├── ESRNN
├── utils
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── config.py
│ ├── losses.py
│ ├── data.py
│ ├── ESRNN.py
│ └── DRNN.py
├── __init__.py
├── tests
│ └── test_esrnn.py
├── utils_visualization.py
├── m4_run.py
├── utils_configs.py
├── m4_data.py
├── utils_evaluation.py
├── ESRNNensemble.py
└── ESRNN.py
├── requirements.txt
├── .github
├── images
│ ├── metrics.png
│ ├── x_test.png
│ ├── x_train.png
│ ├── y_test.png
│ ├── y_train.png
│ ├── test-data-example.png
│ └── train-data-example.png
└── workflows
│ └── pythonpackage.yml
├── .gitignore
├── setup.py
├── LICENSE
└── README.md
/ESRNN/utils/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ESRNN/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from ESRNN.ESRNN import *
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/requirements.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | numpy>=1.16.1
2 | pandas>=0.25.2
3 | torch>=1.3.1
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/images/metrics.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kdgutier/esrnn_torch/HEAD/.github/images/metrics.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/images/x_test.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kdgutier/esrnn_torch/HEAD/.github/images/x_test.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/images/x_train.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kdgutier/esrnn_torch/HEAD/.github/images/x_train.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/images/y_test.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kdgutier/esrnn_torch/HEAD/.github/images/y_test.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/images/y_train.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kdgutier/esrnn_torch/HEAD/.github/images/y_train.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/images/test-data-example.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kdgutier/esrnn_torch/HEAD/.github/images/test-data-example.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/images/train-data-example.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kdgutier/esrnn_torch/HEAD/.github/images/train-data-example.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | *.pyc
2 | *.DS_Store
3 | *.vscode
4 | *.ipynb_checkpoints
5 | data/
6 | !results/
7 | results/*
8 | literature/*
9 | plots/
10 | statistics/
11 | dynet/
12 | theory/
13 | *.so
14 | *.dll
15 | *.exe
16 | *.c
17 | build/
18 | ESRNN/hyperpar_tunning_m4.py
19 | logs/*
20 | configs/*
21 | setup.sh
22 | server_results.sh
23 | test.py
24 |
25 | # Setuptools distribution folder.
26 | /dist/
27 |
28 | # Python egg metadata, regenerated from source files by setuptools.
29 | /*.egg-info
30 | /*.egg
31 | ESRNN/r
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/pythonpackage.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # This workflow will install Python dependencies, run tests and lint with a variety of Python versions
2 | # For more information see: https://help.github.com/actions/language-and-framework-guides/using-python-with-github-actions
3 |
4 | name: Python package
5 |
6 | on:
7 | push:
8 | branches: [ master, pip ]
9 | pull_request:
10 | branches: [ master ]
11 |
12 | jobs:
13 | build:
14 |
15 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
16 | strategy:
17 | matrix:
18 | python-version: [3.6, 3.7, 3.8]
19 |
20 | steps:
21 | - uses: actions/checkout@v2
22 | - name: Set up Python ${{ matrix.python-version }}
23 | uses: actions/setup-python@v1
24 | with:
25 | python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
26 | - name: Install dependencies
27 | run: |
28 | python -m pip install --upgrade pip
29 | pip install -r requirements.txt
30 | - name: Test with pytest
31 | run: |
32 | pip install pytest
33 | pytest -s
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import setuptools
2 |
3 | with open("README.md", "r") as fh:
4 | long_description = fh.read()
5 |
6 | setuptools.setup(
7 | name="ESRNN",
8 | version="0.1.3",
9 | author="Kin Gutierrez, Cristian Challu, Federico Garza",
10 | author_email="kdgutier@cs.cmu.edu, cchallu@andrew.cmu.edu, fede.garza.ramirez@gmail.com",
11 | description="Pytorch implementation of the ESRNN",
12 | long_description=long_description,
13 | long_description_content_type="text/markdown",
14 | url="https://github.com/kdgutier/esrnn_torch",
15 | packages=setuptools.find_packages(),
16 | classifiers=[
17 | "Programming Language :: Python :: 3",
18 | "License :: OSI Approved :: MIT License",
19 | "Operating System :: OS Independent",
20 | ],
21 | python_requires='>=3.6',
22 | install_requires =[
23 | "numpy>=1.16.1",
24 | "pandas>=0.25.2",
25 | "torch>=1.3.1"
26 | ],
27 | entry_points='''
28 | [console_scripts]
29 | m4_run=ESRNN.m4_run:cli
30 | '''
31 | )
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2020 Kin Gutierrez and Cristian Challu
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ESRNN/utils/config.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | class ModelConfig(object):
2 | def __init__(self, max_epochs, batch_size, batch_size_test, freq_of_test,
3 | learning_rate, lr_scheduler_step_size, lr_decay,
4 | per_series_lr_multip, gradient_eps, gradient_clipping_threshold,
5 | rnn_weight_decay,
6 | noise_std,
7 | level_variability_penalty,
8 | testing_percentile, training_percentile, ensemble,
9 | cell_type,
10 | state_hsize, dilations, add_nl_layer, seasonality, input_size, output_size,
11 | frequency, max_periods, random_seed, device, root_dir):
12 |
13 | # Train Parameters
14 | self.max_epochs = max_epochs
15 | self.batch_size = batch_size
16 | self.batch_size_test = batch_size_test
17 | self.freq_of_test = freq_of_test
18 | self.learning_rate = learning_rate
19 | self.lr_scheduler_step_size = lr_scheduler_step_size
20 | self.lr_decay = lr_decay
21 | self.per_series_lr_multip = per_series_lr_multip
22 | self.gradient_eps = gradient_eps
23 | self.gradient_clipping_threshold = gradient_clipping_threshold
24 | self.rnn_weight_decay = rnn_weight_decay
25 | self.noise_std = noise_std
26 | self.level_variability_penalty = level_variability_penalty
27 | self.testing_percentile = testing_percentile
28 | self.training_percentile = training_percentile
29 | self.ensemble = ensemble
30 | self.device = device
31 |
32 | # Model Parameters
33 | self.cell_type = cell_type
34 | self.state_hsize = state_hsize
35 | self.dilations = dilations
36 | self.add_nl_layer = add_nl_layer
37 | self.random_seed = random_seed
38 |
39 | # Data Parameters
40 | self.seasonality = seasonality
41 | if len(seasonality)>0:
42 | self.naive_seasonality = seasonality[0]
43 | else:
44 | self.naive_seasonality = 1
45 | self.input_size = input_size
46 | self.input_size_i = self.input_size
47 | self.output_size = output_size
48 | self.output_size_i = self.output_size
49 | self.frequency = frequency
50 | self.min_series_length = self.input_size_i + self.output_size_i
51 | self.max_series_length = (max_periods * self.input_size) + self.min_series_length
52 | self.max_periods = max_periods
53 | self.root_dir = root_dir
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ESRNN/tests/test_esrnn.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #Testing ESRNN
2 | import runpy
3 | import os
4 |
5 | print('\n')
6 | print(10*'='+'TEST ESRNN'+10*'=')
7 | print('\n')
8 |
9 | def test_esrnn_hourly():
10 | if not os.path.exists('./data'):
11 | os.mkdir('./data')
12 |
13 | print('\n')
14 | print(10*'='+'HOURLY'+10*'=')
15 | print('\n')
16 |
17 | exec_str = 'python -m ESRNN.m4_run --dataset Hourly '
18 | exec_str += '--results_directory ./data --gpu_id 0 '
19 | exec_str += '--use_cpu 1 --num_obs 100 --test 1'
20 | results = os.system(exec_str)
21 |
22 | if results==0:
23 | print('Test completed')
24 | else:
25 | raise Exception('Something went wrong')
26 |
27 | def test_esrnn_weekly():
28 | if not os.path.exists('./data'):
29 | os.mkdir('./data')
30 |
31 | print('\n')
32 | print(10*'='+'WEEKLY'+10*'=')
33 | print('\n')
34 |
35 | exec_str = 'python -m ESRNN.m4_run --dataset Weekly '
36 | exec_str += '--results_directory ./data --gpu_id 0 '
37 | exec_str += '--use_cpu 1 --num_obs 100 --test 1'
38 | results = os.system(exec_str)
39 |
40 | if results==0:
41 | print('Test completed')
42 | else:
43 | raise Exception('Something went wrong')
44 |
45 |
46 | def test_esrnn_daily():
47 | if not os.path.exists('./data'):
48 | os.mkdir('./data')
49 |
50 | print('\n')
51 | print(10*'='+'DAILY'+10*'=')
52 | print('\n')
53 |
54 | exec_str = 'python -m ESRNN.m4_run --dataset Daily '
55 | exec_str += '--results_directory ./data --gpu_id 0 '
56 | exec_str += '--use_cpu 1 --num_obs 100 --test 1'
57 | results = os.system(exec_str)
58 |
59 | if results==0:
60 | print('Test completed')
61 | else:
62 | raise Exception('Something went wrong')
63 |
64 |
65 | def test_esrnn_monthly():
66 | if not os.path.exists('./data'):
67 | os.mkdir('./data')
68 |
69 |
70 | print('\n')
71 | print(10*'='+'MONTHLY'+10*'=')
72 | print('\n')
73 |
74 | exec_str = 'python -m ESRNN.m4_run --dataset Monthly '
75 | exec_str += '--results_directory ./data --gpu_id 0 '
76 | exec_str += '--use_cpu 1 --num_obs 100 --test 1'
77 | results = os.system(exec_str)
78 |
79 | if results==0:
80 | print('Test completed')
81 | else:
82 | raise Exception('Something went wrong')
83 |
84 |
85 | def test_esrnn_quarterly():
86 | if not os.path.exists('./data'):
87 | os.mkdir('./data')
88 |
89 | print('\n')
90 | print(10*'='+'QUARTERLY'+10*'=')
91 | print('\n')
92 |
93 | exec_str = 'python -m ESRNN.m4_run --dataset Quarterly '
94 | exec_str += '--results_directory ./data --gpu_id 0 '
95 | exec_str += '--use_cpu 1 --num_obs 100 --test 1'
96 | results = os.system(exec_str)
97 |
98 | if results==0:
99 | print('Test completed')
100 | else:
101 | raise Exception('Something went wrong')
102 |
103 |
104 | def test_esrnn_yearly():
105 | if not os.path.exists('./data'):
106 | os.mkdir('./data')
107 |
108 | print('\n')
109 | print(10*'='+'YEARLY'+10*'=')
110 | print('\n')
111 |
112 | exec_str = 'python -m ESRNN.m4_run --dataset Yearly '
113 | exec_str += '--results_directory ./data --gpu_id 0 '
114 | exec_str += '--use_cpu 1 --num_obs 100 --test 1'
115 | results = os.system(exec_str)
116 |
117 | if results==0:
118 | print('Test completed')
119 | else:
120 | raise Exception('Something went wrong')
121 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ESRNN/utils/losses.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 |
4 | class PinballLoss(nn.Module):
5 | """ Pinball Loss
6 | Computes the pinball loss between y and y_hat.
7 |
8 | Parameters
9 | ----------
10 | y: tensor
11 | actual values in torch tensor.
12 | y_hat: tensor (same shape as y)
13 | predicted values in torch tensor.
14 | tau: float, between 0 and 1
15 | the slope of the pinball loss, in the context of
16 | quantile regression, the value of tau determines the
17 | conditional quantile level.
18 |
19 | Returns
20 | ----------
21 | pinball_loss:
22 | average accuracy for the predicted quantile
23 | """
24 | def __init__(self, tau=0.5):
25 | super(PinballLoss, self).__init__()
26 | self.tau = tau
27 |
28 | def forward(self, y, y_hat):
29 | delta_y = torch.sub(y, y_hat)
30 | pinball = torch.max(torch.mul(self.tau, delta_y), torch.mul((self.tau-1), delta_y))
31 | pinball = pinball.mean()
32 | return pinball
33 |
34 | class LevelVariabilityLoss(nn.Module):
35 | """ Level Variability Loss
36 | Computes the variability penalty for the level.
37 |
38 | Parameters
39 | ----------
40 | levels: tensor with shape (batch, n_time)
41 | levels obtained from exponential smoothing component of ESRNN
42 | level_variability_penalty: float
43 | this parameter controls the strength of the penalization
44 | to the wigglines of the level vector, induces smoothness
45 | in the output
46 |
47 | Returns
48 | ----------
49 | level_var_loss:
50 | wiggliness loss for the level vector
51 | """
52 | def __init__(self, level_variability_penalty):
53 | super(LevelVariabilityLoss, self).__init__()
54 | self.level_variability_penalty = level_variability_penalty
55 |
56 | def forward(self, levels):
57 | assert levels.shape[1] > 2
58 | level_prev = torch.log(levels[:, :-1])
59 | level_next = torch.log(levels[:, 1:])
60 | log_diff_of_levels = torch.sub(level_prev, level_next)
61 |
62 | log_diff_prev = log_diff_of_levels[:, :-1]
63 | log_diff_next = log_diff_of_levels[:, 1:]
64 | diff = torch.sub(log_diff_prev, log_diff_next)
65 | level_var_loss = diff**2
66 | level_var_loss = level_var_loss.mean() * self.level_variability_penalty
67 | return level_var_loss
68 |
69 | class StateLoss(nn.Module):
70 | pass
71 |
72 | class SmylLoss(nn.Module):
73 | """Computes the Smyl Loss that combines level variability with
74 | with Pinball loss.
75 | windows_y: tensor of actual values,
76 | shape (n_windows, batch_size, window_size).
77 | windows_y_hat: tensor of predicted values,
78 | shape (n_windows, batch_size, window_size).
79 | levels: levels obtained from exponential smoothing component of ESRNN.
80 | tensor with shape (batch, n_time).
81 | return: smyl_loss.
82 | """
83 | def __init__(self, tau, level_variability_penalty=0.0):
84 | super(SmylLoss, self).__init__()
85 | self.pinball_loss = PinballLoss(tau)
86 | self.level_variability_loss = LevelVariabilityLoss(level_variability_penalty)
87 |
88 | def forward(self, windows_y, windows_y_hat, levels):
89 | smyl_loss = self.pinball_loss(windows_y, windows_y_hat)
90 | if self.level_variability_loss.level_variability_penalty>0:
91 | log_diff_of_levels = self.level_variability_loss(levels)
92 | smyl_loss += log_diff_of_levels
93 | return smyl_loss
94 |
95 |
96 | class DisaggregatedPinballLoss(nn.Module):
97 | """ Pinball Loss
98 | Computes the pinball loss between y and y_hat.
99 |
100 | Parameters
101 | ----------
102 | y: tensor
103 | actual values in torch tensor.
104 | y_hat: tensor (same shape as y)
105 | predicted values in torch tensor.
106 | tau: float, between 0 and 1
107 | the slope of the pinball loss, in the context of
108 | quantile regression, the value of tau determines the
109 | conditional quantile level.
110 |
111 | Returns
112 | ----------
113 | pinball_loss:
114 | average accuracy for the predicted quantile
115 | """
116 | def __init__(self, tau=0.5):
117 | super(DisaggregatedPinballLoss, self).__init__()
118 | self.tau = tau
119 |
120 | def forward(self, y, y_hat):
121 | delta_y = torch.sub(y, y_hat)
122 | pinball = torch.max(torch.mul(self.tau, delta_y), torch.mul((self.tau-1), delta_y))
123 | pinball = pinball.mean(axis=0).mean(axis=1)
124 | return pinball
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ESRNN/utils_visualization.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import pandas as pd
4 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
5 | plt.style.use('ggplot')
6 |
7 | import seaborn as sns
8 | from itertools import product
9 | import random
10 |
11 |
12 | def plot_prediction(y, y_hat):
13 | """
14 | y: pandas df
15 | panel with columns unique_id, ds, y
16 | y_hat: pandas df
17 | panel with columns unique_id, ds, y_hat
18 | """
19 | pd.plotting.register_matplotlib_converters()
20 |
21 | plt.plot(y.ds, y.y, label = 'y')
22 | plt.plot(y_hat.ds, y_hat.y_hat, label='y_hat')
23 | plt.legend(loc='upper left')
24 | plt.show()
25 |
26 | def plot_grid_prediction(y, y_hat, plot_random=True, unique_ids=None, save_file_name = None):
27 | """
28 | y: pandas df
29 | panel with columns unique_id, ds, y
30 | y_hat: pandas df
31 | panel with columns unique_id, ds, y_hat
32 | plot_random: bool
33 | if unique_ids will be sampled
34 | unique_ids: list
35 | unique_ids to plot
36 | save_file_name: str
37 | file name to save plot
38 | """
39 | pd.plotting.register_matplotlib_converters()
40 |
41 | fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 4, figsize = (24,8))
42 |
43 | if not unique_ids:
44 | unique_ids = y['unique_id'].unique()
45 |
46 | assert len(unique_ids) >= 8, "Must provide at least 8 ts"
47 |
48 | if plot_random:
49 | unique_ids = random.sample(set(unique_ids), k=8)
50 |
51 | for i, (idx, idy) in enumerate(product(range(2), range(4))):
52 | y_uid = y[y.unique_id == unique_ids[i]]
53 | y_uid_hat = y_hat[y_hat.unique_id == unique_ids[i]]
54 |
55 | axes[idx, idy].plot(y_uid.ds, y_uid.y, label = 'y')
56 | axes[idx, idy].plot(y_uid_hat.ds, y_uid_hat.y_hat, label='y_hat')
57 | axes[idx, idy].set_title(unique_ids[i])
58 | axes[idx, idy].legend(loc='upper left')
59 |
60 | plt.show()
61 |
62 | if save_file_name:
63 | fig.savefig(save_file_name, bbox_inches='tight', pad_inches=0)
64 |
65 |
66 | def plot_distributions(distributions_dict, fig_title=None, xlabel=None):
67 | n_distributions = len(distributions_dict.keys())
68 | fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, figsize=(7, 5.5))
69 | plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.35)
70 |
71 | n_colors = len(distributions_dict.keys())
72 | colors = sns.color_palette("hls", n_colors)
73 |
74 | for idx, dist_name in enumerate(distributions_dict.keys()):
75 | train_dist_plot = sns.kdeplot(distributions_dict[dist_name],
76 | bw='silverman',
77 | label=dist_name,
78 | color=colors[idx])
79 | if xlabel is not None:
80 | ax.set_xlabel(xlabel, fontsize=14)
81 | ax.set_ylabel('Density', fontsize=14)
82 | ax.set_title(fig_title, fontsize=15.5)
83 | ax.grid(True)
84 | ax.legend(loc='center left', bbox_to_anchor=(1, 0.5))
85 |
86 | fig.tight_layout()
87 | if fig_title is not None:
88 | fig_title = fig_title.replace(' ', '_')
89 | plot_file = "./results/plots/{}_distributions.png".format(fig_title)
90 | plt.savefig(plot_file, bbox_inches = "tight", dpi=300)
91 | plt.show()
92 |
93 | def plot_cat_distributions(df, cat, var):
94 | unique_cats = df[cat].unique()
95 | cat_dict = {}
96 | for c in unique_cats:
97 | cat_dict[c] = df[df[cat]==c][var].values
98 |
99 | plot_distributions(cat_dict, xlabel=var)
100 |
101 | def plot_single_cat_distributions(distributions_dict, ax, fig_title=None, xlabel=None):
102 | n_distributions = len(distributions_dict.keys())
103 |
104 | n_colors = len(distributions_dict.keys())
105 | colors = sns.color_palette("hls", n_colors)
106 |
107 | for idx, dist_name in enumerate(distributions_dict.keys()):
108 | train_dist_plot = sns.distplot(distributions_dict[dist_name],
109 | #bw='silverman',
110 | #kde=False,
111 | rug=True,
112 | label=dist_name,
113 | color=colors[idx],
114 | ax=ax)
115 | if xlabel is not None:
116 | ax.set_xlabel(xlabel, fontsize=14)
117 | ax.set_ylabel('Density', fontsize=14)
118 | ax.set_title(fig_title, fontsize=15.5)
119 | ax.grid(True)
120 | ax.legend(loc='center left', bbox_to_anchor=(1, 0.5))
121 |
122 | def plot_grid_cat_distributions(df, cats, var):
123 | cols = int(np.ceil(len(cats)/2))
124 | fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, cols, figsize=(4*cols, 5.5))
125 | plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.95)
126 | plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.5)
127 |
128 | for idx, cat in enumerate(cats):
129 | unique_cats = df[cat].unique()
130 | cat_dict = {}
131 | for c in unique_cats:
132 | values = df[df[cat]==c][var].values
133 | values = values[~np.isnan(values)]
134 | if len(values)>0:
135 | cat_dict[c] = values
136 |
137 | row = int(np.round((idx/len(cats))+0.001, 0))
138 | col = idx % cols
139 | plot_single_cat_distributions(cat_dict, axs[row, col],
140 | fig_title=cat, xlabel=var)
141 |
142 | min_owa = math.floor(df.min_owa.min() * 1000) / 1000
143 | suptitle = var + ': ' + str(min_owa)
144 | fig.suptitle(suptitle, fontsize=18)
145 | plt.show()
146 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ESRNN/utils/data.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import torch
3 |
4 |
5 | class Batch():
6 | def __init__(self, mc, y, last_ds, categories, idxs):
7 | # Parse Model config
8 | exogenous_size = mc.exogenous_size
9 | device = mc.device
10 |
11 | # y: time series values
12 | n = len(y)
13 | y = np.float32(y)
14 | self.idxs = torch.LongTensor(idxs).to(device)
15 | self.y = y
16 | if (self.y.shape[1] > mc.max_series_length):
17 | y = y[:, -mc.max_series_length:]
18 | self.y = torch.tensor(y).float()
19 |
20 | # last_ds: last time for prediction purposes
21 | self.last_ds = last_ds
22 |
23 | # categories: exogenous categoric data
24 | if exogenous_size >0:
25 | self.categories = np.zeros((len(idxs), exogenous_size))
26 | cols_idx = np.array([mc.category_to_idx[category] for category in categories])
27 | rows_idx = np.array(range(len(cols_idx)))
28 | self.categories[rows_idx, cols_idx] = 1
29 | self.categories = torch.from_numpy(self.categories).float()
30 |
31 | self.y = self.y.to(device)
32 | self.categories = self.categories.to(device)
33 |
34 |
35 | class Iterator(object):
36 | """ Time Series Iterator.
