├── stringmatch.md
├── find.md
├── res
└── recursion_example.png
├── find
├── ST.cpp
├── main.cpp
└── ST.h
├── alg-cpp.xcodeproj
├── xcuserdata
│ └── junl.xcuserdatad
│ │ └── xcdebugger
│ │ └── Breakpoints_v2.xcbkptlist
└── project.xcworkspace
│ ├── contents.xcworkspacedata
│ ├── xcuserdata
│ ├── junl.xcuserdatad
│ │ ├── UserInterfaceState.xcuserstate
│ │ └── xcdebugger
│ │ │ └── Breakpoints_v2.xcbkptlist
│ └── junlongj.xcuserdatad
│ │ └── UserInterfaceState.xcuserstate
│ └── xcshareddata
│ └── IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist
├── stack+queue
├── queue.cpp
├── leetcode
│ ├── MyCircularDeque.cpp
│ ├── maxSlidingWindow.h
│ ├── MyCircularDeque.h
│ ├── evalRPN.h
│ └── longestValidParentheses.h
├── itinterviews
│ ├── getMaxRectSize.h
│ ├── TwoStacksQueue.h
│ └── sortStackByStack.h
├── sampleBrowser.h
├── coding-interviews
│ ├── validateStackSequences.h
│ └── queueByStack.h
└── stack.h
├── tiny_stl
├── src
│ ├── map.h
│ └── type_traits.h
├── main.cpp
└── test
│ ├── all_test.h
│ ├── forward_test.h
│ └── allocator_test.h
├── dp
├── leetcode
│ ├── minPathSum.h
│ └── easy
│ │ └── climbStairs.h
├── main.cpp
└── coinChange.h
├── sort
├── main.cpp
├── select.c
├── bubble.c
├── insert.c
├── bucketSort.h
├── sort.h
├── heap.c
├── kthSmallest.h
├── merge.c
├── quick.c
├── countingSort.h
└── sort.c
├── bit
├── main.cpp
└── maximizingXor.h
├── divideandconquer
├── closestPair.h
└── main.cpp
├── skip_list.md
├── array
├── linearList.h
├── leetcode
│ ├── easy
│ │ ├── twoSum.h
│ │ ├── searchInsert.h
│ │ ├── plusOne.h
│ │ ├── pascals_triangle_ii.h
│ │ ├── twoSum_ii.h
│ │ ├── majorityElement.h
│ │ ├── best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock.h
│ │ ├── pascals_triangle.h
│ │ ├── removeDuplicates.h
│ │ ├── removeElement.h
│ │ ├── maxSubArray.h
│ │ └── best_time_to_buy_and_sell_stock_ii.h
│ ├── maxArea.h
│ ├── moveZeroes.h
│ └── medium
│ │ └── 3sum.h
├── coding-interviews
│ ├── FindNumsAppearOnce.h
│ ├── ReOrder.h
│ ├── Find.h
│ ├── GetNumberOfK.h
│ ├── MoreThanHalfNum_Solution.h
│ └── minNumberInRotateArray.h
├── DSIterator.h
└── DSArray.h
├── hashTable
└── main.cpp
├── hash.md
├── base
├── illegalParameterValue.h
└── base.h
├── string
├── coding-interviews
│ ├── removeRepeatChar.h
│ ├── FirstNotRepeatingChar.h
│ ├── StrToInt.h
│ └── match.h
├── leetcode
│ ├── easy
│ │ ├── lengthOfLastWord.h
│ │ ├── strStr.h
│ │ └── romanToInt.h
│ └── medium
│ │ └── lengthOfLongestSubstring.h
└── matching.h
├── recursion
├── coding-interviews
│ ├── jumpFloorII.h
│ ├── rectCover.h
│ ├── jumpFloor.h
│ └── Fibonacci.h
├── main.cpp
└── leetcode
│ └── medium
│ └── longestUnivaluePath.h
├── bsearch
├── bsearch_findLastElementLessOrEqual.h
├── bsearch_findLastElement.h
├── bsearch_findFirstElement.h
├── bsearch_findFirstElementGreaterOrEqual.h
├── leetcode
│ ├── isPerfectSquare.h
│ ├── mySqrt.h
│ └── medium
│ │ ├── searchInRotatedSortedArray.h
│ │ └── searchRange.h
├── bsearch.h
└── main.cpp
├── tree
├── Tree.h
├── leetcode
│ ├── maxDepth.h
│ ├── minDepth.h
│ ├── invertTree.h
│ └── easy
│ │ └── isSameTree.h
├── coding-interviews
│ ├── treeToDoublyList.h
│ ├── VerifySquenceOfBST.h
│ ├── GetNext.h
│ └── HasSubtree.h
└── heap.h
├── linkedList
├── leetcode
│ ├── easy
│ │ ├── deleteDuplicates.h
│ │ ├── getIntersectionNode.h
│ │ └── hasCycle.h
│ ├── reverseList.h
│ ├── medium
│ │ └── addTwoNumbers.h
│ ├── isPalindrome.h
│ ├── middleNode.h
│ └── removeNthFromEnd.h
├── coding-interviews
│ ├── creatlist.h
│ ├── printListFromTailToHead.h
│ ├── DeleteNodeO1.h
│ ├── FindKthToTail.h
│ ├── FindFirstCommonNode.h
│ ├── Clone.h
│ ├── deleteDuplication.h
│ └── LastRemaining_Solution.h
└── itinterviews
│ ├── printCommonPart.h
│ └── josephusKill.h
├── greed
├── coin_dispenser.h
├── shared_the_sweets.h
├── main.cpp
├── region_overlapping.h
└── leetcode
│ └── medium
│ └── jump_game.h
├── backtracking
├── knapsack.h
├── coding-interviews
│ └── hasPath.h
├── Pattern.h
├── leetcode
│ └── medium
│ │ ├── subsets.h
│ │ ├── permutations.h
│ │ ├── combinationSum.h
│ │ └── subsets_ii.h
├── main.cpp
└── eightQueens.h
├── other
├── leetcode
│ ├── easy
│ │ ├── reverse_integer.h
│ │ ├── palindrome_number.h
│ │ └── romanToInt.h
│ └── medium
│ │ └── next_permutation.h
└── coding-interviews
│ ├── IsContinuous2.h
│ ├── NumberOf1.h
│ ├── Power.h
│ ├── GetUglyNumber_Solution.h
│ ├── IsContinuous.h
│ ├── NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution.h
│ └── FindNumbersWithSum.h
├── README.md
├── greed.md
└── divideandconquer.md
/stringmatch.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/find.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 本模块内容为《算法4》第3章内容,原书算法是用java实现,所以各API都为java规范,迁移到C++实现后,难免会跟C++规范有差异,后面有时间在纠正这一块.
2 |
3 |
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/res/recursion_example.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jincc/iOS-Algorithm/HEAD/res/recursion_example.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/find/ST.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // ST.cpp
3 | // find
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2020/12/2.
6 | // Copyright © 2020 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #include "ST.h"
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/alg-cpp.xcodeproj/xcuserdata/junl.xcuserdatad/xcdebugger/Breakpoints_v2.xcbkptlist:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/stack+queue/queue.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // queue.cpp
3 | // stack+queue
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/7/18.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #include "queue.h"
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/alg-cpp.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/contents.xcworkspacedata:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
4 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/alg-cpp.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcuserdata/junl.xcuserdatad/UserInterfaceState.xcuserstate:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jincc/iOS-Algorithm/HEAD/alg-cpp.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcuserdata/junl.xcuserdatad/UserInterfaceState.xcuserstate
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/stack+queue/leetcode/MyCircularDeque.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // MyCircularDeque.cpp
3 | // stack+queue
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/7/18.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #include "MyCircularDeque.h"
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/alg-cpp.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcuserdata/junlongj.xcuserdatad/UserInterfaceState.xcuserstate:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jincc/iOS-Algorithm/HEAD/alg-cpp.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcuserdata/junlongj.xcuserdatad/UserInterfaceState.xcuserstate
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/alg-cpp.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcuserdata/junl.xcuserdatad/xcdebugger/Breakpoints_v2.xcbkptlist:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
6 |
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tiny_stl/src/map.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // map.h
3 | // tiny_stl
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2020/11/21.
