernelList.get(str(i+1))
24 | svdd.fit(X_train, y_train)
25 | svdd.plot_boundary(X_train, y_train)
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/svdd_example_unlabeled_data.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 | """
3 |
4 | An example for SVDD model fitting with negataive samples
5 |
6 | """
7 | import sys
8 | sys.path.append("..")
9 | import numpy as np
10 | from src.BaseSVDD import BaseSVDD
11 |
12 | # create 100 points with 2 dimensions
13 | n = 100
14 | dim = 2
15 | X = np.r_[np.random.randn(n, dim)]
16 |
17 | # svdd object using rbf kernel
18 | svdd = BaseSVDD(C=0.9, gamma=0.3, kernel='rbf', display='on')
19 |
20 | # fit the SVDD model
21 | svdd.fit(X)
22 |
23 | # predict the label
24 | y_predict = svdd.predict(X)
25 |
26 | # plot the boundary
27 | svdd.plot_boundary(X)
28 |
29 | # plot the distance
30 | radius = svdd.radius
31 | distance = svdd.get_distance(X)
32 | svdd.plot_distance(radius, distance)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/requirements.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | cvxopt==1.2.7
2 | matplotlib==3.4.2
3 | numpy==1.22.0
4 | scikit_learn==1.0.1
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/BaseSVDD.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 | """
3 | Created on Sun Feb 27 00:37:30 2022
4 |
5 | @author: iqiukp
6 | """
7 |
8 | import numpy as np
9 | import time
10 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
11 | from collections import defaultdict
12 | import warnings
13 | from cvxopt import matrix, solvers
14 | from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator, OutlierMixin
15 | from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
16 | from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import pairwise_kernels
17 | from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
18 |
19 | class BaseSVDD(BaseEstimator, OutlierMixin):
20 | """One-Classification using Support Vector Data Description (SVDD).
21 |
22 | Parameters
23 | ----------
24 | C : float, default=1.0
25 | Regularization parameter. The strength of the regularization is
26 | inversely proportional to C. Must be strictly positive. The penalty
27 | is a squared l2 penalty.
28 | kernel : {'linear', 'poly', 'rbf', 'sigmoid'}, default='rbf'
29 | Specifies the kernel type to be used in the algorithm.
30 | It must be one of 'linear', 'poly', 'rbf', 'sigmoid'.
31 | degree : int, default=3
32 | Degree of the polynomial kernel function ('poly').
33 | Ignored by all other kernels.
34 | gamma : {'scale', 'auto'} or float, default='scale'
35 | Kernel coefficient for 'rbf', 'poly' and 'sigmoid'.
36 | - if ``gamma='scale'`` (default) is passed then it uses
37 | 1 / (n_features * X.var()) as value of gamma,
38 | - if 'auto', uses 1 / n_features.
39 | coef0 : float, default=0.0
40 | Independent term in kernel function.
41 | It is only significant in 'poly' and 'sigmoid'.
42 |
43 | n_jobs : int, default=None
44 | The number of parallel jobs to run.
45 | ``None`` means 1 unless in a :obj:`joblib.parallel_backend` context.
46 | ``-1`` means using all processors. See :term:`Glossary `
47 | for more details.
48 |
49 | """
50 |
51 | def __init__(self,
52 | C=0.9,
53 | kernel='rbf',
54 | degree=3,
55 | gamma=None,
56 | coef0=1,
57 | display='on',
58 | n_jobs=None):
59 |
60 | self.C = C
61 | self.kernel = kernel
62 | self.degree = degree
63 | self.gamma = gamma
64 | self.coef0 = coef0
65 | self.n_jobs = n_jobs
66 | self.display = display
67 | self.X = None
68 | self.y = None
69 | self.weight = None
70 | self.exist_label = True
71 | self.label_type = None
72 | self.support_vectors = None
73 | self.support_vector_indices = None
74 | self.n_support_vectors = None
75 | self.n_iterations = None
76 | self.object_value = None
77 | self.alpha = None
78 | self.alpha_tolerance = 1e-6
79 | self.support_vector_alpha = None
80 | self.n_support_vectors_ratio = None
81 | self.radius = None
82 | self.center = None
83 | self.offset = None
84 | self.distance = None
85 | self.accuracy = None
86 | self.predicted_y = None
87 | self.running_time = None
88 | self.boundary_indices = None
89 | self.classes_ = None
90 |
91 |
92 |
93 | @property
94 | def n_samples(self):
95 | return self.X.shape[0]
96 | @property
97 | def n_features(self):
98 | return self.X.shape[1]
99 | @property
100 | def n_positive_samples(self):
101 | return np.sum(self.y == 1)
102 | @property
103 | def n_negative_samples(self):
104 | return np.sum(self.y == -1)
105 |
106 |
107 | def fit(self, X, y=None, weight=None):
108 | """Fit the model from data in X.
