├── .gitignore
├── .idea
├── .gitignore
├── BERT-chinese-text-classification-pytorch.iml
├── inspectionProfiles
│ └── profiles_settings.xml
├── misc.xml
├── modules.xml
└── vcs.xml
├── README.md
├── __init__.py
├── pybert
├── __init__.py
├── callback
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── earlystopping.py
│ ├── lrscheduler.py
│ ├── modelcheckpoint.py
│ ├── optimizater.py
│ ├── progressbar.py
│ └── trainingmonitor.py
├── common
│ └── tools.py
├── configs
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── base.py
├── dataset
│ └── __init__.py
├── io
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── bert_processor.py
│ └── task_data.py
├── model
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── nn
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ └── bert_for_multi_class.py
├── output
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── checkpoints
│ │ └── __init__.py
│ ├── embedding
│ │ └── __init__.py
│ ├── feature
│ │ └── __init__.py
│ ├── figure
│ │ └── __init__.py
│ ├── log
│ │ └── __init__.py
│ └── result
│ │ └── __init__.py
├── preprocessing
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── augmentation.py
│ └── preprocessor.py
├── pretrain
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── bert
│ │ └── base-chinese
│ │ └── __init__.py
├── test
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── predictor.py
└── train
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── losses.py
│ ├── metrics.py
│ └── trainer.py
└── run_bert.py
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
2 | __pycache__/
3 | *.py[cod]
4 | *$py.class
5 |
6 | # C extensions
7 | *.so
8 |
9 | # Distribution / packaging
10 | .Python
11 | build/
12 | develop-eggs/
13 | dist/
14 | downloads/
15 | eggs/
16 | .eggs/
17 | lib/
18 | lib64/
19 | parts/
20 | sdist/
21 | var/
22 | wheels/
23 | *.egg-info/
24 | .installed.cfg
25 | *.egg
26 | MANIFEST
27 |
28 | # PyInstaller
29 | # Usually these files are written by a python script from a template
30 | # before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it.
31 | *.manifest
32 | *.spec
33 |
34 | # Installer logs
35 | pip-log.txt
36 | pip-delete-this-directory.txt
37 |
38 | # Unit test / coverage reports
39 | htmlcov/
40 | .tox/
41 | .coverage
42 | .coverage.*
43 | .cache
44 | nosetests.xml
45 | coverage.xml
46 | *.cover
47 | .hypothesis/
48 | .pytest_cache/
49 |
50 | # Translations
51 | *.mo
52 | *.pot
53 |
54 | # Django stuff:
55 | *.log
56 | local_settings.py
57 | db.sqlite3
58 |
59 | # Flask stuff:
60 | instance/
61 | .webassets-cache
62 |
63 | # Scrapy stuff:
64 | .scrapy
65 |
66 | # Sphinx documentation
67 | docs/_build/
68 |
69 | # PyBuilder
70 | target/
71 |
72 | # Jupyter Notebook
73 | .ipynb_checkpoints
74 |
75 | # pyenv
76 | .python-version
77 |
78 | # celery beat schedule file
79 | celerybeat-schedule
80 |
81 | # SageMath parsed files
82 | *.sage.py
83 |
84 | # Environments
85 | .env
86 | .venv
87 | env/
88 | venv/
89 | ENV/
90 | env.bak/
91 | venv.bak/
92 |
93 | # Spyder project settings
94 | .spyderproject
95 | .spyproject
96 |
97 | # Rope project settings
98 | .ropeproject
99 |
100 | # mkdocs documentation
101 | /site
102 |
103 | # mypy
104 | .mypy_cache/
105 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # Default ignored files
3 | /workspace.xml
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/BERT-chinese-text-classification-pytorch.iml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/inspectionProfiles/profiles_settings.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/misc.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/modules.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/vcs.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # BERT Chinese text classification by PyTorch
2 |
3 | This repo contains a PyTorch implementation of a pretrained BERT model for chinese text classification.
4 |
5 | ## Structure of the code
6 |
7 | At the root of the project, you will see:
8 |
9 | ```text
10 | ├── pybert
11 | | └── callback
12 | | | └── lrscheduler.py
13 | | | └── trainingmonitor.py
14 | | | └── ...
15 | | └── config
16 | | | └── base.py #a configuration file for storing model parameters
17 | | └── dataset
18 | | └── io
19 | | | └── bert_processor.py
20 | | └── model
21 | | | └── nn
22 | | | └── pretrain
23 | | └── output #save the ouput of model
24 | | └── preprocessing #text preprocessing
25 | | └── train #used for training a model
26 | | | └── trainer.py
27 | | | └── ...
28 | | └── utils # a set of utility functions
29 | ├── run_bert.py
30 | ```
31 | ## Dependencies
32 |
33 | - csv
34 | - tqdm
35 | - numpy
36 | - pickle
37 | - scikit-learn
38 | - PyTorch 1.0
39 | - matplotlib
40 | - pytorch_transformers=1.1.0
41 |
42 | ## How to use the code
43 |
44 | you need download pretrained chinese bert model
45 |
46 | 1. Download the Bert pretrained model from [s3](https://s3.amazonaws.com/models.huggingface.co/bert/bert-base-chinese-pytorch_model.bin)
47 | 2. Download the Bert config file from [s3](https://s3.amazonaws.com/models.huggingface.co/bert/bert-base-chinese-config.json)
48 | 3. Download the Bert vocab file from [s3](https://s3.amazonaws.com/models.huggingface.co/bert/bert-base-chinese-vocab.txt)
49 | 4. modify `bert-base-chinese-pytorch_model.bin` to `pytorch_model.bin` , `bert-base-chinese-config.json` to `config.json` ,`bert-base-chinese-vocab.txt` to `vocab.txt`
50 | 5. place `model` ,`config` and `vocab` file into the `/pybert/pretrain/bert/base-uncased` directory.
51 | 2. `pip install pytorch-transformers` from [github](https://github.com/huggingface/pytorch-transformers).
52 | 4. Prepare [BaiduNet](https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Gn0rHHhrod6ed8LDTJ-rtA){password:ruxu}, you can modify the `io.bert_processor.py` to adapt your data.
53 | 5. Modify configuration information in `pybert/config/base.py`(the path of data,...).
