├── tests
├── __init__.py
├── test_common.py
├── test_lie_group.py
├── test_manifold.py
├── test_pca.py
├── test_backend_tensorflow.py
├── test_template.py
├── test_connection.py
├── test_visualization.py
├── helper.py
├── test_examples.py
├── test_matrices_space.py
├── test_backend_numpy.py
├── test_general_linear_group.py
├── test_stiefel.py
├── test_minkowski_space.py
└── test_spd_matrices_space.py
├── geomstats
├── backend
│ ├── common.py
│ ├── tensorflow_testing.py
│ ├── numpy_testing.py
│ ├── pytorch_testing.py
│ ├── numpy_random.py
│ ├── pytorch_random.py
│ ├── tensorflow_random.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── pytorch_linalg.py
│ ├── numpy_linalg.py
│ ├── tensorflow_linalg.py
│ ├── tensorflow.py
│ ├── numpy.py
│ └── pytorch.py
├── learning
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── _template.py
│ ├── mean_shift.py
│ └── pca.py
├── __init__.py
├── __about__.py
├── embedded_manifold.py
├── manifold.py
├── tests.py
├── matrices_space.py
├── euclidean_space.py
├── general_linear_group.py
├── minkowski_space.py
├── lie_group.py
├── spd_matrices_space.py
└── connection.py
├── .gitignore
├── docs
├── troubleshooting.rst
├── requirements.doc.txt
├── changelog.rst
├── install.rst
├── index.rst
├── Makefile
├── conf.py
├── tutorials.rst
└── api-reference.rst
├── examples
├── imgs
│ ├── h2_grid.png
│ ├── gradient_descent.gif
│ └── gradient_descent.png
├── plot_geodesics_so3.py
├── plot_geodesics_se3.py
├── plot_geodesics_s2.py
├── plot_quantization_s1.py
├── plot_quantization_s2.py
├── plot_square_h2_poincare_disk.py
├── plot_square_h2_poincare_half_plane.py
├── plot_grid_h2.py
├── plot_square_h2_klein_disk.py
├── tangent_pca_so3.py
├── plot_geodesics_h2.py
├── loss_and_gradient_so3.py
├── gradient_descent_s2.py
└── loss_and_gradient_se3.py
├── requirements.txt
├── .travis.yml
├── setup.py
├── LICENSE.md
├── README.md
└── CONTRIBUTING.md
/tests/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/backend/common.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 |
3 | pi = np.pi
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | build
2 | dist
3 | *.mp4
4 | *egg-info
5 | *.egg
6 | *.pyc
7 | *.png
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/troubleshooting.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Troubleshooting
2 | ===============
3 |
4 | Trouble shooting.
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/imgs/h2_grid.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lmcinnes/geomstats/master/examples/imgs/h2_grid.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/imgs/gradient_descent.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lmcinnes/geomstats/master/examples/imgs/gradient_descent.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/imgs/gradient_descent.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lmcinnes/geomstats/master/examples/imgs/gradient_descent.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/requirements.doc.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | numpydoc==0.8
2 | sphinx
3 | dask_sphinx_theme>=1.1.0
4 | sphinx-click
5 | toolz
6 | cloudpickle
7 | pandas>=0.19.0
8 | distributed
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/requirements.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | autograd
2 | codecov
3 | coverage
4 | h5py==2.8.0
5 | matplotlib
6 | nose2
7 | numpy>=1.14.1
8 | scikit-learn
9 | scipy
10 | tensorflow>=1.12
11 | torch==0.4.0
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/backend/tensorflow_testing.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Testing backend."""
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 |
5 |
6 | def assert_allclose(*args, **kwargs):
7 | return np.testing.assert_allclose(*args, **kwargs)
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/backend/numpy_testing.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Numpy based testing backend."""
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 |
5 |
6 | def assert_allclose(*args, **kwargs):
7 | return np.testing.assert_allclose(*args, **kwargs)
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/backend/pytorch_testing.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Pytorch based testing backend."""
2 |
3 | import torch
4 |
5 |
6 | def assert_allclose(*args, **kwargs):
7 | return torch.testing.assert_allclose(*args, **kwargs)
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/changelog.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Changelog
2 | =========
3 |
4 | **0.1.7**
5 |
6 | * Bugfixes
7 | * Default arguments on the API
8 | * Better command line argument parsing
9 |
10 | **0.1.6**
11 |
12 | * Cleaner API.
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/learning/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from ._template import TemplateEstimator
2 | from ._template import TemplateClassifier
3 | from ._template import TemplateTransformer
4 |
5 | __all__ = ['TemplateEstimator', 'TemplateClassifier', 'TemplateTransformer',
6 | '__version__']
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/install.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Install Geomstats
2 | =================
3 |
4 |
5 | You can install geomstats with ``pip3`` as follows::
6 |
7 | pip3 install geomstats
8 |
9 | You should choose your backend by setting the environment variable GEOMSTATS_BACKEND to numpy, tensorflow or pytorch::
10 |
11 | export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND=numpy
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/backend/numpy_random.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Numpy based random backend."""
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 |
5 |
6 | def rand(*args, **kwargs):
7 | return np.random.rand(*args, **kwargs)
8 |
9 |
10 | def randint(*args, **kwargs):
11 | return np.random.randint(*args, **kwargs)
12 |
13 |
14 | def seed(*args, **kwargs):
15 | return np.random.seed(*args, **kwargs)
16 |
17 |
18 | def normal(*args, **kwargs):
19 | return np.random.normal(*args, **kwargs)
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .__about__ import __version__
2 |
3 | import geomstats.manifold
4 | import geomstats.euclidean_space
5 | import geomstats.hyperbolic_space
6 | import geomstats.hypersphere
7 | import geomstats.invariant_metric
8 | import geomstats.lie_group
9 | import geomstats.minkowski_space
10 | import geomstats.spd_matrices_space
11 | import geomstats.special_euclidean_group
12 | import geomstats.special_orthogonal_group
13 | import geomstats.riemannian_metric
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/backend/pytorch_random.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Torch based random backend."""
2 |
3 | import torch
4 |
5 |
6 | def rand(*args, **kwargs):
7 | return torch.rand(*args, **kwargs)
8 |
9 |
10 | def randint(*args, **kwargs):
11 | return torch.randint(*args, **kwargs)
12 |
13 |
14 | def seed(*args, **kwargs):
15 | return torch.manual_seed(*args, **kwargs)
16 |
17 |
18 | def normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=(1, 1)):
19 | return torch.normal(torch.zeros(size), torch.ones(size))
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/__about__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Remove -dev before releasing
2 | __version__ = '1.15'
3 |
4 | from itertools import chain
5 |
6 | install_requires = [
7 | 'autograd',
8 | 'h5py==2.8.0',
9 | 'matplotlib',
10 | 'numpy>=1.14.1',
11 | 'scipy',
12 | ]
13 |
14 | extras_require = {
15 | 'test': ['codecov', 'coverage', 'nose2'],
16 | 'tf': ['tensorflow>=1.12'],
17 | 'torch': ['torch==0.4.0'],
18 | }
19 | extras_require['all'] = list(chain(*extras_require.values()))
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_common.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import pytest
2 |
3 | from sklearn.utils.estimator_checks import check_estimator
4 |
5 | from geomstats.learning._template import TemplateEstimator
6 | from geomstats.learning._template import TemplateClassifier
7 | from geomstats.learning._template import TemplateTransformer
8 |
9 |
10 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
11 | "Estimator", [TemplateEstimator, TemplateTransformer, TemplateClassifier]
12 | )
13 | def test_all_estimators(Estimator):
14 | return check_estimator(Estimator)
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/index.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Geomstats
2 | =========
3 |
4 | *Geomstats provides code for computations and statistics on manifolds with geometric structures.*
5 |
6 | **Quick install**
7 |
8 | .. code-block:: bash
9 |
10 | pip3 install geomstats
11 | export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND=numpy
12 |
13 | .. toctree::
14 | :maxdepth: 1
15 | :caption: Getting Started
16 |
17 | install.rst
18 | api-reference.rst
19 | contributing.rst
20 | tutorials.rst
21 | changelog.rst
22 |
23 | .. toctree::
24 | :maxdepth: 1
25 | :caption: Support
26 |
27 | troubleshooting.rst
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.travis.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | sudo: false
2 | dist: trusty
3 | cache: pip
4 | language: python
5 | python:
6 | - "3.5"
7 | - "3.5-dev"
8 | - "3.6"
9 | - "3.6-dev"
10 |
11 | install:
12 | - pip install --upgrade pip setuptools wheel
13 | - pip install -q -r requirements.txt --only-binary=numpy,scipy
14 | script:
15 | - nose2 --with-coverage --verbose
16 | env:
17 | - GEOMSTATS_BACKEND=numpy
18 | - GEOMSTATS_BACKEND=pytorch
19 | - GEOMSTATS_BACKEND=tensorflow
20 |
21 | after_success:
22 | - bash <(curl -s https://codecov.io/bash) -c -F $GEOMSTATS_BACKEND
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_lie_group.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for Lie groups.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.tests
6 |
7 | from geomstats.lie_group import LieGroup
8 |
9 |
10 | class TestLieGroupMethods(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
11 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
12 |
13 | dimension = 4
14 | group = LieGroup(dimension=dimension)
15 |
16 | def test_dimension(self):
17 | result = self.group.dimension
18 | expected = self.dimension
19 |
20 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
21 |
22 |
23 | if __name__ == '__main__':
24 | geomstats.tests.main()
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Makefile:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Minimal makefile for Sphinx documentation
2 | #
3 |
4 | # You can set these variables from the command line.
5 | SPHINXOPTS =
6 | SPHINXBUILD = sphinx-build
7 | SOURCEDIR = .
8 | BUILDDIR = build
9 |
10 | # Put it first so that "make" without argument is like "make help".
11 | help:
12 | @$(SPHINXBUILD) -M help "$(SOURCEDIR)" "$(BUILDDIR)" $(SPHINXOPTS) $(O)
13 |
14 | .PHONY: help Makefile
15 |
16 | # Catch-all target: route all unknown targets to Sphinx using the new
17 | # "make mode" option. $(O) is meant as a shortcut for $(SPHINXOPTS).
18 | %: Makefile
19 | @$(SPHINXBUILD) -M $@ "$(SOURCEDIR)" "$(BUILDDIR)" $(SPHINXOPTS) $(O)
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import runpy
3 | from setuptools import setup, find_packages
4 |
5 | base_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
6 | about = runpy.run_path(os.path.join(base_dir, 'geomstats', '__about__.py'))
7 |
8 | setup(name='geomstats',
9 | version=about['__version__'],
10 | install_requires=about['install_requires'],
11 | extras_require=about['extras_require'],
12 | description='Geometric statistics on manifolds',
13 | url='http://github.com/geomstats/geomstats',
14 | author='Nina Miolane',
15 | author_email='ninamio78@gmail.com',
16 | license='MIT',
17 | packages=find_packages(),
18 | zip_safe=False)
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/backend/tensorflow_random.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Tensorflow based random backend."""
2 |
3 | import tensorflow as tf
4 |
5 |
6 | def randint(low, high=None, size=None):
7 | if size is None:
8 | size = (1,)
9 | maxval = high
10 | minval = low
11 | if high is None:
12 | maxval = low - 1
13 | minval = 0
14 | return tf.random_uniform(
15 | shape=size,
16 | minval=minval,
17 | maxval=maxval, dtype=tf.int32, seed=None, name=None)
18 |
19 |
20 | def rand(*args):
21 | return tf.random_uniform(shape=args)
22 |
23 |
24 | def seed(*args):
25 | return tf.set_random_seed(*args)
26 |
27 |
28 | def normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=(1, 1)):
29 | return tf.random_normal(mean=loc, stddev=scale, shape=size)
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_manifold.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for manifolds.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 | import geomstats.tests
7 |
8 | from geomstats.manifold import Manifold
9 |
10 |
11 | class TestManifoldMethods(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
12 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
13 |
14 | def setUp(self):
15 | self.dimension = 4
16 | self.manifold = Manifold(self.dimension)
17 |
18 | def test_dimension(self):
19 | result = self.manifold.dimension
20 | expected = self.dimension
21 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
22 |
23 | def test_belongs(self):
24 | point = gs.array([1., 2., 3.])
25 | self.assertRaises(NotImplementedError,
26 | lambda: self.manifold.belongs(point))
27 |
28 | def test_regularize(self):
29 | point = gs.array([1., 2., 3.])
30 | result = self.manifold.regularize(point)
31 | expected = point
32 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
33 |
34 |
35 | if __name__ == '__main__':
36 | geomstats.test.main()
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2018 Nina Miolane
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/backend/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import sys
3 |
4 | _default_backend = 'numpy'
5 | if 'GEOMSTATS_BACKEND' in os.environ:
6 | _backend = os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND']
7 |
8 | else:
9 | _backend = _default_backend
10 |
11 | _BACKEND = _backend
12 |
13 | from .common import * # NOQA
14 |
15 | if _BACKEND == 'numpy':
16 | sys.stderr.write('Using numpy backend\n')
17 | from .numpy import * # NOQA
18 | from . import numpy_linalg as linalg
19 | from . import numpy_random as random
20 | from . import numpy_testing as testing
21 | elif _BACKEND == 'pytorch':
22 | sys.stderr.write('Using pytorch backend\n')
23 | from .pytorch import * # NOQA
24 | from . import pytorch_linalg as linalg # NOQA
25 | from . import pytorch_random as random # NOQA
26 | from . import pytorch_testing as testing # NOQA
27 | elif _BACKEND == 'tensorflow':
28 | sys.stderr.write('Using tensorflow backend\n')
29 | from .tensorflow import * # NOQA
30 | from . import tensorflow_linalg as linalg # NOQA
31 | from . import tensorflow_random as random # NOQA
32 | from . import tensorflow_testing as testing # NOQA
33 |
34 |
35 | def backend():
36 | return _BACKEND
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/plot_geodesics_so3.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Plot a geodesic of SO(3) equipped
3 | with its left-invariant canonical METRIC.
4 | """
5 |
6 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
7 | import numpy as np
8 | import os
9 |
10 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
11 |
12 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
13 |
14 | SO3_GROUP = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=3)
15 | METRIC = SO3_GROUP.bi_invariant_metric
16 |
17 |
18 | def main():
19 | initial_point = SO3_GROUP.identity
20 | initial_tangent_vec = [0.5, 0.5, 0.8]
21 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=initial_point,
22 | initial_tangent_vec=initial_tangent_vec)
23 |
24 | n_steps = 10
25 | t = np.linspace(0, 1, n_steps)
26 |
27 | points = geodesic(t)
28 | visualization.plot(points, space='SO3_GROUP')
29 | plt.show()
30 |
31 |
32 | if __name__ == "__main__":
33 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
34 | print('Examples with visualizations are only implemented '
35 | 'with numpy backend.\n'
36 | 'To change backend, write: '
37 | 'export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND = \'numpy\'.')
38 | else:
39 | main()
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/plot_geodesics_se3.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Plot a geodesic of SE(3) equipped
3 | with its left-invariant canonical METRIC.
4 | """
5 |
6 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
7 | import numpy as np
8 | import os
9 |
10 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
11 |
12 | from geomstats.special_euclidean_group import SpecialEuclideanGroup
13 |
14 | SE3_GROUP = SpecialEuclideanGroup(n=3)
15 | METRIC = SE3_GROUP.left_canonical_metric
16 |
17 |
18 | def main():
19 | initial_point = SE3_GROUP.identity
20 | initial_tangent_vec = [1.8, 0.2, 0.3, 3., 3., 1.]
21 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=initial_point,
22 | initial_tangent_vec=initial_tangent_vec)
23 |
24 | n_steps = 40
25 | t = np.linspace(-3, 3, n_steps)
26 |
27 | points = geodesic(t)
28 |
29 | visualization.plot(points, space='SE3_GROUP')
30 | plt.show()
31 |
32 |
33 | if __name__ == "__main__":
34 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
35 | print('Examples with visualizations are only implemented '
36 | 'with numpy backend.\n'
37 | 'To change backend, write: '
38 | 'export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND = \'numpy\'.')
39 | else:
40 | main()
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_pca.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import pytest
2 | import numpy as np
3 |
4 | from sklearn.utils.testing import assert_allclose
5 |
6 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
7 |
8 | from geomstats.learning.pca import TangentPCA
9 |
10 |
11 | SO3_GROUP = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=3)
12 | METRIC = SO3_GROUP.bi_invariant_metric
13 | N_SAMPLES = 10
14 | N_COMPONENTS = 2
15 |
16 |
17 | @pytest.fixture
18 | def data():
19 | data = SO3_GROUP.random_uniform(n_samples=N_SAMPLES)
20 | return data
21 |
22 |
23 | def test_tangent_pca_error(data):
24 | X = data
25 | trans = TangentPCA(n_components=N_COMPONENTS)
26 | trans.fit(X)
27 | with pytest.raises(ValueError, match="Shape of input is different"):
28 | X_diff_size = np.ones((10, X.shape[1] + 1))
29 | trans.transform(X_diff_size)
30 |
31 |
32 | def test_tangent_pca(data):
33 | X = data
34 | trans = TangentPCA(n_components=N_COMPONENTS)
35 | assert trans.demo_param == 'demo'
36 |
37 | trans.fit(X)
38 | assert trans.n_features_ == X.shape[1]
39 |
40 | X_trans = trans.transform(X)
41 | assert_allclose(X_trans, np.sqrt(X))
42 |
43 | X_trans = trans.fit_transform(X)
44 | assert_allclose(X_trans, np.sqrt(X))
45 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/embedded_manifold.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Manifold embedded in another manifold.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import math
6 |
7 | from geomstats.manifold import Manifold
8 |
9 |
10 | class EmbeddedManifold(Manifold):
11 | """
12 | Class for manifolds embedded in another manifold.
13 | """
14 |
15 | def __init__(self, dimension, embedding_manifold):
16 | assert isinstance(dimension, int) or dimension == math.inf
17 | assert dimension > 0
18 | super(EmbeddedManifold, self).__init__(
19 | dimension=dimension)
20 | self.embedding_manifold = embedding_manifold
21 |
22 | def intrinsic_to_extrinsic_coords(self, point_intrinsic):
23 | raise NotImplementedError(
24 | 'intrinsic_to_extrinsic_coords is not implemented.')
25 |
26 | def extrinsic_to_intrinsic_coords(self, point_extrinsic):
27 | raise NotImplementedError(
28 | 'extrinsic_to_intrinsic_coords is not implemented.')
29 |
30 | def projection(self, point):
31 | raise NotImplementedError(
32 | 'projection is not implemented.')
33 |
34 | def projection_to_tangent_space(self, vector, base_point):
35 | raise NotImplementedError(
36 | 'projection_to_tangent_space is not implemented.')
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/plot_geodesics_s2.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Plot a geodesic on the sphere S2
3 | """
4 |
5 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
6 | import numpy as np
7 | import os
8 |
9 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
10 |
11 | from geomstats.hypersphere import Hypersphere
12 |
13 | SPHERE2 = Hypersphere(dimension=2)
14 | METRIC = SPHERE2.metric
15 |
16 |
17 | def main():
18 | initial_point = [1., 0., 0.]
19 | initial_tangent_vec = SPHERE2.projection_to_tangent_space(
20 | vector=[1., 2., 0.8],
21 | base_point=initial_point)
22 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=initial_point,
23 | initial_tangent_vec=initial_tangent_vec)
24 |
25 | n_steps = 10
26 | t = np.linspace(0, 1, n_steps)
27 |
28 | points = geodesic(t)
29 | visualization.plot(points, space='S2')
30 | plt.show()
31 |
32 |
33 | if __name__ == "__main__":
34 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
35 | print('Examples with visualizations are only implemented '
36 | 'with numpy backend.\n'
37 | 'To change backend, write: '
38 | 'export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND = \'numpy\'.')
39 | else:
40 | main()
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/backend/pytorch_linalg.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Pytorch based linear algebra backend."""
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 | import scipy.linalg
5 | import torch
6 |
7 |
8 | def expm(x):
9 | np_expm = np.vectorize(
10 | scipy.linalg.expm, signature='(n,m)->(n,m)')(x)
11 | return torch.from_numpy(np_expm)
12 |
13 |
14 | def inv(*args, **kwargs):
15 | return torch.from_numpy(np.linalg.inv(*args, **kwargs))
16 |
17 |
18 | def eigvalsh(*args, **kwargs):
19 | return torch.from_numpy(np.linalg.eigvalsh(*args, **kwargs))
20 |
21 |
22 | def eigh(*args, **kwargs):
23 | eigs = np.linalg.eigh(*args, **kwargs)
24 | return torch.from_numpy(eigs[0]), torch.from_numpy(eigs[1])
25 |
26 |
27 | def svd(*args, **kwargs):
28 | svds = np.linalg.svd(*args, **kwargs)
29 | return (torch.from_numpy(svds[0]),
30 | torch.from_numpy(svds[1]),
31 | torch.from_numpy(svds[2]))
32 |
33 |
34 | def det(*args, **kwargs):
35 | return torch.from_numpy(np.linalg.det(*args, **kwargs))
36 |
37 |
38 | def norm(x, ord=2, axis=None, keepdims=False):
39 | if axis is None:
40 | return torch.norm(x, p=ord)
41 | return torch.norm(x, p=ord, dim=axis)
42 |
43 |
44 | def qr(*args, **kwargs):
45 | return torch.from_numpy(np.linalg.qr(*args, **kwargs))
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/conf.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | project = 'Geomstats'
2 | copyright = '2019, Geomstats, Inc.'
3 | author = 'Geomstats Team'
4 |
5 | version = '0.1'
6 | # The full version, including alpha/beta/rc tags
7 | release = '0.1'
8 |
9 |
10 | extensions = [
11 | 'sphinx.ext.autodoc',
12 | 'sphinx.ext.doctest',
13 | 'sphinx.ext.coverage',
14 | 'sphinx.ext.mathjax',
15 | 'sphinx.ext.viewcode',
16 | 'sphinx.ext.githubpages',
17 | ]
18 |
19 | templates_path = ['templates']
20 |
21 | source_suffix = '.rst'
22 |
23 | master_doc = 'index'
24 |
25 | language = None
26 |
27 | exclude_patterns = ['build', 'Thumbs.db', '.DS_Store']
28 |
29 | pygments_style = None
30 |
31 | html_theme = 'sphinx_rtd_theme'
32 |
33 | html_static_path = ['static']
34 |
35 | htmlhelp_basename = 'geomstatsdoc'
36 |
37 | latex_elements = {
38 | }
39 |
40 |
41 | latex_documents = [
42 | (master_doc, 'geomstats.tex', 'geomstats Documentation',
43 | 'Geomstats Team', 'manual'),
44 | ]
45 |
46 | man_pages = [
47 | (master_doc, 'geomstats', 'geomstats Documentation',
48 | [author], 1)
49 | ]
50 |
51 | texinfo_documents = [
52 | (master_doc, 'geomstats', 'geomstats Documentation',
53 | author, 'geomstats', 'One line description of project.',
54 | 'Miscellaneous'),
55 | ]
56 |
57 | epub_title = project
58 | epub_exclude_files = ['search.html']
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/manifold.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Manifold, i.e. a topological space that locally resembles
3 | Euclidean space near each point.
4 | """
5 |
6 | import math
7 |
8 |
9 | class Manifold(object):
10 | """
11 | Class for manifolds.
12 | """
13 |
14 | def __init__(self, dimension):
15 |
16 | assert isinstance(dimension, int) or dimension == math.inf
17 | assert dimension > 0
18 |
19 | self.dimension = dimension
20 |
21 | def belongs(self, point, point_type=None):
22 | """
23 | Evaluate if a point belongs to the manifold.
24 |
25 | Parameters
26 | ----------
27 | points : array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
28 | Input points.
29 |
30 | Returns
31 | -------
32 | belongs : array-like, shape=[n_samples, 1]
33 | """
34 | raise NotImplementedError('belongs is not implemented.')
35 |
36 | def regularize(self, point, point_type=None):
37 | """
38 | Regularize a point to the canonical representation
39 | chosen for the manifold.
40 |
41 | Parameters
42 | ----------
43 | points : array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
44 | Input points.
45 |
46 | Returns
47 | -------
48 | regularized_point : array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
49 | """
50 | regularized_point = point
51 | return regularized_point
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/backend/numpy_linalg.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Numpy based linear algebra backend."""
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 | import scipy.linalg
5 |
6 |
7 | def expm(x):
8 | return np.vectorize(
9 | scipy.linalg.expm, signature='(n,m)->(n,m)')(x)
10 |
11 |
12 | def logm(x):
13 | return np.vectorize(
14 | scipy.linalg.logm, signature='(n,m)->(n,m)')(x)
15 |
16 |
17 | def sqrtm(x):
18 | return np.vectorize(
19 | scipy.linalg.sqrtm, signature='(n,m)->(n,m)')(x)
20 |
21 |
22 | def det(*args, **kwargs):
23 | return np.linalg.det(*args, **kwargs)
24 |
25 |
26 | def norm(*args, **kwargs):
27 | return np.linalg.norm(*args, **kwargs)
28 |
29 |
30 | def inv(*args, **kwargs):
31 | return np.linalg.inv(*args, **kwargs)
32 |
33 |
34 | def matrix_rank(*args, **kwargs):
35 | return np.linalg.matrix_rank(*args, **kwargs)
36 |
37 |
38 | def eigvalsh(*args, **kwargs):
39 | return np.linalg.eigvalsh(*args, **kwargs)
40 |
41 |
42 | def svd(*args, **kwargs):
43 | return np.linalg.svd(*args, **kwargs)
44 |
45 |
46 | def eigh(*args, **kwargs):
47 | return np.linalg.eigh(*args, **kwargs)
48 |
49 |
50 | def eig(*args, **kwargs):
51 | return np.linalg.eig(*args, **kwargs)
52 |
53 |
54 | def exp(*args, **kwargs):
55 | return np.exp(*args, **kwargs)
56 |
57 |
58 | def qr(*args, **kwargs):
59 | return np.vectorize(
60 | np.linalg.qr,
61 | signature='(n,m)->(n,k),(k,m)',
62 | excluded=['mode'])(*args, **kwargs)
63 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/plot_quantization_s1.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Plot the result of optimal quantization of the uniform distribution
3 | on the circle.
4 | """
5 |
6 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
7 | import os
8 |
9 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
10 |
11 | from geomstats.hypersphere import Hypersphere
12 |
13 | CIRCLE = Hypersphere(dimension=1)
14 | METRIC = CIRCLE.metric
15 | N_POINTS = 1000
16 | N_CENTERS = 5
17 | N_REPETITIONS = 20
18 | TOLERANCE = 1e-6
19 |
20 |
21 | def main():
22 | points = CIRCLE.random_uniform(n_samples=N_POINTS, bound=None)
23 |
24 | centers, weights, clusters, n_iterations = METRIC.optimal_quantization(
25 | points=points, n_centers=N_CENTERS,
26 | n_repetitions=N_REPETITIONS, tolerance=TOLERANCE
27 | )
28 |
29 | plt.figure(0)
30 | visualization.plot(points=centers, space='S1', color='red')
31 | plt.show()
32 |
33 | plt.figure(1)
34 | ax = plt.axes()
35 | circle = visualization.Circle()
36 | circle.draw(ax=ax)
37 | for i in range(N_CENTERS):
38 | circle.draw_points(ax=ax, points=clusters[i])
39 | plt.show()
40 |
41 |
42 | if __name__ == "__main__":
43 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
44 | print('Examples with visualizations are only implemented '
45 | 'with numpy backend.\n'
46 | 'To change backend, write: '
47 | 'export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND = \'numpy\'.')
48 | else:
49 | main()
50 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_backend_tensorflow.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for tensorflow backend.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import importlib
6 | import os
7 | import tensorflow as tf
8 |
9 | import geomstats.backend as gs
10 |
11 |
12 | class TestBackendTensorFlow(tf.test.TestCase):
13 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
14 |
15 | @classmethod
16 | def setUpClass(cls):
17 | cls.initial_backend = os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND']
18 | os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] = 'tensorflow'
19 | os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
20 | importlib.reload(gs)
21 |
22 | @classmethod
23 | def tearDownClass(cls):
24 | os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] = cls.initial_backend
25 | importlib.reload(gs)
26 |
27 | def test_vstack(self):
28 | with self.test_session():
29 | tensor_1 = tf.convert_to_tensor([[1., 2., 3.], [4., 5., 6.]])
30 | tensor_2 = tf.convert_to_tensor([[7., 8., 9.]])
31 |
32 | result = gs.vstack([tensor_1, tensor_2])
33 | expected = tf.convert_to_tensor([
34 | [1., 2., 3.],
35 | [4., 5., 6.],
36 | [7., 8., 9.]])
37 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
38 |
39 | def test_tensor_addition(self):
40 | with self.test_session():
41 | tensor_1 = gs.ones((1, 1))
42 | tensor_2 = gs.ones((0, 1))
43 |
44 | result = tensor_1 + tensor_2
45 |
46 |
47 | if __name__ == '__main__':
48 | tf.test.main()
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/plot_quantization_s2.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Plot the result of optimal quantization of the von Mises Fisher distribution
3 | on the sphere
4 | """
5 |
6 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
7 | import os
8 |
9 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
10 |
11 | from geomstats.hypersphere import Hypersphere
12 |
13 | SPHERE2 = Hypersphere(dimension=2)
14 | METRIC = SPHERE2.metric
15 | N_POINTS = 1000
16 | N_CENTERS = 4
17 | N_REPETITIONS = 20
18 | KAPPA = 10
19 |
20 |
21 | def main():
22 | points = SPHERE2.random_von_mises_fisher(kappa=KAPPA, n_samples=N_POINTS)
23 |
24 | centers, weights, clusters, n_steps = METRIC.optimal_quantization(
25 | points=points, n_centers=N_CENTERS,
26 | n_repetitions=N_REPETITIONS
27 | )
28 |
29 | plt.figure(0)
30 | ax = plt.subplot(111, projection="3d")
31 | visualization.plot(points=centers, ax=ax, space='S2', c='r')
32 | plt.show()
33 |
34 | plt.figure(1)
35 | ax = plt.subplot(111, projection="3d")
36 | sphere = visualization.Sphere()
37 | sphere.draw(ax=ax)
38 | for i in range(N_CENTERS):
39 | sphere.draw_points(ax=ax, points=clusters[i])
40 | plt.show()
41 |
42 |
43 | if __name__ == "__main__":
44 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
45 | print('Examples with visualizations are only implemented '
46 | 'with numpy backend.\n'
47 | 'To change backend, write: '
48 | 'export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND = \'numpy\'.')
49 | else:
50 | main()
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/tutorials.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Tutorials
2 | =========
3 |
4 | **Choosing the backend.**
5 |
6 | You need to set the environment variable GEOMSTATS_BACKEND to numpy, tensorflow or pytorch. Only use the numpy backend for examples with visualizations.
7 |
8 | .. code-block:: bash
9 |
10 | export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND=numpy
11 |
12 | **A first python example.**
13 |
14 | This example shows how to compute a geodesic on the Lie group SE(3), which is the group of rotations and translations in 3D.
15 |
16 | .. code-block:: python
17 |
18 | """
19 | Plot a geodesic of SE(3) equipped
20 | with its left-invariant canonical metric.
21 | """
22 |
23 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
24 | import numpy as np
25 | import os
26 |
27 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
28 |
29 | from geomstats.special_euclidean_group import SpecialEuclideanGroup
30 |
31 | SE3_GROUP = SpecialEuclideanGroup(n=3)
32 | METRIC = SE3_GROUP.left_canonical_metric
33 |
34 | initial_point = SE3_GROUP.identity
35 | initial_tangent_vec = [1.8, 0.2, 0.3, 3., 3., 1.]
36 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=initial_point,
37 | initial_tangent_vec=initial_tangent_vec)
38 |
39 | n_steps = 40
40 | t = np.linspace(-3, 3, n_steps)
41 |
42 | points = geodesic(t)
43 |
44 | visualization.plot(points, space='SE3_GROUP')
45 | plt.show()
46 |
47 | **More examples.**
48 |
49 | You can find more examples in the repository "examples" of geomstats. You can run them from the command line as follows.
50 |
51 | .. code-block:: bash
52 |
53 | python3 examples/plot_grid_h2.py
54 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/plot_square_h2_poincare_disk.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Plot a square on H2 with Poincare Disk visualization.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
6 | import numpy as np
7 | import os
8 |
9 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
10 |
11 | from geomstats.hyperbolic_space import HyperbolicSpace
12 |
13 | H2 = HyperbolicSpace(dimension=2)
14 | METRIC = H2.metric
15 |
16 | SQUARE_SIZE = 50
17 |
18 |
19 | def main():
20 | top = SQUARE_SIZE / 2.0
21 | bot = - SQUARE_SIZE / 2.0
22 | left = - SQUARE_SIZE / 2.0
23 | right = SQUARE_SIZE / 2.0
24 | corners_int = [(bot, left), (bot, right), (top, right), (top, left)]
25 | corners_ext = H2.intrinsic_to_extrinsic_coords(corners_int)
26 | n_steps = 20
27 | ax = plt.gca()
28 | for i, src in enumerate(corners_ext):
29 | dst_id = (i+1) % len(corners_ext)
30 | dst = corners_ext[dst_id]
31 | tangent_vec = METRIC.log(point=dst, base_point=src)
32 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=src,
33 | initial_tangent_vec=tangent_vec)
34 | t = np.linspace(0, 1, n_steps)
35 | edge_points = geodesic(t)
36 |
37 | visualization.plot(
38 | edge_points,
39 | ax=ax,
40 | space='H2_poincare_disk',
41 | marker='.',
42 | color='black')
43 |
44 | plt.show()
45 |
46 |
47 | if __name__ == "__main__":
48 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
49 | print('Examples with visualizations are only implemented '
50 | 'with numpy backend.\n'
51 | 'To change backend, write: '
52 | 'export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND = \'numpy\'.')
53 | else:
54 | main()
55 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/plot_square_h2_poincare_half_plane.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Plot a square on H2 with Poincare Disk visualization.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
6 | import numpy as np
7 | import os
8 |
9 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
10 |
11 | from geomstats.hyperbolic_space import HyperbolicSpace
12 |
13 | H2 = HyperbolicSpace(dimension=2)
14 | METRIC = H2.metric
15 |
16 | SQUARE_SIZE = 50
17 |
18 |
19 | def main():
20 | top = SQUARE_SIZE / 2.0
21 | bot = - SQUARE_SIZE / 2.0
22 | left = - SQUARE_SIZE / 2.0
23 | right = SQUARE_SIZE / 2.0
24 | corners_int = [(bot, left), (bot, right), (top, right), (top, left)]
25 | corners_ext = H2.intrinsic_to_extrinsic_coords(corners_int)
26 | n_steps = 20
27 | ax = plt.gca()
28 | for i, src in enumerate(corners_ext):
29 | dst_id = (i+1) % len(corners_ext)
30 | dst = corners_ext[dst_id]
31 | tangent_vec = METRIC.log(point=dst, base_point=src)
32 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=src,
33 | initial_tangent_vec=tangent_vec)
34 | t = np.linspace(0, 1, n_steps)
35 | edge_points = geodesic(t)
36 |
37 | visualization.plot(
38 | edge_points,
39 | ax=ax,
40 | space='H2_poincare_half_plane',
41 | marker='.',
42 | color='black')
43 |
44 | plt.show()
45 |
46 |
47 | if __name__ == "__main__":
48 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
49 | print('Examples with visualizations are only implemented '
50 | 'with numpy backend.\n'
51 | 'To change backend, write: '
52 | 'export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND = \'numpy\'.')
53 | else:
54 | main()
55 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/plot_grid_h2.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Plot a grid on H2
3 | with Poincare Disk visualization.
4 | """
5 |
6 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
7 | import numpy as np
8 | import os
9 |
10 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
11 |
12 | from geomstats.hyperbolic_space import HyperbolicSpace
13 |
14 | H2 = HyperbolicSpace(dimension=2)
15 | METRIC = H2.metric
16 |
17 |
18 | def main(left=-128,
19 | right=128,
20 | bottom=-128,
21 | top=128,
22 | grid_size=32,
23 | n_steps=512):
24 | starts = []
25 | ends = []
26 | for p in np.linspace(left, right, grid_size):
27 | starts.append(np.array([top, p]))
28 | ends.append(np.array([bottom, p]))
29 | for p in np.linspace(top, bottom, grid_size):
30 | starts.append(np.array([p, left]))
31 | ends.append(np.array([p, right]))
32 | starts = [H2.intrinsic_to_extrinsic_coords(s) for s in starts]
33 | ends = [H2.intrinsic_to_extrinsic_coords(e) for e in ends]
34 | ax = plt.gca()
35 | for start, end in zip(starts, ends):
36 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=start,
37 | end_point=end)
38 |
39 | t = np.linspace(0, 1, n_steps)
40 | points_to_plot = geodesic(t)
41 | visualization.plot(
42 | points_to_plot, ax=ax, space='H2_poincare_disk', marker='.', s=1)
43 | plt.show()
44 |
45 |
46 | if __name__ == "__main__":
47 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
48 | print('Examples with visualizations are only implemented '
49 | 'with numpy backend.\n'
50 | 'To change backend, write: '
51 | 'export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND = \'numpy\'.')
52 | else:
53 | main()
54 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/plot_square_h2_klein_disk.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Plot a square on H2 with Poincare Disk visualization.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
6 | import numpy as np
7 | import os
8 |
9 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
10 |
11 | from geomstats.hyperbolic_space import HyperbolicSpace
12 |
13 | H2 = HyperbolicSpace(dimension=2)
14 | METRIC = H2.metric
15 |
16 | SQUARE_SIZE = 50
17 |
18 |
19 | def main():
20 | top = SQUARE_SIZE / 2.0
21 | bot = - SQUARE_SIZE / 2.0
22 | left = - SQUARE_SIZE / 2.0
23 | right = SQUARE_SIZE / 2.0
24 | corners_int = [(bot, left), (bot, right), (top, right), (top, left)]
25 | corners_ext = H2.intrinsic_to_extrinsic_coords(corners_int)
26 | n_steps = 20
27 | ax = plt.gca()
28 | for i, src in enumerate(corners_ext):
29 | dst_id = (i+1) % len(corners_ext)
30 | dst = corners_ext[dst_id]
31 | tangent_vec = METRIC.log(point=dst, base_point=src)
32 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=src,
33 | initial_tangent_vec=tangent_vec)
34 | t = np.linspace(0, 1, n_steps)
35 | edge_points = geodesic(t)
36 |
37 | visualization.plot(edge_points,
38 | ax=ax,
39 | space='H2_klein_disk',
40 | marker='.',
41 | color='black')
42 | plt.show()
43 |
44 |
45 | if __name__ == "__main__":
46 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
47 | print('Examples with visualizations are only implemented '
48 | 'with numpy backend.\n'
49 | 'To change backend, write: '
50 | 'export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND = \'numpy\'.')
51 | else:
52 | main()
53 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/tangent_pca_so3.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Compute the mean of a data set of 3D rotations.
3 | Performs tangent PCA at the mean.
4 | """
5 |
6 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
7 | import numpy as np
8 |
9 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
10 |
11 | from geomstats.learning.pca import TangentPCA
12 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
13 |
14 | SO3_GROUP = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=3)
15 | METRIC = SO3_GROUP.bi_invariant_metric
16 |
17 | N_SAMPLES = 10
18 | N_COMPONENTS = 2
19 |
20 |
21 | def main():
22 | fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))
23 |
24 | data = SO3_GROUP.random_uniform(n_samples=N_SAMPLES)
25 | mean = METRIC.mean(data)
26 |
27 | tpca = TangentPCA(metric=METRIC, n_components=N_COMPONENTS)
28 | tpca = tpca.fit(data, base_point=mean)
29 | tangent_projected_data = tpca.transform(data)
30 | print(
31 | 'Coordinates of the Log of the first 5 data points at the mean, '
32 | 'projected on the principal components:')
33 | print(tangent_projected_data[:5])
34 |
35 | ax_var = fig.add_subplot(121)
36 | xticks = np.arange(1, N_COMPONENTS+1, 1)
37 | ax_var.xaxis.set_ticks(xticks)
38 | ax_var.set_title('Explained variance')
39 | ax_var.set_xlabel('Number of Principal Components')
40 | ax_var.set_ylim((0, 1))
41 | ax_var.plot(xticks, tpca.explained_variance_ratio_)
42 |
43 | ax = fig.add_subplot(122, projection="3d")
44 | plt.setp(ax, xlabel="X", ylabel="Y", zlabel="Z")
45 |
46 | ax.set_title('Data in SO3 (black) and Frechet mean (color)')
47 | visualization.plot(data, ax, space='SO3_GROUP', color='black')
48 | visualization.plot(mean, ax, space='SO3_GROUP', linewidth=3)
49 | ax.set_xlim((-2, 2))
50 | ax.set_ylim((-2, 2))
51 | ax.set_zlim((-2, 2))
52 | plt.show()
53 |
54 |
55 | if __name__ == "__main__":
56 | main()
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/backend/tensorflow_linalg.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Tensorflow based linear algebra backend."""
2 |
3 | import tensorflow as tf
4 |
5 | from geomstats.backend.tensorflow import to_ndarray
6 |
7 |
8 | def sqrtm(sym_mat):
9 | sym_mat = to_ndarray(sym_mat, to_ndim=3)
10 |
11 | [eigenvalues, vectors] = tf.linalg.eigh(sym_mat)
12 |
13 | sqrt_eigenvalues = tf.sqrt(eigenvalues)
14 |
15 | aux = tf.einsum('ijk,ik->ijk', vectors, sqrt_eigenvalues)
16 | sqrt_mat = tf.einsum('ijk,ilk->ijl', aux, vectors)
17 |
18 | sqrt_mat = to_ndarray(sqrt_mat, to_ndim=3)
19 | return sqrt_mat
20 |
21 |
22 | def expm(x):
23 | return tf.linalg.expm(x)
24 |
25 |
26 | def logm(x):
27 | return tf.linalg.expm(x)
28 |
29 |
30 | def logm(x):
31 | x = tf.cast(x, tf.complex64)
32 | logm = tf.linalg.logm(x)
33 | logm = tf.cast(logm, tf.float32)
34 | return logm
35 |
36 |
37 | def det(x):
38 | return tf.linalg.det(x)
39 |
40 |
41 | def eigh(x):
42 | return tf.linalg.eigh(x)
43 |
44 |
45 | def eig(x):
46 | return tf.linalg.eig(x)
47 |
48 |
49 | def svd(x):
50 | s, u, v_t = tf.svd(x, full_matrices=True)
51 | return u, s, tf.transpose(v_t, perm=(0, 2, 1))
52 |
53 |
54 | def norm(x, axis=None):
55 | return tf.linalg.norm(x, axis=axis)
56 |
57 |
58 | def inv(x):
59 | return tf.linalg.inv(x)
60 |
61 |
62 | def matrix_rank(x):
63 | return tf.rank(x)
64 |
65 |
66 | def eigvalsh(x):
67 | return tf.linalg.eigvalsh(x)
68 |
69 |
70 | def qr(*args, mode='reduced'):
71 | def qr_aux(x, mode):
72 | if mode == 'complete':
73 | aux = tf.linalg.qr(x, full_matrices=True)
74 | else:
75 | aux = tf.linalg.qr(x)
76 |
77 | return (aux.q, aux.r)
78 |
79 | qr = tf.map_fn(
80 | lambda x: qr_aux(x, mode),
81 | *args,
82 | dtype=(tf.float32, tf.float32))
83 |
84 | return qr
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_template.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import pytest
2 | import numpy as np
3 |
4 | from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
5 | from sklearn.utils.testing import assert_array_equal
6 | from sklearn.utils.testing import assert_allclose
7 |
8 | from geomstats.learning._template import TemplateEstimator
9 | from geomstats.learning._template import TemplateTransformer
10 | from geomstats.learning._template import TemplateClassifier
11 |
12 |
13 | @pytest.fixture
14 | def data():
15 | return load_iris(return_X_y=True)
16 |
17 |
18 | def test_template_estimator(data):
19 | est = TemplateEstimator()
20 | assert est.demo_param == 'demo_param'
21 |
22 | est.fit(*data)
23 | assert hasattr(est, 'is_fitted_')
24 |
25 | X = data[0]
26 | y_pred = est.predict(X)
27 | assert_array_equal(y_pred, np.ones(X.shape[0], dtype=np.int64))
28 |
29 |
30 | def test_template_transformer_error(data):
31 | X, y = data
32 | trans = TemplateTransformer()
33 | trans.fit(X)
34 | with pytest.raises(ValueError, match="Shape of input is different"):
35 | X_diff_size = np.ones((10, X.shape[1] + 1))
36 | trans.transform(X_diff_size)
37 |
38 |
39 | def test_template_transformer(data):
40 | X, y = data
41 | trans = TemplateTransformer()
42 | assert trans.demo_param == 'demo'
43 |
44 | trans.fit(X)
45 | assert trans.n_features_ == X.shape[1]
46 |
47 | X_trans = trans.transform(X)
48 | assert_allclose(X_trans, np.sqrt(X))
49 |
50 | X_trans = trans.fit_transform(X)
51 | assert_allclose(X_trans, np.sqrt(X))
52 |
53 |
54 | def test_template_classifier(data):
55 | X, y = data
56 | clf = TemplateClassifier()
57 | assert clf.demo_param == 'demo'
58 |
59 | clf.fit(X, y)
60 | assert hasattr(clf, 'classes_')
61 | assert hasattr(clf, 'X_')
62 | assert hasattr(clf, 'y_')
63 |
64 | y_pred = clf.predict(X)
65 | assert y_pred.shape == (X.shape[0],)
66 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_connection.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for the affine connections.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 | import geomstats.tests
7 |
8 | from geomstats.connection import LeviCivitaConnection
9 | from geomstats.euclidean_space import EuclideanMetric
10 |
11 |
12 | class TestConnectionMethods(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
13 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
14 |
15 | def setUp(self):
16 | self.dimension = 4
17 | self.metric = EuclideanMetric(dimension=self.dimension)
18 | self.connection = LeviCivitaConnection(self.metric)
19 |
20 | def test_metric_matrix(self):
21 | base_point = gs.array([0., 1., 0., 0.])
22 |
23 | result = self.connection.metric_matrix(base_point)
24 | expected = gs.array([gs.eye(self.dimension)])
25 |
26 | with self.session():
27 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
28 |
29 | def test_cometric_matrix(self):
30 | base_point = gs.array([0., 1., 0., 0.])
31 |
32 | result = self.connection.cometric_matrix(base_point)
33 | expected = gs.array([gs.eye(self.dimension)])
34 |
35 | with self.session():
36 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
37 |
38 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
39 | def test_metric_derivative(self):
40 | base_point = gs.array([0., 1., 0., 0.])
41 |
42 | result = self.connection.metric_derivative(base_point)
43 | expected = gs.zeros((1,) + (self.dimension, ) * 3)
44 |
45 | gs.testing.assert_allclose(result, expected)
46 |
47 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
48 | def test_christoffel_symbols(self):
49 | base_point = gs.array([0., 1., 0., 0.])
50 |
51 | result = self.connection.christoffel_symbols(base_point)
52 | expected = gs.zeros((1,) + (self.dimension, ) * 3)
53 |
54 | gs.testing.assert_allclose(result, expected)
55 |
56 |
57 | if __name__ == '__main__':
58 | geomstats.tests.main()
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Geomstats
2 | [](https://travis-ci.org/geomstats/geomstats)[](https://codecov.io/gh/geomstats/geomstats)[](https://codecov.io/gh/geomstats/geomstats)[](https://codecov.io/gh/geomstats/geomstats) (Coverages for: numpy, tensorflow, pytorch)
3 |
4 |
5 | Computations and statistics on manifolds with geometric structures.
6 |
7 | - To get started with ```geomstats```, see the [examples directory](https://github.com/geomstats/geomstats/examples).
8 | - For more in-depth applications of ``geomstats``, see the [applications repository](https://github.com/geomstats/applications/).
9 | - The documentation of ```geomstats``` can be found on the [documentation website](https://geomstats.github.io/).
10 | - If you use ``geomstats``, please kindly cite our [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1805.08308).
11 |
12 | 
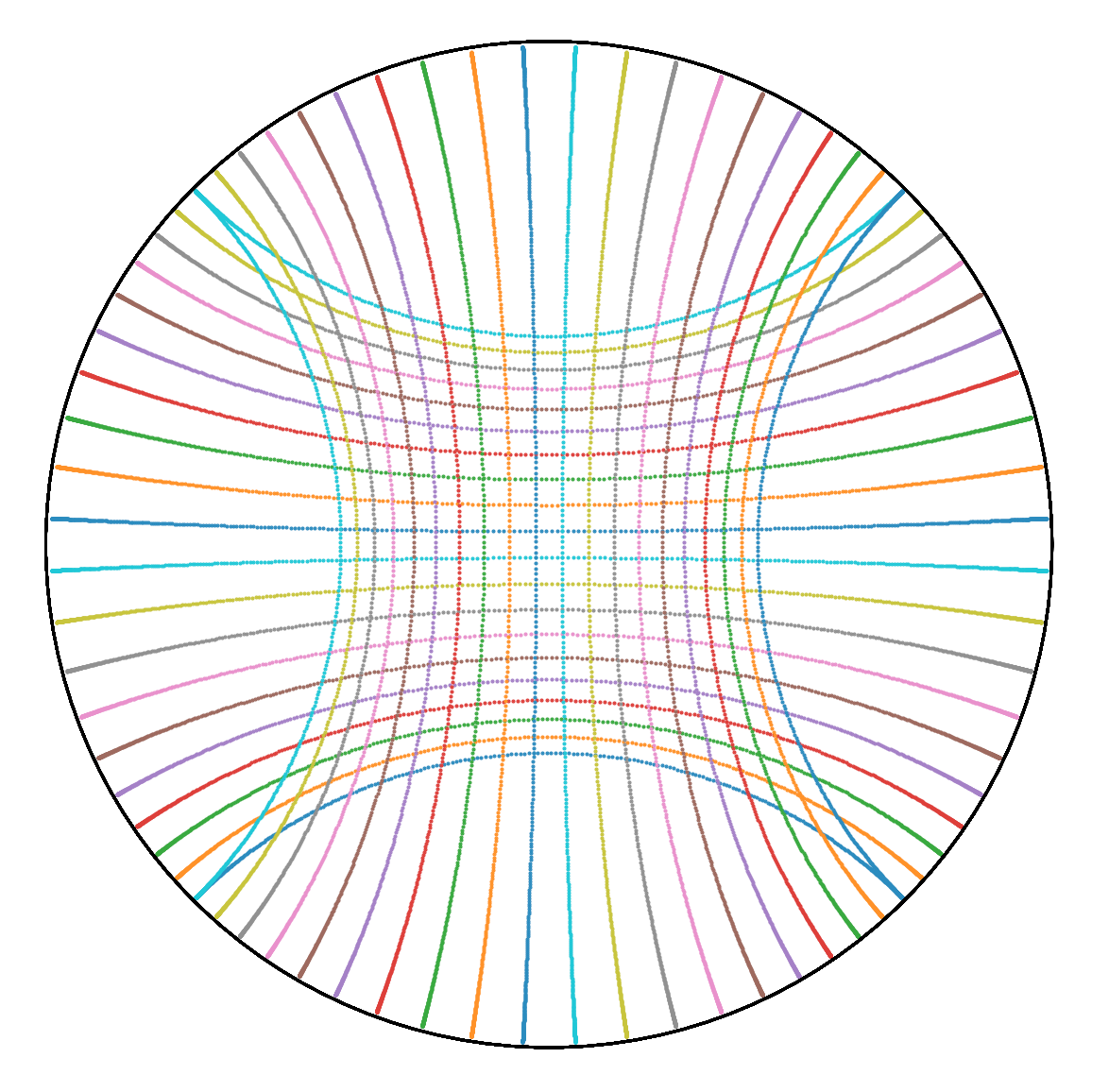 13 |
14 |
15 | ## Installation
16 |
17 | OS X & Linux:
18 |
19 | ```
20 | pip3 install geomstats
21 | ```
22 |
23 | ## Running tests
24 |
25 | ```
26 | pip3 install nose2
27 | nose2
28 | ```
29 |
30 | ## Getting started
31 |
32 | Define your backend by setting the environment variable ```GEOMSTATS_BACKEND``` to ```numpy```, ```tensorflow```, or ```pytorch```:
33 |
34 | ```
35 | export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND=numpy
36 | ```
37 |
38 | Then, run example scripts:
39 |
40 | ```
41 | python3 examples/plot_grid_h2.py
42 | ```
43 |
44 | ## Contributing
45 |
46 | See our [CONTRIBUTING.md][link_contributing] file!
47 |
48 | ## Authors & Contributors
49 |
50 | * Alice Le Brigant
51 | * Claire Donnat
52 | * Oleg Kachan
53 | * Benjamin Hou
54 | * Johan Mathe
55 | * Nina Miolane
56 | * Xavier Pennec
57 |
58 | ## Acknowledgements
59 |
60 | This work is partially supported by the National Science Foundation, grant NSF DMS RTG 1501767.
61 |
62 | [link_contributing]: https://github.com/geomstats/geomstats/CONTRIBUTING.md
63 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_visualization.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for visualization.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import matplotlib
6 | matplotlib.use('Agg') # NOQA
7 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
8 |
9 | import geomstats.tests
10 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
11 |
12 | from geomstats.hyperbolic_space import HyperbolicSpace
13 | from geomstats.hypersphere import Hypersphere
14 | from geomstats.special_euclidean_group import SpecialEuclideanGroup
15 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
16 |
17 |
18 | class TestVisualizationMethods(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
19 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
20 |
21 | def setUp(self):
22 | self.n_samples = 10
23 | self.SO3_GROUP = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=3)
24 | self.SE3_GROUP = SpecialEuclideanGroup(n=3)
25 | self.S1 = Hypersphere(dimension=1)
26 | self.S2 = Hypersphere(dimension=2)
27 | self.H2 = HyperbolicSpace(dimension=2)
28 |
29 | plt.figure()
30 |
31 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
32 | def test_plot_points_so3(self):
33 | points = self.SO3_GROUP.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
34 | visualization.plot(points, space='SO3_GROUP')
35 |
36 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
37 | def test_plot_points_se3(self):
38 | points = self.SE3_GROUP.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
39 | visualization.plot(points, space='SE3_GROUP')
40 |
41 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
42 | def test_plot_points_s1(self):
43 | points = self.S1.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
44 | visualization.plot(points, space='S1')
45 |
46 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
47 | def test_plot_points_s2(self):
48 | points = self.S2.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
49 | visualization.plot(points, space='S2')
50 |
51 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
52 | def test_plot_points_h2_poincare_disk(self):
53 | points = self.H2.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
54 | visualization.plot(points, space='H2_poincare_disk')
55 |
56 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
57 | def test_plot_points_h2_poincare_half_plane(self):
58 | points = self.H2.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
59 | visualization.plot(points, space='H2_poincare_half_plane')
60 |
61 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
62 | def test_plot_points_h2_klein_disk(self):
63 | points = self.H2.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
64 | visualization.plot(points, space='H2_klein_disk')
65 |
66 |
67 | if __name__ == '__main__':
68 | geomstats.tests.main()
69 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/tests.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Testing class for geomstats.