6 | // Copyright © 2020 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef map_hpp
10 | #define map_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 |
14 | #endif /* map_hpp */
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dp/leetcode/minPathSum.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // minPathSum.h
3 | // dp
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/7/26.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef minPathSum_hpp
10 | #define minPathSum_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 |
14 | #endif /* minPathSum_hpp */
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/alg-cpp.xcodeproj/project.xcworkspace/xcshareddata/IDEWorkspaceChecks.plist:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 | IDEDidComputeMac32BitWarning
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/find/main.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // main.cpp
3 | // find
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2020/12/2.
6 | // Copyright © 2020 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #include
10 | #include "ST.h"
11 | int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
12 | // insert code here...
13 | std::cout << "Hello, World!\n";
14 | return 0;
15 | }
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sort/main.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // main.cpp
3 | // sort
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/7/18.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #include
10 | #include "sort.h"
11 | using namespace std;
12 | int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
13 | // insert code here...
14 | test_sort_drive();
15 | return 0;
16 | }
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/bit/main.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // main.cpp
3 | // bit
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2020/5/14.
6 | // Copyright © 2020 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #include
10 | #include "maximizingXor.h"
11 | int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
12 | // insert code here...
13 | int v = maxXor(1, 10);
14 | printf("%d\n", v);
15 | return 0;
16 | }
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/divideandconquer/closestPair.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // closestPair.h
3 | // divideConquer
4 | //
5 | // Created by junlongj on 2019/7/25.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef closestPair_hpp
10 | #define closestPair_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 |
14 | /*
15 | 二维平面上有n个点,如何快速求出最近的两个点之间的距离
16 | */
17 |
18 | //TODO:
19 | #endif /* closestPair_hpp */
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tiny_stl/main.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // main.cpp
3 | // tiny_stl
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2020/11/9.
6 | // Copyright © 2020 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #include
10 | #include "test.h"
11 | #include "all_test.h"
12 | #include
13 | int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
14 | // insert code here...
15 | std::cout << "Hello, World!\n";
16 | RUN_ALL_TESTS();
17 | return 0;
18 | }
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/stack+queue/itinterviews/getMaxRectSize.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // getMaxRectSize.h
3 | // stack+queue
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/10/23.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef getMaxRectSize_hpp
10 | #define getMaxRectSize_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | /*
14 | 求最大矩阵的大小
15 |
16 | 给定一个整形矩阵,其中的值只有0和1两种,求其中全是1的所有矩阵区域中,最大矩形区域为1的数量.
17 |
18 | 1 0 1 1 最大区域为6
19 | 1 1 1 1
20 | 1 1 1 0
21 | */
22 | #endif /* getMaxRectSize_hpp */
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sort/select.c:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // select.c
3 | // sort
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2020/12/1.
6 | // Copyright © 2020 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #include "sort.h"
10 | void sort_select(ItemType a[], int l, int r){
11 | int i, j, min;
12 | for (i = l; i <= r; i++) {
13 | min = i;
14 | for (j = i+1; j <= r; j++) {
15 | if (less(a[j], a[min]))
16 | min = j;
17 | }
18 | exch(a[min], a[i]);
19 | }
20 | }
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tiny_stl/test/all_test.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // all_test.h
3 | // tiny_stl
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2020/11/11.
6 | // Copyright © 2020 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef all_test_h
10 | #define all_test_h
11 |
12 | #include "allocator_test.h"
13 | #include "forward_test.h"
14 | #include "pair_test.h"
15 | #include "iterator_test.h"
16 | #include "vector_test.h"
17 | #include "list_test.h"
18 | #include "deque_test.h"
19 | #include "unordered_map_test.h"
20 | #include "map_test.h"
21 | #endif /* all_test_h */
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sort/bubble.c:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // sort.c
3 | // sort
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2020/12/1.
6 | // Copyright © 2020 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #include "sort.h"
10 | void sort_bubble(ItemType a[], int l, int r){
11 | int i, j, changed;
12 | for (i = l ; i < r; i++) {
13 | for (j = r, changed = 0; j > i; j--) {
14 | if (less(a[j], a[j-1])) {
15 | exch(a[j], a[j-1]);
16 | changed = 1;
17 | }
18 | }
19 | if (!changed) break;
20 | }
21 | }
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/find/ST.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // ST.h
3 | // find
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2020/12/2.
6 | // Copyright © 2020 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef ST_h
10 | #define ST_h
11 |
12 | template
13 | class ST {