37 |
38 | Parameters
39 | ----------
40 | mc: ModelConfig object
41 | ModelConfig object with inherited hyperparameters:
42 | batch_size, and exogenous_size, from the ESRNN
43 | initialization.
44 | X: array, shape (n_unique_id, 3)
45 | Panel array with unique_id, last date stamp and
46 | exogenous variable.
47 | y: array, shape (n_unique_id, n_time)
48 | Panel array in wide format with unique_id, last
49 | date stamp and time series values.
50 | Returns
51 | ----------
52 | self : object
53 | Iterator method get_batch() returns a batch of time
54 | series objects defined by the Batch class.
55 | """
56 | def __init__(self, mc, X, y, weights=None):
57 | if weights is not None:
58 | assert len(weights)==len(X)
59 | train_ids = np.where(weights==1)[0]
60 | self.X = X[train_ids,:]
61 | self.y = y[train_ids,:]
62 | else:
63 | self.X = X
64 | self.y = y
65 | assert len(X)==len(y)
66 |
67 | # Parse Model config
68 | self.mc = mc
69 | self.batch_size = mc.batch_size
70 |
71 | self.unique_idxs = np.unique(self.X[:, 0])
72 | assert len(self.unique_idxs)==len(self.X)
73 | self.n_series = len(self.unique_idxs)
74 |
75 | #assert self.batch_size <= self.n_series
76 |
77 | # Initialize batch iterator
78 | self.b = 0
79 | self.n_batches = int(np.ceil(self.n_series / self.batch_size))
80 | shuffle = list(range(self.n_series))
81 | self.sort_key = {'unique_id': [self.unique_idxs[i] for i in shuffle],
82 | 'sort_key': shuffle}
83 |
84 | def update_batch_size(self, new_batch_size):
85 | self.batch_size = new_batch_size
86 | assert self.batch_size <= self.n_series
87 | self.n_batches = int(np.ceil(self.n_series / self.batch_size))
88 |
89 | def shuffle_dataset(self, random_seed=1):
90 | """Return the examples in the dataset in order, or shuffled."""
91 | # Random Seed
92 | np.random.seed(random_seed)
93 | self.random_seed = random_seed
94 | shuffle = np.random.choice(self.n_series, self.n_series, replace=False)
95 | self.X = self.X[shuffle]
96 | self.y = self.y[shuffle]
97 |
98 | old_sort_key = self.sort_key['sort_key']
99 | old_unique_idxs = self.sort_key['unique_id']
100 | self.sort_key = {'unique_id': [old_unique_idxs[i] for i in shuffle],
101 | 'sort_key': [old_sort_key[i] for i in shuffle]}
102 |
103 | def get_trim_batch(self, unique_id):
104 | if unique_id==None:
105 | # Compute the indexes of the minibatch.
106 | first = (self.b * self.batch_size)
107 | last = min((first + self.batch_size), self.n_series)
108 | else:
109 | # Obtain unique_id index
110 | assert unique_id in self.sort_key['unique_id'], "unique_id, not fitted"
111 | first = self.sort_key['unique_id'].index(unique_id)
112 | last = first+1
113 |
114 | # Extract values for batch
115 | unique_idxs = self.sort_key['unique_id'][first:last]
116 | batch_idxs = self.sort_key['sort_key'][first:last]
117 |
118 | batch_y = self.y[first:last]
119 | batch_categories = self.X[first:last, 1]
120 | batch_last_ds = self.X[first:last, 2]
121 |
122 | len_series = np.count_nonzero(~np.isnan(batch_y), axis=1)
123 | min_len = min(len_series)
124 | last_numeric = (~np.isnan(batch_y)).cumsum(1).argmax(1)+1
125 |
126 | # Trimming to match min_len
127 | y_b = np.zeros((batch_y.shape[0], min_len))
128 | for i in range(batch_y.shape[0]):
129 | y_b[i] = batch_y[i,(last_numeric[i]-min_len):last_numeric[i]]
130 | batch_y = y_b
131 |
132 | assert not np.isnan(batch_y).any(), \
133 | "clean np.nan's from unique_idxs: {}".format(unique_idxs)
134 | assert batch_y.shape[0]==len(batch_idxs)==len(batch_last_ds)==len(batch_categories)
135 | assert batch_y.shape[1]>=1
136 |
137 | # Feed to Batch
138 | batch = Batch(mc=self.mc, y=batch_y, last_ds=batch_last_ds,
139 | categories=batch_categories, idxs=batch_idxs)
140 | self.b = (self.b + 1) % self.n_batches
141 | return batch
142 |
143 | def get_batch(self, unique_id=None):
144 | return self.get_trim_batch(unique_id)
145 |
146 | def __len__(self):
147 | return self.n_batches
148 |
149 | def __iter__(self):
150 | pass
151 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ESRNN/m4_run.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import argparse
3 | import itertools
4 | import ast
5 | import pickle
6 | import time
7 |
8 | import os
9 | import numpy as np
10 | import pandas as pd
11 |
12 | from ESRNN.m4_data import prepare_m4_data
13 | from ESRNN.utils_evaluation import evaluate_prediction_owa
14 | from ESRNN.utils_configs import get_config
15 |
16 | from ESRNN import ESRNN
17 |
18 | import torch
19 |
20 | def main(args):
21 | config = get_config(args.dataset)
22 | if config['data_parameters']['frequency'] == 'Y':
23 | config['data_parameters']['frequency'] = None
24 |
25 | #Setting needed parameters
26 | os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = str(args.gpu_id)
27 |
28 | if args.num_obs:
29 | num_obs = args.num_obs
30 | else:
31 | num_obs = 100000
32 |
33 | if args.use_cpu == 1:
34 | config['device'] = 'cpu'
35 | else:
36 | assert torch.cuda.is_available(), 'No cuda devices detected. You can try using CPU instead.'
37 |
38 | #Reading data
39 | print('Reading data')
40 | X_train_df, y_train_df, X_test_df, y_test_df = prepare_m4_data(dataset_name=args.dataset,
41 | directory=args.results_directory,
42 | num_obs=num_obs)
43 |
44 | # Instantiate model
45 | model = ESRNN(max_epochs=config['train_parameters']['max_epochs'],
46 | batch_size=config['train_parameters']['batch_size'],
47 | freq_of_test=config['train_parameters']['freq_of_test'],
48 | learning_rate=float(config['train_parameters']['learning_rate']),
49 | lr_scheduler_step_size=config['train_parameters']['lr_scheduler_step_size'],
50 | lr_decay=config['train_parameters']['lr_decay'],
51 | per_series_lr_multip=config['train_parameters']['per_series_lr_multip'],
52 | gradient_clipping_threshold=config['train_parameters']['gradient_clipping_threshold'],
53 | rnn_weight_decay=config['train_parameters']['rnn_weight_decay'],
54 | noise_std=config['train_parameters']['noise_std'],
55 | level_variability_penalty=config['train_parameters']['level_variability_penalty'],
56 | testing_percentile=config['train_parameters']['testing_percentile'],
57 | training_percentile=config['train_parameters']['training_percentile'],
58 | ensemble=config['train_parameters']['ensemble'],
59 | max_periods=config['data_parameters']['max_periods'],
60 | seasonality=config['data_parameters']['seasonality'],
61 | input_size=config['data_parameters']['input_size'],
62 | output_size=config['data_parameters']['output_size'],
63 | frequency=config['data_parameters']['frequency'],
64 | cell_type=config['model_parameters']['cell_type'],
65 | state_hsize=config['model_parameters']['state_hsize'],
66 | dilations=config['model_parameters']['dilations'],
67 | add_nl_layer=config['model_parameters']['add_nl_layer'],
68 | random_seed=config['model_parameters']['random_seed'],
69 | device=config['device'])
70 |
71 | if args.test == 1:
72 | model = ESRNN(max_epochs=1,
73 | batch_size=20,
74 | seasonality=config['data_parameters']['seasonality'],
75 | input_size=config['data_parameters']['input_size'],
76 | output_size=config['data_parameters']['output_size'],
77 | frequency=config['data_parameters']['frequency'],
78 | device=config['device'])
79 |
80 | # Fit model
81 | # If y_test_df is provided the model will evaluate predictions on this set every freq_test epochs
82 | model.fit(X_train_df, y_train_df, X_test_df, y_test_df)
83 |
84 | # Predict on test set
85 | print('\nForecasting')
86 | y_hat_df = model.predict(X_test_df)
87 |
88 | # Evaluate predictions
89 | print(15*'=', ' Final evaluation ', 14*'=')
90 | seasonality = config['data_parameters']['seasonality']
91 | if not seasonality:
92 | seasonality = 1
93 | else:
94 | seasonality = seasonality[0]
95 |
96 | final_owa, final_mase, final_smape = evaluate_prediction_owa(y_hat_df, y_train_df,
97 | X_test_df, y_test_df,
98 | naive2_seasonality=seasonality)
99 |
100 | if __name__ == '__main__':
101 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Replicate M4 results for the ESRNN model')
102 | parser.add_argument("--dataset", required=True, type=str,
103 | choices=['Yearly', 'Quarterly', 'Monthly', 'Weekly', 'Hourly', 'Daily'],
104 | help="set of M4 time series to be tested")
105 | parser.add_argument("--results_directory", required=True, type=str,
106 | help="directory where M4 data will be downloaded")
107 | parser.add_argument("--gpu_id", required=False, type=int,
108 | help="an integer that specify which GPU will be used")
109 | parser.add_argument("--use_cpu", required=False, type=int,
110 | help="1 to use CPU instead of GPU (uses GPU by default)")
111 | parser.add_argument("--num_obs", required=False, type=int,
112 | help="number of M4 time series to be tested (uses all data by default)")
113 | parser.add_argument("--test", required=False, type=int,
114 | help="run fast for tests (no test by default)")
115 | args = parser.parse_args()
116 |
117 | main(args)
118 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ESRNN/utils_configs.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | def get_config(dataset_name):
2 | """
3 | Returns dict config
4 |
5 | Parameters
6 | ----------
7 | dataset_name: str
8 | """
9 | allowed_dataset_names = ('Yearly', 'Monthly', 'Weekly', 'Hourly', 'Quarterly', 'Daily')
10 | if dataset_name not in allowed_dataset_names:
11 | raise ValueError(f'kind must be one of {allowed_kinds}')
12 |
13 | if dataset_name == 'Yearly':
14 | return YEARLY
15 | elif dataset_name == 'Monthly':
16 | return MONTHLY
17 | elif dataset_name == 'Weekly':
18 | return WEEKLY
19 | elif dataset_name == 'Hourly':
20 | return HOURLY
21 | elif dataset_name == 'Quarterly':
22 | return QUARTERLY
23 | elif dataset_name == 'Daily':
24 | return DAILY
25 |
26 | YEARLY = {
27 | 'device': 'cuda',
28 | 'train_parameters': {
29 | 'max_epochs': 25,
30 | 'batch_size': 4,
31 | 'freq_of_test': 5,
32 | 'learning_rate': '1e-4',
33 | 'lr_scheduler_step_size': 10,
34 | 'lr_decay': 0.1,
35 | 'per_series_lr_multip': 0.8,
36 | 'gradient_clipping_threshold': 50,
37 | 'rnn_weight_decay': 0,
38 | 'noise_std': 0.001,
39 | 'level_variability_penalty': 100,
40 | 'testing_percentile': 50,
41 | 'training_percentile': 50,
42 | 'ensemble': False
43 | },
44 | 'data_parameters': {
45 | 'max_periods': 25,
46 | 'seasonality': [],
47 | 'input_size': 4,
48 | 'output_size': 6,
49 | 'frequency': 'Y'
50 | },
51 | 'model_parameters': {
52 | 'cell_type': 'LSTM',
53 | 'state_hsize': 40,
54 | 'dilations': [[1], [6]],
55 | 'add_nl_layer': False,
56 | 'random_seed': 117982
57 | }
58 | }
59 |
60 | MONTHLY = {
61 | 'device': 'cuda',
62 | 'train_parameters': {
63 | 'max_epochs': 15,
64 | 'batch_size': 64,
65 | 'freq_of_test': 4,
66 | 'learning_rate': '7e-4',
67 | 'lr_scheduler_step_size': 12,
68 | 'lr_decay': 0.2,
69 | 'per_series_lr_multip': 0.5,
70 | 'gradient_clipping_threshold': 20,
71 | 'rnn_weight_decay': 0,
72 | 'noise_std': 0.001,
73 | 'level_variability_penalty': 50,
74 | 'testing_percentile': 50,
75 | 'training_percentile': 45,
76 | 'ensemble': False
77 | },
78 | 'data_parameters': {
79 | 'max_periods': 36,
80 | 'seasonality': [12],
81 | 'input_size': 12,
82 | 'output_size': 18,
83 | 'frequency': 'M'
84 | },
85 | 'model_parameters': {
86 | 'cell_type': 'LSTM',
87 | 'state_hsize': 50,
88 | 'dilations': [[1, 3, 6, 12]],
89 | 'add_nl_layer': False,
90 | 'random_seed': 1
91 | }
92 | }
93 |
94 |
95 | WEEKLY = {
96 | 'device': 'cuda',
97 | 'train_parameters': {
98 | 'max_epochs': 50,
99 | 'batch_size': 32,
100 | 'freq_of_test': 10,
101 | 'learning_rate': '1e-2',
102 | 'lr_scheduler_step_size': 10,
103 | 'lr_decay': 0.5,
104 | 'per_series_lr_multip': 1.0,
105 | 'gradient_clipping_threshold': 20,
106 | 'rnn_weight_decay': 0,
107 | 'noise_std': 0.001,
108 | 'level_variability_penalty': 100,
109 | 'testing_percentile': 50,
110 | 'training_percentile': 50,
111 | 'ensemble': True
112 | },
113 | 'data_parameters': {
114 | 'max_periods': 31,
115 | 'seasonality': [],
116 | 'input_size': 10,
117 | 'output_size': 13,
118 | 'frequency': 'W'
119 | },
120 | 'model_parameters': {
121 | 'cell_type': 'ResLSTM',
122 | 'state_hsize': 40,
123 | 'dilations': [[1, 52]],
124 | 'add_nl_layer': False,
125 | 'random_seed': 2
126 | }
127 | }
128 |
129 | HOURLY = {
130 | 'device': 'cuda',
131 | 'train_parameters': {
132 | 'max_epochs': 20,
133 | 'batch_size': 32,
134 | 'freq_of_test': 5,
135 | 'learning_rate': '1e-2',
136 | 'lr_scheduler_step_size': 7,
137 | 'lr_decay': 0.5,
138 | 'per_series_lr_multip': 1.0,
139 | 'gradient_clipping_threshold': 50,
140 | 'rnn_weight_decay': 0,
141 | 'noise_std': 0.001,
142 | 'level_variability_penalty': 30,
143 | 'testing_percentile': 50,
144 | 'training_percentile': 50,
145 | 'ensemble': True
146 | },
147 | 'data_parameters': {
148 | 'max_periods': 371,
149 | 'seasonality': [24, 168],
150 | 'input_size': 24,
151 | 'output_size': 48,
152 | 'frequency': 'H'
153 | },
154 | 'model_parameters': {
155 | 'cell_type': 'LSTM',
156 | 'state_hsize': 40,
157 | 'dilations': [[1, 4, 24, 168]],
158 | 'add_nl_layer': False,
159 | 'random_seed': 1
160 | }
161 | }
162 |
163 | QUARTERLY = {
164 | 'device': 'cuda',
165 | 'train_parameters': {
166 | 'max_epochs': 30,
167 | 'batch_size': 16,
168 | 'freq_of_test': 5,
169 | 'learning_rate': '5e-4',
170 | 'lr_scheduler_step_size': 10,
171 | 'lr_decay': 0.5,
172 | 'per_series_lr_multip': 1.0,
173 | 'gradient_clipping_threshold': 20,
174 | 'rnn_weight_decay': 0,
175 | 'noise_std': 0.001,
176 | 'level_variability_penalty': 100,
177 | 'testing_percentile': 50,
178 | 'training_percentile': 50,
179 | 'ensemble': False
180 | },
181 | 'data_parameters': {
182 | 'max_periods': 20,
183 | 'seasonality': [4],
184 | 'input_size': 4,
185 | 'output_size': 8,
186 | 'frequency': 'Q'
187 | },
188 | 'model_parameters': {
189 | 'cell_type': 'LSTM',
190 | 'state_hsize': 40,
191 | 'dilations': [[1, 2, 4, 8]],
192 | 'add_nl_layer': False,
193 | 'random_seed': 3
194 | }
195 | }
196 |
197 | DAILY = {
198 | 'device': 'cuda',
199 | 'train_parameters': {
200 | 'max_epochs': 20,
201 | 'batch_size': 64,
202 | 'freq_of_test': 2,
203 | 'learning_rate': '1e-2',
204 | 'lr_scheduler_step_size': 4,
205 | 'lr_decay': 0.3333,
206 | 'per_series_lr_multip': 0.5,
207 | 'gradient_clipping_threshold': 50,
208 | 'rnn_weight_decay': 0,
209 | 'noise_std': 0.0001,
210 | 'level_variability_penalty': 100,
211 | 'testing_percentile': 50,
212 | 'training_percentile': 65,
213 | 'ensemble': False
214 | },
215 | 'data_parameters': {
216 | 'max_periods': 15,
217 | 'seasonality': [7],
218 | 'input_size': 7,
219 | 'output_size': 14,
220 | 'frequency': 'D'
221 | },
222 | 'model_parameters': {
223 | 'n_models': 5,
224 | 'n_top': 4,
225 | 'cell_type':
226 | 'LSTM',
227 | 'state_hsize': 40,
228 | 'dilations': [[1, 7, 28]],
229 | 'add_nl_layer': True,
230 | 'random_seed': 1
231 | }
232 | }
233 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [](https://github.com/kdgutier/esrnn_torch/tree/master)
2 | [](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/ESRNN/)
3 | [](https://pepy.tech/project/esrnn)
4 | [](https://www.python.org/downloads/release/python-360+/)
5 | [](https://github.com/kdgutier/esrnn_torch/blob/master/LICENSE)
6 |
7 |
8 | # Pytorch Implementation of the ES-RNN
9 | Pytorch implementation of the ES-RNN algorithm proposed by Smyl, winning submission of the M4 Forecasting Competition. The class wraps fit and predict methods to facilitate interaction with Machine Learning pipelines along with evaluation and data wrangling utility. Developed by [Autonlab](https://www.autonlab.org/)’s members at Carnegie Mellon University.
