├── .gitignore
├── .vscode
├── launch.json
└── settings.json
├── CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
├── QUESTIONS_AND_ANSWERS.md
├── QUESTIONS_AND_ANSWERS.pdf
├── QUESTIONS_AND_ANSWERS_02.md
├── README.md
├── database
├── README.md
├── code
│ ├── create_database.sql
│ ├── generate_data.py
│ ├── models.py
│ ├── pwiz.py
│ └── read_files.ipynb
├── data
│ ├── batches.csv
│ ├── mentors.csv
│ └── students.csv
├── docker-compose.yml
├── mcqs
│ ├── 01-database-fundamentals.md
│ ├── 02-integrity-er-diagram.md
│ └── 03-normalisation-acid.md
├── media
│ ├── .DS_Store
│ ├── attributes.png
│ ├── duplicate-error.png
│ ├── fk-error.png
│ ├── many-to-many.png
│ ├── one-to-many.png
│ ├── one-to-one.png
│ ├── partial-er.drawio
│ ├── schema.diagram
│ ├── schema.png
│ ├── student-batch-er.png
│ ├── student-er-full.drawio
│ ├── student-er.drawio
│ ├── student-er.png
│ ├── students-table.png
│ ├── subset.png
│ ├── subsets-and.png
│ └── type-error.png
└── notes
│ ├── 01-database-fundamentals-hw.pdf
│ ├── 01-database-fundamentals.md
│ ├── 01-database-fundamentals.pdf
│ ├── 02-integrity-er-diagram-hw-02.pdf
│ ├── 02-integrity-er-diagram-hw.pdf
│ ├── 02-integrity-er-diagram.md
│ ├── 02-integrity-er-diagram.pdf
│ ├── 02-schema-design-hw.pdf
│ ├── 02-schema-design.md
│ ├── 02-schema-design.pdf
│ ├── 03-normalisation-acid-hw.pdf
│ ├── 03-normalisation-acid.md
│ ├── 03-normalisation-acid.pdf
│ ├── 03-normalisation-sql-hw.pdf
│ ├── 03-normalisation-sql.md
│ ├── 03-normalisation-sql.pdf
│ ├── 04-transactions-indexes-hw-03.pdf
│ ├── 04-transactions-indexes-hw.pdf
│ ├── 04-transactions-indexes-hw02.pdf
│ ├── 04-transactions-indexes.md
│ ├── 04-transactions-indexes.pdf
│ ├── 05-sql-primer-hw-01.pdf
│ ├── 05-sql-primer-hw.pdf
│ ├── 05-sql-primer-worksheet-answers.md
│ ├── 05-sql-primer-worksheet.md
│ ├── 05-sql-primer.md
│ ├── 05-sql-primer.pdf
│ ├── 06-sql-joins-aggregation-hw.pdf
│ ├── 06-sql-joins-aggregation-hw02.pdf
│ ├── 06-sql-joins-aggregation-worksheet-answers.md
│ ├── 06-sql-joins-aggregation-worksheet.md
│ ├── 06-sql-joins-aggregation.md
│ ├── 06-sql-joins-aggregation.pdf
│ ├── 07-groupby-functions-hw.pdf
│ ├── 07-groupby-functions-worksheet-answers.md
│ ├── 07-groupby-functions-worksheet.md
│ ├── 07-groupby-functions.md
│ ├── 07-groupby-functions.pdf
│ ├── 07-subqueries-functions-hw.pdf
│ ├── 07-subqueries-functions-worksheet-answers.md
│ ├── 07-subqueries-functions-worksheet.md
│ ├── 07-subqueries-functions.md
│ ├── 07-subqueries-functions.pdf
│ ├── 08-window-fuctions-indexes-hw.pdf
│ ├── 08-window-fuctions-indexes.md
│ ├── 08-window-fuctions-indexes.pdf
│ ├── 08-window-function-query-optimisation-hw.pdf
│ ├── 08-window-function-query-optimisation.md
│ ├── 08-window-function-query-optimisation.pdf
│ ├── 08-window-functions-worksheet-answers.md
│ ├── 08-window-functions-worksheet.md
│ ├── 09-subqueries-views-hw.pdf
│ ├── 09-subqueries-views-worksheet-answers.md
│ ├── 09-subqueries-views-worksheet.md
│ ├── 09-subqueries-views.md
│ └── 09-subqueries-views.pdf
├── networks
├── .DS_Store
├── README.md
├── code
│ ├── client.py
│ ├── port-scanner.py
│ └── server.py
└── notes
│ ├── 01-introduction-OSI-model-hw.pdf
│ ├── 01-introduction-OSI-model.md
│ ├── 01-introduction-OSI-model.pdf
│ ├── 02-application-layer-hw.pdf
│ ├── 02-application-layer.md
│ ├── 02-application-layer.pdf
│ ├── 03-cookies-dns-tcp-hw.pdf
│ ├── 03-cookies-dns-tcp.md
│ ├── 03-cookies-dns-tcp.pdf
│ ├── 04-sockets-primer-hw-02.pdf
│ ├── 04-sockets-primer-hw.pdf
│ ├── 04-sockets-primer.md
│ └── 04-sockets-primer.pdf
├── oop
├── README.md
├── code
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── oop
│ │ ├── pom.xml
│ │ └── src
│ │ │ ├── main
│ │ │ └── java
│ │ │ │ └── com
│ │ │ │ └── scaler
│ │ │ │ └── lld
│ │ │ │ ├── App.java
│ │ │ │ ├── basics
│ │ │ │ └── OopBankAccount.java
│ │ │ │ ├── bird
│ │ │ │ ├── Bird.java
│ │ │ │ ├── BirdType.java
│ │ │ │ ├── Eagle.java
│ │ │ │ ├── Parrot.java
│ │ │ │ └── Runner.java
│ │ │ │ ├── questions
│ │ │ │ ├── Book.java
│ │ │ │ └── Invoice.java
│ │ │ │ └── scaler
│ │ │ │ ├── Mentor.java
│ │ │ │ ├── Student.java
│ │ │ │ ├── StudentStatus.java
│ │ │ │ └── User.java
│ │ │ └── test
│ │ │ └── java
│ │ │ └── com
│ │ │ └── scaler
│ │ │ └── lld
│ │ │ ├── AppTest.java
│ │ │ └── scaler
│ │ │ └── StudentTest.java
│ ├── procedural_transfer.py
│ └── python_code
│ │ ├── main.py
│ │ └── oop
│ │ ├── SOLID
│ │ └── bird
│ │ │ ├── Bird.py
│ │ │ ├── BirdType.py
│ │ │ ├── Eagle.py
│ │ │ ├── FlappingBehaviour.py
│ │ │ ├── GlidingBehaviour.py
│ │ │ ├── Parrot.py
│ │ │ ├── Penguin.py
│ │ │ ├── Runner.py
│ │ │ └── interfaces
│ │ │ ├── FlyableInterface.py
│ │ │ ├── FlyingBehaviourInterface.py
│ │ │ ├── SwimmableInterface.py
│ │ │ └── __init__.py
│ │ ├── basic
│ │ ├── OopBankAccount.py
│ │ └── __init__.py
│ │ └── inheritance
│ │ ├── Student.py
│ │ ├── StudentStatus.py
│ │ └── User.py
└── notes
│ ├── 01-oop-introduction-hw.pdf
│ ├── 01-oop-introduction.md
│ ├── 01-oop-introduction.pdf
│ ├── 02-constructors-inheritance-hw.pdf
│ ├── 02-constructors-inheritance.md
│ ├── 02-constructors-inheritance.pdf
│ ├── 03-polymorphism-hw.pdf
│ ├── 03-polymorphism.md
│ ├── 03-polymorphism.pdf
│ ├── 04-interfaces-abstract.md
│ ├── 04-solid-01-hw.pdf
│ ├── 04-solid-01.md
│ ├── 04-solid-01.pdf
│ ├── 05-solid-02-hw.pdf
│ ├── 05-solid-02.md
│ └── 05-solid-02.pdf
├── os
├── README.md
├── code
│ └── os
│ │ ├── pom.xml
│ │ ├── src
│ │ ├── main
│ │ │ └── java
│ │ │ │ └── com
│ │ │ │ └── scaler
│ │ │ │ ├── App.java
│ │ │ │ ├── TextPrinter.java
│ │ │ │ ├── addersubtractor
│ │ │ │ ├── Adder.java
│ │ │ │ ├── Count.java
│ │ │ │ ├── Runner.java
│ │ │ │ └── Subtractor.java
│ │ │ │ ├── mergesort
│ │ │ │ ├── Runner.java
│ │ │ │ └── Sorter.java
│ │ │ │ ├── producerconsumer
│ │ │ │ ├── Consumer.java
│ │ │ │ ├── Producer.java
│ │ │ │ ├── Runner.java
│ │ │ │ └── UnitOfWork.java
│ │ │ │ ├── scheduling
│ │ │ │ ├── FirstComeFirstServe.java
│ │ │ │ └── models
│ │ │ │ │ ├── IncomingProcess.java
│ │ │ │ │ └── ScheduledProcess.java
│ │ │ │ └── threads
│ │ │ │ └── Printer.java
│ │ └── test
│ │ │ └── java
│ │ │ └── com
│ │ │ └── scaler
│ │ │ ├── AppTest.java
│ │ │ └── scheduling
│ │ │ └── FirstComeFirstServeTest.java
│ │ └── target
│ │ ├── classes
│ │ └── com
│ │ │ └── scaler
│ │ │ ├── App.class
│ │ │ └── producerconsumer
│ │ │ └── UnitOfWork.class
│ │ └── test-classes
│ │ └── com
│ │ └── scaler
│ │ └── AppTest.class
└── notes
│ ├── 01-os-primer-hw.pdf
│ ├── 01-os-primer.md
│ ├── 01-os-primer.pdf
│ ├── 02-round-robin-threads-hw.pdf
│ ├── 02-round-robin-threads.md
│ ├── 02-round-robin-threads.pdf
│ ├── 03-thread-synchronisation-hw.pdf
│ ├── 03-thread-synchronisation.md
│ ├── 03-thread-synchronisation.pdf
│ ├── 03-threads-synchronisation-hw-02.pdf
│ ├── 03-threads-synchronisation-hw.pdf
│ ├── 03-threads-synchronisation.md
│ ├── 04-memory-management-hw.pdf
│ ├── 04-memory-management.md
│ ├── 04-memory-management.pdf
│ ├── 04-synchronisation.md
│ └── threads-consolidated.md
└── process.md
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | os/code/os/target/*
2 | os/code/os/target/
3 | database/code/__pycache__
4 | *.class
5 | __pycache__/
6 | *.py[cod]
7 | *$py.class
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.vscode/launch.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | // Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
3 | // Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
4 | // For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
5 | "version": "0.2.0",
6 | "configurations": [
7 | {
8 | "type": "java",
9 | "name": "Launch App",
10 | "request": "launch",
11 | "mainClass": "com.scaler.App",
12 | "projectName": "os"
13 | },
14 | {
15 | "name": "Python: Current File",
16 | "type": "python",
17 | "request": "launch",
18 | "program": "${file}",
19 | "console": "integratedTerminal",
20 | "justMyCode": true,
21 | "args": [
22 | "-H",
23 | "127.0.0.1",
24 | "-p",
25 | "5001"
26 | ]
27 | }
28 | ]
29 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.vscode/settings.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "python.formatting.provider": "black",
3 | "java.configuration.updateBuildConfiguration": "interactive"
4 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Contributor Covenant Code of Conduct
2 |
3 | ## Our Pledge
4 |
5 | We as members, contributors, and leaders pledge to make participation in our
6 | community a harassment-free experience for everyone, regardless of age, body
7 | size, visible or invisible disability, ethnicity, sex characteristics, gender
8 | identity and expression, level of experience, education, socio-economic status,
9 | nationality, personal appearance, race, religion, or sexual identity
10 | and orientation.
11 |
12 | We pledge to act and interact in ways that contribute to an open, welcoming,
13 | diverse, inclusive, and healthy community.
14 |
15 | ## Our Standards
16 |
17 | Examples of behavior that contributes to a positive environment for our
18 | community include:
19 |
20 | * Demonstrating empathy and kindness toward other people
21 | * Being respectful of differing opinions, viewpoints, and experiences
22 | * Giving and gracefully accepting constructive feedback
23 | * Accepting responsibility and apologizing to those affected by our mistakes,
24 | and learning from the experience
25 | * Focusing on what is best not just for us as individuals, but for the
26 | overall community
27 |
28 | Examples of unacceptable behavior include:
29 |
30 | * The use of sexualized language or imagery, and sexual attention or
31 | advances of any kind
32 | * Trolling, insulting or derogatory comments, and personal or political attacks
33 | * Public or private harassment
34 | * Publishing others' private information, such as a physical or email
35 | address, without their explicit permission
36 | * Other conduct which could reasonably be considered inappropriate in a
37 | professional setting
38 |
39 | ## Enforcement Responsibilities
40 |
41 | Community leaders are responsible for clarifying and enforcing our standards of
42 | acceptable behavior and will take appropriate and fair corrective action in
43 | response to any behavior that they deem inappropriate, threatening, offensive,
44 | or harmful.
45 |
46 | Community leaders have the right and responsibility to remove, edit, or reject
47 | comments, commits, code, wiki edits, issues, and other contributions that are
48 | not aligned to this Code of Conduct, and will communicate reasons for moderation
49 | decisions when appropriate.
50 |
51 | ## Scope
52 |
53 | This Code of Conduct applies within all community spaces, and also applies when
54 | an individual is officially representing the community in public spaces.
55 | Examples of representing our community include using an official e-mail address,
56 | posting via an official social media account, or acting as an appointed
57 | representative at an online or offline event.
58 |
59 | ## Enforcement
60 |
61 | Instances of abusive, harassing, or otherwise unacceptable behavior may be
62 | reported to the community leaders responsible for enforcement at
63 | tanmaykacker40@gmail.com.
64 | All complaints will be reviewed and investigated promptly and fairly.
65 |
66 | All community leaders are obligated to respect the privacy and security of the
67 | reporter of any incident.
68 |
69 | ## Enforcement Guidelines
70 |
71 | Community leaders will follow these Community Impact Guidelines in determining
72 | the consequences for any action they deem in violation of this Code of Conduct:
73 |
74 | ### 1. Correction
75 |
76 | **Community Impact**: Use of inappropriate language or other behavior deemed
77 | unprofessional or unwelcome in the community.
78 |
79 | **Consequence**: A private, written warning from community leaders, providing
80 | clarity around the nature of the violation and an explanation of why the
81 | behavior was inappropriate. A public apology may be requested.
82 |
83 | ### 2. Warning
84 |
85 | **Community Impact**: A violation through a single incident or series
86 | of actions.
87 |
88 | **Consequence**: A warning with consequences for continued behavior. No
89 | interaction with the people involved, including unsolicited interaction with
90 | those enforcing the Code of Conduct, for a specified period of time. This
91 | includes avoiding interactions in community spaces as well as external channels
92 | like social media. Violating these terms may lead to a temporary or
93 | permanent ban.
94 |
95 | ### 3. Temporary Ban
96 |
97 | **Community Impact**: A serious violation of community standards, including
98 | sustained inappropriate behavior.
99 |
100 | **Consequence**: A temporary ban from any sort of interaction or public
101 | communication with the community for a specified period of time. No public or
102 | private interaction with the people involved, including unsolicited interaction
103 | with those enforcing the Code of Conduct, is allowed during this period.
104 | Violating these terms may lead to a permanent ban.
105 |
106 | ### 4. Permanent Ban
107 |
108 | **Community Impact**: Demonstrating a pattern of violation of community
109 | standards, including sustained inappropriate behavior, harassment of an
110 | individual, or aggression toward or disparagement of classes of individuals.
111 |
112 | **Consequence**: A permanent ban from any sort of public interaction within
113 | the community.
114 |
115 | ## Attribution
116 |
117 | This Code of Conduct is adapted from the [Contributor Covenant][homepage],
118 | version 2.0, available at
119 | https://www.contributor-covenant.org/version/2/0/code_of_conduct.html.
120 |
121 | Community Impact Guidelines were inspired by [Mozilla's code of conduct
122 | enforcement ladder](https://github.com/mozilla/diversity).
123 |
124 | [homepage]: https://www.contributor-covenant.org
125 |
126 | For answers to common questions about this code of conduct, see the FAQ at
127 | https://www.contributor-covenant.org/faq. Translations are available at
128 | https://www.contributor-covenant.org/translations.
129 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/QUESTIONS_AND_ANSWERS.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/QUESTIONS_AND_ANSWERS.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # fundamentals
2 | A collection of tutorials on computer fundamentals
3 |
4 | ## Table of Contents
5 |
6 | - [DBMS](database/)
7 | - [Operating Systems](os/)
8 | - [Computer Networks](networks/)
9 | - [Object Oriented Programming](oop/)
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Notes
2 |
3 | | Name | .md | .pdf | Handwritten | MCQs | Worksheet | Worksheet with Answers |
4 | | ---------------------------- | -------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------- | --------- | ---------------------- |
5 | | Database Fundamentals | [1](notes/01-database-fundamentals.md) | [2](notes/01-database-fundamentals.pdf) | [3](notes/01-database-fundamentals-hw.pdf) | [4](mcqs/01-database-fundamentals.md) | _ | _ |
6 | | Data Integrity & ER Diagrams | [1](notes/02-integrity-er-diagram.md) | [2](notes/02-integrity-er-diagram.pdf) | [3](notes/02-integrity-er-diagram-hw.pdf) | [4](mcqs/02-integrity-er-diagram.md) | _ | _ |
7 | | Data Normalisation and ACID | [1](notes/03-normalisation-acid.md) | [2](notes/03-normalisation-acid.pdf) | [3](notes/03-normalisation-acid-hw.pdf) | [4](mcqs/03-normalisation-acid.md) |_ | _ |
8 | | Transactions and Indexes | [1](notes/04-transactions-indexes.md) | [2](notes/04-transactions-indexes.pdf) | [3](notes/04-transactions-indexes-hw.pdf) | [4](mcqs/04-transactions-indexes.md) | _ | _ |
9 | | SQL Primer | [1](notes/05-sql-primer.md) | [2](notes/05-sql-primer.pdf) | [3](notes/05-sql-primer-hw.pdf) | [4](mcqs/05-sql-primer.md) | [5](notes/05-sql-primer-worksheet.md) | [6](notes/05-sql-primer-worksheet-answers.md) |
10 | | SQL Joins and Aggregation | [1](notes/06-sql-joins-aggregation.md) | [2](notes/06-sql-joins-aggregation.pdf) | [3](notes/06-sql-joins-aggregation-hw.pdf) | [4](mcqs/06-sql-joins-aggregation.md) | [5](notes/06-sql-joins-aggregation-worksheet.md) | [6](notes/06-sql-joins-aggregation-worksheet-answers.md) |
11 | | Subqueries and Functions | [1](notes/07-subqueries-functions.md) | [2](notes/07-subqueries-functions.pdf) | [3](notes/07-subqueries-functions-hw.pdf) | [4](mcqs/07-subqueries-functions.md) | [5](notes/07-subqueries-functions-worksheet.md) | [6](notes/07-subqueries-functions-worksheet-answers.md) |
12 |
13 |
14 | ## Assignments
15 |
16 | ### ER Diagram
17 | Download the ER diagram from [here](media/student-er.drawio) and import it into [draw.io](https://www.draw.io/).
18 |
19 | * Add the `mentor` entity
20 | * Modify `batch` to add more attributes
21 | * Add relationships between the `mentor` and `batch` entities. A mentor can be assigned to multiple batches and a batch can have multiple mentors.
22 |
23 |
24 | ### Problem sets
25 | 1. [**Simple - I**](https://leetcode.com/problems/big-countries/)
26 | 2. [Simple - II](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-customer-referee/)
27 | 3. [**Joins - I**](https://leetcode.com/problems/employees-earning-more-than-their-managers/)
28 | 4. [Joins - II](https://leetcode.com/problems/combine-two-tables/)
29 | 5. [**Aggregation - I**](https://leetcode.com/problems/duplicate-emails/)
30 | 6. [Join - III](https://leetcode.com/problems/delete-duplicate-emails/)
31 | 7. [Aggregation - II](https://leetcode.com/problems/customer-placing-the-largest-number-of-orders/)
32 | 8. [Aggregation - III](https://leetcode.com/problems/classes-more-than-5-students/)
33 | 9. [Subqueries - I](https://leetcode.com/problems/customers-who-never-order/)
34 | 10. [Subqueries - II](https://leetcode.com/problems/sales-person/)
35 | 11. [Dates - I](https://leetcode.com/problems/rising-temperature/)
36 |
37 | Bold problems were solved during the session.
38 |
39 | ## RDBMS
40 | * [MySQL](https://www.mysql.com/)
41 | * [PostgreSQL](https://www.postgresql.org/)
42 | * [SQLite](https://www.sqlite.org/)
43 |
44 | ## SQL clients
45 | * [TablePlus](https://www.tableplus.com/)
46 | * [MySQL Workbench](https://www.mysql.com/products/workbench/)
47 |
48 | ## Online Playgrounds
49 | * [SQL Fiddle](http://sqlfiddle.com/)
50 |
51 | ## Links
52 | * [Awesome database learning](https://github.com/pingcap/awesome-database-learning)
53 | * [SQL Cheat Sheet](https://learnsql.com/blog/sql-basics-cheat-sheet/sql-basics-cheat-sheet-a4.pdf)
54 | * [SQL Tutorial](https://www.scaler.com/topics/sql/)
55 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/code/create_database.sql:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS `jedi_academy`;
2 |
3 | CREATE DATABASE `jedi_academy`;
4 |
5 | USE `jedi_academy`;
6 |
7 | SET
8 | NAMES utf8;
9 |
10 | SET
11 | character_set_client = utf8mb4;
12 |
13 | -- CREATE TABLES --
14 | CREATE TABLE `students` (
15 | `id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
16 | `first_name` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
17 | `last_name` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
18 | `email` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
19 | `phone` varchar(255),
20 | `birth_date` date,
21 | `address` varchar(255),
22 | `iq` int,
23 | `batch_id` int,
24 | PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
25 | );
26 |
27 | CREATE TABLE `batches` (
28 | `id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
29 | `name` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
30 | `start_date` date NOT NULL,
31 | `description` varchar(255),
32 | `instructor_id` int,
33 | PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
34 | );
35 |
36 | CREATE TABLE `instructors` (
37 | `id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
38 | `first_name` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
39 | `last_name` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
40 | `email` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
41 | `phone` varchar(255),
42 | PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
43 | );
44 |
45 | -- ADD FOREIGN KEYS --
46 | ALTER TABLE
47 | `students`
48 | ADD
49 | FOREIGN KEY (`batch_id`) REFERENCES `batches`(`id`);
50 |
51 | ALTER TABLE
52 | `batches`
53 | ADD
54 | FOREIGN KEY (`instructor_id`) REFERENCES `instructors`(`id`);
55 |
56 | -- INSERT DATA --
57 | -- Instructors --
58 | INSERT INTO
59 | `instructors` (`first_name`, `last_name`, `email`, `phone`)
60 | VALUES
61 | ('Master', 'Yoda', 'y@jedi.com', '123-456-7890'),
62 | (
63 | 'Obi-Wan',
64 | 'Kenobi',
65 | 'o@jedi.com',
66 | '123-456-7890'
67 | ),
68 | (
69 | 'Sherlock',
70 | 'Holmes',
71 | 's@sherlock.ed',
72 | '123-456-7890'
73 | ),
74 | (
75 | 'Rani',
76 | 'Laxmi Bai',
77 | 'r@rebelli.on',
78 | '123-456-7890'
79 | ),
80 | (
81 | 'Thor',
82 | 'Odinson',
83 | 't@thunder.com',
84 | '123-456-7890'
85 | );
86 |
87 | -- Batches --
88 | INSERT INTO
89 | `batches` (
90 | `name`,
91 | `start_date`,
92 | `instructor_id`
93 | )
94 | VALUES
95 | (
96 | 'Jedi Academy 1',
97 | '2012-01-01',
98 | 1
99 | ),
100 | (
101 | 'Jedi Academy 2',
102 | '2014-01-01',
103 | 2
104 | ),
105 | (
106 | 'Sherlock Academy',
107 | '2017-01-01',
108 | 3
109 | ),
110 | (
111 | 'Independence Academy',
112 | '1857-01-01',
113 | 4
114 | ),
115 | (
116 | 'Love and Thunder Academy',
117 | '2022-01-01',
118 | 5
119 | );
120 |
121 | -- Students --
122 | INSERT INTO
123 | `students` (
124 | `first_name`,
125 | `last_name`,
126 | `email`,
127 | `phone`,
128 | `birth_date`,
129 | `address`,
130 | `iq`,
131 | `batch_id`
132 | )
133 | VALUES
134 | (
135 | 'Anakin',
136 | 'Skywalker',
137 | 'darth@empire.blr',
138 | '123-456-7890',
139 | '1973-01-01',
140 | 'Tatooine',
141 | 130,
142 | 1
143 | ),
144 | (
145 | 'Luke',
146 | 'Skywalker',
147 | 'luke@resistance.com',
148 | '123-456-7890',
149 | '1994-01-01',
150 | 'Tatooine',
151 | 120,
152 | 2
153 | ),
154 | (
155 | 'Leia',
156 | 'Organa',
157 | 'leia@resistance.com',
158 | '123-456-7890',
159 | '1994-01-01',
160 | 'Alderaan',
161 | 130,
162 | 2
163 | ),
164 | (
165 | 'John',
166 | 'Watson',
167 | 'j@sherlock.ed',
168 | '123-456-7890',
169 | '1657-01-01',
170 | 'London',
171 | 130,
172 | 3
173 | ),
174 | (
175 | 'Mycroft',
176 | 'Holmes',
177 | 'm@sherlock.ed',
178 | '123-456-7890',
179 | '1657-01-01',
180 | 'London',
181 | 150,
182 | 3
183 | ),
184 | (
185 | 'Tantia',
186 | 'Tope',
187 | 't@rebelli.on',
188 | '123-456-7890',
189 | '1657-01-01',
190 | 'Jhansi',
191 | 130,
192 | 4
193 | ),
194 | (
195 | 'Jane',
196 | 'Foster',
197 | 'jane@th.or',
198 | '123-456-7890',
199 | '2022-01-01',
200 | 'New Asgard',
201 | 160,
202 | 5
203 | ),
204 | (
205 | 'Korg',
206 | 'Rock',
207 | 'korg@th.or',
208 | '123-456-7890',
209 | '2022-01-01',
210 | 'New Asgard',
211 | 80,
212 | 5
213 | );
214 |
215 | INSERT INTO
216 | students (first_name, last_name, email, iq)
217 | VALUES ("Moriarty", "Patel", "mo@sherlock.ed", 170);
218 |
219 | INSERT INTO
220 | batches (name, start_date)
221 | VALUES ("Crime Academy", "2022-10-01");
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/code/generate_data.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import argparse
2 | import random
3 | from typing import List
4 | from urllib import request, error
5 | import json
6 | from models import Students
7 |
8 | API_URL = "https://randomuser.me/api"
9 |
10 |
11 | def generate_user(count: int):
12 | url = API_URL + f"?results={count}"
13 | users = json.loads(request.urlopen(url).read())
14 | return users['results']
15 |
16 | def to_student(user: dict) -> Students:
17 | student = Students()
18 | student.first_name = user['name']['first']
19 | student.last_name = user['name']['last']
20 | student.email = user['email']
21 | # random choice from batches 1 - 6
22 | student.batch = random.randint(1, 6)
23 | student.address = f"{user['location']['city']}, {user['location']['state']}, {user['location']['country']}"
24 | student.birth_date = user['dob']['date'].split("T")[0]
25 | return student
26 |
27 | def main(count: int, filename: str) -> None:
28 | with open(filename, "w") as f:
29 | users = generate_user(count)
30 | print(f"Generated {len(users)} users")
31 |
32 | students: List[Students] = [to_student(user) for user in users]
33 | Students.bulk_create(students, batch_size=100)
34 | print(f"Saved {len(students)} students")
35 |
36 | if __name__ == "__main__":
37 |
38 | # Declare arguments
39 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Student generator")
40 | parser.add_argument(
41 | "-n", "--number", type=int, default=10, help="Number of students to generate"
42 | )
43 | parser.add_argument(
44 | "-f", "--file", type=str, default="students.txt", help="File to write to"
45 | )
46 | args = parser.parse_args()
47 |
48 | students_count, file_name = args.number, args.file
49 | main(students_count, file_name)
50 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/code/models.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from peewee import *
2 | database = MySQLDatabase('jedi_academy', **{'charset': 'utf8', 'sql_mode': 'PIPES_AS_CONCAT', 'use_unicode': True, 'user': 'root'})
3 |
4 | class UnknownField(object):
5 | def __init__(self, *_, **__): pass
6 |
7 | class BaseModel(Model):
8 | class Meta:
9 | database = database
10 |
11 | class Instructors(BaseModel):
12 | email = CharField()
13 | first_name = CharField()
14 | last_name = CharField()
15 | phone = CharField(null=True)
16 |
17 | class Meta:
18 | table_name = 'instructors'
19 |
20 | class Batches(BaseModel):
21 | description = CharField(null=True)
22 | instructor = ForeignKeyField(column_name='instructor_id', field='id', model=Instructors, null=True)
23 | name = CharField()
24 | start_date = DateField()
25 |
26 | class Meta:
27 | table_name = 'batches'
28 |
29 | class Students(BaseModel):
30 | address = CharField(null=True)
31 | batch = ForeignKeyField(column_name='batch_id', field='id', model=Batches, null=True)
32 | birth_date = DateField(null=True)
33 | email = CharField()
34 | first_name = CharField()
35 | iq = IntegerField(null=True)
36 | last_name = CharField()
37 | phone = CharField(null=True)
38 |
39 | class Meta:
40 | table_name = 'students'
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/code/pwiz.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python
2 |
3 | import datetime
4 | import os
5 | import sys
6 | from getpass import getpass
7 | from optparse import OptionParser
8 |
9 | from peewee import *
10 | from peewee import print_
11 | from peewee import __version__ as peewee_version
12 | from playhouse.cockroachdb import CockroachDatabase
13 | from playhouse.reflection import *
14 |
15 |
16 | HEADER = """from peewee import *%s
17 | database = %s('%s'%s)
18 | """
19 |
20 | BASE_MODEL = """\
21 | class BaseModel(Model):
22 | class Meta:
23 | database = database
24 | """
25 |
26 | UNKNOWN_FIELD = """\
27 | class UnknownField(object):
28 | def __init__(self, *_, **__): pass
29 | """
30 |
31 | DATABASE_ALIASES = {
32 | CockroachDatabase: ['cockroach', 'cockroachdb', 'crdb'],
33 | MySQLDatabase: ['mysql', 'mysqldb'],
34 | PostgresqlDatabase: ['postgres', 'postgresql'],
35 | SqliteDatabase: ['sqlite', 'sqlite3'],
36 | }
37 |
38 | DATABASE_MAP = dict((value, key)
39 | for key in DATABASE_ALIASES
40 | for value in DATABASE_ALIASES[key])
41 |
42 | def make_introspector(database_type, database_name, **kwargs):
43 | if database_type not in DATABASE_MAP:
44 | err('Unrecognized database, must be one of: %s' %
45 | ', '.join(DATABASE_MAP.keys()))
46 | sys.exit(1)
47 |
48 | schema = kwargs.pop('schema', None)
49 | DatabaseClass = DATABASE_MAP[database_type]
50 | db = DatabaseClass(database_name, **kwargs)
51 | return Introspector.from_database(db, schema=schema)
52 |
53 | def print_models(introspector, tables=None, preserve_order=False,
54 | include_views=False, ignore_unknown=False, snake_case=True):
55 | database = introspector.introspect(table_names=tables,
56 | include_views=include_views,
57 | snake_case=snake_case)
58 |
59 | db_kwargs = introspector.get_database_kwargs()
60 | header = HEADER % (
61 | introspector.get_additional_imports(),
62 | introspector.get_database_class().__name__,
63 | introspector.get_database_name(),
64 | ', **%s' % repr(db_kwargs) if db_kwargs else '')
65 | print_(header)
66 |
67 | if not ignore_unknown:
68 | print_(UNKNOWN_FIELD)
69 |
70 | print_(BASE_MODEL)
71 |
72 | def _print_table(table, seen, accum=None):
73 | accum = accum or []
74 | foreign_keys = database.foreign_keys[table]
75 | for foreign_key in foreign_keys:
76 | dest = foreign_key.dest_table
77 |
78 | # In the event the destination table has already been pushed
79 | # for printing, then we have a reference cycle.