109 |
110 | Parameters
111 | ----------
112 | X : {array-like, sparse matrix}, shape (n_samples, n_features)
113 | The training input samples.
114 | y : array-like, shape (n_samples, 1)
115 | The target values (class labels in classification,
116 | 1 for positive samples and -1 for negative samples)
117 | weight : array-like of shape (n_samples, 1), default=None
118 |
119 | Returns
120 | -------
121 | self : object
122 | Returns self.
123 | """
124 |
125 | start_time = time.time()
126 | # parameter preprocessing
127 | self.X, self.y, self.y_type, self.exist_y = self._check_X_y(X, y)
128 |
129 | if self.y_type == 'single':
130 | self.C = [self.C, 1]
131 |
132 | if self.y_type == 'hybrid':
133 | self.C = [self.C, 2/self.n_negative_samples]
134 |
135 | if weight is None:
136 | self.weight = np.ones((self.n_samples, 1), dtype=np.int64)
137 | else:
138 | self.weight = weight
139 |
140 | # check 'gamma'
141 | if self.gamma == 0:
142 | raise ValueError(
143 | "The gamma value of 0.0 is invalid. Use 'auto' to set"
144 | " gamma to a value of 1 / n_features.")
145 | if self.gamma is None:
146 | self.gamma = 'scale'
147 | if isinstance(self.gamma, str):
148 | if self.gamma == "scale":
149 | X_var = X.var()
150 | self.gamma = 1.0 / (X.shape[1] * X_var) if X_var != 0 else 1.0
151 | elif self.gamma == "auto":
152 | self.gamma = 1.0 / X.shape[1]
153 | else:
154 | raise ValueError(
155 | "When 'gamma' is a string, it should be either 'scale' or 'auto'.")
156 |
157 | # get SVDD model
158 | self.get_model()
159 | display_ = self.display
160 | self.display = 'off'
161 | self.predicted_y_ = self.predict(self.X, self.y)
162 | self.accuracy = accuracy_score(self.y, self.predicted_y_)
163 | self.display = display_
164 | end_time = time.time()
165 | self.running_time = end_time - start_time
166 |
167 | # display
168 | if self.display == 'on':
169 | self.display_fit()
170 | return self
171 |
172 | def get_model(self):
173 | #
174 | K = self._get_kernel(self.X, self.X)
175 | self.solve_problem(K)
176 |
177 | def _get_kernel(self, X, Y=None):
178 | # get kernel matrix
179 | if callable(self.kernel):
180 | params = self.kernel_params or {}
181 | else:
182 | params = {"gamma": self.gamma, "degree": self.degree, "coef0": self.coef0}
183 |
184 | return pairwise_kernels(
185 | X, Y, metric=self.kernel, filter_params=True, n_jobs=self.n_jobs, **params)
186 |
187 | def solve_problem(self, K):
188 | """
189 | DESCRIPTION
190 |
191 | Solve the Lagrange dual problem using cvxopt
192 |
193 |
194 | minimize (1/2)*x'*P*x + q'*x
195 | subject to G*x <= h
196 | A*x = b
197 | --------------------------------------------------
198 |
199 | """
200 |
201 | solvers.options['show_progress'] = False
202 | K = np.multiply(self.y * self.y.T, K)
203 |
204 | # P
205 | n = K.shape[0]
206 | P = K + K.T
207 |
208 | # q