10 |
11 | ## Installation Prerequisites
12 | * numpy>=1.16.1
13 | * pandas>=0.25.2
14 | * pytorch>=1.3.1
15 |
16 | ## Installation
17 |
18 | This code is a work in progress, any contributions or issues are welcome on
19 | GitHub at: https://github.com/kdgutier/esrnn_torch
20 |
21 | You can install the *released version* of `ESRNN` from the [Python package index](https://pypi.org) with:
22 |
23 | ```python
24 | pip install ESRNN
25 | ```
26 |
27 | ## Usage
28 |
29 | ### Input data
30 |
31 | The fit method receives `X_df`, `y_df` training pandas dataframes in long format. Optionally `X_test_df` and `y_test_df` to compute out of sample performance.
32 | - `X_df` must contain the columns `['unique_id', 'ds', 'x']`
33 | - `y_df` must contain the columns `['unique_id', 'ds', 'y']`
34 | - `X_test_df` must contain the columns `['unique_id', 'ds', 'x']`
35 | - `y_test_df` must contain the columns `['unique_id', 'ds', 'y']` and a benchmark model to compare against (default `'y_hat_naive2'`).
36 |
37 | For all the above:
38 | - The column `'unique_id'` is a time series identifier, the column `'ds'` stands for the datetime.
39 | - Column `'x'` is an exogenous categorical feature.
40 | - Column `'y'` is the target variable.
41 | - Column `'y'` **does not allow negative values** and the first entry for all series must be **grater than 0**.
42 |
43 | The `X` and `y` dataframes must contain the same values for `'unique_id'`, `'ds'` columns and be **balanced**, ie.no *gaps* between dates for the frequency.
44 |
45 |
46 |
47 |
48 | |`X_df`|`y_df` |`X_test_df`| `y_test_df`|
49 | |:-----------:|:-----------:|:-----------:|:-----------:|
50 | |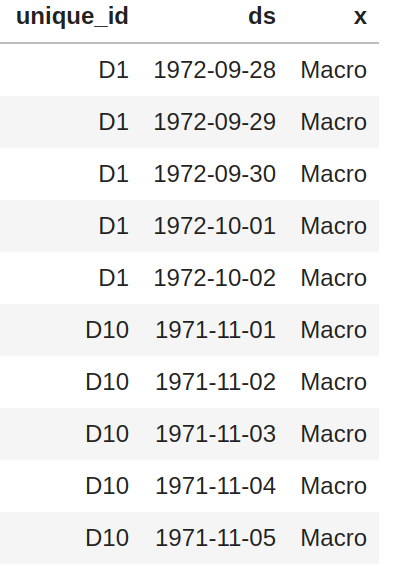 |
| 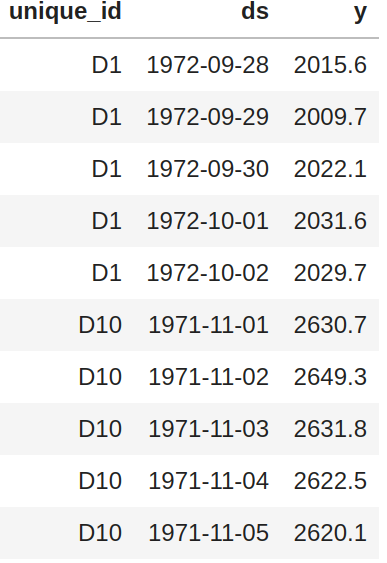 |
| 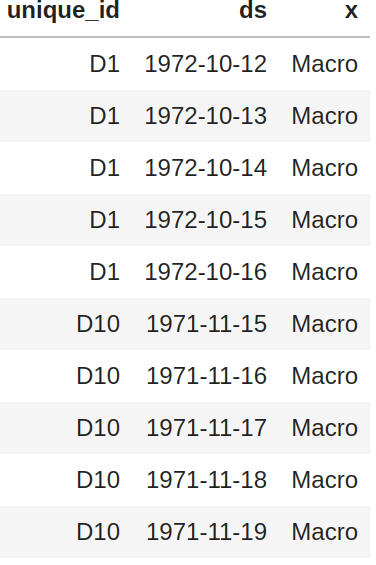 |
| 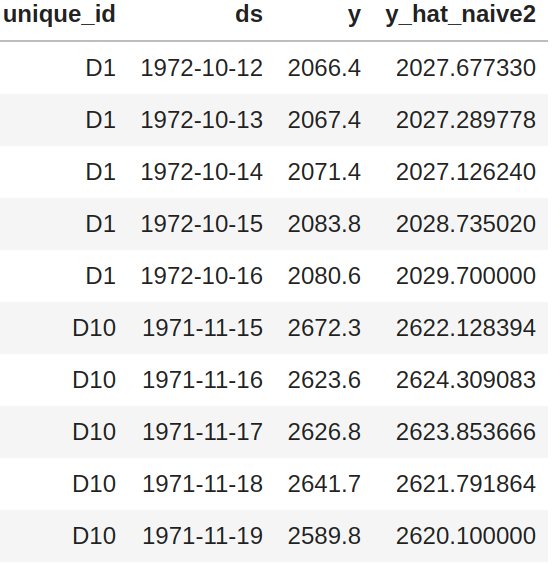 |
51 |
52 |
53 |
54 |
55 | ### M4 example
56 |
57 |
58 | ```python
59 | from ESRNN.m4_data import prepare_m4_data
60 | from ESRNN.utils_evaluation import evaluate_prediction_owa
61 |
62 | from ESRNN import ESRNN
63 |
64 | X_train_df, y_train_df, X_test_df, y_test_df = prepare_m4_data(dataset_name='Yearly',
65 | directory = './data',
66 | num_obs=1000)
67 |
68 | # Instantiate model
69 | model = ESRNN(max_epochs=25, freq_of_test=5, batch_size=4, learning_rate=1e-4,
70 | per_series_lr_multip=0.8, lr_scheduler_step_size=10,
71 | lr_decay=0.1, gradient_clipping_threshold=50,
72 | rnn_weight_decay=0.0, level_variability_penalty=100,
73 | testing_percentile=50, training_percentile=50,
74 | ensemble=False, max_periods=25, seasonality=[],
75 | input_size=4, output_size=6,
76 | cell_type='LSTM', state_hsize=40,
77 | dilations=[[1], [6]], add_nl_layer=False,
78 | random_seed=1, device='cpu')
79 |
80 | # Fit model
81 | # If y_test_df is provided the model
82 | # will evaluate predictions on
83 | # this set every freq_test epochs
84 | model.fit(X_train_df, y_train_df, X_test_df, y_test_df)
85 |
86 | # Predict on test set
87 | y_hat_df = model.predict(X_test_df)
88 |
89 | # Evaluate predictions
90 | final_owa, final_mase, final_smape = evaluate_prediction_owa(y_hat_df, y_train_df,
91 | X_test_df, y_test_df,
92 | naive2_seasonality=1)
93 | ```
94 | ## Overall Weighted Average
95 |
96 | A metric that is useful for quantifying the aggregate error of a specific model for various time series is the Overall Weighted Average (OWA) proposed for the M4 competition. This metric is calculated by obtaining the average of the symmetric mean absolute percentage error (sMAPE) and the mean absolute scaled error (MASE) for all the time series of the model and also calculating it for the Naive2 predictions. Both sMAPE and MASE are scale independent. These measurements are calculated as follows:
97 |
98 | 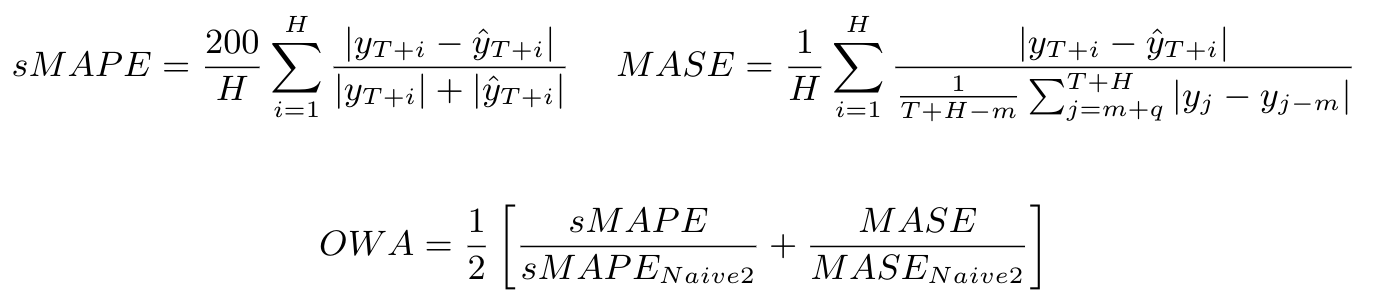
99 |
100 |
101 |
102 | ## Current Results
103 | Here we used the model directly to compare to the original implementation. It is worth noticing that these results do not include the ensemble methods mentioned in the [ESRNN paper](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169207019301153).
|
51 |
52 |
53 |
54 |
55 | ### M4 example
56 |
57 |
58 | ```python
59 | from ESRNN.m4_data import prepare_m4_data
60 | from ESRNN.utils_evaluation import evaluate_prediction_owa
61 |
62 | from ESRNN import ESRNN
63 |
64 | X_train_df, y_train_df, X_test_df, y_test_df = prepare_m4_data(dataset_name='Yearly',
65 | directory = './data',
66 | num_obs=1000)
67 |
68 | # Instantiate model
69 | model = ESRNN(max_epochs=25, freq_of_test=5, batch_size=4, learning_rate=1e-4,
70 | per_series_lr_multip=0.8, lr_scheduler_step_size=10,
71 | lr_decay=0.1, gradient_clipping_threshold=50,
72 | rnn_weight_decay=0.0, level_variability_penalty=100,
73 | testing_percentile=50, training_percentile=50,
74 | ensemble=False, max_periods=25, seasonality=[],
75 | input_size=4, output_size=6,
76 | cell_type='LSTM', state_hsize=40,
77 | dilations=[[1], [6]], add_nl_layer=False,
78 | random_seed=1, device='cpu')
79 |
80 | # Fit model
81 | # If y_test_df is provided the model
82 | # will evaluate predictions on
83 | # this set every freq_test epochs
84 | model.fit(X_train_df, y_train_df, X_test_df, y_test_df)
85 |
86 | # Predict on test set
87 | y_hat_df = model.predict(X_test_df)
88 |
89 | # Evaluate predictions
90 | final_owa, final_mase, final_smape = evaluate_prediction_owa(y_hat_df, y_train_df,
91 | X_test_df, y_test_df,
92 | naive2_seasonality=1)
93 | ```
94 | ## Overall Weighted Average
95 |
96 | A metric that is useful for quantifying the aggregate error of a specific model for various time series is the Overall Weighted Average (OWA) proposed for the M4 competition. This metric is calculated by obtaining the average of the symmetric mean absolute percentage error (sMAPE) and the mean absolute scaled error (MASE) for all the time series of the model and also calculating it for the Naive2 predictions. Both sMAPE and MASE are scale independent. These measurements are calculated as follows:
97 |
98 | 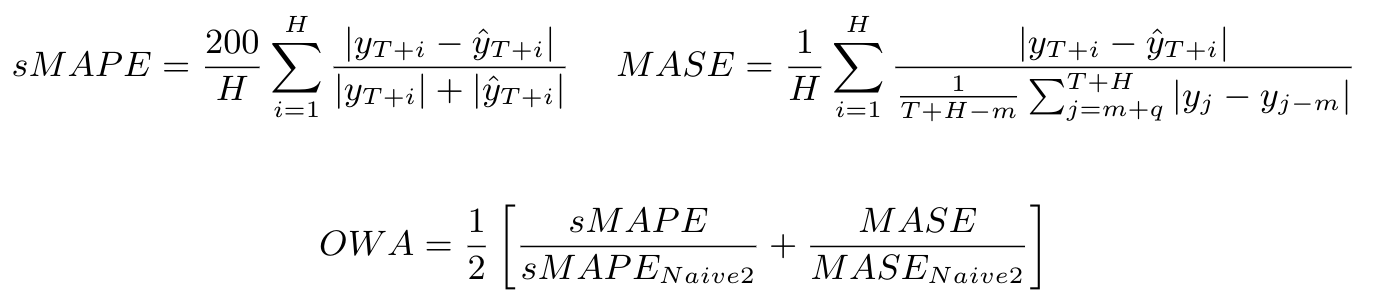
99 |
100 |
101 |
102 | ## Current Results
103 | Here we used the model directly to compare to the original implementation. It is worth noticing that these results do not include the ensemble methods mentioned in the [ESRNN paper](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169207019301153).
104 | [Results of the M4 competition](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/325901666_The_M4_Competition_Results_findings_conclusion_and_way_forward).
105 |
106 |
107 | | DATASET | OUR OWA | M4 OWA (Smyl) |
108 | |-----------|:---------:|:--------:|
109 | | Yearly | 0.785 | 0.778 |
110 | | Quarterly | 0.879 | 0.847 |
111 | | Monthly | 0.872 | 0.836 |
112 | | Hourly | 0.615 | 0.920 |
113 | | Weekly | 0.952 | 0.920 |
114 | | Daily | 0.968 | 0.920 |
115 |
116 |
117 | ## Replicating M4 results
118 |
119 |
120 | Replicating the M4 results is as easy as running the following line of code (for each frequency) after installing the package via pip:
121 |
122 | ```console
123 | python -m ESRNN.m4_run --dataset 'Yearly' --results_directory '/some/path' \
124 | --gpu_id 0 --use_cpu 0
125 | ```
126 |
127 | Use `--help` to get the description of each argument:
128 |
129 | ```console
130 | python -m ESRNN.m4_run --help
131 | ```
132 |
133 | ## Authors
134 | This repository was developed with joint efforts from AutonLab researchers at Carnegie Mellon University and Orax data scientists.
135 | * **Kin Gutierrez** - [kdgutier](https://github.com/kdgutier)
136 | * **Cristian Challu** - [cristianchallu](https://github.com/cristianchallu)
137 | * **Federico Garza** - [FedericoGarza](https://github.com/FedericoGarza) - [mail](fede.garza.ramirez@gmail.com)
138 | * **Max Mergenthaler** - [mergenthaler](https://github.com/mergenthaler)
139 |
140 | ## License
141 | This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the [LICENSE](https://github.com/kdgutier/esrnn_torch/blob/master/LICENSE) file for details.
142 |
143 |
144 | ## REFERENCES
145 | 1. [A hybrid method of exponential smoothing and recurrent neural networks for time series forecasting](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169207019301153)
146 | 2. [The M4 Competition: Results, findings, conclusion and way forward](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/325901666_The_M4_Competition_Results_findings_conclusion_and_way_forward)
147 | 3. [M4 Competition Data](https://github.com/M4Competition/M4-methods/tree/master/Dataset)
148 | 4. [Dilated Recurrent Neural Networks](https://papers.nips.cc/paper/6613-dilated-recurrent-neural-networks.pdf)
149 | 5. [Residual LSTM: Design of a Deep Recurrent Architecture for Distant Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.03360)
150 | 6. [A Dual-Stage Attention-Based recurrent neural network for time series prediction](https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.02971)
151 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ESRNN/m4_data.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | from six.moves import urllib
3 | import subprocess
4 |
5 | import numpy as np
6 | import pandas as pd
7 |
8 | from ESRNN.utils_evaluation import Naive2
9 |
10 |
11 | seas_dict = {'Hourly': {'seasonality': 24, 'input_size': 24,
12 | 'output_size': 48, 'freq': 'H'},
13 | 'Daily': {'seasonality': 7, 'input_size': 7,
14 | 'output_size': 14, 'freq': 'D'},
15 | 'Weekly': {'seasonality': 52, 'input_size': 52,
16 | 'output_size': 13, 'freq': 'W'},
17 | 'Monthly': {'seasonality': 12, 'input_size': 12,
18 | 'output_size':18, 'freq': 'M'},
19 | 'Quarterly': {'seasonality': 4, 'input_size': 4,
20 | 'output_size': 8, 'freq': 'Q'},
21 | 'Yearly': {'seasonality': 1, 'input_size': 4,
22 | 'output_size': 6, 'freq': 'D'}}
23 |
24 | SOURCE_URL = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Mcompetitions/M4-methods/master/Dataset/'
25 |
26 |
27 | def maybe_download(filename, directory):
28 | """
29 | Download the data from M4's website, unless it's already here.
30 |
31 | Parameters
32 | ----------
33 | filename: str
34 | Filename of M4 data with format /Type/Frequency.csv. Example: /Test/Daily-train.csv
35 | directory: str
36 | Custom directory where data will be downloaded.
