4 | * Copyright (C) 2007 Petr Chmelar 5 | *
6 | * By downloading, copying, installing or using the software you agree to 7 | * the license in licenseIntel.txt or in licenseGNU.txt 8 | *
9 | * *************************************************************************** 10 | */ 11 | 12 | package net.kibotu.kalmanrx.jkalman; 13 | 14 | import net.kibotu.kalmanrx.jama.Matrix; 15 | 16 | import org.junit.Test; 17 | 18 | import java.util.Random; 19 | 20 | 21 | /** 22 | * JKalman TestBench 23 | */ 24 | public class KalmanTest { 25 | 26 | @Test 27 | public void random() { 28 | 29 | try { 30 | JKalman kalman = new JKalman(4, 2); 31 | 32 | Random rand = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis() % 2011); 33 | double x = 0; 34 | double y = 0; 35 | // constant velocity 36 | double dx = rand.nextDouble(); 37 | double dy = rand.nextDouble(); 38 | 39 | // init 40 | Matrix s = new Matrix(4, 1); // state [x, y, dx, dy, dxy] 41 | Matrix c = new Matrix(4, 1); // corrected state [x, y, dx, dy, dxy] 42 | 43 | Matrix m = new Matrix(2, 1); // measurement [x] 44 | m.set(0, 0, x); 45 | m.set(1, 0, y); 46 | 47 | // transitions for x, y, dx, dy 48 | double[][] tr = {{1, 0, 1, 0}, 49 | {0, 1, 0, 1}, 50 | {0, 0, 1, 0}, 51 | {0, 0, 0, 1}}; 52 | kalman.setTransition_matrix(new Matrix(tr)); 53 | 54 | // 1s somewhere? 55 | kalman.setError_cov_post(kalman.getError_cov_post().identity()); 56 | 57 | // init first assumption similar to first observation (cheat :) 58 | // kalman.setState_post(kalman.getState_post()); 59 | 60 | // report what happend first :) 61 | System.out.println("first x:" + x + ", y:" + y + ", dx:" + dx + ", dy:" + dy); 62 | System.out.println("no; x; y; dx; dy; predictionX; predictionY; predictionDx; predictionDy; correctionX; correctionY; correctionDx; correctionDy;"); 63 | 64 | // For debug only 65 | for (int i = 0; i < 200; ++i) { 66 | 67 | // check state before 68 | s = kalman.Predict(); 69 | 70 | // function init :) 71 | // m.set(1, 0, rand.nextDouble()); 72 | x = rand.nextGaussian(); 73 | y = rand.nextGaussian(); 74 | 75 | m.set(0, 0, m.get(0, 0) + dx + rand.nextGaussian()); 76 | m.set(1, 0, m.get(1, 0) + dy + rand.nextGaussian()); 77 | 78 | // a missing value (more then 1/4 times) 79 | if (rand.nextGaussian() < -0.8) { 80 | System.out.println("" + i + ";;;;;" 81 | + s.get(0, 0) + ";" + s.get(1, 0) + ";" + s.get(2, 0) + ";" + s.get(3, 0) + ";"); 82 | } else { // measurement is ok :) 83 | // look better 84 | c = kalman.Correct(m); 85 | 86 | System.out.println("" + i + ";" + m.get(0, 0) + ";" + m.get(1, 0) + ";" + x + ";" + y + ";" 87 | + s.get(0, 0) + ";" + s.get(1, 0) + ";" + s.get(2, 0) + ";" + s.get(3, 0) + ";" 88 | + c.get(0, 0) + ";" + c.get(1, 0) + ";" + c.get(2, 0) + ";" + c.get(3, 0) + ";"); 89 | } 90 | 91 | } 92 | } catch (Exception ex) { 93 | System.out.println(ex.getMessage()); 94 | } 95 | } 96 | } 97 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /.gitignore: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | 2 | # Created by https://www.gitignore.io/api/android,jetbrains,windows,osx,java,gradle 3 | .idea 4 | ### Android ### 5 | # Built application files 6 | *.apk 7 | *.ap_ 8 | 9 | # Files for the ART/Dalvik VM 10 | *.dex 11 | 12 | # Java class files 13 | *.class 14 | 15 | # Generated files 16 | bin/ 17 | gen/ 18 | out/ 19 | 20 | # Gradle files 21 | .gradle/ 22 | build/ 23 | 24 | # Local configuration file (sdk path, etc) 25 | local.properties 26 | 27 | # Proguard folder generated by Eclipse 28 | proguard/ 29 | 30 | # Log Files 31 | *.log 32 | 33 | # Android Studio Navigation editor temp files 34 | .navigation/ 35 | 36 | # Android Studio captures folder 37 | captures/ 38 | 39 | # Intellij 40 | *.iml 41 | .idea/workspace.xml 42 | .idea/libraries 43 | 44 | # Keystore files 45 | *.jks 46 | 47 | ### Android Patch ### 48 | gen-external-apklibs 49 | 50 | 51 | ### JetBrains ### 52 | # Covers JetBrains IDEs: IntelliJ, RubyMine, PhpStorm, AppCode, PyCharm, CLion, Android Studio and Webstorm 53 | # Reference: https://intellij-support.jetbrains.com/hc/en-us/articles/206544839 54 | 55 | # User-specific stuff: 56 | .idea/workspace.xml 57 | .idea/tasks.xml 58 | .idea/dictionaries 59 | .idea/vcs.xml 60 | .idea/jsLibraryMappings.xml 61 | 62 | # Sensitive or high-churn files: 63 | .idea/dataSources.ids 64 | .idea/dataSources.xml 65 | .idea/dataSources.local.xml 66 | .idea/sqlDataSources.xml 67 | .idea/dynamic.xml 68 | .idea/uiDesigner.xml 69 | 70 | # Gradle: 71 | .idea/gradle.xml 72 | .idea/libraries 73 | 74 | # Mongo Explorer plugin: 75 | .idea/mongoSettings.xml 76 | 77 | ## File-based project format: 78 | *.iws 79 | 80 | ## Plugin-specific files: 81 | 82 | # IntelliJ 83 | /out/ 84 | 85 | # mpeltonen/sbt-idea plugin 86 | .idea_modules/ 87 | 88 | # JIRA plugin 89 | atlassian-ide-plugin.xml 90 | 91 | # Crashlytics plugin (for Android Studio and IntelliJ) 92 | com_crashlytics_export_strings.xml 93 | crashlytics.properties 94 | crashlytics-build.properties 95 | fabric.properties 96 | 97 | ### JetBrains Patch ### 98 | # Comment Reason: https://github.com/joeblau/gitignore.io/issues/186#issuecomment-215987721 99 | 100 | # *.iml 101 | # modules.xml 102 | # .idea/misc.xml 103 | # *.ipr 104 | 105 | 106 | ### Windows ### 107 | # Windows image file caches 108 | Thumbs.db 109 | ehthumbs.db 110 | 111 | # Folder config file 112 | Desktop.ini 113 | 114 | # Recycle Bin used on file shares 115 | $RECYCLE.BIN/ 116 | 117 | # Windows Installer files 118 | *.cab 119 | *.msi 120 | *.msm 121 | *.msp 122 | 123 | # Windows shortcuts 124 | *.lnk 125 | 126 | 127 | ### OSX ### 128 | *.DS_Store 129 | .AppleDouble 130 | .LSOverride 131 | 132 | # Icon must end with two \r 133 | Icon 134 | 135 | 136 | # Thumbnails 137 | ._* 138 | 139 | # Files that might appear in the root of a volume 140 | .DocumentRevisions-V100 141 | .fseventsd 142 | .Spotlight-V100 143 | .TemporaryItems 144 | .Trashes 145 | .VolumeIcon.icns 146 | .com.apple.timemachine.donotpresent 147 | 148 | # Directories potentially created on remote AFP share 149 | .AppleDB 150 | .AppleDesktop 151 | Network Trash Folder 152 | Temporary Items 153 | .apdisk 154 | 155 | 156 | ### Java ### 157 | *.class 158 | 159 | # Mobile Tools for Java (J2ME) 160 | .mtj.tmp/ 161 | 162 | # Package Files # 163 | *.jar 164 | *.war 165 | *.ear 166 | 167 | # virtual machine crash logs, see http://www.java.com/en/download/help/error_hotspot.xml 168 | hs_err_pid* 169 | 170 | 171 | ### Gradle ### 172 | .gradle 173 | /build/ 174 | 175 | # Ignore Gradle GUI config 176 | gradle-app.setting 177 | 178 | # Avoid ignoring Gradle wrapper jar file (.jar files are usually ignored) 179 | !gradle-wrapper.jar 180 | 181 | # Cache of project 182 | .gradletasknamecache 183 | 184 | # # Work around https://youtrack.jetbrains.com/issue/IDEA-116898 185 | # gradle/wrapper/gradle-wrapper.properties -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /README.md: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | [](https://www.paypal.me/janrabe/5) [](https://about.me/janrabe) 2 | # KalmanRx [](http://android-arsenal.com/details/1/4539) [](https://jitpack.io/#kibotu/KalmanRx) [](https://jitpack.io/#kibotu/KalmanRx) [](https://jitpack.io/com/github/kibotu/KalmanRx/master-SNAPSHOT/javadoc/index.html) [](https://travis-ci.org/kibotu/KalmanRx) [](https://android-arsenal.com/api?level=15) [](https://docs.gradle.org/current/release-notes) [](https://kotlinlang.org/) [](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kibotu/KalmanRx/master/LICENSE) [](https://developer.android.com/topic/libraries/support-library/refactor) 3 | 4 | ## Introduction 5 | 6 | Removes the noise from float streams using [Kalman Filter](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kalman_filter). Useful to smoothen sensory data e.g.: [gps location](https://github.com/villoren/KalmanLocationManager), or [Accelerometer](https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/sensors/sensors_motion.html#sensors-motion-accel). 7 | 8 | is an open-source library for Android that provides a set of classes and utilities for implementing Kalman filtering in reactive programming applications using the RxJava library. 9 | 10 | Kalman filtering is a mathematical technique that is used to estimate the state of a dynamic system based on a series of noisy measurements. It is commonly used in signal processing, control systems, and navigation applications. 11 | 12 | The KalmanRx library provides a set of reactive operators that can be used to implement Kalman filtering in RxJava applications. These operators allow you to easily filter noisy data streams, estimate the state of dynamic systems, and make predictions about future states. 13 | 14 | Some of the key features of the KalmanRx library are: 15 | 16 | Integration with RxJava: The library is designed to work seamlessly with the RxJava library, which allows you to easily combine Kalman filtering with other reactive programming techniques. 17 | Support for multiple Kalman filter models: The library provides a set of pre-defined Kalman filter models that can be used to filter different types of data streams, including scalar, vector, and matrix data. 18 | Configurable filter parameters: The library allows you to configure the filter parameters, such as the process noise, measurement noise, and initial state, to optimize the filter performance for your specific application. 19 | Real-time filtering: The library is optimized for real-time applications, and provides a set of utilities to measure the filter performance, detect anomalies, and adjust the filter parameters in real-time. 20 | Overall, the KalmanRx library can be a useful tool for implementing Kalman filtering in reactive programming applications on the Android platform, especially for developers who are working with dynamic systems and noisy data streams. 21 | 22 | 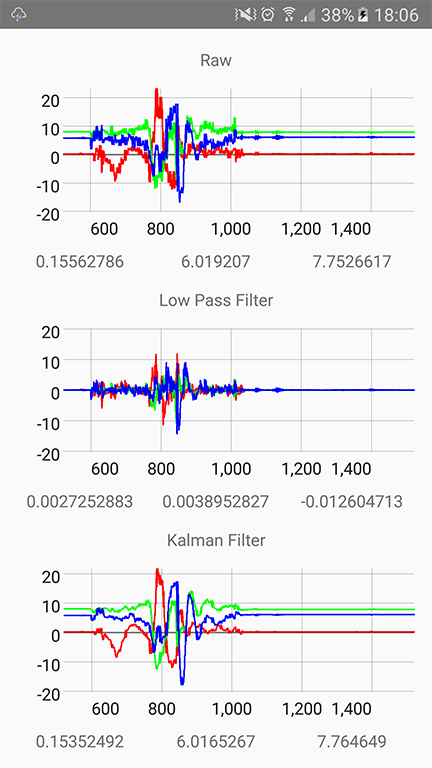 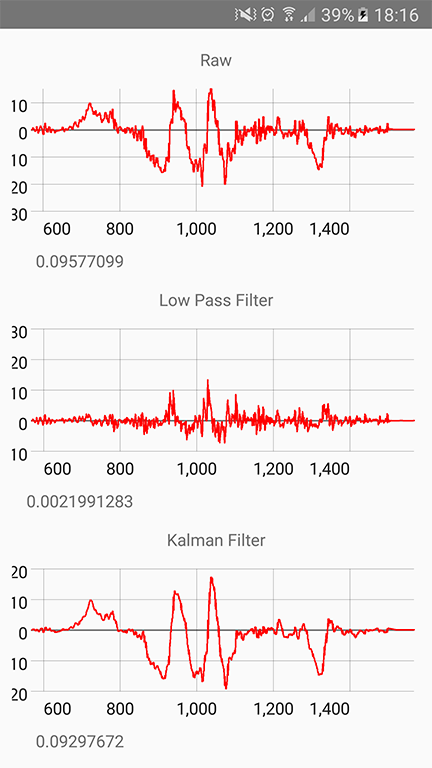 23 | 24 | ## [How to use](https://github.com/kibotu/KalmanRx/blob/master/app/src/main/java/net/kibotu/kalmanrx/app/ui/AccelerationSensorKalmanFragment.java#L16-L19) 25 | 26 | Library is supporting up to 3 values smoothened from a stream. 27 | 28 | (float) stream 29 | 30 | ```java 31 | KalmanRx.createFrom1D(floatObservable.map(e -> e.value)) 32 | .subscribe(value->{}, Throwable::printStackTrace); 33 | ``` 34 | 35 | (float, float) stream 36 | 37 | ```java 38 | KalmanRx.createFrom2D(floatObservable.map(e -> e.values)) 39 | .subscribe(values->{}, Throwable::printStackTrace); 40 | ``` 41 | 42 | (float, float, float) stream 43 | 44 | ```java 45 | KalmanRx.createFrom3D(floatObservable.map(e -> e.values)) 46 | .subscribe(value->{}, Throwable::printStackTrace); 47 | ``` 48 | 49 | ## How to install 50 | 51 | ```groovy 52 | implementation 'com.github.kibotu:KalmanRx:-SNAPSHOT' 53 | ``` 54 | 55 | ## How to build 56 | 57 | ```bash 58 | graldew clean build 59 | ``` 60 | 61 | ### CI 62 | 63 | ```bash 64 | gradlew clean assembleRelease test javadoc 65 | ``` 66 | 67 | #### Build Requirements 68 | 69 | - JDK8 70 | - Android Build Tools 27.0.3 71 | - Android SDK 27 72 | 73 | ### Notes 74 | 75 | Follow me on Twitter: [@wolkenschauer](https://twitter.com/wolkenschauer) 76 | 77 | Let me know what you think: [jan.rabe@kibotu.net](mailto:jan.rabe@kibotu.net) 78 | 79 | Contributions welcome! 80 | 81 | ### License 82 |
83 | Copyright 2016 Jan Rabe 84 | 85 | Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); 86 | you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. 87 | You may obtain a copy of the License at 88 | 89 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 90 | 91 | Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software 92 | distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, 93 | WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. 94 | See the License for the specific language governing permissions and 95 | limitations under the License. 96 |97 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /gradlew: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | #!/usr/bin/env sh 2 | 3 | # 4 | # Copyright 2015 the original author or authors. 5 | # 6 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); 7 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. 8 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at 9 | # 10 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 11 | # 12 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software 13 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, 14 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. 15 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and 16 | # limitations under the License. 17 | # 18 | 19 | ############################################################################## 20 | ## 21 | ## Gradle start up script for UN*X 22 | ## 23 | ############################################################################## 24 | 25 | # Attempt to set APP_HOME 26 | # Resolve links: $0 may be a link 27 | PRG="$0" 28 | # Need this for relative symlinks. 29 | while [ -h "$PRG" ] ; do 30 | ls=`ls -ld "$PRG"` 31 | link=`expr "$ls" : '.*-> \(.*\)$'` 32 | if expr "$link" : '/.*' > /dev/null; then 33 | PRG="$link" 34 | else 35 | PRG=`dirname "$PRG"`"/$link" 36 | fi 37 | done 38 | SAVED="`pwd`" 39 | cd "`dirname \"$PRG\"`/" >/dev/null 40 | APP_HOME="`pwd -P`" 41 | cd "$SAVED" >/dev/null 42 | 43 | APP_NAME="Gradle" 44 | APP_BASE_NAME=`basename "$0"` 45 | 46 | # Add default JVM options here. You can also use JAVA_OPTS and GRADLE_OPTS to pass JVM options to this script. 47 | DEFAULT_JVM_OPTS='"-Xmx64m" "-Xms64m"' 48 | 49 | # Use the maximum available, or set MAX_FD != -1 to use that value. 50 | MAX_FD="maximum" 51 | 52 | warn () { 53 | echo "$*" 54 | } 55 | 56 | die () { 57 | echo 58 | echo "$*" 59 | echo 60 | exit 1 61 | } 62 | 63 | # OS specific support (must be 'true' or 'false'). 64 | cygwin=false 65 | msys=false 66 | darwin=false 67 | nonstop=false 68 | case "`uname`" in 69 | CYGWIN* ) 70 | cygwin=true 71 | ;; 72 | Darwin* ) 73 | darwin=true 74 | ;; 75 | MINGW* ) 76 | msys=true 77 | ;; 78 | NONSTOP* ) 79 | nonstop=true 80 | ;; 81 | esac 82 | 83 | CLASSPATH=$APP_HOME/gradle/wrapper/gradle-wrapper.jar 84 | 85 | # Determine the Java command to use to start the JVM. 86 | if [ -n "$JAVA_HOME" ] ; then 87 | if [ -x "$JAVA_HOME/jre/sh/java" ] ; then 88 | # IBM's JDK on AIX uses strange locations for the executables 89 | JAVACMD="$JAVA_HOME/jre/sh/java" 90 | else 91 | JAVACMD="$JAVA_HOME/bin/java" 92 | fi 93 | if [ ! -x "$JAVACMD" ] ; then 94 | die "ERROR: JAVA_HOME is set to an invalid directory: $JAVA_HOME 95 | 96 | Please set the JAVA_HOME variable in your environment to match the 97 | location of your Java installation." 98 | fi 99 | else 100 | JAVACMD="java" 101 | which java >/dev/null 2>&1 || die "ERROR: JAVA_HOME is not set and no 'java' command could be found in your PATH. 102 | 103 | Please set the JAVA_HOME variable in your environment to match the 104 | location of your Java installation." 105 | fi 106 | 107 | # Increase the maximum file descriptors if we can. 108 | if [ "$cygwin" = "false" -a "$darwin" = "false" -a "$nonstop" = "false" ] ; then 109 | MAX_FD_LIMIT=`ulimit -H -n` 110 | if [ $? -eq 0 ] ; then 111 | if [ "$MAX_FD" = "maximum" -o "$MAX_FD" = "max" ] ; then 112 | MAX_FD="$MAX_FD_LIMIT" 113 | fi 114 | ulimit -n $MAX_FD 115 | if [ $? -ne 0 ] ; then 116 | warn "Could not set maximum file descriptor limit: $MAX_FD" 117 | fi 118 | else 119 | warn "Could not query maximum file descriptor limit: $MAX_FD_LIMIT" 120 | fi 121 | fi 122 | 123 | # For Darwin, add options to specify how the application appears in the dock 124 | if $darwin; then 125 | GRADLE_OPTS="$GRADLE_OPTS \"-Xdock:name=$APP_NAME\" \"-Xdock:icon=$APP_HOME/media/gradle.icns\"" 126 | fi 127 | 128 | # For Cygwin, switch paths to Windows format before running java 129 | if $cygwin ; then 130 | APP_HOME=`cygpath --path --mixed "$APP_HOME"` 131 | CLASSPATH=`cygpath --path --mixed "$CLASSPATH"` 132 | JAVACMD=`cygpath --unix "$JAVACMD"` 133 | 134 | # We build the pattern for arguments to be converted via cygpath 135 | ROOTDIRSRAW=`find -L / -maxdepth 1 -mindepth 1 -type d 2>/dev/null` 136 | SEP="" 137 | for dir in $ROOTDIRSRAW ; do 138 | ROOTDIRS="$ROOTDIRS$SEP$dir" 139 | SEP="|" 140 | done 141 | OURCYGPATTERN="(^($ROOTDIRS))" 142 | # Add a user-defined pattern to the cygpath arguments 143 | if [ "$GRADLE_CYGPATTERN" != "" ] ; then 144 | OURCYGPATTERN="$OURCYGPATTERN|($GRADLE_CYGPATTERN)" 145 | fi 146 | # Now convert the arguments - kludge to limit ourselves to /bin/sh 147 | i=0 148 | for arg in "$@" ; do 149 | CHECK=`echo "$arg"|egrep -c "$OURCYGPATTERN" -` 150 | CHECK2=`echo "$arg"|egrep -c "^-"` ### Determine if an option 151 | 152 | if [ $CHECK -ne 0 ] && [ $CHECK2 -eq 0 ] ; then ### Added a condition 153 | eval `echo args$i`=`cygpath --path --ignore --mixed "$arg"` 154 | else 155 | eval `echo args$i`="\"$arg\"" 156 | fi 157 | i=$((i+1)) 158 | done 159 | case $i in 160 | (0) set -- ;; 161 | (1) set -- "$args0" ;; 162 | (2) set -- "$args0" "$args1" ;; 163 | (3) set -- "$args0" "$args1" "$args2" ;; 164 | (4) set -- "$args0" "$args1" "$args2" "$args3" ;; 165 | (5) set -- "$args0" "$args1" "$args2" "$args3" "$args4" ;; 166 | (6) set -- "$args0" "$args1" "$args2" "$args3" "$args4" "$args5" ;; 167 | (7) set -- "$args0" "$args1" "$args2" "$args3" "$args4" "$args5" "$args6" ;; 168 | (8) set -- "$args0" "$args1" "$args2" "$args3" "$args4" "$args5" "$args6" "$args7" ;; 169 | (9) set -- "$args0" "$args1" "$args2" "$args3" "$args4" "$args5" "$args6" "$args7" "$args8" ;; 170 | esac 171 | fi 172 | 173 | # Escape application args 174 | save () { 175 | for i do printf %s\\n "$i" | sed "s/'/'\\\\''/g;1s/^/'/;\$s/\$/' \\\\/" ; done 176 | echo " " 177 | } 178 | APP_ARGS=$(save "$@") 179 | 180 | # Collect all arguments for the java command, following the shell quoting and substitution rules 181 | eval set -- $DEFAULT_JVM_OPTS $JAVA_OPTS $GRADLE_OPTS "\"-Dorg.gradle.appname=$APP_BASE_NAME\"" -classpath "\"$CLASSPATH\"" org.gradle.wrapper.GradleWrapperMain "$APP_ARGS" 182 | 183 | # by default we should be in the correct project dir, but when run from Finder on Mac, the cwd is wrong 184 | if [ "$(uname)" = "Darwin" ] && [ "$HOME" = "$PWD" ]; then 185 | cd "$(dirname "$0")" 186 | fi 187 | 188 | exec "$JAVACMD" "$@" 189 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /lib/src/main/java/net/kibotu/kalmanrx/KalmanRx.java: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | package net.kibotu.kalmanrx; 2 | 3 | import net.kibotu.kalmanrx.jama.Matrix; 4 | import net.kibotu.kalmanrx.jkalman.JKalman; 5 | 6 | import rx.Observable; 7 | 8 | /** 9 | * Created by jan.rabe on 11/10/16. 10 | *
11 | */
12 |
13 | public class KalmanRx {
14 |
15 | /**
16 | * Smoothens float value stream using kalman filter.