54 | 6. Run `python run_bert.py --do_data` to preprocess data.
55 | 7. Run `python run_bert.py --do_train --save_best` to fine tuning bert model.
56 | 8. Run `run_bert.py --do_test --do_lower_case` to predict new data.
57 |
58 | ## Fine-tuning result
59 |
60 | ### training
61 |
62 | Epoch: 3 - loss: 0.0222 acc: 0.9939 - f1: 0.9911 val_loss: 0.0785 - val_acc: 0.9799 - val_f1: 0.9800
63 |
64 | ### classify_report
65 |
66 | | label | precision | recall | f1-score | support |
67 | | :---------: | :-------: | :----: | :------: | :-----: |
68 | | 财经 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 1500 |
69 | | 体育 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1500 |
70 | | 娱乐 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1500 |
71 | | 家居 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1500 |
72 | | 房产 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 1500 |
73 | | 教育 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 1500 |
74 | | 时尚 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 1500 |
75 | | 时政 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 1500 |
76 | | 游戏 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1500 |
77 | | 科技 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 1500 |
78 | | avg / total | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 15000 |
79 |
80 | ### training figure
81 |
82 | 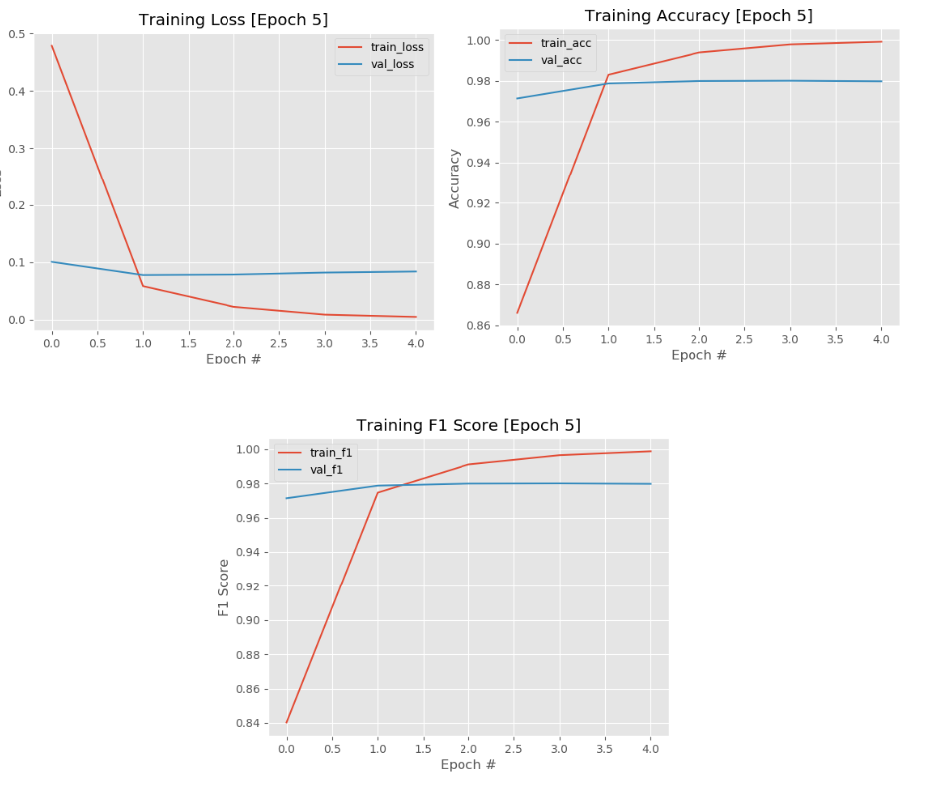
83 |
84 | ## Tips
85 |
86 | - When converting the tensorflow checkpoint into the pytorch, it's expected to choice the "bert_model.ckpt", instead of "bert_model.ckpt.index", as the input file. Otherwise, you will see that the model can learn nothing and give almost same random outputs for any inputs. This means, in fact, you have not loaded the true ckpt for your model
87 | - When using multiple GPUs, the non-tensor calculations, such as accuracy and f1_score, are not supported by DataParallel instance
88 | - As recommanded by Jocob in his paper https://arxiv.org/pdf/1810.04805.pdf, in fine-tuning tasks, the hyperparameters are expected to set as following: **Batch_size**: 16 or 32, **learning_rate**: 5e-5 or 2e-5 or 3e-5, **num_train_epoch**: 3 or 4
89 | - The pretrained model has a limit for the sentence of input that its length should is not larger than 512, the max position embedding dim. The data flows into the model as: Raw_data -> WordPieces -> Model. Note that the length of wordPieces is generally larger than that of raw_data, so a safe max length of raw_data is at ~128 - 256
90 | - Upon testing, we found that fine-tuning all layers could get much better results than those of only fine-tuning the last classfier layer. The latter is actually a feature-based way
91 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/earlystopping.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from ..common.tools import logger
3 | class EarlyStopping(object):
4 | '''
5 | """Stop training when a monitored quantity has stopped improving.
6 | # Arguments
7 | monitor: quantity to be monitored.
8 | min_delta: minimum change in the monitored quantity
9 | to qualify as an improvement, i.e. an absolute
10 | change of less than min_delta, will count as no
11 | improvement.
12 | patience: number of epochs with no improvement
13 | after which training will be stopped.
14 | verbose: verbosity mode.
15 | mode: one of {auto, min, max}. In `min` mode,
16 | training will stop when the quantity
17 | monitored has stopped decreasing; in `max`
18 | mode it will stop when the quantity
19 | monitored has stopped increasing; in `auto`
20 | mode, the direction is automatically inferred
21 | from the name of the monitored quantity.
22 | baseline: Baseline value for the monitored quantity to reach.
23 | Training will stop if the model doesn't show improvement
24 | over the baseline.
25 | restore_best_weights: whether to restore model weights from
26 | the epoch with the best value of the monitored quantity.
27 | If False, the model weights obtained at the last step of
28 | training are used.
