├── .gitignore
├── CITATION.cff
├── HideQuiz.ipynb
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── examples
├── mc-example.gif
├── num-example.gif
└── questions.json
├── jupyterquiz
├── __init__.py
├── dynamic
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── capture.py
│ ├── display.py
│ ├── loader.py
│ └── renderer.py
├── js
│ ├── async_suffix.js.tpl
│ ├── helpers.js
│ ├── multiple_choice.js
│ ├── numeric.js
│ ├── show_questions.js
│ ├── static_suffix.js.tpl
│ └── string.js
└── styles.css
├── mve.ipynb
├── preserve-responses.ipynb
├── previews
├── github-preview.png
└── github-preview.psd
├── pyproject.toml
├── schema
├── README
├── mc_schema.json
├── mc_schema.png
├── mc_schema.svg
├── num_schema.json
├── num_schema.png
├── schema.ipynb
├── string_schema.json
└── string_schema.png
└── test.ipynb
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
2 | __pycache__/
3 | *.py[cod]
4 | *$py.class
5 |
6 | # C extensions
7 | *.so
8 |
9 | # Distribution / packaging
10 | .Python
11 | build/
12 | develop-eggs/
13 | dist/
14 | downloads/
15 | eggs/
16 | .eggs/
17 | lib/
18 | lib64/
19 | parts/
20 | sdist/
21 | var/
22 | wheels/
23 | pip-wheel-metadata/
24 | share/python-wheels/
25 | *.egg-info/
26 | .installed.cfg
27 | *.egg
28 | MANIFEST
29 |
30 | # PyInstaller
31 | # Usually these files are written by a python script from a template
32 | # before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it.
33 | *.manifest
34 | *.spec
35 |
36 | # Installer logs
37 | pip-log.txt
38 | pip-delete-this-directory.txt
39 |
40 | # Unit test / coverage reports
41 | htmlcov/
42 | .tox/
43 | .nox/
44 | .coverage
45 | .coverage.*
46 | .cache
47 | nosetests.xml
48 | coverage.xml
49 | *.cover
50 | *.py,cover
51 | .hypothesis/
52 | .pytest_cache/
53 |
54 | # Translations
55 | *.mo
56 | *.pot
57 |
58 | # Django stuff:
59 | *.log
60 | local_settings.py
61 | db.sqlite3
62 | db.sqlite3-journal
63 |
64 | # Flask stuff:
65 | instance/
66 | .webassets-cache
67 |
68 | # Scrapy stuff:
69 | .scrapy
70 |
71 | # Sphinx documentation
72 | docs/_build/
73 |
74 | # PyBuilder
75 | target/
76 |
77 | # Jupyter Notebook
78 | .ipynb_checkpoints
79 |
80 | # IPython
81 | profile_default/
82 | ipython_config.py
83 |
84 | # pyenv
85 | .python-version
86 |
87 | # pipenv
88 | # According to pypa/pipenv#598, it is recommended to include Pipfile.lock in version control.
89 | # However, in case of collaboration, if having platform-specific dependencies or dependencies
90 | # having no cross-platform support, pipenv may install dependencies that don't work, or not
91 | # install all needed dependencies.
92 | #Pipfile.lock
93 |
94 | # PEP 582; used by e.g. github.com/David-OConnor/pyflow
95 | __pypackages__/
96 |
97 | # Celery stuff
98 | celerybeat-schedule
99 | celerybeat.pid
100 |
101 | # SageMath parsed files
102 | *.sage.py
103 |
104 | # Environments
105 | .env
106 | .venv
107 | env/
108 | venv/
109 | ENV/
110 | env.bak/
111 | venv.bak/
112 |
113 | # Spyder project settings
114 | .spyderproject
115 | .spyproject
116 |
117 | # Rope project settings
118 | .ropeproject
119 |
120 | # mkdocs documentation
121 | /site
122 |
123 | # mypy
124 | .mypy_cache/
125 | .dmypy.json
126 | dmypy.json
127 |
128 | # Pyre type checker
129 | .pyre/
130 |
131 | .DS_Store
132 |
133 | .vscode/
134 |
135 | .#*
136 |
137 | .virtual_documents/
138 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/CITATION.cff:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | cff-version: 1.1.0
2 | message: If you use this software, please cite it as below.
3 | authors:
4 | - family-names: Shea
5 | given-names: John
6 | title: JupyterQuiz
7 | version: 2.9.3
8 | date-released: 2025-04-26
9 |
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2021-2025 John M. Shea
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # JupyterQuiz
2 | *JupyterQuiz* is a tool for displaying **interactive self-assessment quizzes in Jupyter notebooks and Jupyter Book**. JupyterQuiz was created to enable interactive quizzes for readers of my book [*Foundations of Data Science with Python*](https://t.co/ES9zBUMSQF) [Affiliate Link]
3 |
4 | **Important Note for JupyterLab 4 Users:** *TLDR*: Make sure you are using Jupyter Quiz version 2.8.0 or later.
5 |
6 | There have been two significant changes to Jupyter Lab recently:
7 |
8 | 1) Changes to the math rendering system in JupyterLab 4 have broken the LaTeX
9 | rendering in JupyterQuiz. There is not currently a simple solution, but I have
10 | opened an issue requesting that the necessary methods be made available. Math
11 | should still work in Jupyter Book. A very hacky solution for Jupyter Lab has now
12 | been moved to the main branch staring with 2.8.0. This loads MathJax 3 on top of
13 | the JupyterLab MathJax version. Although this is not the ideal solution, the upstream
14 | problem has not been fixed after many months, and so I felt I had to take this step.
15 | If it breaks anything for you, please let me know.
16 |
17 | 2) Starting with Jupyter 4.2.5, when Markdown cells are rendered, the id tags
18 | will be stripped from any HTML elements. These id tags were needed by
19 | JupyterQuiz users who use hidden spans to embed quizzes in Jupyter notebooks.
20 | This probably affects a small number of JupyterQuiz users. If you are affected,
21 | update to JupyterQuiz 2.8.0 or later and change your `id` tags to `class`, and
22 | everything should work again.
