12 | '''.strip()
13 |
14 | class HeadersTest(TestCase):
15 | def setUp(self):
16 | self.maxDiff = None
17 | self.context = {'object_list': Book.objects.all}
18 | author = Author.objects.create(name='MyAuthor', rating=2)
19 | for i in range(11):
20 | Book.objects.create(author=author, title='B'+str(i), rating=10)
21 |
22 | def testHeaders1(self):
23 | result = render_to_string('django_find/headers.html', self.context)
24 | self.assertEqual(result.strip(), expected_headers, result)
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/django_find/parsers/parser.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | class Parser(object):
2 | """
3 | The base class for all parsers.
4 | """
5 |
6 | def __init__(self, token_list):
7 | self.token_list = token_list
8 | self._reset()
9 |
10 | def _reset(self):
11 | self.offset = 0
12 | self.line = 0
13 | self.error = ''
14 |
15 | def _get_next_token(self):
16 | if len(self.input) <= self.offset:
17 | return 'EOF', None
18 |
19 | # Walk through the list of tokens, trying to find a match.
20 | for token_name, token_regex in self.token_list:
21 | match = token_regex.match(self.input, self.offset)
22 | if not match:
23 | continue
24 |
25 | string = match.group(0)
26 | self.offset += len(string)
27 | self.line += string.count('\n')
28 | return token_name, match
29 |
30 | # Ending up here no matching token was found.
31 | return None, None
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
2 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
3 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
4 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
5 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
6 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
7 |
8 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
9 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
10 |
11 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
12 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
13 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
14 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
15 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
16 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
17 | SOFTWARE.
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/parsers/test_json.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | from django.test import TestCase
3 | from django_find.parsers.json import JSONParser
4 |
5 | query1 = '''
6 | {
7 | "Author":{"name":[[["equals","test"]]]},
8 | "Book": {"title":[[["notcontains","c"]]]},
9 | "Chapter": {"comment":[[["startswith","The "]]]}
10 | }
11 | '''
12 | expected1 = """Group(root)
13 | Term: Author.name equals 'test'
14 | Not
15 | Term: Book.title contains 'c'
16 | Term: Chapter.comment startswith 'The '"""
17 |
18 | query2 = '''
19 | {
20 | "Chapter": {"title":[[["contains","foo"]]]}
21 | }
22 | '''
23 | expected2 = """Group(root)
24 | Term: Chapter.title contains 'foo'"""
25 |
26 | query3 = '''
27 | {
28 | "Book": {"title":[[["contains","foo"]]]},
29 | "Chapter": {"title":[[]]}
30 | }
31 | '''
32 | expected3 = """Group(root)
33 | Term: Book.title contains 'foo'
34 | Term: Chapter.title any ''"""
35 |
36 | class JSONParserTest(TestCase):
37 | def setUp(self):
38 | self.maxDiff = None
39 | self.parser = JSONParser()
40 |
41 | def testParser(self):
42 | dom = self.parser.parse(query1)
43 | self.assertEqual(expected1, dom.dump())
44 |
45 | dom = self.parser.parse(query2)
46 | self.assertEqual(expected2, dom.dump())
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/django_find/templatetags/find_tags.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | from django import template
3 | from django.template.loader import render_to_string
4 |
5 | class SearchNode(template.Node):
6 | def __init__(self, queryset_var, fields):
7 | self.queryset_var = template.Variable(queryset_var)
8 | self.fields = fields
9 |
10 | def render(self, context):
11 | request = context['request']
12 | getvars = request.GET.copy()
13 |
14 | if 'q' in getvars:
15 | # Search, and store the resulting queryset in the current
16 | # context.
17 | query = getvars['q']
18 | queryset = self.queryset_var.resolve(context)
19 | q_obj = queryset.model.q_from_query(query, self.fields)
20 | context[self.queryset_var.var] = queryset.filter(q_obj)
21 |
22 | return render_to_string('django_find/form.html',
23 | {'getvars': getvars})
24 |
25 | def find(parser, token):
26 | contents = token.split_contents()
27 | if len(contents) < 2:
28 | raise template.TemplateSyntaxError(
29 | "%r tag requires at least 1 argument, " +
30 | "in the form of {%% %r model.objects.all [alias1 alias2 ...] %%}" % contents[0])
31 |
32 | return SearchNode(contents[1], contents[2:])
33 |
34 | register = template.Library()
35 | register.tag('find', find)
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/django_find/tree.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | class Node(object):
4 | def __init__(self, children=None, is_root=False):
5 | if isinstance(children, Node):
6 | children = [children]
7 | self.is_root = is_root
8 | self.children = list(children) if children else []
9 |
10 | @classmethod
11 | def precedence(self):
12 | return 0
13 |
14 | @classmethod
15 | def is_logical(self):
16 | return False
17 |
18 | def add(self, child):
19 | self.children.append(child)
20 | return child
21 |
22 | def pop(self):
23 | return self.children.pop()
24 |
25 | def dump(self, indent=0):
26 | isroot = '(root)' if self.is_root else ''
27 | result = [(indent * ' ') + self.__class__.__name__ + isroot]
28 | for child in self.children:
29 | result += child.dump(indent+1)
30 | if self.is_root:
31 | return '\n'.join(result)
32 | return result
33 |
34 | def each(self, func, node_type=None):
35 | """
36 | Runs func once for every node in the object tree.
37 | If node_type is not None, only call func for nodes with the given
38 | type.
39 | """
40 | if node_type is None or isinstance(self, node_type):
41 | func(self)
42 | for child in self.children:
43 | child.each(func, node_type)
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_handlers.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | from copy import copy
3 | from django.test import TestCase
4 | from django_find.handlers import type_registry, LowerCaseStrFieldHandler
5 | from .models import Author
6 |
7 | nicknames = {'robbie': 'Robert Frost'}
8 |
9 | class AuthorNameFieldHandler(LowerCaseStrFieldHandler):
10 | @classmethod
11 | def handles(cls, model, field):
12 | return model._meta.model_name == 'author' and field.name == 'name'
13 |
14 | @classmethod
15 | def prepare(cls, data):
16 | return nicknames.get(data, data)
17 |
18 | class HandlersTest(TestCase):
19 | def setUp(self):
20 | self.maxDiff = None
21 | self.old_type_registry = copy(type_registry)
22 |
23 | def tearDown(self):
24 | del type_registry[:]
25 | type_registry.extend(self.old_type_registry)
26 |
27 | def testTypeRegistry(self):
28 | func = Author.get_field_handler_from_alias
29 | self.assertEqual(func('name'), LowerCaseStrFieldHandler)
30 |
31 | type_registry.insert(0, AuthorNameFieldHandler)
32 | self.assertEqual(func('name'), AuthorNameFieldHandler)
33 |
34 | def testCustomHandler(self):
35 | query = str(Author.q_from_query('name:robbie'))
36 | self.assertEqual(query, "(AND: ('name__icontains', 'robbie'))")
37 |
38 | type_registry.insert(0, AuthorNameFieldHandler)
39 | query = str(Author.q_from_query('name:robbie'))
40 | self.assertEqual(query, "(AND: ('name__icontains', 'Robert Frost'))")
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/handlers.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Custom Handlers
2 | ===============
3 |
4 | What are handlers?
5 | ------------------
6 |
7 | A handler is an object that you can use to define custom
8 | behavior when searching a field of a model.
9 |
10 | You might want to use a handler if you are using a custom
11 | model field, or if your query contains information that
12 | requires client-side processing before being passed to
13 | the database.
14 |
15 | Example
16 | -------
17 |
18 | Lets say you have the following model::
19 |
20 | from django.db import models
21 | from django_find import Searchable
22 |
23 | class Author(models.Model, Searchable):
24 | name = models.CharField("Author Name", max_length=50)
25 |
26 | Author.objects.create(name='Robert Frost')
27 |
28 | Assuming you want to be able to filter for author names, but need
29 | to translate the name first, e.g.::
30 |
31 | Author.by_query('name:robbie')
32 |
33 | You can achieve this by defining a custom handler::
34 |
35 | from django_find.handlers import type_registry, LowerCaseStrFieldHandler
36 |
37 | nicknames = {'robbie': 'Robert Frost'}
38 |
39 | class AuthorNameFieldHandler(LowerCaseStrFieldHandler):
40 | @classmethod
41 | def handles(cls, model, field):
42 | return model._meta.model_name == 'author' and field.name == 'name'
43 |
44 | @classmethod
45 | def prepare(cls, data):
46 | return nicknames.get(data, data)
47 |
48 | type_registry.insert(0, AuthorNameFieldHandler)
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/version.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/sh
2 | # Tag revisions like this:
3 | # $ git tag -a -m "v0.2" v0.2
4 | VERSION_IN=VERSION.in
5 | VERSION_FILE=django_find/version.py
6 |
7 | # Check that we are actually in a git managed project.
8 | if [ ! -e .git -a -z "$1" ]; then
9 | echo >&2 Not a git repository.
10 | exit 1
11 | fi
12 |
13 | # Make sure that we have permission to modify the version file.
14 | if [ -r $VERSION_FILE -a ! -w $VERSION_FILE ]; then
15 | echo >&2 No permission to modify $VERSION_FILE.
16 | exit 1
17 | fi
18 |
19 | # By default, get the version number from "git describe".
20 | if [ ! -z "$1" ]; then
21 | VERSION=$1
22 | else
23 | HEAD=`git log -1 --pretty=format:%H HEAD`
24 | VERSION=`git describe $HEAD --tags --match "v[0-9]*" | sed 's/^v//;s/-[^\-]*$//;s/-/./' 2>/dev/null`
25 | if [ -z "$VERSION" ]; then
26 | echo >&2 No matching tag was found.
27 | exit 1
28 | fi
29 | fi
30 |
31 | # If the --reset switch was given, reset the version number to 'DEVELOPMENT'.
32 | [ "$1" = "--reset" ] && VERSION='DEVELOPMENT'
33 |
34 | # If there is no version file, we are already done.
35 | echo Version is $VERSION
36 | [ ! -r $VERSION_FILE ] && exit 0
37 |
38 | # Check whether the version file already contains this number,
39 | # and only touch it if there is a change to avoid changing
40 | # the timestamp.
41 | VERSION_FILE_TMP=`mktemp`
42 | cat $VERSION_IN | sed "s/@VERSION@/$VERSION/g" > $VERSION_FILE_TMP
43 | if diff -q $VERSION_FILE_TMP $VERSION_FILE; then
44 | echo Version file unchanged.
45 | rm $VERSION_FILE_TMP
46 | exit 0
47 | fi
48 |
49 | mv $VERSION_FILE_TMP $VERSION_FILE
50 | echo Version file updated.
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/parsers/test_query.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | from django.test import TestCase
3 | from django_find.parsers.query import QueryParser
4 |
5 | name_map = {'host': 'Device.metadata_id',
6 | 'model': 'Device.model',
7 | 'interface': 'Unit.interface'}
8 |
9 | query1 = 'host:^test (model:foo or interface:bar)'
10 | expected_dom1 = """Group(root)
11 | Term: Device.metadata_id startswith 'test'
12 | Or
13 | Term: Device.model contains 'foo'
14 | Term: Unit.interface contains 'bar'"""
15 |
16 | query2 = 'test (model:foo or interface:bar$)'
17 | expected_dom2 = """Group(root)
18 | Or
19 | Term: Device.metadata_id contains 'test'
20 | Term: Device.model contains 'test'
21 | Term: Device.model contains 'foo'
22 | Term: Unit.interface endswith 'bar'"""
23 |
24 | query3 = 'hosta host!:no host:yes host!=no host=yes host>=c host<=g host<>no'
25 | expected_dom3 = """Group(root)
26 | Term: Device.metadata_id lt 'z'
27 | Term: Device.metadata_id gt 'a'
28 | Not
29 | Term: Device.metadata_id contains 'no'
30 | Term: Device.metadata_id contains 'yes'
31 | Not
32 | Term: Device.metadata_id equals 'no'
33 | Term: Device.metadata_id equals 'yes'
34 | Term: Device.metadata_id gte 'c'
35 | Term: Device.metadata_id lte 'g'
36 | Not
37 | Term: Device.metadata_id equals 'no'"""
38 |
39 | class QueryParserTest(TestCase):
40 | def setUp(self):
41 | self.maxDiff = None
42 | self.parser = QueryParser(name_map, ('host', 'model'))
43 |
44 | def testParser(self):
45 | dom = self.parser.parse(query1)
46 | self.assertEqual(expected_dom1, dom.dump())
47 |
48 | dom = self.parser.parse(query2)
49 | self.assertEqual(expected_dom2, dom.dump())
50 |
51 | dom1 = self.parser.parse("host:^test$")
52 | dom2 = self.parser.parse("host=test")
53 | self.assertEqual(dom1.dump(), dom2.dump())
54 |
55 | dom = self.parser.parse(query3)
56 | self.assertEqual(expected_dom3, dom.dump())
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Makefile:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | NAME=django_find
2 | VERSION=`python setup.py --version | sed s/^v//`
3 | PREFIX=/usr/local/
4 | BIN_DIR=$(PREFIX)/bin
5 | SITE_DIR=$(PREFIX)`python -c "from __future__ import print_function; import sys; from distutils.sysconfig import get_python_lib; print(get_python_lib()[len(sys.prefix):])"`
6 |
7 | ###################################################################
8 | # Standard targets.
9 | ###################################################################
10 | .PHONY : clean
11 | clean:
12 | find . -name "*.pyc" -o -name "*.pyo" | xargs -n1 rm -f
13 | rm -Rf build *.egg-info
14 | cd docs; make clean
15 |
16 | .PHONY : dist-clean
17 | dist-clean: clean
18 | rm -Rf dist
19 |
20 | .PHONY : doc
21 | doc:
22 | cd doc; make
23 |
24 | install:
25 | mkdir -p $(SITE_DIR)
26 | ./version.sh
27 | export PYTHONPATH=$(SITE_DIR):$(PYTHONPATH); \
28 | python setup.py install --prefix $(PREFIX) \
29 | --install-scripts $(BIN_DIR) \
30 | --install-lib $(SITE_DIR)
31 | ./version.sh --reset
32 |
33 | uninstall:
34 | # Sorry, Python's distutils support no such action yet.
35 |
36 | .PHONY : tests
37 | tests:
38 | ./runtests.py
39 |
40 | ###################################################################
41 | # Package builders.
42 | ###################################################################
43 | targz: clean
44 | ./version.sh
45 | python setup.py sdist --formats gztar
46 | ./version.sh --reset
47 |
48 | tarbz: clean
49 | ./version.sh
50 | python setup.py sdist --formats bztar
51 | ./version.sh --reset
52 |
53 | wheel: clean
54 | ./version.sh
55 | python setup.py bdist_wheel --universal
56 | ./version.sh --reset
57 |
58 | deb: clean
59 | ./version.sh
60 | debuild -S -sa
61 | cd ..; sudo pbuilder build $(NAME)_$(VERSION)-0ubuntu1.dsc; cd -
62 | ./version.sh --reset
63 |
64 | dist: targz tarbz wheel
65 |
66 | ###################################################################
67 | # Publishers.
68 | ###################################################################
69 | dist-publish:
70 | ./version.sh
71 | twine upload dist/*
72 | ./version.sh --reset
73 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/django_find/parsers/json.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | import json
3 | from collections import OrderedDict
4 | from ..dom import Group, And, Or, Not, Term
5 |
6 | class JSONParser(object):
7 | """
8 | Transforms a JSON string into a DOM. The DOM is identical to what
9 | QueryParser generates. Example JSON input::
10 |
11 | {
12 | "Device":
13 | {
14 | "Hostname":
15 | [
16 | [["contains": "s-"],["contains": "-ea1"]],
17 | [["startswith", ""]]
18 | ],
19 | "Tags":
20 | [
21 | [["neq":"asdasd"]]
22 | ]
23 | }
24 | "Component":
25 | {
26 | "Slot": [[]]
27 | }
28 | }
29 | """
30 |
31 | def parse_operators(self, termgroup, term, fieldname):
32 | for operator, value in term:
33 | if operator.startswith('not'):
34 | term = Not(Term(fieldname, operator[3:], value))
35 | else:
36 | term = Term(fieldname, operator, value)
37 | termgroup.add(term)
38 |
39 | def parse_terms(self, fieldgroup, terms, fieldname):
40 | for term in terms:
41 | termgroup = And()
42 | fieldgroup.add(termgroup)
43 | if not term:
44 | termgroup.add(Term(fieldname, 'any', ''))
45 | continue
46 | self.parse_operators(termgroup, term, fieldname)
47 |
48 | def parse_criteria(self, clsgroup, criteria, clsname):
49 | for fieldname, terms in criteria.items():
50 | fieldname = clsname + '.' + fieldname
51 | fieldgroup = Or()
52 | clsgroup.add(fieldgroup)
53 | self.parse_terms(fieldgroup, terms, fieldname)
54 |
55 | def parse(self, json_string):
56 | json_tree = json.loads(json_string, object_pairs_hook=OrderedDict)
57 | result = Group(is_root=True)
58 |
59 | for clsname, criteria in json_tree.items():
60 | clsgroup = And()
61 | result.add(clsgroup)
62 | self.parse_criteria(clsgroup, criteria, clsname)
63 |
64 | return result.optimize()
65 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/django_find/handlers.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from django.db import models
2 |
3 | class FieldHandler(object):
4 | """
5 | Abstract base type for all field handlers.