17 | *
18 | * @param stream Float Stream.
19 | * @return Observable.
20 | */
21 | public static Observable
6 | * For a symmetric, positive definite matrix A, the Cholesky decomposition
7 | * is an lower triangular matrix L so that A = L*L'.
8 | *
9 | * If the matrix is not symmetric or positive definite, the constructor
10 | * returns a partial decomposition and sets an internal flag that may
11 | * be queried by the isSPD() method.
12 | */
13 |
14 | public class CholeskyDecomposition implements java.io.Serializable {
15 |
16 | /* ------------------------
17 | Class variables
18 | * ------------------------ */
19 |
20 | /**
21 | * Array for internal storage of decomposition.
22 | *
23 | * @serial internal array storage.
24 | */
25 | private double[][] L;
26 |
27 | /**
28 | * Row and column dimension (square matrix).
29 | *
30 | * @serial matrix dimension.
31 | */
32 | private int n;
33 |
34 | /**
35 | * Symmetric and positive definite flag.
36 | *
37 | * @serial is symmetric and positive definite flag.
38 | */
39 | private boolean isspd;
40 |
41 | /* ------------------------
42 | Constructor
43 | * ------------------------ */
44 |
45 | /**
46 | * Cholesky algorithm for symmetric and positive definite matrix.
47 | *
48 | * @param A Square, symmetric matrix.
49 | * @return Structure to access L and isspd flag.
50 | */
51 |
52 | public CholeskyDecomposition(Matrix Arg) {
53 |
54 |
55 | // Initialize.
56 | double[][] A = Arg.getArray();
57 | n = Arg.getRowDimension();
58 | L = new double[n][n];
59 | isspd = (Arg.getColumnDimension() == n);
60 | // Main loop.
61 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
62 | double[] Lrowj = L[j];
63 | double d = 0.0;
64 | for (int k = 0; k < j; k++) {
65 | double[] Lrowk = L[k];
66 | double s = 0.0;
67 | for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
68 | s += Lrowk[i] * Lrowj[i];
69 | }
70 | Lrowj[k] = s = (A[j][k] - s) / L[k][k];
71 | d = d + s * s;
72 | isspd = isspd & (A[k][j] == A[j][k]);
73 | }
74 | d = A[j][j] - d;
75 | isspd = isspd & (d > 0.0);
76 | L[j][j] = Math.sqrt(Math.max(d, 0.0));
77 | for (int k = j + 1; k < n; k++) {
78 | L[j][k] = 0.0;
79 | }
80 | }
81 | }
82 |
83 | /* ------------------------
84 | Temporary, experimental code.
85 | * ------------------------ *\
86 |
87 | \** Right Triangular Cholesky Decomposition.
88 |
89 | For a symmetric, positive definite matrix A, the Right Cholesky
90 | decomposition is an upper triangular matrix R so that A = R'*R.
91 | This constructor computes R with the Fortran inspired column oriented
92 | algorithm used in LINPACK and MATLAB. In Java, we suspect a row oriented,
93 | lower triangular decomposition is faster. We have temporarily included
94 | this constructor here until timing experiments confirm this suspicion.
95 | *\
96 |
97 | \** Array for internal storage of right triangular decomposition. **\
98 | private transient double[][] R;
99 |
100 | \** Cholesky algorithm for symmetric and positive definite matrix.
101 | @param A Square, symmetric matrix.
102 | @param rightflag Actual value ignored.
103 | @return Structure to access R and isspd flag.
104 | *\
105 |
106 | public CholeskyDecomposition (Matrix Arg, int rightflag) {
107 | // Initialize.
108 | double[][] A = Arg.getArray();
109 | n = Arg.getColumnDimension();
110 | R = new double[n][n];
111 | isspd = (Arg.getColumnDimension() == n);
112 | // Main loop.
113 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
114 | double d = 0.0;
115 | for (int k = 0; k < j; k++) {
116 | double s = A[k][j];
117 | for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
118 | s = s - R[i][k]*R[i][j];
119 | }
120 | R[k][j] = s = s/R[k][k];
121 | d = d + s*s;
122 | isspd = isspd & (A[k][j] == A[j][k]);
123 | }
124 | d = A[j][j] - d;
125 | isspd = isspd & (d > 0.0);
126 | R[j][j] = Math.sqrt(Math.max(d,0.0));
127 | for (int k = j+1; k < n; k++) {
128 | R[k][j] = 0.0;
129 | }
130 | }
131 | }
132 |
133 | \** Return upper triangular factor.
134 | @return R
135 | *\
136 |
137 | public Matrix getR () {
138 | return new Matrix(R,n,n);
139 | }
140 |
141 | \* ------------------------
142 | End of temporary code.
143 | * ------------------------ */
144 |
145 | /* ------------------------
146 | Public Methods
147 | * ------------------------ */
148 |
149 | /**
150 | * Is the matrix symmetric and positive definite?
151 | *
152 | * @return true if A is symmetric and positive definite.
153 | */
154 |
155 | public boolean isSPD() {
156 | return isspd;
157 | }
158 |
159 | /**
160 | * Return triangular factor.
161 | *
162 | * @return L
163 | */
164 |
165 | public Matrix getL() {
166 | return new Matrix(L, n, n);
167 | }
168 |
169 | /**
170 | * Solve A*X = B
171 | *
172 | * @param B A Matrix with as many rows as A and any number of columns.
173 | * @return X so that L*L'*X = B
174 | * @throws IllegalArgumentException Matrix row dimensions must agree.
175 | * @throws RuntimeException Matrix is not symmetric positive definite.
176 | */
177 |
178 | public Matrix solve(Matrix B) {
179 | if (B.getRowDimension() != n) {
180 | throw new IllegalArgumentException("Matrix row dimensions must agree.");
181 | }
182 | if (!isspd) {
183 | throw new RuntimeException("Matrix is not symmetric positive definite.");
184 | }
185 |
186 | // Copy right hand side.
187 | double[][] X = B.getArrayCopy();
188 | int nx = B.getColumnDimension();
189 |
190 | // Solve L*Y = B;
191 | for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
192 | for (int j = 0; j < nx; j++) {
193 | for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
194 | X[k][j] -= X[i][j] * L[k][i];
195 | }
196 | X[k][j] /= L[k][k];
197 | }
198 | }
199 |
200 | // Solve L'*X = Y;
201 | for (int k = n - 1; k >= 0; k--) {
202 | for (int j = 0; j < nx; j++) {
203 | for (int i = k + 1; i < n; i++) {
204 | X[k][j] -= X[i][j] * L[i][k];
205 | }
206 | X[k][j] /= L[k][k];
207 | }
208 | }
209 |
210 |
211 | return new Matrix(X, n, nx);
212 | }
213 | }
214 |
215 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/lib/src/main/java/net/kibotu/kalmanrx/jama/QRDecomposition.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package net.kibotu.kalmanrx.jama;
2 |
3 | import net.kibotu.kalmanrx.jama.util.Maths;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | * QR Decomposition.
7 | *
8 | * For an m-by-n matrix A with m >= n, the QR decomposition is an m-by-n
9 | * orthogonal matrix Q and an n-by-n upper triangular matrix R so that
10 | * A = Q*R.
11 | *
12 | * The QR decompostion always exists, even if the matrix does not have
13 | * full rank, so the constructor will never fail. The primary use of the
14 | * QR decomposition is in the least squares solution of nonsquare systems
15 | * of simultaneous linear equations. This will fail if isFullRank()
16 | * returns false.
17 | */
18 |
19 | public class QRDecomposition implements java.io.Serializable {
20 |
21 | /* ------------------------
22 | Class variables
23 | * ------------------------ */
24 |
25 | /**
26 | * Array for internal storage of decomposition.
27 | *
28 | * @serial internal array storage.
29 | */
30 | private double[][] QR;
31 |
32 | /**
33 | * Row and column dimensions.
34 | *
35 | * @serial column dimension.
36 | * @serial row dimension.
37 | */
38 | private int m, n;
39 |
40 | /**
41 | * Array for internal storage of diagonal of R.
42 | *
43 | * @serial diagonal of R.
44 | */
45 | private double[] Rdiag;
46 |
47 | /* ------------------------
48 | Constructor
49 | * ------------------------ */
50 |
51 | /**
52 | * QR Decomposition, computed by Householder reflections.
53 | *
54 | * @param A Rectangular matrix
55 | * @return Structure to access R and the Householder vectors and compute Q.
56 | */
57 |
58 | public QRDecomposition(Matrix A) {
59 | // Initialize.
60 | QR = A.getArrayCopy();
61 | m = A.getRowDimension();
62 | n = A.getColumnDimension();
63 | Rdiag = new double[n];
64 |
65 | // Main loop.
66 | for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
67 | // Compute 2-norm of k-th column without under/overflow.
68 | double nrm = 0;
69 | for (int i = k; i < m; i++) {
70 | nrm = Maths.hypot(nrm, QR[i][k]);
71 | }
72 |
73 | if (nrm != 0.0) {
74 | // Form k-th Householder vector.
75 | if (QR[k][k] < 0) {
76 | nrm = -nrm;
77 | }
78 | for (int i = k; i < m; i++) {
79 | QR[i][k] /= nrm;
80 | }
81 | QR[k][k] += 1.0;
82 |
83 | // Apply transformation to remaining columns.
84 | for (int j = k + 1; j < n; j++) {
85 | double s = 0.0;
86 | for (int i = k; i < m; i++) {
87 | s += QR[i][k] * QR[i][j];
88 | }
89 | s = -s / QR[k][k];
90 | for (int i = k; i < m; i++) {
91 | QR[i][j] += s * QR[i][k];
92 | }
93 | }
94 | }
95 | Rdiag[k] = -nrm;
96 | }
97 | }
98 |
99 | /* ------------------------
100 | Public Methods
101 | * ------------------------ */
102 |
103 | /**
104 | * Is the matrix full rank?
105 | *
106 | * @return true if R, and hence A, has full rank.
107 | */
108 |
109 | public boolean isFullRank() {
110 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
111 | if (Rdiag[j] == 0)
112 | return false;
113 | }
114 | return true;
115 | }
116 |
117 | /**
118 | * Return the Householder vectors
119 | *
120 | * @return Lower trapezoidal matrix whose columns define the reflections
121 | */
122 |
123 | public Matrix getH() {
124 | Matrix X = new Matrix(m, n);
125 | double[][] H = X.getArray();
126 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
127 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
128 | if (i >= j) {
129 | H[i][j] = QR[i][j];
130 | } else {
131 | H[i][j] = 0.0;
132 | }
133 | }
134 | }
135 | return X;
136 | }
137 |
138 | /**
139 | * Return the upper triangular factor
140 | *
141 | * @return R
142 | */
143 |
144 | public Matrix getR() {
145 | Matrix X = new Matrix(n, n);
146 | double[][] R = X.getArray();
147 | for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
148 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
149 | if (i < j) {
150 | R[i][j] = QR[i][j];
151 | } else if (i == j) {
152 | R[i][j] = Rdiag[i];
153 | } else {
154 | R[i][j] = 0.0;
155 | }
156 | }
157 | }
158 | return X;
159 | }
160 |
161 | /**
162 | * Generate and return the (economy-sized) orthogonal factor
163 | *
164 | * @return Q
165 | */
166 |
167 | public Matrix getQ() {
168 | Matrix X = new Matrix(m, n);
169 | double[][] Q = X.getArray();
170 | for (int k = n - 1; k >= 0; k--) {
171 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
172 | Q[i][k] = 0.0;
173 | }
174 | Q[k][k] = 1.0;
175 | for (int j = k; j < n; j++) {
176 | if (QR[k][k] != 0) {
177 | double s = 0.0;
178 | for (int i = k; i < m; i++) {
179 | s += QR[i][k] * Q[i][j];
180 | }
181 | s = -s / QR[k][k];
182 | for (int i = k; i < m; i++) {
183 | Q[i][j] += s * QR[i][k];
184 | }
185 | }
186 | }
187 | }
188 | return X;
189 | }
190 |
191 | /**
192 | * Least squares solution of A*X = B
193 | *
194 | * @param B A Matrix with as many rows as A and any number of columns.
195 | * @return X that minimizes the two norm of Q*R*X-B.
196 | * @throws IllegalArgumentException Matrix row dimensions must agree.
197 | * @throws RuntimeException Matrix is rank deficient.
198 | */
199 |
200 | public Matrix solve(Matrix B) {
201 | if (B.getRowDimension() != m) {
202 | throw new IllegalArgumentException("Matrix row dimensions must agree.");
203 | }
204 | if (!this.isFullRank()) {
205 | throw new RuntimeException("Matrix is rank deficient.");
206 | }
207 |
208 | // Copy right hand side
209 | int nx = B.getColumnDimension();
210 | double[][] X = B.getArrayCopy();
211 |
212 | // Compute Y = transpose(Q)*B
213 | for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
214 | for (int j = 0; j < nx; j++) {
215 | double s = 0.0;
216 | for (int i = k; i < m; i++) {
217 | s += QR[i][k] * X[i][j];
218 | }
219 | s = -s / QR[k][k];
220 | for (int i = k; i < m; i++) {
221 | X[i][j] += s * QR[i][k];
222 | }
223 | }
224 | }
225 | // Solve R*X = Y;
226 | for (int k = n - 1; k >= 0; k--) {
227 | for (int j = 0; j < nx; j++) {
228 | X[k][j] /= Rdiag[k];
229 | }
230 | for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
231 | for (int j = 0; j < nx; j++) {
232 | X[i][j] -= X[k][j] * QR[i][k];
233 | }
234 | }
235 | }
236 | return (new Matrix(X, n, nx).getMatrix(0, n - 1, 0, nx - 1));
237 | }
238 | }
239 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/lib/src/main/java/net/kibotu/kalmanrx/jama/LUDecomposition.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package net.kibotu.kalmanrx.jama;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | * LU Decomposition.