23 |
24 | **Change to precision parameter:** Starting with 2.7.0a3 and 2.8.0, I changed
25 | how the precision parameter effects numerical answers. Prior to these versions,
26 | precision specified a decimal place; from these versions on, it specifies a number of
27 | significant digits. )
28 |
29 | *JupyterQuiz* is part of my effort to make **open source tools for developing
30 | modern, interactive textbooks**.
31 | * The other part of this effort is my interactive flashcards tool,
32 | [JupyterCards](https://github.com/jmshea/jupytercards).
33 | * You can see both tools in action in the online resources for my textbook [Foundations of Data Science with Python](https://www.fdsp.net).
34 |
35 | If you would like to see a video that introduces these tools and discusses *why* I made them, check out my [JupyterCon 2023 talk on Tools for Interactive Education Experiences in Jupyter Notebooks and Jupyter Books](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MDMUiQ2_ZWE).
36 |
37 | These animated GIFs illustrate two of the basic question types in *JupyterQuiz* (a third String type of question was added in April 2025, and I have not created an animated GIF for it yet):
38 |
39 | **Many Choice Question**
40 |
41 | 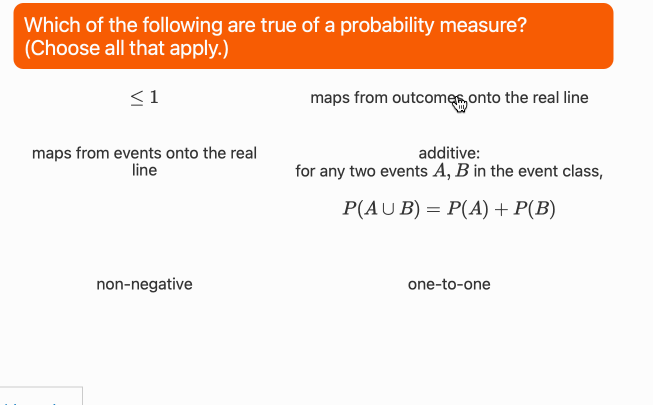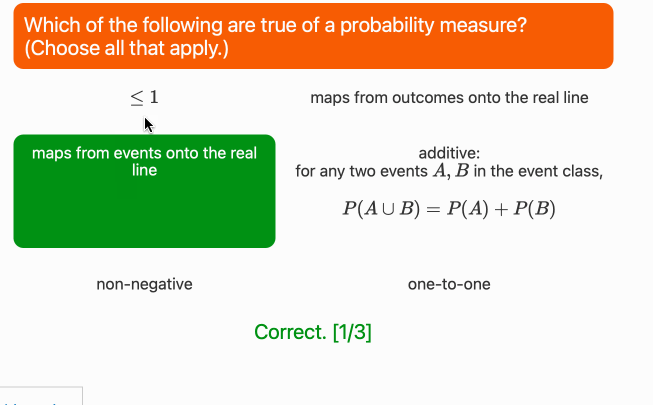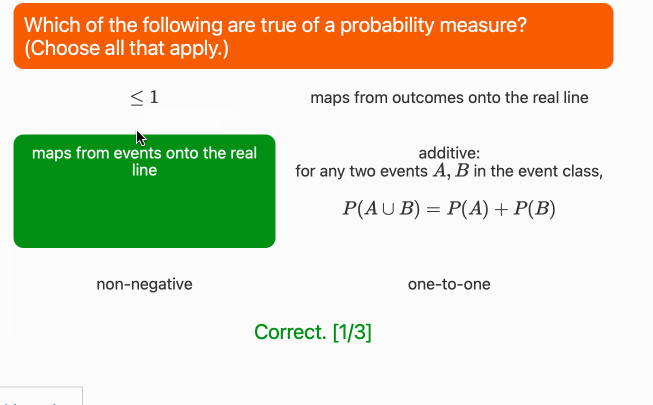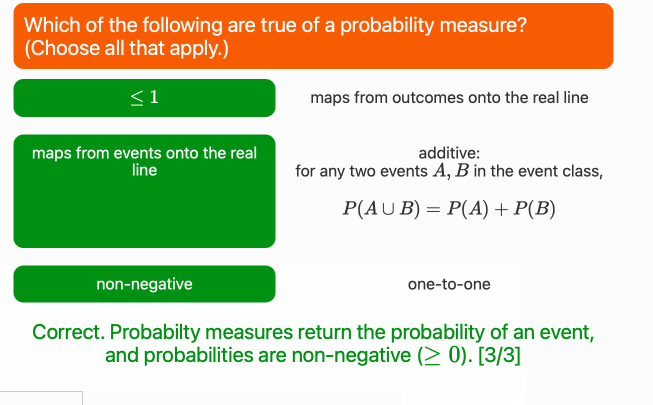
42 |
43 | ---
44 |
45 | **Numerical Answer Question**
46 |
47 | 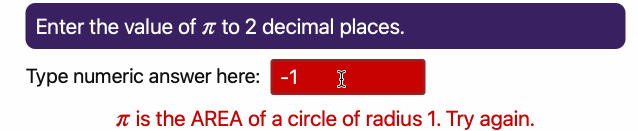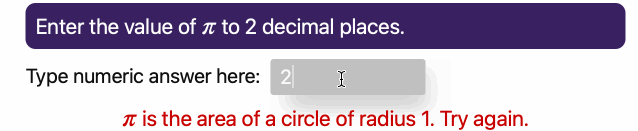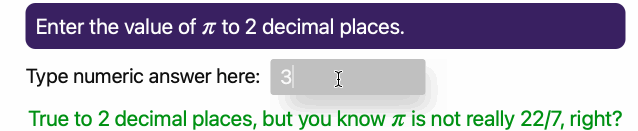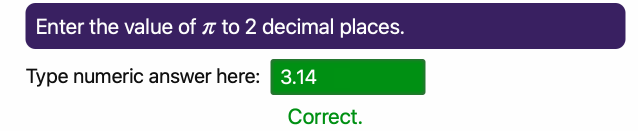
48 |
49 | ---
50 |
51 | **Examples using JupyterQuiz**
52 |
53 | This library was built to create interactive questions for the [*Foundations of Data Science with Python*](https://www.amazon.com/Foundations-Data-Science-Python-Chapman/dp/1032350423) book by John M. Shea. Example: [Chapter 3 Self-Assessment Questions](https://www.fdsp.net/03-first-data/summary.html#terminology-review)
54 |
55 | Some other examples I have seen around the web include:
56 | * *Introduction to Python for Humanists* book by W.J.B. Mattingly. Example: [Section 2.2 Introduction to Data Structures, ](https://python-textbook.pythonhumanities.com/01_intro/01_02-03_data_structures.html)
57 | * *Groundwater I* by P. K. Yadav, T. Reimann, and others. Example: [Lecture 1: Course Introduction/Water Cycle of ](https://vibhubatheja.github.io/GW-Book/content/background/03_basic_hydrogeology.html)
58 | * *Sizing and optimization of mechatronic systems* course by Marc Budinger, Scott Delbecq and Félix Pollet. Example: [Lecture 1 Quiz](https://sizinglab.github.io/sizing_course/class/Lecture1/4-quizz.html)
59 | * *Linux en Bioinformatique* by Thomas Denecker & Claire Toffano-Nioche. Example: [Quizz 1](https://ifb-elixirfr.github.io/LinuxEBAII/quizz_01.html)
60 | * *Programmering i Kjemi (Programming in Chemistry?)* by Andreas Haraldsrud. Example: [Quiz 1: Variabler og aritmetikk](https://andreasdh.github.io/programmering-i-kjemi/docs/grunnleggende_programmering/quiz1.html)
61 | * *AnIML: Another Introduction to Machine Learning* by Hunter Schafer. Example: [Chapter 2: Assessing Performance](https://animlbook.com/regression/assessing_performance/index.html)
62 |
63 | If you using JupyterQuiz in a Jupyter Book or other way that is useable on the web, please clone this repository, add your information to the bulleted list in the README.md, and make a pull request for me to include a link to your use of this library.