80 | if dest in accum and table not in accum:
81 | print_('# Possible reference cycle: %s' % dest)
82 |
83 | # If this is not a self-referential foreign key, and we have
84 | # not already processed the destination table, do so now.
85 | if dest not in seen and dest not in accum:
86 | seen.add(dest)
87 | if dest != table:
88 | _print_table(dest, seen, accum + [table])
89 |
90 | print_('class %s(BaseModel):' % database.model_names[table])
91 | columns = database.columns[table].items()
92 | if not preserve_order:
93 | columns = sorted(columns)
94 | primary_keys = database.primary_keys[table]
95 | for name, column in columns:
96 | skip = all([
97 | name in primary_keys,
98 | name == 'id',
99 | len(primary_keys) == 1,
100 | column.field_class in introspector.pk_classes])
101 | if skip:
102 | continue
103 | if column.primary_key and len(primary_keys) > 1:
104 | # If we have a CompositeKey, then we do not want to explicitly
105 | # mark the columns as being primary keys.
106 | column.primary_key = False
107 |
108 | is_unknown = column.field_class is UnknownField
109 | if is_unknown and ignore_unknown:
110 | disp = '%s - %s' % (column.name, column.raw_column_type or '?')
111 | print_(' # %s' % disp)
112 | else:
113 | print_(' %s' % column.get_field())
114 |
115 | print_('')
116 | print_(' class Meta:')
117 | print_(' table_name = \'%s\'' % table)
118 | multi_column_indexes = database.multi_column_indexes(table)
119 | if multi_column_indexes:
120 | print_(' indexes = (')
121 | for fields, unique in sorted(multi_column_indexes):
122 | print_(' ((%s), %s),' % (
123 | ', '.join("'%s'" % field for field in fields),
124 | unique,
125 | ))
126 | print_(' )')
127 |
128 | if introspector.schema:
129 | print_(' schema = \'%s\'' % introspector.schema)
130 | if len(primary_keys) > 1:
131 | pk_field_names = sorted([
132 | field.name for col, field in columns
133 | if col in primary_keys])
134 | pk_list = ', '.join("'%s'" % pk for pk in pk_field_names)
135 | print_(' primary_key = CompositeKey(%s)' % pk_list)
136 | elif not primary_keys:
137 | print_(' primary_key = False')
138 | print_('')
139 |
140 | seen.add(table)
141 |
142 | seen = set()
143 | for table in sorted(database.model_names.keys()):
144 | if table not in seen:
145 | if not tables or table in tables:
146 | _print_table(table, seen)
147 |
148 | def print_header(cmd_line, introspector):
149 | timestamp = datetime.datetime.now()
150 | print_('# Code generated by:')
151 | print_('# python -m pwiz %s' % cmd_line)
152 | print_('# Date: %s' % timestamp.strftime('%B %d, %Y %I:%M%p'))
153 | print_('# Database: %s' % introspector.get_database_name())
154 | print_('# Peewee version: %s' % peewee_version)
155 | print_('')
156 |
157 |
158 | def err(msg):
159 | sys.stderr.write('\033[91m%s\033[0m\n' % msg)
160 | sys.stderr.flush()
161 |
162 | def get_option_parser():
163 | parser = OptionParser(usage='usage: %prog [options] database_name')
164 | ao = parser.add_option
165 | ao('-H', '--host', dest='host')
166 | ao('-p', '--port', dest='port', type='int')
167 | ao('-u', '--user', dest='user')
168 | ao('-P', '--password', dest='password', action='store_true')
169 | engines = sorted(DATABASE_MAP)
170 | ao('-e', '--engine', dest='engine', choices=engines,
171 | help=('Database type, e.g. sqlite, mysql, postgresql or cockroachdb. '
172 | 'Default is "postgresql".'))
173 | ao('-s', '--schema', dest='schema')
174 | ao('-t', '--tables', dest='tables',
175 | help=('Only generate the specified tables. Multiple table names should '
176 | 'be separated by commas.'))
177 | ao('-v', '--views', dest='views', action='store_true',
178 | help='Generate model classes for VIEWs in addition to tables.')
179 | ao('-i', '--info', dest='info', action='store_true',
180 | help=('Add database information and other metadata to top of the '
181 | 'generated file.'))
182 | ao('-o', '--preserve-order', action='store_true', dest='preserve_order',
183 | help='Model definition column ordering matches source table.')
184 | ao('-I', '--ignore-unknown', action='store_true', dest='ignore_unknown',
185 | help='Ignore fields whose type cannot be determined.')
186 | ao('-L', '--legacy-naming', action='store_true', dest='legacy_naming',
187 | help='Use legacy table- and column-name generation.')
188 | return parser
189 |
190 | def get_connect_kwargs(options):
191 | ops = ('host', 'port', 'user', 'schema')
192 | kwargs = dict((o, getattr(options, o)) for o in ops if getattr(options, o))
193 | if options.password:
194 | kwargs['password'] = getpass()
195 | return kwargs
196 |
197 |
198 | if __name__ == '__main__':
199 | raw_argv = sys.argv
200 |
201 | parser = get_option_parser()
202 | options, args = parser.parse_args()
203 |
204 | if len(args) < 1:
205 | err('Missing required parameter "database"')
206 | parser.print_help()
207 | sys.exit(1)
208 |
209 | connect = get_connect_kwargs(options)
210 | database = args[-1]
211 |
212 | tables = None
213 | if options.tables:
214 | tables = [table.strip() for table in options.tables.split(',')
215 | if table.strip()]
216 |
217 | engine = options.engine
218 | if engine is None:
219 | engine = 'sqlite' if os.path.exists(database) else 'postgresql'
220 |
221 | introspector = make_introspector(engine, database, **connect)
222 | if options.info:
223 | cmd_line = ' '.join(raw_argv[1:])
224 | print_header(cmd_line, introspector)
225 |
226 | print_models(introspector, tables, options.preserve_order, options.views,
227 | options.ignore_unknown, not options.legacy_naming)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/code/read_files.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "code",
5 | "execution_count": 1,
6 | "metadata": {},
7 | "outputs": [],
8 | "source": [
9 | "STUDENTS_FILE = \"../data/students.csv\""
10 | ]
11 | },
12 | {
13 | "cell_type": "code",
14 | "execution_count": 10,
15 | "metadata": {},
16 | "outputs": [
17 | {
18 | "name": "stdout",
19 | "output_type": "stream",
20 | "text": [
21 | "Name\n",
22 | "Tantia Tope\n",
23 | "Kilvish\n",
24 | "John Watson\n"
25 | ]
26 | }
27 | ],
28 | "source": [
29 | "# Read file and print out name of students\n",
30 | "with open(STUDENTS_FILE, \"r\") as file:\n",
31 | " for line in file:\n",
32 | " name = line.split(\",\")[0]\n",
33 | " print(name)"
34 | ]
35 | },
36 | {
37 | "cell_type": "code",
38 | "execution_count": 11,
39 | "metadata": {},
40 | "outputs": [
41 | {
42 | "name": "stdout",
43 | "output_type": "stream",
44 | "text": [
45 | "Tantia Tope\n",
46 | "Kilvish\n",
47 | "John Watson\n"
48 | ]
49 | }
50 | ],
51 | "source": [
52 | "# Read file and print just names of students\n",
53 | "with open(STUDENTS_FILE, \"r\") as file:\n",
54 | " for index, line, in enumerate(file):\n",
55 | " if index == 0:\n",
56 | " continue\n",
57 | " name = line.split(\",\")[0]\n",
58 | " print(name)"
59 | ]
60 | },
61 | {
62 | "cell_type": "code",
63 | "execution_count": 14,
64 | "metadata": {},
65 | "outputs": [
66 | {
67 | "name": "stdout",
68 | "output_type": "stream",
69 | "text": [
70 | "Tantia Tope 20\n",
71 | "Kilvish 21\n"
72 | ]
73 | }
74 | ],
75 | "source": [
76 | "# Read file and only print users with age less than 25\n",
77 | "with open(STUDENTS_FILE, \"r\") as file:\n",
78 | " for index, line, in enumerate(file):\n",
79 | " if index == 0:\n",
80 | " continue\n",
81 | " name = line.split(\",\")[0]\n",
82 | " age = line.split(\",\")[3]\n",
83 | " if int(age) < 25:\n",
84 | " print(name, age)"
85 | ]
86 | },
87 | {
88 | "cell_type": "code",
89 | "execution_count": null,
90 | "metadata": {},
91 | "outputs": [],
92 | "source": []
93 | }
94 | ],
95 | "metadata": {
96 | "kernelspec": {
97 | "display_name": "Python 3.9.13 64-bit",
98 | "language": "python",
99 | "name": "python3"
100 | },
101 | "language_info": {
102 | "codemirror_mode": {
103 | "name": "ipython",
104 | "version": 3
105 | },
106 | "file_extension": ".py",
107 | "mimetype": "text/x-python",
108 | "name": "python",
109 | "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
110 | "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
111 | "version": "3.9.13"
112 | },
113 | "orig_nbformat": 4,
114 | "vscode": {
115 | "interpreter": {
116 | "hash": "b0fa6594d8f4cbf19f97940f81e996739fb7646882a419484c72d19e05852a7e"
117 | }
118 | }
119 | },
120 | "nbformat": 4,
121 | "nbformat_minor": 2
122 | }
123 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/data/batches.csv:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Name,Start,Type,Mentor
2 | Rebellion,01/01/1967,Advanced,Rani Bai
3 | Doordashan,01/01/1994,Beginner,Shaktimaan
4 | Sherlock Season 5,01/01/2031,Intermediate,Sherlock Holmes
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/data/mentors.csv:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Name,Email,Phone,Age,Address
2 | Rani Lakshmi Bai,rani@rani.bai,123456789,20,Jhansi
3 | Shaktimaan,shakti@ma.an,987654321,21,Earth
4 | Sherlock Holmes,i.am@sherlock.ed,123456789,30,221B Baker Street
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/data/students.csv:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Name,Email,Phone,Age,Address
2 | Tantia Tope,tantia@rani.bai,123456789,20,Jhansi
3 | Kilvish,kil@vi.sh,987654321,21,Andhera
4 | John Watson,i.am@sherlock.ed,123456789,30,221B Baker Street
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/docker-compose.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | version: '3.8'
2 |
3 | services:
4 | db:
5 | image: mysql:8.0
6 | container_name: mysql_container
7 | environment:
8 | MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: rootpassword
9 | MYSQL_DATABASE: jedi_academy
10 | volumes:
11 | - ./code/create_database.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/create_database.sql
12 | ports:
13 | - "3306:3306"
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/mcqs/01-database-fundamentals.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Questions
2 | 1. Joe Bloggs wants to create a website which returns the factorial of a number given by the user.
3 | Should Joe store this result in a database?
4 | >A. Yes \
5 | B. No
6 | ---
7 | 2. The website is a hit. Now Joe wants to show user their past results. So he has the store the values in a database.
8 | Which of the following should not be in the database?
9 |
10 | >A. User details \
11 | B. Input and Output (number and factorial) \
12 | C. User's Amazon orders
13 | ---
14 | 3. Joe Bloggs decides to use a MySql database. But he puts all his data in the database. Which of the following can he store as file?
15 | >A. User details \
16 | B. Input and Output (number and factorial) \
17 | C. AWS credentials \
18 | D. Passwords
19 | ---
20 | 4. Joe Bloggs want to uniquely identify whenever a user ran a calculation. What feature of a database can he use to achieve that?
21 | >A. Primary key \
22 | B. Foreign key \
23 | C. Tuple \
24 | D. Index
25 |
26 | ---
27 | # Answers
28 | 1. A. `Yes`
29 | 2. C `User's Amazon orders`
30 | 3. C `AWS credentials`
31 | 4. A `Primary key`
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/mcqs/02-integrity-er-diagram.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Questions
2 | 1. Joe Bloggs is helping us build Scaler. He is trying to delete some batches but the database throws an error that the batch is used by a tuple in another table. Which type of integrity constraint is being enforced here?
3 | >A. User-defined integrity \
4 | B. Domain integrity \
5 | C. Entity integrity \
6 | D. Referential integrity
7 | ---
8 | 2. Which of the following is not an example of domain integrity constraints?
9 |
10 | >A. Validating that input is correct data type \
11 | B. Ensuring value is not null if a non-nullable column \
12 | C. Making sure each row is unique \
13 | D. Checking if the value exceeds maximum length
14 | ---
15 | 3. Joe Bloggs is taking some time off to build his house. A house can have many rooms. What is the cardinality of house to room?
16 | >A. One to Many (1:m) \
17 | B. One to One (1:1) \
18 | C. Many to Many (m:n)
19 | ---
20 | 4. Let us say a house has a house_id and a room has room_id.
21 | Given the cardinality of house to room, which is the ideal place to store their relationship i.e. reference?
22 | >A. room_id in house \
23 | B. Separate table for room_id and house_id \
24 | C. Array of room_ids in house \
25 | D. house_id in room
26 |
27 | ---
28 | # Answers
29 | 1. D. `Referential integrity`
30 | 2. C `Making sure each row is unique`
31 | 3. A `One to Many (1:m)`
32 | 4. D `house_id in room`
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/mcqs/03-normalisation-acid.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Questions
2 | 1. Joe Bloggs is creating a social media today. However, Joe has kept user and group information in the same table. Now whenever Joe removes a user, the group information is also gone. Which type of anomaly is this?
3 | >A. Insertion \
4 | B. Updation \
5 | C. Deletion
6 | ---
7 | 2. A user has an ID, name, email and group ID. One user can only have one email and it is unique.
8 | Which of the following dependencies is not correct?
9 |
10 | >A. ID -> NAME \
11 | B. EMAIL -> NAME \
12 | C. EMAIL -> GROUP ID \
13 | D. NAME -> GROUP ID
14 | ---
15 | 3. Joe has created a table for group members where the columns are `Group ID, User ID, Rating, Group Name`. The primary key here is `Group ID, User ID`.
16 | Which type of functional dependency exists?
17 | >A. No functional dependency \
18 | B. Transitive \
19 | C. Partial
20 | ---
21 | 4. Joe has identified that one of his tables does not satisfy 1NF constraints. Which of the following types of ERD attributes are allowed under 1NF?