29 |
30 | # Arguments
31 | min_delta: 最小变化
32 | patience: 多少个epoch未提高,就停止训练
33 | verbose: 信息大于,默认打印信息
34 | mode: 计算模式
35 | monitor: 计算指标
36 | baseline: 基线
37 | '''
38 | def __init__(self,
39 | min_delta = 0,
40 | patience = 10,
41 | verbose = 1,
42 | mode = 'min',
43 | monitor = 'loss',
44 | baseline = None):
45 |
46 | self.baseline = baseline
47 | self.patience = patience
48 | self.verbose = verbose
49 | self.min_delta = min_delta
50 | self.monitor = monitor
51 |
52 | assert mode in ['min','max']
53 |
54 | if mode == 'min':
55 | self.monitor_op = np.less
56 | elif mode == 'max':
57 | self.monitor_op = np.greater
58 | if self.monitor_op == np.greater:
59 | self.min_delta *= 1
60 | else:
61 | self.min_delta *= -1
62 | self.reset()
63 |
64 | def reset(self):
65 | # Allow instances to be re-used
66 | self.wait = 0
67 | self.stop_training = False
68 | if self.baseline is not None:
69 | self.best = self.baseline
70 | else:
71 | self.best = np.Inf if self.monitor_op == np.less else -np.Inf
72 |
73 | def epoch_step(self,current):
74 | if self.monitor_op(current - self.min_delta, self.best):
75 | self.best = current
76 | self.wait = 0
77 | else:
78 | self.wait += 1
79 | if self.wait >= self.patience:
80 | if self.verbose >0:
81 | logger.info(f"{self.patience} epochs with no improvement after which training will be stopped")
82 | self.stop_training = True
83 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/lrscheduler.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import warnings
4 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
5 |
6 | __all__ = ['CustomDecayLR',
7 | 'BertLR',
8 | 'CyclicLR',
9 | 'ReduceLROnPlateau',
10 | 'ReduceLRWDOnPlateau',
11 | 'CosineLRWithRestarts',
12 | ]
13 |
14 | class CustomDecayLR(object):
15 | '''
16 | 自定义学习率变化机制
17 | Example:
18 | >>> scheduler = CustomDecayLR(optimizer)
19 | >>> for epoch in range(100):
20 | >>> scheduler.epoch_step()
21 | >>> train(...)
22 | >>> ...
23 | >>> optimizer.zero_grad()
24 | >>> loss.backward()
25 | >>> optimizer.step()
26 | >>> validate(...)
27 | '''
28 | def __init__(self,optimizer,lr):
29 | self.optimizer = optimizer
30 | self.lr = lr
31 |
32 | def epoch_step(self,epoch):
33 | lr = self.lr
34 | if epoch > 12:
35 | lr = lr / 1000
36 | elif epoch > 8:
37 | lr = lr / 100
38 | elif epoch > 4:
39 | lr = lr / 10
40 | for param_group in self.optimizer.param_groups:
41 | param_group['lr'] = lr
42 |
43 | class BertLR(object):
44 | '''
45 | Bert模型内定的学习率变化机制
46 | Example:
47 | >>> scheduler = BertLR(optimizer)
48 | >>> for epoch in range(100):
49 | >>> scheduler.step()
50 | >>> train(...)
51 | >>> ...
52 | >>> optimizer.zero_grad()
53 | >>> loss.backward()
54 | >>> optimizer.step()
55 | >>> scheduler.batch_step()
56 | >>> validate(...)
57 | '''
58 | def __init__(self,optimizer,learning_rate,t_total,warmup):
59 | self.learning_rate = learning_rate
60 | self.optimizer = optimizer
61 | self.t_total = t_total
62 | self.warmup = warmup
63 |
64 | # 线性预热方式
65 | def warmup_linear(self,x, warmup=0.002):
66 | if x < warmup:
67 | return x / warmup
68 | return 1.0 - x
69 |
70 | def batch_step(self,training_step):
71 | lr_this_step = self.learning_rate * self.warmup_linear(training_step / self.t_total,self.warmup)
72 | for param_group in self.optimizer.param_groups:
73 | param_group['lr'] = lr_this_step
74 |
75 | class CyclicLR(object):
76 | '''
77 | Cyclical learning rates for training neural networks
78 | Example:
79 | >>> scheduler = CyclicLR(optimizer)
80 | >>> for epoch in range(100):
81 | >>> scheduler.step()
82 | >>> train(...)
83 | >>> ...
84 | >>> optimizer.zero_grad()
85 | >>> loss.backward()
86 | >>> optimizer.step()
87 | >>> scheduler.batch_step()
88 | >>> validate(...)
89 | '''
90 | def __init__(self, optimizer, base_lr=1e-3, max_lr=6e-3,
91 | step_size=2000, mode='triangular', gamma=1.,
92 | scale_fn=None, scale_mode='cycle', last_batch_iteration=-1):
93 |
94 | if not isinstance(optimizer, Optimizer):
95 | raise TypeError('{} is not an Optimizer'.format(
96 | type(optimizer).__name__))
97 |
98 | self.optimizer = optimizer
99 |
100 | if isinstance(base_lr, list) or isinstance(base_lr, tuple):
101 | if len(base_lr) != len(optimizer.param_groups):
102 | raise ValueError("expected {} base_lr, got {}".format(
103 | len(optimizer.param_groups), len(base_lr)))
104 | self.base_lrs = list(base_lr)
105 | else:
106 | self.base_lrs = [base_lr] * len(optimizer.param_groups)
107 |
108 | if isinstance(max_lr, list) or isinstance(max_lr, tuple):
109 | if len(max_lr) != len(optimizer.param_groups):
110 | raise ValueError("expected {} max_lr, got {}".format(
111 | len(optimizer.param_groups), len(max_lr)))
112 | self.max_lrs = list(max_lr)
113 | else:
114 | self.max_lrs = [max_lr] * len(optimizer.param_groups)
115 |
116 | self.step_size = step_size
117 |
118 | if mode not in ['triangular', 'triangular2', 'exp_range'] \
119 | and scale_fn is None:
120 | raise ValueError('mode is invalid and scale_fn is None')
121 |
122 | self.mode = mode
123 | self.gamma = gamma
124 |
125 | if scale_fn is None:
126 | if self.mode == 'triangular':
127 | self.scale_fn = self._triangular_scale_fn
128 | self.scale_mode = 'cycle'
129 | elif self.mode == 'triangular2':
130 | self.scale_fn = self._triangular2_scale_fn
131 | self.scale_mode = 'cycle'
132 | elif self.mode == 'exp_range':
133 | self.scale_fn = self._exp_range_scale_fn
134 | self.scale_mode = 'iterations'
135 | else:
136 | self.scale_fn = scale_fn
137 | self.scale_mode = scale_mode
138 |
139 | self.batch_step(last_batch_iteration + 1)
140 | self.last_batch_iteration = last_batch_iteration
141 |
142 | def _triangular_scale_fn(self, x):
143 | return 1.