64 |
65 | The notebook [test.ipynb](test.ipynb) shows more features but must be run on your own local Jupyter or in nbviewer -- GitHub only renders the static HTML that does not include the interactive quizzes. (If viewing on GitHub, there should be a little circle with a minus sign at the top of the file that offers you the ability to launch the notebook in nbviewer.)
66 |
67 | It currently supports two types of quiz questions:
68 | 1. **Multiple/ Many Choice Questions:** Users are given a predefined set of choices and click on answer(s) they believe are correct.
69 | 2. **Numerical:** Users are given a text box in which they can submit answers in decimal or fraction form.
70 |
71 | Each type of question offers different ways to provide feedback to help users understand what they did wrong (or right).
72 |
73 | Quesitons can be loaded from:
74 | * a Python list of dicts,
75 | * a JSON local file,
76 | * via a URL to a JSON file.
77 |
78 | **New as of version 1.6 (9/26/2021): You can now embed the question source (most importantly, the answers) in Jupyter Notebook so that they will not be directly visibile to users!**
79 |
80 | Question source data can be stored in any Markdown cell in a hidden HTML element (such as a span with the display style set to "none"). Questions can be stored as either JSON or base64-encoded JSON (to make them non-human readable). Please see the notebook [HideQuiz.ipynb](HideQuiz.ipynb) for examples of how to use this.
81 |
82 | ## Quiz options
83 |
84 | JupyterQuiz supports a few options:
85 | * num = Number of questions to present. If this option is chosen, the set of questions will be selected at random.
86 | * shuffle_questions = boolean, whether to shuffle order of questions (default False)
87 | * shuffle_answers = boolean, whether to shuffle answers for multiple-choice questions (default True)
88 | * preserve_responses = boolean, whether to output the user responses in a way that is preserved upon reload of the notebook (default False) -- see below
89 |
90 | ### Quiz Formatting
91 | In addtion, it supports additional options for controlling the formatting of the quiz options.
92 |
93 | * `border_radius` = boolean, border radius of question boxes
94 | * `question_alignment` = string, alignment of question text (e.g., "left", "right)
95 | * `max_width` = int, max width of question boxes
96 |
97 | For more fine-grained formatting control of the question text, leaving the
98 | question field the empty string (`""`) will result in only the answers being
99 | displayed. This allows for custom question formatting such as including images,
100 | tables, more complex code examples, etc. Note that this feature works better for
101 | a single question quiz and may not work as well with shuffled quizzes or quiz
102 | questions selected at random.
103 |
104 | Colors can be changed by passing the `colors` keyword argument. Pass in a dictionary of colors that you would like to change. Here is the default dictionary for reference:
105 |
106 | ```{Python}
107 | color_dict = {
108 | '--jq-multiple-choice-bg': '#6f78ffff', # Background for the question part of multiple-choice questions
109 | '--jq-mc-button-bg': '#fafafa', # Background for the buttons when not pressed
110 | '--jq-mc-button-border': '#e0e0e0e0', # Border of the buttons
111 | '--jq-mc-button-inset-shadow': '#555555', # Color of inset shadow for pressed buttons
112 | '--jq-many-choice-bg': '#f75c03ff', # Background for question part of many-choice questions
113 | '--jq-numeric-bg': '#392061ff', # Background for question part of numeric questions
114 | '--jq-numeric-input-bg': '#c0c0c0', # Background for input area of numeric questions
115 | '--jq-numeric-input-label': '#101010', # Color for input of numeric questions
116 | '--jq-numeric-input-shadow': '#999999', # Color for shadow of input area of numeric questions when selected
117 | '--jq-incorrect-color': '#c80202', # Color for incorrect answers
118 | '--jq-correct-color': '#009113', # Color for correct answers
119 | '--jq-text-color': '#fafafa' # Color for question text
120 | }
121 | ```
122 |
123 | There is one included alternative set of colors to the default colors, which be selected by passing `colors='fdsp'`.
124 |
125 | ## Preserving student responses
126 |
127 | **New as of version 2.0 (7/26/2022): There is now code to enable preserving student responses (for instance, for checking/grading their quizzes). If you want to use this functionality, please read this carefully!**
128 |
129 | To enable this behavior, set `preserve_responses=True` in `display_quiz()`
130 |
131 | This option produces a text ouptut that consists of a question number (based on the question order) along with the chosen answer. Instructions are given at the end of the quiz on how to copy the text output and paste it into a pre-prepared Markdown cell. See [preserve-responses.ipynb](preserve-responses.ipynb) for an example.