3 |
4 | This class abstracts the backend type.
5 | """
6 |
7 | import os
8 | import tensorflow as tf
9 | import unittest
10 |
11 | import geomstats.backend as gs
12 |
13 |
14 | def pytorch_backend():
15 | return os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'pytorch'
16 |
17 |
18 | def tf_backend():
19 | return os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow'
20 |
21 |
22 | def np_backend():
23 | return os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'numpy'
24 |
25 |
26 | test_class = unittest.TestCase
27 | if tf_backend():
28 | test_class = tf.test.TestCase
29 |
30 |
31 | def np_only(test_item):
32 | """Decorator to filter tests for numpy only."""
33 | if not np_backend():
34 | test_item.__unittest_skip__ = True
35 | test_item.__unittest_skip_why__ = (
36 | 'Test for numpy backend only.')
37 | return test_item
38 |
39 |
40 | def np_and_tf_only(test_item):
41 | """Decorator to filter tests for numpy and tensorflow only."""
42 | if not (np_backend() or tf_backend()):
43 | test_item.__unittest_skip__ = True
44 | test_item.__unittest_skip_why__ = (
45 | 'Test for numpy and tensorflow backends only.')
46 | return test_item
47 |
48 |
49 | def np_and_pytorch_only(test_item):
50 | """Decorator to filter tests for numpy and pytorch only."""
51 | if not (np_backend() or pytorch_backend()):
52 | test_item.__unittest_skip__ = True
53 | test_item.__unittest_skip_why__ = (
54 | 'Test for numpy and pytorch backends only.')
55 | return test_item
56 |
57 |
58 | class DummySession():
59 | def __enter__(self):
60 | pass
61 |
62 | def __exit__(self, a, b, c):
63 | pass
64 |
65 |
66 | class TestCase(test_class):
67 |
68 | def assertAllClose(self, a, b, rtol=1e-6, atol=1e-6):
69 | if tf_backend():
70 | return super().assertAllClose(a, b, rtol=rtol, atol=atol)
71 | return self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(a, b, rtol=rtol, atol=atol))
72 |
73 | def session(self):
74 | if tf_backend():
75 | return super().test_session()
76 | return DummySession()
77 |
78 | def assertShapeEqual(self, a, b):
79 | if tf_backend():
80 | return super().assertShapeEqual(a, b)
81 | super().assertEqual(a.shape, b.shape)
82 |
83 | @classmethod
84 | def setUpClass(cls):
85 | if tf_backend():
86 | os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
87 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/plot_geodesics_h2.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Plot a geodesic on the Hyperbolic space H2,
3 | with Poincare Disk visualization.
4 | """
5 |
6 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
7 | import numpy as np
8 | import os
9 |
10 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
11 |
12 | from geomstats.hyperbolic_space import HyperbolicSpace
13 |
14 | H2 = HyperbolicSpace(dimension=2)
15 | METRIC = H2.metric
16 |
17 |
18 | def plot_geodesic_between_two_points(initial_point,
19 | end_point,
20 | n_steps=10,
21 | ax=None):
22 | assert H2.belongs(initial_point)
23 | assert H2.belongs(end_point)
24 |
25 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=initial_point,
26 | end_point=end_point)
27 |
28 | t = np.linspace(0, 1, n_steps)
29 | points = geodesic(t)
30 | visualization.plot(points, ax=ax, space='H2_poincare_disk')
31 |
32 |
33 | def plot_geodesic_with_initial_tangent_vector(initial_point,
34 | initial_tangent_vec,
35 | n_steps=10,
36 | ax=None):
37 | assert H2.belongs(initial_point)
38 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=initial_point,
39 | initial_tangent_vec=initial_tangent_vec)
40 | n_steps = 10
41 | t = np.linspace(0, 1, n_steps)
42 |
43 | points = geodesic(t)
44 | visualization.plot(points, ax=ax, space='H2_poincare_disk')
45 |
46 |
47 | def main():
48 | initial_point = [np.sqrt(2), 1., 0.]
49 | end_point = H2.intrinsic_to_extrinsic_coords([1.5, 1.5])
50 | initial_tangent_vec = H2.projection_to_tangent_space(
51 | vector=[3.5, 0.6, 0.8],
52 | base_point=initial_point)
53 |
54 | ax = plt.gca()
55 | plot_geodesic_between_two_points(initial_point,
56 | end_point,
57 | ax=ax)
58 | plot_geodesic_with_initial_tangent_vector(initial_point,
59 | initial_tangent_vec,
60 | ax=ax)
61 | plt.show()
62 |
63 |
64 | if __name__ == "__main__":
65 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
66 | print('Examples with visualizations are only implemented '
67 | 'with numpy backend.\n'
68 | 'To change backend, write: '
69 | 'export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND = \'numpy\'.')
70 | else:
71 | main()
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/helper.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Helper functions for unit tests.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 |
7 |
8 | def to_scalar(expected):
9 | expected = gs.to_ndarray(expected, to_ndim=1)
10 | expected = gs.to_ndarray(expected, to_ndim=2, axis=-1)
11 | return expected
12 |
13 |
14 | def to_vector(expected):
15 | expected = gs.to_ndarray(expected, to_ndim=2)
16 | return expected
17 |
18 |
19 | def to_matrix(expected):
20 | expected = gs.to_ndarray(expected, to_ndim=3)
21 | return expected
22 |
23 |
24 | def left_log_then_exp_from_identity(metric, point):
25 | aux = metric.left_log_from_identity(point=point)
26 | result = metric.left_exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=aux)
27 | return result
28 |
29 |
30 | def left_exp_then_log_from_identity(metric, tangent_vec):
31 | aux = metric.left_exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=tangent_vec)
32 | result = metric.left_log_from_identity(point=aux)
33 | return result
34 |
35 |
36 | def log_then_exp_from_identity(metric, point):
37 | aux = metric.log_from_identity(point=point)
38 | result = metric.exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=aux)
39 | return result
40 |
41 |
42 | def exp_then_log_from_identity(metric, tangent_vec):
43 | aux = metric.exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=tangent_vec)
44 | result = metric.log_from_identity(point=aux)
45 | return result
46 |
47 |
48 | def log_then_exp(metric, point, base_point):
49 | aux = metric.log(point=point,
50 | base_point=base_point)
51 | result = metric.exp(tangent_vec=aux,
52 | base_point=base_point)
53 | return result
54 |
55 |
56 | def exp_then_log(metric, tangent_vec, base_point):
57 | aux = metric.exp(tangent_vec=tangent_vec,
58 | base_point=base_point)
59 | result = metric.log(point=aux,
60 | base_point=base_point)
61 | return result
62 |
63 |
64 | def group_log_then_exp_from_identity(group, point):
65 | aux = group.group_log_from_identity(point=point)
66 | result = group.group_exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=aux)
67 | return result
68 |
69 |
70 | def group_exp_then_log_from_identity(group, tangent_vec):
71 | aux = group.group_exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=tangent_vec)
72 | result = group.group_log_from_identity(point=aux)
73 | return result
74 |
75 |
76 | def group_log_then_exp(group, point, base_point):
77 | aux = group.group_log(point=point,
78 | base_point=base_point)
79 | result = group.group_exp(tangent_vec=aux,
80 | base_point=base_point)
81 | return result
82 |
83 |
84 | def group_exp_then_log(group, tangent_vec, base_point):
85 | aux = group.group_exp(tangent_vec=tangent_vec,
86 | base_point=base_point)
87 | result = group.group_log(point=aux,
88 | base_point=base_point)
89 | return result
90 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/api-reference.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | *************
2 | API reference
3 | *************
4 |
5 | .. automodule:: geomstats
6 | :members:
7 |
8 | The "manifold" module
9 | ---------------------
10 |
11 | .. automodule:: geomstats.manifold
12 | :members:
13 |
14 | The "connection" module
15 | -----------------------
16 |
17 | .. automodule:: geomstats.connection
18 | :members:
19 |
20 | The "riemannian_metric" module
21 | ------------------------------
22 |
23 | .. automodule:: geomstats.riemannian_metric
24 | :members:
25 |
26 | Spaces of constant curvatures
27 | =============================
28 |
29 | The "embedded_manifold" module
30 | ------------------------------
31 |
32 | .. automodule:: geomstats.embedded_manifold
33 | :members:
34 |
35 | The "euclidean_space" module
36 | ----------------------------
37 |
38 | .. automodule:: geomstats.euclidean_space
39 | :members:
40 |
41 | The "minkowski_space" module
42 | ----------------------------
43 |
44 | .. automodule:: geomstats.minkowski_space
45 | :members:
46 |
47 | The "hypersphere" module
48 | ------------------------
49 |
50 | .. automodule:: geomstats.hypersphere
51 | :members:
52 |
53 | The "hyperbolic_space" module
54 | -----------------------------
55 |
56 | .. automodule:: geomstats.hyperbolic_space
57 | :members:
58 |
59 | Lie groups
60 | ==========
61 |
62 | The "lie_group" module
63 | ----------------------
64 |
65 | .. automodule:: geomstats.lie_group
66 | :members:
67 |
68 | The "matrices_space" module
69 | ---------------------------
70 |
71 | .. automodule:: geomstats.matrices_space
72 | :members:
73 |
74 | The "general_linear_group" module
75 | ---------------------------------
76 |
77 | .. automodule:: geomstats.general_linear_group
78 | :members:
79 |
80 | The "invariant_metric" module
81 | -----------------------------
82 |
83 | .. automodule:: geomstats.invariant_metric
84 | :members:
85 |
86 | The "special_euclidean_group" module
87 | ------------------------------------
88 |
89 | .. automodule:: geomstats.special_euclidean_group
90 | :members:
91 |
92 | The "special_orthogonal_group" module
93 | -------------------------------------
94 |
95 | .. automodule:: geomstats.special_orthogonal_group
96 | :members:
97 |
98 | More manifolds
99 | ==============
100 |
101 | The "discretized_curves_space" module
102 | -------------------------------------
103 |
104 | .. automodule:: geomstats.discretized_curves_space
105 | :members:
106 |
107 | The "spd_matrices_space" module
108 | -------------------------------
109 |
110 | .. automodule:: geomstats.spd_matrices_space
111 | :members:
112 |
113 | The "stiefel" module
114 | --------------------
115 |
116 | .. automodule:: geomstats.stiefel
117 | :members:
118 |
119 | Visualization implementations
120 | =============================
121 |
122 | .. automodule:: geomstats.visualization
123 | :members:
124 |
125 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_examples.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for the examples.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import matplotlib
6 | matplotlib.use('Agg') # NOQA
7 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
8 | import os
9 | import sys
10 | import warnings
11 |
12 | import examples.gradient_descent_s2 as gradient_descent_s2
13 | import examples.loss_and_gradient_se3 as loss_and_gradient_se3
14 | import examples.loss_and_gradient_so3 as loss_and_gradient_so3
15 | import examples.plot_geodesics_h2 as plot_geodesics_h2
16 | import examples.plot_geodesics_s2 as plot_geodesics_s2
17 | import examples.plot_geodesics_se3 as plot_geodesics_se3
18 | import examples.plot_geodesics_so3 as plot_geodesics_so3
19 | import examples.plot_grid_h2 as plot_grid_h2
20 | import examples.plot_square_h2_poincare_disk as plot_square_h2_poincare_disk
21 | import examples.plot_square_h2_poincare_half_plane as plot_square_h2_poincare_half_plane # NOQA
22 | import examples.plot_square_h2_klein_disk as plot_square_h2_klein_disk
23 | import examples.plot_quantization_s1 as plot_quantization_s1
24 | import examples.plot_quantization_s2 as plot_quantization_s2
25 | import examples.tangent_pca_so3 as tangent_pca_so3
26 | import geomstats.tests
27 |
28 |
29 | class TestExamples(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
30 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
31 |
32 | @classmethod
33 | def setUpClass(cls):
34 | sys.stdout = open(os.devnull, 'w')
35 |
36 | def setUp(self):
37 | warnings.simplefilter('ignore', category=ImportWarning)
38 | plt.figure()
39 |
40 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
41 | def test_gradient_descent_s2(self):
42 | gradient_descent_s2.main(max_iter=32, output_file=None)
43 |
44 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
45 | def test_loss_and_gradient_so3(self):
46 | loss_and_gradient_so3.main()
47 |
48 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
49 | def test_loss_and_gradient_se3(self):
50 | loss_and_gradient_se3.main()
51 |
52 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
53 | def test_plot_geodesics_h2(self):
54 | plot_geodesics_h2.main()
55 |
56 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
57 | def test_plot_geodesics_s2(self):
58 | plot_geodesics_s2.main()
59 |
60 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
61 | def test_plot_geodesics_se3(self):
62 | plot_geodesics_se3.main()
63 |
64 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
65 | def test_plot_geodesics_so3(self):
66 | plot_geodesics_so3.main()
67 |
68 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
69 | def test_plot_grid_h2(self):
70 | plot_grid_h2.main()
71 |
72 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
73 | def test_plot_square_h2_square_poincare_disk(self):
74 | plot_square_h2_poincare_disk.main()
75 |
76 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
77 | def test_plot_square_h2_square_poincare_half_plane(self):
78 | plot_square_h2_poincare_half_plane.main()
79 |
80 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
81 | def test_plot_square_h2_square_klein_disk(self):
82 | plot_square_h2_klein_disk.main()
83 |
84 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
85 | def test_tangent_pca_so3(self):
86 | tangent_pca_so3.main()
87 |
88 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
89 | def test_plot_quantization_s1(self):
90 | plot_quantization_s1.main()
91 |
92 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
93 | def test_plot_quantization_s2(self):
94 | plot_quantization_s2.main()
95 |
96 |
97 | if __name__ == '__main__':
98 | geomstats.tests.main()
99 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/matrices_space.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | The space of matrices (m, n), which is the Euclidean space R^{mn}.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 |
7 | from geomstats.euclidean_space import EuclideanSpace
8 | from geomstats.riemannian_metric import RiemannianMetric
9 |
10 |
11 | TOLERANCE = 1e-5
12 |
13 |
14 | class MatricesSpace(EuclideanSpace):
15 | """Class for the space of matrices (m, n)."""
16 |
17 | def __init__(self, m, n):
18 | assert isinstance(m, int) and isinstance(n, int) and m > 0 and n > 0
19 | super(MatricesSpace, self).__init__(dimension=m*n)
20 | self.m = m
21 | self.n = n
22 | self.default_point_type = 'matrix'
23 | self.metric = MatricesMetric(m, n)
24 |
25 | def belongs(self, point):
26 | """
27 | Check if point belongs to the Matrix space.
28 | """
29 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=3)
30 | _, mat_dim_1, mat_dim_2 = point.shape
31 | return mat_dim_1 == self.m & mat_dim_2 == self.n
32 |
33 | @staticmethod
34 | def vector_from_matrix(matrix):
35 | """
36 | Conversion function from (_, m, n) to (_, mn).
37 | """
38 | matrix = gs.to_ndarray(matrix, to_ndim=3)
39 | n_mats, m, n = matrix.shape
40 | return gs.reshape(matrix, (n_mats, m*n))
41 |
42 | @staticmethod
43 | def is_symmetric(matrix, tolerance=TOLERANCE):
44 | """Check if a matrix is symmetric."""
45 | matrix = gs.to_ndarray(matrix, to_ndim=3)
46 | n_mats, m, n = matrix.shape
47 | assert m == n
48 | matrix_transpose = gs.transpose(matrix, axes=(0, 2, 1))
49 |
50 | mask = gs.isclose(matrix, matrix_transpose, atol=tolerance)
51 | mask = gs.all(mask, axis=(1, 2))
52 |
53 | mask = gs.to_ndarray(mask, to_ndim=1)
54 | mask = gs.to_ndarray(mask, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
55 | return mask
56 |
57 | @staticmethod
58 | def make_symmetric(matrix):
59 | """Make a matrix fully symmetric to avoid numerical issues."""
60 | matrix = gs.to_ndarray(matrix, to_ndim=3)
61 | n_mats, m, n = matrix.shape
62 | assert m == n
63 | matrix = gs.to_ndarray(matrix, to_ndim=3)
64 | return (matrix + gs.transpose(matrix, axes=(0, 2, 1))) / 2
65 |
66 | def random_uniform(self, n_samples=1):
67 | point = gs.random.rand(n_samples, self.m, self.n)
68 | return point
69 |
70 |
71 | class MatricesMetric(RiemannianMetric):
72 | """
73 | Euclidean metric on matrices given by the Frobenius inner product.
74 | """
75 | def __init__(self, m, n):
76 | dimension = m*n
77 | super(MatricesMetric, self).__init__(
78 | dimension=dimension,
79 | signature=(dimension, 0, 0))
80 |
81 | def inner_product(self, tangent_vec_a, tangent_vec_b, base_point=None):
82 | """
83 | Compute the Frobenius inner product of tangent_vec_a and tangent_vec_b
84 | at base_point.
85 | """
86 | tangent_vec_a = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec_a, to_ndim=3)
87 | n_tangent_vecs_a, _, _ = tangent_vec_a.shape
88 |
89 | tangent_vec_b = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec_b, to_ndim=3)
90 | n_tangent_vecs_b, _, _ = tangent_vec_b.shape
91 |
92 | assert n_tangent_vecs_a == n_tangent_vecs_b
93 |
94 | inner_prod = gs.einsum("nij,nij->n", tangent_vec_a, tangent_vec_b)
95 | inner_prod = gs.to_ndarray(inner_prod, to_ndim=1)
96 | inner_prod = gs.to_ndarray(inner_prod, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
97 | return inner_prod
98 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_matrices_space.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for the manifold of matrices.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 | import geomstats.tests
7 | import tests.helper as helper
8 |
9 | from geomstats.matrices_space import MatricesSpace
10 |
11 |
12 | class TestMatricesSpaceMethods(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
13 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
14 |
15 | def setUp(self):
16 | gs.random.seed(1234)
17 |
18 | self.n = 3
19 | self.space = MatricesSpace(m=self.n, n=self.n)
20 | self.metric = self.space.metric
21 | self.n_samples = 2
22 |
23 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
24 | def test_is_symmetric(self):
25 | sym_mat = gs.array([[1., 2.],
26 | [2., 1.]])
27 | result = self.space.is_symmetric(sym_mat)
28 | expected = gs.array([True])
29 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
30 |
31 | not_a_sym_mat = gs.array([[1., 0.6, -3.],
32 | [6., -7., 0.],
33 | [0., 7., 8.]])
34 | result = self.space.is_symmetric(not_a_sym_mat)
35 | expected = gs.array([False])
36 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
37 |
38 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
39 | def test_is_symmetric_vectorization(self):
40 | points = gs.array([
41 | [[1., 2.],
42 | [2., 1.]],
43 | [[3., 4.],
44 | [4., 5.]]])
45 | result = gs.all(self.space.is_symmetric(points))
46 | expected = True
47 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
48 |
49 | def test_make_symmetric(self):
50 | sym_mat = gs.array([[1., 2.],
51 | [2., 1.]])
52 | result = self.space.make_symmetric(sym_mat)
53 | expected = helper.to_matrix(sym_mat)
54 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
55 |
56 | mat = gs.array([[1., 2., 3.],
57 | [0., 0., 0.],
58 | [3., 1., 1.]])
59 | result = self.space.make_symmetric(mat)
60 | expected = gs.array([[[1., 1., 3.],
61 | [1., 0., 0.5],
62 | [3., 0.5, 1.]]])
63 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
64 |
65 | mat = gs.array([[[1e100, 1e-100, 1e100],
66 | [1e100, 1e-100, 1e100],
67 | [1e-100, 1e-100, 1e100]]])
68 | result = self.space.make_symmetric(mat)
69 |
70 | res = 0.5 * (1e100 + 1e-100)
71 |
72 | expected = gs.array([[[1e100, res, res],
73 | [res, 1e-100, res],
74 | [res, res, 1e100]]])
75 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
76 |
77 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
78 | def test_make_symmetric_and_is_symmetric_vectorization(self):
79 | points = gs.array([
80 | [[1., 2.],
81 | [3., 4.]],
82 | [[5., 6.],
83 | [4., 9.]]])
84 |
85 | sym_points = self.space.make_symmetric(points)
86 | result = gs.all(self.space.is_symmetric(sym_points))
87 | expected = True
88 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
89 |
90 | def test_inner_product(self):
91 | base_point = gs.array([
92 | [1., 2., 3.],
93 | [0., 0., 0.],
94 | [3., 1., 1.]])
95 |
96 | tangent_vector_1 = gs.array([
97 | [1., 2., 3.],
98 | [0., -10., 0.],
99 | [30., 1., 1.]])
100 |
101 | tangent_vector_2 = gs.array([
102 | [1., 4., 3.],
103 | [5., 0., 0.],
104 | [3., 1., 1.]])
105 |
106 | result = self.metric.inner_product(
107 | tangent_vector_1,
108 | tangent_vector_2,
109 | base_point=base_point)
110 |
111 | expected = gs.trace(
112 | gs.matmul(
113 | gs.transpose(tangent_vector_1),
114 | tangent_vector_2))
115 | expected = helper.to_scalar(expected)
116 |
117 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
118 |
119 |
120 | if __name__ == '__main__':
121 | geomstats.tests.main()
122 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/euclidean_space.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Euclidean space.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 |
7 | from geomstats.manifold import Manifold
8 | from geomstats.riemannian_metric import RiemannianMetric
9 |
10 |
11 | class EuclideanSpace(Manifold):
12 | """
13 | Class for Euclidean spaces.
14 |
15 | By definition, a Euclidean space is a vector space of a given
16 | dimension, equipped with a Euclidean metric.
17 | """
18 |
19 | def __init__(self, dimension):
20 | assert isinstance(dimension, int) and dimension > 0
21 | self.dimension = dimension
22 | self.metric = EuclideanMetric(dimension)
23 |
24 | def belongs(self, point):
25 | """
26 | Evaluate if a point belongs to the Euclidean space.
27 |
28 | Parameters
29 | ----------
30 | point : array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
31 | Input points.
32 |
33 | Returns
34 | -------
35 | belongs : array-like, shape=[n_samples, 1]
36 | """
37 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=2)
38 | n_points, point_dim = point.shape
39 | belongs = point_dim == self.dimension
40 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=1)
41 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
42 | belongs = gs.tile(belongs, (n_points, 1))
43 |
44 | return belongs
45 |
46 | def random_uniform(self, n_samples=1, bound=1.):
47 | """
48 | Sample in the Euclidean space with the uniform distribution.
49 | """
50 | size = (n_samples, self.dimension)
51 | point = bound * (gs.random.rand(*size) - 0.5) * 2
52 |
53 | return point
54 |
55 |
56 | class EuclideanMetric(RiemannianMetric):
57 | """
58 | Class for Euclidean metrics.
59 |
60 | As a Riemannian metric, the Euclidean metric is:
61 | - flat: the inner product is independent of the base point.
62 | - positive definite: it has signature (0, dimension),
63 | where dimension is the dimension of the Euclidean space.
64 | """
65 | def __init__(self, dimension):
66 | assert isinstance(dimension, int) and dimension > 0
67 | super(EuclideanMetric, self).__init__(
68 | dimension=dimension,
69 | signature=(dimension, 0, 0))
70 |
71 | def inner_product_matrix(self, base_point=None):
72 | """
73 | Inner product matrix, independent of the base point.
74 | """
75 | mat = gs.eye(self.dimension)
76 | mat = gs.to_ndarray(mat, to_ndim=3)
77 | return mat
78 |
79 | def exp(self, tangent_vec, base_point):
80 | """
81 | The Riemannian exponential is the addition in the Euclidean space.
82 | """
83 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=2)
84 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=2)
85 | exp = base_point + tangent_vec
86 | return exp
87 |
88 | def log(self, point, base_point):
89 | """
90 | The Riemannian logarithm is the subtraction in the Euclidean space.
91 | """
92 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=2)
93 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=2)
94 | log = point - base_point
95 | return log
96 |
97 | def mean(self, points, weights=None):
98 | """
99 | The Frechet mean of (weighted) points computed with the
100 | Euclidean metric is the weighted average of the points
101 | in the Euclidean space.
102 | """
103 | if isinstance(points, list):
104 | points = gs.vstack(points)
105 | points = gs.to_ndarray(points, to_ndim=2)
106 | n_points = gs.shape(points)[0]
107 |
108 | if isinstance(weights, list):
109 | weights = gs.vstack(weights)
110 | elif weights is None:
111 | weights = gs.ones((n_points,))
112 |
113 | weighted_points = gs.einsum('n,nj->nj', weights, points)
114 | mean = (gs.sum(weighted_points, axis=0)
115 | / gs.sum(weights))
116 | mean = gs.to_ndarray(mean, to_ndim=2)
117 | return mean
118 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_backend_numpy.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for numpy backend.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import importlib
6 | import os
7 | import unittest
8 | import warnings
9 |
10 | import geomstats.backend as gs
11 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
12 |
13 |
14 | class TestBackendNumpy(unittest.TestCase):
15 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
16 |
17 | @classmethod
18 | def setUpClass(cls):
19 | cls.initial_backend = os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND']
20 | os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] = 'numpy'
21 | importlib.reload(gs)
22 |
23 | @classmethod
24 | def tearDownClass(cls):
25 | os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] = cls.initial_backend
26 | importlib.reload(gs)
27 |
28 | def setUp(self):
29 | warnings.simplefilter('ignore', category=ImportWarning)
30 |
31 | self.so3_group = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=3)
32 | self.n_samples = 2
33 |
34 | def test_logm(self):
35 | point = gs.array([[2., 0., 0.],
36 | [0., 3., 0.],
37 | [0., 0., 4.]])
38 | result = gs.linalg.logm(point)
39 | expected = gs.array([[0.693147180, 0., 0.],
40 | [0., 1.098612288, 0.],
41 | [0., 0., 1.38629436]])
42 |
43 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
44 |
45 | def test_expm_and_logm(self):
46 | point = gs.array([[2., 0., 0.],
47 | [0., 3., 0.],
48 | [0., 0., 4.]])
49 | result = gs.linalg.expm(gs.linalg.logm(point))
50 | expected = point
51 |
52 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
53 |
54 | def test_expm_vectorization(self):
55 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
56 | [0., 3., 0.],
57 | [0., 0., 4.]],
58 | [[1., 0., 0.],
59 | [0., 5., 0.],
60 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
61 |
62 | expected = gs.array([[[7.38905609, 0., 0.],
63 | [0., 20.0855369, 0.],
64 | [0., 0., 54.5981500]],
65 | [[2.718281828, 0., 0.],
66 | [0., 148.413159, 0.],
67 | [0., 0., 403.42879349]]])
68 |
69 | result = gs.linalg.expm(point)
70 |
71 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
72 |
73 | def test_logm_vectorization_diagonal(self):
74 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
75 | [0., 3., 0.],
76 | [0., 0., 4.]],
77 | [[1., 0., 0.],
78 | [0., 5., 0.],
79 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
80 |
81 | expected = gs.array([[[0.693147180, 0., 0.],
82 | [0., 1.09861228866, 0.],
83 | [0., 0., 1.38629436]],
84 | [[0., 0., 0.],
85 | [0., 1.609437912, 0.],
86 | [0., 0., 1.79175946]]])
87 |
88 | result = gs.linalg.logm(point)
89 |
90 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
91 |
92 | def test_expm_and_logm_vectorization_random_rotation(self):
93 | point = self.so3_group.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
94 | point = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(point)
95 |
96 | result = gs.linalg.expm(gs.linalg.logm(point))
97 | expected = point
98 |
99 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
100 |
101 | def test_expm_and_logm_vectorization(self):
102 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
103 | [0., 3., 0.],
104 | [0., 0., 4.]],
105 | [[1., 0., 0.],
106 | [0., 5., 0.],
107 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
108 | result = gs.linalg.expm(gs.linalg.logm(point))
109 | expected = point
110 |
111 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
112 |
113 |
114 | if __name__ == '__main__':
115 | unittest.main()
116 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/general_linear_group.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | The General Linear Group, i.e. the matrix group GL(n).
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 |
7 | from geomstats.lie_group import LieGroup
8 | from geomstats.matrices_space import MatricesSpace
9 |
10 |
11 | class GeneralLinearGroup(LieGroup, MatricesSpace):
12 | """
13 | Class for the General Linear Group, i.e. the matrix group GL(n).
14 |
15 |
16 | Note: The default representation for elements of GL(n)
17 | are matrices.
18 | For now, SO(n) and SE(n) elements are represented
19 | by a vector by default.
20 | """
21 |
22 | def __init__(self, n):
23 | assert isinstance(n, int) and n > 0
24 | LieGroup.__init__(self, dimension=n*n)
25 | MatricesSpace.__init__(self, m=n, n=n)
26 |
27 | def get_identity(self, point_type=None):
28 | if point_type is None:
29 | point_type = self.default_point_type
30 | if point_type == 'matrix':
31 | return gs.eye(self.n)
32 | else:
33 | raise NotImplementedError(
34 | 'The identity of the general linear group is not'
35 | ' implemented for a point_type that is not \'matrix\'.')
36 | identity = property(get_identity)
37 |
38 | def belongs(self, mat):
39 | """
40 | Check if mat belongs to GL(n).
41 | """
42 | mat = gs.to_ndarray(mat, to_ndim=3)
43 |
44 | det = gs.linalg.det(mat)
45 | belongs = ~gs.isclose(det, 0.)
46 |
47 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=1)
48 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
49 |
50 | return belongs
51 |
52 | def compose(self, mat_a, mat_b):
53 | """
54 | Matrix composition.
55 | """
56 | mat_a = gs.to_ndarray(mat_a, to_ndim=3)
57 | mat_b = gs.to_ndarray(mat_b, to_ndim=3)
58 | composition = gs.einsum('nij,njk->nik', mat_a, mat_b)
59 | return composition
60 |
61 | def inverse(self, mat):
62 | """
63 | Matrix inverse.
64 | """
65 | mat = gs.to_ndarray(mat, to_ndim=3)
66 | return gs.linalg.inv(mat)
67 |
68 | def group_exp_from_identity(self, tangent_vec, point_type=None):
69 | """
70 | Group exponential of the Lie group of
71 | all invertible matrices at the identity.
72 | """
73 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=3)
74 | group_exp = gs.linalg.expm(tangent_vec)
75 |
76 | return gs.real(group_exp)
77 |
78 | def group_exp_not_from_identity(
79 | self, tangent_vec, base_point, point_type=None):
80 | """
81 | Group exponential of the Lie group of
82 | all invertible matrices.
83 | """
84 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=3)
85 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=3)
86 |
87 | tangent_vec_at_identity = self.compose(
88 | self.inverse(base_point), tangent_vec)
89 |
90 | group_exp_from_identity = self.group_exp_from_identity(
91 | tangent_vec_at_identity)
92 |
93 | group_exp = self.compose(
94 | base_point, group_exp_from_identity)
95 |
96 | return group_exp
97 |
98 | def group_log_from_identity(self, point, point_type=None):
99 | """
100 | Group logarithm of the Lie group of
101 | all invertible matrices at the identity.
102 | """
103 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=3)
104 | group_log = gs.linalg.logm(point)
105 |
106 | return gs.real(group_log)
107 |
108 | def group_log_not_from_identity(
109 | self, point, base_point, point_type=None):
110 | """
111 | Group logarithm of the Lie group of
112 | all invertible matrices.
113 | """
114 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=3)
115 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=3)
116 |
117 | point_near_identity = self.compose(
118 | self.inverse(base_point), point)
119 |
120 | group_log_from_identity = self.group_log_from_identity(
121 | point_near_identity)
122 |
123 | group_log = self.compose(
124 | base_point, group_log_from_identity)
125 |
126 | return group_log
127 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/loss_and_gradient_so3.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Predict on manifolds: losses.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import os
6 | import tensorflow as tf
7 |
8 | import geomstats.backend as gs
9 | import geomstats.lie_group as lie_group
10 |
11 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
12 |
13 |
14 | SO3 = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=3)
15 |
16 |
17 | def loss(y_pred, y_true,
18 | metric=SO3.bi_invariant_metric,
19 | representation='vector'):
20 |
21 | if representation == 'quaternion':
22 | y_pred = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_pred)
23 | y_true = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_true)
24 |
25 | loss = lie_group.loss(y_pred, y_true, SO3, metric)
26 | return loss
27 |
28 |
29 | def grad(y_pred, y_true,
30 | metric=SO3.bi_invariant_metric,
31 | representation='vector'):
32 |
33 | y_pred = gs.expand_dims(y_pred, axis=0)
34 | y_true = gs.expand_dims(y_true, axis=0)
35 |
36 | if representation == 'vector':
37 | grad = lie_group.grad(y_pred, y_true, SO3, metric)
38 |
39 | if representation == 'quaternion':
40 | quat_scalar = y_pred[:, :1]
41 | quat_vec = y_pred[:, 1:]
42 |
43 | quat_vec_norm = gs.linalg.norm(quat_vec, axis=1)
44 | quat_sq_norm = quat_vec_norm ** 2 + quat_scalar ** 2
45 |
46 | quat_arctan2 = gs.arctan2(quat_vec_norm, quat_scalar)
47 | differential_scalar = - 2 * quat_vec / (quat_sq_norm)
48 | differential_scalar = gs.to_ndarray(differential_scalar, to_ndim=2)
49 | differential_scalar = gs.transpose(differential_scalar)
50 |
51 | differential_vec = (2 * (quat_scalar / quat_sq_norm
52 | - 2 * quat_arctan2 / quat_vec_norm)
53 | * (gs.einsum('ni,nj->nij', quat_vec, quat_vec)
54 | / quat_vec_norm ** 2)
55 | + 2 * quat_arctan2 / quat_vec_norm * gs.eye(3))
56 | differential_vec = gs.squeeze(differential_vec)
57 |
58 | differential = gs.concatenate(
59 | [differential_scalar, differential_vec],
60 | axis=1)
61 |
62 | y_pred = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_pred)
63 | y_true = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_true)
64 |
65 | grad = lie_group.grad(y_pred, y_true, SO3, metric)
66 |
67 | grad = gs.matmul(grad, differential)
68 |
69 | grad = gs.squeeze(grad, axis=0)
70 | return grad
71 |
72 |
73 | def main():
74 | y_pred = gs.array([1., 1.5, -0.3])
75 | y_true = gs.array([0.1, 1.8, -0.1])
76 |
77 | loss_rot_vec = loss(y_pred, y_true)
78 | grad_rot_vec = grad(y_pred, y_true)
79 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
80 | with tf.Session() as sess:
81 | loss_rot_vec = sess.run(loss_rot_vec)
82 | grad_rot_vec = sess.run(grad_rot_vec)
83 | print('The loss between the rotation vectors is: {}'.format(
84 | loss_rot_vec[0, 0]))
85 | print('The riemannian gradient is: {}'.format(
86 | grad_rot_vec))
87 |
88 | angle = gs.pi / 6
89 | cos = gs.cos(angle / 2)
90 | sin = gs.sin(angle / 2)
91 | u = gs.array([1., 2., 3.])
92 | u = u / gs.linalg.norm(u)
93 | scalar = gs.to_ndarray(cos, to_ndim=1)
94 | vec = sin * u
95 | y_pred_quaternion = gs.concatenate([scalar, vec], axis=0)
96 |
97 | angle = gs.pi / 7
98 | cos = gs.cos(angle / 2)
99 | sin = gs.sin(angle / 2)
100 | u = gs.array([1., 2., 3.])
101 | u = u / gs.linalg.norm(u)
102 | scalar = gs.to_ndarray(cos, to_ndim=1)
103 | vec = sin * u
104 | y_true_quaternion = gs.concatenate([scalar, vec], axis=0)
105 |
106 | loss_quaternion = loss(y_pred_quaternion, y_true_quaternion,
107 | representation='quaternion')
108 | grad_quaternion = grad(y_pred_quaternion, y_true_quaternion,
109 | representation='quaternion')
110 |
111 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
112 | with tf.Session() as sess:
113 | loss_quaternion = sess.run(loss_quaternion)
114 | grad_quaternion = sess.run(grad_quaternion)
115 | print('The loss between the quaternions is: {}'.format(
116 | loss_quaternion[0, 0]))
117 | print('The riemannian gradient is: {}'.format(
118 | grad_quaternion))
119 |
120 |
121 | if __name__ == "__main__":
122 | main()
123 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/gradient_descent_s2.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Gradient descent on a sphere.
3 |
4 | We solve the following optimization problem:
5 |
6 | minimize: x^{T}Ax
7 | such than: x^{T}x = 1
8 |
9 | Using by operating a gradient descent of the quadratic form
10 | on the sphere. We solve this in 3 dimension on the 2-sphere
11 | manifold so that we can visualize and render the path as a video.
12 | """
13 |
14 | import matplotlib
15 | matplotlib.use("Agg") # NOQA
16 | import matplotlib.animation as animation
17 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
18 | import numpy as np
19 |
20 | import geomstats.backend as gs
21 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
22 |
23 | from geomstats.hypersphere import Hypersphere
24 | from geomstats.spd_matrices_space import SPDMatricesSpace
25 |
26 |
27 | SPHERE2 = Hypersphere(dimension=2)
28 | METRIC = SPHERE2.metric
29 |
30 |
31 | def gradient_descent(start,
32 | loss,
33 | grad,
34 | manifold,
35 | lr=0.01,
36 | max_iter=256,
37 | precision=1e-5):
38 | """Operate a gradient descent on a given manifold until either max_iter or
39 | a given precision is reached."""
40 | x = start
41 | for i in range(max_iter):
42 | x_prev = x
43 | euclidean_grad = - lr * grad(x)
44 | tangent_vec = manifold.projection_to_tangent_space(
45 | vector=euclidean_grad, base_point=x)
46 | x = manifold.metric.exp(base_point=x, tangent_vec=tangent_vec)[0]
47 | if (gs.abs(loss(x, use_gs=True) - loss(x_prev, use_gs=True))
48 | <= precision):
49 | print('x: %s' % x)
50 | print('reached precision %s' % precision)
51 | print('iterations: %d' % i)
52 | break
53 | yield x, loss(x)
54 |
55 |
56 | def plot_and_save_video(geodesics,
57 | loss,
58 | size=20,
59 | fps=10,
60 | dpi=100,
61 | out='out.mp4',
62 | color='red'):
63 | """Render a set of geodesics and save it to an mpeg 4 file."""
64 | FFMpegWriter = animation.writers['ffmpeg']
65 | writer = FFMpegWriter(fps=fps)
66 | fig = plt.figure(figsize=(size, size))
67 | ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d', aspect='equal')
68 | sphere = visualization.Sphere()
69 | sphere.plot_heatmap(ax, loss)
70 | points = gs.to_ndarray(geodesics[0], to_ndim=2)
71 | sphere.add_points(points)
72 | sphere.draw(ax, color=color, marker='.')
73 | with writer.saving(fig, out, dpi=dpi):
74 | for points in geodesics[1:]:
75 | points = gs.to_ndarray(points, to_ndim=2)
76 | sphere.draw_points(ax, points=points, color=color, marker='.')
77 | writer.grab_frame()
78 |
79 |
80 | def generate_well_behaved_matrix():
81 | """Generate a matrix with real eigenvalues."""
82 | matrix = 2 * SPDMatricesSpace(n=3).random_uniform()[0]
83 | assert np.linalg.det(matrix) > 0
84 | return matrix
85 |
86 |
87 | def main(output_file='out.mp4', max_iter=128):
88 | gs.random.seed(1985)
89 | A = generate_well_behaved_matrix()
90 |
91 | def grad(x):
92 | return 2 * gs.matmul(A, x)
93 |
94 | def loss(x, use_gs=False):
95 | if use_gs:
96 | return gs.matmul(x, gs.matmul(A, x))
97 | return np.matmul(x, np.matmul(A, x))
98 |
99 | initial_point = gs.array([0., 1., 0.])
100 | previous_x = initial_point
101 | geodesics = []
102 | n_steps = 20
103 | for x, fx in gradient_descent(initial_point,
104 | loss,
105 | grad,
106 | max_iter=max_iter,
107 | manifold=SPHERE2):
108 | initial_tangent_vec = METRIC.log(point=x, base_point=previous_x)
109 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=previous_x,
110 | initial_tangent_vec=initial_tangent_vec)
111 |
112 | t = np.linspace(0, 1, n_steps)
113 | geodesics.append(geodesic(t))
114 | previous_x = x
115 | if output_file:
116 | plot_and_save_video(geodesics, loss, out=output_file)
117 | eig, _ = np.linalg.eig(A)
118 | np.testing.assert_almost_equal(loss(x), np.min(eig), decimal=2)
119 |
120 |
121 | if __name__ == "__main__":
122 | main()
123 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/minkowski_space.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Minkowski space.
3 | """
4 |
5 |
6 | from geomstats.manifold import Manifold
7 | from geomstats.riemannian_metric import RiemannianMetric
8 | import geomstats.backend as gs
9 |
10 |
11 | class MinkowskiSpace(Manifold):
12 | """Class for Minkowski Space."""
13 |
14 | def __init__(self, dimension):
15 | assert isinstance(dimension, int) and dimension > 0
16 | self.dimension = dimension
17 | self.metric = MinkowskiMetric(dimension)
18 |
19 | def belongs(self, point):
20 | """
21 | Evaluate if a point belongs to the Minkowski space.
22 |
23 | Parameters
24 | ----------
25 | point : array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
26 | Input points.
27 |
28 | Returns
29 | -------
30 | belongs : array-like, shape=[n_samples, 1]
31 | """
32 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=2)
33 | n_points, point_dim = point.shape
34 | belongs = point_dim == self.dimension
35 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=1)
36 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
37 | belongs = gs.tile(belongs, (n_points, 1))
38 |
39 | return belongs
40 |
41 | def random_uniform(self, n_samples=1, bound=1.):
42 | """
43 | Sample in the Minkowski space with the uniform distribution.
44 |
45 | Returns
46 | -------
47 | points : array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
48 | Sampled points.
49 | """
50 | size = (n_samples, self.dimension)
51 | point = bound * gs.random.rand(*size) * 2 - 1
52 |
53 | return point
54 |
55 |
56 | class MinkowskiMetric(RiemannianMetric):
57 | """
58 | Class for the pseudo-Riemannian Minkowski metric.
59 | The metric is flat: the inner product is independent of the base point.
60 | """
61 | def __init__(self, dimension):
62 | super(MinkowskiMetric, self).__init__(
63 | dimension=dimension,
64 | signature=(dimension - 1, 1, 0))
65 |
66 | def inner_product_matrix(self, base_point=None):
67 | """
68 | Inner product matrix, independent of the base point.
69 |
70 | Parameters
71 | ----------
72 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
73 | """
74 | inner_prod_mat = gs.eye(self.dimension-1, self.dimension-1)
75 | first_row = gs.array([0.] * (self.dimension - 1))
76 | first_row = gs.to_ndarray(first_row, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
77 | inner_prod_mat = gs.vstack([gs.transpose(first_row),
78 | inner_prod_mat])
79 |
80 | first_column = gs.array([-1.] + [0.] * (self.dimension - 1))
81 | first_column = gs.to_ndarray(first_column, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
82 | inner_prod_mat = gs.hstack([first_column,
83 | inner_prod_mat])
84 |
85 | return inner_prod_mat
86 |
87 | def exp(self, tangent_vec, base_point):
88 | """
89 | The Riemannian exponential is the addition in the Minkowski space.
90 |
91 | Parameters
92 | ----------
93 | tangent_vec: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
94 | or shape=[1, dimension]
95 |
96 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
97 | or shape=[1, dimension]
98 | """
99 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=2)
100 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=2)
101 | return base_point + tangent_vec
102 |
103 | def log(self, point, base_point):
104 | """
105 | The Riemannian logarithm is the subtraction in the Minkowski space.
106 |
107 | Parameters
108 | ----------
109 | point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
110 | or shape=[1, dimension]
111 |
112 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
113 | or shape=[1, dimension]
114 | """
115 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=2)
116 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=2)
117 | return point - base_point
118 |
119 | def mean(self, points, weights=None):
120 | """
121 | The Frechet mean of (weighted) points is the weighted average of
122 | the points in the Minkowski space.
123 |
124 | Parameters
125 | ----------
126 | points: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
127 |
128 | weights: array-like, shape=[n_samples, 1], optional
129 | """
130 | if isinstance(points, list):
131 | points = gs.vstack(points)
132 | points = gs.to_ndarray(points, to_ndim=2)
133 | n_points = gs.shape(points)[0]
134 |
135 | if isinstance(weights, list):
136 | weights = gs.vstack(weights)
137 | elif weights is None:
138 | weights = gs.ones((n_points,))
139 |
140 | weighted_points = gs.einsum('n,nj->nj', weights, points)
141 | mean = (gs.sum(weighted_points, axis=0)
142 | / gs.sum(weights))
143 | mean = gs.to_ndarray(mean, to_ndim=2)
144 | return mean
145 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/loss_and_gradient_se3.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Predict on SE3: losses.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import os
6 | import tensorflow as tf
7 |
8 | import geomstats.backend as gs
9 | import geomstats.lie_group as lie_group
10 |
11 | from geomstats.special_euclidean_group import SpecialEuclideanGroup
12 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
13 |
14 |
15 | SE3 = SpecialEuclideanGroup(n=3)
16 | SO3 = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=3)
17 |
18 |
19 | def loss(y_pred, y_true,
20 | metric=SE3.left_canonical_metric,
21 | representation='vector'):
22 | """
23 | Loss function given by a riemannian metric on a Lie group,
24 | by default the left-invariant canonical metric.
25 | """
26 | if gs.ndim(y_pred) == 1:
27 | y_pred = gs.expand_dims(y_pred, axis=0)
28 | if gs.ndim(y_true) == 1:
29 | y_true = gs.expand_dims(y_true, axis=0)
30 |
31 | if representation == 'quaternion':
32 | y_pred_rot_vec = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_pred[:, :4])
33 | y_pred = gs.hstack([y_pred_rot_vec, y_pred[:, 4:]])
34 | y_true_rot_vec = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_true[:, :4])
35 | y_true = gs.hstack([y_true_rot_vec, y_true[:, 4:]])
36 |
37 | loss = lie_group.loss(y_pred, y_true, SE3, metric)
38 | return loss
39 |
40 |
41 | def grad(y_pred, y_true,
42 | metric=SE3.left_canonical_metric,
43 | representation='vector'):
44 | """
45 | Closed-form for the gradient of pose_loss.
46 |
47 | :return: tangent vector at point y_pred.
48 | """
49 | if gs.ndim(y_pred) == 1:
50 | y_pred = gs.expand_dims(y_pred, axis=0)
51 | if gs.ndim(y_true) == 1:
52 | y_true = gs.expand_dims(y_true, axis=0)
53 |
54 | if representation == 'vector':
55 | grad = lie_group.grad(y_pred, y_true, SE3, metric)
56 |
57 | if representation == 'quaternion':
58 |
59 | y_pred_rot_vec = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_pred[:, :4])
60 | y_pred_pose = gs.hstack([y_pred_rot_vec, y_pred[:, 4:]])
61 | y_true_rot_vec = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_true[:, :4])
62 | y_true_pose = gs.hstack([y_true_rot_vec, y_true[:, 4:]])
63 | grad = lie_group.grad(y_pred_pose, y_true_pose, SE3, metric)
64 |
65 | quat_scalar = y_pred[:, :1]
66 | quat_vec = y_pred[:, 1:4]
67 |
68 | quat_vec_norm = gs.linalg.norm(quat_vec, axis=1)
69 | quat_sq_norm = quat_vec_norm ** 2 + quat_scalar ** 2
70 |
71 | quat_arctan2 = gs.arctan2(quat_vec_norm, quat_scalar)
72 | differential_scalar = - 2 * quat_vec / (quat_sq_norm)
73 | differential_vec = (2 * (quat_scalar / quat_sq_norm
74 | - 2 * quat_arctan2 / quat_vec_norm)
75 | * (gs.einsum('ni,nj->nij', quat_vec, quat_vec)
76 | / quat_vec_norm * quat_vec_norm)
77 | + 2 * quat_arctan2 / quat_vec_norm * gs.eye(3))
78 |
79 | differential_scalar_t = gs.transpose(differential_scalar, axes=(1, 0))
80 |
81 | upper_left_block = gs.hstack(
82 | (differential_scalar_t, differential_vec[0]))
83 | upper_right_block = gs.zeros((3, 3))
84 | lower_right_block = gs.eye(3)
85 | lower_left_block = gs.zeros((3, 4))
86 |
87 | top = gs.hstack((upper_left_block, upper_right_block))
88 | bottom = gs.hstack((lower_left_block, lower_right_block))
89 |
90 | differential = gs.vstack((top, bottom))
91 | differential = gs.expand_dims(differential, axis=0)
92 |
93 | grad = gs.einsum('ni,nij->ni', grad, differential)
94 |
95 | grad = gs.squeeze(grad, axis=0)
96 | return grad
97 |
98 |
99 | def main():
100 | y_pred = gs.array([1., 1.5, -0.3, 5., 6., 7.])
101 | y_true = gs.array([0.1, 1.8, -0.1, 4., 5., 6.])
102 |
103 | loss_rot_vec = loss(y_pred, y_true)
104 | grad_rot_vec = grad(y_pred, y_true)
105 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
106 | with tf.Session() as sess:
107 | loss_rot_vec = sess.run(loss_rot_vec)
108 | grad_rot_vec = sess.run(grad_rot_vec)
109 | print('The loss between the poses using rotation vectors is: {}'.format(
110 | loss_rot_vec[0, 0]))
111 | print('The riemannian gradient is: {}'.format(grad_rot_vec))
112 |
113 | angle = gs.pi / 6
114 | cos = gs.cos(angle / 2)
115 | sin = gs.sin(angle / 2)
116 | u = gs.array([1., 2., 3.])
117 | u = u / gs.linalg.norm(u)
118 | scalar = gs.array(cos)
119 | vec = sin * u
120 | translation = gs.array([5., 6., 7.])
121 | y_pred_quaternion = gs.concatenate([[scalar], vec, translation], axis=0)
122 |
123 | angle = gs.pi / 7
124 | cos = gs.cos(angle / 2)
125 | sin = gs.sin(angle / 2)
126 | u = gs.array([1., 2., 3.])
127 | u = u / gs.linalg.norm(u)
128 | scalar = gs.array(cos)
129 | vec = sin * u
130 | translation = gs.array([4., 5., 6.])
131 | y_true_quaternion = gs.concatenate([[scalar], vec, translation], axis=0)
132 |
133 | loss_quaternion = loss(y_pred_quaternion, y_true_quaternion,
134 | representation='quaternion')
135 | grad_quaternion = grad(y_pred_quaternion, y_true_quaternion,
136 | representation='quaternion')
137 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
138 | with tf.Session() as sess:
139 | loss_quaternion = sess.run(loss_quaternion)
140 | grad_quaternion = sess.run(grad_quaternion)
141 | print('The loss between the poses using quaternions is: {}'.format(
142 | loss_quaternion[0, 0]))
143 | print('The riemannian gradient is: {}'.format(
144 | grad_quaternion))
145 |
146 |
147 | if __name__ == "__main__":
148 | main()
149 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_general_linear_group.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for General Linear group.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import warnings
6 |
7 | import geomstats.backend as gs
8 | import geomstats.tests
9 | import tests.helper as helper
10 |
11 | from geomstats.general_linear_group import GeneralLinearGroup
12 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
13 |
14 | RTOL = 1e-5
15 |
16 |
17 | class TestGeneralLinearGroupMethods(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
18 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
19 |
20 | def setUp(self):
21 | gs.random.seed(1234)
22 | self.n = 3
23 | self.n_samples = 2
24 | self.group = GeneralLinearGroup(n=self.n)
25 | # We generate invertible matrices using so3_group
26 | self.so3_group = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=self.n)
27 |
28 | warnings.simplefilter('ignore', category=ImportWarning)
29 |
30 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
31 | def test_belongs(self):
32 | """
33 | A rotation matrix belongs to the matrix Lie group
34 | of invertible matrices.
35 | """
36 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.2, -0.1, 0.1])
37 | rot_mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
38 | result = self.group.belongs(rot_mat)
39 | expected = gs.array([True])
40 |
41 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
42 |
43 | def test_compose(self):
44 | # 1. Composition by identity, on the right
45 | # Expect the original transformation
46 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.2, -0.1, 0.1])
47 | mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
48 |
49 | result = self.group.compose(mat, self.group.identity)
50 | expected = mat
51 | expected = helper.to_matrix(mat)
52 |
53 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
54 |
55 | # 2. Composition by identity, on the left
56 | # Expect the original transformation
57 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.2, 0.1, -0.1])
58 | mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
59 |
60 | result = self.group.compose(self.group.identity, mat)
61 | expected = mat
62 |
63 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
64 |
65 | def test_inverse(self):
66 | mat = gs.array([
67 | [1., 2., 3.],
68 | [4., 5., 6.],
69 | [7., 8., 10.]])
70 | result = self.group.inverse(mat)
71 | expected = 1. / 3. * gs.array([
72 | [-2., -4., 3.],
73 | [-2., 11., -6.],
74 | [3., -6., 3.]])