6 |
7 | A field handler is an object that you can use to define custom
8 | behavior when searching a field of a model.
9 |
10 | You might want to use a field handler if you are using a custom
11 | model field, or if your query contains information that
12 | requires client-side processing before being passed to
13 | the database.
14 | """
15 | db_type = None
16 |
17 | @classmethod
18 | def handles(cls, model, field):
19 | raise NotImplemented
20 |
21 | @classmethod
22 | def prepare(cls, value):
23 | return value
24 |
25 | class StrFieldHandler(FieldHandler):
26 | db_type = 'STR'
27 |
28 | @classmethod
29 | def handles(cls, model, field):
30 | return isinstance(field, (models.CharField, models.TextField))
31 |
32 | class LowerCaseStrFieldHandler(StrFieldHandler):
33 | db_type = 'LCSTR'
34 |
35 | class IPAddressFieldHandler(LowerCaseStrFieldHandler):
36 | @classmethod
37 | def handles(cls, model, field):
38 | return isinstance(field, models.GenericIPAddressField)
39 |
40 | class BooleanFieldHandler(FieldHandler):
41 | db_type = 'BOOL'
42 |
43 | @classmethod
44 | def handles(cls, model, field):
45 | return isinstance(field, models.BooleanField)
46 |
47 | class IntegerFieldHandler(FieldHandler):
48 | db_type = 'INT'
49 |
50 | @classmethod
51 | def handles(cls, model, field):
52 | return isinstance(field, (models.IntegerField, models.AutoField))
53 |
54 | class DateFieldHandler(FieldHandler):
55 | db_type = 'DATE'
56 |
57 | @classmethod
58 | def handles(cls, model, field):
59 | return isinstance(field, models.DateField)
60 |
61 | class DateTimeFieldHandler(FieldHandler):
62 | db_type = 'DATETIME'
63 |
64 | @classmethod
65 | def handles(cls, model, field):
66 | return isinstance(field, models.DateTimeField)
67 |
68 | type_registry = [
69 | LowerCaseStrFieldHandler,
70 | IPAddressFieldHandler,
71 | BooleanFieldHandler,
72 | IntegerFieldHandler,
73 | DateTimeFieldHandler,
74 | DateFieldHandler,
75 | ]
76 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/serializers/test_django.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | from datetime import date, datetime
3 | import datetime
4 | from django.test import TestCase
5 | from django_find.parsers.json import JSONParser
6 | from django_find.serializers.django import DjangoSerializer
7 | from ..models import Author, DummyModel
8 | from ..parsers.test_json import query1, query2
9 |
10 | expected_query1 = """(AND: ('name__iexact', 'test'), (NOT (AND: ('book__title__icontains', 'c'))), ('book__chapter__comment__istartswith', 'The '))"""
11 |
12 | expected_query2 = """(AND: ('book__chapter__title__icontains', 'foo'))"""
13 |
14 | query3 = 'test and updated:"2018-02-01" or updated:^2018-02-02$ added:"^2018-01-01" added:2018-01-02$'
15 | expected_query3 = """(AND: (OR: (AND: (OR: ('hostname__icontains', 'test'), ('address__icontains', 'test'), ('model__icontains', 'test'), ('hostname__icontains', 'test')), ('updated__year', 2018), ('updated__day', 1), ('updated__month', 2)), (AND: ('updated__year', 2018), ('updated__day', 2), ('updated__month', 2), ('updated__hour', 0), ('updated__minute', 0)), ('added__gte', datetime.date(2018, 1, 1)), ('added__lte', datetime.date(2018, 1, 2))))"""
16 |
17 | def to_list_recursive(tpl):
18 | if not isinstance(tpl, tuple):
19 | return tpl
20 | return [to_list_recursive(t) for t in sorted(tpl, key=str)]
21 |
22 | def prep_result(result_str):
23 | result_str = result_str.replace('AND:', "'AND',")
24 | result_str = result_str.replace('OR:', "'OR',")
25 | tuple_in = eval(result_str)
26 | return to_list_recursive(tuple_in)
27 |
28 | class DjangoSerializerTest(TestCase):
29 | def setUp(self):
30 | self.maxDiff = None
31 |
32 | def testDjangoSQLSerializer(self):
33 | parser = JSONParser()
34 | dom = parser.parse(query1)
35 | query = dom.serialize(DjangoSerializer(Author))
36 | self.assertEqual(str(query), expected_query1)
37 |
38 | parser = JSONParser()
39 | dom = parser.parse(query2)
40 | query = dom.serialize(DjangoSerializer(Author))
41 | self.assertEqual(str(query), expected_query2)
42 |
43 | query = DummyModel.q_from_query(query3)
44 | query = prep_result(str(query))
45 | expected = prep_result(expected_query3)
46 | self.assertListEqual(query, expected)
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/install.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Installation
2 | ============
3 |
4 | Prerequisites
5 | -------------
6 |
7 | django-find requires Python 2.7 or Python 3.5 or greater.
8 |
9 | Getting started
10 | ---------------
11 |
12 | Download and install the module
13 | ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
14 |
15 | Download and install using PIP::
16 |
17 | sudo pip3 install django-find
18 |
19 | Alternatively, you may also install the latest development version
20 | from GitHub::
21 |
22 | git clone git://github.com/knipknap/django-find
23 | cd django-find
24 | sudo make install
25 |
26 | Add it to your Django project
27 | ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
28 |
29 | Add "django_find" to your ``INSTALLED_APPS`` setting like this::
30 |
31 | INSTALLED_APPS = [
32 | ...
33 | 'django_find',
34 | ]
35 |
36 | Make sure that the request object is available to templates!
37 | ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
38 |
39 | If you haven't already, you should also install Django's
40 | `django.template.context_processors.request `_
41 | and
42 | `django.template.context_processors.i18n `_.
43 |
44 | In other words, your settings need to set the TEMPLATES
45 | variable to include the context_processors like so::
46 |
47 | TEMPLATES = [
48 | {
49 | 'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
50 | 'DIRS': [
51 | # ...
52 | ],
53 | 'APP_DIRS': True,
54 | 'OPTIONS': {
55 | 'context_processors': [
56 | # ...
57 | 'django.template.context_processors.i18n',
58 | 'django.template.context_processors.request',
59 | ],
60 | },
61 | },
62 | ]
63 |
64 | Add it to your models
65 | ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
66 |
67 | You are now ready to start using the Searchable mixin.
68 | For more information, please continue with the
69 | :doc:`tutorial `.
70 |
71 | Running the automated test suite
72 | --------------------------------
73 |
74 | If you installed from GitHub, you can run the integrated test suite::
75 |
76 | make tests
77 |
78 | There shouldn't be any errors, so if something comes up,
79 | `please file a bug `_.
80 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/models.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from django.db import models
2 | from django_find import Searchable
3 |
4 | class DummyModel(models.Model, Searchable):
5 | hostname = models.CharField(max_length=10)
6 | address = models.CharField(max_length=10)
7 | model = models.CharField(max_length=10)
8 | added = models.DateField(auto_now_add=True, blank=True)
9 | updated = models.DateTimeField(auto_now=True, blank=True)
10 |
11 | searchable = [
12 | ('host', 'hostname'),
13 | ]
14 |
15 | class Meta:
16 | app_label = 'search_tests'
17 |
18 | class Author(models.Model, Searchable):
19 | name = models.CharField("Name", max_length=10)
20 | rating = models.IntegerField("Stars")
21 |
22 | searchable = [
23 | ('author', 'name'),
24 | ('writer', 'name'),
25 | ]
26 |
27 | class Meta:
28 | app_label = 'search_tests'
29 |
30 | class DerivedAuthor(Author):
31 | class Meta:
32 | app_label = 'search_tests'
33 |
34 | class Book(models.Model, Searchable):
35 | author = models.ForeignKey(Author, on_delete=models.CASCADE, verbose_name='AuthorID')
36 | title = models.CharField("The title", max_length=10)
37 | comment = models.CharField("Comment", max_length=10)
38 | rating = models.IntegerField("Stars")
39 |
40 | searchable = [
41 | ('author', 'author__name'),
42 | ('something', 'author'),
43 | ]
44 |
45 | class Meta:
46 | app_label = 'search_tests'
47 |
48 | class Chapter(models.Model, Searchable):
49 | book = models.ManyToManyField(Book)
50 | title = models.CharField(max_length=10)
51 | comment = models.CharField(max_length=10)
52 |
53 | searchable = [
54 | ('book', 'book__title'),
55 | ]
56 |
57 | class Meta:
58 | app_label = 'search_tests'
59 |
60 | class SecondAuthor(models.Model, Searchable):
61 | author = models.ForeignKey(Author, related_name='author2', on_delete=models.CASCADE)
62 | book = models.ForeignKey(Book, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
63 |
64 | searchable = [
65 | ('author', 'author__name'),
66 | ('book', 'book_title'),
67 | ]
68 |
69 | class Meta:
70 | app_label = 'search_tests'
71 |
72 | class SimpleModel(models.Model, Searchable):
73 | title = models.CharField(max_length=10)
74 | comment = models.CharField(max_length=10)
75 | yesno = models.BooleanField("Choose yes or no")
76 |
77 | class Meta:
78 | app_label = 'search_tests'
79 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import sys
3 | from setuptools import find_packages, setup
4 | sys.path.insert(0, 'django_find')
5 | from version import __version__
6 |
7 | descr = '''
8 | django-find is a Django app that makes it easy to add complex
9 | search functionality to your project. It supports two different ways
10 | to search your Django models: Query-based, or JSON-based.
11 |
12 | By query-based, we mean that you can use statements like these
13 | to search (filter) your model:
14 |
15 | - `hello world`
16 | - `author:"robert frost" and (title:road or chapter:2)`
17 |
18 | You can also create complex multi-model searches/filters by
19 | using a JSON-based query.
20 |
21 | Checkout the README.md on Github for more information.
22 | '''.strip()
23 |
24 | # allow setup.py to be run from any path
25 | os.chdir(os.path.normpath(os.path.join(os.path.abspath(__file__), os.pardir)))
26 |
27 | setup(
28 | name='django-find',
29 | version=__version__,
30 | packages=find_packages(),
31 | include_package_data=True,
32 | license='MIT License',
33 | description='Simple but powerful search/filter functionality to Django projects',
34 | long_description=descr,
35 | url='https://github.com/knipknap/django-find',
36 | author='Samuel Abels',
37 | author_email='knipknap@gmail.com',
38 | install_requires=['future',
39 | 'Django>=1.11,<2',
40 | 'mysqlclient',
41 | 'dateparser'],
42 | keywords=' '.join(['django',
43 | 'search',
44 | 'find',
45 | 'filter',
46 | 'query',
47 | 'json',
48 | 'sql',
49 | 'app']),
50 | classifiers=[
51 | 'Environment :: Web Environment',
52 | 'Development Status :: 5 - Production/Stable',
53 | 'Framework :: Django',
54 | 'Framework :: Django :: 1.9',
55 | 'Framework :: Django :: 1.10',
56 | 'Framework :: Django :: 1.11',
57 | 'Intended Audience :: Developers',
58 | 'License :: OSI Approved :: MIT License',
59 | 'Operating System :: OS Independent',
60 | 'Programming Language :: Python',
61 | 'Programming Language :: Python :: 2.7',
62 | 'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.4',
63 | 'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.5',
64 | 'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.6',
65 | 'Topic :: Internet :: WWW/HTTP',
66 | 'Topic :: Internet :: WWW/HTTP :: Dynamic Content',
67 | 'Topic :: Text Processing :: Filters',
68 | ],
69 | )
70 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_tags.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | from django.test import TestCase
3 | from django.test.client import RequestFactory
4 | from django.template import Template, Context
5 | from .models import Author
6 |
7 | form_tmpl = '''
8 | {% load find_tags %}
9 | {% find object_list %}
10 | {% for obj in object_list %}{{ obj.name }},{% endfor %}
11 | '''.strip()
12 |
13 | expected_form1 = '''
14 |
19 |
20 | '''.lstrip()
21 |
22 | expected_form2 = '''
23 |
30 |
31 | '''.lstrip()
32 |
33 | expected_form3 = '''
34 |
41 |
42 | '''.lstrip()
43 |
44 | expected_headers1 = '''
45 |
46 | '''.lstrip()
47 |
48 | class TemplateTagFindTest(TestCase):
49 | def setUp(self):
50 | self.maxDiff = None
51 | self.factory = RequestFactory()
52 | self.template = Template(form_tmpl)
53 | self.context = Context()
54 | self.context['object_list'] = Author.objects.all
55 | for i in range(11):
56 | Author.objects.create(name='A'+str(i), rating=10)
57 |
58 | def testFind1(self):
59 | self.context['request'] = self.factory.get('/')
60 | result = self.template.render(self.context).strip()
61 | expected = expected_form1+'A0,A1,A2,A3,A4,A5,A6,A7,A8,A9,A10,'
62 | self.assertEqual(result, expected, result)
63 |
64 | def testFind2(self):
65 | self.context['request'] = self.factory.get('/?test=test-value')
66 | result = self.template.render(self.context).strip()
67 | expected = expected_form2+'A0,A1,A2,A3,A4,A5,A6,A7,A8,A9,A10,'
68 | self.assertEqual(result, expected, result)
69 |
70 | def testFind3(self):
71 | self.context['request'] = self.factory.get('/?test=test-value&q=A1')
72 | result = self.template.render(self.context).strip()
73 | expected = expected_form3+'A1,A10,'
74 | self.assertEqual(result, expected, result)
75 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/django_find/rawquery.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from django.db import connection
2 |
3 | SQL_MAXINT=9223372036854775807 # SQLite maxint
4 |
5 | def assert_positive_slice(slc):
6 | if (slc.start is not None and slc.start < 0) or \
7 | (slc.stop is not None and slc.stop < 0):
8 | raise IndexError("Negative indexing is not supported")
9 |
10 | class PaginatedRawQuerySet(object):
11 | def __init__(self, model, raw_query, args=None, limit=None, offset=None):
12 | self.model = model
13 | self.raw_query = raw_query
14 | self.args = args if args else []
15 | self.limit = limit
16 | self.offset = offset or 0
17 | self.result_cache = None
18 | self.count_cache = None
19 |
20 | def __copy__(self):
21 | return self.__class__(self.model,
22 | self.raw_query,
23 | self.args,
24 | limit=self.limit,
25 | offset=self.offset)
26 |
27 | def _getslice(self, slc):
28 | assert_positive_slice(slc)
29 | qs = self.__copy__()
30 | qs.offset = slc.start or 0
31 | qs.limit = None if slc.stop is None else (slc.stop-qs.offset)
32 | return qs
33 |
34 | def _getindex(self, idx):
35 | if idx < 0:
36 | raise IndexError("Negative indexing is not supported")
37 | qs = self.__copy__()
38 | qs.offset = self.offset+idx if self.offset else idx
39 | qs.limit = 1
40 | return list(qs)[idx]
41 |
42 | def __getitem__(self, k):
43 | """
44 | Retrieves an item or slice from the set of results.