132 |
133 | *The requirement that the student copy and paste the text output to preserve it is because of limitations in the exchange of information from the JavaScript side to the Python side. As far as I know, the only way around this requires a plug-in, and I do not want to require that. I will continue to investigate solutions to this in the future.*
134 |
135 | This option is not compatible with `shuffle_questions = True` or setting `num` because these result in the order of the questions being random, which makes no sense when reporting answers vs question number.
136 |
137 | ## Tool for making Multiple/Many Choice Questions
138 |
139 | Dr. WJB Mattingly (@wjbmattingly) has made a [Streamlit App for creating JupyterQuiz question files](https://github.com/wjbmattingly/quiz-generator) in an interactive way without having to edit a JSON file.
140 | It currently supports multiple/many choice questions.
141 |
142 |
143 | ## Installation
144 |
145 | *JupyterQuiz* is available via pip:
146 |
147 | ``` pip install jupyterquiz```
148 |
149 | ## Multiple/Many Choice Questions
150 |
151 | Multiple/Many Choice questions are defined by a Question, an optional Code block, and a list of possible Answers. Answers include a text component and/or a code block, details on whether the Answer is correct, and Feedback to be displayed for that Answer. The schema for Multiple/Many Choice Questions is shown below:
152 | 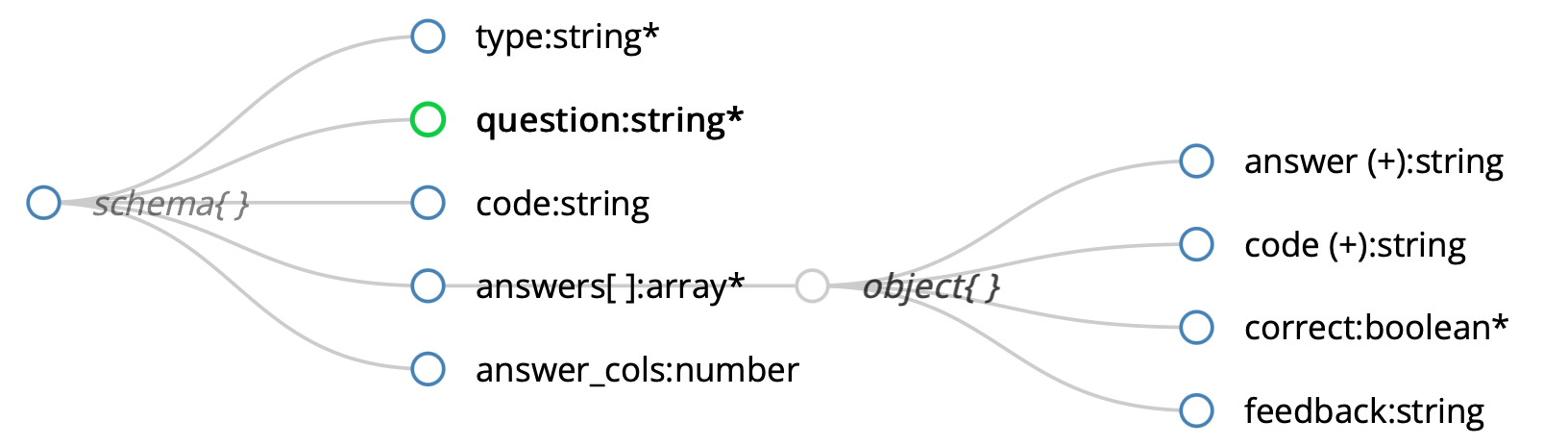
153 |
154 | \* = Required parameter, (+) = At least one of these parameters is required
155 |
156 |
157 |
158 | Example JSON for a many-choice question is below:
159 | ```json
160 | {
161 | "question": "Choose all of the following that can be included in Jupyter notebooks?",
162 | "type": "many_choice",
163 | "answers": [
164 | {
165 | "answer": "Text and graphics output from Python",
166 | "correct": true,
167 | "feedback": "Correct."
168 | },
169 | {
170 | "answer": "Typeset mathematics",
171 | "correct": true,
172 | "feedback": "Correct."
173 | },
174 | {
175 | "answer": "Python executable code",
176 | "correct": true,
177 | "feedback": "Correct."
178 | },
179 | {
180 | "answer": "Formatted text",
181 | "correct": true,
182 | "feedback": "Correct."
183 | },
184 | {
185 | "answer": "Live snakes via Python",
186 | "correct": false,
187 | "feedback": "I hope not."