37 | """
38 | data_directory = directory + "/m4"
39 | train_directory = data_directory + "/Train/"
40 | test_directory = data_directory + "/Test/"
41 |
42 | if not os.path.exists(data_directory):
43 | os.mkdir(data_directory)
44 | if not os.path.exists(train_directory):
45 | os.mkdir(train_directory)
46 | if not os.path.exists(test_directory):
47 | os.mkdir(test_directory)
48 |
49 | filepath = os.path.join(data_directory, filename)
50 | if not os.path.exists(filepath):
51 | filepath, _ = urllib.request.urlretrieve(SOURCE_URL + filename, filepath)
52 | size = os.path.getsize(filepath)
53 | print('Successfully downloaded', filename, size, 'bytes.')
54 | return filepath
55 |
56 | def m4_parser(dataset_name, directory, num_obs=1000000):
57 | """
58 | Transform M4 data into a panel.
59 |
60 | Parameters
61 | ----------
62 | dataset_name: str
63 | Frequency of the data. Example: 'Yearly'.
64 | directory: str
65 | Custom directory where data will be saved.
66 | num_obs: int
67 | Number of time series to return.
68 | """
69 | data_directory = directory + "/m4"
70 | train_directory = data_directory + "/Train/"
71 | test_directory = data_directory + "/Test/"
72 | freq = seas_dict[dataset_name]['freq']
73 |
74 | m4_info = pd.read_csv(data_directory+'/M4-info.csv', usecols=['M4id','category'])
75 | m4_info = m4_info[m4_info['M4id'].str.startswith(dataset_name[0])].reset_index(drop=True)
76 |
77 | # Train data
78 | train_path='{}{}-train.csv'.format(train_directory, dataset_name)
79 |
80 | train_df = pd.read_csv(train_path, nrows=num_obs)
81 | train_df = train_df.rename(columns={'V1':'unique_id'})
82 |
83 | train_df = pd.wide_to_long(train_df, stubnames=["V"], i="unique_id", j="ds").reset_index()
84 | train_df = train_df.rename(columns={'V':'y'})
85 | train_df = train_df.dropna()
86 | train_df['split'] = 'train'
87 | train_df['ds'] = train_df['ds']-1
88 | # Get len of series per unique_id
89 | len_series = train_df.groupby('unique_id').agg({'ds': 'max'}).reset_index()
90 | len_series.columns = ['unique_id', 'len_serie']
91 |
92 | # Test data
93 | test_path='{}{}-test.csv'.format(test_directory, dataset_name)
94 |
95 | test_df = pd.read_csv(test_path, nrows=num_obs)
96 | test_df = test_df.rename(columns={'V1':'unique_id'})
97 |
98 | test_df = pd.wide_to_long(test_df, stubnames=["V"], i="unique_id", j="ds").reset_index()
99 | test_df = test_df.rename(columns={'V':'y'})
100 | test_df = test_df.dropna()
101 | test_df['split'] = 'test'
102 | test_df = test_df.merge(len_series, on='unique_id')
103 | test_df['ds'] = test_df['ds'] + test_df['len_serie'] - 1
104 | test_df = test_df[['unique_id','ds','y','split']]
105 |
106 | df = pd.concat((train_df,test_df))
107 | df = df.sort_values(by=['unique_id', 'ds']).reset_index(drop=True)
108 |
109 | # Create column with dates with freq of dataset
110 | len_series = df.groupby('unique_id').agg({'ds': 'max'}).reset_index()
111 | dates = []
112 | for i in range(len(len_series)):
113 | len_serie = len_series.iloc[i,1]
114 | ranges = pd.date_range(start='1970/01/01', periods=len_serie, freq=freq)
115 | dates += list(ranges)
116 | df.loc[:,'ds'] = dates
117 |
118 | df = df.merge(m4_info, left_on=['unique_id'], right_on=['M4id'])
119 | df.drop(columns=['M4id'], inplace=True)
120 | df = df.rename(columns={'category': 'x'})
121 |
122 | X_train_df = df[df['split']=='train'].filter(items=['unique_id', 'ds', 'x'])
123 | y_train_df = df[df['split']=='train'].filter(items=['unique_id', 'ds', 'y'])
124 | X_test_df = df[df['split']=='test'].filter(items=['unique_id', 'ds', 'x'])
125 | y_test_df = df[df['split']=='test'].filter(items=['unique_id', 'ds', 'y'])
126 |
127 | X_train_df = X_train_df.reset_index(drop=True)
128 | y_train_df = y_train_df.reset_index(drop=True)
129 | X_test_df = X_test_df.reset_index(drop=True)
130 | y_test_df = y_test_df.reset_index(drop=True)
131 |
132 | return X_train_df, y_train_df, X_test_df, y_test_df
133 |
134 | def naive2_predictions(dataset_name, directory, num_obs, y_train_df = None, y_test_df = None):
135 | """
136 | Computes Naive2 predictions.
137 |
138 | Parameters
139 | ----------
140 | dataset_name: str
141 | Frequency of the data. Example: 'Yearly'.
142 | directory: str
143 | Custom directory where data will be saved.
144 | num_obs: int
145 | Number of time series to return.
146 | y_train_df: DataFrame
147 | Y train set returned by m4_parser
148 | y_test_df: DataFrame
149 | Y test set returned by m4_parser
150 | """
151 | # Read train and test data
152 | if (y_train_df is None) or (y_test_df is None):
153 | _, y_train_df, _, y_test_df = m4_parser(dataset_name, directory, num_obs)
154 |
155 | seasonality = seas_dict[dataset_name]['seasonality']
156 | input_size = seas_dict[dataset_name]['input_size']
157 | output_size = seas_dict[dataset_name]['output_size']
158 | freq = seas_dict[dataset_name]['freq']
159 |
160 | print('Preparing {} dataset'.format(dataset_name))
161 | print('Preparing Naive2 {} dataset predictions'.format(dataset_name))
162 |
163 | # Naive2
164 | y_naive2_df = pd.DataFrame(columns=['unique_id', 'ds', 'y_hat'])
165 |
166 | # Sort X by unique_id for faster loop
167 | y_train_df = y_train_df.sort_values(by=['unique_id', 'ds'])
168 | # List of uniques ids
169 | unique_ids = y_train_df['unique_id'].unique()
170 | # Panel of fitted models
171 | for unique_id in unique_ids:
172 | # Fast filter X and y by id.
173 | top_row = np.asscalar(y_train_df['unique_id'].searchsorted(unique_id, 'left'))
174 | bottom_row = np.asscalar(y_train_df['unique_id'].searchsorted(unique_id, 'right'))
175 | y_id = y_train_df[top_row:bottom_row]
176 |
177 | y_naive2 = pd.DataFrame(columns=['unique_id', 'ds', 'y_hat'])
178 | y_naive2['ds'] = pd.date_range(start=y_id.ds.max(),
179 | periods=output_size+1, freq=freq)[1:]
180 | y_naive2['unique_id'] = unique_id
181 | y_naive2['y_hat'] = Naive2(seasonality).fit(y_id.y.to_numpy()).predict(output_size)
182 | y_naive2_df = y_naive2_df.append(y_naive2)
183 |
184 | y_naive2_df = y_test_df.merge(y_naive2_df, on=['unique_id', 'ds'], how='left')
185 | y_naive2_df.rename(columns={'y_hat': 'y_hat_naive2'}, inplace=True)
186 |
187 | results_dir = directory + '/results'
188 | naive2_file = results_dir + '/{}-naive2predictions_{}.csv'.format(dataset_name, num_obs)
189 | y_naive2_df.to_csv(naive2_file, encoding='utf-8', index=None)
190 |
191 | return y_naive2_df
192 |
193 | def prepare_m4_data(dataset_name, directory, num_obs):
194 | """
195 | Pipeline that obtains M4 times series, tranforms it and gets naive2 predictions.
196 |
197 | Parameters
198 | ----------
199 | dataset_name: str
200 | Frequency of the data. Example: 'Yearly'.
201 | directory: str
202 | Custom directory where data will be saved.
203 | num_obs: int
204 | Number of time series to return.
205 | py_predictions: bool
206 | whether use python or r predictions
207 | """
208 | m4info_filename = maybe_download('M4-info.csv', directory)
209 |
210 | dailytrain_filename = maybe_download('Train/Daily-train.csv', directory)
211 | hourlytrain_filename = maybe_download('Train/Hourly-train.csv', directory)
212 | monthlytrain_filename = maybe_download('Train/Monthly-train.csv', directory)
213 | quarterlytrain_filename = maybe_download('Train/Quarterly-train.csv', directory)
214 | weeklytrain_filename = maybe_download('Train/Weekly-train.csv', directory)
215 | yearlytrain_filename = maybe_download('Train/Yearly-train.csv', directory)
216 |
217 | dailytest_filename = maybe_download('Test/Daily-test.csv', directory)
218 | hourlytest_filename = maybe_download('Test/Hourly-test.csv', directory)
219 | monthlytest_filename = maybe_download('Test/Monthly-test.csv', directory)
220 | quarterlytest_filename = maybe_download('Test/Quarterly-test.csv', directory)
221 | weeklytest_filename = maybe_download('Test/Weekly-test.csv', directory)
222 | yearlytest_filename = maybe_download('Test/Yearly-test.csv', directory)
223 | print('\n')
224 |
225 | X_train_df, y_train_df, X_test_df, y_test_df = m4_parser(dataset_name, directory, num_obs)
226 |
227 | results_dir = directory + '/results'
228 | if not os.path.exists(results_dir):
229 | os.mkdir(results_dir)
230 |
231 | naive2_file = results_dir + '/{}-naive2predictions_{}.csv'
232 | naive2_file = naive2_file.format(dataset_name, num_obs)
233 |
234 | if not os.path.exists(naive2_file):
235 | y_naive2_df = naive2_predictions(dataset_name, directory, num_obs, y_train_df, y_test_df)
236 | else:
237 | y_naive2_df = pd.read_csv(naive2_file)
238 | y_naive2_df['ds'] = pd.to_datetime(y_naive2_df['ds'])
239 |
240 | return X_train_df, y_train_df, X_test_df, y_naive2_df
241 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ESRNN/utils/ESRNN.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | from ESRNN.utils.DRNN import DRNN
4 | import numpy as np
5 |
6 | #import torch.jit as jit
7 |
8 |
9 | class _ES(nn.Module):
10 | def __init__(self, mc):
11 | super(_ES, self).__init__()
12 | self.mc = mc
13 | self.n_series = self.mc.n_series
14 | self.output_size = self.mc.output_size
15 | assert len(self.mc.seasonality) in [0, 1, 2]
16 |
17 | def gaussian_noise(self, input_data, std=0.2):
18 | size = input_data.size()
19 | noise = torch.autograd.Variable(input_data.data.new(size).normal_(0, std))
20 | return input_data + noise
21 |
22 | #@jit.script_method
23 | def compute_levels_seasons(self, y, idxs):
24 | pass
25 |
26 | def normalize(self, y, level, seasonalities):
27 | pass
28 |
29 | def predict(self, trend, levels, seasonalities):
30 | pass
31 |
32 | def forward(self, ts_object):
33 | # parse mc
34 | input_size = self.mc.input_size
35 | output_size = self.mc.output_size
36 | exogenous_size = self.mc.exogenous_size
37 | noise_std = self.mc.noise_std
38 | seasonality = self.mc.seasonality
39 | batch_size = len(ts_object.idxs)
40 |
41 | # Parse ts_object
42 | y = ts_object.y
43 | idxs = ts_object.idxs
44 | n_series, n_time = y.shape
45 | if self.training:
46 | windows_end = n_time-input_size-output_size+1
47 | windows_range = range(windows_end)
48 | else:
49 | windows_start = n_time-input_size-output_size+1
50 | windows_end = n_time-input_size+1
51 |
52 | windows_range = range(windows_start, windows_end)
53 | n_windows = len(windows_range)
54 | assert n_windows>0
55 |
56 | # Initialize windows, levels and seasonalities
57 | levels, seasonalities = self.compute_levels_seasons(y, idxs)
58 | windows_y_hat = torch.zeros((n_windows, batch_size, input_size+exogenous_size),
59 | device=self.mc.device)
60 | windows_y = torch.zeros((n_windows, batch_size, output_size),
61 | device=self.mc.device)
62 |
63 | for i, window in enumerate(windows_range):
64 | # Windows yhat
65 | y_hat_start = window
66 | y_hat_end = input_size + window
67 |
68 | # Y_hat deseasonalization and normalization
69 | window_y_hat = self.normalize(y=y[:, y_hat_start:y_hat_end],
70 | level=levels[:, [y_hat_end-1]],
71 | seasonalities=seasonalities,
72 | start=y_hat_start, end=y_hat_end)
73 |
74 | if self.training:
75 | window_y_hat = self.gaussian_noise(window_y_hat, std=noise_std)
76 |
77 | # Concatenate categories
78 | if exogenous_size>0:
79 | window_y_hat = torch.cat((window_y_hat, ts_object.categories), 1)
80 |
81 | windows_y_hat[i, :, :] += window_y_hat
82 |
83 | # Windows y (for loss during train)
84 | if self.training:
85 | y_start = y_hat_end
86 | y_end = y_start+output_size
87 | # Y deseasonalization and normalization
88 | window_y = self.normalize(y=y[:, y_start:y_end],
89 | level=levels[:, [y_start]],
90 | seasonalities=seasonalities,
91 | start=y_start, end=y_end)
92 | windows_y[i, :, :] += window_y
93 |
94 | return windows_y_hat, windows_y, levels, seasonalities
95 |
96 | class _ESM(_ES):
97 | def __init__(self, mc):
98 | super(_ESM, self).__init__(mc)
99 | # Level and Seasonality Smoothing parameters
100 | # 1 level, S seasonalities, S init_seas
101 | embeds_size = 1 + len(self.mc.seasonality) + sum(self.mc.seasonality)
102 | init_embeds = torch.ones((self.n_series, embeds_size)) * 0.5
103 | self.embeds = nn.Embedding(self.n_series, embeds_size)
104 | self.embeds.weight.data.copy_(init_embeds)
105 | self.register_buffer('seasonality', torch.LongTensor(self.mc.seasonality))
106 |
107 | #@jit.script_method
108 | def compute_levels_seasons(self, y, idxs):
109 | """
110 | Computes levels and seasons
111 | """
112 | # Lookup parameters per serie
113 | #seasonality = self.seasonality
114 | embeds = self.embeds(idxs)
115 | lev_sms = torch.sigmoid(embeds[:, 0])
116 |
117 | # Initialize seasonalities
118 | seas_prod = torch.ones(len(y[:,0])).to(y.device)
119 | #seasonalities1 = torch.jit.annotate(List[Tensor], [])
120 | #seasonalities2 = torch.jit.annotate(List[Tensor], [])
121 | seasonalities1 = []
122 | seasonalities2 = []
123 | seas_sms1 = torch.ones(1).to(y.device)
124 | seas_sms2 = torch.ones(1).to(y.device)
125 |
126 | if len(self.seasonality)>0:
127 | seas_sms1 = torch.sigmoid(embeds[:, 1])
128 | init_seas1 = torch.exp(embeds[:, 2:(2+self.seasonality[0])]).unbind(1)
129 | assert len(init_seas1) == self.seasonality[0]
130 |
131 | for i in range(len(init_seas1)):
132 | seasonalities1 += [init_seas1[i]]
133 | seasonalities1 += [init_seas1[0]]
134 | seas_prod = seas_prod * init_seas1[0]
135 |
136 | if len(self.seasonality)==2:
137 | seas_sms2 = torch.sigmoid(embeds[:, 2+self.seasonality[0]])
138 | init_seas2 = torch.exp(embeds[:, 3+self.seasonality[0]:]).unbind(1)
139 | assert len(init_seas2) == self.seasonality[1]
140 |
141 | for i in range(len(init_seas2)):
142 | seasonalities2 += [init_seas2[i]]
143 | seasonalities2 += [init_seas2[0]]
144 | seas_prod = seas_prod * init_seas2[0]
145 |
146 | # Initialize levels
147 | #levels = torch.jit.annotate(List[Tensor], [])
148 | levels = []
149 | levels += [y[:,0]/seas_prod]
150 |
151 | # Recursive seasonalities and levels
152 | ys = y.unbind(1)
153 | n_time = len(ys)
154 | for t in range(1, n_time):
155 |
156 | seas_prod_t = torch.ones(len(y[:,t])).to(y.device)
157 | if len(self.seasonality)>0:
158 | seas_prod_t = seas_prod_t * seasonalities1[t]
159 | if len(self.seasonality)==2:
160 | seas_prod_t = seas_prod_t * seasonalities2[t]
161 |
162 | newlev = lev_sms * (ys[t] / seas_prod_t) + (1-lev_sms) * levels[t-1]
163 | levels += [newlev]
164 |
165 | if len(self.seasonality)==1:
166 | newseason1 = seas_sms1 * (ys[t] / newlev) + (1-seas_sms1) * seasonalities1[t]
167 | seasonalities1 += [newseason1]
168 |
169 | if len(self.seasonality)==2:
170 | newseason1 = seas_sms1 * (ys[t] / (newlev * seasonalities2[t])) + \
171 | (1-seas_sms1) * seasonalities1[t]
172 | seasonalities1 += [newseason1]
173 | newseason2 = seas_sms2 * (ys[t] / (newlev * seasonalities1[t])) + \
174 | (1-seas_sms2) * seasonalities2[t]
175 | seasonalities2 += [newseason2]
176 |
177 | levels = torch.stack(levels).transpose(1,0)
178 |
179 | #seasonalities = torch.jit.annotate(List[Tensor], [])
180 | seasonalities = []
181 |
182 | if len(self.seasonality)>0:
183 | seasonalities += [torch.stack(seasonalities1).transpose(1,0)]
184 |
185 | if len(self.seasonality)==2:
186 | seasonalities += [torch.stack(seasonalities2).transpose(1,0)]
187 |
188 | return levels, seasonalities
189 |
190 | def normalize(self, y, level, seasonalities, start, end):
191 | # Deseasonalization and normalization
192 | y_n = y / level
193 | for s in range(len(self.seasonality)):
194 | y_n /= seasonalities[s][:, start:end]
195 | y_n = torch.log(y_n)
196 | return y_n
197 |
198 | def predict(self, trend, levels, seasonalities):
199 | output_size = self.mc.output_size
200 | seasonality = self.mc.seasonality
201 | n_time = levels.shape[1]
202 |
203 | # Denormalize
204 | trend = torch.exp(trend)
205 |
206 | # Completion of seasonalities if prediction horizon is larger than seasonality
207 | # Naive2 like prediction, to avoid recursive forecasting
208 | for s in range(len(seasonality)):
209 | if output_size > seasonality[s]:
210 | repetitions = int(np.ceil(output_size/seasonality[s]))-1
211 | last_season = seasonalities[s][:, -seasonality[s]:]
212 | extra_seasonality = last_season.repeat((1, repetitions))
213 | seasonalities[s] = torch.cat((seasonalities[s], extra_seasonality), 1)
214 |
215 | # Deseasonalization and normalization (inverse)
216 | y_hat = trend * levels[:,[n_time-1]]
217 | for s in range(len(seasonality)):
218 | y_hat *= seasonalities[s][:, n_time:(n_time+output_size)]
219 |
220 | return y_hat
221 |
222 | class _RNN(nn.Module):
223 | def __init__(self, mc):
224 | super(_RNN, self).__init__()
225 | self.mc = mc
226 | self.layers = len(mc.dilations)
227 |
228 | layers = []
229 | for grp_num in range(len(mc.dilations)):
230 | if grp_num == 0:
231 | input_size = mc.input_size + mc.exogenous_size
232 | else:
233 | input_size = mc.state_hsize