75 | expected = helper.to_matrix(expected)
76 |
77 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
78 |
79 | def test_compose_and_inverse(self):
80 | # 1. Compose transformation by its inverse on the right
81 | # Expect the group identity
82 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.2, 0.1, 0.1])
83 | mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
84 | inv_mat = self.group.inverse(mat)
85 |
86 | result = self.group.compose(mat, inv_mat)
87 | expected = self.group.identity
88 | expected = helper.to_matrix(expected)
89 |
90 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
91 |
92 | # 2. Compose transformation by its inverse on the left
93 | # Expect the group identity
94 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.7, 0.1, 0.1])
95 | mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
96 | inv_mat = self.group.inverse(mat)
97 |
98 | result = self.group.compose(inv_mat, mat)
99 | expected = self.group.identity
100 | expected = helper.to_matrix(expected)
101 |
102 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
103 |
104 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
105 | def test_group_log_and_exp(self):
106 | point = 5 * gs.eye(self.n)
107 |
108 | group_log = self.group.group_log(point)
109 | result = self.group.group_exp(group_log)
110 | expected = point
111 | expected = helper.to_matrix(expected)
112 |
113 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
114 |
115 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
116 | def test_group_exp_vectorization(self):
117 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
118 | [0., 3., 0.],
119 | [0., 0., 4.]],
120 | [[1., 0., 0.],
121 | [0., 5., 0.],
122 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
123 |
124 | expected = gs.array([[[7.38905609, 0., 0.],
125 | [0., 20.0855369, 0.],
126 | [0., 0., 54.5981500]],
127 | [[2.718281828, 0., 0.],
128 | [0., 148.413159, 0.],
129 | [0., 0., 403.42879349]]])
130 |
131 | result = self.group.group_exp(point)
132 |
133 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected, rtol=1e-3)
134 |
135 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
136 | def test_group_log_vectorization(self):
137 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
138 | [0., 3., 0.],
139 | [0., 0., 4.]],
140 | [[1., 0., 0.],
141 | [0., 5., 0.],
142 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
143 |
144 | expected = gs.array([[[0.693147180, 0., 0.],
145 | [0., 1.09861228866, 0.],
146 | [0., 0., 1.38629436]],
147 | [[0., 0., 0.],
148 | [0., 1.609437912, 0.],
149 | [0., 0., 1.79175946]]])
150 |
151 | result = self.group.group_log(point)
152 |
153 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected, atol=1e-4)
154 |
155 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
156 | def test_expm_and_logm_vectorization_symmetric(self):
157 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
158 | [0., 3., 0.],
159 | [0., 0., 4.]],
160 | [[1., 0., 0.],
161 | [0., 5., 0.],
162 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
163 | result = self.group.group_exp(self.group.group_log(point))
164 | expected = point
165 |
166 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
167 |
168 |
169 | if __name__ == '__main__':
170 | geomstats.tests.main()
171 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/backend/tensorflow.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Tensorflow based computation backend."""
2 |
3 | import tensorflow as tf
4 |
5 |
6 | int8 = tf.int8
7 | int32 = tf.int32
8 | int64 = tf.int64
9 | float16 = tf.float16
10 | float32 = tf.float32
11 | float64 = tf.float64
12 |
13 |
14 | def while_loop(*args, **kwargs):
15 | return tf.while_loop(*args, **kwargs)
16 |
17 |
18 | def logical_or(x, y):
19 | return tf.logical_or(x, y)
20 |
21 |
22 | def get_mask_i_float(i, n):
23 | range_n = arange(n)
24 | i_float = cast(array([i]), int32)[0]
25 | mask_i = equal(range_n, i_float)
26 | mask_i_float = cast(mask_i, float32)
27 | return mask_i_float
28 |
29 |
30 | def gather(*args, **kwargs):
31 | return tf.gather(*args, **kwargs)
32 |
33 |
34 | def where(*args, **kwargs):
35 | return tf.where(*args, **kwargs)
36 |
37 |
38 | def vectorize(x, pyfunc, multiple_args=False, dtype=None, **kwargs):
39 | if multiple_args:
40 | return tf.map_fn(lambda x: pyfunc(*x), elems=x, dtype=dtype)
41 | return tf.map_fn(pyfunc, elems=x, dtype=dtype)
42 |
43 |
44 | def sign(x):
45 | return tf.sign(x)
46 |
47 |
48 | def hsplit(x, n_splits):
49 | return tf.split(x, num_or_size_splits=n_splits, axis=1)
50 |
51 |
52 | def amax(x):
53 | return tf.reduce_max(x)
54 |
55 |
56 | def real(x):
57 | return tf.real(x)
58 |
59 |
60 | def cond(*args, **kwargs):
61 | return tf.cond(*args, **kwargs)
62 |
63 |
64 | def reshape(*args, **kwargs):
65 | return tf.reshape(*args, **kwargs)
66 |
67 |
68 | def arange(*args, **kwargs):
69 | return tf.range(*args, **kwargs)
70 |
71 |
72 | def outer(x, y):
73 | return tf.einsum('i,j->ij', x, y)
74 |
75 |
76 | def copy(x):
77 | return tf.Variable(x)
78 |
79 |
80 | def linspace(start, stop, num):
81 | return tf.linspace(start, stop, num)
82 |
83 |
84 | def mod(x, y):
85 | return tf.mod(x, y)
86 |
87 |
88 | def boolean_mask(x, mask, name='boolean_mask', axis=None):
89 | return tf.boolean_mask(x, mask, name, axis)
90 |
91 |
92 | def exp(x):
93 | return tf.exp(x)
94 |
95 |
96 | def log(x):
97 | return tf.log(x)
98 |
99 |
100 | def hstack(x):
101 | return tf.concat(x, axis=1)
102 |
103 |
104 | def vstack(x):
105 | return tf.concat(x, axis=0)
106 |
107 |
108 | def cast(x, dtype):
109 | return tf.cast(x, dtype)
110 |
111 |
112 | def divide(x1, x2):
113 | return tf.divide(x1, x2)
114 |
115 |
116 | def tile(x, reps):
117 | return tf.tile(x, reps)
118 |
119 |
120 | def eval(x):
121 | if tf.executing_eagerly():
122 | return x
123 | return x.eval()
124 |
125 |
126 | def abs(x):
127 | return tf.abs(x)
128 |
129 |
130 | def zeros(x):
131 | return tf.zeros(x)
132 |
133 |
134 | def ones(x):
135 | return tf.ones(x)
136 |
137 |
138 | def sin(x):
139 | return tf.sin(x)
140 |
141 |
142 | def cos(x):
143 | return tf.cos(x)
144 |
145 |
146 | def cosh(x):
147 | return tf.cosh(x)
148 |
149 |
150 | def sinh(x):
151 | return tf.sinh(x)
152 |
153 |
154 | def tanh(x):
155 | return tf.tanh(x)
156 |
157 |
158 | def arccosh(x):
159 | return tf.acosh(x)
160 |
161 |
162 | def tan(x):
163 | return tf.tan(x)
164 |
165 |
166 | def arcsin(x):
167 | return tf.asin(x)
168 |
169 |
170 | def arccos(x):
171 | return tf.acos(x)
172 |
173 |
174 | def shape(x):
175 | return tf.shape(x)
176 |
177 |
178 | def ndim(x):
179 | x = array(x)
180 | dims = x.get_shape()._dims
181 | if dims is not None:
182 | return len(dims)
183 | return None
184 |
185 |
186 | def dot(x, y):
187 | return tf.tensordot(x, y, axes=1)
188 |
189 |
190 | def maximum(x, y):
191 | return tf.maximum(x, y)
192 |
193 |
194 | def greater(x, y):
195 | return tf.greater(x, y)
196 |
197 |
198 | def greater_equal(x, y):
199 | return tf.greater_equal(x, y)
200 |
201 |
202 | def equal(x, y):
203 | return tf.equal(x, y)
204 |
205 |
206 | def to_ndarray(x, to_ndim, axis=0):
207 | if ndim(x) == to_ndim - 1:
208 | x = tf.expand_dims(x, axis=axis)
209 |
210 | return x
211 |
212 |
213 | def sqrt(x):
214 | return tf.sqrt(x)
215 |
216 |
217 | def isclose(x, y, rtol=1e-05, atol=1e-08):
218 | rhs = tf.constant(atol) + tf.constant(rtol) * tf.abs(y)
219 | return tf.less_equal(tf.abs(tf.subtract(x, y)), rhs)
220 |
221 |
222 | def allclose(x, y, rtol=1e-05, atol=1e-08):
223 | return tf.reduce_all(isclose(x, y, rtol=rtol, atol=atol))
224 |
225 |
226 | def less(x, y):
227 | return tf.less(x, y)
228 |
229 |
230 | def less_equal(x, y):
231 | return tf.less_equal(x, y)
232 |
233 |
234 | def eye(n, m=None):
235 | if m is None:
236 | m = n
237 | n = cast(n, dtype=int32)
238 | m = cast(m, dtype=int32)
239 | return tf.eye(num_rows=n, num_columns=m)
240 |
241 |
242 | def matmul(x, y):
243 | return tf.matmul(x, y)
244 |
245 |
246 | def argmax(*args, **kwargs):
247 | return tf.argmax(*args, **kwargs)
248 |
249 |
250 | def sum(*args, **kwargs):
251 | return tf.reduce_sum(*args, **kwargs)
252 |
253 |
254 | def einsum(equation, *inputs, **kwargs):
255 | return tf.einsum(equation, *inputs, **kwargs)
256 |
257 |
258 | def transpose(x, axes=None):
259 | return tf.transpose(x, perm=axes)
260 |
261 |
262 | def squeeze(x, **kwargs):
263 | return tf.squeeze(x, **kwargs)
264 |
265 |
266 | def zeros_like(x):
267 | return tf.zeros_like(x)
268 |
269 |
270 | def ones_like(x):
271 | return tf.ones_like(x)
272 |
273 |
274 | def trace(x, **kwargs):
275 | return tf.trace(x)
276 |
277 |
278 | def array(x):
279 | return tf.convert_to_tensor(x)
280 |
281 |
282 | def all(bool_tensor, axis=None, keepdims=False):
283 | bool_tensor = tf.cast(bool_tensor, tf.bool)
284 | all_true = tf.reduce_all(bool_tensor, axis, keepdims)
285 | return all_true
286 |
287 |
288 | def concatenate(*args, **kwargs):
289 | return tf.concat(*args, **kwargs)
290 |
291 |
292 | def asarray(x):
293 | return x
294 |
295 |
296 | def expand_dims(x, axis=None):
297 | return tf.expand_dims(x, axis)
298 |
299 |
300 | def clip(x, min_value, max_value):
301 | return tf.clip_by_value(x, min_value, max_value)
302 |
303 |
304 | def floor(x):
305 | return tf.floor(x)
306 |
307 |
308 | def diag(a):
309 | return tf.map_fn(
310 | lambda x: tf.diag(x),
311 | a)
312 |
313 |
314 | def cross(a, b):
315 | return tf.cross(a, b)
316 |
317 |
318 | def stack(*args, **kwargs):
319 | return tf.stack(*args, **kwargs)
320 |
321 |
322 | def arctan2(*args, **kwargs):
323 | return tf.atan2(*args, **kwargs)
324 |
325 |
326 | def diagonal(*args, **kwargs):
327 | return tf.linalg.diag_part(*args)
328 |
329 |
330 | def mean(x, axis=None):
331 | return tf.reduce_mean(x, axis)
332 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/CONTRIBUTING.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Contributing to Geomstats
2 |
3 | Welcome to the geomstats repository!
4 | We are excited you are here and want to contribute.
5 |
6 | More details on contributing can be found on the [documentation website][link_doc].
7 |
8 | ## Practical Guide to Submitting your Contribution
9 |
10 | These guidelines are designed to make it as easy as possible to get involved.
11 | If you have any questions that are not discussed below,
12 | please let us know by opening an [issue][link_issues]!
13 |
14 | Before you start you will need to set up a free [GitHub][link_github] account and sign in.
15 | Here are some [instructions][link_signupinstructions].
16 |
17 |
18 | ## Joining the Conversation
19 |
20 | `geomstats` is maintained by a growing group of enthusiastic developers!
21 | Most of our discussions take place on [issues][link_issues].
22 |
23 |
24 | ## Contributing through GitHub
25 |
26 | [git][link_git] is a really useful tool for version control.
27 | [GitHub][link_github] sits on top of git and supports collaborative and distributed working.
28 |
29 | If you are not yet familiar with `git`, there are lots of great resources to help you *git* started!
30 | Some of our favorites include the [git Handbook][link_handbook] and
31 | the [Software Carpentry introduction to git][link_swc_intro].
32 |
33 | On GitHub, you will use [Markdown][markdown] to chat in issues and pull requests.
34 |
35 | GitHub has a really helpful page for getting started with
36 | [writing and formatting Markdown on GitHub][writing_formatting_github].
37 |
38 |
39 | ## Understanding Issues
40 |
41 | Every project on GitHub uses [issues][link_issues] slightly differently.
42 |
43 | The following outlines how ``geomstats`` developers think about these tools.
44 |
45 | * **Issues** are individual pieces of work that need to be completed to move the project forwards.
46 | A general guideline: if you find yourself tempted to write a great big issue that
47 | is difficult to describe as one unit of work, please consider splitting it into two or more issues.
48 |
49 | * Issues are assigned [labels](#issue-labels) which explain how they relate to the overall project's
50 | goals and immediate next steps.
51 |
52 |
53 | ## Making a Change
54 |
55 | We appreciate all contributions to ``geomstats``,
56 | but those accepted fastest will follow a workflow similar to the following:
57 |
58 | **1. Comment on an existing issue or open a new issue referencing your addition.**
59 |
60 | This allows other members of the ``geomstats`` development team to confirm that you are not
61 | overlapping with work that is currently underway and that everyone is on the same page
62 | with the goal of the work you are going to carry out.
63 |
64 | [This blog][link_pushpullblog] is a nice explanation of why putting this work in up front
65 | is so useful to everyone involved.
66 |
67 | **2. [Fork][link_fork] the [geomstats repository][link_geomstats] to your profile.**
68 |
69 | This is now your own unique copy of ``geomstats``.
70 | Changes here will not effect anyone else's work, so it is a safe space to explore edits to the code!
71 |
72 | Make sure to [keep your fork up to date][link_updateupstreamwiki] with the master repository.
73 |
74 | **3. Make the changes you have discussed, following the [geomstats coding style guide](#geomstats-coding-style-guide).**
75 |
76 | - Create your feature branch (`git checkout -b feature/fooBar`)
77 | - Commit your changes (`git commit -am 'Add some fooBar'`)
78 | - Push to the branch (`git push origin feature/fooBar`)
79 |
80 | Try to keep the changes focused.
81 | If you feel tempted to "branch out" then please make a [new branch][link_branches].
82 |
83 | **4. Add the corresponding unit tests.**
84 |
85 | If you are adding a new feature, do not forget to add the corresponding [unit tests][link_unit_tests].
86 | As ``geomstats`` enables numpy and tensorflow, your unit tests should run on these two backends.
87 |
88 | **5. Ensure Geomstats Coding Style Guide.**
89 |
90 | Ensure that your code is compliant with [PEP8][link_pep8],
91 | the coding style guide for python.
92 |
93 | Use [flake8][link_flake8] or [yapf][link_yapf] to automatically enforces this style.
94 |
95 |
96 | **6. Submit a [pull request][link_pullrequest].**
97 |
98 | A member of the development team will review your changes to confirm
99 | that they can be merged into the main code base.
100 |
101 | Use the Github labels to label your pull request:
102 | * ``enhancement``: enhancements or new features
103 | * ``bug``: bug fixes
104 | * ``test``: new or updated tests
105 | * ``documentation``: new or updated documentation
106 | * ``style``: style changes
107 | * ``refactoring``: refactoring existing code
108 | * ``continuous integration``: updates to continous integration infrastructure
109 |
110 |
111 | ## Recognizing Contributions
112 |
113 | We welcome and recognize all contributions from documentation to testing to code development.
114 | You can see a list of current contributors in our [README.md][link_readme].
115 | If you are new to the project, do not forget to add your name and affiliation there!
116 |
117 | ## Thank You!
118 |
119 |
13 |
14 |
15 | ## Installation
16 |
17 | OS X & Linux:
18 |
19 | ```
20 | pip3 install geomstats
21 | ```
22 |
23 | ## Running tests
24 |
25 | ```
26 | pip3 install nose2
27 | nose2
28 | ```
29 |
30 | ## Getting started
31 |
32 | Define your backend by setting the environment variable ```GEOMSTATS_BACKEND``` to ```numpy```, ```tensorflow```, or ```pytorch```:
33 |
34 | ```
35 | export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND=numpy
36 | ```
37 |
38 | Then, run example scripts:
39 |
40 | ```
41 | python3 examples/plot_grid_h2.py
42 | ```
43 |
44 | ## Contributing
45 |
46 | See our [CONTRIBUTING.md][link_contributing] file!
47 |
48 | ## Authors & Contributors
49 |
50 | * Alice Le Brigant
51 | * Claire Donnat
52 | * Oleg Kachan
53 | * Benjamin Hou
54 | * Johan Mathe
55 | * Nina Miolane
56 | * Xavier Pennec
57 |
58 | ## Acknowledgements
59 |
60 | This work is partially supported by the National Science Foundation, grant NSF DMS RTG 1501767.
61 |
62 | [link_contributing]: https://github.com/geomstats/geomstats/CONTRIBUTING.md
63 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_visualization.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for visualization.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import matplotlib
6 | matplotlib.use('Agg') # NOQA
7 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
8 |
9 | import geomstats.tests
10 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
11 |
12 | from geomstats.hyperbolic_space import HyperbolicSpace
13 | from geomstats.hypersphere import Hypersphere
14 | from geomstats.special_euclidean_group import SpecialEuclideanGroup
15 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
16 |
17 |
18 | class TestVisualizationMethods(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
19 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
20 |
21 | def setUp(self):
22 | self.n_samples = 10
23 | self.SO3_GROUP = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=3)
24 | self.SE3_GROUP = SpecialEuclideanGroup(n=3)
25 | self.S1 = Hypersphere(dimension=1)
26 | self.S2 = Hypersphere(dimension=2)
27 | self.H2 = HyperbolicSpace(dimension=2)
28 |
29 | plt.figure()
30 |
31 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
32 | def test_plot_points_so3(self):
33 | points = self.SO3_GROUP.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
34 | visualization.plot(points, space='SO3_GROUP')
35 |
36 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
37 | def test_plot_points_se3(self):
38 | points = self.SE3_GROUP.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
39 | visualization.plot(points, space='SE3_GROUP')
40 |
41 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
42 | def test_plot_points_s1(self):
43 | points = self.S1.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
44 | visualization.plot(points, space='S1')
45 |
46 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
47 | def test_plot_points_s2(self):
48 | points = self.S2.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
49 | visualization.plot(points, space='S2')
50 |
51 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
52 | def test_plot_points_h2_poincare_disk(self):
53 | points = self.H2.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
54 | visualization.plot(points, space='H2_poincare_disk')
55 |
56 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
57 | def test_plot_points_h2_poincare_half_plane(self):
58 | points = self.H2.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
59 | visualization.plot(points, space='H2_poincare_half_plane')
60 |
61 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
62 | def test_plot_points_h2_klein_disk(self):
63 | points = self.H2.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
64 | visualization.plot(points, space='H2_klein_disk')
65 |
66 |
67 | if __name__ == '__main__':
68 | geomstats.tests.main()
69 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/tests.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Testing class for geomstats.
3 |
4 | This class abstracts the backend type.
5 | """
6 |
7 | import os
8 | import tensorflow as tf
9 | import unittest
10 |
11 | import geomstats.backend as gs
12 |
13 |
14 | def pytorch_backend():
15 | return os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'pytorch'
16 |
17 |
18 | def tf_backend():
19 | return os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow'
20 |
21 |
22 | def np_backend():
23 | return os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'numpy'
24 |
25 |
26 | test_class = unittest.TestCase
27 | if tf_backend():
28 | test_class = tf.test.TestCase
29 |
30 |
31 | def np_only(test_item):
32 | """Decorator to filter tests for numpy only."""
33 | if not np_backend():
34 | test_item.__unittest_skip__ = True
35 | test_item.__unittest_skip_why__ = (
36 | 'Test for numpy backend only.')
37 | return test_item
38 |
39 |
40 | def np_and_tf_only(test_item):
41 | """Decorator to filter tests for numpy and tensorflow only."""
42 | if not (np_backend() or tf_backend()):
43 | test_item.__unittest_skip__ = True
44 | test_item.__unittest_skip_why__ = (
45 | 'Test for numpy and tensorflow backends only.')
46 | return test_item
47 |
48 |
49 | def np_and_pytorch_only(test_item):
50 | """Decorator to filter tests for numpy and pytorch only."""
51 | if not (np_backend() or pytorch_backend()):
52 | test_item.__unittest_skip__ = True
53 | test_item.__unittest_skip_why__ = (
54 | 'Test for numpy and pytorch backends only.')
55 | return test_item
56 |
57 |
58 | class DummySession():
59 | def __enter__(self):
60 | pass
61 |
62 | def __exit__(self, a, b, c):
63 | pass
64 |
65 |
66 | class TestCase(test_class):
67 |
68 | def assertAllClose(self, a, b, rtol=1e-6, atol=1e-6):
69 | if tf_backend():
70 | return super().assertAllClose(a, b, rtol=rtol, atol=atol)
71 | return self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(a, b, rtol=rtol, atol=atol))
72 |
73 | def session(self):
74 | if tf_backend():
75 | return super().test_session()
76 | return DummySession()
77 |
78 | def assertShapeEqual(self, a, b):
79 | if tf_backend():
80 | return super().assertShapeEqual(a, b)
81 | super().assertEqual(a.shape, b.shape)
82 |
83 | @classmethod
84 | def setUpClass(cls):
85 | if tf_backend():
86 | os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
87 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/plot_geodesics_h2.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Plot a geodesic on the Hyperbolic space H2,
3 | with Poincare Disk visualization.
4 | """
5 |
6 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
7 | import numpy as np
8 | import os
9 |
10 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
11 |
12 | from geomstats.hyperbolic_space import HyperbolicSpace
13 |
14 | H2 = HyperbolicSpace(dimension=2)
15 | METRIC = H2.metric
16 |
17 |
18 | def plot_geodesic_between_two_points(initial_point,
19 | end_point,
20 | n_steps=10,
21 | ax=None):
22 | assert H2.belongs(initial_point)
23 | assert H2.belongs(end_point)
24 |
25 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=initial_point,
26 | end_point=end_point)
27 |
28 | t = np.linspace(0, 1, n_steps)
29 | points = geodesic(t)
30 | visualization.plot(points, ax=ax, space='H2_poincare_disk')
31 |
32 |
33 | def plot_geodesic_with_initial_tangent_vector(initial_point,
34 | initial_tangent_vec,
35 | n_steps=10,
36 | ax=None):
37 | assert H2.belongs(initial_point)
38 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=initial_point,
39 | initial_tangent_vec=initial_tangent_vec)
40 | n_steps = 10
41 | t = np.linspace(0, 1, n_steps)
42 |
43 | points = geodesic(t)
44 | visualization.plot(points, ax=ax, space='H2_poincare_disk')
45 |
46 |
47 | def main():
48 | initial_point = [np.sqrt(2), 1., 0.]
49 | end_point = H2.intrinsic_to_extrinsic_coords([1.5, 1.5])
50 | initial_tangent_vec = H2.projection_to_tangent_space(
51 | vector=[3.5, 0.6, 0.8],
52 | base_point=initial_point)
53 |
54 | ax = plt.gca()
55 | plot_geodesic_between_two_points(initial_point,
56 | end_point,
57 | ax=ax)
58 | plot_geodesic_with_initial_tangent_vector(initial_point,
59 | initial_tangent_vec,
60 | ax=ax)
61 | plt.show()
62 |
63 |
64 | if __name__ == "__main__":
65 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
66 | print('Examples with visualizations are only implemented '
67 | 'with numpy backend.\n'
68 | 'To change backend, write: '
69 | 'export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND = \'numpy\'.')
70 | else:
71 | main()
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/helper.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Helper functions for unit tests.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 |
7 |
8 | def to_scalar(expected):
9 | expected = gs.to_ndarray(expected, to_ndim=1)
10 | expected = gs.to_ndarray(expected, to_ndim=2, axis=-1)
11 | return expected
12 |
13 |
14 | def to_vector(expected):
15 | expected = gs.to_ndarray(expected, to_ndim=2)
16 | return expected
17 |
18 |
19 | def to_matrix(expected):
20 | expected = gs.to_ndarray(expected, to_ndim=3)
21 | return expected
22 |
23 |
24 | def left_log_then_exp_from_identity(metric, point):
25 | aux = metric.left_log_from_identity(point=point)
26 | result = metric.left_exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=aux)
27 | return result
28 |
29 |
30 | def left_exp_then_log_from_identity(metric, tangent_vec):
31 | aux = metric.left_exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=tangent_vec)
32 | result = metric.left_log_from_identity(point=aux)
33 | return result
34 |
35 |
36 | def log_then_exp_from_identity(metric, point):
37 | aux = metric.log_from_identity(point=point)
38 | result = metric.exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=aux)
39 | return result
40 |
41 |
42 | def exp_then_log_from_identity(metric, tangent_vec):
43 | aux = metric.exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=tangent_vec)
44 | result = metric.log_from_identity(point=aux)
45 | return result
46 |
47 |
48 | def log_then_exp(metric, point, base_point):
49 | aux = metric.log(point=point,
50 | base_point=base_point)
51 | result = metric.exp(tangent_vec=aux,
52 | base_point=base_point)
53 | return result
54 |
55 |
56 | def exp_then_log(metric, tangent_vec, base_point):
57 | aux = metric.exp(tangent_vec=tangent_vec,
58 | base_point=base_point)
59 | result = metric.log(point=aux,
60 | base_point=base_point)
61 | return result
62 |
63 |
64 | def group_log_then_exp_from_identity(group, point):
65 | aux = group.group_log_from_identity(point=point)
66 | result = group.group_exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=aux)
67 | return result
68 |
69 |
70 | def group_exp_then_log_from_identity(group, tangent_vec):
71 | aux = group.group_exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=tangent_vec)
72 | result = group.group_log_from_identity(point=aux)
73 | return result
74 |
75 |
76 | def group_log_then_exp(group, point, base_point):
77 | aux = group.group_log(point=point,
78 | base_point=base_point)
79 | result = group.group_exp(tangent_vec=aux,
80 | base_point=base_point)
81 | return result
82 |
83 |
84 | def group_exp_then_log(group, tangent_vec, base_point):
85 | aux = group.group_exp(tangent_vec=tangent_vec,
86 | base_point=base_point)
87 | result = group.group_log(point=aux,
88 | base_point=base_point)
89 | return result
90 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/api-reference.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | *************
2 | API reference
3 | *************
4 |
5 | .. automodule:: geomstats
6 | :members:
7 |
8 | The "manifold" module
9 | ---------------------
10 |
11 | .. automodule:: geomstats.manifold
12 | :members:
13 |
14 | The "connection" module
15 | -----------------------
16 |
17 | .. automodule:: geomstats.connection
18 | :members:
19 |
20 | The "riemannian_metric" module
21 | ------------------------------
22 |
23 | .. automodule:: geomstats.riemannian_metric
24 | :members:
25 |
26 | Spaces of constant curvatures
27 | =============================
28 |
29 | The "embedded_manifold" module
30 | ------------------------------
31 |
32 | .. automodule:: geomstats.embedded_manifold
33 | :members:
34 |
35 | The "euclidean_space" module
36 | ----------------------------
37 |
38 | .. automodule:: geomstats.euclidean_space
39 | :members:
40 |
41 | The "minkowski_space" module
42 | ----------------------------
43 |
44 | .. automodule:: geomstats.minkowski_space
45 | :members:
46 |
47 | The "hypersphere" module
48 | ------------------------
49 |
50 | .. automodule:: geomstats.hypersphere
51 | :members:
52 |
53 | The "hyperbolic_space" module
54 | -----------------------------
55 |
56 | .. automodule:: geomstats.hyperbolic_space
57 | :members:
58 |
59 | Lie groups
60 | ==========
61 |
62 | The "lie_group" module
63 | ----------------------
64 |
65 | .. automodule:: geomstats.lie_group
66 | :members:
67 |
68 | The "matrices_space" module
69 | ---------------------------
70 |
71 | .. automodule:: geomstats.matrices_space
72 | :members:
73 |
74 | The "general_linear_group" module
75 | ---------------------------------
76 |
77 | .. automodule:: geomstats.general_linear_group
78 | :members:
79 |
80 | The "invariant_metric" module
81 | -----------------------------
82 |
83 | .. automodule:: geomstats.invariant_metric
84 | :members:
85 |
86 | The "special_euclidean_group" module
87 | ------------------------------------
88 |
89 | .. automodule:: geomstats.special_euclidean_group
90 | :members:
91 |
92 | The "special_orthogonal_group" module
93 | -------------------------------------
94 |
95 | .. automodule:: geomstats.special_orthogonal_group
96 | :members:
97 |
98 | More manifolds
99 | ==============
100 |
101 | The "discretized_curves_space" module
102 | -------------------------------------
103 |
104 | .. automodule:: geomstats.discretized_curves_space
105 | :members:
106 |
107 | The "spd_matrices_space" module
108 | -------------------------------
109 |
110 | .. automodule:: geomstats.spd_matrices_space
111 | :members:
112 |
113 | The "stiefel" module
114 | --------------------
115 |
116 | .. automodule:: geomstats.stiefel
117 | :members:
118 |
119 | Visualization implementations
120 | =============================
121 |
122 | .. automodule:: geomstats.visualization
123 | :members:
124 |
125 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_examples.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for the examples.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import matplotlib
6 | matplotlib.use('Agg') # NOQA
7 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
8 | import os
9 | import sys
10 | import warnings
11 |
12 | import examples.gradient_descent_s2 as gradient_descent_s2
13 | import examples.loss_and_gradient_se3 as loss_and_gradient_se3
14 | import examples.loss_and_gradient_so3 as loss_and_gradient_so3
15 | import examples.plot_geodesics_h2 as plot_geodesics_h2
16 | import examples.plot_geodesics_s2 as plot_geodesics_s2
17 | import examples.plot_geodesics_se3 as plot_geodesics_se3
18 | import examples.plot_geodesics_so3 as plot_geodesics_so3
19 | import examples.plot_grid_h2 as plot_grid_h2
20 | import examples.plot_square_h2_poincare_disk as plot_square_h2_poincare_disk
21 | import examples.plot_square_h2_poincare_half_plane as plot_square_h2_poincare_half_plane # NOQA
22 | import examples.plot_square_h2_klein_disk as plot_square_h2_klein_disk
23 | import examples.plot_quantization_s1 as plot_quantization_s1
24 | import examples.plot_quantization_s2 as plot_quantization_s2
25 | import examples.tangent_pca_so3 as tangent_pca_so3
26 | import geomstats.tests
27 |
28 |
29 | class TestExamples(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
30 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
31 |
32 | @classmethod
33 | def setUpClass(cls):
34 | sys.stdout = open(os.devnull, 'w')
35 |
36 | def setUp(self):
37 | warnings.simplefilter('ignore', category=ImportWarning)
38 | plt.figure()
39 |
40 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
41 | def test_gradient_descent_s2(self):
42 | gradient_descent_s2.main(max_iter=32, output_file=None)
43 |
44 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
45 | def test_loss_and_gradient_so3(self):
46 | loss_and_gradient_so3.main()
47 |
48 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
49 | def test_loss_and_gradient_se3(self):
50 | loss_and_gradient_se3.main()
51 |
52 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
53 | def test_plot_geodesics_h2(self):
54 | plot_geodesics_h2.main()
55 |
56 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
57 | def test_plot_geodesics_s2(self):
58 | plot_geodesics_s2.main()
59 |
60 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
61 | def test_plot_geodesics_se3(self):
62 | plot_geodesics_se3.main()
63 |
64 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
65 | def test_plot_geodesics_so3(self):
66 | plot_geodesics_so3.main()
67 |
68 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
69 | def test_plot_grid_h2(self):
70 | plot_grid_h2.main()
71 |
72 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
73 | def test_plot_square_h2_square_poincare_disk(self):
74 | plot_square_h2_poincare_disk.main()
75 |
76 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
77 | def test_plot_square_h2_square_poincare_half_plane(self):
78 | plot_square_h2_poincare_half_plane.main()
79 |
80 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
81 | def test_plot_square_h2_square_klein_disk(self):
82 | plot_square_h2_klein_disk.main()
83 |
84 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
85 | def test_tangent_pca_so3(self):
86 | tangent_pca_so3.main()
87 |
88 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
89 | def test_plot_quantization_s1(self):
90 | plot_quantization_s1.main()
91 |
92 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
93 | def test_plot_quantization_s2(self):
94 | plot_quantization_s2.main()
95 |
96 |
97 | if __name__ == '__main__':
98 | geomstats.tests.main()
99 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/matrices_space.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | The space of matrices (m, n), which is the Euclidean space R^{mn}.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 |
7 | from geomstats.euclidean_space import EuclideanSpace
8 | from geomstats.riemannian_metric import RiemannianMetric
9 |
10 |
11 | TOLERANCE = 1e-5
12 |
13 |
14 | class MatricesSpace(EuclideanSpace):
15 | """Class for the space of matrices (m, n)."""
16 |
17 | def __init__(self, m, n):
18 | assert isinstance(m, int) and isinstance(n, int) and m > 0 and n > 0
19 | super(MatricesSpace, self).__init__(dimension=m*n)
20 | self.m = m
21 | self.n = n
22 | self.default_point_type = 'matrix'
23 | self.metric = MatricesMetric(m, n)
24 |
25 | def belongs(self, point):
26 | """
27 | Check if point belongs to the Matrix space.
28 | """
29 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=3)
30 | _, mat_dim_1, mat_dim_2 = point.shape
31 | return mat_dim_1 == self.m & mat_dim_2 == self.n
32 |
33 | @staticmethod
34 | def vector_from_matrix(matrix):
35 | """
36 | Conversion function from (_, m, n) to (_, mn).
37 | """
38 | matrix = gs.to_ndarray(matrix, to_ndim=3)
39 | n_mats, m, n = matrix.shape
40 | return gs.reshape(matrix, (n_mats, m*n))
41 |
42 | @staticmethod
43 | def is_symmetric(matrix, tolerance=TOLERANCE):
44 | """Check if a matrix is symmetric."""
45 | matrix = gs.to_ndarray(matrix, to_ndim=3)
46 | n_mats, m, n = matrix.shape
47 | assert m == n
48 | matrix_transpose = gs.transpose(matrix, axes=(0, 2, 1))
49 |
50 | mask = gs.isclose(matrix, matrix_transpose, atol=tolerance)
51 | mask = gs.all(mask, axis=(1, 2))
52 |
53 | mask = gs.to_ndarray(mask, to_ndim=1)
54 | mask = gs.to_ndarray(mask, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
55 | return mask
56 |
57 | @staticmethod
58 | def make_symmetric(matrix):
59 | """Make a matrix fully symmetric to avoid numerical issues."""
60 | matrix = gs.to_ndarray(matrix, to_ndim=3)
61 | n_mats, m, n = matrix.shape
62 | assert m == n
63 | matrix = gs.to_ndarray(matrix, to_ndim=3)
64 | return (matrix + gs.transpose(matrix, axes=(0, 2, 1))) / 2
65 |
66 | def random_uniform(self, n_samples=1):
67 | point = gs.random.rand(n_samples, self.m, self.n)
68 | return point
69 |
70 |
71 | class MatricesMetric(RiemannianMetric):
72 | """
73 | Euclidean metric on matrices given by the Frobenius inner product.
74 | """
75 | def __init__(self, m, n):
76 | dimension = m*n
77 | super(MatricesMetric, self).__init__(
78 | dimension=dimension,
79 | signature=(dimension, 0, 0))
80 |
81 | def inner_product(self, tangent_vec_a, tangent_vec_b, base_point=None):
82 | """
83 | Compute the Frobenius inner product of tangent_vec_a and tangent_vec_b
84 | at base_point.
85 | """
86 | tangent_vec_a = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec_a, to_ndim=3)
87 | n_tangent_vecs_a, _, _ = tangent_vec_a.shape
88 |
89 | tangent_vec_b = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec_b, to_ndim=3)
90 | n_tangent_vecs_b, _, _ = tangent_vec_b.shape
91 |
92 | assert n_tangent_vecs_a == n_tangent_vecs_b
93 |
94 | inner_prod = gs.einsum("nij,nij->n", tangent_vec_a, tangent_vec_b)
95 | inner_prod = gs.to_ndarray(inner_prod, to_ndim=1)
96 | inner_prod = gs.to_ndarray(inner_prod, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
97 | return inner_prod
98 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_matrices_space.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for the manifold of matrices.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 | import geomstats.tests
7 | import tests.helper as helper
8 |
9 | from geomstats.matrices_space import MatricesSpace
10 |
11 |
12 | class TestMatricesSpaceMethods(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
13 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
14 |
15 | def setUp(self):
16 | gs.random.seed(1234)
17 |
18 | self.n = 3
19 | self.space = MatricesSpace(m=self.n, n=self.n)
20 | self.metric = self.space.metric
21 | self.n_samples = 2
22 |
23 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
24 | def test_is_symmetric(self):
25 | sym_mat = gs.array([[1., 2.],
26 | [2., 1.]])
27 | result = self.space.is_symmetric(sym_mat)
28 | expected = gs.array([True])
29 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
30 |
31 | not_a_sym_mat = gs.array([[1., 0.6, -3.],
32 | [6., -7., 0.],
33 | [0., 7., 8.]])
34 | result = self.space.is_symmetric(not_a_sym_mat)
35 | expected = gs.array([False])
36 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
37 |
38 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
39 | def test_is_symmetric_vectorization(self):
40 | points = gs.array([
41 | [[1., 2.],
42 | [2., 1.]],
43 | [[3., 4.],
44 | [4., 5.]]])
45 | result = gs.all(self.space.is_symmetric(points))
46 | expected = True
47 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
48 |
49 | def test_make_symmetric(self):
50 | sym_mat = gs.array([[1., 2.],
51 | [2., 1.]])
52 | result = self.space.make_symmetric(sym_mat)
53 | expected = helper.to_matrix(sym_mat)
54 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
55 |
56 | mat = gs.array([[1., 2., 3.],
57 | [0., 0., 0.],
58 | [3., 1., 1.]])
59 | result = self.space.make_symmetric(mat)
60 | expected = gs.array([[[1., 1., 3.],
61 | [1., 0., 0.5],
62 | [3., 0.5, 1.]]])
63 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
64 |
65 | mat = gs.array([[[1e100, 1e-100, 1e100],
66 | [1e100, 1e-100, 1e100],
67 | [1e-100, 1e-100, 1e100]]])
68 | result = self.space.make_symmetric(mat)
69 |
70 | res = 0.5 * (1e100 + 1e-100)
71 |
72 | expected = gs.array([[[1e100, res, res],
73 | [res, 1e-100, res],
74 | [res, res, 1e100]]])
75 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
76 |
77 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
78 | def test_make_symmetric_and_is_symmetric_vectorization(self):
79 | points = gs.array([
80 | [[1., 2.],
81 | [3., 4.]],
82 | [[5., 6.],
83 | [4., 9.]]])
84 |
85 | sym_points = self.space.make_symmetric(points)
86 | result = gs.all(self.space.is_symmetric(sym_points))
87 | expected = True
88 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
89 |
90 | def test_inner_product(self):
91 | base_point = gs.array([
92 | [1., 2., 3.],
93 | [0., 0., 0.],
94 | [3., 1., 1.]])
95 |
96 | tangent_vector_1 = gs.array([
97 | [1., 2., 3.],
98 | [0., -10., 0.],
99 | [30., 1., 1.]])
100 |
101 | tangent_vector_2 = gs.array([
102 | [1., 4., 3.],
103 | [5., 0., 0.],
104 | [3., 1., 1.]])
105 |
106 | result = self.metric.inner_product(
107 | tangent_vector_1,
108 | tangent_vector_2,
109 | base_point=base_point)
110 |
111 | expected = gs.trace(
112 | gs.matmul(
113 | gs.transpose(tangent_vector_1),
114 | tangent_vector_2))
115 | expected = helper.to_scalar(expected)
116 |
117 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
118 |
119 |
120 | if __name__ == '__main__':
121 | geomstats.tests.main()
122 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/euclidean_space.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Euclidean space.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 |
7 | from geomstats.manifold import Manifold
8 | from geomstats.riemannian_metric import RiemannianMetric
9 |
10 |
11 | class EuclideanSpace(Manifold):
12 | """
13 | Class for Euclidean spaces.
14 |
15 | By definition, a Euclidean space is a vector space of a given
16 | dimension, equipped with a Euclidean metric.
17 | """
18 |
19 | def __init__(self, dimension):
20 | assert isinstance(dimension, int) and dimension > 0
21 | self.dimension = dimension
22 | self.metric = EuclideanMetric(dimension)
23 |
24 | def belongs(self, point):
25 | """
26 | Evaluate if a point belongs to the Euclidean space.
27 |
28 | Parameters
29 | ----------
30 | point : array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
31 | Input points.
32 |
33 | Returns
34 | -------
35 | belongs : array-like, shape=[n_samples, 1]
36 | """
37 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=2)
38 | n_points, point_dim = point.shape
39 | belongs = point_dim == self.dimension
40 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=1)
41 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
42 | belongs = gs.tile(belongs, (n_points, 1))
43 |
44 | return belongs
45 |
46 | def random_uniform(self, n_samples=1, bound=1.):
47 | """
48 | Sample in the Euclidean space with the uniform distribution.
49 | """
50 | size = (n_samples, self.dimension)
51 | point = bound * (gs.random.rand(*size) - 0.5) * 2
52 |
53 | return point
54 |
55 |
56 | class EuclideanMetric(RiemannianMetric):
57 | """
58 | Class for Euclidean metrics.
59 |
60 | As a Riemannian metric, the Euclidean metric is:
61 | - flat: the inner product is independent of the base point.
62 | - positive definite: it has signature (0, dimension),
63 | where dimension is the dimension of the Euclidean space.
64 | """
65 | def __init__(self, dimension):
66 | assert isinstance(dimension, int) and dimension > 0
67 | super(EuclideanMetric, self).__init__(
68 | dimension=dimension,
69 | signature=(dimension, 0, 0))
70 |
71 | def inner_product_matrix(self, base_point=None):
72 | """
73 | Inner product matrix, independent of the base point.
74 | """
75 | mat = gs.eye(self.dimension)
76 | mat = gs.to_ndarray(mat, to_ndim=3)
77 | return mat
78 |
79 | def exp(self, tangent_vec, base_point):
80 | """
81 | The Riemannian exponential is the addition in the Euclidean space.
82 | """
83 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=2)
84 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=2)
85 | exp = base_point + tangent_vec
86 | return exp
87 |
88 | def log(self, point, base_point):
89 | """
90 | The Riemannian logarithm is the subtraction in the Euclidean space.
91 | """
92 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=2)
93 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=2)
94 | log = point - base_point
95 | return log
96 |
97 | def mean(self, points, weights=None):
98 | """
99 | The Frechet mean of (weighted) points computed with the
100 | Euclidean metric is the weighted average of the points
101 | in the Euclidean space.
102 | """
103 | if isinstance(points, list):
104 | points = gs.vstack(points)
105 | points = gs.to_ndarray(points, to_ndim=2)
106 | n_points = gs.shape(points)[0]
107 |
108 | if isinstance(weights, list):
109 | weights = gs.vstack(weights)
110 | elif weights is None:
111 | weights = gs.ones((n_points,))
112 |
113 | weighted_points = gs.einsum('n,nj->nj', weights, points)
114 | mean = (gs.sum(weighted_points, axis=0)
115 | / gs.sum(weights))
116 | mean = gs.to_ndarray(mean, to_ndim=2)
117 | return mean
118 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_backend_numpy.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for numpy backend.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import importlib
6 | import os
7 | import unittest
8 | import warnings
9 |
10 | import geomstats.backend as gs
11 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
12 |
13 |
14 | class TestBackendNumpy(unittest.TestCase):
15 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
16 |
17 | @classmethod
18 | def setUpClass(cls):
19 | cls.initial_backend = os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND']
20 | os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] = 'numpy'
21 | importlib.reload(gs)
22 |
23 | @classmethod
24 | def tearDownClass(cls):
25 | os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] = cls.initial_backend
26 | importlib.reload(gs)
27 |
28 | def setUp(self):
29 | warnings.simplefilter('ignore', category=ImportWarning)
30 |
31 | self.so3_group = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=3)
32 | self.n_samples = 2
33 |
34 | def test_logm(self):
35 | point = gs.array([[2., 0., 0.],
36 | [0., 3., 0.],
37 | [0., 0., 4.]])
38 | result = gs.linalg.logm(point)
39 | expected = gs.array([[0.693147180, 0., 0.],
40 | [0., 1.098612288, 0.],
41 | [0., 0., 1.38629436]])
42 |
43 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
44 |
45 | def test_expm_and_logm(self):
46 | point = gs.array([[2., 0., 0.],
47 | [0., 3., 0.],
48 | [0., 0., 4.]])
49 | result = gs.linalg.expm(gs.linalg.logm(point))
50 | expected = point
51 |
52 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
53 |
54 | def test_expm_vectorization(self):
55 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
56 | [0., 3., 0.],
57 | [0., 0., 4.]],
58 | [[1., 0., 0.],
59 | [0., 5., 0.],
60 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
61 |
62 | expected = gs.array([[[7.38905609, 0., 0.],
63 | [0., 20.0855369, 0.],
64 | [0., 0., 54.5981500]],
65 | [[2.718281828, 0., 0.],
66 | [0., 148.413159, 0.],
67 | [0., 0., 403.42879349]]])
68 |
69 | result = gs.linalg.expm(point)
70 |
71 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
72 |
73 | def test_logm_vectorization_diagonal(self):
74 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
75 | [0., 3., 0.],
76 | [0., 0., 4.]],
77 | [[1., 0., 0.],
78 | [0., 5., 0.],
79 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
80 |
81 | expected = gs.array([[[0.693147180, 0., 0.],
82 | [0., 1.09861228866, 0.],
83 | [0., 0., 1.38629436]],
84 | [[0., 0., 0.],
85 | [0., 1.609437912, 0.],
86 | [0., 0., 1.79175946]]])
87 |
88 | result = gs.linalg.logm(point)
89 |
90 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
91 |
92 | def test_expm_and_logm_vectorization_random_rotation(self):
93 | point = self.so3_group.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
94 | point = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(point)
95 |
96 | result = gs.linalg.expm(gs.linalg.logm(point))
97 | expected = point
98 |
99 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
100 |
101 | def test_expm_and_logm_vectorization(self):
102 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
103 | [0., 3., 0.],
104 | [0., 0., 4.]],
105 | [[1., 0., 0.],
106 | [0., 5., 0.],
107 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
108 | result = gs.linalg.expm(gs.linalg.logm(point))
109 | expected = point
110 |
111 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
112 |
113 |
114 | if __name__ == '__main__':
115 | unittest.main()
116 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/general_linear_group.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | The General Linear Group, i.e. the matrix group GL(n).
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 |
7 | from geomstats.lie_group import LieGroup
8 | from geomstats.matrices_space import MatricesSpace
9 |
10 |
11 | class GeneralLinearGroup(LieGroup, MatricesSpace):
12 | """
13 | Class for the General Linear Group, i.e. the matrix group GL(n).
14 |
15 |
16 | Note: The default representation for elements of GL(n)
17 | are matrices.
18 | For now, SO(n) and SE(n) elements are represented
19 | by a vector by default.
20 | """
21 |
22 | def __init__(self, n):
23 | assert isinstance(n, int) and n > 0
24 | LieGroup.__init__(self, dimension=n*n)
25 | MatricesSpace.__init__(self, m=n, n=n)
26 |
27 | def get_identity(self, point_type=None):
28 | if point_type is None:
29 | point_type = self.default_point_type
30 | if point_type == 'matrix':
31 | return gs.eye(self.n)
32 | else:
33 | raise NotImplementedError(
34 | 'The identity of the general linear group is not'
35 | ' implemented for a point_type that is not \'matrix\'.')
36 | identity = property(get_identity)
37 |
38 | def belongs(self, mat):
39 | """
40 | Check if mat belongs to GL(n).
41 | """
42 | mat = gs.to_ndarray(mat, to_ndim=3)
43 |
44 | det = gs.linalg.det(mat)
45 | belongs = ~gs.isclose(det, 0.)
46 |
47 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=1)
48 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
49 |
50 | return belongs
51 |
52 | def compose(self, mat_a, mat_b):
53 | """
54 | Matrix composition.
55 | """
56 | mat_a = gs.to_ndarray(mat_a, to_ndim=3)
57 | mat_b = gs.to_ndarray(mat_b, to_ndim=3)
58 | composition = gs.einsum('nij,njk->nik', mat_a, mat_b)
59 | return composition
60 |
61 | def inverse(self, mat):
62 | """
63 | Matrix inverse.
64 | """
65 | mat = gs.to_ndarray(mat, to_ndim=3)
66 | return gs.linalg.inv(mat)
67 |
68 | def group_exp_from_identity(self, tangent_vec, point_type=None):
69 | """
70 | Group exponential of the Lie group of
71 | all invertible matrices at the identity.
72 | """
73 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=3)
74 | group_exp = gs.linalg.expm(tangent_vec)
75 |
76 | return gs.real(group_exp)
77 |
78 | def group_exp_not_from_identity(
79 | self, tangent_vec, base_point, point_type=None):
80 | """
81 | Group exponential of the Lie group of
82 | all invertible matrices.
83 | """
84 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=3)
85 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=3)
86 |
87 | tangent_vec_at_identity = self.compose(
88 | self.inverse(base_point), tangent_vec)
89 |
90 | group_exp_from_identity = self.group_exp_from_identity(
91 | tangent_vec_at_identity)
92 |
93 | group_exp = self.compose(
94 | base_point, group_exp_from_identity)
95 |
96 | return group_exp
97 |
98 | def group_log_from_identity(self, point, point_type=None):
99 | """
100 | Group logarithm of the Lie group of
101 | all invertible matrices at the identity.
102 | """
103 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=3)
104 | group_log = gs.linalg.logm(point)
105 |
106 | return gs.real(group_log)
107 |
108 | def group_log_not_from_identity(
109 | self, point, base_point, point_type=None):
110 | """
111 | Group logarithm of the Lie group of
112 | all invertible matrices.
113 | """
114 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=3)
115 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=3)
116 |
117 | point_near_identity = self.compose(
118 | self.inverse(base_point), point)
119 |
120 | group_log_from_identity = self.group_log_from_identity(
121 | point_near_identity)
122 |
123 | group_log = self.compose(
124 | base_point, group_log_from_identity)
125 |
126 | return group_log
127 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/loss_and_gradient_so3.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Predict on manifolds: losses.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import os
6 | import tensorflow as tf
7 |
8 | import geomstats.backend as gs
9 | import geomstats.lie_group as lie_group
10 |
11 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
12 |
13 |
14 | SO3 = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=3)
15 |
16 |
17 | def loss(y_pred, y_true,
18 | metric=SO3.bi_invariant_metric,
19 | representation='vector'):
20 |
21 | if representation == 'quaternion':
22 | y_pred = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_pred)
23 | y_true = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_true)
24 |
25 | loss = lie_group.loss(y_pred, y_true, SO3, metric)
26 | return loss
27 |
28 |
29 | def grad(y_pred, y_true,
30 | metric=SO3.bi_invariant_metric,
31 | representation='vector'):
32 |
33 | y_pred = gs.expand_dims(y_pred, axis=0)
34 | y_true = gs.expand_dims(y_true, axis=0)
35 |
36 | if representation == 'vector':
37 | grad = lie_group.grad(y_pred, y_true, SO3, metric)
38 |
39 | if representation == 'quaternion':
40 | quat_scalar = y_pred[:, :1]
41 | quat_vec = y_pred[:, 1:]
42 |
43 | quat_vec_norm = gs.linalg.norm(quat_vec, axis=1)
44 | quat_sq_norm = quat_vec_norm ** 2 + quat_scalar ** 2
45 |
46 | quat_arctan2 = gs.arctan2(quat_vec_norm, quat_scalar)
47 | differential_scalar = - 2 * quat_vec / (quat_sq_norm)
48 | differential_scalar = gs.to_ndarray(differential_scalar, to_ndim=2)
49 | differential_scalar = gs.transpose(differential_scalar)
50 |
51 | differential_vec = (2 * (quat_scalar / quat_sq_norm
52 | - 2 * quat_arctan2 / quat_vec_norm)
53 | * (gs.einsum('ni,nj->nij', quat_vec, quat_vec)
54 | / quat_vec_norm ** 2)
55 | + 2 * quat_arctan2 / quat_vec_norm * gs.eye(3))
56 | differential_vec = gs.squeeze(differential_vec)
57 |
58 | differential = gs.concatenate(
59 | [differential_scalar, differential_vec],
60 | axis=1)
61 |
62 | y_pred = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_pred)
63 | y_true = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_true)
64 |
65 | grad = lie_group.grad(y_pred, y_true, SO3, metric)
66 |
67 | grad = gs.matmul(grad, differential)
68 |
69 | grad = gs.squeeze(grad, axis=0)
70 | return grad
71 |
72 |
73 | def main():
74 | y_pred = gs.array([1., 1.5, -0.3])
75 | y_true = gs.array([0.1, 1.8, -0.1])
76 |
77 | loss_rot_vec = loss(y_pred, y_true)
78 | grad_rot_vec = grad(y_pred, y_true)
79 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
80 | with tf.Session() as sess:
81 | loss_rot_vec = sess.run(loss_rot_vec)
82 | grad_rot_vec = sess.run(grad_rot_vec)
83 | print('The loss between the rotation vectors is: {}'.format(
84 | loss_rot_vec[0, 0]))
85 | print('The riemannian gradient is: {}'.format(
86 | grad_rot_vec))
87 |
88 | angle = gs.pi / 6
89 | cos = gs.cos(angle / 2)
90 | sin = gs.sin(angle / 2)
91 | u = gs.array([1., 2., 3.])
92 | u = u / gs.linalg.norm(u)
93 | scalar = gs.to_ndarray(cos, to_ndim=1)
94 | vec = sin * u
95 | y_pred_quaternion = gs.concatenate([scalar, vec], axis=0)
96 |
97 | angle = gs.pi / 7
98 | cos = gs.cos(angle / 2)
99 | sin = gs.sin(angle / 2)
100 | u = gs.array([1., 2., 3.])
101 | u = u / gs.linalg.norm(u)
102 | scalar = gs.to_ndarray(cos, to_ndim=1)
103 | vec = sin * u
104 | y_true_quaternion = gs.concatenate([scalar, vec], axis=0)
105 |
106 | loss_quaternion = loss(y_pred_quaternion, y_true_quaternion,
107 | representation='quaternion')
108 | grad_quaternion = grad(y_pred_quaternion, y_true_quaternion,
109 | representation='quaternion')
110 |
111 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
112 | with tf.Session() as sess:
113 | loss_quaternion = sess.run(loss_quaternion)
114 | grad_quaternion = sess.run(grad_quaternion)
115 | print('The loss between the quaternions is: {}'.format(
116 | loss_quaternion[0, 0]))
117 | print('The riemannian gradient is: {}'.format(
118 | grad_quaternion))
119 |
120 |
121 | if __name__ == "__main__":
122 | main()
123 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/gradient_descent_s2.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Gradient descent on a sphere.
3 |
4 | We solve the following optimization problem:
5 |
6 | minimize: x^{T}Ax
7 | such than: x^{T}x = 1
8 |
9 | Using by operating a gradient descent of the quadratic form
10 | on the sphere. We solve this in 3 dimension on the 2-sphere
11 | manifold so that we can visualize and render the path as a video.