14 | public:
15 | ST();
16 | void put(Key key, Value value);
17 | Value get(Key key);
18 | void remove(Key key);
19 | bool contains(Key key) {
20 | return get(key);
21 | };
22 | bool isEmpty();
23 | int size();
24 | virtual ~ST(){}
25 | };
26 |
27 | #endif /* ST_h */
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/skip_list.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 背景
2 | 为什么要有跳表这样的结构?
3 |
4 | 拿一个单链表来说,即便单链表的数据是有序的,如果我们想从里面查找一个指定的数,那么时间复杂度任然是O(N). 那么怎么才能是链表的查询速度变快呢?
5 |
6 | 这就是跳表这个数据结构,跳表就是在链表的基础上增加多级索引,从而提高查询速度的.
7 |
8 | 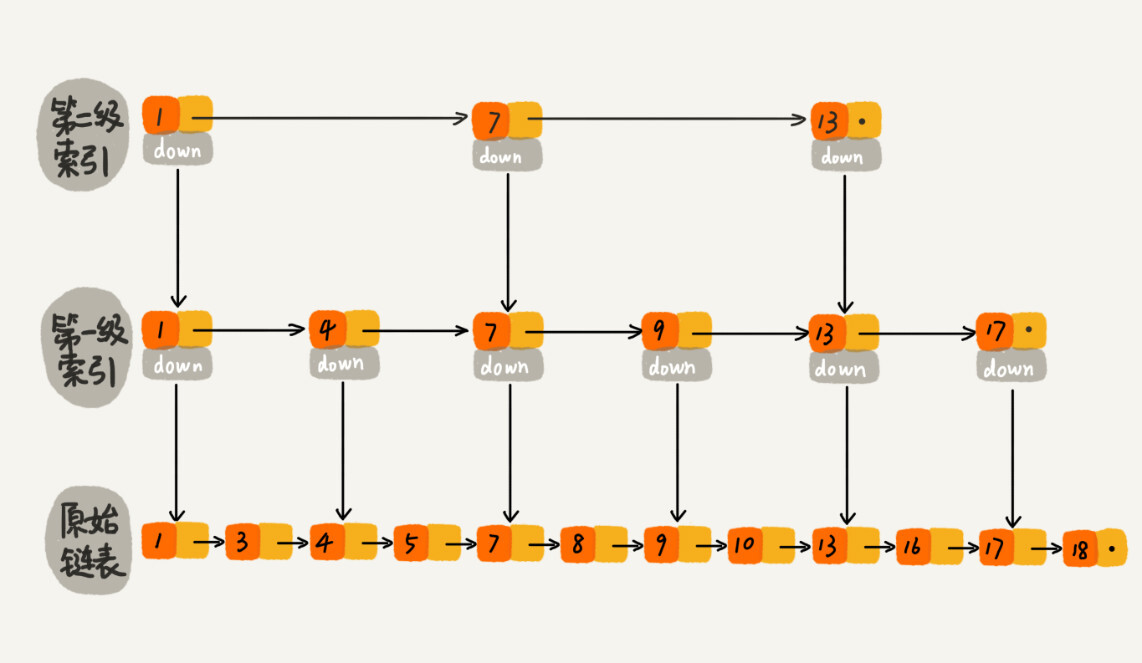
9 | 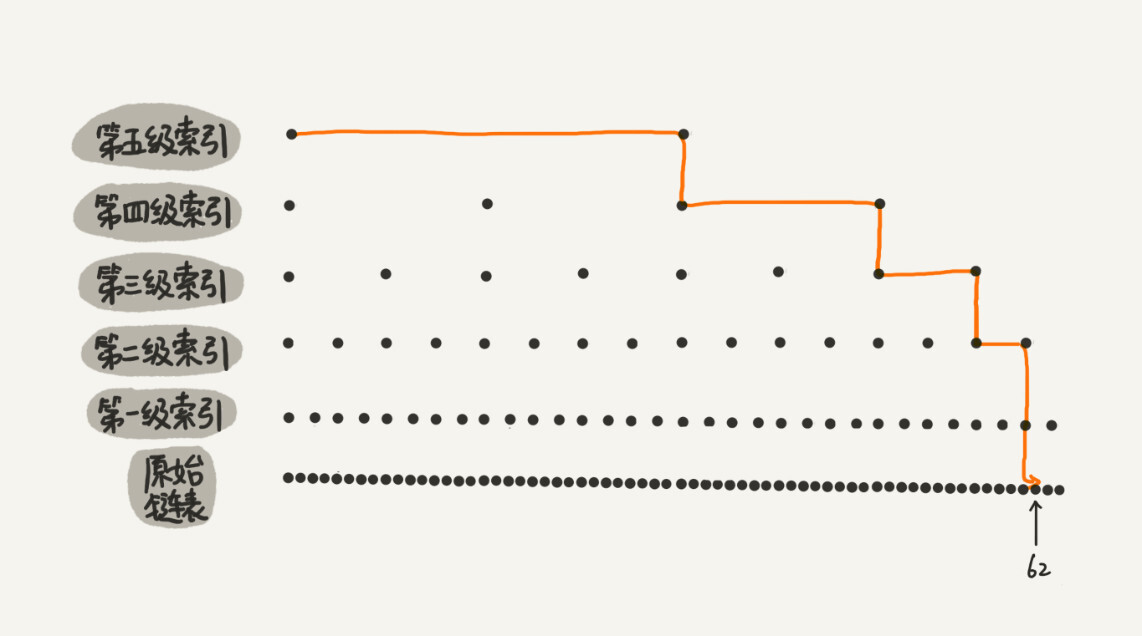
10 |
11 |
12 | # 查询速度
13 |
14 | 跳表结构,每两个节点会抽出一个节点来作为上一级索引的节点,那么第一级节点的个数就是n/2, 第二级n/4..... 那么跳表的高度时间就是log2(N).
15 |
16 | 查询16的路径分析:
17 |
18 | 1->7->13->13(down)->13(down)->16
19 |
20 | 整个查询是log(N)级别的.
21 |
22 |
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/stack+queue/leetcode/maxSlidingWindow.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // maxSlidingWindow.h
3 | // stack+queue
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/7/18.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef maxSlidingWindow_hpp
10 | #define maxSlidingWindow_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 |
14 | /*
15 | 239.给定一个数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口 k 内的数字。滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。
16 |
17 | 返回滑动窗口最大值。
18 |
19 | 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
20 | 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sliding-window-maximum
21 | 著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
22 | */
23 | #endif /* maxSlidingWindow_hpp */
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tiny_stl/src/type_traits.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // type_traits.h
3 | // tiny_stl
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2020/11/13.
6 | // Copyright © 2020 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef type_traits_hpp
10 | #define type_traits_hpp
11 |
12 | namespace tiny{
13 | template
14 | struct m_integer_constant{
15 | static constexpr T value = v;
16 | };
17 | template
18 | using m_bool_constant = m_integer_constant;
19 |
20 | typedef m_bool_constant m_true_type;
21 | typedef m_bool_constant m_false_type;
22 | }
23 | #endif /* type_traits_hpp */
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/array/linearList.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // linearList.h
3 | // ALG-DS
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/4/29.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef linearList_h
10 | #define linearList_h
11 |
12 | // 线性表抽象描述 base ADT
13 | template
14 | class linearList {
15 | public:
16 | virtual ~linearList(){};
17 | virtual bool empty() const = 0;
18 | virtual int size() const = 0;
19 | virtual T& get(int index) = 0;
20 | virtual int indexOf(const T& element) const = 0;
21 | virtual void earse(int index) = 0;
22 | virtual void insert(int index, const T& element) = 0;
23 | };
24 | #endif /* linearList_h */
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sort/insert.c:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // insert.c
3 | // sort
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2020/12/1.
6 | // Copyright © 2020 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #include "sort.h"
10 | //依次将未排序数组中的元素插入到已排序数组中的指定位置
11 | void sort_insert(ItemType a[], int l, int r){
12 | int i, j, min = l, v;
13 | for (i = l+1; i <= r; i++) {
14 | if (less(a[i], a[min])) min = i;
15 | }
16 | //数组a的第一个元素为最小元素, 避免内层循环的判断
17 | exch(a[min], a[l]);
18 |
19 | for (i = l + 2; i <= r ; i++) {
20 | v = a[i];
21 | for (j = i; less(v, a[j-1]); j--) {
22 | a[j] = a[j-1];//如果v比前一个元素小,向后移动一位
23 | }
24 | a[j] = v;
25 | }
26 | }
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/hashTable/main.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // main.cpp
3 | // hasTable
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/7/20.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #include
10 | #include "hash_map.h"
11 |
12 | class SampleHash {
13 | public:
14 | size_t operator()(const int &s) const
15 | {
16 | return s % 3;
17 | }
18 | };
19 | int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
20 | // insert code here...
21 | std::cout << "Hello, World!\n";
22 |
23 | hash_map test;
24 | for (int i=0; i<20; i++) {
25 | test[i] = i;
26 | }
27 | std::cout << test[1] << ' ' << test[2] << std::endl;
28 | return 0;
29 | }
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dp/main.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // main.cpp
3 | // dp
4 | //
5 | // Created by junlongj on 2019/7/23.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #include
10 | #include "knapsack.h"
11 | #include "minPathSum.h"
12 | #include "climbStairs.h"
13 | #include "double11advance.h"
14 | #include "coinChange.h"
15 | #include "levenshtein_distance.h"
16 | #include "pascals_triangle.h"
17 | #include "matrix_move.h"
18 | int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
19 | // insert code here...
20 | using namespace std;
21 | test_double11advance();
22 | test_knapsack();
23 | test_coinChange();
24 | test_levenshtein_distance();
25 | test_pascals_triangle();
26 | test_matrix_move();
27 | return 0;
28 | }
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/hash.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # 哈希算法
3 |
4 | 定义: 将任意长度的二进制值串映射为固定长度的二进制串,这个映射的规则就是哈希算法。哈希算法要满足几个要求:
5 |
6 | * 输入数据不管长短,输出都是固定的长度.
7 | * 对输入数据铭感,哪怕只是修改了一个bit,最后的哈希值也不一样
8 | * 哈希算法是单向的,就是说原始数据可以映射到哈希值,但是不能反向推导
9 | * 哈希冲突的概率要很小,劲量避免冲突
10 | * 执行效率要竟可能高效,不管是多长的文本,也能快速计算出哈希值。
11 |
12 |
13 | ## 哈希函数的应用
14 |
15 |
16 | [网络安全——数据的加密与签名,RSA介绍](https://www.cnblogs.com/mddblog/p/5380556.html)
17 |
18 |
19 | 1. 哈希算法可以对大数据做信息摘要,通过一个较短的摘要来作为唯一标识,作为身份的象征。比如:我们可以对图库里面的所有图片做hash运算,然后将结果保存到散列表中。这样当我们想要判断某张图片是否在图库中,就可以通过hash值来判断了,非常高效.