209 | q = -np.multiply(self.y, np.mat(np.diagonal(K)).T)
210 |
211 | # G
212 | G1 = -np.eye(n)
213 | G2 = np.eye(n)
214 | G = np.append(G1, G2, axis=0)
215 |
216 | # h
217 | h1 = np.zeros([n, 1])
218 | h2 = np.ones([n, 1])
219 |
220 | if self.y_type == 'single':
221 | h2[self.y == 1] = self.C[0] * self.weight[self.y == 1]
222 |
223 | if self.y_type == 'hybrid':
224 | h2[self.y == 1] = self.C[0] * self.weight[self.y == 1]
225 | h2[self.y == -1] = self.C[1] * self.weight[self.y == -1]
226 |
227 | h = np.append(h1, h2, axis=0)
228 | h2_ = h2
229 |
230 | # A, b
231 | A = np.ones([n, 1]).T
232 | b = np.ones([1, 1])
233 |
234 | #
235 | P = matrix(P)
236 | q = matrix(q)
237 | G = matrix(G)
238 | h = matrix(h)
239 | A = matrix(A)
240 | b = matrix(b)
241 |
242 | #
243 | sol = solvers.qp(P, q, G, h, A, b)
244 |
245 | self.object_value = np.array(sol['dual objective'])
246 | self.n_iterations = np.array(sol['iterations'])
247 |
248 | if len(np.array(sol['x'])) == 0:
249 | warnings.warn("No solution for the SVDD model could be found.\n")
250 | self.alpha = np.zeros((self.n_samples, 1))
251 | self.alpha[0][0] = 1
252 | else:
253 | self.alpha = np.array(sol['x'])
254 |
255 | self.alpha = self.y * self.alpha
256 | self.support_vector_indices = np.where(np.abs(self.alpha) > self.alpha_tolerance)[0][:]
257 |
258 | # boundary indices
259 | tmp_1 = self.alpha[self.support_vector_indices, 0]
260 | tmp_2 = h2_[self.support_vector_indices, 0]
261 | tmp_3 = np.where(tmp_1 < tmp_2)[0][:]
262 | tmp_4 = np.where(tmp_1 > self.alpha_tolerance)[0][:]
263 | self.boundary_indices = self.support_vector_indices[np.array(list(set(tmp_3) & set(tmp_4)))]
264 |
265 | # support vectors
266 | self.alpha[np.where(np.abs(self.alpha) < self.alpha_tolerance)[0][:]] = 0
267 | self.support_vectors = self.X[self.support_vector_indices, :]
268 | self.support_vector_alpha = self.alpha[self.support_vector_indices]
269 | self.n_support_vectors = self.support_vector_indices.shape[0]
270 | self.n_support_vectors_ratio = self.n_support_vectors/self.n_samples
271 |
272 | if self.n_support_vectors_ratio > 0.5:
273 | warnings.warn("The fitted SVDD model may be overfitting.\n")
274 |
275 | # offset, center, radius
276 | tmp_5 = np.dot(np.ones((self.n_samples, 1)), self.alpha.T)
277 | tmp_6 = np.multiply(tmp_5, K)
278 | tmp_ = -2*np.sum(tmp_6, axis=1, keepdims=True)
279 | self.offset = np.sum(np.multiply(np.dot(self.alpha, self.alpha.T), K))
280 | self.center = np.dot(self.alpha.T, self.X)
281 | self.radius = np.sqrt(np.mean(np.diag(K)[self.boundary_indices]) + self.offset + np.mean(tmp_[self.boundary_indices, 0]))
282 |
283 | def predict(self, X, y=None):
284 | """Predict the class labels for the provided data.
285 |
286 | Parameters
287 | ----------
288 | X : array-like of shape (n_queries, n_features)
289 | Test samples.