45 | """
46 | if isinstance(k, slice):
47 | return self._getslice(k)
48 | if isinstance(k, int):
49 | return self._getindex(k)
50 | raise TypeError
51 |
52 | @property
53 | def query(self):
54 | query = self.raw_query
55 | if self.limit is None:
56 | query += ' LIMIT '+str(SQL_MAXINT-self.offset)+' OFFSET '+str(int(self.offset))
57 | else:
58 | query += ' LIMIT '+str(int(self.limit))+' OFFSET '+str(int(self.offset))
59 | return query
60 |
61 | def __iter__(self):
62 | if self.result_cache is None:
63 | with connection.cursor() as cursor:
64 | cursor.execute(self.query, self.args)
65 | self.result_cache = cursor.fetchall()
66 | return iter(self.result_cache)
67 |
68 | def __len__(self):
69 | if self.count_cache is not None:
70 | return self.count_cache
71 | query = 'SELECT COUNT(*) FROM (' + self.query + ') c'
72 | with connection.cursor() as cursor:
73 | cursor.execute(query, self.args)
74 | row = cursor.fetchone()
75 | self.count_cache = int(row[0])
76 | return self.count_cache
77 |
78 | count = property(__len__) # For better compatibility to Django's QuerySet
79 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_rawquery.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | from django.test import TestCase
3 | from django_find.rawquery import PaginatedRawQuerySet
4 | from .models import Author
5 |
6 | class PaginatedRawQuerySetTest(TestCase):
7 | def setUp(self):
8 | self.maxDiff = None
9 | for i in range(10):
10 | Author.objects.create(name='Foo'+str(i), rating=10)
11 | sql = 'SELECT name, rating FROM '+Author._meta.db_table+' ORDER BY name'
12 | self.query = PaginatedRawQuerySet(Author, sql)
13 |
14 | def testModel(self):
15 | self.assertEqual(self.query.model, Author)
16 |
17 | def testGetItem(self):
18 | self.assertEqual(self.query[0], ('Foo0', 10))
19 | self.assertEqual(list(self.query[0:0]), [])
20 | self.assertEqual(list(self.query[0:2]), [('Foo0', 10), ('Foo1', 10)])
21 | self.assertEqual(list(self.query[1:3]), [('Foo1', 10), ('Foo2', 10)])
22 | self.assertEqual(list(self.query[9:12]), [('Foo9', 10),])
23 | self.assertEqual(list(self.query[10:11]), [])
24 | self.assertRaises(IndexError, self.query.__getitem__, -1)
25 | self.assertRaises(IndexError, self.query.__getitem__, slice(-1, 0))
26 | self.assertRaises(IndexError, self.query.__getitem__, slice(0, -1))
27 | self.assertRaises(IndexError, self.query.__getitem__, slice(None, -1))
28 | self.assertRaises(TypeError, self.query.__getitem__, 'a')
29 |
30 | # Test the result cache.
31 | self.assertEqual(self.query[0], ('Foo0', 10))
32 | self.assertEqual(self.query[0], ('Foo0', 10))
33 | self.assertEqual(list(self.query[0:2]), [('Foo0', 10), ('Foo1', 10)])
34 | self.assertEqual(list(self.query[0:2]), [('Foo0', 10), ('Foo1', 10)])
35 |
36 | def testQuery(self):
37 | expected = "SELECT name, rating FROM search_tests_author ORDER BY name"
38 | self.assertTrue(self.query.query.startswith(expected), self.query.query)
39 |
40 | expected = "SELECT name, rating FROM search_tests_author ORDER BY name LIMIT 3 OFFSET 2"
41 | self.assertEqual(self.query[2:5].query, expected)
42 |
43 | expected = "SELECT name, rating FROM search_tests_author ORDER BY name"
44 | self.assertTrue(self.query[:].query.startswith(expected), self.query.query)
45 |
46 | def testLen(self):
47 | self.assertEqual(len(self.query), 10)
48 | self.assertEqual(len(self.query), 10) # Cached
49 | self.assertEqual(len(self.query[2:8]), 6)
50 | self.assertEqual(len(self.query[:8]), 8)
51 | self.assertEqual(len(self.query[:]), 10)
52 | self.assertEqual(len(self.query[1:]), 9)
53 |
54 | def testCount(self):
55 | self.assertEqual(self.query.count, 10)
56 | self.assertEqual(self.query.count, 10) # Cached
57 | self.assertEqual(self.query[2:8].count, 6)
58 | self.assertEqual(self.query[:8].count, 8)
59 | self.assertEqual(self.query[:].count, 10)
60 | self.assertEqual(self.query[1:].count, 9)
61 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/index.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. image:: _static/logo.png
2 | :target: http://django-find.readthedocs.io
3 |
4 | |
5 |
6 | .. image:: https://travis-ci.org/knipknap/django-find.svg?branch=master
7 | :target: https://travis-ci.org/knipknap/django-find
8 |
9 | .. image:: https://coveralls.io/repos/github/knipknap/django-find/badge.svg?branch=master
10 | :target: https://coveralls.io/github/knipknap/django-find?branch=master
11 |
12 | .. image:: https://lima.codeclimate.com/github/knipknap/django-find/badges/gpa.svg
13 | :target: https://lima.codeclimate.com/github/knipknap/django-find
14 | :alt: Code Climate
15 |
16 | .. image:: https://img.shields.io/github/stars/knipknap/django-find.svg
17 | :target: https://github.com/knipknap/django-find/stargazers
18 |
19 | .. image:: https://img.shields.io/github/license/knipknap/django-find.svg
20 | :target: https://github.com/knipknap/django-find/blob/master/COPYING
21 |
22 | django-find
23 | ===========
24 |
25 | What is django-find?
26 | --------------------
27 |
28 | **django-find** is a Django app that makes it easy to add complex
29 | search functionality for the models in your project.
30 |
31 | **django-find** supports two different ways to search your Django models:
32 | Query-based, or JSON-based.
33 |
34 | By query-based, we mean that you can use statements like these
35 | to search your model::
36 |
37 | author:"robert frost" and (title:road or chapter:2)
38 |
39 | To make it easy to do complex searches spanning multiple models, another
40 | method is provided. For example, you may want to allow for custom searches
41 | that let the user choose which models and columns to include.
42 | In other words, a user interface like this:
43 |
44 | .. image:: _static/custom.png
45 | :alt: Custom Search
46 |
47 | For this, a JSON-based search functionality is provided::
48 |
49 | {
50 | "Author":{"name":[[["equals","test"]]]},
51 | "Book": {"title":[[["notcontains","c"]]]},
52 | "Chapter": {"content":[[["startswith","The "]]]}
53 | }
54 |
55 | django-find is smart in figuring out how to join those models
56 | together and return a useful result.
57 |
58 | django-find also provides a template tag that you can use to
59 | render a search field::
60 |
61 | {% load find_tags %}
62 | {% find object_list %}
63 | {% for obj in object_list %}
64 | {{ obj.name }}
65 | {% endfor %}
66 |
67 | What isn't django-find?
68 | =======================
69 |
70 | **django-find** is not a full text search engine, it searches the fields
71 | of your models. In other words, it searches and provides tabular data.
72 |
73 | Contents
74 | --------
75 |
76 | .. toctree::
77 | :maxdepth: 2
78 |
79 | install
80 | tutorial
81 | query
82 | API Documentation
83 |
84 | Development
85 | -----------
86 |
87 | django-find is on `GitHub `_.
88 |
89 | License
90 | -------
91 | django-find is published under the `MIT licence `_.
92 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/runtests.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python2
2 | import glob
3 | import os
4 | import sys
5 |
6 | import django
7 | from django.conf import settings
8 | from django.core.management import execute_from_command_line
9 |
10 |
11 | BASE_DIR = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__))
12 | sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(BASE_DIR, '..')))
13 |
14 | # Unfortunately, apps can not be installed via ``modify_settings``
15 | # decorator, because it would miss the database setup.
16 | CUSTOM_INSTALLED_APPS = (
17 | 'django_find',
18 | 'tests',
19 | 'django.contrib.admin',
20 | )
21 |
22 | ALWAYS_INSTALLED_APPS = (
23 | 'django.contrib.auth',
24 | 'django.contrib.contenttypes',
25 | 'django.contrib.sessions',
26 | 'django.contrib.messages',
27 | 'django.contrib.staticfiles',
28 | )
29 |
30 | ALWAYS_MIDDLEWARE_CLASSES = (
31 | 'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware',
32 | 'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware',
33 | 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',
34 | 'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware',
35 | 'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware',
36 | 'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware',
37 | )
38 |
39 | TEMPLATES = [
40 | {
41 | 'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
42 | 'DIRS': [
43 | ],
44 | 'APP_DIRS': True,
45 | 'OPTIONS': {
46 | 'context_processors': [
47 | 'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',
48 | 'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth',
49 | 'django.template.context_processors.i18n',
50 | 'django.template.context_processors.request',
51 | ],
52 | },
53 | },
54 | ]
55 |
56 | settings.configure(
57 | SECRET_KEY="django_tests_secret_key",
58 | DEBUG=False,
59 | TEMPLATE_DEBUG=False,
60 | ALLOWED_HOSTS=[],
61 | INSTALLED_APPS=ALWAYS_INSTALLED_APPS + CUSTOM_INSTALLED_APPS,
62 | MIDDLEWARE=ALWAYS_MIDDLEWARE_CLASSES,
63 | TEMPLATES=TEMPLATES,
64 | ROOT_URLCONF='tests.urls',
65 | DATABASES={
66 | 'default': {
67 | 'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.sqlite3',
68 | }
69 | },
70 | LANGUAGE_CODE='en-us',
71 | TIME_ZONE='UTC',
72 | USE_I18N=True,
73 | USE_L10N=True,
74 | USE_TZ=True,
75 | STATIC_URL='/static/',
76 | # Use a fast hasher to speed up tests.
77 | PASSWORD_HASHERS=(
78 | 'django.contrib.auth.hashers.MD5PasswordHasher',
79 | ),
80 | FIXTURE_DIRS=glob.glob(BASE_DIR + '/' + '*/fixtures/')
81 |
82 | )
83 |
84 | django.setup()
85 | args = [sys.argv[0], 'test']
86 | # Current module (``tests``) and its submodules.
87 | test_cases = '.'
88 |
89 | # Allow accessing test options from the command line.
90 | offset = 1
91 | try:
92 | sys.argv[1]
93 | except IndexError:
94 | pass
95 | else:
96 | option = sys.argv[1].startswith('-')
97 | if not option:
98 | test_cases = sys.argv[1]
99 | offset = 2
100 |
101 | args.append(test_cases)
102 | # ``verbosity`` can be overwritten from command line.
103 | args.append('--verbosity=2')
104 | args.extend(sys.argv[offset:])
105 |
106 | execute_from_command_line(args)
107 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_refs.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | from django.test import TestCase
3 | from django_find import Searchable
4 | from django_find.refs import get_subclasses, child_classes, parent_classes, \
5 | get_field_to, get_join_for, get_object_vector_to
6 | from .models import Author, DerivedAuthor, SecondAuthor, Book, Chapter
7 |
8 | class RefsTest(TestCase):
9 | def setUp(self):
10 | self.maxDiff = None
11 |
12 | def testGetSubClasses(self):
13 | result = get_subclasses(Searchable)
14 | self.assertIn(Author, result)
15 | self.assertIn(Book, result)
16 | self.assertIn(DerivedAuthor, result)
17 | self.assertNotIn(RefsTest, result)
18 |
19 | def testChildClasses(self):
20 | #children = child_classes(Author)
21 | #self.assertEqual(children, [Book, SecondAuthor])
22 | children = child_classes(Book)
23 | self.assertEqual(children, [Chapter, SecondAuthor])
24 |
25 | def testParentClasses(self):
26 | parents = parent_classes(Author)
27 | self.assertEqual(parents, [])
28 | parents = parent_classes(Book)
29 | self.assertEqual(parents, [Author])
30 | parents = parent_classes(SecondAuthor)
31 | self.assertEqual(parents, [Author, Book])
32 |
33 | def testGetFieldTo(self):
34 | field = get_field_to(Author, Book)
35 | self.assertEqual(field, None)
36 | field = get_field_to(Book, Author)
37 | self.assertEqual(field, Book._meta.get_field('author'))
38 |
39 | def testGetObjectVectorTo(self):
40 | self.assertEqual(get_object_vector_to(Author, Book, Searchable),
41 | [(Author, Book),
42 | (Author, DerivedAuthor, Book),
43 | (Author, SecondAuthor, Book),
44 | (Author, DerivedAuthor, SecondAuthor, Book)])
45 |
46 | self.assertEqual(get_object_vector_to(Author, Chapter, Searchable),
47 | [(Author, Book, Chapter),
48 | (Author, DerivedAuthor, Book, Chapter),
49 | (Author, SecondAuthor, Book, Chapter),
50 | (Author, DerivedAuthor, SecondAuthor, Book, Chapter)])
51 |
52 | self.assertEqual(get_object_vector_to(Author, SecondAuthor, Searchable),
53 | [(Author, SecondAuthor),
54 | (Author, DerivedAuthor, SecondAuthor),
55 | (Author, Book, SecondAuthor),
56 | (Author, DerivedAuthor, Book, SecondAuthor)])
57 |
58 | def testGetJoinFor(self):
59 | expected = [('search_tests_author', None, None),
60 | ('search_tests_book', 'author_id', 'search_tests_author.id'),
61 | ('search_tests_chapter_book', 'book_id', 'search_tests_book.id'),
62 | ('search_tests_chapter', 'id', 'search_tests_chapter_book.chapter_id')]
63 | self.assertEqual(get_join_for((Author, Book, Chapter)), expected)
64 |
65 | expected = [('search_tests_chapter', None, None),
66 | ('search_tests_chapter_book', 'chapter_id', 'search_tests_chapter.id'),
67 | ('search_tests_book', 'id', 'search_tests_chapter_book.book_id'),
68 | ('search_tests_author', 'id', 'search_tests_book.author_id'),
69 | ('search_tests_secondauthor', 'author_id', 'search_tests_author.id')]
70 | self.assertEqual(get_join_for((Chapter, Book, Author, SecondAuthor)), expected)
71 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # django-find
2 |
3 | [](https://travis-ci.org/knipknap/django-find)
4 | [](https://coveralls.io/github/knipknap/django-find?branch=master)
5 | [](https://lima.codeclimate.com/github/knipknap/django-find)
6 | [](http://django-find.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
7 |
8 | ## Summary
9 |
10 | **django-find** is a Django app that makes it easy to add complex
11 | search/filter functionality for the models in your project.
12 | It supports two different ways to search your Django models:
13 | Query-based, or JSON-based.
14 |
15 | **django-find** is not a full text search engine, it searches the fields
16 | of your models. In other words, it filters on your models and provides
17 | tabular data as a result.
18 |
19 | ## Features
20 |
21 | ### Query-based search
22 |
23 | By query-based, we mean that you can use statements like these
24 | to search your models:
25 |
26 | ```
27 | author:"robert frost" and (title:road or chapter:2)
28 | ```
29 |
30 | ### Add a search field to your template using a single tag
31 |
32 | ```
33 | {% load find_tags %}
34 | {% find object_list %}
35 | {% for obj in object_list %}
36 | {{ obj.name }}
37 | {% endfor %}
38 | ```
39 |
40 | (object\_list is a queryset that is passed to the template)
41 |
42 | ### Query in your code
43 |
44 | Just add the Searchable mixin:
45 |
46 | ```python
47 | from django_find import Searchable
48 |
49 | class Author(models.Model, Searchable):
50 | name = models.CharField("Author Name", max_length=10)
51 | ...
52 | ```
53 |
54 | And you are good to go:
55 |
56 | ```python
57 | # Query-based search returns a standard Django QuerySet that you
58 | # can .filter() and work with as usual.
59 | query = Book.by_query('author:"robert frost" and title:"the road"')
60 |
61 | # You can also get a Django Q object for the statements.
62 | q_obj = Book.q_from_query('author:"robert frost" and title:"the road"')
63 | ```
64 |
65 | ### Query using JSON
66 |
67 | To make it easy to do complex searches spanning multiple models, JSON-based
68 | query method is provided. It allows your to make custom searches like these:
69 |
70 | 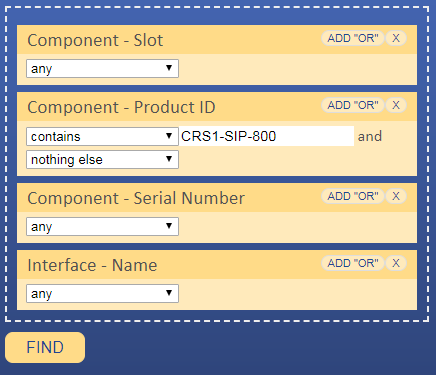
71 |
72 | For this, a JSON-based search functionality is provided:
73 |
74 | ```
75 | {
76 | "Author":{"name":[[["equals","test"]]]},
77 | "Book": {"title":[[["notcontains","c"]]]},
78 | "Chapter": {"content":[[["startswith","The "]]]}
79 | }
80 | ```
81 |
82 | django-find is smart in figuring out how to join those models
83 | together and return a useful result.