20 |
21 |
22 | 2. 哈希算法可以用来做数据校验,比如BT下载种子里面保存了源文件的哈希值,当用户下载完文件后,可以对下载后文件进行hash,然后比较判断是否文件下载成功或是否被篡改过。
23 |
24 | 3. 散列函数也是哈希函数的一种应用。散列函数对算法冲突的要求比较低,同时也并不关心是否能反向解密,它更关心的是散列后的值是否能平均分布,并且这种计算要足够高效,不然就会影响散列表的性能
25 | 4. hash + salt可以避免字典攻击
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/base/illegalParameterValue.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // illegalParameterValue.hpp
3 | // ALG-DS
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/4/22.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef illegalParameterValue_hpp
10 | #define illegalParameterValue_hpp
11 | #include
12 | #include
13 |
14 | class illegalParameterValue {
15 | public:
16 | illegalParameterValue(): message("Illegal parameter value"){}
17 | illegalParameterValue(const std::string& theMessage) {message = theMessage;}
18 | void outputMessage() {std::cout << message << std::endl;}
19 | private:
20 | std::string message;
21 | };
22 |
23 | class stackEmpty {
24 |
25 | public:
26 |
27 | };
28 |
29 |
30 | #endif /* illegalParameterValue_hpp */
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/bit/maximizingXor.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // maximizingXor.h
3 | // bit
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2020/5/14.
6 | // Copyright © 2020 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef maximizingXor_h
10 | #define maximizingXor_h
11 |
12 | /*
13 | 题目:https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/maximizing-xor/problem
14 | 先通过异或运算求出a和b有哪些位不一样,这样我们就知道最左边的1位于什么位置了,通过不断的右移,这样就可以定位到最左边的位置. 那么最大值就为最左位为0,后面全为1. 因为
15 |
16 | LxorR可以知道不变位。从L到R的范围内,任意两个整数异或的结果可能都不一样,但是必然存在前几位相同的特性。例如:L= 11110,R=11010.在其范围内的AxorB的结果一定是00xxx的模式
17 | */
18 |
19 | int maxXor(int a, int b){
20 | int value = a ^ b, result = 1;
21 | while(value){
22 | value = value >> 1;
23 | result = result << 1;
24 | }
25 | return result - 1;
26 | }
27 | #endif /* maximizingXor_h */
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/divideandconquer/main.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // main.cpp
3 | // divideConquer
4 | //
5 | // Created by junlongj on 2019/7/25.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #include
10 | #include "reversedOrderPairs.h"
11 | int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
12 | // insert code here...
13 | using namespace std;
14 | cout << "数组里面的逆序对 starting.........." << endl;
15 |
16 | {
17 | int nums[] = {7,5,6,4,3,2,1};
18 | printf("%d\n", reversedOrderPairs(nums, 7));
19 | for(int i=0; i < 7; i++)
20 | printf(" %d",nums[i]);
21 | };
22 | {
23 | int nums[] = {7,5,6,4,3,2,1};
24 | printf("\n%d\n", reversePairs(nums, 7));
25 | for(int i=0; i < 7; i++)
26 | printf(" %d",nums[i]);
27 | };
28 | return 0;
29 | }
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/stack+queue/leetcode/MyCircularDeque.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // MyCircularDeque.h
3 | // stack+queue
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/7/18.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef MyCircularDeque_hpp
10 | #define MyCircularDeque_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 |
14 | /*
15 | 641.设计实现双端队列。
16 | 你的实现需要支持以下操作:
17 |
18 | MyCircularDeque(k):构造函数,双端队列的大小为k。
19 | insertFront():将一个元素添加到双端队列头部。 如果操作成功返回 true。
20 | insertLast():将一个元素添加到双端队列尾部。如果操作成功返回 true。
21 | deleteFront():从双端队列头部删除一个元素。 如果操作成功返回 true。
22 | deleteLast():从双端队列尾部删除一个元素。如果操作成功返回 true。
23 | getFront():从双端队列头部获得一个元素。如果双端队列为空,返回 -1。
24 | getRear():获得双端队列的最后一个元素。 如果双端队列为空,返回 -1。
25 | isEmpty():检查双端队列是否为空。
26 | isFull():检查双端队列是否满了。
27 |
28 | 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
29 | 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/design-circular-deque
30 | 著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
31 | */
32 |
33 |
34 | #endif /* MyCircularDeque_hpp */
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sort/bucketSort.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // bucketSort.h
3 | // sort
4 | //
5 | // Created by junlongj on 2019/9/2.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef bucketSort_hpp
10 | #define bucketSort_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | #include
14 |
15 | void test_bucketsort(){
16 | using namespace std;
17 | int ages[] = {15,78,24,26,67,90,1,56,78};
18 | const int bucket_cout = 100;
19 | int buckets[bucket_cout];//创建100个桶,代表0-99个年龄
20 | memset(buckets, 0, sizeof(buckets));
21 | for (auto &age : ages) {
22 | buckets[age]+=1;
23 | }
24 |
25 | //依次从桶里面读出
26 | printf("test_bucketsort starting.........\n");
27 | for (int i=0; i0) {
29 | printf("%i,",i);
30 | buckets[i]-=1;
31 | }
32 | }
33 | printf("\n");
34 | }
35 |
36 |
37 |
38 | #endif /* bucketSort_hpp */
39 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/string/coding-interviews/removeRepeatChar.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // removeRepeatChar.h
3 | // string
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2020/5/18.
6 | // Copyright © 2020 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef removeRepeatChar_h
10 | #define removeRepeatChar_h
11 |
12 | namespace codinginterviews {
13 | void removeRepeatChar(char *s){
14 | if (s == NULL) return ;
15 |
16 | bool hashMap[256];
17 | memset(hashMap, false, sizeof(hashMap));
18 |
19 | char *ptr0 , *ptr1;
20 | ptr0 = ptr1 = s;
21 | while (*ptr1 != '\0') {
22 | if (!hashMap[*ptr1]) {
23 | hashMap[*ptr1] = true;
24 | *ptr0++ = *ptr1;
25 | }
26 | ptr1++;
27 | }
28 | *ptr0 = '\0';
29 | }
30 | void test_removeRepeatChar(){
31 | printf("test_removeRepeatChar\n");
32 | char s[] = "google";
33 | removeRepeatChar(s);
34 | puts(s);
35 | }
36 | }
37 |
38 | #endif /* removeRepeatChar_h */
39 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sort/sort.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // sort.h
3 | // sort
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2020/12/1.
6 | // Copyright © 2020 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef sort_h
10 | #define sort_h
11 |
12 | #include
13 |
14 | typedef int ItemType;
15 | #define key(A) (A)
16 | #define less(A, B) (key(A) < key(B))
17 | #define exch(A, B) {ItemType t = A; A = B; B = t;}
18 | #define compexch(A, B) if (less(B, A)) exch(A, B)
19 |
20 | #ifdef __cplusplus
21 | extern "C" {
22 | #endif
23 | void sort_bubble(ItemType a[], int l, int r);
24 | void sort_insert(ItemType a[], int l, int r);
25 | void sort_select(ItemType a[], int l, int r);
26 | void sort_merge(ItemType a[], int l, int r);
27 | void sort_quick(ItemType a[], int l, int r);
28 | void sort_heap(ItemType a[], int l, int r);
29 |
30 | typedef int(*Compare)(ItemType a[], int i, int j);
31 | //驱动程序
32 | void test_sort_drive(void);
33 | #ifdef __cplusplus
34 | }
35 | #endif
36 | #endif /* sort_h */
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/array/leetcode/easy/twoSum.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // twoSum.h
3 | // array
4 | //
5 | // Created by junlongj on 2019/8/6.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef twoSum_hpp
10 | #define twoSum_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | #include
14 | namespace leetcode {
15 | /*
16 | 1.两数之和
17 |
18 | 思路:通过集合来保存之前遍历过的元素,这样每次查找的时候先判断target-当前值的元素在不在hash table里面,就可以计算出结果了.