290 | y : (optional) array-like, shape (n_samples, 1)
291 | The target values (class labels in classification,
292 | 1 for positive samples and -1 for negative samples)
293 |
294 | Returns
295 | -------
296 | predicted_y : array-like, shape (n_samples, 1)
297 | The predicted target values
298 | """
299 |
300 | start_time = time.time()
301 | results = {}
302 | results['X'], results['y'], results['y_type'], results['exist_y'] = self._check_X_y(X, y)
303 | results['n_samples'] = results['X'].shape[0]
304 | results['distance'] = self.get_distance(X)
305 | results['predicted_y'] = np.mat(np.ones(results['n_samples'])).T
306 | index_ = results['distance'] > self.radius
307 | results['predicted_y'][index_] = -1
308 | results['predicted_y'] = np.asarray(results['predicted_y'])
309 | results['n_alarm'] = np.sum(index_==True)
310 |
311 | if results['exist_y'] == True:
312 | results['accuracy'] = accuracy_score(results['y'], results['predicted_y'])
313 |
314 | end_time = time.time()
315 | results['running_time'] = end_time - start_time
316 | # display
317 | if self.display == 'on':
318 | self.display_predict(results)
319 | return results['predicted_y']
320 |
321 | def get_distance(self, X):
322 | # compute the distance between the samples and the center
323 | K = self._get_kernel(X, self.X)
324 | K_ = self._get_kernel(X, X)
325 | tmp_1 = np.dot(np.ones((X.shape[0], 1), dtype=np.int64), self.alpha.T)
326 | tmp_2 = np.multiply(tmp_1, K)
327 | tmp_ = -2*np.sum(tmp_2, axis=1, keepdims=True)
328 | distance = np.sqrt(np.mat(np.diag(K_)).T+self.offset+tmp_)
329 | return distance
330 |
331 | def fit_predict(self, X, y=None, weight=None):
332 | # Perform fit on X and returns labels for X.
333 | self.fit(X, y, weight)
334 | return self.predict(X, y)
335 |
336 | def decision_function(self, X):
337 | """Signed distance to the separating hyperplane.
338 | Signed distance is positive for an inlier and negative for an outlier.
339 | Parameters
340 | ----------
341 | X : array-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
342 | The data matrix.
343 | Returns
344 | -------
345 | dec : ndarray of shape (n_samples, 1)
346 | Returns the decision function of the samples.
347 | The anomaly score of the input samples. The lower,
348 | the more abnormal. Negative scores represent outliers,
349 | positive scores represent inliers.
350 |
351 | """
352 | return np.asarray(self.radius-self.get_distance(X))
353 |
354 | def get_params(self, deep=True):
355 | """
356 | Get parameters for this estimator.
357 | Parameters
358 | ----------
359 | deep : bool, default=True
360 | If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and
361 | contained subobjects that are estimators.
362 | Returns
363 | -------
364 | params : dict
365 | Parameter names mapped to their values.
366 | """
367 | out = dict()
368 | for key in self._get_param_names():
369 | value = getattr(self, key)
370 | if deep and hasattr(value, "get_params"):
371 | deep_items = value.get_params().items()
372 | out.update((key + "__" + k, val) for k, val in deep_items)
373 | out[key] = value
374 | return out
375 |
376 | def set_params(self, **params):
377 | """
378 | Set the parameters of this estimator.
379 | The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects
380 | (such as :class:`~sklearn.pipeline.Pipeline`). The latter have
381 | parameters of the form ``__`` so that it's
382 | possible to update each component of a nested object.
383 | Parameters
384 | ----------
385 | **params : dict
386 | Estimator parameters.
387 | Returns
388 | -------
389 | self : estimator instance
390 | Estimator instance.