5 | *
6 | * For an m-by-n matrix A with m >= n, the LU decomposition is an m-by-n
7 | * unit lower triangular matrix L, an n-by-n upper triangular matrix U,
8 | * and a permutation vector piv of length m so that A(piv,:) = L*U.
9 | * If m < n, then L is m-by-m and U is m-by-n.
10 | *
11 | * The LU decompostion with pivoting always exists, even if the matrix is
12 | * singular, so the constructor will never fail. The primary use of the
13 | * LU decomposition is in the solution of square systems of simultaneous
14 | * linear equations. This will fail if isNonsingular() returns false.
15 | */
16 |
17 | public class LUDecomposition implements java.io.Serializable {
18 |
19 | /* ------------------------
20 | Class variables
21 | * ------------------------ */
22 |
23 | /**
24 | * Array for internal storage of decomposition.
25 | *
26 | * @serial internal array storage.
27 | */
28 | private double[][] LU;
29 |
30 | /**
31 | * Row and column dimensions, and pivot sign.
32 | *
33 | * @serial column dimension.
34 | * @serial row dimension.
35 | * @serial pivot sign.
36 | */
37 | private int m, n, pivsign;
38 |
39 | /**
40 | * Internal storage of pivot vector.
41 | *
42 | * @serial pivot vector.
43 | */
44 | private int[] piv;
45 |
46 | /* ------------------------
47 | Constructor
48 | * ------------------------ */
49 |
50 | /**
51 | * LU Decomposition
52 | *
53 | * @param A Rectangular matrix
54 | * @return Structure to access L, U and piv.
55 | */
56 |
57 | public LUDecomposition(Matrix A) {
58 |
59 | // Use a "left-looking", dot-product, Crout/Doolittle algorithm.
60 |
61 | LU = A.getArrayCopy();
62 | m = A.getRowDimension();
63 | n = A.getColumnDimension();
64 | piv = new int[m];
65 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
66 | piv[i] = i;
67 | }
68 | pivsign = 1;
69 | double[] LUrowi;
70 | double[] LUcolj = new double[m];
71 |
72 | // Outer loop.
73 |
74 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
75 |
76 | // Make a copy of the j-th column to localize references.
77 |
78 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
79 | LUcolj[i] = LU[i][j];
80 | }
81 |
82 | // Apply previous transformations.
83 |
84 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
85 | LUrowi = LU[i];
86 |
87 | // Most of the time is spent in the following dot product.
88 |
89 | int kmax = Math.min(i, j);
90 | double s = 0.0;
91 | for (int k = 0; k < kmax; k++) {
92 | s += LUrowi[k] * LUcolj[k];
93 | }
94 |
95 | LUrowi[j] = LUcolj[i] -= s;
96 | }
97 |
98 | // Find pivot and exchange if necessary.
99 |
100 | int p = j;
101 | for (int i = j + 1; i < m; i++) {
102 | if (Math.abs(LUcolj[i]) > Math.abs(LUcolj[p])) {
103 | p = i;
104 | }
105 | }
106 | if (p != j) {
107 | for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
108 | double t = LU[p][k];
109 | LU[p][k] = LU[j][k];
110 | LU[j][k] = t;
111 | }
112 | int k = piv[p];
113 | piv[p] = piv[j];
114 | piv[j] = k;
115 | pivsign = -pivsign;
116 | }
117 |
118 | // Compute multipliers.
119 |
120 | if (j < m & LU[j][j] != 0.0) {
121 | for (int i = j + 1; i < m; i++) {
122 | LU[i][j] /= LU[j][j];
123 | }
124 | }
125 | }
126 | }
127 |
128 | /* ------------------------
129 | Temporary, experimental code.
130 | ------------------------ *\
131 |
132 | \** LU Decomposition, computed by Gaussian elimination.
133 |
134 | This constructor computes L and U with the "daxpy"-based elimination
135 | algorithm used in LINPACK and MATLAB. In Java, we suspect the dot-product,
136 | Crout algorithm will be faster. We have temporarily included this
137 | constructor until timing experiments confirm this suspicion.
138 |
139 | @param A Rectangular matrix
140 | @param linpackflag Use Gaussian elimination. Actual value ignored.
141 | @return Structure to access L, U and piv.
142 | *\
143 |
144 | public LUDecomposition (Matrix A, int linpackflag) {
145 | // Initialize.
146 | LU = A.getArrayCopy();
147 | m = A.getRowDimension();
148 | n = A.getColumnDimension();
149 | piv = new int[m];
150 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
151 | piv[i] = i;
152 | }
153 | pivsign = 1;
154 | // Main loop.
155 | for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
156 | // Find pivot.
157 | int p = k;
158 | for (int i = k+1; i < m; i++) {
159 | if (Math.abs(LU[i][k]) > Math.abs(LU[p][k])) {
160 | p = i;
161 | }
162 | }
163 | // Exchange if necessary.
164 | if (p != k) {
165 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
166 | double t = LU[p][j]; LU[p][j] = LU[k][j]; LU[k][j] = t;
167 | }
168 | int t = piv[p]; piv[p] = piv[k]; piv[k] = t;
169 | pivsign = -pivsign;
170 | }
171 | // Compute multipliers and eliminate k-th column.
172 | if (LU[k][k] != 0.0) {
173 | for (int i = k+1; i < m; i++) {
174 | LU[i][k] /= LU[k][k];
175 | for (int j = k+1; j < n; j++) {
176 | LU[i][j] -= LU[i][k]*LU[k][j];
177 | }
178 | }
179 | }
180 | }
181 | }
182 |
183 | \* ------------------------
184 | End of temporary code.
185 | * ------------------------ */
186 |
187 | /* ------------------------
188 | Public Methods
189 | * ------------------------ */
190 |
191 | /**
192 | * Is the matrix nonsingular?
193 | *
194 | * @return true if U, and hence A, is nonsingular.
195 | */
196 |
197 | public boolean isNonsingular() {
198 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
199 | if (LU[j][j] == 0)
200 | return false;
201 | }
202 | return true;
203 | }
204 |
205 | /**
206 | * Return lower triangular factor
207 | *
208 | * @return L
209 | */
210 |
211 | public Matrix getL() {
212 | Matrix X = new Matrix(m, n);
213 | double[][] L = X.getArray();
214 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
215 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
216 | if (i > j) {
217 | L[i][j] = LU[i][j];
218 | } else if (i == j) {
219 | L[i][j] = 1.0;
220 | } else {
221 | L[i][j] = 0.0;
222 | }
223 | }
224 | }
225 | return X;
226 | }
227 |
228 | /**
229 | * Return upper triangular factor
230 | *
231 | * @return U
232 | */
233 |
234 | public Matrix getU() {
235 | Matrix X = new Matrix(n, n);
236 | double[][] U = X.getArray();
237 | for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
238 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
239 | if (i <= j) {
240 | U[i][j] = LU[i][j];
241 | } else {
242 | U[i][j] = 0.0;
243 | }
244 | }
245 | }
246 | return X;
247 | }
248 |
249 | /**
250 | * Return pivot permutation vector
251 | *
252 | * @return piv
253 | */
254 |
255 | public int[] getPivot() {
256 | int[] p = new int[m];
257 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
258 | p[i] = piv[i];
259 | }
260 | return p;
261 | }
262 |
263 | /**
264 | * Return pivot permutation vector as a one-dimensional double array
265 | *
266 | * @return (double) piv
267 | */
268 |
269 | public double[] getDoublePivot() {
270 | double[] vals = new double[m];
271 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
272 | vals[i] = (double) piv[i];
273 | }
274 | return vals;
275 | }
276 |
277 | /**
278 | * Determinant
279 | *
280 | * @return det(A)
281 | * @throws IllegalArgumentException Matrix must be square
282 | */
283 |
284 | public double det() {
285 | if (m != n) {
286 | throw new IllegalArgumentException("Matrix must be square.");
287 | }
288 | double d = (double) pivsign;
289 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
290 | d *= LU[j][j];
291 | }
292 | return d;
293 | }
294 |
295 | /**
296 | * Solve A*X = B
297 | *
298 | * @param B A Matrix with as many rows as A and any number of columns.
299 | * @return X so that L*U*X = B(piv,:)
300 | * @throws IllegalArgumentException Matrix row dimensions must agree.
301 | * @throws RuntimeException Matrix is singular.
302 | */
303 |
304 | public Matrix solve(Matrix B) {
305 | if (B.getRowDimension() != m) {
306 | throw new IllegalArgumentException("Matrix row dimensions must agree.");
307 | }
308 | if (!this.isNonsingular()) {
309 | throw new RuntimeException("Matrix is singular.");
310 | }
311 |
312 | // Copy right hand side with pivoting
313 | int nx = B.getColumnDimension();
314 | Matrix Xmat = B.getMatrix(piv, 0, nx - 1);
315 | double[][] X = Xmat.getArray();
316 |
317 | // Solve L*Y = B(piv,:)
318 | for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
319 | for (int i = k + 1; i < n; i++) {
320 | for (int j = 0; j < nx; j++) {
321 | X[i][j] -= X[k][j] * LU[i][k];
322 | }
323 | }
324 | }
325 | // Solve U*X = Y;
326 | for (int k = n - 1; k >= 0; k--) {
327 | for (int j = 0; j < nx; j++) {
328 | X[k][j] /= LU[k][k];
329 | }
330 | for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
331 | for (int j = 0; j < nx; j++) {
332 | X[i][j] -= X[k][j] * LU[i][k];
333 | }
334 | }
335 | }
336 | return Xmat;
337 | }
338 | }
339 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Apache License
2 | Version 2.0, January 2004
3 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/
4 |
5 | TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR USE, REPRODUCTION, AND DISTRIBUTION
6 |
7 | 1. Definitions.
8 |
9 | "License" shall mean the terms and conditions for use, reproduction,
10 | and distribution as defined by Sections 1 through 9 of this document.
11 |
12 | "Licensor" shall mean the copyright owner or entity authorized by
13 | the copyright owner that is granting the License.
14 |
15 | "Legal Entity" shall mean the union of the acting entity and all
16 | other entities that control, are controlled by, or are under common
17 | control with that entity. For the purposes of this definition,
18 | "control" means (i) the power, direct or indirect, to cause the
19 | direction or management of such entity, whether by contract or
20 | otherwise, or (ii) ownership of fifty percent (50%) or more of the
21 | outstanding shares, or (iii) beneficial ownership of such entity.
22 |
23 | "You" (or "Your") shall mean an individual or Legal Entity
24 | exercising permissions granted by this License.
25 |
26 | "Source" form shall mean the preferred form for making modifications,
27 | including but not limited to software source code, documentation
28 | source, and configuration files.
29 |
30 | "Object" form shall mean any form resulting from mechanical
31 | transformation or translation of a Source form, including but
32 | not limited to compiled object code, generated documentation,
33 | and conversions to other media types.
34 |
35 | "Work" shall mean the work of authorship, whether in Source or
36 | Object form, made available under the License, as indicated by a
37 | copyright notice that is included in or attached to the work
38 | (an example is provided in the Appendix below).
39 |
40 | "Derivative Works" shall mean any work, whether in Source or Object
41 | form, that is based on (or derived from) the Work and for which the
42 | editorial revisions, annotations, elaborations, or other modifications
43 | represent, as a whole, an original work of authorship. For the purposes
44 | of this License, Derivative Works shall not include works that remain
45 | separable from, or merely link (or bind by name) to the interfaces of,
46 | the Work and Derivative Works thereof.
47 |
48 | "Contribution" shall mean any work of authorship, including
49 | the original version of the Work and any modifications or additions
50 | to that Work or Derivative Works thereof, that is intentionally
51 | submitted to Licensor for inclusion in the Work by the copyright owner
52 | or by an individual or Legal Entity authorized to submit on behalf of
53 | the copyright owner. For the purposes of this definition, "submitted"
54 | means any form of electronic, verbal, or written communication sent
55 | to the Licensor or its representatives, including but not limited to
56 | communication on electronic mailing lists, source code control systems,
57 | and issue tracking systems that are managed by, or on behalf of, the
58 | Licensor for the purpose of discussing and improving the Work, but
59 | excluding communication that is conspicuously marked or otherwise
60 | designated in writing by the copyright owner as "Not a Contribution."
61 |
62 | "Contributor" shall mean Licensor and any individual or Legal Entity
63 | on behalf of whom a Contribution has been received by Licensor and
64 | subsequently incorporated within the Work.
65 |
66 | 2. Grant of Copyright License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
67 | this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
68 | worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
69 | copyright license to reproduce, prepare Derivative Works of,
70 | publicly display, publicly perform, sublicense, and distribute the
71 | Work and such Derivative Works in Source or Object form.
72 |
73 | 3. Grant of Patent License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
74 | this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
75 | worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
76 | (except as stated in this section) patent license to make, have made,
77 | use, offer to sell, sell, import, and otherwise transfer the Work,
78 | where such license applies only to those patent claims licensable
79 | by such Contributor that are necessarily infringed by their
80 | Contribution(s) alone or by combination of their Contribution(s)
81 | with the Work to which such Contribution(s) was submitted. If You
82 | institute patent litigation against any entity (including a
83 | cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that the Work
84 | or a Contribution incorporated within the Work constitutes direct
85 | or contributory patent infringement, then any patent licenses
86 | granted to You under this License for that Work shall terminate
87 | as of the date such litigation is filed.
88 |
89 | 4. Redistribution. You may reproduce and distribute copies of the
90 | Work or Derivative Works thereof in any medium, with or without
91 | modifications, and in Source or Object form, provided that You
92 | meet the following conditions:
93 |
94 | (a) You must give any other recipients of the Work or
95 | Derivative Works a copy of this License; and
96 |
97 | (b) You must cause any modified files to carry prominent notices
98 | stating that You changed the files; and
99 |
100 | (c) You must retain, in the Source form of any Derivative Works
101 | that You distribute, all copyright, patent, trademark, and
102 | attribution notices from the Source form of the Work,
103 | excluding those notices that do not pertain to any part of
104 | the Derivative Works; and
105 |
106 | (d) If the Work includes a "NOTICE" text file as part of its
107 | distribution, then any Derivative Works that You distribute must
108 | include a readable copy of the attribution notices contained
109 | within such NOTICE file, excluding those notices that do not
110 | pertain to any part of the Derivative Works, in at least one
111 | of the following places: within a NOTICE text file distributed
112 | as part of the Derivative Works; within the Source form or
113 | documentation, if provided along with the Derivative Works; or,
114 | within a display generated by the Derivative Works, if and
115 | wherever such third-party notices normally appear. The contents
116 | of the NOTICE file are for informational purposes only and
117 | do not modify the License. You may add Your own attribution
118 | notices within Derivative Works that You distribute, alongside
119 | or as an addendum to the NOTICE text from the Work, provided
120 | that such additional attribution notices cannot be construed
121 | as modifying the License.
122 |
123 | You may add Your own copyright statement to Your modifications and
124 | may provide additional or different license terms and conditions
125 | for use, reproduction, or distribution of Your modifications, or
126 | for any such Derivative Works as a whole, provided Your use,
127 | reproduction, and distribution of the Work otherwise complies with
128 | the conditions stated in this License.
129 |
130 | 5. Submission of Contributions. Unless You explicitly state otherwise,
131 | any Contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the Work
132 | by You to the Licensor shall be under the terms and conditions of
133 | this License, without any additional terms or conditions.
134 | Notwithstanding the above, nothing herein shall supersede or modify
135 | the terms of any separate license agreement you may have executed
136 | with Licensor regarding such Contributions.
137 |
138 | 6. Trademarks. This License does not grant permission to use the trade
139 | names, trademarks, service marks, or product names of the Licensor,
140 | except as required for reasonable and customary use in describing the
141 | origin of the Work and reproducing the content of the NOTICE file.
142 |
143 | 7. Disclaimer of Warranty. Unless required by applicable law or
144 | agreed to in writing, Licensor provides the Work (and each
145 | Contributor provides its Contributions) on an "AS IS" BASIS,
146 | WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or
147 | implied, including, without limitation, any warranties or conditions
148 | of TITLE, NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, or FITNESS FOR A
149 | PARTICULAR PURPOSE. You are solely responsible for determining the
150 | appropriateness of using or redistributing the Work and assume any
151 | risks associated with Your exercise of permissions under this License.
152 |
153 | 8. Limitation of Liability. In no event and under no legal theory,
154 | whether in tort (including negligence), contract, or otherwise,
155 | unless required by applicable law (such as deliberate and grossly
156 | negligent acts) or agreed to in writing, shall any Contributor be
157 | liable to You for damages, including any direct, indirect, special,
158 | incidental, or consequential damages of any character arising as a
159 | result of this License or out of the use or inability to use the
160 | Work (including but not limited to damages for loss of goodwill,
161 | work stoppage, computer failure or malfunction, or any and all
162 | other commercial damages or losses), even if such Contributor
163 | has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
164 |
165 | 9. Accepting Warranty or Additional Liability. While redistributing
166 | the Work or Derivative Works thereof, You may choose to offer,
167 | and charge a fee for, acceptance of support, warranty, indemnity,
168 | or other liability obligations and/or rights consistent with this
169 | License. However, in accepting such obligations, You may act only
170 | on Your own behalf and on Your sole responsibility, not on behalf
171 | of any other Contributor, and only if You agree to indemnify,
172 | defend, and hold each Contributor harmless for any liability
173 | incurred by, or claims asserted against, such Contributor by reason
174 | of your accepting any such warranty or additional liability.
175 |
176 | END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
177 |
178 | APPENDIX: How to apply the Apache License to your work.
179 |
180 | To apply the Apache License to your work, attach the following
181 | boilerplate notice, with the fields enclosed by brackets "{}"
182 | replaced with your own identifying information. (Don't include
183 | the brackets!) The text should be enclosed in the appropriate
184 | comment syntax for the file format. We also recommend that a
185 | file or class name and description of purpose be included on the
186 | same "printed page" as the copyright notice for easier
187 | identification within third-party archives.
188 |
189 | Copyright {yyyy} {name of copyright owner}
190 |
191 | Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
192 | you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
193 | You may obtain a copy of the License at
194 |
195 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
196 |
197 | Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
198 | distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
199 | WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
200 | See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
201 | limitations under the License.