19 | */
20 | std::vector twoSum(std::vector& nums, int target) {
21 | std::map mm;//key为当前值,value为下标
22 | std::vector result;
23 | for (int i=0;i
13 | #include
14 | #include
15 | #include "stack.h"
16 | class sampleBrowser {
17 | public:
18 | void open(const std::string &url){
19 | aStack.push(url);
20 | }
21 | void goBack(){
22 | std::string &url = aStack.pop();
23 | bStack.push(url);
24 | }
25 | void goForward(){
26 | std::string &url = bStack.pop();
27 | aStack.push(url);
28 | }
29 | void checkCurrentPage(){
30 | std::cout << "checkCurrentPage : " << aStack.topElement() << std::endl;
31 | }
32 |
33 | private:
34 | stack aStack;
35 | stack bStack;
36 | };
37 |
38 | #endif /* sampleBrowser_hpp */
39 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/recursion/coding-interviews/jumpFloorII.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // jumpFloorII.h
3 | // recursion
4 | //
5 | // Created by junlongj on 2019/8/4.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef jumpFloorII_hpp
10 | #define jumpFloorII_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | /*
14 | 剑指Offer(九):变态跳台阶
15 | 一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级……它也可以跳上n级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
16 | https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/22243d016f6b47f2a6928b4313c85387?tpId=13&tqId=11162&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=%2Fta%2Fcoding-interviews&qru=%2Fta%2Fcoding-interviews%2Fquestion-ranking
17 |
18 | */
19 | namespace codinginterviews {
20 | /*
21 | n == 1 1
22 | n == 2 2
23 | n == 3 4
24 | .....
25 | */
26 | int jumpFloorII(int number) {
27 | if (number == 0)return 0;
28 | int step = 1;
29 | for (int i= 1; i
13 | /*
14 | 查找最后一个小于等于给定值的元素
15 | */
16 | int bsearch_findLastElementLessOrEqual(int nums[], int n,int target){
17 | if (n <= 0) return -1;
18 | int left = 0;
19 | int right = n-1;
20 | while(left<=right){
21 | int mid = left+((right-left)>>1);
22 | if (nums[mid] <= target){
23 | //已经是小于等于给定值的元素,找到最后一个
24 | if (mid == n-1 || nums[mid+1] > target){
25 | return mid;
26 | }
27 | left = mid + 1;
28 | }else{
29 | right = mid -1;
30 | }
31 | }
32 | return -1;
33 | }
34 |
35 | #endif /* bsearch_findLastElementLessOrEqual_hpp */
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tree/Tree.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // Tree.h
3 | // tree
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2020/5/13.
6 | // Copyright © 2020 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef Tree_h
10 | #define Tree_h
11 |
12 | #ifdef __cplusplus
13 | extern "C" {
14 | #endif
15 | typedef struct BTreeNode BTreeNode;
16 | struct BTreeNode{
17 | int val;
18 | BTreeNode *left;
19 | BTreeNode *right;
20 | };
21 | BTreeNode *creatTreeNode(int val);
22 | BTreeNode *creatTree(int vals[], int n);
23 | void preOrder(BTreeNode *pTree);
24 | void preOrderIterate(BTreeNode *pTree);
25 | void inOrder(BTreeNode *pTree);
26 | void inOrderIterate(BTreeNode *pTree);
27 | void postOrder(BTreeNode *pTree);
28 | void postOrderIterate(BTreeNode *pTree);
29 | void levelOrder(BTreeNode *pTree);
30 |
31 | //根据前序遍历和中序遍历构建二叉树
32 | BTreeNode *construct(int preorder[], int inorder[], int size);
33 | #ifdef __cplusplus
34 | }
35 | #endif
36 |
37 | #endif /* Tree_h */
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tree/leetcode/maxDepth.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // maxDepth.h
3 | // tree
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/8/1.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef maxDepth_hpp
10 | #define maxDepth_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | /*
14 | 104.给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
15 |
16 | 二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
17 |
18 | 说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
19 |
20 | 示例:
21 | 给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
22 |
23 | 3
24 | / \
25 | 9 20
26 | / \
27 | 15 7
28 | 返回它的最大深度 3 。
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 | 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
33 | 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree
34 | 著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
35 | */
36 |
37 | namespace leetcode {
38 | int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
39 | if (!root) {
40 | return 0;
41 | }
42 | int leftDepth = maxDepth(root->lchild);
43 | int rightDepth = maxDepth(root->rchild);
44 | return std::max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
45 | }
46 | }
47 | #endif /* maxDepth_hpp */
48 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dp/leetcode/easy/climbStairs.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // climbStairs.h
3 | // dp
4 | //
5 | // Created by junlongj on 2019/8/14.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef climbStairs_hpp
10 | #define climbStairs_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | /*
14 | 70.爬楼梯
15 | 假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
16 |
17 | 每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
18 |
19 | 注意:给定 n 是一个正整数。
20 |
21 | 示例 1:
22 |
23 | 输入: 2
24 | 输出: 2
25 | 解释: 有两种方法可以爬到楼顶。
26 | 1. 1 阶 + 1 阶
27 | 2. 2 阶
28 |
29 | 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
30 | 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/climbing-stairs
31 | 著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
32 | */
33 | namespace leetcode {
34 | int climbStairs(int n) {
35 | if (n == 0) return 0;
36 | if (n == 1) return 1;
37 | if (n == 2) return 2;
38 | int dp[n];
39 | dp[0] = 1;
40 | dp[1] = 2;
41 | for (int i=2;i
13 | /*
14 | 给定一个排序链表,删除所有重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次。
15 |
16 | 示例 1:
17 |
18 | 输入: 1->1->2
19 | 输出: 1->2
20 | 示例 2:
21 |
22 | 输入: 1->1->2->3->3
23 | 输出: 1->2->3
24 |
25 | 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
26 | 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list
27 | 著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
28 | */
29 |
30 | namespace leetcode {
31 | ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
32 | ListNode *ct=head;
33 | while(ct && ct->next){
34 | if (ct->val == ct->next->val){
35 | ct->next=ct->next->next;
36 | }else{
37 | ct=ct->next;
38 | }
39 | }
40 | return head;
41 | }
42 | }
43 | #endif /* deleteDuplicates_hpp */
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/bsearch/bsearch_findLastElement.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // bsearch_findLastElement.h
3 | // bsearch
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/9/4.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef bsearch_findLastElement_hpp
10 | #define bsearch_findLastElement_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | /*
14 | 有序数组中,存在着相同的元素,找到最后一个值等于指定元素的位置
15 | */
16 |
17 | int bsearch_findLastElement(int nums[], int n,int target){
18 | if (n <= 0) {
19 | return -1;
20 | }
21 | int left=0;
22 | int right=n-1;
23 | while (left<=right) {
24 | int mid = left+((right-left)>>1);
25 | if (nums[mid] < target) {
26 | left = mid+1;
27 | }else if (nums[mid] > target){
28 | right=mid-1;
29 | }else{
30 | //找到了target,我们判断它是否是最后一个
31 | if (mid == n-1 || nums[mid+1] !=target) {
32 | return mid;
33 | }
34 | left=mid+1;
35 | }
36 | }
37 | return -1;
38 | }
39 |
40 | #endif /* bsearch_findLastElement_hpp */
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/bsearch/bsearch_findFirstElement.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // bsearch_findFirstElement.h
3 | // bsearch
4 | //
5 | // Created by junlongj on 2019/9/4.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef bsearch_findFirstElement_hpp
10 | #define bsearch_findFirstElement_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 |
14 | /*
15 | 有序数组中,存在着相同的元素,找到指定元素的第一个值.