188 | }
189 | ]
190 | }
191 | ```
192 |
193 | ## Numerical Questions
194 |
195 | Numerical questions consist of a Question, an optional Precision, and one or more Answers. Each Answer can be a Value, a Range, or the Default, and each of these can include Feedback text. Values and Ranges can be marked as correct or incorrect. Ranges are in the form [A,B), where endpoint A is included in the range and endpoint B is not included in the range. When Precision is specified, numerical inputs are rounded to the specified precision before comparing to the Answers. The schema for Numerical questions is shown below:
196 |
197 | 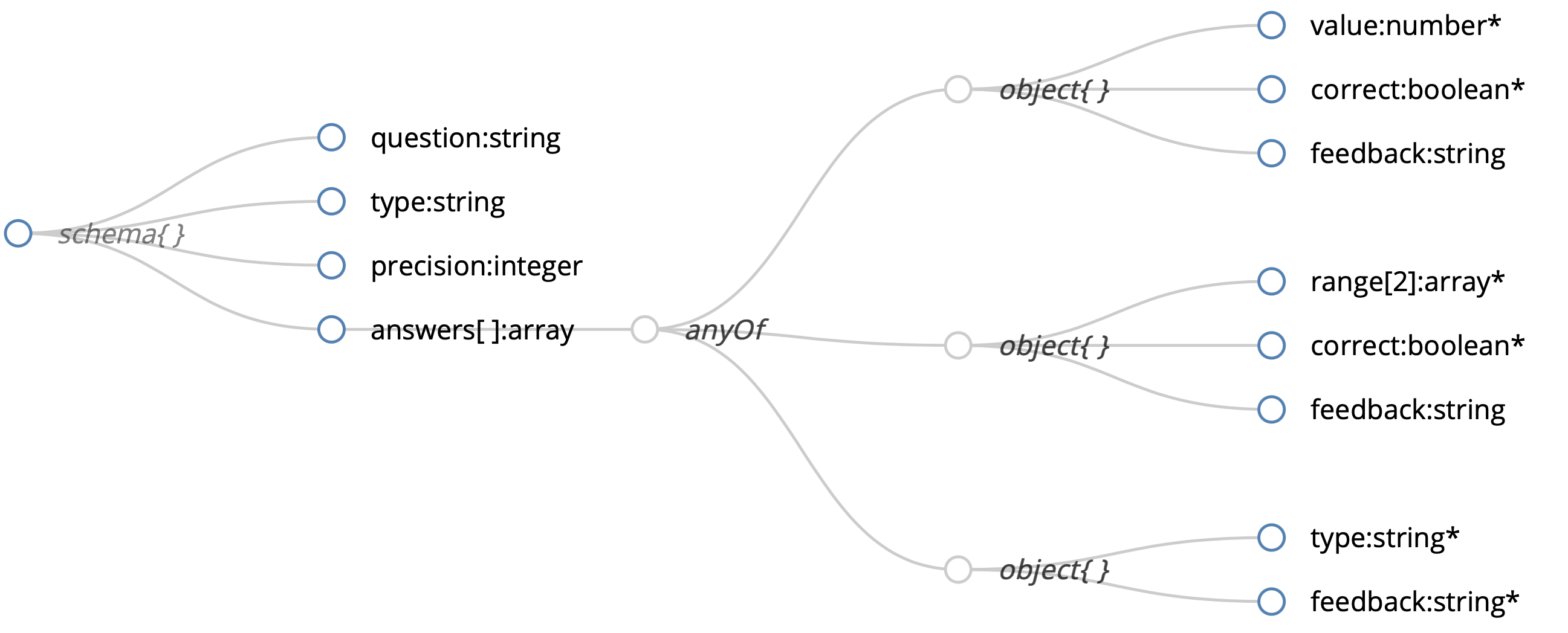
198 |
199 | \* = Required parameter
200 |
201 | Example JSON for a numerical question is below:
202 | ```json
203 | {
204 | "question": "Enter the value of pi (will be checked to 2 decimal places):",
205 | "type": "numeric",
206 | "precision": 2,
207 | "answers": [
208 | {
209 | "type": "value",
210 | "value": 3.14,
211 | "correct": true,
212 | "feedback": "Correct."
213 | },
214 | {
215 | "type": "range",
216 | "range": [ 3.142857, 3.142858],
217 | "correct": true,
218 | "feedback": "True to 2 decimal places, but you know pi is not really 22/7, right?"
219 | },
220 | {
221 | "type": "range",
222 | "range": [ -100000000, 0],
223 | "correct": false,
224 | "feedback": "pi is the AREA of a circle of radius 1. Try again."
225 | },
226 | {
227 | "type": "default",
228 | "feedback": "pi is the area of a circle of radius 1. Try again."
229 | }
230 | ]
231 | }
232 | ```
233 |
234 | ## String Questions
235 |
236 | String questions are specified by setting the "type" property to "string". These questions offer a single question prompt that is specified by the "question" property, but may have multiple possible answers specified by the Answers array. Each Answer in the Answers array is an object that consists of an "answer" (string), a Boolean called "correct", and several optional properties. By default answers case is ignored in comparing submissions to the Answers; however, this can be changed using the boolean "match_case" property. Each answer can have a string "feedback" that is displayed when this answer is matched. Fuzzy matching can be used by specifying a value for the "fuzzy_threshold" property, which should take values between 0 and 1. Fuzzy matching calculates the Levenshtein distance, dividing that by the string length, and then subtracting the result from 1. The resulting value is 1 when the strings match exactly and decreases when the strings are more different.
237 |
238 | You can optionally include a default answer pattern by specifying an object with a "type" property set to "default" and a "feedback" string. If no other answer patterns match the user's submission, the question will be marked incorrect and the provided feedback will be displayed.
239 |
240 | You can also specify an `input_width` property (integer, approximate number of characters) on the question to control the width of the text input field (in em units) in the rendered quiz.
241 |
242 | The schema for String Questions is shown below:
243 |
244 | 
245 |
246 | Example JSON for a string question is below:
247 | ```json
248 | {
249 | "question": "Who was the 35th president (1961-63) of the US?",
250 | "type": "string",
251 | "answers": [
252 | {
253 | "answer": "John F. Kennedy",
254 | "correct": true,
255 | "feedback": "Correct. John F. Kennedy was the 35th president of the U.S.",
256 | "match_case": false,
257 | "fuzzy_threshold": 0.80
258 | },
259 | {
260 | "answer": "JFK",
261 | "correct": true,
262 | "feedback": "Correct. John F. Kennedy was the 35th president of the U.S."
263 | },
264 | {
265 | "answer": "Kennedy",
266 | "correct": false,
267 | "feedback": "Please also provide the first name.",
268 | "match_case": false
269 | }
270 | ]
271 | }
272 | ```
273 |
274 | ## Working with JupyterLite
275 |
276 | This should work with JupyterLite as of version 2.1.2. Here is an example that should work on JupyterLite:
277 |
278 |
279 | ```
280 | import micropip
281 | await micropip.install('jupyterquiz')
282 |
283 | from jupyterquiz import display_quiz
284 | git_url='https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jmshea/Foundations-of-Data-Science-with-Python/main/questions/'
285 |
286 | display_quiz(git_url+'ch1.json')
287 | ```
288 |
289 |
290 | **As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.**
291 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/mc-example.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jmshea/jupyterquiz/a9d18e2eba2e0d76a2ff5782138f105e7b71638d/examples/mc-example.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/num-example.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jmshea/jupyterquiz/a9d18e2eba2e0d76a2ff5782138f105e7b71638d/examples/num-example.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/questions.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [
2 | {
3 | "question": "Choose all of the following that can be included in Jupyter notebooks?",
4 | "type": "many_choice",
5 | "answers": [
6 | {
7 | "answer": "Text and graphics output from Python",
8 | "correct": true,
9 | "feedback": "Correct."
