├── README.md
├── images
├── all_in_one_256s.png
├── all_in_one_header.png
├── cornell_all.png
├── cornell_with_without_photon.png
├── dof_256s.png
├── final_scene.jpg
├── glossy_256s.png
├── material_file.png
├── noise_bump_256s.png
├── texturing_100s.png
├── texturing_bump_100s.png
├── txt_001_diff.jpg
└── txt_002_bump.jpg
├── index.html
└── sources
├── BLPatch.cpp
├── BLPatch.h
├── BVH.cpp
├── BVH.h
├── BoundingBox.cpp
├── BoundingBox.h
├── Box.cpp
├── Box.h
├── Camera.cpp
├── Camera.h
├── CellularStoneTexture.cpp
├── CellularStoneTexture.h
├── Console.cpp
├── Console.h
├── Image.cpp
├── Image.h
├── IntersectObjects.h
├── Makedefs
├── Makefile
├── Material.cpp
├── Material.h
├── Matrix4x4.h
├── Miro.h
├── MiroWindow.cpp
├── MiroWindow.h
├── MyBoost.h
├── Object.h
├── OpenGL.h
├── PFMLoader.cpp
├── PFMLoader.h
├── Perlin.cpp
├── Perlin.h
├── Phong.cpp
├── Phong.h
├── PhotonMap.cpp
├── PhotonMap.h
├── PointLight.h
├── Ray.h
├── SSE.cpp
├── SSE.h
├── SSEObject.h
├── Scene.cpp
├── Scene.h
├── Sphere.cpp
├── Sphere.h
├── Texture.cpp
├── Texture.h
├── Triangle.cpp
├── Triangle.h
├── TriangleMesh.cpp
├── TriangleMesh.h
├── TriangleMeshLoad.cpp
├── Vector3.h
├── Vector4.h
├── Worley.cpp
├── Worley.h
├── assignment1.cpp
├── assignment1.h
├── assignment2.cpp
├── assignment2.h
├── boost
├── threadpool.hpp
└── threadpool
│ ├── detail
│ ├── future.hpp
│ ├── locking_ptr.hpp
│ ├── pool_core.hpp
│ ├── scope_guard.hpp
│ └── worker_thread.hpp
│ ├── future.hpp
│ ├── pool.hpp
│ ├── pool_adaptors.hpp
│ ├── scheduling_policies.hpp
│ ├── shutdown_policies.hpp
│ ├── size_policies.hpp
│ └── task_adaptors.hpp
├── freeglut.h
├── freeglut_ext.h
├── freeglut_std.h
├── future.hpp
├── gl
└── include
│ └── GL
│ ├── freeglut.h
│ ├── freeglut_ext.h
│ ├── freeglut_std.h
│ └── glut.h
├── glut.h
├── locking_ptr.hpp
├── main.cpp
├── pool.hpp
├── pool_adaptors.hpp
├── pool_core.hpp
├── scheduling_policies.hpp
├── scope_guard.hpp
├── shutdown_policies.hpp
├── size_policies.hpp
├── task_adaptors.hpp
├── threadpool.hpp
└── worker_thread.hpp
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #UC San Diego - Rendering Algorithms
2 | ####Authors: Fabrice Bascoulergue & Adrien Ecoffet
3 |
4 | 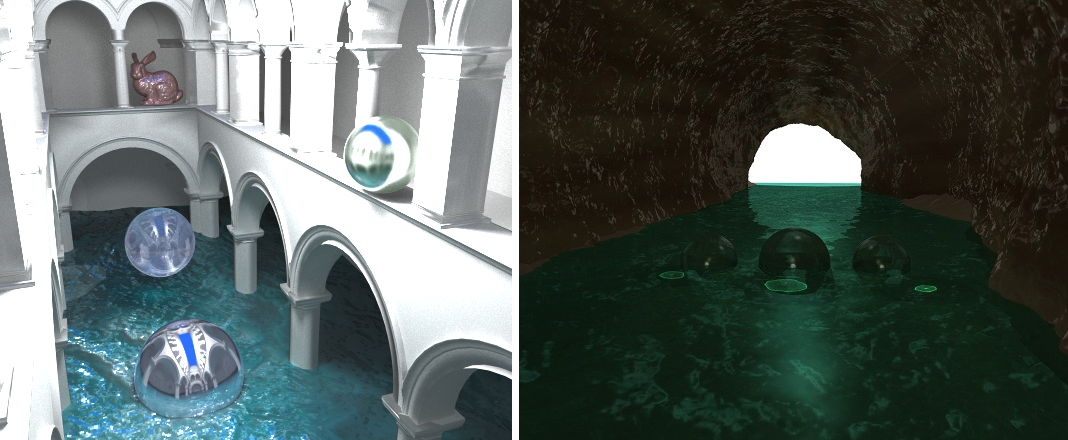
5 |
6 | ##Depth of field
7 | One of the first algorithm we implemented is the Depth of field to render realistic scenes. To achieve that, our raytracer use to variables:
8 | - Focal length: The distance between the eye and the focused objects
9 | - Aperture size: Define the amount of blur effect applied on objects depending of their distance with the focal length
10 |
11 | Smooth shadow follow almost the same principle and are applied to the scene.
12 |
13 | Cellular texturing is applied on the floor to create the stone patterns.
14 |
15 | 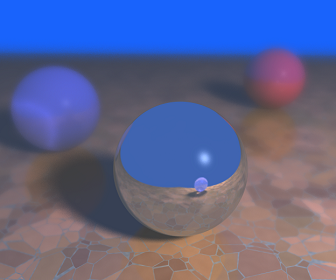
16 |
17 |
18 | ##Texturing and bump mapping
19 | ###UV Texture mapping
20 | We used flat projection to display images on a triangle mesh. The surface on the right is a triangle mesh with an ocean texture applied. The texture is defined by the following image:
21 |
22 | 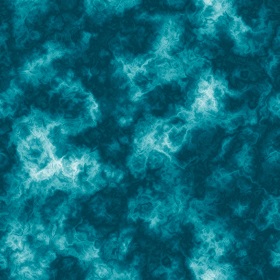
23 | 
24 |
25 | ###Bump mapping
26 | The same image with bump mapping enabled.
27 | The bump map is defined by the following image:
28 |
29 | 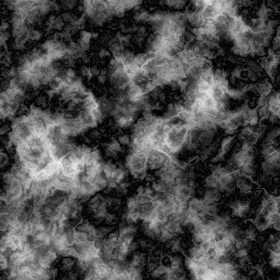
30 | 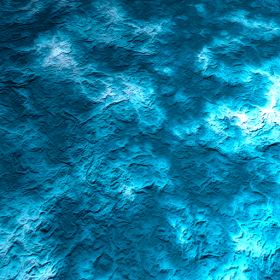
31 |
32 | ###Noise: turbulence and bump mapping
33 | In order to render more realistic scenes with water, we implemented an other version of the bump mapping using noise and turbulence.
34 | Our raytracer use a specific percentage to define the importance of the bump on the surface, 0% has no effect on the normal and 100% generate a full bumped normal.
35 | The three spheres on the right share the same noise with turbulence but with different levels of bump noise (from left to right):
36 | - Bump from noise disabled
37 | - Bump with 20% importance
38 | - Bump with 40% importance
39 |
40 | 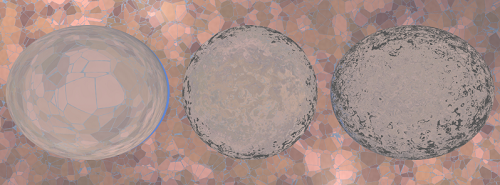
41 |
42 |
43 | ##Glossy reflection
44 | The image on the right show our implementation of the glossy reflection.
45 | From left to right we have:
46 | - Highly glossy sphere
47 | - Glossy sphere
48 | - Sphere without glossy reflection
49 |
50 | 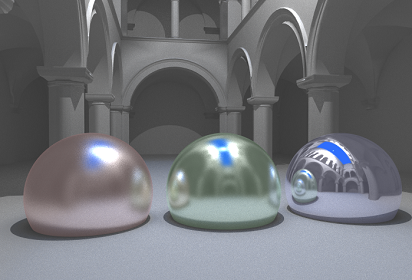
51 |
52 |
53 | ##Photon mapping
54 | ###Global illumination
55 | We implemented the photon mapping and caustics to render global illumination:
56 | On the left, the scene is darker because the global illumination is disabled
57 | On the right, the same scene with global illumination
58 |
59 | 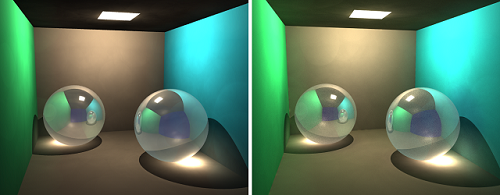
60 |
61 | ###Caustics
62 | The two spheres on those scenes on the right create caustics.
63 | Caustics are independent of the number of sample, that is why on the four images on the right, the caustic stay almost the same:
64 | - The global illumination make it brighter (with all the rest of the scene)
65 | - The caustic is a bit more precise with a lot more samples
66 |
67 | ###Sampling
68 | Here are some tests with different numbers of sample to show the importance of sampling with photon mapping:
69 | - Top left: 16 samples per pixel
70 | - Top right: 64 samples per pixel
71 | - Bottom left: 128 samples per pixel
72 | - Bottom right: 256 samples per pixel
73 |
74 | 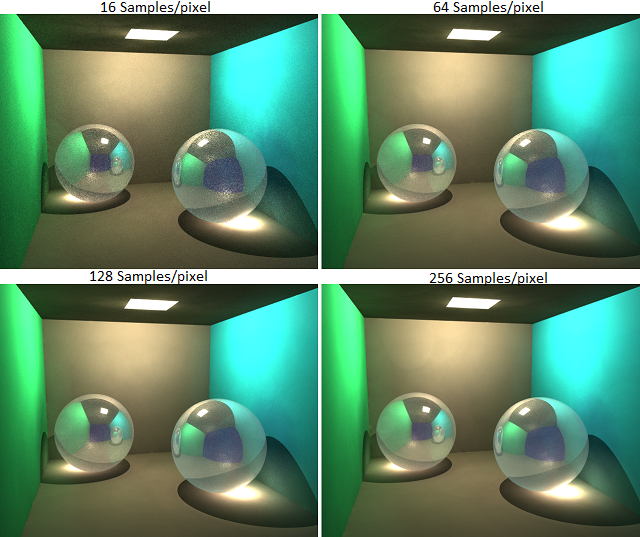
75 |
76 |
77 | ##Wavefront Obj and materials
78 | In order to render complex scenes with realistic materials like the cave (final image on the right), we improved the .obj file parser to also load the .mtl files with the materials.
79 |
80 | Those material files describe each features to enable and each parameters to apply on the triangles such as:
81 | - Ns: Specifies the specular exponent for the current material.
82 | - Ni: Specifies the index of refraction for the surface.
83 | - d: Opacity of the material.
84 | - Ka: Ambient color.
85 | - map_Kd: Texture to apply on the diffuse reflectivity of the material.
86 | - map_bump: Bump map to apply on the normals of the surface.
87 | - ...
88 |
89 | With this parser, we were able to create scenes with any 3D software (blender, 3ds max) and export them in the .obj format.
90 | The main challenge after that was to check manually for each material if all the properties were properly exported (and this is not often the case).