16 | */
17 |
18 | int bsearch_findFirstElement(int nums[], int n,int target){
19 | if (n <= 0) {
20 | return -1;
21 | }
22 | int left=0;
23 | int right=n-1;
24 | while (left<=right) {
25 | int mid = left+((right-left)>>1);
26 | if (nums[mid] < target) {
27 | left = mid+1;
28 | }else if (nums[mid] > target){
29 | right=mid-1;
30 | }else{
31 | //找到了target,我们判断它是否是第一个
32 | if (mid == 0 || nums[mid-1] != target) {
33 | return mid;
34 | }
35 | right = mid-1;
36 | }
37 | }
38 | return -1;
39 | }
40 | #endif /* bsearch_findFirstElement_hpp */
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/bsearch/bsearch_findFirstElementGreaterOrEqual.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // bsearch_findFirstElementGreaterOrEqual.h
3 | // bsearch
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/9/4.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef bsearch_findFirstElementGreaterOrEqual_hpp
10 | #define bsearch_findFirstElementGreaterOrEqual_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | /*
14 | 有序数组中,存在着相同的元素, 查找第一个大于等于指定元素的值.
15 | */
16 | int bsearch_findFirstElementGreaterOrEqual(int nums[], int n,int target){
17 | //首先找到大于等于指定元素的值,然后判断它是否是第一个.
18 | if (n <= 0) return -1;
19 | int left = 0;
20 | int right = n-1;
21 | while(left<=right){
22 | int mid = left+((right-left)>>1);
23 | if (nums[mid] >= target){
24 | //已经是大于等于target的值了,找到第一个
25 | if (mid == 0 || nums[mid-1] < target){
26 | return mid;
27 | }
28 | right = mid -1;
29 | }else{
30 | left = mid+1;
31 | }
32 | }
33 | return -1;
34 |
35 | }
36 |
37 |
38 |
39 | #endif /* bsearch_findFirstElementGreaterOrEqual_hpp */
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/bsearch/leetcode/isPerfectSquare.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // isPerfectSquare.h
3 | // bsearch
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/7/19.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef isPerfectSquare_hpp
10 | #define isPerfectSquare_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | /*
14 | 367.给定一个正整数 num,编写一个函数,如果 num 是一个完全平方数,则返回 True,否则返回 False。
15 |
16 | 说明:不要使用任何内置的库函数,如 sqrt。
17 |
18 | 示例 1:
19 |
20 | 输入:16
21 | 输出:True
22 | 示例 2:
23 |
24 | 输入:14
25 | 输出:False
26 |
27 | 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
28 | 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-perfect-square
29 | 著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
30 | */
31 |
32 | bool isPerfectSquare(int num) {
33 | if (num<=1) return true;
34 | int left=1;
35 | int right=num/2;
36 | while (left=num/mid) {
39 | //至少mid^2大于num
40 | right=mid;
41 | } else {
42 | //mid^2无限逼近num
43 | left=mid+1;
44 | }
45 | }
46 | return (long)left*left == num;
47 | }
48 |
49 | #endif /* isPerfectSquare_hpp */
50 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/recursion/coding-interviews/rectCover.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // rectCover.h
3 | // recursion
4 | //
5 | // Created by junlongj on 2019/8/4.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef rectCover_hpp
10 | #define rectCover_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | /*
14 | 剑指Offer(十):矩形覆盖
15 | 我们可以用2*1的小矩形横着或者竖着去覆盖更大的矩形。请问用n个2*1的小矩形无重叠地覆盖一个2*n的大矩形,总共有多少种方法?
16 | https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/72a5a919508a4251859fb2cfb987a0e6?tpId=13&tqId=11163&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=%2Fta%2Fcoding-interviews&qru=%2Fta%2Fcoding-interviews%2Fquestion-ranking
17 | */
18 |
19 | namespace codinginterviews {
20 | /*
21 | 这个问题实际上就是Fibonacci数列的问题。
22 | 就拿2*5的格子来说,定义为f(5).第一行我们可以顺着放,那么f5=f(4).
23 | 如果第一行我们横着放,占用了两格,那么f5=f3;
24 | 所以f5=f4+f3.
25 | */
26 | int rectCover(int n) {
27 | int f0,f1,f2;
28 | f0 = 0;
29 | f1 = 1;
30 | if (n == 0) return f0;
31 | if (n == 1) return f1;
32 | for (int i=2; i<=n; i++) {
33 | f2 = f0+f1;
34 | f0 = f1;
35 | f1 = f2;
36 | }
37 | return f2;
38 | }
39 | }
40 |
41 | #endif /* rectCover_hpp */
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/greed/coin_dispenser.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // coin_dispenser.h
3 | // greed
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/9/9.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef coin_dispenser_hpp
10 | #define coin_dispenser_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | #include
14 | using namespace std;
15 |
16 | /**
17 | 假设我们有100元,50,20,10,5,2,1这些面额的纸币,它们分别的张数为a1,a2,a3....张.
18 | 题目是使用最少的纸币数目来支付K元.
19 | */
20 | int coin_dispenser(vector &cointypes,vector &coincounts, int targetmoney){
21 | /*
22 | 限制值:筹齐这targetmoney
23 | 期望值: 纸币数量最小
24 | 贪心思想:对于贡献一张纸币来说(期望值),我们肯定希望它的价值越大,因为这样意味着更少的张数.
25 | */
26 | int count=0;
27 | for (size_t i=cointypes.size()-1; i>=0;) {
28 | if (targetmoney <= 0 )
29 | break;
30 |
31 | if (targetmoney >= cointypes[i] && coincounts[i]>0) {
32 | count++;
33 | coincounts[i]--;
34 | targetmoney -= cointypes[i];
35 | }else{
36 | i--;
37 | }
38 | }
39 | if (targetmoney > 0) {
40 | throw "钱不够啊";
41 | }
42 | return count;
43 | }
44 |
45 | #endif /* coin_dispenser_hpp */
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/linkedList/coding-interviews/creatlist.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // creatlist.h
3 | // linkedList
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/8/2.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef creatlist_hpp
10 | #define creatlist_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | #include
14 |
15 | namespace codinginterviews {
16 | ListNode *creatLists(const std::vector &s){
17 | ListNode *root = new ListNode(0);
18 | ListNode *node = root;
19 | auto it = s.begin();
20 | while (it != s.end()) {
21 | node->next = new ListNode(*it);
22 | node = node->next;
23 | it++;
24 | }
25 | return root;
26 | }
27 | DoubleNode *creatDoubleLists(const std::vector &s){
28 | DoubleNode *root = new DoubleNode(0);
29 | DoubleNode *node = root;
30 | auto it = s.begin();
31 | while (it != s.end()) {
32 | node->next = new DoubleNode(*it);
33 | node->next->pre = node;
34 | node = node->next;
35 | it++;
36 | }
37 | return root;
38 | }
39 | }
40 |
41 | #endif /* creatlist_hpp */
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/backtracking/knapsack.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // knapsack.h
3 | // backtracking
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/7/25.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef knapsack_hpp
10 | #define knapsack_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | /**
14 | 0-1背包问题. 对于一组不同质量,不可分割的物品,我们需要选择一些放入背包中,在满足最大重量限制的条件下,背包中所能放入的最大值是多少?