12 | """
13 |
14 | import matplotlib
15 | matplotlib.use("Agg") # NOQA
16 | import matplotlib.animation as animation
17 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
18 | import numpy as np
19 |
20 | import geomstats.backend as gs
21 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
22 |
23 | from geomstats.hypersphere import Hypersphere
24 | from geomstats.spd_matrices_space import SPDMatricesSpace
25 |
26 |
27 | SPHERE2 = Hypersphere(dimension=2)
28 | METRIC = SPHERE2.metric
29 |
30 |
31 | def gradient_descent(start,
32 | loss,
33 | grad,
34 | manifold,
35 | lr=0.01,
36 | max_iter=256,
37 | precision=1e-5):
38 | """Operate a gradient descent on a given manifold until either max_iter or
39 | a given precision is reached."""
40 | x = start
41 | for i in range(max_iter):
42 | x_prev = x
43 | euclidean_grad = - lr * grad(x)
44 | tangent_vec = manifold.projection_to_tangent_space(
45 | vector=euclidean_grad, base_point=x)
46 | x = manifold.metric.exp(base_point=x, tangent_vec=tangent_vec)[0]
47 | if (gs.abs(loss(x, use_gs=True) - loss(x_prev, use_gs=True))
48 | <= precision):
49 | print('x: %s' % x)
50 | print('reached precision %s' % precision)
51 | print('iterations: %d' % i)
52 | break
53 | yield x, loss(x)
54 |
55 |
56 | def plot_and_save_video(geodesics,
57 | loss,
58 | size=20,
59 | fps=10,
60 | dpi=100,
61 | out='out.mp4',
62 | color='red'):
63 | """Render a set of geodesics and save it to an mpeg 4 file."""
64 | FFMpegWriter = animation.writers['ffmpeg']
65 | writer = FFMpegWriter(fps=fps)
66 | fig = plt.figure(figsize=(size, size))
67 | ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d', aspect='equal')
68 | sphere = visualization.Sphere()
69 | sphere.plot_heatmap(ax, loss)
70 | points = gs.to_ndarray(geodesics[0], to_ndim=2)
71 | sphere.add_points(points)
72 | sphere.draw(ax, color=color, marker='.')
73 | with writer.saving(fig, out, dpi=dpi):
74 | for points in geodesics[1:]:
75 | points = gs.to_ndarray(points, to_ndim=2)
76 | sphere.draw_points(ax, points=points, color=color, marker='.')
77 | writer.grab_frame()
78 |
79 |
80 | def generate_well_behaved_matrix():
81 | """Generate a matrix with real eigenvalues."""
82 | matrix = 2 * SPDMatricesSpace(n=3).random_uniform()[0]
83 | assert np.linalg.det(matrix) > 0
84 | return matrix
85 |
86 |
87 | def main(output_file='out.mp4', max_iter=128):
88 | gs.random.seed(1985)
89 | A = generate_well_behaved_matrix()
90 |
91 | def grad(x):
92 | return 2 * gs.matmul(A, x)
93 |
94 | def loss(x, use_gs=False):
95 | if use_gs:
96 | return gs.matmul(x, gs.matmul(A, x))
97 | return np.matmul(x, np.matmul(A, x))
98 |
99 | initial_point = gs.array([0., 1., 0.])
100 | previous_x = initial_point
101 | geodesics = []
102 | n_steps = 20
103 | for x, fx in gradient_descent(initial_point,
104 | loss,
105 | grad,
106 | max_iter=max_iter,
107 | manifold=SPHERE2):
108 | initial_tangent_vec = METRIC.log(point=x, base_point=previous_x)
109 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=previous_x,
110 | initial_tangent_vec=initial_tangent_vec)
111 |
112 | t = np.linspace(0, 1, n_steps)
113 | geodesics.append(geodesic(t))
114 | previous_x = x
115 | if output_file:
116 | plot_and_save_video(geodesics, loss, out=output_file)
117 | eig, _ = np.linalg.eig(A)
118 | np.testing.assert_almost_equal(loss(x), np.min(eig), decimal=2)
119 |
120 |
121 | if __name__ == "__main__":
122 | main()
123 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/minkowski_space.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Minkowski space.
3 | """
4 |
5 |
6 | from geomstats.manifold import Manifold
7 | from geomstats.riemannian_metric import RiemannianMetric
8 | import geomstats.backend as gs
9 |
10 |
11 | class MinkowskiSpace(Manifold):
12 | """Class for Minkowski Space."""
13 |
14 | def __init__(self, dimension):
15 | assert isinstance(dimension, int) and dimension > 0
16 | self.dimension = dimension
17 | self.metric = MinkowskiMetric(dimension)
18 |
19 | def belongs(self, point):
20 | """
21 | Evaluate if a point belongs to the Minkowski space.
22 |
23 | Parameters
24 | ----------
25 | point : array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
26 | Input points.
27 |
28 | Returns
29 | -------
30 | belongs : array-like, shape=[n_samples, 1]
31 | """
32 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=2)
33 | n_points, point_dim = point.shape
34 | belongs = point_dim == self.dimension
35 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=1)
36 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
37 | belongs = gs.tile(belongs, (n_points, 1))
38 |
39 | return belongs
40 |
41 | def random_uniform(self, n_samples=1, bound=1.):
42 | """
43 | Sample in the Minkowski space with the uniform distribution.
44 |
45 | Returns
46 | -------
47 | points : array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
48 | Sampled points.
49 | """
50 | size = (n_samples, self.dimension)
51 | point = bound * gs.random.rand(*size) * 2 - 1
52 |
53 | return point
54 |
55 |
56 | class MinkowskiMetric(RiemannianMetric):
57 | """
58 | Class for the pseudo-Riemannian Minkowski metric.
59 | The metric is flat: the inner product is independent of the base point.
60 | """
61 | def __init__(self, dimension):
62 | super(MinkowskiMetric, self).__init__(
63 | dimension=dimension,
64 | signature=(dimension - 1, 1, 0))
65 |
66 | def inner_product_matrix(self, base_point=None):
67 | """
68 | Inner product matrix, independent of the base point.
69 |
70 | Parameters
71 | ----------
72 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
73 | """
74 | inner_prod_mat = gs.eye(self.dimension-1, self.dimension-1)
75 | first_row = gs.array([0.] * (self.dimension - 1))
76 | first_row = gs.to_ndarray(first_row, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
77 | inner_prod_mat = gs.vstack([gs.transpose(first_row),
78 | inner_prod_mat])
79 |
80 | first_column = gs.array([-1.] + [0.] * (self.dimension - 1))
81 | first_column = gs.to_ndarray(first_column, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
82 | inner_prod_mat = gs.hstack([first_column,
83 | inner_prod_mat])
84 |
85 | return inner_prod_mat
86 |
87 | def exp(self, tangent_vec, base_point):
88 | """
89 | The Riemannian exponential is the addition in the Minkowski space.
90 |
91 | Parameters
92 | ----------
93 | tangent_vec: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
94 | or shape=[1, dimension]
95 |
96 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
97 | or shape=[1, dimension]
98 | """
99 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=2)
100 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=2)
101 | return base_point + tangent_vec
102 |
103 | def log(self, point, base_point):
104 | """
105 | The Riemannian logarithm is the subtraction in the Minkowski space.
106 |
107 | Parameters
108 | ----------
109 | point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
110 | or shape=[1, dimension]
111 |
112 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
113 | or shape=[1, dimension]
114 | """
115 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=2)
116 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=2)
117 | return point - base_point
118 |
119 | def mean(self, points, weights=None):
120 | """
121 | The Frechet mean of (weighted) points is the weighted average of
122 | the points in the Minkowski space.
123 |
124 | Parameters
125 | ----------
126 | points: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
127 |
128 | weights: array-like, shape=[n_samples, 1], optional
129 | """
130 | if isinstance(points, list):
131 | points = gs.vstack(points)
132 | points = gs.to_ndarray(points, to_ndim=2)
133 | n_points = gs.shape(points)[0]
134 |
135 | if isinstance(weights, list):
136 | weights = gs.vstack(weights)
137 | elif weights is None:
138 | weights = gs.ones((n_points,))
139 |
140 | weighted_points = gs.einsum('n,nj->nj', weights, points)
141 | mean = (gs.sum(weighted_points, axis=0)
142 | / gs.sum(weights))
143 | mean = gs.to_ndarray(mean, to_ndim=2)
144 | return mean
145 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/loss_and_gradient_se3.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Predict on SE3: losses.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import os
6 | import tensorflow as tf
7 |
8 | import geomstats.backend as gs
9 | import geomstats.lie_group as lie_group
10 |
11 | from geomstats.special_euclidean_group import SpecialEuclideanGroup
12 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
13 |
14 |
15 | SE3 = SpecialEuclideanGroup(n=3)
16 | SO3 = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=3)
17 |
18 |
19 | def loss(y_pred, y_true,
20 | metric=SE3.left_canonical_metric,
21 | representation='vector'):
22 | """
23 | Loss function given by a riemannian metric on a Lie group,
24 | by default the left-invariant canonical metric.
25 | """
26 | if gs.ndim(y_pred) == 1:
27 | y_pred = gs.expand_dims(y_pred, axis=0)
28 | if gs.ndim(y_true) == 1:
29 | y_true = gs.expand_dims(y_true, axis=0)
30 |
31 | if representation == 'quaternion':
32 | y_pred_rot_vec = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_pred[:, :4])
33 | y_pred = gs.hstack([y_pred_rot_vec, y_pred[:, 4:]])
34 | y_true_rot_vec = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_true[:, :4])
35 | y_true = gs.hstack([y_true_rot_vec, y_true[:, 4:]])
36 |
37 | loss = lie_group.loss(y_pred, y_true, SE3, metric)
38 | return loss
39 |
40 |
41 | def grad(y_pred, y_true,
42 | metric=SE3.left_canonical_metric,
43 | representation='vector'):
44 | """
45 | Closed-form for the gradient of pose_loss.
46 |
47 | :return: tangent vector at point y_pred.
48 | """
49 | if gs.ndim(y_pred) == 1:
50 | y_pred = gs.expand_dims(y_pred, axis=0)
51 | if gs.ndim(y_true) == 1:
52 | y_true = gs.expand_dims(y_true, axis=0)
53 |
54 | if representation == 'vector':
55 | grad = lie_group.grad(y_pred, y_true, SE3, metric)
56 |
57 | if representation == 'quaternion':
58 |
59 | y_pred_rot_vec = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_pred[:, :4])
60 | y_pred_pose = gs.hstack([y_pred_rot_vec, y_pred[:, 4:]])
61 | y_true_rot_vec = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_true[:, :4])
62 | y_true_pose = gs.hstack([y_true_rot_vec, y_true[:, 4:]])
63 | grad = lie_group.grad(y_pred_pose, y_true_pose, SE3, metric)
64 |
65 | quat_scalar = y_pred[:, :1]
66 | quat_vec = y_pred[:, 1:4]
67 |
68 | quat_vec_norm = gs.linalg.norm(quat_vec, axis=1)
69 | quat_sq_norm = quat_vec_norm ** 2 + quat_scalar ** 2
70 |
71 | quat_arctan2 = gs.arctan2(quat_vec_norm, quat_scalar)
72 | differential_scalar = - 2 * quat_vec / (quat_sq_norm)
73 | differential_vec = (2 * (quat_scalar / quat_sq_norm
74 | - 2 * quat_arctan2 / quat_vec_norm)
75 | * (gs.einsum('ni,nj->nij', quat_vec, quat_vec)
76 | / quat_vec_norm * quat_vec_norm)
77 | + 2 * quat_arctan2 / quat_vec_norm * gs.eye(3))
78 |
79 | differential_scalar_t = gs.transpose(differential_scalar, axes=(1, 0))
80 |
81 | upper_left_block = gs.hstack(
82 | (differential_scalar_t, differential_vec[0]))
83 | upper_right_block = gs.zeros((3, 3))
84 | lower_right_block = gs.eye(3)
85 | lower_left_block = gs.zeros((3, 4))
86 |
87 | top = gs.hstack((upper_left_block, upper_right_block))
88 | bottom = gs.hstack((lower_left_block, lower_right_block))
89 |
90 | differential = gs.vstack((top, bottom))
91 | differential = gs.expand_dims(differential, axis=0)
92 |
93 | grad = gs.einsum('ni,nij->ni', grad, differential)
94 |
95 | grad = gs.squeeze(grad, axis=0)
96 | return grad
97 |
98 |
99 | def main():
100 | y_pred = gs.array([1., 1.5, -0.3, 5., 6., 7.])
101 | y_true = gs.array([0.1, 1.8, -0.1, 4., 5., 6.])
102 |
103 | loss_rot_vec = loss(y_pred, y_true)
104 | grad_rot_vec = grad(y_pred, y_true)
105 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
106 | with tf.Session() as sess:
107 | loss_rot_vec = sess.run(loss_rot_vec)
108 | grad_rot_vec = sess.run(grad_rot_vec)
109 | print('The loss between the poses using rotation vectors is: {}'.format(
110 | loss_rot_vec[0, 0]))
111 | print('The riemannian gradient is: {}'.format(grad_rot_vec))
112 |
113 | angle = gs.pi / 6
114 | cos = gs.cos(angle / 2)
115 | sin = gs.sin(angle / 2)
116 | u = gs.array([1., 2., 3.])
117 | u = u / gs.linalg.norm(u)
118 | scalar = gs.array(cos)
119 | vec = sin * u
120 | translation = gs.array([5., 6., 7.])
121 | y_pred_quaternion = gs.concatenate([[scalar], vec, translation], axis=0)
122 |
123 | angle = gs.pi / 7
124 | cos = gs.cos(angle / 2)
125 | sin = gs.sin(angle / 2)
126 | u = gs.array([1., 2., 3.])
127 | u = u / gs.linalg.norm(u)
128 | scalar = gs.array(cos)
129 | vec = sin * u
130 | translation = gs.array([4., 5., 6.])
131 | y_true_quaternion = gs.concatenate([[scalar], vec, translation], axis=0)
132 |
133 | loss_quaternion = loss(y_pred_quaternion, y_true_quaternion,
134 | representation='quaternion')
135 | grad_quaternion = grad(y_pred_quaternion, y_true_quaternion,
136 | representation='quaternion')
137 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
138 | with tf.Session() as sess:
139 | loss_quaternion = sess.run(loss_quaternion)
140 | grad_quaternion = sess.run(grad_quaternion)
141 | print('The loss between the poses using quaternions is: {}'.format(
142 | loss_quaternion[0, 0]))
143 | print('The riemannian gradient is: {}'.format(
144 | grad_quaternion))
145 |
146 |
147 | if __name__ == "__main__":
148 | main()
149 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_general_linear_group.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for General Linear group.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import warnings
6 |
7 | import geomstats.backend as gs
8 | import geomstats.tests
9 | import tests.helper as helper
10 |
11 | from geomstats.general_linear_group import GeneralLinearGroup
12 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
13 |
14 | RTOL = 1e-5
15 |
16 |
17 | class TestGeneralLinearGroupMethods(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
18 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
19 |
20 | def setUp(self):
21 | gs.random.seed(1234)
22 | self.n = 3
23 | self.n_samples = 2
24 | self.group = GeneralLinearGroup(n=self.n)
25 | # We generate invertible matrices using so3_group
26 | self.so3_group = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=self.n)
27 |
28 | warnings.simplefilter('ignore', category=ImportWarning)
29 |
30 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
31 | def test_belongs(self):
32 | """
33 | A rotation matrix belongs to the matrix Lie group
34 | of invertible matrices.
35 | """
36 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.2, -0.1, 0.1])
37 | rot_mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
38 | result = self.group.belongs(rot_mat)
39 | expected = gs.array([True])
40 |
41 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
42 |
43 | def test_compose(self):
44 | # 1. Composition by identity, on the right
45 | # Expect the original transformation
46 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.2, -0.1, 0.1])
47 | mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
48 |
49 | result = self.group.compose(mat, self.group.identity)
50 | expected = mat
51 | expected = helper.to_matrix(mat)
52 |
53 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
54 |
55 | # 2. Composition by identity, on the left
56 | # Expect the original transformation
57 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.2, 0.1, -0.1])
58 | mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
59 |
60 | result = self.group.compose(self.group.identity, mat)
61 | expected = mat
62 |
63 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
64 |
65 | def test_inverse(self):
66 | mat = gs.array([
67 | [1., 2., 3.],
68 | [4., 5., 6.],
69 | [7., 8., 10.]])
70 | result = self.group.inverse(mat)
71 | expected = 1. / 3. * gs.array([
72 | [-2., -4., 3.],
73 | [-2., 11., -6.],
74 | [3., -6., 3.]])
75 | expected = helper.to_matrix(expected)
76 |
77 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
78 |
79 | def test_compose_and_inverse(self):
80 | # 1. Compose transformation by its inverse on the right
81 | # Expect the group identity
82 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.2, 0.1, 0.1])
83 | mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
84 | inv_mat = self.group.inverse(mat)
85 |
86 | result = self.group.compose(mat, inv_mat)
87 | expected = self.group.identity
88 | expected = helper.to_matrix(expected)
89 |
90 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
91 |
92 | # 2. Compose transformation by its inverse on the left
93 | # Expect the group identity
94 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.7, 0.1, 0.1])
95 | mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
96 | inv_mat = self.group.inverse(mat)
97 |
98 | result = self.group.compose(inv_mat, mat)
99 | expected = self.group.identity
100 | expected = helper.to_matrix(expected)
101 |
102 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
103 |
104 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
105 | def test_group_log_and_exp(self):
106 | point = 5 * gs.eye(self.n)
107 |
108 | group_log = self.group.group_log(point)
109 | result = self.group.group_exp(group_log)
110 | expected = point
111 | expected = helper.to_matrix(expected)
112 |
113 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
114 |
115 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
116 | def test_group_exp_vectorization(self):
117 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
118 | [0., 3., 0.],
119 | [0., 0., 4.]],
120 | [[1., 0., 0.],
121 | [0., 5., 0.],
122 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
123 |
124 | expected = gs.array([[[7.38905609, 0., 0.],
125 | [0., 20.0855369, 0.],
126 | [0., 0., 54.5981500]],
127 | [[2.718281828, 0., 0.],
128 | [0., 148.413159, 0.],
129 | [0., 0., 403.42879349]]])
130 |
131 | result = self.group.group_exp(point)
132 |
133 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected, rtol=1e-3)
134 |
135 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
136 | def test_group_log_vectorization(self):
137 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
138 | [0., 3., 0.],
139 | [0., 0., 4.]],
140 | [[1., 0., 0.],
141 | [0., 5., 0.],
142 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
143 |
144 | expected = gs.array([[[0.693147180, 0., 0.],
145 | [0., 1.09861228866, 0.],
146 | [0., 0., 1.38629436]],
147 | [[0., 0., 0.],
148 | [0., 1.609437912, 0.],
149 | [0., 0., 1.79175946]]])
150 |
151 | result = self.group.group_log(point)
152 |
153 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected, atol=1e-4)
154 |
155 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
156 | def test_expm_and_logm_vectorization_symmetric(self):
157 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
158 | [0., 3., 0.],
159 | [0., 0., 4.]],
160 | [[1., 0., 0.],
161 | [0., 5., 0.],
162 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
163 | result = self.group.group_exp(self.group.group_log(point))
164 | expected = point
165 |
166 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
167 |
168 |
169 | if __name__ == '__main__':
170 | geomstats.tests.main()
171 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/backend/tensorflow.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Tensorflow based computation backend."""
2 |
3 | import tensorflow as tf
4 |
5 |
6 | int8 = tf.int8
7 | int32 = tf.int32
8 | int64 = tf.int64
9 | float16 = tf.float16
10 | float32 = tf.float32
11 | float64 = tf.float64
12 |
13 |
14 | def while_loop(*args, **kwargs):
15 | return tf.while_loop(*args, **kwargs)
16 |
17 |
18 | def logical_or(x, y):
19 | return tf.logical_or(x, y)
20 |
21 |
22 | def get_mask_i_float(i, n):
23 | range_n = arange(n)
24 | i_float = cast(array([i]), int32)[0]
25 | mask_i = equal(range_n, i_float)
26 | mask_i_float = cast(mask_i, float32)
27 | return mask_i_float
28 |
29 |
30 | def gather(*args, **kwargs):
31 | return tf.gather(*args, **kwargs)
32 |
33 |
34 | def where(*args, **kwargs):
35 | return tf.where(*args, **kwargs)
36 |
37 |
38 | def vectorize(x, pyfunc, multiple_args=False, dtype=None, **kwargs):
39 | if multiple_args:
40 | return tf.map_fn(lambda x: pyfunc(*x), elems=x, dtype=dtype)
41 | return tf.map_fn(pyfunc, elems=x, dtype=dtype)
42 |
43 |
44 | def sign(x):
45 | return tf.sign(x)
46 |
47 |
48 | def hsplit(x, n_splits):
49 | return tf.split(x, num_or_size_splits=n_splits, axis=1)
50 |
51 |
52 | def amax(x):
53 | return tf.reduce_max(x)
54 |
55 |
56 | def real(x):
57 | return tf.real(x)
58 |
59 |
60 | def cond(*args, **kwargs):
61 | return tf.cond(*args, **kwargs)
62 |
63 |
64 | def reshape(*args, **kwargs):
65 | return tf.reshape(*args, **kwargs)
66 |
67 |
68 | def arange(*args, **kwargs):
69 | return tf.range(*args, **kwargs)
70 |
71 |
72 | def outer(x, y):
73 | return tf.einsum('i,j->ij', x, y)
74 |
75 |
76 | def copy(x):
77 | return tf.Variable(x)
78 |
79 |
80 | def linspace(start, stop, num):
81 | return tf.linspace(start, stop, num)
82 |
83 |
84 | def mod(x, y):
85 | return tf.mod(x, y)
86 |
87 |
88 | def boolean_mask(x, mask, name='boolean_mask', axis=None):
89 | return tf.boolean_mask(x, mask, name, axis)
90 |
91 |
92 | def exp(x):
93 | return tf.exp(x)
94 |
95 |
96 | def log(x):
97 | return tf.log(x)
98 |
99 |
100 | def hstack(x):
101 | return tf.concat(x, axis=1)
102 |
103 |
104 | def vstack(x):
105 | return tf.concat(x, axis=0)
106 |
107 |
108 | def cast(x, dtype):
109 | return tf.cast(x, dtype)
110 |
111 |
112 | def divide(x1, x2):
113 | return tf.divide(x1, x2)
114 |
115 |
116 | def tile(x, reps):
117 | return tf.tile(x, reps)
118 |
119 |
120 | def eval(x):
121 | if tf.executing_eagerly():
122 | return x
123 | return x.eval()
124 |
125 |
126 | def abs(x):
127 | return tf.abs(x)
128 |
129 |
130 | def zeros(x):
131 | return tf.zeros(x)
132 |
133 |
134 | def ones(x):
135 | return tf.ones(x)
136 |
137 |
138 | def sin(x):
139 | return tf.sin(x)
140 |
141 |
142 | def cos(x):
143 | return tf.cos(x)
144 |
145 |
146 | def cosh(x):
147 | return tf.cosh(x)
148 |
149 |
150 | def sinh(x):
151 | return tf.sinh(x)
152 |
153 |
154 | def tanh(x):
155 | return tf.tanh(x)
156 |
157 |
158 | def arccosh(x):
159 | return tf.acosh(x)
160 |
161 |
162 | def tan(x):
163 | return tf.tan(x)
164 |
165 |
166 | def arcsin(x):
167 | return tf.asin(x)
168 |
169 |
170 | def arccos(x):
171 | return tf.acos(x)
172 |
173 |
174 | def shape(x):
175 | return tf.shape(x)
176 |
177 |
178 | def ndim(x):
179 | x = array(x)
180 | dims = x.get_shape()._dims
181 | if dims is not None:
182 | return len(dims)
183 | return None
184 |
185 |
186 | def dot(x, y):
187 | return tf.tensordot(x, y, axes=1)
188 |
189 |
190 | def maximum(x, y):
191 | return tf.maximum(x, y)
192 |
193 |
194 | def greater(x, y):
195 | return tf.greater(x, y)
196 |
197 |
198 | def greater_equal(x, y):
199 | return tf.greater_equal(x, y)
200 |
201 |
202 | def equal(x, y):
203 | return tf.equal(x, y)
204 |
205 |
206 | def to_ndarray(x, to_ndim, axis=0):
207 | if ndim(x) == to_ndim - 1:
208 | x = tf.expand_dims(x, axis=axis)
209 |
210 | return x
211 |
212 |
213 | def sqrt(x):
214 | return tf.sqrt(x)
215 |
216 |
217 | def isclose(x, y, rtol=1e-05, atol=1e-08):
218 | rhs = tf.constant(atol) + tf.constant(rtol) * tf.abs(y)
219 | return tf.less_equal(tf.abs(tf.subtract(x, y)), rhs)
220 |
221 |
222 | def allclose(x, y, rtol=1e-05, atol=1e-08):
223 | return tf.reduce_all(isclose(x, y, rtol=rtol, atol=atol))
224 |
225 |
226 | def less(x, y):
227 | return tf.less(x, y)
228 |
229 |
230 | def less_equal(x, y):
231 | return tf.less_equal(x, y)
232 |
233 |
234 | def eye(n, m=None):
235 | if m is None:
236 | m = n
237 | n = cast(n, dtype=int32)
238 | m = cast(m, dtype=int32)
239 | return tf.eye(num_rows=n, num_columns=m)
240 |
241 |
242 | def matmul(x, y):
243 | return tf.matmul(x, y)
244 |
245 |
246 | def argmax(*args, **kwargs):
247 | return tf.argmax(*args, **kwargs)
248 |
249 |
250 | def sum(*args, **kwargs):
251 | return tf.reduce_sum(*args, **kwargs)
252 |
253 |
254 | def einsum(equation, *inputs, **kwargs):
255 | return tf.einsum(equation, *inputs, **kwargs)
256 |
257 |
258 | def transpose(x, axes=None):
259 | return tf.transpose(x, perm=axes)
260 |
261 |
262 | def squeeze(x, **kwargs):
263 | return tf.squeeze(x, **kwargs)
264 |
265 |
266 | def zeros_like(x):
267 | return tf.zeros_like(x)
268 |
269 |
270 | def ones_like(x):
271 | return tf.ones_like(x)
272 |
273 |
274 | def trace(x, **kwargs):
275 | return tf.trace(x)
276 |
277 |
278 | def array(x):
279 | return tf.convert_to_tensor(x)
280 |
281 |
282 | def all(bool_tensor, axis=None, keepdims=False):
283 | bool_tensor = tf.cast(bool_tensor, tf.bool)
284 | all_true = tf.reduce_all(bool_tensor, axis, keepdims)
285 | return all_true
286 |
287 |
288 | def concatenate(*args, **kwargs):
289 | return tf.concat(*args, **kwargs)
290 |
291 |
292 | def asarray(x):
293 | return x
294 |
295 |
296 | def expand_dims(x, axis=None):
297 | return tf.expand_dims(x, axis)
298 |
299 |
300 | def clip(x, min_value, max_value):
301 | return tf.clip_by_value(x, min_value, max_value)
302 |
303 |
304 | def floor(x):
305 | return tf.floor(x)
306 |
307 |
308 | def diag(a):
309 | return tf.map_fn(
310 | lambda x: tf.diag(x),
311 | a)
312 |
313 |
314 | def cross(a, b):
315 | return tf.cross(a, b)
316 |
317 |
318 | def stack(*args, **kwargs):
319 | return tf.stack(*args, **kwargs)
320 |
321 |
322 | def arctan2(*args, **kwargs):
323 | return tf.atan2(*args, **kwargs)
324 |
325 |
326 | def diagonal(*args, **kwargs):
327 | return tf.linalg.diag_part(*args)
328 |
329 |
330 | def mean(x, axis=None):
331 | return tf.reduce_mean(x, axis)
332 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/CONTRIBUTING.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Contributing to Geomstats
2 |
3 | Welcome to the geomstats repository!
4 | We are excited you are here and want to contribute.
5 |
6 | More details on contributing can be found on the [documentation website][link_doc].
7 |
8 | ## Practical Guide to Submitting your Contribution
9 |
10 | These guidelines are designed to make it as easy as possible to get involved.
11 | If you have any questions that are not discussed below,
12 | please let us know by opening an [issue][link_issues]!
13 |
14 | Before you start you will need to set up a free [GitHub][link_github] account and sign in.
15 | Here are some [instructions][link_signupinstructions].
16 |
17 |
18 | ## Joining the Conversation
19 |
20 | `geomstats` is maintained by a growing group of enthusiastic developers!
21 | Most of our discussions take place on [issues][link_issues].
22 |
23 |
24 | ## Contributing through GitHub
25 |
26 | [git][link_git] is a really useful tool for version control.
27 | [GitHub][link_github] sits on top of git and supports collaborative and distributed working.
28 |
29 | If you are not yet familiar with `git`, there are lots of great resources to help you *git* started!
30 | Some of our favorites include the [git Handbook][link_handbook] and
31 | the [Software Carpentry introduction to git][link_swc_intro].
32 |
33 | On GitHub, you will use [Markdown][markdown] to chat in issues and pull requests.
34 |
35 | GitHub has a really helpful page for getting started with
36 | [writing and formatting Markdown on GitHub][writing_formatting_github].
37 |
38 |
39 | ## Understanding Issues
40 |
41 | Every project on GitHub uses [issues][link_issues] slightly differently.
42 |
43 | The following outlines how ``geomstats`` developers think about these tools.
44 |
45 | * **Issues** are individual pieces of work that need to be completed to move the project forwards.
46 | A general guideline: if you find yourself tempted to write a great big issue that
47 | is difficult to describe as one unit of work, please consider splitting it into two or more issues.
48 |
49 | * Issues are assigned [labels](#issue-labels) which explain how they relate to the overall project's
50 | goals and immediate next steps.
51 |
52 |
53 | ## Making a Change
54 |
55 | We appreciate all contributions to ``geomstats``,
56 | but those accepted fastest will follow a workflow similar to the following:
57 |
58 | **1. Comment on an existing issue or open a new issue referencing your addition.**
59 |
60 | This allows other members of the ``geomstats`` development team to confirm that you are not
61 | overlapping with work that is currently underway and that everyone is on the same page
62 | with the goal of the work you are going to carry out.
63 |
64 | [This blog][link_pushpullblog] is a nice explanation of why putting this work in up front
65 | is so useful to everyone involved.
66 |
67 | **2. [Fork][link_fork] the [geomstats repository][link_geomstats] to your profile.**
68 |
69 | This is now your own unique copy of ``geomstats``.
70 | Changes here will not effect anyone else's work, so it is a safe space to explore edits to the code!
71 |
72 | Make sure to [keep your fork up to date][link_updateupstreamwiki] with the master repository.
73 |
74 | **3. Make the changes you have discussed, following the [geomstats coding style guide](#geomstats-coding-style-guide).**
75 |
76 | - Create your feature branch (`git checkout -b feature/fooBar`)
77 | - Commit your changes (`git commit -am 'Add some fooBar'`)
78 | - Push to the branch (`git push origin feature/fooBar`)
79 |
80 | Try to keep the changes focused.
81 | If you feel tempted to "branch out" then please make a [new branch][link_branches].
82 |
83 | **4. Add the corresponding unit tests.**
84 |
85 | If you are adding a new feature, do not forget to add the corresponding [unit tests][link_unit_tests].
86 | As ``geomstats`` enables numpy and tensorflow, your unit tests should run on these two backends.
87 |
88 | **5. Ensure Geomstats Coding Style Guide.**
89 |
90 | Ensure that your code is compliant with [PEP8][link_pep8],
91 | the coding style guide for python.
92 |
93 | Use [flake8][link_flake8] or [yapf][link_yapf] to automatically enforces this style.
94 |
95 |
96 | **6. Submit a [pull request][link_pullrequest].**
97 |
98 | A member of the development team will review your changes to confirm
99 | that they can be merged into the main code base.
100 |
101 | Use the Github labels to label your pull request:
102 | * ``enhancement``: enhancements or new features
103 | * ``bug``: bug fixes
104 | * ``test``: new or updated tests
105 | * ``documentation``: new or updated documentation
106 | * ``style``: style changes
107 | * ``refactoring``: refactoring existing code
108 | * ``continuous integration``: updates to continous integration infrastructure
109 |
110 |
111 | ## Recognizing Contributions
112 |
113 | We welcome and recognize all contributions from documentation to testing to code development.
114 | You can see a list of current contributors in our [README.md][link_readme].
115 | If you are new to the project, do not forget to add your name and affiliation there!
116 |
117 | ## Thank You!
118 |
119 |
120 |
121 | *— Based on contributing guidelines from the [fMRIprep][link_fmriprep] project.*
122 |
123 | [link_github]: https://github.com/
124 | [link_geomstats]: https://github.com/geomstats/geomstats
125 | [link_signupinstructions]: https://help.github.com/articles/signing-up-for-a-new-github-account
126 |
127 | [link_git]: https://git-scm.com/
128 | [link_handbook]: https://guides.github.com/introduction/git-handbook/
129 | [link_swc_intro]: http://swcarpentry.github.io/git-novice/
130 |
131 | [writing_formatting_github]: https://help.github.com/articles/getting-started-with-writing-and-formatting-on-github
132 | [markdown]: https://daringfireball.net/projects/markdown
133 | [rick_roll]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQw4w9WgXcQ
134 |
135 | [link_issues]: https://github.com/geomstats/geomstats/issues
136 | [link_labels]: https://github.com/geomstats/geomstats/labels
137 | [link_discussingissues]: https://help.github.com/articles/discussing-projects-in-issues-and-pull-requests
138 |
139 | [link_pullrequest]: https://help.github.com/articles/creating-a-pull-request/
140 | [link_fork]: https://help.github.com/articles/fork-a-repo/
141 | [link_pushpullblog]: https://www.igvita.com/2011/12/19/dont-push-your-pull-requests/
142 | [link_branches]: https://help.github.com/articles/creating-and-deleting-branches-within-your-repository/
143 | [link_unit_tests]: https://github.com/geomstats/geomstats/tree/master/tests
144 | [link_updateupstreamwiki]: https://help.github.com/articles/syncing-a-fork/
145 | [link_pep8]: https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/
146 | [link_linters]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lint_(software)
147 | [link_flake8]: http://flake8.pycqa.org/en/latest/
148 | [link_yapf]: https://github.com/google/yapf
149 | [link_readme]: https://github.com/geomstats/geomstats/blob/master/README.md
150 | [link_fmriprep]: https://github.com/poldracklab/fmriprep/
151 | [link_doc]: https://geomstats.github.io/contributing.html
152 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/learning/_template.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | This is a module to be used as a reference for building other modules
3 | """
4 | import numpy as np
5 | from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator, ClassifierMixin, TransformerMixin
6 | from sklearn.utils.validation import check_X_y, check_array, check_is_fitted
7 | from sklearn.utils.multiclass import unique_labels
8 | from sklearn.metrics import euclidean_distances
9 |
10 |
11 | class TemplateEstimator(BaseEstimator):
12 | """ A template estimator to be used as a reference implementation.
13 |
14 | For more information regarding how to build your own estimator, read more
15 | in the :ref:`User Guide `.
16 |
17 | Parameters
18 | ----------
19 | demo_param : str, default='demo_param'
20 | A parameter used for demonstation of how to pass and store paramters.
21 | """
22 | def __init__(self, demo_param='demo_param'):
23 | self.demo_param = demo_param
24 |
25 | def fit(self, X, y):
26 | """A reference implementation of a fitting function.
27 |
28 | Parameters
29 | ----------
30 | X : {array-like, sparse matrix}, shape (n_samples, n_features)
31 | The training input samples.
32 | y : array-like, shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs)
33 | The target values (class labels in classification, real numbers in
34 | regression).
35 |
36 | Returns
37 | -------
38 | self : object
39 | Returns self.
40 | """
41 | X, y = check_X_y(X, y, accept_sparse=True)
42 | self.is_fitted_ = True
43 | # `fit` should always return `self`
44 | return self
45 |
46 | def predict(self, X):
47 | """ A reference implementation of a predicting function.
48 |
49 | Parameters
50 | ----------
51 | X : {array-like, sparse matrix}, shape (n_samples, n_features)
52 | The training input samples.
53 |
54 | Returns
55 | -------
56 | y : ndarray, shape (n_samples,)
57 | Returns an array of ones.
58 | """
59 | X = check_array(X, accept_sparse=True)
60 | check_is_fitted(self, 'is_fitted_')
61 | return np.ones(X.shape[0], dtype=np.int64)
62 |
63 |
64 | class TemplateClassifier(BaseEstimator, ClassifierMixin):
65 | """ An example classifier which implements a 1-NN algorithm.
66 |
67 | For more information regarding how to build your own classifier, read more
68 | in the :ref:`User Guide `.
69 |
70 | Parameters
71 | ----------
72 | demo_param : str, default='demo'
73 | A parameter used for demonstation of how to pass and store paramters.
74 |
75 | Attributes
76 | ----------
77 | X_ : ndarray, shape (n_samples, n_features)
78 | The input passed during :meth:`fit`.
79 | y_ : ndarray, shape (n_samples,)
80 | The labels passed during :meth:`fit`.
81 | classes_ : ndarray, shape (n_classes,)
82 | The classes seen at :meth:`fit`.
83 | """
84 | def __init__(self, demo_param='demo'):
85 | self.demo_param = demo_param
86 |
87 | def fit(self, X, y):
88 | """A reference implementation of a fitting function for a classifier.
89 |
90 | Parameters
91 | ----------
92 | X : array-like, shape (n_samples, n_features)
93 | The training input samples.
94 | y : array-like, shape (n_samples,)
95 | The target values. An array of int.
96 |
97 | Returns
98 | -------
99 | self : object
100 | Returns self.
101 | """
102 | # Check that X and y have correct shape
103 | X, y = check_X_y(X, y)
104 | # Store the classes seen during fit
105 | self.classes_ = unique_labels(y)
106 |
107 | self.X_ = X
108 | self.y_ = y
109 | # Return the classifier
110 | return self
111 |
112 | def predict(self, X):
113 | """ A reference implementation of a prediction for a classifier.
114 |
115 | Parameters
116 | ----------
117 | X : array-like, shape (n_samples, n_features)
118 | The input samples.
119 |
120 | Returns
121 | -------
122 | y : ndarray, shape (n_samples,)
123 | The label for each sample is the label of the closest sample
124 | seen during fit.
125 | """
126 | # Check is fit had been called
127 | check_is_fitted(self, ['X_', 'y_'])
128 |
129 | # Input validation
130 | X = check_array(X)
131 |
132 | closest = np.argmin(euclidean_distances(X, self.X_), axis=1)
133 | return self.y_[closest]
134 |
135 |
136 | class TemplateTransformer(BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin):
137 | """ An example transformer that returns the element-wise square root.
138 |
139 | For more information regarding how to build your own transformer, read more
140 | in the :ref:`User Guide `.
141 |
142 | Parameters
143 | ----------
144 | demo_param : str, default='demo'
145 | A parameter used for demonstation of how to pass and store paramters.
146 |
147 | Attributes
148 | ----------
149 | n_features_ : int
150 | The number of features of the data passed to :meth:`fit`.
151 | """
152 | def __init__(self, demo_param='demo'):
153 | self.demo_param = demo_param
154 |
155 | def fit(self, X, y=None):
156 | """A reference implementation of a fitting function for a transformer.
157 |
158 | Parameters
159 | ----------
160 | X : {array-like, sparse matrix}, shape (n_samples, n_features)
161 | The training input samples.
162 | y : None
163 | There is no need of a target in a transformer, yet the pipeline API
164 | requires this parameter.
165 |
166 | Returns
167 | -------
168 | self : object
169 | Returns self.
170 | """
171 | X = check_array(X, accept_sparse=True)
172 |
173 | self.n_features_ = X.shape[1]
174 |
175 | # Return the transformer
176 | return self
177 |
178 | def transform(self, X):
179 | """ A reference implementation of a transform function.
180 |
181 | Parameters
182 | ----------
183 | X : {array-like, sparse-matrix}, shape (n_samples, n_features)
184 | The input samples.
185 |
186 | Returns
187 | -------
188 | X_transformed : array, shape (n_samples, n_features)
189 | The array containing the element-wise square roots of the values
190 | in ``X``.
191 | """
192 | # Check is fit had been called
193 | check_is_fitted(self, 'n_features_')
194 |
195 | # Input validation
196 | X = check_array(X, accept_sparse=True)
197 |
198 | # Check that the input is of the same shape as the one passed
199 | # during fit.
200 | if X.shape[1] != self.n_features_:
201 | raise ValueError('Shape of input is different from what was seen'
202 | 'in `fit`')
203 | return np.sqrt(X)
204 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/learning/mean_shift.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Mean shift clustering algorithm on Manifolds.
2 | """
3 |
4 |
5 | from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator, ClusterMixin
6 | from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import pairwise_distances_argmin
7 | from sklearn.utils import check_array
8 | from sklearn.utils.validation import check_is_fitted
9 |
10 |
11 | def mean_shift(X, bandwidth=None, seeds=None, bin_seeding=False,
12 | min_bin_freq=1, cluster_all=True, max_iter=300,
13 | n_jobs=None):
14 | """Perform mean shift clustering of data.
15 |
16 | Parameters
17 | ----------
18 |
19 | X : array-like, shape=[n_samples, n_features]
20 | Input data.
21 |
22 | bandwidth : float, optional
23 | Kernel bandwidth.
24 |
25 | If bandwidth is not given, it is determined using a heuristic based on
26 | the median of all pairwise distances. This will take quadratic time in
27 | the number of samples. The sklearn.cluster.estimate_bandwidth function
28 | can be used to do this more efficiently.
29 |
30 | seeds : array-like, shape=[n_seeds, n_features] or None
31 | Point used as initial kernel locations. If None and bin_seeding=False,
32 | each data point is used as a seed. If None and bin_seeding=True,
33 | see bin_seeding.
34 |
35 | bin_seeding : boolean, default=False
36 | If true, initial kernel locations are not locations of all
37 | points, but rather the location of the discretized version of
38 | points, where points are binned onto a grid whose coarseness
39 | corresponds to the bandwidth. Setting this option to True will speed
40 | up the algorithm because fewer seeds will be initialized.
41 | Ignored if seeds argument is not None.
42 |
43 | min_bin_freq : int, default=1
44 | To speed up the algorithm, accept only those bins with at least
45 | min_bin_freq points as seeds.
46 |
47 | cluster_all : boolean, default True
48 | If true, then all points are clustered, even those orphans that are
49 | not within any kernel. Orphans are assigned to the nearest kernel.
50 | If false, then orphans are given cluster label -1.
51 |
52 | max_iter : int, default 300
53 | Maximum number of iterations, per seed point before the clustering
54 | operation terminates (for that seed point), if has not converged yet.
55 |
56 | n_jobs : int or None, optional (default=None)
57 | The number of jobs to use for the computation. This works by computing
58 | each of the n_init runs in parallel.
59 |
60 | ``None`` means 1 unless in a :obj:`joblib.parallel_backend` context.
61 | ``-1`` means using all processors. See :term:`Glossary `
62 | for more details.
63 |
64 | .. versionadded:: 0.17
65 | Parallel Execution using *n_jobs*.
66 |
67 | Returns
68 | -------
69 |
70 | cluster_centers : array, shape=[n_clusters, n_features]
71 | Coordinates of cluster centers.
72 |
73 | labels : array, shape=[n_samples]
74 | Cluster labels for each point.
75 |
76 | """
77 | raise NotImplementedError()
78 |
79 |
80 | class MeanShift(BaseEstimator, ClusterMixin):
81 | """Mean shift clustering using a flat kernel.
82 |
83 | Mean shift clustering aims to discover "blobs" in a smooth density of
84 | samples. It is a centroid-based algorithm, which works by updating
85 | candidates for centroids to be the mean of the points within a given
86 | region. These candidates are then filtered in a post-processing stage to
87 | eliminate near-duplicates to form the final set of centroids.
88 |
89 | Seeding is performed using a binning technique for scalability.
90 |
91 | Parameters
92 | ----------
93 | bandwidth : float, optional
94 | Bandwidth used in the RBF kernel.
95 |
96 | If not given, the bandwidth is estimated using
97 | sklearn.cluster.estimate_bandwidth; see the documentation for that
98 | function for hints on scalability (see also the Notes, below).
99 |
100 | seeds : array, shape=[n_samples, n_features], optional
101 | Seeds used to initialize kernels. If not set,
102 | the seeds are calculated by clustering.get_bin_seeds
103 | with bandwidth as the grid size and default values for
104 | other parameters.
105 |
106 | bin_seeding : boolean, optional
107 | If true, initial kernel locations are not locations of all
108 | points, but rather the location of the discretized version of
109 | points, where points are binned onto a grid whose coarseness
110 | corresponds to the bandwidth. Setting this option to True will speed
111 | up the algorithm because fewer seeds will be initialized.
112 | default value: False
113 | Ignored if seeds argument is not None.
114 |
115 | min_bin_freq : int, optional
116 | To speed up the algorithm, accept only those bins with at least
117 | min_bin_freq points as seeds. If not defined, set to 1.
118 |
119 | cluster_all : boolean, default True
120 | If true, then all points are clustered, even those orphans that are
121 | not within any kernel. Orphans are assigned to the nearest kernel.
122 | If false, then orphans are given cluster label -1.
123 |
124 | n_jobs : int or None, optional (default=None)
125 | The number of jobs to use for the computation. This works by computing
126 | each of the n_init runs in parallel.
127 |
128 | ``None`` means 1 unless in a :obj:`joblib.parallel_backend` context.
129 | ``-1`` means using all processors. See :term:`Glossary `
130 | for more details.
131 |
132 | Attributes
133 | ----------
134 | cluster_centers_ : array, [n_clusters, n_features]
135 | Coordinates of cluster centers.
136 |
137 | labels_ :
138 | Labels of each point.
139 | """
140 | def __init__(self, bandwidth=None, seeds=None, bin_seeding=False,
141 | min_bin_freq=1, cluster_all=True, n_jobs=None):
142 | self.bandwidth = bandwidth
143 | self.seeds = seeds
144 | self.bin_seeding = bin_seeding
145 | self.cluster_all = cluster_all
146 | self.min_bin_freq = min_bin_freq
147 | self.n_jobs = n_jobs
148 |
149 | def fit(self, X, y=None):
150 | """Perform clustering.
151 |
152 | Parameters
153 | ----------
154 | X : array-like, shape=[n_samples, n_features]
155 | Samples to cluster.
156 |
157 | y : Ignored
158 |
159 | """
160 | X = check_array(X)
161 | self.cluster_centers_, self.labels_ = \
162 | mean_shift(X, bandwidth=self.bandwidth, seeds=self.seeds,
163 | min_bin_freq=self.min_bin_freq,
164 | bin_seeding=self.bin_seeding,
165 | cluster_all=self.cluster_all, n_jobs=self.n_jobs)
166 | return self
167 |
168 | def predict(self, X):
169 | """Predict the closest cluster each sample in X belongs to.
170 |
171 | Parameters
172 | ----------
173 | X : {array-like, sparse matrix}, shape=[n_samples, n_features]
174 | New data to predict.
175 |
176 | Returns
177 | -------
178 | labels : array, shape [n_samples,]
179 | Index of the cluster each sample belongs to.
180 | """
181 | check_is_fitted(self, "cluster_centers_")
182 |
183 | return pairwise_distances_argmin(X, self.cluster_centers_)
184 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/backend/numpy.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Numpy based computation backend."""
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 |
5 |
6 | int32 = np.int32
7 | int8 = np.int8
8 | float32 = np.float32
9 | float64 = np.float64
10 |
11 |
12 | def while_loop(cond, body, loop_vars, maximum_iterations):
13 | iteration = 0
14 | while cond(*loop_vars):
15 | loop_vars = body(*loop_vars)
16 | iteration += 1
17 | if iteration >= maximum_iterations:
18 | break
19 | return loop_vars
20 |
21 |
22 | def logical_or(x, y):
23 | bool_result = x or y
24 | return bool_result
25 |
26 |
27 | def get_mask_i_float(i, n):
28 | range_n = arange(n)
29 | i_float = cast(array([i]), int32)[0]
30 | mask_i = equal(range_n, i_float)
31 | mask_i_float = cast(mask_i, float32)
32 | return mask_i_float
33 |
34 |
35 | def gather(x, indices):
36 | return x[indices]
37 |
38 |
39 | def vectorize(x, pyfunc, multiple_args=False, signature=None, **kwargs):
40 | if multiple_args:
41 | return np.vectorize(pyfunc, signature=signature)(*x)
42 | return np.vectorize(pyfunc, signature=signature)(x)
43 |
44 |
45 | def cond(pred, true_fn, false_fn):
46 | if pred:
47 | return true_fn()
48 | return false_fn()
49 |
50 |
51 | def real(x):
52 | return np.real(x)
53 |
54 |
55 | def reshape(*args, **kwargs):
56 | return np.reshape(*args, **kwargs)
57 |
58 |
59 | def cast_to_complex(x):
60 | return np.vectorize(complex)(x)
61 |
62 |
63 | def boolean_mask(x, mask):
64 | return x[mask]
65 |
66 |
67 | def flip(*args, **kwargs):
68 | return np.flip(*args, **kwargs)
69 |
70 |
71 | def amax(*args, **kwargs):
72 | return np.amax(*args, **kwargs)
73 |
74 |
75 | def arctan2(*args, **kwargs):
76 | return np.arctan2(*args, **kwargs)
77 |
78 |
79 | def cast(x, dtype):
80 | return x.astype(dtype)
81 |
82 |
83 | def divide(*args, **kwargs):
84 | return np.divide(*args, **kwargs)
85 |
86 |
87 | def repeat(*args, **kwargs):
88 | return np.repeat(*args, **kwargs)
89 |
90 |
91 | def asarray(*args, **kwargs):
92 | return np.asarray(*args, **kwargs)
93 |
94 |
95 | def concatenate(*args, **kwargs):
96 | return np.concatenate(*args, **kwargs)
97 |
98 |
99 | def identity(val):
100 | return np.identity(val)
101 |
102 |
103 | def hstack(val):
104 | return np.hstack(val)
105 |
106 |
107 | def stack(*args, **kwargs):
108 | return np.stack(*args, **kwargs)
109 |
110 |
111 | def vstack(val):
112 | return np.vstack(val)
113 |
114 |
115 | def array(val):
116 | return np.array(val)
117 |
118 |
119 | def abs(val):
120 | return np.abs(val)
121 |
122 |
123 | def zeros(val):
124 | return np.zeros(val)
125 |
126 |
127 | def ones(val):
128 | return np.ones(val)
129 |
130 |
131 | def ones_like(*args, **kwargs):
132 | return np.ones_like(*args, **kwargs)
133 |
134 |
135 | def empty_like(*args, **kwargs):
136 | return np.empty_like(*args, **kwargs)
137 |
138 |
139 | def all(*args, **kwargs):
140 | return np.all(*args, **kwargs)
141 |
142 |
143 | def allclose(a, b, **kwargs):
144 | return np.allclose(a, b, **kwargs)
145 |
146 |
147 | def sin(val):
148 | return np.sin(val)
149 |
150 |
151 | def cos(val):
152 | return np.cos(val)
153 |
154 |
155 | def cosh(*args, **kwargs):
156 | return np.cosh(*args, **kwargs)
157 |
158 |
159 | def sinh(*args, **kwargs):
160 | return np.sinh(*args, **kwargs)
161 |
162 |
163 | def tanh(*args, **kwargs):
164 | return np.tanh(*args, **kwargs)
165 |
166 |
167 | def arccosh(*args, **kwargs):
168 | return np.arccosh(*args, **kwargs)
169 |
170 |
171 | def tan(val):
172 | return np.tan(val)
173 |
174 |
175 | def arcsin(val):
176 | return np.arcsin(val)
177 |
178 |
179 | def arccos(val):
180 | return np.arccos(val)
181 |
182 |
183 | def shape(val):
184 | return val.shape
185 |
186 |
187 | def dot(a, b):
188 | return np.dot(a, b)
189 |
190 |
191 | def maximum(a, b):
192 | return np.maximum(a, b)
193 |
194 |
195 | def greater(a, b):
196 | return np.greater(a, b)
197 |
198 |
199 | def greater_equal(a, b):
200 | return np.greater_equal(a, b)
201 |
202 |
203 | def to_ndarray(x, to_ndim, axis=0):
204 | x = np.asarray(x)
205 | if x.ndim == to_ndim - 1:
206 | x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=axis)
207 | assert x.ndim >= to_ndim
208 | return x
209 |
210 |
211 | def sqrt(val):
212 | return np.sqrt(val)
213 |
214 |
215 | def norm(val, axis):
216 | return np.linalg.norm(val, axis=axis)
217 |
218 |
219 | def rand(*args, **largs):
220 | return np.random.rand(*args, **largs)
221 |
222 |
223 | def randint(*args, **kwargs):
224 | return np.random.randint(*args, **kwargs)
225 |
226 |
227 | def isclose(*args, **kwargs):
228 | return np.isclose(*args, **kwargs)
229 |
230 |
231 | def less_equal(a, b):
232 | return np.less_equal(a, b)
233 |
234 |
235 | def less(a, b):
236 | return np.less(a, b)
237 |
238 |
239 | def eye(*args, **kwargs):
240 | return np.eye(*args, **kwargs)
241 |
242 |
243 | def average(*args, **kwargs):
244 | return np.average(*args, **kwargs)
245 |
246 |
247 | def matmul(*args, **kwargs):
248 | return np.matmul(*args, **kwargs)
249 |
250 |
251 | def sum(*args, **kwargs):
252 | return np.sum(*args, **kwargs)
253 |
254 |
255 | def einsum(*args, **kwargs):
256 | return np.einsum(*args, **kwargs)
257 |
258 |
259 | def transpose(*args, **kwargs):
260 | return np.transpose(*args, **kwargs)
261 |
262 |
263 | def squeeze(*args, **kwargs):
264 | return np.squeeze(*args, **kwargs)
265 |
266 |
267 | def zeros_like(*args, **kwargs):
268 | return np.zeros_like(*args, **kwargs)
269 |
270 |
271 | def trace(*args, **kwargs):
272 | return np.trace(*args, **kwargs)
273 |
274 |
275 | def mod(*args, **kwargs):
276 | return np.mod(*args, **kwargs)
277 |
278 |
279 | def linspace(*args, **kwargs):
280 | return np.linspace(*args, **kwargs)
281 |
282 |
283 | def equal(*args, **kwargs):
284 | return np.equal(*args, **kwargs)
285 |
286 |
287 | def floor(*args, **kwargs):
288 | return np.floor(*args, **kwargs)
289 |
290 |
291 | def cross(*args, **kwargs):
292 | return np.cross(*args, **kwargs)
293 |
294 |
295 | def triu_indices(*args, **kwargs):
296 | return np.triu_indices(*args, **kwargs)
297 |
298 |
299 | def where(*args, **kwargs):
300 | return np.where(*args, **kwargs)
301 |
302 |
303 | def tile(*args, **kwargs):
304 | return np.tile(*args, **kwargs)
305 |
306 |
307 | def clip(*args, **kwargs):
308 | return np.clip(*args, **kwargs)
309 |
310 |
311 | def diag(x):
312 | x = to_ndarray(x, to_ndim=2)
313 | _, n = shape(x)
314 | aux = np.vectorize(
315 | np.diagflat,
316 | signature='(m,n)->(k,k)')(x)
317 | k, k = shape(aux)
318 | m = int(k / n)
319 | result = zeros((m, n, n))
320 | for i in range(m):
321 | result[i] = aux[i*n:(i+1)*n, i*n:(i+1)*n]
322 | return result
323 |
324 |
325 | def any(*args, **kwargs):
326 | return np.any(*args, **kwargs)
327 |
328 |
329 | def expand_dims(*args, **kwargs):
330 | return np.expand_dims(*args, **kwargs)
331 |
332 |
333 | def outer(*args, **kwargs):
334 | return np.outer(*args, **kwargs)
335 |
336 |
337 | def hsplit(*args, **kwargs):
338 | return np.hsplit(*args, **kwargs)
339 |
340 |
341 | def argmax(*args, **kwargs):
342 | return np.argmax(*args, **kwargs)
343 |
344 |
345 | def argmin(*args, **kwargs):
346 | return np.argmin(*args, **kwargs)
347 |
348 |
349 | def diagonal(*args, **kwargs):
350 | return np.diagonal(*args, **kwargs)
351 |
352 |
353 | def exp(*args, **kwargs):
354 | return np.exp(*args, **kwargs)
355 |
356 |
357 | def log(*args, **kwargs):
358 | return np.log(*args, **kwargs)
359 |
360 |
361 | def cov(*args, **kwargs):
362 | return np.cov(*args, **kwargs)
363 |
364 |
365 | def eval(x):
366 | return x
367 |
368 |
369 | def ndim(x):
370 | return x.ndim
371 |
372 |
373 | def nonzero(x):
374 | return np.nonzero(x)
375 |
376 |
377 | def copy(x):
378 | return np.copy(x)
379 |
380 |
381 | def ix_(*args):
382 | return np.ix_(*args)
383 |
384 |
385 | def arange(*args, **kwargs):
386 | return np.arange(*args, **kwargs)
387 |
388 |
389 | def prod(x, axis=None):
390 | return np.prod(x, axis=axis)
391 |
392 |
393 | def sign(*args, **kwargs):
394 | return np.sign(*args, **kwargs)
395 |
396 |
397 | def mean(x, axis=None):
398 | return np.mean(x, axis)
399 |
400 |
401 | def normal(*args, **kwargs):
402 | return np.random.normal(*args, **kwargs)
403 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/learning/pca.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """ Principal Component Analysis on Manifolds
2 | """
3 |
4 | from math import log
5 | import numbers
6 |
7 | import numpy as np
8 | from scipy import linalg
9 | from scipy.special import gammaln
10 |
11 | from sklearn.decomposition.base import _BasePCA
12 | from sklearn.utils.extmath import svd_flip
13 | from sklearn.utils.extmath import stable_cumsum
14 | from sklearn.utils.validation import check_array
15 |
16 |
17 | def _assess_dimension_(spectrum, rank, n_samples, n_features):
18 | """Compute the likelihood of a rank ``rank`` dataset
19 |
20 | The dataset is assumed to be embedded in gaussian noise of shape(n,
21 | dimf) having spectrum ``spectrum``.