391 | """
392 | if not params:
393 | # Simple optimization to gain speed (inspect is slow)
394 | return self
395 | valid_params = self.get_params(deep=True)
396 |
397 | nested_params = defaultdict(dict) # grouped by prefix
398 | for key, value in params.items():
399 | key, delim, sub_key = key.partition("__")
400 | if key not in valid_params:
401 | raise ValueError(
402 | "Invalid parameter %s for estimator %s. "
403 | "Check the list of available parameters "
404 | "with `estimator.get_params().keys()`." % (key, self)
405 | )
406 |
407 | if delim:
408 | nested_params[key][sub_key] = value
409 | else:
410 | setattr(self, key, value)
411 | valid_params[key] = value
412 |
413 | for key, sub_params in nested_params.items():
414 | valid_params[key].set_params(**sub_params)
415 |
416 | return self
417 |
418 | def _check_X_y(self, X, y):
419 |
420 | # check for labels
421 | if y is None:
422 | y = np.ones((X.shape[0], 1))
423 | exist_y = False
424 | else:
425 | exist_y = True
426 |
427 | # check for object type (numpy.ndarray)
428 | if type(X) is not np.ndarray or type(y) is not np.ndarray:
429 | raise SyntaxError("The type of X and y must be 'numpy.ndarray'.\n")
430 |
431 | # check for data dimensionality
432 | if len(X.shape) != 2 or len(y.shape) != 2:
433 | raise SyntaxError("The X and y must be 2D.\n")
434 |
435 | # check for data length
436 | if X.shape[0] != y.shape[0]:
437 | raise SyntaxError("The length of X and y must the same.\n")
438 |
439 | # check for label values
440 | tmp_ = np.unique(y)
441 | if np.all(tmp_ == np.array([1])) or np.all(tmp_ == np.array([-1])):
442 | y_type = 'single'
443 |
444 | elif np.all(tmp_ == np.array([1, -1])) or np.all(tmp_ == np.array([-1, 1])):
445 | y_type = 'hybrid'
446 |
447 | else:
448 | errorText = "SVDD is only supported for one-class or binary classification. "\
449 | "The label must be 1 for positive samples or -1 for negative samples.\n"
450 | raise SyntaxError(errorText)
451 |
452 | self.classes_ = np.unique(y)
453 |
454 | return X, y, y_type, exist_y
455 |
456 | def display_fit(self):
457 | # display the fitting results
458 | print('\n')
459 | print('*** Fitting of the SVDD model is completed. ***\n')
460 | print('running time = %.4f seconds' % self.running_time)
461 | print('kernel function = %s' % self.kernel)
462 | print('iterations = %d' % self.n_iterations)
463 | print('number of samples = %d' % self.n_samples)
464 | print('number of features = %d' % self.n_features)
465 | print('number of SVs = %d' % self.n_support_vectors)
466 | print('ratio of SVs = %.4f %%' % (100*self.n_support_vectors_ratio))
467 | print('accuracy = %.4f %%' % (100*self.accuracy))
468 | print('\n')
469 |
470 | def display_predict(self, results):
471 | # display test results
472 | print('\n')
473 | print('*** Prediction of the provided data is completed. ***\n')
474 | print('running time = %.4f seconds' % results['running_time'])
475 | print('number of samples = %d' % results['n_samples'])
476 | print('number of alarm = %d' % results['n_alarm'])
477 | if results['exist_y'] == True:
478 | print('accuracy = %.4f %%' % (100*results['accuracy']))
479 | print('\n')
480 |
481 | def plot_distance(self, radius, distance):
482 | """
483 | DESCRIPTION
484 |
485 | Plot the curve of distance
486 | ---------------------------------------------------------------
487 |
488 | """
489 |
490 | n = distance.shape[0]
491 | fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
492 | ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
493 | radius = np.ones((n, 1))*radius
494 |
495 | ax.plot(radius,
496 | color='r',
497 | linestyle='-',
498 | marker='None',
499 | linewidth=3,
500 | markeredgecolor='k',
501 | markerfacecolor='w',
502 | markersize=6)
503 |
504 | ax.plot(distance,
505 | color='k',
506 | linestyle=':',
507 | marker='o',
508 | linewidth=1,
509 | markeredgecolor='k',
510 | markerfacecolor='C4',
511 | markersize=6)
512 |
513 | ax.set_xlabel('Samples')