15 | */
16 |
17 | void backpack01_bt(int weights[], int n, int level, int ctweight,int limitweight, int *result);
18 | int backpack01(int weights[], int n, int limitweight){
19 | int result = 0;
20 | backpack01_bt(weights, n, 0, 0, limitweight, &result);
21 | return result;
22 | }
23 | void backpack01_bt(int weights[], int n,int level, int ctweight,int limitweight, int *result){
24 | if (level == n || *result == limitweight){
25 | if (*result < ctweight){
26 | *result = ctweight;
27 | }
28 | return;
29 | }
30 |
31 | backpack01_bt(weights, n, level+1, ctweight, limitweight, result);
32 | if (ctweight + weights[level] <= limitweight)
33 | backpack01_bt(weights, n, level+1, ctweight + weights[level], limitweight, result);
34 |
35 | }
36 | #endif /* knapsack_hpp */
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/bsearch/leetcode/mySqrt.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // mySqrt.h
3 | // bsearch
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/7/19.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef mySqrt_hpp
10 | #define mySqrt_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | /*
14 | 69.实现 int sqrt(int x) 函数。
15 |
16 | 计算并返回 x 的平方根,其中 x 是非负整数。
17 |
18 | 由于返回类型是整数,结果只保留整数的部分,小数部分将被舍去。
19 |
20 | 示例 1:
21 |
22 | 输入: 4
23 | 输出: 2
24 | 示例 2:
25 |
26 | 输入: 8
27 | 输出: 2
28 | 说明: 8 的平方根是 2.82842...,
29 | 由于返回类型是整数,小数部分将被舍去。
30 |
31 |
32 | 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
33 | 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sqrtx
34 | 著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
35 |
36 | */
37 |
38 | int mySqrt(int x) {
39 | if (x==1)
40 | return 1;
41 | int start=0;
42 | //the sqt is not greater than x/2+1
43 | int end=x/2+1;
44 | while (start <= end) {
45 | int mid = start + ((end-start)>>1);
46 |
47 | if (mid < x / mid) {//用除法不用乘法防止越界
48 | start = mid+1;
49 | }else if (mid > x / mid){
50 | end = mid-1;
51 | }else{
52 | return mid;
53 | }
54 | }
55 | return end;
56 | }
57 | #endif /* mySqrt_hpp */
58 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/greed/shared_the_sweets.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // shared_the_sweets.h
3 | // greed
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/9/9.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef shared_the_sweets_hpp
10 | #define shared_the_sweets_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | #include
14 |
15 | using namespace std;
16 |
17 | /**
18 | 分糖果. 把m个糖果分给n个孩子,只有当糖果的大小大于孩子期望的大小时,孩子才会得到满足.
19 |
20 | @param sweets m个糖果分别的大小
21 | @param childwants 孩子们每个人期望的糖果大小.
22 | @return 能得到满足的孩子数量
23 | */
24 | int shared_the_sweets(vector &sweets, vector &childwants){
25 | /*
26 | 限制条件:一共只有m个糖果。
27 | 期望值: 希望得到满足的孩子数量最大.
28 | 贪心思想: 要求糖果大小越小的孩子越容易满足,对于期望值来说,满足它跟满足要大糖果的孩子是一样的,所以我们优先满足它。
29 | */
30 | sort(sweets.begin(), sweets.end());
31 | sort(childwants.begin(), childwants.end());
32 | int count = 0;
33 | for (int i=0,j=0; i= childwants[i]) {
36 | count++;//孩子得到了满足
37 | i++;
38 | }else{
39 | }
40 | }
41 | return count;
42 | }
43 |
44 | #endif /* shared_the_sweets_hpp */
45 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/array/leetcode/easy/searchInsert.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // searchInsert.h
3 | // array
4 | //
5 | // Created by junlongj on 2019/8/7.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef searchInsert_hpp
10 | #define searchInsert_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | #include
14 | /*
15 | 35. 搜索插入位置
16 |
17 | 给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引。如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置。
18 |
19 | 你可以假设数组中无重复元素。
20 |
21 | 示例 1:
22 |
23 | 输入: [1,3,5,6], 5
24 | 输出: 2
25 |
26 | 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
27 | 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/search-insert-position
28 | 著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
29 | */
30 | namespace leetcode {
31 | int searchInsert(std::vector& nums, int target) {
32 | if (nums.empty())
33 | return 0;
34 | int l=0;
35 | int r=nums.size()-1;
36 | while(l<=r){
37 | int mid = l+(r-l)/2;
38 | if (nums[mid] == target){
39 | return mid;
40 | }else if (nums[mid] < target){
41 | l = mid+1;
42 | }else{
43 | r = mid-1;
44 | }
45 | }
46 | return l;
47 | }
48 | }
49 | #endif /* searchInsert_hpp */
50 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/other/leetcode/easy/reverse_integer.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // reverse_integer.h
3 | // other
4 | //
5 | // Created by junlongj on 2019/8/11.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef reverse_integer_hpp
10 | #define reverse_integer_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | /*
14 | 7. 整数反转
15 |
16 | 给出一个 32 位的有符号整数,你需要将这个整数中每位上的数字进行反转。
17 |
18 | 示例 1:
19 |
20 | 输入: 123
21 | 输出: 321
22 | 示例 2:
23 |
24 | 输入: -123
25 | 输出: -321
26 | 示例 3:
27 |
28 | 输入: 120
29 | 输出: 21
30 |
31 | 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
32 | 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-integer
33 | 著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
34 | */
35 |
36 | namespace leetcode {
37 | //这个题提交失败了多次,关键在于如何确保数据不会溢出。
38 | int reverse(int x) {
39 | int result=0;
40 | while(x){
41 | int v=x%10;
42 | //int最大值是2147483647,最小值是-2147483648
43 | if (result > INT_MAX/10){
44 | return 0;
45 | }
46 | if (result < INT_MIN/10){
47 | return 0;
48 | }
49 | result=result*10+v;
50 | x/=10;
51 | }
52 | return result;
53 | }
54 | }
55 | #endif /* reverse_integer_hpp */
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/string/leetcode/easy/lengthOfLastWord.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // lengthOfLastWord.h
3 | // string
4 | //
5 | // Created by junlongj on 2019/8/14.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef lengthOfLastWord_hpp
10 | #define lengthOfLastWord_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | #include
14 | /*
15 | 58. 最后一个单词的长度
16 | 给定一个仅包含大小写字母和空格 ' ' 的字符串,返回其最后一个单词的长度。
17 |
18 | 如果不存在最后一个单词,请返回 0 。
19 |
20 | 说明:一个单词是指由字母组成,但不包含任何空格的字符串。
21 |
22 | 示例:
23 |
24 | 输入: "Hello World"
25 | 输出: 5
26 |
27 |
28 | 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
29 | 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/length-of-last-word
30 | 著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
31 | */
32 | namespace leetcode {
33 | int lengthOfLastWord(std::string s) {
34 | int length=0;
35 | if (s.empty()) return 0;
36 | bool ch = false;//是否已经出现过字符
37 | for(int i=s.length()-1;i>=0;i--){
38 | if (s[i] == ' '){
39 | if (ch){
40 | return length;
41 | }
42 | }else{
43 | ch = true;
44 | length++;
45 | }
46 | }
47 | return ch ? length : 0 ;
48 | }
49 | }
50 | #endif /* lengthOfLastWord_hpp */
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/other/coding-interviews/IsContinuous2.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // IsContinuous2.h
3 | // other
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2020/1/13.
6 | // Copyright © 2020 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef IsContinuous2_hpp
10 | #define IsContinuous2_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | #include
14 |
15 | namespace codinginterviews {
16 | using namespace std;
17 | bool IsContinuous2( vector numbers ) {
18 | sort(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
19 |
20 | int offset = 0;
21 | int zerocount = numbers[0] == 0;
22 | for (int i=1;i < numbers.size();i++){
23 | if (numbers[i] == 0){
24 | zerocount++;
25 | continue;
26 | }
27 | if (numbers[i] == numbers[i-1]){
28 | return false;
29 | }
30 | offset += numbers[i] - numbers[i-1] - 1;
31 | }
32 | return offset <= zerocount ? true : false ;
33 | }
34 |
35 | void test_IsContinuous2(){
36 | vector nums{1,3,4,6,0};
37 | cout << "-------test_IsContinuous2------" << endl;
38 | cout << IsContinuous2(nums) << endl;
39 | }
40 | }
41 |
42 | #endif /* IsContinuous2_hpp */
43 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sort/heap.c:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // heap.c
3 | // sort
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2020/12/2.