84 | In your code, you can load the JSON and get back the search
85 | result:
86 |
87 | ```python
88 | # JSON-based search exhausts what Django's ORM can do, so it does
89 | # not return a Django QuerySet, but a row-based PaginatedRawQuerySet:
90 | query, field_list = Book.by_json_raw('''{
91 | "Chapter": {"title":[[["contains","foo"]]]}
92 | }''')
93 | print('|'.join(field_list))
94 | for row in query:
95 | print('|'.join(row))
96 | ```
97 |
98 | ## Documentation
99 |
100 | Full documentation, including installation instructions, is here:
101 |
102 | http://django-find.readthedocs.io
103 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/serializers/test_sql.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | from django.test import TestCase
3 | from django_find.parsers.json import JSONParser
4 | from django_find.serializers.sql import SQLSerializer
5 | from ..models import Author, DummyModel
6 | from ..parsers.test_json import query1, expected1, query2, expected2, \
7 | query3, expected3
8 |
9 | expected_select1 = """SELECT DISTINCT search_tests_author.name search_tests_author_name, search_tests_book.title search_tests_book_title, search_tests_chapter.comment search_tests_chapter_comment FROM search_tests_author LEFT JOIN search_tests_book ON search_tests_book.author_id=search_tests_author.id LEFT JOIN search_tests_chapter_book ON search_tests_chapter_book.book_id=search_tests_book.id LEFT JOIN search_tests_chapter ON search_tests_chapter.id=search_tests_chapter_book.chapter_id WHERE (search_tests_author.name LIKE 'test' AND NOT(search_tests_book.title LIKE '%c%') AND search_tests_chapter.comment LIKE 'the %')"""
10 |
11 | expected_select2 = """SELECT DISTINCT search_tests_chapter.title search_tests_chapter_title FROM search_tests_chapter WHERE (search_tests_chapter.title LIKE '%foo%')"""
12 |
13 | expected_select3 = """SELECT DISTINCT search_tests_book.title search_tests_book_title, search_tests_chapter.title search_tests_chapter_title FROM search_tests_book LEFT JOIN search_tests_chapter_book ON search_tests_chapter_book.book_id=search_tests_book.id LEFT JOIN search_tests_chapter ON search_tests_chapter.id=search_tests_chapter_book.chapter_id WHERE (search_tests_book.title LIKE '%foo%' AND 1)"""
14 |
15 | query4 = 'test and updated:"2018-02-01" or updated:^2018-02-02$ added:"^2018-01-01" added:2018-01-02$'
16 | expected_select4 = """SELECT DISTINCT search_tests_dummymodel.hostname search_tests_dummymodel_hostname, search_tests_dummymodel.address search_tests_dummymodel_address, search_tests_dummymodel.model search_tests_dummymodel_model, search_tests_dummymodel.added search_tests_dummymodel_added, search_tests_dummymodel.updated search_tests_dummymodel_updated, search_tests_dummymodel.hostname search_tests_dummymodel_hostname__1 FROM search_tests_dummymodel WHERE (((search_tests_dummymodel.hostname LIKE '%test%' OR search_tests_dummymodel.address LIKE '%test%' OR search_tests_dummymodel.model LIKE '%test%' OR search_tests_dummymodel.hostname LIKE '%test%') AND search_tests_dummymodel.updated='2018-02-01T00:00:00') OR search_tests_dummymodel.updated='2018-02-02T00:00:00' OR search_tests_dummymodel.added>='2018-01-01' OR search_tests_dummymodel.added<='2018-01-02')"""
17 |
18 | class SQLSerializerTest(TestCase):
19 | def setUp(self):
20 | self.maxDiff = None
21 |
22 | def testSerialize(self):
23 | parser = JSONParser()
24 | dom = parser.parse(query1)
25 | self.assertEqual(expected1, dom.dump())
26 | select, args = dom.serialize(SQLSerializer(Author))
27 | self.assertEqual(expected_select1, select % tuple(args))
28 |
29 | parser = JSONParser()
30 | dom = parser.parse(query2)
31 | self.assertEqual(expected2, dom.dump())
32 | select, args = dom.serialize(SQLSerializer(Author))
33 | self.assertEqual(expected_select2, select % tuple(args))
34 |
35 | parser = JSONParser()
36 | dom = parser.parse(query3)
37 | self.assertEqual(expected3, dom.dump())
38 | select, args = dom.serialize(SQLSerializer(Author))
39 | self.assertEqual(expected_select3, select % tuple(args))
40 |
41 | dom = DummyModel.dom_from_query(query4)
42 | select, args = dom.serialize(SQLSerializer(DummyModel))
43 | self.assertEqual(expected_select4, select % tuple(args))
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/django_find/serializers/django.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | from functools import reduce
3 | from django.db.models import Q
4 | from .serializer import Serializer
5 | from .util import parse_date, parse_datetime
6 |
7 | int_op_map = {'equals': 'exact',
8 | 'contains': 'exact',
9 | 'startswith': 'gte',
10 | 'endswith': 'lte'}
11 |
12 | str_op_map = {'equals': 'exact',
13 | 'gt': 'startswith',
14 | 'gte': 'startswith',
15 | 'lt': 'endswith',
16 | 'lte': 'endswith'}
17 |
18 | date_op_map = {'startswith': 'gte',
19 | 'endswith': 'lte'}
20 |
21 | class DjangoSerializer(Serializer):
22 | def __init__(self, model):
23 | Serializer.__init__(self)
24 | self.model = model
25 |
26 | def logical_and(self, terms):
27 | terms = [t for t in terms if t]
28 | return reduce(lambda x, y: x.__and__(y), terms, Q())
29 |
30 | def logical_or(self, terms):
31 | terms = [t for t in terms if t]
32 | if not terms:
33 | return Q()
34 | return reduce(lambda x, y: x.__or__(y), terms)
35 |
36 | def logical_not(self, terms):
37 | if len(terms) == 1:
38 | return ~terms[0]
39 | return ~self.logical_and(terms)
40 |
41 | def boolean_term(self, selector, operator, data):
42 | value = data.lower() == 'true'
43 | return Q(**{selector: value})
44 |
45 | def int_term(self, selector, operator, data):
46 | try:
47 | value = int(data)
48 | except ValueError:
49 | return Q()
50 | operator = int_op_map.get(operator, operator)
51 | if operator == 'exact':
52 | return Q(**{selector: value})
53 | return Q(**{selector+'__'+operator: value})
54 |
55 | def str_term(self, selector, operator, data):
56 | operator = str_op_map.get(operator, operator)
57 | return Q(**{selector+'__'+operator: data})
58 |
59 | def lcstr_term(self, selector, operator, data):
60 | operator = str_op_map.get(operator, operator)
61 | return Q(**{selector+'__i'+operator: data})
62 |
63 | def date_datetime_common(self, selector, operator, thedatetime):
64 | if not thedatetime:
65 | return Q()
66 | operator = date_op_map.get(operator, operator)
67 | if operator in ('contains', 'equals'):
68 | return Q(**{selector+'__year': thedatetime.year,
69 | selector+'__month': thedatetime.month,
70 | selector+'__day': thedatetime.day})
71 | return Q(**{selector+'__'+operator: thedatetime})
72 |
73 | def date_term(self, selector, operator, data):
74 | thedate = parse_date(data)
75 | return self.date_datetime_common(selector, operator, thedate)
76 |
77 | def datetime_term(self, selector, operator, data):
78 | thedatetime = parse_datetime(data)
79 | result = self.date_datetime_common(selector, operator, thedatetime)
80 | if operator != 'equals' or not result:
81 | return result
82 | return result&Q(**{selector+'__hour': thedatetime.hour,
83 | selector+'__minute': thedatetime.minute})
84 |
85 | def term(self, name, operator, data):
86 | if operator == 'any':
87 | return Q()
88 |
89 | cls, alias = self.model.get_class_from_fullname(name)
90 | handler = cls.get_field_handler_from_alias(alias)
91 | selector = self.model.get_selector_from_fullname(name)
92 |
93 | type_map = {'BOOL': self.boolean_term,
94 | 'INT': self.int_term,
95 | 'STR': self.str_term,
96 | 'LCSTR': self.lcstr_term,
97 | 'DATE': self.date_term,
98 | 'DATETIME': self.datetime_term}
99 |
100 | func = type_map.get(handler.db_type)
101 | if not func:
102 | raise TypeError('unsupported field type: '+repr(field_type))
103 | return func(selector, operator, handler.prepare(data))
104 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/django_find/dom.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from builtins import str
2 | from .tree import Node
3 |
4 | operators = [
5 | 'contains',
6 | 'equals',
7 | 'startswith',
8 | 'endswith',
9 | 'regex',
10 | 'gt',
11 | 'gte',
12 | 'lt',
13 | 'lte',
14 | 'any'
15 | ]
16 |
17 | class Group(Node):
18 | def translate_term_names(self, name_map):
19 | def translate(dom_obj):
20 | dom_obj.name = name_map.get(dom_obj.name, dom_obj.name)
21 | self.each(translate, Term)
22 |
23 | def get_term_names(self):
24 | """
25 | Returns a flat list of the names of all Terms in the query, in
26 | the order in which they appear. Filters duplicates.
27 | """
28 | field_names = []
29 | def collect_field_names(dom_obj):
30 | if not dom_obj.name in field_names:
31 | field_names.append(dom_obj.name)
32 | self.each(collect_field_names, Term)
33 | return field_names
34 |
35 | def auto_leave_scope(self):
36 | return False
37 |
38 | def optimize(self):
39 | children = [c.optimize() for c in self.children]
40 | self.children = [c for c in children if c is not None]
41 | children = []
42 | for child in self.children:
43 | if type(child) == type(self):
44 | for grandchild in child.children:
45 | children.append(grandchild)
46 | else:
47 | children.append(child)
48 | self.children = children
49 | if not self.children and not self.is_root:
50 | return None
51 | if len(self.children) == 1 and not self.is_root:
52 | return self.children[0]
53 | return self
54 |
55 | def serialize(self, strategy):
56 | results = [c.serialize(strategy) for c in self.children]
57 | if self.is_root:
58 | return strategy.logical_root_group(self, results)
59 | return strategy.logical_group(results)
60 |
61 | class And(Group):
62 | @classmethod
63 | def is_logical(self):
64 | return True
65 |
66 | @classmethod
67 | def precedence(self):
68 | return 2
69 |
70 | def serialize(self, strategy):
71 | return strategy.logical_and(c.serialize(strategy)
72 | for c in self.children)
73 |
74 | class Or(Group):
75 | @classmethod
76 | def is_logical(self):
77 | return True
78 |
79 | @classmethod
80 | def precedence(self):
81 | return 1
82 |
83 | def serialize(self, strategy):
84 | return strategy.logical_or(c.serialize(strategy)
85 | for c in self.children)
86 |
87 | class Not(Group):
88 | @classmethod
89 | def precedence(self):
90 | return 3
91 |
92 | def auto_leave_scope(self):
93 | return True
94 |
95 | def optimize(self):
96 | children = [c.optimize() for c in self.children]
97 | self.children = [c for c in children if c is not None]
98 | if not self.children and not self.is_root:
99 | return None
100 | return self
101 |
102 | def serialize(self, strategy):
103 | children = [c.serialize(strategy) for c in self.children]
104 | return strategy.logical_not(children)
105 |
106 | class Term(Node):
107 | def __init__(self, name, operator, data):
108 | assert operator in operators, "unsupported operator {}".format(operator)
109 | Node.__init__(self)
110 | self.name = name
111 | self.operator = str(operator)
112 | self.data = str(data)
113 |
114 | def optimize(self):
115 | return self
116 |
117 | def each(self, func, node_type):
118 | if node_type is None or isinstance(self, node_type):
119 | func(self)
120 |
121 | def dump(self, indent=0):
122 | return [(indent * ' ')
123 | + self.__class__.__name__ + ': '
124 | + self.name + ' ' + self.operator + ' ' + repr(self.data)]
125 |
126 | def serialize(self, strategy):
127 | return strategy.term(self.name, self.operator, self.data)
128 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/tutorial.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Tutorial
2 | ========
3 |
4 | Introduction
5 | ------------
6 |
7 | We'll assume that django-find is already installed, and added
8 | to your Django project. The instructions are :doc:`here `.
9 |
10 | Motivation
11 | ----------
12 |
13 | Assume you want to add a search box to your user interface, where
14 | your users can search your models using a simple query language.
15 | For example:
16 |
17 | - ``hello world`` (searches all fields for hello and world)
18 | - ``robert OR title:road`` (searches all fields for "robert", and "title" for "road")
19 |
20 | The documentation of the query language is :doc:`here `.
21 |
22 | Alternatively, you may want to allow the user to specify the
23 | models and columns to display with a UI like this:
24 |
25 | .. image:: _static/custom.png
26 | :target: http://django-find.readthedocs.io
27 |
28 | django-find supports JSON-based queries for this purpose.
29 |
30 | Getting started
31 | ---------------
32 |
33 | Enabling the functionality is as simple as adding the "Searchable"
34 | mixin to your models. Example::
35 |
36 | from django.db import models
37 | from django_find import Searchable
38 |
39 | class Author(models.Model, Searchable):
40 | name = models.CharField("Author Name", max_length=10)
41 |
42 | class Book(models.Model, Searchable):
43 | author = models.ForeignKey(Author, on_delete=models.CASCADE, verbose_name='Author')
44 | title = models.CharField("Title", max_length=80)
45 | rating = models.IntegerField("Rating")
46 | internal_id = models.CharField(max_length=10)
47 |
48 | That is all, you are now ready to query your models using your own code,
49 | or in your templates.
50 |
51 | Query from your own code
52 | ------------------------
53 |
54 | All models having the Searchable mixin added provide the following methods::
55 |
56 | # Query-based search returns a standard Django QuerySet that you
57 | # can .filter() and work with as usual.
58 | query = Book.by_query('author:"robert frost" and title:"the road"')
59 |
60 | # You can also get a Django Q object for the statements.
61 | q_obj = Book.q_from_query('author:"robert frost" and title:"the road"')
62 |
63 | # JSON-based search exhausts what Django's ORM can do, so it does
64 | # not return a Django QuerySet, but a row-based PaginatedRawQuerySet:
65 | query, field_list = Book.by_json_raw('''{
66 | "Chapter": {"title":[[["contains","foo"]]]}
67 | }''')
68 | print('|'.join(field_list))
69 | for row in query:
70 | print('|'.join(row))
71 |
72 | You can pass the PaginatedRawQuerySet to Django templates as you
73 | would with a Django QuerySet, as it supports slicing and
74 | pagination.
75 |
76 | In most cases, you also want to specify some other, related
77 | fields that can be searched, or exclude some columns from the search.
78 | The following example shows how to do that::
79 |
80 | class Book(models.Model, Searchable):
81 | author = models.ForeignKey(Author, on_delete=models.CASCADE, verbose_name='Author')
82 | title = models.CharField("Title", max_length=10)
83 | rating = models.IntegerField("Rating")
84 | internal_id = models.CharField(max_length=10)
85 |
86 | searchable = [
87 | ('author', 'author__name'), # Search the name instead of the id of the related model. Note the selector syntax
88 | ('stars', 'rating'), # Add an extra alias for "rating" that can be used in a query.
89 | ('internal_id', False), # Exclude from search
90 | ]
91 |
92 | In other words, add a "searchable" attribute to your models, that lists the
93 | aliases and maps them to a Django field using Django's selector syntax
94 | (underscore-separated field names).
95 |
96 | Query from within templates
97 | ---------------------------
98 |
99 | Using the template tag
100 | ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
101 |
102 | django-find also provides a template tag that you can use to
103 | render a search field::
104 |
105 | {% load find_tags %}
106 | {% find object_list %}
107 | {% for obj in object_list %}
108 | {{ obj.name }}
109 | {% endfor %}
110 |
111 | You will probably want to use this together with
112 | `dj-pagination `_ like so::
113 |
114 | {% load find_tags %}
115 | {% load pagination_tags %}
116 |
117 | {% find object_list %}
118 | Found {{ object_list.count }} results.
119 |
120 | {% autopaginate object_list %}
121 |
122 | {% for obj in object_list %}
123 |
{{ obj.name }}
124 | {% endfor %}
125 |
126 |
127 | {% paginate %}
128 |
129 | Using provided templates
130 | ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
131 |
132 | django-find comes with some templates that you may find useful::
133 |
134 | {% include 'django_find/headers.html' with object_list=author.objects.all %}
135 |
136 | This produces a ``
`` that contains the column headers as returned
137 | by ``Searchable.table_headers()``, e.g.::
138 |
139 |
140 |
Name
The title
Comment
Stars
141 |
142 |
143 | Custom field types
144 | ------------------
145 |
146 | To support your own field types, check the documentation for
147 | :doc:`handlers `.