22 |
23 | Parameters
24 | ----------
25 | spectrum : array of shape (n)
26 | Data spectrum.
27 | rank : int
28 | Tested rank value.
29 | n_samples : int
30 | Number of samples.
31 | n_features : int
32 | Number of features.
33 |
34 | Returns
35 | -------
36 | ll : float,
37 | The log-likelihood
38 |
39 | Notes
40 | -----
41 | This implements the method of `Thomas P. Minka:
42 | Automatic Choice of Dimensionality for PCA. NIPS 2000: 598-604`
43 | """
44 | if rank > len(spectrum):
45 | raise ValueError("The tested rank cannot exceed the rank of the"
46 | " dataset")
47 |
48 | pu = -rank * log(2.)
49 | for i in range(rank):
50 | pu += (gammaln((n_features - i) / 2.) -
51 | log(np.pi) * (n_features - i) / 2.)
52 |
53 | pl = np.sum(np.log(spectrum[:rank]))
54 | pl = -pl * n_samples / 2.
55 |
56 | if rank == n_features:
57 | pv = 0
58 | v = 1
59 | else:
60 | v = np.sum(spectrum[rank:]) / (n_features - rank)
61 | pv = -np.log(v) * n_samples * (n_features - rank) / 2.
62 |
63 | m = n_features * rank - rank * (rank + 1.) / 2.
64 | pp = log(2. * np.pi) * (m + rank + 1.) / 2.
65 |
66 | pa = 0.
67 | spectrum_ = spectrum.copy()
68 | spectrum_[rank:n_features] = v
69 | for i in range(rank):
70 | for j in range(i + 1, len(spectrum)):
71 | pa += log((spectrum[i] - spectrum[j]) *
72 | (1. / spectrum_[j] - 1. / spectrum_[i])) + log(n_samples)
73 |
74 | ll = pu + pl + pv + pp - pa / 2. - rank * log(n_samples) / 2.
75 |
76 | return ll
77 |
78 |
79 | def _infer_dimension_(spectrum, n_samples, n_features):
80 | """Infers the dimension of a dataset of shape (n_samples, n_features)
81 |
82 | The dataset is described by its spectrum `spectrum`.
83 | """
84 | n_spectrum = len(spectrum)
85 | ll = np.empty(n_spectrum)
86 | for rank in range(n_spectrum):
87 | ll[rank] = _assess_dimension_(spectrum, rank, n_samples, n_features)
88 | return ll.argmax()
89 |
90 |
91 | class TangentPCA(_BasePCA):
92 | """Tangent Principal component analysis (tPCA)
93 |
94 | Linear dimensionality reduction using
95 | Singular Value Decomposition of the
96 | Riemannian Log of the data at the tangent space
97 | of the mean.
98 | """
99 |
100 | def __init__(self, metric, n_components=None, copy=True,
101 | whiten=False, tol=0.0, iterated_power='auto',
102 | random_state=None):
103 | self.metric = metric
104 | self.n_components = n_components
105 | self.copy = copy
106 | self.whiten = whiten
107 | self.tol = tol
108 | self.iterated_power = iterated_power
109 | self.random_state = random_state
110 |
111 | def fit(self, X,
112 | base_point=None, point_type='vector', y=None):
113 | """Fit the model with X.
114 |
115 | Parameters
116 | ----------
117 | X : array-like, shape (n_samples, n_features)
118 | Training data, where n_samples is the number of samples
119 | and n_features is the number of features.
120 |
121 | y : Ignored
122 |
123 | Returns
124 | -------
125 | self : object
126 | Returns the instance itself.
127 | """
128 | self._fit(X, base_point, point_type)
129 | return self
130 |
131 | def fit_transform(self, X,
132 | base_point=None, point_type='vector',
133 | y=None):
134 | """Fit the model with X and apply the dimensionality reduction on X.
135 |
136 | Parameters
137 | ----------
138 | X : array-like, shape (n_samples, n_features)
139 | Training data, where n_samples is the number of samples
140 | and n_features is the number of features.
141 |
142 | y : Ignored
143 |
144 | Returns
145 | -------
146 | X_new : array-like, shape (n_samples, n_components)
147 |
148 | """
149 | U, S, V = self._fit(X, base_point, point_type)
150 | U = U[:, :self.n_components_]
151 |
152 | U *= S[:self.n_components_]
153 |
154 | return U
155 |
156 | def _fit(self, X, base_point=None, point_type='vector'):
157 | """Fit the model by computing full SVD on X"""
158 | if point_type == 'matrix':
159 | raise NotImplementedError(
160 | 'This is currently only implemented for vectors.')
161 | if base_point is None:
162 | base_point = self.metric.mean(X)
163 |
164 | tangent_vecs = self.metric.log(X, base_point=base_point)
165 |
166 | # Convert to sklearn format
167 | X = tangent_vecs
168 |
169 | X = check_array(X, dtype=[np.float64, np.float32], ensure_2d=True,
170 | copy=self.copy)
171 |
172 | # Handle n_components==None
173 | if self.n_components is None:
174 | n_components = min(X.shape)
175 | else:
176 | n_components = self.n_components
177 | n_samples, n_features = X.shape
178 |
179 | if n_components == 'mle':
180 | if n_samples < n_features:
181 | raise ValueError("n_components='mle' is only supported "
182 | "if n_samples >= n_features")
183 | elif not 0 <= n_components <= min(n_samples, n_features):
184 | raise ValueError("n_components=%r must be between 0 and "
185 | "min(n_samples, n_features)=%r with "
186 | "svd_solver='full'"
187 | % (n_components, min(n_samples, n_features)))
188 | elif n_components >= 1:
189 | if not isinstance(n_components, (numbers.Integral, np.integer)):
190 | raise ValueError("n_components=%r must be of type int "
191 | "when greater than or equal to 1, "
192 | "was of type=%r"
193 | % (n_components, type(n_components)))
194 |
195 | # Center data
196 | self.mean_ = np.mean(X, axis=0)
197 | X -= self.mean_
198 |
199 | U, S, V = linalg.svd(X, full_matrices=False)
200 | # flip eigenvectors' sign to enforce deterministic output
201 | U, V = svd_flip(U, V)
202 |
203 | components_ = V
204 |
205 | # Get variance explained by singular values
206 | explained_variance_ = (S ** 2) / (n_samples - 1)
207 | total_var = explained_variance_.sum()
208 | explained_variance_ratio_ = explained_variance_ / total_var
209 | singular_values_ = S.copy() # Store the singular values.
210 |
211 | # Postprocess the number of components required
212 | if n_components == 'mle':
213 | n_components = \
214 | _infer_dimension_(explained_variance_, n_samples, n_features)
215 | elif 0 < n_components < 1.0:
216 | # number of components for which the cumulated explained
217 | # variance percentage is superior to the desired threshold
218 | ratio_cumsum = stable_cumsum(explained_variance_ratio_)
219 | n_components = np.searchsorted(ratio_cumsum, n_components) + 1
220 |
221 | # Compute noise covariance using Probabilistic PCA model
222 | # The sigma2 maximum likelihood (cf. eq. 12.46)
223 | if n_components < min(n_features, n_samples):
224 | self.noise_variance_ = explained_variance_[n_components:].mean()
225 | else:
226 | self.noise_variance_ = 0.
227 |
228 | self.n_samples_, self.n_features_ = n_samples, n_features
229 | self.components_ = components_[:n_components]
230 | self.n_components_ = n_components
231 | self.explained_variance_ = explained_variance_[:n_components]
232 | self.explained_variance_ratio_ = \
233 | explained_variance_ratio_[:n_components]
234 | self.singular_values_ = singular_values_[:n_components]
235 |
236 | return U, S, V
237 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/backend/pytorch.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Pytorch based computation backend."""
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 | import torch
5 |
6 | double = 'torch.DoubleTensor'
7 | float16 = 'torch.Float'
8 | float32 = 'torch.FloatTensor'
9 | float64 = 'torch.DoubleTensor'
10 | int32 = 'torch.LongTensor'
11 | int8 = 'torch.ByteTensor'
12 |
13 |
14 | def cond(pred, true_fn, false_fn):
15 | if pred:
16 | return true_fn()
17 | return false_fn()
18 |
19 |
20 | def amax(x):
21 | return torch.max(x)
22 |
23 |
24 | def boolean_mask(x, mask):
25 | idx = np.argwhere(np.asarray(mask))
26 | return x[idx]
27 |
28 |
29 | def arctan2(*args, **kwargs):
30 | return torch.arctan2(*args, **kwargs)
31 |
32 |
33 | def cast(x, dtype):
34 | x = array(x)
35 | return x.type(dtype)
36 |
37 |
38 | def divide(*args, **kwargs):
39 | return torch.div(*args, **kwargs)
40 |
41 |
42 | def repeat(*args, **kwargs):
43 | return torch.repeat(*args, **kwargs)
44 |
45 |
46 | def asarray(x):
47 | return np.asarray(x)
48 |
49 |
50 | def concatenate(seq, axis=0, out=None):
51 | seq = [t.float() for t in seq]
52 | return torch.cat(seq, dim=axis, out=out)
53 |
54 |
55 | def identity(val):
56 | return torch.eye(val)
57 |
58 |
59 | def hstack(seq):
60 | return concatenate(seq, axis=1)
61 |
62 |
63 | def stack(*args, **kwargs):
64 | return torch.stack(*args, **kwargs)
65 |
66 |
67 | def vstack(seq):
68 | return concatenate(seq)
69 |
70 |
71 | def array(val):
72 | if type(val) == list:
73 | if type(val[0]) != torch.Tensor:
74 | val = np.copy(np.array(val))
75 | else:
76 | val = concatenate(val)
77 |
78 | if type(val) == bool:
79 | val = np.array(val)
80 | if type(val) == np.ndarray:
81 | if val.dtype == bool:
82 | val = torch.from_numpy(np.array(val, dtype=np.uint8))
83 | elif val.dtype == np.float32 or val.dtype == np.float64:
84 | val = torch.from_numpy(np.array(val, dtype=np.float32))
85 | else:
86 | val = torch.from_numpy(val)
87 |
88 | if type(val) != torch.Tensor:
89 | val = torch.Tensor([val])
90 | if val.dtype == torch.float64:
91 | val = val.float()
92 | return val
93 |
94 |
95 | def abs(val):
96 | return torch.abs(val)
97 |
98 |
99 | def zeros(*args):
100 | return torch.from_numpy(np.zeros(*args)).float()
101 |
102 |
103 | def ones(*args):
104 | return torch.from_numpy(np.ones(*args)).float()
105 |
106 |
107 | def ones_like(*args, **kwargs):
108 | return torch.ones_like(*args, **kwargs)
109 |
110 |
111 | def empty_like(*args, **kwargs):
112 | return torch.empty_like(*args, **kwargs)
113 |
114 |
115 | def all(x, axis=None):
116 | if axis is None:
117 | return x.byte().all()
118 | return torch.from_numpy(np.all(x, axis=axis).astype(int))
119 |
120 |
121 | def allclose(a, b, **kwargs):
122 | a = torch.tensor(a)
123 | b = torch.tensor(b)
124 | a = a.float()
125 | b = b.float()
126 | a = to_ndarray(a, to_ndim=1)
127 | b = to_ndarray(b, to_ndim=1)
128 | n_a = a.shape[0]
129 | n_b = b.shape[0]
130 | ndim = len(a.shape)
131 | if n_a > n_b:
132 | reps = (int(n_a / n_b),) + (ndim-1) * (1,)
133 | b = tile(b, reps)
134 | elif n_a < n_b:
135 | reps = (int(n_b / n_a),) + (ndim-1) * (1,)
136 | a = tile(a, reps)
137 | return torch.allclose(a, b, **kwargs)
138 |
139 |
140 | def sin(val):
141 | return torch.sin(val)
142 |
143 |
144 | def cos(val):
145 | return torch.cos(val)
146 |
147 |
148 | def cosh(*args, **kwargs):
149 | return torch.cosh(*args, **kwargs)
150 |
151 |
152 | def arccosh(x):
153 | c0 = torch.log(x)
154 | c1 = torch.log1p(torch.sqrt(x * x - 1) / x)
155 | return c0 + c1
156 |
157 |
158 | def sinh(*args, **kwargs):
159 | return torch.sinh(*args, **kwargs)
160 |
161 |
162 | def tanh(*args, **kwargs):
163 | return torch.tanh(*args, **kwargs)
164 |
165 |
166 | def arcsinh(x):
167 | return torch.log(x + torch.sqrt(x*x+1))
168 |
169 |
170 | def arcosh(x):
171 | return torch.log(x + torch.sqrt(x*x-1))
172 |
173 |
174 | def tan(val):
175 | return torch.tan(val)
176 |
177 |
178 | def arcsin(val):
179 | return torch.asin(val)
180 |
181 |
182 | def arccos(val):
183 | return torch.acos(val)
184 |
185 |
186 | def shape(val):
187 | return val.shape
188 |
189 |
190 | def dot(a, b):
191 | dot = np.dot(a, b)
192 | return torch.from_numpy(np.array(dot)).float()
193 |
194 |
195 | def maximum(a, b):
196 | return torch.max(array(a), array(b))
197 |
198 |
199 | def greater(a, b):
200 | return torch.gt(a, b)
201 |
202 |
203 | def greater_equal(a, b):
204 | return torch.greater_equal(a, b)
205 |
206 |
207 | def to_ndarray(x, to_ndim, axis=0):
208 | x = array(x)
209 | if x.dim() == to_ndim - 1:
210 | x = torch.unsqueeze(x, dim=axis)
211 | assert x.dim() >= to_ndim
212 | return x
213 |
214 |
215 | def sqrt(val):
216 | return torch.sqrt(torch.tensor(val).float())
217 |
218 |
219 | def norm(val, axis):
220 | return torch.linalg.norm(val, axis=axis)
221 |
222 |
223 | def rand(*args, **largs):
224 | return torch.random.rand(*args, **largs)
225 |
226 |
227 | def isclose(*args, **kwargs):
228 | return torch.from_numpy(np.isclose(*args, **kwargs).astype(int)).byte()
229 |
230 |
231 | def less(a, b):
232 | return torch.le(a, b)
233 |
234 |
235 | def less_equal(a, b):
236 | return np.less_equal(a, b)
237 |
238 |
239 | def eye(*args, **kwargs):
240 | return torch.eye(*args, **kwargs)
241 |
242 |
243 | def average(*args, **kwargs):
244 | return torch.average(*args, **kwargs)
245 |
246 |
247 | def matmul(*args, **kwargs):
248 | return torch.matmul(*args, **kwargs)
249 |
250 |
251 | def sum(x, axis=None, **kwargs):
252 | if axis is None:
253 | return torch.sum(x, **kwargs)
254 | return torch.sum(x, dim=axis, **kwargs)
255 |
256 |
257 | def einsum(*args, **kwargs):
258 | return torch.from_numpy(np.einsum(*args, **kwargs)).float()
259 |
260 |
261 | def T(x):
262 | return torch.t(x)
263 |
264 |
265 | def transpose(x, axes=None):
266 | if axes:
267 | return x.permute(axes)
268 | if len(shape(x)) == 1:
269 | return x
270 | return x.t()
271 |
272 |
273 | def squeeze(x, axis=None):
274 | return torch.squeeze(x, dim=axis)
275 |
276 |
277 | def zeros_like(*args, **kwargs):
278 | return torch.zeros_like(*args, **kwargs)
279 |
280 |
281 | def trace(*args, **kwargs):
282 | trace = np.trace(*args, **kwargs)
283 | return torch.from_numpy(np.array(trace)).float()
284 |
285 |
286 | def mod(*args, **kwargs):
287 | return torch.fmod(*args, **kwargs)
288 |
289 |
290 | def linspace(start, stop, num):
291 | return torch.linspace(start=start, end=stop, steps=num)
292 |
293 |
294 | def equal(a, b, **kwargs):
295 | if a.dtype == torch.ByteTensor:
296 | a = cast(a, torch.uint8).float()
297 | if b.dtype == torch.ByteTensor:
298 | b = cast(b, torch.uint8).float()
299 | return torch.equal(a, b, **kwargs)
300 |
301 |
302 | def floor(*args, **kwargs):
303 | return torch.floor(*args, **kwargs)
304 |
305 |
306 | def cross(x, y):
307 | return torch.from_numpy(np.cross(x, y))
308 |
309 |
310 | def triu_indices(*args, **kwargs):
311 | return torch.triu_indices(*args, **kwargs)
312 |
313 |
314 | def where(*args, **kwargs):
315 | return torch.where(*args, **kwargs)
316 |
317 |
318 | def tile(x, y):
319 | # TODO(johmathe): Native tile implementation
320 | return array(np.tile(x, y))
321 |
322 |
323 | def clip(x, amin, amax):
324 | return np.clip(x, amin, amax)
325 |
326 |
327 | def diag(*args, **kwargs):
328 | return torch.diag(*args, **kwargs)
329 |
330 |
331 | def any(x):
332 | return x.byte().any()
333 |
334 |
335 | def expand_dims(x, axis=0):
336 | return torch.unsqueeze(x, dim=axis)
337 |
338 |
339 | def outer(*args, **kwargs):
340 | return torch.ger(*args, **kwargs)
341 |
342 |
343 | def hsplit(*args, **kwargs):
344 | return torch.hsplit(*args, **kwargs)
345 |
346 |
347 | def argmax(*args, **kwargs):
348 | return torch.argmax(*args, **kwargs)
349 |
350 |
351 | def diagonal(*args, **kwargs):
352 | return torch.diagonal(*args, **kwargs)
353 |
354 |
355 | def exp(*args, **kwargs):
356 | return torch.exp(*args, **kwargs)
357 |
358 |
359 | def log(*args, **kwargs):
360 | return torch.log(*args, **kwargs)
361 |
362 |
363 | def cov(*args, **kwargs):
364 | return torch.cov(*args, **kwargs)
365 |
366 |
367 | def eval(x):
368 | return x
369 |
370 |
371 | def ndim(x):
372 | return x.dim()
373 |
374 |
375 | def gt(*args, **kwargs):
376 | return torch.gt(*args, **kwargs)
377 |
378 |
379 | def eq(*args, **kwargs):
380 | return torch.eq(*args, **kwargs)
381 |
382 |
383 | def nonzero(*args, **kwargs):
384 | return torch.nonzero(*args, **kwargs)
385 |
386 |
387 | def copy(x):
388 | return x.clone()
389 |
390 |
391 | def seed(x):
392 | torch.manual_seed(x)
393 |
394 |
395 | def sign(*args, **kwargs):
396 | return torch.sign(*args, **kwargs)
397 |
398 |
399 | def mean(x, axis=None):
400 | if axis is None:
401 | return torch.mean(x)
402 | else:
403 | return np.mean(x, axis)
404 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/lie_group.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Lie groups."""
2 |
3 |
4 | import geomstats.backend as gs
5 | import geomstats.riemannian_metric as riemannian_metric
6 |
7 | from geomstats.invariant_metric import InvariantMetric
8 | from geomstats.manifold import Manifold
9 |
10 |
11 | def loss(y_pred, y_true, group, metric=None):
12 | """
13 | Loss function given by a riemannian metric.
14 | """
15 | if metric is None:
16 | metric = group.left_invariant_metric
17 | loss = riemannian_metric.loss(y_pred, y_true, metric)
18 | return loss
19 |
20 |
21 | def grad(y_pred, y_true, group, metric=None):
22 | """
23 | Closed-form for the gradient of the loss function.
24 |
25 | :return: tangent vector at point y_pred.
26 | """
27 | if metric is None:
28 | metric = group.left_invariant_metric
29 | grad = riemannian_metric.grad(y_pred, y_true, metric)
30 | return grad
31 |
32 |
33 | class LieGroup(Manifold):
34 | """ Class for Lie groups."""
35 |
36 | def __init__(self, dimension):
37 | assert dimension > 0
38 | Manifold.__init__(self, dimension)
39 |
40 | self.left_canonical_metric = InvariantMetric(
41 | group=self,
42 | inner_product_mat_at_identity=gs.eye(self.dimension),
43 | left_or_right='left')
44 |
45 | self.right_canonical_metric = InvariantMetric(
46 | group=self,
47 | inner_product_mat_at_identity=gs.eye(self.dimension),
48 | left_or_right='right')
49 |
50 | self.metrics = []
51 |
52 | def get_identity(self, point_type=None):
53 | """
54 | Get the identity of the group.
55 | """
56 | raise NotImplementedError('The Lie group identity'
57 | ' is not implemented.')
58 | identity = property(get_identity)
59 |
60 | def compose(self, point_a, point_b, point_type=None):
61 | """
62 | Composition of the Lie group.
63 | """
64 | raise NotImplementedError('The Lie group composition'
65 | ' is not implemented.')
66 |
67 | def inverse(self, point, point_type=None):
68 | """
69 | Inverse law of the Lie group.
70 | """
71 | raise NotImplementedError('The Lie group inverse is not implemented.')
72 |
73 | def jacobian_translation(
74 | self, point, left_or_right='left', point_type=None):
75 | """
76 | Compute the jacobian matrix of the differential
77 | of the left translation by the point.
78 | """
79 | raise NotImplementedError(
80 | 'The jacobian of the Lie group translation is not implemented.')
81 |
82 | def group_exp_from_identity(self, tangent_vec, point_type=None):
83 | """
84 | Compute the group exponential
85 | of tangent vector tangent_vec from the identity.
86 | """
87 | raise NotImplementedError(
88 | 'The group exponential from the identity is not implemented.')
89 |
90 | def group_exp_not_from_identity(self, tangent_vec, base_point, point_type):
91 | jacobian = self.jacobian_translation(
92 | point=base_point,
93 | left_or_right='left',
94 | point_type=point_type)
95 |
96 | if point_type == 'vector':
97 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=2)
98 | inv_jacobian = gs.linalg.inv(jacobian)
99 |
100 | tangent_vec_at_id = gs.einsum('ni,nij->nj',
101 | tangent_vec,
102 | gs.transpose(inv_jacobian,
103 | axes=(0, 2, 1)))
104 | group_exp_from_identity = self.group_exp_from_identity(
105 | tangent_vec=tangent_vec_at_id,
106 | point_type=point_type)
107 | group_exp = self.compose(base_point,
108 | group_exp_from_identity,
109 | point_type=point_type)
110 | group_exp = self.regularize(group_exp, point_type=point_type)
111 | return group_exp
112 |
113 | elif point_type == 'matrix':
114 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=3)
115 | raise NotImplementedError()
116 |
117 | def group_exp(self, tangent_vec, base_point=None, point_type=None):
118 | """
119 | Compute the group exponential at point base_point
120 | of tangent vector tangent_vec.
121 | """
122 | if point_type is None:
123 | point_type = self.default_point_type
124 |
125 | identity = self.get_identity(point_type=point_type)
126 | identity = self.regularize(identity, point_type=point_type)
127 | if base_point is None:
128 | base_point = identity
129 | base_point = self.regularize(base_point, point_type=point_type)
130 |
131 | if point_type == 'vector':
132 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=2)
133 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=2)
134 | if point_type == 'matrix':
135 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=3)
136 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=3)
137 |
138 | n_tangent_vecs = tangent_vec.shape[0]
139 | n_base_points = base_point.shape[0]
140 |
141 | assert (tangent_vec.shape == base_point.shape
142 | or n_tangent_vecs == 1
143 | or n_base_points == 1)
144 |
145 | if n_tangent_vecs == 1:
146 | tangent_vec = gs.array([tangent_vec[0]] * n_base_points)
147 |
148 | if n_base_points == 1:
149 | base_point = gs.array([base_point[0]] * n_tangent_vecs)
150 |
151 | result = gs.cond(
152 | pred=gs.allclose(base_point, identity),
153 | true_fn=lambda: self.group_exp_from_identity(
154 | tangent_vec, point_type=point_type),
155 | false_fn=lambda: self.group_exp_not_from_identity(
156 | tangent_vec, base_point, point_type))
157 | return result
158 |
159 | def group_log_from_identity(self, point, point_type=None):
160 | """
161 | Compute the group logarithm
162 | of the point point from the identity.
163 | """
164 | raise NotImplementedError(
165 | 'The group logarithm from the identity is not implemented.')
166 |
167 | def group_log_not_from_identity(self, point, base_point, point_type):
168 | jacobian = self.jacobian_translation(point=base_point,
169 | left_or_right='left',
170 | point_type=point_type)
171 | point_near_id = self.compose(
172 | self.inverse(base_point), point, point_type=point_type)
173 | group_log_from_id = self.group_log_from_identity(
174 | point=point_near_id,
175 | point_type=point_type)
176 |
177 | group_log = gs.einsum('ni,nij->nj',
178 | group_log_from_id,
179 | gs.transpose(jacobian, axes=(0, 2, 1)))
180 |
181 | assert gs.ndim(group_log) == 2
182 | return group_log
183 |
184 | def group_log(self, point, base_point=None, point_type=None):
185 | """
186 | Compute the group logarithm at point base_point
187 | of the point point.
188 | """
189 | if point_type is None:
190 | point_type = self.default_point_type
191 |
192 | identity = self.get_identity(point_type=point_type)
193 | if base_point is None:
194 | base_point = identity
195 |
196 | if point_type == 'vector':
197 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=2)
198 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=2)
199 | if point_type == 'matrix':
200 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=3)
201 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=3)
202 |
203 | point = self.regularize(point, point_type=point_type)
204 | base_point = self.regularize(base_point, point_type=point_type)
205 |
206 | n_points = point.shape[0]
207 | n_base_points = base_point.shape[0]
208 |
209 | assert (point.shape == base_point.shape
210 | or n_points == 1
211 | or n_base_points == 1)
212 |
213 | if n_points == 1:
214 | point = gs.array([point[0]] * n_base_points)
215 |
216 | if n_base_points == 1:
217 | base_point = gs.array([base_point[0]] * n_points)
218 |
219 | result = gs.cond(
220 | pred=gs.allclose(base_point, identity),
221 | true_fn=lambda: self.group_log_from_identity(
222 | point, point_type=point_type),
223 | false_fn=lambda: self.group_log_not_from_identity(
224 | point, base_point, point_type))
225 |
226 | return result
227 |
228 | def group_exponential_barycenter(
229 | self, points, weights=None, point_type=None):
230 | """
231 | Compute the group exponential barycenter.
232 | """
233 | raise NotImplementedError(
234 | 'The group exponential barycenter is not implemented.')
235 |
236 | def add_metric(self, metric):
237 | self.metrics.append(metric)
238 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_stiefel.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for Stiefel manifolds.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import warnings
6 |
7 | import geomstats.backend as gs
8 | import geomstats.tests
9 | import tests.helper as helper
10 |
11 | from geomstats.stiefel import Stiefel
12 |
13 | ATOL = 1e-6
14 |
15 |
16 | class TestStiefelMethods(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
17 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
18 |
19 | def setUp(self):
20 | """
21 | Tangent vectors constructed following:
22 | http://noodle.med.yale.edu/hdtag/notes/steifel_notes.pdf
23 | """
24 | warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
25 |
26 | gs.random.seed(1234)
27 |
28 | self.p = 3
29 | self.n = 4
30 | self.space = Stiefel(self.n, self.p)
31 | self.n_samples = 10
32 | self.dimension = int(
33 | self.p * self.n - (self.p * (self.p + 1) / 2))
34 |
35 | self.point_a = gs.array([
36 | [1., 0., 0.],
37 | [0., 1., 0.],
38 | [0., 0., 1.],
39 | [0., 0., 0.]])
40 |
41 | self.point_b = gs.array([
42 | [1. / gs.sqrt(2.), 0., 0.],
43 | [0., 1., 0.],
44 | [0., 0., 1.],
45 | [1. / gs.sqrt(2.), 0., 0.]])
46 |
47 | point_perp = gs.array([
48 | [0.],
49 | [0.],
50 | [0.],
51 | [1.]])
52 |
53 | matrix_a_1 = gs.array([
54 | [0., 2., -5.],
55 | [-2., 0., -1.],
56 | [5., 1., 0.]])
57 |
58 | matrix_b_1 = gs.array([
59 | [-2., 1., 4.]])
60 |
61 | matrix_a_2 = gs.array([
62 | [0., 2., -5.],
63 | [-2., 0., -1.],
64 | [5., 1., 0.]])
65 |
66 | matrix_b_2 = gs.array([
67 | [-2., 1., 4.]])
68 |
69 | self.tangent_vector_1 = (
70 | gs.matmul(self.point_a, matrix_a_1)
71 | + gs.matmul(point_perp, matrix_b_1))
72 |
73 | self.tangent_vector_2 = (
74 | gs.matmul(self.point_a, matrix_a_2)
75 | + gs.matmul(point_perp, matrix_b_2))
76 |
77 | self.metric = self.space.canonical_metric
78 |
79 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
80 | def test_belongs(self):
81 | point = self.space.random_uniform()
82 | belongs = self.space.belongs(point)
83 |
84 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(belongs), (1, 1))
85 |
86 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
87 | def test_random_uniform_and_belongs(self):
88 | point = self.space.random_uniform()
89 | result = self.space.belongs(point)
90 | expected = gs.array([[True]])
91 |
92 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
93 |
94 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
95 | def test_random_uniform(self):
96 | result = self.space.random_uniform()
97 |
98 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (1, self.n, self.p))
99 |
100 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
101 | def test_log_and_exp(self):
102 | """
103 | Test that the riemannian exponential
104 | and the riemannian logarithm are inverse.
105 |
106 | Expect their composition to give the identity function.
107 | """
108 | # Riemannian Log then Riemannian Exp
109 | # General case
110 | base_point = self.point_a
111 | point = self.point_b
112 |
113 | log = self.metric.log(point=point, base_point=base_point)
114 | result = self.metric.exp(tangent_vec=log, base_point=base_point)
115 | expected = helper.to_matrix(point)
116 |
117 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected, atol=ATOL)
118 |
119 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
120 | def test_exp_and_belongs(self):
121 | base_point = self.point_a
122 | tangent_vec = self.tangent_vector_1
123 |
124 | exp = self.metric.exp(
125 | tangent_vec=tangent_vec,
126 | base_point=base_point)
127 | result = self.space.belongs(exp)
128 | expected = gs.array([[True]])
129 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
130 |
131 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
132 | def test_exp_vectorization(self):
133 | n_samples = self.n_samples
134 | n = self.n
135 | p = self.p
136 |
137 | one_base_point = self.point_a
138 | n_base_points = gs.tile(
139 | gs.to_ndarray(self.point_a, to_ndim=3),
140 | (n_samples, 1, 1))
141 |
142 | one_tangent_vec = self.tangent_vector_1
143 | result = self.metric.exp(one_tangent_vec, one_base_point)
144 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (1, n, p))
145 |
146 | n_tangent_vecs = gs.tile(
147 | gs.to_ndarray(self.tangent_vector_2, to_ndim=3),
148 | (n_samples, 1, 1))
149 |
150 | result = self.metric.exp(n_tangent_vecs, one_base_point)
151 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, n, p))
152 |
153 | result = self.metric.exp(one_tangent_vec, n_base_points)
154 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, n, p))
155 |
156 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
157 | def test_log_vectorization(self):
158 | n_samples = self.n_samples
159 | n = self.n
160 | p = self.p
161 |
162 | one_point = self.space.random_uniform()
163 | one_base_point = self.space.random_uniform()
164 | n_points = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=n_samples)
165 | n_base_points = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=n_samples)
166 |
167 | result = self.metric.log(one_point, one_base_point)
168 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (1, n, p))
169 |
170 | result = self.metric.log(n_points, one_base_point)
171 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, n, p))
172 |
173 | result = self.metric.log(one_point, n_base_points)
174 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, n, p))
175 |
176 | result = self.metric.log(n_points, n_base_points)
177 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, n, p))
178 |
179 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
180 | def test_retractation_and_lifting(self):
181 | """
182 | Test that the riemannian exponential
183 | and the riemannian logarithm are inverse.
184 |
185 | Expect their composition to give the identity function.
186 | """
187 | # Riemannian Log then Riemannian Exp
188 | # General case
189 | base_point = self.point_a
190 | point = self.point_b
191 | tangent_vec = self.tangent_vector_1
192 |
193 | lifted = self.metric.lifting(point=point, base_point=base_point)
194 | result = self.metric.retraction(
195 | tangent_vec=lifted, base_point=base_point)
196 | expected = helper.to_matrix(point)
197 |
198 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected, atol=ATOL)
199 |
200 | retract = self.metric.retraction(
201 | tangent_vec=tangent_vec, base_point=base_point)
202 | result = self.metric.lifting(point=retract, base_point=base_point)
203 | expected = helper.to_matrix(tangent_vec)
204 |
205 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected, atol=ATOL)
206 |
207 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
208 | def test_lifting_vectorization(self):
209 | n_samples = self.n_samples
210 | n = self.n
211 | p = self.p
212 |
213 | one_point = self.point_a
214 | one_base_point = self.point_b
215 | n_points = gs.tile(
216 | gs.to_ndarray(self.point_a, to_ndim=3),
217 | (n_samples, 1, 1))
218 | n_base_points = gs.tile(
219 | gs.to_ndarray(self.point_b, to_ndim=3),
220 | (n_samples, 1, 1))
221 |
222 | result = self.metric.lifting(one_point, one_base_point)
223 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (1, n, p))
224 |
225 | result = self.metric.lifting(n_points, one_base_point)
226 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, n, p))
227 |
228 | result = self.metric.lifting(one_point, n_base_points)
229 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, n, p))
230 |
231 | result = self.metric.lifting(n_points, n_base_points)
232 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, n, p))
233 |
234 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
235 | def test_retraction_vectorization(self):
236 | n_samples = self.n_samples
237 | n = self.n
238 | p = self.p
239 |
240 | one_point = self.point_a
241 | n_points = gs.tile(
242 | gs.to_ndarray(one_point, to_ndim=3),
243 | (n_samples, 1, 1))
244 | one_tangent_vec = self.tangent_vector_1
245 | n_tangent_vecs = gs.tile(
246 | gs.to_ndarray(self.tangent_vector_2, to_ndim=3),
247 | (n_samples, 1, 1))
248 |
249 | result = self.metric.retraction(one_tangent_vec, one_point)
250 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (1, n, p))
251 |
252 | result = self.metric.retraction(n_tangent_vecs, one_point)
253 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, n, p))
254 |
255 | result = self.metric.retraction(one_tangent_vec, n_points)
256 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, n, p))
257 |
258 | result = self.metric.retraction(n_tangent_vecs, n_points)
259 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, n, p))
260 |
261 | def test_inner_product(self):
262 | base_point = self.point_a
263 | tangent_vector_1 = self.tangent_vector_1
264 | tangent_vector_2 = self.tangent_vector_2
265 |
266 | result = self.metric.inner_product(
267 | tangent_vector_1,
268 | tangent_vector_2,
269 | base_point=base_point)
270 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (1, 1))
271 |
272 |
273 | if __name__ == '__main__':
274 | geomstats.tests.main()
275 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/spd_matrices_space.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | The manifold of symmetric positive definite (SPD) matrices.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 |
7 | from geomstats.embedded_manifold import EmbeddedManifold
8 | from geomstats.general_linear_group import GeneralLinearGroup
9 | from geomstats.riemannian_metric import RiemannianMetric
10 |
11 | EPSILON = 1e-6
12 | TOLERANCE = 1e-12
13 |
14 |
15 | class SPDMatricesSpace(EmbeddedManifold):
16 | """
17 | Class for the manifold of symmetric positive definite (SPD) matrices.
18 | """
19 | def __init__(self, n):
20 | assert isinstance(n, int) and n > 0
21 | super(SPDMatricesSpace, self).__init__(
22 | dimension=int(n * (n + 1) / 2),
23 | embedding_manifold=GeneralLinearGroup(n=n))
24 | self.n = n
25 | self.metric = SPDMetric(n=n)
26 |
27 | def belongs(self, mat, tolerance=TOLERANCE):
28 | """
29 | Check if a matrix belongs to the manifold of
30 | symmetric positive definite matrices.
31 | """
32 | mat = gs.to_ndarray(mat, to_ndim=3)
33 | n_mats, mat_dim, _ = mat.shape
34 |
35 | mask_is_symmetric = self.embedding_manifold.is_symmetric(
36 | mat, tolerance=tolerance)
37 | mask_is_invertible = self.embedding_manifold.belongs(mat)
38 |
39 | belongs = mask_is_symmetric & mask_is_invertible
40 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=1)
41 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
42 | return belongs
43 |
44 | def vector_from_symmetric_matrix(self, mat):
45 | """
46 | Convert the symmetric part of a symmetric matrix
47 | into a vector.
48 | """
49 | mat = gs.to_ndarray(mat, to_ndim=3)
50 | assert gs.all(self.embedding_manifold.is_symmetric(mat))
51 | mat = self.embedding_manifold.make_symmetric(mat)
52 |
53 | _, mat_dim, _ = mat.shape
54 | vec_dim = int(mat_dim * (mat_dim + 1) / 2)
55 | vec = gs.zeros(vec_dim)
56 |
57 | idx = 0
58 | for i in range(mat_dim):
59 | for j in range(i + 1):
60 | if i == j:
61 | vec[idx] = mat[j, j]
62 | else:
63 | vec[idx] = mat[j, i]
64 | idx += 1
65 |
66 | return vec
67 |
68 | def symmetric_matrix_from_vector(self, vec):
69 | """
70 | Convert a vector into a symmetric matrix.
71 | """
72 | vec = gs.to_ndarray(vec, to_ndim=2)
73 | _, vec_dim = vec.shape
74 | mat_dim = int((gs.sqrt(8 * vec_dim + 1) - 1) / 2)
75 | mat = gs.zeros((mat_dim,) * 2)
76 |
77 | lower_triangle_indices = gs.tril_indices(mat_dim)
78 | diag_indices = gs.diag_indices(mat_dim)
79 |
80 | mat[lower_triangle_indices] = 2 * vec
81 | mat[diag_indices] = vec
82 |
83 | mat = self.embedding_manifold.make_symmetric(mat)
84 | return mat
85 |
86 | def random_uniform(self, n_samples=1):
87 | mat = 2 * gs.random.rand(n_samples, self.n, self.n) - 1
88 |
89 | spd_mat = self.embedding_manifold.group_exp(
90 | mat + gs.transpose(mat, axes=(0, 2, 1)))
91 | return spd_mat
92 |
93 | def random_tangent_vec_uniform(self, n_samples=1, base_point=None):
94 | if base_point is None:
95 | base_point = gs.eye(self.n)
96 |
97 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=3)
98 | n_base_points, _, _ = base_point.shape
99 |
100 | assert n_base_points == n_samples or n_base_points == 1
101 | if n_base_points == 1:
102 | base_point = gs.tile(base_point, (n_samples, 1, 1))
103 |
104 | sqrt_base_point = gs.linalg.sqrtm(base_point)
105 |
106 | tangent_vec_at_id = (2 * gs.random.rand(n_samples,
107 | self.n,
108 | self.n)
109 | - 1)
110 | tangent_vec_at_id = (tangent_vec_at_id
111 | + gs.transpose(tangent_vec_at_id,
112 | axes=(0, 2, 1)))
113 |
114 | tangent_vec = gs.matmul(sqrt_base_point, tangent_vec_at_id)
115 | tangent_vec = gs.matmul(tangent_vec, sqrt_base_point)
116 |
117 | return tangent_vec
118 |
119 |
120 | class SPDMetric(RiemannianMetric):
121 |
122 | def __init__(self, n):
123 | super(SPDMetric, self).__init__(
124 | dimension=int(n * (n + 1) / 2),
125 | signature=(int(n * (n + 1) / 2), 0, 0))
126 | self.n = n
127 |
128 | def inner_product(self, tangent_vec_a, tangent_vec_b, base_point):
129 | """
130 | Compute the inner product of tangent_vec_a and tangent_vec_b
131 | at point base_point using the affine invariant Riemannian metric.
132 | """
133 | tangent_vec_a = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec_a, to_ndim=3)
134 | n_tangent_vecs_a, _, _ = tangent_vec_a.shape
135 | tangent_vec_b = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec_b, to_ndim=3)
136 | n_tangent_vecs_b, _, _ = tangent_vec_b.shape
137 |
138 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=3)
139 | n_base_points, _, _ = base_point.shape
140 |
141 | assert (n_tangent_vecs_a == n_tangent_vecs_b == n_base_points
142 | or n_tangent_vecs_a == n_tangent_vecs_b and n_base_points == 1
143 | or n_base_points == n_tangent_vecs_a and n_tangent_vecs_b == 1
144 | or n_base_points == n_tangent_vecs_b and n_tangent_vecs_a == 1
145 | or n_tangent_vecs_a == 1 and n_tangent_vecs_b == 1
146 | or n_base_points == 1 and n_tangent_vecs_a == 1
147 | or n_base_points == 1 and n_tangent_vecs_b == 1)
148 |
149 | if n_tangent_vecs_a == 1:
150 | tangent_vec_a = gs.tile(
151 | tangent_vec_a,
152 | (gs.maximum(n_base_points, n_tangent_vecs_b), 1, 1))
153 |
154 | if n_tangent_vecs_b == 1:
155 | tangent_vec_b = gs.tile(
156 | tangent_vec_b,
157 | (gs.maximum(n_base_points, n_tangent_vecs_a), 1, 1))
158 |
159 | if n_base_points == 1:
160 | base_point = gs.tile(
161 | base_point,
162 | (gs.maximum(n_tangent_vecs_a, n_tangent_vecs_b), 1, 1))
163 |
164 | inv_base_point = gs.linalg.inv(base_point)
165 |
166 | aux_a = gs.matmul(inv_base_point, tangent_vec_a)
167 | aux_b = gs.matmul(inv_base_point, tangent_vec_b)
168 | inner_product = gs.trace(gs.matmul(aux_a, aux_b), axis1=1, axis2=2)
169 | inner_product = gs.to_ndarray(inner_product, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
170 | return inner_product
171 |
172 | def exp(self, tangent_vec, base_point):
173 | """
174 | Compute the Riemannian exponential at point base_point
175 | of tangent vector tangent_vec wrt the metric
176 | defined in inner_product.
177 |
178 | This gives a symmetric positive definite matrix.
179 | """
180 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=3)
181 | n_tangent_vecs, _, _ = tangent_vec.shape
182 |
183 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=3)
184 | n_base_points, mat_dim, _ = base_point.shape
185 |
186 | assert (n_tangent_vecs == n_base_points
187 | or n_tangent_vecs == 1
188 | or n_base_points == 1)
189 |
190 | if n_tangent_vecs == 1:
191 | tangent_vec = gs.tile(tangent_vec, (n_base_points, 1, 1))
192 | if n_base_points == 1:
193 | base_point = gs.tile(base_point, (n_tangent_vecs, 1, 1))
194 |
195 | sqrt_base_point = gs.linalg.sqrtm(base_point)
196 |
197 | inv_sqrt_base_point = gs.linalg.inv(sqrt_base_point)
198 |
199 | tangent_vec_at_id = gs.matmul(inv_sqrt_base_point,
200 | tangent_vec)
201 | tangent_vec_at_id = gs.matmul(tangent_vec_at_id,
202 | inv_sqrt_base_point)
203 | exp_from_id = gs.linalg.expm(tangent_vec_at_id)
204 |
205 | exp = gs.matmul(exp_from_id, sqrt_base_point)
206 | exp = gs.matmul(sqrt_base_point, exp)
207 |
208 | return exp
209 |
210 | def log(self, point, base_point):
211 | """
212 | Compute the Riemannian logarithm at point base_point,
213 | of point wrt the metric defined in inner_product.
214 |
215 | This gives a tangent vector at point base_point.
216 | """
217 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=3)
218 | n_points, _, _ = point.shape
219 |
220 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=3)
221 | n_base_points, mat_dim, _ = base_point.shape
222 |
223 | assert (n_points == n_base_points
224 | or n_points == 1
225 | or n_base_points == 1)
226 |
227 | if n_points == 1:
228 | point = gs.tile(point, (n_base_points, 1, 1))
229 | if n_base_points == 1:
230 | base_point = gs.tile(base_point, (n_points, 1, 1))
231 |
232 | sqrt_base_point = gs.zeros((n_base_points,) + (mat_dim,) * 2)
233 | sqrt_base_point = gs.linalg.sqrtm(base_point)
234 |
235 | inv_sqrt_base_point = gs.linalg.inv(sqrt_base_point)
236 | point_near_id = gs.matmul(inv_sqrt_base_point, point)
237 | point_near_id = gs.matmul(point_near_id, inv_sqrt_base_point)
238 | log_at_id = gs.linalg.logm(point_near_id)
239 |
240 | log = gs.matmul(sqrt_base_point, log_at_id)
241 | log = gs.matmul(log, sqrt_base_point)
242 |
243 | return log
244 |
245 | def geodesic(self, initial_point, initial_tangent_vec):
246 | return super(SPDMetric, self).geodesic(
247 | initial_point=initial_point,
248 | initial_tangent_vec=initial_tangent_vec,
249 | point_type='matrix')
250 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_minkowski_space.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for Minkowski space.
3 | """
4 | import math
5 | import numpy as np
6 |
7 | import geomstats.backend as gs
8 | import geomstats.tests
9 | import tests.helper as helper
10 |
11 | from geomstats.minkowski_space import MinkowskiSpace
12 |
13 |
14 | class TestMinkowskiSpaceMethods(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
15 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
16 |
17 | def setUp(self):
18 | gs.random.seed(1234)
19 |
20 | self.time_like_dim = 0
21 | self.dimension = 2
22 | self.space = MinkowskiSpace(self.dimension)
23 | self.metric = self.space.metric
24 | self.n_samples = 10
25 |
26 | def test_belongs(self):
27 | point = gs.array([-1., 3.])
28 | result = self.space.belongs(point)
29 | expected = gs.array([[True]])
30 |
31 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
32 |
33 | def test_random_uniform(self):
34 | point = self.space.random_uniform()
35 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(point), (1, self.dimension))
36 |
37 | def test_random_uniform_and_belongs(self):
38 | point = self.space.random_uniform()
39 | result = self.space.belongs(point)
40 | expected = gs.array([[True]])
41 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
42 |
43 | def test_inner_product_matrix(self):
44 | result = self.metric.inner_product_matrix()
45 |
46 | expected = gs.array([[-1., 0.], [0., 1.]])
47 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
48 |
49 | def test_inner_product(self):
50 | point_a = gs.array([0., 1.])
51 | point_b = gs.array([2., 10.])
52 |
53 | result = self.metric.inner_product(point_a, point_b)
54 | expected = helper.to_scalar(gs.dot(point_a, point_b))
55 | expected -= (2 * point_a[self.time_like_dim]
56 | * point_b[self.time_like_dim])
57 |
58 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
59 |
60 | def test_inner_product_vectorization(self):
61 | n_samples = 3
62 | one_point_a = gs.array([[-1., 0.]])
63 | one_point_b = gs.array([[1.0, 0.]])
64 |
65 | n_points_a = gs.array([
66 | [-1., 0.],
67 | [1., 0.],
68 | [2., math.sqrt(3)]])
69 | n_points_b = gs.array([
70 | [2., -math.sqrt(3)],
71 | [4.0, math.sqrt(15)],
72 | [-4.0, math.sqrt(15)]])
73 |
74 | result = self.metric.inner_product(one_point_a, one_point_b)
75 | expected = gs.dot(one_point_a, gs.transpose(one_point_b))
76 | expected -= (2 * one_point_a[:, self.time_like_dim]
77 | * one_point_b[:, self.time_like_dim])
78 | expected = helper.to_scalar(expected)
79 |
80 | result_no = self.metric.inner_product(n_points_a,
81 | one_point_b)
82 | result_on = self.metric.inner_product(one_point_a, n_points_b)
83 |
84 | result_nn = self.metric.inner_product(n_points_a, n_points_b)
85 |
86 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
87 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result_no), (n_samples, 1))
88 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result_on), (n_samples, 1))
89 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result_nn), (n_samples, 1))
90 |
91 | with self.session():
92 | expected = np.zeros(n_samples)
93 | for i in range(n_samples):
94 | expected[i] = gs.eval(gs.dot(n_points_a[i],
95 | n_points_b[i]))
96 | expected[i] -= (2 * gs.eval(n_points_a[i, self.time_like_dim])
97 | * gs.eval(n_points_b[i, self.time_like_dim]))
98 | expected = helper.to_scalar(gs.array(expected))
99 |
100 | self.assertAllClose(result_nn, expected)
101 |
102 | def test_squared_norm(self):
103 | point = gs.array([-2., 4.])
104 |
105 | result = self.metric.squared_norm(point)
106 | expected = gs.array([[12.]])
107 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
108 |
109 | def test_squared_norm_vectorization(self):
110 | n_samples = 3
111 | n_points = gs.array([
112 | [-1., 0.],
113 | [1., 0.],
114 | [2., math.sqrt(3)]])
115 |
116 | result = self.metric.squared_norm(n_points)
117 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, 1))
118 |
119 | def test_exp(self):
120 | base_point = gs.array([1.0, 0.])
121 | vector = gs.array([2., math.sqrt(3)])
122 |
123 | result = self.metric.exp(tangent_vec=vector,
124 | base_point=base_point)
125 | expected = base_point + vector
126 | expected = helper.to_vector(expected)
127 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
128 |
129 | def test_exp_vectorization(self):
130 | dim = self.dimension
131 | n_samples = 3
132 | one_tangent_vec = gs.array([[-1., 0.]])
133 | one_base_point = gs.array([[1.0, 0.]])
134 |
135 | n_tangent_vecs = gs.array([
136 | [-1., 0.],
137 | [1., 0.],
138 | [2., math.sqrt(3)]])
139 | n_base_points = gs.array([
140 | [2., -math.sqrt(3)],
141 | [4.0, math.sqrt(15)],
142 | [-4.0, math.sqrt(15)]])
143 |
144 | result = self.metric.exp(one_tangent_vec, one_base_point)
145 | expected = one_tangent_vec + one_base_point
146 | expected = helper.to_vector(expected)
147 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
148 |
149 | result = self.metric.exp(n_tangent_vecs, one_base_point)
150 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, dim))
151 |
152 | result = self.metric.exp(one_tangent_vec, n_base_points)
153 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, dim))
154 |
155 | result = self.metric.exp(n_tangent_vecs, n_base_points)
156 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, dim))
157 |
158 | def test_log(self):
159 | base_point = gs.array([-1., 0.])
160 | point = gs.array([2., math.sqrt(3)])
161 |
162 | result = self.metric.log(point=point, base_point=base_point)
163 | expected = point - base_point
164 | expected = helper.to_vector(expected)
165 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
166 |
167 | def test_log_vectorization(self):
168 | dim = self.dimension
169 | n_samples = 3
170 | one_point = gs.array([[-1., 0.]])
171 | one_base_point = gs.array([[1.0, 0.]])
172 |
173 | n_points = gs.array([
174 | [-1., 0.],
175 | [1., 0.],
176 | [2., math.sqrt(3)]])
177 | n_base_points = gs.array([
178 | [2., -math.sqrt(3)],
179 | [4.0, math.sqrt(15)],
180 | [-4.0, math.sqrt(15)]])
181 |
182 | result = self.metric.log(one_point, one_base_point)
183 | expected = one_point - one_base_point
184 | expected = helper.to_vector(expected)
185 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
186 |
187 | result = self.metric.log(n_points, one_base_point)
188 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, dim))
189 |
190 | result = self.metric.log(one_point, n_base_points)
191 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, dim))
192 |
193 | result = self.metric.log(n_points, n_base_points)
194 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, dim))
195 |
196 | def test_squared_dist(self):
197 | point_a = gs.array([2., -math.sqrt(3)])
198 | point_b = gs.array([4.0, math.sqrt(15)])
199 |
200 | result = self.metric.squared_dist(point_a, point_b)
201 | vec = point_b - point_a
202 | expected = gs.dot(vec, vec)
203 | expected -= 2 * vec[self.time_like_dim] * vec[self.time_like_dim]
204 | expected = helper.to_scalar(expected)
205 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
206 |
207 | def test_geodesic_and_belongs(self):
208 | n_geodesic_points = 100
209 | initial_point = gs.array([2., -math.sqrt(3)])
210 | initial_tangent_vec = gs.array([2., 0.])