10 | },
11 | {
12 | "answer": "Typeset mathematics",
13 | "correct": true,
14 | "feedback": "Correct."
15 | },
16 | {
17 | "answer": "Python executable code",
18 | "correct": true,
19 | "feedback": "Correct."
20 | },
21 | {
22 | "answer": "Formatted text",
23 | "correct": true,
24 | "feedback": "Correct."
25 | },
26 | {
27 | "answer": "Live snakes via Python",
28 | "correct": false,
29 | "feedback": "I hope not."
30 | }
31 | ]
32 | },
33 | {
34 | "question": "Testing parameter to change number of colums for answers: Choose all of the following that can be included in Jupyter notebooks?",
35 | "type": "many_choice",
36 | "answer_cols": 4,
37 | "answers": [
38 | {
39 | "answer": "Text and graphics output from Python",
40 | "correct": true,
41 | "feedback": "Correct."
42 | },
43 | {
44 | "answer": "Typeset mathematics",
45 | "correct": true,
46 | "feedback": "Correct."
47 | },
48 | {
49 | "answer": "Python executable code",
50 | "correct": true,
51 | "feedback": "Correct."
52 | },
53 | {
54 | "answer": "Formatted text",
55 | "correct": true,
56 | "feedback": "Correct."
57 | },
58 | {
59 | "answer": "Live snakes via Python",
60 | "correct": false,
61 | "feedback": "I hope not."
62 | }
63 | ]
64 | },
65 | {
66 | "question": "Which of these are used to create formatted text in Jupyter notebooks?",
67 | "type": "multiple_choice",
68 | "answers": [
69 | {
70 | "answer": "Wiki markup",
71 | "correct": false,
72 | "feedback": "False."
73 | },
74 | {
75 | "answer": "SVG",
76 | "correct": false,
77 | "feedback": "False."
78 | },
79 | {
80 | "answer": "Markdown",
81 | "correct": true,
82 | "feedback": "Correct."
83 | },
84 | {
85 | "answer": "Rich Text",
86 | "correct": false,
87 | "feedback": "False."
88 | }
89 | ]
90 | },
91 | {
92 | "question": "Enter the value of $\\pi$ to 2 decimal places.",
93 | "type": "numeric",
94 | "answers": [
95 | {
96 | "type": "value",
97 | "value": 3.14,
98 | "correct": true,
99 | "feedback": "Correct."
100 | },
101 | {
102 | "type": "range",
103 | "range": [
104 | 3.142857,
105 | 3.142858
106 | ],
107 | "correct": true,
108 | "feedback": "True to 2 decimal places, but you know $\\pi$ is not really 22/7, right?"
109 | },
110 | {
111 | "type": "range",
112 | "range": [
113 | -100000000,
114 | 0
115 | ],
116 | "correct": false,
117 | "feedback": "$\\pi$ is the AREA of a circle of radius 1. Try again."
118 | },
119 | {
120 | "type": "default",
121 | "feedback": "$\\pi$ is the area of a circle of radius 1. Try again."
122 | }
123 | ]
124 | },
125 | {
126 | "question": "Enter the value of $\\pi$ to 2 decimal places.",
127 | "type": "numeric",
128 | "precision": 3,
129 | "answers": [
130 | {
131 | "type": "value",
132 | "value": 3.14,
133 | "correct": true,
134 | "feedback": "Correct."
135 | },
136 | {
137 | "type": "range",
138 | "range": [
139 | 3.142857,
140 | 3.142858
141 | ],
142 | "correct": true,
143 | "feedback": "True to 2 decimal places, but you know $\\pi$ is not really 22/7, right?"
144 | },
145 | {
146 | "type": "range",
147 | "range": [
148 | -100000000,
149 | 0
150 | ],
151 | "correct": false,
152 | "feedback": "$\\pi$ is the AREA of a circle of radius 1. Try again."
153 | },
154 | {
155 | "type": "default",
156 | "feedback": "$\\pi$ is the area of a circle of radius 1. Try again."
157 | }
158 | ]
159 | },
160 | {
161 | "question": "Determine the output of the following Python code:",
162 | "code": "a=\"1\"\nb=\"2\"\nprint(a+b)",
163 | "type": "multiple_choice",
164 | "answers": [
165 | {
166 | "answer": "1",
167 | "correct": false,
168 | "feedback": "No. When strings are operated on by +, they are concatenated."
169 | },
170 | {
171 | "answer": "2",
172 | "correct": false,
173 | "feedback": "No. When strings are operated on by +, they are concatenated."
174 | },
175 | {
176 | "answer": "3",
177 | "correct": false,
178 | "feedback": "No. When strings are operated on by +, they are concatenated."
179 | },
180 | {
181 | "answer": "12",
182 | "correct": true,
183 | "feedback": "Yes. The + operator will concatenate the strings \"1\" and \"2\"."
184 | },
185 | {
186 | "answer": "error",
187 | "correct": false,
188 | "feedback": "No. The + operator for strings performs string concatenation."
189 | }
190 | ]
191 | },
192 | {
193 | "question": "The variable mylist is a Python list. Choose which code snippet will append the item 3 to mylist.",
194 | "type": "multiple_choice",
195 | "answers": [
196 | {
197 | "code": "mylist+=3",
198 | "correct": false
199 | },
200 | {
201 | "code": "mylist+=[3]",
202 | "correct": true
203 | },
204 | {
205 | "code": "mylist+={3}",
206 | "correct": false
207 | }
208 | ]
209 | },
210 | {
211 | "question": "Which of these is the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter?",
212 | "type": "multiple_choice",
213 | "answers": [
214 | {
215 | "answer": "$\\pi$",
216 | "correct": true,
217 | "feedback": "Correct."
218 | },
219 | {
220 | "answer": "$\\frac{22}{7}$",
221 | "correct": false,
222 | "feedback": "$\\frac{22}{7}$ is only an approximation to the true value."
223 | },
224 | {
225 | "answer": "3",
226 | "correct": false,
227 | "feedback": "This is a crude approximation to the true value."
228 | },
229 | {
230 | "answer": "$\\tau$",
231 | "correct": false,
232 | "feedback": "True for the ratio of the circle's circumference to its radius, not diameter."