202 |
203 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/lib/src/main/java/net/kibotu/kalmanrx/jkalman/JKalman.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*******************************************************************************
2 | * JKalman - KALMAN FILTER (Java)
3 | *
4 | * Copyright (C) 2007 Petr Chmelar
5 | *
6 | * By downloading, copying, installing or using the software you agree to
7 | * the license in licenseIntel.txt or in licenseGNU.txt
8 | *
9 | * ***************************************************************************
10 | */
11 |
12 | package net.kibotu.kalmanrx.jkalman;
13 |
14 | import net.kibotu.kalmanrx.jama.Matrix;
15 |
16 | /**
17 | * Kalman filter (state).
18 | *
19 | * The structure
23 | * Normally, the structure is used for standard JKalman filter
24 | * (notation and the formulae below are borrowed from the JKalman
25 | * tutorial [Welch95]):
26 | * where:
31 | *
43 | * In case of standard JKalman filter, all the matrices: A, B, H, Q and R
44 | * are initialized once after JKalman structure is allocated via constructor.
45 | * However, the same structure and the same functions may be used to simulate
46 | * extended JKalman filter by linearizing extended JKalman filter equation in the
47 | * current system state neighborhood, in this case A, B, H (and, probably,
48 | * Q and R) should be updated on every step.
49 | */
50 | public class JKalman {
51 |
52 | /**
53 | * number of measurement vector dimensions
54 | */
55 | int mp;
56 | /**
57 | * number of state vector dimensions
58 | */
59 | int dp;
60 | /**
61 | * number of control vector dimensions
62 | */
63 | int cp;
64 |
65 | /**
66 | * predicted state (x'(k)): x(k)=A*x(k-1)+B*u(k)
67 | */
68 | Matrix state_pre;
69 | /**
70 | * corrected state (x(k)): x(k)=x'(k)+K(k)*(z(k)-H*x'(k))
71 | */
72 | Matrix state_post;
73 | /**
74 | * state transition matrix (A)
75 | */
76 | Matrix transition_matrix;
77 | /**
78 | * control matrix (B) (it is not used if there is no control)
79 | */
80 | Matrix control_matrix;
81 | /**
82 | * measurement matrix (H)
83 | */
84 | Matrix measurement_matrix;
85 | /**
86 | * process noise covariance matrix (Q)
87 | */
88 | Matrix process_noise_cov;
89 | /**
90 | * measurement noise covariance matrix (R)
91 | */
92 | Matrix measurement_noise_cov;
93 | /**
94 | * priori error estimate covariance matrix (P'(k)): P'(k)=A*P(k-1)*At + Q)
95 | */
96 | Matrix error_cov_pre;
97 | /**
98 | * Kalman gain matrix (K(k)): K(k)=P'(k)*Ht*inv(H*P'(k)*Ht+R)
99 | */
100 | Matrix gain;
101 | /**
102 | * posteriori error estimate covariance matrix (P(k)): P(k)=(I-K(k)*H)*P'(k)
103 | */
104 | Matrix error_cov_post;
105 |
106 | /**
107 | * temporary matrices
108 | */
109 | Matrix temp1;
110 | Matrix temp2;
111 | Matrix temp3;
112 | Matrix temp4;
113 | Matrix temp5;
114 |
115 | /**
116 | * The construstor allocates JKalman filter and all its matrices and
117 | * initializes them somehow.
118 | *
119 | * @param dynam_params
120 | * @param measure_params
121 | * @param control_params
122 | * @throws IllegalArgumentException Kalman filter dimensions exception.
123 | */
124 | public JKalman(int dynam_params, int measure_params, int control_params)
125 | throws IllegalArgumentException {
126 |
127 | if (dynam_params <= 0 || measure_params <= 0) {
128 | throw new IllegalArgumentException("Kalman filter: Illegal dimensions.");
129 | }
130 |
131 | if (control_params < 0) {
132 | control_params = dynam_params;
133 | }
134 |
135 | // init
136 | dp = dynam_params;
137 | mp = measure_params;
138 | cp = control_params;
139 |
140 | state_pre = new Matrix(dp, 1); // init by transition _matrix*state_post
141 |
142 | // following variables must be initialized properly in advance
143 | state_post = new Matrix(dp, 1); // init by the first measurement!!!
144 | transition_matrix = Matrix.identity(dp, dp); // or init the matrix as:
145 | /* double[][] tr = { {1, 0, 1, 0}, // { {1, 1}, // x
146 | {0, 1, 0, 1}, // {0, 1} }; // dx
147 | {0, 0, 1, 0},
148 | {0, 0, 0, 1} };
149 | kalman.transition_matrix = new Matrix(tr);
150 | */
151 | process_noise_cov = Matrix.identity(dp, dp, 1e-3); // 1e-5 (1 in OpenCV)
152 |
153 | measurement_matrix = Matrix.identity(mp, dp); // 1 (0 in OpenCV)
154 | measurement_noise_cov = Matrix.identity(mp, mp, 1e-1); // 1e-1 (1 in OpenCV)
155 |
156 | error_cov_pre = new Matrix(dp, dp); // initialized in Predict
157 | error_cov_post = Matrix.identity(dp, dp); // 1 (0 in OpenCV)
158 |
159 | gain = new Matrix(dp, mp);
160 |
161 | if (cp > 0) {
162 | control_matrix = new Matrix(dp, cp);
163 | } else { // TODO possibly an error in OpenCV
164 | control_matrix = null;
165 | }
166 |
167 | temp1 = new Matrix(dp, dp);
168 | temp2 = new Matrix(mp, dp);
169 | temp3 = new Matrix(mp, mp);
170 | temp4 = new Matrix(mp, dp);
171 | temp5 = new Matrix(mp, 1);
172 | }
173 |
174 | /**
175 | * Constructor in case of no control.
176 | *
177 | * @param dynam_params
178 | * @param measure_params
179 | */
180 | public JKalman(int dynam_params, int measure_params) throws IllegalArgumentException {
181 | this(dynam_params, measure_params, 0);
182 | }
183 |
184 |
185 | /**
186 | * Alias for prediction with no control.
187 | *
188 | * @return Predict(no control).
189 | */
190 | public Matrix Predict() {
191 | return Predict(null);
192 | }
193 |
194 | /**
195 | * Estimates subsequent model state.
196 | * The function estimates the subsequent
197 | * stochastic model state by its current state and stores it at
198 | * JKalman is used to keep
20 | * Kalman filter state. It is created by constructor function, updated by
21 | * Predict and Correct functions.
22 | *
27 | * xk=A*xk-1+B*uk+wk
28 | * zk=Hxk+vk,
29 | *
30 | *
32 | * xk (xk-1) - state of the system at the moment k (k-1)
33 | * zk - measurement of the system state at the moment k
34 | * uk - external control applied at the moment k
35 | * wk and vk are normally-distributed process and measurement noise, respectively:
36 | * p(w) ~ N(0,Q)
37 | * p(v) ~ N(0,R),
38 | * that is,
39 | * Q - process noise covariance matrix, constant or variable,
40 | * R - measurement noise covariance matrix, constant or variable
41 | *
42 | * state_pre:
199 | *
200 | * x'k=A*xk+B*uk
201 | * P'k=A*Pk-1*AT + Q,
202 | * where
203 | * x'k is predicted state (state_pre),
204 | * xk-1 is corrected state on the previous step (state_post)
205 | * (should be initialized somehow in the beginning, zero vector by default),
206 | * uk is external control (
211 | *
212 | * @param control Control vector (uk), should be NULL if there
213 | * is no external control (control parameter),
207 | * P'k is prior error covariance matrix (error_cov_pre)
208 | * Pk-1 is posteriori error covariance matrix on the previous step (error_cov_post)
209 | * (should be initialized somehow in the beginning, identity matrix by default),
210 | * control_params=0).
214 | * @return The function returns the estimated state.
215 | */
216 | public Matrix Predict(Matrix control) {
217 |
218 | // (1) Project the state ahead
219 | // update the state: x'(k) = A*x(k)
220 | state_pre = transition_matrix.times(state_post);
221 | if (control != null && cp > 0) {
222 | // x'(k) = x'(k) + B*u(k)
223 | state_pre = control_matrix.gemm(control, state_pre, 1, 1);
224 | }
225 |
226 | // (2) Project the error covariance ahead
227 | // update error covariance matrices: temp1 = A*P(k)
228 | temp1 = transition_matrix.times(error_cov_post);
229 | // P'(k) = temp1*At + Q
230 | error_cov_pre = temp1.gemm(transition_matrix.transpose(), process_noise_cov, 1, 1);
231 |
232 | return state_pre;
233 | }
234 |
235 | /**
236 | * Adjusts model state.
237 | * The function KalmanCorrect adjusts stochastic model state
238 | * on the basis of the given measurement of the model state:
240 | * Kk=P'k*HT*(H*P'k*HT+R)-1
241 | * xk=x'k+Kk*(zk-H*x'k)
242 | * Pk=(I-Kk*H)*P'k
243 | * where
244 | * zk - given measurement (mesurement parameter)
245 | * Kk - JKalman "gain" matrix.
246 | *
247 | * The function stores adjusted state at state_post and
248 | * returns it on output.
249 | *
250 | * @param measurement Matrix containing the measurement vector.
251 | * @return
252 | */
253 | public Matrix Correct(final Matrix measurement) {
254 |
255 | // (1) Compute the Kalman gain
256 | // temp2 = H*P'(k)
257 | temp2 = measurement_matrix.times(error_cov_pre);
258 |
259 | // temp3 = temp2*Ht + R
260 | temp3 = temp2.gemm(measurement_matrix.transpose(), measurement_noise_cov, 1, 1);
261 |
262 | // temp4 = inv(temp3)*temp2 = Kt(k)
263 | temp4 = temp3.solve(temp2);
264 | // hokus pokus...
265 | // temp4 = temp3.svd().getU().times(temp2);
266 |
267 | // K(k)
268 | gain = temp4.transpose();
269 |
270 | // (2) Update estimate with measurement z(k)
271 | // temp5 = z(k) - H*x'(k)
272 | temp5 = measurement_matrix.gemm(state_pre, measurement, -1, 1);
273 |
274 | // x(k) = x'(k) + K(k)*temp5
275 | state_post = gain.gemm(temp5, state_pre, 1, 1);
276 |
277 | // (3) Update the error covariance.
278 | // P(k) = P'(k) - K(k)*temp2
279 | error_cov_post = gain.gemm(temp2, error_cov_pre, -1, 1);
280 |
281 | return state_post;
282 | }
283 |
284 | /**
285 | * Setter
286 | *
287 | * @param state_pre
288 | */
289 | public void setState_pre(Matrix state_pre) {
290 | this.state_pre = state_pre;
291 | }
292 |
293 | /**
294 | * Getter
295 | *
296 | * @return
297 | */
298 | public Matrix getState_pre() {
299 | return state_pre;
300 | }
301 |
302 | /**
303 | * Setter
304 | *
305 | * @param state_post
306 | */
307 | public void setState_post(Matrix state_post) {
308 | this.state_post = state_post;
309 | }
310 |
311 | public Matrix getState_post() {
312 | return state_post;
313 | }
314 |
315 | /**
316 | * Getter
317 | *
318 | * @param transition_matrix
319 | */
320 | public void setTransition_matrix(Matrix transition_matrix) {
321 | this.transition_matrix = transition_matrix;
322 | }
323 |
324 | public Matrix getTransition_matrix() {
325 | return transition_matrix;
326 | }
327 |
328 | /**
329 | * Setter
330 | *
331 | * @param control_matrix
332 | */
333 | public void setControl_matrix(Matrix control_matrix) {
334 | this.control_matrix = control_matrix;
335 | }
336 |
337 | /**
338 | * Getter
339 | *
340 | * @return
341 | */
342 | public Matrix getControl_matrix() {
343 | return control_matrix;
344 | }
345 |
346 | /**
347 | * Setter
348 | *
349 | * @param measurement_matrix
350 | */
351 | public void setMeasurement_matrix(Matrix measurement_matrix) {
352 | this.measurement_matrix = measurement_matrix;
353 | }
354 |
355 | /**
356 | * Getter
357 | *
358 | * @return
359 | */
360 | public Matrix getMeasurement_matrix() {
361 | return measurement_matrix;
362 | }
363 |
364 | /**
365 | * Setter
366 | *
367 | * @param process_noise_cov
368 | */
369 | public void setProcess_noise_cov(Matrix process_noise_cov) {
370 | this.process_noise_cov = process_noise_cov;
371 | }
372 |
373 | /**
374 | * Getter
375 | *
376 | * @return
377 | */
378 | public Matrix getProcess_noise_cov() {
379 | return process_noise_cov;
380 | }
381 |
382 | /**
383 | * Setter
384 | *
385 | * @param measurement_noise_cov
386 | */
387 | public void setMeasurement_noise_cov(Matrix measurement_noise_cov) {
388 | this.measurement_noise_cov = measurement_noise_cov;
389 | }
390 |
391 | /**
392 | * Getter
393 | *
394 | * @return
395 | */
396 | public Matrix getMeasurement_noise_cov() {
397 | return measurement_noise_cov;
398 | }
399 |
400 | /**
401 | * Setter
402 | *
403 | * @param error_cov_pre
404 | */
405 | public void setError_cov_pre(Matrix error_cov_pre) {
406 | this.error_cov_pre = error_cov_pre;
407 | }
408 |
409 | /**
410 | * Getter
411 | *
412 | * @return
413 | */
414 | public Matrix getError_cov_pre() {
415 | return error_cov_pre;
416 | }
417 |
418 | /**
419 | * Setter
420 | *
421 | * @param gain
422 | */
423 | public void setGain(Matrix gain) {
424 | this.gain = gain;
425 | }
426 |
427 | /**
428 | * Getter
429 | *
430 | * @return
431 | */
432 | public Matrix getGain() {
433 | return gain;
434 | }
435 |
436 | /**
437 | * Setter
438 | *
439 | * @param error_cov_post
440 | */
441 | public void setError_cov_post(Matrix error_cov_post) {
442 | this.error_cov_post = error_cov_post;
443 | }
444 |
445 | /**
446 | * Getter
447 | *
448 | * @return
449 | */
450 | public Matrix getError_cov_post() {
451 | return error_cov_post;
452 | }
453 | }
454 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/lib/src/main/java/net/kibotu/kalmanrx/jama/SingularValueDecomposition.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package net.kibotu.kalmanrx.jama;
2 |
3 | import net.kibotu.kalmanrx.jama.util.Maths;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | * Singular Value Decomposition.
7 | *
8 | * For an m-by-n matrix A with m >= n, the singular value decomposition is 9 | * an m-by-n orthogonal matrix U, an n-by-n diagonal matrix S, and 10 | * an n-by-n orthogonal matrix V so that A = U*S*V'. 11 | *
12 | * The singular values, sigma[k] = S[k][k], are ordered so that 13 | * sigma[0] >= sigma[1] >= ... >= sigma[n-1]. 14 | *
15 | * The singular value decompostion always exists, so the constructor will
16 | * never fail. The matrix condition number and the effective numerical
17 | * rank can be computed from this decomposition.
18 | */
19 |
20 | public class SingularValueDecomposition implements java.io.Serializable {
21 |
22 | /* ------------------------
23 | Class variables
24 | * ------------------------ */
25 |
26 | /**
27 | * Arrays for internal storage of U and V.
28 | *
29 | * @serial internal storage of U.
30 | * @serial internal storage of V.
31 | */
32 | private double[][] U, V;
33 |
34 | /**
35 | * Array for internal storage of singular values.
36 | *
37 | * @serial internal storage of singular values.
38 | */
39 | private double[] s;
40 |
41 | /**
42 | * Row and column dimensions.
43 | *
44 | * @serial row dimension.
45 | * @serial column dimension.
46 | */
47 | private int m, n;
48 |
49 | /* ------------------------
50 | Constructor
51 | * ------------------------ */
52 |
53 | /**
54 | * Construct the singular value decomposition
55 | *
56 | * @param A Rectangular matrix
57 | * @return Structure to access U, S and V.
58 | */
59 |
60 | public SingularValueDecomposition(Matrix Arg) {
61 |
62 | // Derived from LINPACK code.
63 | // Initialize.
64 | double[][] A = Arg.getArrayCopy();
65 | m = Arg.getRowDimension();
66 | n = Arg.getColumnDimension();
67 |
68 | /* Apparently the failing cases are only a proper subset of (m = -1; k--) {
283 | if (k == -1) {
284 | break;
285 | }
286 | if (Math.abs(e[k]) <=
287 | tiny + eps * (Math.abs(s[k]) + Math.abs(s[k + 1]))) {
288 | e[k] = 0.0;
289 | break;
290 | }
291 | }
292 | if (k == p - 2) {
293 | kase = 4;
294 | } else {
295 | int ks;
296 | for (ks = p - 1; ks >= k; ks--) {
297 | if (ks == k) {
298 | break;
299 | }
300 | double t = (ks != p ? Math.abs(e[ks]) : 0.) +
301 | (ks != k + 1 ? Math.abs(e[ks - 1]) : 0.);
302 | if (Math.abs(s[ks]) <= tiny + eps * t) {
303 | s[ks] = 0.0;
304 | break;
305 | }
306 | }
307 | if (ks == k) {
308 | kase = 3;
309 | } else if (ks == p - 1) {
310 | kase = 1;
311 | } else {
312 | kase = 2;
313 | k = ks;
314 | }
315 | }
316 | k++;
317 |
318 | // Perform the task indicated by kase.
319 |
320 | switch (kase) {
321 |
322 | // Deflate negligible s(p).
323 |
324 | case 1: {
325 | double f = e[p - 2];
326 | e[p - 2] = 0.0;
327 | for (int j = p - 2; j >= k; j--) {
328 | double t = Maths.hypot(s[j], f);
329 | double cs = s[j] / t;
330 | double sn = f / t;
331 | s[j] = t;
332 | if (j != k) {
333 | f = -sn * e[j - 1];
334 | e[j - 1] = cs * e[j - 1];
335 | }
336 | if (wantv) {
337 | for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
338 | t = cs * V[i][j] + sn * V[i][p - 1];
339 | V[i][p - 1] = -sn * V[i][j] + cs * V[i][p - 1];
340 | V[i][j] = t;
341 | }
342 | }
343 | }
344 | }
345 | break;
346 |
347 | // Split at negligible s(k).