211 |
212 | geodesic = self.metric.geodesic(
213 | initial_point=initial_point,
214 | initial_tangent_vec=initial_tangent_vec)
215 |
216 | t = gs.linspace(start=0., stop=1., num=n_geodesic_points)
217 | points = geodesic(t)
218 |
219 | result = self.space.belongs(points)
220 | expected = gs.array(n_geodesic_points * [[True]])
221 |
222 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
223 |
224 | def test_mean(self):
225 | point = gs.array([[2., -math.sqrt(3)]])
226 | result = self.metric.mean(points=[point, point, point])
227 | expected = point
228 | expected = helper.to_vector(expected)
229 |
230 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
231 |
232 | points = gs.array([
233 | [1., 0.],
234 | [2., math.sqrt(3)],
235 | [3., math.sqrt(8)],
236 | [4., math.sqrt(24)]])
237 | weights = gs.array([1., 2., 1., 2.])
238 | result = self.metric.mean(points, weights)
239 | result = self.space.belongs(result)
240 | expected = gs.array([[True]])
241 |
242 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
243 |
244 | def test_variance(self):
245 | points = gs.array([
246 | [1., 0.],
247 | [2., math.sqrt(3)],
248 | [3., math.sqrt(8)],
249 | [4., math.sqrt(24)]])
250 | weights = gs.array([1., 2., 1., 2.])
251 | base_point = gs.array([-1., 0.])
252 | variance = self.metric.variance(points, weights, base_point)
253 | result = helper.to_scalar(variance != 0)
254 | # we expect the average of the points' Minkowski sq norms.
255 | expected = helper.to_scalar(gs.array([True]))
256 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
257 |
258 |
259 | if __name__ == '__main__':
260 | geomstats.tests.main()
261 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_spd_matrices_space.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for the manifold of symmetric positive definite matrices.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import warnings
6 |
7 | import geomstats.backend as gs
8 | import geomstats.tests
9 | import tests.helper as helper
10 |
11 | from geomstats.spd_matrices_space import SPDMatricesSpace
12 |
13 |
14 | class TestSPDMatricesSpaceMethods(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
15 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
16 |
17 | def setUp(self):
18 | warnings.simplefilter('ignore', category=ImportWarning)
19 |
20 | gs.random.seed(1234)
21 |
22 | self.n = 3
23 | self.space = SPDMatricesSpace(n=self.n)
24 | self.metric = self.space.metric
25 | self.n_samples = 4
26 |
27 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
28 | def test_random_uniform_and_belongs(self):
29 | point = self.space.random_uniform()
30 | result = self.space.belongs(point)
31 | expected = gs.array([[True]])
32 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
33 |
34 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
35 | def test_random_uniform_and_belongs_vectorization(self):
36 | """
37 | Test that the random uniform method samples
38 | on the hypersphere space.
39 | """
40 | n_samples = self.n_samples
41 | points = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=n_samples)
42 | result = self.space.belongs(points)
43 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, 1))
44 |
45 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
46 | def vector_from_symmetric_matrix_and_symmetric_matrix_from_vector(self):
47 | sym_mat_1 = gs.array([[1., 0.6, -3.],
48 | [0.6, 7., 0.],
49 | [-3., 0., 8.]])
50 | vector_1 = self.space.vector_from_symmetric_matrix(sym_mat_1)
51 | result_1 = self.space.symmetric_matrix_from_vector(vector_1)
52 | expected_1 = sym_mat_1
53 |
54 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result_1, expected_1))
55 |
56 | vector_2 = gs.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
57 | sym_mat_2 = self.space.symmetric_matrix_from_vector(vector_2)
58 | result_2 = self.space.vector_from_symmetric_matrix(sym_mat_2)
59 | expected_2 = vector_2
60 |
61 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result_2, expected_2))
62 |
63 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
64 | def vector_and_symmetric_matrix_vectorization(self):
65 | n_samples = self.n_samples
66 | vector = gs.random.rand(n_samples, 6)
67 | sym_mat = self.space.symmetric_matrix_from_vector(vector)
68 | result = self.space.vector_from_symmetric_matrix(sym_mat)
69 | expected = vector
70 |
71 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
72 |
73 | sym_mat = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples)
74 | vector = self.space.vector_from_symmetric_matrix(sym_mat)
75 | result = self.space.symmetric_matrix_from_vector(vector)
76 | expected = sym_mat
77 |
78 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
79 |
80 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
81 | def test_log_and_exp(self):
82 | base_point = gs.array([[5., 0., 0.],
83 | [0., 7., 2.],
84 | [0., 2., 8.]])
85 | point = gs.array([[9., 0., 0.],
86 | [0., 5., 0.],
87 | [0., 0., 1.]])
88 |
89 | log = self.metric.log(point=point, base_point=base_point)
90 | result = self.metric.exp(tangent_vec=log, base_point=base_point)
91 | expected = helper.to_matrix(point)
92 |
93 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
94 |
95 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
96 | def test_exp_and_belongs(self):
97 | n_samples = self.n_samples
98 | base_point = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=1)
99 | tangent_vec = self.space.random_tangent_vec_uniform(
100 | n_samples=n_samples,
101 | base_point=base_point)
102 | exps = self.metric.exp(tangent_vec, base_point)
103 | result = self.space.belongs(exps)
104 | expected = gs.array([[True]] * n_samples)
105 |
106 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
107 |
108 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
109 | def test_exp_vectorization(self):
110 | n_samples = self.n_samples
111 | one_base_point = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=1)
112 | n_base_point = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=n_samples)
113 |
114 | n_tangent_vec_same_base = self.space.random_tangent_vec_uniform(
115 | n_samples=n_samples,
116 | base_point=one_base_point)
117 | n_tangent_vec = self.space.random_tangent_vec_uniform(
118 | n_samples=n_samples,
119 | base_point=n_base_point)
120 |
121 | # Test with the 1 base_point, and several different tangent_vecs
122 | result = self.metric.exp(n_tangent_vec_same_base, one_base_point)
123 |
124 | self.assertAllClose(
125 | gs.shape(result), (n_samples, self.space.n, self.space.n))
126 |
127 | # Test with the same number of base_points and tangent_vecs
128 | result = self.metric.exp(n_tangent_vec, n_base_point)
129 |
130 | self.assertAllClose(
131 | gs.shape(result), (n_samples, self.space.n, self.space.n))
132 |
133 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
134 | def test_log_vectorization(self):
135 | n_samples = self.n_samples
136 | one_base_point = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=1)
137 | n_base_point = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=n_samples)
138 |
139 | one_point = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=1)
140 | n_point = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=n_samples)
141 |
142 | # Test with different points, one base point
143 | result = self.metric.log(n_point, one_base_point)
144 |
145 | self.assertAllClose(
146 | gs.shape(result), (n_samples, self.space.n, self.space.n))
147 |
148 | # Test with the same number of points and base points
149 | result = self.metric.log(n_point, n_base_point)
150 |
151 | self.assertAllClose(
152 | gs.shape(result), (n_samples, self.space.n, self.space.n))
153 |
154 | # Test with the one point and n base points
155 | result = self.metric.log(one_point, n_base_point)
156 |
157 | self.assertAllClose(
158 | gs.shape(result), (n_samples, self.space.n, self.space.n))
159 |
160 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
161 | def test_geodesic_and_belongs(self):
162 | initial_point = self.space.random_uniform()
163 | initial_tangent_vec = self.space.random_tangent_vec_uniform(
164 | n_samples=1,
165 | base_point=initial_point)
166 | geodesic = self.metric.geodesic(
167 | initial_point=initial_point,
168 | initial_tangent_vec=initial_tangent_vec)
169 |
170 | n_points = 10
171 | t = gs.linspace(start=0., stop=1., num=n_points)
172 | points = geodesic(t)
173 | result = self.space.belongs(points)
174 | expected = gs.array([[True]] * n_points)
175 |
176 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
177 |
178 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
179 | def test_squared_dist_is_symmetric(self):
180 | n_samples = self.n_samples
181 |
182 | point_1 = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=1)
183 | point_2 = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=1)
184 |
185 | sq_dist_1_2 = self.metric.squared_dist(point_1, point_2)
186 | sq_dist_2_1 = self.metric.squared_dist(point_2, point_1)
187 |
188 | self.assertAllClose(sq_dist_1_2, sq_dist_2_1)
189 |
190 | point_1 = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=1)
191 | point_2 = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=n_samples)
192 |
193 | sq_dist_1_2 = self.metric.squared_dist(point_1, point_2)
194 | sq_dist_2_1 = self.metric.squared_dist(point_2, point_1)
195 |
196 | self.assertAllClose(sq_dist_1_2, sq_dist_2_1)
197 |
198 | point_1 = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=n_samples)
199 | point_2 = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=1)
200 |
201 | sq_dist_1_2 = self.metric.squared_dist(point_1, point_2)
202 | sq_dist_2_1 = self.metric.squared_dist(point_2, point_1)
203 |
204 | self.assertAllClose(sq_dist_1_2, sq_dist_2_1)
205 |
206 | point_1 = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=n_samples)
207 | point_2 = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=n_samples)
208 |
209 | sq_dist_1_2 = self.metric.squared_dist(point_1, point_2)
210 | sq_dist_2_1 = self.metric.squared_dist(point_2, point_1)
211 |
212 | self.assertAllClose(sq_dist_1_2, sq_dist_2_1)
213 |
214 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
215 | def test_squared_dist_vectorization(self):
216 | n_samples = self.n_samples
217 | point_1 = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=n_samples)
218 | point_2 = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=n_samples)
219 |
220 | result = self.metric.squared_dist(point_1, point_2)
221 |
222 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, 1))
223 |
224 | point_1 = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=1)
225 | point_2 = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=n_samples)
226 |
227 | result = self.metric.squared_dist(point_1, point_2)
228 |
229 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, 1))
230 |
231 | point_1 = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=n_samples)
232 | point_2 = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=1)
233 |
234 | result = self.metric.squared_dist(point_1, point_2)
235 |
236 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (n_samples, 1))
237 |
238 | point_1 = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=1)
239 | point_2 = self.space.random_uniform(n_samples=1)
240 |
241 | result = self.metric.squared_dist(point_1, point_2)
242 |
243 | self.assertAllClose(gs.shape(result), (1, 1))
244 |
245 |
246 | if __name__ == '__main__':
247 | geomstats.tests.main()
248 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/connection.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Affine connections.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import autograd
6 |
7 | import geomstats.backend as gs
8 |
9 |
10 | class Connection(object):
11 |
12 | def __init__(self, dimension):
13 | self.dimension = dimension
14 |
15 | def christoffel_symbol(self, base_point):
16 | """
17 | Christoffel symbols associated with the connection.
18 |
19 | Parameters
20 | ----------
21 | base_point : array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
22 | """
23 | raise NotImplementedError(
24 | 'The Christoffel symbols are not implemented.')
25 |
26 | def connection(self, tangent_vector_a, tangent_vector_b, base_point):
27 | """
28 | Connection applied to tangent_vector_b in the direction of
29 | tangent_vector_a, both tangent at base_point.
30 |
31 | Parameters
32 | ----------
33 | tangent_vec_a: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
34 | or shape=[1, dimension]
35 |
36 | tangent_vec_b: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
37 | or shape=[1, dimension]
38 |
39 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
40 | or shape=[1, dimension]
41 | """
42 | raise NotImplementedError(
43 | 'connection is not implemented.')
44 |
45 | def exp(self, tangent_vector, base_point):
46 | """
47 | Exponential map associated to the affine connection.
48 |
49 | Parameters
50 | ----------
51 | tangent_vec: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
52 | or shape=[1, dimension]
53 |
54 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
55 | or shape=[1, dimension]
56 | """
57 | raise NotImplementedError(
58 | 'The affine connection exponential is not implemented.')
59 |
60 | def log(self, point, base_point):
61 | """
62 | Logarithm map associated to the affine connection.
63 |
64 | Parameters
65 | ----------
66 | point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
67 | or shape=[1, dimension]
68 |
69 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
70 | or shape=[1, dimension]
71 | """
72 | raise NotImplementedError(
73 | 'The affine connection logarithm is not implemented.')
74 |
75 | def pole_ladder_transport(
76 | self, tangent_vector_a, tangent_vector_b, base_point):
77 | """
78 | One step of pole ladder (parallel transport associated with the
79 | symmetric part of the connection using transvections).
80 |
81 | Parameters
82 | ----------
83 | tangent_vec_a: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
84 | or shape=[1, dimension]
85 |
86 | tangent_vec_b: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
87 | or shape=[1, dimension]
88 |
89 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
90 | or shape=[1, dimension]
91 | """
92 | half_tangent_vector_b = 1. / 2. * tangent_vector_b
93 | mid_point = self.exp(
94 | base_point=base_point,
95 | tangent_vector=half_tangent_vector_b)
96 |
97 | mid_tangent_vector = - self.log(
98 | base_point=mid_point,
99 | point=base_point)
100 | end_point = self.exp(
101 | base_point=mid_point,
102 | tangent_vector=mid_tangent_vector)
103 |
104 | base_shoot = self.exp(
105 | base_point=base_point,
106 | tangent_vector=tangent_vector_a)
107 | mid_tangent_vector_to_shoot = - self.log(
108 | base_point=mid_point,
109 | end_point=base_shoot)
110 | end_shoot = self.exp(
111 | base_point=mid_point,
112 | tangent_vector=mid_tangent_vector_to_shoot)
113 |
114 | tangent_vector = - self.log(base_point=end_point, point=end_shoot)
115 | return tangent_vector
116 |
117 | def parallel_transport(
118 | self, tangent_vector_a, tangent_vector_b, base_point, n_points=1):
119 | """
120 | Parallel transport of tangent vector a integrating the connection
121 | along the (affine connection) geodesic starting at the initial point
122 | base_point with initial tangent vector the tangent vector b.
123 |
124 | Returns a tangent vector at the point
125 | exp_(base_point)(tangent_vector_b).
126 |
127 | Parameters
128 | ----------
129 | tangent_vec_a: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
130 | or shape=[1, dimension]
131 |
132 | tangent_vec_b: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
133 | or shape=[1, dimension]
134 |
135 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
136 | or shape=[1, dimension]
137 | """
138 | current_point = gs.copy(base_point)
139 | geodesic_tangent_vector = 1. / n_points * tangent_vector_b
140 | transported_tangent_vector = gs.copy(tangent_vector_a)
141 | for i_point in range(1, n_points):
142 | transported_tangent_vector = self.pole_ladder_transport(
143 | tangent_vector_a=transported_tangent_vector,
144 | tangent_vector_b=geodesic_tangent_vector,
145 | base_point=current_point)
146 | current_point = self.exp(
147 | base_point=current_point,
148 | tangent_vector=geodesic_tangent_vector)
149 |
150 | frac_tangent_vector_b = (i_point + 1) / n_points * tangent_vector_b
151 | next_point = self.exp(
152 | base_point=base_point,
153 | tangent_vector=frac_tangent_vector_b)
154 | geodesic_tangent_vector = self.log(
155 | base_point=current_point,
156 | point=next_point)
157 |
158 | return transported_tangent_vector
159 |
160 | def riemannian_curvature(self, base_point):
161 | """
162 | Riemannian curvature tensor associated with the connection.
163 |
164 | Parameters
165 | ----------
166 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
167 | or shape=[1, dimension]
168 | """
169 | raise NotImplementedError(
170 | 'The Riemannian curvature tensor is not implemented.')
171 |
172 | def geodesic_equation(self):
173 | """
174 | The geodesic ordinary differential equation associated
175 | with the connection.
176 | """
177 | raise NotImplementedError(
178 | 'The geodesic equation tensor is not implemented.')
179 |
180 | def geodesic(self, initial_point,
181 | end_point=None, initial_tangent_vec=None, point_ndim=1):
182 | """
183 | Geodesic associated with the connection.
184 | """
185 | raise NotImplementedError(
186 | 'Geodesics are not implemented.')
187 |
188 | def torsion(self, base_point):
189 | """
190 | Torsion tensor associated with the connection.
191 |
192 | Parameters
193 | ----------
194 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
195 | or shape=[1, dimension]
196 | """
197 | raise NotImplementedError(
198 | 'The torsion tensor is not implemented.')
199 |
200 |
201 | class LeviCivitaConnection(Connection):
202 | """
203 | Levi-Civita connection associated with a Riemannian metric.
204 | """
205 | def __init__(self, metric):
206 | self.metric = metric
207 | self.dimension = metric.dimension
208 |
209 | def metric_matrix(self, base_point):
210 | metric_matrix = self.metric.inner_product_matrix(base_point)
211 | return metric_matrix
212 |
213 | def cometric_matrix(self, base_point):
214 | """
215 | The cometric is the inverse of the metric.
216 |
217 | Parameters
218 | ----------
219 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
220 | or shape=[1, dimension]
221 | """
222 | metric_matrix = self.metric_matrix(base_point)
223 | cometric_matrix = gs.linalg.inv(metric_matrix)
224 | return cometric_matrix
225 |
226 | def metric_derivative(self, base_point):
227 | """
228 |
229 | Parameters
230 | ----------
231 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
232 | or shape=[1, dimension]
233 | """
234 | metric_derivative = autograd.jacobian(self.metric_matrix)
235 | return metric_derivative(base_point)
236 |
237 | def christoffel_symbols(self, base_point):
238 | """
239 | Christoffel symbols associated with the connection.
240 |
241 | Parameters
242 | ----------
243 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
244 | or shape=[1, dimension]
245 | """
246 | term_1 = gs.einsum('nim,nmkl->nikl',
247 | self.cometric_matrix(base_point),
248 | self.metric_derivative(base_point))
249 | term_2 = gs.einsum('nim,nmlk->nilk',
250 | self.cometric_matrix(base_point),
251 | self.metric_derivative(base_point))
252 | term_3 = - gs.einsum('nim,nklm->nikl',
253 | self.cometric_matrix(base_point),
254 | self.metric_derivative(base_point))
255 |
256 | christoffel_symbols = 0.5 * (term_1 + term_2 + term_3)
257 | return christoffel_symbols
258 |
259 | def torsion(self, base_point):
260 | """
261 | Torsion tensor associated with the Levi-Civita connection is zero.
262 |
263 | Parameters
264 | ----------
265 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
266 | or shape=[1, dimension]
267 | """
268 | return gs.zeros((self.dimension,) * 3)
269 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 13 |
14 |
15 | ## Installation
16 |
17 | OS X & Linux:
18 |
19 | ```
20 | pip3 install geomstats
21 | ```
22 |
23 | ## Running tests
24 |
25 | ```
26 | pip3 install nose2
27 | nose2
28 | ```
29 |
30 | ## Getting started
31 |
32 | Define your backend by setting the environment variable ```GEOMSTATS_BACKEND``` to ```numpy```, ```tensorflow```, or ```pytorch```:
33 |
34 | ```
35 | export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND=numpy
36 | ```
37 |
38 | Then, run example scripts:
39 |
40 | ```
41 | python3 examples/plot_grid_h2.py
42 | ```
43 |
44 | ## Contributing
45 |
46 | See our [CONTRIBUTING.md][link_contributing] file!
47 |
48 | ## Authors & Contributors
49 |
50 | * Alice Le Brigant
51 | * Claire Donnat
52 | * Oleg Kachan
53 | * Benjamin Hou
54 | * Johan Mathe
55 | * Nina Miolane
56 | * Xavier Pennec
57 |
58 | ## Acknowledgements
59 |
60 | This work is partially supported by the National Science Foundation, grant NSF DMS RTG 1501767.
61 |
62 | [link_contributing]: https://github.com/geomstats/geomstats/CONTRIBUTING.md
63 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_visualization.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for visualization.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import matplotlib
6 | matplotlib.use('Agg') # NOQA
7 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
8 |
9 | import geomstats.tests
10 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
11 |
12 | from geomstats.hyperbolic_space import HyperbolicSpace
13 | from geomstats.hypersphere import Hypersphere
14 | from geomstats.special_euclidean_group import SpecialEuclideanGroup
15 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
16 |
17 |
18 | class TestVisualizationMethods(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
19 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
20 |
21 | def setUp(self):
22 | self.n_samples = 10
23 | self.SO3_GROUP = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=3)
24 | self.SE3_GROUP = SpecialEuclideanGroup(n=3)
25 | self.S1 = Hypersphere(dimension=1)
26 | self.S2 = Hypersphere(dimension=2)
27 | self.H2 = HyperbolicSpace(dimension=2)
28 |
29 | plt.figure()
30 |
31 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
32 | def test_plot_points_so3(self):
33 | points = self.SO3_GROUP.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
34 | visualization.plot(points, space='SO3_GROUP')
35 |
36 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
37 | def test_plot_points_se3(self):
38 | points = self.SE3_GROUP.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
39 | visualization.plot(points, space='SE3_GROUP')
40 |
41 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
42 | def test_plot_points_s1(self):
43 | points = self.S1.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
44 | visualization.plot(points, space='S1')
45 |
46 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
47 | def test_plot_points_s2(self):
48 | points = self.S2.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
49 | visualization.plot(points, space='S2')
50 |
51 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
52 | def test_plot_points_h2_poincare_disk(self):
53 | points = self.H2.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
54 | visualization.plot(points, space='H2_poincare_disk')
55 |
56 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
57 | def test_plot_points_h2_poincare_half_plane(self):
58 | points = self.H2.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
59 | visualization.plot(points, space='H2_poincare_half_plane')
60 |
61 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
62 | def test_plot_points_h2_klein_disk(self):
63 | points = self.H2.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
64 | visualization.plot(points, space='H2_klein_disk')
65 |
66 |
67 | if __name__ == '__main__':
68 | geomstats.tests.main()
69 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/tests.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Testing class for geomstats.
3 |
4 | This class abstracts the backend type.
5 | """
6 |
7 | import os
8 | import tensorflow as tf
9 | import unittest
10 |
11 | import geomstats.backend as gs
12 |
13 |
14 | def pytorch_backend():
15 | return os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'pytorch'
16 |
17 |
18 | def tf_backend():
19 | return os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow'
20 |
21 |
22 | def np_backend():
23 | return os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'numpy'
24 |
25 |
26 | test_class = unittest.TestCase
27 | if tf_backend():
28 | test_class = tf.test.TestCase
29 |
30 |
31 | def np_only(test_item):
32 | """Decorator to filter tests for numpy only."""
33 | if not np_backend():
34 | test_item.__unittest_skip__ = True
35 | test_item.__unittest_skip_why__ = (
36 | 'Test for numpy backend only.')
37 | return test_item
38 |
39 |
40 | def np_and_tf_only(test_item):
41 | """Decorator to filter tests for numpy and tensorflow only."""
42 | if not (np_backend() or tf_backend()):
43 | test_item.__unittest_skip__ = True
44 | test_item.__unittest_skip_why__ = (
45 | 'Test for numpy and tensorflow backends only.')
46 | return test_item
47 |
48 |
49 | def np_and_pytorch_only(test_item):
50 | """Decorator to filter tests for numpy and pytorch only."""
51 | if not (np_backend() or pytorch_backend()):
52 | test_item.__unittest_skip__ = True
53 | test_item.__unittest_skip_why__ = (
54 | 'Test for numpy and pytorch backends only.')
55 | return test_item
56 |
57 |
58 | class DummySession():
59 | def __enter__(self):
60 | pass
61 |
62 | def __exit__(self, a, b, c):
63 | pass
64 |
65 |
66 | class TestCase(test_class):
67 |
68 | def assertAllClose(self, a, b, rtol=1e-6, atol=1e-6):
69 | if tf_backend():
70 | return super().assertAllClose(a, b, rtol=rtol, atol=atol)
71 | return self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(a, b, rtol=rtol, atol=atol))
72 |
73 | def session(self):
74 | if tf_backend():
75 | return super().test_session()
76 | return DummySession()
77 |
78 | def assertShapeEqual(self, a, b):
79 | if tf_backend():
80 | return super().assertShapeEqual(a, b)
81 | super().assertEqual(a.shape, b.shape)
82 |
83 | @classmethod
84 | def setUpClass(cls):
85 | if tf_backend():
86 | os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
87 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/plot_geodesics_h2.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Plot a geodesic on the Hyperbolic space H2,
3 | with Poincare Disk visualization.
4 | """
5 |
6 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
7 | import numpy as np
8 | import os
9 |
10 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
11 |
12 | from geomstats.hyperbolic_space import HyperbolicSpace
13 |
14 | H2 = HyperbolicSpace(dimension=2)
15 | METRIC = H2.metric
16 |
17 |
18 | def plot_geodesic_between_two_points(initial_point,
19 | end_point,
20 | n_steps=10,
21 | ax=None):
22 | assert H2.belongs(initial_point)
23 | assert H2.belongs(end_point)
24 |
25 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=initial_point,
26 | end_point=end_point)
27 |
28 | t = np.linspace(0, 1, n_steps)
29 | points = geodesic(t)
30 | visualization.plot(points, ax=ax, space='H2_poincare_disk')
31 |
32 |
33 | def plot_geodesic_with_initial_tangent_vector(initial_point,
34 | initial_tangent_vec,
35 | n_steps=10,
36 | ax=None):
37 | assert H2.belongs(initial_point)
38 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=initial_point,
39 | initial_tangent_vec=initial_tangent_vec)
40 | n_steps = 10
41 | t = np.linspace(0, 1, n_steps)
42 |
43 | points = geodesic(t)
44 | visualization.plot(points, ax=ax, space='H2_poincare_disk')
45 |
46 |
47 | def main():
48 | initial_point = [np.sqrt(2), 1., 0.]
49 | end_point = H2.intrinsic_to_extrinsic_coords([1.5, 1.5])
50 | initial_tangent_vec = H2.projection_to_tangent_space(
51 | vector=[3.5, 0.6, 0.8],
52 | base_point=initial_point)
53 |
54 | ax = plt.gca()
55 | plot_geodesic_between_two_points(initial_point,
56 | end_point,
57 | ax=ax)
58 | plot_geodesic_with_initial_tangent_vector(initial_point,
59 | initial_tangent_vec,
60 | ax=ax)
61 | plt.show()
62 |
63 |
64 | if __name__ == "__main__":
65 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
66 | print('Examples with visualizations are only implemented '
67 | 'with numpy backend.\n'
68 | 'To change backend, write: '
69 | 'export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND = \'numpy\'.')
70 | else:
71 | main()
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/helper.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Helper functions for unit tests.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 |
7 |
8 | def to_scalar(expected):
9 | expected = gs.to_ndarray(expected, to_ndim=1)
10 | expected = gs.to_ndarray(expected, to_ndim=2, axis=-1)
11 | return expected
12 |
13 |
14 | def to_vector(expected):
15 | expected = gs.to_ndarray(expected, to_ndim=2)
16 | return expected
17 |
18 |
19 | def to_matrix(expected):
20 | expected = gs.to_ndarray(expected, to_ndim=3)
21 | return expected
22 |
23 |
24 | def left_log_then_exp_from_identity(metric, point):
25 | aux = metric.left_log_from_identity(point=point)
26 | result = metric.left_exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=aux)
27 | return result
28 |
29 |
30 | def left_exp_then_log_from_identity(metric, tangent_vec):
31 | aux = metric.left_exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=tangent_vec)
32 | result = metric.left_log_from_identity(point=aux)
33 | return result
34 |
35 |
36 | def log_then_exp_from_identity(metric, point):
37 | aux = metric.log_from_identity(point=point)
38 | result = metric.exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=aux)
39 | return result
40 |
41 |
42 | def exp_then_log_from_identity(metric, tangent_vec):
43 | aux = metric.exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=tangent_vec)
44 | result = metric.log_from_identity(point=aux)
45 | return result
46 |
47 |
48 | def log_then_exp(metric, point, base_point):
49 | aux = metric.log(point=point,
50 | base_point=base_point)
51 | result = metric.exp(tangent_vec=aux,
52 | base_point=base_point)
53 | return result
54 |
55 |
56 | def exp_then_log(metric, tangent_vec, base_point):
57 | aux = metric.exp(tangent_vec=tangent_vec,
58 | base_point=base_point)
59 | result = metric.log(point=aux,
60 | base_point=base_point)
61 | return result
62 |
63 |
64 | def group_log_then_exp_from_identity(group, point):
65 | aux = group.group_log_from_identity(point=point)
66 | result = group.group_exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=aux)
67 | return result
68 |
69 |
70 | def group_exp_then_log_from_identity(group, tangent_vec):
71 | aux = group.group_exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=tangent_vec)
72 | result = group.group_log_from_identity(point=aux)
73 | return result
74 |
75 |
76 | def group_log_then_exp(group, point, base_point):
77 | aux = group.group_log(point=point,
78 | base_point=base_point)
79 | result = group.group_exp(tangent_vec=aux,
80 | base_point=base_point)
81 | return result
82 |
83 |
84 | def group_exp_then_log(group, tangent_vec, base_point):
85 | aux = group.group_exp(tangent_vec=tangent_vec,
86 | base_point=base_point)
87 | result = group.group_log(point=aux,
88 | base_point=base_point)
89 | return result
90 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/api-reference.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | *************
2 | API reference
3 | *************
4 |
5 | .. automodule:: geomstats
6 | :members:
7 |
8 | The "manifold" module
9 | ---------------------
10 |
11 | .. automodule:: geomstats.manifold
12 | :members:
13 |
14 | The "connection" module
15 | -----------------------
16 |
17 | .. automodule:: geomstats.connection
18 | :members:
19 |
20 | The "riemannian_metric" module
21 | ------------------------------
22 |
23 | .. automodule:: geomstats.riemannian_metric
24 | :members:
25 |
26 | Spaces of constant curvatures
27 | =============================
28 |
29 | The "embedded_manifold" module
30 | ------------------------------
31 |
32 | .. automodule:: geomstats.embedded_manifold
33 | :members:
34 |
35 | The "euclidean_space" module
36 | ----------------------------
37 |
38 | .. automodule:: geomstats.euclidean_space
39 | :members:
40 |
41 | The "minkowski_space" module
42 | ----------------------------
43 |
44 | .. automodule:: geomstats.minkowski_space
45 | :members:
46 |
47 | The "hypersphere" module
48 | ------------------------
49 |
50 | .. automodule:: geomstats.hypersphere
51 | :members:
52 |
53 | The "hyperbolic_space" module
54 | -----------------------------
55 |
56 | .. automodule:: geomstats.hyperbolic_space
57 | :members:
58 |
59 | Lie groups
60 | ==========
61 |
62 | The "lie_group" module
63 | ----------------------
64 |
65 | .. automodule:: geomstats.lie_group
66 | :members:
67 |
68 | The "matrices_space" module
69 | ---------------------------
70 |
71 | .. automodule:: geomstats.matrices_space
72 | :members:
73 |
74 | The "general_linear_group" module
75 | ---------------------------------
76 |
77 | .. automodule:: geomstats.general_linear_group
78 | :members:
79 |
80 | The "invariant_metric" module
81 | -----------------------------
82 |
83 | .. automodule:: geomstats.invariant_metric
84 | :members:
85 |
86 | The "special_euclidean_group" module
87 | ------------------------------------
88 |
89 | .. automodule:: geomstats.special_euclidean_group
90 | :members:
91 |
92 | The "special_orthogonal_group" module
93 | -------------------------------------
94 |
95 | .. automodule:: geomstats.special_orthogonal_group
96 | :members:
97 |
98 | More manifolds
99 | ==============
100 |
101 | The "discretized_curves_space" module
102 | -------------------------------------
103 |
104 | .. automodule:: geomstats.discretized_curves_space
105 | :members:
106 |
107 | The "spd_matrices_space" module
108 | -------------------------------
109 |
110 | .. automodule:: geomstats.spd_matrices_space
111 | :members:
112 |
113 | The "stiefel" module
114 | --------------------
115 |
116 | .. automodule:: geomstats.stiefel
117 | :members:
118 |
119 | Visualization implementations
120 | =============================
121 |
122 | .. automodule:: geomstats.visualization
123 | :members:
124 |
125 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_examples.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for the examples.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import matplotlib
6 | matplotlib.use('Agg') # NOQA
7 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
8 | import os
9 | import sys
10 | import warnings
11 |
12 | import examples.gradient_descent_s2 as gradient_descent_s2
13 | import examples.loss_and_gradient_se3 as loss_and_gradient_se3
14 | import examples.loss_and_gradient_so3 as loss_and_gradient_so3
15 | import examples.plot_geodesics_h2 as plot_geodesics_h2
16 | import examples.plot_geodesics_s2 as plot_geodesics_s2
17 | import examples.plot_geodesics_se3 as plot_geodesics_se3
18 | import examples.plot_geodesics_so3 as plot_geodesics_so3
19 | import examples.plot_grid_h2 as plot_grid_h2
20 | import examples.plot_square_h2_poincare_disk as plot_square_h2_poincare_disk
21 | import examples.plot_square_h2_poincare_half_plane as plot_square_h2_poincare_half_plane # NOQA
22 | import examples.plot_square_h2_klein_disk as plot_square_h2_klein_disk
23 | import examples.plot_quantization_s1 as plot_quantization_s1
24 | import examples.plot_quantization_s2 as plot_quantization_s2
25 | import examples.tangent_pca_so3 as tangent_pca_so3
26 | import geomstats.tests
27 |
28 |
29 | class TestExamples(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
30 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
31 |
32 | @classmethod
33 | def setUpClass(cls):
34 | sys.stdout = open(os.devnull, 'w')
35 |
36 | def setUp(self):
37 | warnings.simplefilter('ignore', category=ImportWarning)
38 | plt.figure()
39 |
40 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
41 | def test_gradient_descent_s2(self):
42 | gradient_descent_s2.main(max_iter=32, output_file=None)
43 |
44 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
45 | def test_loss_and_gradient_so3(self):
46 | loss_and_gradient_so3.main()
47 |
48 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
49 | def test_loss_and_gradient_se3(self):
50 | loss_and_gradient_se3.main()
51 |
52 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
53 | def test_plot_geodesics_h2(self):
54 | plot_geodesics_h2.main()
55 |
56 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
57 | def test_plot_geodesics_s2(self):
58 | plot_geodesics_s2.main()
59 |
60 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
61 | def test_plot_geodesics_se3(self):
62 | plot_geodesics_se3.main()
63 |
64 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
65 | def test_plot_geodesics_so3(self):
66 | plot_geodesics_so3.main()
67 |
68 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
69 | def test_plot_grid_h2(self):
70 | plot_grid_h2.main()
71 |
72 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
73 | def test_plot_square_h2_square_poincare_disk(self):
74 | plot_square_h2_poincare_disk.main()
75 |
76 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
77 | def test_plot_square_h2_square_poincare_half_plane(self):
78 | plot_square_h2_poincare_half_plane.main()
79 |
80 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
81 | def test_plot_square_h2_square_klein_disk(self):
82 | plot_square_h2_klein_disk.main()
83 |
84 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
85 | def test_tangent_pca_so3(self):
86 | tangent_pca_so3.main()
87 |
88 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
89 | def test_plot_quantization_s1(self):
90 | plot_quantization_s1.main()
91 |
92 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
93 | def test_plot_quantization_s2(self):
94 | plot_quantization_s2.main()
95 |
96 |
97 | if __name__ == '__main__':
98 | geomstats.tests.main()
99 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/matrices_space.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | The space of matrices (m, n), which is the Euclidean space R^{mn}.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 |
7 | from geomstats.euclidean_space import EuclideanSpace
8 | from geomstats.riemannian_metric import RiemannianMetric
9 |
10 |
11 | TOLERANCE = 1e-5
12 |
13 |
14 | class MatricesSpace(EuclideanSpace):
15 | """Class for the space of matrices (m, n)."""
16 |
17 | def __init__(self, m, n):
18 | assert isinstance(m, int) and isinstance(n, int) and m > 0 and n > 0
19 | super(MatricesSpace, self).__init__(dimension=m*n)
20 | self.m = m
21 | self.n = n
22 | self.default_point_type = 'matrix'
23 | self.metric = MatricesMetric(m, n)
24 |
25 | def belongs(self, point):
26 | """
27 | Check if point belongs to the Matrix space.
28 | """
29 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=3)
30 | _, mat_dim_1, mat_dim_2 = point.shape
31 | return mat_dim_1 == self.m & mat_dim_2 == self.n
32 |
33 | @staticmethod
34 | def vector_from_matrix(matrix):
35 | """
36 | Conversion function from (_, m, n) to (_, mn).
37 | """
38 | matrix = gs.to_ndarray(matrix, to_ndim=3)
39 | n_mats, m, n = matrix.shape
40 | return gs.reshape(matrix, (n_mats, m*n))
41 |
42 | @staticmethod
43 | def is_symmetric(matrix, tolerance=TOLERANCE):
44 | """Check if a matrix is symmetric."""
45 | matrix = gs.to_ndarray(matrix, to_ndim=3)
46 | n_mats, m, n = matrix.shape
47 | assert m == n
48 | matrix_transpose = gs.transpose(matrix, axes=(0, 2, 1))
49 |
50 | mask = gs.isclose(matrix, matrix_transpose, atol=tolerance)
51 | mask = gs.all(mask, axis=(1, 2))
52 |
53 | mask = gs.to_ndarray(mask, to_ndim=1)
54 | mask = gs.to_ndarray(mask, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
55 | return mask
56 |
57 | @staticmethod
58 | def make_symmetric(matrix):
59 | """Make a matrix fully symmetric to avoid numerical issues."""
60 | matrix = gs.to_ndarray(matrix, to_ndim=3)
61 | n_mats, m, n = matrix.shape
62 | assert m == n
63 | matrix = gs.to_ndarray(matrix, to_ndim=3)
64 | return (matrix + gs.transpose(matrix, axes=(0, 2, 1))) / 2
65 |
66 | def random_uniform(self, n_samples=1):
67 | point = gs.random.rand(n_samples, self.m, self.n)
68 | return point
69 |
70 |
71 | class MatricesMetric(RiemannianMetric):
72 | """
73 | Euclidean metric on matrices given by the Frobenius inner product.
74 | """
75 | def __init__(self, m, n):
76 | dimension = m*n
77 | super(MatricesMetric, self).__init__(
78 | dimension=dimension,
79 | signature=(dimension, 0, 0))
80 |
81 | def inner_product(self, tangent_vec_a, tangent_vec_b, base_point=None):
82 | """
83 | Compute the Frobenius inner product of tangent_vec_a and tangent_vec_b
84 | at base_point.
85 | """
86 | tangent_vec_a = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec_a, to_ndim=3)
87 | n_tangent_vecs_a, _, _ = tangent_vec_a.shape
88 |
89 | tangent_vec_b = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec_b, to_ndim=3)
90 | n_tangent_vecs_b, _, _ = tangent_vec_b.shape
91 |
92 | assert n_tangent_vecs_a == n_tangent_vecs_b
93 |
94 | inner_prod = gs.einsum("nij,nij->n", tangent_vec_a, tangent_vec_b)
95 | inner_prod = gs.to_ndarray(inner_prod, to_ndim=1)
96 | inner_prod = gs.to_ndarray(inner_prod, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
97 | return inner_prod
98 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_matrices_space.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for the manifold of matrices.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 | import geomstats.tests
7 | import tests.helper as helper
8 |
9 | from geomstats.matrices_space import MatricesSpace
10 |
11 |
12 | class TestMatricesSpaceMethods(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
13 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
14 |
15 | def setUp(self):
16 | gs.random.seed(1234)
17 |
18 | self.n = 3
19 | self.space = MatricesSpace(m=self.n, n=self.n)
20 | self.metric = self.space.metric
21 | self.n_samples = 2
22 |
23 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
24 | def test_is_symmetric(self):
25 | sym_mat = gs.array([[1., 2.],
26 | [2., 1.]])
27 | result = self.space.is_symmetric(sym_mat)
28 | expected = gs.array([True])
29 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
30 |
31 | not_a_sym_mat = gs.array([[1., 0.6, -3.],
32 | [6., -7., 0.],
33 | [0., 7., 8.]])
34 | result = self.space.is_symmetric(not_a_sym_mat)
35 | expected = gs.array([False])
36 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
37 |
38 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
39 | def test_is_symmetric_vectorization(self):
40 | points = gs.array([
41 | [[1., 2.],
42 | [2., 1.]],
43 | [[3., 4.],
44 | [4., 5.]]])
45 | result = gs.all(self.space.is_symmetric(points))
46 | expected = True
47 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
48 |
49 | def test_make_symmetric(self):
50 | sym_mat = gs.array([[1., 2.],
51 | [2., 1.]])
52 | result = self.space.make_symmetric(sym_mat)
53 | expected = helper.to_matrix(sym_mat)
54 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
55 |
56 | mat = gs.array([[1., 2., 3.],
57 | [0., 0., 0.],
58 | [3., 1., 1.]])
59 | result = self.space.make_symmetric(mat)
60 | expected = gs.array([[[1., 1., 3.],
61 | [1., 0., 0.5],
62 | [3., 0.5, 1.]]])
63 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
64 |
65 | mat = gs.array([[[1e100, 1e-100, 1e100],
66 | [1e100, 1e-100, 1e100],
67 | [1e-100, 1e-100, 1e100]]])
68 | result = self.space.make_symmetric(mat)
69 |
70 | res = 0.5 * (1e100 + 1e-100)
71 |
72 | expected = gs.array([[[1e100, res, res],
73 | [res, 1e-100, res],
74 | [res, res, 1e100]]])
75 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
76 |
77 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
78 | def test_make_symmetric_and_is_symmetric_vectorization(self):
79 | points = gs.array([
80 | [[1., 2.],
81 | [3., 4.]],
82 | [[5., 6.],
83 | [4., 9.]]])
84 |
85 | sym_points = self.space.make_symmetric(points)
86 | result = gs.all(self.space.is_symmetric(sym_points))
87 | expected = True
88 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
89 |
90 | def test_inner_product(self):
91 | base_point = gs.array([
92 | [1., 2., 3.],
93 | [0., 0., 0.],
94 | [3., 1., 1.]])
95 |
96 | tangent_vector_1 = gs.array([
97 | [1., 2., 3.],
98 | [0., -10., 0.],
99 | [30., 1., 1.]])
100 |
101 | tangent_vector_2 = gs.array([
102 | [1., 4., 3.],
103 | [5., 0., 0.],
104 | [3., 1., 1.]])
105 |
106 | result = self.metric.inner_product(
107 | tangent_vector_1,
108 | tangent_vector_2,
109 | base_point=base_point)
110 |
111 | expected = gs.trace(
112 | gs.matmul(
113 | gs.transpose(tangent_vector_1),
114 | tangent_vector_2))
115 | expected = helper.to_scalar(expected)
116 |
117 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
118 |
119 |
120 | if __name__ == '__main__':
121 | geomstats.tests.main()
122 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/euclidean_space.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Euclidean space.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 |
7 | from geomstats.manifold import Manifold
8 | from geomstats.riemannian_metric import RiemannianMetric
9 |
10 |
11 | class EuclideanSpace(Manifold):
12 | """
13 | Class for Euclidean spaces.
14 |
15 | By definition, a Euclidean space is a vector space of a given
16 | dimension, equipped with a Euclidean metric.
17 | """
18 |
19 | def __init__(self, dimension):
20 | assert isinstance(dimension, int) and dimension > 0
21 | self.dimension = dimension
22 | self.metric = EuclideanMetric(dimension)
23 |
24 | def belongs(self, point):
25 | """
26 | Evaluate if a point belongs to the Euclidean space.
27 |
28 | Parameters
29 | ----------
30 | point : array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
31 | Input points.
32 |
33 | Returns
34 | -------
35 | belongs : array-like, shape=[n_samples, 1]
36 | """
37 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=2)
38 | n_points, point_dim = point.shape
39 | belongs = point_dim == self.dimension
40 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=1)
41 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
42 | belongs = gs.tile(belongs, (n_points, 1))
43 |
44 | return belongs
45 |
46 | def random_uniform(self, n_samples=1, bound=1.):
47 | """
48 | Sample in the Euclidean space with the uniform distribution.
49 | """
50 | size = (n_samples, self.dimension)
51 | point = bound * (gs.random.rand(*size) - 0.5) * 2
52 |
53 | return point
54 |
55 |
56 | class EuclideanMetric(RiemannianMetric):
57 | """
58 | Class for Euclidean metrics.
59 |
60 | As a Riemannian metric, the Euclidean metric is:
61 | - flat: the inner product is independent of the base point.
62 | - positive definite: it has signature (0, dimension),
63 | where dimension is the dimension of the Euclidean space.
64 | """
65 | def __init__(self, dimension):
66 | assert isinstance(dimension, int) and dimension > 0
67 | super(EuclideanMetric, self).__init__(
68 | dimension=dimension,
69 | signature=(dimension, 0, 0))
70 |
71 | def inner_product_matrix(self, base_point=None):
72 | """
73 | Inner product matrix, independent of the base point.
74 | """
75 | mat = gs.eye(self.dimension)
76 | mat = gs.to_ndarray(mat, to_ndim=3)
77 | return mat
78 |
79 | def exp(self, tangent_vec, base_point):
80 | """
81 | The Riemannian exponential is the addition in the Euclidean space.
82 | """
83 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=2)
84 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=2)
85 | exp = base_point + tangent_vec
86 | return exp
87 |
88 | def log(self, point, base_point):
89 | """
90 | The Riemannian logarithm is the subtraction in the Euclidean space.
91 | """
92 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=2)
93 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=2)
94 | log = point - base_point
95 | return log
96 |
97 | def mean(self, points, weights=None):
98 | """
99 | The Frechet mean of (weighted) points computed with the
100 | Euclidean metric is the weighted average of the points
101 | in the Euclidean space.
102 | """
103 | if isinstance(points, list):
104 | points = gs.vstack(points)
105 | points = gs.to_ndarray(points, to_ndim=2)
106 | n_points = gs.shape(points)[0]
107 |
108 | if isinstance(weights, list):
109 | weights = gs.vstack(weights)
110 | elif weights is None:
111 | weights = gs.ones((n_points,))
112 |
113 | weighted_points = gs.einsum('n,nj->nj', weights, points)
114 | mean = (gs.sum(weighted_points, axis=0)
115 | / gs.sum(weights))
116 | mean = gs.to_ndarray(mean, to_ndim=2)
117 | return mean
118 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_backend_numpy.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for numpy backend.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import importlib
6 | import os
7 | import unittest
8 | import warnings
9 |
10 | import geomstats.backend as gs
11 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
12 |
13 |
14 | class TestBackendNumpy(unittest.TestCase):
15 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
16 |
17 | @classmethod
18 | def setUpClass(cls):
19 | cls.initial_backend = os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND']
20 | os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] = 'numpy'
21 | importlib.reload(gs)
22 |
23 | @classmethod
24 | def tearDownClass(cls):
25 | os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] = cls.initial_backend
26 | importlib.reload(gs)
27 |
28 | def setUp(self):
29 | warnings.simplefilter('ignore', category=ImportWarning)
30 |
31 | self.so3_group = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=3)
32 | self.n_samples = 2
33 |
34 | def test_logm(self):
35 | point = gs.array([[2., 0., 0.],
36 | [0., 3., 0.],
37 | [0., 0., 4.]])
38 | result = gs.linalg.logm(point)
39 | expected = gs.array([[0.693147180, 0., 0.],
40 | [0., 1.098612288, 0.],
41 | [0., 0., 1.38629436]])
42 |
43 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
44 |
45 | def test_expm_and_logm(self):
46 | point = gs.array([[2., 0., 0.],
47 | [0., 3., 0.],
48 | [0., 0., 4.]])
49 | result = gs.linalg.expm(gs.linalg.logm(point))
50 | expected = point
51 |
52 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
53 |
54 | def test_expm_vectorization(self):
55 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
56 | [0., 3., 0.],
57 | [0., 0., 4.]],
58 | [[1., 0., 0.],
59 | [0., 5., 0.],
60 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
61 |
62 | expected = gs.array([[[7.38905609, 0., 0.],
63 | [0., 20.0855369, 0.],
64 | [0., 0., 54.5981500]],
65 | [[2.718281828, 0., 0.],
66 | [0., 148.413159, 0.],
67 | [0., 0., 403.42879349]]])
68 |
69 | result = gs.linalg.expm(point)
70 |
71 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
72 |
73 | def test_logm_vectorization_diagonal(self):
74 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
75 | [0., 3., 0.],
76 | [0., 0., 4.]],
77 | [[1., 0., 0.],
78 | [0., 5., 0.],
79 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
80 |
81 | expected = gs.array([[[0.693147180, 0., 0.],
82 | [0., 1.09861228866, 0.],
83 | [0., 0., 1.38629436]],
84 | [[0., 0., 0.],
85 | [0., 1.609437912, 0.],
86 | [0., 0., 1.79175946]]])
87 |
88 | result = gs.linalg.logm(point)
89 |
90 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
91 |
92 | def test_expm_and_logm_vectorization_random_rotation(self):
93 | point = self.so3_group.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
94 | point = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(point)
95 |
96 | result = gs.linalg.expm(gs.linalg.logm(point))
97 | expected = point
98 |
99 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
100 |
101 | def test_expm_and_logm_vectorization(self):
102 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
103 | [0., 3., 0.],
104 | [0., 0., 4.]],
105 | [[1., 0., 0.],
106 | [0., 5., 0.],
107 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
108 | result = gs.linalg.expm(gs.linalg.logm(point))
109 | expected = point
110 |
111 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
112 |
113 |
114 | if __name__ == '__main__':
115 | unittest.main()
116 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/general_linear_group.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | The General Linear Group, i.e. the matrix group GL(n).
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 |
7 | from geomstats.lie_group import LieGroup
8 | from geomstats.matrices_space import MatricesSpace
9 |
10 |
11 | class GeneralLinearGroup(LieGroup, MatricesSpace):
12 | """
13 | Class for the General Linear Group, i.e. the matrix group GL(n).
14 |
15 |
16 | Note: The default representation for elements of GL(n)
17 | are matrices.
18 | For now, SO(n) and SE(n) elements are represented
19 | by a vector by default.
20 | """
21 |
22 | def __init__(self, n):
23 | assert isinstance(n, int) and n > 0
24 | LieGroup.__init__(self, dimension=n*n)
25 | MatricesSpace.__init__(self, m=n, n=n)
26 |
27 | def get_identity(self, point_type=None):
28 | if point_type is None:
29 | point_type = self.default_point_type
30 | if point_type == 'matrix':
31 | return gs.eye(self.n)
32 | else:
33 | raise NotImplementedError(
34 | 'The identity of the general linear group is not'
35 | ' implemented for a point_type that is not \'matrix\'.')
36 | identity = property(get_identity)
37 |
38 | def belongs(self, mat):
39 | """
40 | Check if mat belongs to GL(n).
41 | """
42 | mat = gs.to_ndarray(mat, to_ndim=3)
43 |
44 | det = gs.linalg.det(mat)
45 | belongs = ~gs.isclose(det, 0.)
46 |
47 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=1)
48 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
49 |
50 | return belongs
51 |
52 | def compose(self, mat_a, mat_b):
53 | """
54 | Matrix composition.
55 | """
56 | mat_a = gs.to_ndarray(mat_a, to_ndim=3)
57 | mat_b = gs.to_ndarray(mat_b, to_ndim=3)
58 | composition = gs.einsum('nij,njk->nik', mat_a, mat_b)
59 | return composition
60 |
61 | def inverse(self, mat):
62 | """
63 | Matrix inverse.
64 | """
65 | mat = gs.to_ndarray(mat, to_ndim=3)
66 | return gs.linalg.inv(mat)
67 |
68 | def group_exp_from_identity(self, tangent_vec, point_type=None):
69 | """
70 | Group exponential of the Lie group of
71 | all invertible matrices at the identity.
72 | """
73 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=3)
74 | group_exp = gs.linalg.expm(tangent_vec)
75 |
76 | return gs.real(group_exp)
77 |
78 | def group_exp_not_from_identity(
79 | self, tangent_vec, base_point, point_type=None):
80 | """
81 | Group exponential of the Lie group of
82 | all invertible matrices.
83 | """
84 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=3)
85 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=3)
86 |
87 | tangent_vec_at_identity = self.compose(
88 | self.inverse(base_point), tangent_vec)
89 |
90 | group_exp_from_identity = self.group_exp_from_identity(
91 | tangent_vec_at_identity)
92 |
93 | group_exp = self.compose(
94 | base_point, group_exp_from_identity)
95 |
96 | return group_exp
97 |
98 | def group_log_from_identity(self, point, point_type=None):
99 | """
100 | Group logarithm of the Lie group of
101 | all invertible matrices at the identity.
102 | """
103 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=3)
104 | group_log = gs.linalg.logm(point)
105 |
106 | return gs.real(group_log)
107 |
108 | def group_log_not_from_identity(
109 | self, point, base_point, point_type=None):
110 | """
111 | Group logarithm of the Lie group of
112 | all invertible matrices.