233 | }
234 | ]
235 | }
236 | ]
237 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/jupyterquiz/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | '''Module to display dynamic quizzes in Jupyter notebooks and Jupyter Books. Uses JavaScript to provide
2 | interactivity across these different formats and to dynamically update questions from a given URL and
3 | randomly select questions from a pool (if desired) when the cell is rerun (Jupyter notebook) or
4 | page is reloaded Jupyter Book (HTML format).
5 |
6 | Currently supports two question types: Multiple/Many Choice and Numeric
7 |
8 | Created by John M. Shea, copyright 2021-2024
9 | for the book Foundations of Data Science with Python: https://fdsp.net
10 |
11 | All files in the package are distributed under the MIT License
12 | '''
13 |
14 | __version__ = '2.9.6.2'
15 | from .dynamic import display_quiz, capture_responses
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/jupyterquiz/dynamic/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | dynamic subpackage splitting responsibilities of dynamic.py.
3 | """
4 | from .display import display_quiz
5 | from .capture import capture_responses
6 |
7 | __all__ = ["display_quiz", "capture_responses"]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/jupyterquiz/dynamic/capture.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Module for capturing user responses to quizzes.
3 | """
4 | import string
5 | import random
6 | from IPython.display import display, Javascript, HTML
7 |
8 | def capture_responses(prev_div_id):
9 | """
10 | Attempt to capture and display responses from a previous quiz container.
11 | """
12 | letters = string.ascii_letters
13 | div_id = ''.join(random.choice(letters) for _ in range(12))
14 |
15 | mydiv = f''
16 | javascript = f"""
17 | {{
18 | var prev = {prev_div_id};
19 | var container = document.getElementById("{div_id}");
20 | var responses = prev.querySelector('.JCResponses');
21 | if (responses) {{
22 | var respStr = responses.dataset.responses;
23 | container.setAttribute('data-responses', respStr);
24 | var iDiv = document.createElement('div');
25 | iDiv.id = 'responses' + '{div_id}';
26 | iDiv.innerText = respStr;
27 | container.appendChild(iDiv);
28 | }} else {{
29 | container.innerText = 'No Responses Found';
30 | }}
31 | }}
32 | """
33 | display(HTML(mydiv))
34 | display(Javascript(javascript))
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/jupyterquiz/dynamic/display.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Entry point for displaying quizzes in Jupyter environments.
3 | """
4 | import string
5 | import random
6 | from IPython.display import display, Javascript, HTML
7 |
8 | from .loader import load_questions_script
9 | from .renderer import render_div, build_styles, build_script
10 |
11 | def display_quiz(ref, num=1_000_000, shuffle_questions=False,
12 | shuffle_answers=True, preserve_responses=False,
13 | border_radius=10, question_alignment="left",
14 | max_width=600, colors=None, load_js=True):
15 | """
16 | Display an interactive quiz in a Jupyter notebook.
17 |
18 | Parameters are the same as documented in the original dynamic.py.
19 | """
20 | assert not (shuffle_questions and preserve_responses), \
21 | "Preserving responses not supported when shuffling questions."
22 | assert num == 1_000_000 or (not preserve_responses), \
23 | "Preserving responses not supported when num is set."
24 | assert question_alignment in ['left', 'right', 'center'], \
25 | "question_alignment must be 'left', 'center', or 'right'"
26 |
27 | # Unique identifier for container
28 | letters = string.ascii_letters
29 | div_id = ''.join(random.choice(letters) for _ in range(12))
30 |
31 | preserve_json = 'true' if preserve_responses else 'false'
32 |
33 | # Default color palette
34 | color_dict = {
35 | '--jq-multiple-choice-bg': '#6f78ffff',
36 | '--jq-mc-button-bg': '#fafafa',
37 | '--jq-mc-button-border': '#e0e0e0e0',
38 | '--jq-mc-button-inset-shadow': '#555555',
39 | '--jq-many-choice-bg': '#f75c03ff',
40 | '--jq-numeric-bg': '#392061ff',
41 | '--jq-numeric-input-bg': '#c0c0c0',
42 | '--jq-numeric-input-label': '#101010',
43 | '--jq-numeric-input-shadow': '#999999',
44 | '--jq-string-bg': '#4c1a57',
45 | '--jq-incorrect-color': '#c80202',
46 | '--jq-correct-color': '#009113',
47 | '--jq-text-color': '#fafafa'
48 | }
49 | # Alternative palette
50 | fdsp_dict = {
51 | '--jq-multiple-choice-bg': '#345995',
52 | '--jq-mc-button-bg': '#fafafa',
53 | '--jq-mc-button-border': '#e0e0e0e0',
54 | '--jq-mc-button-inset-shadow': '#555555',
55 | '--jq-many-choice-bg': '#e26d5a',
56 | '--jq-numeric-bg': '#5bc0eb',
57 | '--jq-numeric-input-bg': '#c0c0c0',
58 | '--jq-numeric-input-label': '#101010',
59 | '--jq-numeric-input-shadow': '#999999',
60 | '--jq-string-bg': '#861657',
61 | '--jq-incorrect-color': '#666666',
62 | '--jq-correct-color': '#87a878',
63 | '--jq-text-color': '#fafafa'
64 | }
65 | if colors == 'fdsp':
66 | color_dict = fdsp_dict
67 | elif isinstance(colors, dict):
68 | color_dict.update(colors)
69 |
70 | # Build loading script
71 | prefix_script, static, url = load_questions_script(ref, div_id)
72 |
73 | # Render HTML container and styles
74 | mydiv = render_div(div_id, shuffle_questions, shuffle_answers,
75 | preserve_responses, num,
76 | max_width, border_radius, question_alignment)
77 | styles = build_styles(div_id, color_dict)
78 |
79 | # Combine all JavaScript
80 | javascript = build_script(prefix_script, static, url, div_id, load_js)
81 |
82 | # Display in notebook
83 | display(HTML(mydiv + styles))
84 | display(Javascript(javascript))
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/jupyterquiz/dynamic/loader.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Module for loading question data from list, file, URL, or DOM element.