348 |
349 | case 2: {
350 | double f = e[k - 1];
351 | e[k - 1] = 0.0;
352 | for (int j = k; j < p; j++) {
353 | double t = Maths.hypot(s[j], f);
354 | double cs = s[j] / t;
355 | double sn = f / t;
356 | s[j] = t;
357 | f = -sn * e[j];
358 | e[j] = cs * e[j];
359 | if (wantu) {
360 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
361 | t = cs * U[i][j] + sn * U[i][k - 1];
362 | U[i][k - 1] = -sn * U[i][j] + cs * U[i][k - 1];
363 | U[i][j] = t;
364 | }
365 | }
366 | }
367 | }
368 | break;
369 |
370 | // Perform one qr step.
371 |
372 | case 3: {
373 |
374 | // Calculate the shift.
375 |
376 | double scale = Math.max(Math.max(Math.max(Math.max(
377 | Math.abs(s[p - 1]), Math.abs(s[p - 2])), Math.abs(e[p - 2])),
378 | Math.abs(s[k])), Math.abs(e[k]));
379 | double sp = s[p - 1] / scale;
380 | double spm1 = s[p - 2] / scale;
381 | double epm1 = e[p - 2] / scale;
382 | double sk = s[k] / scale;
383 | double ek = e[k] / scale;
384 | double b = ((spm1 + sp) * (spm1 - sp) + epm1 * epm1) / 2.0;
385 | double c = (sp * epm1) * (sp * epm1);
386 | double shift = 0.0;
387 | if ((b != 0.0) | (c != 0.0)) {
388 | shift = Math.sqrt(b * b + c);
389 | if (b < 0.0) {
390 | shift = -shift;
391 | }
392 | shift = c / (b + shift);
393 | }
394 | double f = (sk + sp) * (sk - sp) + shift;
395 | double g = sk * ek;
396 |
397 | // Chase zeros.
398 |
399 | for (int j = k; j < p - 1; j++) {
400 | double t = Maths.hypot(f, g);
401 | double cs = f / t;
402 | double sn = g / t;
403 | if (j != k) {
404 | e[j - 1] = t;
405 | }
406 | f = cs * s[j] + sn * e[j];
407 | e[j] = cs * e[j] - sn * s[j];
408 | g = sn * s[j + 1];
409 | s[j + 1] = cs * s[j + 1];
410 | if (wantv) {
411 | for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
412 | t = cs * V[i][j] + sn * V[i][j + 1];
413 | V[i][j + 1] = -sn * V[i][j] + cs * V[i][j + 1];
414 | V[i][j] = t;
415 | }
416 | }
417 | t = Maths.hypot(f, g);
418 | cs = f / t;
419 | sn = g / t;
420 | s[j] = t;
421 | f = cs * e[j] + sn * s[j + 1];
422 | s[j + 1] = -sn * e[j] + cs * s[j + 1];
423 | g = sn * e[j + 1];
424 | e[j + 1] = cs * e[j + 1];
425 | if (wantu && (j < m - 1)) {
426 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
427 | t = cs * U[i][j] + sn * U[i][j + 1];
428 | U[i][j + 1] = -sn * U[i][j] + cs * U[i][j + 1];
429 | U[i][j] = t;
430 | }
431 | }
432 | }
433 | e[p - 2] = f;
434 | iter = iter + 1;
435 | }
436 | break;
437 |
438 | // Convergence.
439 |
440 | case 4: {
441 |
442 | // Make the singular values positive.
443 |
444 | if (s[k] <= 0.0) {
445 | s[k] = (s[k] < 0.0 ? -s[k] : 0.0);
446 | if (wantv) {
447 | for (int i = 0; i <= pp; i++) {
448 | V[i][k] = -V[i][k];
449 | }
450 | }
451 | }
452 |
453 | // Order the singular values.
454 |
455 | while (k < pp) {
456 | if (s[k] >= s[k + 1]) {
457 | break;
458 | }
459 | double t = s[k];
460 | s[k] = s[k + 1];
461 | s[k + 1] = t;
462 | if (wantv && (k < n - 1)) {
463 | for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
464 | t = V[i][k + 1];
465 | V[i][k + 1] = V[i][k];
466 | V[i][k] = t;
467 | }
468 | }
469 | if (wantu && (k < m - 1)) {
470 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
471 | t = U[i][k + 1];
472 | U[i][k + 1] = U[i][k];
473 | U[i][k] = t;
474 | }
475 | }
476 | k++;
477 | }
478 | iter = 0;
479 | p--;
480 | }
481 | break;
482 | }
483 | }
484 | }
485 |
486 | /* ------------------------
487 | Public Methods
488 | * ------------------------ */
489 |
490 | /**
491 | * Return the left singular vectors
492 | *
493 | * @return U
494 | */
495 |
496 | public Matrix getU() {
497 | return new Matrix(U, m, Math.min(m + 1, n));
498 | }
499 |
500 | /**
501 | * Return the right singular vectors
502 | *
503 | * @return V
504 | */
505 |
506 | public Matrix getV() {
507 | return new Matrix(V, n, n);
508 | }
509 |
510 | /**
511 | * Return the one-dimensional array of singular values
512 | *
513 | * @return diagonal of S.
514 | */
515 |
516 | public double[] getSingularValues() {
517 | return s;
518 | }
519 |
520 | /**
521 | * Return the diagonal matrix of singular values
522 | *
523 | * @return S
524 | */
525 |
526 | public Matrix getS() {
527 | Matrix X = new Matrix(n, n);
528 | double[][] S = X.getArray();
529 | for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
530 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
531 | S[i][j] = 0.0;
532 | }
533 | S[i][i] = this.s[i];
534 | }
535 | return X;
536 | }
537 |
538 | /**
539 | * Two norm
540 | *
541 | * @return max(S)
542 | */
543 |
544 | public double norm2() {
545 | return s[0];
546 | }
547 |
548 | /**
549 | * Two norm condition number
550 | *
551 | * @return max(S)/min(S)
552 | */
553 |
554 | public double cond() {
555 | return s[0] / s[Math.min(m, n) - 1];
556 | }
557 |
558 | /**
559 | * Effective numerical matrix rank
560 | *
561 | * @return Number of nonnegligible singular values.
562 | */
563 |
564 | public int rank() {
565 | double eps = Math.pow(2.0, -52.0);
566 | double tol = Math.max(m, n) * s[0] * eps;
567 | int r = 0;
568 | for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
569 | if (s[i] > tol) {
570 | r++;
571 | }
572 | }
573 | return r;
574 | }
575 | }
576 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/lib/src/main/java/net/kibotu/kalmanrx/jama/EigenValueDecomposition.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package net.kibotu.kalmanrx.jama;
2 |
3 | import net.kibotu.kalmanrx.jama.util.Maths;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | * Eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a real matrix.
7 | *
8 | * If A is symmetric, then A = V*D*V' where the eigenvalue matrix D is
9 | * diagonal and the eigenvector matrix V is orthogonal.
10 | * I.e. A = V.times(D.times(V.transpose())) and
11 | * V.times(V.transpose()) equals the identity matrix.
12 | *
13 | * If A is not symmetric, then the eigenvalue matrix D is block diagonal
14 | * with the real eigenvalues in 1-by-1 blocks and any complex eigenvalues,
15 | * lambda + i*mu, in 2-by-2 blocks, [lambda, mu; -mu, lambda]. The
16 | * columns of V represent the eigenvectors in the sense that A*V = V*D,
17 | * i.e. A.times(V) equals V.times(D). The matrix V may be badly
18 | * conditioned, or even singular, so the validity of the equation
19 | * A = V*D*inverse(V) depends upon V.cond().
20 | **/
21 |
22 | public class EigenValueDecomposition implements java.io.Serializable {
23 |
24 | /* ------------------------
25 | Class variables
26 | * ------------------------ */
27 |
28 | /**
29 | * Row and column dimension (square matrix).
30 | *
31 | * @serial matrix dimension.
32 | */
33 | private int n;
34 |
35 | /**
36 | * Symmetry flag.
37 | *
38 | * @serial internal symmetry flag.
39 | */
40 | private boolean issymmetric;
41 |
42 | /**
43 | * Arrays for internal storage of eigenvalues.
44 | *
45 | * @serial internal storage of eigenvalues.
46 | */
47 | private double[] d, e;
48 |
49 | /**
50 | * Array for internal storage of eigenvectors.
51 | *
52 | * @serial internal storage of eigenvectors.
53 | */
54 | private double[][] V;
55 |
56 | /**
57 | * Array for internal storage of nonsymmetric Hessenberg form.
58 | *
59 | * @serial internal storage of nonsymmetric Hessenberg form.
60 | */
61 | private double[][] H;
62 |
63 | /**
64 | * Working storage for nonsymmetric algorithm.
65 | *
66 | * @serial working storage for nonsymmetric algorithm.
67 | */
68 | private double[] ort;
69 |
70 | /* ------------------------
71 | Private Methods
72 | * ------------------------ */
73 |
74 | // Symmetric Householder reduction to tridiagonal form.
75 |
76 | private void tred2() {
77 |
78 | // This is derived from the Algol procedures tred2 by
79 | // Bowdler, Martin, Reinsch, and Wilkinson, Handbook for
80 | // Auto. Comp., Vol.ii-Linear Algebra, and the corresponding
81 | // Fortran subroutine in EISPACK.
82 |
83 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
84 | d[j] = V[n - 1][j];
85 | }
86 |
87 | // Householder reduction to tridiagonal form.
88 |
89 | for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i--) {
90 |
91 | // Scale to avoid under/overflow.
92 |
93 | double scale = 0.0;
94 | double h = 0.0;
95 | for (int k = 0; k < i; k++) {
96 | scale = scale + Math.abs(d[k]);
97 | }
98 | if (scale == 0.0) {
99 | e[i] = d[i - 1];
100 | for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
101 | d[j] = V[i - 1][j];
102 | V[i][j] = 0.0;
103 | V[j][i] = 0.0;
104 | }
105 | } else {
106 |
107 | // Generate Householder vector.
108 |
109 | for (int k = 0; k < i; k++) {
110 | d[k] /= scale;
111 | h += d[k] * d[k];
112 | }
113 | double f = d[i - 1];
114 | double g = Math.sqrt(h);
115 | if (f > 0) {
116 | g = -g;
117 | }
118 | e[i] = scale * g;
119 | h = h - f * g;
120 | d[i - 1] = f - g;
121 | for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
122 | e[j] = 0.0;
123 | }
124 |
125 | // Apply similarity transformation to remaining columns.
126 |
127 | for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
128 | f = d[j];
129 | V[j][i] = f;
130 | g = e[j] + V[j][j] * f;
131 | for (int k = j + 1; k <= i - 1; k++) {
132 | g += V[k][j] * d[k];
133 | e[k] += V[k][j] * f;
134 | }
135 | e[j] = g;
136 | }
137 | f = 0.0;
138 | for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
139 | e[j] /= h;
140 | f += e[j] * d[j];
141 | }
142 | double hh = f / (h + h);
143 | for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
144 | e[j] -= hh * d[j];
145 | }
146 | for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
147 | f = d[j];
148 | g = e[j];
149 | for (int k = j; k <= i - 1; k++) {
150 | V[k][j] -= (f * e[k] + g * d[k]);
151 | }
152 | d[j] = V[i - 1][j];
153 | V[i][j] = 0.0;
154 | }
155 | }
156 | d[i] = h;
157 | }
158 |
159 | // Accumulate transformations.
160 |
161 | for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
162 | V[n - 1][i] = V[i][i];
163 | V[i][i] = 1.0;
164 | double h = d[i + 1];
165 | if (h != 0.0) {
166 | for (int k = 0; k <= i; k++) {
167 | d[k] = V[k][i + 1] / h;
168 | }
169 | for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
170 | double g = 0.0;
171 | for (int k = 0; k <= i; k++) {
172 | g += V[k][i + 1] * V[k][j];
173 | }
174 | for (int k = 0; k <= i; k++) {
175 | V[k][j] -= g * d[k];
176 | }
177 | }
178 | }
179 | for (int k = 0; k <= i; k++) {
180 | V[k][i + 1] = 0.0;
181 | }
182 | }
183 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
184 | d[j] = V[n - 1][j];
185 | V[n - 1][j] = 0.0;
186 | }
187 | V[n - 1][n - 1] = 1.0;
188 | e[0] = 0.0;
189 | }
190 |
191 | // Symmetric tridiagonal QL algorithm.
192 |
193 | private void tql2() {
194 |
195 | // This is derived from the Algol procedures tql2, by
196 | // Bowdler, Martin, Reinsch, and Wilkinson, Handbook for
197 | // Auto. Comp., Vol.ii-Linear Algebra, and the corresponding
198 | // Fortran subroutine in EISPACK.
199 |
200 | for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
201 | e[i - 1] = e[i];
202 | }
203 | e[n - 1] = 0.0;
204 |
205 | double f = 0.0;
206 | double tst1 = 0.0;
207 | double eps = Math.pow(2.0, -52.0);
208 | for (int l = 0; l < n; l++) {
209 |
210 | // Find small subdiagonal element
211 |
212 | tst1 = Math.max(tst1, Math.abs(d[l]) + Math.abs(e[l]));
213 | int m = l;
214 | while (m < n) {
215 | if (Math.abs(e[m]) <= eps * tst1) {
216 | break;
217 | }
218 | m++;
219 | }
220 |
221 | // If m == l, d[l] is an eigenvalue,
222 | // otherwise, iterate.
223 |
224 | if (m > l) {
225 | int iter = 0;
226 | do {
227 | iter = iter + 1; // (Could check iteration count here.)
228 |
229 | // Compute implicit shift
230 |
231 | double g = d[l];
232 | double p = (d[l + 1] - g) / (2.0 * e[l]);
233 | double r = Maths.hypot(p, 1.0);
234 | if (p < 0) {
235 | r = -r;
236 | }
237 | d[l] = e[l] / (p + r);
238 | d[l + 1] = e[l] * (p + r);
239 | double dl1 = d[l + 1];
240 | double h = g - d[l];
241 | for (int i = l + 2; i < n; i++) {
242 | d[i] -= h;
243 | }
244 | f = f + h;
245 |
246 | // Implicit QL transformation.
247 |
248 | p = d[m];
249 | double c = 1.0;
250 | double c2 = c;
251 | double c3 = c;
252 | double el1 = e[l + 1];
253 | double s = 0.0;
254 | double s2 = 0.0;
255 | for (int i = m - 1; i >= l; i--) {
256 | c3 = c2;
257 | c2 = c;
258 | s2 = s;
259 | g = c * e[i];
260 | h = c * p;
261 | r = Maths.hypot(p, e[i]);
262 | e[i + 1] = s * r;
263 | s = e[i] / r;
264 | c = p / r;
265 | p = c * d[i] - s * g;
266 | d[i + 1] = h + s * (c * g + s * d[i]);
267 |
268 | // Accumulate transformation.
269 |
270 | for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
271 | h = V[k][i + 1];
272 | V[k][i + 1] = s * V[k][i] + c * h;
273 | V[k][i] = c * V[k][i] - s * h;
274 | }
275 | }
276 | p = -s * s2 * c3 * el1 * e[l] / dl1;
277 | e[l] = s * p;
278 | d[l] = c * p;
279 |
280 | // Check for convergence.
281 |
282 | } while (Math.abs(e[l]) > eps * tst1);
283 | }
284 | d[l] = d[l] + f;
285 | e[l] = 0.0;
286 | }
287 |
288 | // Sort eigenvalues and corresponding vectors.
289 |
290 | for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
291 | int k = i;
292 | double p = d[i];
293 | for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
294 | if (d[j] < p) {
295 | k = j;
296 | p = d[j];
297 | }
298 | }
299 | if (k != i) {
300 | d[k] = d[i];
301 | d[i] = p;
302 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
303 | p = V[j][i];
304 | V[j][i] = V[j][k];
305 | V[j][k] = p;
306 | }
307 | }
308 | }
309 | }
310 |
311 | // Nonsymmetric reduction to Hessenberg form.
312 |
313 | private void orthes() {
314 |
315 | // This is derived from the Algol procedures orthes and ortran,
316 | // by Martin and Wilkinson, Handbook for Auto. Comp.,
317 | // Vol.ii-Linear Algebra, and the corresponding
318 | // Fortran subroutines in EISPACK.
319 |
320 | int low = 0;
321 | int high = n - 1;
322 |
323 | for (int m = low + 1; m <= high - 1; m++) {
324 |
325 | // Scale column.
326 |
327 | double scale = 0.0;
328 | for (int i = m; i <= high; i++) {
329 | scale = scale + Math.abs(H[i][m - 1]);
330 | }
331 | if (scale != 0.0) {
332 |
333 | // Compute Householder transformation.
334 |
335 | double h = 0.0;
336 | for (int i = high; i >= m; i--) {
337 | ort[i] = H[i][m - 1] / scale;
338 | h += ort[i] * ort[i];
339 | }
340 | double g = Math.sqrt(h);
341 | if (ort[m] > 0) {
342 | g = -g;
343 | }
344 | h = h - ort[m] * g;
345 | ort[m] = ort[m] - g;
346 |
347 | // Apply Householder similarity transformation
348 | // H = (I-u*u'/h)*H*(I-u*u')/h)
349 |
350 | for (int j = m; j < n; j++) {
351 | double f = 0.0;
352 | for (int i = high; i >= m; i--) {
353 | f += ort[i] * H[i][j];
354 | }
355 | f = f / h;
356 | for (int i = m; i <= high; i++) {
357 | H[i][j] -= f * ort[i];
358 | }
359 | }
360 |
361 | for (int i = 0; i <= high; i++) {
362 | double f = 0.0;
363 | for (int j = high; j >= m; j--) {
364 | f += ort[j] * H[i][j];
365 | }
366 | f = f / h;
367 | for (int j = m; j <= high; j++) {
368 | H[i][j] -= f * ort[j];
369 | }
370 | }
371 | ort[m] = scale * ort[m];
372 | H[m][m - 1] = scale * g;
373 | }
374 | }
375 |
376 | // Accumulate transformations (Algol's ortran).
377 |
378 | for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
379 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
380 | V[i][j] = (i == j ? 1.0 : 0.0);
381 | }
382 | }
383 |
384 | for (int m = high - 1; m >= low + 1; m--) {
385 | if (H[m][m - 1] != 0.0) {
386 | for (int i = m + 1; i <= high; i++) {
387 | ort[i] = H[i][m - 1];
388 | }
389 | for (int j = m; j <= high; j++) {
390 | double g = 0.0;
391 | for (int i = m; i <= high; i++) {
392 | g += ort[i] * V[i][j];
393 | }
394 | // Double division avoids possible underflow
395 | g = (g / ort[m]) / H[m][m - 1];
396 | for (int i = m; i <= high; i++) {
397 | V[i][j] += g * ort[i];
398 | }
399 | }
400 | }
401 | }
402 | }
403 |
404 |
405 | // Complex scalar division.