144 |
145 | def _triangular2_scale_fn(self, x):
146 | return 1 / (2. ** (x - 1))
147 |
148 | def _exp_range_scale_fn(self, x):
149 | return self.gamma**(x)
150 |
151 | def get_lr(self):
152 | step_size = float(self.step_size)
153 | cycle = np.floor(1 + self.last_batch_iteration / (2 * step_size))
154 | x = np.abs(self.last_batch_iteration / step_size - 2 * cycle + 1)
155 |
156 | lrs = []
157 | param_lrs = zip(self.optimizer.param_groups, self.base_lrs, self.max_lrs)
158 | for param_group, base_lr, max_lr in param_lrs:
159 | base_height = (max_lr - base_lr) * np.maximum(0, (1 - x))
160 | if self.scale_mode == 'cycle':
161 | lr = base_lr + base_height * self.scale_fn(cycle)
162 | else:
163 | lr = base_lr + base_height * self.scale_fn(self.last_batch_iteration)
164 | lrs.append(lr)
165 | return lrs
166 |
167 | def batch_step(self, batch_iteration=None):
168 | if batch_iteration is None:
169 | batch_iteration = self.last_batch_iteration + 1
170 | self.last_batch_iteration = batch_iteration
171 | for param_group, lr in zip(self.optimizer.param_groups, self.get_lr()):
172 | param_group['lr'] = lr
173 |
174 | class ReduceLROnPlateau(object):
175 | """Reduce learning rate when a metric has stopped improving.
176 | Models often benefit from reducing the learning rate by a factor
177 | of 2-10 once learning stagnates. This scheduler reads a metrics
178 | quantity and if no improvement is seen for a 'patience' number
179 | of epochs, the learning rate is reduced.
180 |
181 | Args:
182 | factor: factor by which the learning rate will
183 | be reduced. new_lr = lr * factor
184 | patience: number of epochs with no improvement
185 | after which learning rate will be reduced.
186 | verbose: int. 0: quiet, 1: update messages.
187 | mode: one of {min, max}. In `min` mode,
188 | lr will be reduced when the quantity
189 | monitored has stopped decreasing; in `max`
190 | mode it will be reduced when the quantity
191 | monitored has stopped increasing.
192 | epsilon: threshold for measuring the new optimum,
193 | to only focus on significant changes.
194 | cooldown: number of epochs to wait before resuming
195 | normal operation after lr has been reduced.
196 | min_lr: lower bound on the learning rate.
197 |
198 |
199 | Example:
200 | >>> optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1, momentum=0.9)
201 | >>> scheduler = ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, 'min')
202 | >>> for epoch in range(10):
203 | >>> train(...)
204 | >>> val_acc, val_loss = validate(...)
205 | >>> scheduler.epoch_step(val_loss, epoch)
206 | """
207 |
208 | def __init__(self, optimizer, mode='min', factor=0.1, patience=10,
209 | verbose=0, epsilon=1e-4, cooldown=0, min_lr=0,eps=1e-8):
210 |
211 | super(ReduceLROnPlateau, self).__init__()
212 | assert isinstance(optimizer, Optimizer)
213 | if factor >= 1.0:
214 | raise ValueError('ReduceLROnPlateau '
215 | 'does not support a factor >= 1.0.')
216 | self.factor = factor
217 | self.min_lr = min_lr
218 | self.epsilon = epsilon
219 | self.patience = patience
220 | self.verbose = verbose
221 | self.cooldown = cooldown
222 | self.cooldown_counter = 0 # Cooldown counter.
223 | self.monitor_op = None
224 | self.wait = 0
225 | self.best = 0
226 | self.mode = mode
227 | self.optimizer = optimizer
228 | self.eps = eps
229 | self._reset()
230 |
231 | def _reset(self):
232 | """Resets wait counter and cooldown counter.
233 | """
234 | if self.mode not in ['min', 'max']:
235 | raise RuntimeError('Learning Rate Plateau Reducing mode %s is unknown!')
236 | if self.mode == 'min':
237 | self.monitor_op = lambda a, b: np.less(a, b - self.epsilon)
238 | self.best = np.Inf
239 | else:
240 | self.monitor_op = lambda a, b: np.greater(a, b + self.epsilon)
241 | self.best = -np.Inf
242 | self.cooldown_counter = 0
243 | self.wait = 0
244 |
245 | def reset(self):
246 | self._reset()
247 |
248 | def epoch_step(self, metrics, epoch):
249 | current = metrics
250 | if current is None:
251 | warnings.warn('Learning Rate Plateau Reducing requires metrics available!', RuntimeWarning)
252 | else:
253 | if self.in_cooldown():
254 | self.cooldown_counter -= 1
255 | self.wait = 0
256 |
257 | if self.monitor_op(current, self.best):
258 | self.best = current
259 | self.wait = 0
260 | elif not self.in_cooldown():
261 | if self.wait >= self.patience:
262 | for param_group in self.optimizer.param_groups:
263 | old_lr = float(param_group['lr'])
264 | if old_lr > self.min_lr + self.eps:
265 | new_lr = old_lr * self.factor
266 | new_lr = max(new_lr, self.min_lr)
267 | param_group['lr'] = new_lr
268 | if self.verbose > 0:
269 | print('\nEpoch %05d: reducing learning rate to %s.' % (epoch, new_lr))
270 | self.cooldown_counter = self.cooldown
271 | self.wait = 0
272 | self.wait += 1
273 |
274 | def in_cooldown(self):
275 | return self.cooldown_counter > 0
276 |
277 | class ReduceLRWDOnPlateau(ReduceLROnPlateau):
278 | """Reduce learning rate and weight decay when a metric has stopped
279 | improving. Models often benefit from reducing the learning rate by
280 | a factor of 2-10 once learning stagnates. This scheduler reads a metric
281 | quantity and if no improvement is seen for a 'patience' number
282 | of epochs, the learning rate and weight decay factor is reduced for
283 | optimizers that implement the the weight decay method from the paper
284 | `Fixing Weight Decay Regularization in Adam`_.