113 | """
114 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=3)
115 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=3)
116 |
117 | point_near_identity = self.compose(
118 | self.inverse(base_point), point)
119 |
120 | group_log_from_identity = self.group_log_from_identity(
121 | point_near_identity)
122 |
123 | group_log = self.compose(
124 | base_point, group_log_from_identity)
125 |
126 | return group_log
127 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/loss_and_gradient_so3.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Predict on manifolds: losses.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import os
6 | import tensorflow as tf
7 |
8 | import geomstats.backend as gs
9 | import geomstats.lie_group as lie_group
10 |
11 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
12 |
13 |
14 | SO3 = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=3)
15 |
16 |
17 | def loss(y_pred, y_true,
18 | metric=SO3.bi_invariant_metric,
19 | representation='vector'):
20 |
21 | if representation == 'quaternion':
22 | y_pred = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_pred)
23 | y_true = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_true)
24 |
25 | loss = lie_group.loss(y_pred, y_true, SO3, metric)
26 | return loss
27 |
28 |
29 | def grad(y_pred, y_true,
30 | metric=SO3.bi_invariant_metric,
31 | representation='vector'):
32 |
33 | y_pred = gs.expand_dims(y_pred, axis=0)
34 | y_true = gs.expand_dims(y_true, axis=0)
35 |
36 | if representation == 'vector':
37 | grad = lie_group.grad(y_pred, y_true, SO3, metric)
38 |
39 | if representation == 'quaternion':
40 | quat_scalar = y_pred[:, :1]
41 | quat_vec = y_pred[:, 1:]
42 |
43 | quat_vec_norm = gs.linalg.norm(quat_vec, axis=1)
44 | quat_sq_norm = quat_vec_norm ** 2 + quat_scalar ** 2
45 |
46 | quat_arctan2 = gs.arctan2(quat_vec_norm, quat_scalar)
47 | differential_scalar = - 2 * quat_vec / (quat_sq_norm)
48 | differential_scalar = gs.to_ndarray(differential_scalar, to_ndim=2)
49 | differential_scalar = gs.transpose(differential_scalar)
50 |
51 | differential_vec = (2 * (quat_scalar / quat_sq_norm
52 | - 2 * quat_arctan2 / quat_vec_norm)
53 | * (gs.einsum('ni,nj->nij', quat_vec, quat_vec)
54 | / quat_vec_norm ** 2)
55 | + 2 * quat_arctan2 / quat_vec_norm * gs.eye(3))
56 | differential_vec = gs.squeeze(differential_vec)
57 |
58 | differential = gs.concatenate(
59 | [differential_scalar, differential_vec],
60 | axis=1)
61 |
62 | y_pred = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_pred)
63 | y_true = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_true)
64 |
65 | grad = lie_group.grad(y_pred, y_true, SO3, metric)
66 |
67 | grad = gs.matmul(grad, differential)
68 |
69 | grad = gs.squeeze(grad, axis=0)
70 | return grad
71 |
72 |
73 | def main():
74 | y_pred = gs.array([1., 1.5, -0.3])
75 | y_true = gs.array([0.1, 1.8, -0.1])
76 |
77 | loss_rot_vec = loss(y_pred, y_true)
78 | grad_rot_vec = grad(y_pred, y_true)
79 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
80 | with tf.Session() as sess:
81 | loss_rot_vec = sess.run(loss_rot_vec)
82 | grad_rot_vec = sess.run(grad_rot_vec)
83 | print('The loss between the rotation vectors is: {}'.format(
84 | loss_rot_vec[0, 0]))
85 | print('The riemannian gradient is: {}'.format(
86 | grad_rot_vec))
87 |
88 | angle = gs.pi / 6
89 | cos = gs.cos(angle / 2)
90 | sin = gs.sin(angle / 2)
91 | u = gs.array([1., 2., 3.])
92 | u = u / gs.linalg.norm(u)
93 | scalar = gs.to_ndarray(cos, to_ndim=1)
94 | vec = sin * u
95 | y_pred_quaternion = gs.concatenate([scalar, vec], axis=0)
96 |
97 | angle = gs.pi / 7
98 | cos = gs.cos(angle / 2)
99 | sin = gs.sin(angle / 2)
100 | u = gs.array([1., 2., 3.])
101 | u = u / gs.linalg.norm(u)
102 | scalar = gs.to_ndarray(cos, to_ndim=1)
103 | vec = sin * u
104 | y_true_quaternion = gs.concatenate([scalar, vec], axis=0)
105 |
106 | loss_quaternion = loss(y_pred_quaternion, y_true_quaternion,
107 | representation='quaternion')
108 | grad_quaternion = grad(y_pred_quaternion, y_true_quaternion,
109 | representation='quaternion')
110 |
111 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
112 | with tf.Session() as sess:
113 | loss_quaternion = sess.run(loss_quaternion)
114 | grad_quaternion = sess.run(grad_quaternion)
115 | print('The loss between the quaternions is: {}'.format(
116 | loss_quaternion[0, 0]))
117 | print('The riemannian gradient is: {}'.format(
118 | grad_quaternion))
119 |
120 |
121 | if __name__ == "__main__":
122 | main()
123 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/gradient_descent_s2.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Gradient descent on a sphere.
3 |
4 | We solve the following optimization problem:
5 |
6 | minimize: x^{T}Ax
7 | such than: x^{T}x = 1
8 |
9 | Using by operating a gradient descent of the quadratic form
10 | on the sphere. We solve this in 3 dimension on the 2-sphere
11 | manifold so that we can visualize and render the path as a video.
12 | """
13 |
14 | import matplotlib
15 | matplotlib.use("Agg") # NOQA
16 | import matplotlib.animation as animation
17 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
18 | import numpy as np
19 |
20 | import geomstats.backend as gs
21 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
22 |
23 | from geomstats.hypersphere import Hypersphere
24 | from geomstats.spd_matrices_space import SPDMatricesSpace
25 |
26 |
27 | SPHERE2 = Hypersphere(dimension=2)
28 | METRIC = SPHERE2.metric
29 |
30 |
31 | def gradient_descent(start,
32 | loss,
33 | grad,
34 | manifold,
35 | lr=0.01,
36 | max_iter=256,
37 | precision=1e-5):
38 | """Operate a gradient descent on a given manifold until either max_iter or
39 | a given precision is reached."""
40 | x = start
41 | for i in range(max_iter):
42 | x_prev = x
43 | euclidean_grad = - lr * grad(x)
44 | tangent_vec = manifold.projection_to_tangent_space(
45 | vector=euclidean_grad, base_point=x)
46 | x = manifold.metric.exp(base_point=x, tangent_vec=tangent_vec)[0]
47 | if (gs.abs(loss(x, use_gs=True) - loss(x_prev, use_gs=True))
48 | <= precision):
49 | print('x: %s' % x)
50 | print('reached precision %s' % precision)
51 | print('iterations: %d' % i)
52 | break
53 | yield x, loss(x)
54 |
55 |
56 | def plot_and_save_video(geodesics,
57 | loss,
58 | size=20,
59 | fps=10,
60 | dpi=100,
61 | out='out.mp4',
62 | color='red'):
63 | """Render a set of geodesics and save it to an mpeg 4 file."""
64 | FFMpegWriter = animation.writers['ffmpeg']
65 | writer = FFMpegWriter(fps=fps)
66 | fig = plt.figure(figsize=(size, size))
67 | ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d', aspect='equal')
68 | sphere = visualization.Sphere()
69 | sphere.plot_heatmap(ax, loss)
70 | points = gs.to_ndarray(geodesics[0], to_ndim=2)
71 | sphere.add_points(points)
72 | sphere.draw(ax, color=color, marker='.')
73 | with writer.saving(fig, out, dpi=dpi):
74 | for points in geodesics[1:]:
75 | points = gs.to_ndarray(points, to_ndim=2)
76 | sphere.draw_points(ax, points=points, color=color, marker='.')
77 | writer.grab_frame()
78 |
79 |
80 | def generate_well_behaved_matrix():
81 | """Generate a matrix with real eigenvalues."""
82 | matrix = 2 * SPDMatricesSpace(n=3).random_uniform()[0]
83 | assert np.linalg.det(matrix) > 0
84 | return matrix
85 |
86 |
87 | def main(output_file='out.mp4', max_iter=128):
88 | gs.random.seed(1985)
89 | A = generate_well_behaved_matrix()
90 |
91 | def grad(x):
92 | return 2 * gs.matmul(A, x)
93 |
94 | def loss(x, use_gs=False):
95 | if use_gs:
96 | return gs.matmul(x, gs.matmul(A, x))
97 | return np.matmul(x, np.matmul(A, x))
98 |
99 | initial_point = gs.array([0., 1., 0.])
100 | previous_x = initial_point
101 | geodesics = []
102 | n_steps = 20
103 | for x, fx in gradient_descent(initial_point,
104 | loss,
105 | grad,
106 | max_iter=max_iter,
107 | manifold=SPHERE2):
108 | initial_tangent_vec = METRIC.log(point=x, base_point=previous_x)
109 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=previous_x,
110 | initial_tangent_vec=initial_tangent_vec)
111 |
112 | t = np.linspace(0, 1, n_steps)
113 | geodesics.append(geodesic(t))
114 | previous_x = x
115 | if output_file:
116 | plot_and_save_video(geodesics, loss, out=output_file)
117 | eig, _ = np.linalg.eig(A)
118 | np.testing.assert_almost_equal(loss(x), np.min(eig), decimal=2)
119 |
120 |
121 | if __name__ == "__main__":
122 | main()
123 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/minkowski_space.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Minkowski space.
3 | """
4 |
5 |
6 | from geomstats.manifold import Manifold
7 | from geomstats.riemannian_metric import RiemannianMetric
8 | import geomstats.backend as gs
9 |
10 |
11 | class MinkowskiSpace(Manifold):
12 | """Class for Minkowski Space."""
13 |
14 | def __init__(self, dimension):
15 | assert isinstance(dimension, int) and dimension > 0
16 | self.dimension = dimension
17 | self.metric = MinkowskiMetric(dimension)
18 |
19 | def belongs(self, point):
20 | """
21 | Evaluate if a point belongs to the Minkowski space.
22 |
23 | Parameters
24 | ----------
25 | point : array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
26 | Input points.
27 |
28 | Returns
29 | -------
30 | belongs : array-like, shape=[n_samples, 1]
31 | """
32 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=2)
33 | n_points, point_dim = point.shape
34 | belongs = point_dim == self.dimension
35 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=1)
36 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
37 | belongs = gs.tile(belongs, (n_points, 1))
38 |
39 | return belongs
40 |
41 | def random_uniform(self, n_samples=1, bound=1.):
42 | """
43 | Sample in the Minkowski space with the uniform distribution.
44 |
45 | Returns
46 | -------
47 | points : array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
48 | Sampled points.
49 | """
50 | size = (n_samples, self.dimension)
51 | point = bound * gs.random.rand(*size) * 2 - 1
52 |
53 | return point
54 |
55 |
56 | class MinkowskiMetric(RiemannianMetric):
57 | """
58 | Class for the pseudo-Riemannian Minkowski metric.
59 | The metric is flat: the inner product is independent of the base point.
60 | """
61 | def __init__(self, dimension):
62 | super(MinkowskiMetric, self).__init__(
63 | dimension=dimension,
64 | signature=(dimension - 1, 1, 0))
65 |
66 | def inner_product_matrix(self, base_point=None):
67 | """
68 | Inner product matrix, independent of the base point.
69 |
70 | Parameters
71 | ----------
72 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
73 | """
74 | inner_prod_mat = gs.eye(self.dimension-1, self.dimension-1)
75 | first_row = gs.array([0.] * (self.dimension - 1))
76 | first_row = gs.to_ndarray(first_row, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
77 | inner_prod_mat = gs.vstack([gs.transpose(first_row),
78 | inner_prod_mat])
79 |
80 | first_column = gs.array([-1.] + [0.] * (self.dimension - 1))
81 | first_column = gs.to_ndarray(first_column, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
82 | inner_prod_mat = gs.hstack([first_column,
83 | inner_prod_mat])
84 |
85 | return inner_prod_mat
86 |
87 | def exp(self, tangent_vec, base_point):
88 | """
89 | The Riemannian exponential is the addition in the Minkowski space.
90 |
91 | Parameters
92 | ----------
93 | tangent_vec: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
94 | or shape=[1, dimension]
95 |
96 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
97 | or shape=[1, dimension]
98 | """
99 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=2)
100 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=2)
101 | return base_point + tangent_vec
102 |
103 | def log(self, point, base_point):
104 | """
105 | The Riemannian logarithm is the subtraction in the Minkowski space.
106 |
107 | Parameters
108 | ----------
109 | point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
110 | or shape=[1, dimension]
111 |
112 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
113 | or shape=[1, dimension]
114 | """
115 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=2)
116 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=2)
117 | return point - base_point
118 |
119 | def mean(self, points, weights=None):
120 | """
121 | The Frechet mean of (weighted) points is the weighted average of
122 | the points in the Minkowski space.
123 |
124 | Parameters
125 | ----------
126 | points: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
127 |
128 | weights: array-like, shape=[n_samples, 1], optional
129 | """
130 | if isinstance(points, list):
131 | points = gs.vstack(points)
132 | points = gs.to_ndarray(points, to_ndim=2)
133 | n_points = gs.shape(points)[0]
134 |
135 | if isinstance(weights, list):
136 | weights = gs.vstack(weights)
137 | elif weights is None:
138 | weights = gs.ones((n_points,))
139 |
140 | weighted_points = gs.einsum('n,nj->nj', weights, points)
141 | mean = (gs.sum(weighted_points, axis=0)
142 | / gs.sum(weights))
143 | mean = gs.to_ndarray(mean, to_ndim=2)
144 | return mean
145 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/loss_and_gradient_se3.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Predict on SE3: losses.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import os
6 | import tensorflow as tf
7 |
8 | import geomstats.backend as gs
9 | import geomstats.lie_group as lie_group
10 |
11 | from geomstats.special_euclidean_group import SpecialEuclideanGroup
12 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
13 |
14 |
15 | SE3 = SpecialEuclideanGroup(n=3)
16 | SO3 = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=3)
17 |
18 |
19 | def loss(y_pred, y_true,
20 | metric=SE3.left_canonical_metric,
21 | representation='vector'):
22 | """
23 | Loss function given by a riemannian metric on a Lie group,
24 | by default the left-invariant canonical metric.
25 | """
26 | if gs.ndim(y_pred) == 1:
27 | y_pred = gs.expand_dims(y_pred, axis=0)
28 | if gs.ndim(y_true) == 1:
29 | y_true = gs.expand_dims(y_true, axis=0)
30 |
31 | if representation == 'quaternion':
32 | y_pred_rot_vec = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_pred[:, :4])
33 | y_pred = gs.hstack([y_pred_rot_vec, y_pred[:, 4:]])
34 | y_true_rot_vec = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_true[:, :4])
35 | y_true = gs.hstack([y_true_rot_vec, y_true[:, 4:]])
36 |
37 | loss = lie_group.loss(y_pred, y_true, SE3, metric)
38 | return loss
39 |
40 |
41 | def grad(y_pred, y_true,
42 | metric=SE3.left_canonical_metric,
43 | representation='vector'):
44 | """
45 | Closed-form for the gradient of pose_loss.
46 |
47 | :return: tangent vector at point y_pred.
48 | """
49 | if gs.ndim(y_pred) == 1:
50 | y_pred = gs.expand_dims(y_pred, axis=0)
51 | if gs.ndim(y_true) == 1:
52 | y_true = gs.expand_dims(y_true, axis=0)
53 |
54 | if representation == 'vector':
55 | grad = lie_group.grad(y_pred, y_true, SE3, metric)
56 |
57 | if representation == 'quaternion':
58 |
59 | y_pred_rot_vec = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_pred[:, :4])
60 | y_pred_pose = gs.hstack([y_pred_rot_vec, y_pred[:, 4:]])
61 | y_true_rot_vec = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_true[:, :4])
62 | y_true_pose = gs.hstack([y_true_rot_vec, y_true[:, 4:]])
63 | grad = lie_group.grad(y_pred_pose, y_true_pose, SE3, metric)
64 |
65 | quat_scalar = y_pred[:, :1]
66 | quat_vec = y_pred[:, 1:4]
67 |
68 | quat_vec_norm = gs.linalg.norm(quat_vec, axis=1)
69 | quat_sq_norm = quat_vec_norm ** 2 + quat_scalar ** 2
70 |
71 | quat_arctan2 = gs.arctan2(quat_vec_norm, quat_scalar)
72 | differential_scalar = - 2 * quat_vec / (quat_sq_norm)
73 | differential_vec = (2 * (quat_scalar / quat_sq_norm
74 | - 2 * quat_arctan2 / quat_vec_norm)
75 | * (gs.einsum('ni,nj->nij', quat_vec, quat_vec)
76 | / quat_vec_norm * quat_vec_norm)
77 | + 2 * quat_arctan2 / quat_vec_norm * gs.eye(3))
78 |
79 | differential_scalar_t = gs.transpose(differential_scalar, axes=(1, 0))
80 |
81 | upper_left_block = gs.hstack(
82 | (differential_scalar_t, differential_vec[0]))
83 | upper_right_block = gs.zeros((3, 3))
84 | lower_right_block = gs.eye(3)
85 | lower_left_block = gs.zeros((3, 4))
86 |
87 | top = gs.hstack((upper_left_block, upper_right_block))
88 | bottom = gs.hstack((lower_left_block, lower_right_block))
89 |
90 | differential = gs.vstack((top, bottom))
91 | differential = gs.expand_dims(differential, axis=0)
92 |
93 | grad = gs.einsum('ni,nij->ni', grad, differential)
94 |
95 | grad = gs.squeeze(grad, axis=0)
96 | return grad
97 |
98 |
99 | def main():
100 | y_pred = gs.array([1., 1.5, -0.3, 5., 6., 7.])
101 | y_true = gs.array([0.1, 1.8, -0.1, 4., 5., 6.])
102 |
103 | loss_rot_vec = loss(y_pred, y_true)
104 | grad_rot_vec = grad(y_pred, y_true)
105 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
106 | with tf.Session() as sess:
107 | loss_rot_vec = sess.run(loss_rot_vec)
108 | grad_rot_vec = sess.run(grad_rot_vec)
109 | print('The loss between the poses using rotation vectors is: {}'.format(
110 | loss_rot_vec[0, 0]))
111 | print('The riemannian gradient is: {}'.format(grad_rot_vec))
112 |
113 | angle = gs.pi / 6
114 | cos = gs.cos(angle / 2)
115 | sin = gs.sin(angle / 2)
116 | u = gs.array([1., 2., 3.])
117 | u = u / gs.linalg.norm(u)
118 | scalar = gs.array(cos)
119 | vec = sin * u
120 | translation = gs.array([5., 6., 7.])
121 | y_pred_quaternion = gs.concatenate([[scalar], vec, translation], axis=0)
122 |
123 | angle = gs.pi / 7
124 | cos = gs.cos(angle / 2)
125 | sin = gs.sin(angle / 2)
126 | u = gs.array([1., 2., 3.])
127 | u = u / gs.linalg.norm(u)
128 | scalar = gs.array(cos)
129 | vec = sin * u
130 | translation = gs.array([4., 5., 6.])
131 | y_true_quaternion = gs.concatenate([[scalar], vec, translation], axis=0)
132 |
133 | loss_quaternion = loss(y_pred_quaternion, y_true_quaternion,
134 | representation='quaternion')
135 | grad_quaternion = grad(y_pred_quaternion, y_true_quaternion,
136 | representation='quaternion')
137 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
138 | with tf.Session() as sess:
139 | loss_quaternion = sess.run(loss_quaternion)
140 | grad_quaternion = sess.run(grad_quaternion)
141 | print('The loss between the poses using quaternions is: {}'.format(
142 | loss_quaternion[0, 0]))
143 | print('The riemannian gradient is: {}'.format(
144 | grad_quaternion))
145 |
146 |
147 | if __name__ == "__main__":
148 | main()
149 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_general_linear_group.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for General Linear group.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import warnings
6 |
7 | import geomstats.backend as gs
8 | import geomstats.tests
9 | import tests.helper as helper
10 |
11 | from geomstats.general_linear_group import GeneralLinearGroup
12 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
13 |
14 | RTOL = 1e-5
15 |
16 |
17 | class TestGeneralLinearGroupMethods(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
18 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
19 |
20 | def setUp(self):
21 | gs.random.seed(1234)
22 | self.n = 3
23 | self.n_samples = 2
24 | self.group = GeneralLinearGroup(n=self.n)
25 | # We generate invertible matrices using so3_group
26 | self.so3_group = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=self.n)
27 |
28 | warnings.simplefilter('ignore', category=ImportWarning)
29 |
30 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
31 | def test_belongs(self):
32 | """
33 | A rotation matrix belongs to the matrix Lie group
34 | of invertible matrices.
35 | """
36 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.2, -0.1, 0.1])
37 | rot_mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
38 | result = self.group.belongs(rot_mat)
39 | expected = gs.array([True])
40 |
41 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
42 |
43 | def test_compose(self):
44 | # 1. Composition by identity, on the right
45 | # Expect the original transformation
46 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.2, -0.1, 0.1])
47 | mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
48 |
49 | result = self.group.compose(mat, self.group.identity)
50 | expected = mat
51 | expected = helper.to_matrix(mat)
52 |
53 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
54 |
55 | # 2. Composition by identity, on the left
56 | # Expect the original transformation
57 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.2, 0.1, -0.1])
58 | mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
59 |
60 | result = self.group.compose(self.group.identity, mat)
61 | expected = mat
62 |
63 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
64 |
65 | def test_inverse(self):
66 | mat = gs.array([
67 | [1., 2., 3.],
68 | [4., 5., 6.],
69 | [7., 8., 10.]])
70 | result = self.group.inverse(mat)
71 | expected = 1. / 3. * gs.array([
72 | [-2., -4., 3.],
73 | [-2., 11., -6.],
74 | [3., -6., 3.]])
75 | expected = helper.to_matrix(expected)
76 |
77 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
78 |
79 | def test_compose_and_inverse(self):
80 | # 1. Compose transformation by its inverse on the right
81 | # Expect the group identity
82 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.2, 0.1, 0.1])
83 | mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
84 | inv_mat = self.group.inverse(mat)
85 |
86 | result = self.group.compose(mat, inv_mat)
87 | expected = self.group.identity
88 | expected = helper.to_matrix(expected)
89 |
90 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
91 |
92 | # 2. Compose transformation by its inverse on the left
93 | # Expect the group identity
94 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.7, 0.1, 0.1])
95 | mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
96 | inv_mat = self.group.inverse(mat)
97 |
98 | result = self.group.compose(inv_mat, mat)
99 | expected = self.group.identity
100 | expected = helper.to_matrix(expected)
101 |
102 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
103 |
104 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
105 | def test_group_log_and_exp(self):
106 | point = 5 * gs.eye(self.n)
107 |
108 | group_log = self.group.group_log(point)
109 | result = self.group.group_exp(group_log)
110 | expected = point
111 | expected = helper.to_matrix(expected)
112 |
113 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
114 |
115 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
116 | def test_group_exp_vectorization(self):
117 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
118 | [0., 3., 0.],
119 | [0., 0., 4.]],
120 | [[1., 0., 0.],
121 | [0., 5., 0.],
122 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
123 |
124 | expected = gs.array([[[7.38905609, 0., 0.],
125 | [0., 20.0855369, 0.],
126 | [0., 0., 54.5981500]],
127 | [[2.718281828, 0., 0.],
128 | [0., 148.413159, 0.],
129 | [0., 0., 403.42879349]]])
130 |
131 | result = self.group.group_exp(point)
132 |
133 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected, rtol=1e-3)
134 |
135 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
136 | def test_group_log_vectorization(self):
137 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
138 | [0., 3., 0.],
139 | [0., 0., 4.]],
140 | [[1., 0., 0.],
141 | [0., 5., 0.],
142 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
143 |
144 | expected = gs.array([[[0.693147180, 0., 0.],
145 | [0., 1.09861228866, 0.],
146 | [0., 0., 1.38629436]],
147 | [[0., 0., 0.],
148 | [0., 1.609437912, 0.],
149 | [0., 0., 1.79175946]]])
150 |
151 | result = self.group.group_log(point)
152 |
153 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected, atol=1e-4)
154 |
155 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
156 | def test_expm_and_logm_vectorization_symmetric(self):
157 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
158 | [0., 3., 0.],
159 | [0., 0., 4.]],
160 | [[1., 0., 0.],
161 | [0., 5., 0.],
162 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
163 | result = self.group.group_exp(self.group.group_log(point))
164 | expected = point
165 |
166 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
167 |
168 |
169 | if __name__ == '__main__':
170 | geomstats.tests.main()
171 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/backend/tensorflow.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Tensorflow based computation backend."""
2 |
3 | import tensorflow as tf
4 |
5 |
6 | int8 = tf.int8
7 | int32 = tf.int32
8 | int64 = tf.int64
9 | float16 = tf.float16
10 | float32 = tf.float32
11 | float64 = tf.float64
12 |
13 |
14 | def while_loop(*args, **kwargs):
15 | return tf.while_loop(*args, **kwargs)
16 |
17 |
18 | def logical_or(x, y):
19 | return tf.logical_or(x, y)
20 |
21 |
22 | def get_mask_i_float(i, n):
23 | range_n = arange(n)
24 | i_float = cast(array([i]), int32)[0]
25 | mask_i = equal(range_n, i_float)
26 | mask_i_float = cast(mask_i, float32)
27 | return mask_i_float
28 |
29 |
30 | def gather(*args, **kwargs):
31 | return tf.gather(*args, **kwargs)
32 |
33 |
34 | def where(*args, **kwargs):
35 | return tf.where(*args, **kwargs)
36 |
37 |
38 | def vectorize(x, pyfunc, multiple_args=False, dtype=None, **kwargs):
39 | if multiple_args:
40 | return tf.map_fn(lambda x: pyfunc(*x), elems=x, dtype=dtype)
41 | return tf.map_fn(pyfunc, elems=x, dtype=dtype)
42 |
43 |
44 | def sign(x):
45 | return tf.sign(x)
46 |
47 |
48 | def hsplit(x, n_splits):
49 | return tf.split(x, num_or_size_splits=n_splits, axis=1)
50 |
51 |
52 | def amax(x):
53 | return tf.reduce_max(x)
54 |
55 |
56 | def real(x):
57 | return tf.real(x)
58 |
59 |
60 | def cond(*args, **kwargs):
61 | return tf.cond(*args, **kwargs)
62 |
63 |
64 | def reshape(*args, **kwargs):
65 | return tf.reshape(*args, **kwargs)
66 |
67 |
68 | def arange(*args, **kwargs):
69 | return tf.range(*args, **kwargs)
70 |
71 |
72 | def outer(x, y):
73 | return tf.einsum('i,j->ij', x, y)
74 |
75 |
76 | def copy(x):
77 | return tf.Variable(x)
78 |
79 |
80 | def linspace(start, stop, num):
81 | return tf.linspace(start, stop, num)
82 |
83 |
84 | def mod(x, y):
85 | return tf.mod(x, y)
86 |
87 |
88 | def boolean_mask(x, mask, name='boolean_mask', axis=None):
89 | return tf.boolean_mask(x, mask, name, axis)
90 |
91 |
92 | def exp(x):
93 | return tf.exp(x)
94 |
95 |
96 | def log(x):
97 | return tf.log(x)
98 |
99 |
100 | def hstack(x):
101 | return tf.concat(x, axis=1)
102 |
103 |
104 | def vstack(x):
105 | return tf.concat(x, axis=0)
106 |
107 |
108 | def cast(x, dtype):
109 | return tf.cast(x, dtype)
110 |
111 |
112 | def divide(x1, x2):
113 | return tf.divide(x1, x2)
114 |
115 |
116 | def tile(x, reps):
117 | return tf.tile(x, reps)
118 |
119 |
120 | def eval(x):
121 | if tf.executing_eagerly():
122 | return x
123 | return x.eval()
124 |
125 |
126 | def abs(x):
127 | return tf.abs(x)
128 |
129 |
130 | def zeros(x):
131 | return tf.zeros(x)
132 |
133 |
134 | def ones(x):
135 | return tf.ones(x)
136 |
137 |
138 | def sin(x):
139 | return tf.sin(x)
140 |
141 |
142 | def cos(x):
143 | return tf.cos(x)
144 |
145 |
146 | def cosh(x):
147 | return tf.cosh(x)
148 |
149 |
150 | def sinh(x):
151 | return tf.sinh(x)
152 |
153 |
154 | def tanh(x):
155 | return tf.tanh(x)
156 |
157 |
158 | def arccosh(x):
159 | return tf.acosh(x)
160 |
161 |
162 | def tan(x):
163 | return tf.tan(x)
164 |
165 |
166 | def arcsin(x):
167 | return tf.asin(x)
168 |
169 |
170 | def arccos(x):
171 | return tf.acos(x)
172 |
173 |
174 | def shape(x):
175 | return tf.shape(x)
176 |
177 |
178 | def ndim(x):
179 | x = array(x)
180 | dims = x.get_shape()._dims
181 | if dims is not None:
182 | return len(dims)
183 | return None
184 |
185 |
186 | def dot(x, y):
187 | return tf.tensordot(x, y, axes=1)
188 |
189 |
190 | def maximum(x, y):
191 | return tf.maximum(x, y)
192 |
193 |
194 | def greater(x, y):
195 | return tf.greater(x, y)
196 |
197 |
198 | def greater_equal(x, y):
199 | return tf.greater_equal(x, y)
200 |
201 |
202 | def equal(x, y):
203 | return tf.equal(x, y)
204 |
205 |
206 | def to_ndarray(x, to_ndim, axis=0):
207 | if ndim(x) == to_ndim - 1:
208 | x = tf.expand_dims(x, axis=axis)
209 |
210 | return x
211 |
212 |
213 | def sqrt(x):
214 | return tf.sqrt(x)
215 |
216 |
217 | def isclose(x, y, rtol=1e-05, atol=1e-08):
218 | rhs = tf.constant(atol) + tf.constant(rtol) * tf.abs(y)
219 | return tf.less_equal(tf.abs(tf.subtract(x, y)), rhs)
220 |
221 |
222 | def allclose(x, y, rtol=1e-05, atol=1e-08):
223 | return tf.reduce_all(isclose(x, y, rtol=rtol, atol=atol))
224 |
225 |
226 | def less(x, y):
227 | return tf.less(x, y)
228 |
229 |
230 | def less_equal(x, y):
231 | return tf.less_equal(x, y)
232 |
233 |
234 | def eye(n, m=None):
235 | if m is None:
236 | m = n
237 | n = cast(n, dtype=int32)
238 | m = cast(m, dtype=int32)
239 | return tf.eye(num_rows=n, num_columns=m)
240 |
241 |
242 | def matmul(x, y):
243 | return tf.matmul(x, y)
244 |
245 |
246 | def argmax(*args, **kwargs):
247 | return tf.argmax(*args, **kwargs)
248 |
249 |
250 | def sum(*args, **kwargs):
251 | return tf.reduce_sum(*args, **kwargs)
252 |
253 |
254 | def einsum(equation, *inputs, **kwargs):
255 | return tf.einsum(equation, *inputs, **kwargs)
256 |
257 |
258 | def transpose(x, axes=None):
259 | return tf.transpose(x, perm=axes)
260 |
261 |
262 | def squeeze(x, **kwargs):
263 | return tf.squeeze(x, **kwargs)
264 |
265 |
266 | def zeros_like(x):
267 | return tf.zeros_like(x)
268 |
269 |
270 | def ones_like(x):
271 | return tf.ones_like(x)
272 |
273 |
274 | def trace(x, **kwargs):
275 | return tf.trace(x)
276 |
277 |
278 | def array(x):
279 | return tf.convert_to_tensor(x)
280 |
281 |
282 | def all(bool_tensor, axis=None, keepdims=False):
283 | bool_tensor = tf.cast(bool_tensor, tf.bool)
284 | all_true = tf.reduce_all(bool_tensor, axis, keepdims)
285 | return all_true
286 |
287 |
288 | def concatenate(*args, **kwargs):
289 | return tf.concat(*args, **kwargs)
290 |
291 |
292 | def asarray(x):
293 | return x
294 |
295 |
296 | def expand_dims(x, axis=None):
297 | return tf.expand_dims(x, axis)
298 |
299 |
300 | def clip(x, min_value, max_value):
301 | return tf.clip_by_value(x, min_value, max_value)
302 |
303 |
304 | def floor(x):
305 | return tf.floor(x)
306 |
307 |
308 | def diag(a):
309 | return tf.map_fn(
310 | lambda x: tf.diag(x),
311 | a)
312 |
313 |
314 | def cross(a, b):
315 | return tf.cross(a, b)
316 |
317 |
318 | def stack(*args, **kwargs):
319 | return tf.stack(*args, **kwargs)
320 |
321 |
322 | def arctan2(*args, **kwargs):
323 | return tf.atan2(*args, **kwargs)
324 |
325 |
326 | def diagonal(*args, **kwargs):
327 | return tf.linalg.diag_part(*args)
328 |
329 |
330 | def mean(x, axis=None):
331 | return tf.reduce_mean(x, axis)
332 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/CONTRIBUTING.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Contributing to Geomstats
2 |
3 | Welcome to the geomstats repository!
4 | We are excited you are here and want to contribute.
5 |
6 | More details on contributing can be found on the [documentation website][link_doc].
7 |
8 | ## Practical Guide to Submitting your Contribution
9 |
10 | These guidelines are designed to make it as easy as possible to get involved.
11 | If you have any questions that are not discussed below,
12 | please let us know by opening an [issue][link_issues]!
13 |
14 | Before you start you will need to set up a free [GitHub][link_github] account and sign in.
15 | Here are some [instructions][link_signupinstructions].
16 |
17 |
18 | ## Joining the Conversation
19 |
20 | `geomstats` is maintained by a growing group of enthusiastic developers!
21 | Most of our discussions take place on [issues][link_issues].
22 |
23 |
24 | ## Contributing through GitHub
25 |
26 | [git][link_git] is a really useful tool for version control.
27 | [GitHub][link_github] sits on top of git and supports collaborative and distributed working.
28 |
29 | If you are not yet familiar with `git`, there are lots of great resources to help you *git* started!
30 | Some of our favorites include the [git Handbook][link_handbook] and
31 | the [Software Carpentry introduction to git][link_swc_intro].
32 |
33 | On GitHub, you will use [Markdown][markdown] to chat in issues and pull requests.
34 |
35 | GitHub has a really helpful page for getting started with
36 | [writing and formatting Markdown on GitHub][writing_formatting_github].
37 |
38 |
39 | ## Understanding Issues
40 |
41 | Every project on GitHub uses [issues][link_issues] slightly differently.
42 |
43 | The following outlines how ``geomstats`` developers think about these tools.
44 |
45 | * **Issues** are individual pieces of work that need to be completed to move the project forwards.
46 | A general guideline: if you find yourself tempted to write a great big issue that
47 | is difficult to describe as one unit of work, please consider splitting it into two or more issues.
48 |
49 | * Issues are assigned [labels](#issue-labels) which explain how they relate to the overall project's
50 | goals and immediate next steps.
51 |
52 |
53 | ## Making a Change
54 |
55 | We appreciate all contributions to ``geomstats``,
56 | but those accepted fastest will follow a workflow similar to the following:
57 |
58 | **1. Comment on an existing issue or open a new issue referencing your addition.**
59 |
60 | This allows other members of the ``geomstats`` development team to confirm that you are not
61 | overlapping with work that is currently underway and that everyone is on the same page
62 | with the goal of the work you are going to carry out.
63 |
64 | [This blog][link_pushpullblog] is a nice explanation of why putting this work in up front
65 | is so useful to everyone involved.
66 |
67 | **2. [Fork][link_fork] the [geomstats repository][link_geomstats] to your profile.**
68 |
69 | This is now your own unique copy of ``geomstats``.
70 | Changes here will not effect anyone else's work, so it is a safe space to explore edits to the code!
71 |
72 | Make sure to [keep your fork up to date][link_updateupstreamwiki] with the master repository.
73 |
74 | **3. Make the changes you have discussed, following the [geomstats coding style guide](#geomstats-coding-style-guide).**
75 |
76 | - Create your feature branch (`git checkout -b feature/fooBar`)
77 | - Commit your changes (`git commit -am 'Add some fooBar'`)
78 | - Push to the branch (`git push origin feature/fooBar`)
79 |
80 | Try to keep the changes focused.
81 | If you feel tempted to "branch out" then please make a [new branch][link_branches].
82 |
83 | **4. Add the corresponding unit tests.**
84 |
85 | If you are adding a new feature, do not forget to add the corresponding [unit tests][link_unit_tests].
86 | As ``geomstats`` enables numpy and tensorflow, your unit tests should run on these two backends.
87 |
88 | **5. Ensure Geomstats Coding Style Guide.**
89 |
90 | Ensure that your code is compliant with [PEP8][link_pep8],
91 | the coding style guide for python.
92 |
93 | Use [flake8][link_flake8] or [yapf][link_yapf] to automatically enforces this style.
94 |
95 |
96 | **6. Submit a [pull request][link_pullrequest].**
97 |
98 | A member of the development team will review your changes to confirm
99 | that they can be merged into the main code base.
100 |
101 | Use the Github labels to label your pull request:
102 | * ``enhancement``: enhancements or new features
103 | * ``bug``: bug fixes
104 | * ``test``: new or updated tests
105 | * ``documentation``: new or updated documentation
106 | * ``style``: style changes
107 | * ``refactoring``: refactoring existing code
108 | * ``continuous integration``: updates to continous integration infrastructure
109 |
110 |
111 | ## Recognizing Contributions
112 |
113 | We welcome and recognize all contributions from documentation to testing to code development.
114 | You can see a list of current contributors in our [README.md][link_readme].
115 | If you are new to the project, do not forget to add your name and affiliation there!
116 |
117 | ## Thank You!
118 |
119 |
13 |
14 |
15 | ## Installation
16 |
17 | OS X & Linux:
18 |
19 | ```
20 | pip3 install geomstats
21 | ```
22 |
23 | ## Running tests
24 |
25 | ```
26 | pip3 install nose2
27 | nose2
28 | ```
29 |
30 | ## Getting started
31 |
32 | Define your backend by setting the environment variable ```GEOMSTATS_BACKEND``` to ```numpy```, ```tensorflow```, or ```pytorch```:
33 |
34 | ```
35 | export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND=numpy
36 | ```
37 |
38 | Then, run example scripts:
39 |
40 | ```
41 | python3 examples/plot_grid_h2.py
42 | ```
43 |
44 | ## Contributing
45 |
46 | See our [CONTRIBUTING.md][link_contributing] file!
47 |
48 | ## Authors & Contributors
49 |
50 | * Alice Le Brigant
51 | * Claire Donnat
52 | * Oleg Kachan
53 | * Benjamin Hou
54 | * Johan Mathe
55 | * Nina Miolane
56 | * Xavier Pennec
57 |
58 | ## Acknowledgements
59 |
60 | This work is partially supported by the National Science Foundation, grant NSF DMS RTG 1501767.
61 |
62 | [link_contributing]: https://github.com/geomstats/geomstats/CONTRIBUTING.md
63 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_visualization.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for visualization.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import matplotlib
6 | matplotlib.use('Agg') # NOQA
7 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
8 |
9 | import geomstats.tests
10 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
11 |
12 | from geomstats.hyperbolic_space import HyperbolicSpace
13 | from geomstats.hypersphere import Hypersphere
14 | from geomstats.special_euclidean_group import SpecialEuclideanGroup
15 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
16 |
17 |
18 | class TestVisualizationMethods(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
19 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
20 |
21 | def setUp(self):
22 | self.n_samples = 10
23 | self.SO3_GROUP = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=3)
24 | self.SE3_GROUP = SpecialEuclideanGroup(n=3)
25 | self.S1 = Hypersphere(dimension=1)
26 | self.S2 = Hypersphere(dimension=2)
27 | self.H2 = HyperbolicSpace(dimension=2)
28 |
29 | plt.figure()
30 |
31 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
32 | def test_plot_points_so3(self):
33 | points = self.SO3_GROUP.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
34 | visualization.plot(points, space='SO3_GROUP')
35 |
36 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
37 | def test_plot_points_se3(self):
38 | points = self.SE3_GROUP.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
39 | visualization.plot(points, space='SE3_GROUP')
40 |
41 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
42 | def test_plot_points_s1(self):
43 | points = self.S1.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
44 | visualization.plot(points, space='S1')
45 |
46 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
47 | def test_plot_points_s2(self):
48 | points = self.S2.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
49 | visualization.plot(points, space='S2')
50 |
51 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
52 | def test_plot_points_h2_poincare_disk(self):
53 | points = self.H2.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
54 | visualization.plot(points, space='H2_poincare_disk')
55 |
56 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
57 | def test_plot_points_h2_poincare_half_plane(self):
58 | points = self.H2.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
59 | visualization.plot(points, space='H2_poincare_half_plane')
60 |
61 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
62 | def test_plot_points_h2_klein_disk(self):
63 | points = self.H2.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
64 | visualization.plot(points, space='H2_klein_disk')
65 |
66 |
67 | if __name__ == '__main__':
68 | geomstats.tests.main()
69 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/tests.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Testing class for geomstats.
3 |
4 | This class abstracts the backend type.
5 | """
6 |
7 | import os
8 | import tensorflow as tf
9 | import unittest
10 |
11 | import geomstats.backend as gs
12 |
13 |
14 | def pytorch_backend():
15 | return os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'pytorch'
16 |
17 |
18 | def tf_backend():
19 | return os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow'
20 |
21 |
22 | def np_backend():
23 | return os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'numpy'
24 |
25 |
26 | test_class = unittest.TestCase
27 | if tf_backend():
28 | test_class = tf.test.TestCase
29 |
30 |
31 | def np_only(test_item):
32 | """Decorator to filter tests for numpy only."""
33 | if not np_backend():
34 | test_item.__unittest_skip__ = True
35 | test_item.__unittest_skip_why__ = (
36 | 'Test for numpy backend only.')
37 | return test_item
38 |
39 |
40 | def np_and_tf_only(test_item):
41 | """Decorator to filter tests for numpy and tensorflow only."""
42 | if not (np_backend() or tf_backend()):
43 | test_item.__unittest_skip__ = True
44 | test_item.__unittest_skip_why__ = (
45 | 'Test for numpy and tensorflow backends only.')
46 | return test_item
47 |
48 |
49 | def np_and_pytorch_only(test_item):
50 | """Decorator to filter tests for numpy and pytorch only."""
51 | if not (np_backend() or pytorch_backend()):
52 | test_item.__unittest_skip__ = True
53 | test_item.__unittest_skip_why__ = (
54 | 'Test for numpy and pytorch backends only.')
55 | return test_item
56 |
57 |
58 | class DummySession():
59 | def __enter__(self):
60 | pass
61 |
62 | def __exit__(self, a, b, c):
63 | pass
64 |
65 |
66 | class TestCase(test_class):
67 |
68 | def assertAllClose(self, a, b, rtol=1e-6, atol=1e-6):
69 | if tf_backend():
70 | return super().assertAllClose(a, b, rtol=rtol, atol=atol)
71 | return self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(a, b, rtol=rtol, atol=atol))
72 |
73 | def session(self):
74 | if tf_backend():
75 | return super().test_session()
76 | return DummySession()
77 |
78 | def assertShapeEqual(self, a, b):
79 | if tf_backend():
80 | return super().assertShapeEqual(a, b)
81 | super().assertEqual(a.shape, b.shape)
82 |
83 | @classmethod
84 | def setUpClass(cls):
85 | if tf_backend():
86 | os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
87 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/plot_geodesics_h2.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Plot a geodesic on the Hyperbolic space H2,
3 | with Poincare Disk visualization.
4 | """
5 |
6 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
7 | import numpy as np
8 | import os
9 |
10 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
11 |
12 | from geomstats.hyperbolic_space import HyperbolicSpace
13 |
14 | H2 = HyperbolicSpace(dimension=2)
15 | METRIC = H2.metric
16 |
17 |
18 | def plot_geodesic_between_two_points(initial_point,
19 | end_point,
20 | n_steps=10,
21 | ax=None):
22 | assert H2.belongs(initial_point)
23 | assert H2.belongs(end_point)
24 |
25 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=initial_point,
26 | end_point=end_point)
27 |
28 | t = np.linspace(0, 1, n_steps)
29 | points = geodesic(t)
30 | visualization.plot(points, ax=ax, space='H2_poincare_disk')
31 |
32 |
33 | def plot_geodesic_with_initial_tangent_vector(initial_point,
34 | initial_tangent_vec,
35 | n_steps=10,
36 | ax=None):
37 | assert H2.belongs(initial_point)
38 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=initial_point,
39 | initial_tangent_vec=initial_tangent_vec)
40 | n_steps = 10
41 | t = np.linspace(0, 1, n_steps)
42 |
43 | points = geodesic(t)
44 | visualization.plot(points, ax=ax, space='H2_poincare_disk')
45 |
46 |
47 | def main():
48 | initial_point = [np.sqrt(2), 1., 0.]
49 | end_point = H2.intrinsic_to_extrinsic_coords([1.5, 1.5])
50 | initial_tangent_vec = H2.projection_to_tangent_space(
51 | vector=[3.5, 0.6, 0.8],
52 | base_point=initial_point)
53 |
54 | ax = plt.gca()
55 | plot_geodesic_between_two_points(initial_point,
56 | end_point,
57 | ax=ax)
58 | plot_geodesic_with_initial_tangent_vector(initial_point,
59 | initial_tangent_vec,
60 | ax=ax)
61 | plt.show()
62 |
63 |
64 | if __name__ == "__main__":
65 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
66 | print('Examples with visualizations are only implemented '
67 | 'with numpy backend.\n'
68 | 'To change backend, write: '
69 | 'export GEOMSTATS_BACKEND = \'numpy\'.')
70 | else:
71 | main()
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/helper.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Helper functions for unit tests.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 |
7 |
8 | def to_scalar(expected):
9 | expected = gs.to_ndarray(expected, to_ndim=1)
10 | expected = gs.to_ndarray(expected, to_ndim=2, axis=-1)
11 | return expected
12 |
13 |
14 | def to_vector(expected):
15 | expected = gs.to_ndarray(expected, to_ndim=2)
16 | return expected
17 |
18 |
19 | def to_matrix(expected):
20 | expected = gs.to_ndarray(expected, to_ndim=3)
21 | return expected
22 |
23 |
24 | def left_log_then_exp_from_identity(metric, point):
25 | aux = metric.left_log_from_identity(point=point)
26 | result = metric.left_exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=aux)
27 | return result
28 |
29 |
30 | def left_exp_then_log_from_identity(metric, tangent_vec):
31 | aux = metric.left_exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=tangent_vec)
32 | result = metric.left_log_from_identity(point=aux)
33 | return result
34 |
35 |
36 | def log_then_exp_from_identity(metric, point):
37 | aux = metric.log_from_identity(point=point)
38 | result = metric.exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=aux)
39 | return result
40 |
41 |
42 | def exp_then_log_from_identity(metric, tangent_vec):
43 | aux = metric.exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=tangent_vec)
44 | result = metric.log_from_identity(point=aux)
45 | return result
46 |
47 |
48 | def log_then_exp(metric, point, base_point):
49 | aux = metric.log(point=point,
50 | base_point=base_point)
51 | result = metric.exp(tangent_vec=aux,
52 | base_point=base_point)
53 | return result
54 |
55 |
56 | def exp_then_log(metric, tangent_vec, base_point):
57 | aux = metric.exp(tangent_vec=tangent_vec,
58 | base_point=base_point)
59 | result = metric.log(point=aux,
60 | base_point=base_point)
61 | return result
62 |
63 |
64 | def group_log_then_exp_from_identity(group, point):
65 | aux = group.group_log_from_identity(point=point)
66 | result = group.group_exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=aux)
67 | return result
68 |
69 |
70 | def group_exp_then_log_from_identity(group, tangent_vec):
71 | aux = group.group_exp_from_identity(tangent_vec=tangent_vec)
72 | result = group.group_log_from_identity(point=aux)
73 | return result
74 |
75 |
76 | def group_log_then_exp(group, point, base_point):
77 | aux = group.group_log(point=point,
78 | base_point=base_point)
79 | result = group.group_exp(tangent_vec=aux,
80 | base_point=base_point)
81 | return result
82 |
83 |
84 | def group_exp_then_log(group, tangent_vec, base_point):
85 | aux = group.group_exp(tangent_vec=tangent_vec,
86 | base_point=base_point)
87 | result = group.group_log(point=aux,
88 | base_point=base_point)
89 | return result
90 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/api-reference.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | *************
2 | API reference
3 | *************
4 |
5 | .. automodule:: geomstats
6 | :members:
7 |
8 | The "manifold" module
9 | ---------------------
10 |
11 | .. automodule:: geomstats.manifold
12 | :members:
13 |
14 | The "connection" module
15 | -----------------------
16 |
17 | .. automodule:: geomstats.connection
18 | :members:
19 |
20 | The "riemannian_metric" module
21 | ------------------------------
22 |
23 | .. automodule:: geomstats.riemannian_metric
24 | :members:
25 |
26 | Spaces of constant curvatures
27 | =============================
28 |
29 | The "embedded_manifold" module
30 | ------------------------------
31 |
32 | .. automodule:: geomstats.embedded_manifold
33 | :members:
34 |
35 | The "euclidean_space" module
36 | ----------------------------
37 |
38 | .. automodule:: geomstats.euclidean_space
39 | :members:
40 |
41 | The "minkowski_space" module
42 | ----------------------------
43 |
44 | .. automodule:: geomstats.minkowski_space
45 | :members:
46 |
47 | The "hypersphere" module
48 | ------------------------
49 |
50 | .. automodule:: geomstats.hypersphere
51 | :members:
52 |
53 | The "hyperbolic_space" module
54 | -----------------------------
55 |
56 | .. automodule:: geomstats.hyperbolic_space
57 | :members:
58 |
59 | Lie groups
60 | ==========
61 |
62 | The "lie_group" module
63 | ----------------------
64 |
65 | .. automodule:: geomstats.lie_group
66 | :members:
67 |
68 | The "matrices_space" module
69 | ---------------------------
70 |
71 | .. automodule:: geomstats.matrices_space
72 | :members:
73 |
74 | The "general_linear_group" module
75 | ---------------------------------
76 |
77 | .. automodule:: geomstats.general_linear_group
78 | :members:
79 |
80 | The "invariant_metric" module
81 | -----------------------------
82 |
83 | .. automodule:: geomstats.invariant_metric
84 | :members:
85 |
86 | The "special_euclidean_group" module
87 | ------------------------------------
88 |
89 | .. automodule:: geomstats.special_euclidean_group
90 | :members:
91 |
92 | The "special_orthogonal_group" module
93 | -------------------------------------
94 |
95 | .. automodule:: geomstats.special_orthogonal_group
96 | :members:
97 |
98 | More manifolds
99 | ==============
100 |
101 | The "discretized_curves_space" module
102 | -------------------------------------
103 |
104 | .. automodule:: geomstats.discretized_curves_space
105 | :members:
106 |
107 | The "spd_matrices_space" module
108 | -------------------------------
109 |
110 | .. automodule:: geomstats.spd_matrices_space
111 | :members:
112 |
113 | The "stiefel" module
114 | --------------------
115 |
116 | .. automodule:: geomstats.stiefel
117 | :members:
118 |
119 | Visualization implementations
120 | =============================
121 |
122 | .. automodule:: geomstats.visualization
123 | :members:
124 |
125 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_examples.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for the examples.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import matplotlib
6 | matplotlib.use('Agg') # NOQA
7 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
8 | import os
9 | import sys
10 | import warnings
11 |
12 | import examples.gradient_descent_s2 as gradient_descent_s2
13 | import examples.loss_and_gradient_se3 as loss_and_gradient_se3
14 | import examples.loss_and_gradient_so3 as loss_and_gradient_so3
15 | import examples.plot_geodesics_h2 as plot_geodesics_h2
16 | import examples.plot_geodesics_s2 as plot_geodesics_s2
17 | import examples.plot_geodesics_se3 as plot_geodesics_se3
18 | import examples.plot_geodesics_so3 as plot_geodesics_so3
19 | import examples.plot_grid_h2 as plot_grid_h2
20 | import examples.plot_square_h2_poincare_disk as plot_square_h2_poincare_disk
21 | import examples.plot_square_h2_poincare_half_plane as plot_square_h2_poincare_half_plane # NOQA
22 | import examples.plot_square_h2_klein_disk as plot_square_h2_klein_disk
23 | import examples.plot_quantization_s1 as plot_quantization_s1
24 | import examples.plot_quantization_s2 as plot_quantization_s2
25 | import examples.tangent_pca_so3 as tangent_pca_so3
26 | import geomstats.tests
27 |
28 |
29 | class TestExamples(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
30 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
31 |
32 | @classmethod
33 | def setUpClass(cls):
34 | sys.stdout = open(os.devnull, 'w')
35 |
36 | def setUp(self):
37 | warnings.simplefilter('ignore', category=ImportWarning)
38 | plt.figure()
39 |
40 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
41 | def test_gradient_descent_s2(self):
42 | gradient_descent_s2.main(max_iter=32, output_file=None)
43 |
44 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
45 | def test_loss_and_gradient_so3(self):
46 | loss_and_gradient_so3.main()
47 |
48 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
49 | def test_loss_and_gradient_se3(self):
50 | loss_and_gradient_se3.main()
51 |
52 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
53 | def test_plot_geodesics_h2(self):
54 | plot_geodesics_h2.main()
55 |
56 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
57 | def test_plot_geodesics_s2(self):
58 | plot_geodesics_s2.main()
59 |
60 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
61 | def test_plot_geodesics_se3(self):
62 | plot_geodesics_se3.main()
63 |
64 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
65 | def test_plot_geodesics_so3(self):
66 | plot_geodesics_so3.main()
67 |
68 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
69 | def test_plot_grid_h2(self):
70 | plot_grid_h2.main()
71 |
72 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
73 | def test_plot_square_h2_square_poincare_disk(self):
74 | plot_square_h2_poincare_disk.main()
75 |
76 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
77 | def test_plot_square_h2_square_poincare_half_plane(self):
78 | plot_square_h2_poincare_half_plane.main()
79 |
80 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
81 | def test_plot_square_h2_square_klein_disk(self):
82 | plot_square_h2_klein_disk.main()
83 |
84 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
85 | def test_tangent_pca_so3(self):
86 | tangent_pca_so3.main()
87 |
88 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
89 | def test_plot_quantization_s1(self):
90 | plot_quantization_s1.main()
91 |
92 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
93 | def test_plot_quantization_s2(self):
94 | plot_quantization_s2.main()
95 |
96 |
97 | if __name__ == '__main__':
98 | geomstats.tests.main()
99 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/matrices_space.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | The space of matrices (m, n), which is the Euclidean space R^{mn}.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 |
7 | from geomstats.euclidean_space import EuclideanSpace
8 | from geomstats.riemannian_metric import RiemannianMetric
9 |
10 |
11 | TOLERANCE = 1e-5
12 |
13 |
14 | class MatricesSpace(EuclideanSpace):
15 | """Class for the space of matrices (m, n)."""
16 |
17 | def __init__(self, m, n):
18 | assert isinstance(m, int) and isinstance(n, int) and m > 0 and n > 0
19 | super(MatricesSpace, self).__init__(dimension=m*n)
20 | self.m = m
21 | self.n = n
22 | self.default_point_type = 'matrix'
23 | self.metric = MatricesMetric(m, n)
24 |
25 | def belongs(self, point):
26 | """
27 | Check if point belongs to the Matrix space.
28 | """
29 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=3)
30 | _, mat_dim_1, mat_dim_2 = point.shape
31 | return mat_dim_1 == self.m & mat_dim_2 == self.n
32 |
33 | @staticmethod
34 | def vector_from_matrix(matrix):
35 | """
36 | Conversion function from (_, m, n) to (_, mn).
37 | """
38 | matrix = gs.to_ndarray(matrix, to_ndim=3)
39 | n_mats, m, n = matrix.shape
40 | return gs.reshape(matrix, (n_mats, m*n))
41 |
42 | @staticmethod
43 | def is_symmetric(matrix, tolerance=TOLERANCE):
44 | """Check if a matrix is symmetric."""