406 |
407 | private transient double cdivr, cdivi;
408 |
409 | private void cdiv(double xr, double xi, double yr, double yi) {
410 | double r, d;
411 | if (Math.abs(yr) > Math.abs(yi)) {
412 | r = yi / yr;
413 | d = yr + r * yi;
414 | cdivr = (xr + r * xi) / d;
415 | cdivi = (xi - r * xr) / d;
416 | } else {
417 | r = yr / yi;
418 | d = yi + r * yr;
419 | cdivr = (r * xr + xi) / d;
420 | cdivi = (r * xi - xr) / d;
421 | }
422 | }
423 |
424 |
425 | // Nonsymmetric reduction from Hessenberg to real Schur form.
426 |
427 | private void hqr2() {
428 |
429 | // This is derived from the Algol procedure hqr2,
430 | // by Martin and Wilkinson, Handbook for Auto. Comp.,
431 | // Vol.ii-Linear Algebra, and the corresponding
432 | // Fortran subroutine in EISPACK.
433 |
434 | // Initialize
435 |
436 | int nn = this.n;
437 | int n = nn - 1;
438 | int low = 0;
439 | int high = nn - 1;
440 | double eps = Math.pow(2.0, -52.0);
441 | double exshift = 0.0;
442 | double p = 0, q = 0, r = 0, s = 0, z = 0, t, w, x, y;
443 |
444 | // Store roots isolated by balanc and compute matrix norm
445 |
446 | double norm = 0.0;
447 | for (int i = 0; i < nn; i++) {
448 | if (i < low | i > high) {
449 | d[i] = H[i][i];
450 | e[i] = 0.0;
451 | }
452 | for (int j = Math.max(i - 1, 0); j < nn; j++) {
453 | norm = norm + Math.abs(H[i][j]);
454 | }
455 | }
456 |
457 | // Outer loop over eigenvalue index
458 |
459 | int iter = 0;
460 | while (n >= low) {
461 |
462 | // Look for single small sub-diagonal element
463 |
464 | int l = n;
465 | while (l > low) {
466 | s = Math.abs(H[l - 1][l - 1]) + Math.abs(H[l][l]);
467 | if (s == 0.0) {
468 | s = norm;
469 | }
470 | if (Math.abs(H[l][l - 1]) < eps * s) {
471 | break;
472 | }
473 | l--;
474 | }
475 |
476 | // Check for convergence
477 | // One root found
478 |
479 | if (l == n) {
480 | H[n][n] = H[n][n] + exshift;
481 | d[n] = H[n][n];
482 | e[n] = 0.0;
483 | n--;
484 | iter = 0;
485 |
486 | // Two roots found
487 |
488 | } else if (l == n - 1) {
489 | w = H[n][n - 1] * H[n - 1][n];
490 | p = (H[n - 1][n - 1] - H[n][n]) / 2.0;
491 | q = p * p + w;
492 | z = Math.sqrt(Math.abs(q));
493 | H[n][n] = H[n][n] + exshift;
494 | H[n - 1][n - 1] = H[n - 1][n - 1] + exshift;
495 | x = H[n][n];
496 |
497 | // Real pair
498 |
499 | if (q >= 0) {
500 | if (p >= 0) {
501 | z = p + z;
502 | } else {
503 | z = p - z;
504 | }
505 | d[n - 1] = x + z;
506 | d[n] = d[n - 1];
507 | if (z != 0.0) {
508 | d[n] = x - w / z;
509 | }
510 | e[n - 1] = 0.0;
511 | e[n] = 0.0;
512 | x = H[n][n - 1];
513 | s = Math.abs(x) + Math.abs(z);
514 | p = x / s;
515 | q = z / s;
516 | r = Math.sqrt(p * p + q * q);
517 | p = p / r;
518 | q = q / r;
519 |
520 | // Row modification
521 |
522 | for (int j = n - 1; j < nn; j++) {
523 | z = H[n - 1][j];
524 | H[n - 1][j] = q * z + p * H[n][j];
525 | H[n][j] = q * H[n][j] - p * z;
526 | }
527 |
528 | // Column modification
529 |
530 | for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
531 | z = H[i][n - 1];
532 | H[i][n - 1] = q * z + p * H[i][n];
533 | H[i][n] = q * H[i][n] - p * z;
534 | }
535 |
536 | // Accumulate transformations
537 |
538 | for (int i = low; i <= high; i++) {
539 | z = V[i][n - 1];
540 | V[i][n - 1] = q * z + p * V[i][n];
541 | V[i][n] = q * V[i][n] - p * z;
542 | }
543 |
544 | // Complex pair
545 |
546 | } else {
547 | d[n - 1] = x + p;
548 | d[n] = x + p;
549 | e[n - 1] = z;
550 | e[n] = -z;
551 | }
552 | n = n - 2;
553 | iter = 0;
554 |
555 | // No convergence yet
556 |
557 | } else {
558 |
559 | // Form shift
560 |
561 | x = H[n][n];
562 | y = 0.0;
563 | w = 0.0;
564 | if (l < n) {
565 | y = H[n - 1][n - 1];
566 | w = H[n][n - 1] * H[n - 1][n];
567 | }
568 |
569 | // Wilkinson's original ad hoc shift
570 |
571 | if (iter == 10) {
572 | exshift += x;
573 | for (int i = low; i <= n; i++) {
574 | H[i][i] -= x;
575 | }
576 | s = Math.abs(H[n][n - 1]) + Math.abs(H[n - 1][n - 2]);
577 | x = y = 0.75 * s;
578 | w = -0.4375 * s * s;
579 | }
580 |
581 | // MATLAB's new ad hoc shift
582 |
583 | if (iter == 30) {
584 | s = (y - x) / 2.0;
585 | s = s * s + w;
586 | if (s > 0) {
587 | s = Math.sqrt(s);
588 | if (y < x) {
589 | s = -s;
590 | }
591 | s = x - w / ((y - x) / 2.0 + s);
592 | for (int i = low; i <= n; i++) {
593 | H[i][i] -= s;
594 | }
595 | exshift += s;
596 | x = y = w = 0.964;
597 | }
598 | }
599 |
600 | iter = iter + 1; // (Could check iteration count here.)
601 |
602 | // Look for two consecutive small sub-diagonal elements
603 |
604 | int m = n - 2;
605 | while (m >= l) {
606 | z = H[m][m];
607 | r = x - z;
608 | s = y - z;
609 | p = (r * s - w) / H[m + 1][m] + H[m][m + 1];
610 | q = H[m + 1][m + 1] - z - r - s;
611 | r = H[m + 2][m + 1];
612 | s = Math.abs(p) + Math.abs(q) + Math.abs(r);
613 | p = p / s;
614 | q = q / s;
615 | r = r / s;
616 | if (m == l) {
617 | break;
618 | }
619 | if (Math.abs(H[m][m - 1]) * (Math.abs(q) + Math.abs(r)) <
620 | eps * (Math.abs(p) * (Math.abs(H[m - 1][m - 1]) + Math.abs(z) +
621 | Math.abs(H[m + 1][m + 1])))) {
622 | break;
623 | }
624 | m--;
625 | }
626 |
627 | for (int i = m + 2; i <= n; i++) {
628 | H[i][i - 2] = 0.0;
629 | if (i > m + 2) {
630 | H[i][i - 3] = 0.0;
631 | }
632 | }
633 |
634 | // Double QR step involving rows l:n and columns m:n
635 |
636 | for (int k = m; k <= n - 1; k++) {
637 | boolean notlast = (k != n - 1);
638 | if (k != m) {
639 | p = H[k][k - 1];
640 | q = H[k + 1][k - 1];
641 | r = (notlast ? H[k + 2][k - 1] : 0.0);
642 | x = Math.abs(p) + Math.abs(q) + Math.abs(r);
643 | if (x != 0.0) {
644 | p = p / x;
645 | q = q / x;
646 | r = r / x;
647 | }
648 | }
649 | if (x == 0.0) {
650 | break;
651 | }
652 | s = Math.sqrt(p * p + q * q + r * r);
653 | if (p < 0) {
654 | s = -s;
655 | }
656 | if (s != 0) {
657 | if (k != m) {
658 | H[k][k - 1] = -s * x;
659 | } else if (l != m) {
660 | H[k][k - 1] = -H[k][k - 1];
661 | }
662 | p = p + s;
663 | x = p / s;
664 | y = q / s;
665 | z = r / s;
666 | q = q / p;
667 | r = r / p;
668 |
669 | // Row modification
670 |
671 | for (int j = k; j < nn; j++) {
672 | p = H[k][j] + q * H[k + 1][j];
673 | if (notlast) {
674 | p = p + r * H[k + 2][j];
675 | H[k + 2][j] = H[k + 2][j] - p * z;
676 | }
677 | H[k][j] = H[k][j] - p * x;
678 | H[k + 1][j] = H[k + 1][j] - p * y;
679 | }
680 |
681 | // Column modification
682 |
683 | for (int i = 0; i <= Math.min(n, k + 3); i++) {
684 | p = x * H[i][k] + y * H[i][k + 1];
685 | if (notlast) {
686 | p = p + z * H[i][k + 2];
687 | H[i][k + 2] = H[i][k + 2] - p * r;
688 | }
689 | H[i][k] = H[i][k] - p;
690 | H[i][k + 1] = H[i][k + 1] - p * q;
691 | }
692 |
693 | // Accumulate transformations
694 |
695 | for (int i = low; i <= high; i++) {
696 | p = x * V[i][k] + y * V[i][k + 1];
697 | if (notlast) {
698 | p = p + z * V[i][k + 2];
699 | V[i][k + 2] = V[i][k + 2] - p * r;
700 | }
701 | V[i][k] = V[i][k] - p;
702 | V[i][k + 1] = V[i][k + 1] - p * q;
703 | }
704 | } // (s != 0)
705 | } // k loop
706 | } // check convergence
707 | } // while (n >= low)
708 |
709 | // Backsubstitute to find vectors of upper triangular form
710 |
711 | if (norm == 0.0) {
712 | return;
713 | }
714 |
715 | for (n = nn - 1; n >= 0; n--) {
716 | p = d[n];
717 | q = e[n];
718 |
719 | // Real vector
720 |
721 | if (q == 0) {
722 | int l = n;
723 | H[n][n] = 1.0;
724 | for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
725 | w = H[i][i] - p;
726 | r = 0.0;
727 | for (int j = l; j <= n; j++) {
728 | r = r + H[i][j] * H[j][n];
729 | }
730 | if (e[i] < 0.0) {
731 | z = w;
732 | s = r;
733 | } else {
734 | l = i;
735 | if (e[i] == 0.0) {
736 | if (w != 0.0) {
737 | H[i][n] = -r / w;
738 | } else {
739 | H[i][n] = -r / (eps * norm);
740 | }
741 |
742 | // Solve real equations
743 |
744 | } else {
745 | x = H[i][i + 1];
746 | y = H[i + 1][i];
747 | q = (d[i] - p) * (d[i] - p) + e[i] * e[i];
748 | t = (x * s - z * r) / q;
749 | H[i][n] = t;
750 | if (Math.abs(x) > Math.abs(z)) {
751 | H[i + 1][n] = (-r - w * t) / x;
752 | } else {
753 | H[i + 1][n] = (-s - y * t) / z;
754 | }
755 | }
756 |
757 | // Overflow control
758 |
759 | t = Math.abs(H[i][n]);
760 | if ((eps * t) * t > 1) {
761 | for (int j = i; j <= n; j++) {
762 | H[j][n] = H[j][n] / t;
763 | }
764 | }
765 | }
766 | }
767 |
768 | // Complex vector
769 |
770 | } else if (q < 0) {
771 | int l = n - 1;
772 |
773 | // Last vector component imaginary so matrix is triangular
774 |
775 | if (Math.abs(H[n][n - 1]) > Math.abs(H[n - 1][n])) {
776 | H[n - 1][n - 1] = q / H[n][n - 1];
777 | H[n - 1][n] = -(H[n][n] - p) / H[n][n - 1];
778 | } else {
779 | cdiv(0.0, -H[n - 1][n], H[n - 1][n - 1] - p, q);
780 | H[n - 1][n - 1] = cdivr;
781 | H[n - 1][n] = cdivi;
782 | }
783 | H[n][n - 1] = 0.0;
784 | H[n][n] = 1.0;
785 | for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
786 | double ra, sa, vr, vi;
787 | ra = 0.0;
788 | sa = 0.0;
789 | for (int j = l; j <= n; j++) {
790 | ra = ra + H[i][j] * H[j][n - 1];
791 | sa = sa + H[i][j] * H[j][n];
792 | }
793 | w = H[i][i] - p;
794 |
795 | if (e[i] < 0.0) {
796 | z = w;
797 | r = ra;
798 | s = sa;
799 | } else {
800 | l = i;
801 | if (e[i] == 0) {
802 | cdiv(-ra, -sa, w, q);
803 | H[i][n - 1] = cdivr;
804 | H[i][n] = cdivi;
805 | } else {
806 |
807 | // Solve complex equations
808 |
809 | x = H[i][i + 1];
810 | y = H[i + 1][i];
811 | vr = (d[i] - p) * (d[i] - p) + e[i] * e[i] - q * q;
812 | vi = (d[i] - p) * 2.0 * q;
813 | if (vr == 0.0 & vi == 0.0) {
814 | vr = eps * norm * (Math.abs(w) + Math.abs(q) +
815 | Math.abs(x) + Math.abs(y) + Math.abs(z));
816 | }
817 | cdiv(x * r - z * ra + q * sa, x * s - z * sa - q * ra, vr, vi);
818 | H[i][n - 1] = cdivr;
819 | H[i][n] = cdivi;
820 | if (Math.abs(x) > (Math.abs(z) + Math.abs(q))) {
821 | H[i + 1][n - 1] = (-ra - w * H[i][n - 1] + q * H[i][n]) / x;
822 | H[i + 1][n] = (-sa - w * H[i][n] - q * H[i][n - 1]) / x;
823 | } else {
824 | cdiv(-r - y * H[i][n - 1], -s - y * H[i][n], z, q);
825 | H[i + 1][n - 1] = cdivr;
826 | H[i + 1][n] = cdivi;
827 | }
828 | }
829 |
830 | // Overflow control
831 |
832 | t = Math.max(Math.abs(H[i][n - 1]), Math.abs(H[i][n]));
833 | if ((eps * t) * t > 1) {
834 | for (int j = i; j <= n; j++) {
835 | H[j][n - 1] = H[j][n - 1] / t;
836 | H[j][n] = H[j][n] / t;
837 | }
838 | }
839 | }
840 | }
841 | }
842 | }
843 |
844 | // Vectors of isolated roots
845 |
846 | for (int i = 0; i < nn; i++) {
847 | if (i < low | i > high) {
848 | for (int j = i; j < nn; j++) {
849 | V[i][j] = H[i][j];
850 | }
851 | }
852 | }
853 |
854 | // Back transformation to get eigenvectors of original matrix
855 |
856 | for (int j = nn - 1; j >= low; j--) {
857 | for (int i = low; i <= high; i++) {
858 | z = 0.0;
859 | for (int k = low; k <= Math.min(j, high); k++) {
860 | z = z + V[i][k] * H[k][j];
861 | }
862 | V[i][j] = z;
863 | }
864 | }
865 | }
866 |
867 |
868 | /* ------------------------
869 | Constructor
870 | * ------------------------ */
871 |
872 | /**
873 | * Check for symmetry, then construct the eigenvalue decomposition
874 | *
875 | * @param A Square matrix
876 | * @return Structure to access D and V.
877 | */
878 |
879 | public EigenValueDecomposition(Matrix Arg) {
880 | double[][] A = Arg.getArray();
881 | n = Arg.getColumnDimension();
882 | V = new double[n][n];
883 | d = new double[n];
884 | e = new double[n];
885 |
886 | issymmetric = true;
887 | for (int j = 0; (j < n) & issymmetric; j++) {
888 | for (int i = 0; (i < n) & issymmetric; i++) {
889 | issymmetric = (A[i][j] == A[j][i]);
890 | }
891 | }
892 |
893 | if (issymmetric) {
894 | for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
895 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
896 | V[i][j] = A[i][j];
897 | }
898 | }
899 |
900 | // Tridiagonalize.
901 | tred2();
902 |
903 | // Diagonalize.
904 | tql2();
905 |
906 | } else {
907 | H = new double[n][n];
908 | ort = new double[n];
909 |
910 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
911 | for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
912 | H[i][j] = A[i][j];
913 | }
914 | }
915 |
916 | // Reduce to Hessenberg form.
917 | orthes();
918 |
919 | // Reduce Hessenberg to real Schur form.
920 | hqr2();
921 | }
922 | }
923 |
924 | /* ------------------------
925 | Public Methods
926 | * ------------------------ */
927 |
928 | /**
929 | * Return the eigenvector matrix
930 | *
931 | * @return V
932 | */
933 |
934 | public Matrix getV() {
935 | return new Matrix(V, n, n);
936 | }
937 |
938 | /**
939 | * Return the real parts of the eigenvalues
940 | *
941 | * @return real(diag(D))
942 | */
943 |
944 | public double[] getRealEigenvalues() {
945 | return d;
946 | }
947 |
948 | /**
949 | * Return the imaginary parts of the eigenvalues
950 | *
951 | * @return imag(diag(D))
952 | */
953 |
954 | public double[] getImagEigenvalues() {
955 | return e;
956 | }
957 |
958 | /**
959 | * Return the block diagonal eigenvalue matrix
960 | *
961 | * @return D
962 | */
963 |
964 | public Matrix getD() {
965 | Matrix X = new Matrix(n, n);
966 | double[][] D = X.getArray();
967 | for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
968 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
969 | D[i][j] = 0.0;
970 | }
971 | D[i][i] = d[i];
972 | if (e[i] > 0) {
973 | D[i][i + 1] = e[i];
974 | } else if (e[i] < 0) {
975 | D[i][i - 1] = e[i];
976 | }
977 | }
978 | return X;
979 | }
980 | }
981 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/lib/src/main/java/net/kibotu/kalmanrx/jama/Matrix.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package net.kibotu.kalmanrx.jama;
2 |
3 | import net.kibotu.kalmanrx.jama.util.Maths;
4 |
5 | import java.io.BufferedReader;
6 | import java.io.PrintWriter;
7 | import java.io.StreamTokenizer;
8 | import java.text.DecimalFormat;
9 | import java.text.DecimalFormatSymbols;
10 | import java.text.NumberFormat;
11 | import java.util.Locale;
12 |
13 | /**
14 | * Jama = Java Matrix class.