91 |
92 | 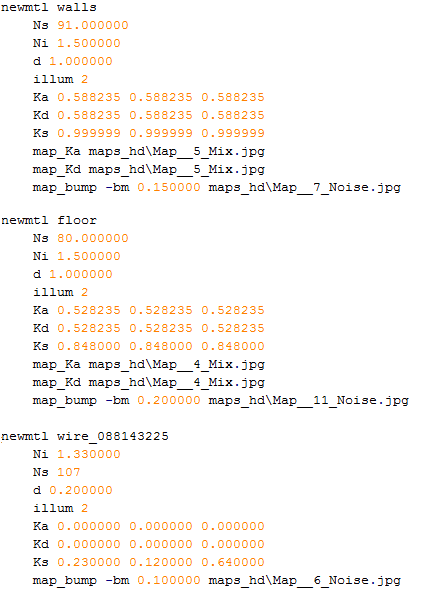
93 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/all_in_one_256s.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lebascou/Raytracer/5f7fd9ec2fa7d178d0b9509e2bdbc74beb408551/images/all_in_one_256s.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/all_in_one_header.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lebascou/Raytracer/5f7fd9ec2fa7d178d0b9509e2bdbc74beb408551/images/all_in_one_header.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/cornell_all.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lebascou/Raytracer/5f7fd9ec2fa7d178d0b9509e2bdbc74beb408551/images/cornell_all.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/cornell_with_without_photon.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lebascou/Raytracer/5f7fd9ec2fa7d178d0b9509e2bdbc74beb408551/images/cornell_with_without_photon.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/dof_256s.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lebascou/Raytracer/5f7fd9ec2fa7d178d0b9509e2bdbc74beb408551/images/dof_256s.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/final_scene.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lebascou/Raytracer/5f7fd9ec2fa7d178d0b9509e2bdbc74beb408551/images/final_scene.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/glossy_256s.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lebascou/Raytracer/5f7fd9ec2fa7d178d0b9509e2bdbc74beb408551/images/glossy_256s.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/material_file.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lebascou/Raytracer/5f7fd9ec2fa7d178d0b9509e2bdbc74beb408551/images/material_file.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/noise_bump_256s.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lebascou/Raytracer/5f7fd9ec2fa7d178d0b9509e2bdbc74beb408551/images/noise_bump_256s.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/texturing_100s.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lebascou/Raytracer/5f7fd9ec2fa7d178d0b9509e2bdbc74beb408551/images/texturing_100s.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/texturing_bump_100s.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lebascou/Raytracer/5f7fd9ec2fa7d178d0b9509e2bdbc74beb408551/images/texturing_bump_100s.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/txt_001_diff.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lebascou/Raytracer/5f7fd9ec2fa7d178d0b9509e2bdbc74beb408551/images/txt_001_diff.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/txt_002_bump.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lebascou/Raytracer/5f7fd9ec2fa7d178d0b9509e2bdbc74beb408551/images/txt_002_bump.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/BLPatch.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "BLPatch.h"
2 | #include "Ray.h"
3 | #include "Console.h"
4 |
5 | BLPatch::BLPatch()
6 | {
7 | }
8 |
9 | BLPatch::~BLPatch()
10 | {
11 | }
12 |
13 | void
14 | BLPatch::renderGL()
15 | {
16 |
17 | }
18 |
19 | ObjType BLPatch::type() const { return BLPATCH; }
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/BLPatch.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef CSE168_BL_PATCH_H_INCLUDED
2 | #define CSE168_BL_PATCH_H_INCLUDED
3 |
4 | #include "Vector3.h"
5 | #include "Object.h"
6 |
7 | class BLPatch : public Object
8 | {
9 | public:
10 | BLPatch();
11 | virtual ~BLPatch();
12 |
13 | Vector3 & vertex(int i) {return m_verts[i];}
14 | const Vector3 & vertex(int i) const {return m_verts[i];}
15 |
16 | virtual void renderGL();
17 |
18 | virtual ObjType type() const;
19 |
20 | virtual void *selfPtr() { return this; }
21 | protected:
22 | Vector3 m_verts[4];
23 | };
24 |
25 | #endif // CSE168_BL_PATCH_H_INCLUDED
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/BVH.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "BVH.h"
2 | #include "Ray.h"
3 | #include "Console.h"
4 | #include "Sphere.h"
5 | #include "Triangle.h"
6 | #include "Box.h"
7 | #include "BoundingBox.h"
8 | #include
9 | #include
10 | #include
11 |
12 | #define INF std::numeric_limits::infinity()
13 |
14 | #define CBOX 4.f
15 | #define CTRI 1.f
16 | #define SIZE_LEAF 8
17 |
18 | static float costNTris(int n)
19 | {
20 | return (n / 4 + (n % 4 != 0)) * CTRI;
21 | }
22 |
23 | static float cost(float areaA, int objA, float areaB, int objB, float areaCinv)
24 | {
25 | return 2 * CBOX + (areaA * costNTris(objA) + areaB * costNTris(objB)) * areaCinv;
26 | }
27 |
28 | void BVH::splitBox(AxisData const &data, BoundingBox &abox, BoundingBox &bbox, ObjectsWithBoxes::iterator begin, ObjectsWithBoxes::iterator end, float areaCinv, boost::function f)
29 | {
30 | Vector3 v(INF);
31 | abox.setA(v);
32 | bbox.setA(v);
33 | v.set(-INF);
34 | abox.setB(v);
35 | bbox.setB(v);
36 | int a = 0, b = 0;
37 | for (ObjectsWithBoxes::iterator it = begin; it != end;)
38 | {
39 | Vector3 const &min = it->min;
40 | Vector3 const &max = it->max;
41 | if (min[data.axis] > data.pos || (max[data.axis] > data.pos && max[data.axis] - data.pos > data.pos - min[data.axis]))
42 | {
43 | bbox.setA(bbox.getA().min(min));
44 | bbox.setB(bbox.getB().max(max));
45 | f(1, it, end);
46 | b++;
47 | continue;
48 | }
49 | else
50 | {
51 | abox.setA(abox.getA().min(min));
52 | abox.setB(abox.getB().max(max));
53 | f(0, it, end);
54 | a++;
55 | continue;
56 | }
57 | }
58 | }
59 |
60 | void BVH::buildLeaf(ObjectsWithBoxes::iterator begin, ObjectsWithBoxes::iterator end, BVH::BBoxNode *prev_node)
61 | {
62 | prev_node->objs = new std::vector();
63 | prev_node->objs->resize(NB_OBJS);
64 | for (ObjectsWithBoxes::iterator it = begin; it != end; ++it)
65 | {
66 | (*prev_node->objs)[it->obj->type()].plain.push_back(it->obj->ptr());
67 | }
68 | (*prev_node->objs)[TRIANGLE].sse_preprocessed = Triangle::preProcess((*prev_node->objs)[TRIANGLE].plain);
69 | }
70 |
71 | void BVH::recBuildBBox(ObjectsWithBoxes::iterator begin, ObjectsWithBoxes::iterator end, BVH::BBoxNode *prev_node, int depth)
72 | {
73 | if (end - begin <= SIZE_LEAF)
74 | {
75 | buildLeaf(begin, end, prev_node);
76 | return;
77 | }
78 | BoundingBox abox;
79 | BoundingBox bbox;
80 | float areaCinv = 1.f / prev_node->box.area();
81 | AxisData minsplit;
82 | minsplit.axis = -1;
83 | minsplit.cost = INF;
84 | for (int axis = 0; axis < 3; ++axis)
85 | {
86 | AxisData data;
87 | data.lowest = prev_node->box.getA()[axis];
88 | data.highest = prev_node->box.getB()[axis];
89 | if (data.lowest > data.highest)
90 | std::swap(data.lowest, data.highest);
91 | data.interval = (data.highest - data.lowest) / 10;
92 | if (data.interval < EPSILON)
93 | continue;
94 | data.axis = axis;
95 | for (data.pos = data.lowest + data.interval; data.pos < data.highest; data.pos += data.interval)
96 | {
97 | int cnts[2] = {0, 0};
98 | splitBox(data, abox, bbox, begin, end, areaCinv, [&](int n, ObjectsWithBoxes::iterator &it, ObjectsWithBoxes::iterator &)
99 | {
100 | cnts[n]++;
101 | ++it;
102 | });
103 | data.cost = cost(abox.area(), cnts[0], bbox.area(), cnts[1], areaCinv);
104 | minsplit = std::min(minsplit, data);
105 | }
106 | }
107 | if (minsplit.axis == -1)
108 | {
109 | buildLeaf(begin, end, prev_node);
110 | return;
111 | }
112 | ObjectsWithBoxes::iterator middle = begin, last = begin + (end - begin - 1);
113 | splitBox(minsplit, abox, bbox, begin, end, areaCinv, [&](int n, ObjectsWithBoxes::iterator &it, ObjectsWithBoxes::iterator &curend)
114 | {
115 | if (n == 0)
116 | {
117 | ++it;
118 | ++middle;
119 | }
120 | else
121 | {
122 | std::swap(*it, *last);
123 | --last;
124 | curend = last + 1;
125 | }
126 | });
127 | prev_node->a = new BBoxNode;
128 | prev_node->a->box = abox;
129 | prev_node->b = new BBoxNode;
130 | prev_node->b->box = bbox;
131 | if (1 << depth <= nCpus())
132 | {
133 | boost::thread t([&]() {recBuildBBox(begin, middle, prev_node->a, depth + 1);});
134 | recBuildBBox(middle, end, prev_node->b, depth + 1);
135 | t.join();
136 | }
137 | else
138 | {
139 | recBuildBBox(begin, middle, prev_node->a, depth + 1);
140 | recBuildBBox(middle, end, prev_node->b, depth + 1);
141 | }
142 | }
143 |
144 | BoundingBox BVH::objectBox(ObjectsWithBoxes *objs)
145 | {
146 | Vector3 min = Vector3(INF, INF, INF);
147 | Vector3 max = Vector3(-INF, -INF, -INF);
148 | for (ObjectsWithBoxes::const_iterator it = objs->begin(); it != objs->end(); ++it)
149 | {
150 | min = min.min(it->min);
151 | max = max.max(it->max);
152 | }
153 | return BoundingBox(min, max);
154 | }
155 |
156 | void BVH::printHierarchy(BBoxNode *node, int ind)
157 | {
158 | printf("%f\n", node->box.area());
159 | if (node->a && node->b)
160 | {
161 | printHierarchy(node->a, ind + 1);
162 | printHierarchy(node->b, ind + 1);
163 | }
164 | else
165 | printf("%f\n", (*node->objs)[TRIANGLE].plain.size());
166 | }
167 |
168 | void
169 | BVH::build(Objects * objs)
170 | {
171 | // construct the bounding volume hierarchy
172 |
173 | ObjectsWithBoxes objs_boxes;
174 | std::transform(objs->begin(), objs->end(), std::back_inserter(objs_boxes), [](Object *o) -> ObjectWithBox
175 | {
176 | ObjectWithBox res;
177 | res.min = o->minVector();
178 | res.max = o->maxVector();
179 | res.obj = o;
180 | return res;
181 | });
182 |
183 | m_root = new BBoxNode;
184 | m_root->box = objectBox(&objs_boxes);
185 | recBuildBBox(objs_boxes.begin(), objs_boxes.end(), m_root);
186 | //printHierarchy(m_root, 0);
187 |
188 | m_objects = objs;
189 |
190 | // OBSOLETE: start
191 | //m_categories_objects.resize(NB_OBJS);
192 | //for (size_t i = 0; i < m_objects->size(); ++i)
193 | //{
194 | // m_categories_objects[(*m_objects)[i]->type()].plain.push_back((*m_objects)[i]->ptr());
195 | //}
196 | //m_categories_objects[TRIANGLE].sse_preprocessed = Triangle::preProcess(m_categories_objects[TRIANGLE].plain);
197 | // OBSOLETE: stop
198 |
199 | m_intersect_fcts.resize(NB_OBJS);
200 | m_intersect_fcts[TRIANGLE] = &Triangle::doIntersect;
201 | m_intersect_fcts[SPHERE] = &Sphere::doIntersect;
202 | m_intersect_fcts[BOX] = &Box::doIntersect;
203 | }
204 |
205 | bool
206 | BVH::rec_intersect(BBoxNode *node, HitInfo& minHit, const Ray& ray, float tMin, float tMax) const
207 | {
208 | bool hit = false;
209 | HitInfo tempMinHit;
210 | minHit.t = MIRO_TMAX;
211 |
212 | if (node->a == NULL && node->b == NULL)
213 | {
214 | for (size_t i = 0; i < NB_OBJS; ++i)
215 | {
216 | if (m_intersect_fcts[i] && m_intersect_fcts[i]((*node->objs)[i], tempMinHit, ray, tMin, tMax) && tempMinHit.t < minHit.t)
217 | {
218 | minHit = tempMinHit;
219 | hit = true;
220 | }
221 | }
222 |
223 | }
224 | else
225 | {
226 | if (node->a && node->a->box.doIntersect(tempMinHit, ray, tMin, tMax))
227 | {
228 | hit = rec_intersect(node->a, minHit, ray, tMin, tMax);
229 | }
230 | if (node->b && node->b->box.doIntersect(tempMinHit, ray, tMin, tMax))
231 | {
232 | bool tmpHit = rec_intersect(node->b, tempMinHit, ray, tMin, tMax);
233 | if (tmpHit && (!hit || (hit && tempMinHit.t < minHit.t)))
234 | {
235 | minHit = tempMinHit;
236 | hit = true;
237 | }
238 | }
239 | }
240 | if (hit)
241 | {
242 | if (minHit.N.dot(ray.d) > 0)
243 | {
244 | minHit.N.negate();
245 | }
246 | }
247 | return hit;
248 | }
249 |
250 | bool
251 | BVH::intersect(HitInfo& minHit, const Ray& ray, float tMin, float tMax) const
252 | {
253 | // Here you would need to traverse the BVH to perform ray-intersection
254 | // acceleration. For now we just intersect every object.
255 |
256 | bool hit = false;
257 | HitInfo tempMinHit;
258 | minHit.t = MIRO_TMAX;
259 |
260 | return rec_intersect(m_root, minHit, ray, tMin, tMax);
261 | }
262 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/BVH.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef CSE168_BVH_H_INCLUDED
2 | #define CSE168_BVH_H_INCLUDED
3 |
4 | #include "Miro.h"
5 | #include "Object.h"
6 | #include "BoundingBox.h"
7 | #include "IntersectObjects.h"
8 | #include
9 |
10 | class BVH
11 | {
12 | public:
13 | void build(Objects * objs);
14 |
15 | bool intersect(HitInfo& result, const Ray& ray,
16 | float tMin = 0.0f, float tMax = MIRO_TMAX) const;
17 |
18 | protected:
19 | struct BBoxNode
20 | {
21 | BoundingBox box;
22 | std::vector *objs;
23 | BBoxNode *a;
24 | BBoxNode *b;
25 |
26 | BBoxNode() : a(0), b(0), objs(0) {}
27 |
28 | ~BBoxNode() { delete a; delete b; delete objs; }
29 | };
30 |
31 | struct AxisData
32 | {
33 | float lowest;
34 | float highest;
35 | float interval;
36 | float pos;
37 | int axis;
38 | float cost;
39 |
40 | bool operator<(AxisData const &other) const
41 | {
42 | return cost < other.cost;
43 | }
44 | };
45 |
46 | struct ObjectWithBox
47 | {
48 | Object *obj;
49 | Vector3 min, max;
50 | };
51 | typedef std::vector ObjectsWithBoxes;
52 |
53 | void splitBox(AxisData const &data, BoundingBox &abox, BoundingBox &bbox, ObjectsWithBoxes::iterator begin, ObjectsWithBoxes::iterator end, float areaCinv, boost::function f);
54 | void buildLeaf(ObjectsWithBoxes::iterator begin, ObjectsWithBoxes::iterator end, BVH::BBoxNode *prev_node);
55 |
56 | void recBuildBBox(ObjectsWithBoxes::iterator begin, ObjectsWithBoxes::iterator end, BVH::BBoxNode *prev_node, int depth = 0);
57 | BoundingBox objectBox(ObjectsWithBoxes *objs);
58 | void printHierarchy(BBoxNode *node, int ind);
59 |
60 | Objects * m_objects;
61 | std::vector m_categories_objects;
62 | typedef bool (*Intersect)(IntersectObjects const &objects, HitInfo& result,
63 | const Ray& ray, float tMin, float tMax);
64 | std::vector m_intersect_fcts;
65 |
66 | BBoxNode *m_root;
67 |
68 | public:
69 | bool rec_intersect(BBoxNode *node, HitInfo& result, const Ray& ray,
70 | float tMin = 0.0f, float tMax = MIRO_TMAX) const;
71 | };
72 |
73 | #endif // CSE168_BVH_H_INCLUDED
74 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/BoundingBox.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "BoundingBox.h"
2 | #include "Ray.h"
3 | #include
4 |
5 | BoundingBox::BoundingBox(const Vector3& a, const Vector3& b) : _a(a), _b(b)
6 | {
7 | }
8 |
9 |
10 | BoundingBox::~BoundingBox(void)
11 | {
12 | }
13 |
14 | bool BoundingBox::doIntersect(HitInfo &result, const Ray &ray, float tMin, float tMax)
15 | {
16 | Vector3 t1 = (_a - ray.o) / ray.d;
17 | Vector3 t2 = (_b - ray.o) / ray.d;
18 |
19 | float t_min = std::max(std::min(t1.x, t2.x), std::max(std::min(t1.y, t2.y), std::min(t1.z, t2.z)));
20 | float t_max = std::min(std::max(t1.x, t2.x), std::min(std::max(t1.y, t2.y), std::max(t1.z, t2.z)));
21 |
22 | if (t_max < 0 || t_min > t_max)
23 | return false;
24 | result.t = t_min < 0 ? t_max : t_min;
25 | return true;
26 | }
27 |
28 | float BoundingBox::area() const
29 | {
30 | Vector3 segments = (_a - _b).abs();
31 | return (segments.x * segments.y + segments.x * segments.z + segments.y * segments.z) * 2;
32 | }
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/BoundingBox.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #pragma once
2 | #include "Object.h"
3 |
4 | class BoundingBox
5 | {
6 | public:
7 | BoundingBox(const Vector3& a, const Vector3& b);
8 | BoundingBox() {}
9 | virtual ~BoundingBox();
10 |
11 | bool doIntersect(HitInfo &, const Ray &, float, float);
12 |
13 | void setA(const Vector3 & v) {_a = v;}
14 | const Vector3& getA() const { return _a; }
15 | void setB(const Vector3 & v) {_b = v;}
16 | const Vector3& getB() const { return _b; }
17 |