22 | >A. Composite \
23 | B. Multivalued \
24 | C. Derived \
25 | D. Index
26 |
27 | ---
28 | # Answers
29 | 1. A. `Deletion`
30 | 2. D `NAME -> GROUP ID`
31 | 3. C `Partial`
32 | 4. C `Derived`
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/media/.DS_Store:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/media/.DS_Store
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/media/attributes.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/media/attributes.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/media/duplicate-error.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/media/duplicate-error.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/media/fk-error.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/media/fk-error.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/media/many-to-many.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/media/many-to-many.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/media/one-to-many.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/media/one-to-many.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/media/one-to-one.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/media/one-to-one.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/media/partial-er.drawio:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 5Vptc6IwEP41fKwDBBA/atVeb6rtnHbuet8iROAKxAmx6v36CxJAiPWlhWKvM50pu0kWeHafzWZRAtfB+obAhTvCNvIlVbbXEuhLqqq0TcD+xZoN18iAaxzi2VyXKybeX5RO5NqlZ6OoMJFi7FNvUVRaOAyRRQs6SAheFafNsV+86wI6SFBMLOiL2p+eTd1Ea+pyrv+GPMdN76zIfCSA6WSuiFxo41VBhdZ0iEPKH/EBkQCGKKRsZATJMyKSPnApjd+0K6lD9jePZ7ccjB0fwYUXtSwcMLUVsSnDOQw8P8Z5x1CPG2K3AwMJXBOMaXIVrK+RHzsrdUPyTMNXRjMcSGz3hAXj6ez5EfTcvo7Vq1HwdPfb7F0p3ExENynAyGZ4cxET6mIHh9Af5NoewcvQRrFZmUn5nDuMF0ypMOUfROmGBw9cUsxULg18PorWHv0VL2/pXHraGemvueWtsEmFkJLNzqJYfNody5dtpXQdd6wtRFWOW4oBXhILHQKLhzskDqIH5hmZdxkNEQ4Qex62jiAfUu+l+ByQx5qTzctdyC64F8/waGr4BfpLfqsmXFw17O+Aky99wN6WyTwVAo1zPk2EHbloInEzX1VySvYY7/ATaJR5O7zLWXiEeUqBdzkNL4d5oFHmGZfi0f8mkyqNplIxk06mj/3BeCr4eeV6FE0WcPvSK1Z5FX0Efc8J2bXFgGJ7fwrlCyIUrQ+DKb47X6B2ivlLNbi8yquirPZxdyoiTa4JLiDAddsXGeH7rFKMI/9czOJSK+WSVg2GinppGBoChuPuaFAhijVEHug0jZoiwta/770dtSpCC5RAMkWQOnsw0uvCKC0DdzDq3lQZWTaM3O1GVhGC5TBT9KbDTG0LEH6/vx1PBBCJi4PZMvqQQNPMUg7TRJjMPSiZtW0DmoCSGGWf6gACTi4/G60/gZgFvwzweqPAm18X+HajwIsVeg9SyxXQrz8NG+VSct9upe7Jw0ZteVisx99XS9aA0t7S8WNR0gWUJtPuD3bEk/vdabNomZcXU2IFdOlnPANcWhmpndKhDe1u/LGESSEOURG24k6Rt3POa8+ljaO0WXRKK7DCLSYtpo9vMfX0f4W6ud1p6UUjyTsIHWDBlCGXTJVr65pbyZp4tBM/6xAUeX/hbCvK+2lIkuDvxXzzLOh3uX6GKcVB5n7+ZY/bkrKPZ0doeoALr5+iEzMfU01opxxc3sDLM9vmb2nRN8HLmmhZ4lImn0tKrXPEUN2kFAuL0WchpVYpKff7Ry25A8/nETrTE0zMv58n0/NfPYDBPw==
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/media/schema.diagram:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {"type":"edit","version":3,"columns":[{"id":0,"value":{"id":"0","name":"name","type":"string"}},{"id":1,"value":{"id":"1","name":"type","type":"string"}},{"id":2,"value":{"id":"2","name":"nullable","type":"boolean"}}],"tables":[{"value":{"rows":[{"id":0,"value":{"id":"id","name":"id","type":"int","nullable":"true"}},{"id":1,"value":{"id":"name","name":"name","type":"varchar(255)","nullable":"true"}},{"id":2,"value":{"id":"start_date","name":"start_date","type":"timestamp","nullable":"true"}},{"id":3,"value":{"id":"type","name":"type","type":"varchar(255)","nullable":"true"}},{"id":4,"value":{"id":"mentor_id","name":"mentor_id","type":"int","nullable":"true"}}],"name":"batches","id":"batches","schema":"db"},"position":{"top":96,"left":448},"id":0,"rowsExpanded":false,"selected":false},{"value":{"rows":[{"id":0,"value":{"id":"id","name":"id","type":"int","nullable":"true"}},{"id":1,"value":{"id":"name","name":"name","type":"varchar(255)","nullable":"true"}},{"id":2,"value":{"id":"age","name":"age","type":"int","nullable":"true"}},{"id":3,"value":{"id":"phone","name":"phone","type":"int","nullable":"true"}},{"id":4,"value":{"id":"address","name":"address","type":"varchar(255)","nullable":"true"}},{"id":5,"value":{"id":"email","name":"email","type":"varchar(255)","nullable":"true"}}],"name":"mentors","id":"mentors","schema":"db"},"position":{"top":80,"left":832},"id":1,"rowsExpanded":false,"selected":false},{"value":{"rows":[{"id":0,"value":{"id":"id","name":"id","type":"int","nullable":"true"}},{"id":1,"value":{"id":"name","name":"name","type":"varchar(255)","nullable":"true"}},{"id":2,"value":{"id":"age","name":"age","type":"int","nullable":"true"}},{"id":3,"value":{"id":"phone","name":"phone","type":"int","nullable":"true"}},{"id":4,"value":{"id":"email","name":"email","type":"varchar(255)","nullable":"true"}},{"id":5,"value":{"id":"address","name":"address","type":"varchar(255)","nullable":"true"}},{"id":6,"value":{"id":"batch_id","name":"batch_id","type":"int","nullable":"true"}}],"name":"students","id":"students","schema":"db"},"position":{"top":64,"left":64},"id":2,"rowsExpanded":false,"selected":false}],"refs":[{"id":0,"from":{"table":0,"rows":[4]},"to":{"table":1,"rows":[0]},"selected":false},{"id":1,"from":{"table":2,"rows":[6]},"to":{"table":0,"rows":[0]},"selected":false}],"size":{"width":1568,"height":1003},"schema":"db"}
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/media/schema.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/media/schema.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/media/student-batch-er.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/media/student-batch-er.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/media/student-er-full.drawio:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 5Vtbc6o6FP41PrYDBBAf8dLLGXuZ6pmz+9SJEoVuIA7GqvvXnyABgUTrBQR3ZzodskgC+VbWyrfWwgboeKv7AM7sJ2wht6FI1qoBug1FaUky/R8K1pFAl7VIMA0cKxLJW8HA+YOYUGLShWOheaYjwdglziwrHGPfR2OSkcEgwMtstwl2s0+dwSniBIMxdHnpf45F7EhqaNJW/oCcqR0/WZbYHQ/GnZlgbkMLLzMitCJ32CfsFV9R4EEf+YTeeYLBbxQ0tJ5NSLhSs6Hc0b9J2Pt2ivHURXDmzG/H2KPi8Zx2uZtAz3FDmFMTtdlE9HGg1wCdAGMSXXmrDnJDVcVqiN7pbsfdBIcgnPeAAe+a5/ZfvOEHmNro5nPS1DvoBkSzfEF3wfBl2JB1DDiyKP6siQNi4yn2odvbStsBXvgWCh8j0da2Tx/jGRXKVPiJCFmzzQQXBFORTTyX3eWXwlY3x4tgjPa8f7wDYTBFZE8/tqxwLakHMKDuEfYQCda0Q4BcSJyv7F6DbD9Mk35bmOkFQ/oI1LUfgrpaK9Rl+YfAHrvquuD+U5yMXJmXUXtt4C/6b6+K+aFh5/Nx3V/eVIIyWjnkFxseXr+H17caa3VXqVvdddzw6XJ/xROEjdSosLkdtmnF44Rol6xitVJL4gxpMPy323secppe2g5BgxncLHpJiWBWS9B1pj69HlOgKBkB7Ynjuh3s4mAzHFgaMiyVyuckwL9R6o6hjICu7zOnLxQQtNq7/9ldoDJHxahowjGXW2KX0Dc7RericYUDrHAAP3Z5K3JdSnZDazkaZcoWY/tTedQn0GpZmgh1iFQZKMWg3sqC3qwa8+aVnw7qga5Dr9Wh3PohqBu1Ql3lUH82n3qne5icAxnJljWRRA5ElpqghQpy2yDrQYAicCGKwIXoZbkQnYO1bw7ooSgVii51z004FqE7UnVNUstBV9WrRtfg0L17fLtWeOXabd6Y9KTw7b60rwxWJQdr5Zs2jsVSqJr3Z2xWjstZcG5vjj6RH4ZjwwIizCnnVTWrGMzVHH02qmZyMn+89Z7Mx/4e1Oc2nIVCCy9GLuolco+e606INziFZme1gWQazjRF2mjpTQALCmb0XCwjsoCytCEM//msyz8vj88DThmBjb3RYn60Y7EgMiZCx6KPDTSaJLByGAqQ3gmrlnMscovH1RDAapQFa62yWcfmPoQr0sQKOJgRs6Gv2NlUSpjimnnFKTmNRNSdjcopJXmNM/TE05a/QU/ZkEe88uaZCj3PPlpVwBynHePr90Yqz7g/6ZjKM743UjnIQpOO5yn0XAs9S6F8saptDjsPnJaPPD0OzTCedXrozdypLF2QlwrRPCTb5VtmWCinLR/7KAtj1lK2m7iszPm3m7Oc00OXc4pTWrdadpLIvLjzg59Kyx1EzcseRPw59MxzMDR3/sDRpimJ2W0Qbc52aA/OGLomk48wIdhLdMo+u2BzNZIvG74xo917dXckHc1ypqKT8DcegieTOSqHEfCBdiG2d2TV6pQKWYGHDuDtenetqXi7VnJ2DU63ayM3VT6SKptg8tW4pysx7MgSSrbsPN8v0bD5vEMty3aFUhlR3U7EZLTSAmGeGFaTDz4LViMH6yUTl3uit1yR33wbfnTN4bWDWz39VngO8GAOqMDkXXet82J6royflI2qyospdaooF8KU4gV8GwIphlhVl4nPQZ0+a7ws8GAHj7kQ8HX6jPfCwIMqgY9fM828e8/DlzcO/mvISWnVH4o8f+Y38hGBcRzgJkHt99nYIjfxuU5hRz0jl0ZS84mLQ+PWfGGE02vJcavCu61riVuVHV/flhK3rrPN8sNYhf+M6dJmWIOiyOGsqyQ732aaY0tvnWrp/FQXLoIqfDApc3uqprauX97W88FRibYuqApcX/IkT2V0tWoqA/j4/rtPkOoIbD5xUj1HBPxnL39fjjWBOYFd42GXBbCfkGSlze1vfyO3sv29Nuj9Dw==
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/media/student-er.drawio:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 5Zlbc6IwFMc/jY92uGsfVbDtjLSd6l76tJNKhLSBOCFe6KffIImIYV3bdRdnnelMycnJgfzOPycBW+YgXt9QMI98EkDcMrRg3TLdlmHoluHwf7klKyyda6swhBQFwqk0jNE7FEZNWBcogGnFkRGCGZpXjVOSJHDKKjZAKVlV3WYEV+86ByFUDOMpwKr1GwpYVFi7tlbabyEKI3lnXRM9MZDOwpBGICCrigmu2ZAkTDziI6QxSGDCeI8P6BukLduLGMtn2msZQ/43y72vQkJCDMEcpVdTEnPzNOUuwxmIEc4x7wTqi0D8dqbXMgeUEFZcxesBxHmuZBqKZxr+onfLgeZxjxgwaC+z0ZvGktuV+ZX5fvjYeWnrRhFmCfBCABZwWCaJw4AnQDT5vRDLniAGDJHEK3v6MAl6eXq5k/f0DimZEB8kfPb9lAHKyj6SCPch4s9nurp0EW2Nt9W5SakBGkJ2aEIdkcmgIiOB5AaSGDKacYdVKZ6tRKJd4Ugj3Ux2WZUfEBIJtwG393gkaKMYseI6Mo5Yb7pjV0OkZEGnUIzazd9eIMupBjK0vUAFGyUQv9iZeGnayKNeKs92jEcP8eSHGUaw/TrrOAPYNj+mFEJZREKSALyrEkoWSQADkebSZ0TIXGjhFTKWiboDFoxwU8RiqZTa7NZKpeB6YEI1kqr1M+oFdLQuKon4KHX7UqlbTVLX9UvFXmzzjXG/2CKjN1pldLsJzBwmzb6L8ZvGc964smXTXe92ulnldPBv09NsOVJWxXjyxfXuJ0rWVhFicDwHm0mv+BtAlTjAKEz49ZSD4odQiXIJKYPrwzDVuYsBprV3LpFvCr87YclxJ8elnmnvXFXfGPNXllzHH2WWn/nlyrBOw1A3z41h538rxNaRK91pcqFfXyr1bpPULYX6fc/3Pl8xTlFU9wqCadQUBKOmIDh/qyA4CqRRb8w3IO3sWG1flBtj1VVYDe+ezgPW/k7TvLDkVrdDy33on5Wiuo0zUo80vZs/EJJypglAGm22jBMRtM/uQKOrVd7ze3ejAxDTCMxzY0AWLxh6W3vMdzOU4zM/QfoUcPe+BJp243DV3aHfmwxuFbgN0DKuq7ScutV8Ilq8WX7QLz68lr/CmN5P
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/media/student-er.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/media/student-er.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/media/students-table.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/media/students-table.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/media/subset.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/media/subset.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/media/subsets-and.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/media/subsets-and.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/media/type-error.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/media/type-error.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/01-database-fundamentals-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/01-database-fundamentals-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/01-database-fundamentals.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/01-database-fundamentals.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/02-integrity-er-diagram-hw-02.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/02-integrity-er-diagram-hw-02.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/02-integrity-er-diagram-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/02-integrity-er-diagram-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/02-integrity-er-diagram.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/02-integrity-er-diagram.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/02-schema-design-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/02-schema-design-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/02-schema-design.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/02-schema-design.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/03-normalisation-acid-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/03-normalisation-acid-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/03-normalisation-acid.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/03-normalisation-acid.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/03-normalisation-sql-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/03-normalisation-sql-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/03-normalisation-sql.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/03-normalisation-sql.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/04-transactions-indexes-hw-03.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/04-transactions-indexes-hw-03.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/04-transactions-indexes-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/04-transactions-indexes-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/04-transactions-indexes-hw02.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/04-transactions-indexes-hw02.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/04-transactions-indexes.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/04-transactions-indexes.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/05-sql-primer-hw-01.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/05-sql-primer-hw-01.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/05-sql-primer-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/05-sql-primer-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/05-sql-primer-worksheet-answers.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # Queries
3 |
4 | ## Insert queries
5 | 1. Insert a row with all columns
6 | ```sql
7 | INSERT INTO students
8 | VALUES (1, 'Tantia', 'Tope', 't@t.com', '1234567890', 1);
9 | ```
10 |
11 | 2. Insert a row with some columns
12 | ```sql
13 | INSERT INTO students (first_name, last_name)
14 | VALUES ('Tantia', 'Tope');
15 | ```
16 |
17 | ---
18 |
19 | ## Select Queries
20 | 1. Get all students
21 |
22 | ```sql
23 | SELECT *
24 | FROM students;
25 | ```
26 |
27 | 2. Get first and last name of all students
28 |
29 | ```sql
30 | SELECT first_name, last_name
31 | FROM students;
32 | ```
33 |
34 | 3. Get first name of all students with output column name as `Student Name`
35 |
36 | ```sql
37 | SELECT first_name AS "Student Name"
38 | FROM students;
39 | ```
40 | 4. Get all unique addresses of all students
41 |
42 | ```sql
43 | SELECT DISTINCT address FROM students;
44 | ```
45 | 5. Get all students with ID equal to 1
46 |
47 | ```sql
48 | SELECT * FROM students WHERE id = 1;
49 | ```
50 | 6. Get all students with IQ greater than 150
51 |
52 | ```sql
53 | SELECT * FROM students WHERE iq > 150;
54 | ```
55 | 7. Get all students with IQ less than 100
56 |
57 | ```sql
58 | SELECT * FROM students WHERE iq < 100;
59 | ```
60 | 8. Get all students with IQ greater than 100 and less than150
61 |
62 | ```sql
63 | SELECT * FROM students
64 | WHERE iq > 100 AND iq < 150;
65 | ```
66 | 9. Get all students with IQ greater than 100 or less than 150
67 |
68 | ```sql
69 | SELECT * FROM students
70 | WHERE iq BETWEEN 100 AND 150;
71 | ```
72 | 10. Get all students with first name `Tantia`
73 |
74 | ```sql
75 | SELECT * FROM students WHERE first_name = 'Tantia';
76 | ```
77 | 11. Get all students with first name `Tantia` and last name `Tope`
78 |
79 | ```sql
80 | SELECT * FROM students
81 | WHERE first_name = 'Tantia' AND last_name = 'Tope';
82 | ```
83 | 12. Get all students with first name `John` or first name `Mycroft`
84 |
85 | ```sql
86 | SELECT * FROM students
87 | WHERE first_name = 'John' OR first_name = 'Mycroft';
88 | ```
89 | 13. Get all students with name `John Watson` or `Mycroft Holmes`
90 |
91 | ```sql
92 | SELECT * FROM students
93 | WHERE (first_name = 'John' AND last_name = 'Watson')
94 | OR (first_name = 'Mycroft' AND last_name = 'Holmes');
95 | ```
96 | 14. Get all students without the first name `John`
97 |
98 | ```sql
99 | SELECT * FROM students WHERE first_name <> 'John';
100 | ```
101 | 15. Get all students without the first name `John` or last name `Mycroft`
102 |
103 | ```sql
104 | SELECT * FROM students
105 | WHERE first_name <> 'John' AND last_name <> 'Mycroft';
106 | ```
107 | 16. Get all students with first name starting with `T`
108 |
109 | ```sql
110 | SELECT * FROM students WHERE first_name LIKE 'T%';
111 | ```
112 | 17. Get all students with last name ending with `walker`
113 |
114 | ```sql
115 | SELECT * FROM students WHERE last_name LIKE '%walker';
116 | ```
117 | 18. Get all students with first name containing `T`
118 |
119 | ```sql
120 | SELECT * FROM students WHERE first_name LIKE '%T%';
121 | ```
122 | 19. Get all students with last name in the format `___walker`
123 | ```sql
124 | SELECT * FROM students WHERE last_name LIKE '___walker';
125 | ```
126 | 20. Get all students in Jhansi and London
127 |
128 | ```sql
129 | SELECT * FROM students
130 | WHERE address IN ('Jhansi', 'London');
131 | ```
132 | 21. Get all students which do not have a batch id
133 |
134 | ```sql
135 | SELECT * FROM students WHERE batch_id IS NULL;
136 | ```
137 | 22. Get the first 5 students
138 |
139 | ```sql
140 | SELECT * FROM students LIMIT 5;
141 | ```
142 | 23. Get the first 5 students sorted by IQ
143 |
144 |
145 | ```sql
146 | SELECT * FROM students ORDER BY iq LIMIT 5;
147 | ```
148 | 24. Get the first 5 students sorted by IQ in descending order
149 |
150 | ```sql
151 | SELECT * FROM students ORDER BY iq DESC LIMIT 5;
152 | ```
153 | 25. Get the first 5 students sorted by IQ in descending order and then by first name
154 |
155 | ```sql
156 | SELECT * FROM students
157 | ORDER BY iq DESC, first_name LIMIT 5;
158 | ```
159 |
160 | ---
161 |
162 | ## Update Queries
163 |
164 | 1. Update a row
165 |
166 | ```sql
167 | UPDATE students SET first_name = 'Tantia' WHERE id = 1;
168 | ```
169 | 2. Update a row with a condition
170 |
171 | ```sql
172 | UPDATE students SET first_name = 'Tantia' WHERE id = 1 AND first_name = 'John';
173 | ```
174 |
175 | 3. Update multiple columns
176 |
177 | ```sql
178 | UPDATE students SET first_name = 'Tantia', last_name = 'Tope' WHERE id = 1 AND first_name = 'John';
179 | ```
180 |
181 | ## Delete Queries
182 |
183 | 1. Delete a row with a condition
184 |
185 | ```sql
186 | DELETE FROM students
187 | WHERE id = 1 AND first_name = 'John';
188 | ```
189 |
190 | 2. Delete a multiple rows
191 |
192 | ```sql
193 | DELETE FROM students WHERE id IN (1, 2, 3);
194 | ```
195 |
196 | ## Joining Queries
197 |
198 | 1. Get first name and last name of all students and their batch names
199 |
200 | ```sql
201 | SELECT students.first_name, students.last_name, batches.name FROM students JOIN batches ON students.batch_id = batches.id;
202 | ```
203 | 2. Get first name and last name of all students and their instructor names
204 |
205 | ```sql
206 | SELECT s.first_name, s.last_name, i.first_name, b.name, i.last_name
207 | FROM students s
208 | JOIN batches b ON s.batch_id = b.id
209 | JOIN instructors i ON b.instructor_id = i.id;
210 | ```
211 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/05-sql-primer-worksheet.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # Queries
3 |
4 | ## Insert queries
5 | 1. Insert a row with your name and all the other fields in **students** table
6 | ```sql
7 |
8 | ```
9 |
10 | 2. Insert a row with just mandatory fields in **students** table
11 | ```sql
12 |
13 | ```
14 |
15 | ---
16 |
17 | ## Select Queries
18 | 1. Get all students
19 |
20 | ```sql
21 |
22 | ```
23 |
24 | 2. Get first and last name of all students
25 |
26 | ```sql
27 |
28 | ```
29 |
30 | 3. Get first name of all students with output column name as `Student Name`
31 |
32 | ```sql
33 |
34 | ```
35 | 4. Get all unique addresses of all students
36 |
37 | ```sql
38 |
39 | ```
40 | 5. Get all students with ID equal to 1
41 |
42 | ```sql
43 |
44 | ```
45 | 6. Get all students with IQ greater than 150
46 |
47 | ```sql
48 |
49 | ```
50 | 7. Get all students with IQ less than 100
51 |
52 | ```sql
53 |
54 | ```
55 | 8. Get all students with IQ greater than 100 and less than150
56 |
57 | ```sql
58 |
59 | ```
60 | 9. Get all students with IQ greater than 100 or less than 150
61 |
62 | ```sql
63 |
64 | ```
65 | 10. Get all students with first name `Tantia`
66 |
67 | ```sql
68 |
69 | ```
70 | 11. Get all students with first name `Tantia` and last name `Tope`
71 |
72 | ```sql
73 |
74 | ```
75 | 12. Get all students with first name `John` or first name `Mycroft`
76 |
77 | ```sql
78 |
79 | ```
80 | 13. Get all students with name `John Watson` or `Mycroft Holmes`
81 |
82 | ```sql
83 |
84 | ```
85 | 14. Get all students without the first name `John`
86 |
87 | ```sql
88 |
89 | ```
90 | 15. Get all students without the first name `John` or first name `Mycroft`
91 |
92 | ```sql
93 |
94 | ```
95 | 16. Get all students with first name starting with `T`
96 |
97 | ```sql
98 |
99 | ```
100 | 17. Get all students with last name ending with `walker`
101 |
102 | ```sql
103 |
104 | ```
105 | 18. Get all students with first name containing `T`
106 |
107 | ```sql
108 |
109 | ```
110 | 19. Get all students with last name in the format `___walker`
111 | ```sql
112 |
113 | ```
114 | 20. Get all students from Jhansi and London
115 |
116 | ```sql
117 |
118 | ```
119 | 21. Get all students which do not have a batch id
120 |
121 | ```sql
122 |
123 | ```
124 | 22. Get the first 5 students
125 |
126 | ```sql
127 |
128 | ```
129 | 23. Get the first 5 students sorted by IQ
130 |
131 |
132 | ```sql
133 |
134 | ```
135 | 24. Get the first 5 students sorted by IQ in descending order
136 |
137 | ```sql
138 |
139 | ```
140 | 25. Get the first 5 students sorted by IQ in descending order and then by first name
141 |
142 | ```sql
143 |
144 | ```
145 |
146 | ---
147 |
148 | ## Update Queries
149 |
150 | 1. Update a row
151 |
152 | ```sql
153 |
154 | ```
155 | 2. Update a row with a condition
156 |
157 | ```sql
158 |
159 | ```
160 |
161 | 3. Update multiple columns
162 |
163 | ```sql
164 |
165 | ```
166 |
167 | ## Delete Queries
168 |
169 | 1. Delete a row with a condition
170 |
171 | ```sql
172 |
173 | ```
174 |
175 | 2. Delete multiple rows
176 |
177 | ```sql
178 |
179 | ```
180 |
181 | ## Joining Queries
182 |
183 | 1. Get first name and last name of all students and their batch names
184 |
185 | ```sql
186 |
187 | ```
188 | 2. Get first name and last name of all students and their instructor names
189 |
190 | ```sql
191 | ```
192 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/05-sql-primer.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/05-sql-primer.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/06-sql-joins-aggregation-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/06-sql-joins-aggregation-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/06-sql-joins-aggregation-hw02.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/06-sql-joins-aggregation-hw02.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/06-sql-joins-aggregation-worksheet-answers.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Queries
2 |
3 | ## Joins
4 |
5 | 1. Get all batch names along with their instructor names.
6 |
7 | ```sql
8 | SELECT
9 | b.name, i.first_name, i.last_name
10 | FROM
11 | batches b
12 | JOIN
13 | instructors i ON b.instructor_id = i.id;
14 | ```
15 |
16 | 2. Get all students along with their batch names if present else `NULL`.
17 |
18 | ```sql
19 | SELECT
20 | s.first_name, s.last_name, b.name
21 | FROM
22 | students s
23 | LEFT JOIN
24 | batches b ON s.batch_id = b.id;
25 | ```
26 | 3. Get all students along with their batch names. Also, fetch all the batches which have no students.
27 |
28 | ```sql
29 | SELECT
30 | s.first_name, s.last_name, b.name
31 | FROM
32 | students s
33 | RIGHT JOIN
34 | batches b ON s.batch_id = b.id
35 | ```
36 | 4. Get all the combinations of batches and instructors.
37 |
38 | ```sql
39 | SELECT
40 | b.name, i.first_name, i.last_name
41 | FROM
42 | batches b, instructors i
43 | ```
44 | 5. Get all students with their instructors. If a student has no instructor, then show `NULL` for the instructor's name.
45 |
46 | ```sql
47 | SELECT
48 | s.first_name, s.last_name, i.first_name, i.last_name
49 | FROM
50 | students s
51 | LEFT JOIN
52 | batches b ON s.batch_id = b.id
53 | LEFT JOIN
54 | instructors i ON b.instructor_id = i.id;
55 | ```
56 |
57 | ## Aggregation
58 | 1. Get the maximum IQ in all students (Try without aggregation first).
59 |
60 | ```sql
61 | SELECT
62 | first_name, iq
63 | FROM
64 | students
65 | ORDER BY iq DESC
66 | LIMIT 1;
67 | ```
68 |
69 | 2. Get the maximum IQ in all students (With aggregation).
70 |
71 | ```sql
72 | SELECT
73 | MAX(IQ) AS 'IQ'
74 | FROM
75 | students;
76 | ```
77 |
78 | 3. Get the oldest batch from the batches table.
79 |
80 | ```sql
81 | SELECT
82 | MIN(start_date) AS 'start date'
83 | FROM
84 | batches;
85 | ```
86 |
87 | 4. Fetch the number of batches that start with the word `Jedi`.
88 |
89 | ```sql
90 | SELECT
91 | COUNT(id)
92 | FROM
93 | batches
94 | WHERE
95 | name LIKE 'Jedi%';
96 | ```
97 |
98 | 5. Get the average IQ of all students (Without using `AVG`)
99 |
100 | ```sql
101 | SELECT
102 | SUM(iq) / COUNT(iq) as 'Average IQ'
103 | FROM
104 | students;
105 | ```
106 |
107 | 6. Get the average IQ of students in all batches.
108 |
109 | ```sql
110 | SELECT
111 | AVG(IQ) AS 'IQ'
112 | FROM
113 | students
114 | WHERE
115 | batch_id IS NOT NULL;
116 | ```
117 | 7. Find the average IQ of students in each batch.
118 |
119 | ```sql
120 | SELECT
121 | batch_id, AVG(iq)
122 | FROM
123 | students
124 | GROUP BY batch_id;
125 | ```
126 |
127 | 8. Find the total number of students in each batch.
128 |
129 | ```sql
130 | SELECT
131 | b.name, COUNT(s.id)
132 | FROM
133 | batches b
134 | LEFT JOIN
135 | students s ON b.id = s.batch_id
136 | GROUP BY b.id;
137 | ```
138 |
139 | 9. Get the total number of batches taught by each instructor.
140 |
141 | ```sql
142 | SELECT
143 | i.first_name, COUNT(b.id)
144 | FROM
145 | instructors i
146 | LEFT JOIN
147 | batches b ON i.id = b.instructor_id
148 | GROUP BY i.id;
149 | ```
150 |
151 | 10. Find the average IQ of students in batches with batch ID `1` and `2`.
152 |
153 | ```sql
154 | SELECT
155 | batch_id, AVG(iq)
156 | FROM
157 | students
158 | WHERE batch_id IN (1, 2)
159 | GROUP BY batch_id;
160 | ```
161 |
162 | 11. Find count of students that are part of batches that have average IQ greater than `120`.
163 |
164 | ```sql
165 | SELECT
166 | batch_id, AVG(iq) as avg_iq, COUNT(iq)
167 | FROM
168 | students
169 | GROUP BY batch_id
170 | HAVING avg_iq > 130;
171 | ```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/06-sql-joins-aggregation-worksheet.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Queries
2 |
3 | ## Joins
4 |
5 | 1. Get all batch names along with their instructor names.
6 |
7 | ```sql
8 | ```
9 |
10 | 2. Get all students along with their batch names if present else `NULL`.
11 |
12 | ```sql
13 | ```
14 | 3. Get all students along with their batch names. Also, fetch all the batches which have no students.
15 |
16 | ```sql
17 | ```
18 | 4. Get all the combinations of batches and instructors.
19 |
20 | ```sql
21 | ```
22 | 5. Get all students with their instructors. If a student has no instructor, then show `NULL` for the instructor's name.
23 |
24 | ```sql
25 | ```
26 |
27 | ## Aggregation
28 | 1. Get the maximum IQ in all students (Try without aggregation first).
29 |
30 | ```sql
31 | ```
32 |
33 | 2. Get the maximum IQ in all students (With aggregation).
34 |
35 | ```sql
36 | ```
37 |
38 | 3. Get the oldest batch from the batches table.
39 |
40 | ```sql
41 | ```
42 |
43 | 4. Fetch the number of batches that start with the word `Jedi`.
44 |
45 | ```sql
46 | ```
47 |
48 | 5. Get the average IQ of all students (Without using `AVG`)
49 |
50 | ```sql
51 | ```
52 |
53 | 6. Get the average IQ of students in all batches.
54 |
55 | ```sql
56 | ```
57 | 7. Find the average IQ of students in each batch.
58 |
59 | ```sql
60 | ```
61 |
62 | 8. Find the total number of students in each batch.
63 |
64 | ```sql
65 | ```
66 |
67 | 9. Get the total number of batches taught by each instructor.
68 |
69 | ```sql
70 | ```
71 |
72 | 10. Find the average IQ of students in batches with batch ID `1` and `2`.
73 |
74 | ```sql
75 | ```
76 |
77 | 11. Find count of students that are part of batches that have average IQ greater than `120`.
78 |
79 | ```sql
80 | ```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/06-sql-joins-aggregation.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/06-sql-joins-aggregation.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/07-groupby-functions-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/07-groupby-functions-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/07-groupby-functions-worksheet-answers.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Queries
2 |
3 | ## Aggregation
4 | 1. Get the maximum IQ in all students (Try without aggregation first).
5 |
6 | ```sql
7 | SELECT
8 | first_name, iq
9 | FROM
10 | students
11 | ORDER BY iq DESC
12 | LIMIT 1;
13 | ```
14 |
15 | 2. Get the maximum IQ in all students (With aggregation).
16 |
17 | ```sql
18 | SELECT
19 | MAX(IQ) AS 'IQ'
20 | FROM
21 | students;
22 | ```
23 |
24 | 3. Get the oldest batch from the batches table.
25 |
26 | ```sql
27 | SELECT
28 | MIN(start_date) AS 'start date'
29 | FROM
30 | batches;
31 | ```
32 |
33 | 4. Fetch the number of batches that start with the word `Jedi`.
34 |
35 | ```sql
36 | SELECT
37 | COUNT(id)
38 | FROM
39 | batches
40 | WHERE
41 | name LIKE 'Jedi%';
42 | ```
43 |
44 | 5. Get the average IQ of all students (Without using `AVG`)
45 |
46 | ```sql
47 | SELECT
48 | SUM(iq) / COUNT(iq) as 'Average IQ'
49 | FROM
50 | students;
51 | ```
52 |
53 | 6. Get the average IQ of students in all batches.