148 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/query.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | The django-find Query Language
2 | ==============================
3 |
4 | Introduction
5 | ------------
6 |
7 | In this chapter, we explain the query language that can be passed to
8 | ``Searchable.by_query()``.
9 |
10 | For example:
11 |
12 | - ``hello world`` (searches all fields for hello and world)
13 | - ``robert OR title:road`` (searches all fields for "robert", and "title" for "road")
14 |
15 | The basics
16 | ----------
17 |
18 | To search all available fields, simply enter a word. For example,
19 | the following query searches all fields for "test"::
20 |
21 | test
22 |
23 | When using multiple words, the query returns all entries that match
24 | all of the words. In other words, the following query returns all
25 | entries that have both, 'foo' in any field AND 'bar' in any field::
26 |
27 | foo bar
28 |
29 | To search for strings including whitespace, use double quotes. The
30 | following string returns all models that have a field containing
31 | "foo bar" (without quotes)::
32 |
33 | "foo bar"
34 |
35 | Search individual fields
36 | ------------------------
37 |
38 | To limit your search to a specific field, you can
39 | use the following syntax::
40 |
41 | author:robert
42 | author:"robert frost"
43 | author:robert author:frost title:road
44 |
45 | Limiting a search to the beginning or end of a string
46 | -----------------------------------------------------
47 |
48 | To search a string in a particular location of a field, use the
49 | ``^`` and ``$`` operators. To search at the beginning, use::
50 |
51 | ^test
52 | author:^robert
53 |
54 | To search a string at the end of a field, use::
55 |
56 | test$
57 | author:frost$
58 |
59 | To look for an exact match, use either both, ``^`` and ``$``, or
60 | use an equal sign (``=``) instead. The following queries all look
61 | for an exact match::
62 |
63 | ^test$
64 | author:^frost$
65 | author=frost
66 | author:"^robert frost$"
67 | author="robert frost"
68 |
69 | Boolean operators
70 | -----------------
71 |
72 | Boolean AND
73 | ~~~~~~~~~~~
74 |
75 | When you specify multiple words, django-find by default returns
76 | all entries that match all of the words. In other words, django-find
77 | behaves like a boolean AND. The following queries are all equivalent::
78 |
79 | foo bar
80 | foo AND bar
81 | foo and bar
82 | "foo" and "bar"
83 |
84 | Boolean OR
85 | ~~~~~~~~~~
86 |
87 | You can also use boolean OR operators. Here are some examples::
88 |
89 | "robert frost" OR "mark twain"
90 | robert or mark
91 | ^robert or twain$ or foo or title:test
92 | author:^robert or author:twain$
93 |
94 | Boolean NOT
95 | ~~~~~~~~~~~
96 |
97 | To find fields that DON'T match a particular string, use NOT::
98 |
99 | "robert frost" not title:"the road"
100 | "robert frost" and not title:"the road"
101 | not foo or not bar
102 |
103 | Grouping
104 | --------
105 |
106 | For more complex searches, you can use brackets to group sub-expressions.
107 | Arbitrary nesting is supported::
108 |
109 | author:robert and not (title:"the road" or title:"yellow")
110 | test (name:foo and (book:one or book:two) and (chapter:10 or chapter:12 or chapter:13))
111 |
112 | Searching dates and times
113 | -------------------------
114 |
115 | Date formats
116 | ~~~~~~~~~~~~
117 |
118 | django-find accepts all formats that are supported by the
119 | `dateparser `_ python module.
120 | Some examples::
121 |
122 | 12/12/12
123 | 2018-01-22
124 | "2018-01-22 10:00"
125 | "10:40 pm"
126 | "August 14, 2015 EST"
127 | "1 min ago"
128 | "2 weeks ago"
129 | "3 months, 1 week and 1 day ago"
130 | "in 2 days"
131 | tomorrow
132 |
133 | For a full list of supported formats, please check the
134 | `dateparser documentation `_.
135 |
136 | Searching for ranges
137 | ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
138 |
139 | You can use them to look for time ranges. The following query
140 | returns all entries that were updated after the beginning of
141 | January 1st, 12:00am::
142 |
143 | updated>=2018-1-1
144 |
145 | Similarly, you can get the entries that were updated before 2018::
146 |
147 | updated<2018-1-1
148 |
149 | To look for a range, use AND::
150 |
151 | updated>=2018-1-1 updated<=2019-1-1
152 | updated>=2018-1-1 AND updated<=2019-1-1
153 |
154 | When searching for dates and times, the ``^`` and ``$`` characters
155 | have special meanings: They are equivalent to ``<=`` and ``>=``. In
156 | other words, the following queries are equivalent when used on a
157 | DateField or DateTimeField::
158 |
159 | updated:^2018-1-1
160 | updated>=2018-1-1
161 |
162 | To look for an exact match, use both::
163 |
164 | updated:"^2018-1-1 11:00$"
165 |
166 | Operator list
167 | -------------
168 |
169 | Here is the full list of operators supported by **django-find**::
170 |
171 | name=foo -> Name matching "foo" exactly
172 | name:^foo$ -> Equivalent to the previous query
173 | name!=foo -> Name not matching "foo" exactly
174 | name<>foo -> Equivalent to the previous query
175 |
176 | name:foo -> Name containing the substring "foo"
177 | name!:foo -> Name not containing the substring "foo"
178 | name:^foo -> Name starting with the substring "foo"
179 | name!:^foo -> Name not starting the substring "foo"
180 | name:foo$ -> Name ending with the substring "foo"
181 | name!:foo$ -> Name not ending the substring "foo"
182 |
183 | id>1 -> Greater than
184 | id>=1 -> Greater than or equal
185 | id=>1 -> Greater than or equal
186 | id<5 -> Less than
187 | id<=5 -> Less than or equal
188 | id=>5 -> Less than or equal
189 | id<>5 -> Unequal
190 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/django_find/parsers/query.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import re
2 | from ..refs import get_subclasses
3 | from django_find import models
4 | from collections import OrderedDict
5 | from .parser import Parser
6 | from ..dom import Group, And, Or, Not, Term
7 |
8 | operators = OrderedDict((
9 | ('!=', 'notequals'),
10 | ('<>', 'notequals'),
11 | ('>=', 'gte'),
12 | ('=>', 'gte'),
13 | ('>', 'gt'),
14 | ('<=', 'lte'),
15 | ('=<', 'lte'),
16 | ('<', 'lt'),
17 | (':', 'contains'),
18 | ('!:', 'notcontains'),
19 | ('=', 'equals'),
20 | ))
21 |
22 | operators_str = '|'.join(list(operators.keys()))
23 | tokens = [
24 | ('and', re.compile(r'and\b', re.I)),
25 | ('or', re.compile(r'or\b', re.I)),
26 | ('not', re.compile(r'not\b', re.I)),
27 | ('openbracket', re.compile(r'\(')),
28 | ('closebracket', re.compile(r'\)')),
29 | ('whitespace', re.compile(r'\s+')),
30 | ('field', re.compile(r'([\w\-]+)({})'.format(operators_str))),
31 | ('word', re.compile(r'"([^"]*)"')),
32 | ('word', re.compile(r'([^"\s\\\'\)]+)')),
33 | ('unknown', re.compile(r'.'))
34 | ]
35 |
36 | def open_scope(scopes, scope):
37 | scopes.append(scopes[-1].add(scope))
38 |
39 | def close_scope(scopes):
40 | while scopes[-1].auto_leave_scope() and not scopes[-1].is_root:
41 | scopes.pop()
42 |
43 | def op_from_word(word):
44 | if word.startswith('^') and word.endswith('$'):
45 | return word[1:-1], 'equals'
46 | elif word.startswith('^'):
47 | return word[1:], 'startswith'
48 | elif word.endswith('$'):
49 | return word[:-1], 'endswith'
50 | return word, 'contains'
51 |
52 | def get_term_from_op(field, operator, value):
53 | op = operators.get(operator)
54 |
55 | if op == 'contains':
56 | value, op = op_from_word(value)
57 | if op == 'notcontains':
58 | value, op = op_from_word(value)
59 | op = 'not'+op
60 |
61 | if op.startswith('not'):
62 | return Not(Term(field, op[3:], value))
63 | return Term(field, op, value)
64 |
65 | class QueryParser(Parser):
66 | def __init__(self, fields, default):
67 | """
68 | Fields is a map that translates aliases to something like
69 | Book.author.
70 | """
71 | Parser.__init__(self, tokens)
72 | self.fields = fields
73 | self.default = default or fields
74 | for name in self.default:
75 | if name not in self.fields:
76 | raise AttributeError('constructor argument "default" contains'\
77 | +' "{}", which is not also in "fields"'.format(name))
78 |
79 | def parse_word(self, scopes, match):
80 | self.parse_or(scopes, ())
81 | child = Or()
82 | for name in self.default:
83 | name = self.fields[name]
84 | value, operator = op_from_word(match.group(1))
85 | child.add(Term(name, operator, value))
86 | scopes[-1].add(child)
87 | close_scope(scopes)
88 |
89 | def parse_field(self, scopes, match):
90 | field_name = match.group(1).lower()
91 | field = self.fields.get(field_name)
92 | if field is None:
93 | self.parse_word(scopes, match)
94 | return
95 |
96 | # A field value is required.
97 | op = match.group(2)
98 | token, match = self._get_next_token()
99 | try:
100 | value = match.group(1)
101 | except IndexError:
102 | return
103 |
104 | for subclass in get_subclasses(models.Searchable):
105 | try:
106 | for k, v in subclass._meta.get_field(field_name).choices:
107 | if value == v:
108 | value = k
109 | break
110 | except:
111 | continue
112 |
113 | term = get_term_from_op(field, op, value)
114 | scopes[-1].add(term)
115 | close_scope(scopes)
116 |
117 | def parse_boolean(self, scopes, dom_cls, match):
118 | try:
119 | if scopes[-1].is_logical() and dom_cls.precedence() < scopes[-1].precedence():
120 | scopes.pop()
121 | if type(scopes[-1]).__name__ == dom_cls.__name__:
122 | return
123 | last_term = scopes[-1].pop()
124 | except IndexError:
125 | open_scope(scopes, dom_cls())
126 | else:
127 | open_scope(scopes, dom_cls(last_term))
128 |
129 | def parse_and(self, scopes, match):
130 | self.parse_boolean(scopes, And, match)
131 |
132 | def parse_or(self, scopes, match):
133 | self.parse_boolean(scopes, Or, match)
134 |
135 | def parse_not(self, scopes, match):
136 | open_scope(scopes, Not())
137 |
138 | def parse_openbracket(self, scopes, match):
139 | open_scope(scopes, Group())
140 |
141 | def parse_closebracket(self, scopes, match):
142 | # Leave the current group.
143 | while type(scopes[-1]).__name__ != Group.__name__ and not scopes[-1].is_root:
144 | scopes.pop()
145 | if not scopes[-1].is_root:
146 | scopes.pop()
147 |
148 | # Auto-leave the parent scope (if necessary).
149 | close_scope(scopes)
150 |
151 | def parse(self, query):
152 | self._reset()
153 | self.input = query.strip()
154 | result = Group(is_root=True)
155 | scopes = [result]
156 | token, match = self._get_next_token()
157 |
158 | while token != 'EOF':
159 | try:
160 | parse_func = getattr(self, 'parse_'+token)
161 | parse_func(scopes, match)
162 | except AttributeError:
163 | pass
164 | finally:
165 | token, match = self._get_next_token()
166 |
167 | return result.optimize()
168 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_searchable.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | from django.test import TestCase
3 | from django_find.handlers import LowerCaseStrFieldHandler, IntegerFieldHandler
4 | from .models import Author, DerivedAuthor, SecondAuthor, Book, Chapter, \
5 | DummyModel, SimpleModel
6 |
7 | class SearchableTest(TestCase):
8 | def setUp(self):
9 | self.maxDiff = None
10 |
11 | def testGetAliases(self):
12 | expected = ['name', 'rating', 'author', 'writer']
13 | self.assertEqual(expected, Author.get_aliases())
14 |
15 | expected = ['author', 'title', 'comment', 'rating', 'something']
16 | self.assertEqual(expected, Book.get_aliases())
17 |
18 | def testGetFullNames(self):
19 | expected = ['Author.name', 'Author.rating', 'Author.author', 'Author.writer']
20 | self.assertEqual(expected, Author.get_fullnames())
21 |
22 | expected = ['Author.name', 'Author.rating']
23 | self.assertEqual(expected, Author.get_fullnames(True))
24 |
25 |
26 | expected = ['Book.author', 'Book.title', 'Book.comment',
27 | 'Book.rating', 'Book.something']
28 | self.assertEqual(expected, Book.get_fullnames())
29 |
30 | def testTableHeaders(self):
31 | expected = ['Name', 'Stars']
32 | self.assertEqual(expected, Author.table_headers())
33 |
34 | expected = ['Name', 'The title', 'Comment', 'Stars', 'AuthorID']
35 | self.assertEqual(expected, Book.table_headers())
36 |
37 | def testGetFieldFromSelector(self):
38 | func = SecondAuthor.get_field_from_selector
39 | self.assertRaises(Exception, func, 'foo')
40 | self.assertEqual(func('book__author__name'),
41 | (Author, Author._meta.get_field('name')))
42 |
43 | def testGetCaptionFromSelector(self):
44 | func = SecondAuthor.get_caption_from_selector
45 | self.assertRaises(Exception, func, 'foo')
46 | self.assertEqual(func('book__author__name'), 'Name')
47 |
48 | def testGetFieldHandlerFromAlias(self):
49 | func = Author.get_field_handler_from_alias
50 | self.assertRaises(KeyError, func, 'foo')
51 | self.assertEqual(func('name'), LowerCaseStrFieldHandler)
52 | self.assertEqual(func('author'), LowerCaseStrFieldHandler)
53 | self.assertEqual(func('rating'), IntegerFieldHandler)
54 |
55 | def testGetFieldHandlerFromFullname(self):
56 | func = Author.get_field_handler_from_fullname
57 | self.assertRaises(AttributeError, func, 'foo')
58 | self.assertEqual(func('Author.name'), LowerCaseStrFieldHandler)
59 | self.assertEqual(func('Book.author'), LowerCaseStrFieldHandler)
60 | self.assertEqual(func('Book.rating'), IntegerFieldHandler)
61 |
62 | def testGetSelectorFromAlias(self):
63 | func = Author.get_selector_from_alias
64 | self.assertRaises(KeyError, func, 'foo')
65 | self.assertEqual(func('name'), 'name')
66 | self.assertEqual(func('author'), 'name')
67 | self.assertEqual(func('rating'), 'rating')
68 |
69 | def testGetClassFromFieldName(self):
70 | func = Author.get_class_from_fullname
71 | self.assertRaises(KeyError, func, 'no.foo')
72 | self.assertRaises(AttributeError, func, 'name')
73 | self.assertEqual(func('Author.name'), (Author, 'name'))
74 | self.assertEqual(func('Author.author'), (Author, 'author'))
75 | self.assertEqual(func('Author.rating'), (Author, 'rating'))
76 | self.assertEqual(func('Book.name'), (Book, 'name'))
77 | self.assertEqual(func('Book.author'), (Book, 'author'))
78 | self.assertEqual(func('Book.rating'), (Book, 'rating'))
79 |
80 | def testGetSelectorFromFullname(self):
81 | func = DummyModel.get_selector_from_fullname
82 | self.assertRaises(AttributeError, func, 'foo')
83 | self.assertRaises(KeyError, func, 'DummyModel.foo')
84 | self.assertEqual(func('DummyModel.host'), 'hostname')
85 | self.assertEqual(func('DummyModel.model'), 'model')
86 |
87 | def testGetObjectVectorTo(self):
88 | func = Author.get_object_vector_to
89 | self.assertEqual(func(Book), [(Author, Book),
90 | (Author, DerivedAuthor, Book),
91 | (Author, SecondAuthor, Book),
92 | (Author, DerivedAuthor, SecondAuthor, Book)])
93 | self.assertEqual(func(Chapter), [(Author, Book, Chapter),
94 | (Author, DerivedAuthor, Book, Chapter),
95 | (Author, SecondAuthor, Book, Chapter),
96 | (Author, DerivedAuthor, SecondAuthor, Book, Chapter)])
97 |
98 | def testGetQFromQuery(self):
99 | result = Author.q_from_query('testme AND name:foo')
100 | query = str(Author.objects.filter(result).query)
101 | self.assertTrue('WHERE ' in query)
102 | self.assertTrue('%testme%' in query)
103 |
104 | def testByQueryRaw(self):
105 | query, fields = SimpleModel.by_query_raw('testme AND comment:foo')
106 | self.assertTrue('WHERE ' in query.raw_query)
107 | self.assertTrue('%testme%' in query.raw_query)
108 | self.failIf('SimpleModel' in query.raw_query)
109 | self.assertEqual(['SimpleModel.title',
110 | 'SimpleModel.comment',
111 | 'SimpleModel.yesno'], fields)
112 |
113 | query, fields = Author.by_query_raw('testme AND name:foo')
114 | self.assertTrue('WHERE ' in query.raw_query)
115 | self.assertTrue('%testme%' in query.raw_query)
116 | self.failIf('Author' in query.raw_query)
117 | self.failIf('Book' in query.raw_query)
118 | self.assertEqual(['Author.name', 'Author.rating', 'Author.author', 'Author.writer'], fields)
119 |
120 | query, fields = Book.by_query_raw('rating:5')
121 | self.assertTrue('WHERE ' in query.raw_query)
122 | self.assertTrue('5' in query.raw_query)
123 | self.failIf('Author' in query.raw_query)
124 | self.failIf('Book' in query.raw_query)
125 | self.assertEqual(['Book.rating'], fields)
126 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/django_find/serializers/sql.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from builtins import str
2 | from collections import defaultdict, OrderedDict
3 | from MySQLdb import escape_string
4 | from ..refs import get_join_for
5 | from .serializer import Serializer
6 | from .util import parse_date, parse_datetime
7 |
8 | int_op_map = {
9 | 'equals': 'equals',
10 | 'contains': 'equals',
11 | 'startswith': 'gte',
12 | 'endswith': 'lte'
13 | }
14 |
15 | str_op_map = {
16 | 'gt': 'startswith',
17 | 'gte': 'startswith',
18 | 'lt': 'endswith',
19 | 'lte': 'endswith'
20 | }
21 |
22 | date_op_map = {
23 | 'contains': 'equals',
24 | 'startswith': 'gte',
25 | 'endswith': 'lte'
26 | }
27 |
28 | operator_map = {
29 | 'equals': "='{}'",
30 | 'iequals': " LIKE '{}'",
31 | 'lt': "<'{}'",
32 | 'lte': "<='{}'",
33 | 'gt': ">'{}'",
34 | 'gte': ">='{}'",
35 | 'startswith': " LIKE '{}%%'",
36 | 'endswith': " LIKE '%%{}'",
37 | 'contains': " LIKE '%%{}%%'",
38 | 'regex': " REGEXP '%%{}%%'"
39 | }
40 |
41 | def _mkcol(tbl, name, alias):
42 | return tbl+'.'+name+' '+tbl+'_'+alias
43 |
44 | def _mk_condition(db_column, operator, data):
45 | op = operator_map.get(operator)
46 | if not op:
47 | raise Exception('unsupported operator:' + str(operator))
48 |
49 | # I would prefer to use a prepared statement, but collecting arguments
50 | # and passing them back along the string everywhere would be awful design.