234 | layer = DRNN(input_size,
235 | mc.state_hsize,
236 | n_layers=len(mc.dilations[grp_num]),
237 | dilations=mc.dilations[grp_num],
238 | cell_type=mc.cell_type)
239 | layers.append(layer)
240 |
241 | self.rnn_stack = nn.Sequential(*layers)
242 |
243 | if self.mc.add_nl_layer:
244 | self.MLPW = nn.Linear(mc.state_hsize, mc.state_hsize)
245 |
246 | self.adapterW = nn.Linear(mc.state_hsize, mc.output_size)
247 |
248 | def forward(self, input_data):
249 | for layer_num in range(len(self.rnn_stack)):
250 | residual = input_data
251 | output, _ = self.rnn_stack[layer_num](input_data)
252 | if layer_num > 0:
253 | output += residual
254 | input_data = output
255 |
256 | if self.mc.add_nl_layer:
257 | input_data = self.MLPW(input_data)
258 | input_data = torch.tanh(input_data)
259 |
260 | input_data = self.adapterW(input_data)
261 | return input_data
262 |
263 |
264 | class _ESRNN(nn.Module):
265 | def __init__(self, mc):
266 | super(_ESRNN, self).__init__()
267 | self.mc = mc
268 | self.es = _ESM(mc).to(self.mc.device)
269 | self.rnn = _RNN(mc).to(self.mc.device)
270 |
271 | def forward(self, ts_object):
272 | # ES Forward
273 | windows_y_hat, windows_y, levels, seasonalities = self.es(ts_object)
274 |
275 | # RNN Forward
276 | windows_y_hat = self.rnn(windows_y_hat)
277 |
278 | return windows_y, windows_y_hat, levels
279 |
280 | def predict(self, ts_object):
281 | # ES Forward
282 | windows_y_hat, _, levels, seasonalities = self.es(ts_object)
283 |
284 | # RNN Forward
285 | windows_y_hat = self.rnn(windows_y_hat)
286 | trend = windows_y_hat[-1,:,:] # Last observation prediction
287 |
288 | y_hat = self.es.predict(trend, levels, seasonalities)
289 | return y_hat
290 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ESRNN/utils/DRNN.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Dilated Recurrent Neural Networks. https://papers.nips.cc/paper/6613-dilated-recurrent-neural-networks.pdf
2 | # implementation from https://github.com/zalandoresearch/pytorch-dilated-rnn
3 | # Residual LSTM: Design of a Deep Recurrent Architecture for Distant Speech Recognition. https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.03360
4 | # A Dual-Stage Attention-Based recurrent neural network for time series prediction. https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.02971
5 |
6 | import torch
7 | import torch.nn as nn
8 | import torch.autograd as autograd
9 |
10 | #import torch.jit as jit
11 |
12 | use_cuda = torch.cuda.is_available()
13 |
14 |
15 | class LSTMCell(nn.Module): #jit.ScriptModule
16 | def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, dropout=0.):
17 | super(LSTMCell, self).__init__()
18 | self.input_size = input_size
19 | self.hidden_size = hidden_size
20 | self.weight_ih = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(4 * hidden_size, input_size))
21 | self.weight_hh = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(4 * hidden_size, hidden_size))
22 | self.bias_ih = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(4 * hidden_size))
23 | self.bias_hh = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(4 * hidden_size))
24 | self.dropout = dropout
25 |
26 | #@jit.script_method
27 | def forward(self, input, hidden):
28 | # type: (Tensor, Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]]
29 | hx, cx = hidden[0].squeeze(0), hidden[1].squeeze(0)
30 | gates = (torch.matmul(input, self.weight_ih.t()) + self.bias_ih +
31 | torch.matmul(hx, self.weight_hh.t()) + self.bias_hh)
32 | ingate, forgetgate, cellgate, outgate = gates.chunk(4, 1)
33 |
34 | ingate = torch.sigmoid(ingate)
35 | forgetgate = torch.sigmoid(forgetgate)
36 | cellgate = torch.tanh(cellgate)
37 | outgate = torch.sigmoid(outgate)
38 |
39 | cy = (forgetgate * cx) + (ingate * cellgate)
40 | hy = outgate * torch.tanh(cy)
41 |
42 | return hy, (hy, cy)
43 |
44 |
45 | class ResLSTMCell(nn.Module):
46 | def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, dropout=0.):
47 | super(ResLSTMCell, self).__init__()
48 | self.register_buffer('input_size', torch.Tensor([input_size]))
49 | self.register_buffer('hidden_size', torch.Tensor([hidden_size]))
50 | self.weight_ii = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(3 * hidden_size, input_size))
51 | self.weight_ic = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(3 * hidden_size, hidden_size))
52 | self.weight_ih = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(3 * hidden_size, hidden_size))
53 | self.bias_ii = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(3 * hidden_size))
54 | self.bias_ic = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(3 * hidden_size))
55 | self.bias_ih = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(3 * hidden_size))
56 | self.weight_hh = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1 * hidden_size, hidden_size))
57 | self.bias_hh = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1 * hidden_size))
58 | self.weight_ir = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(hidden_size, input_size))
59 | self.dropout = dropout
60 |
61 | #@jit.script_method
62 | def forward(self, input, hidden):
63 | # type: (Tensor, Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]]
64 | hx, cx = hidden[0].squeeze(0), hidden[1].squeeze(0)
65 |
66 | ifo_gates = (torch.matmul(input, self.weight_ii.t()) + self.bias_ii +
67 | torch.matmul(hx, self.weight_ih.t()) + self.bias_ih +
68 | torch.matmul(cx, self.weight_ic.t()) + self.bias_ic)
69 | ingate, forgetgate, outgate = ifo_gates.chunk(3, 1)
70 |
71 | cellgate = torch.matmul(hx, self.weight_hh.t()) + self.bias_hh
72 |
73 | ingate = torch.sigmoid(ingate)
74 | forgetgate = torch.sigmoid(forgetgate)
75 | cellgate = torch.tanh(cellgate)
76 | outgate = torch.sigmoid(outgate)
77 |
78 | cy = (forgetgate * cx) + (ingate * cellgate)
79 | ry = torch.tanh(cy)
80 |
81 | if self.input_size == self.hidden_size:
82 | hy = outgate * (ry + input)
83 | else:
84 | hy = outgate * (ry + torch.matmul(input, self.weight_ir.t()))
85 | return hy, (hy, cy)
86 |
87 |
88 | class ResLSTMLayer(nn.Module):
89 | def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, dropout=0.):
90 | super(ResLSTMLayer, self).__init__()
91 | self.input_size = input_size
92 | self.hidden_size = hidden_size
93 | self.cell = ResLSTMCell(input_size, hidden_size, dropout=0.)
94 |
95 | #@jit.script_method
96 | def forward(self, input, hidden):
97 | # type: (Tensor, Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]]
98 | inputs = input.unbind(0)
99 | #outputs = torch.jit.annotate(List[Tensor], [])
100 | outputs = []
101 | for i in range(len(inputs)):
102 | out, hidden = self.cell(inputs[i], hidden)
103 | outputs += [out]
104 | outputs = torch.stack(outputs)
105 | return outputs, hidden
106 |
107 |
108 | class AttentiveLSTMLayer(nn.Module):
109 | def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, dropout=0.0):
110 | super(AttentiveLSTMLayer, self).__init__()
111 | self.input_size = input_size
112 | self.hidden_size = hidden_size
113 | attention_hsize = hidden_size
114 | self.attention_hsize = attention_hsize
115 |
116 | self.cell = LSTMCell(input_size, hidden_size)
117 | self.attn_layer = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(2 * hidden_size + input_size, attention_hsize),
118 | nn.Tanh(),
119 | nn.Linear(attention_hsize, 1))
120 | self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=0)
121 | self.dropout = dropout
122 |
123 | #@jit.script_method
124 | def forward(self, input, hidden):
125 | inputs = input.unbind(0)
126 | #outputs = torch.jit.annotate(List[Tensor], [])
127 | outputs = []
128 |
129 | for t in range(len(input)):
130 | # attention on windows
131 | hx, cx = hidden[0].squeeze(0), hidden[1].squeeze(0)
132 | hx_rep = hx.repeat(len(inputs), 1, 1)
133 | cx_rep = cx.repeat(len(inputs), 1, 1)
134 | x = torch.cat((input, hx_rep, cx_rep), dim=-1)
135 | l = self.attn_layer(x)
136 | beta = self.softmax(l)
137 | context = torch.bmm(beta.permute(1, 2, 0),
138 | input.permute(1, 0, 2)).squeeze(1)
139 | out, hidden = self.cell(context, hidden)
140 | outputs += [out]
141 | outputs = torch.stack(outputs)
142 | return outputs, hidden
143 |
144 |
145 | class DRNN(nn.Module):
146 |
147 | def __init__(self, n_input, n_hidden, n_layers, dilations, dropout=0, cell_type='GRU', batch_first=False):
148 |
149 | super(DRNN, self).__init__()
150 |
151 | self.dilations = dilations
152 | self.cell_type = cell_type
153 | self.batch_first = batch_first
154 |
155 | layers = []
156 | if self.cell_type == "GRU":
157 | cell = nn.GRU
158 | elif self.cell_type == "RNN":
159 | cell = nn.RNN
160 | elif self.cell_type == "LSTM":
161 | cell = nn.LSTM
162 | elif self.cell_type == "ResLSTM":
163 | cell = ResLSTMLayer
164 | elif self.cell_type == "AttentiveLSTM":
165 | cell = AttentiveLSTMLayer
166 | else:
167 | raise NotImplementedError
168 |
169 | for i in range(n_layers):
170 | if i == 0:
171 | c = cell(n_input, n_hidden, dropout=dropout)
172 | else:
173 | c = cell(n_hidden, n_hidden, dropout=dropout)
174 | layers.append(c)
175 | self.cells = nn.Sequential(*layers)
176 |
177 | def forward(self, inputs, hidden=None):
178 | if self.batch_first:
179 | inputs = inputs.transpose(0, 1)
180 | outputs = []
181 | for i, (cell, dilation) in enumerate(zip(self.cells, self.dilations)):
182 | if hidden is None:
183 | inputs, _ = self.drnn_layer(cell, inputs, dilation)
184 | else:
185 | inputs, hidden[i] = self.drnn_layer(cell, inputs, dilation, hidden[i])
186 |
187 | outputs.append(inputs[-dilation:])
188 |
189 | if self.batch_first:
190 | inputs = inputs.transpose(0, 1)
191 | return inputs, outputs
192 |
193 | def drnn_layer(self, cell, inputs, rate, hidden=None):
194 |
195 | n_steps = len(inputs)
196 | batch_size = inputs[0].size(0)
197 | hidden_size = cell.hidden_size
198 |
199 | inputs, dilated_steps = self._pad_inputs(inputs, n_steps, rate)
200 | dilated_inputs = self._prepare_inputs(inputs, rate)
201 |
202 | if hidden is None:
203 | dilated_outputs, hidden = self._apply_cell(dilated_inputs, cell, batch_size, rate, hidden_size)
204 | else:
205 | hidden = self._prepare_inputs(hidden, rate)
206 | dilated_outputs, hidden = self._apply_cell(dilated_inputs, cell, batch_size, rate, hidden_size,
207 | hidden=hidden)
208 |
209 | splitted_outputs = self._split_outputs(dilated_outputs, rate)
210 | outputs = self._unpad_outputs(splitted_outputs, n_steps)
211 |
212 | return outputs, hidden
213 |
214 | def _apply_cell(self, dilated_inputs, cell, batch_size, rate, hidden_size, hidden=None):
215 | if hidden is None:
216 | if self.cell_type == 'LSTM' or self.cell_type == 'ResLSTM' or self.cell_type == 'AttentiveLSTM':
217 | c, m = self.init_hidden(batch_size * rate, hidden_size)
218 | hidden = (c.unsqueeze(0), m.unsqueeze(0))
219 | else:
220 | hidden = self.init_hidden(batch_size * rate, hidden_size).unsqueeze(0)
221 |
222 | dilated_outputs, hidden = cell(dilated_inputs, hidden) # compatibility hack
223 |
224 | return dilated_outputs, hidden
225 |
226 | def _unpad_outputs(self, splitted_outputs, n_steps):
227 | return splitted_outputs[:n_steps]
228 |
229 | def _split_outputs(self, dilated_outputs, rate):
230 | batchsize = dilated_outputs.size(1) // rate
231 |
232 | blocks = [dilated_outputs[:, i * batchsize: (i + 1) * batchsize, :] for i in range(rate)]
233 |
234 | interleaved = torch.stack((blocks)).transpose(1, 0).contiguous()
235 | interleaved = interleaved.view(dilated_outputs.size(0) * rate,
236 | batchsize,
237 | dilated_outputs.size(2))
238 | return interleaved
239 |
240 | def _pad_inputs(self, inputs, n_steps, rate):
241 | iseven = (n_steps % rate) == 0
242 |
243 | if not iseven:
244 | dilated_steps = n_steps // rate + 1
245 |
246 | zeros_ = torch.zeros(dilated_steps * rate - inputs.size(0),
247 | inputs.size(1),
248 | inputs.size(2))
249 | if use_cuda:
250 | zeros_ = zeros_.cuda()
251 |
252 | inputs = torch.cat((inputs, autograd.Variable(zeros_)))
253 | else:
254 | dilated_steps = n_steps // rate
255 |
256 | return inputs, dilated_steps
257 |
258 | def _prepare_inputs(self, inputs, rate):
259 | dilated_inputs = torch.cat([inputs[j::rate, :, :] for j in range(rate)], 1)
260 | return dilated_inputs
261 |
262 | def init_hidden(self, batch_size, hidden_dim):
263 | hidden = autograd.Variable(torch.zeros(batch_size, hidden_dim))
264 | if use_cuda:
265 | hidden = hidden.cuda()
266 | if self.cell_type == "LSTM" or self.cell_type == 'ResLSTM' or self.cell_type == 'AttentiveLSTM':
267 | memory = autograd.Variable(torch.zeros(batch_size, hidden_dim))
268 | if use_cuda:
269 | memory = memory.cuda()
270 | return hidden, memory
271 | else:
272 | return hidden
273 |
274 |
275 | if __name__ == '__main__':
276 | n_inp = 4
277 | n_hidden = 4
278 | n_layers = 2
279 | batch_size = 3
280 | n_windows = 2
281 | cell_type = 'ResLSTM'
282 |
283 | model = DRNN(n_inp, n_hidden, n_layers=n_layers, cell_type=cell_type, dilations=[1,2])
284 |
285 | test_x1 = torch.autograd.Variable(torch.randn(n_windows, batch_size, n_inp))
286 | test_x2 = torch.autograd.Variable(torch.randn(n_windows, batch_size, n_inp))
287 |
288 | out, hidden = model(test_x1)
289 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ESRNN/utils_evaluation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from numpy.random import seed
3 | seed(1)
4 |
5 | import pandas as pd
6 | from math import sqrt
7 |
8 |
9 | ########################
10 | # UTILITY MODELS
11 | ########################
12 |
13 | def detrend(insample_data):
14 | """
15 | Calculates a & b parameters of LRL
16 | :param insample_data:
17 | :return:
18 | """
19 | x = np.arange(len(insample_data))
20 | a, b = np.polyfit(x, insample_data, 1)
21 | return a, b
22 |
23 | def deseasonalize(original_ts, ppy):
24 | """
25 | Calculates and returns seasonal indices
26 | :param original_ts: original data
27 | :param ppy: periods per year
28 | :return:
29 | """
30 | """
31 | # === get in-sample data
32 | original_ts = original_ts[:-out_of_sample]
33 | """
34 | if seasonality_test(original_ts, ppy):
35 | # ==== get moving averages
36 | ma_ts = moving_averages(original_ts, ppy)
37 |
38 | # ==== get seasonality indices
39 | le_ts = original_ts * 100 / ma_ts
40 | le_ts = np.hstack((le_ts, np.full((ppy - (len(le_ts) % ppy)), np.nan)))
41 | le_ts = np.reshape(le_ts, (-1, ppy))
42 | si = np.nanmean(le_ts, 0)
43 | norm = np.sum(si) / (ppy * 100)
44 | si = si / norm
45 | else:
46 | si = np.ones(ppy)
47 |
48 | return si
49 |
50 | def moving_averages(ts_init, window):
51 | """
52 | Calculates the moving averages for a given TS
53 | :param ts_init: the original time series
54 | :param window: window length
55 | :return: moving averages ts
56 | """
57 | """
58 | As noted by Professor Isidro Lloret Galiana:
59 | line 82:
60 | if len(ts_init) % 2 == 0:
61 |
62 | should be changed to
63 | if window % 2 == 0:
64 |
65 | This change has a minor (less then 0.05%) impact on the calculations of the seasonal indices
66 | In order for the results to be fully replicable this change is not incorporated into the code below
67 | """
68 | ts_init = pd.Series(ts_init)
69 |
70 | if len(ts_init) % 2 == 0:
71 | ts_ma = ts_init.rolling(window, center=True).mean()
72 | ts_ma = ts_ma.rolling(2, center=True).mean()
73 | ts_ma = np.roll(ts_ma, -1)
74 | else:
75 | ts_ma = ts_init.rolling(window, center=True).mean()
76 |
77 | return ts_ma
78 |
79 | def seasonality_test(original_ts, ppy):
80 | """
81 | Seasonality test
82 | :param original_ts: time series
83 | :param ppy: periods per year
84 | :return: boolean value: whether the TS is seasonal
85 | """
86 | s = acf(original_ts, 1)
87 | for i in range(2, ppy):
88 | s = s + (acf(original_ts, i) ** 2)
89 |
90 | limit = 1.645 * (sqrt((1 + 2 * s) / len(original_ts)))
91 |
92 | return (abs(acf(original_ts, ppy))) > limit
93 |
94 | def acf(data, k):
95 | """
96 | Autocorrelation function
97 | :param data: time series
98 | :param k: lag
99 | :return:
100 | """
101 | m = np.mean(data)
102 | s1 = 0
103 | for i in range(k, len(data)):
104 | s1 = s1 + ((data[i] - m) * (data[i - k] - m))
105 |
106 | s2 = 0
107 | for i in range(0, len(data)):
108 | s2 = s2 + ((data[i] - m) ** 2)
109 |
110 | return float(s1 / s2)
111 |
112 | class Naive:
113 | """
114 | Naive model.
115 | This benchmark model produces a forecast that is equal to
116 | the last observed value for a given time series.
117 | """
118 | def __init__(self):
119 | pass
120 |
121 | def fit(self, ts_init):
122 | """
123 | ts_init: the original time series
124 | ts_naive: last observations of time series
125 | """
126 | self.ts_naive = [ts_init[-1]]
127 | return self
128 |
129 | def predict(self, h):
130 | return np.array(self.ts_naive * h)
131 |
132 | class SeasonalNaive:
133 | """
134 | Seasonal Naive model.