54 |
55 | ```sql
56 | SELECT
57 | AVG(IQ) AS 'IQ'
58 | FROM
59 | students
60 | WHERE
61 | batch_id IS NOT NULL;
62 | ```
63 | 7. Find the average IQ of students in each batch.
64 |
65 | ```sql
66 | SELECT
67 | batch_id, AVG(iq)
68 | FROM
69 | students
70 | GROUP BY batch_id;
71 | ```
72 |
73 | 8. Find the total number of students in each batch.
74 |
75 | ```sql
76 | SELECT
77 | b.name, COUNT(s.id)
78 | FROM
79 | batches b
80 | LEFT JOIN
81 | students s ON b.id = s.batch_id
82 | GROUP BY b.id;
83 | ```
84 |
85 | 9. Get the total number of batches taught by each instructor.
86 |
87 | ```sql
88 | SELECT
89 | i.first_name, COUNT(b.id)
90 | FROM
91 | instructors i
92 | LEFT JOIN
93 | batches b ON i.id = b.instructor_id
94 | GROUP BY i.id;
95 | ```
96 |
97 | 10. Find the average IQ of students in batches with batch ID `1` and `2`.
98 |
99 | ```sql
100 | SELECT
101 | batch_id, AVG(iq)
102 | FROM
103 | students
104 | WHERE batch_id IN (1, 2)
105 | GROUP BY batch_id;
106 | ```
107 |
108 | 11. Find count of students that are part of batches that have average IQ greater than `120`.
109 |
110 | ```sql
111 | SELECT
112 | batch_id, AVG(iq) as avg_iq, COUNT(iq)
113 | FROM
114 | students
115 | GROUP BY batch_id
116 | HAVING avg_iq > 130;
117 | ```
118 |
119 | ## Built-in Functions
120 | 1. Get the average IQ of all the students rounded to the nearest integer.
121 |
122 | ```sql
123 | SELECT
124 | ROUND(AVG(iq))
125 | FROM
126 | students;
127 | ```
128 | 2. Find all batches whose name is longer than 10 characters.
129 |
130 | ```sql
131 | SELECT
132 | id, name
133 | FROM
134 | batches
135 | WHERE
136 | LENGTH(name) > 10;
137 | ```
138 |
139 | 3. Find all batches whose name's first 10 characters contains the string `sher`
140 |
141 | ```sql
142 | SELECT
143 | id, name
144 | FROM
145 | batches
146 | WHERE
147 | LOCATE('sher', SUBSTR(name, 1, 10)) > 0;
148 | ```
149 |
150 | 4. Get all batches that have started on a Sunday
151 |
152 | ```sql
153 | SELECT
154 | id, name
155 | FROM
156 | batches
157 | WHERE
158 | DAYNAME(start_date) = 'Sunday';
159 | ```
160 |
161 | 5. Get all batches that have been running for more than 10 years
162 |
163 | ```sql
164 | SELECT
165 | id, name, start_date
166 | FROM
167 | batches
168 | WHERE
169 | (DATEDIFF(NOW(), start_date) / 365) > 10;
170 | ```
171 | 6. Print the name and the instructor's id for each batch. If no instructor is assigned, print `NO INSTRUCTOR`.
172 |
173 | ```sql
174 | SELECT
175 | name, IFNULL(instructor_id, 'NO INSTRUCTOR')
176 | FROM
177 | batches;
178 | ```
179 |
180 | 7. Print the name and IQ of each student. If the IQ of the student is less than 100, print `LOW IQ` instead.
181 |
182 | ```sql
183 | SELECT
184 | first_name, last_name, IF(iq < 100, 'LOW IQ', iq)
185 | FROM
186 | students;
187 | ```
188 |
189 | 8. For each student print the name and their IQ category.
190 |
191 | | IQ | Category |
192 | | --------- | -------- |
193 | | < 100 | LOW IQ |
194 | | 100 - 150 | MEDIUM |
195 | | > 150 | HIGH |
196 |
197 | ```sql
198 | SELECT
199 | first_name,
200 | last_name,
201 | CASE
202 | WHEN iq > 150 THEN 'HIGH IQ'
203 | WHEN iq BETWEEN 100 AND 150 THEN 'MEDIUM IQ'
204 | ELSE 'LOW IQ'
205 | END
206 | FROM
207 | students;
208 | ```
209 |
210 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/07-groupby-functions-worksheet.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Queries
2 |
3 | ## Aggregation
4 | 1. Get the maximum IQ in all students (Try without aggregation first).
5 |
6 | ```sql
7 | ```
8 |
9 | 2. Get the maximum IQ in all students (With aggregation).
10 |
11 | ```sql
12 | ```
13 |
14 | 3. Get the oldest batch from the batches table.
15 |
16 | ```sql
17 | ```
18 |
19 | 4. Fetch the number of batches that start with the word `Jedi`.
20 |
21 | ```sql
22 | ```
23 |
24 | 5. Get the average IQ of all students (Without using `AVG`)
25 |
26 | ```sql
27 | ```
28 |
29 | 6. Get the average IQ of students in all batches.
30 |
31 | ```sql
32 | ```
33 | 7. Find the average IQ of students in each batch.
34 |
35 | ```sql
36 | ```
37 |
38 | 8. Find the total number of students in each batch.
39 |
40 | ```sql
41 | ```
42 |
43 | 9. Get the total number of batches taught by each instructor.
44 |
45 | ```sql
46 | ```
47 |
48 | 10. Find the average IQ of students in batches with batch ID `1` and `2`.
49 |
50 | ```sql
51 | ```
52 |
53 | 11. Find count of students that are part of batches that have average IQ greater than `120`.
54 |
55 | ```sql
56 | ```
57 |
58 | ## Built-in Functions
59 | 1. Get the average IQ of all the students rounded to the nearest integer.
60 |
61 | ```sql
62 |
63 | ```
64 | 2. Find all batches whose name is longer than 10 characters.
65 |
66 | ```sql
67 |
68 | ```
69 |
70 | 3. Find all batches whose name's first 10 characters contains the string `sher`
71 |
72 | ```sql
73 |
74 | ```
75 |
76 | 4. Get all batches that have started on a Sunday
77 |
78 | ```sql
79 |
80 | ```
81 |
82 | 5. Get all batches that have been running for more than 10 years
83 |
84 | ```sql
85 |
86 | ```
87 | 6. Print the name and the instructor's id for each batch. If no instructor is assigned, print `NO INSTRUCTOR`.
88 |
89 | ```sql
90 |
91 | ```
92 |
93 | 7. Print the name and IQ of each student. If the IQ of the student is less than 100, print `LOW IQ` instead.
94 |
95 | ```sql
96 |
97 | ```
98 |
99 | 8. For each student print the name and their IQ category.
100 |
101 | | IQ | Category |
102 | | --------- | -------- |
103 | | < 100 | LOW IQ |
104 | | 100 - 150 | MEDIUM |
105 | | > 150 | HIGH |
106 |
107 | ```sql
108 |
109 | ```
110 |
111 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/07-groupby-functions.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Group by and built-in functions
2 |
3 | - [Group by and built-in functions](#group-by-and-built-in-functions)
4 | - [GROUP BY clause](#group-by-clause)
5 | - [Problems](#problems)
6 | - [MySQL functions](#mysql-functions)
7 | - [Numeric functions](#numeric-functions)
8 | - [String functions](#string-functions)
9 | - [Date and time functions](#date-and-time-functions)
10 | - [Miscellaneous functions](#miscellaneous-functions)
11 |
12 |
13 | ## GROUP BY clause
14 |
15 | The GROUP BY clause groups a set of rows into a set of summary rows by values of columns or expressions. The GROUP BY clause returns one row for each group. In other words, it reduces the number of rows in the result set
16 |
17 | **Keyword**: `GROUP BY`
18 | **Syntax**: `SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name GROUP BY column1, column2, ...`
19 |
20 | In this syntax, you place the GROUP BY clause after the FROM and WHERE clauses. After the GROUP BY keywords, you place is a list of comma-separated columns or expressions to group rows.
21 |
22 | > MySQL evaluates the GROUP BY clause after the FROM and WHERE clauses and before the HAVING, SELECT, DISTINCT, ORDER BY and LIMIT clauses
23 |
24 | 
25 |
26 | Fields that are not encapsulated within an aggregate function and must be included in the GROUP BY Clause at the end of the SQL statement.
27 |
28 | For example, the following query will return the number of students in each batch:
29 |
30 | ```sql
31 | SELECT
32 | batch_id, AVG(iq)
33 | FROM
34 | students
35 | GROUP BY batch_id;
36 | ```
37 |
38 | You can also use the `HAVING` clause to filter the result set.
39 | For example, the following query will return the number of students in each batch where each batches average IQ is greater than or equal to 100:
40 | ```sql
41 | SELECT
42 | batch_id, AVG(iq)
43 | FROM
44 | students
45 | GROUP BY batch_id
46 | HAVING AVG(iq) >= 100;
47 | ```
48 |
49 | ### Problems
50 | 1. [Aggregation - I](https://leetcode.com/problems/duplicate-emails/)
51 | 2. [Aggregation - II](https://leetcode.com/problems/customer-placing-the-largest-number-of-orders/)
52 | 3. [Aggregation - III](https://leetcode.com/problems/classes-more-than-5-students/)
53 |
54 | ---
55 |
56 | ## MySQL functions
57 |
58 | MySQL has a number of built-in functions that can be used to perform common tasks.
59 | They are divided in the following categories:
60 | 1. Numeric
61 | 2. String
62 | 3. Date and time
63 | 4. Miscellaneous
64 |
65 |
66 | ## Numeric functions
67 |
68 | | Function | Description | Example |
69 | | -------- | --------------------------------- | ------------------------ |
70 | | ABS | Absolute value | SELECT ABS(-1) |
71 | | CEIL | Round up to the nearest integer | SELECT CEIL(1.5) |
72 | | FLOOR | Round down to the nearest integer | SELECT FLOOR(1.5) |
73 | | ROUND | Round to the given precision | SELECT ROUND(1.54, 1) |
74 | | TRUNCATE | Truncate to the given precision | SELECT TRUNCATE(1.54, 1) |
75 | | RAND | Generate a random number | SELECT RAND() |
76 |
77 | See more function [here](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/numeric-functions.html).
78 |
79 | ## String functions
80 |
81 | | Function | Description | Example |
82 | | -------- | -------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------- |
83 | | LENGTH | Length of the string | SELECT LENGTH('Kattapa') |
84 | | LOWER | Convert to lowercase | SELECT LOWER('Kattapa') |
85 | | UPPER | Convert to uppercase | SELECT UPPER('Kattapa') |
86 | | LTRIM | Trim leading spaces | SELECT LTRIM(' Kattapa') |
87 | | RTRIM | Trim trailing spaces | SELECT RTRIM('Kattapa ') |
88 | | TRIM | Trim leading and trailing spaces | SELECT TRIM(' Kattapa ') |
89 | | SUBSTR | Extract a substring | SELECT SUBSTR('Namma Bengaluru', 1, 3) |
90 | | LEFT | Extract left substring | SELECT LEFT('Namma Bengaluru', 3) |
91 | | RIGHT | Extract right substring | SELECT RIGHT('Namma Bengaluru', 3) |
92 | | LOCATE | Find the position of a substring | SELECT LOCATE('Bengaluru', 'Namma Bengaluru') |
93 |
94 | See more function [here](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/string-functions.html).
95 |
96 | ## Date and time functions
97 |
98 | | Function | Description | Example |
99 | | --------- | ---------------------------- | --------------------------------------------- |
100 | | NOW | Current date and time | SELECT NOW() |
101 | | CURDATE | Current date | SELECT CURDATE() |
102 | | CURTIME | Current time | SELECT CURTIME() |
103 | | YEAR | Year of the date | SELECT YEAR('2020-01-01') |
104 | | MONTH | Month of the date | SELECT MONTH('2020-01-01') |
105 | | DAY | Day of the date | SELECT DAY('2020-01-01') |
106 | | DAYNAME | Day of the week | SELECT DAYNAME('2020-01-01') |
107 | | DAYOFWEEK | Day of the week | SELECT DAYOFWEEK('2020-01-01') |
108 | | DATE_ADD | Add a date | SELECT DATE_ADD('2020-01-01', INTERVAL 1 DAY) |
109 | | DATE_SUB | Subtract a date | SELECT DATE_SUB('2020-01-01', INTERVAL 1 DAY) |
110 | | DATEDIFF | Difference between two dates | SELECT DATEDIFF('2020-01-01', '2020-01-02') |
111 |
112 | ## Miscellaneous functions
113 |
114 | | Function | Description | Example |
115 | | -------- | ------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------ |
116 | | IFNULL | Replace NULL values | SELECT IFNULL(batch_id, 'NO BATCH') |
117 | | COALESCE | Replace NULL values recursively | SELECT COALESCE(batch_id, phone, email, first_name) |
118 | | IF | Conditional expression | SELECT IF(batch_id = 1, 'YES', 'NO') |
119 | | CASE | Conditional expression | SELECT CASE WHEN batch_id = 1 THEN 'YES' ELSE 'NO' END |
120 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/07-groupby-functions.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/07-groupby-functions.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/07-subqueries-functions-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/07-subqueries-functions-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/07-subqueries-functions-worksheet-answers.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Queries
2 |
3 | ## Sub-queries
4 |
5 | 1. Get all the students whose IQ is greater than the average IQ.
6 |
7 | ```sql
8 | SELECT
9 | first_name, last_name, iq
10 | FROM
11 | students
12 | WHERE
13 | iq > (SELECT
14 | AVG(iq)
15 | FROM
16 | students);
17 | ```
18 |
19 | 2. Get all the students whose IQ is greater than the highest IQ of the batch_id `2` students.
20 |
21 | ```sql
22 | SELECT
23 | *
24 | FROM
25 | students
26 | WHERE
27 | iq > (SELECT
28 | MAX(iq)
29 | FROM
30 | students
31 | WHERE
32 | batch_id = 2);
33 | ```
34 |
35 | 3. Get all the students whose IQ is greater than `all` the IQs of the batch_id `2` students.
36 |
37 | ```sql
38 | SELECT
39 | *
40 | FROM
41 | students
42 | WHERE
43 | iq > ALL (SELECT
44 | iq
45 | FROM
46 | students
47 | WHERE
48 | batch_id = 2);
49 | ```
50 |
51 | 4. Find all the students who are in batches that start with the word `Jedi` (Without JOIN)
52 |
53 | ```sql
54 | SELECT
55 | *
56 | FROM
57 | students
58 | WHERE
59 | batch_id IN (SELECT
60 | id
61 | FROM
62 | batches
63 | WHERE
64 | name LIKE 'Jedi%');
65 | ```
66 |
67 | 5. Find all the students whose IQ is greater than the average IQ of their batch.
68 |
69 | ```sql
70 | SELECT
71 | *
72 | FROM
73 | students;
74 |
75 | SELECT
76 | first_name, last_name, batch_id, iq
77 | FROM
78 | students s
79 | WHERE
80 | s.iq > (SELECT
81 | AVG(iq)
82 | FROM
83 | students e
84 | WHERE
85 | e.batch_id = s.batch_id);
86 | ```
87 |
88 | 6. Get all the instructors that have at least one batch (Without using joins)
89 |
90 | ```sql
91 | SELECT
92 | *
93 | FROM
94 | instructors i
95 | WHERE
96 | EXISTS( SELECT
97 | id
98 | FROM
99 | batches
100 | WHERE
101 | instructor_id = i.id);
102 | ```
103 |
104 | 7. Print all the names, batch ID and average IQ of the batch for each student
105 |
106 | ```sql
107 | SELECT
108 | id,
109 | first_name,
110 | last_name,
111 | iq,
112 | batch_id,
113 | (SELECT
114 | AVG(iq)
115 | FROM
116 | students
117 | WHERE batch_id = s.batch_id
118 | )
119 | FROM
120 | students s;
121 | ```
122 |
123 | ## Built-in Functions
124 | 1. Get the average IQ of all the students rounded to the nearest integer.
125 |
126 | ```sql
127 | SELECT
128 | ROUND(AVG(iq))
129 | FROM
130 | students;
131 | ```
132 | 2. Find all batches whose name is longer than 10 characters.
133 |
134 | ```sql
135 | SELECT
136 | id, name
137 | FROM
138 | batches
139 | WHERE
140 | LENGTH(name) > 10;
141 | ```
142 |
143 | 3. Find all batches whose name's first 10 characters contains the string `sher`
144 |
145 | ```sql
146 | SELECT
147 | id, name
148 | FROM
149 | batches
150 | WHERE
151 | LOCATE('sher', SUBSTR(name, 1, 10)) > 0;
152 | ```
153 |
154 | 4. Get all batches that have started on a Sunday
155 |
156 | ```sql
157 | SELECT
158 | id, name
159 | FROM
160 | batches
161 | WHERE
162 | DAYNAME(start_date) = 'Sunday';
163 | ```
164 |
165 | 5. Get all batches that have been running for more than 10 years
166 |
167 | ```sql
168 | SELECT
169 | id, name, start_date
170 | FROM
171 | batches
172 | WHERE
173 | (DATEDIFF(NOW(), start_date) / 365) > 10;
174 | ```
175 | 6. Print the name and the instructor's id for each batch. If no instructor is assigned, print `NO INSTRUCTOR`.
176 |
177 | ```sql
178 | SELECT
179 | name, IFNULL(instructor_id, 'NO INSTRUCTOR')
180 | FROM
181 | batches;
182 | ```
183 |
184 | 7. Print the name and IQ of each student. If the IQ of the student is less than 100, print `LOW IQ` instead.
185 |
186 | ```sql
187 | SELECT
188 | first_name, last_name, IF(iq < 100, 'LOW IQ', iq)
189 | FROM
190 | students;
191 | ```
192 |
193 | 8. For each student print the name and their IQ category.
194 |
195 | | IQ | Category |
196 | | --------- | -------- |
197 | | < 100 | LOW IQ |
198 | | 100 - 150 | MEDIUM |
199 | | > 150 | HIGH |
200 |
201 | ```sql
202 | SELECT
203 | first_name,
204 | last_name,
205 | CASE
206 | WHEN iq > 150 THEN 'HIGH IQ'
207 | WHEN iq BETWEEN 100 AND 150 THEN 'MEDIUM IQ'
208 | ELSE 'LOW IQ'
209 | END
210 | FROM
211 | students;
212 | ```
213 |
214 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/07-subqueries-functions-worksheet.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Queries
2 |
3 | ## Sub-queries
4 |
5 | 1. Get all the students whose IQ is greater than the average IQ.
6 |
7 | ```sql
8 |
9 | ```
10 |
11 | 2. Get all the students whose IQ is greater than the highest IQ of the batch_id `2` students.
12 |
13 | ```sql
14 |
15 | ```
16 |
17 | 3. Get all the students whose IQ is greater than `all` the IQs of the batch_id `2` students.
18 |
19 | ```sql
20 |
21 | ```
22 |
23 | 4. Find all the students who are in batches that start with the word `Jedi` (Without JOIN)
24 |
25 | ```sql
26 |
27 | ```
28 |
29 | 5. Find all the students whose IQ is greater than the average IQ of their batch.
30 |
31 | ```sql
32 |
33 | ```
34 |
35 | 6. Get all the instructors that have at least one batch (Without using joins)
36 |
37 | ```sql
38 |
39 | ```
40 |
41 | 7. Print all the names, batch ID and average IQ of the batch for each student
42 |
43 | ```sql
44 |
45 | ```
46 |
47 | ## Built-in Functions
48 | 1. Get the average IQ of all the students rounded to the nearest integer.
49 |
50 | ```sql
51 |
52 | ```
53 | 2. Find all batches whose name is longer than 10 characters.
54 |
55 | ```sql
56 |
57 | ```
58 |
59 | 3. Find all batches whose name's first 10 characters contains the string `sher`
60 |
61 | ```sql
62 |
63 | ```
64 |
65 | 4. Get all batches that have started on a Sunday
66 |
67 | ```sql
68 |
69 | ```
70 |
71 | 5. Get all batches that have been running for more than 10 years
72 |
73 | ```sql
74 |
75 | ```
76 | 6. Print the name and the instructor's id for each batch. If no instructor is assigned, print `NO INSTRUCTOR`.
77 |
78 | ```sql
79 |
80 | ```
81 |
82 | 7. Print the name and IQ of each student. If the IQ of the student is less than 100, print `LOW IQ` instead.
83 |
84 | ```sql
85 |
86 | ```
87 |
88 | 8. For each student print the name and their IQ category.
89 |
90 | | IQ | Category |
91 | | --------- | -------- |
92 | | < 100 | LOW IQ |
93 | | 100 - 150 | MEDIUM |
94 | | > 150 | HIGH |
95 |
96 | ```sql
97 |
98 | ```
99 |
100 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/07-subqueries-functions.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Sub-queries and Views
2 |
3 | ## Agenda
4 | * Sub-queries
5 | * Built-in string functions
6 |
7 | ## Sub-queries
8 |
9 | > A subquery is a SQL query nested inside a larger query.
10 | > A subquery is used to return data that will be used in the main query as a condition to further restrict the data to be retrieved.
11 |
12 |
13 | You can use a sub-query in a SELECT, INSERT, DELETE, or UPDATE statement to perform the following tasks:
14 |
15 | * Compare an expression to the result of the query.
16 | * Determine if an expression is included in the results of the query.
17 | * Check whether the query selects any rows.
18 |
19 | A sub-query may occur in :
20 | * A SELECT clause
21 | * A FROM clause
22 | * A WHERE clause
23 |
24 | There are a few rules that sub-queries must follow −
25 |
26 | * Sub-queries must be enclosed within parentheses.
27 | * A sub-query can have only one column in the SELECT clause, unless multiple columns are in the main query for the sub-query to compare its selected columns.
28 | * An ORDER BY command cannot be used in a subquery, although the main query can use an ORDER BY.
29 | * Sub-queries that return more than one row can only be used with multiple value operators such as the IN operator.
30 | * The BETWEEN operator cannot be used with a subquery. However, the BETWEEN operator can be used within the subquery.
31 |
32 | Let us consider the `students` table below
33 |
34 | | id | first_name | last_name | batch_id | iq |
35 | | --- | ---------- | --------- | -------- | --- |
36 | | 1 | John | Watson | 1 | 120 |
37 | | 2 | Mycroft | Holmes | 1 | 160 |
38 | | 3 | Moriarty | Patel | 2 | 160 |
39 |
40 |
41 | Now, we want all the students who are greater than the average IQ.
42 | We can compute the average IQ using the `AVG` function but the aggregated value can not be used within the WHERE clause. So, let us try to use a sub-query.
43 |
44 | ```sql
45 | SELECT
46 | first_name, last_name, iq
47 | FROM
48 | students
49 | WHERE
50 | iq > (SELECT
51 | AVG(iq)
52 | FROM
53 | students);
54 | ```
55 |
56 | This would first compute the average IQ of all the students and then compare the average IQ to the IQ of the current student. Since the sub-query returns a single value, it can be used in the WHERE clause without any special handling.
57 |
58 | Let us modify the original query to see an example where the sub-query returns multiple values.
59 | We want all the students who have IQs greater than the students of batch_id 2;
60 |
61 | One way to handle this query is to use the MAX function to get the highest IQ of the batch_id 2 students.
62 |
63 | ```sql
64 | SELECT
65 | *
66 | FROM
67 | students
68 | WHERE
69 | iq > (SELECT
70 | MAX(iq)
71 | FROM
72 | students
73 | WHERE
74 | batch_id = 2);
75 | ```
76 |
77 | Another way would be to use the `ALL` keyword. ALL means that the condition will be true only if the operation is true for all values in the range.
78 |
79 | ```sql
80 | SELECT
81 | *
82 | FROM
83 | students
84 | WHERE
85 | iq > ALL (SELECT
86 | iq
87 | FROM
88 | students
89 | WHERE
90 | batch_id = 2);
91 | ```
92 |
93 | ### Correlated Sub-queries
94 |
95 | > A correlated subquery (also known as a synchronized subquery) is a subquery (a query nested inside another query) that uses values from the outer query. Because the subquery may be evaluated once for each row processed by the outer query, it can be slow.
96 |
97 |
98 | > Correlated subqueries are used for row-by-row processing. Each subquery is executed once for every row of the outer query.
99 |
100 | 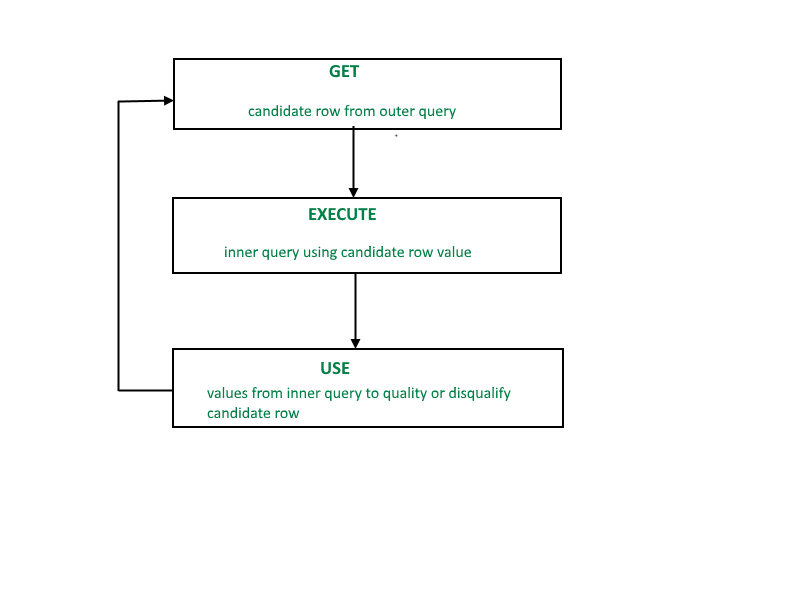
101 |
102 | A correlated subquery is one way of reading every row in a table and comparing values in each row against related data. It is used whenever a subquery must return a different result or set of results for each candidate row considered by the main query.
103 |
104 | In other words, you can use a correlated subquery to answer a multipart question whose answer depends on the value in each row processed by the parent statement.
105 |
106 | **EXISTS operator**
107 |
108 | The EXISTS operator tests for existence of rows in the results set of the subquery. If a subquery row value is found the condition is flagged TRUE and the search does not continue in the inner query, and if it is not found then the condition is flagged FALSE and the search continues in the inner query.
109 |
110 | ---
111 |
112 | ## MySQL functions
113 |
114 | MySQL has a number of built-in functions that can be used to perform common tasks.