51 | # (Also, I didn't find any API from Django to generate a prepared statement
52 | # without already executing it, e.g. django.db.connection.execute())
53 | if isinstance(data, int):
54 | return db_column+op.format(data)
55 | return db_column+op.format(escape_string(data).decode('utf-8'))
56 |
57 | class SQLSerializer(Serializer):
58 | def __init__(self, model, mode='SELECT', fullnames=None, extra_model=None):
59 | modes = 'SELECT', 'WHERE'
60 | if mode not in modes:
61 | raise AttributeError('invalid mode: {}. Must be one of {}'.format(mode, modes))
62 | Serializer.__init__(self)
63 | self.model = model
64 | self.mode = mode
65 | self.fullnames = fullnames
66 | self.extra_model = extra_model
67 |
68 | def _create_db_column_list(self, dom):
69 | fullnames = self.fullnames if self.fullnames else dom.get_term_names()
70 | result = []
71 | for fullname in fullnames:
72 | model, alias = self.model.get_class_from_fullname(fullname)
73 | selector = model.get_selector_from_alias(alias)
74 | target_model, field = model.get_field_from_selector(selector)
75 | result.append((target_model, target_model._meta.db_table, field.column))
76 | return result
77 |
78 | def _create_select(self, fields):
79 | # Create the "SELECT DISTINCT table1.col1, table2.col2, ..."
80 | # part of the SQL.
81 | col_numbers = defaultdict(int)
82 | fullfields = []
83 | for field in fields:
84 | table, column = field[1:3]
85 | key = "%s.%s" % (table, column)
86 | col_number = col_numbers[key]
87 | col_numbers[key] += 1
88 | if len(field) == 3:
89 | field = (field[0], table, column, column if col_number == 0 else "%s__%d" % (column, col_number))
90 | fullfields.append(field)
91 |
92 | select = 'SELECT DISTINCT '+_mkcol(fullfields[0][1], fullfields[0][2], fullfields[0][3])
93 | for target_model, table, column, alias in fullfields[1:]:
94 | select += ', '+_mkcol(table, column, alias)
95 |
96 | # Find the best way to join the tables.
97 | target_models = [r[0] for r in fullfields]
98 | if self.extra_model:
99 | target_models.append(self.extra_model)
100 | vector = self.model.get_object_vector_for(target_models)
101 | join_path = get_join_for(vector)
102 |
103 | # Create the "table1 LEFT JOIN table2 ON table1.col1=table2.col1"
104 | # part of the SQL.
105 | select += ' FROM '+join_path[0][0]
106 | for table, left, right in join_path[1:]:
107 | select += ' LEFT JOIN {} ON {}={}'.format(table,
108 | table+'.'+left,
109 | right)
110 | return select
111 |
112 | def logical_root_group(self, root_group, terms):
113 | fields = self._create_db_column_list(root_group)
114 |
115 | # Create the SELECT part of the query.
116 | if self.mode == 'SELECT':
117 | select = self._create_select(fields)+' WHERE '
118 | else:
119 | select = ''
120 |
121 | where = (' AND '.join(terms) if terms else '1')
122 | if where.startswith('(') and where.endswith(')'):
123 | select += where
124 | else:
125 | select += '('+where+')'
126 | return select, []
127 |
128 | def logical_group(self, terms):
129 | terms = [t for t in terms if t]
130 | if not terms:
131 | return ''
132 | return ' AND '.join(terms)
133 |
134 | def logical_and(self, terms):
135 | terms = [t for t in terms if t]
136 | if not terms:
137 | return '()'
138 | return '(' + self.logical_group(terms) + ')'
139 |
140 | def logical_or(self, terms):
141 | terms = [t for t in terms if t]
142 | if not terms:
143 | return ''
144 | return '(' + ' OR '.join(terms) + ')'
145 |
146 | def logical_not(self, terms):
147 | if not terms:
148 | return ''
149 | if len(terms) == 1:
150 | return 'NOT(' + terms[0] + ')'
151 | return 'NOT ' + self.logical_and(terms)
152 |
153 | def boolean_term(self, db_column, operator, data):
154 | value = 'TRUE' if data.lower() == 'true' else 'FALSE'
155 | return _mk_condition(db_column, operator, value)
156 |
157 | def int_term(self, db_column, operator, data):
158 | try:
159 | value = int(data)
160 | except ValueError:
161 | return '1'
162 | operator = int_op_map.get(operator, operator)
163 | return _mk_condition(db_column, operator, value)
164 |
165 | def str_term(self, db_column, operator, data):
166 | operator = str_op_map.get(operator, operator)
167 | return _mk_condition(db_column, operator, data)
168 |
169 | def lcstr_term(self, db_column, operator, data):
170 | operator = str_op_map.get(operator, operator)
171 | if operator == 'equals':
172 | operator = 'iequals'
173 | return _mk_condition(db_column, operator, data.lower())
174 |
175 | def date_datetime_common(self, db_column, operator, thedatetime):
176 | if not thedatetime:
177 | return ''
178 | operator = date_op_map.get(operator, operator)
179 | return _mk_condition(db_column, operator, thedatetime.isoformat())
180 |
181 | def date_term(self, db_column, operator, data):
182 | thedate = parse_date(data)
183 | return self.date_datetime_common(db_column, operator, thedate)
184 |
185 | def datetime_term(self, db_column, operator, data):
186 | thedatetime = parse_datetime(data)
187 | return self.date_datetime_common(db_column, operator, thedatetime)
188 |
189 | def term(self, term_name, operator, data):
190 | if operator == 'any':
191 | return '1'
192 |
193 | model, alias = self.model.get_class_from_fullname(term_name)
194 | selector = model.get_selector_from_alias(alias)
195 | target_model, field = model.get_field_from_selector(selector)
196 | db_column = target_model._meta.db_table + '.' + field.column
197 | handler = model.get_field_handler_from_alias(alias)
198 |
199 | type_map = {'BOOL': self.boolean_term,
200 | 'INT': self.int_term,
201 | 'STR': self.str_term,
202 | 'LCSTR': self.lcstr_term,
203 | 'DATE': self.date_term,
204 | 'DATETIME': self.datetime_term}
205 |
206 | func = type_map.get(handler.db_type)
207 | if not func:
208 | raise TypeError('unsupported field type: '+repr(field_type))
209 | return func(db_column, operator, handler.prepare(data))
210 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Makefile:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Makefile for Sphinx documentation
2 | #
3 |
4 | # You can set these variables from the command line.
5 | SPHINXOPTS =
6 | SPHINXBUILD = sphinx-build
7 | PAPER =
8 | BUILDDIR = _build
9 |
10 | # User-friendly check for sphinx-build
11 | ifeq ($(shell which $(SPHINXBUILD) >/dev/null 2>&1; echo $$?), 1)
12 | $(error The '$(SPHINXBUILD)' command was not found. Make sure you have Sphinx installed, then set the SPHINXBUILD environment variable to point to the full path of the '$(SPHINXBUILD)' executable. Alternatively you can add the directory with the executable to your PATH. If you don't have Sphinx installed, grab it from http://sphinx-doc.org/)
13 | endif
14 |
15 | # Internal variables.
16 | PAPEROPT_a4 = -D latex_paper_size=a4
17 | PAPEROPT_letter = -D latex_paper_size=letter
18 | ALLSPHINXOPTS = -d $(BUILDDIR)/doctrees $(PAPEROPT_$(PAPER)) $(SPHINXOPTS) .
19 | # the i18n builder cannot share the environment and doctrees with the others
20 | I18NSPHINXOPTS = $(PAPEROPT_$(PAPER)) $(SPHINXOPTS) .
21 |
22 | .PHONY: help
23 | help:
24 | @echo "Please use \`make ' where is one of"
25 | @echo " html to make standalone HTML files"
26 | @echo " dirhtml to make HTML files named index.html in directories"
27 | @echo " singlehtml to make a single large HTML file"
28 | @echo " pickle to make pickle files"
29 | @echo " json to make JSON files"
30 | @echo " htmlhelp to make HTML files and a HTML help project"
31 | @echo " qthelp to make HTML files and a qthelp project"
32 | @echo " applehelp to make an Apple Help Book"
33 | @echo " devhelp to make HTML files and a Devhelp project"
34 | @echo " epub to make an epub"
35 | @echo " latex to make LaTeX files, you can set PAPER=a4 or PAPER=letter"
36 | @echo " latexpdf to make LaTeX files and run them through pdflatex"
37 | @echo " latexpdfja to make LaTeX files and run them through platex/dvipdfmx"
38 | @echo " text to make text files"
39 | @echo " man to make manual pages"
40 | @echo " texinfo to make Texinfo files"
41 | @echo " info to make Texinfo files and run them through makeinfo"
42 | @echo " gettext to make PO message catalogs"
43 | @echo " changes to make an overview of all changed/added/deprecated items"
44 | @echo " xml to make Docutils-native XML files"
45 | @echo " pseudoxml to make pseudoxml-XML files for display purposes"
46 | @echo " linkcheck to check all external links for integrity"
47 | @echo " doctest to run all doctests embedded in the documentation (if enabled)"
48 | @echo " coverage to run coverage check of the documentation (if enabled)"
49 |
50 | .PHONY: clean
51 | clean:
52 | rm -rf $(BUILDDIR)/*
53 |
54 | .PHONY: apidoc
55 | apidoc:
56 | sphinx-apidoc -d5 -Mefo . ../django_find/searchable.py `realpath ../django_find/parsers` `realpath ../django_find/serializers`
57 |
58 | .PHONY: html
59 | html:
60 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b html $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/html
61 | @echo
62 | @echo "Build finished. The HTML pages are in $(BUILDDIR)/html."
63 |
64 | .PHONY: dirhtml
65 | dirhtml:
66 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b dirhtml $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/dirhtml
67 | @echo
68 | @echo "Build finished. The HTML pages are in $(BUILDDIR)/dirhtml."
69 |
70 | .PHONY: singlehtml
71 | singlehtml:
72 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b singlehtml $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/singlehtml
73 | @echo
74 | @echo "Build finished. The HTML page is in $(BUILDDIR)/singlehtml."
75 |
76 | .PHONY: pickle
77 | pickle:
78 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b pickle $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/pickle
79 | @echo
80 | @echo "Build finished; now you can process the pickle files."
81 |
82 | .PHONY: json
83 | json:
84 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b json $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/json
85 | @echo
86 | @echo "Build finished; now you can process the JSON files."
87 |
88 | .PHONY: htmlhelp
89 | htmlhelp:
90 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b htmlhelp $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/htmlhelp
91 | @echo
92 | @echo "Build finished; now you can run HTML Help Workshop with the" \
93 | ".hhp project file in $(BUILDDIR)/htmlhelp."
94 |
95 | .PHONY: qthelp
96 | qthelp:
97 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b qthelp $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/qthelp
98 | @echo
99 | @echo "Build finished; now you can run "qcollectiongenerator" with the" \
100 | ".qhcp project file in $(BUILDDIR)/qthelp, like this:"
101 | @echo "# qcollectiongenerator $(BUILDDIR)/qthelp/django_find.qhcp"
102 | @echo "To view the help file:"
103 | @echo "# assistant -collectionFile $(BUILDDIR)/qthelp/django_find.qhc"
104 |
105 | .PHONY: applehelp
106 | applehelp:
107 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b applehelp $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/applehelp
108 | @echo
109 | @echo "Build finished. The help book is in $(BUILDDIR)/applehelp."
110 | @echo "N.B. You won't be able to view it unless you put it in" \
111 | "~/Library/Documentation/Help or install it in your application" \
112 | "bundle."
113 |
114 | .PHONY: devhelp
115 | devhelp:
116 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b devhelp $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/devhelp
117 | @echo
118 | @echo "Build finished."
119 | @echo "To view the help file:"
120 | @echo "# mkdir -p $$HOME/.local/share/devhelp/django_find"
121 | @echo "# ln -s $(BUILDDIR)/devhelp $$HOME/.local/share/devhelp/django_find"
122 | @echo "# devhelp"
123 |
124 | .PHONY: epub
125 | epub:
126 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b epub $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/epub
127 | @echo
128 | @echo "Build finished. The epub file is in $(BUILDDIR)/epub."
129 |
130 | .PHONY: latex
131 | latex:
132 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b latex $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/latex
133 | @echo
134 | @echo "Build finished; the LaTeX files are in $(BUILDDIR)/latex."
135 | @echo "Run \`make' in that directory to run these through (pdf)latex" \
136 | "(use \`make latexpdf' here to do that automatically)."
137 |
138 | .PHONY: latexpdf
139 | latexpdf:
140 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b latex $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/latex
141 | @echo "Running LaTeX files through pdflatex..."
142 | $(MAKE) -C $(BUILDDIR)/latex all-pdf
143 | @echo "pdflatex finished; the PDF files are in $(BUILDDIR)/latex."
144 |
145 | .PHONY: latexpdfja
146 | latexpdfja:
147 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b latex $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/latex
148 | @echo "Running LaTeX files through platex and dvipdfmx..."
149 | $(MAKE) -C $(BUILDDIR)/latex all-pdf-ja
150 | @echo "pdflatex finished; the PDF files are in $(BUILDDIR)/latex."
151 |
152 | .PHONY: text
153 | text:
154 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b text $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/text
155 | @echo
156 | @echo "Build finished. The text files are in $(BUILDDIR)/text."