15 | *
16 | * The Java Matrix Class provides the fundamental operations of numerical
17 | * linear algebra. Various constructors create Matrices from two dimensional
18 | * arrays of double precision floating point numbers. Various "gets" and
19 | * "sets" provide access to submatrices and matrix elements. Several methods
20 | * implement basic matrix arithmetic, including matrix addition and
21 | * multiplication, matrix norms, and element-by-element array operations.
22 | * Methods for reading and printing matrices are also included. All the
23 | * operations in this version of the Matrix Class involve real matrices.
24 | * Complex matrices may be handled in a future version.
25 | *
26 | * Five fundamental matrix decompositions, which consist of pairs or triples
27 | * of matrices, permutation vectors, and the like, produce results in five
28 | * decomposition classes. These decompositions are accessed by the Matrix
29 | * class to compute solutions of simultaneous linear equations, determinants,
30 | * inverses and other matrix functions. The five decompositions are:
31 | *
41 | *
1123 | * Matrix shapes: A(m x n), B(n x p), C(m x p).
1124 | *
1125 | * After potential transpositions and shape conformance check;
1126 | * C[i,j] = alpha*Sum(A[i,k] * B[k,j]) + beta*C[i,j], k=0..n-1.
1127 | *
1128 | * Use:
32 | *
38 | *
39 | *
51 | *
52 | * @author The MathWorks, Inc. and the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
53 | * @version 5 August 1998
54 | */
55 | public class Matrix implements Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
56 |
57 | /* ------------------------
58 | Class variables
59 | * ------------------------ */
60 |
61 | /**
62 | * Array for internal storage of elements.
63 | *
64 | * @serial internal array storage.
65 | */
66 | private double[][] A;
67 |
68 | /**
69 | * Row and column dimensions.
70 | *
71 | * @serial row dimension.
72 | * @serial column dimension.
73 | */
74 | private int m, n;
75 |
76 | /* ------------------------
77 | Constructors
78 | * ------------------------ */
79 |
80 | /**
81 | * Construct an m-by-n matrix of zeros.
82 | *
83 | * @param m Number of rows.
84 | * @param n Number of colums.
85 | */
86 | public Matrix(int m, int n) {
87 | this.m = m;
88 | this.n = n;
89 | A = new double[m][n];
90 | }
91 |
92 | /**
93 | * Construct an m-by-n constant matrix.
94 | *
95 | * @param m Number of rows.
96 | * @param n Number of colums.
97 | * @param s Fill the matrix with this scalar value.
98 | */
99 | public Matrix(int m, int n, double s) {
100 | this.m = m;
101 | this.n = n;
102 | A = new double[m][n];
103 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
104 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
105 | A[i][j] = s;
106 | }
107 | }
108 | }
109 |
110 | /**
111 | * Construct a matrix from a 2-D array.
112 | *
113 | * @param A Two-dimensional array of doubles.
114 | * @throws IllegalArgumentException All rows must have the same length
115 | * @see #constructWithCopy
116 | */
117 | public Matrix(double[][] A) {
118 | m = A.length;
119 | n = A[0].length;
120 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
121 | if (A[i].length != n) {
122 | throw new IllegalArgumentException("All rows must have the same length.");
123 | }
124 | }
125 | this.A = A;
126 | }
127 |
128 | /**
129 | * Construct a matrix quickly without checking arguments.
130 | *
131 | * @param A Two-dimensional array of doubles.
132 | * @param m Number of rows.
133 | * @param n Number of colums.
134 | */
135 | public Matrix(double[][] A, int m, int n) {
136 | this.A = A;
137 | this.m = m;
138 | this.n = n;
139 | }
140 |
141 | /**
142 | * Construct a matrix from a one-dimensional packed array
143 | *
144 | * @param vals One-dimensional array of doubles, packed by columns (ala Fortran).
145 | * @param m Number of rows.
146 | * @throws IllegalArgumentException Array length must be a multiple of m.
147 | */
148 | public Matrix(double[] vals, int m) {
149 | this.m = m;
150 | n = (m != 0 ? vals.length / m : 0);
151 | if (m * n != vals.length) {
152 | throw new IllegalArgumentException("Array length must be a multiple of m.");
153 | }
154 | A = new double[m][n];
155 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
156 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
157 | A[i][j] = vals[i + j * m];
158 | }
159 | }
160 | }
161 |
162 | /* ------------------------
163 | Public Methods
164 | * ------------------------ */
165 |
166 | /**
167 | * Construct a matrix from a copy of a 2-D array.
168 | *
169 | * @param A Two-dimensional array of doubles.
170 | * @throws IllegalArgumentException All rows must have the same length
171 | */
172 | public static Matrix constructWithCopy(double[][] A) {
173 | int m = A.length;
174 | int n = A[0].length;
175 | Matrix X = new Matrix(m, n);
176 | double[][] C = X.getArray();
177 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
178 | if (A[i].length != n) {
179 | throw new IllegalArgumentException("All rows must have the same length.");
180 | }
181 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
182 | C[i][j] = A[i][j];
183 | }
184 | }
185 | return X;
186 | }
187 |
188 | /**
189 | * Make a deep copy of a matrix
190 | */
191 | public Matrix copy() {
192 | Matrix X = new Matrix(m, n);
193 | double[][] C = X.getArray();
194 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
195 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
196 | C[i][j] = A[i][j];
197 | }
198 | }
199 | return X;
200 | }
201 |
202 | /**
203 | * Clone the Matrix object.
204 | */
205 | public Object clone() {
206 | return this.copy();
207 | }
208 |
209 | /**
210 | * Access the internal two-dimensional array.
211 | *
212 | * @return Pointer to the two-dimensional array of matrix elements.
213 | */
214 | public double[][] getArray() {
215 | return A;
216 | }
217 |
218 | /**
219 | * Copy the internal two-dimensional array.
220 | *
221 | * @return Two-dimensional array copy of matrix elements.
222 | */
223 | public double[][] getArrayCopy() {
224 | double[][] C = new double[m][n];
225 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
226 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
227 | C[i][j] = A[i][j];
228 | }
229 | }
230 | return C;
231 | }
232 |
233 | /**
234 | * Make a one-dimensional column packed copy of the internal array.
235 | *
236 | * @return Matrix elements packed in a one-dimensional array by columns.
237 | */
238 | public double[] getColumnPackedCopy() {
239 | double[] vals = new double[m * n];
240 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
241 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
242 | vals[i + j * m] = A[i][j];
243 | }
244 | }
245 | return vals;
246 | }
247 |
248 | /**
249 | * Make a one-dimensional row packed copy of the internal array.
250 | *
251 | * @return Matrix elements packed in a one-dimensional array by rows.
252 | */
253 | public double[] getRowPackedCopy() {
254 | double[] vals = new double[m * n];
255 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
256 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
257 | vals[i * n + j] = A[i][j];
258 | }
259 | }
260 | return vals;
261 | }
262 |
263 | /**
264 | * Get row dimension.
265 | *
266 | * @return m, the number of rows.
267 | */
268 | public int getRowDimension() {
269 | return m;
270 | }
271 |
272 | /**
273 | * Get column dimension.
274 | *
275 | * @return n, the number of columns.
276 | */
277 | public int getColumnDimension() {
278 | return n;
279 | }
280 |
281 | /**
282 | * Get a single element.
283 | *
284 | * @param i Row index.
285 | * @param j Column index.
286 | * @return A(i, j)
287 | * @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
288 | */
289 | public double get(int i, int j) {
290 | return A[i][j];
291 | }
292 |
293 | /**
294 | * Get a submatrix.
295 | *
296 | * @param i0 Initial row index
297 | * @param i1 Final row index
298 | * @param j0 Initial column index
299 | * @param j1 Final column index
300 | * @return A(i0:i1, j0:j1)
301 | * @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException Submatrix indices
302 | */
303 | public Matrix getMatrix(int i0, int i1, int j0, int j1) {
304 | Matrix X = new Matrix(i1 - i0 + 1, j1 - j0 + 1);
305 | double[][] B = X.getArray();
306 | try {
307 | for (int i = i0; i <= i1; i++) {
308 | for (int j = j0; j <= j1; j++) {
309 | B[i - i0][j - j0] = A[i][j];
310 | }
311 | }
312 | } catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
313 | throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("Submatrix indices");
314 | }
315 | return X;
316 | }
317 |
318 | /**
319 | * Get a submatrix.
320 | *
321 | * @param r Array of row indices.
322 | * @param c Array of column indices.
323 | * @return A(r(:), c(:))
324 | * @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException Submatrix indices
325 | */
326 | public Matrix getMatrix(int[] r, int[] c) {
327 | Matrix X = new Matrix(r.length, c.length);
328 | double[][] B = X.getArray();
329 | try {
330 | for (int i = 0; i < r.length; i++) {
331 | for (int j = 0; j < c.length; j++) {
332 | B[i][j] = A[r[i]][c[j]];
333 | }
334 | }
335 | } catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
336 | throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("Submatrix indices");
337 | }
338 | return X;
339 | }
340 |
341 | /**
342 | * Get a submatrix.
343 | *
344 | * @param i0 Initial row index
345 | * @param i1 Final row index
346 | * @param c Array of column indices.
347 | * @return A(i0:i1, c(:))
348 | * @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException Submatrix indices
349 | */
350 | public Matrix getMatrix(int i0, int i1, int[] c) {
351 | Matrix X = new Matrix(i1 - i0 + 1, c.length);
352 | double[][] B = X.getArray();
353 | try {
354 | for (int i = i0; i <= i1; i++) {
355 | for (int j = 0; j < c.length; j++) {
356 | B[i - i0][j] = A[i][c[j]];
357 | }
358 | }
359 | } catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
360 | throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("Submatrix indices");
361 | }
362 | return X;
363 | }
364 |
365 | /**
366 | * Get a submatrix.
367 | *
368 | * @param r Array of row indices.
369 | * @param i0 Initial column index
370 | * @param i1 Final column index
371 | * @return A(r(:), j0:j1)
372 | * @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException Submatrix indices
373 | */
374 | public Matrix getMatrix(int[] r, int j0, int j1) {
375 | Matrix X = new Matrix(r.length, j1 - j0 + 1);
376 | double[][] B = X.getArray();
377 | try {
378 | for (int i = 0; i < r.length; i++) {
379 | for (int j = j0; j <= j1; j++) {
380 | B[i][j - j0] = A[r[i]][j];
381 | }
382 | }
383 | } catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
384 | throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("Submatrix indices");
385 | }
386 | return X;
387 | }
388 |
389 | /**
390 | * Set a single element.
391 | *
392 | * @param i Row index.
393 | * @param j Column index.
394 | * @param s A(i,j).
395 | * @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
396 | */
397 | public void set(int i, int j, double s) {
398 | A[i][j] = s;
399 | }
400 |
401 | /**
402 | * Set a submatrix.
403 | *
404 | * @param i0 Initial row index
405 | * @param i1 Final row index
406 | * @param j0 Initial column index
407 | * @param j1 Final column index
408 | * @param X A(i0:i1,j0:j1)
409 | * @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException Submatrix indices
410 | */
411 | public void setMatrix(int i0, int i1, int j0, int j1, Matrix X) {
412 | try {
413 | for (int i = i0; i <= i1; i++) {
414 | for (int j = j0; j <= j1; j++) {
415 | A[i][j] = X.get(i - i0, j - j0);
416 | }
417 | }
418 | } catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
419 | throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("Submatrix indices");
420 | }
421 | }
422 |
423 | /**
424 | * Set a submatrix.
425 | *
426 | * @param r Array of row indices.
427 | * @param c Array of column indices.
428 | * @param X A(r(:),c(:))
429 | * @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException Submatrix indices
430 | */
431 | public void setMatrix(int[] r, int[] c, Matrix X) {
432 | try {
433 | for (int i = 0; i < r.length; i++) {
434 | for (int j = 0; j < c.length; j++) {
435 | A[r[i]][c[j]] = X.get(i, j);
436 | }
437 | }
438 | } catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
439 | throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("Submatrix indices");
440 | }
441 | }
442 |
443 | /**
444 | * Set a submatrix.
445 | *
446 | * @param r Array of row indices.
447 | * @param j0 Initial column index
448 | * @param j1 Final column index
449 | * @param X A(r(:),j0:j1)
450 | * @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException Submatrix indices
451 | */
452 | public void setMatrix(int[] r, int j0, int j1, Matrix X) {
453 | try {
454 | for (int i = 0; i < r.length; i++) {
455 | for (int j = j0; j <= j1; j++) {
456 | A[r[i]][j] = X.get(i, j - j0);
457 | }
458 | }
459 | } catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
460 | throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("Submatrix indices");
461 | }
462 | }
463 |
464 | /**
465 | * Set a submatrix.
466 | *
467 | * @param i0 Initial row index
468 | * @param i1 Final row index
469 | * @param c Array of column indices.
470 | * @param X A(i0:i1,c(:))
471 | * @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException Submatrix indices
472 | */
473 | public void setMatrix(int i0, int i1, int[] c, Matrix X) {
474 | try {
475 | for (int i = i0; i <= i1; i++) {
476 | for (int j = 0; j < c.length; j++) {
477 | A[i][c[j]] = X.get(i - i0, j);
478 | }
479 | }
480 | } catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
481 | throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("Submatrix indices");
482 | }
483 | }
484 |
485 | /**
486 | * Matrix transpose.
487 | *
488 | * @return A'
489 | */
490 | public Matrix transpose() {
491 | Matrix X = new Matrix(n, m);
492 | double[][] C = X.getArray();
493 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
494 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
495 | C[j][i] = A[i][j];
496 | }
497 | }
498 | return X;
499 | }
500 |
501 | /**
502 | * One norm
503 | *
504 | * @return maximum column sum.
505 | */
506 | public double norm1() {
507 | double f = 0;
508 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
509 | double s = 0;
510 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
511 | s += Math.abs(A[i][j]);
512 | }
513 | f = Math.max(f, s);
514 | }
515 | return f;
516 | }
517 |
518 | /**
519 | * Two norm
520 | *
521 | * @return maximum singular value.
522 | */
523 | public double norm2() {
524 | return (new SingularValueDecomposition(this).norm2());
525 | }
526 |
527 | /**
528 | * Infinity norm
529 | *
530 | * @return maximum row sum.
531 | */
532 | public double normInf() {
533 | double f = 0;
534 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
535 | double s = 0;
536 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
537 | s += Math.abs(A[i][j]);
538 | }
539 | f = Math.max(f, s);
540 | }
541 | return f;
542 | }
543 |
544 | /**
545 | * Frobenius norm
546 | *
547 | * @return sqrt of sum of squares of all elements.
548 | */
549 | public double normF() {
550 | double f = 0;
551 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
552 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
553 | f = Maths.hypot(f, A[i][j]);
554 | }
555 | }
556 | return f;
557 | }
558 |
559 | /**
560 | * Unary minus
561 | *
562 | * @return -A
563 | */
564 | public Matrix uminus() {
565 | Matrix X = new Matrix(m, n);
566 | double[][] C = X.getArray();
567 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
568 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
569 | C[i][j] = -A[i][j];
570 | }
571 | }
572 | return X;
573 | }
574 |
575 | /**
576 | * C = A + B
577 | *
578 | * @param B another matrix
579 | * @return A + B
580 | */
581 | public Matrix plus(Matrix B) {
582 | checkMatrixDimensions(B);
583 | Matrix X = new Matrix(m, n);
584 | double[][] C = X.getArray();
585 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
586 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
587 | C[i][j] = A[i][j] + B.A[i][j];
588 | }
589 | }
590 | return X;
591 | }
592 |
593 | /**
594 | * A = A + B
595 | *
596 | * @param B another matrix
597 | * @return A + B
598 | */
599 | public Matrix plusEquals(Matrix B) {
600 | checkMatrixDimensions(B);
601 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
602 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
603 | A[i][j] = A[i][j] + B.A[i][j];
604 | }
605 | }
606 | return this;
607 | }
608 |
609 | /**
610 | * C = A - B
611 | *
612 | * @param B another matrix
613 | * @return A - B
614 | */
615 | public Matrix minus(Matrix B) {
616 | checkMatrixDimensions(B);
617 | Matrix X = new Matrix(m, n);
618 | double[][] C = X.getArray();
619 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
620 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
621 | C[i][j] = A[i][j] - B.A[i][j];
622 | }
623 | }
624 | return X;
625 | }
626 |
627 | /**
628 | * A = A - B
629 | *
630 | * @param B another matrix
631 | * @return A - B
632 | */
633 | public Matrix minusEquals(Matrix B) {
634 | checkMatrixDimensions(B);
635 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
636 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
637 | A[i][j] = A[i][j] - B.A[i][j];
638 | }
639 | }
640 | return this;
641 | }
642 |
643 | /**
644 | * Element-by-element multiplication, C = A.*B
645 | *
646 | * @param B another matrix
647 | * @return A.*B
648 | */
649 | public Matrix arrayTimes(Matrix B) {
650 | checkMatrixDimensions(B);
651 | Matrix X = new Matrix(m, n);
652 | double[][] C = X.getArray();
653 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
654 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
655 | C[i][j] = A[i][j] * B.A[i][j];
656 | }
657 | }
658 | return X;
659 | }
660 |
661 | /**
662 | * Element-by-element multiplication in place, A = A.*B
663 | *
664 | * @param B another matrix
665 | * @return A.*B
666 | */
667 | public Matrix arrayTimesEquals(Matrix B) {
668 | checkMatrixDimensions(B);
669 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
670 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
671 | A[i][j] = A[i][j] * B.A[i][j];
672 | }
673 | }
674 | return this;
675 | }
676 |
677 | /**
678 | * Element-by-element right division, C = A./B
679 | *
680 | * @param B another matrix
681 | * @return A./B
682 | */
683 | public Matrix arrayRightDivide(Matrix B) {
684 | checkMatrixDimensions(B);
685 | Matrix X = new Matrix(m, n);
686 | double[][] C = X.getArray();
687 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
688 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
689 | C[i][j] = A[i][j] / B.A[i][j];
690 | }
691 | }
692 | return X;
693 | }
694 |
695 | /**
696 | * Element-by-element right division in place, A = A./B
697 | *
698 | * @param B another matrix
699 | * @return A./B
700 | */
701 | public Matrix arrayRightDivideEquals(Matrix B) {
702 | checkMatrixDimensions(B);
703 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
704 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
705 | A[i][j] = A[i][j] / B.A[i][j];
706 | }
707 | }
708 | return this;
709 | }
710 |
711 | /**
712 | * Element-by-element left division, C = A.\B
713 | *
714 | * @param B another matrix
715 | * @return A.\B
716 | */
717 | public Matrix arrayLeftDivide(Matrix B) {
718 | checkMatrixDimensions(B);
719 | Matrix X = new Matrix(m, n);
720 | double[][] C = X.getArray();
721 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
722 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
723 | C[i][j] = B.A[i][j] / A[i][j];
724 | }
725 | }
726 | return X;
727 | }
728 |
729 | /**
730 | * Element-by-element left division in place, A = A.\B
731 | *
732 | * @param B another matrix
733 | * @return A.\B
734 | */
735 | public Matrix arrayLeftDivideEquals(Matrix B) {
736 | checkMatrixDimensions(B);
737 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
738 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
739 | A[i][j] = B.A[i][j] / A[i][j];
740 | }
741 | }
742 | return this;
743 | }
744 |
745 | /**
746 | * Multiply a matrix by a scalar, C = s*A
747 | *
748 | * @param s scalar
749 | * @return s*A
750 | */
751 | public Matrix times(double s) {
752 | Matrix X = new Matrix(m, n);
753 | double[][] C = X.getArray();
754 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
755 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
756 | C[i][j] = s * A[i][j];
757 | }
758 | }
759 | return X;
760 | }
761 |
762 | /**
763 | * Multiply a matrix by a scalar in place, A = s*A
764 | *
765 | * @param s scalar
766 | * @return replace A by s*A
767 | */
768 | public Matrix timesEquals(double s) {
769 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
770 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
771 | A[i][j] = s * A[i][j];
772 | }
773 | }
774 | return this;
775 | }
776 |
777 | /**
778 | * Linear algebraic matrix multiplication, A * B
779 | *
780 | * @param B another matrix
781 | * @return Matrix product, A * B
782 | * @throws IllegalArgumentException Matrix inner dimensions must agree.