115 | They are divided in the following categories:
116 | 1. Numeric
117 | 2. String
118 | 3. Date and time
119 | 4. Miscellaneous
120 |
121 |
122 | ## Numeric functions
123 |
124 | | Function | Description | Example |
125 | | -------- | --------------------------------- | ------------------------ |
126 | | ABS | Absolute value | SELECT ABS(-1) |
127 | | CEIL | Round up to the nearest integer | SELECT CEIL(1.5) |
128 | | FLOOR | Round down to the nearest integer | SELECT FLOOR(1.5) |
129 | | ROUND | Round to the given precision | SELECT ROUND(1.54, 1) |
130 | | TRUNCATE | Truncate to the given precision | SELECT TRUNCATE(1.54, 1) |
131 | | RAND | Generate a random number | SELECT RAND() |
132 |
133 | See more function [here](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/numeric-functions.html).
134 |
135 | ## String functions
136 |
137 | | Function | Description | Example |
138 | | -------- | -------------------- | ------------------------ |
139 | | LENGTH | Length of the string | SELECT LENGTH('Kattapa') |
140 | | LOWER | Convert to lowercase | SELECT LOWER('Kattapa') |
141 | | UPPER | Convert to uppercase | SELECT UPPER('Kattapa') |
142 | | LTRIM | Trim leading spaces | SELECT LTRIM(' Kattapa') |
143 | | RTRIM | Trim trailing spaces | SELECT RTRIM('Kattapa ') |
144 | | TRIM | Trim leading and trailing spaces | SELECT TRIM(' Kattapa ') |
145 | | SUBSTR | Extract a substring | SELECT SUBSTR('Namma Bengaluru', 1, 3) |
146 | | LEFT | Extract left substring | SELECT LEFT('Namma Bengaluru', 3) |
147 | | RIGHT | Extract right substring | SELECT RIGHT('Namma Bengaluru', 3) |
148 | | LOCATE | Find the position of a substring | SELECT LOCATE('Bengaluru', 'Namma Bengaluru') |
149 |
150 | See more function [here](https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/string-functions.html).
151 |
152 | ## Date and time functions
153 |
154 | | Function | Description | Example |
155 | | -------- | -------------------- | ------------------------ |
156 | | NOW | Current date and time | SELECT NOW() |
157 | | CURDATE | Current date | SELECT CURDATE() |
158 | | CURTIME | Current time | SELECT CURTIME() |
159 | | YEAR | Year of the date | SELECT YEAR('2020-01-01') |
160 | | MONTH | Month of the date | SELECT MONTH('2020-01-01') |
161 | | DAY | Day of the date | SELECT DAY('2020-01-01') |
162 | | DAYNAME | Day of the week | SELECT DAYNAME('2020-01-01') |
163 | | DAYOFWEEK | Day of the week | SELECT DAYOFWEEK('2020-01-01') |
164 | | DATE_ADD | Add a date | SELECT DATE_ADD('2020-01-01', INTERVAL 1 DAY) |
165 | | DATE_SUB | Subtract a date | SELECT DATE_SUB('2020-01-01', INTERVAL 1 DAY) |
166 | | DATEDIFF | Difference between two dates | SELECT DATEDIFF('2020-01-01', '2020-01-02') |
167 |
168 | ## Miscellaneous functions
169 |
170 | | Function | Description | Example |
171 | | -------- | -------------------- | ------------------------ |
172 | | IFNULL | Replace NULL values | SELECT IFNULL(batch_id, 'NO BATCH') |
173 | | COALESCE | Replace NULL values recursively | SELECT COALESCE(batch_id, phone, email, first_name) |
174 | | IF | Conditional expression | SELECT IF(batch_id = 1, 'YES', 'NO') |
175 | | CASE | Conditional expression | SELECT CASE WHEN batch_id = 1 THEN 'YES' ELSE 'NO' END |
176 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/07-subqueries-functions.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/07-subqueries-functions.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/08-window-fuctions-indexes-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/08-window-fuctions-indexes-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/08-window-fuctions-indexes.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/08-window-fuctions-indexes.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/08-window-function-query-optimisation-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/08-window-function-query-optimisation-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/08-window-function-query-optimisation.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/08-window-function-query-optimisation.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/08-window-functions-worksheet-answers.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Window functions worksheet
2 |
3 | 1. Print the student names along with the number of students in their batch.
4 |
5 | ```sql
6 | SELECT
7 | id,
8 | first_name,
9 | last_name,
10 | batch_id,
11 | iq,
12 | COUNT(*) OVER (PARTITION BY batch_id) AS batch_size
13 | FROM
14 | students;
15 | ```
16 |
17 | 2. Print the student names along with the average IQ of their batch.
18 |
19 | ```sql
20 | SELECT
21 | id,
22 | first_name,
23 | last_name,
24 | batch_id,
25 | iq,
26 | AVG(iq) OVER (PARTITION BY batch_id) AS batch_avg_iq
27 | FROM
28 | students;
29 | ```
30 |
31 | 3. Print the student names along with the maximum IQ of their batch.
32 |
33 | ```sql
34 | SELECT
35 | id,
36 | first_name,
37 | last_name,
38 | batch_id,
39 | iq,
40 | MAX(iq) OVER (PARTITION BY batch_id) AS batch_max_iq
41 | FROM
42 | students;
43 | ```
44 |
45 | 4. Print the student names along with their rank based on IQ.
46 |
47 | ```sql
48 | SELECT
49 | id,
50 | first_name,
51 | last_name,
52 | batch_id,
53 | iq,
54 | RANK() OVER (ORDER BY iq) AS iq_rank
55 | FROM
56 | students;
57 | ```
58 |
59 | 5. Print the student names along with their rank in their batch based on IQ.
60 |
61 | ```sql
62 | SELECT
63 | id,
64 | first_name,
65 | last_name,
66 | batch_id,
67 | iq,
68 | RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY batch_id ORDER BY iq) AS batch_iq_rank
69 | FROM
70 | students;
71 | ```
72 |
73 | 6. Print the student names along with their rank in their batch based on IQ. Ties should not increase the rank.
74 |
75 | ```sql
76 | SELECT
77 | id,
78 | first_name,
79 | last_name,
80 | batch_id,
81 | iq,
82 | DENSE_RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY batch_id ORDER BY iq) AS batch_iq_rank
83 | FROM
84 | students;
85 | ```
86 |
87 | 7. Print the student names along with their rank in their batch based on IQ. Ties should not be counted and broken by ID.
88 |
89 | ```sql
90 | SELECT
91 | id,
92 | first_name,
93 | last_name,
94 | batch_id,
95 | iq,
96 | ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY batch_id ORDER BY iq, id) AS batch_iq_rank
97 | FROM
98 | students;
99 | ```
100 |
101 | 8. Find the rank of batches based on the start date of the batch.
102 |
103 | ```sql
104 | SELECT
105 | id,
106 | name,
107 | start_date,
108 | RANK() OVER (ORDER BY start_date) AS batch_rank
109 | FROM
110 | batches;
111 | ```
112 |
113 | 9. Sort the instructors by the first and last name and assign them a roll number.
114 |
115 | ```sql
116 | SELECT
117 | id,
118 | first_name,
119 | last_name,
120 | ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY first_name, last_name) AS roll_number
121 | FROM
122 | instructors;
123 | ```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/08-window-functions-worksheet.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Window functions worksheet
2 |
3 | 1. Print the student names along with the number of students in their batch.
4 |
5 | ```sql
6 | ```
7 |
8 | 2. Print the student names along with the average IQ of their batch.
9 |
10 | ```sql
11 | ```
12 |
13 | 3. Print the student names along with the maximum IQ of their batch.
14 |
15 | ```sql
16 | ```
17 |
18 | 4. Print the student names along with their rank based on IQ.
19 |
20 | ```sql
21 | ```
22 |
23 | 5. Print the student names along with their rank in their batch based on IQ.
24 |
25 | ```sql
26 | ```
27 |
28 | 6. Print the student names along with their rank in their batch based on IQ. Ties should not increase the rank.
29 |
30 | ```sql
31 | ```
32 |
33 | 7. Print the student names along with their rank in their batch based on IQ. Ties should not be counted and broken by ID.
34 |
35 | ```sql
36 | ```
37 |
38 | 8. Find the rank of batches based on the start date of the batch.
39 |
40 | ```sql
41 | ```
42 |
43 | 9. Sort the instructors by the first and last name and assign them a roll number.
44 |
45 | ```sql
46 | ```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/09-subqueries-views-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/09-subqueries-views-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/09-subqueries-views-worksheet-answers.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Sub-queries and views worksheet
2 | ## Sub-queries
3 |
4 | 1. Get all the students whose IQ is greater than the average IQ.
5 |
6 | ```sql
7 | SELECT
8 | first_name, last_name, iq
9 | FROM
10 | students
11 | WHERE
12 | iq > (SELECT
13 | AVG(iq)
14 | FROM
15 | students);
16 | ```
17 |
18 | 2. Get all the students whose IQ is greater than the highest IQ of the batch_id `2` students.
19 |
20 | ```sql
21 | SELECT
22 | *
23 | FROM
24 | students
25 | WHERE
26 | iq > (SELECT
27 | MAX(iq)
28 | FROM
29 | students
30 | WHERE
31 | batch_id = 2);
32 | ```
33 |
34 | 3. Get all the students whose IQ is greater than `all` the IQs of the batch_id `2` students.
35 |
36 | ```sql
37 | SELECT
38 | *
39 | FROM
40 | students
41 | WHERE
42 | iq > ALL (SELECT
43 | iq
44 | FROM
45 | students
46 | WHERE
47 | batch_id = 2);
48 | ```
49 |
50 | 4. Find all the students who are in batches that start with the word `Jedi` (Without JOIN)
51 |
52 | ```sql
53 | SELECT
54 | *
55 | FROM
56 | students
57 | WHERE
58 | batch_id IN (SELECT
59 | id
60 | FROM
61 | batches
62 | WHERE
63 | name LIKE 'Jedi%');
64 | ```
65 |
66 | 5. Find all the students whose IQ is greater than the average IQ of their batch.
67 |
68 | ```sql
69 | SELECT
70 | *
71 | FROM
72 | students;
73 |
74 | SELECT
75 | first_name, last_name, batch_id, iq
76 | FROM
77 | students s
78 | WHERE
79 | s.iq > (SELECT
80 | AVG(iq)
81 | FROM
82 | students e
83 | WHERE
84 | e.batch_id = s.batch_id);
85 | ```
86 |
87 | 6. Get all the instructors that have at least one batch (Without using joins)
88 |
89 | ```sql
90 | SELECT
91 | *
92 | FROM
93 | instructors i
94 | WHERE
95 | EXISTS( SELECT
96 | id
97 | FROM
98 | batches
99 | WHERE
100 | instructor_id = i.id);
101 | ```
102 |
103 | 7. Print all the names, batch ID and average IQ of the batch for each student
104 |
105 | ```sql
106 | SELECT
107 | id,
108 | first_name,
109 | last_name,
110 | iq,
111 | batch_id,
112 | (SELECT
113 | AVG(iq)
114 | FROM
115 | students
116 | WHERE batch_id = s.batch_id
117 | )
118 | FROM
119 | students s;
120 | ```
121 |
122 | ## Views
123 |
124 | 1. Create a view that shows the students and their batches.
125 |
126 | ```sql
127 | CREATE VIEW students_and_batches AS
128 | SELECT
129 | s.id,
130 | s.first_name,
131 | s.last_name,
132 | s.iq,
133 | b.name AS batch_name
134 | FROM
135 | students s
136 | JOIN
137 | batches b ON s.batch_id = b.id;
138 | ```
139 |
140 | 2. Create a view that shows the students and their batches, but only for batches that start with the word `Jedi`.
141 |
142 | ```sql
143 | CREATE VIEW students_and_batches AS
144 | SELECT
145 | s.id,
146 | s.first_name,
147 | s.last_name,
148 | s.iq,
149 | b.name AS batch_name
150 | FROM
151 | students s
152 | JOIN
153 | batches b ON s.batch_id = b.id
154 | WHERE
155 | b.name LIKE 'Jedi%';
156 | ```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/09-subqueries-views-worksheet.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Sub-queries and views worksheet
2 | ## Sub-queries
3 |
4 | 1. Get all the students whose IQ is greater than the average IQ.
5 |
6 | ```sql
7 |
8 | ```
9 |
10 | 2. Get all the students whose IQ is greater than the highest IQ of the batch_id `2` students.
11 |
12 | ```sql
13 |
14 | ```
15 |
16 | 3. Get all the students whose IQ is greater than `all` the IQs of the batch_id `2` students.
17 |
18 | ```sql
19 |
20 | ```
21 |
22 | 4. Find all the students who are in batches that start with the word `Jedi` (Without JOIN)
23 |
24 | ```sql
25 |
26 | ```
27 |
28 | 5. Find all the students whose IQ is greater than the average IQ of their batch.
29 |
30 | ```sql
31 |
32 | ```
33 |
34 | 6. Get all the instructors that have at least one batch (Without using joins)
35 |
36 | ```sql
37 |
38 | ```
39 |
40 | 7. Print all the names, batch ID and average IQ of the batch for each student
41 |
42 | ```sql
43 |
44 | ```
45 |
46 | ## Views
47 |
48 | 1. Create a view that shows the students and their batches.
49 |
50 | ```sql
51 |
52 | ```
53 |
54 | 2. Create a view that shows the students and their batches, but only for batches that start with the word `Jedi`.
55 |
56 | ```sql
57 |
58 | ```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/database/notes/09-subqueries-views.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/database/notes/09-subqueries-views.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/networks/.DS_Store:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/networks/.DS_Store
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/networks/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Notes
2 |
3 | | Name | .md | .pdf | Handwritten | MCQs | Worksheet | Worksheet with Answers |
4 | | ---------------------------- | -------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------- | --------- | ---------------------- |
5 | | Network Fundamentals and the OSI model | [1](notes/01-introduction-OSI-model.md) | [2](notes/01-introduction-OSI-model.pdf) | [3](notes/01-introduction-OSI-model-hw.pdf) | _ | _ | _ |
6 | | Application architecture and HTTP | [1](notes/02-application-layer.md) | [2](notes/02-application-layer.pdf) | [3](notes/02-application-layer-hw.pdf) | _ | _ | _ |
7 | | Cookies, DNS and TCP | [1](notes/03-cookies-dns-tcp.md) | [2](notes/03-cookies-dns-tcp.pdf) | [3](notes/03-cookies-dns-tcp-hw.pdf) | _ | _ | _ |
8 | | Socket programming with Python | [1](notes/04-sockets-primer.md) | [2](notes/04-sockets-primer.pdf) | [3](notes/04-sockets-primer-hw.pdf) | _ | _ | _ |
9 |
10 |
11 | ## Must read
12 | * [What happens when you type google.com into your browser and press enter?](https://github.com/alex/what-happens-when)
13 |
14 |
15 | ## Resources
16 | * [Awesome networking](https://github.com/facyber/awesome-networking)
17 | * [Awesome tools](https://github.com/nyquist/awesome-networking)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/networks/code/client.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from concurrent.futures import thread
2 | import socket
3 | import argparse
4 | from threading import Thread
5 | import time
6 |
7 | def main(host: str, port: int, index: int) -> None:
8 |
9 | # Create a socket object
10 | sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
11 |
12 | sock.connect((host, port))
13 | print(f"Connected socket {sock.getsockname()} to {sock.getpeername()}")
14 |
15 | data_to_send = bytes(f"Hello, world {index}".encode('utf-8'))
16 | print(f"Sending data: {data_to_send}")
17 | sock.sendall(data_to_send)
18 |
19 | data = sock.recv(1024)
20 | print(f"Received data: {data} \n")
21 |
22 | sock.close()
23 |
24 |
25 | if __name__ == '__main__':
26 |
27 | # Declare arguments
28 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Socket server')
29 | parser.add_argument('-H', '--host', help='Target host', default='127.0.0.1', type=str)
30 | parser.add_argument('-p', '--port', help='Target port', required=True, type=int)
31 |
32 | # Parse arguments
33 | args = parser.parse_args()
34 | host, port = args.host, args.port
35 |
36 | for index in range(10):
37 | thread = Thread(target=main, args=(host, port, index + 1))
38 | thread.start()
39 | time.sleep(0.2)
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/networks/code/port-scanner.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import argparse
2 | import socket
3 | from colorama import init, Fore
4 |
5 | def is_port_open(host: str, port: int) -> bool:
6 | """
7 | Checks if a port is open on a host.
8 | """
9 | sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
10 | try:
11 | sock.connect((host, port))
12 | sock.settimeout(0.5)
13 | except:
14 | return False
15 | else:
16 | return True
17 |
18 |
19 | if __name__ == '__main__':
20 |
21 | init() # initialize colorama
22 |
23 | # Declare arguments
24 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Port Scanner')
25 | parser.add_argument('-H', '--host', help='Host to scan', required=True, type=str)
26 | parser.add_argument('-s', '--start', help='Starting port', default=1, type=int)
27 | parser.add_argument('-e', '--end', help='Ending port', default=1024, type=int)
28 |
29 | # Parse arguments
30 | args = parser.parse_args()
31 | host, start, end = args.host, args.start, args.end
32 |
33 | for port in range(start, end):
34 | if not is_port_open(host, port):
35 | print(f'{Fore.RED}Port {port} is closed{Fore.RESET}')
36 | continue
37 | print(f'{Fore.GREEN}Port {port} is open{Fore.RESET}')
38 |
39 |
40 |
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/networks/code/server.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import socket
2 | import argparse
3 | from threading import Thread
4 |
5 | def handleConnection(conn) -> None:
6 | print(f"Connection from {conn.getsockname()} to {conn.getpeername()}")
7 |
8 | data = conn.recv(1024)
9 | print(f"Received data: {data}")
10 |
11 | conn.sendall(data.upper())
12 | conn.close()
13 |
14 | def main(host: str, port:int) -> None:
15 |
16 | # Create a socket object
17 | sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
18 | # Bind the socket to the port
19 | try:
20 | sock.bind((host, port))
21 | except socket.error as e :
22 | print(f"Error in binding host and port: {e}")
23 |
24 | # Listen for incoming connections
25 | sock.listen()
26 | print(f"Server is listening on port {port}")
27 |
28 | while True:
29 | # Accept connections from outside
30 | conn, _ = sock.accept()
31 |
32 | # Delegate the connection to a thread
33 | thread = Thread(target=handleConnection, args=(conn,))
34 | thread.start()
35 |
36 |
37 |
38 | if __name__ == '__main__':
39 |
40 | # Declare arguments
41 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Socket server')
42 | parser.add_argument('-p', '--port', help='Port to bind to', required=True, type=int)
43 | parser.add_argument('-H', '--host', help='Host to bind to', default='127.0.0.1', type=str)
44 |
45 | # Parse arguments
46 | args = parser.parse_args()
47 | host, port = args.host, args.port
48 |
49 | main(host, port)
50 |
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/networks/notes/01-introduction-OSI-model-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/networks/notes/01-introduction-OSI-model-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/networks/notes/01-introduction-OSI-model.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/networks/notes/01-introduction-OSI-model.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/networks/notes/02-application-layer-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/networks/notes/02-application-layer-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/networks/notes/02-application-layer.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/networks/notes/02-application-layer.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/networks/notes/03-cookies-dns-tcp-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/networks/notes/03-cookies-dns-tcp-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/networks/notes/03-cookies-dns-tcp.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/networks/notes/03-cookies-dns-tcp.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/networks/notes/04-sockets-primer-hw-02.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/networks/notes/04-sockets-primer-hw-02.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/networks/notes/04-sockets-primer-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/networks/notes/04-sockets-primer-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/networks/notes/04-sockets-primer.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Socket programming with Python
2 |
3 | ## Agenda
4 | * Understanding sockets
5 | * Types of sockets
6 | * Local and remote addresses
7 | * Ephemeral ports
8 | * Creating an echo client-server
9 | * Single connection
10 | * Multi connection
11 | * Multi-threaded
12 |
13 | ## Key terms
14 | ### Socket
15 | > A network socket is a software structure within a network node of a computer network that serves as an endpoint for sending and receiving data across the network
16 |
17 | ### Ephemeral port
18 | > A port that is dynamically allocated by the system and is used for a short period of time
19 |
20 | ## What are sockets?
21 | > Sockets and the socket API are used to send messages across a network. They provide a form of inter-process communication (IPC).
22 |
23 | **Sockets are nothing but interfaces provided to developers transfer data over the network.**
24 | Any message sent from one process to another, must go through the underlying layers. The software interface between these layers is called a **socket**.
25 | Socket programming is a way of connecting two nodes on a network to communicate with each other.
26 |
27 | 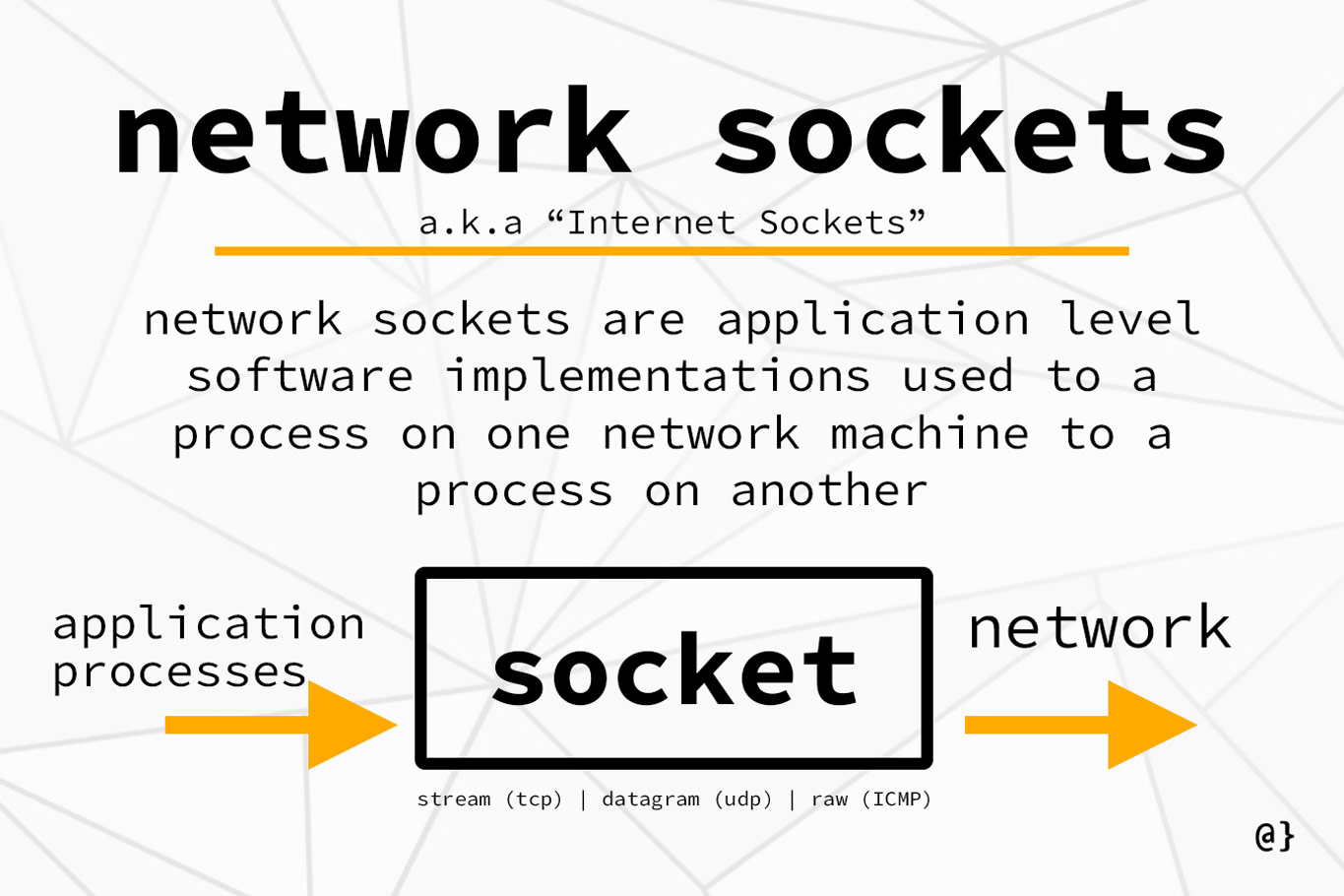
28 |
29 | One socket(node) listens on a particular port at an IP, while the other socket reaches out to the other to form a connection. The server forms the listener socket while the client reaches out to the server.
30 |
31 | > As developers, we have control over everything that happens before the message is sent through the socket, and everything that happens after the message is received from a socket. The only control we have over the transport layer is maybe choosing the protocol (TCP, UDP…) or some parameters.
32 |
33 |
34 | > A socket is an endpoint instance defined by an IP address and a port in the context of either a particular connection or the listening state
35 |
36 | A socket comprises 5 things:
37 | 1. Local address
38 | 2. Local port
39 | 3. Remote address
40 | 4. Remote port
41 | 5. Protocol
42 |
43 | ### Types of sockets
44 | 1. `Stream socket`: a socket that is used to send and receive data using TCP in a connection-oriented manner.
45 | 2. `Datagram socket`: Datagram sockets are used to support User Datagram Protocol (UDP) applications that rely on connectionless data transfer. Each packet sent via datagram sockets is individually addressed and routed but takes no measure to ensure order or arrival. Datagram sockets are considered to be “unreliable” transport services.
46 | 3. `Raw socket`: Raw sockets allow the send/receive of Internet Protocol packets from the network layer without any specific constraint on protocol (TCP, UDP, etc.). As such, header specifications are made at the application layer when sending and much of the encapsulation is left up to application developers.