18 | float area() const;
19 |
20 | protected:
21 | Vector3 _a;
22 | Vector3 _b;
23 | };
24 |
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Box.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "Box.h"
2 | #include "Ray.h"
3 |
4 | Box::Box(const Vector3& a, const Vector3& b) : BoundingBox(a, b)
5 | {
6 | }
7 |
8 |
9 | Box::~Box(void)
10 | {
11 | }
12 |
13 | void Box::renderGL()
14 | {
15 | Vector3 v[16];
16 |
17 | v[0] = Vector3(_a.x, _a.y, _a.z);
18 | v[1] = Vector3(_a.x + _b.x, _a.y, _a.z);
19 | v[2] = Vector3(_a.x + _b.x, _a.y, _a.z + _b.z);
20 | v[3] = Vector3(_a.x, _a.y, _a.z + _b.z);
21 |
22 | v[4] = Vector3(_a.x, _a.y, _a.z + _b.z);
23 | v[5] = Vector3(_a.x, _a.y + _b.y, _a.z + _b.z);
24 | v[6] = Vector3(_a.x, _a.y + _b.y, _a.z);
25 | v[7] = Vector3(_a.x, _a.y, _a.z);
26 |
27 | v[8] = Vector3(_a.x, _a.y + _b.y, _a.z);
28 | v[9] = Vector3(_a.x + _b.x, _a.y + _b.y, _a.z);
29 | v[10] = Vector3(_a.x + _b.x, _a.y + _b.y, _a.z + _b.z);
30 | v[11] = Vector3(_a.x, _a.y + _b.y, _a.z + _b.z);
31 |
32 | v[12] = Vector3(_a.x + _b.x, _a.y, _a.z + _b.z);
33 | v[13] = Vector3(_a.x + _b.x, _a.y + _b.y, _a.z + _b.z);
34 | v[14] = Vector3(_a.x + _b.x, _a.y + _b.y, _a.z);
35 | v[15] = Vector3(_a.x + _b.x, _a.y, _a.z);
36 |
37 | glBegin(GL_QUADS);
38 | for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++)
39 | glVertex3f(v[i].x, v[i].y, v[i].z);
40 | glEnd();
41 | }
42 |
43 | bool Box::doIntersect(IntersectObjects const &objects, HitInfo& result, const Ray& ray, float tMin, float tMax)
44 | {
45 | bool hit = false;
46 | int idx = 0;
47 |
48 | for (int i = 0; i < objects.plain.size(); i++)
49 | {
50 | Box *cur = (Box*) objects.plain[i];
51 | HitInfo cur_result;
52 |
53 | if (((BoundingBox*)cur)->doIntersect(cur_result, ray, tMin, tMax) && cur_result.t > tMin && cur_result.t < tMax)
54 | {
55 | result = cur_result;
56 | result.material = cur->m_material;
57 | hit = true;
58 | idx = i;
59 | }
60 | }
61 | if (hit == true)
62 | {
63 | result.P = ray.o + (ray.d * result.t);
64 | Vector3 p = (((Box*)objects.plain[idx])->getA() + ((Box*)objects.plain[idx])->getB()) / 2.f;
65 | p = result.P - p;
66 |
67 | if (std::abs(p.x) >= std::abs(p.y) && std::abs(p.x) >= std::abs(p.z))
68 | {
69 | p.y = 0;
70 | p.z = 0;
71 | }
72 | else if (std::abs(p.y) >= std::abs(p.x) && std::abs(p.y) >= std::abs(p.z))
73 | {
74 | p.x = 0;
75 | p.z = 0;
76 | }
77 | else
78 | {
79 | p.x = 0;
80 | p.y = 0;
81 | }
82 | p.normalize();
83 | result.N = p;
84 | }
85 | return hit;
86 | }
87 |
88 | Vector3 Box::maxVector() const
89 | {
90 | return _a.max(_b);
91 | }
92 |
93 | Vector3 Box::minVector() const
94 | {
95 | return _a.min(_b);
96 | }
97 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Box.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #pragma once
2 | #include "Object.h"
3 | #include "BoundingBox.h"
4 |
5 | class Box : public Object, public BoundingBox
6 | {
7 | public:
8 | Box(const Vector3& a, const Vector3& b);
9 | virtual ~Box();
10 |
11 | void renderGL();
12 | static bool doIntersect(IntersectObjects const &objects, HitInfo &, const Ray &, float, float);
13 |
14 | virtual ObjType type() const { return BOX; }
15 |
16 | virtual void *ptr() { return this; }
17 |
18 | virtual Vector3 minVector() const;
19 | virtual Vector3 maxVector() const;
20 | };
21 |
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Camera.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include
2 | #include
3 | #include "Miro.h"
4 | #include "Camera.h"
5 | #include "Image.h"
6 | #include "Scene.h"
7 | #include "Console.h"
8 | #include "OpenGL.h"
9 |
10 | Camera * g_camera = 0;
11 |
12 | static bool firstRayTrace = true;
13 |
14 | const float HalfDegToRad = DegToRad/2.0f;
15 |
16 | Camera::Camera() :
17 | m_renderer(RENDER_OPENGL),
18 | m_eye(0,0,0),
19 | m_viewDir(0,0,-1),
20 | m_up(0,1,0),
21 | m_lookAt(FLT_MAX, FLT_MAX, FLT_MAX),
22 | m_fov((45.)*(PI/180.))
23 | {
24 | calcLookAt();
25 | }
26 |
27 |
28 | Camera::~Camera()
29 | {
30 |
31 | }
32 |
33 |
34 | void
35 | Camera::click(Scene* pScene, Image* pImage)
36 | {
37 | calcLookAt();
38 | static bool firstRayTrace = false;
39 |
40 | if (m_renderer == RENDER_OPENGL)
41 | {
42 | glDrawBuffer(GL_BACK);
43 | pScene->openGL(this);
44 | firstRayTrace = true;
45 | }
46 | else if (m_renderer == RENDER_RAYTRACE)
47 | {
48 | glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
49 | glLoadIdentity();
50 | glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
51 | glLoadIdentity();
52 |
53 | glDrawBuffer(GL_FRONT);
54 | if (firstRayTrace)
55 | {
56 | pImage->clear(pScene->bgColor());
57 | pScene->raytraceImage(this, g_image);
58 | firstRayTrace = false;
59 | }
60 |
61 | g_image->draw();
62 | }
63 | }
64 |
65 |
66 | void
67 | Camera::calcLookAt()
68 | {
69 | // this is true when a "lookat" is not used in the config file
70 | if (m_lookAt.x != FLT_MAX)
71 | {
72 | setLookAt(m_lookAt);
73 | m_lookAt.set(FLT_MAX, FLT_MAX, FLT_MAX);
74 | }
75 | }
76 |
77 |
78 | void
79 | Camera::drawGL()
80 | {
81 | // set up the screen with our camera parameters
82 | glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
83 | glLoadIdentity();
84 | gluPerspective(fov(), g_image->width()/(float)g_image->height(),
85 | 0.01, 10000);
86 |
87 | glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
88 | glLoadIdentity();
89 | Vector3 vCenter = eye() + viewDir();
90 | gluLookAt(eye().x, eye().y, eye().z,
91 | vCenter.x, vCenter.y, vCenter.z,
92 | up().x, up().y, up().z);
93 | }
94 |
95 |
96 | Ray
97 | Camera::eyeRay(float x, float y, int imageWidth, int imageHeight) const
98 | {
99 | // first compute the camera coordinate system
100 | // ------------------------------------------
101 |
102 | // wDir = e - (e+m_viewDir) = -m_vView
103 | const Vector3 wDir = Vector3(-m_viewDir).normalize();
104 | const Vector3 uDir = cross(m_up, wDir).normalize();
105 | const Vector3 vDir = cross(wDir, uDir);
106 |
107 |
108 |
109 | // next find the corners of the image plane in camera space
110 | // --------------------------------------------------------
111 |
112 | const float aspectRatio = (float)imageWidth/(float)imageHeight;
113 |
114 |
115 | const float top = tan(m_fov*HalfDegToRad);
116 | const float right = aspectRatio*top;
117 |
118 | const float bottom = -top;
119 | const float left = -right;
120 |
121 |
122 |
123 | // transform x and y into camera space
124 | // -----------------------------------
125 |
126 | const float imPlaneUPos = left + (right - left)*(((float)x+0.5f)/(float)imageWidth);
127 | const float imPlaneVPos = bottom + (top - bottom)*(((float)y+0.5f)/(float)imageHeight);
128 |
129 | return Ray(m_eye, (imPlaneUPos*uDir + imPlaneVPos*vDir - wDir).normalize());
130 | }
131 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Camera.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef CSE168_CAMERA_H_INCLUDED
2 | #define CSE168_CAMERA_H_INCLUDED
3 |
4 | #include "Vector3.h"
5 | #include "Miro.h"
6 | #include "Ray.h"
7 |
8 | class Camera
9 | {
10 | public:
11 | Camera();
12 | virtual ~Camera();
13 |
14 | enum
15 | {
16 | RENDER_OPENGL = 0,
17 | RENDER_RAYTRACE = 1
18 | };
19 |
20 | void click(Scene* pScene, Image* pImage);
21 |
22 | inline bool isOpenGL() const {return m_renderer == RENDER_OPENGL;}
23 | inline void setRenderer(int i) {m_renderer = i;}
24 |
25 | inline void setEye(float x, float y, float z);
26 | inline void setEye(const Vector3& eye);
27 | inline void setUp(float x, float y, float z);
28 | inline void setUp(const Vector3& up);
29 | inline void setViewDir(float x, float y, float z);
30 | inline void setViewDir(const Vector3& vd);
31 | inline void setLookAt(float x, float y, float z);
32 | inline void setLookAt(const Vector3& look);
33 | inline void setFOV(float fov) {m_fov = fov;}
34 |
35 | inline float fov() const {return m_fov;}
36 | inline const Vector3 & viewDir() const {return m_viewDir;}
37 | inline const Vector3 & lookAt() const {return m_lookAt;}
38 | inline const Vector3 & up() const {return m_up;}
39 | inline const Vector3 & eye() const {return m_eye;}
40 |
41 | Ray eyeRay(float x, float y, int imageWidth, int imageHeight) const;
42 |
43 | void drawGL();
44 |
45 | private:
46 |
47 | void calcLookAt();
48 |
49 | int m_renderer;
50 |
51 | // main screen params
52 | Vector3 m_eye;
53 | Vector3 m_up;
54 | Vector3 m_viewDir;
55 | Vector3 m_lookAt;
56 | float m_fov;
57 | };
58 |
59 | extern Camera * g_camera;
60 |
61 | //--------------------------------------------------------
62 |
63 | inline void Camera::setEye(float x, float y, float z)
64 | {
65 | Vector3 v(x, y, z);
66 | setEye(v);
67 | }
68 |
69 | inline void Camera::setEye(const Vector3& eye)
70 | {
71 | m_eye.set(eye);
72 | }
73 |
74 | inline void Camera::setUp(float x, float y, float z)
75 | {
76 | Vector3 v(x, y, z);
77 | setUp(v);
78 | }
79 |
80 | inline void Camera::setUp(const Vector3& up)
81 | {
82 | m_up.set(up);
83 | m_up.normalize();
84 | }
85 |
86 | inline void Camera::setViewDir(float x, float y, float z)
87 | {
88 | Vector3 v(x, y, z);
89 | setViewDir(v);
90 | }
91 |
92 | inline void Camera::setViewDir(const Vector3& vd)
93 | {
94 | m_viewDir.set(vd);
95 | m_viewDir.normalize();
96 | }
97 |
98 | inline void Camera::setLookAt(float x, float y, float z)
99 | {
100 | Vector3 v(x, y, z);
101 | setLookAt(v);
102 | }
103 |
104 | inline void Camera::setLookAt(const Vector3& vd)
105 | {
106 | Vector3 dir = vd - m_eye;
107 | setViewDir(dir);
108 | }
109 |
110 | #endif // CSE168_CAMERA_H_INCLUDED
111 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/CellularStoneTexture.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "CellularStoneTexture.h"
2 | #include "Ray.h"
3 | #include "Scene.h"
4 | #include "Perlin.h"
5 | #include "Worley.h"
6 | #include
7 |
8 | CellularStoneTexture::CellularStoneTexture(float tile_size, float sep_size, const Vector3& sep_color)
9 | {
10 | m_tile_size = 1.0f / tile_size;
11 | m_sep_delta = sep_size;
12 | m_tiles_colors.push_back(Vector3(0.6, 0.35, 0.19));
13 | m_tiles_colors.push_back(Vector3(0.68, 0.41, 0.21));
14 | m_tiles_colors.push_back(Vector3(0.82, 0.49, 0.35));
15 | m_tiles_colors.push_back(Vector3(0.5, 0.33, 0.16));
16 | m_tiles_colors.push_back(Vector3(0.42, 0.23, 0.14));
17 | m_sep_color = sep_color;
18 | }
19 |
20 | CellularStoneTexture::~CellularStoneTexture()
21 | {
22 | }
23 |
24 | Vector3
25 | CellularStoneTexture::getTextureColorAt(const Vector3& pos) const
26 | {
27 | Vector3 color(m_sep_color);
28 | Vector3 npos(pos);
29 |
30 | float at[] = {npos.x * m_tile_size, npos.y * m_tile_size, npos.z * m_tile_size};
31 | float F[m_max_order];
32 | float delta[m_max_order][3];
33 | unsigned int ID[m_max_order];
34 | float noise_scale = 0.2f;
35 | float p_noise = 0;
36 |
37 | WorleyNoise::noise3D(at, m_max_order, F, delta, ID);
38 | if(F[2] - F[1] < -m_sep_delta || F[2] - F[1] > m_sep_delta)
39 | {
40 | color = m_tiles_colors[ID[1] % m_tiles_colors.size()] + m_tiles_colors[ID[0] % m_tiles_colors.size()];
41 | npos *= 6;
42 | noise_scale = 0.05;
43 | p_noise = (PerlinNoise::noise(npos.x, npos.y, npos.z));
44 | }
45 | else
46 | {
47 | npos *= 18;
48 | p_noise = (PerlinNoise::noise(npos.x, npos.y, npos.z)) + 0.6;
49 | }
50 | color = (1.0f - noise_scale) * color + noise_scale * p_noise;
51 | return color;
52 | }
53 |
54 | Vector3
55 | CellularStoneTexture::shade(const Ray& ray, const HitInfo& hit, const Scene& scene) const
56 | {
57 | return getTextureColorAt(hit.P);
58 | }
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/CellularStoneTexture.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef CSE168_CELLULAR_STONE_TEXTURE_H_INCLUDED
2 | #define CSE168_CELLULAR_STONE_TEXTURE_H_INCLUDED
3 |
4 | #include "Material.h"
5 | #include
6 |
7 | class CellularStoneTexture : public Material
8 | {
9 | public:
10 | // tile_size: value between 0(small tiles) and 1(normal tiles)
11 | // sep_size: Separator between tiles (0.03 is a good value)
12 | CellularStoneTexture(float tile_size = 1.0f, float sep_size = 0.03f, const Vector3& sep_color = Vector3(0.9f));
13 | virtual ~CellularStoneTexture();
14 |
15 | virtual void preCalc() {}
16 |
17 | virtual Vector3 shade(const Ray& ray, const HitInfo& hit,
18 | const Scene& scene) const;
19 |
20 | protected:
21 | Vector3 getTextureColorAt(const Vector3& pos) const;
22 |
23 | protected:
24 | std::vector m_tiles_colors;
25 | float m_tile_size;
26 | static const int m_max_order = 3;
27 | float m_sep_delta;
28 | Vector3 m_sep_color;
29 | };
30 |
31 | #endif // CSE168_CELLULAR_STONE_TEXTURE_H_INCLUDED
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Console.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // you probably dont want to modify this file
2 |
3 | #include
4 | #include
5 | #include
6 | #include "Console.h"
7 |
8 | #ifdef WIN32
9 | #include
10 | //#include
11 |
12 | // disable useless warnings
13 | #pragma warning(disable:4996)
14 | #endif
15 |
16 | static char __internal_console_buffer__[8192] = {'\0'};
17 |
18 | #define TEXT_NORMAL "\033[0m"
19 | #define TEXT_RED "\033[1;31m"
20 | #define TEXT_GREEN "\033[1;32m"
21 | #define TEXT_PINK "\033[1;35m"
22 |
23 |
24 | #ifdef WIN32
25 | static void cprintf(const char *s) {
26 | unsigned short attr = 0;
27 | int code = 0, state = 0;
28 | while (*s) {
29 | char ch = *s++;
30 | if (ch == 27)
31 | state = 1;
32 | else if (state == 1) {
33 | if (ch == '[') {
34 | state = 2;
35 | code = 0;
36 | }
37 | else
38 | state = 0;
39 | }
40 | else if (state == 2) {
41 | if (ch == ';' || ch == 'm') { // finished with this one
42 | fflush(stdout);
43 | switch (code) {
44 | case 0: attr = FOREGROUND_RED | FOREGROUND_GREEN | FOREGROUND_BLUE; break;
45 | case 1: attr |= FOREGROUND_INTENSITY; break;
46 | case 3: attr |= COMMON_LVB_UNDERSCORE; break;
47 | case 7: attr |= COMMON_LVB_REVERSE_VIDEO; break;
48 | case 31: attr |= FOREGROUND_RED; break;
49 | case 32: attr |= FOREGROUND_GREEN; break;
50 | case 33: attr |= FOREGROUND_RED | FOREGROUND_GREEN; break;
51 | case 34: attr |= FOREGROUND_BLUE | FOREGROUND_INTENSITY; break;
52 | case 35: attr |= FOREGROUND_RED | FOREGROUND_BLUE; break;
53 | case 36: attr |= FOREGROUND_GREEN | FOREGROUND_BLUE; break;
54 | case 37: attr |= FOREGROUND_RED | FOREGROUND_GREEN | FOREGROUND_BLUE; break;
55 | case 38: attr |= FOREGROUND_BLUE | FOREGROUND_BLUE; break;
56 | case 41: attr |= BACKGROUND_INTENSITY | BACKGROUND_RED; break;
57 | case 42: attr |= BACKGROUND_INTENSITY | BACKGROUND_GREEN; break;
58 | case 43: attr |= BACKGROUND_INTENSITY | BACKGROUND_RED | BACKGROUND_GREEN; break;
59 | case 44: attr |= BACKGROUND_INTENSITY | BACKGROUND_BLUE; break;
60 | case 45: attr |= BACKGROUND_INTENSITY | BACKGROUND_RED | BACKGROUND_BLUE; break;
61 | case 46: attr |= BACKGROUND_INTENSITY | BACKGROUND_GREEN | BACKGROUND_BLUE; break;
62 | case 47: attr |= BACKGROUND_INTENSITY | BACKGROUND_RED | BACKGROUND_GREEN | BACKGROUND_BLUE; break;
63 | }
64 | code = 0;
65 | if (ch == 'm') {
66 | //setConsoleTextAttribute(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE),attr);
67 | state = 0;
68 | }
69 | }
70 | else
71 | code = (code * 10) + (ch - '0'); // leading digit
72 | } else {
73 | putchar(ch);
74 | attr = 0;
75 | }
76 | }
77 | }
78 | #else
79 | #define cprintf printf
80 | #define _vsnprintf vsnprintf
81 | #endif
82 |
83 | void warning(const char *fmt,...)