135 | This benchmark model produces a forecast that is equal to
136 | the last observed value of the same season for a given time
137 | series.
138 | """
139 | def __init__(self):
140 | pass
141 |
142 | def fit(self, ts_init, seasonality):
143 | """
144 | ts_init: the original time series
145 | frcy: frequency of the time series
146 | ts_naive: last observations of time series
147 | """
148 | self.ts_seasonal_naive = ts_init[-seasonality:]
149 | return self
150 |
151 | def predict(self, h):
152 | repetitions = int(np.ceil(h/len(self.ts_seasonal_naive)))
153 | y_hat = np.tile(self.ts_seasonal_naive, reps=repetitions)[:h]
154 | return y_hat
155 |
156 | class Naive2:
157 | """
158 | Naive2 model.
159 | Popular benchmark model for time series forecasting that automatically adapts
160 | to the potential seasonality of a series based on an autocorrelation test.
161 | If the series is seasonal the model composes the predictions of Naive and SeasonalNaive,
162 | else the model predicts on the simple Naive.
163 | """
164 | def __init__(self, seasonality):
165 | self.seasonality = seasonality
166 |
167 | def fit(self, ts_init):
168 | seasonality_in = deseasonalize(ts_init, ppy=self.seasonality)
169 | windows = int(np.ceil(len(ts_init) / self.seasonality))
170 |
171 | self.ts_init = ts_init
172 | self.s_hat = np.tile(seasonality_in, reps=windows)[:len(ts_init)]
173 | self.ts_des = ts_init / self.s_hat
174 |
175 | return self
176 |
177 | def predict(self, h):
178 | s_hat = SeasonalNaive().fit(self.s_hat,
179 | seasonality=self.seasonality).predict(h)
180 | r_hat = Naive().fit(self.ts_des).predict(h)
181 | y_hat = s_hat * r_hat
182 | return y_hat
183 |
184 | ########################
185 | # METRICS
186 | ########################
187 |
188 | def mse(y, y_hat):
189 | """
190 | Calculates Mean Squared Error.
191 |
192 | Parameters
193 | ----------
194 | y: numpy array
195 | actual test values
196 | y_hat: numpy array
197 | predicted values
198 |
199 | Returns
200 | -------
201 | mse: float
202 | mean squared error
203 | """
204 | y = np.reshape(y, (-1,))
205 | y_hat = np.reshape(y_hat, (-1,))
206 | mse = np.mean(np.square(y - y_hat)).item()
207 | return mse
208 |
209 | def mape(y, y_hat):
210 | """
211 | Calculates Mean Absolute Percentage Error.
212 |
213 | Parameters
214 | ----------
215 | y: numpy array
216 | actual test values
217 | y_hat: numpy array
218 | predicted values
219 |
220 | Returns
221 | -------
222 | mape: float
223 | mean absolute percentage error
224 | """
225 | y = np.reshape(y, (-1,))
226 | y_hat = np.reshape(y_hat, (-1,))
227 | mape = np.mean(np.abs(y - y_hat) / np.abs(y))
228 | return mape
229 |
230 | def smape(y, y_hat):
231 | """
232 | Calculates Symmetric Mean Absolute Percentage Error.
233 |
234 | Parameters
235 | ----------
236 | y: numpy array
237 | actual test values
238 | y_hat: numpy array
239 | predicted values
240 |
241 | Returns
242 | -------
243 | smape: float
244 | symmetric mean absolute percentage error
245 | """
246 | y = np.reshape(y, (-1,))
247 | y_hat = np.reshape(y_hat, (-1,))
248 | smape = np.mean(2.0 * np.abs(y - y_hat) / (np.abs(y) + np.abs(y_hat)))
249 | return smape
250 |
251 | def mase(y, y_hat, y_train, seasonality):
252 | """
253 | Calculates Mean Absolute Scaled Error.
254 |
255 | Parameters
256 | ----------
257 | y: numpy array
258 | actual test values
259 | y_hat: numpy array
260 | predicted values
261 | y_train: numpy array
262 | actual train values for Naive1 predictions
263 | seasonality: int
264 | main frequency of the time series
265 | Quarterly 4, Daily 7, Monthly 12
266 |
267 | Returns
268 | -------
269 | mase: float
270 | mean absolute scaled error
271 | """
272 | y_hat_naive = []
273 | for i in range(seasonality, len(y_train)):
274 | y_hat_naive.append(y_train[(i - seasonality)])
275 |
276 | masep = np.mean(abs(y_train[seasonality:] - y_hat_naive))
277 | mase = np.mean(abs(y - y_hat)) / masep
278 | return mase
279 |
280 | ########################
281 | # PANEL EVALUATION
282 | ########################
283 |
284 | def evaluate_panel(y_panel, y_hat_panel, metric,
285 | y_insample=None, seasonality=None):
286 | """
287 | Calculates metric for y_panel and y_hat_panel
288 | y_panel: pandas df
289 | panel with columns unique_id, ds, y
290 | y_naive2_panel: pandas df
291 | panel with columns unique_id, ds, y_hat
292 | y_insample: pandas df
293 | panel with columns unique_id, ds, y (train)
294 | this is used in the MASE
295 | seasonality: int
296 | main frequency of the time series
297 | Quarterly 4, Daily 7, Monthly 12
298 | return: list of metric evaluations
299 | """
300 | metric_name = metric.__code__.co_name
301 |
302 | y_panel = y_panel.sort_values(['unique_id', 'ds'])
303 | y_hat_panel = y_hat_panel.sort_values(['unique_id', 'ds'])
304 | if y_insample is not None:
305 | y_insample = y_insample.sort_values(['unique_id', 'ds'])
306 |
307 | assert len(y_panel)==len(y_hat_panel)
308 | assert all(y_panel.unique_id.unique() == y_hat_panel.unique_id.unique()), "not same u_ids"
309 |
310 | evaluation = []
311 | for u_id in y_panel.unique_id.unique():
312 | top_row = np.asscalar(y_panel['unique_id'].searchsorted(u_id, 'left'))
313 | bottom_row = np.asscalar(y_panel['unique_id'].searchsorted(u_id, 'right'))
314 | y_id = y_panel[top_row:bottom_row].y.to_numpy()
315 |
316 | top_row = np.asscalar(y_hat_panel['unique_id'].searchsorted(u_id, 'left'))
317 | bottom_row = np.asscalar(y_hat_panel['unique_id'].searchsorted(u_id, 'right'))
318 | y_hat_id = y_hat_panel[top_row:bottom_row].y_hat.to_numpy()
319 | assert len(y_id)==len(y_hat_id)
320 |
321 | if metric_name == 'mase':
322 | assert (y_insample is not None) and (seasonality is not None)
323 | top_row = np.asscalar(y_insample['unique_id'].searchsorted(u_id, 'left'))
324 | bottom_row = np.asscalar(y_insample['unique_id'].searchsorted(u_id, 'right'))
325 | y_insample_id = y_insample[top_row:bottom_row].y.to_numpy()
326 | evaluation_id = metric(y_id, y_hat_id, y_insample_id, seasonality)
327 | else:
328 | evaluation_id = metric(y_id, y_hat_id)
329 | evaluation.append(evaluation_id)
330 | return evaluation
331 |
332 | def owa(y_panel, y_hat_panel, y_naive2_panel, y_insample, seasonality):
333 | """
334 | Calculates MASE, sMAPE for Naive2 and current model
335 | then calculatess Overall Weighted Average.
336 | y_panel: pandas df
337 | panel with columns unique_id, ds, y
338 | y_hat_panel: pandas df
339 | panel with columns unique_id, ds, y_hat
340 | y_naive2_panel: pandas df
341 | panel with columns unique_id, ds, y_hat
342 | y_insample: pandas df
343 | panel with columns unique_id, ds, y (train)
344 | this is used in the MASE
345 | seasonality: int
346 | main frequency of the time series
347 | Quarterly 4, Daily 7, Monthly 12
348 | return: OWA
349 | """
350 | total_mase = evaluate_panel(y_panel, y_hat_panel, mase,
351 | y_insample, seasonality)
352 | total_mase_naive2 = evaluate_panel(y_panel, y_naive2_panel, mase,
353 | y_insample, seasonality)
354 | total_smape = evaluate_panel(y_panel, y_hat_panel, smape)
355 | total_smape_naive2 = evaluate_panel(y_panel, y_naive2_panel, smape)
356 |
357 | assert len(total_mase) == len(total_mase_naive2)
358 | assert len(total_smape) == len(total_smape_naive2)
359 | assert len(total_mase) == len(total_smape)
360 |
361 | naive2_mase = np.mean(total_mase_naive2)
362 | naive2_smape = np.mean(total_smape_naive2) * 100
363 |
364 | model_mase = np.mean(total_mase)
365 | model_smape = np.mean(total_smape) * 100
366 |
367 | model_owa = ((model_mase/naive2_mase) + (model_smape/naive2_smape))/2
368 | return model_owa, model_mase, model_smape
369 |
370 | def evaluate_prediction_owa(y_hat_df, y_train_df, X_test_df, y_test_df,
371 | naive2_seasonality):
372 | """
373 | y_hat_df: pandas df
374 | panel with columns unique_id, ds, y_hat
375 | y_train_df: pandas df
376 | panel with columns unique_id, ds, y
377 | X_test_df: pandas df
378 | panel with columns unique_id, ds, x
379 | y_test_df: pandas df
380 | panel with columns unique_id, ds, y, y_hat_naive2
381 | naive2_seasonality: int
382 | seasonality for the Naive2 predictions (needed for owa)
383 | model: python class
384 | python class with predict method
385 | """
386 | y_panel = y_test_df.filter(['unique_id', 'ds', 'y'])
387 | y_naive2_panel = y_test_df.filter(['unique_id', 'ds', 'y_hat_naive2'])
388 | y_naive2_panel.rename(columns={'y_hat_naive2': 'y_hat'}, inplace=True)
389 | y_hat_panel = y_hat_df
390 | y_insample = y_train_df.filter(['unique_id', 'ds', 'y'])
391 |
392 | model_owa, model_mase, model_smape = owa(y_panel, y_hat_panel,
393 | y_naive2_panel, y_insample,
394 | seasonality=naive2_seasonality)
395 |
396 | print(15*'=', ' Model evaluation ', 14*'=')
397 | print('OWA: {} '.format(np.round(model_owa, 3)))
398 | print('SMAPE: {} '.format(np.round(model_smape, 3)))
399 | print('MASE: {} '.format(np.round(model_mase, 3)))
400 | return model_owa, model_mase, model_smape
401 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ESRNN/ESRNNensemble.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import time
3 | import random
4 |
5 | import numpy as np
6 | import pandas as pd
7 |
8 | import torch
9 |
10 | from pathlib import Path
11 |
12 | from ESRNN.utils.config import ModelConfig
13 | from ESRNN.utils.losses import DisaggregatedPinballLoss
14 | from ESRNN.utils.data import Iterator
15 |
16 | from ESRNN.ESRNN import ESRNN
17 |
18 | from ESRNN.utils_evaluation import owa
19 |
20 | class ESRNNensemble(object):
21 | """ Exponential Smoothing Recurrent Neural Network Ensemble
22 |
23 | Pytorch Implementation of the M4 time series forecasting competition winner.
24 | Proposed by Smyl. The model ensembles multiple ESRNNs that use a hybrid approach
25 | of Machine Learning and statistical methods by combining recurrent neural networks
26 | to model a common trend with shared parameters across series, and multiplicative
27 | Holt-Winter exponential smoothing.
28 |
29 | Parameters
30 | ----------
31 | n_models: int
32 | the number of ESRNNs in the ensemble.
33 | n_top: int
34 | the number of ESRNNs from the n_models pool, to which a
35 | particular time series gets assigned during fitting procedure.
36 | max_epochs: int
37 | maximum number of complete passes to train data during fit
38 | freq_of_test: int
39 | period for the diagnostic evaluation of the model.
40 | learning_rate: float
41 | size of the stochastic gradient descent steps
42 | lr_scheduler_step_size: int
43 | this step_size is the period for each learning rate decay
44 | per_series_lr_multip: float
45 | multiplier for per-series parameters smoothing and initial
46 | seasonalities learning rate (default 1.0)
47 | gradient_eps: float
48 | term added to the Adam optimizer denominator to improve
49 | numerical stability (default: 1e-8)
50 | gradient_clipping_threshold: float
51 | max norm of gradient vector, with all parameters treated
52 | as a single vector
53 | rnn_weight_decay: float
54 | parameter to control classic L2/Tikhonov regularization
55 | of the rnn parameters
56 | noise_std: float
57 | standard deviation of white noise added to input during
58 | fit to avoid the model from memorizing the train data
59 | level_variability_penalty: float
60 | this parameter controls the strength of the penalization
61 | to the wigglines of the level vector, induces smoothness
62 | in the output
63 | testing_percentile: float
64 | This value is only for diagnostic evaluation.
65 | In case of percentile predictions this parameter controls
66 | for the value predicted, when forecasting point value,
67 | the forecast is the median, so percentile=50.
68 | training_percentile: float
69 | To reduce the model's tendency to over estimate, the
70 | training_percentile can be set to fit a smaller value
71 | through the Pinball Loss.
72 | batch_size: int
73 | number of training examples for the stochastic gradient steps
74 | seasonality: int list
75 | list of seasonalities of the time series
76 | Hourly [24, 168], Daily [7], Weekly [52], Monthly [12],
77 | Quarterly [4], Yearly [].
78 | input_size: int
79 | input size of the recurrent neural network, usually a
80 | multiple of seasonality
81 | output_size: int
82 | output_size or forecast horizon of the recurrent neural
83 | network, usually multiple of seasonality
84 | random_seed: int
85 | random_seed for pseudo random pytorch initializer and
86 | numpy random generator
87 | exogenous_size: int
88 | size of one hot encoded categorical variable, invariannt
89 | per time series of the panel
90 | min_inp_seq_length: int
91 | description
92 | max_periods: int
93 | Parameter to chop longer series, to last max_periods,
94 | max e.g. 40 years
95 | cell_type: str
96 | Type of RNN cell, available GRU, LSTM, RNN, ResidualLSTM.
97 | state_hsize: int
98 | dimension of hidden state of the recurrent neural network
99 | dilations: int list
100 | each list represents one chunk of Dilated LSTMS, connected in
101 | standard ResNet fashion
102 | add_nl_layer: bool
103 | whether to insert a tanh() layer between the RNN stack and the
104 | linear adaptor (output) layers
105 | device: str
106 | pytorch device either 'cpu' or 'cuda'
107 | Notes
108 | -----
109 | **References:**
110 | `M4 Competition Conclusions
111 | `__
112 | `Original Dynet Implementation of ESRNN
113 | `__
114 | """
115 | def __init__(self, n_models=1, n_top=1, max_epochs=15, batch_size=1, batch_size_test=128,
116 | freq_of_test=-1, learning_rate=1e-3, lr_scheduler_step_size=9, lr_decay=0.9,
117 | per_series_lr_multip=1.0, gradient_eps=1e-8, gradient_clipping_threshold=20,
118 | rnn_weight_decay=0, noise_std=0.001, level_variability_penalty=80,
119 | testing_percentile=50, training_percentile=50, ensemble=False, cell_type='LSTM',
120 | state_hsize=40, dilations=[[1, 2], [4, 8]],
121 | add_nl_layer=False, seasonality=[4], input_size=4, output_size=8,
122 | frequency='D', max_periods=20, random_seed=1,
123 | device='cuda', root_dir='./'):
124 | super(ESRNNensemble, self).__init__()
125 |
126 | self.n_models = n_models
127 | self.n_top = n_top
128 | assert n_models>=2, "Number of models for ensemble should be greater than 1"
129 | assert n_top<=n_models, "Number of top models should be smaller than models to ensemble"
130 | self.big_float = 1e6
131 | self.mc = ModelConfig(max_epochs=max_epochs, batch_size=batch_size, batch_size_test=batch_size_test,
132 | freq_of_test=freq_of_test, learning_rate=learning_rate,
133 | lr_scheduler_step_size=lr_scheduler_step_size, lr_decay=lr_decay,
134 | per_series_lr_multip=per_series_lr_multip,
135 | gradient_eps=gradient_eps, gradient_clipping_threshold=gradient_clipping_threshold,
136 | rnn_weight_decay=rnn_weight_decay, noise_std=noise_std,
137 | level_variability_penalty=level_variability_penalty,
138 | testing_percentile=testing_percentile, training_percentile=training_percentile,
139 | ensemble=ensemble, cell_type=cell_type,
140 | state_hsize=state_hsize, dilations=dilations, add_nl_layer=add_nl_layer,
141 | seasonality=seasonality, input_size=input_size, output_size=output_size,
142 | frequency=frequency, max_periods=max_periods, random_seed=random_seed,
143 | device=device, root_dir=root_dir)
144 | self._fitted = False
145 |
146 | def fit(self, X_df, y_df, X_test_df=None, y_test_df=None, shuffle=True):
147 | """
148 | Fit ESRNN ensemble.
149 |
150 | Parameters
151 | ----------
152 | X_df : pandas dataframe
153 | Train dataframe in long format with columns 'unique_id', 'ds'
154 | and 'x'.
155 | - 'unique_id' an identifier of each independent time series.
156 | - 'ds' is a datetime column
157 | - 'x' is a single exogenous variable
158 | y_df : pandas dataframe
159 | Train dataframe in long format with columns 'unique_id', 'ds' and 'y'.
160 | - 'unique_id' an identifier of each independent time series.
161 | - 'ds' is a datetime column
162 | - 'y' is the column with the target values
163 | X_test_df: pandas dataframe
164 | Optional test dataframe with columns 'unique_id', 'ds' and 'x'.
165 | If provided the fit procedure will evaluate the intermediate
166 | performance within training epochs.
167 | y_test_df: pandas dataframe
168 | Optional test dataframe with columns 'unique_id', 'ds' and 'x' and
169 | y_hat_benchmark column.
170 | If provided the fit procedure will evaluate the intermediate
171 | performance within training epochs.
172 | shuffle: boolean
173 | Name of the benchmark model for the comparison of the relative
174 | improvement of the model.
175 |
176 | Returns
177 | -------
178 | self : returns an instance of self.