157 |
158 | .PHONY: man
159 | man:
160 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b man $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/man
161 | @echo
162 | @echo "Build finished. The manual pages are in $(BUILDDIR)/man."
163 |
164 | .PHONY: texinfo
165 | texinfo:
166 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b texinfo $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/texinfo
167 | @echo
168 | @echo "Build finished. The Texinfo files are in $(BUILDDIR)/texinfo."
169 | @echo "Run \`make' in that directory to run these through makeinfo" \
170 | "(use \`make info' here to do that automatically)."
171 |
172 | .PHONY: info
173 | info:
174 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b texinfo $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/texinfo
175 | @echo "Running Texinfo files through makeinfo..."
176 | make -C $(BUILDDIR)/texinfo info
177 | @echo "makeinfo finished; the Info files are in $(BUILDDIR)/texinfo."
178 |
179 | .PHONY: gettext
180 | gettext:
181 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b gettext $(I18NSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/locale
182 | @echo
183 | @echo "Build finished. The message catalogs are in $(BUILDDIR)/locale."
184 |
185 | .PHONY: changes
186 | changes:
187 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b changes $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/changes
188 | @echo
189 | @echo "The overview file is in $(BUILDDIR)/changes."
190 |
191 | .PHONY: linkcheck
192 | linkcheck:
193 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b linkcheck $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/linkcheck
194 | @echo
195 | @echo "Link check complete; look for any errors in the above output " \
196 | "or in $(BUILDDIR)/linkcheck/output.txt."
197 |
198 | .PHONY: doctest
199 | doctest:
200 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b doctest $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/doctest
201 | @echo "Testing of doctests in the sources finished, look at the " \
202 | "results in $(BUILDDIR)/doctest/output.txt."
203 |
204 | .PHONY: coverage
205 | coverage:
206 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b coverage $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/coverage
207 | @echo "Testing of coverage in the sources finished, look at the " \
208 | "results in $(BUILDDIR)/coverage/python.txt."
209 |
210 | .PHONY: xml
211 | xml:
212 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b xml $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/xml
213 | @echo
214 | @echo "Build finished. The XML files are in $(BUILDDIR)/xml."
215 |
216 | .PHONY: pseudoxml
217 | pseudoxml:
218 | $(SPHINXBUILD) -b pseudoxml $(ALLSPHINXOPTS) $(BUILDDIR)/pseudoxml
219 | @echo
220 | @echo "Build finished. The pseudo-XML files are in $(BUILDDIR)/pseudoxml."
221 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/django_find/refs.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from copy import copy
2 | from itertools import chain
3 | from django.db import models
4 | from django.db.models.fields.related import ManyToOneRel, ManyToManyRel
5 |
6 | def get_subclasses(cls):
7 | """
8 | Recursively finds all subclasses of the current class.
9 | Like Python's __class__.__subclasses__(), but recursive.
10 | Returns a list containing all subclasses.
11 |
12 | @type cls: object
13 | @param cls: A Python class.
14 | @rtype: list(object)
15 | @return: A list containing all subclasses.
16 | """
17 | result = set()
18 | path = [cls]
19 | while path:
20 | parent = path.pop()
21 | for child in parent.__subclasses__():
22 | if not '.' in str(child):
23 | # In a multi inheritance scenario, __subclasses__()
24 | # also returns interim-classes that don't have all the
25 | # methods. With this hack, we skip them.
26 | continue
27 | if child not in result:
28 | result.add(child)
29 | path.append(child)
30 | return result
31 |
32 | def child_classes(cls):
33 | """
34 | Returns all models that have a foreign key pointing to cls.
35 | """
36 | children = []
37 | for field in cls._meta.get_fields():
38 | if isinstance(field, (ManyToOneRel, ManyToManyRel)):
39 | children.append(field.related_model)
40 | return children
41 |
42 | def parent_classes(cls):
43 | """
44 | Returns all models that are referenced by a foreign key of the
45 | given class.
46 | """
47 | parents = []
48 | for field in cls._meta.get_fields():
49 | if isinstance(field, (models.ForeignKey, models.ManyToManyField)):
50 | parents.append(field.remote_field.model)
51 | return parents
52 |
53 | def get_field_to(cls, target_cls):
54 | for field in cls._meta.get_fields():
55 | if not isinstance(field, (models.ForeignKey, models.ManyToManyField)):
56 | continue
57 | if field.remote_field.model is target_cls:
58 | return field
59 | return None
60 |
61 | def get_object_vector_to(cls, search_cls, subtype, avoid=None):
62 | """
63 | Returns a list of all possible paths to the given class.
64 | Only searches classes that are subtype of the given class.
65 | """
66 | # Does the name point to this class? Then we are done.
67 | if search_cls == cls:
68 | return [(cls,)]
69 |
70 | # Avoid endless recursion.
71 | if avoid is None:
72 | avoid = set()
73 | else:
74 | avoid = copy(avoid)
75 | avoid.add(cls)
76 |
77 | # So the name does not point to this class. Delegate the request to
78 | # each of our connected classes, collecting all possible paths.
79 | path_list = []
80 | for thecls in chain(child_classes(cls), parent_classes(cls)):
81 | if thecls in avoid:
82 | continue
83 | if subtype in thecls.__mro__:
84 | child_path_list = get_object_vector_to(thecls, search_cls, subtype, copy(avoid))
85 | elif thecls == search_cls:
86 | child_path_list = [(thecls,)]
87 | else:
88 | continue
89 | for path in child_path_list:
90 | path_list.append((cls,)+path)
91 | path_list.sort(key=len)
92 | return path_list
93 |
94 | def yield_all_vectors(search_cls_list, subtype):
95 | """
96 | Yields all possible vectors between all given classes.
97 | """
98 | for target_cls in search_cls_list[:]:
99 | for thecls in search_cls_list:
100 | vectors = get_object_vector_to(thecls, target_cls, subtype)
101 | for vector in vectors:
102 | yield vector
103 |
104 | def yield_matching_vectors(vectors, search_cls_list):
105 | """
106 | Yields all possible vectors that connect all of the given classes.
107 | The result is sorted by the position of the primary class, and
108 | the vector length.
109 | """
110 | for vector in vectors:
111 | for target_cls in search_cls_list:
112 | if target_cls not in vector:
113 | break
114 | else:
115 | yield vector
116 |
117 | def sort_vectors_by_primary_cls(vectors, primary_cls):
118 | """
119 | Sort the vectors by the position of the primary class, and
120 | the vector length.
121 | """
122 | def sort_by_length_and_pos_of_primary_cls(vector):
123 | try:
124 | pos = vector.index(primary_cls)
125 | except ValueError:
126 | pos = 0
127 | return float('{}.{}'.format(pos, len(vector)))
128 | return sorted(vectors, key=sort_by_length_and_pos_of_primary_cls)
129 |
130 | def get_object_vector_for(cls, search_cls_list, subtype, avoid=None):
131 | """
132 | Like get_object_vector_to(), but returns a single vector that reaches
133 | all of the given classes, if it exists.
134 | Only searches classes that are subtype of the given class.
135 | """
136 | vectors = list(yield_all_vectors(search_cls_list, subtype))
137 | matching = list(yield_matching_vectors(vectors, search_cls_list))
138 | if not matching:
139 | return None # No vector contains all classes
140 |
141 | # Prefer the path where the classes appear in the same order as in
142 | # search_cls_list.
143 | primary_cls = search_cls_list[0]
144 | matching = sort_vectors_by_primary_cls(matching, primary_cls)
145 | for vector in matching:
146 | # Remove extra classes that are not explicitly requested.
147 | clean_vector = [c for c in vector if c in search_cls_list]
148 | if clean_vector == search_cls_list:
149 | return vector
150 |
151 | return matching[0] # No vector contains all classes in the same order.
152 |
153 | def _class2through_columns(from_cls, through_model):
154 | table_name = from_cls._meta.db_table
155 | through_table = through_model._meta.db_table
156 | through_left = get_field_to(through_model, from_cls).column
157 | through_right = table_name+'.'+from_cls._meta.pk.column
158 | return through_table, through_left, through_right
159 |
160 | def _through2class_columns(through_model, target_cls):
161 | # From through-table to target class.
162 | through_table = through_model._meta.db_table
163 | from_field = get_field_to(through_model, target_cls)
164 | through_join = from_field.get_reverse_joining_columns()
165 | left, right = through_join[0]
166 | right = through_table+'.'+right
167 | return left, right
168 |
169 | def _get_through_model(cls, field):
170 | if isinstance(field, models.fields.related.ManyToManyField):
171 | return getattr(cls, field.attname).through
172 | return None
173 |
174 | def _get_join_data(last_cls, to_cls):
175 | result = []
176 | last_table_name = last_cls._meta.db_table
177 |
178 | # Two options: The current class has a reference to the other table,
179 | # or the other way around.
180 | field = get_field_to(last_cls, to_cls)
181 | if field:
182 | through_model = _get_through_model(last_cls, field)
183 | if through_model:
184 | result.append(_class2through_columns(last_cls, through_model))
185 | left, right = _through2class_columns(through_model, to_cls)
186 | else:
187 | left, right = field.get_reverse_joining_columns()[0]
188 | right = last_table_name+'.'+right
189 |
190 | else:
191 | field = get_field_to(to_cls, last_cls)
192 | if field is None:
193 | raise AttributeError('JOIN for unconnected objects is not possible')
194 |
195 | through_model = _get_through_model(to_cls, field)
196 | if through_model:
197 | result.append(_class2through_columns(last_cls, through_model))
198 | left, right = _through2class_columns(through_model, to_cls)
199 | else:
200 | left, right = field.get_joining_columns()[0]
201 | right = last_table_name+'.'+right
202 |
203 | table_name = to_cls._meta.db_table
204 | result.append((table_name, left, right))
205 | return result
206 |
207 | def get_join_for(vector):
208 | """
209 | Given a vector as returned by get_object_vector_for(), this function
210 | returns a list of tuples that explain how to join the models (tables)
211 | together on the SQL layer. Each tuple has three elements::
212 |
213 | (table_name, left_key, right_key)
214 |
215 | In the first tuple of the list, left_key is always None.
216 | In the second tuple of the list, right_key is always None.
217 | All other tuples required both keys to join them.
218 |
219 | Complete example (keep in mind that the connection between Component
220 | and Unit is many-to-many, so there's a helper table here)::
221 |
222 | get_join_path_for((Device, Component, Unit))
223 |
224 | This returns::
225 |
226 | [
227 | ('inventory_device', None, None),
228 | ('inventory_component', 'device_id', 'inventory_device.metadata_id'),
229 | ('inventory_unit_component', 'component_id', 'inventory_component.id'),
230 | ('inventory_unit', 'id', 'inventory_unit_component.unit_id')
231 | ]
232 |
233 | Which means that the following SQL JOIN could be used::
234 |
235 | SELECT *
236 | FROM inventory_device
237 | LEFT JOIN inventory_component ON inventory_component.device_id=inventory_device.metadata_id
238 | LEFT JOIN inventory_unit_component ON inventory_unit_component.component_id=inventory_component.id
239 | LEFT JOIN inventory_unit ON inventory_unit.id=inventory_unit_component.unit_id
240 | """
241 | result = [(vector[0]._meta.db_table, None, None)]
242 | for pos, thecls in enumerate(vector[1:]):
243 | last_cls = vector[pos]
244 | result += _get_join_data(last_cls, thecls)
245 | return result
246 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/conf.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 | #
3 | # django-find documentation build configuration file, created by
4 | # sphinx-quickstart on Tue Sep 4 14:21:46 2012.
5 | #
6 | # This file is execfile()d with the current directory set to its containing dir.
7 | #
8 | # Note that not all possible configuration values are present in this
9 | # autogenerated file.
10 | #
11 | # All configuration values have a default; values that are commented out
12 | # serve to show the default.
13 |
14 | import sys, os
15 |
16 | # If extensions (or modules to document with autodoc) are in another directory,
17 | # add these directories to sys.path here. If the directory is relative to the
18 | # documentation root, use os.path.abspath to make it absolute, like shown here.
19 | sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath('..'))
20 |
21 | # Auto-generate API documentation.
22 | from sphinx.apidoc import main
23 | apidoc_exclude = [os.path.join('..', 'django_find', 'urls.py')]
24 | main(['-d5', '-Mef', '-o', '.', '../django_find']
25 | + [os.path.abspath(p) for p in apidoc_exclude])
26 |
27 | # -- General configuration -----------------------------------------------------
28 |
29 | # If your documentation needs a minimal Sphinx version, state it here.
30 | #needs_sphinx = '1.0'
31 |
32 | # Add any Sphinx extension module names here, as strings. They can be extensions
33 | # coming with Sphinx (named 'sphinx.ext.*') or your custom ones.
34 | #extensions = ['sphinx.ext.autodoc', 'sphinx.ext.doctest', 'sphinx.ext.todo', 'sphinx.ext.coverage', 'sphinx.ext.pngmath', 'sphinx.ext.mathjax', 'sphinx.ext.ifconfig', 'sphinx.ext.viewcode']
35 | extensions = ['sphinx.ext.autodoc', # 'sphinx.ext.coverage',
36 | 'sphinx.ext.viewcode',
37 | 'sphinx.ext.autosummary',
38 | #'sphinx.ext.intersphinx',
39 | ]
40 |
41 | # Add any paths that contain templates here, relative to this directory.
42 | templates_path = ['_templates']
43 |
44 | # The suffix of source filenames.
45 | source_suffix = '.rst'
46 |
47 | # The encoding of source files.
48 | #source_encoding = 'utf-8-sig'
49 |
50 | # The master toctree document.
51 | master_doc = 'index'
52 |
53 | # General information about the project.
54 | project = 'django-find'
55 | copyright = '2018, Samuel Abels'
56 |
57 | # The version info for the project you're documenting, acts as replacement for
58 | # |version| and |release|, also used in various other places throughout the
59 | # built documents.
60 | #
61 | # The short X.Y version.
62 | version = '0.3'
63 | # The full version, including alpha/beta/rc tags.
64 | release = '0.3.4'
65 |
66 | # The language for content autogenerated by Sphinx. Refer to documentation
67 | # for a list of supported languages.
68 | #language = None
69 |
70 | # There are two options for replacing |today|: either, you set today to some
71 | # non-false value, then it is used:
72 | #today = ''
73 | # Else, today_fmt is used as the format for a strftime call.
74 | #today_fmt = '%B %d, %Y'
75 |
76 | # List of patterns, relative to source directory, that match files and
77 | # directories to ignore when looking for source files.
78 | exclude_patterns = ['_build']
79 |
80 | # The reST default role (used for this markup: `text`) to use for all documents.
81 | #default_role = None
82 |
83 | # If true, '()' will be appended to :func: etc. cross-reference text.
84 | #add_function_parentheses = True
85 |
86 | # If true, the current module name will be prepended to all description
87 | # unit titles (such as .. function::).
88 | #add_module_names = True
89 |
90 | # If true, sectionauthor and moduleauthor directives will be shown in the
91 | # output. They are ignored by default.
92 | #show_authors = False
93 |
94 | # The name of the Pygments (syntax highlighting) style to use.
95 | pygments_style = 'sphinx'
96 |
97 | # A list of ignored prefixes for module index sorting.
98 | #modindex_common_prefix = []
99 |
100 |
101 | # -- Options for HTML output ---------------------------------------------------
102 |
103 | # The theme to use for HTML and HTML Help pages. See the documentation for
104 | # a list of builtin themes.
105 | html_theme = 'default'
106 |
107 | # Theme options are theme-specific and customize the look and feel of a theme
108 | # further. For a list of options available for each theme, see the
109 | # documentation.
110 | #html_theme_options = {}
111 |
112 | # Add any paths that contain custom themes here, relative to this directory.
113 | #html_theme_path = []
114 |
115 | # The name for this set of Sphinx documents. If None, it defaults to
116 | # " v documentation".
117 | #html_title = None
118 |
119 | # A shorter title for the navigation bar. Default is the same as html_title.
120 | #html_short_title = None
121 |
122 | # The name of an image file (relative to this directory) to place at the top
123 | # of the sidebar.
124 | #html_logo = None
125 |
126 | # The name of an image file (within the static path) to use as favicon of the
127 | # docs. This file should be a Windows icon file (.ico) being 16x16 or 32x32
128 | # pixels large.
129 | #html_favicon = None
130 |
131 | # Add any paths that contain custom static files (such as style sheets) here,
132 | # relative to this directory. They are copied after the builtin static files,
133 | # so a file named "default.css" will overwrite the builtin "default.css".