84 | {
85 | va_list msg;
86 | va_start (msg, fmt);
87 | _vsnprintf(__internal_console_buffer__, 8191, fmt, msg);
88 | va_end (msg);
89 |
90 | cprintf(TEXT_PINK "warning: " TEXT_NORMAL);
91 | cprintf(__internal_console_buffer__);
92 | }
93 |
94 | void error(const char *fmt,...)
95 | {
96 | va_list msg;
97 | va_start (msg, fmt);
98 | _vsnprintf(__internal_console_buffer__, 8191, fmt, msg);
99 | va_end (msg);
100 |
101 | cprintf(TEXT_RED "error: " TEXT_NORMAL);
102 | cprintf(__internal_console_buffer__);
103 | }
104 |
105 | void debug(const char *fmt,...)
106 | {
107 | va_list msg;
108 | va_start (msg, fmt);
109 | _vsnprintf(__internal_console_buffer__, 8191, fmt, msg);
110 | va_end (msg);
111 |
112 | cprintf(TEXT_GREEN "debug: " TEXT_NORMAL);
113 | cprintf(__internal_console_buffer__);
114 | }
115 |
116 | void fatal(const char *fmt,...)
117 | {
118 | va_list msg;
119 | va_start (msg, fmt);
120 | _vsnprintf(__internal_console_buffer__, 8191, fmt, msg);
121 | va_end (msg);
122 |
123 | cprintf(TEXT_RED "fatal error: " TEXT_NORMAL);
124 | cprintf(__internal_console_buffer__);
125 | exit(-1);
126 | }
127 |
128 | /*
129 | cprintf(" Misc Options\n"
130 | "\033[7m Hi-Lite Font = \\033[7m \033[0m\n"
131 | "\033[4mUnderLine Font = \\033[4m \033[0m\n"
132 | "\033[0mBack To Normal = \\033[0m \033[0m\n\n"
133 |
134 | " Font Colors\n"
135 | "\033[40m\033[1;37m White = \\033[1;37m \033[0m\n"
136 | "\033[40m\033[1;30m Gray = \\033[1;30m \033[0m\n"
137 | "\033[40m\033[37m Light Gray = \\033[37m \033[0m\n"
138 | "\033[47m\033[30m Black = \\033[30m \033[0m\n"
139 | "\033[40m\033[31m Red = \\033[31m \033[0m\n"
140 | "\033[40m\033[1;31m Light Red = \\033[1;31m \033[0m\n"
141 | "\033[40m\033[32m Green = \\033[32m \033[0m\n"
142 | "\033[40m\033[1;32m Light Green = \\033[1;32m \033[0m\n"
143 | "\033[40m\033[33m Yellow = \\033[33m \033[0m\n"
144 | "\033[40m\033[1;33m Light Yellow = \\033[1;33m \033[0m\n"
145 | "\033[40m\033[34m Blue = \\033[34m \033[0m\n"
146 | "\033[40m\033[1;34m Light Blue = \\033[1;34m \033[0m\n"
147 | "\033[40m\033[35m Purple = \\033[35m \033[0m\n"
148 | "\033[40m\033[1;35m Pink = \\033[1;35m \033[0m\n"
149 | "\033[40m\033[36m Cyan = \\033[36m \033[0m\n"
150 | "\033[40m\033[1;36m Light Cyan = \\033[1;36m \033[0m\n"
151 | "\033[40m\033[0mBack To Normal = \\033[0m \033[0m\n");
152 |
153 | cprintf("\n BackGround Colors\n"
154 | "\033[1;37m\033[40m Black = \\033[40m \033[0m\n"
155 | "\033[1;37m\033[41m Red = \\033[41m \033[0m\n"
156 | "\033[1;37m\033[42m Green = \\033[42m \033[0m\n"
157 | "\033[1;37m\033[43m Yellow = \\033[43m \033[0m\n"
158 | "\033[1;37m\033[44m Blue = \\033[44m \033[0m\n"
159 | "\033[1;37m\033[45m Purple = \\033[45m \033[0m\n"
160 | "\033[1;37m\033[46m Cyan = \\033[46m \033[0m\n"
161 | "\033[1;37m\033[47m Gray = \\033[47m \033[0m\n"
162 | "\033[1;30m\033[5;47m White = \\033[5;47m \033[0m\n");
163 | cprintf("\033[1;37m\033[0mBack To Normal = \\033[0m \033[0m\n\n");
164 |
165 | */
166 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Console.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef CSE168_CONSOLE_H_INCLUDED
2 |
3 | void warning(const char *fmt,...);
4 | void error(const char *fmt,...);
5 | void debug(const char *fmt,...);
6 | void fatal(const char *fmt,...);
7 |
8 | #endif // CSE168_CONSOLE_H_INCLUDED
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Image.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "Miro.h"
2 | #include "Image.h"
3 | #include
4 | #include
5 | #include
6 |
7 | #ifdef WIN32
8 | // disable useless warnings
9 | #pragma warning(disable:4996)
10 | #endif
11 |
12 | Image * g_image = 0;
13 |
14 | Image::Image()
15 | {
16 | m_pixels = 0;
17 | m_width = 1;
18 | m_height = 1;
19 | }
20 |
21 | Image::~Image()
22 | {
23 | if (m_pixels)
24 | delete [] m_pixels;
25 | }
26 |
27 | void Image::resize(int width, int height)
28 | {
29 | if (m_pixels)
30 | delete [] m_pixels;
31 | m_pixels = 0;
32 | m_pixels = new Pixel[width*height];
33 | memset(m_pixels, 0, width*height*sizeof(Pixel));
34 | m_width = width;
35 | m_height = height;
36 | }
37 |
38 | void Image::clear(const Vector3& c)
39 | {
40 | // should be bg color
41 | for (int y=0; y255?255:(unsigned char)rMap;
51 | return c;
52 | }
53 |
54 | void Image::setPixel(int x, int y, const Vector3& p)
55 | {
56 | // do some tone mapping
57 | if (x >= 0 && x < m_width && y < m_height && y >= 0)
58 | {
59 | m_pixels[y*m_width+x].r = Map(p.x);
60 | m_pixels[y*m_width+x].g = Map(p.y);
61 | m_pixels[y*m_width+x].b = Map(p.z);
62 | }
63 | }
64 |
65 | void Image::setPixel(int x, int y, const Pixel& p)
66 | {
67 | // do some tone mapping
68 | if (x >= 0 && x < m_width && y < m_height && y >= 0)
69 | {
70 | m_pixels[y*m_width+x]= p;
71 | }
72 | }
73 |
74 | void Image::drawScanline(int y)
75 | {
76 | glRasterPos2f(-1, -1 + 2*y / (float)m_height);
77 | glDrawPixels(m_width, 1, GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, &m_pixels[y*m_width]);
78 | }
79 |
80 | void Image::draw()
81 | {
82 | for (int i = 0; i < m_height; i++)
83 | drawScanline(i);
84 | }
85 |
86 | void Image::writePPM(char* pcFile)
87 | {
88 | writePPM(pcFile, (unsigned char*)m_pixels, m_width, m_height);
89 | }
90 |
91 | void Image::writePPM(char *pcFile, unsigned char *data, int width, int height)
92 | {
93 | FILE *fp = fopen(pcFile, "wb");
94 | if (!fp)
95 | fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't open PPM file %s for writing\n", pcFile);
96 | else
97 | {
98 | fprintf(fp, "P6\n");
99 | fprintf(fp, "%d %d\n", width, height );
100 | fprintf(fp, "255\n" );
101 |
102 | // invert image
103 | int stride = width*3;
104 | for (int i = height-1; i >= 0; i--)
105 | fwrite(&data[stride*i], stride, 1, fp);
106 | fclose(fp);
107 | }
108 | }
109 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Image.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef CSE168_IMAGE_H_INCLUDED
2 | #define CSE168_IMAGE_H_INCLUDED
3 |
4 | #include "Vector3.h"
5 |
6 | class Image
7 | {
8 | public:
9 | struct Pixel
10 | {
11 | unsigned char r, g, b;
12 | Pixel(unsigned char ir, unsigned char ig, unsigned char ib) {set(ir, ig, ib);}
13 | Pixel() : r(0), g(0), b(0) {}
14 | void set(unsigned char ir, unsigned char ig, unsigned char ib) {r = ir; g = ig; b = ib;}
15 | };
16 |
17 | Image();
18 | ~Image();
19 |
20 | void resize(int width, int height);
21 | void setPixel(int x, int y, const Vector3& p);
22 | void setPixel(int x, int y, const Pixel& p);
23 |
24 | void draw();
25 | void drawScanline(int y);
26 | void clear(const Vector3& c);
27 | void writePPM(char* pcFile); // write data to a ppm image file
28 | void writePPM(char *pcName, unsigned char *data, int width, int height);
29 |
30 | unsigned char* getCharPixels() {return (unsigned char*)m_pixels;}
31 | int width() const {return m_width;}
32 | int height() const {return m_height;}
33 |
34 | private:
35 | Pixel* m_pixels;
36 | int m_width;
37 | int m_height;
38 | };
39 |
40 | extern Image * g_image;
41 |
42 | #endif // CSE168_IMAGE_H_INCLUDED
43 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/IntersectObjects.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #pragma once
2 |
3 | #include
4 | #include "SSEObject.h"
5 |
6 | struct IntersectObjects
7 | {
8 | IntersectObjects() : sse_preprocessed(0) {}
9 |
10 | void *sse_preprocessed;
11 | std::vector plain;
12 | };
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Makedefs:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MAKE = make
2 | AR = @ar
3 | CC = @clang++
4 | MV = @mv
5 | RM = @rm -rf
6 | MKDIR = @mkdir
7 | MKDEP = @mkdep
8 | ECHO = @echo
9 | INCDIRS = -I/usr/X11R6/include
10 | #use the following LIBS line for GNU/Linux
11 | LIBS = -lm -lX11 -lXmu -lXi -lXext -lGL -lGLU -lglut -lboost_thread-mt -lboost_system-mt -lboost_exception-mt -lboost_timer-mt -lpthread -ljpeg
12 | #use this one instead for Mac OSX
13 | #LIBS = -lm -framework GLUT --lobjc -framework OpenGL
14 | LIBDIRS = -L. -L/usr/X11R6/lib
15 | LDFLAGS = $(LIBDIRS) $(LIBS)
16 | CFLAGS = $(INCDIRS) -march=native -std=c++11 -O3 \
17 | -Wno-deprecated -D_FILE_OFFSET_BITS=64 -D_LARGEFILE_SOURCE -D_GNU_SOURCE -g
18 |
19 | .SUFFIXES: .cpp .h .d .o
20 |
21 | .cpp.o:
22 | $(ECHO) "Compiling $<"
23 | $(CC) $(CFLAGS) -c -o $@ $<
24 | .d.o:
25 | $(ECHO) "Finding dependancies for $<"
26 | $(CC) $(CFLAGS) -MD -E $<
27 |
28 | SOURCES = $(wildcard *.cpp)
29 | OBJS = $(patsubst %.cpp, %.o, $(SOURCES))
30 | DEPS = $(patsubst %.cpp, %.d, $(SOURCES))
31 |
32 | clean:
33 | $(RM) core .deps *.o $(NAME)
34 | $(RM) lexer.cpp parse.cpp parse.cpp.h
35 | $(ECHO) "All clean!"
36 |
37 | deps:
38 | $(ECHO) "Finding dependancies in `pwd`..."