514 | ax.set_ylabel('Distance')
515 |
516 | ax.legend(["Radius", "Distance"],
517 | ncol=1, loc=0,
518 | edgecolor='black',
519 | markerscale=1, fancybox=True)
520 | ax.yaxis.grid()
521 | plt.show()
522 |
523 | def plot_boundary(self, X, y=None, expand_ratio=0.2, n_grids=50,
524 | color_map='RdYlBu', n_level=6):
525 | """
526 | DESCRIPTION
527 |
528 | Plot the boundary
529 | ---------------------------------------------------------------
530 |
531 | """
532 | start_time = time.time()
533 | dim = X.shape[1]
534 | if dim != 2:
535 | raise SyntaxError('Visualization of decision boundary only supports for 2D data')
536 | x_range = np.zeros(shape=(n_grids, 2))
537 | for i in range(2):
538 | _tmp_ = (np.max(X[:, i])-np.min(X[:, i]))*expand_ratio
539 | xlim_1 = np.min(X[:, i])-_tmp_
540 | xlim_2 = np.max(X[:, i])+_tmp_
541 | x_range[:, i] = np.linspace(xlim_1, xlim_2, n_grids)
542 |
543 | # grid
544 | xv, yv = np.meshgrid(x_range[:, 0], x_range[:, 1])
545 | num1 = xv.shape[0]
546 | num2 = yv.shape[0]
547 | print('Calculating the grid scores (%04d*%04d)...\n' %(num1, num2))
548 | distance_ = self.get_distance(np.c_[xv.ravel(), yv.ravel()])
549 | distance = distance_.reshape(xv.shape)
550 | end_time = time.time()
551 | print('Calculation of the grid scores is completed. Time cost %.4f seconds\n' % (end_time-start_time))
552 |
553 | fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20, 6))
554 |
555 | # figure 1: the 3D contour
556 | ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 1, projection='3d')
557 | ax1.plot_surface(xv, yv, distance, cmap=color_map)
558 | ax1.contourf(xv, yv, distance.A, n_level, zdir='z', offset=np.min(distance)*0.9, cmap=color_map)
559 | ax1.set_zlim(np.min(distance)*0.9, np.max(distance)*1.05)
560 |
561 | # figure 2: the 2D contour
562 | ax2 = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 2)
563 | ctf1 = ax2.contourf(xv, yv, distance, n_level, alpha=0.8, cmap=color_map)
564 | ctf2 = ax2.contour(xv, yv, distance, n_level, colors='black', linewidths=1)
565 | plt.clabel(ctf2, inline=True)
566 | plt.colorbar(ctf1)
567 |
568 | # figure 3: the 2D contour and data
569 | ax3 = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 3)
570 | _, y, _, _ = self._check_X_y(X, y)
571 | tmp_1 = y == 1
572 | tmp_2 = y == -1
573 | positive_indices = tmp_1[:, 0]
574 | negative_indices = tmp_2[:, 0]
575 |
576 | if self.y_type == 'single':
577 |
578 | ax3.scatter(X[:, 0],
579 | X[:, 1],
580 | facecolor='C0', marker='o', s=100, linewidths=2,
581 | edgecolor='black', zorder=2)
582 |
583 | ax3.scatter(X[self.support_vector_indices, 0],
584 | X[self.support_vector_indices, 1],
585 | facecolor='C2', marker='o', s=144, linewidths=2,
586 | edgecolor='black', zorder=2)
587 |
588 | ax3.contour(xv, yv, distance, levels=[self.radius],
589 | colors='C3', linewidths=7, zorder=1)
590 |
591 | ax3.legend(["Data", "Support vectors"],
592 | ncol=1, loc='upper left', edgecolor='black',
593 | markerscale=1.2, fancybox=True)
594 |
595 | else:
596 | ax3.scatter(X[positive_indices, 0],
597 | X[positive_indices, 1],
598 | facecolor='C0', marker='o', s=100, linewidths=2,
599 | edgecolor='black', zorder=2)
600 |
601 | ax3.scatter(X[negative_indices, 0],
602 | X[negative_indices, 1],
603 | facecolor='C4', marker='s', s =100, linewidths=2,
604 | edgecolor='black', zorder=2)
605 |
606 | ax3.scatter(X[self.support_vector_indices, 0],
607 | X[self.support_vector_indices, 1],
608 | facecolor='C2', marker='o', s=144, linewidths=2,
609 | edgecolor='black', zorder=2)
610 |
611 | ax3.contour(xv, yv, distance, levels=[self.radius],
612 | colors='C3', linewidths=7, zorder=1)
613 |
614 | ax3.legend(["Data (+)", "Data (-)", "Support vectors"],
615 | ncol=1, loc='upper left', edgecolor='black',
616 | markerscale=1.2, fancybox=True)
617 |
618 | plt.grid()
619 | plt.show()
620 |
621 | class BananaDataset():
622 | """
623 | Banana-shaped dataset generation and partitioning.