285 |
286 | .. _Fixing Weight Decay Regularization in Adam:
287 | https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.05101
288 | for AdamW or SGDW
289 | Example:
290 | >>> optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=0.1, weight_decay=1e-3)
291 | >>> scheduler = ReduceLRWDOnPlateau(optimizer, 'min')
292 | >>> for epoch in range(10):
293 | >>> train(...)
294 | >>> val_loss = validate(...)
295 | >>> # Note that step should be called after validate()
296 | >>> scheduler.epoch_step(val_loss)
297 | """
298 | def epoch_step(self, metrics, epoch):
299 | current = metrics
300 | if current is None:
301 | warnings.warn('Learning Rate Plateau Reducing requires metrics available!', RuntimeWarning)
302 | else:
303 | if self.in_cooldown():
304 | self.cooldown_counter -= 1
305 | self.wait = 0
306 |
307 | if self.monitor_op(current, self.best):
308 | self.best = current
309 | self.wait = 0
310 | elif not self.in_cooldown():
311 | if self.wait >= self.patience:
312 | for param_group in self.optimizer.param_groups:
313 | old_lr = float(param_group['lr'])
314 | if old_lr > self.min_lr + self.eps:
315 | new_lr = old_lr * self.factor
316 | new_lr = max(new_lr, self.min_lr)
317 | param_group['lr'] = new_lr
318 | if self.verbose > 0:
319 | print('\nEpoch %d: reducing learning rate to %s.' % (epoch, new_lr))
320 | if param_group['weight_decay'] != 0:
321 | old_weight_decay = float(param_group['weight_decay'])
322 | new_weight_decay = max(old_weight_decay * self.factor, self.min_lr)
323 | if old_weight_decay > new_weight_decay + self.eps:
324 | param_group['weight_decay'] = new_weight_decay
325 | if self.verbose:
326 | print('\nEpoch {epoch}: reducing weight decay factor of group {i} to {new_weight_decay:.4e}.')
327 | self.cooldown_counter = self.cooldown
328 | self.wait = 0
329 | self.wait += 1
330 |
331 | class CosineLRWithRestarts(object):
332 | """Decays learning rate with cosine annealing, normalizes weight decay
333 | hyperparameter value, implements restarts.
334 | https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.05101
335 |
336 | Args:
337 | optimizer (Optimizer): Wrapped optimizer.
338 | batch_size: minibatch size
339 | epoch_size: training samples per epoch
340 | restart_period: epoch count in the first restart period
341 | t_mult: multiplication factor by which the next restart period will extend/shrink
342 |
343 | Example:
344 | >>> scheduler = CosineLRWithRestarts(optimizer, 32, 1024, restart_period=5, t_mult=1.2)
345 | >>> for epoch in range(100):
346 | >>> scheduler.step()
347 | >>> train(...)
348 | >>> ...
349 | >>> optimizer.zero_grad()
350 | >>> loss.backward()
351 | >>> optimizer.step()
352 | >>> scheduler.batch_step()
353 | >>> validate(...)
354 | """
355 |
356 | def __init__(self, optimizer, batch_size, epoch_size, restart_period=100,
357 | t_mult=2, last_epoch=-1, eta_threshold=1000, verbose=False):
358 | if not isinstance(optimizer, Optimizer):
359 | raise TypeError('{} is not an Optimizer'.format(
360 | type(optimizer).__name__))
361 | self.optimizer = optimizer
362 | if last_epoch == -1:
363 | for group in optimizer.param_groups:
364 | group.setdefault('initial_lr', group['lr'])
365 | else:
366 | for i, group in enumerate(optimizer.param_groups):
367 | if 'initial_lr' not in group:
368 | raise KeyError("param 'initial_lr' is not specified "
369 | "in param_groups[{}] when resuming an"
370 | " optimizer".format(i))
371 | self.base_lrs = list(map(lambda group: group['initial_lr'],
372 | optimizer.param_groups))
373 |
374 | self.last_epoch = last_epoch
375 | self.batch_size = batch_size
376 | self.iteration = 0
377 | self.epoch_size = epoch_size
378 | self.eta_threshold = eta_threshold
379 | self.t_mult = t_mult
380 | self.verbose = verbose
381 | self.base_weight_decays = list(map(lambda group: group['weight_decay'],
382 | optimizer.param_groups))
383 | self.restart_period = restart_period
384 | self.restarts = 0
385 | self.t_epoch = -1
386 | self.batch_increments = []
387 | self._set_batch_increment()
388 |
389 | def _schedule_eta(self):
390 | """
391 | Threshold value could be adjusted to shrink eta_min and eta_max values.
392 | """
393 | eta_min = 0
394 | eta_max = 1
395 | if self.restarts <= self.eta_threshold:
396 | return eta_min, eta_max
397 | else:
398 | d = self.restarts - self.eta_threshold
399 | k = d * 0.09
400 | return (eta_min + k, eta_max - k)
401 |
402 | def get_lr(self, t_cur):
403 | eta_min, eta_max = self._schedule_eta()
404 |
405 | eta_t = (eta_min + 0.5 * (eta_max - eta_min)
406 | * (1. + math.cos(math.pi *
407 | (t_cur / self.restart_period))))
408 |
409 | weight_decay_norm_multi = math.sqrt(self.batch_size /
410 | (self.epoch_size *
411 | self.restart_period))
412 | lrs = [base_lr * eta_t for base_lr in self.base_lrs]
413 | weight_decays = [base_weight_decay * eta_t * weight_decay_norm_multi
414 | for base_weight_decay in self.base_weight_decays]
415 |
416 | if self.t_epoch % self.restart_period < self.t_epoch:
417 | if self.verbose:
418 | print("Restart at epoch {}".format(self.last_epoch))
419 | self.restart_period *= self.t_mult
420 | self.restarts += 1
421 | self.t_epoch = 0
422 |
423 | return zip(lrs, weight_decays)
424 |
425 | def _set_batch_increment(self):
426 | d, r = divmod(self.epoch_size, self.batch_size)
427 | batches_in_epoch = d + 2 if r > 0 else d + 1
428 | self.iteration = 0
429 | self.batch_increments = list(np.linspace(0, 1, batches_in_epoch))
430 |
431 | def batch_step(self):
432 | self.last_epoch += 1
433 | self.t_epoch += 1
434 | self._set_batch_increment()
435 | try:
436 | t_cur = self.t_epoch + self.batch_increments[self.iteration]
437 | self.iteration += 1
438 | except (IndexError):
439 | raise RuntimeError("Epoch size and batch size used in the "
440 | "training loop and while initializing "
441 | "scheduler should be the same.")