39 | $(RM) .deps
40 | $(CC) $(CFLAGS) -MD -E $(SOURCES) > /dev/null
41 | $(MKDIR) .deps
42 | $(MV) $(DEPS) .deps
43 |
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Makefile:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | NAME = miro
2 |
3 | all: $(NAME)
4 |
5 | include Makedefs
6 | SOURCES -= parse.cpp lexer.cpp
7 | OBJS -= parse.o lexer.o
8 | #
9 | # lexer.cpp: lexer.lex
10 | # $(ECHO) "Flex-ing lexer.lex"
11 | # $(FLEX) -o$@ lexer.lex
12 | #
13 | # parse.cpp: parse.y
14 | # $(ECHO) "Bison-ing parse.y"
15 | # $(BISON) -d -o $@ parse.y
16 | # @if [ -f parse.hpp ]; then \
17 | # mv parse.hpp parse.cpp.h; \
18 | # fi
19 | # @if [ -f parse.tab.hpp ]; then \
20 | # mv parse.tab.hpp parse.cpp.h; \
21 | # fi
22 | # @if [ -f parse.tab.h ]; then \
23 | # mv parse.tab.h parse.cpp.h; \
24 | # fi
25 |
26 | -include .deps/*.d
27 |
28 | $(NAME): $(OBJS)
29 | $(ECHO) "Linking $@..."
30 | $(CC) -o $@ *.o $(LIBS) $(LIBDIRS) #$(OBJS)
31 | $(ECHO) "Built $@!"
32 |
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Material.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "Material.h"
2 |
3 | Material::Material() : m_castShadow(true)
4 | {
5 | m_color = Vector3(1, 1, 1);
6 | }
7 |
8 | Material::~Material()
9 | {
10 | }
11 |
12 | Vector3
13 | Material::shade(const Ray&, const HitInfo&, const Scene&) const
14 | {
15 | return m_color;
16 | }
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Material.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef CSE168_MATERIAL_H_INCLUDED
2 | #define CSE168_MATERIAL_H_INCLUDED
3 |
4 | #include "Miro.h"
5 | #include "Vector3.h"
6 | #include "PhotonMap.h"
7 | #include
8 |
9 | class Material
10 | {
11 | public:
12 | Material();
13 | virtual ~Material();
14 |
15 | virtual void preCalc() {}
16 |
17 | virtual Vector3 shade(const Ray& ray, const HitInfo& hit,
18 | const Scene& scene) const;
19 |
20 | virtual void shadePhoton(const Ray &ray, const HitInfo &hit, const Scene &scene, Vector3 const &power, Photon_map *map) const {throw std::runtime_error("Not implemented");}
21 |
22 | virtual bool castShadow() const {return m_castShadow;}
23 | virtual void setCastShadow(bool b) {m_castShadow = b;}
24 |
25 | virtual bool hasBump() const { return false; }
26 |
27 | protected:
28 | Vector3 m_color;
29 | bool m_castShadow;
30 | };
31 |
32 | #endif // CSE168_MATERIAL_H_INCLUDED
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Miro.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef __MIRO_H__
2 | #define __MIRO_H__
3 | #include
4 | #include
5 | #include
6 |
7 | using boost::shared_ptr;
8 |
9 | // #ifndef max
10 | // #define max(a,b) ((a>b)?a:b)
11 | // #endif
12 |
13 | const float MIRO_TMAX = 1e12f;
14 | const float epsilon = 0.001f;
15 | const float PI = 3.1415926535897932384626433832795028841972f;
16 | const float DegToRad = PI/180.0f;
17 | const float RadToDeg = 180.0f/PI;
18 |
19 | #include
20 | #include "OpenGL.h"
21 | #include
22 | #include
23 |
24 | class Ray;
25 | class HitInfo;
26 |
27 | class Object;
28 | class Sphere;
29 | class Triangle;
30 | class TriangleMesh;
31 | class Instance;
32 |
33 | class PointLight;
34 |
35 | class Camera;
36 | class Image;
37 | class Scene;
38 | class Material;
39 | class Photon_map;
40 |
41 | extern void ParseFile(FILE* fp);
42 | extern void initOpenGL();
43 | extern Camera* g_camera;
44 | extern Scene* g_scene;
45 | extern Image* g_image;
46 | extern Photon_map* g_global_illum_map;
47 | extern Photon_map* g_caustics_map;
48 |
49 | extern boost::mt19937 g_rng;
50 | //extern boost::uniform_01 randone;
51 |
52 | inline float randone(const boost::mt19937& g_rng)
53 | {
54 | #ifdef WIN32
55 | unsigned int r;
56 | rand_s(&r);
57 | return ((float)r)/UINT_MAX;
58 | #else
59 | return drand48();
60 | #endif
61 | }
62 |
63 | #endif
64 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/MiroWindow.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "MiroWindow.h"
2 | #include "OpenGL.h"
3 | #include "Miro.h"
4 | #include "Camera.h"
5 | #include "Image.h"
6 | #include
7 | #include
8 |
9 | #define ANGFACT 1.0
10 | #define LEFT 4
11 | #define MIDDLE 2
12 | #define RIGHT 1
13 |
14 | #ifdef WIN32
15 | // disable useless warnings
16 | #pragma warning(disable:4996)
17 | #endif
18 |
19 |
20 | namespace
21 | {
22 |
23 | // Non-member functions used as proxy callbacks to our real C++ member functions
24 | MiroWindow *g_miroWindow;
25 | void display() {g_miroWindow->display();}
26 | void resize(int x,int y) {g_miroWindow->reshape(x,y);}
27 | void keyboard(unsigned char key, int x, int y) {g_miroWindow->keyboard(key,x,y);}
28 | void mouse(int btn,int state,int x,int y) {g_miroWindow->mouse(btn,state,x,y);}
29 | void motion(int x, int y) {g_miroWindow->motion(x,y);}
30 |
31 | } // namespace
32 |
33 |
34 | MiroWindow::MiroWindow(int * argc, char* argv[]) :
35 | m_scaleFact(0.1f),
36 | m_activeButton(0),
37 | m_mouseX(0),
38 | m_mouseY(0)
39 | {
40 | // Initialize GLUT
41 | glutInit(argc, argv);
42 |
43 | // Create the window
44 | glutInitWindowSize(g_image->width(), g_image->height());
45 | glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_RGB | GLUT_DOUBLE);
46 | glutInitWindowPosition(200, 200);
47 | glutCreateWindow("miro");
48 |
49 | // Initialize some OpenGL state
50 | glClearColor(0.25f, 0.25f, 0.25f, 1);
51 | glDisable(GL_LIGHTING);
52 | glDisable(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
53 | glShadeModel(GL_SMOOTH);
54 | glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT_AND_BACK, GL_LINE); // draw outlines only
55 | }
56 |
57 |
58 | void
59 | MiroWindow::mainLoop()
60 | {
61 | // Setup callback functions
62 | g_miroWindow = this;
63 | glutDisplayFunc(::display);
64 | glutKeyboardFunc(::keyboard);
65 | glutMouseFunc(::mouse);
66 | glutMotionFunc(::motion);
67 | glutReshapeFunc(::resize);
68 |
69 | // Start the glut main loop, never returns
70 | glutMainLoop();
71 | }
72 |
73 |
74 | void
75 | MiroWindow::display()
76 | {
77 | g_camera->click(g_scene, g_image); // take a snapshot of the scene
78 |
79 | glFinish(); // flush the openGL pipeline
80 | }
81 |
82 |
83 | void
84 | MiroWindow::motion(int x, int y)
85 | {
86 | int dx, dy; // change in mouse coordinates
87 |
88 | dx = x - m_mouseX; // change in mouse coords
89 | dy = y - m_mouseY;
90 |
91 | if (m_activeButton & LEFT)
92 | {
93 | float xfact = -ANGFACT*dy;
94 | float yfact = -ANGFACT*dx;
95 | // construct a coordinate system from up and viewdir
96 | Vector3 vRight = cross(g_camera->viewDir(), g_camera->up());
97 | // now rotate everything
98 | Vector3 v = g_camera->viewDir();
99 | v.rotate(xfact*PI/180., vRight);
100 | v.rotate(yfact*PI/180., g_camera->up());
101 | g_camera->setViewDir(v);
102 | }
103 |
104 | m_mouseX = x; // new current position
105 | m_mouseY = y;
106 |
107 | glutPostRedisplay();
108 | }
109 |
110 |
111 | void
112 | MiroWindow::mouse(int button, int state, int x, int y)
113 | {
114 | int b; // LEFT, MIDDLE, or RIGHT
115 |
116 | switch (button)
117 | {
118 | case GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON:
119 | b = LEFT;
120 | break;
121 |
122 | case GLUT_MIDDLE_BUTTON:
123 | b = MIDDLE;
124 | break;
125 |
126 | case GLUT_RIGHT_BUTTON:
127 | b = RIGHT;
128 | break;
129 |
130 | default:
131 | b = 0;
132 | }
133 |
134 | if (state == GLUT_DOWN)
135 | {
136 | m_mouseX = x;
137 | m_mouseY = y;
138 | m_activeButton |= b; /* set the proper bit */
139 | }
140 | else
141 | m_activeButton &= ~b; /* clear the proper bit */
142 | }
143 |
144 | void
145 | MiroWindow::keyboard(unsigned char key, int x, int y)
146 | {
147 | switch (key)
148 | {
149 | case 27:
150 | exit(0);
151 | break;
152 |
153 | case 'i':
154 | case 'I':
155 | {
156 | char str[1024];
157 | sprintf(str, "miro_%d.ppm", time(0));
158 | if (g_camera->isOpenGL())
159 | {
160 | unsigned char* buf = new unsigned char[g_image->width()*g_image->height()*3];
161 | glReadPixels(0, 0, g_image->width(), g_image->height(),
162 | GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, buf);
163 | g_image->writePPM(str, buf, g_image->width(), g_image->height());
164 | }
165 | else
166 | {
167 | g_image->writePPM(str);
168 | }
169 | break;
170 | }
171 |
172 | case 'r':
173 | case 'R':
174 | g_camera->setRenderer(Camera::RENDER_RAYTRACE);
175 | break;
176 |
177 | case 'g':
178 | case 'G':
179 | g_camera->setRenderer(Camera::RENDER_OPENGL);
180 | break;
181 |
182 | case '+':
183 | m_scaleFact *= 1.5;
184 | break;
185 |
186 | case '-':
187 | m_scaleFact /= 1.5;
188 | break;
189 |
190 | case 'w':
191 | case 'W':
192 | g_camera->setEye(g_camera->eye() + m_scaleFact*g_camera->viewDir());
193 | break;
194 |
195 | case 's':
196 | case 'S':
197 | g_camera->setEye(g_camera->eye() - m_scaleFact*g_camera->viewDir());
198 | break;
199 |
200 | case 'q':
201 | case 'Q':
202 | g_camera->setEye(g_camera->eye() + m_scaleFact*g_camera->up());
203 | break;
204 |
205 | case 'z':
206 | case 'Z':
207 | g_camera->setEye(g_camera->eye() - m_scaleFact*g_camera->up());
208 | break;
209 |
210 | case 'a':
211 | case 'A':
212 | {
213 | Vector3 vRight = cross(g_camera->viewDir(), g_camera->up());
214 | g_camera->setEye(g_camera->eye() - m_scaleFact*vRight);
215 | break;
216 | }
217 |
218 | case 'd':
219 | case 'D':
220 | {
221 | Vector3 vRight = cross(g_camera->viewDir(), g_camera->up());
222 | g_camera->setEye(g_camera->eye() + m_scaleFact*vRight);
223 | break;
224 | }
225 | break;
226 |
227 | default:
228 | break;
229 | }
230 | printf("Eye: %f, %f, %f\n", g_camera->eye()[0], g_camera->eye()[1], g_camera->eye()[2]);
231 |
232 | glutPostRedisplay();
233 | }
234 |
235 |
236 | void
237 | MiroWindow::reshape(int w, int h)
238 | {
239 | g_image->resize(w, h);
240 | glViewport(0, 0, w, h);
241 | g_camera->setRenderer(Camera::RENDER_OPENGL);
242 | glutPostRedisplay();
243 | }
244 |
245 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/MiroWindow.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef CSE168_MIRO_GLUT_WINDOW_H_INCLUDED
2 | #define CSE168_MIRO_GLUT_WINDOW_H_INCLUDED
3 |
4 | class MiroWindow
5 | {
6 | public:
7 | MiroWindow(int * argc, char* argv[]);
8 |
9 | void mainLoop();
10 |
11 | // GLUT Event handlers
12 | void display();
13 | void reshape(int x, int y);
14 | void keyboard(unsigned char key, int x, int y);
15 | void mouse(int btn, int state, int x, int y);
16 | void motion(int x, int y);
17 |
18 | protected:
19 | float m_scaleFact;
20 | int m_activeButton;
21 | int m_mouseX, m_mouseY;
22 | };
23 |
24 | #endif // CSE168_MIRO_GLUT_WINDOW_H_INCLUDED
25 |
26 |
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/MyBoost.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #pragma once
2 |
3 | #ifdef __GNUC__
4 | #define LIKELY(cond) __builtin_expect(cond, 1)
5 | #define UNLIKELY(cond) __builtin_expect(cond, 0)
6 | #else
7 | #define LIKELY(cond) (cond)
8 | #define UNLIKELY(cond) (cond)
9 | #endif
10 |
11 | class Nothing {};
12 |
13 | // member_if::type is the type if Cond is true, or a zero length array if Cond is false.
14 | // This way, if cond is false, you can declare a member that is unusable and takes 0 bytes.
15 | // Not standard: zero length arrays are "illegal", but work in GCC and Visual Studio (2012 at least).