624 |
625 | """
626 | def generate(**kwargs):
627 | # Banana-shaped dataset generation
628 | number = kwargs['number']
629 | display = kwargs['display']
630 |
631 | # parameters for banana-shaped dataset
632 | sizeBanana = 3
633 | varBanana = 1.2
634 | param_1 = 0.02
635 | param_2 = 0.02
636 | param_3 = 0.98
637 | param_4 = -0.8 # x-axsis shift
638 | # generate
639 | class_p = param_1 * np.pi+np.random.rand(number, 1) * param_3 * np.pi
640 | data_p = np.append(sizeBanana * np.sin(class_p), sizeBanana * np.cos(class_p), axis=1)
641 | data_p = data_p + np.random.rand(number, 2) * varBanana
642 | data_p[:, 0] = data_p[:, 0] - sizeBanana * 0.5
643 | label_p = np.ones((number, 1), dtype=np.int64)
644 |
645 | class_n = param_2 * np.pi - np.random.rand(number, 1) * param_3 * np.pi
646 | data_n = np.append(sizeBanana * np.sin(class_n), sizeBanana * np.cos(class_n), axis=1)
647 | data_n = data_n + np.random.rand(number, 2)*varBanana
648 | data_n = data_n + np.ones((number, 1)) * [sizeBanana * param_4, sizeBanana * param_4]
649 | data_n[:, 0] = data_n[:, 0] + sizeBanana * 0.5
650 | label_n = -np.ones((number, 1), dtype=np.int64)
651 |
652 | # banana-shaped dataset
653 | data = np.append(data_p, data_n, axis=0)
654 | label = np.append(label_p, label_n, axis=0)
655 |
656 | if display == 'on':
657 | pIndex = label == 1
658 | nIndex = label == -1
659 | fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
660 | ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
661 | ax.scatter(data[pIndex[:, 0], 0], data[pIndex[:, 0], 1],
662 | facecolor='C0', marker='o', s=100, linewidths=2,
663 | edgecolor='black', zorder=2)
664 |
665 | ax.scatter(data[nIndex[:, 0], 0], data[nIndex[:, 0], 1],
666 | facecolor='C3', marker='o', s = 100, linewidths=2,
667 | edgecolor='black', zorder=2)
668 |
669 | ax.set_xlim([-6, 5])
670 | ax.set_ylim([-7, 7])
671 |
672 | return data, label
673 |
674 | def split(data, label, **kwargs):
675 | # Banana-shaped dataset partitioning.
676 |
677 | ratio = kwargs['ratio']
678 | X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data, label, test_size=ratio,
679 | random_state=None, shuffle=True, stratify=label)
680 | pIndex = y_train == 1
681 | nIndex = y_train == -1
682 | X_train = np.append(X_train[pIndex[:, 0], :], X_train[nIndex[:, 0], :], axis=0)
683 | y_train = np.append(y_train[pIndex[:, 0], :], y_train[nIndex[:, 0], :], axis=0)
684 |
685 | pIndex = y_test == 1
686 | nIndex = y_test == -1
687 | X_test = np.append(X_test[pIndex[:, 0], :], X_test[nIndex[:, 0], :], axis=0)
688 | y_test = np.append(y_test[pIndex[:, 0], :], y_test[nIndex[:, 0], :], axis=0)
689 |
690 | return X_train, X_test ,y_train, y_test
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/__pycache__/BananaDataset.cpython-38.pyc:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/iqiukp/SVDD-Python/e24837efaed0ed2054da151aeb558b6ece23e23c/src/__pycache__/BananaDataset.cpython-38.pyc
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/__pycache__/BaseSVDD.cpython-38.pyc:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/iqiukp/SVDD-Python/e24837efaed0ed2054da151aeb558b6ece23e23c/src/__pycache__/BaseSVDD.cpython-38.pyc
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/__pycache__/testmodel.cpython-38.pyc:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/iqiukp/SVDD-Python/e24837efaed0ed2054da151aeb558b6ece23e23c/src/__pycache__/testmodel.cpython-38.pyc
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 3 |
3 |  3 |
3 |  14 |
14 |  15 |
15 |  16 |
16 |  17 |
17 |  18 |
18 |  19 |
19 |  51 |
51 |  52 |
52 |  88 |
88 |  89 |
89 |  119 |
119 |  120 |
120 |  121 |
121 |  166 |
166 |  167 |
167 |  215 |
215 |  223 |
223 |  224 |
224 |