442 |
443 | for param_group, (lr, weight_decay) in zip(self.optimizer.param_groups,self.get_lr(t_cur)):
444 | param_group['lr'] = lr
445 | param_group['weight_decay'] = weight_decay
446 |
447 |
448 | class NoamLR(object):
449 | '''
450 | 主要参考论文<< Attention Is All You Need>>中的学习更新方式
451 | Example:
452 | >>> scheduler = NoamLR(d_model,factor,warm_up,optimizer)
453 | >>> for epoch in range(100):
454 | >>> scheduler.step()
455 | >>> train(...)
456 | >>> ...
457 | >>> glopab_step += 1
458 | >>> optimizer.zero_grad()
459 | >>> loss.backward()
460 | >>> optimizer.step()
461 | >>> scheduler.batch_step(global_step)
462 | >>> validate(...)
463 | '''
464 | def __init__(self,d_model,factor,warm_up,optimizer):
465 | self.optimizer = optimizer
466 | self.warm_up = warm_up
467 | self.factor = factor
468 | self.d_model = d_model
469 | self._lr = 0
470 |
471 | def get_lr(self,step):
472 | lr = self.factor * (self.d_model ** (-0.5) * min(step ** (-0.5),step * self.warm_up ** (-1.5)))
473 | return lr
474 |
475 | def batch_step(self,step):
476 | '''
477 | update parameters and rate
478 | :return:
479 | '''
480 | lr = self.get_lr(step)
481 | for p in self.optimizer.param_groups:
482 | p['lr'] = lr
483 | self._lr = lr
484 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/modelcheckpoint.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from pathlib import Path
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import torch
4 | from ..common.tools import logger
5 |
6 | class ModelCheckpoint(object):
7 | """Save the model after every epoch.
8 | # Arguments
9 | checkpoint_dir: string, path to save the model file.
10 | monitor: quantity to monitor.
11 | verbose: verbosity mode, 0 or 1.
12 | save_best_only: if `save_best_only=True`,
13 | the latest best model according to
14 | the quantity monitored will not be overwritten.
15 | mode: one of {auto, min, max}.
16 | If `save_best_only=True`, the decision
17 | to overwrite the current save file is made
18 | based on either the maximization or the
19 | minimization of the monitored quantity. For `val_acc`,
20 | this should be `max`, for `val_loss` this should
21 | be `min`, etc. In `auto` mode, the direction is
22 | automatically inferred from the name of the monitored quantity.
23 | """
24 | def __init__(self, checkpoint_dir,
25 | monitor,
26 | arch,
27 | mode='min',
28 | epoch_freq=1,
29 | best = None,
30 | save_best_only = True):
31 | if isinstance(checkpoint_dir,Path):
32 | checkpoint_dir = checkpoint_dir
33 | else:
34 | checkpoint_dir = Path(checkpoint_dir)
35 | assert checkpoint_dir.is_dir()
36 | checkpoint_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
37 | self.base_path = checkpoint_dir
38 | self.arch = arch
39 | self.monitor = monitor
40 | self.epoch_freq = epoch_freq
41 | self.save_best_only = save_best_only
42 |
43 | # 计算模式
44 | if mode == 'min':
45 | self.monitor_op = np.less
46 | self.best = np.Inf
47 |
48 | elif mode == 'max':
49 | self.monitor_op = np.greater
50 | self.best = -np.Inf
51 | # 这里主要重新加载模型时候
52 | #对best重新赋值
53 | if best:
54 | self.best = best
55 |
56 | if save_best_only:
57 | self.model_name = f"BEST_{arch}_MODEL.pth"
58 |
59 | def epoch_step(self, state,current):
60 | '''
61 | :param state: 需要保存的信息
62 | :param current: 当前判断指标
63 | :return:
64 | '''
65 | if self.save_best_only:
66 | if self.monitor_op(current, self.best):
67 | logger.info(f"\nEpoch {state['epoch']}: {self.monitor} improved from {self.best:.5f} to {current:.5f}")
68 | self.best = current
69 | state['best'] = self.best
70 | best_path = self.base_path/ self.model_name
71 | torch.save(state, str(best_path))
72 |
73 | else:
74 | filename = self.base_path / f"epoch_{state['epoch']}_{state[self.monitor]}_{self.arch}_model.bin"
75 | if state['epoch'] % self.epoch_freq == 0:
76 | logger.info(f"\nEpoch {state['epoch']}: save model to disk.")
77 | torch.save(state, str(filename))
78 |
79 | def bert_epoch_step(self, state,current):
80 | model_to_save = state['model']
81 | if self.save_best_only:
82 | if self.monitor_op(current, self.best):
83 | logger.info(f"\nEpoch {state['epoch']}: {self.monitor} improved from {self.best:.5f} to {current:.5f}")
84 | self.best = current
85 | state['best'] = self.best
86 | model_to_save.save_pretrained(str(self.base_path))
87 | output_config_file = self.base_path / 'configs.json'
88 | with open(str(output_config_file), 'w') as f:
89 | f.write(model_to_save.config.to_json_string())
90 | state.pop("model")
91 | torch.save(state,self.base_path / 'checkpoint_info.bin')
92 |
93 |
94 | else:
95 | if state['epoch'] % self.epoch_freq == 0:
96 | save_path = self.base_path / f"checkpoint-epoch-{state['epoch']}"
97 | save_path.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
98 | logger.info(f"\nEpoch {state['epoch']}: save model to disk.")