3 | """
4 | import json
5 | import sys
6 | import urllib.request
7 |
8 | # Try to import open_url for Pyodide environments
9 | try:
10 | from pyodide.http import open_url
11 | except ImportError:
12 | try:
13 | from pyodide import open_url
14 | except ImportError:
15 | open_url = None
16 |
17 | def load_questions_script(ref, div_id):
18 | """
19 | Build JavaScript code prefix to load questions into a variable questions{div_id}.
20 | Returns (script_prefix, static, url), where static is True if questions are embedded,
21 | and url is the reference URL for async loading when static is False.
22 | """
23 | script = ''
24 | static = True
25 | url = ''
26 | # List of question dicts
27 | if isinstance(ref, list):
28 | script = f"var questions{div_id}=" + json.dumps(ref)
29 | # String reference: DOM id, URL, or filename
30 | elif isinstance(ref, str):
31 | # DOM element containing JSON or base64-encoded JSON
32 | if ref.startswith('#'):
33 | element_id = ref[1:]
34 | script = (
35 | f'var element = document.getElementById("{element_id}");\n'
36 | f'if (element == null) {{ console.log("ID failed, trying class"); '
37 | f'var elems = document.getElementsByClassName("{element_id}"); '
38 | f'element = elems[0]; }}\n'
39 | f'if (element == null) {{ throw new Error("Cannot find element {element_id}"); }}\n'
40 | f'var questions{div_id};\n'
41 | f'try {{ questions{div_id} = JSON.parse(window.atob(element.innerHTML)); }} '
42 | f'catch(err) {{ console.log("Parsing error, using raw innerHTML"); '
43 | f'questions{div_id} = JSON.parse(element.innerHTML); }}\n'
44 | f'console.log(questions{div_id});'
45 | )
46 | # URL fetched asynchronously, with fallback to embedded content
47 | elif ref.lower().startswith("http"):
48 | script = f"var questions{div_id}="
49 | url = ref
50 | # Embed initial data for fallback
51 | if sys.platform == 'emscripten' and open_url:
52 | text = open_url(url).read()
53 | script += text
54 | else:
55 | with urllib.request.urlopen(url) as response:
56 | for line in response:
57 | script += line.decode('utf-8')
58 | static = False
59 | # Local file path
60 | else:
61 | script = f"var questions{div_id}="
62 | with open(ref, 'r') as f:
63 | for line in f:
64 | script += line
65 | static = True
66 | else:
67 | raise Exception("First argument must be list, URL, or file ref")
68 | # Terminate statement
69 | script += ";\n\nif (typeof Question === 'undefined') {\n"
70 | return script, static, url
71 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/jupyterquiz/dynamic/renderer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Module for rendering HTML, CSS, and JavaScript components of the quiz display.
3 | """
4 | import importlib.resources
5 | from string import Template
6 |
7 | def render_div(div_id, shuffle_questions, shuffle_answers,
8 | preserve_responses, num, max_width,
9 | border_radius, question_alignment):
10 | """
11 | Build the HTML container div with data attributes and inline style.
12 | """
13 | preserve_json = 'true' if preserve_responses else 'false'
14 | return (
15 | f'
"
253 | ],
254 | "text/plain": [
255 | ""
256 | ]
257 | },
258 | "metadata": {},
259 | "output_type": "display_data"
260 | },
261 | {
262 | "data": {
263 | "application/javascript": [
264 | "var questionsHkGwvkyiZWoc=[{\"question\": \"Which of these is the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter?\", \"type\": \"multiple_choice\", \"answers\": [{\"answer\": \"pi\", \"correct\": true, \"feedback\": \"Correct.\"}, {\"answer\": \"frac227\", \"correct\": false, \"feedback\": \"frac227 is only an approximation to the true value.\"}, {\"answer\": \"3\", \"correct\": false, \"feedback\": \"This is a crude approximation to the true value.\"}, {\"answer\": \"tau\", \"correct\": false, \"feedback\": \"True for the ratio of the circle's circumference to its radius, not diameter.\"}]}, {\"question\": \"Enter the value of pi to 2 decimal places.\", \"type\": \"numeric\", \"answers\": [{\"type\": \"value\", \"value\": 3.14, \"correct\": true, \"feedback\": \"Correct.\"}, {\"type\": \"range\", \"range\": [3.142857, 3.142858], \"correct\": true, \"feedback\": \"True to 2 decimal places, but you know pi is not really 22/7, right?\"}, {\"type\": \"range\", \"range\": [-100000000, 0], \"correct\": false, \"feedback\": \"pi is the AREA of a circle of radius 1. Try again.\"}, {\"type\": \"default\", \"feedback\": \"pi is the area of a circle of radius 1. Try again.\"}]}];\n",
265 | " // Make a random ID\n",
266 | "function makeid(length) {\n",
267 | " var result = [];\n",
268 | " var characters = 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz';\n",
269 | " var charactersLength = characters.length;\n",
270 | " for (var i = 0; i < length; i++) {\n",
271 | " result.push(characters.charAt(Math.floor(Math.random() * charactersLength)));\n",
272 | " }\n",
273 | " return result.join('');\n",
274 | "}\n",
275 | "\n",
276 | "// Choose a random subset of an array. Can also be used to shuffle the array\n",
277 | "function getRandomSubarray(arr, size) {\n",
278 | " var shuffled = arr.slice(0), i = arr.length, temp, index;\n",
279 | " while (i--) {\n",
280 | " index = Math.floor((i + 1) * Math.random());\n",
281 | " temp = shuffled[index];\n",
282 | " shuffled[index] = shuffled[i];\n",
283 | " shuffled[i] = temp;\n",
284 | " }\n",
285 | " return shuffled.slice(0, size);\n",
286 | "}\n",
287 | "\n",
288 | "function printResponses(responsesContainer) {\n",
289 | " var responses=JSON.parse(responsesContainer.dataset.responses);\n",
290 | " var stringResponses='IMPORTANT!To preserve this answer sequence for submission, when you have finalized your answers:
Copy the text in this cell below \"Answer String\"
Double click on the cell directly below the Answer String, labeled \"Replace Me\"
Select the whole \"Replace Me\" text
Paste in your answer string and press shift-Enter.
Save the notebook using the save icon or File->Save Notebook menu item