16 | template
17 | struct member_if
18 | {
19 | typedef T type;
20 | };
21 |
22 | template
23 | struct member_if<0, T>
24 | {
25 | typedef Nothing type[0];
26 | };
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Object.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef CSE168_OBJECT_H_INCLUDED
2 | #define CSE168_OBJECT_H_INCLUDED
3 |
4 | #include
5 | #include "Miro.h"
6 | #include "Material.h"
7 | #include "IntersectObjects.h"
8 |
9 | enum ObjType
10 | {
11 | SPHERE,
12 | TRIANGLE,
13 | BLPATCH,
14 | BOUNDING_BOX,
15 | BOX,
16 | NB_OBJS
17 | };
18 |
19 | class ObjBundle;
20 |
21 | class Object
22 | {
23 | public:
24 | Object() {}
25 | virtual ~Object() {}
26 |
27 | void setMaterial(const Material* m) {m_material = m;}
28 |
29 | virtual void renderGL() {}
30 | virtual void preCalc() {}
31 |
32 | // Needs a static function that intersects a bunch of objects of the same type
33 |
34 | virtual ObjType type() const = 0;
35 |
36 | virtual void *ptr() = 0;
37 |
38 | virtual Vector3 minVector() const = 0;
39 | virtual Vector3 maxVector() const = 0;
40 |
41 | protected:
42 | const Material* m_material;
43 | };
44 |
45 | typedef std::vector Objects;
46 |
47 | #endif // CSE168_OBJECT_H_INCLUDED
48 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/OpenGL.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef CSE168_OPENGL_H_INCLUDED
2 | #define CSE168_OPENGL_H_INCLUDED
3 |
4 | // use the following on Windows or GNU/Linux
5 | #ifndef __APPLE__
6 |
7 | #ifndef GLUT_BUILDING_LIB
8 | #define GLUT_BUILDING_LIB
9 | #endif // GLUT_BUILDING_LIB
10 | #include
11 |
12 | #else
13 |
14 | // use this on Mac OSX
15 | #include
16 |
17 | #endif
18 |
19 | #endif // CSE168_OPENGL_H_INCLUDED
20 |
21 |
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/PFMLoader.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "PFMLoader.h"
2 | #include
3 |
4 | // define this to 1 if you are running on a big-endian machine (e.g. PPC Macs)
5 | // #if WORDS_BIGENDIAN
6 |
7 | namespace
8 | {
9 |
10 | inline void
11 | byteSwapFloat(float& f)
12 | {
13 | union {float f; unsigned char b[4];} u1, u2;
14 |
15 | u1.f = f;
16 | u2.b[0] = u1.b[3];
17 | u2.b[1] = u1.b[2];
18 | u2.b[2] = u1.b[1];
19 | u2.b[3] = u1.b[0];
20 | f = u2.f;
21 | }
22 |
23 |
24 | #if WORDS_BIGENDIAN
25 | // big endian system, need to swap bytes to convert into
26 | // external little-endian representation
27 |
28 | inline void littleEndianFloat(float& f) {byteSwapFloat (f);}
29 | inline void bigEndianFloat(float) {}
30 |
31 | #else
32 |
33 | // little endian, no need to swap
34 | inline void littleEndianFloat(float) {}
35 | inline void bigEndianFloat(float& f) {byteSwapFloat(f);}
36 |
37 | #endif
38 |
39 | }
40 |
41 |
42 | Vector3*
43 | readPFMImage(const char * filename, int * width, int * height)
44 | {
45 | FILE *infile = 0;
46 | float *lineBuffer = 0;
47 | Vector3 *img = 0;
48 | char junk;
49 |
50 | try
51 | {
52 | infile = fopen(filename, "rb");
53 | if (!infile)
54 | throw std::runtime_error("cannot open file.");
55 |
56 | int a = fgetc(infile);
57 | int b = fgetc(infile);
58 | fgetc(infile);
59 |
60 | if ((a != 'P') || ((b != 'F') && (b != 'f')))
61 | throw std::runtime_error("not a PFM image file.");
62 |
63 | b = (b == 'F'); // 'F' = RGB, 'f' = monochrome
64 |
65 | fscanf(infile, "%d %d%c", width, height, &junk);
66 | if ((*width <= 0) || (*height <= 0))
67 | throw std::runtime_error("invalid width or height.");
68 |
69 | float scaleFactor;
70 | fscanf(infile, "%f%c", &scaleFactor, &junk);
71 |
72 | img = new Vector3[*width * *height];
73 |
74 | a = *width * (b ? 3 : 1);
75 | lineBuffer = new float[a];
76 | for (int y = 0; y < *height; ++y)
77 | {
78 | Vector3 *cur = &img[y * *width];
79 | if (fread(lineBuffer, sizeof(float), a, infile) != (size_t) a)
80 | throw std::runtime_error("cannot read pixel data.");
81 |
82 | float *temp = lineBuffer;
83 | for (int x = 0; x < *width; x++)
84 | {
85 | if (b)
86 | { // color
87 | (*cur)[0] = *temp++;
88 | (*cur)[1] = *temp++;
89 | (*cur)[2] = *temp++;
90 |
91 | if (scaleFactor > 0.0)
92 | {
93 | bigEndianFloat((*cur)[0]);
94 | bigEndianFloat((*cur)[1]);
95 | bigEndianFloat((*cur)[2]);
96 | }
97 | else
98 | {
99 | littleEndianFloat((*cur)[0]);
100 | littleEndianFloat((*cur)[1]);
101 | littleEndianFloat((*cur)[2]);
102 | }
103 | }
104 | else
105 | { // black and white
106 | float c = *temp++;
107 |
108 | if (scaleFactor > 0.0)
109 | bigEndianFloat (c);
110 | else
111 | littleEndianFloat (c);
112 |
113 | (*cur)[0] = (*cur)[1] = (*cur)[2] = c;
114 | }
115 | cur++;
116 | }
117 | }
118 |
119 | delete [] lineBuffer;
120 | fclose(infile);
121 |
122 | return img;
123 | }
124 | catch (const std::exception &e)
125 | {
126 | printf("Unable to read image file \"%s\": %s",
127 | filename, e.what());
128 | delete [] lineBuffer;
129 | delete [] img;
130 | if (infile)
131 | fclose (infile);
132 | return 0;
133 | }
134 | catch (...)
135 | {
136 | printf("Unable to read image file \"%s\".", filename);
137 | delete [] lineBuffer;
138 | delete [] img;
139 | if (infile)
140 | fclose (infile);
141 | return 0;
142 | }
143 | }
144 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/PFMLoader.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef CSE168_PFM_LOADER_H_INCLUDED
2 | #define CSE168_PFM_LOADER_H_INCLUDED
3 |
4 | #include "Vector3.h"
5 |
6 | Vector3* readPFMImage(const char * filename, int * width, int * height);
7 |
8 | #endif // CSE168_PFM_LOADER_H_INCLUDED
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Perlin.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "Perlin.h"
2 |
3 | const unsigned char PerlinNoise::p[512] =
4 | {
5 | 151,160,137, 91, 90, 15,131, 13,201, 95, 96, 53,194,233, 7,225,
6 | 140, 36,103, 30, 69,142, 8, 99, 37,240, 21, 10, 23,190, 6,148,
7 | 247,120,234, 75, 0, 26,197, 62, 94,252,219,203,117, 35, 11, 32,
8 | 57,177, 33, 88,237,149, 56, 87,174, 20,125,136,171,168, 68,175,
9 | 74,165, 71,134,139, 48, 27,166, 77,146,158,231, 83,111,229,122,
10 | 60,211,133,230,220,105, 92, 41, 55, 46,245, 40,244,102,143, 54,
11 | 65, 25, 63,161, 1,216, 80, 73,209, 76,132,187,208, 89, 18,169,
12 | 200,196,135,130,116,188,159, 86,164,100,109,198,173,186, 3, 64,
13 | 52,217,226,250,124,123, 5,202, 38,147,118,126,255, 82, 85,212,
14 | 207,206, 59,227, 47, 16, 58, 17,182,189, 28, 42,223,183,170,213,
15 | 119,248,152, 2, 44,154,163, 70,221,153,101,155,167, 43,172, 9,
16 | 129, 22, 39,253, 19, 98,108,110, 79,113,224,232,178,185,112,104,
17 | 218,246, 97,228,251, 34,242,193,238,210,144, 12,191,179,162,241,
18 | 81, 51,145,235,249, 14,239,107, 49,192,214, 31,181,199,106,157,
19 | 184, 84,204,176,115,121, 50, 45,127, 4,150,254,138,236,205, 93,
20 | 222,114, 67, 29, 24, 72,243,141,128,195, 78, 66,215, 61,156,180,
21 |
22 | 151,160,137, 91, 90, 15,131, 13,201, 95, 96, 53,194,233, 7,225,
23 | 140, 36,103, 30, 69,142, 8, 99, 37,240, 21, 10, 23,190, 6,148,
24 | 247,120,234, 75, 0, 26,197, 62, 94,252,219,203,117, 35, 11, 32,
25 | 57,177, 33, 88,237,149, 56, 87,174, 20,125,136,171,168, 68,175,
26 | 74,165, 71,134,139, 48, 27,166, 77,146,158,231, 83,111,229,122,
27 | 60,211,133,230,220,105, 92, 41, 55, 46,245, 40,244,102,143, 54,
28 | 65, 25, 63,161, 1,216, 80, 73,209, 76,132,187,208, 89, 18,169,
29 | 200,196,135,130,116,188,159, 86,164,100,109,198,173,186, 3, 64,
30 | 52,217,226,250,124,123, 5,202, 38,147,118,126,255, 82, 85,212,
31 | 207,206, 59,227, 47, 16, 58, 17,182,189, 28, 42,223,183,170,213,
32 | 119,248,152, 2, 44,154,163, 70,221,153,101,155,167, 43,172, 9,
33 | 129, 22, 39,253, 19, 98,108,110, 79,113,224,232,178,185,112,104,
34 | 218,246, 97,228,251, 34,242,193,238,210,144, 12,191,179,162,241,
35 | 81, 51,145,235,249, 14,239,107, 49,192,214, 31,181,199,106,157,
36 | 184, 84,204,176,115,121, 50, 45,127, 4,150,254,138,236,205, 93,
37 | 222,114, 67, 29, 24, 72,243,141,128,195, 78, 66,215, 61,156,180,
38 | };
39 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Perlin.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef CSE168_PERLIN_H_INCLUDED
2 | #define CSE168_PERLIN_H_INCLUDED
3 |
4 | #include
5 | #include "Vector3.h"
6 |
7 | //! Perlin noise class
8 | /*!
9 | Based on Java reference implementation of:
10 | Improved Noise - Copyright 2002 Ken Perlin.
11 |
12 | (http://mrl.nyu.edu/~perlin/noise/)
13 | */
14 | class PerlinNoise
15 | {
16 | public:
17 | static float noise(float x, float y, float z)
18 | {
19 | int X = int(floor(x)) & 255,
20 | Y = int(floor(y)) & 255,
21 | Z = int(floor(z)) & 255;
22 |
23 | x -= floor(x);
24 | y -= floor(y);
25 | z -= floor(z);
26 | float u = fade(x),
27 | v = fade(y),
28 | w = fade(z);
29 |
30 | int A = p[X ]+Y, AA = p[A]+Z, AB = p[A+1]+Z,
31 | B = p[X+1]+Y, BA = p[B]+Z, BB = p[B+1]+Z;
32 |
33 | return lerp(w, lerp(v, lerp(u, grad(p[AA ], x , y , z ),
34 | grad(p[BA ], x-1, y , z )),
35 | lerp(u, grad(p[AB ], x , y-1, z ),
36 | grad(p[BB ], x-1, y-1, z ))),
37 | lerp(v, lerp(u, grad(p[AA+1], x , y , z-1 ),
38 | grad(p[BA+1], x-1, y , z-1 )),
39 | lerp(u, grad(p[AB+1], x , y-1, z-1 ),
40 | grad(p[BB+1], x-1, y-1, z-1 ))));
41 | }
42 | static float turbulence(const Vector3& pos, int freq)
43 | {
44 | float turb = 0;
45 |
46 | for (int i = 1; i <= freq; i++)
47 | {
48 | turb += noise(pos.x * i, pos.y * i, pos.z * i) / i;
49 | }
50 | return turb;
51 | }
52 |
53 | private:
54 | static float fade(float t) {return t * t * t * (t * (t * 6 - 15) + 10);}
55 | static float lerp(float t, float a, float b) {return a + t * (b - a);}
56 | static float grad(int hash, float x, float y, float z)
57 | {
58 | int h = hash & 15;
59 | float u = h<8 ? x : y,
60 | v = h<4 ? y : h==12||h==14 ? x : z;
61 | return ((h&1) == 0 ? u : -u) + ((h&2) == 0 ? v : -v);
62 | }
63 |
64 | static const unsigned char p[512];
65 | };
66 |
67 | #endif // CSE168_PERLIN_H_INCLUDED
68 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Phong.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef CSE168_LAMBERT_H_INCLUDED
2 | #define CSE168_LAMBERT_H_INCLUDED
3 |
4 | #include "Material.h"
5 | #include "Texture.h"
6 | #include "Ray.h"
7 | #include "Scene.h"
8 | #include "Perlin.h"
9 |
10 | class Phong : public Material
11 | {
12 | public:
13 | Phong(const Vector3 & diffuse, const Vector3 &specular, const Vector3 &ambient);
14 | Phong(shared_ptr kd, shared_ptr ks, const Vector3 &ambient);
15 | Phong(shared_ptr kd, const Vector3 &ambient = Vector3(0.f));
16 | virtual ~Phong();
17 |
18 | void setPhong(float f) {m_phong = f;}
19 | void setRefraction(float indice) {m_refr = indice;}
20 | void setIndirectLighting(bool value) {m_indirect = value;}
21 |
22 | virtual void preCalc() {}
23 |
24 | virtual Vector3 shade(const Ray& ray, const HitInfo& hit,
25 | const Scene& scene) const;
26 | virtual void shadePhoton(const Ray &ray, const HitInfo &hit, const Scene &scene, Vector3 const &power, Photon_map *map) const;
27 |
28 | void setTransparency(float tp) { m_tp = tp; }
29 |
30 | void setKa(const Vector3& ka) { m_ka = ka; }
31 | void setKs(const Vector3& ks) { m_ks = ks; }
32 | const Vector3& getKs() { return m_ks; }
33 | void setKd(const Vector3& kd) { m_kd = kd; }
34 | void setBm(float bm) { m_bm = bm; }
35 | void setGlossy(bool is_glossy) { m_is_glossy = true; }
36 | bool isGlossy() { return m_is_glossy; }
37 | void setBumpNoisy(float height, int turbulence = 1) { m_is_bump_noisy = true; m_bump_noise_height = height; m_bump_noise_turbulence = turbulence; }
38 | bool isBumpNoisy() { return m_is_bump_noisy; }
39 | void setIsBumpNoisy(bool is_noisy) { m_is_bump_noisy = is_noisy; }
40 |
41 | virtual bool hasBump() const {return m_texture_bump;}
42 |
43 | void setKaTexture(shared_ptr ka_texture) { m_texture_ka = ka_texture; }
44 | void setKsTexture(shared_ptr ks_texture) { m_texture_ks = ks_texture; }
45 | void setKdTexture(shared_ptr kd_texture) { m_texture_kd = kd_texture; }
46 | void setBumpTexture(shared_ptr bump_texture) { m_texture_bump = bump_texture; }
47 |
48 | protected:
49 | HitInfo bumpHit(HitInfo const &rhit) const;
50 |
51 | protected:
52 | shared_ptr m_texture_ka;
53 | shared_ptr m_texture_ks;
54 | shared_ptr m_texture_kd;
55 | shared_ptr m_texture_bump;
56 |
57 | Vector3 m_ka;
58 | Vector3 m_ks; // old: m_sp
59 | Vector3 m_kd; // old: m_dp
60 | float m_bm;
61 |
62 | float m_tp;
63 | float m_phong;
64 | float m_refr;
65 |
66 | bool m_indirect;
67 | bool m_is_glossy;
68 |
69 | bool m_is_bump_noisy;
70 | float m_bump_noise_height;
71 | int m_bump_noise_turbulence;
72 | };
73 |
74 | #endif // CSE168_LAMBERT_H_INCLUDED
75 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/PhotonMap.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #pragma once
2 |
3 | #include
4 | #include
5 | #include
6 | #include
7 |
8 |
9 | /* This is the photon
10 | * The power is not compressed so the
11 | * size is 28 bytes
12 | */
13 | //**********************
14 | typedef struct Photon {
15 | //**********************
16 | float pos[3]; // photon position
17 | short plane; // splitting plane for kd-tree
18 | unsigned char theta, phi; // incoming direction
19 | float power[3]; // photon power (uncompressed)
20 | } Photon;
21 |
22 |
23 | /* This structure is used only to locate the
24 | * nearest photons
25 | */
26 | //******************************
27 | typedef struct NearestPhotons {
28 | //******************************
29 | int max;
30 | int found;
31 | int got_heap;
32 | float pos[3];
33 | float *dist2;
34 | const Photon **index;
35 | } NearestPhotons;
36 |
37 |
38 | /* This is the Photon_map class
39 | */
40 | //*****************
41 | class Photon_map {
42 | //*****************
43 | public:
44 | Photon_map( int max_phot );
45 | ~Photon_map();
46 |
47 | void store(
48 | const float power[3], // photon power
49 | const float pos[3], // photon position
50 | const float dir[3] ); // photon direction
51 |
52 | void scale_photon_power(
53 | const float scale ); // 1/(number of emitted photons)
54 |
55 | void balance(void); // balance the kd-tree (before use!)