47 |
48 |
49 | ### Life cycle of a socket
50 |
51 | 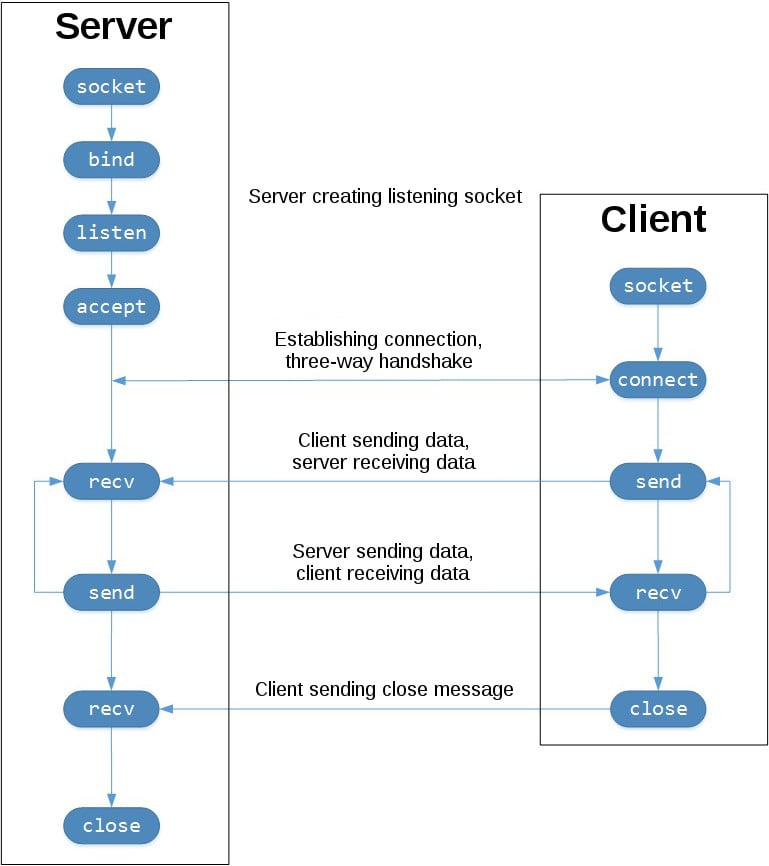
52 |
53 | #### Server
54 |
55 | 1. Create a socket
56 | 2. Bind the socket to a local address and port
57 | 3. Start listening for incoming connections
58 | 4. Accept incoming connections
59 | 5. Receive data
60 | 6. Send data
61 | 7. Close the socket when done
62 |
63 | #### Client
64 | 1. Create a socket
65 | 2. Connect to a remote address and port
66 | 3. Send data
67 | 4. Receive data
68 | 5. Close the socket when done
69 |
70 | #### Ephemeral ports
71 | The server port is one that cannot be instantly changed since it is being used by multiple clients. However, the client port is one whose value is not of importance. As long as the client port is present, the connection and data transmission will be successful. So to avoid the overhead of binding a socket to the port, the system will automatically allocate a port for the client. This is a short-lived port and is hence known as an ephemeral port.
72 |
73 | ## Socket programming with Python
74 |
75 | ### Creating a socket
76 |
77 | ```python
78 | import socket
79 |
80 | socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
81 | ```
82 |
83 | Here, we create a socket object with the address family `AF_INET` and the socket type `SOCK_STREAM`.
84 | This means that the socket will use the IPv4 protocol and will be a TCP socket.
85 |
86 | If we want to use the UDP protocol, we would use the socket type `SOCK_DGRAM`.
87 |
88 | ### Binding a socket to a local address and port
89 |
90 | ```python
91 | sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
92 | sock.bind(('127.0.0.1', 5000))
93 | ```
94 |
95 | ### Listening for incoming connections
96 |
97 | ```python
98 | sock.listen(1)
99 | ```
100 | The parameter `1` specifies the maximum number of queued connections.
101 | It specifies the number of unaccepted connections that the system will allow before refusing new connections. Starting in Python 3.5, it’s optional. If not specified, a default backlog value is chosen
102 |
103 | Find out more about the parameter [here](https://tangentsoft.net/wskfaq/advanced.html#backlog).
104 |
105 | ### Accepting incoming connections
106 |
107 | ```python
108 | conn, addr = sock.accept()
109 | ```
110 |
111 | The `accept` method blocks execution and waits for an incoming connection. When a client connects, it returns a new socket object representing the connection and a tuple holding the address of the client
112 |
113 | The `conn` variable is the new connection (socket) object and the `addr` variable is the address of the client. We can use the `conn` variable to send and receive data. The difference between the `conn` and `sock` variables is that `sock` is the listening socket and `conn` is the new connection that has both local and remote addresses.
114 |
115 | ### Connecting to a remote address and port
116 |
117 | ```python
118 | sock.connect(('127.0.0.1', 5000))
119 | ```
120 |
121 | The connect method is used by the client to connect to the server.
122 |
123 |
124 | ### Receiving and sending data
125 |
126 | ```python
127 | data = conn.recv(1024)
128 | ```
129 | The `recv` method is used to receive data from the socket. The parameter specifies the maximum number of bytes to be received.
130 |
131 | ```python
132 | conn.sendall(b'Hello World')
133 | ```
134 | Unlike `send`, this method continues to send data from bytes until either all data has been sent or an error occurs. None is returned on success.
135 |
136 | ### Closing the socket
137 |
138 | ```python
139 | sock.close()
140 | ```
141 | ---
142 |
143 | ## Further reading
144 | * [Detailed Socket programming with Python](https://realpython.com/python-sockets/#background)
145 | * [Creating a port scanner with Python](https://www.thepythoncode.com/article/make-port-scanner-python)
146 | * [Non-blocking sockets](https://docs.python.org/3/howto/sockets.html#non-blocking-sockets)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/networks/notes/04-sockets-primer.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/networks/notes/04-sockets-primer.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/oop/README.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Code snippets across topics
2 |
3 | ## Bank transfers in procedural and object-oriented programming
4 | * [Procedural programming](../code/procedural_transfer.py)
5 | * [Object-oriented programming](oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/basics/OopBankAccount.java)
6 | * [Unit test](oop/src/test/java/com/scaler/lld/basics/OopBankAccountTest.java)
7 |
8 | ## Object-oriented programming
9 | ### Encapsulation
10 | * [Default constructor](https://github.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/blob/oop-default-ctor/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/scaler/Student.java)
11 | * [Unit test](https://github.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/blob/oop-default-ctor/oop/code/oop/src/test/java/com/scaler/lld/scaler/StudentTest.java)
12 | * [Parametrised constructor](https://github.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/blob/oop-para-ctor/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/scaler/Student.java)
13 | * [Unit test](https://github.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/blob/oop-para-ctor/oop/code/oop/src/test/java/com/scaler/lld/scaler/StudentTest.java)
14 |
15 | ### Inheritance
16 | * [User - Parent class](https://github.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/blob/oop-inheritance/oop/code/oop/src/test/java/com/scaler/lld/scaler/StudentTest.java)
17 | * [Student - Child class](https://github.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/blob/oop-inheritance/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/scaler/Student.java)
18 | * [Unit Test](https://github.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/blob/oop-inheritance/oop/code/oop/src/test/java/com/scaler/lld/scaler/StudentTest.java)
19 |
20 | ### Polymorphism
21 | * [Mentor class](https://github.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/tree/master/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/scaler)
22 | * [Subtyping - Mentor and Student as User](https://github.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/blob/master/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/App.java#L18)
23 | * [Method overloading - `printInfo`](https://github.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/blob/master/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/scaler/User.java#L26-L31)
24 | * [Method overriding - Overriding `printInfo` in Student](https://github.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/blob/master/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/scaler/Student.java#L34)
25 |
26 | ## SOLID principles
27 | * [Bird - v0](https://github.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/blob/bird-v0/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/bird/Bird.java)
28 | * `Bird - v1 - After fixing SRP and OCP`
29 | * [Bird Class](../code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/bird/Bird.java)
30 | * [Parrot/Sparrow child classes](oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/bird/Parrot.java)
31 |
32 | ### Assignment for SOLID - I
33 | * Find where [the code](oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/questions/Invoice.java) violates SRP
34 | * Fix the code to make it adhere to SRP
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/oop/pom.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
5 | 4.0.0
6 |
7 | com.scaler.lld
8 | oop
9 | 1.0-SNAPSHOT
10 |
11 | oop
12 |
13 | http://www.example.com
14 |
15 |
16 | UTF-8
17 | 1.8
18 | 1.8
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 | junit
24 | junit
25 | 4.11
26 | test
27 |
28 |
29 | org.projectlombok
30 | lombok
31 | 1.18.24
32 | provided
33 |
34 |
35 |
36 |
37 |
38 |
39 |
40 |
41 |
42 | maven-clean-plugin
43 | 3.1.0
44 |
45 |
46 |
47 | maven-resources-plugin
48 | 3.0.2
49 |
50 |
51 | maven-compiler-plugin
52 | 3.8.0
53 |
54 |
55 | maven-surefire-plugin
56 | 2.22.1
57 |
58 |
59 | maven-jar-plugin
60 | 3.0.2
61 |
62 |
63 | maven-install-plugin
64 | 2.5.2
65 |
66 |
67 | maven-deploy-plugin
68 | 2.8.2
69 |
70 |
71 |
72 | maven-site-plugin
73 | 3.7.1
74 |
75 |
76 | maven-project-info-reports-plugin
77 | 3.0.0
78 |
79 |
80 |
81 |
82 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/App.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.lld;
2 |
3 | import java.util.List;
4 |
5 | import com.scaler.lld.scaler.Student;
6 | import com.scaler.lld.scaler.User;
7 |
8 | /**
9 | * Hello world!
10 | *
11 | */
12 | public class App {
13 | public static void main(String[] args) {
14 | User student = new Student("student", "student@scaler.in", "batch", 100);
15 | student.printInfo(); // inheritance
16 | }
17 |
18 | public static void resetEmail(List users) {
19 | for (User user : users) {
20 | user.changeEmail("");
21 |
22 | if (user instanceof Student) {
23 | Student student = (Student) user;
24 |
25 | System.out.println("Name :" + student.getName() + " " + student.getPsp());
26 |
27 | student.setPsp(0);
28 | System.out.println("Name :" + student.getName() + " " + student.getPsp());
29 |
30 | }
31 |
32 | }
33 |
34 | }
35 | }
36 |
37 | // Reusable code
38 | // In order to reset email, I just had to call the parent's changeEmail fn
39 | // Instead of defining a method for each class
40 | // instanceof
41 | // A a = (A) b;
42 | // 6:05
43 | // 10:35
44 | // Three types of DP
45 | // 1. Creational - OOP
46 | // Factory - Simple Factory - No OOP
47 | // 2. Structural -
48 | // 3. Behavioural -
49 |
50 | // 1. Subtyping
51 | // - Compile and run time
52 |
53 | // Method overloading - Compile time
54 | // 2. Generic Polymorphism
55 | // 3. Adhoc polymorphism - Duck Typing
56 |
57 | // PATCH /edit-student (JSON patchBody)
58 | // { field: "name", op: "set", value: "Tanmay"}
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/basics/OopBankAccount.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.lld.basics;
2 |
3 | public class OopBankAccount {
4 | private Integer number;
5 | private String name;
6 | private Integer balance;
7 |
8 | public OopBankAccount(Integer number, Integer balance, String name) {
9 | this.number = number;
10 | this.balance = balance;
11 | this.name = name;
12 | }
13 |
14 | // GETTERS AND SETTERS START
15 | public Integer getNumber() {
16 | return this.number;
17 | }
18 |
19 | public void setNumber(Integer number) {
20 | this.number = number;
21 | }
22 |
23 | public String getName() {
24 | return this.name;
25 | }
26 |
27 | public void setName(String name) {
28 | this.name = name;
29 | }
30 |
31 | public Integer getBalance() {
32 | return this.balance;
33 | }
34 |
35 | public void setBalance(Integer balance) {
36 | this.balance = balance;
37 | }
38 |
39 | // GETTERS AND SETTERS END
40 |
41 |
42 | public void deposit(Integer amount) {
43 | this.balance += amount;
44 | }
45 |
46 | public void withdraw(Integer amount) {
47 | this.balance -= amount;
48 | }
49 |
50 | public void transfer(OopBankAccount destination, Integer amount) {
51 | this.withdraw(amount);
52 | destination.deposit(amount);
53 | }
54 |
55 | }
56 |
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/bird/Bird.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.lld.bird;
2 |
3 | import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
4 | import lombok.Getter;
5 |
6 | @AllArgsConstructor
7 | @Getter
8 | public abstract class Bird {
9 | private Integer weight;
10 | private String colour;
11 | private String size;
12 | private String beakType;
13 | private BirdType type;
14 |
15 | public abstract void fly();
16 | }
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/bird/BirdType.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.lld.bird;
2 |
3 | public enum BirdType {
4 | Eagle, Penguin, Parrot
5 | }
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/bird/Eagle.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.lld.bird;
2 |
3 | public class Eagle extends Bird {
4 |
5 | public Eagle(Integer weight, String colour, String size, String beakType, BirdType type) {
6 | super(weight, colour, size, beakType, type);
7 | }
8 |
9 | @Override
10 | public void fly() {
11 | System.out.println("\nEagle is flying");
12 | }
13 |
14 | }
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/bird/Parrot.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.lld.bird;
2 |
3 | public class Parrot extends Bird {
4 |
5 | public Parrot(Integer weight, String colour, String size, String beakType, BirdType type) {
6 | super(weight, colour, size, beakType, type);
7 | }
8 |
9 | @Override
10 | public void fly() {
11 | System.out.println("\nParrot is flying");
12 | }
13 |
14 | }
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/bird/Runner.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.lld.bird;
2 |
3 | public class Runner {
4 | public static void main(String[] args) {
5 | Bird parrot = new Parrot(10, "Green", "Small", "Sharp", BirdType.Parrot);
6 | parrot.fly();
7 |
8 | Bird eagle = new Eagle(20, "Brown", "Medium", "Sharp", BirdType.Eagle);
9 | eagle.fly();
10 | }
11 | }
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/questions/Book.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.lld.questions;
2 |
3 | import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
4 | import lombok.Getter;
5 | import lombok.Setter;
6 |
7 | @AllArgsConstructor
8 | @Getter
9 | @Setter
10 | public class Book {
11 | private String name;
12 | private String authorName;
13 | private int year;
14 | private int price;
15 | private String isbn;
16 | }
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/questions/Invoice.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.lld.questions;
2 |
3 | import lombok.AccessLevel;
4 | import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
5 | import lombok.Getter;
6 |
7 | @Getter
8 | @AllArgsConstructor
9 | public class Invoice {
10 | private Book book;
11 | private Integer quantity;
12 | private Double discountRate;
13 | private Double taxRate;
14 |
15 | @Getter(AccessLevel.NONE)
16 | private double total; // Will not generate a getter
17 |
18 | public Double getTotal() {
19 | double price = ((book.getPrice() - book.getPrice() * discountRate) * this.quantity);
20 | return price * (1 + taxRate);
21 | }
22 |
23 | public void printInvoice() {
24 | System.out.println(quantity + "x " + book.getName() + " " + book.getPrice() + "$");
25 | System.out.println("Discount Rate: " + discountRate);
26 | System.out.println("Tax Rate: " + taxRate);
27 | System.out.println("Total: " + total);
28 | }
29 |
30 | public void saveToFile(String filename) {
31 | // Creates a file with given name and writes the invoice
32 | }
33 |
34 | }
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/scaler/Mentor.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.lld.scaler;
2 |
3 | import java.util.ArrayList;
4 | import java.util.List;
5 |
6 | import lombok.Getter;
7 | import lombok.Setter;
8 |
9 | // Step 1 - Extend parent class
10 | @Getter
11 | @Setter
12 | public class Mentor extends User {
13 | private List mentees = new ArrayList<>();
14 | private String company;
15 |
16 | public Mentor(String name, String email, List mentees, String company) {
17 | super(name, email);
18 | this.mentees = mentees;
19 | this.company = company;
20 | }
21 |
22 | }
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/scaler/Student.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.lld.scaler;
2 |
3 | import lombok.Getter;
4 | import lombok.Setter;
5 |
6 | @Getter
7 | @Setter
8 | public class Student extends User {
9 |
10 | private String batchName;
11 | private Integer psp;
12 | private StudentStatus status = StudentStatus.ACTIVE; // ACTIVE, PAUSED, COMPLETED
13 |
14 | // Define parametrised constructor
15 |
16 | public Student(String name, String email, String batchName, Integer psp) {
17 | super(name, email);
18 | this.batchName = batchName;
19 |
20 | if (psp < 0 || psp > 100) {
21 | throw new IllegalArgumentException("PSP should be between 0 and 100");
22 | }
23 | this.psp = psp;
24 | }
25 |
26 | public Student() {
27 | }
28 |
29 | void changeBatch(String batchName) {
30 | this.batchName = batchName;
31 | }
32 |
33 | @Override
34 | public void printInfo() {
35 | System.out.println("\nStudent: " + getName() + " " + getBatchName());
36 | }
37 |
38 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/scaler/StudentStatus.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.lld.scaler;
2 |
3 | public enum StudentStatus {
4 | ACTIVE, PAUSED, COMPLETED, EDGE
5 | }
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/oop/src/main/java/com/scaler/lld/scaler/User.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.lld.scaler;
2 |
3 | import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
4 | import lombok.Getter;
5 | import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
6 | import lombok.Setter;
7 |
8 | @Getter
9 | @Setter
10 | @AllArgsConstructor
11 | @NoArgsConstructor
12 | public class User {
13 | private String name;
14 | private String email;
15 |
16 | public void changeEmail(String email) {
17 | this.email = email;
18 | }
19 |
20 | // Method overloading
21 | // Method signature:
22 | // 1. Method name
23 | // 2. # of args
24 | // 3. Data type of args
25 |
26 | public void printInfo() {
27 | }
28 |
29 | public void printInfo(String title) {
30 | System.out.println(" \n User: " + title + " " + this.getName());
31 | }
32 | }
33 |
34 | // Interfaces
35 | // Class - Blueprint
36 | // Interface - Blue print of behaviour
37 | // Database db = new MySqlDB();
38 | // Interfaces - define methods with an impl.
39 | // Abstract - mixture of interface and class
40 | // implemented methods + not-implemented
41 | // Abstract classes - state
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/oop/src/test/java/com/scaler/lld/AppTest.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.lld;
2 |
3 | import static org.junit.Assert.assertTrue;
4 |
5 | import org.junit.Test;
6 |
7 | /**
8 | * Unit test for simple App.
9 | */
10 | public class AppTest
11 | {
12 | /**
13 | * Rigorous Test :-)
14 | */
15 | @Test
16 | public void shouldAnswerWithTrue()
17 | {
18 | assertTrue( true );
19 | }
20 | }
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/oop/src/test/java/com/scaler/lld/scaler/StudentTest.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.lld.scaler;
2 |
3 | import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
4 | import static org.junit.Assert.assertNotNull;
5 | import static org.junit.Assert.assertNull;
6 |
7 | import org.junit.Test;
8 |
9 | public class StudentTest {
10 |
11 | @Test
12 | public void testDefaultCtor() {
13 | Student student = new Student();
14 |
15 | assertNotNull("If the ctor is called, then object must be returned",
16 | student);
17 | assertNull("If default ctor is used, name should be null", student.getName());
18 | assertEquals("If default ctor is used, status should be active", StudentStatus.ACTIVE, student.getStatus());
19 | }
20 |
21 | @Test
22 | public void testParametrisedCtor() {
23 | Student student = new Student("John Doe", "john@doe.in", "Batch 1", 100);
24 |
25 | assertNotNull("If the ctor is called, then object must be returned",
26 | student);
27 | assertEquals("If name ctor is passed to ctor, name should be set in instance", "John Doe", student.getName());
28 | assertEquals("If status is not passed to ctor, status should be active", StudentStatus.ACTIVE,
29 | student.getStatus());
30 | }
31 |
32 | @Test(expected = IllegalArgumentException.class)
33 | public void testParametrisedCtorWithInvalidPsp() {
34 | new Student("John Doe", "john@doe.in", "Batch 1", 101);
35 | }
36 |
37 | @Test
38 | public void testParentFields() {
39 | Student student = new Student("John Doe", "john@doe.in", "Batch 1", 100);
40 | assertEquals("If name ctor is passed to ctor, name should be set in instance", "John Doe", student.getName());
41 |
42 | String newEmail = "john@doe.com";
43 | student.changeEmail(newEmail);
44 | assertEquals("If email is changed, then email should be updated", newEmail, student.getEmail());
45 | }
46 |
47 | }
48 |
49 | // Coverage - % of code your test cases cover - 80%
50 | // pytest > junit
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/procedural_transfer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | accounts = []
3 |
4 | def transfer(source: int, destination: int, amount: int) -> None:
5 |
6 | source_account = get_account(source)
7 | update_account(source_account, -amount)
8 |
9 | destination_account = get_account(destination)
10 | update_account(destination_account, amount)
11 |
12 | def get_account(number: int) -> dict:
13 | return list(filter(lambda account: account['number'] == number, accounts))[0]
14 |
15 | def update_account(account: int, delta: int) -> None:
16 | account['balance'] += delta
17 |
18 | if __name__ == '__main__':
19 | accounts.append({'number': 1, 'balance': 100})
20 | accounts.append({'number': 2, 'balance': 200})
21 |
22 | transfer(1, 2, 50)
23 | print(accounts)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/python_code/main.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from oop.basic.OopBankAccount import OopBankAccount
2 |
3 | from oop.inheritance.Student import *
4 | from oop.inheritance.User import *
5 | from oop.inheritance.StudentStatus import *
6 |
7 | def main():
8 | #oop - basic
9 | abhi = OopBankAccount(100, 1)
10 | bob = OopBankAccount(200, 2)
11 |
12 | abhi.transfer(bob, 50)
13 |
14 | print(abhi.getBalance())
15 |
16 | #oop - inheritance
17 |
18 | sam = Student("sam", "abhi@a.cm", 25, "khulri", "Oct", 90, StudentStatus.ACTIVE)
19 | sam.print_details()
20 |
21 | # oop - inheritance and polymorphism
22 |
23 | student = Student("Student", "stu@scaler", "batch", 100)
24 | student.__class__ = User
25 | student.print_details()
26 |
27 | user = User("user", "user@gmail")
28 | # user.print_details() Python does not support method overloading like java or C++
29 | # we need to define method with default arguments
30 | if __name__ == '__main__':
31 | main()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/python_code/oop/SOLID/bird/Bird.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
2 | import BirdType
3 |
4 | class Bird(ABC):
5 | def __init__(self, weight: int, colour: str, size: int, beakType : str, birdType : BirdType) -> None:
6 | self.__weight = weight
7 | self.__colour = colour
8 | self.__size = size
9 | self.__beakType = beakType
10 | self.__birdType = birdType
11 |
12 | @abstractmethod
13 | def makeSound(self) -> None:
14 | ...
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/python_code/oop/SOLID/bird/BirdType.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from enum import Enum
2 |
3 | class BirdType(Enum):
4 | Eagle = 0
5 | Penguin = 1
6 | Parrot = 2
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/python_code/oop/SOLID/bird/Eagle.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from Bird import *
2 | from BirdType import *
3 | from interfaces.FlyableInterface import *
4 | from interfaces.FlyingBehaviourInterface import *
5 |
6 | class Eagle(Bird, FlyableInterface):
7 | __flyingBehaviour: FlyingBehaviourInterface = None
8 | def __init__(self, weight: int, colour: str, size: int, beakType: str, birdType: BirdType, flyingBehaviour: FlyingBehaviourInterface) -> None:
9 | super().__init__(weight, colour, size, beakType, birdType)
10 | self.__flyingBehaviour = flyingBehaviour
11 |
12 | def fly(self) -> None:
13 | self.__flyingBehaviour.makeFly()
14 |
15 | def makeSound(self) -> None:
16 | ...
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/python_code/oop/SOLID/bird/FlappingBehaviour.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from Bird import *
2 | from BirdType import *
3 | from interfaces.FlyingBehaviourInterface import *
4 |
5 | class FlappingBehaviour(FlyingBehaviourInterface):
6 | def makeFly(self) -> None:
7 | print("Flapping")
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/python_code/oop/SOLID/bird/GlidingBehaviour.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from Bird import *
2 | from BirdType import *
3 | from interfaces.FlyingBehaviourInterface import *
4 |
5 | class GlidingBehaviour(FlyingBehaviourInterface):
6 | def makeFly(self) -> None:
7 | print("Gliding")
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/python_code/oop/SOLID/bird/Parrot.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from Bird import *
2 | from BirdType import *
3 | from interfaces.FlyableInterface import *
4 | from interfaces.FlyingBehaviourInterface import *
5 |
6 | class Parrot(Bird, FlyableInterface):
7 | __flyingBehaviour: FlyingBehaviourInterface = None
8 | def __init__(self, weight: int, colour: str, size: int, beakType: str, birdType: BirdType, flyingBehaviour: FlyingBehaviourInterface) -> None:
9 | super().__init__(weight, colour, size, beakType, birdType)
10 | self.__flyingBehaviour = flyingBehaviour
11 |
12 | def fly(self) -> None:
13 | self.__flyingBehaviour.makeFly()
14 |
15 | def makeSound(self) -> None:
16 | ...
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/python_code/oop/SOLID/bird/Penguin.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from Bird import *
2 | from BirdType import *
3 | from interfaces.SwimmableInterface import *
4 | from interfaces.FlyingBehaviourInterface import *
5 |
6 | class Penguin(Bird, SwimmableInterface):
7 | def __init__(self, weight: int, colour: str, size: int, beakType: str, birdType: BirdType) -> None:
8 | super().__init__(weight, colour, size, beakType, birdType)
9 |
10 | def fly(self) -> None:
11 | self.__flyingBehaviour.makeFly()
12 |
13 | def makeSound(self) -> None:
14 | ...
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/python_code/oop/SOLID/bird/Runner.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from distutils.ccompiler import gen_lib_options
2 | from Parrot import *
3 | from Eagle import *
4 | from Penguin import *
5 | from BirdType import *
6 | from interfaces.FlyableInterface import *
7 | from interfaces.SwimmableInterface import *
8 | from FlappingBehaviour import *
9 | from GlidingBehaviour import *
10 |
11 | #import FlappingBehaviour gives error bcoz bird is package
12 |
13 | parrot = Parrot(10, "Green", "Small", "Sharp", BirdType.Parrot, FlappingBehaviour())
14 | parrot.fly()
15 |
16 | eagle = Eagle(20, "Brown", "Medium", "Sharp", BirdType.Eagle, GlidingBehaviour())
17 | eagle.fly()
18 |
19 | penguin = Penguin(30, "Black", "Large", "Sharp", BirdType.Penguin)
20 | penguin.makeSound()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/python_code/oop/SOLID/bird/interfaces/FlyableInterface.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
2 |
3 | class FlyableInterface(ABC):
4 | @abstractmethod
5 | def fly() -> None:
6 | ...
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/python_code/oop/SOLID/bird/interfaces/FlyingBehaviourInterface.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
2 |
3 | class FlyingBehaviourInterface(ABC):
4 | @abstractmethod
5 | def makeFly() -> None:
6 | ...
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/python_code/oop/SOLID/bird/interfaces/SwimmableInterface.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
2 |
3 | class SwimmableInterface:
4 | @abstractmethod
5 | def swim() -> None:
6 | ...