134 | html_static_path = ['_static']
135 |
136 | # If not '', a 'Last updated on:' timestamp is inserted at every page bottom,
137 | # using the given strftime format.
138 | #html_last_updated_fmt = '%b %d, %Y'
139 |
140 | # If true, SmartyPants will be used to convert quotes and dashes to
141 | # typographically correct entities.
142 | #html_use_smartypants = True
143 |
144 | # Custom sidebar templates, maps document names to template names.
145 | #html_sidebars = {}
146 |
147 | # Additional templates that should be rendered to pages, maps page names to
148 | # template names.
149 | #html_additional_pages = {}
150 |
151 | # If false, no module index is generated.
152 | #html_domain_indices = True
153 |
154 | # If false, no index is generated.
155 | #html_use_index = True
156 |
157 | # If true, the index is split into individual pages for each letter.
158 | #html_split_index = False
159 |
160 | # If true, links to the reST sources are added to the pages.
161 | #html_show_sourcelink = True
162 |
163 | # If true, "Created using Sphinx" is shown in the HTML footer. Default is True.
164 | #html_show_sphinx = True
165 |
166 | # If true, "(C) Copyright ..." is shown in the HTML footer. Default is True.
167 | #html_show_copyright = True
168 |
169 | # If true, an OpenSearch description file will be output, and all pages will
170 | # contain a tag referring to it. The value of this option must be the
171 | # base URL from which the finished HTML is served.
172 | #html_use_opensearch = ''
173 |
174 | # This is the file name suffix for HTML files (e.g. ".xhtml").
175 | #html_file_suffix = None
176 |
177 | # Output file base name for HTML help builder.
178 | htmlhelp_basename = 'django-find'
179 |
180 |
181 | # -- Options for LaTeX output --------------------------------------------------
182 |
183 | latex_elements = {
184 | # The paper size ('letterpaper' or 'a4paper').
185 | #'papersize': 'letterpaper',
186 |
187 | # The font size ('10pt', '11pt' or '12pt').
188 | #'pointsize': '10pt',
189 |
190 | # Additional stuff for the LaTeX preamble.
191 | #'preamble': '',
192 | }
193 |
194 | # Grouping the document tree into LaTeX files. List of tuples
195 | # (source start file, target name, title, author, documentclass [howto/manual]).
196 | latex_documents = [
197 | ('index', 'django-find.tex', 'django-find Documentation',
198 | 'Samuel Abels', 'manual'),
199 | ]
200 |
201 | # The name of an image file (relative to this directory) to place at the top of
202 | # the title page.
203 | #latex_logo = None
204 |
205 | # For "manual" documents, if this is true, then toplevel headings are parts,
206 | # not chapters.
207 | #latex_use_parts = False
208 |
209 | # If true, show page references after internal links.
210 | #latex_show_pagerefs = False
211 |
212 | # If true, show URL addresses after external links.
213 | #latex_show_urls = False
214 |
215 | # Documents to append as an appendix to all manuals.
216 | #latex_appendices = []
217 |
218 | # If false, no module index is generated.
219 | #latex_domain_indices = True
220 |
221 |
222 | # -- Options for manual page output --------------------------------------------
223 |
224 | # One entry per manual page. List of tuples
225 | # (source start file, name, description, authors, manual section).
226 | man_pages = [
227 | ('index', 'django-find', 'django-find Documentation',
228 | ['Samuel Abels'], 1)
229 | ]
230 |
231 | # If true, show URL addresses after external links.
232 | #man_show_urls = False
233 |
234 |
235 | # -- Options for Texinfo output ------------------------------------------------
236 |
237 | # Grouping the document tree into Texinfo files. List of tuples
238 | # (source start file, target name, title, author,
239 | # dir menu entry, description, category)
240 | texinfo_documents = [
241 | ('index', 'django-find', 'django-find Documentation',
242 | 'Samuel Abels', 'django-find', 'Query your models using human-friendly query language',
243 | 'Miscellaneous'),
244 | ]
245 |
246 | # Documents to append as an appendix to all manuals.
247 | #texinfo_appendices = []
248 |
249 | # If false, no module index is generated.
250 | #texinfo_domain_indices = True
251 |
252 | # How to display URL addresses: 'footnote', 'no', or 'inline'.
253 | #texinfo_show_urls = 'footnote'
254 |
255 |
256 | # -- Options for Epub output ---------------------------------------------------
257 |
258 | # Bibliographic Dublin Core info.
259 | epub_title = 'django-find'
260 | epub_author = 'Samuel Abels'
261 | epub_publisher = 'Samuel Abels'
262 | epub_copyright = '2018, Samuel Abels'
263 |
264 | # The language of the text. It defaults to the language option
265 | # or en if the language is not set.
266 | #epub_language = ''
267 |
268 | # The scheme of the identifier. Typical schemes are ISBN or URL.
269 | #epub_scheme = ''
270 |
271 | # The unique identifier of the text. This can be a ISBN number
272 | # or the project homepage.
273 | #epub_identifier = ''
274 |
275 | # A unique identification for the text.
276 | #epub_uid = ''
277 |
278 | # A tuple containing the cover image and cover page html template filenames.
279 | #epub_cover = ()
280 |
281 | # HTML files that should be inserted before the pages created by sphinx.
282 | # The format is a list of tuples containing the path and title.
283 | #epub_pre_files = []
284 |
285 | # HTML files shat should be inserted after the pages created by sphinx.
286 | # The format is a list of tuples containing the path and title.
287 | #epub_post_files = []
288 |
289 | # A list of files that should not be packed into the epub file.
290 | #epub_exclude_files = []
291 |
292 | # The depth of the table of contents in toc.ncx.
293 | #epub_tocdepth = 3
294 |
295 | # Allow duplicate toc entries.
296 | #epub_tocdup = True
297 |
298 |
299 | # Example configuration for intersphinx: refer to the Python standard library.
300 | intersphinx_mapping = {'http://docs.python.org/': None}
301 |
302 | def skip(app, what, name, obj, skip, options):
303 | if name == "__init__":
304 | return False
305 | return skip
306 |
307 | def setup(app):
308 | app.connect("autodoc-skip-member", skip)
309 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/django_find/models.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | This module contains the Searchable mixin, the main public API of
3 | django-find.
4 | """
5 | from collections import OrderedDict
6 | from django.apps import AppConfig
7 | from django.db import models
8 | from .parsers.query import QueryParser
9 | from .parsers.json import JSONParser
10 | from .serializers.django import DjangoSerializer
11 | from .refs import get_subclasses, get_object_vector_to, get_object_vector_for
12 | from .rawquery import PaginatedRawQuerySet
13 | from .model_helpers import sql_from_dom
14 | from .handlers import type_registry
15 |
16 | class Searchable(object):
17 | """
18 | This class is a mixin for Django models that provides methods for
19 | searching the model using query strings and other tools.
20 | """
21 |
22 | searchable_labels = {} # Override the verbose_name for the given aliases
23 | searchable = () # Contains two-tuples, mapping aliases to Django selectors
24 |
25 | @classmethod
26 | def get_default_searchable(cls):
27 | return OrderedDict((f.name, f.name) for f in cls._meta.get_fields()
28 | if not f.auto_created)
29 |
30 | @classmethod
31 | def get_searchable(cls):
32 | result = cls.get_default_searchable()
33 | if hasattr(cls, 'searchable'):
34 | result.update(OrderedDict(cls.searchable))
35 | return tuple(i for i in result.items() if i[1])
36 |
37 | @classmethod
38 | def get_caption_from_selector(cls, selector):
39 | caption = cls.searchable_labels.get(selector)
40 | if caption:
41 | return caption
42 | field = cls.get_field_from_selector(selector)[1]
43 | if hasattr(field, 'verbose_name'):
44 | return field.verbose_name
45 | return field.name.capitalize()
46 |
47 | @classmethod
48 | def get_field_handler_from_field(cls, field):
49 | if isinstance(field, models.ForeignKey):
50 | field = field.target_field
51 | for handler in type_registry:
52 | if handler.handles(cls, field):
53 | return handler
54 | msg = 'field {}.{} is of type {}'.format(cls.__name__,
55 | field.name,
56 | type(field))
57 | raise TypeError(msg + ', which has no field handler. Consider adding a '
58 | + 'django_find.handlers.FieldHandler to the '
59 | + 'django_find.handlers.type_registry. See the docs for'
60 | + 'more information')
61 |
62 | @classmethod
63 | def get_aliases(cls):
64 | """
65 | Returns a list of the aliases, that is, the names of the
66 | fields that can be used in a query.
67 | """
68 | return list(OrderedDict(cls.get_searchable()).keys())
69 |
70 | @classmethod
71 | def get_fullnames(cls, unique=False):
72 | """
73 | Like get_aliases(), but returns the aliases prefixed by the class
74 | name.
75 | """
76 | if unique:
77 | selectors = set()
78 | result = []
79 | for item in cls.get_searchable():
80 | selector = item[1]
81 | if selector in selectors:
82 | continue
83 | selectors.add(selector)
84 | result.append(cls.__name__+'.'+item[0])
85 | return result
86 | else:
87 | aliases = cls.get_aliases()
88 | return [cls.__name__+'.'+alias for alias in aliases]
89 |
90 | @classmethod
91 | def table_headers(cls):
92 | selectors = set()
93 | result = []
94 | for item in cls.get_searchable():
95 | selector = item[1]
96 | if selector in selectors:
97 | continue
98 | selectors.add(selector)
99 | result.append(cls.get_caption_from_selector(selector))
100 | return result
101 |
102 | @classmethod
103 | def get_field_from_selector(cls, selector):
104 | """
105 | Given a django selector, e.g. device__metadata__name, this returns the class
106 | and the Django field of the model, as returned by Model._meta.get_field().
107 | Example::
108 |
109 | device__metadata__name -> (SeedDevice, SeeDevice.name)
110 | """
111 | if not '__' in selector:
112 | return cls, cls._meta.get_field(selector)
113 |
114 | model = cls
115 | while '__' in selector:
116 | model_name, selector = selector.split('__', 1)
117 | model = model._meta.get_field(model_name).remote_field.model
118 |
119 | return model, model._meta.get_field(selector)
120 |
121 | @classmethod
122 | def get_field_handler_from_alias(cls, alias):
123 | """
124 | Given an alias, e.g. 'host', 'name',
125 | this function returns the handler.FieldHandler.
126 |
127 | @type name: str
128 | @param name: e.g. 'address', or 'name'
129 | """
130 | selector = cls.get_selector_from_alias(alias)
131 | field = cls.get_field_from_selector(selector)[1]
132 | return cls.get_field_handler_from_field(field)
133 |
134 | @classmethod
135 | def get_field_handler_from_fullname(cls, fullname):
136 | """
137 | Given a fullname, e.g. 'Device.host', 'Author.name',
138 | this function returns the handler.FieldHandler.
139 |
140 | @type name: str
141 | @param name: e.g. 'address', or 'name'
142 | """
143 | thecls, alias = cls.get_class_from_fullname(fullname)
144 | return thecls.get_field_handler_from_alias(alias)
145 |
146 | @classmethod
147 | def get_selector_from_alias(cls, alias):
148 | """
149 | Given alias (not a fullname), this function returns the
150 | selector in the following form::
151 |
152 | component__device__host
153 |
154 | @type name: str
155 | @param name: e.g. 'address', or 'name'
156 | """
157 | return dict(cls.get_searchable())[alias]
158 |
159 | @classmethod
160 | def get_object_vector_to(cls, search_cls):
161 | return get_object_vector_to(cls, search_cls, Searchable)
162 |
163 | @classmethod
164 | def get_object_vector_for(cls, search_cls_list):
165 | return get_object_vector_for(cls, search_cls_list, Searchable)
166 |
167 | @classmethod
168 | def get_class_from_fullname(cls, fullname):
169 | """
170 | Given a name in the format "Model.hostname", this
171 | function returns a tuple, where the first element is the Model
172 | class, and the second is the field name "hostname".
173 |
174 | The Model class must inherit from Searchable to be found.
175 | """
176 | if '.' not in fullname:
177 | raise AttributeError('class name is required, format should be "Class.alias"')
178 |
179 | # Search the class.
180 | clsname, alias = fullname.split('.', 1)
181 | thecls = None
182 | for subclass in get_subclasses(Searchable):
183 | if subclass.__module__ == '__fake__':
184 | # Skip Django-internal models
185 | continue
186 | if subclass.__name__ == clsname:
187 | thecls = subclass
188 | break
189 | if thecls is None:
190 | raise KeyError('no such class: ', clsname)
191 |
192 | return subclass, alias
193 |
194 | @classmethod
195 | def get_selector_from_fullname(cls, fullname):
196 | """
197 | Given a name in the form 'Unit.hostname', this function returns
198 | a Django selector that can be used for filtering.
199 | Example (assuming the models are Book and Author)::
200 |
201 | Book.get_selector_from_fullname('Author.birthdate')
202 | # returns 'author__birthdate'
203 |
204 | Example for the models Blog, Entry, Comment::
205 |
206 | Blog.get_selector_from_fullname('Comment.author')
207 | # returns 'entry__comment__author'
208 |
209 | @type name: str
210 | @param name: The field to select for
211 | @rtype: str
212 | @return: The Django selector
213 | """
214 | # Get the target class and attribute by parsing the name.
215 | target_cls, alias = cls.get_class_from_fullname(fullname)
216 | selector = target_cls.get_selector_from_alias(alias)
217 | if target_cls == cls:
218 | return selector
219 |
220 | # Prefix the target by the class names.
221 | path_list = get_object_vector_to(cls, target_cls, Searchable)
222 | path = path_list[0]
223 | prefix = ''
224 | for thecls in path[1:]:
225 | prefix += thecls.__name__.lower() + '__'
226 | if thecls == target_cls:
227 | return prefix+selector
228 |
229 | raise Exception('BUG: class %s not in path %s' % (target_cls, path))
230 |
231 | @classmethod
232 | def get_primary_class_from_fullnames(cls, fullnames):
233 | if not fullnames:
234 | return cls
235 | return cls.get_class_from_fullname(fullnames[0])[0]
236 |
237 | @classmethod
238 | def by_fullnames(cls, fullnames):
239 | """
240 | Returns a unfiltered values_list() of all given field names.
241 | """
242 | selectors = [cls.get_selector_from_fullname(f) for f in fullnames]
243 | primary_cls = cls.get_primary_class_from_fullnames(fullnames)
244 | return primary_cls.objects.values_list(*selectors)
245 |
246 | @classmethod
247 | def dom_from_query(cls, query, aliases=None):
248 | if not aliases:
249 | aliases = cls.get_aliases()
250 | fields = {}
251 | for alias in aliases:
252 | fields[alias] = cls.__name__+'.'+alias
253 | query_parser = QueryParser(fields, aliases)
254 | return query_parser.parse(query)
255 |
256 | @classmethod
257 | def q_from_query(cls, query, aliases=None):
258 | """
259 | Returns a Q-Object for the given query.
260 | """
261 | dom = cls.dom_from_query(query, aliases)
262 | serializer = DjangoSerializer(cls)
263 | return dom.serialize(serializer)
264 |
265 | @classmethod
266 | def by_query(cls, query, aliases=None):
267 | return cls.objects.filter(cls.q_from_query(query, aliases))
268 |
269 | @classmethod
270 | def sql_from_query(cls, query, mode='SELECT', fullnames=None, extra_model=None):
271 | """
272 | Returns an SQL statement for the given query.
273 | """
274 | dom = cls.dom_from_query(query)
275 | return sql_from_dom(cls, dom,
276 | mode=mode,
277 | fullnames=fullnames,
278 | extra_model=extra_model)
279 |
280 | @classmethod
281 | def by_query_raw(cls, query, mode='SELECT', fullnames=None, extra_model=None):
282 | """
283 | Returns a PaginatedRawQuerySet for the given query.
284 | """
285 | sql, args, fields = cls.sql_from_query(query,
286 | mode=mode,
287 | fullnames=fullnames,
288 | extra_model=extra_model)
289 | return PaginatedRawQuerySet(cls, sql, args), fields
290 |
291 | @classmethod
292 | def sql_from_json(cls, json_string, mode='SELECT', extra_model=None):
293 | dom = JSONParser().parse(json_string)
294 | return sql_from_dom(cls, dom, extra_model=extra_model)
295 |
296 | @classmethod
297 | def by_json_raw(cls, json_string, extra_model=None):
298 | sql, args, fields = cls.sql_from_json(json_string,
299 | extra_model=extra_model)
300 | return PaginatedRawQuerySet(cls, sql, args), fields
301 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------