179 | """
180 |
181 | # Transform long dfs to wide numpy
182 | assert type(X_df) == pd.core.frame.DataFrame
183 | assert type(y_df) == pd.core.frame.DataFrame
184 | assert all([(col in X_df) for col in ['unique_id', 'ds', 'x']])
185 | assert all([(col in y_df) for col in ['unique_id', 'ds', 'y']])
186 |
187 | # Storing dfs for OWA evaluation, initializing min_owa
188 | self.y_train_df = y_df
189 | self.X_test_df = X_test_df
190 | self.y_test_df = y_test_df
191 | self.min_owa = 4.0
192 | self.min_epoch = 0
193 |
194 | # Exogenous variables
195 | unique_categories = X_df['x'].unique()
196 | self.mc.category_to_idx = dict((word, index) for index, word in enumerate(unique_categories))
197 | self.mc.exogenous_size = len(unique_categories)
198 |
199 | self.unique_ids = X_df['unique_id'].unique()
200 | self.mc.n_series = len(self.unique_ids)
201 |
202 | # Set seeds
203 | self.shuffle = shuffle
204 | torch.manual_seed(self.mc.random_seed)
205 | np.random.seed(self.mc.random_seed)
206 |
207 | # Initial series random assignment to models
208 | self.series_models_map = np.zeros((self.mc.n_series, self.n_models))
209 | n_initial_models = int(np.ceil(self.n_models/2))
210 | for i in range(self.mc.n_series):
211 | id_models = np.random.choice(self.n_models, n_initial_models)
212 | self.series_models_map[i,id_models] = 1
213 |
214 | self.esrnn_ensemble = []
215 | for _ in range(self.n_models):
216 | esrnn = ESRNN(max_epochs=self.mc.max_epochs, batch_size=self.mc.batch_size, batch_size_test=self.mc.batch_size_test,
217 | freq_of_test=-1, learning_rate=self.mc.learning_rate,
218 | lr_scheduler_step_size=self.mc.lr_scheduler_step_size, lr_decay=self.mc.lr_decay,
219 | per_series_lr_multip=self.mc.per_series_lr_multip,
220 | gradient_eps=self.mc.gradient_eps, gradient_clipping_threshold=self.mc.gradient_clipping_threshold,
221 | rnn_weight_decay=self.mc.rnn_weight_decay, noise_std=self.mc.noise_std,
222 | level_variability_penalty=self.mc.level_variability_penalty,
223 | testing_percentile=self.mc.testing_percentile,
224 | training_percentile=self.mc.training_percentile, ensemble=self.mc.ensemble,
225 | cell_type=self.mc.cell_type,
226 | state_hsize=self.mc.state_hsize, dilations=self.mc.dilations, add_nl_layer=self.mc.add_nl_layer,
227 | seasonality=self.mc.seasonality, input_size=self.mc.input_size, output_size=self.mc.output_size,
228 | frequency=self.mc.frequency, max_periods=self.mc.max_periods, random_seed=self.mc.random_seed,
229 | device=self.mc.device, root_dir=self.mc.root_dir)
230 |
231 | # To instantiate _ESRNN object within ESRNN class we need n_series
232 | esrnn.instantiate_esrnn(self.mc.exogenous_size, self.mc.n_series)
233 | esrnn._fitted = True
234 | self.esrnn_ensemble.append(esrnn)
235 |
236 | self.X, self.y = esrnn.long_to_wide(X_df, y_df)
237 | assert len(self.X)==len(self.y)
238 | assert self.X.shape[1]>=3
239 |
240 | # Train model
241 | self._fitted = True
242 | self.train()
243 |
244 | def train(self):
245 | """
246 | Auxiliary function, pytorch train procedure for the ESRNN ensemble
247 |
248 | Parameters:
249 | -------
250 | self: instance of self.
251 |
252 | Returns
253 | -------
254 | self : returns an instance of self.
255 | """
256 |
257 | # Initial performance matrix
258 | self.performance_matrix = np.ones((self.mc.n_series, self.n_models)) * self.big_float
259 | warm_start = False
260 | train_tau = self.mc.training_percentile/100
261 | criterion = DisaggregatedPinballLoss(train_tau)
262 |
263 | # Train epoch loop
264 | for epoch in range(self.mc.max_epochs):
265 | start = time.time()
266 |
267 | # Solve degenerate models
268 | for model_id in range(self.n_models):
269 | if np.sum(self.series_models_map[:,model_id])==0:
270 | print('Reassigning random series to model ', model_id)
271 | n_sample_series= int(self.mc.n_series/2)
272 | index_series = np.random.choice(self.mc.n_series, n_sample_series, replace=False)
273 | self.series_models_map[index_series, model_id] = 1
274 |
275 | # Model loop
276 | for model_id, esrnn in enumerate(self.esrnn_ensemble):
277 | # Train model with subset data
278 | dataloader = Iterator(mc = self.mc, X=self.X, y=self.y,
279 | weights=self.series_models_map[:, model_id])
280 | esrnn.train(dataloader, max_epochs=1, warm_start=warm_start, shuffle=self.shuffle, verbose=False)
281 |
282 | # Compute model performance for each series
283 | dataloader = Iterator(mc=self.mc, X=self.X, y=self.y)
284 | per_series_evaluation = esrnn.per_series_evaluation(dataloader, criterion=criterion)
285 | self.performance_matrix[:, model_id] = per_series_evaluation
286 |
287 | # Reassign series to models
288 | self.series_models_map = np.zeros((self.mc.n_series, self.n_models))
289 | top_models = np.argpartition(self.performance_matrix, self.n_top)[:, :self.n_top]
290 | for i in range(self.mc.n_series):
291 | self.series_models_map[i, top_models[i,:]] = 1
292 |
293 | warm_start = True
294 |
295 | print("========= Epoch {} finished =========".format(epoch))
296 | print("Training time: {}".format(round(time.time()-start, 5)))
297 | self.train_loss = np.einsum('ij,ij->i',self.performance_matrix, self.series_models_map)/self.n_top
298 | self.train_loss = np.mean(self.train_loss)
299 | print("Training loss ({} prc): {:.5f}".format(self.mc.training_percentile,
300 | self.train_loss))
301 | print('Models num series', np.sum(self.series_models_map, axis=0))
302 |
303 | if (epoch % self.mc.freq_of_test == 0) and (self.mc.freq_of_test > 0):
304 | if self.y_test_df is not None:
305 | self.evaluate_model_prediction(self.y_train_df, self.X_test_df,
306 | self.y_test_df, epoch=epoch)
307 | print('Train finished! \n')
308 |
309 | def predict(self, X_df):
310 | """
311 | Predict using the ESRNN ensemble.
312 |
313 | Parameters
314 | ----------
315 | X_df : pandas dataframe
316 | Dataframe in LONG format with columns 'unique_id', 'ds'
317 | and 'x'.
318 | - 'unique_id' an identifier of each independent time series.
319 | - 'ds' is a datetime column
320 | - 'x' is a single exogenous variable
321 |
322 | Returns
323 | -------
324 | Y_hat_panel : pandas dataframe
325 | Dataframe in LONG format with columns 'unique_id', 'ds'
326 | and 'x'.
327 | - 'unique_id' an identifier of each independent time series.
328 | - 'ds' datetime columnn that matches the dates in X_df
329 | - 'y_hat' is the column with the predicted target values
330 | """
331 |
332 | assert type(X_df) == pd.core.frame.DataFrame
333 | assert 'unique_id' in X_df
334 | assert self._fitted, "Model not fitted yet"
335 |
336 | dataloader = Iterator(mc=self.mc, X=self.X, y=self.y)
337 |
338 | output_size = self.mc.output_size
339 | n_unique_id = len(dataloader.sort_key['unique_id'])
340 |
341 | ensemble_y_hat = np.zeros((self.n_models, n_unique_id, output_size))
342 |
343 | for model_id, esrnn in enumerate(self.esrnn_ensemble):
344 | esrnn.esrnn.eval()
345 |
346 | # Predict ALL series
347 | count = 0
348 | for j in range(dataloader.n_batches):
349 | batch = dataloader.get_batch()
350 | batch_size = batch.y.shape[0]
351 |
352 | y_hat = esrnn.esrnn.predict(batch)
353 |
354 | y_hat = y_hat.data.cpu().numpy()
355 |
356 | ensemble_y_hat[model_id, count:count+batch_size, :] = y_hat
357 | count += batch_size
358 |
359 | # Weighted average of prediction for n_top best models per series
360 | # (n_models x n_unique_id x output_size) (n_unique_id x n_models)
361 | y_hat = np.einsum('ijk,ji->jk', ensemble_y_hat, self.series_models_map) / self.n_top
362 | y_hat = y_hat.flatten()
363 |
364 | panel_unique_id = pd.Series(dataloader.sort_key['unique_id']).repeat(output_size)
365 | panel_last_ds = pd.Series(dataloader.X[:, 2]).repeat(output_size)
366 |
367 | panel_delta = list(range(1, output_size+1)) * n_unique_id
368 | panel_delta = pd.to_timedelta(panel_delta, unit=self.mc.frequency)
369 | panel_ds = panel_last_ds + panel_delta
370 |
371 | assert len(panel_ds) == len(y_hat) == len(panel_unique_id)
372 |
373 | Y_hat_panel_dict = {'unique_id': panel_unique_id,
374 | 'ds': panel_ds,
375 | 'y_hat': y_hat}
376 |
377 | Y_hat_panel = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(Y_hat_panel_dict)
378 |
379 | if 'ds' in X_df:
380 | Y_hat_panel = X_df.merge(Y_hat_panel, on=['unique_id', 'ds'], how='left')
381 | else:
382 | Y_hat_panel = X_df.merge(Y_hat_panel, on=['unique_id'], how='left')
383 |
384 | return Y_hat_panel
385 |
386 | def evaluate_model_prediction(self, y_train_df, X_test_df, y_test_df, epoch=None):
387 | """
388 | Evaluate ESRNN model against benchmark in y_test_df
389 |
390 | Parameters
391 | ----------
392 | y_train_df: pandas dataframe
393 | panel with columns 'unique_id', 'ds', 'y'
394 | X_test_df: pandas dataframe
395 | panel with columns 'unique_id', 'ds', 'x'
396 | y_test_df: pandas dataframe
397 | panel with columns 'unique_id', 'ds', 'y' and a column
398 | y_hat_naive2 identifying benchmark predictions
399 | epoch: int
400 | the number of epoch to check early stopping results
401 |
402 | Returns
403 | -------
404 | model_owa : float
405 | relative improvement of model with respect to benchmark, measured with
406 | the M4 overall weighted average.
407 | smape: float
408 | relative improvement of model with respect to benchmark, measured with
409 | the symmetric mean absolute percentage error.
410 | mase: float
411 | relative improvement of model with respect to benchmark, measured with
412 | the M4 mean absolute scaled error.
413 | """
414 |
415 | assert self._fitted, "Model not fitted yet"
416 |
417 | y_panel = y_test_df.filter(['unique_id', 'ds', 'y'])
418 | y_naive2_panel = y_test_df.filter(['unique_id', 'ds', 'y_hat_naive2'])
419 | y_naive2_panel.rename(columns={'y_hat_naive2': 'y_hat'}, inplace=True)
420 | y_hat_panel = self.predict(X_test_df)
421 | y_insample = y_train_df.filter(['unique_id', 'ds', 'y'])
422 |
423 | model_owa, model_mase, model_smape = owa(y_panel, y_hat_panel,
424 | y_naive2_panel, y_insample,
425 | seasonality=self.mc.naive_seasonality)
426 |
427 | if self.min_owa > model_owa:
428 | self.min_owa = model_owa
429 | if epoch is not None:
430 | self.min_epoch = epoch
431 |
432 | print('OWA: {} '.format(np.round(model_owa, 3)))
433 | print('SMAPE: {} '.format(np.round(model_smape, 3)))
434 | print('MASE: {} '.format(np.round(model_mase, 3)))
435 |
436 | return model_owa, model_mase, model_smape
437 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ESRNN/ESRNN.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import time
3 |
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import pandas as pd
6 |
7 | import torch
8 | import torch.nn as nn
9 | import torch.optim as optim
10 | from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import StepLR
11 |
12 | from pathlib import Path
13 | from copy import deepcopy
14 |
15 | from ESRNN.utils.config import ModelConfig
16 | from ESRNN.utils.ESRNN import _ESRNN
17 | from ESRNN.utils.losses import SmylLoss, PinballLoss
18 | from ESRNN.utils.data import Iterator
19 |
20 | from ESRNN.utils_evaluation import owa
21 |
22 |
23 | class ESRNN(object):
24 | """ Exponential Smoothing Recurrent Neural Network
25 |
26 | Pytorch Implementation of the M4 time series forecasting competition winner.
27 | Proposed by Smyl. The model uses a hybrid approach of Machine Learning and
28 | statistical methods by combining recurrent neural networks to model a common
29 | trend with shared parameters across series, and multiplicative Holt-Winter
30 | exponential smoothing.
31 |
32 | Parameters
33 | ----------
34 | max_epochs: int
35 | maximum number of complete passes to train data during fit
36 | freq_of_test: int
37 | period for the diagnostic evaluation of the model.
38 | learning_rate: float
39 | size of the stochastic gradient descent steps
40 | lr_scheduler_step_size: int
41 | this step_size is the period for each learning rate decay
42 | per_series_lr_multip: float
43 | multiplier for per-series parameters smoothing and initial
44 | seasonalities learning rate (default 1.0)
45 | gradient_eps: float
46 | term added to the Adam optimizer denominator to improve
47 | numerical stability (default: 1e-8)
48 | gradient_clipping_threshold: float
49 | max norm of gradient vector, with all parameters treated
50 | as a single vector
51 | rnn_weight_decay: float
52 | parameter to control classic L2/Tikhonov regularization
53 | of the rnn parameters
54 | noise_std: float
55 | standard deviation of white noise added to input during
56 | fit to avoid the model from memorizing the train data
57 | level_variability_penalty: float
58 | this parameter controls the strength of the penalization
59 | to the wigglines of the level vector, induces smoothness
60 | in the output
61 | testing_percentile: float
62 | This value is only for diagnostic evaluation.
63 | In case of percentile predictions this parameter controls
64 | for the value predicted, when forecasting point value,
65 | the forecast is the median, so percentile=50.
66 | training_percentile: float
67 | To reduce the model's tendency to over estimate, the
68 | training_percentile can be set to fit a smaller value
69 | through the Pinball Loss.
70 | batch_size: int
71 | number of training examples for the stochastic gradient steps
72 | seasonality: int list
73 | list of seasonalities of the time series
74 | Hourly [24, 168], Daily [7], Weekly [52], Monthly [12],
75 | Quarterly [4], Yearly [].
76 | input_size: int
77 | input size of the recurrent neural network, usually a
78 | multiple of seasonality
79 | output_size: int
80 | output_size or forecast horizon of the recurrent neural
81 | network, usually multiple of seasonality
82 | random_seed: int
83 | random_seed for pseudo random pytorch initializer and
84 | numpy random generator
85 | exogenous_size: int
86 | size of one hot encoded categorical variable, invariannt
87 | per time series of the panel
88 | min_inp_seq_length: int
89 | description
90 | max_periods: int
91 | Parameter to chop longer series, to last max_periods,
92 | max e.g. 40 years
93 | cell_type: str
94 | Type of RNN cell, available GRU, LSTM, RNN, ResidualLSTM.
95 | state_hsize: int
96 | dimension of hidden state of the recurrent neural network
97 | dilations: int list
98 | each list represents one chunk of Dilated LSTMS, connected in
99 | standard ResNet fashion
100 | add_nl_layer: bool
101 | whether to insert a tanh() layer between the RNN stack and the
102 | linear adaptor (output) layers
103 | device: str
104 | pytorch device either 'cpu' or 'cuda'
105 | Notes
106 | -----
107 | **References:**
108 | `M4 Competition Conclusions
109 | `__
110 | `Original Dynet Implementation of ESRNN
111 | `__
112 | """
113 | def __init__(self, max_epochs=15, batch_size=1, batch_size_test=64, freq_of_test=-1,
114 | learning_rate=1e-3, lr_scheduler_step_size=9, lr_decay=0.9,
115 | per_series_lr_multip=1.0, gradient_eps=1e-8, gradient_clipping_threshold=20,
116 | rnn_weight_decay=0, noise_std=0.001,
117 | level_variability_penalty=80,
118 | testing_percentile=50, training_percentile=50, ensemble=False,
119 | cell_type='LSTM',
120 | state_hsize=40, dilations=[[1, 2], [4, 8]],
121 | add_nl_layer=False, seasonality=[4], input_size=4, output_size=8,
122 | frequency=None, max_periods=20, random_seed=1,
123 | device='cpu', root_dir='./'):
124 | super(ESRNN, self).__init__()
125 | self.mc = ModelConfig(max_epochs=max_epochs, batch_size=batch_size, batch_size_test=batch_size_test,
126 | freq_of_test=freq_of_test, learning_rate=learning_rate,
127 | lr_scheduler_step_size=lr_scheduler_step_size, lr_decay=lr_decay,
128 | per_series_lr_multip=per_series_lr_multip,
129 | gradient_eps=gradient_eps, gradient_clipping_threshold=gradient_clipping_threshold,
130 | rnn_weight_decay=rnn_weight_decay, noise_std=noise_std,
131 | level_variability_penalty=level_variability_penalty,
132 | testing_percentile=testing_percentile, training_percentile=training_percentile,
133 | ensemble=ensemble,
134 | cell_type=cell_type,
135 | state_hsize=state_hsize, dilations=dilations, add_nl_layer=add_nl_layer,
136 | seasonality=seasonality, input_size=input_size, output_size=output_size,
137 | frequency=frequency, max_periods=max_periods, random_seed=random_seed,
138 | device=device, root_dir=root_dir)
139 | self._fitted = False
140 |
141 | def train(self, dataloader, max_epochs,
142 | warm_start=False, shuffle=True, verbose=True):
143 | """
144 | Auxiliary function, pytorch train procedure for the ESRNN model
145 |
146 | Parameters:
147 | -------
148 | dataloader: pytorch dataloader
149 | max_epochs: int
150 | warm_start: bool
151 | shuffle: bool
152 | verbose: bool
153 |
154 | Returns
155 | -------
156 | self : returns an instance of self.