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/python_code/oop/SOLID/bird/interfaces/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/oop/code/python_code/oop/SOLID/bird/interfaces/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/python_code/oop/basic/OopBankAccount.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | class OopBankAccount:
2 | def __init__(self, balance, number):
3 | self.__number = number
4 | self.__balance = balance
5 |
6 | def getNumber(self):
7 | return self.__number
8 |
9 | def setNumber(self, number):
10 | self.__number = number
11 |
12 | def getBalance(self):
13 | return self.__balance
14 |
15 | def setBalance(self, balance):
16 | self.__balance = balance
17 |
18 | def deposit(self, amount):
19 | self.__balance += amount
20 |
21 | def withdraw(self, amount):
22 | self.__balance -= amount
23 |
24 | def transfer(self, destination, amount):
25 | self.withdraw(amount)
26 | destination.deposit(amount)
27 |
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/python_code/oop/basic/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/oop/code/python_code/oop/basic/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/python_code/oop/inheritance/Student.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from oop.inheritance.User import *
2 | from oop.inheritance.StudentStatus import *
3 |
4 | class Student(User):
5 |
6 | __status = StudentStatus.ACTIVE
7 |
8 | def __init__(self, name: str, email: str, batch_name: str, psp: int) -> None:
9 | super().__init__(name, email)
10 | self.__batch_name = batch_name
11 |
12 | if (psp < 0 or psp > 100):
13 | raise Exception("PSP should be between 0 and 100")
14 | self.__psp = psp
15 |
16 | def print_details(self) -> None:
17 | print("In Student", self.get_name(), self.__batch_name)
18 |
19 | def change_batch(self, batch_name: str) -> None:
20 | self.batch_name = batch_name
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/python_code/oop/inheritance/StudentStatus.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from enum import Enum
2 |
3 | class StudentStatus(Enum):
4 | ACTIVE = 1
5 | PAUSED = 1
6 | COMPLETED = 1
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/code/python_code/oop/inheritance/User.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | class User:
2 | def __init__(self, name: str, email: str) -> None:
3 | self.__name = name
4 | self.__email = email
5 |
6 | def change_email(self, email: str) -> None:
7 | self.__email = email
8 |
9 | def get_name(self) -> str:
10 | return self.__name
11 |
12 | def print_details(self) -> None:
13 | print("Print with no args")
14 |
15 | def print_details(self, title: str) -> None:
16 | print("\n In User:", title, self.get_name())
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/notes/01-oop-introduction-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/oop/notes/01-oop-introduction-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/notes/01-oop-introduction.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/oop/notes/01-oop-introduction.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/notes/02-constructors-inheritance-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/oop/notes/02-constructors-inheritance-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/notes/02-constructors-inheritance.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/oop/notes/02-constructors-inheritance.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/notes/03-polymorphism-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/oop/notes/03-polymorphism-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/notes/03-polymorphism.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Polymorphism
2 |
3 | ## What is Polymorphism?
4 |
5 | Polymorphism is one of the main aspects of Object-Oriented Programming(OOP). The word polymorphism can be broken down into “Poly” and “morphs”, as “Poly” means many and “Morphs” means forms. In simple words, we can say that ability of a message to be represented in many forms.
6 |
7 | Polymorphism is often referred to as the third pillar of object-oriented programming, after encapsulation and inheritance. Polymorphism is a Greek word that means "many-shaped" and it has two distinct aspects:
8 |
9 | * At run time, objects of a derived class may be treated as objects of a base class in places such as method parameters and collections or arrays. When this polymorphism occurs, the object's declared type is no longer identical to its run-time type
10 | * Base classes may define methods, and derived classes can override them, which means they provide their own definition and implementation. At run-time, when client code calls the method, the CLR looks up the run-time type of the object, and invokes that override of the virtual method. In your source code you can call a method on a base class, and cause a derived class's version of the method to be executed.
11 |
12 | Polymorphism in Java can be achieved in two ways i.e., method overloading and method overriding.
13 |
14 | Polymorphism in Java is mainly divided into two types.
15 |
16 | * Compile-time polymorphism
17 | * Runtime polymorphism
18 |
19 | Compile-time polymorphism can be achieved by method overloading, and Runtime polymorphism can be achieved by method overriding.
20 |
21 | ### Subtyping
22 |
23 | Subtyping is a concept in object-oriented programming that allows a variable of a base class to reference a derived class object. This is called polymorphism, because the variable can take on many forms. The variable can be used to call methods that are defined in the base class, but the actual implementation of the method is defined in the derived class.
24 |
25 | For example, the following is our User class:
26 |
27 | ```java
28 | public class User {
29 | private String name;
30 | private String email;
31 | }
32 | ```
33 |
34 | The user class is extended by the Student class:
35 |
36 | ```java
37 | public class Student extends User {
38 | private String batchName;
39 | private Integer psp;
40 | }
41 | ```
42 |
43 | The Student class inherits the name and email properties from the User class. The Student class also has its own properties batchName and psp. The Student class can be used in place of the User class, because the Student class is a subtype of the User class. The following is an example of how this works:
44 |
45 | ```java
46 | User user = new Student();
47 | ```
48 |
49 | ### Method Overloading
50 |
51 | Method overloading is a feature that allows a class to have more than one method having the same name, if their argument lists are different. It is similar to constructor overloading in Java, that allows a class to have more than one constructor having different argument lists.
52 |
53 | Let's take an example of a class that has two methods having the same name but different in parameters.
54 |
55 | ```java
56 | public class User {
57 | private String name;
58 | private String email;
59 |
60 | public void printUser() {
61 | System.out.println("Name: " + name + ", Email: " + email);
62 | }
63 |
64 | public void printUser(String name, String email) {
65 | System.out.println("Name: " + name + ", Email: " + email);
66 | }
67 | }
68 | ```
69 |
70 | In the above example, the class has two methods with the same name printUser but different in parameters. The first method has no parameters, and the second method has two parameters. This is called method overloading.
71 |
72 | **The compiler distinguishes these two methods by the number of parameters in the list and their data types. The return type of the method does not matter.**
73 |
74 | ### Method Overriding
75 |
76 | Runtime polymorphism is also called Dynamic method dispatch. Instead of resolving the overridden method at compile-time, it is resolved at runtime.
77 |
78 | Here, an overridden child class method is called through its parent's reference. Then the method is evoked according to the type of object. In runtime, JVM figures out the object type and the method belonging to that object.
79 |
80 | Runtime polymorphism in Java occurs when we have two or more classes, and all are interrelated through inheritance. To achieve runtime polymorphism, we must build an "IS-A" relationship between classes and override a method.
81 |
82 | If a child class has a method as its parent class, it is called method overriding.
83 |
84 | If the derived class has a specific implementation of the method that has been declared in its parent class is known as method overriding.
85 |
86 | Rules for overriding a method in Java
87 | * There must be inheritance between classes.
88 | * The method between the classes must be the same(name of the class, number, and type of arguments must be the same).
89 |
90 | Let's add a method to our User class:
91 |
92 | ```java
93 | public class User {
94 | private String name;
95 | private String email;
96 |
97 | public void printUser() {
98 | System.out.println("Name: " + name + ", Email: " + email);
99 | }
100 | }
101 | ```
102 |
103 | Now, let's add a method to our Student class:
104 |
105 | ```java
106 | public class Student extends User {
107 | private String batchName;
108 | private Integer psp;
109 |
110 | @Override
111 | public void printUser() {
112 | System.out.println("Name: " + name + ", Email: " + email + ", Batch: " + batchName + ", PSP: " + psp);
113 | }
114 | }
115 | ```
116 |
117 | In the above example, we have added a method to the Student class that overrides the method in the User class. The Student class has a method with the same name and parameters as the User class. The Student class method has an additional print statement that prints the batchName and psp properties.
118 |
119 | The @Override annotation is optional, but it is a good practice to use it. It is used to ensure that the method is actually being overridden. If the method is not being overridden, the compiler will throw an error.
120 |
121 | ### Advantages of Polymorphism
122 | * Code reusability is the main advantage of polymorphism; once a class is defined, it can be used multiple times to create an object.
123 | * In compile-time polymorphism, the readability of code increases, as nearly similar functions can have the same name, so it becomes easy to understand the functions.
124 | * The same method can be created in the child class as in the parent class in runtime polymorphism.
125 | * Easy to debug the code. You might have intermediate results stored in arbitrary memory locations while executing code, which might get misused by other parts of the program. Polymorphism adds necessary structure and regularity to computation, so it is easier to debug.
126 |
127 | ### Problems with Polymorphism
128 | * Implementing code is complex because understanding the hierarchy of classes and its overridden method is quite difficult.
129 | * Problems during downcasting because implicitly downcasting is not possible. Casting to a child type or casting a common type to an individual type is known as downcasting.
130 | * Sometimes, when the parent class design is not built correctly, subclasses of a superclass use superclass in unexpected ways. This leads to broken code.
131 | * Runtime polymorphism can lead to the real-time performance issue (during the process), it basically degrades the performances as decisions are taken at run time because, machine needs to decide which method or variable to invoke
132 |
133 |
134 | ## Interface
135 |
136 | An interface is a reference type in Java. It is similar to a class, but it cannot be instantiated. It can contain only constants, method signatures, default methods, static methods, and nested types. Method bodies exist only for default methods and static methods.
137 |
138 | It can be thought of as a blueprint of behavior. It is used to achieve abstraction and multiple inheritance in Java.
139 |
140 | ### Why use an interface?
141 |
142 | * It is used to achieve abstraction.
143 | * Due to multiple inheritance, it can achieve loose coupling.
144 | * Define a common behavior for unrelated classes.
145 |
146 | ### How to create an interface?
147 |
148 | Let us create an interface for a Person
149 |
150 | ```java
151 | public interface Person {
152 | String getName();
153 | String getEmail();
154 | }
155 | ```
156 |
157 | Now let's create a class that implements the Person interface:
158 |
159 | ```java
160 | public class User implements Person {
161 | private String name;
162 | private String email;
163 |
164 | public User(String name, String email) {
165 | this.name = name;
166 | this.email = email;
167 | }
168 |
169 | @Override
170 | public String getName() {
171 | return name;
172 | }
173 |
174 | @Override
175 | public String getEmail() {
176 | return email;
177 | }
178 | }
179 | ```
180 |
181 | ## Reading List
182 | * [Duck Typing](https://realpython.com/lessons/duck-typing/#:~:text=Duck%20typing%20is%20a%20concept,a%20given%20method%20or%20attribute.)
183 | * [OOP in Python](https://gist.github.com/kanmaytacker/e6ed49131970c67588fba9164fbc45d4)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/notes/03-polymorphism.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/oop/notes/03-polymorphism.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/notes/04-interfaces-abstract.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Interfaces, Abstract Classes, and Static Methods
2 |
3 | ## Interfaces
4 |
5 | An interface is a reference type in Java. It is similar to a class, but it cannot be instantiated. It can contain only constants, method signatures, default methods, static methods, and nested types. Method bodies exist only for default methods and static methods.
6 |
7 | It can be thought of as a blueprint of behavior. It is used to achieve abstraction and multiple inheritance in Java.
8 |
9 | ### Why use an interface?
10 |
11 | * It is used to achieve abstraction.
12 | * Due to multiple inheritance, it can achieve loose coupling.
13 | * Define a common behavior for unrelated classes.
14 |
15 | ### How to create an interface?
16 |
17 | Let us create an interface for a Person
18 |
19 | ```java
20 | public interface Person {
21 | String getName();
22 | String getEmail();
23 | }
24 | ```
25 |
26 | Now let's create a class that implements the Person interface:
27 |
28 | ```java
29 | public class User implements Person {
30 | private String name;
31 | private String email;
32 |
33 | public User(String name, String email) {
34 | this.name = name;
35 | this.email = email;
36 | }
37 |
38 | @Override
39 | public String getName() {
40 | return name;
41 | }
42 |
43 | @Override
44 | public String getEmail() {
45 | return email;
46 | }
47 | }
48 | ```
49 |
50 | ## Abstract Classes
51 |
52 | An abstract class is a class that is declared abstract. It may or may not include abstract methods. Abstract classes cannot be instantiated, but they can be subclassed. When an abstract class is subclassed, the subclass usually provides implementations for all of the abstract methods in its parent class. However, if it does not, then the subclass must also be declared abstract.
53 |
54 | ### Why use an abstract class?
55 |
56 | * It is used to achieve abstraction.
57 | * It can have abstract methods and non-abstract methods.
58 | * When you don't want to provide the implementation of a method, you can make it abstract.
59 | * When you don't want to allow the instantiation of a class, you can make it abstract.
60 |
61 | ### How to create an abstract class?
62 |
63 | Let us create an abstract class for a Person
64 | You can create an abstract class by using the abstract keyword.
65 | Similarly, you can create an abstract method by using the abstract keyword.
66 |
67 | ```java
68 | public abstract Person {
69 |
70 | public abstract String getName();
71 | public abstract String getEmail();
72 | }
73 | ```
74 |
75 | Now let's create a class that extends the Person abstract class:
76 |
77 | ```java
78 | public class User extends Person {
79 | private String name;
80 | private String email;
81 |
82 | public User(String name, String email) {
83 | this.name = name;
84 | this.email = email;
85 | }
86 |
87 | @Override
88 | public String getName() {
89 | return name;
90 | }
91 |
92 | @Override
93 | public String getEmail() {
94 | return email;
95 | }
96 | }
97 | ```
98 |
99 | ## Static Methods
100 |
101 | Static methods are methods that can be called without creating an instance of the class. They are declared using the static keyword.
102 |
103 | ### Why use a static method?
104 |
105 | * You can call a static method without creating an instance of the class.
106 | * You don't need to have separate implementations of the same method for each instance of the class.
107 |
108 | ### How to create a static method?
109 |
110 | Let us create a static method for a Person
111 |
112 | ```java
113 | public class Person {
114 | private String name;
115 | private String email;
116 |
117 | public Person(String name, String email) {
118 | this.name = name;
119 | this.email = email;
120 | }
121 |
122 | public static String getPersonInfo(Person person) {
123 | return person.getName() + " " + person.getEmail();
124 | }
125 | }
126 | ```
127 |
128 | Now let's create a class that uses the static method:
129 |
130 | ```java
131 | public class User {
132 | public static void main(String[] args) {
133 | Person person = new Person("John", "Doee");
134 |
135 | System.out.println(Person.getPersonInfo(person));
136 | }
137 | }
138 | ```
139 |
140 |
141 |
142 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/notes/04-solid-01-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/oop/notes/04-solid-01-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/notes/04-solid-01.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/oop/notes/04-solid-01.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/notes/05-solid-02-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/oop/notes/05-solid-02-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/oop/notes/05-solid-02.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/oop/notes/05-solid-02.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Notes
2 |
3 | | Name | .md | .pdf | Handwritten | MCQs | Worksheet | Worksheet with Answers |
4 | | -------------------------- | --------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------ | --------- | ---------------------- |
5 | | Operating Systems - Primer | [1](notes/01-os-primer.md) | [2](notes/01-os-primer.pdf) | [3](notes/01-os-primer-hw.pdf) | [4](notes/01-os-primer-mcqs.pdf) | - | - |
6 | | Round Robin and Threads | [1](notes/02-round-robin-threads.md) | [2](notes/02-round-robin-threads.pdf) | [3](notes/02-round-robin-threads-hw.pdf) | [4](notes/02-round-robin-threads-mcqs.pdf) | - | - |
7 | | Thread Synchronisation | [1](notes/03-thread-synchronisation.md) | [2](notes/03-thread-synchronisation.pdf) | [3](notes/03-thread-synchronisation-hw.pdf) | [4](mcqs/03-thread-synchronisation.md) | _ | _ |
8 | | Memory management | [1](notes/04-memory-management.md) | [2](notes/04-memory-management.pdf) | [3](notes/04-memory-management-hw.pdf) | [4](mcqs/04-memory-management.md) | _ | _ |
9 |
10 | ## Problem sets
11 | 1. [**Print in order**](https://leetcode.com/problems/print-in-order/submissions/)
12 | 2. [Dining philosopher's problem](https://leetcode.com/problems/the-dining-philosophers/)
13 | 3. [Print Zero even odd](https://leetcode.com/problems/print-zero-even-odd/)
14 | 4. [Foo Bar](https://leetcode.com/problems/print-foobar-alternately/)
15 | 5. [Traffic Light](https://leetcode.com/problems/traffic-light-controlled-intersection/)
16 |
17 | Bold problems were solved during the session.
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/pom.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 | 4.0.0
5 |
6 | com.scaler
7 | os
8 | pyenv shell 3.9.7
9 |
10 | os
11 |
12 | http://www.example.com
13 |
14 |
15 | UTF-8
16 | 1.9
17 | 1.9
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 | junit
23 | junit
24 | 4.11
25 | test
26 |
27 |
28 | org.projectlombok
29 | lombok
30 | 1.18.24
31 | provided
32 |
33 |
34 | org.javatuples
35 | javatuples
36 | 1.2
37 |
38 |
39 |
40 |
41 |
42 |
43 |
44 |
45 |
46 | maven-clean-plugin
47 | 3.1.0
48 |
49 |
50 |
51 | maven-resources-plugin
52 | 3.0.2
53 |
54 |
55 | maven-compiler-plugin
56 | 3.8.0
57 |
58 |
59 | maven-surefire-plugin
60 | 2.22.1
61 |
62 |
63 | maven-jar-plugin
64 | 3.0.2
65 |
66 |
67 | maven-install-plugin
68 | 2.5.2
69 |
70 |
71 | maven-deploy-plugin
72 | 2.8.2
73 |
74 |
75 |
76 | maven-site-plugin
77 | 3.7.1
78 |
79 |
80 | maven-project-info-reports-plugin
81 | 3.0.0
82 |
83 |
84 |
85 |
86 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/src/main/java/com/scaler/App.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler;
2 |
3 | import com.scaler.threads.Printer;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | * Hello world!
7 | *
8 | */
9 | public class App {
10 |
11 | public static void main(String[] args) {
12 | System.out.println("Hello world. Printed by :" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
13 | for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
14 | Printer printer = new Printer(String.valueOf(i));
15 | Thread thread = new Thread(printer);
16 | thread.start();
17 | }
18 | }
19 | }
20 |
21 | // Print number 1 to 10 on a single thread
22 | // Print number 1 to 10 each on different threads
23 | // 1 - Thread 1
24 | // 2 - Thread 2
25 | // ...
26 | // 10 Thread 10
27 |
28 | //
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/src/main/java/com/scaler/TextPrinter.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler;
2 |
3 | import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
4 |
5 | @AllArgsConstructor
6 | public class TextPrinter implements Runnable {
7 |
8 | private String text;
9 |
10 | @Override
11 | public void run() {
12 | System.out.println(text + " printed by: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
13 | }
14 | }
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/src/main/java/com/scaler/addersubtractor/Adder.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.addersubtractor;
2 |
3 | import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
4 |
5 | @AllArgsConstructor
6 | public class Adder implements Runnable {
7 | private Count count;
8 |
9 | @Override
10 | public void run() {
11 |
12 | for (int i = 1; i <= 100; ++i) {
13 |
14 | int value = count.getValue();
15 | try {
16 | Thread.sleep(50);
17 | } catch (Exception e) {
18 | System.out.println("Something wrong happened");
19 | }
20 |
21 | int nextValue = value + i;
22 | count.setValue(nextValue);
23 |
24 | try {
25 | Thread.sleep(10);
26 | } catch (Exception e) {
27 | System.out.println("Something wrong happened");
28 | }
29 | }
30 |
31 | }
32 | }
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/src/main/java/com/scaler/addersubtractor/Count.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.addersubtractor;
2 |
3 | public class Count {
4 | private volatile int value = 0;
5 |
6 | public int getValue() {
7 | return value;
8 | }
9 |
10 | public void setValue(int value) {
11 | this.value = value;
12 | }
13 | }
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/src/main/java/com/scaler/addersubtractor/Runner.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.addersubtractor;
2 |
3 | import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
4 | import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
5 | import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
6 |
7 | public class Runner {
8 | public static void main(String[] args) {
9 | Count count = new Count();
10 |
11 | Adder adder = new Adder(count);
12 | Subtractor subtractor = new Subtractor(count);
13 |
14 | ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
15 | executor.execute(adder);
16 | executor.execute(subtractor);
17 |
18 | executor.shutdown();
19 | try {
20 | executor.awaitTermination(100, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
21 | } catch (Exception e) {
22 | System.out.println("Something wrong happened");
23 | }
24 |
25 | System.out.println(count.getValue());
26 | }
27 | }
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/src/main/java/com/scaler/addersubtractor/Subtractor.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.addersubtractor;
2 |
3 | import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
4 |
5 | @AllArgsConstructor
6 | public class Subtractor implements Runnable {
7 | private Count count;
8 |
9 | @Override
10 | public void run() {
11 |
12 | for (int i = 1; i <= 100; ++i) {
13 |
14 | int value = count.getValue();
15 | try {
16 | Thread.sleep(50);
17 | } catch (Exception e) {
18 | System.out.println("Something wrong happened");
19 | }
20 |
21 | int nextValue = value - i;
22 | count.setValue(nextValue);
23 |
24 | try {
25 | Thread.sleep(10);
26 | } catch (Exception e) {
27 | System.out.println("Something wrong happened");
28 | }
29 |
30 | for (int j = 0; j < 10000; ++j) {
31 | // do something
32 | }
33 | }
34 |
35 | }
36 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/src/main/java/com/scaler/mergesort/Runner.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.mergesort;
2 |
3 | import java.util.List;
4 | import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
5 | import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
6 | import java.util.concurrent.Future;
7 |
8 | public class Runner {
9 | public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
10 | List values = List.of(
11 | 10, 9, 8, 7, 1, 2, 3, 4);
12 |
13 | ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
14 | Sorter sorter = new Sorter(values, executor);
15 | Future> sortedValues = executor.submit(sorter);
16 | System.out.println(sortedValues.get());
17 | }
18 | }
19 |
20 | // Assignment - Implement quick sort
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/src/main/java/com/scaler/mergesort/Sorter.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.mergesort;
2 |
3 | import java.util.ArrayList;
4 | import java.util.List;
5 | import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
6 | import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
7 | import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
8 | import java.util.concurrent.Future;
9 |
10 | import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
11 |
12 | @AllArgsConstructor
13 | public class Sorter implements Callable> {
14 | private List values = new ArrayList<>();
15 | private ExecutorService executorService;
16 |
17 | @Override
18 | public List call() throws Exception {
19 |
20 | // Base case - If size of array 1 is return
21 | if (values.size() <= 1) {
22 | return values;
23 | }
24 |
25 | // Split the array
26 | int mid = values.size() / 2;
27 |
28 | List leftArray = values.subList(0, mid);
29 | List rightArray = values.subList(mid, values.size());
30 |
31 | Sorter leftSorter = new Sorter(leftArray, executorService);
32 | Sorter rightSorter = new Sorter(rightArray, executorService);
33 |
34 | Future> sortedLeft = executorService.submit(leftSorter);
35 | Future> sortedRight = executorService.submit(rightSorter);
36 |
37 | // Merge the array
38 | return merge(sortedLeft, sortedRight);
39 | }
40 |
41 | private List merge(Future> sortedLeftFuture, Future> sortedRightFuture)
42 | throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
43 | List sortedArray = new ArrayList<>();
44 | int first = 0;
45 | int second = 0;
46 |
47 | List sortedLeft = sortedLeftFuture.get();
48 | List sortedRight = sortedRightFuture.get();
49 |
50 | // Compare values from both the arrays
51 | while (first < sortedLeft.size() && second < sortedRight.size()) {
52 | // If left is smaller, add to sorted array
53 | // increment first
54 | if (sortedLeft.get(first) < sortedRight.get(second)) {
55 | sortedArray.add(sortedLeft.get(first));
56 | ++first;
57 | } else {
58 | // Add the right one to the sorted array
59 | // increment second
60 | sortedArray.add(sortedRight.get(second));
61 | ++second;
62 | }
63 | }
64 |
65 | while (first < sortedLeft.size()) {
66 | sortedArray.add(sortedLeft.get(first));
67 | ++first;
68 | }
69 |
70 | while (second < sortedRight.size()) {
71 | sortedArray.add(sortedRight.get(second));
72 | ++second;
73 | }
74 |
75 | return sortedArray;
76 | }
77 |
78 | }
79 |
80 | // Parallel - multiple tasks at same time instant
81 | // 7:11 - Task 1
82 | // 7:11 - Task 2
83 |
84 | // Person 1 Done
85 | // Person 2 IN PROCESS
86 | // Person 3 NOT started
87 |
88 | // Concurrency - Two tasks at different stages of execution
89 | // Person 1 - Intro 10% IN PROCESS
90 | // Person 2 - intro 10% IN PROCESS
91 | // Person 3 - intro 10% IN PROCESS
92 |
93 | // Person 1 - Query
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/src/main/java/com/scaler/producerconsumer/Consumer.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.producerconsumer;
2 |
3 | import java.util.Queue;
4 | import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
5 |
6 | import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
7 | import lombok.Getter;
8 |
9 | @AllArgsConstructor
10 | @Getter
11 | public class Consumer implements Runnable {
12 |
13 | private Queue store;
14 | private String name;
15 | private Semaphore forProducer;
16 | private Semaphore forConsumer;
17 |
18 | @Override
19 | public void run() {
20 | while (true) {
21 | try {
22 | forConsumer.acquire();
23 | } catch (InterruptedException e) {
24 | throw new RuntimeException("Error acquiring semaphore " + e);
25 | }
26 |
27 | store.remove();
28 | System.out.println("Consumed: " + name + " Left units :" + store.size());
29 |
30 | forProducer.release();
31 |
32 | }
33 |
34 | }
35 |
36 | }
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/src/main/java/com/scaler/producerconsumer/Producer.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.producerconsumer;
2 |
3 | import java.util.Queue;
4 | import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
5 |
6 | import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
7 | import lombok.Getter;
8 |
9 | @AllArgsConstructor
10 | @Getter
11 | public class Producer implements Runnable {
12 |
13 | private Queue store;
14 | private int maxSize;
15 | private String name;
16 | private Semaphore forProducer;
17 | private Semaphore forConsumer;
18 |
19 | @Override
20 | public void run() {
21 | while (true) {
22 | try {
23 | forProducer.acquire();
24 | } catch (InterruptedException e) {
25 | throw new RuntimeException("Error acquiring semaphore " + e);
26 | }
27 |
28 | store.add(new UnitOfWork());
29 | System.out.println("Produced: " + name + " Left units :" + store.size());
30 |
31 | forConsumer.release();
32 | }
33 |
34 | }
35 |
36 | }
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/src/main/java/com/scaler/producerconsumer/Runner.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.producerconsumer;
2 |
3 | import java.util.Queue;
4 | import java.util.Set;
5 | import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedDeque;
6 | import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
7 | import java.util.stream.Collectors;
8 |
9 | public class Runner {
10 |
11 | private static final Set producerNames = Set.of("p1", "p2", "p3");
12 | private static final Set consumerNames = Set.of("c1", "c2", "c3", "c4");
13 |
14 | public static void main(String[] args) {
15 | Queue store = new ConcurrentLinkedDeque<>();
16 | int maxSize = 20;
17 |
18 | Semaphore forProducer = new Semaphore(maxSize);
19 | Semaphore forConsumer = new Semaphore(0);
20 |
21 | Set producers = producerNames
22 | .stream()
23 | .map(name -> new Producer(store, maxSize, name, forProducer, forConsumer))
24 | .collect(Collectors.toSet());
25 |
26 | Set consumers = consumerNames
27 | .stream()
28 | .map(name -> new Consumer(store, name, forProducer, forConsumer))
29 | .collect(Collectors.toSet());
30 |
31 | producers.forEach(producer -> new Thread(producer).start());
32 | consumers.forEach(consumer -> new Thread(consumer).start());
33 |
34 | }
35 | }
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/src/main/java/com/scaler/producerconsumer/UnitOfWork.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.producerconsumer;
2 |
3 | public class UnitOfWork {
4 |
5 | }
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/src/main/java/com/scaler/scheduling/FirstComeFirstServe.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.scheduling;
2 |
3 | import java.util.LinkedList;
4 | import java.util.List;
5 | import java.util.Queue;
6 |
7 | import com.scaler.scheduling.models.IncomingProcess;
8 | import com.scaler.scheduling.models.ScheduledProcess;
9 |
10 | public class FirstComeFirstServe {
11 |
12 | public List schedule(List processes) {
13 |
14 | // Get a sorted list of processes
15 | Queue queue = prepareQueue(processes);
16 | List scheduledProcesses = new LinkedList<>();
17 |
18 | int time = 0;
19 | int index = 0;
20 |
21 | // Check if there are any processes in the queue
22 | while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
23 | IncomingProcess process = queue.poll();
24 |
25 | // Increment elapsed time by the burst time of the process
26 | time += process.getBurstTime();
27 | index += 1;
28 |
29 | process.setCompletedAt(time);
30 |
31 | // Add the process to the list of scheduled processes
32 | scheduledProcesses.add(new ScheduledProcess(index, process));
33 | }
34 |
35 | return scheduledProcesses;
36 | }
37 |
38 | // When ever we get a new process, we add it to the queue
39 | private Queue prepareQueue(List processes) {
40 | // Simulate a queue using a linked list
41 | Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
42 |
43 | List sortedProcesses = new LinkedList<>(processes);
44 |
45 | // Sort the processes by arrival time to simulate FCFS
46 | sortedProcesses.sort((p1, p2) -> p1.getArrivalTime() - p2.getArrivalTime());
47 |
48 | for (IncomingProcess process : sortedProcesses) {
49 | queue.add(process);
50 | }
51 | return queue;
52 | }
53 | }
54 |
55 | // Side-assignment
56 | // Implement tie breaking in scheduling
57 | // If two processes have the same arrival time
58 | // * Check the id
59 | // * Also, you can check the burst time
60 | // One line code
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/src/main/java/com/scaler/scheduling/models/IncomingProcess.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.scheduling.models;
2 |
3 | import lombok.Getter;
4 | import lombok.Setter;
5 |
6 | @Getter
7 | @Setter
8 | public class IncomingProcess {
9 | private int id;
10 | private int arrivalTime;
11 | private int burstTime; // How long the process will take to complete
12 |
13 | private int completedAt;
14 |
15 | public IncomingProcess(int id, int arrivalTime, int burstTime) {
16 | this.id = id;
17 | this.arrivalTime = arrivalTime;
18 | this.burstTime = burstTime;
19 | }
20 | }
21 |
22 | // List schedule(List)
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/src/main/java/com/scaler/scheduling/models/ScheduledProcess.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.scheduling.models;
2 |
3 | import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
4 | import lombok.Getter;
5 |
6 | @AllArgsConstructor
7 | @Getter
8 | public class ScheduledProcess {
9 |
10 | private int index;
11 | private IncomingProcess process;
12 |
13 | public int getId() {
14 | return process.getId();
15 | }
16 | }
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/src/main/java/com/scaler/threads/Printer.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.threads;
2 |
3 | import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
4 |
5 | @AllArgsConstructor
6 | public class Printer implements Runnable {
7 |
8 | private String text;
9 |
10 | @Override
11 | public void run() {
12 | System.out.println(text + " Printed by " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
13 | }
14 | }
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/src/test/java/com/scaler/AppTest.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler;
2 |
3 | import static org.junit.Assert.assertTrue;
4 |
5 | import org.junit.Test;
6 |
7 | /**
8 | * Unit test for simple App.