56 |
57 | void irradiance_estimate(
58 | float irrad[3], // returned irradiance
59 | const float pos[3], // surface position
60 | const float normal[3], // surface normal at pos
61 | const float max_dist, // max distance to look for photons
62 | const int nphotons ) const; // number of photons to use
63 |
64 | void locate_photons(
65 | NearestPhotons *const np, // np is used to locate the photons
66 | const int index ) const; // call with index = 1
67 |
68 | void photon_dir(
69 | float *dir, // direction of photon (returned)
70 | const Photon *p ) const; // the photon
71 |
72 | void renderGL() const;
73 |
74 | bool isCaustics() const {return m_caustics;}
75 | void setCaustics(bool c) {m_caustics = c;}
76 |
77 | private:
78 |
79 | void balance_segment(
80 | Photon **pbal,
81 | Photon **porg,
82 | const int index,
83 | const int start,
84 | const int end );
85 |
86 | void median_split(
87 | Photon **p,
88 | const int start,
89 | const int end,
90 | const int median,
91 | const int axis );
92 |
93 | Photon *photons;
94 |
95 | int stored_photons;
96 | int half_stored_photons;
97 | int max_photons;
98 | int prev_scale;
99 |
100 | float costheta[256];
101 | float sintheta[256];
102 | float cosphi[256];
103 | float sinphi[256];
104 |
105 | float bbox_min[3]; // use bbox_min;
106 | float bbox_max[3]; // use bbox_max;
107 | bool m_caustics;
108 | };
109 |
110 | // #include
111 | // #include
112 | // #include
113 | // #include
114 | // #include "Vector3.h"
115 | // #include "Miro.h"
116 |
117 | // struct Photon
118 | // {
119 | // Vector3 position;
120 | // Vector3 power;
121 | // Vector3 dir;
122 | // };
123 |
124 | // class Photon_map
125 | // {
126 | // public:
127 | // Photon_map() : m_root(0) {}
128 |
129 | // void addPhoton(Photon const &ph) {m_photons.push_back(new Photon(ph));}
130 |
131 | // void build();
132 |
133 | // void kNearest(Vector3 const &v, int k, std::vector &result) const;
134 |
135 | // void renderGL() const;
136 |
137 | // ~Photon_map() {delete m_root;}
138 |
139 | // private:
140 | // struct PhotonNode
141 | // {
142 | // Photon *photon;
143 | // PhotonNode *left;
144 |
145 | // PhotonNode() : photon(0), left(0) {}
146 |
147 | // ~PhotonNode()
148 | // {
149 | // delete photon;
150 | // if (left)
151 | // {
152 | // delete[] (PhotonNode*)((uintptr_t) left & ~3);
153 | // }
154 | // }
155 | // };
156 |
157 | // typedef std::priority_queue, boost::function > Heap;
158 | // void tryInsertPhoton(Vector3 const &p, int k, Photon *photon, Heap &result) const;
159 | // void recKNearest(PhotonNode *node, Vector3 const &v, int k, Heap &result) const;
160 | // void recursiveBuild(PhotonNode *node, int axis, std::vector::iterator start, std::vector::iterator end);
161 |
162 | // std::vector m_photons;
163 | // PhotonNode *m_root;
164 | // };
165 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/PointLight.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef CSE168_POINTLIGHT_H_INCLUDED
2 | #define CSE168_POINTLIGHT_H_INCLUDED
3 |
4 | #include
5 | #include "Vector3.h"
6 |
7 | class PointLight
8 | {
9 | public:
10 | PointLight(): m_sphere(0), m_samples(1) {}
11 | void setPosition(const Vector3& v) {m_position = v;}
12 | void setColor(const Vector3& v) {m_color = v;}
13 | void setWattage(float f) {m_wattage = f;}
14 | void setBlur(float sphere, int samples) {m_sphere = sphere; m_samples = samples;}
15 |
16 | float wattage() const {return m_wattage;}
17 | const Vector3 & color() const {return m_color;}
18 | const Vector3& position() const {return m_position;}
19 | float sphere() const {return m_sphere;}
20 | int samples() const {return m_samples;}
21 |
22 | void preCalc() {} // use this if you need to
23 |
24 | protected:
25 | Vector3 m_position;
26 | Vector3 m_color;
27 | float m_wattage;
28 | float m_sphere;
29 | int m_samples;
30 | };
31 |
32 | typedef std::vector Lights;
33 |
34 | #endif // CSE168_POINTLIGHT_H_INCLUDED
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Ray.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef CSE168_RAY_H_INCLUDED
2 | #define CSE168_RAY_H_INCLUDED
3 |
4 | #include "Vector3.h"
5 | #include
6 |
7 | #define MAX_RAY_ITER 6
8 |
9 | class Ray
10 | {
11 | public:
12 | Vector3 o, //!< Origin of ray
13 | d; //!< Direction of ray
14 | int iter;
15 | std::vector *refractionStack;
16 | int refractionIndex;
17 | bool seen_specular; // Only for photon map generation
18 |
19 | Ray() : o(), d(Vector3(0.0f,0.0f,1.0f)), iter(0), seen_specular(false)
20 | {
21 | // empty
22 | }
23 |
24 | Ray(const Vector3& o, const Vector3& d, int i = 0) : o(o), d(d), iter(i)
25 | {
26 | // empty
27 | }
28 | };
29 |
30 |
31 | //! Contains information about a ray hit with a surface.
32 | /*!
33 | HitInfos are used by object intersection routines. They are useful in
34 | order to return more than just the hit distance.
35 | */
36 | class HitInfo
37 | {
38 | public:
39 | float t; //!< The hit distance
40 | Vector3 P; //!< The hit point
41 | Vector3 N; //!< Shading normal vector
42 | const Material* material; //!< Material of the intersected object
43 | Vector3 tangent;
44 | float u;
45 | float v;
46 |
47 | //! Default constructor.
48 | explicit HitInfo(float t = 0.0f,
49 | const Vector3& P = Vector3(),
50 | const Vector3& N = Vector3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f)) :
51 | t(t), P(P), N(N), material (0), u(0), v(0)
52 | {
53 | // empty
54 | }
55 | };
56 |
57 | #endif // CSE168_RAY_H_INCLUDED
58 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/SSE.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "SSE.h"
2 |
3 | #ifdef _WIN32
4 | #include
5 | #define cpuid __cpuid
6 | #else
7 | void cpuid(int CPUInfo[4],int InfoType){
8 | __asm__ __volatile__ (
9 | "cpuid":
10 | "=a" (CPUInfo[0]),
11 | "=b" (CPUInfo[1]),
12 | "=c" (CPUInfo[2]),
13 | "=d" (CPUInfo[3]) :
14 | "a" (InfoType)
15 | );
16 | }
17 | #endif
18 |
19 | SSE sse_info;
20 |
21 | SSE::SSE() : m_hasSSE(false)
22 | {
23 | int info[4];
24 | cpuid(info, 0);
25 | int nIds = info[0];
26 | if (nIds >= 1)
27 | {
28 | cpuid(info, 1);
29 | // This tests for SSE 4.1. We will probably only use SSE2, if so, change that later.
30 | m_hasSSE = (info[2] & ((int)1 << 19)) != 0;
31 | }
32 | }
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/SSE.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #pragma once
2 |
3 | #include
4 | #include
5 | #include "Miro.h"
6 |
7 | #if defined(WIN32) && defined(SSE)
8 | #define WSSEALIGN __declspec( align( 16 ) )
9 | #else
10 | #define WSSEALIGN
11 | #endif
12 |
13 | inline int nCpus()
14 | {
15 | static int n = -1;
16 | if (n == -1) {
17 | #ifdef WIN32
18 | SYSTEM_INFO sysinfo;
19 | GetSystemInfo( &sysinfo );
20 |
21 | n = sysinfo.dwNumberOfProcessors;
22 | #else
23 | n = sysconf( _SC_NPROCESSORS_ONLN );
24 | #endif
25 | }
26 | return n;
27 | }
28 |
29 | #if defined(__GNUC__) && defined(SSE)
30 | #define GSSEALIGN __attribute__((aligned(16)))
31 | #else
32 | #define GSSEALIGN
33 | #endif
34 |
35 | inline float _mm_extract_ps1(__m128 a, int i)
36 | {
37 | union
38 | {
39 | __m128 m;
40 | float f[4];
41 | } u;
42 | u.m = a;
43 | return u.f[i];
44 | }
45 |
46 | inline int _mm_extract_int(__m128 a, int i)
47 | {
48 | union
49 | {
50 | __m128 m;
51 | int f[4];
52 | } u;
53 | u.m = a;
54 | return u.f[i];
55 | }
56 |
57 | class SSE
58 | {
59 | public:
60 | SSE();
61 |
62 | bool hasSSE() const { return m_hasSSE; }
63 |
64 | private:
65 | bool m_hasSSE;
66 | };
67 |
68 | extern SSE sse_info;
69 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/SSEObject.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #pragma once
2 |
3 | #include "SSE.h"
4 |
5 | struct WSSEALIGN SSEVector4
6 | {
7 | __m128 x, y, z;
8 | } GSSEALIGN;
9 |
10 | class WSSEALIGN SSEObject
11 | {
12 | public:
13 | inline void *operator new[](size_t sz) { return _mm_malloc(sz, 16); }
14 | inline void *operator new(size_t sz) { return _mm_malloc(sz, 16); }
15 | inline void operator delete[](void *p) { if (p) _mm_free(p); }
16 | inline void operator delete(void *p) { if (p) _mm_free(p); }
17 | } GSSEALIGN;
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Scene.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "boost/threadpool.hpp"
2 | #include "Miro.h"
3 | #include "Scene.h"
4 | #include "Camera.h"
5 | #include "Image.h"
6 | #include "Console.h"
7 |
8 | #include
9 |
10 | Scene * g_scene = 0;
11 |
12 | Scene::Scene() : m_bgColor(0.f), m_global_photons(400000), m_caustics_photons(400000), m_samples(1), m_cutoffs(0), m_focus_length(-1.f), m_lens(0.25f) {}
13 |
14 | void
15 | Scene::openGL(Camera *cam)
16 | {
17 | glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
18 |
19 | cam->drawGL();
20 |
21 | // draw objects
22 | for (size_t i = 0; i < m_objects.size(); ++i)
23 | m_objects[i]->renderGL();
24 | for (size_t i = 0; i < m_lights.size(); ++i)
25 | {
26 | glColor3f(1, 1, 0.2);
27 | glPushMatrix();
28 | glTranslatef(m_lights[i]->position().x, m_lights[i]->position().y, m_lights[i]->position().z);
29 | glutSolidSphere(1, 10, 10);
30 | glPopMatrix();
31 | glColor3f(1, 1, 1);
32 | }
33 | g_caustics_map->renderGL();
34 |
35 | glutSwapBuffers();
36 | }
37 |
38 | void Scene::sampleMap(Photon_map *map, int n_photons, float total_wattage)
39 | {
40 | Lights::iterator lit;
41 | std::vector refr_stack;
42 | int total = 0;
43 | for (lit = m_lights.begin(); lit != m_lights.end(); ++lit)
44 | {
45 | int photons = (*lit)->wattage() * n_photons / total_wattage;
46 | float power = (*lit)->wattage() / photons;
47 | for (int i = 0; i < photons; ++i)
48 | {
49 | if (total % 1000 == 0)
50 | {
51 | printf("%.2f%%\r", 100 * total / ((float) n_photons));
52 | fflush(stdout);
53 | }
54 | total++;
55 | Ray ray;
56 | do
57 | {
58 | ray.d.x = 2*randone(g_rng) - 1;
59 | ray.d.y = 2*randone(g_rng) - 1;
60 | ray.d.z = 2*randone(g_rng) - 1;
61 | } while (ray.d.x*ray.d.x + ray.d.y*ray.d.y + ray.d.z*ray.d.z > 1);
62 | ray.d.normalize();
63 | ray.o = (*lit)->position();
64 | refr_stack.clear();
65 | refr_stack.push_back(1.f);
66 | ray.refractionStack = &refr_stack;
67 | ray.refractionIndex = 0;
68 | HitInfo h;
69 | if (trace(h, ray))
70 | h.material->shadePhoton(ray, h, *this, power * (*lit)->color(), map);
71 | }
72 | }
73 | printf("100.00%\n");
74 | map->balance();
75 | }
76 |
77 | void
78 | Scene::preCalc()
79 | {
80 | Objects::iterator it;
81 | for (it = m_objects.begin(); it != m_objects.end(); it++)
82 | {
83 | Object* pObject = *it;
84 | pObject->preCalc();
85 | }
86 | Lights::iterator lit;
87 | float total_wattage = 0.f;
88 | for (lit = m_lights.begin(); lit != m_lights.end(); lit++)
89 | {
90 | PointLight* pLight = *lit;
91 | pLight->preCalc();
92 | total_wattage += pLight->wattage();
93 | }
94 |
95 | m_bvh.build(&m_objects);
96 |
97 | delete g_global_illum_map;
98 | g_global_illum_map = new Photon_map(m_global_photons);
99 | delete g_caustics_map;
100 | g_caustics_map = new Photon_map(m_caustics_photons);
101 | g_caustics_map->setCaustics(true);
102 |
103 | printf("Caustics map:\n");
104 | sampleMap(g_caustics_map, m_caustics_photons, total_wattage);
105 | printf("Global illum map:\n");
106 | sampleMap(g_global_illum_map, m_global_photons, total_wattage);
107 | }
108 |
109 | std::vector Scene::traceLine(Camera const *cam, Image const *img, int j) const
110 | {
111 | std::vector results(img->width());
112 | Ray ray;
113 | HitInfo hitInfo;
114 | Vector3 shadeResult;
115 | std::vector refr_stack;
116 | std::vector colors(m_samples);
117 | for (int i = 0; i < img->width(); ++i)
118 | {
119 | for (int k = 0; k < m_samples; ++k)
120 | {
121 | ray = cam->eyeRay(i + (m_samples == 1 ? 0.5f : randone(g_rng) - 0.5f), j + (m_samples == 1 ? 0.5f : randone(g_rng) - 0.5f), img->width(), img->height());
122 | if (m_focus_length >= 0.f) // if depth of field enabled
123 | {
124 | Vector3 focal_point = ray.o + m_focus_length * ray.d;
125 | Vector3 view_dir = cam->viewDir();
126 | Vector3 d_vec(randone(g_rng) - 0.5f, randone(g_rng) - 0.5f, randone(g_rng) - 0.5f);
127 | d_vec.normalize();
128 | d_vec = view_dir.cross(d_vec);
129 |
130 | ray.o += d_vec * randone(g_rng) * m_lens;
131 | ray.d = focal_point - ray.o;
132 | ray.d.normalize();
133 | }
134 |
135 | refr_stack.clear();
136 | refr_stack.push_back(1.f);
137 | ray.refractionStack = &refr_stack;
138 | ray.refractionIndex = 0;
139 | if (!results[i])
140 | results[i] = new Vector3();
141 | if (trace(hitInfo, ray))
142 | {
143 | colors[k] = hitInfo.material->shade(ray, hitInfo, *this);
144 | }
145 | else
146 | {
147 | colors[k] = bgColor();
148 | }
149 | *results[i] += colors[k];
150 | }
151 | if (m_cutoffs > 0)
152 | {
153 | std::vector biggest(m_cutoffs, -1);