99 | model_to_save.save_pretrained(save_path)
100 | output_config_file = save_path / 'configs.json'
101 | with open(str(output_config_file), 'w') as f:
102 | f.write(model_to_save.config.to_json_string())
103 | state.pop("model")
104 | torch.save(state, save_path / 'checkpoint_info.bin')
105 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/optimizater.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # encofing:utf-8
2 | import math
3 | import torch
4 | import itertools as it
5 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
6 |
7 | __call__ = ['SGDW', 'AdamW', 'AdaBound', 'Lookahead', 'RAdam']
8 |
9 |
10 | class SGDW(Optimizer):
11 | r"""Implements stochastic gradient descent (optionally with momentum) with
12 | weight decay from the paper `Fixing Weight Decay Regularization in Adam`_.
13 |
14 | Nesterov momentum is based on the formula from
15 | `On the importance of initialization and momentum in deep learning`__.
16 |
17 | Args:
18 | params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining
19 | parameter groups
20 | lr (float): learning rate
21 | momentum (float, optional): momentum factor (default: 0)
22 | weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay factor (default: 0)
23 | dampening (float, optional): dampening for momentum (default: 0)
24 | nesterov (bool, optional): enables Nesterov momentum (default: False)
25 |
26 | .. _Fixing Weight Decay Regularization in Adam:
27 | https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.05101
28 |
29 | Example:
30 | >>> model = LSTM()
31 | >>> optimizer = SGDW(model.parameters(), lr=0.1, momentum=0.9,weight_decay=1e-5)
32 | """
33 |
34 | def __init__(self, params, lr=0.1, momentum=0, dampening=0,
35 | weight_decay=0, nesterov=False):
36 | if lr < 0.0:
37 | raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
38 | if momentum < 0.0:
39 | raise ValueError("Invalid momentum value: {}".format(momentum))
40 | if weight_decay < 0.0:
41 | raise ValueError("Invalid weight_decay value: {}".format(weight_decay))
42 |
43 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, momentum=momentum, dampening=dampening,
44 | weight_decay=weight_decay, nesterov=nesterov)
45 | if nesterov and (momentum <= 0 or dampening != 0):
46 | raise ValueError("Nesterov momentum requires a momentum and zero dampening")
47 | super(SGDW, self).__init__(params, defaults)
48 |
49 | def __setstate__(self, state):
50 | super(SGDW, self).__setstate__(state)
51 | for group in self.param_groups:
52 | group.setdefault('nesterov', False)
53 |
54 | def step(self, closure=None):
55 | """Performs a single optimization step.
56 |
57 | Arguments:
58 | closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
59 | and returns the loss.
60 | """
61 | loss = None
62 | if closure is not None:
63 | loss = closure()
64 |
65 | for group in self.param_groups:
66 | weight_decay = group['weight_decay']
67 | momentum = group['momentum']
68 | dampening = group['dampening']
69 | nesterov = group['nesterov']
70 |
71 | for p in group['params']:
72 | if p.grad is None:
73 | continue
74 | d_p = p.grad.data
75 |
76 | if momentum != 0:
77 | param_state = self.state[p]
78 | if 'momentum_buffer' not in param_state:
79 | buf = param_state['momentum_buffer'] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
80 | buf.mul_(momentum).add_(d_p)
81 | else:
82 | buf = param_state['momentum_buffer']
83 | buf.mul_(momentum).add_(1 - dampening, d_p)
84 | if nesterov:
85 | d_p = d_p.add(momentum, buf)
86 | else:
87 | d_p = buf
88 |
89 | if weight_decay != 0:
90 | p.data.add_(-weight_decay, p.data)
91 |
92 | p.data.add_(-group['lr'], d_p)
93 |
94 | return loss
95 |
96 |
97 | class AdamW(Optimizer):
98 | """Implements Adam algorithm.
99 |
100 | Arguments:
101 | params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining
102 | parameter groups
103 | lr (float, optional): learning rate (default: 1e-3)
104 | betas (Tuple[float, float], optional): coefficients used for computing
105 | running averages of gradient and its square (default: (0.9, 0.999))
106 | eps (float, optional): term added to the denominator to improve
107 | numerical stability (default: 1e-8)
108 | weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: 0)
109 | amsgrad (boolean, optional): whether to use the AMSGrad variant of this
110 | algorithm from the paper `On the Convergence of Adam and Beyond`_
111 |
112 | Example:
113 | >>> model = LSTM()
114 | >>> optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3, weight_decay=1e-5)
115 | """
116 |
117 | def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-3, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-8,
118 | weight_decay=0, amsgrad=False):
119 | if lr < 0.0:
120 | raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
121 | if not 0.0 <= betas[0] < 1.0:
122 | raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 0: {}".format(betas[0]))
123 | if not 0.0 <= betas[1] < 1.0:
124 | raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 1: {}".format(betas[1]))
125 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, betas=betas, eps=eps, weight_decay=weight_decay, amsgrad=amsgrad)
126 | # super(AdamW, self).__init__(params, defaults)
127 | super().__init__(params, defaults)
128 |
129 | def step(self, closure=None):
130 | """Performs a single optimization step.
131 |
132 | Arguments:
133 | closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
134 | and returns the loss.