9 | */
10 | public class AppTest
11 | {
12 | /**
13 | * Rigorous Test :-)
14 | */
15 | @Test
16 | public void shouldAnswerWithTrue()
17 | {
18 | assertTrue( true );
19 | }
20 | }
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/src/test/java/com/scaler/scheduling/FirstComeFirstServeTest.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.scaler.scheduling;
2 |
3 | import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
4 |
5 | import java.util.List;
6 | import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
7 | import java.util.stream.Collectors;
8 |
9 | import org.javatuples.Pair;
10 | import org.junit.Test;
11 |
12 | import com.scaler.scheduling.models.IncomingProcess;
13 | import com.scaler.scheduling.models.ScheduledProcess;
14 |
15 | public class FirstComeFirstServeTest {
16 |
17 | private static AtomicInteger generator = new AtomicInteger();
18 |
19 | private List> processTimes = List.of(
20 | Pair.with(2, 6),
21 | Pair.with(1, 8),
22 | Pair.with(0, 3),
23 | Pair.with(4, 4));
24 |
25 | private List expectedOrder = List.of(3, 2, 1, 4);
26 | private List expectedCompletionTimes = List.of(3, 11, 17, 21);
27 |
28 | @Test
29 | public void test() {
30 | FirstComeFirstServe firstComeFirstServe = new FirstComeFirstServe();
31 | List scheduledProcesses = firstComeFirstServe.schedule(incomingProcesses(processTimes));
32 |
33 | assertEquals("If n processes are given, then n processes should be scheduled", processTimes.size(),
34 | scheduledProcesses.size());
35 |
36 | List actualOrder = scheduledProcesses.stream().map(ScheduledProcess::getId)
37 | .collect(Collectors.toList());
38 | assertEquals("The order of the processes should be the same as the order of the input", expectedOrder,
39 | actualOrder);
40 |
41 | List actualCompletionTimes = scheduledProcesses.stream().map(ScheduledProcess::getProcess)
42 | .map(IncomingProcess::getCompletedAt)
43 | .collect(Collectors.toList());
44 |
45 | assertEquals("The completion time of the processes should be the same as the expected completion times",
46 | expectedCompletionTimes,
47 | actualCompletionTimes);
48 |
49 | }
50 |
51 | private static List incomingProcesses(List> processTimes) {
52 |
53 | return processTimes.stream()
54 | .map(p -> new IncomingProcess(generator.incrementAndGet(), p.getValue0(), p.getValue1()))
55 | .collect(Collectors.toList());
56 | }
57 | }
58 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/target/classes/com/scaler/App.class:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/os/code/os/target/classes/com/scaler/App.class
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/target/classes/com/scaler/producerconsumer/UnitOfWork.class:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/os/code/os/target/classes/com/scaler/producerconsumer/UnitOfWork.class
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/code/os/target/test-classes/com/scaler/AppTest.class:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/os/code/os/target/test-classes/com/scaler/AppTest.class
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/notes/01-os-primer-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/os/notes/01-os-primer-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/notes/01-os-primer.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/os/notes/01-os-primer.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/notes/02-round-robin-threads-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/os/notes/02-round-robin-threads-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/notes/02-round-robin-threads.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/os/notes/02-round-robin-threads.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/notes/03-thread-synchronisation-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/os/notes/03-thread-synchronisation-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/notes/03-thread-synchronisation.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Thread synchronisation
2 |
3 | ## Agenda
4 | * Producer-consumer problem
5 | * Semaphores
6 | * Concurrent data structures
7 | * Atomic Integer
8 | * Concurrent Hash Map
9 |
10 |
11 | ## Producer-consumer problem
12 |
13 | The Producer-Consumer problem is a classic synchronization problem in operating systems.
14 |
15 | The problem is defined as follows: there is a fixed-size buffer and a Producer process, and a Consumer process.
16 |
17 | The Producer process creates an item and adds it to the shared buffer. The Consumer process takes items out of the shared buffer and “consumes” them.
18 |
19 | 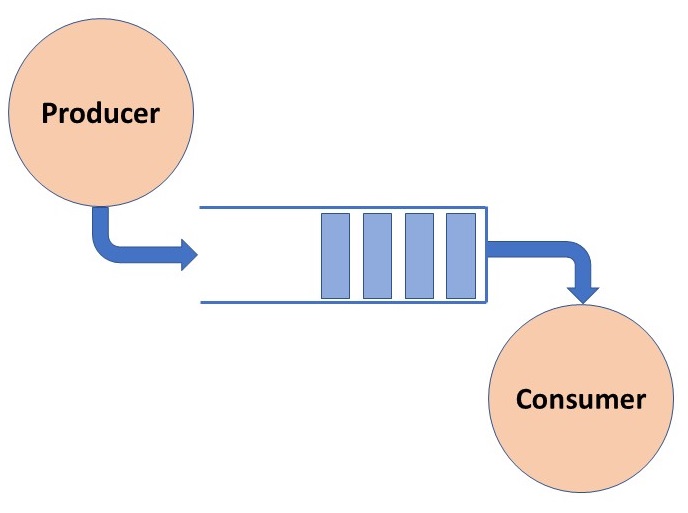
20 |
21 | Certain conditions must be met by the Producer and the Consumer processes to have consistent data synchronisation:
22 |
23 | * The Producer process must not produce an item if the shared buffer is full.
24 |
25 | * The Consumer process must not consume an item if the shared buffer is empty.
26 |
27 |
28 | ### Producer
29 | The task of the producer is to create a unit of work and add it to the store. The consumer will pick that up when it is available. The producer cannot add exceed the number of max units of the store.
30 |
31 | ```java
32 | public void run() {
33 | while (true) {
34 | if (store.size() < maxSizeOfStore) {
35 | store.add(new UnitOfWork());
36 | }
37 | }
38 | }
39 | ```
40 |
41 | ### Consumer
42 | The role of the consumer is to pick up unit of works from the queue or the store once they have been added by the consumer. The consumer can only pick up units if there are any available.
43 |
44 | ```java
45 | public void run() {
46 | while (true) {
47 | if (store.size() > 0) {
48 | store.remove();
49 | }
50 | }
51 | }
52 | ```
53 |
54 | The above code will lead to concurrency issues since multiple thread can access the store at one time.
55 | What happens if there is only one unit present, but two consumers try to acquire it at the same time.
56 | Since the size of the store will be 1, both of them will be allowed to execute, but one will error out.
57 |
58 | ### Base Solution - Mutex
59 |
60 | In order to solver the concurrency issue, we can use mutexes or locks.
61 | In Java this can be achieved by simply wrapping the critical section in a synchronised block.
62 |
63 |
64 | ```java
65 | public void run() {
66 | while (true) {
67 | synchronized (store) {
68 | if (store.size() < maxSizeOfStore) {
69 | store.add(new Shirt());
70 | }
71 | }
72 | }
73 | }
74 | ```
75 |
76 | Now only one thread will be able to access the store at one time. This will solve the concurrency issue, but our execution does not happen in parallel now. Due to the mutex, only one thread can access the store at a time.
77 |
78 | ### Parallel solution - Semaphore
79 |
80 | A semaphore is a variable or abstract data type used to control access to a common resource by multiple threads and avoid critical section problems in a concurrent system such as a multitasking operating system. The main attribute of a semaphore is how many thread does it control. If a semaphore handles just one thread, it is effectively similar to a mutex.
81 |
82 | To solve our producer and consumer problem, we can use two semaphores:
83 | 1. For Producer - This semaphore will control the maximum number of producers and is initialised with the max stor size.
84 | 2. For Consumer - This semaphore controls the maximum number of consumers. This starts with 0 active threads.
85 |
86 | ```java
87 | Semaphore forProducer = new Semaphore(maxSize);
88 | Semaphore forConsumer = new Semaphore(0);
89 | ```
90 |
91 | The ideal situation for us is that:
92 | * There are parallel threads that are able to produce until all the store is filled.
93 | * There are parallel threads that are able to consume until all the store is empty.
94 |
95 | Thus, to achieve this we use each producer thread to signal to the consumer that it has added a new unit. Similarly, once the consumer has reduced the unit of works, it signals it to the producer to start making more.
96 |
97 | ```java
98 |
99 | // Producer
100 |
101 | while (true) {
102 | forProducer.acquire();
103 | store.add(new UnitOfWork());
104 | forConsumer.release();
105 | }
106 | ```
107 |
108 | ```java
109 |
110 | // Consumer
111 |
112 | while (true) {
113 | forConsumer.acquire();
114 | store.add(new UnitOfWork());
115 | forProducer.release();
116 | }
117 | ```
118 |
119 | ## Concurrent Data structures
120 |
121 | A concurrent data structure is a particular way of storing and organizing data for access by multiple computing threads (or processes) on a computer. A shared mutable state very easily leads to problems when concurrency is involved. If access to shared mutable objects is not managed properly, applications can quickly become prone to some hard-to-detect concurrency errors.
122 |
123 | Some common concurrent data structures:
124 | 1. [Atomic Integer](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/atomic/AtomicInteger.html#:~:text=An%20AtomicInteger%20is%20used%20in,deal%20with%20numerically%2Dbased%20classes)
125 | > The AtomicInteger class protects an underlying int value by providing methods that perform atomic operations on the value
126 | 2. [Concurrent hash maps](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/concurrent/ConcurrentHashMap.html)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/notes/03-thread-synchronisation.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/os/notes/03-thread-synchronisation.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/notes/03-threads-synchronisation-hw-02.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/os/notes/03-threads-synchronisation-hw-02.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/notes/03-threads-synchronisation-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/os/notes/03-threads-synchronisation-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/notes/03-threads-synchronisation.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Threads and Synchronisation
2 |
3 | ## Executor
4 |
5 | The `Executor` interface is used to execute tasks. It is a generic interface that can be used to execute any kind of task. The `Executor` interface has only one method:
6 |
7 | ```java
8 | public interface Executor {
9 | void execute(Runnable command);
10 | }
11 | ```
12 |
13 | The `execute` method takes a `Runnable` object as a parameter. The `Runnable` interface is a functional interface that has only one method. Executors internally use a thread pool to execute the tasks. The `execute` method is non-blocking. It returns immediately after submitting the task to the thread pool. The `execute` method is used to execute tasks that do not return a result.
14 |
15 | A thread pool is a collection of threads that are used to execute tasks.
16 | Instead of creating a new thread for each task, a thread pool reuses the existing threads to execute the tasks. This improves the performance of the application.
17 |
18 | The `Executor` interface has a method called `newCachedThreadPool` that returns an `ExecutorService` object. The `ExecutorService` interface extends the `Executor` interface. The `ExecutorService` interface has methods to execute tasks that return a result. The `ExecutorService` interface also has methods to shutdown the thread pool.
19 |
20 | To run a task using the `Executor` interface, we can use the `newCachedThreadPool` method to create an `ExecutorService` object. The `newCachedThreadPool` method returns an `ExecutorService` object that uses a thread pool with a variable number of threads. The `newCachedThreadPool` method creates a new thread for each task if there are no idle threads in the thread pool. If there is an idle thread in the thread pool, the `newCachedThreadPool` method reuses the idle thread to execute the task. The `newCachedThreadPool` method returns an `ExecutorService` object that uses a thread pool with a variable number of threads.
21 |
22 | ```java
23 | Executor executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
24 | executorService.execute(() -> System.out.println("Hello World"));
25 | ```
26 |
27 | ## Callable and Future
28 |
29 | Runnables do not return a result. If we want to execute a task that returns a result, we can use the `Callable` interface. The `Callable` interface is a functional interface that has only one method:
30 |
31 | ```java
32 | public interface Callable {
33 | V call() throws Exception;
34 | }
35 | ```
36 |
37 | The `call` method returns a result of type `V`. The `call` method can throw an exception. The `Callable` interface is used to execute tasks that return a result.
38 | For instance we can use the `Callable` interface to execute a task that returns the sum of two numbers:
39 |
40 | ```java
41 | Callable sumTask = () -> 2 + 3;
42 | ```
43 |
44 | In order to execute a task that returns a result, we can use the `submit` method of the `ExecutorService` interface. The `submit` method takes a `Callable` object as a parameter. The `submit` method returns a `Future` object. The `Future` interface has a method called `get` that returns the result of the task. The `get` method is a blocking method. It waits until the task is completed and then returns the result of the task.
45 |
46 | ```java
47 | ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
48 | Future future = executorService.submit(() -> 2 + 3);
49 | Integer result = future.get();
50 | ```
51 |
52 | Futures can be used to cancel tasks. The `Future` interface has a method called `cancel` that can be used to cancel a task. The `cancel` method takes a boolean parameter. If the boolean parameter is `true`, the task is cancelled even if the task is already running. If the boolean parameter is `false`, the task is cancelled only if the task is not running.
53 |
54 | ```java
55 | ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
56 | Future future = executorService.submit(() -> 2 + 3);
57 | future.cancel(false);
58 | ```
59 |
60 | ## Synchronisation
61 |
62 | Whenever we have multiple threads that access the same resource, we need to make sure that the threads do not interfere with each other. This is called synchronisation.
63 |
64 | Synchronisation can be seen in the adder and subtractor example. The adder and subtractor threads access the same counter variable. If the adder and subtractor threads do not synchronise, the counter variable can be in an inconsistent state.
65 |
66 | * Create a count class that has a count variable.
67 | * Create two different classes `Adder` and `Subtractor`.
68 | * Accept a count object in the constructor of both the classes.
69 | * In `Adder`, iterate from 1 to 100 and increment the count variable by 1 on each iteration.
70 | * In `Subtractor`, iterate from 1 to 100 and decrement the count variable by 1 on each iteration.
71 | * Print the final value of the count variable.
72 | * What would the ideal value of the count variable be?
73 | * What is the actual value of the count variable?
74 | * Try to add some delay in the `Adder` and `Subtractor` classes using inspiration from the code below. What is the value of the count variable now?
75 |
76 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/notes/04-memory-management-hw.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/os/notes/04-memory-management-hw.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/notes/04-memory-management.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kanmaytacker/fundamentals/cf95ff808f840454d89e7e2194e0a4c64776d7f0/os/notes/04-memory-management.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/os/notes/04-synchronisation.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Synchronisation
2 | - [Synchronisation](#synchronisation)
3 | - [Adder and Subtractor problem](#adder-and-subtractor-problem)
4 | - [Adder](#adder)
5 | - [Subtractor](#subtractor)
6 | - [Runner](#runner)
7 | - [Synchronisation](#synchronisation-1)
8 | - [Characteristics of synchronisation problems](#characteristics-of-synchronisation-problems)
9 | - [Properties of a good solution](#properties-of-a-good-solution)
10 | - [Solutions to synchronisation problems](#solutions-to-synchronisation-problems)
11 | - [Mutex Locks](#mutex-locks)
12 | - [Properties of a mutex lock](#properties-of-a-mutex-lock)
13 | - [Syncronised keyword](#syncronised-keyword)
14 | ## Adder and Subtractor problem
15 |
16 | The adder and subtractor problem is a problem that is used to demonstrate the need for synchronisation in a system.
17 | The problem is as follows:
18 | * Create a count class that has a count variable.
19 | * Create two different classes `Adder` and `Subtractor`.
20 | * Accept a count object in the constructor of both the classes.
21 | * In `Adder`, iterate from 1 to 100 and increment the count variable by 1 on each iteration.
22 | * In `Subtractor`, iterate from 1 to 100 and decrement the count variable by 1 on each iteration.
23 | * Print the final value of the count variable.
24 | * What would the ideal value of the count variable be?
25 | * What is the actual value of the count variable?
26 | * Try to add some delay in the `Adder` and `Subtractor` classes using inspiration from the code below. What is the value of the count variable now?
27 |
28 | ### Adder
29 |
30 | ```java
31 | public class Adder implements Runnable {
32 | private Count count;
33 |
34 | public Adder(Count count) {
35 | this.count = count;
36 | }
37 |
38 | @Override
39 | public void run() {
40 | for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
41 | count.increment();
42 | }
43 | }
44 | }
45 | ```
46 |
47 | ### Subtractor
48 |
49 | ```java
50 | public class Subtractor implements Runnable {
51 | private Count count;
52 |
53 | public Subtractor(Count count) {
54 | this.count = count;
55 | }
56 |
57 | @Override
58 | public void run() {
59 | for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
60 | count.decrement();
61 | }
62 | }
63 | }
64 | ```
65 |
66 | ### Runner
67 |
68 | ```java
69 | public class Runner {
70 | public static void main(String[] args) {
71 | Count count = new Count();
72 | Adder adder = new Adder(count);
73 | Subtractor subtractor = new Subtractor(count);
74 |
75 | Thread adderThread = new Thread(adder);
76 | Thread subtractorThread = new Thread(subtractor);
77 |
78 | adderThread.start();
79 | subtractorThread.start();
80 |
81 | adderThread.join();
82 | subtractorThread.join();
83 |
84 | System.out.println(count.getCount());
85 | }
86 | }
87 | ```
88 |
89 | ## Synchronisation
90 |
91 | Running the above code should ideally result in the count variable being 0. However, if you increase the number of iterations in the `Adder` and `Subtractor` classes, you will see that the count variable is not 0. This is because the `Adder` and `Subtractor` classes are running in parallel and are not synchronised. This means that the `Adder` and `Subtractor` classes are not waiting for each other to finish before they start their own iterations. This results in the count variable being incremented and decremented at the same time, resulting in the count variable not being 0.
92 |
93 | The major issue is that multiple threads are accessing a shared resource at the same time.
94 |
95 | ### Characteristics of synchronisation problems
96 | * `Critical section` - A section of code that is accessed by multiple threads. When multiple threads access the same critical section, the result is a synchronisation problem that might yield wrong or inconsistent results.
97 |
98 | ```java
99 | public void run() {
100 | for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
101 | count.increment(); // Critical section
102 | }
103 | }
104 | ```
105 | * `Race Conditions` - When more than one thread tries to enter the critical section at the same time.
106 | * `Preemption` - When a thread is interrupted by another thread. It could be possible that the interrupted thread is in the middle of a critical section. This could result in the interrupted thread not being able to finish the critical section and yield inconsistent results.
107 |
108 | ### Properties of a good solution
109 | * `Mutual Exclusion` - Only one thread can access the critical section at a time.
110 | * `Progress` - If a thread wants to enter the critical section, it will eventually be able to do so.
111 | * `Bounded Waiting` - If a thread wants to enter the critical section, it will eventually be able to do so, but only after a finite number of other threads have entered the critical section.
112 | * `No busy Waiting` - If a thread wants to enter the critical section, it will not be able to do so until the critical section is free. It has to keep checking if the critical section is free. This is called busy waiting.
113 | * `Notification` - If a thread is waiting to enter the critical section, it should be notified when the critical section is free.
114 |
115 | ## Solutions to synchronisation problems
116 |
117 | ### Mutex Locks
118 |
119 | Mutex locks are a way to solve the synchronisation problem. Mutex locks are a way to ensure that only one thread can access a critical section at a time. Mutex locks are also known as `mutual exclusion locks`.
120 |
121 | A thread can only access the critical section if it has the lock. If a thread does not have the lock, it cannot access the critical section. If a thread has the lock, it can access the critical section. If a thread has the lock, it can release the lock and allow another thread to access the critical section.
122 |
123 | Think of a room with a lock. Only one person can enter the room at a time. If a person has the key, they can enter the room. If a person does not have the key, they cannot enter the room. If a person has the key, they can leave the room and give the key to another person. This is the same as a mutex lock.
124 |
125 | #### Properties of a mutex lock
126 | * `Lock` - A thread can only access the critical section if it has the lock.
127 | * Only one thread can have the lock at a time.
128 | * Other threads cannot access the critical section if a thread has the lock and thus have to wait.
129 | * Lock will automatically be released when the thread exits the critical section.
130 |
131 | ### Syncronised keyword
132 |
133 | The `synchronized` keyword is a way to solve the synchronisation problem. The `synchronized` keyword is a way to ensure that only one thread can access a critical section at a time.
134 |
135 | A synchronized method or block can only be accessed by one thread at a time. If a thread is accessing a synchronized method or block, other threads cannot access the synchronized method or block. If a thread is accessing a synchronized method or block, other threads have to wait until the thread exits the synchronized method or block.
136 |
137 | Following is an example of a synchronized method:
138 | ```java
139 | public class Count {
140 | private int count = 0;
141 |
142 | public synchronized void increment() {
143 | count++;
144 | }
145 |
146 | public synchronized void decrement() {
147 | count--;
148 | }
149 |
150 | public int getCount() {
151 | return count;
152 | }
153 | }
154 | ```
155 |
156 | In the above example, the `increment()` and `decrement()` methods are synchronized. This means that only one thread can access the `increment()` and `decrement()` methods at a time. If a thread is accessing the `increment()` method, other threads cannot access the `increment()` method. If a thread is accessing the `decrement()` method, other threads cannot access the `decrement()` method. If a thread is accessing the `increment()` method, other threads have to wait until the thread exits the `increment()` method. If a thread is accessing the `decrement()` method, other threads have to wait until the thread exits the `decrement()` method.
157 |
158 | Similarly, the `synchronized` keyword can be used to synchronize a block of code. Following is an example of a synchronized block:
159 | ```java
160 | public class Count {
161 | private int count = 0;
162 |
163 | public void increment() {
164 | synchronized (this) {
165 | count++;
166 | }
167 | }
168 |
169 | public void decrement() {
170 | synchronized (this) {
171 | count--;
172 | }
173 | }
174 |
175 | public int getCount() {
176 | return count;
177 | }
178 | }
179 | ```
180 |
181 | If you declare a method as `synchronized`, only one thread will be able to access any `synchronized` method in the class. This is because the `synchronized` keyword is associated with the object.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/process.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```mermaid
2 | gantt
3 | title Session Schedule
4 | dateFormat HH:mm
5 | axisFormat %H:%M
6 | AMA : a1, 21:00, 5m
7 | Quiz : a2, after a1, 5m
8 | Show me the code : a3, after a2, 5m
9 | Session : a4, after a3, 75m
10 | Break : a5, 22:30, 5m
11 | Session : a6, after a5, 23:30
12 | Doubt Session : a7, 23:30, 30m
13 | ```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------