45 | matrix = gs.to_ndarray(matrix, to_ndim=3)
46 | n_mats, m, n = matrix.shape
47 | assert m == n
48 | matrix_transpose = gs.transpose(matrix, axes=(0, 2, 1))
49 |
50 | mask = gs.isclose(matrix, matrix_transpose, atol=tolerance)
51 | mask = gs.all(mask, axis=(1, 2))
52 |
53 | mask = gs.to_ndarray(mask, to_ndim=1)
54 | mask = gs.to_ndarray(mask, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
55 | return mask
56 |
57 | @staticmethod
58 | def make_symmetric(matrix):
59 | """Make a matrix fully symmetric to avoid numerical issues."""
60 | matrix = gs.to_ndarray(matrix, to_ndim=3)
61 | n_mats, m, n = matrix.shape
62 | assert m == n
63 | matrix = gs.to_ndarray(matrix, to_ndim=3)
64 | return (matrix + gs.transpose(matrix, axes=(0, 2, 1))) / 2
65 |
66 | def random_uniform(self, n_samples=1):
67 | point = gs.random.rand(n_samples, self.m, self.n)
68 | return point
69 |
70 |
71 | class MatricesMetric(RiemannianMetric):
72 | """
73 | Euclidean metric on matrices given by the Frobenius inner product.
74 | """
75 | def __init__(self, m, n):
76 | dimension = m*n
77 | super(MatricesMetric, self).__init__(
78 | dimension=dimension,
79 | signature=(dimension, 0, 0))
80 |
81 | def inner_product(self, tangent_vec_a, tangent_vec_b, base_point=None):
82 | """
83 | Compute the Frobenius inner product of tangent_vec_a and tangent_vec_b
84 | at base_point.
85 | """
86 | tangent_vec_a = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec_a, to_ndim=3)
87 | n_tangent_vecs_a, _, _ = tangent_vec_a.shape
88 |
89 | tangent_vec_b = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec_b, to_ndim=3)
90 | n_tangent_vecs_b, _, _ = tangent_vec_b.shape
91 |
92 | assert n_tangent_vecs_a == n_tangent_vecs_b
93 |
94 | inner_prod = gs.einsum("nij,nij->n", tangent_vec_a, tangent_vec_b)
95 | inner_prod = gs.to_ndarray(inner_prod, to_ndim=1)
96 | inner_prod = gs.to_ndarray(inner_prod, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
97 | return inner_prod
98 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_matrices_space.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for the manifold of matrices.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 | import geomstats.tests
7 | import tests.helper as helper
8 |
9 | from geomstats.matrices_space import MatricesSpace
10 |
11 |
12 | class TestMatricesSpaceMethods(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
13 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
14 |
15 | def setUp(self):
16 | gs.random.seed(1234)
17 |
18 | self.n = 3
19 | self.space = MatricesSpace(m=self.n, n=self.n)
20 | self.metric = self.space.metric
21 | self.n_samples = 2
22 |
23 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
24 | def test_is_symmetric(self):
25 | sym_mat = gs.array([[1., 2.],
26 | [2., 1.]])
27 | result = self.space.is_symmetric(sym_mat)
28 | expected = gs.array([True])
29 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
30 |
31 | not_a_sym_mat = gs.array([[1., 0.6, -3.],
32 | [6., -7., 0.],
33 | [0., 7., 8.]])
34 | result = self.space.is_symmetric(not_a_sym_mat)
35 | expected = gs.array([False])
36 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
37 |
38 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
39 | def test_is_symmetric_vectorization(self):
40 | points = gs.array([
41 | [[1., 2.],
42 | [2., 1.]],
43 | [[3., 4.],
44 | [4., 5.]]])
45 | result = gs.all(self.space.is_symmetric(points))
46 | expected = True
47 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
48 |
49 | def test_make_symmetric(self):
50 | sym_mat = gs.array([[1., 2.],
51 | [2., 1.]])
52 | result = self.space.make_symmetric(sym_mat)
53 | expected = helper.to_matrix(sym_mat)
54 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
55 |
56 | mat = gs.array([[1., 2., 3.],
57 | [0., 0., 0.],
58 | [3., 1., 1.]])
59 | result = self.space.make_symmetric(mat)
60 | expected = gs.array([[[1., 1., 3.],
61 | [1., 0., 0.5],
62 | [3., 0.5, 1.]]])
63 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
64 |
65 | mat = gs.array([[[1e100, 1e-100, 1e100],
66 | [1e100, 1e-100, 1e100],
67 | [1e-100, 1e-100, 1e100]]])
68 | result = self.space.make_symmetric(mat)
69 |
70 | res = 0.5 * (1e100 + 1e-100)
71 |
72 | expected = gs.array([[[1e100, res, res],
73 | [res, 1e-100, res],
74 | [res, res, 1e100]]])
75 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
76 |
77 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
78 | def test_make_symmetric_and_is_symmetric_vectorization(self):
79 | points = gs.array([
80 | [[1., 2.],
81 | [3., 4.]],
82 | [[5., 6.],
83 | [4., 9.]]])
84 |
85 | sym_points = self.space.make_symmetric(points)
86 | result = gs.all(self.space.is_symmetric(sym_points))
87 | expected = True
88 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
89 |
90 | def test_inner_product(self):
91 | base_point = gs.array([
92 | [1., 2., 3.],
93 | [0., 0., 0.],
94 | [3., 1., 1.]])
95 |
96 | tangent_vector_1 = gs.array([
97 | [1., 2., 3.],
98 | [0., -10., 0.],
99 | [30., 1., 1.]])
100 |
101 | tangent_vector_2 = gs.array([
102 | [1., 4., 3.],
103 | [5., 0., 0.],
104 | [3., 1., 1.]])
105 |
106 | result = self.metric.inner_product(
107 | tangent_vector_1,
108 | tangent_vector_2,
109 | base_point=base_point)
110 |
111 | expected = gs.trace(
112 | gs.matmul(
113 | gs.transpose(tangent_vector_1),
114 | tangent_vector_2))
115 | expected = helper.to_scalar(expected)
116 |
117 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
118 |
119 |
120 | if __name__ == '__main__':
121 | geomstats.tests.main()
122 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/euclidean_space.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Euclidean space.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 |
7 | from geomstats.manifold import Manifold
8 | from geomstats.riemannian_metric import RiemannianMetric
9 |
10 |
11 | class EuclideanSpace(Manifold):
12 | """
13 | Class for Euclidean spaces.
14 |
15 | By definition, a Euclidean space is a vector space of a given
16 | dimension, equipped with a Euclidean metric.
17 | """
18 |
19 | def __init__(self, dimension):
20 | assert isinstance(dimension, int) and dimension > 0
21 | self.dimension = dimension
22 | self.metric = EuclideanMetric(dimension)
23 |
24 | def belongs(self, point):
25 | """
26 | Evaluate if a point belongs to the Euclidean space.
27 |
28 | Parameters
29 | ----------
30 | point : array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
31 | Input points.
32 |
33 | Returns
34 | -------
35 | belongs : array-like, shape=[n_samples, 1]
36 | """
37 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=2)
38 | n_points, point_dim = point.shape
39 | belongs = point_dim == self.dimension
40 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=1)
41 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
42 | belongs = gs.tile(belongs, (n_points, 1))
43 |
44 | return belongs
45 |
46 | def random_uniform(self, n_samples=1, bound=1.):
47 | """
48 | Sample in the Euclidean space with the uniform distribution.
49 | """
50 | size = (n_samples, self.dimension)
51 | point = bound * (gs.random.rand(*size) - 0.5) * 2
52 |
53 | return point
54 |
55 |
56 | class EuclideanMetric(RiemannianMetric):
57 | """
58 | Class for Euclidean metrics.
59 |
60 | As a Riemannian metric, the Euclidean metric is:
61 | - flat: the inner product is independent of the base point.
62 | - positive definite: it has signature (0, dimension),
63 | where dimension is the dimension of the Euclidean space.
64 | """
65 | def __init__(self, dimension):
66 | assert isinstance(dimension, int) and dimension > 0
67 | super(EuclideanMetric, self).__init__(
68 | dimension=dimension,
69 | signature=(dimension, 0, 0))
70 |
71 | def inner_product_matrix(self, base_point=None):
72 | """
73 | Inner product matrix, independent of the base point.
74 | """
75 | mat = gs.eye(self.dimension)
76 | mat = gs.to_ndarray(mat, to_ndim=3)
77 | return mat
78 |
79 | def exp(self, tangent_vec, base_point):
80 | """
81 | The Riemannian exponential is the addition in the Euclidean space.
82 | """
83 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=2)
84 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=2)
85 | exp = base_point + tangent_vec
86 | return exp
87 |
88 | def log(self, point, base_point):
89 | """
90 | The Riemannian logarithm is the subtraction in the Euclidean space.
91 | """
92 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=2)
93 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=2)
94 | log = point - base_point
95 | return log
96 |
97 | def mean(self, points, weights=None):
98 | """
99 | The Frechet mean of (weighted) points computed with the
100 | Euclidean metric is the weighted average of the points
101 | in the Euclidean space.
102 | """
103 | if isinstance(points, list):
104 | points = gs.vstack(points)
105 | points = gs.to_ndarray(points, to_ndim=2)
106 | n_points = gs.shape(points)[0]
107 |
108 | if isinstance(weights, list):
109 | weights = gs.vstack(weights)
110 | elif weights is None:
111 | weights = gs.ones((n_points,))
112 |
113 | weighted_points = gs.einsum('n,nj->nj', weights, points)
114 | mean = (gs.sum(weighted_points, axis=0)
115 | / gs.sum(weights))
116 | mean = gs.to_ndarray(mean, to_ndim=2)
117 | return mean
118 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_backend_numpy.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for numpy backend.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import importlib
6 | import os
7 | import unittest
8 | import warnings
9 |
10 | import geomstats.backend as gs
11 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
12 |
13 |
14 | class TestBackendNumpy(unittest.TestCase):
15 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
16 |
17 | @classmethod
18 | def setUpClass(cls):
19 | cls.initial_backend = os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND']
20 | os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] = 'numpy'
21 | importlib.reload(gs)
22 |
23 | @classmethod
24 | def tearDownClass(cls):
25 | os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] = cls.initial_backend
26 | importlib.reload(gs)
27 |
28 | def setUp(self):
29 | warnings.simplefilter('ignore', category=ImportWarning)
30 |
31 | self.so3_group = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=3)
32 | self.n_samples = 2
33 |
34 | def test_logm(self):
35 | point = gs.array([[2., 0., 0.],
36 | [0., 3., 0.],
37 | [0., 0., 4.]])
38 | result = gs.linalg.logm(point)
39 | expected = gs.array([[0.693147180, 0., 0.],
40 | [0., 1.098612288, 0.],
41 | [0., 0., 1.38629436]])
42 |
43 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
44 |
45 | def test_expm_and_logm(self):
46 | point = gs.array([[2., 0., 0.],
47 | [0., 3., 0.],
48 | [0., 0., 4.]])
49 | result = gs.linalg.expm(gs.linalg.logm(point))
50 | expected = point
51 |
52 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
53 |
54 | def test_expm_vectorization(self):
55 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
56 | [0., 3., 0.],
57 | [0., 0., 4.]],
58 | [[1., 0., 0.],
59 | [0., 5., 0.],
60 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
61 |
62 | expected = gs.array([[[7.38905609, 0., 0.],
63 | [0., 20.0855369, 0.],
64 | [0., 0., 54.5981500]],
65 | [[2.718281828, 0., 0.],
66 | [0., 148.413159, 0.],
67 | [0., 0., 403.42879349]]])
68 |
69 | result = gs.linalg.expm(point)
70 |
71 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
72 |
73 | def test_logm_vectorization_diagonal(self):
74 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
75 | [0., 3., 0.],
76 | [0., 0., 4.]],
77 | [[1., 0., 0.],
78 | [0., 5., 0.],
79 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
80 |
81 | expected = gs.array([[[0.693147180, 0., 0.],
82 | [0., 1.09861228866, 0.],
83 | [0., 0., 1.38629436]],
84 | [[0., 0., 0.],
85 | [0., 1.609437912, 0.],
86 | [0., 0., 1.79175946]]])
87 |
88 | result = gs.linalg.logm(point)
89 |
90 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
91 |
92 | def test_expm_and_logm_vectorization_random_rotation(self):
93 | point = self.so3_group.random_uniform(self.n_samples)
94 | point = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(point)
95 |
96 | result = gs.linalg.expm(gs.linalg.logm(point))
97 | expected = point
98 |
99 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
100 |
101 | def test_expm_and_logm_vectorization(self):
102 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
103 | [0., 3., 0.],
104 | [0., 0., 4.]],
105 | [[1., 0., 0.],
106 | [0., 5., 0.],
107 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
108 | result = gs.linalg.expm(gs.linalg.logm(point))
109 | expected = point
110 |
111 | self.assertTrue(gs.allclose(result, expected))
112 |
113 |
114 | if __name__ == '__main__':
115 | unittest.main()
116 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/general_linear_group.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | The General Linear Group, i.e. the matrix group GL(n).
3 | """
4 |
5 | import geomstats.backend as gs
6 |
7 | from geomstats.lie_group import LieGroup
8 | from geomstats.matrices_space import MatricesSpace
9 |
10 |
11 | class GeneralLinearGroup(LieGroup, MatricesSpace):
12 | """
13 | Class for the General Linear Group, i.e. the matrix group GL(n).
14 |
15 |
16 | Note: The default representation for elements of GL(n)
17 | are matrices.
18 | For now, SO(n) and SE(n) elements are represented
19 | by a vector by default.
20 | """
21 |
22 | def __init__(self, n):
23 | assert isinstance(n, int) and n > 0
24 | LieGroup.__init__(self, dimension=n*n)
25 | MatricesSpace.__init__(self, m=n, n=n)
26 |
27 | def get_identity(self, point_type=None):
28 | if point_type is None:
29 | point_type = self.default_point_type
30 | if point_type == 'matrix':
31 | return gs.eye(self.n)
32 | else:
33 | raise NotImplementedError(
34 | 'The identity of the general linear group is not'
35 | ' implemented for a point_type that is not \'matrix\'.')
36 | identity = property(get_identity)
37 |
38 | def belongs(self, mat):
39 | """
40 | Check if mat belongs to GL(n).
41 | """
42 | mat = gs.to_ndarray(mat, to_ndim=3)
43 |
44 | det = gs.linalg.det(mat)
45 | belongs = ~gs.isclose(det, 0.)
46 |
47 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=1)
48 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
49 |
50 | return belongs
51 |
52 | def compose(self, mat_a, mat_b):
53 | """
54 | Matrix composition.
55 | """
56 | mat_a = gs.to_ndarray(mat_a, to_ndim=3)
57 | mat_b = gs.to_ndarray(mat_b, to_ndim=3)
58 | composition = gs.einsum('nij,njk->nik', mat_a, mat_b)
59 | return composition
60 |
61 | def inverse(self, mat):
62 | """
63 | Matrix inverse.
64 | """
65 | mat = gs.to_ndarray(mat, to_ndim=3)
66 | return gs.linalg.inv(mat)
67 |
68 | def group_exp_from_identity(self, tangent_vec, point_type=None):
69 | """
70 | Group exponential of the Lie group of
71 | all invertible matrices at the identity.
72 | """
73 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=3)
74 | group_exp = gs.linalg.expm(tangent_vec)
75 |
76 | return gs.real(group_exp)
77 |
78 | def group_exp_not_from_identity(
79 | self, tangent_vec, base_point, point_type=None):
80 | """
81 | Group exponential of the Lie group of
82 | all invertible matrices.
83 | """
84 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=3)
85 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=3)
86 |
87 | tangent_vec_at_identity = self.compose(
88 | self.inverse(base_point), tangent_vec)
89 |
90 | group_exp_from_identity = self.group_exp_from_identity(
91 | tangent_vec_at_identity)
92 |
93 | group_exp = self.compose(
94 | base_point, group_exp_from_identity)
95 |
96 | return group_exp
97 |
98 | def group_log_from_identity(self, point, point_type=None):
99 | """
100 | Group logarithm of the Lie group of
101 | all invertible matrices at the identity.
102 | """
103 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=3)
104 | group_log = gs.linalg.logm(point)
105 |
106 | return gs.real(group_log)
107 |
108 | def group_log_not_from_identity(
109 | self, point, base_point, point_type=None):
110 | """
111 | Group logarithm of the Lie group of
112 | all invertible matrices.
113 | """
114 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=3)
115 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=3)
116 |
117 | point_near_identity = self.compose(
118 | self.inverse(base_point), point)
119 |
120 | group_log_from_identity = self.group_log_from_identity(
121 | point_near_identity)
122 |
123 | group_log = self.compose(
124 | base_point, group_log_from_identity)
125 |
126 | return group_log
127 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/loss_and_gradient_so3.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Predict on manifolds: losses.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import os
6 | import tensorflow as tf
7 |
8 | import geomstats.backend as gs
9 | import geomstats.lie_group as lie_group
10 |
11 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
12 |
13 |
14 | SO3 = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=3)
15 |
16 |
17 | def loss(y_pred, y_true,
18 | metric=SO3.bi_invariant_metric,
19 | representation='vector'):
20 |
21 | if representation == 'quaternion':
22 | y_pred = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_pred)
23 | y_true = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_true)
24 |
25 | loss = lie_group.loss(y_pred, y_true, SO3, metric)
26 | return loss
27 |
28 |
29 | def grad(y_pred, y_true,
30 | metric=SO3.bi_invariant_metric,
31 | representation='vector'):
32 |
33 | y_pred = gs.expand_dims(y_pred, axis=0)
34 | y_true = gs.expand_dims(y_true, axis=0)
35 |
36 | if representation == 'vector':
37 | grad = lie_group.grad(y_pred, y_true, SO3, metric)
38 |
39 | if representation == 'quaternion':
40 | quat_scalar = y_pred[:, :1]
41 | quat_vec = y_pred[:, 1:]
42 |
43 | quat_vec_norm = gs.linalg.norm(quat_vec, axis=1)
44 | quat_sq_norm = quat_vec_norm ** 2 + quat_scalar ** 2
45 |
46 | quat_arctan2 = gs.arctan2(quat_vec_norm, quat_scalar)
47 | differential_scalar = - 2 * quat_vec / (quat_sq_norm)
48 | differential_scalar = gs.to_ndarray(differential_scalar, to_ndim=2)
49 | differential_scalar = gs.transpose(differential_scalar)
50 |
51 | differential_vec = (2 * (quat_scalar / quat_sq_norm
52 | - 2 * quat_arctan2 / quat_vec_norm)
53 | * (gs.einsum('ni,nj->nij', quat_vec, quat_vec)
54 | / quat_vec_norm ** 2)
55 | + 2 * quat_arctan2 / quat_vec_norm * gs.eye(3))
56 | differential_vec = gs.squeeze(differential_vec)
57 |
58 | differential = gs.concatenate(
59 | [differential_scalar, differential_vec],
60 | axis=1)
61 |
62 | y_pred = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_pred)
63 | y_true = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_true)
64 |
65 | grad = lie_group.grad(y_pred, y_true, SO3, metric)
66 |
67 | grad = gs.matmul(grad, differential)
68 |
69 | grad = gs.squeeze(grad, axis=0)
70 | return grad
71 |
72 |
73 | def main():
74 | y_pred = gs.array([1., 1.5, -0.3])
75 | y_true = gs.array([0.1, 1.8, -0.1])
76 |
77 | loss_rot_vec = loss(y_pred, y_true)
78 | grad_rot_vec = grad(y_pred, y_true)
79 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
80 | with tf.Session() as sess:
81 | loss_rot_vec = sess.run(loss_rot_vec)
82 | grad_rot_vec = sess.run(grad_rot_vec)
83 | print('The loss between the rotation vectors is: {}'.format(
84 | loss_rot_vec[0, 0]))
85 | print('The riemannian gradient is: {}'.format(
86 | grad_rot_vec))
87 |
88 | angle = gs.pi / 6
89 | cos = gs.cos(angle / 2)
90 | sin = gs.sin(angle / 2)
91 | u = gs.array([1., 2., 3.])
92 | u = u / gs.linalg.norm(u)
93 | scalar = gs.to_ndarray(cos, to_ndim=1)
94 | vec = sin * u
95 | y_pred_quaternion = gs.concatenate([scalar, vec], axis=0)
96 |
97 | angle = gs.pi / 7
98 | cos = gs.cos(angle / 2)
99 | sin = gs.sin(angle / 2)
100 | u = gs.array([1., 2., 3.])
101 | u = u / gs.linalg.norm(u)
102 | scalar = gs.to_ndarray(cos, to_ndim=1)
103 | vec = sin * u
104 | y_true_quaternion = gs.concatenate([scalar, vec], axis=0)
105 |
106 | loss_quaternion = loss(y_pred_quaternion, y_true_quaternion,
107 | representation='quaternion')
108 | grad_quaternion = grad(y_pred_quaternion, y_true_quaternion,
109 | representation='quaternion')
110 |
111 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
112 | with tf.Session() as sess:
113 | loss_quaternion = sess.run(loss_quaternion)
114 | grad_quaternion = sess.run(grad_quaternion)
115 | print('The loss between the quaternions is: {}'.format(
116 | loss_quaternion[0, 0]))
117 | print('The riemannian gradient is: {}'.format(
118 | grad_quaternion))
119 |
120 |
121 | if __name__ == "__main__":
122 | main()
123 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/gradient_descent_s2.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Gradient descent on a sphere.
3 |
4 | We solve the following optimization problem:
5 |
6 | minimize: x^{T}Ax
7 | such than: x^{T}x = 1
8 |
9 | Using by operating a gradient descent of the quadratic form
10 | on the sphere. We solve this in 3 dimension on the 2-sphere
11 | manifold so that we can visualize and render the path as a video.
12 | """
13 |
14 | import matplotlib
15 | matplotlib.use("Agg") # NOQA
16 | import matplotlib.animation as animation
17 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
18 | import numpy as np
19 |
20 | import geomstats.backend as gs
21 | import geomstats.visualization as visualization
22 |
23 | from geomstats.hypersphere import Hypersphere
24 | from geomstats.spd_matrices_space import SPDMatricesSpace
25 |
26 |
27 | SPHERE2 = Hypersphere(dimension=2)
28 | METRIC = SPHERE2.metric
29 |
30 |
31 | def gradient_descent(start,
32 | loss,
33 | grad,
34 | manifold,
35 | lr=0.01,
36 | max_iter=256,
37 | precision=1e-5):
38 | """Operate a gradient descent on a given manifold until either max_iter or
39 | a given precision is reached."""
40 | x = start
41 | for i in range(max_iter):
42 | x_prev = x
43 | euclidean_grad = - lr * grad(x)
44 | tangent_vec = manifold.projection_to_tangent_space(
45 | vector=euclidean_grad, base_point=x)
46 | x = manifold.metric.exp(base_point=x, tangent_vec=tangent_vec)[0]
47 | if (gs.abs(loss(x, use_gs=True) - loss(x_prev, use_gs=True))
48 | <= precision):
49 | print('x: %s' % x)
50 | print('reached precision %s' % precision)
51 | print('iterations: %d' % i)
52 | break
53 | yield x, loss(x)
54 |
55 |
56 | def plot_and_save_video(geodesics,
57 | loss,
58 | size=20,
59 | fps=10,
60 | dpi=100,
61 | out='out.mp4',
62 | color='red'):
63 | """Render a set of geodesics and save it to an mpeg 4 file."""
64 | FFMpegWriter = animation.writers['ffmpeg']
65 | writer = FFMpegWriter(fps=fps)
66 | fig = plt.figure(figsize=(size, size))
67 | ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d', aspect='equal')
68 | sphere = visualization.Sphere()
69 | sphere.plot_heatmap(ax, loss)
70 | points = gs.to_ndarray(geodesics[0], to_ndim=2)
71 | sphere.add_points(points)
72 | sphere.draw(ax, color=color, marker='.')
73 | with writer.saving(fig, out, dpi=dpi):
74 | for points in geodesics[1:]:
75 | points = gs.to_ndarray(points, to_ndim=2)
76 | sphere.draw_points(ax, points=points, color=color, marker='.')
77 | writer.grab_frame()
78 |
79 |
80 | def generate_well_behaved_matrix():
81 | """Generate a matrix with real eigenvalues."""
82 | matrix = 2 * SPDMatricesSpace(n=3).random_uniform()[0]
83 | assert np.linalg.det(matrix) > 0
84 | return matrix
85 |
86 |
87 | def main(output_file='out.mp4', max_iter=128):
88 | gs.random.seed(1985)
89 | A = generate_well_behaved_matrix()
90 |
91 | def grad(x):
92 | return 2 * gs.matmul(A, x)
93 |
94 | def loss(x, use_gs=False):
95 | if use_gs:
96 | return gs.matmul(x, gs.matmul(A, x))
97 | return np.matmul(x, np.matmul(A, x))
98 |
99 | initial_point = gs.array([0., 1., 0.])
100 | previous_x = initial_point
101 | geodesics = []
102 | n_steps = 20
103 | for x, fx in gradient_descent(initial_point,
104 | loss,
105 | grad,
106 | max_iter=max_iter,
107 | manifold=SPHERE2):
108 | initial_tangent_vec = METRIC.log(point=x, base_point=previous_x)
109 | geodesic = METRIC.geodesic(initial_point=previous_x,
110 | initial_tangent_vec=initial_tangent_vec)
111 |
112 | t = np.linspace(0, 1, n_steps)
113 | geodesics.append(geodesic(t))
114 | previous_x = x
115 | if output_file:
116 | plot_and_save_video(geodesics, loss, out=output_file)
117 | eig, _ = np.linalg.eig(A)
118 | np.testing.assert_almost_equal(loss(x), np.min(eig), decimal=2)
119 |
120 |
121 | if __name__ == "__main__":
122 | main()
123 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/minkowski_space.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Minkowski space.
3 | """
4 |
5 |
6 | from geomstats.manifold import Manifold
7 | from geomstats.riemannian_metric import RiemannianMetric
8 | import geomstats.backend as gs
9 |
10 |
11 | class MinkowskiSpace(Manifold):
12 | """Class for Minkowski Space."""
13 |
14 | def __init__(self, dimension):
15 | assert isinstance(dimension, int) and dimension > 0
16 | self.dimension = dimension
17 | self.metric = MinkowskiMetric(dimension)
18 |
19 | def belongs(self, point):
20 | """
21 | Evaluate if a point belongs to the Minkowski space.
22 |
23 | Parameters
24 | ----------
25 | point : array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
26 | Input points.
27 |
28 | Returns
29 | -------
30 | belongs : array-like, shape=[n_samples, 1]
31 | """
32 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=2)
33 | n_points, point_dim = point.shape
34 | belongs = point_dim == self.dimension
35 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=1)
36 | belongs = gs.to_ndarray(belongs, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
37 | belongs = gs.tile(belongs, (n_points, 1))
38 |
39 | return belongs
40 |
41 | def random_uniform(self, n_samples=1, bound=1.):
42 | """
43 | Sample in the Minkowski space with the uniform distribution.
44 |
45 | Returns
46 | -------
47 | points : array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
48 | Sampled points.
49 | """
50 | size = (n_samples, self.dimension)
51 | point = bound * gs.random.rand(*size) * 2 - 1
52 |
53 | return point
54 |
55 |
56 | class MinkowskiMetric(RiemannianMetric):
57 | """
58 | Class for the pseudo-Riemannian Minkowski metric.
59 | The metric is flat: the inner product is independent of the base point.
60 | """
61 | def __init__(self, dimension):
62 | super(MinkowskiMetric, self).__init__(
63 | dimension=dimension,
64 | signature=(dimension - 1, 1, 0))
65 |
66 | def inner_product_matrix(self, base_point=None):
67 | """
68 | Inner product matrix, independent of the base point.
69 |
70 | Parameters
71 | ----------
72 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
73 | """
74 | inner_prod_mat = gs.eye(self.dimension-1, self.dimension-1)
75 | first_row = gs.array([0.] * (self.dimension - 1))
76 | first_row = gs.to_ndarray(first_row, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
77 | inner_prod_mat = gs.vstack([gs.transpose(first_row),
78 | inner_prod_mat])
79 |
80 | first_column = gs.array([-1.] + [0.] * (self.dimension - 1))
81 | first_column = gs.to_ndarray(first_column, to_ndim=2, axis=1)
82 | inner_prod_mat = gs.hstack([first_column,
83 | inner_prod_mat])
84 |
85 | return inner_prod_mat
86 |
87 | def exp(self, tangent_vec, base_point):
88 | """
89 | The Riemannian exponential is the addition in the Minkowski space.
90 |
91 | Parameters
92 | ----------
93 | tangent_vec: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
94 | or shape=[1, dimension]
95 |
96 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
97 | or shape=[1, dimension]
98 | """
99 | tangent_vec = gs.to_ndarray(tangent_vec, to_ndim=2)
100 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=2)
101 | return base_point + tangent_vec
102 |
103 | def log(self, point, base_point):
104 | """
105 | The Riemannian logarithm is the subtraction in the Minkowski space.
106 |
107 | Parameters
108 | ----------
109 | point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
110 | or shape=[1, dimension]
111 |
112 | base_point: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
113 | or shape=[1, dimension]
114 | """
115 | point = gs.to_ndarray(point, to_ndim=2)
116 | base_point = gs.to_ndarray(base_point, to_ndim=2)
117 | return point - base_point
118 |
119 | def mean(self, points, weights=None):
120 | """
121 | The Frechet mean of (weighted) points is the weighted average of
122 | the points in the Minkowski space.
123 |
124 | Parameters
125 | ----------
126 | points: array-like, shape=[n_samples, dimension]
127 |
128 | weights: array-like, shape=[n_samples, 1], optional
129 | """
130 | if isinstance(points, list):
131 | points = gs.vstack(points)
132 | points = gs.to_ndarray(points, to_ndim=2)
133 | n_points = gs.shape(points)[0]
134 |
135 | if isinstance(weights, list):
136 | weights = gs.vstack(weights)
137 | elif weights is None:
138 | weights = gs.ones((n_points,))
139 |
140 | weighted_points = gs.einsum('n,nj->nj', weights, points)
141 | mean = (gs.sum(weighted_points, axis=0)
142 | / gs.sum(weights))
143 | mean = gs.to_ndarray(mean, to_ndim=2)
144 | return mean
145 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/loss_and_gradient_se3.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Predict on SE3: losses.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import os
6 | import tensorflow as tf
7 |
8 | import geomstats.backend as gs
9 | import geomstats.lie_group as lie_group
10 |
11 | from geomstats.special_euclidean_group import SpecialEuclideanGroup
12 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
13 |
14 |
15 | SE3 = SpecialEuclideanGroup(n=3)
16 | SO3 = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=3)
17 |
18 |
19 | def loss(y_pred, y_true,
20 | metric=SE3.left_canonical_metric,
21 | representation='vector'):
22 | """
23 | Loss function given by a riemannian metric on a Lie group,
24 | by default the left-invariant canonical metric.
25 | """
26 | if gs.ndim(y_pred) == 1:
27 | y_pred = gs.expand_dims(y_pred, axis=0)
28 | if gs.ndim(y_true) == 1:
29 | y_true = gs.expand_dims(y_true, axis=0)
30 |
31 | if representation == 'quaternion':
32 | y_pred_rot_vec = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_pred[:, :4])
33 | y_pred = gs.hstack([y_pred_rot_vec, y_pred[:, 4:]])
34 | y_true_rot_vec = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_true[:, :4])
35 | y_true = gs.hstack([y_true_rot_vec, y_true[:, 4:]])
36 |
37 | loss = lie_group.loss(y_pred, y_true, SE3, metric)
38 | return loss
39 |
40 |
41 | def grad(y_pred, y_true,
42 | metric=SE3.left_canonical_metric,
43 | representation='vector'):
44 | """
45 | Closed-form for the gradient of pose_loss.
46 |
47 | :return: tangent vector at point y_pred.
48 | """
49 | if gs.ndim(y_pred) == 1:
50 | y_pred = gs.expand_dims(y_pred, axis=0)
51 | if gs.ndim(y_true) == 1:
52 | y_true = gs.expand_dims(y_true, axis=0)
53 |
54 | if representation == 'vector':
55 | grad = lie_group.grad(y_pred, y_true, SE3, metric)
56 |
57 | if representation == 'quaternion':
58 |
59 | y_pred_rot_vec = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_pred[:, :4])
60 | y_pred_pose = gs.hstack([y_pred_rot_vec, y_pred[:, 4:]])
61 | y_true_rot_vec = SO3.rotation_vector_from_quaternion(y_true[:, :4])
62 | y_true_pose = gs.hstack([y_true_rot_vec, y_true[:, 4:]])
63 | grad = lie_group.grad(y_pred_pose, y_true_pose, SE3, metric)
64 |
65 | quat_scalar = y_pred[:, :1]
66 | quat_vec = y_pred[:, 1:4]
67 |
68 | quat_vec_norm = gs.linalg.norm(quat_vec, axis=1)
69 | quat_sq_norm = quat_vec_norm ** 2 + quat_scalar ** 2
70 |
71 | quat_arctan2 = gs.arctan2(quat_vec_norm, quat_scalar)
72 | differential_scalar = - 2 * quat_vec / (quat_sq_norm)
73 | differential_vec = (2 * (quat_scalar / quat_sq_norm
74 | - 2 * quat_arctan2 / quat_vec_norm)
75 | * (gs.einsum('ni,nj->nij', quat_vec, quat_vec)
76 | / quat_vec_norm * quat_vec_norm)
77 | + 2 * quat_arctan2 / quat_vec_norm * gs.eye(3))
78 |
79 | differential_scalar_t = gs.transpose(differential_scalar, axes=(1, 0))
80 |
81 | upper_left_block = gs.hstack(
82 | (differential_scalar_t, differential_vec[0]))
83 | upper_right_block = gs.zeros((3, 3))
84 | lower_right_block = gs.eye(3)
85 | lower_left_block = gs.zeros((3, 4))
86 |
87 | top = gs.hstack((upper_left_block, upper_right_block))
88 | bottom = gs.hstack((lower_left_block, lower_right_block))
89 |
90 | differential = gs.vstack((top, bottom))
91 | differential = gs.expand_dims(differential, axis=0)
92 |
93 | grad = gs.einsum('ni,nij->ni', grad, differential)
94 |
95 | grad = gs.squeeze(grad, axis=0)
96 | return grad
97 |
98 |
99 | def main():
100 | y_pred = gs.array([1., 1.5, -0.3, 5., 6., 7.])
101 | y_true = gs.array([0.1, 1.8, -0.1, 4., 5., 6.])
102 |
103 | loss_rot_vec = loss(y_pred, y_true)
104 | grad_rot_vec = grad(y_pred, y_true)
105 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
106 | with tf.Session() as sess:
107 | loss_rot_vec = sess.run(loss_rot_vec)
108 | grad_rot_vec = sess.run(grad_rot_vec)
109 | print('The loss between the poses using rotation vectors is: {}'.format(
110 | loss_rot_vec[0, 0]))
111 | print('The riemannian gradient is: {}'.format(grad_rot_vec))
112 |
113 | angle = gs.pi / 6
114 | cos = gs.cos(angle / 2)
115 | sin = gs.sin(angle / 2)
116 | u = gs.array([1., 2., 3.])
117 | u = u / gs.linalg.norm(u)
118 | scalar = gs.array(cos)
119 | vec = sin * u
120 | translation = gs.array([5., 6., 7.])
121 | y_pred_quaternion = gs.concatenate([[scalar], vec, translation], axis=0)
122 |
123 | angle = gs.pi / 7
124 | cos = gs.cos(angle / 2)
125 | sin = gs.sin(angle / 2)
126 | u = gs.array([1., 2., 3.])
127 | u = u / gs.linalg.norm(u)
128 | scalar = gs.array(cos)
129 | vec = sin * u
130 | translation = gs.array([4., 5., 6.])
131 | y_true_quaternion = gs.concatenate([[scalar], vec, translation], axis=0)
132 |
133 | loss_quaternion = loss(y_pred_quaternion, y_true_quaternion,
134 | representation='quaternion')
135 | grad_quaternion = grad(y_pred_quaternion, y_true_quaternion,
136 | representation='quaternion')
137 | if os.environ['GEOMSTATS_BACKEND'] == 'tensorflow':
138 | with tf.Session() as sess:
139 | loss_quaternion = sess.run(loss_quaternion)
140 | grad_quaternion = sess.run(grad_quaternion)
141 | print('The loss between the poses using quaternions is: {}'.format(
142 | loss_quaternion[0, 0]))
143 | print('The riemannian gradient is: {}'.format(
144 | grad_quaternion))
145 |
146 |
147 | if __name__ == "__main__":
148 | main()
149 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_general_linear_group.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Unit tests for General Linear group.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import warnings
6 |
7 | import geomstats.backend as gs
8 | import geomstats.tests
9 | import tests.helper as helper
10 |
11 | from geomstats.general_linear_group import GeneralLinearGroup
12 | from geomstats.special_orthogonal_group import SpecialOrthogonalGroup
13 |
14 | RTOL = 1e-5
15 |
16 |
17 | class TestGeneralLinearGroupMethods(geomstats.tests.TestCase):
18 | _multiprocess_can_split_ = True
19 |
20 | def setUp(self):
21 | gs.random.seed(1234)
22 | self.n = 3
23 | self.n_samples = 2
24 | self.group = GeneralLinearGroup(n=self.n)
25 | # We generate invertible matrices using so3_group
26 | self.so3_group = SpecialOrthogonalGroup(n=self.n)
27 |
28 | warnings.simplefilter('ignore', category=ImportWarning)
29 |
30 | @geomstats.tests.np_only
31 | def test_belongs(self):
32 | """
33 | A rotation matrix belongs to the matrix Lie group
34 | of invertible matrices.
35 | """
36 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.2, -0.1, 0.1])
37 | rot_mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
38 | result = self.group.belongs(rot_mat)
39 | expected = gs.array([True])
40 |
41 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
42 |
43 | def test_compose(self):
44 | # 1. Composition by identity, on the right
45 | # Expect the original transformation
46 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.2, -0.1, 0.1])
47 | mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
48 |
49 | result = self.group.compose(mat, self.group.identity)
50 | expected = mat
51 | expected = helper.to_matrix(mat)
52 |
53 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
54 |
55 | # 2. Composition by identity, on the left
56 | # Expect the original transformation
57 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.2, 0.1, -0.1])
58 | mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
59 |
60 | result = self.group.compose(self.group.identity, mat)
61 | expected = mat
62 |
63 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
64 |
65 | def test_inverse(self):
66 | mat = gs.array([
67 | [1., 2., 3.],
68 | [4., 5., 6.],
69 | [7., 8., 10.]])
70 | result = self.group.inverse(mat)
71 | expected = 1. / 3. * gs.array([
72 | [-2., -4., 3.],
73 | [-2., 11., -6.],
74 | [3., -6., 3.]])
75 | expected = helper.to_matrix(expected)
76 |
77 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
78 |
79 | def test_compose_and_inverse(self):
80 | # 1. Compose transformation by its inverse on the right
81 | # Expect the group identity
82 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.2, 0.1, 0.1])
83 | mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
84 | inv_mat = self.group.inverse(mat)
85 |
86 | result = self.group.compose(mat, inv_mat)
87 | expected = self.group.identity
88 | expected = helper.to_matrix(expected)
89 |
90 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
91 |
92 | # 2. Compose transformation by its inverse on the left
93 | # Expect the group identity
94 | rot_vec = gs.array([0.7, 0.1, 0.1])
95 | mat = self.so3_group.matrix_from_rotation_vector(rot_vec)
96 | inv_mat = self.group.inverse(mat)
97 |
98 | result = self.group.compose(inv_mat, mat)
99 | expected = self.group.identity
100 | expected = helper.to_matrix(expected)
101 |
102 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
103 |
104 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
105 | def test_group_log_and_exp(self):
106 | point = 5 * gs.eye(self.n)
107 |
108 | group_log = self.group.group_log(point)
109 | result = self.group.group_exp(group_log)
110 | expected = point
111 | expected = helper.to_matrix(expected)
112 |
113 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
114 |
115 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
116 | def test_group_exp_vectorization(self):
117 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
118 | [0., 3., 0.],
119 | [0., 0., 4.]],
120 | [[1., 0., 0.],
121 | [0., 5., 0.],
122 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
123 |
124 | expected = gs.array([[[7.38905609, 0., 0.],
125 | [0., 20.0855369, 0.],
126 | [0., 0., 54.5981500]],
127 | [[2.718281828, 0., 0.],
128 | [0., 148.413159, 0.],
129 | [0., 0., 403.42879349]]])
130 |
131 | result = self.group.group_exp(point)
132 |
133 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected, rtol=1e-3)
134 |
135 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
136 | def test_group_log_vectorization(self):
137 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
138 | [0., 3., 0.],
139 | [0., 0., 4.]],
140 | [[1., 0., 0.],
141 | [0., 5., 0.],
142 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
143 |
144 | expected = gs.array([[[0.693147180, 0., 0.],
145 | [0., 1.09861228866, 0.],
146 | [0., 0., 1.38629436]],
147 | [[0., 0., 0.],
148 | [0., 1.609437912, 0.],
149 | [0., 0., 1.79175946]]])
150 |
151 | result = self.group.group_log(point)
152 |
153 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected, atol=1e-4)
154 |
155 | @geomstats.tests.np_and_tf_only
156 | def test_expm_and_logm_vectorization_symmetric(self):
157 | point = gs.array([[[2., 0., 0.],
158 | [0., 3., 0.],
159 | [0., 0., 4.]],
160 | [[1., 0., 0.],
161 | [0., 5., 0.],
162 | [0., 0., 6.]]])
163 | result = self.group.group_exp(self.group.group_log(point))
164 | expected = point
165 |
166 | self.assertAllClose(result, expected)
167 |
168 |
169 | if __name__ == '__main__':
170 | geomstats.tests.main()
171 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geomstats/backend/tensorflow.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Tensorflow based computation backend."""
2 |
3 | import tensorflow as tf
4 |
5 |
6 | int8 = tf.int8
7 | int32 = tf.int32
8 | int64 = tf.int64
9 | float16 = tf.float16
10 | float32 = tf.float32
11 | float64 = tf.float64
12 |
13 |
14 | def while_loop(*args, **kwargs):
15 | return tf.while_loop(*args, **kwargs)
16 |
17 |
18 | def logical_or(x, y):
19 | return tf.logical_or(x, y)
20 |
21 |
22 | def get_mask_i_float(i, n):
23 | range_n = arange(n)
24 | i_float = cast(array([i]), int32)[0]
25 | mask_i = equal(range_n, i_float)
26 | mask_i_float = cast(mask_i, float32)
27 | return mask_i_float
28 |
29 |
30 | def gather(*args, **kwargs):
31 | return tf.gather(*args, **kwargs)
32 |
33 |
34 | def where(*args, **kwargs):
35 | return tf.where(*args, **kwargs)
36 |
37 |
38 | def vectorize(x, pyfunc, multiple_args=False, dtype=None, **kwargs):
39 | if multiple_args:
40 | return tf.map_fn(lambda x: pyfunc(*x), elems=x, dtype=dtype)
41 | return tf.map_fn(pyfunc, elems=x, dtype=dtype)
42 |
43 |
44 | def sign(x):
45 | return tf.sign(x)
46 |
47 |
48 | def hsplit(x, n_splits):
49 | return tf.split(x, num_or_size_splits=n_splits, axis=1)
50 |
51 |
52 | def amax(x):
53 | return tf.reduce_max(x)
54 |
55 |
56 | def real(x):
57 | return tf.real(x)
58 |
59 |
60 | def cond(*args, **kwargs):
61 | return tf.cond(*args, **kwargs)
62 |
63 |
64 | def reshape(*args, **kwargs):
65 | return tf.reshape(*args, **kwargs)
66 |
67 |
68 | def arange(*args, **kwargs):
69 | return tf.range(*args, **kwargs)
70 |
71 |
72 | def outer(x, y):
73 | return tf.einsum('i,j->ij', x, y)
74 |
75 |
76 | def copy(x):
77 | return tf.Variable(x)
78 |
79 |
80 | def linspace(start, stop, num):
81 | return tf.linspace(start, stop, num)
82 |
83 |
84 | def mod(x, y):
85 | return tf.mod(x, y)
86 |
87 |
88 | def boolean_mask(x, mask, name='boolean_mask', axis=None):
89 | return tf.boolean_mask(x, mask, name, axis)
90 |
91 |
92 | def exp(x):
93 | return tf.exp(x)
94 |
95 |
96 | def log(x):
97 | return tf.log(x)
98 |
99 |
100 | def hstack(x):
101 | return tf.concat(x, axis=1)
102 |
103 |
104 | def vstack(x):
105 | return tf.concat(x, axis=0)
106 |
107 |
108 | def cast(x, dtype):
109 | return tf.cast(x, dtype)
110 |
111 |
112 | def divide(x1, x2):
113 | return tf.divide(x1, x2)
114 |
115 |
116 | def tile(x, reps):
117 | return tf.tile(x, reps)
118 |
119 |
120 | def eval(x):
121 | if tf.executing_eagerly():
122 | return x
123 | return x.eval()
124 |
125 |
126 | def abs(x):
127 | return tf.abs(x)
128 |
129 |
130 | def zeros(x):
131 | return tf.zeros(x)
132 |
133 |
134 | def ones(x):
135 | return tf.ones(x)
136 |
137 |
138 | def sin(x):
139 | return tf.sin(x)
140 |
141 |
142 | def cos(x):
143 | return tf.cos(x)
144 |
145 |
146 | def cosh(x):
147 | return tf.cosh(x)
148 |
149 |
150 | def sinh(x):
151 | return tf.sinh(x)
152 |
153 |
154 | def tanh(x):
155 | return tf.tanh(x)
156 |
157 |
158 | def arccosh(x):
159 | return tf.acosh(x)
160 |
161 |
162 | def tan(x):
163 | return tf.tan(x)
164 |
165 |
166 | def arcsin(x):
167 | return tf.asin(x)
168 |
169 |
170 | def arccos(x):
171 | return tf.acos(x)
172 |
173 |
174 | def shape(x):
175 | return tf.shape(x)
176 |
177 |
178 | def ndim(x):
179 | x = array(x)
180 | dims = x.get_shape()._dims
181 | if dims is not None:
182 | return len(dims)
183 | return None
184 |
185 |
186 | def dot(x, y):
187 | return tf.tensordot(x, y, axes=1)
188 |
189 |
190 | def maximum(x, y):
191 | return tf.maximum(x, y)
192 |
193 |
194 | def greater(x, y):
195 | return tf.greater(x, y)
196 |
197 |
198 | def greater_equal(x, y):
199 | return tf.greater_equal(x, y)
200 |
201 |
202 | def equal(x, y):
203 | return tf.equal(x, y)
204 |
205 |
206 | def to_ndarray(x, to_ndim, axis=0):
207 | if ndim(x) == to_ndim - 1:
208 | x = tf.expand_dims(x, axis=axis)
209 |
210 | return x
211 |
212 |
213 | def sqrt(x):
214 | return tf.sqrt(x)
215 |
216 |
217 | def isclose(x, y, rtol=1e-05, atol=1e-08):
218 | rhs = tf.constant(atol) + tf.constant(rtol) * tf.abs(y)
219 | return tf.less_equal(tf.abs(tf.subtract(x, y)), rhs)
220 |
221 |
222 | def allclose(x, y, rtol=1e-05, atol=1e-08):
223 | return tf.reduce_all(isclose(x, y, rtol=rtol, atol=atol))
224 |
225 |
226 | def less(x, y):
227 | return tf.less(x, y)
228 |
229 |
230 | def less_equal(x, y):
231 | return tf.less_equal(x, y)
232 |
233 |
234 | def eye(n, m=None):
235 | if m is None:
236 | m = n
237 | n = cast(n, dtype=int32)
238 | m = cast(m, dtype=int32)
239 | return tf.eye(num_rows=n, num_columns=m)
240 |
241 |
242 | def matmul(x, y):
243 | return tf.matmul(x, y)
244 |
245 |
246 | def argmax(*args, **kwargs):
247 | return tf.argmax(*args, **kwargs)
248 |
249 |
250 | def sum(*args, **kwargs):
251 | return tf.reduce_sum(*args, **kwargs)
252 |
253 |
254 | def einsum(equation, *inputs, **kwargs):
255 | return tf.einsum(equation, *inputs, **kwargs)
256 |
257 |
258 | def transpose(x, axes=None):
259 | return tf.transpose(x, perm=axes)
260 |
261 |
262 | def squeeze(x, **kwargs):
263 | return tf.squeeze(x, **kwargs)
264 |
265 |
266 | def zeros_like(x):
267 | return tf.zeros_like(x)
268 |
269 |
270 | def ones_like(x):
271 | return tf.ones_like(x)
272 |
273 |
274 | def trace(x, **kwargs):
275 | return tf.trace(x)
276 |
277 |
278 | def array(x):
279 | return tf.convert_to_tensor(x)
280 |
281 |
282 | def all(bool_tensor, axis=None, keepdims=False):
283 | bool_tensor = tf.cast(bool_tensor, tf.bool)
284 | all_true = tf.reduce_all(bool_tensor, axis, keepdims)
285 | return all_true
286 |
287 |
288 | def concatenate(*args, **kwargs):
289 | return tf.concat(*args, **kwargs)
290 |
291 |
292 | def asarray(x):
293 | return x
294 |
295 |
296 | def expand_dims(x, axis=None):
297 | return tf.expand_dims(x, axis)
298 |
299 |
300 | def clip(x, min_value, max_value):
301 | return tf.clip_by_value(x, min_value, max_value)
302 |
303 |
304 | def floor(x):
305 | return tf.floor(x)
306 |
307 |
308 | def diag(a):
309 | return tf.map_fn(
310 | lambda x: tf.diag(x),
311 | a)
312 |
313 |
314 | def cross(a, b):
315 | return tf.cross(a, b)
316 |
317 |
318 | def stack(*args, **kwargs):
319 | return tf.stack(*args, **kwargs)
320 |
321 |
322 | def arctan2(*args, **kwargs):
323 | return tf.atan2(*args, **kwargs)
324 |
325 |
326 | def diagonal(*args, **kwargs):
327 | return tf.linalg.diag_part(*args)
328 |
329 |
330 | def mean(x, axis=None):
331 | return tf.reduce_mean(x, axis)
332 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/CONTRIBUTING.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Contributing to Geomstats
2 |
3 | Welcome to the geomstats repository!
4 | We are excited you are here and want to contribute.
5 |
6 | More details on contributing can be found on the [documentation website][link_doc].
7 |
8 | ## Practical Guide to Submitting your Contribution
9 |
10 | These guidelines are designed to make it as easy as possible to get involved.
11 | If you have any questions that are not discussed below,
12 | please let us know by opening an [issue][link_issues]!
13 |
14 | Before you start you will need to set up a free [GitHub][link_github] account and sign in.
15 | Here are some [instructions][link_signupinstructions].
16 |
17 |
18 | ## Joining the Conversation
19 |
20 | `geomstats` is maintained by a growing group of enthusiastic developers!
21 | Most of our discussions take place on [issues][link_issues].
22 |
23 |
24 | ## Contributing through GitHub
25 |
26 | [git][link_git] is a really useful tool for version control.
27 | [GitHub][link_github] sits on top of git and supports collaborative and distributed working.
28 |
29 | If you are not yet familiar with `git`, there are lots of great resources to help you *git* started!
30 | Some of our favorites include the [git Handbook][link_handbook] and
31 | the [Software Carpentry introduction to git][link_swc_intro].
32 |
33 | On GitHub, you will use [Markdown][markdown] to chat in issues and pull requests.
34 |
35 | GitHub has a really helpful page for getting started with
36 | [writing and formatting Markdown on GitHub][writing_formatting_github].
37 |
38 |
39 | ## Understanding Issues
40 |
41 | Every project on GitHub uses [issues][link_issues] slightly differently.
42 |
43 | The following outlines how ``geomstats`` developers think about these tools.
44 |
45 | * **Issues** are individual pieces of work that need to be completed to move the project forwards.
46 | A general guideline: if you find yourself tempted to write a great big issue that
47 | is difficult to describe as one unit of work, please consider splitting it into two or more issues.
48 |
49 | * Issues are assigned [labels](#issue-labels) which explain how they relate to the overall project's
50 | goals and immediate next steps.
51 |
52 |
53 | ## Making a Change
54 |
55 | We appreciate all contributions to ``geomstats``,
56 | but those accepted fastest will follow a workflow similar to the following:
57 |
58 | **1. Comment on an existing issue or open a new issue referencing your addition.**
59 |
60 | This allows other members of the ``geomstats`` development team to confirm that you are not
61 | overlapping with work that is currently underway and that everyone is on the same page
62 | with the goal of the work you are going to carry out.
63 |
64 | [This blog][link_pushpullblog] is a nice explanation of why putting this work in up front
65 | is so useful to everyone involved.
66 |
67 | **2. [Fork][link_fork] the [geomstats repository][link_geomstats] to your profile.**
68 |
69 | This is now your own unique copy of ``geomstats``.
70 | Changes here will not effect anyone else's work, so it is a safe space to explore edits to the code!
71 |
72 | Make sure to [keep your fork up to date][link_updateupstreamwiki] with the master repository.
73 |
74 | **3. Make the changes you have discussed, following the [geomstats coding style guide](#geomstats-coding-style-guide).**
75 |
76 | - Create your feature branch (`git checkout -b feature/fooBar`)
77 | - Commit your changes (`git commit -am 'Add some fooBar'`)
78 | - Push to the branch (`git push origin feature/fooBar`)
79 |
80 | Try to keep the changes focused.
81 | If you feel tempted to "branch out" then please make a [new branch][link_branches].
82 |
83 | **4. Add the corresponding unit tests.**
84 |
85 | If you are adding a new feature, do not forget to add the corresponding [unit tests][link_unit_tests].
86 | As ``geomstats`` enables numpy and tensorflow, your unit tests should run on these two backends.
87 |
88 | **5. Ensure Geomstats Coding Style Guide.**
89 |
90 | Ensure that your code is compliant with [PEP8][link_pep8],
91 | the coding style guide for python.
92 |
93 | Use [flake8][link_flake8] or [yapf][link_yapf] to automatically enforces this style.
94 |
95 |
96 | **6. Submit a [pull request][link_pullrequest].**
97 |
98 | A member of the development team will review your changes to confirm
99 | that they can be merged into the main code base.
100 |
101 | Use the Github labels to label your pull request:
102 | * ``enhancement``: enhancements or new features
103 | * ``bug``: bug fixes
104 | * ``test``: new or updated tests
105 | * ``documentation``: new or updated documentation
106 | * ``style``: style changes
107 | * ``refactoring``: refactoring existing code
108 | * ``continuous integration``: updates to continous integration infrastructure
109 |
110 |
111 | ## Recognizing Contributions
112 |
113 | We welcome and recognize all contributions from documentation to testing to code development.
114 | You can see a list of current contributors in our [README.md][link_readme].
115 | If you are new to the project, do not forget to add your name and affiliation there!
116 |
117 | ## Thank You!
118 |
119 |