6 | // Copyright © 2020 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #include "sort.h"
10 |
11 | int cmp(ItemType a[], int i, int j) {
12 | return less(a[i], a[j]);
13 | }
14 | //上浮操作,将制定元素上浮到它应该在的位置
15 | void swim(ItemType a[], int n, int idx, Compare cmp){
16 | while (idx > 1 && cmp(a, idx/2, idx)) {
17 | exch(a[idx/2], a[idx]);
18 | idx /= 2;
19 | }
20 | }
21 | //下沉操作,将制定元素下沉到它应该在的位置
22 | void sink(ItemType a[], int n, int idx, Compare cmp){
23 | while (2 * idx <= n) {
24 | int j = 2 * idx;
25 | if (j+1 <= n && cmp(a, j, j+1)) {
26 | j++;
27 | }
28 | if (cmp(a, idx, j)) {
29 | //swap
30 | exch(a[idx], a[j]);
31 | idx = j;
32 | }else break;
33 | }
34 | }
35 | void sort_heap(ItemType a[], int l, int r){
36 | //构建初始堆
37 | int k, n;
38 | n = r - l + 1;
39 | for (k = n / 2; k >= 1; k--) {
40 | sink(a, n, k, cmp);
41 | }
42 | //依次将堆首的最大元素放到数组末尾,并将堆的大小缩短,直到堆被缩短完成
43 | for (k = n-1; k>1; ) {
44 | exch(a[1], a[k]);
45 | k--;
46 | sink(a, k, 1, cmp);
47 | }
48 | }
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/array/leetcode/easy/plusOne.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // plusOne.h
3 | // array
4 | //
5 | // Created by junlongj on 2019/7/28.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef plusOne_hpp
10 | #define plusOne_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | #include
14 |
15 | /*
16 | 66.给定一个由整数组成的非空数组所表示的非负整数,在该数的基础上加一。
17 |
18 | 最高位数字存放在数组的首位, 数组中每个元素只存储一个数字。
19 |
20 | 你可以假设除了整数 0 之外,这个整数不会以零开头。
21 |
22 | 示例 1:
23 |
24 | 输入: [1,2,3]
25 | 输出: [1,2,4]
26 | 解释: 输入数组表示数字 123。
27 | 示例 2:
28 |
29 | 输入: [4,3,2,1]
30 | 输出: [4,3,2,2]
31 | 解释: 输入数组表示数字 4321。
32 |
33 | 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
34 | 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/plus-one
35 | 著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
36 |
37 |
38 | */
39 |
40 | std::vector plusOne(std::vector& digits) {
41 | std::vector r;
42 | if (digits.empty()){
43 | return r;
44 | }
45 | int i=digits.size()-1;
46 | int carry = 1;
47 | while (i>=0) {
48 | int t = digits[i] + carry;
49 | carry = t/10;
50 | t = t % 10;
51 | r.insert(r.begin(), t);
52 | i--;
53 | }
54 | if (carry > 0) {
55 | r.insert(r.begin(), carry);
56 | }
57 | return r;
58 | }
59 | #endif /* plusOne_hpp */
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/linkedList/leetcode/reverseList.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // reverseList.h
3 | // linkedList
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2019/7/17.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef reverseList_hpp
10 | #define reverseList_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | #include "singlyLinkedList.h"
14 |
15 | namespace leetcode {
16 | /*
17 | 206.反转一个单链表。
18 |
19 | 示例:
20 |
21 | 输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
22 | 输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
23 | */
24 | ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
25 | ListNode *pre,*ct,*next;
26 | if (!head->next) {
27 | return head;
28 | }
29 |
30 |
31 | ct = head;
32 | pre = nullptr;
33 | while (ct) {
34 | next = ct->next;
35 | ct->next = pre;
36 | pre = ct;
37 | ct = next;
38 | }
39 | return pre;
40 |
41 | }
42 |
43 | void test_reverseList(){
44 | singlyLinkedList ll;
45 | ll.insertTail(3);
46 | ll.insertTail(2);
47 | ll.insertTail(0);
48 | ll.insertTail(-4);
49 | reverseList(ll.start())->print();
50 | }
51 | }
52 |
53 |
54 |
55 | #endif /* reverseList_hpp */
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sort/kthSmallest.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // kthSmallest.h
3 | // sort
4 | //
5 | // Created by junlongj on 2019/7/19.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef kthSmallest_h
10 | #define kthSmallest_h
11 |
12 | /*
13 | 如何在o(n)内查找一个无序数组中的第K大元素.
14 |
15 |
16 | 利用快排分区的思想,将数组一分为3,然后根据pivot和kth的位置关系,继续寻找,最终定位到kth.
17 |
18 | */
19 |
20 | int _partition(int nums[], int start, int end){
21 | int i=start;
22 | int j=start;
23 | for (; j
13 | #include
14 | /*
15 | 119. 杨辉三角 II
16 | 给定一个非负索引 k,其中 k ≤ 33,返回杨辉三角的第 k 行。
17 | https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/pascals-triangle-ii/
18 |
19 | 你可以优化你的算法到 O(k) 空间复杂度吗?
20 | */
21 |
22 | namespace leetcode {
23 | /*
24 | 思路:通过上一行内容推算出下行的内容,比如:
25 | 1,1
26 | 1 , 2 + 1
27 |
28 | 1,2,1 如果j指向这一行的话
29 | 1, 3 3 +1 结果:result[j]=result[j]+result[j-1];
30 | */
31 | std::vector getRow(int rowIndex) {
32 | if (rowIndex<0) return {};
33 | std::vector result;
34 | for (int i=0;i<=rowIndex;i++){
35 | if (i==0) {
36 | result.push_back(1);
37 | }else{
38 | for(int j=i-1;j-1>=0;j--){
39 | result[j]=result[j]+result[j-1];
40 | }
41 | result.push_back(1);
42 | }
43 | }
44 | return result;
45 | }
46 | }
47 |
48 | #endif /* pascals_triangle_ii_hpp */
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sort/merge.c:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // merge.c
3 | // sort
4 | //
5 | // Created by junl on 2020/12/1.
6 | // Copyright © 2020 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #include "sort.h"
10 | void _merge(ItemType a[], ItemType aux[], int l, int mid, int r);
11 | void _sort_merge(ItemType a[], ItemType aux[], int l, int r);
12 | void sort_merge(ItemType a[], int l, int r){
13 | int sz = r - l + 1;
14 | //利用辅助数组,避免频繁创建数组带来的消耗
15 | ItemType aux[sz];
16 | _sort_merge(a, aux, l, r);
17 | }
18 | void _sort_merge(ItemType a[], ItemType aux[], int l, int r){
19 | if (l >= r) return;
20 | int mid = l + (r - l)/2;
21 | //先将左右两半分别排序,然后将结果合并起来
22 | _sort_merge(a, aux, l, mid);
23 | _sort_merge(a, aux, mid+1, r);
24 | _merge(a, aux, l, mid, r);
25 | }
26 | void _merge(ItemType a[], ItemType aux[], int l, int mid, int r){
27 | int i = l, j = mid+1, k;
28 | for (k=l; k<=r; k++) {
29 | aux[k] = a[k];
30 | }
31 | //原地排序
32 | for (k=l; k<=r; k++) {
33 | if (i > mid) {
34 | a[k] = aux[j++];
35 | }else if (j > r){
36 | a[k] = aux[i++];
37 | }else if (less(aux[i], aux[j])) {
38 | a[k] = aux[i++];
39 | }else{
40 | a[k] = aux[j++];
41 | }
42 | }
43 | }
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/array/coding-interviews/FindNumsAppearOnce.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //
2 | // FindNumsAppearOnce.h
3 | // array
4 | //
5 | // Created by junlongj on 2019/8/3.
6 | // Copyright © 2019 junl. All rights reserved.
7 | //
8 |
9 | #ifndef FindNumsAppearOnce_hpp
10 | #define FindNumsAppearOnce_hpp
11 |
12 | #include
13 | #include
14 | #include