783 | */
784 | public Matrix times(Matrix B) {
785 | if (B.m != n) {
786 | throw new IllegalArgumentException("Matrix inner dimensions must agree.");
787 | }
788 | Matrix X = new Matrix(m, B.n);
789 | double[][] C = X.getArray();
790 | double[] Bcolj = new double[n];
791 | for (int j = 0; j < B.n; j++) {
792 | for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
793 | Bcolj[k] = B.A[k][j];
794 | }
795 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
796 | double[] Arowi = A[i];
797 | double s = 0;
798 | for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
799 | s += Arowi[k] * Bcolj[k];
800 | }
801 | C[i][j] = s;
802 | }
803 | }
804 | return X;
805 | }
806 |
807 | /**
808 | * LU Decomposition
809 | *
810 | * @return LUDecomposition
811 | * @see net.kibotu.kalmanrx.jama.LUDecomposition
812 | */
813 | public LUDecomposition lu() {
814 | return new LUDecomposition(this);
815 | }
816 |
817 | /**
818 | * QR Decomposition
819 | *
820 | * @return QRDecomposition
821 | * @see net.kibotu.kalmanrx.jama.QRDecomposition
822 | */
823 | public QRDecomposition qr() {
824 | return new QRDecomposition(this);
825 | }
826 |
827 | /**
828 | * Cholesky Decomposition
829 | *
830 | * @return CholeskyDecomposition
831 | * @see net.kibotu.kalmanrx.jama.CholeskyDecomposition
832 | */
833 | public CholeskyDecomposition chol() {
834 | return new CholeskyDecomposition(this);
835 | }
836 |
837 | /**
838 | * Singular Value Decomposition
839 | *
840 | * @return SingularValueDecomposition
841 | * @see net.kibotu.kalmanrx.jama.SingularValueDecomposition
842 | */
843 | public SingularValueDecomposition svd() {
844 | return new SingularValueDecomposition(this);
845 | }
846 |
847 | /**
848 | * Eigenvalue Decomposition
849 | *
850 | * @return EigenValueDecomposition
851 | * @see EigenValueDecomposition
852 | */
853 | public EigenValueDecomposition eig() {
854 | return new EigenValueDecomposition(this);
855 | }
856 |
857 | /**
858 | * Solve A*X = B
859 | *
860 | * @param B right hand side
861 | * @return solution if A is square, least squares solution otherwise
862 | */
863 | public Matrix solve(Matrix B) {
864 | return (m == n ? (new LUDecomposition(this)).solve(B) :
865 | (new QRDecomposition(this)).solve(B));
866 | }
867 |
868 | /**
869 | * Solve X*A = B, which is also A'*X' = B'
870 | *
871 | * @param B right hand side
872 | * @return solution if A is square, least squares solution otherwise.
873 | */
874 | public Matrix solveTranspose(Matrix B) {
875 | return transpose().solve(B.transpose());
876 | }
877 |
878 | /**
879 | * Matrix inverse or pseudoinverse
880 | *
881 | * @return inverse(A) if A is square, pseudoinverse otherwise.
882 | */
883 | public Matrix inverse() {
884 | return solve(identity(m, m));
885 | }
886 |
887 | /**
888 | * Matrix determinant
889 | *
890 | * @return determinant
891 | */
892 | public double det() {
893 | return new LUDecomposition(this).det();
894 | }
895 |
896 | /**
897 | * Matrix rank
898 | *
899 | * @return effective numerical rank, obtained from SVD.
900 | */
901 | public int rank() {
902 | return new SingularValueDecomposition(this).rank();
903 | }
904 |
905 | /**
906 | * Matrix condition (2 norm)
907 | *
908 | * @return ratio of largest to smallest singular value.
909 | */
910 | public double cond() {
911 | return new SingularValueDecomposition(this).cond();
912 | }
913 |
914 | /**
915 | * Matrix trace.
916 | *
917 | * @return sum of the diagonal elements.
918 | */
919 | public double trace() {
920 | double t = 0;
921 | for (int i = 0; i < Math.min(m, n); i++) {
922 | t += A[i][i];
923 | }
924 | return t;
925 | }
926 |
927 | /**
928 | * Generate matrix with random elements
929 | *
930 | * @param m Number of rows.
931 | * @param n Number of colums.
932 | * @return An m-by-n matrix with uniformly distributed random elements.
933 | */
934 | public static Matrix random(int m, int n) {
935 | Matrix A = new Matrix(m, n);
936 | double[][] X = A.getArray();
937 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
938 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
939 | X[i][j] = Math.random();
940 | }
941 | }
942 | return A;
943 | }
944 |
945 | /**
946 | * Generate identity matrix
947 | *
948 | * @param m Number of rows.
949 | * @param n Number of colums.
950 | * @return An m-by-n matrix with ones on the diagonal and zeros elsewhere.
951 | */
952 | public static Matrix identity(int m, int n) {
953 | Matrix A = new Matrix(m, n);
954 | double[][] X = A.getArray();
955 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
956 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
957 | X[i][j] = (i == j ? 1.0 : 0.0);
958 | }
959 | }
960 | return A;
961 | }
962 |
963 |
964 | /**
965 | * Print the matrix to stdout. Line the elements up in columns
966 | * with a Fortran-like 'Fw.d' style format.
967 | *
968 | * @param w Column width.
969 | * @param d Number of digits after the decimal.
970 | */
971 | public void print(int w, int d) {
972 | print(new PrintWriter(System.out, true), w, d);
973 | }
974 |
975 | /**
976 | * Print the matrix to the output stream. Line the elements up in
977 | * columns with a Fortran-like 'Fw.d' style format.
978 | *
979 | * @param output Output stream.
980 | * @param w Column width.
981 | * @param d Number of digits after the decimal.
982 | */
983 | public void print(PrintWriter output, int w, int d) {
984 | DecimalFormat format = new DecimalFormat();
985 | format.setDecimalFormatSymbols(new DecimalFormatSymbols(Locale.US));
986 | format.setMinimumIntegerDigits(1);
987 | format.setMaximumFractionDigits(d);
988 | format.setMinimumFractionDigits(d);
989 | format.setGroupingUsed(false);
990 | print(output, format, w + 2);
991 | }
992 |
993 | /**
994 | * Print the matrix to stdout. Line the elements up in columns.
995 | * Use the format object, and right justify within columns of width
996 | * characters.
997 | * Note that is the matrix is to be read back in, you probably will want
998 | * to use a NumberFormat that is set to US Locale.
999 | *
1000 | * @param format A Formatting object for individual elements.
1001 | * @param width Field width for each column.
1002 | * @see DecimalFormat#setDecimalFormatSymbols
1003 | */
1004 | public void print(NumberFormat format, int width) {
1005 | print(new PrintWriter(System.out, true), format, width);
1006 | }
1007 |
1008 | // DecimalFormat is a little disappointing coming from Fortran or C's printf.
1009 | // Since it doesn't pad on the left, the elements will come out different
1010 | // widths. Consequently, we'll pass the desired column width in as an
1011 | // argument and do the extra padding ourselves.
1012 |
1013 | /**
1014 | * Print the matrix to the output stream. Line the elements up in columns.
1015 | * Use the format object, and right justify within columns of width
1016 | * characters.
1017 | * Note that is the matrix is to be read back in, you probably will want
1018 | * to use a NumberFormat that is set to US Locale.
1019 | *
1020 | * @param output the output stream.
1021 | * @param format A formatting object to format the matrix elements
1022 | * @param width Column width.
1023 | * @see DecimalFormat#setDecimalFormatSymbols
1024 | */
1025 | public void print(PrintWriter output, NumberFormat format, int width) {
1026 | output.println(); // start on new line.
1027 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
1028 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
1029 | String s = format.format(A[i][j]); // format the number
1030 | int padding =
1031 | Math.max(1, width - s.length()); // At _least_ 1 space
1032 | for (int k = 0; k < padding; k++)
1033 | output.print(' ');
1034 | output.print(s);
1035 | }
1036 | output.println();
1037 | }
1038 | output.println(); // end with blank line.
1039 | }
1040 |
1041 | /**
1042 | * Read a matrix from a stream. The format is the same the print method,
1043 | * so printed matrices can be read back in (provided they were printed using
1044 | * US Locale). Elements are separated by
1045 | * whitespace, all the elements for each row appear on a single line,
1046 | * the last row is followed by a blank line.
1047 | *
1048 | * @param input the input stream.
1049 | */
1050 | public static Matrix read(BufferedReader input) throws java.io.IOException {
1051 | StreamTokenizer tokenizer = new StreamTokenizer(input);
1052 |
1053 | // Although StreamTokenizer will parse numbers, it doesn't recognize
1054 | // scientific notation (E or D); however, Double.valueOf does.
1055 | // The strategy here is to disable StreamTokenizer's number parsing.
1056 | // We'll only get whitespace delimited words, EOL's and EOF's.
1057 | // These words should all be numbers, for Double.valueOf to parse.
1058 |
1059 | tokenizer.resetSyntax();
1060 | tokenizer.wordChars(0, 255);
1061 | tokenizer.whitespaceChars(0, ' ');
1062 | tokenizer.eolIsSignificant(true);
1063 | java.util.Vector v = new java.util.Vector();
1064 |
1065 | // Ignore initial empty lines
1066 | while (tokenizer.nextToken() == StreamTokenizer.TT_EOL)
1067 | ;
1068 | if (tokenizer.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF)
1069 | throw new java.io.IOException("Unexpected EOF on matrix read.");
1070 | do {
1071 | v.addElement(Double.valueOf(tokenizer.sval)); // Read & store 1st row.
1072 | } while (tokenizer.nextToken() == StreamTokenizer.TT_WORD);
1073 |
1074 | int n = v.size(); // Now we've got the number of columns!
1075 | double row[] = new double[n];
1076 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) // extract the elements of the 1st row.
1077 | row[j] = ((Double) v.elementAt(j)).doubleValue();
1078 | v.removeAllElements();
1079 | v.addElement(row); // Start storing rows instead of columns.
1080 | while (tokenizer.nextToken() == StreamTokenizer.TT_WORD) {
1081 | // While non-empty lines
1082 | v.addElement(row = new double[n]);
1083 | int j = 0;
1084 | do {
1085 | if (j >= n)
1086 | throw new java.io.IOException("Row " + v.size() +
1087 | " is too long.");
1088 | row[j++] = Double.valueOf(tokenizer.sval).doubleValue();
1089 | } while (tokenizer.nextToken() == StreamTokenizer.TT_WORD);
1090 | if (j < n)
1091 | throw new java.io.IOException("Row " + v.size() +
1092 | " is too short.");
1093 | }
1094 | int m = v.size(); // Now we've got the number of rows.
1095 | double[][] A = new double[m][];
1096 | v.copyInto(A); // copy the rows out of the vector
1097 | return new Matrix(A);
1098 | }
1099 |
1100 |
1101 | /* ------------------------
1102 | Private Methods
1103 | * ------------------------ */
1104 |
1105 | /**
1106 | * Check if size(A) == size(B)
1107 | **/
1108 | private void checkMatrixDimensions(Matrix B) {
1109 | if (B.m != m || B.n != n) {
1110 | throw new IllegalArgumentException("Matrix dimensions must agree.");
1111 | }
1112 | }
1113 |
1114 |
1115 | /***************************************************************************
1116 | * KALMAN FILTER FUNCTIONS (c) 2007 Petr Chmelar
1117 | **************************************************************************/
1118 |
1119 | /***************************************************************************
1120 | * Generalized linear algebraic matrix-matrix multiplication (of A);
1121 | * C = alpha*A x B + beta*C.
1122 | *
43 | * double[][] vals = {{1.,2.,3},{4.,5.,6.},{7.,8.,10.}};
44 | * Matrix A = new Matrix(vals);
45 | * Matrix b = Matrix.random(3,1);
46 | * Matrix x = A.solve(b);
47 | * Matrix r = A.times(x).minus(b);
48 | * double rnorm = r.normInf();
49 | *
1129 | * C = A.gemm(B, null, 1, 1); // similar to A.times(B);
1130 | * C = A.transpose().gemm(B.transpose(), C, 1, -1);
1131 | *
1132 | * @param B the second source matrix.
1133 | * @param C the matrix where results are to be stored. Set this parameter to
1134 | * null to indicate that a new result matrix shall be constructed.
1135 | * @param alpha a scale factor.
1136 | * @param beta a result scale factor.
1137 | * @return C product matrix (for convenience only).
1138 | * @throws IllegalArgumentException if B.rows() != A.columns().
1139 | * @throws IllegalArgumentException if C.rows() != A.rows() || C.columns() != B.columns().
1140 | * @throws IllegalArgumentException if A == C || B == C.
1141 | */
1142 | public Matrix gemm(Matrix B, Matrix C, double alpha, double beta) {
1143 |
1144 | // m = rows;
1145 | // n = columns;
1146 | int p = B.n; // columns of B
1147 |
1148 | // cannot change C :(
1149 | Matrix X = new Matrix(m, p); // X ~ C
1150 |
1151 | if (C == null) { // multiplication - rare, but necessary :(
1152 |
1153 | if (B.m != n) {
1154 | throw new IllegalArgumentException("Matrix inner dimensions must agree.");
1155 | }
1156 |
1157 | for (int j = p; --j >= 0; ) {
1158 | for (int i = m; --i >= 0; ) {
1159 | double s = 0;
1160 | for (int k = n; --k >= 0; ) {
1161 | s += this.A[i][k] * B.A[k][j];
1162 | }
1163 | X.A[i][j] = alpha * s;
1164 | }
1165 | }
1166 | return X;
1167 |
1168 | } else {
1169 |
1170 | if (B.m != n) {
1171 | throw new IllegalArgumentException("Matrix inner dimensions must agree.");
1172 | }
1173 | if (C.m != m || C.n != p) {
1174 | throw new IllegalArgumentException("Incompatible result matrix.");
1175 | }
1176 |
1177 | for (int j = p; --j >= 0; ) {
1178 | for (int i = m; --i >= 0; ) {
1179 | double s = 0;
1180 | for (int k = n; --k >= 0; ) {
1181 | s += this.A[i][k] * B.A[k][j];
1182 | }
1183 | X.A[i][j] = alpha * s + beta * C.A[i][j];
1184 | }
1185 | }
1186 |
1187 | }
1188 | return X;
1189 | }
1190 |
1191 | /**
1192 | * Hybrid toString.
1193 | *
1194 | * @see print(int w, int d)
1195 | */
1196 | public String toString(int w, int d) {
1197 |
1198 | DecimalFormat format = new DecimalFormat();
1199 | format.setDecimalFormatSymbols(new DecimalFormatSymbols(Locale.US));
1200 | format.setMinimumIntegerDigits(1);
1201 | format.setMaximumFractionDigits(d);
1202 | format.setMinimumFractionDigits(d);
1203 | format.setGroupingUsed(false);
1204 |
1205 | w += 2;
1206 |
1207 | String s;
1208 | String result = "";
1209 |
1210 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
1211 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
1212 | s = format.format(A[i][j]); // format the number
1213 | int padding =
1214 | Math.max(1, w - result.length()); // At _least_ 1 space
1215 |
1216 | result += s;
1217 | for (int k = 0; k < padding; k++)
1218 | result += " ";
1219 | }
1220 | result += "\n";
1221 | }
1222 |
1223 | return result;
1224 | }
1225 |
1226 | /**
1227 | * Overrides the Object {@link Object#toString toString()} method.
1228 | *
1229 | * @return String tab-separated rows on separate lines
1230 | */
1231 | public String toString() {
1232 | String result = "";
1233 |
1234 | for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { // 4 columns
1235 | for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // 4 rows
1236 | // append value
1237 | result += String.valueOf(this.A[j][i]) + "\t";
1238 | }
1239 |
1240 | result += "\n";
1241 | }
1242 | return result;
1243 | }
1244 |
1245 | /**
1246 | * Generate identity matrix
1247 | *
1248 | * @return An m-by-n matrix with ones on the diagonal and zeros elsewhere.
1249 | */
1250 | public Matrix identity() {
1251 | Matrix A = new Matrix(m, n);
1252 | double[][] X = A.getArray();
1253 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
1254 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
1255 | X[i][j] = (i == j ? 1.0 : 0.0);
1256 | }
1257 | }
1258 | return A;
1259 | }
1260 |
1261 | /**
1262 | * Generate identity matrix
1263 | *
1264 | * @param m Number of rows.
1265 | * @param n Number of colums.
1266 | * @return An m-by-n matrix with ones on the diagonal and zeros elsewhere.
1267 | */
1268 | public static Matrix identity(int m, int n, double value) {
1269 | Matrix A = new Matrix(m, n);
1270 | double[][] X = A.getArray();
1271 | for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
1272 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
1273 | X[i][j] = (i == j ? value : 0.0);
1274 | }
1275 | }
1276 | return A;
1277 | }
1278 |
1279 | /** end Petr Chmelar (c) 2007 *************************************************/
1280 |
1281 | }
1282 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------