154 | for (int c = 0; c < m_cutoffs; ++c)
155 | {
156 | if (biggest[0] == -1 || colors[c].length2() > colors[biggest[0]].length2())
157 | {
158 | biggest[0] = c;
159 | for (int k = 1; k < m_cutoffs; ++k)
160 | {
161 | if (biggest[k] == -1 || colors[biggest[k - 1]].length2() > colors[biggest[k]].length2())
162 | std::swap(biggest[k - 1], biggest[k]);
163 | else
164 | break;
165 | }
166 | }
167 | }
168 | for (int k = 0; k < m_cutoffs; ++k)
169 | *results[i] -= colors[biggest[k]];
170 | }
171 | if (results[i])
172 | *results[i] /= m_samples - m_cutoffs;
173 | }
174 | return results;
175 | }
176 |
177 | void
178 | Scene::raytraceImage(Camera *cam, Image *img)
179 | {
180 | boost::timer::auto_cpu_timer t;
181 | boost::threadpool::pool threadpool(7);//nCpus() * 2);
182 | std::vector > * > tasks;
183 | std::vector > * > lines;
184 |
185 | // loop over all pixels in the image
186 | {
187 | for (int j = 0; j < img->height(); ++j)
188 | {
189 | tasks.push_back(new boost::packaged_task >(boost::bind(&Scene::traceLine, this, cam, img, j)));
190 | lines.push_back(new boost::unique_future >(tasks.back()->get_future()));
191 | boost::threadpool::schedule(threadpool, boost::bind(&boost::packaged_task >::operator(), tasks.back()));
192 | }
193 | printf("Rendering Progress: %.3f%%\r", 0.f);
194 | for (int j = 0; j < img->height(); ++j)
195 | {
196 | for (int i = 0; i < img->width(); ++i)
197 | {
198 | if (lines[j]->get()[i])
199 | {
200 | img->setPixel(i, j, *lines[j]->get()[i]);
201 | delete lines[j]->get()[i];
202 | }
203 | }
204 | img->drawScanline(j);
205 | if (j + 1 == img->height() || !lines[j + 1]->has_value())
206 | glFinish();
207 | printf("Rendering Progress: %.3f%%\r", j/float(img->height())*100.0f);
208 | fflush(stdout);
209 | }
210 | }
211 | printf("Rendering Progress: 100.000%\n");
212 | debug("done Raytracing!\n");
213 | }
214 |
215 | bool
216 | Scene::trace(HitInfo& minHit, const Ray& ray, float tMin, float tMax) const
217 | {
218 | return m_bvh.intersect(minHit, ray, tMin, tMax);
219 | }
220 |
221 | void
222 | Scene::setDepthOfField(float focus_length, float lens)
223 | {
224 | m_focus_length = focus_length;
225 | m_lens = lens;
226 | }
227 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Scene.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef CSE168_SCENE_H_INCLUDED
2 | #define CSE168_SCENE_H_INCLUDED
3 |
4 | #include "Miro.h"
5 | #include "Object.h"
6 | #include "PointLight.h"
7 | #include "BVH.h"
8 |
9 | class Camera;
10 | class Image;
11 |
12 | class Scene
13 | {
14 | public:
15 | Scene();
16 |
17 | void addObject(Object* pObj) {m_objects.push_back(pObj);}
18 | const Objects* objects() const {return &m_objects;}
19 |
20 | void addLight(PointLight* pObj) {m_lights.push_back(pObj);}
21 | const Lights* lights() const {return &m_lights;}
22 |
23 | void preCalc();
24 | void openGL(Camera *cam);
25 |
26 | inline void setBGColor(float x, float y, float z);
27 | inline void setBGColor(const Vector3& color);
28 |
29 | inline const Vector3 & bgColor() const {return m_bgColor;}
30 |
31 | inline void setSamples(int n) { m_samples = n; }
32 | inline int samples() const { return m_samples; }
33 |
34 | inline void setAntiAliasing(int a, int b) { m_samples = a * b; }
35 |
36 | inline void setCutoffs(int n) { m_cutoffs = n; }
37 | inline int cutoffs() const { return m_cutoffs; }
38 |
39 | void setDepthOfField(float focus_length, float lens = 1.0f);
40 |
41 | void raytraceImage(Camera *cam, Image *img);
42 |
43 | bool trace(HitInfo& minHit, const Ray& ray,
44 | float tMin = 0.0f, float tMax = MIRO_TMAX) const;
45 |
46 | protected:
47 | std::vector traceLine(Camera const *cam, Image const *img, int j) const;
48 | void sampleMap(Photon_map *map, int n_photons, float total_wattage);
49 |
50 | Vector3 m_bgColor;
51 |
52 | Objects m_objects;
53 | BVH m_bvh;
54 | Lights m_lights;
55 | int m_global_photons;
56 | int m_caustics_photons;
57 |
58 | int m_samples;
59 | int m_cutoffs;
60 |
61 | float m_focus_length;
62 | float m_lens;
63 | };
64 |
65 | extern Scene * g_scene;
66 |
67 | inline void Scene::setBGColor(float x, float y, float z)
68 | {
69 | Vector3 v(x, y, z);
70 | setBGColor(v);
71 | }
72 |
73 | inline void Scene::setBGColor(const Vector3& vd)
74 | {
75 | m_bgColor.set(vd);
76 | }
77 |
78 | #endif // CSE168_SCENE_H_INCLUDED
79 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Sphere.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "Sphere.h"
2 | #include "Ray.h"
3 | #include "Console.h"
4 |
5 | Sphere::Sphere()
6 | {
7 | }
8 |
9 | Sphere::~Sphere()
10 | {
11 | }
12 |
13 | void
14 | Sphere::renderGL()
15 | {
16 | glColor3f(1, 1, 1);
17 | glPushMatrix();
18 | glTranslatef(m_center.x, m_center.y, m_center.z);
19 | glutWireSphere(m_radius, 20, 20);
20 | glPopMatrix();
21 | }
22 |
23 | bool Sphere::doIntersect(IntersectObjects const &objs, HitInfo& result, const Ray& ray,
24 | float tMin, float tMax)
25 | {
26 | bool hit = false;
27 | for (int i = 0; i < objs.plain.size(); ++i)
28 | {
29 | Sphere *s = (Sphere *)objs.plain[i];
30 | const Vector3 toO = ray.o - s->m_center;
31 |
32 | const float a = ray.d.length2();
33 | const float b = dot(2*ray.d, toO);
34 | const float c = toO.length2() - s->m_radius*s->m_radius;
35 |
36 | const float discrim = b*b-4.0f*a*c;
37 |
38 | if (discrim < 0)
39 | {
40 | continue; // quadratic equation would yield imaginary numbers
41 | }
42 |
43 | const float sqrt_discrim = sqrt(discrim);
44 |
45 | // solve the quadratic equation
46 | const float t[2] = {(-b-sqrt_discrim)/(2.0f*a), (-b+sqrt_discrim)/(2.0f*a)};
47 |
48 | // since we know that discrim >= 0, t[0] < t{1]
49 | // return the t closest to us that is within range
50 | if ((t[0] > tMin) && (t[0] < tMax))
51 | {
52 | result.t = t[0];
53 | }
54 | else if((t[1] > tMin) && (t[1] < tMax))
55 | {
56 | result.t = t[1];
57 | }
58 | else
59 | {
60 | // neither of the solutions are in the required range
61 | continue;
62 | }
63 |
64 | hit = true;
65 |
66 | tMax = result.t;
67 | result.P = ray.o + result.t*ray.d;
68 | result.N = (result.P-s->m_center);
69 | result.N.normalize();
70 | result.material = s->m_material;
71 | }
72 | return hit;
73 | }
74 |
75 | Vector3 Sphere::maxVector() const
76 | {
77 | return m_center + Vector3(m_radius);
78 | }
79 |
80 | Vector3 Sphere::minVector() const
81 | {
82 | return m_center - Vector3(m_radius);
83 | }
84 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Sphere.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef CSE168_SPHERE_H_INCLUDED
2 | #define CSE168_SPHERE_H_INCLUDED
3 |
4 | #include "Vector3.h"
5 | #include "Object.h"
6 | #include "IntersectObjects.h"
7 |
8 | class Sphere : public Object
9 | {
10 | public:
11 | Sphere();
12 | virtual ~Sphere();
13 |
14 | void setCenter(const Vector3& v) {m_center = v;}
15 | void setRadius(const float f) {m_radius = f;}
16 |
17 | const Vector3& center() const {return m_center;}
18 | float radius() const {return m_radius;}
19 |
20 | virtual void renderGL();
21 | static bool doIntersect(IntersectObjects const &objects, HitInfo& result, const Ray& ray,
22 | float tMin = 0.0f, float tMax = MIRO_TMAX);
23 |
24 | virtual ObjType type() const { return SPHERE; }
25 | virtual void *ptr() { return this; }
26 |
27 | virtual Vector3 minVector() const;
28 | virtual Vector3 maxVector() const;
29 |
30 | protected:
31 | Vector3 m_center;
32 | float m_radius;
33 | };
34 |
35 | #endif // CSE168_SPHERE_H_INCLUDED
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Texture.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "Texture.h"
2 | #include
3 | using namespace boost::gil;
4 | using boost::algorithm::clamp;
5 |
6 | Texture::Texture(const std::string& texture_path)
7 | {
8 | m_img_loaded = false;
9 | setTexturePath(texture_path);
10 | loadTexture();
11 | }
12 |
13 |
14 | Texture::~Texture(void)
15 | {
16 | }
17 |
18 | void
19 | Texture::loadTexture()
20 | {
21 | if (m_texture_path.empty())
22 | {
23 | m_img_loaded = false;
24 | return;
25 | }
26 | try
27 | {
28 | boost::gil::jpeg_read_image(m_texture_path, m_img);
29 | printf("[Texture] GIL: ('%s') texture map loaded\n", m_texture_path.c_str());
30 | m_img_loaded = true;
31 | }
32 | catch (std::exception &e)
33 | {
34 | printf("[Texture] GIL: ('%s') %s\n", m_texture_path.c_str(), e.what());
35 | m_img_loaded = false;
36 | }
37 | }
38 |
39 | void
40 | Texture::setTexturePath(const std::string& texture_path)
41 | {
42 | m_texture_path = texture_path;
43 | m_texture_path.erase(std::remove(m_texture_path.begin(), m_texture_path.end(), '\n'), m_texture_path.end());
44 | m_texture_path.erase(std::remove(m_texture_path.begin(), m_texture_path.end(), '\r'), m_texture_path.end());
45 | loadTexture();
46 | }
47 |
48 | Vector3
49 | Texture::shade(const Ray& ray, const HitInfo& hit, const Scene& scene) const
50 | {
51 | if (m_img_loaded)
52 | {
53 | boost::gil::rgb8_pixel_t pixel = m_img._view((int) (fmodf(std::abs(hit.u), 1) * m_img.width()), (int) (fmodf(std::abs(hit.v), 1) * m_img.height()));
54 | return Vector3(pixel[0] / 255.f, pixel[1] / 255.f, pixel[2] / 255.f);
55 | }
56 | else
57 | return m_color;
58 | }
59 |
60 | Vector3
61 | Texture::getPixel(float u, float v, int x, int y) const
62 | {
63 | if (m_img_loaded)
64 | {
65 | int posx = fmodf(std::abs(u), 1) * m_img.width() + x;
66 | posx = (posx + m_img.width()) % m_img.width();
67 | int posy = fmodf(std::abs(v), 1) * m_img.height() + y;
68 | posy = (posy + m_img.height()) %m_img.height();
69 | boost::gil::rgb8_pixel_t pixel = m_img._view(posx, posy);
70 | return Vector3(pixel[0] / 255.f, pixel[1] / 255.f, pixel[2] / 255.f);
71 | }
72 | else
73 | {
74 | return m_color;
75 | }
76 | }
77 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Texture.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #pragma once
2 | #include "material.h"
3 | #include "Ray.h"
4 | #include
5 | #include
6 |
7 | class Texture :
8 | public Material
9 | {
10 | public:
11 | Texture() { m_img_loaded = false; }; // A texture without a path is a basic material (one color)
12 | Texture(const std::string& texture_path);
13 | virtual ~Texture(void);
14 |
15 | virtual void preCalc() {}
16 |
17 | virtual Vector3 shade(const Ray& ray, const HitInfo& hit,
18 | const Scene& scene) const;
19 | void setTexturePath(const std::string& texture_path);
20 | const std::string& getTexturePath() { return m_texture_path; }
21 | Vector3 getPixel(float u, float v, int x, int y) const;
22 |
23 | protected:
24 | void loadTexture();
25 |
26 | private:
27 | std::string m_texture_path;
28 | boost::gil::rgb8_image_t m_img;
29 | bool m_img_loaded;
30 | };
31 |
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/Triangle.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef CSE168_TRIANGLE_H_INCLUDED
2 | #define CSE168_TRIANGLE_H_INCLUDED
3 |
4 | #include "SSE.h"
5 | #include "Object.h"
6 | #include "SSEObject.h"
7 |
8 | /*
9 | The Triangle class stores a pointer to a mesh and an index into its
10 | triangle array. The mesh stores all data needed by this Triangle.
11 | */
12 | class Triangle : public Object
13 | {
14 | public:
15 | Triangle(TriangleMesh * m = 0, unsigned int i = 0);
16 | virtual ~Triangle();
17 |
18 | void setIndex(unsigned int i) {m_index = i;}
19 | void setMesh(TriangleMesh* m) {m_mesh = m;}
20 |
21 | virtual void renderGL();
22 |
23 | static bool doIntersect(IntersectObjects const &objects, HitInfo &, const Ray &, float, float);
24 |
25 | virtual ObjType type() const { return TRIANGLE; }
26 | virtual void *ptr() { return this; }
27 | static void * preProcess( std::vector &objects );
28 |
29 | virtual Vector3 minVector() const;
30 | virtual Vector3 maxVector() const;
31 |
32 | protected:
33 | TriangleMesh* m_mesh;
34 | unsigned int m_index;
35 | };
36 |
37 | #endif // CSE168_TRIANGLE_H_INCLUDED
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/TriangleMesh.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "TriangleMesh.h"
2 | #include "Triangle.h"
3 | #include "Scene.h"
4 |
5 |
6 | TriangleMesh::TriangleMesh() :
7 | m_normals(0),
8 | m_vertices(0),
9 | m_texCoords(0),
10 | m_normalIndices(0),
11 | m_vertexIndices(0),
12 | m_texCoordIndices(0)
13 | {
14 |
15 | }
16 |
17 | TriangleMesh::~TriangleMesh()
18 | {
19 | delete [] m_normals;
20 | delete [] m_vertices;
21 | delete [] m_texCoords;
22 | delete [] m_normalIndices;
23 | delete [] m_vertexIndices;
24 | delete [] m_texCoordIndices;
25 | }
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sources/TriangleMesh.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef CSE168_TRIANGLE_MESH_H_INCLUDED
2 | #define CSE168_TRIANGLE_MESH_H_INCLUDED
3 |
4 | #include
5 | #include