157 | """
158 |
159 | if self.mc.ensemble:
160 | self.esrnn_ensemble = [deepcopy(self.esrnn).to(self.mc.device)] * 5
161 |
162 | if verbose: print(15*'='+' Training ESRNN ' + 15*'=' + '\n')
163 |
164 | # Optimizers
165 | if not warm_start:
166 | self.es_optimizer = optim.Adam(params=self.esrnn.es.parameters(),
167 | lr=self.mc.learning_rate*self.mc.per_series_lr_multip,
168 | betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=self.mc.gradient_eps)
169 |
170 | self.es_scheduler = StepLR(optimizer=self.es_optimizer,
171 | step_size=self.mc.lr_scheduler_step_size,
172 | gamma=0.9)
173 |
174 | self.rnn_optimizer = optim.Adam(params=self.esrnn.rnn.parameters(),
175 | lr=self.mc.learning_rate,
176 | betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=self.mc.gradient_eps,
177 | weight_decay=self.mc.rnn_weight_decay)
178 |
179 | self.rnn_scheduler = StepLR(optimizer=self.rnn_optimizer,
180 | step_size=self.mc.lr_scheduler_step_size,
181 | gamma=self.mc.lr_decay)
182 |
183 | # Loss Functions
184 | train_tau = self.mc.training_percentile / 100
185 | train_loss = SmylLoss(tau=train_tau,
186 | level_variability_penalty=self.mc.level_variability_penalty)
187 |
188 | eval_tau = self.mc.testing_percentile / 100
189 | eval_loss = PinballLoss(tau=eval_tau)
190 |
191 | for epoch in range(max_epochs):
192 | self.esrnn.train()
193 | start = time.time()
194 | if shuffle:
195 | dataloader.shuffle_dataset(random_seed=epoch)
196 | losses = []
197 | for j in range(dataloader.n_batches):
198 | self.es_optimizer.zero_grad()
199 | self.rnn_optimizer.zero_grad()
200 |
201 | batch = dataloader.get_batch()
202 | windows_y, windows_y_hat, levels = self.esrnn(batch)
203 |
204 | # Pinball loss on normalized values
205 | loss = train_loss(windows_y, windows_y_hat, levels)
206 | losses.append(loss.data.cpu().numpy())
207 | #print("loss", loss)
208 |
209 | loss.backward()
210 |
211 | torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(self.esrnn.rnn.parameters(),
212 | self.mc.gradient_clipping_threshold)
213 | torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(self.esrnn.es.parameters(),
214 | self.mc.gradient_clipping_threshold)
215 | self.rnn_optimizer.step()
216 | self.es_optimizer.step()
217 |
218 | # Decay learning rate
219 | self.es_scheduler.step()
220 | self.rnn_scheduler.step()
221 |
222 | if self.mc.ensemble:
223 | copy_esrnn = deepcopy(self.esrnn)
224 | copy_esrnn.eval()
225 | self.esrnn_ensemble.pop(0)
226 | self.esrnn_ensemble.append(copy_esrnn)
227 |
228 |
229 | # Evaluation
230 | self.train_loss = np.mean(losses)
231 | if verbose:
232 | print("========= Epoch {} finished =========".format(epoch))
233 | print("Training time: {}".format(round(time.time()-start, 5)))
234 | print("Training loss ({} prc): {:.5f}".format(self.mc.training_percentile,
235 | self.train_loss))
236 |
237 | if (epoch % self.mc.freq_of_test == 0) and (self.mc.freq_of_test > 0):
238 | if self.y_test_df is not None:
239 | self.test_loss = self.model_evaluation(dataloader, eval_loss)
240 | print("Testing loss ({} prc): {:.5f}".format(self.mc.testing_percentile,
241 | self.test_loss))
242 | self.evaluate_model_prediction(self.y_train_df, self.X_test_df,
243 | self.y_test_df, self.y_hat_benchmark, epoch=epoch)
244 | self.esrnn.train()
245 |
246 | if verbose: print('Train finished! \n')
247 |
248 | def per_series_evaluation(self, dataloader, criterion):
249 | """
250 | Auxiliary function, evaluate ESRNN model for training
251 | procedure supervision.
252 |
253 | Parameters
254 | ----------
255 | dataloader: pytorch dataloader
256 | criterion: pytorch test criterion
257 | """
258 |
259 | with torch.no_grad():
260 | # Create fast dataloader
261 | if self.mc.n_series < self.mc.batch_size_test: new_batch_size = self.mc.n_series
262 | else: new_batch_size = self.mc.batch_size_test
263 | dataloader.update_batch_size(new_batch_size)
264 |
265 | per_series_losses = []
266 | for j in range(dataloader.n_batches):
267 | batch = dataloader.get_batch()
268 | windows_y, windows_y_hat, _ = self.esrnn(batch)
269 | loss = criterion(windows_y, windows_y_hat)
270 | per_series_losses += loss.data.cpu().numpy().tolist()
271 |
272 | dataloader.update_batch_size(self.mc.batch_size)
273 | return per_series_losses
274 |
275 | def model_evaluation(self, dataloader, criterion):
276 | """
277 | Auxiliary function, evaluate ESRNN model for training
278 | procedure supervision.
279 |
280 | Parameters
281 | ----------
282 | dataloader: pytorch dataloader
283 | criterion: pytorch test criterion
284 |
285 | Returns
286 | -------
287 | model_loss: float
288 | loss for train supervision purpose.
289 | """
290 |
291 | with torch.no_grad():
292 | # Create fast dataloader
293 | if self.mc.n_series < self.mc.batch_size_test: new_batch_size = self.mc.n_series
294 | else: new_batch_size = self.mc.batch_size_test
295 | dataloader.update_batch_size(new_batch_size)
296 |
297 | model_loss = 0.0
298 | for j in range(dataloader.n_batches):
299 | batch = dataloader.get_batch()
300 | windows_y, windows_y_hat, _ = self.esrnn(batch)
301 | loss = criterion(windows_y, windows_y_hat)
302 | model_loss += loss.data.cpu().numpy()
303 |
304 | model_loss /= dataloader.n_batches
305 | dataloader.update_batch_size(self.mc.batch_size)
306 | return model_loss
307 |
308 | def evaluate_model_prediction(self, y_train_df, X_test_df, y_test_df, y_hat_benchmark='y_hat_naive2', epoch=None):
309 | """
310 | Evaluate ESRNN model against benchmark in y_test_df
311 |
312 | Parameters
313 | ----------
314 | y_train_df: pandas dataframe
315 | panel with columns 'unique_id', 'ds', 'y'
316 | X_test_df: pandas dataframe
317 | panel with columns 'unique_id', 'ds', 'x'
318 | y_test_df: pandas dataframe
319 | panel with columns 'unique_id', 'ds', 'y' and a column
320 | y_hat_benchmark identifying benchmark predictions
321 | y_hat_benchmark: str
322 | column name of benchmark predictions, default y_hat_naive2
323 |
324 | Returns
325 | -------
326 | model_owa : float
327 | relative improvement of model with respect to benchmark, measured with
328 | the M4 overall weighted average.
329 | smape: float
330 | relative improvement of model with respect to benchmark, measured with
331 | the symmetric mean absolute percentage error.
332 | mase: float
333 | relative improvement of model with respect to benchmark, measured with
334 | the M4 mean absolute scaled error.
335 | """
336 |
337 | assert self._fitted, "Model not fitted yet"
338 |
339 | y_panel = y_test_df.filter(['unique_id', 'ds', 'y'])
340 | y_benchmark_panel = y_test_df.filter(['unique_id', 'ds', y_hat_benchmark])
341 | y_benchmark_panel.rename(columns={y_hat_benchmark: 'y_hat'}, inplace=True)
342 | y_hat_panel = self.predict(X_test_df)
343 | y_insample = y_train_df.filter(['unique_id', 'ds', 'y'])
344 |
345 | model_owa, model_mase, model_smape = owa(y_panel, y_hat_panel,
346 | y_benchmark_panel, y_insample,
347 | seasonality=self.mc.naive_seasonality)
348 |
349 | if self.min_owa > model_owa:
350 | self.min_owa = model_owa
351 | if epoch is not None:
352 | self.min_epoch = epoch
353 |
354 | print('OWA: {} '.format(np.round(model_owa, 3)))
355 | print('SMAPE: {} '.format(np.round(model_smape, 3)))
356 | print('MASE: {} '.format(np.round(model_mase, 3)))
357 |
358 | return model_owa, model_mase, model_smape
359 |
360 | def fit(self, X_df, y_df, X_test_df=None, y_test_df=None, y_hat_benchmark='y_hat_naive2',
361 | warm_start=False, shuffle=True, verbose=True):
362 | """
363 | Fit ESRNN model.
364 |
365 | Parameters
366 | ----------
367 | X_df : pandas dataframe
368 | Train dataframe in long format with columns 'unique_id', 'ds'
369 | and 'x'.
370 | - 'unique_id' an identifier of each independent time series.
371 | - 'ds' is a datetime column
372 | - 'x' is a single exogenous variable
373 | y_df : pandas dataframe
374 | Train dataframe in long format with columns 'unique_id', 'ds' and 'y'.
375 | - 'unique_id' an identifier of each independent time series.
376 | - 'ds' is a datetime column
377 | - 'y' is the column with the target values
378 | X_test_df: pandas dataframe
379 | Optional test dataframe with columns 'unique_id', 'ds' and 'x'.
380 | If provided the fit procedure will evaluate the intermediate
381 | performance within training epochs.
382 | y_test_df: pandas dataframe
383 | Optional test dataframe with columns 'unique_id', 'ds' and 'x' and
384 | y_hat_benchmark column.
385 | If provided the fit procedure will evaluate the intermediate
386 | performance within training epochs.
387 | y_hat_benchmark: str
388 | Name of the benchmark model for the comparison of the relative
389 | improvement of the model.
390 |
391 | Returns
392 | -------
393 | self : returns an instance of self.
394 | """
395 |
396 | # Transform long dfs to wide numpy
397 | assert type(X_df) == pd.core.frame.DataFrame
398 | assert type(y_df) == pd.core.frame.DataFrame
399 | assert all([(col in X_df) for col in ['unique_id', 'ds', 'x']])
400 | assert all([(col in y_df) for col in ['unique_id', 'ds', 'y']])
401 | if y_test_df is not None:
402 | assert y_hat_benchmark in y_test_df.columns, 'benchmark is not present in y_test_df, use y_hat_benchmark to define it'
403 |
404 | # Storing dfs for OWA evaluation, initializing min_owa
405 | self.y_train_df = y_df
406 | self.X_test_df = X_test_df
407 | self.y_test_df = y_test_df
408 | self.min_owa = 4.0
409 | self.min_epoch = 0
410 |
411 | self.int_ds = isinstance(self.y_train_df['ds'][0], (int, np.int, np.int64))
412 |
413 | self.y_hat_benchmark = y_hat_benchmark
414 |
415 | X, y = self.long_to_wide(X_df, y_df)
416 | assert len(X)==len(y)
417 | assert X.shape[1]>=3
418 |
419 | # Exogenous variables
420 | unique_categories = np.unique(X[:, 1])
421 | self.mc.category_to_idx = dict((word, index) for index, word in enumerate(unique_categories))
422 | exogenous_size = len(unique_categories)
423 |
424 | # Create batches (device in mc)
425 | self.train_dataloader = Iterator(mc=self.mc, X=X, y=y)
426 |
427 | # Random Seeds (model initialization)
428 | torch.manual_seed(self.mc.random_seed)
429 | np.random.seed(self.mc.random_seed)
430 |
431 | # Initialize model
432 | n_series = self.train_dataloader.n_series
433 | self.instantiate_esrnn(exogenous_size, n_series)
434 |
435 | # Validating frequencies
436 | X_train_frequency = pd.infer_freq(X_df.head()['ds'])
437 | y_train_frequency = pd.infer_freq(y_df.head()['ds'])
438 | self.frequencies = [X_train_frequency, y_train_frequency]
439 |
440 | if (X_test_df is not None) and (y_test_df is not None):
441 | X_test_frequency = pd.infer_freq(X_test_df.head()['ds'])
442 | y_test_frequency = pd.infer_freq(y_test_df.head()['ds'])
443 | self.frequencies += [X_test_frequency, y_test_frequency]
444 |
445 | assert len(set(self.frequencies)) <= 1, \
446 | "Match the frequencies of the dataframes {}".format(self.frequencies)
447 |
448 | self.mc.frequency = self.frequencies[0]
449 | print("Infered frequency: {}".format(self.mc.frequency))
450 |
451 | # Train model
452 | self._fitted = True
453 | self.train(dataloader=self.train_dataloader, max_epochs=self.mc.max_epochs,
454 | warm_start=warm_start, shuffle=shuffle, verbose=verbose)
455 |
456 | def instantiate_esrnn(self, exogenous_size, n_series):
457 | """Auxiliary function used at beginning of train to instantiate ESRNN"""
458 |
459 | self.mc.exogenous_size = exogenous_size
460 | self.mc.n_series = n_series
461 | self.esrnn = _ESRNN(self.mc).to(self.mc.device)
462 |
463 | def predict(self, X_df, decomposition=False):
464 | """
465 | Predict using the ESRNN model.
466 |
467 | Parameters
468 | ----------
469 | X_df : pandas dataframe
470 | Dataframe in LONG format with columns 'unique_id', 'ds'
471 | and 'x'.
472 | - 'unique_id' an identifier of each independent time series.
473 | - 'ds' is a datetime column
474 | - 'x' is a single exogenous variable
475 |
476 | Returns
477 | -------
478 | Y_hat_panel : pandas dataframe
479 | Dataframe in LONG format with columns 'unique_id', 'ds'
480 | and 'x'.
481 | - 'unique_id' an identifier of each independent time series.
482 | - 'ds' datetime columnn that matches the dates in X_df
483 | - 'y_hat' is the column with the predicted target values
484 | """
485 |
486 | #print(9*'='+' Predicting ESRNN ' + 9*'=' + '\n')
487 | assert type(X_df) == pd.core.frame.DataFrame
488 | assert 'unique_id' in X_df
489 | assert self._fitted, "Model not fitted yet"
490 |
491 | self.esrnn.eval()
492 |
493 | # Create fast dataloader
494 | if self.mc.n_series < self.mc.batch_size_test: new_batch_size = self.mc.n_series
495 | else: new_batch_size = self.mc.batch_size_test
496 | self.train_dataloader.update_batch_size(new_batch_size)
497 | dataloader = self.train_dataloader
498 |
499 | # Create Y_hat_panel placeholders
500 | output_size = self.mc.output_size
501 | n_unique_id = len(dataloader.sort_key['unique_id'])
502 | panel_unique_id = pd.Series(dataloader.sort_key['unique_id']).repeat(output_size)
503 |
504 | #access column with last train date
505 | panel_last_ds = pd.Series(dataloader.X[:, 2])
506 | panel_ds = []
507 | for i in range(len(panel_last_ds)):
508 | ranges = pd.date_range(start=panel_last_ds[i], periods=output_size+1, freq=self.mc.frequency)
509 | panel_ds += list(ranges[1:])
510 |
511 | panel_y_hat= np.zeros((output_size * n_unique_id))
512 |
513 | # Predict
514 | count = 0
515 | for j in range(dataloader.n_batches):
516 | batch = dataloader.get_batch()
517 | batch_size = batch.y.shape[0]
518 |
519 | if self.mc.ensemble:
520 | y_hat = torch.zeros((5,batch_size,output_size))
521 | for i in range(5):
522 | y_hat[i,:,:] = self.esrnn_ensemble[i].predict(batch)
523 | y_hat = torch.mean(y_hat,0)
524 | else:
525 | y_hat = self.esrnn.predict(batch)
526 |
527 | y_hat = y_hat.data.cpu().numpy()
528 |
529 | panel_y_hat[count:count+output_size*batch_size] = y_hat.flatten()
530 | count += output_size*batch_size
531 |
532 | Y_hat_panel_dict = {'unique_id': panel_unique_id,
533 | 'ds': panel_ds,
534 | 'y_hat': panel_y_hat}
535 |
536 | assert len(panel_ds) == len(panel_y_hat) == len(panel_unique_id)
537 |
538 | Y_hat_panel = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(Y_hat_panel_dict)
539 |
540 | if 'ds' in X_df:
541 | Y_hat_panel = X_df.merge(Y_hat_panel, on=['unique_id', 'ds'], how='left')
542 | else:
543 | Y_hat_panel = X_df.merge(Y_hat_panel, on=['unique_id'], how='left')
544 |
545 | self.train_dataloader.update_batch_size(self.mc.batch_size)
546 | return Y_hat_panel
547 |
548 | def long_to_wide(self, X_df, y_df):
549 | """
550 | Auxiliary function to wrangle LONG format dataframes
551 | to a wide format compatible with ESRNN inputs.
552 |
553 | Parameters
554 | ----------
555 | X_df : pandas dataframe
556 | Dataframe in long format with columns 'unique_id', 'ds'
557 | and 'x'.
558 | - 'unique_id' an identifier of each independent time series.
559 | - 'ds' is a datetime column
560 | - 'x' is a single exogenous variable
561 | y_df : pandas dataframe
562 | Dataframe in long format with columns 'unique_id', 'ds' and 'y'.
563 | - 'unique_id' an identifier of each independent time series.
564 | - 'ds' is a datetime column
565 | - 'y' is the column with the target values
566 |
567 | Returns
568 | -------
569 | X: numpy array, shape (n_unique_ids, n_time)
570 | y: numpy array, shape (n_unique_ids, n_time)
571 | """
572 | data = X_df.copy()
573 | data['y'] = y_df['y'].copy()
574 | sorted_ds = np.sort(data['ds'].unique())
575 | ds_map = {}
576 | for dmap, t in enumerate(sorted_ds):
577 | ds_map[t] = dmap
578 | data['ds_map'] = data['ds'].map(ds_map)
579 | data = data.sort_values(by=['ds_map','unique_id'])
580 | df_wide = data.pivot(index='unique_id', columns='ds_map')['y']
581 |
582 | x_unique = data[['unique_id', 'x']].groupby('unique_id').first()
583 | last_ds = data[['unique_id', 'ds']].groupby('unique_id').last()
584 | assert len(x_unique)==len(data.unique_id.unique())
585 | df_wide['x'] = x_unique
586 | df_wide['last_ds'] = last_ds
587 | df_wide = df_wide.reset_index().rename_axis(None, axis=1)
588 |
589 | ds_cols = data.ds_map.unique().tolist()
590 | X = df_wide.filter(items=['unique_id', 'x', 'last_ds']).values
591 | y = df_wide.filter(items=ds_cols).values
592 |
593 | return X, y
594 |
595 | def get_dir_name(self, root_dir=None):
596 | """Auxiliary function to save ESRNN model"""
597 | if not root_dir:
598 | assert self.mc.root_dir
599 | root_dir = self.mc.root_dir
600 |
601 | data_dir = self.mc.dataset_name
602 | model_parent_dir = os.path.join(root_dir, data_dir)
603 | model_path = ['esrnn_{}'.format(str(self.mc.copy))]
604 | model_dir = os.path.join(model_parent_dir, '_'.join(model_path))
605 | return model_dir
606 |
607 | def save(self, model_dir=None, copy=None):
608 | """Auxiliary function to save ESRNN model"""
609 | if copy is not None:
610 | self.mc.copy = copy
611 |
612 | if not model_dir:
613 | assert self.mc.root_dir
614 | model_dir = self.get_dir_name()
615 |
616 | if not os.path.exists(model_dir):
617 | os.makedirs(model_dir)
618 |
619 | rnn_filepath = os.path.join(model_dir, "rnn.model")
620 | es_filepath = os.path.join(model_dir, "es.model")
621 |
622 | print('Saving model to:\n {}'.format(model_dir)+'\n')
623 | torch.save({'model_state_dict': self.es.state_dict()}, es_filepath)
624 | torch.save({'model_state_dict': self.rnn.state_dict()}, rnn_filepath)
625 |
626 | def load(self, model_dir=None, copy=None):
627 | """Auxiliary function to load ESRNN model"""
628 | if copy is not None:
629 | self.mc.copy = copy
630 |
631 | if not model_dir:
632 | assert self.mc.root_dir
633 | model_dir = self.get_dir_name()
634 |
635 | rnn_filepath = os.path.join(model_dir, "rnn.model")
636 | es_filepath = os.path.join(model_dir, "es.model")
637 | path = Path(es_filepath)
638 |
639 | if path.is_file():
640 | print('Loading model from:\n {}'.format(model_dir)+'\n')
641 |
642 | checkpoint = torch.load(es_filepath, map_location=self.mc.device)
643 | self.es.load_state_dict(checkpoint['model_state_dict'])
644 | self.es.to(self.mc.device)
645 |
646 | checkpoint = torch.load(rnn_filepath, map_location=self.mc.device)
647 | self.rnn.load_state_dict(checkpoint['model_state_dict'])
648 | self.rnn.to(self.mc.device)
649 | else:
650 | print('Model path {} does not exist'.format(path))
651 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 |
|  |
|  |
|  |
51 |
52 |
|
51 |
52 |  |
|  |
|  |
|  |
51 |
52 |
|
51 |
52 |