135 | """
136 | loss = None
137 | if closure is not None:
138 | loss = closure()
139 |
140 | for group in self.param_groups:
141 | for p in group['params']:
142 | if p.grad is None:
143 | continue
144 | grad = p.grad.data
145 | if grad.is_sparse:
146 | raise RuntimeError('Adam does not support sparse gradients, please consider SparseAdam instead')
147 | amsgrad = group['amsgrad']
148 |
149 | state = self.state[p]
150 |
151 | # State initialization
152 | if len(state) == 0:
153 | state['step'] = 0
154 | # Exponential moving average of gradient values
155 | state['exp_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
156 | # Exponential moving average of squared gradient values
157 | state['exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
158 | if amsgrad:
159 | # Maintains max of all exp. moving avg. of sq. grad. values
160 | state['max_exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
161 |
162 | exp_avg, exp_avg_sq = state['exp_avg'], state['exp_avg_sq']
163 | if amsgrad:
164 | max_exp_avg_sq = state['max_exp_avg_sq']
165 | beta1, beta2 = group['betas']
166 |
167 | state['step'] += 1
168 |
169 | # Decay the first and second moment running average coefficient
170 | exp_avg.mul_(beta1).add_(1 - beta1, grad)
171 | exp_avg_sq.mul_(beta2).addcmul_(1 - beta2, grad, grad)
172 | if amsgrad:
173 | # Maintains the maximum of all 2nd moment running avg. till now
174 | torch.max(max_exp_avg_sq, exp_avg_sq, out=max_exp_avg_sq)
175 | # Use the max. for normalizing running avg. of gradient
176 | denom = max_exp_avg_sq.sqrt().add_(group['eps'])
177 | else:
178 | denom = exp_avg_sq.sqrt().add_(group['eps'])
179 |
180 | bias_correction1 = 1 - beta1 ** state['step']
181 | bias_correction2 = 1 - beta2 ** state['step']
182 | step_size = group['lr'] * math.sqrt(bias_correction2) / bias_correction1
183 |
184 | if group['weight_decay'] != 0:
185 | decayed_weights = torch.mul(p.data, group['weight_decay'])
186 | p.data.addcdiv_(-step_size, exp_avg, denom)
187 | p.data.sub_(decayed_weights)
188 | else:
189 | p.data.addcdiv_(-step_size, exp_avg, denom)
190 |
191 | return loss
192 |
193 |
194 | class AdaBound(Optimizer):
195 | """Implements AdaBound algorithm.
196 | It has been proposed in `Adaptive Gradient Methods with Dynamic Bound of Learning Rate`_.
197 | Arguments:
198 | params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining
199 | parameter groups
200 | lr (float, optional): Adam learning rate (default: 1e-3)
201 | betas (Tuple[float, float], optional): coefficients used for computing
202 | running averages of gradient and its square (default: (0.9, 0.999))
203 | final_lr (float, optional): final (SGD) learning rate (default: 0.1)
204 | gamma (float, optional): convergence speed of the bound functions (default: 1e-3)
205 | eps (float, optional): term added to the denominator to improve
206 | numerical stability (default: 1e-8)
207 | weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: 0)
208 | amsbound (boolean, optional): whether to use the AMSBound variant of this algorithm
209 | .. Adaptive Gradient Methods with Dynamic Bound of Learning Rate:
210 | https://openreview.net/forum?id=Bkg3g2R9FX
211 | Example:
212 | >>> model = LSTM()
213 | >>> optimizer = AdaBound(model.parameters())
214 | """
215 |
216 | def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-3, betas=(0.9, 0.999), final_lr=0.1, gamma=1e-3,
217 | eps=1e-8, weight_decay=0, amsbound=False):
218 | if not 0.0 <= lr:
219 | raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
220 | if not 0.0 <= eps:
221 | raise ValueError("Invalid epsilon value: {}".format(eps))
222 | if not 0.0 <= betas[0] < 1.0:
223 | raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 0: {}".format(betas[0]))
224 | if not 0.0 <= betas[1] < 1.0:
225 | raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 1: {}".format(betas[1]))
226 | if not 0.0 <= final_lr:
227 | raise ValueError("Invalid final learning rate: {}".format(final_lr))
228 | if not 0.0 <= gamma < 1.0:
229 | raise ValueError("Invalid gamma parameter: {}".format(gamma))
230 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, betas=betas, final_lr=final_lr, gamma=gamma, eps=eps,
231 | weight_decay=weight_decay, amsbound=amsbound)
232 | super(AdaBound, self).__init__(params, defaults)
233 |
234 | self.base_lrs = list(map(lambda group: group['lr'], self.param_groups))
235 |
236 | def __setstate__(self, state):
237 | super(AdaBound, self).__setstate__(state)
238 | for group in self.param_groups:
239 | group.setdefault('amsbound', False)
240 |
241 | def step(self, closure=None):
242 | """Performs a single optimization step.
243 | Arguments:
244 | closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
245 | and returns the loss.
246 | Examples:
247 | >>> model = resnet()
248 | >>> optimizer = adabound.AdaBound(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3, final_lr=0.1)
249 | """
250 | loss = None
251 | if closure is not None:
252 | loss = closure()
253 |
254 | for group, base_lr in zip(self.param_groups, self.base_lrs):
255 | for p in group['params']:
256 | if p.grad is None:
257 | continue
258 | grad = p.grad.data
259 | if grad.is_sparse:
260 | raise RuntimeError(
261 | 'Adam does not support sparse gradients, please consider SparseAdam instead')
262 | amsbound = group['amsbound']
263 |
264 | state = self.state[p]
265 |
266 | # State initialization
267 | if len(state) == 0:
268 | state['step'] = 0
269 | # Exponential moving average of gradient values
270 | state['exp_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
271 | # Exponential moving average of squared gradient values
272 | state['exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
273 | if amsbound:
274 | # Maintains max of all exp. moving avg. of sq. grad. values
275 | state['max_exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
276 |
277 | exp_avg, exp_avg_sq = state['exp_avg'], state['exp_avg_sq']
278 | if amsbound:
279 | max_exp_avg_sq = state['max_exp_avg_sq']
280 | beta1, beta2 = group['betas']
281 |
282 | state['step'] += 1
283 |
284 | if group['weight_decay'] != 0:
285 | grad = grad.add(group['weight_decay'], p.data)
286 |
287 | # Decay the first and second moment running average coefficient
288 | exp_avg.mul_(beta1).add_(1 - beta1, grad)
289 | exp_avg_sq.mul_(beta2).addcmul_(1 - beta2, grad, grad)
290 | if amsbound:
291 | # Maintains the maximum of all 2nd moment running avg. till now
292 | torch.max(max_exp_avg_sq, exp_avg_sq, out=max_exp_avg_sq)
293 | # Use the max. for normalizing running avg. of gradient
294 | denom = max_exp_avg_sq.sqrt().add_(group['eps'])
295 | else:
296 | denom = exp_avg_sq.sqrt().add_(group['eps'])
297 |
298 | bias_correction1 = 1 - beta1 ** state['step']
299 | bias_correction2 = 1 - beta2 ** state['step']
300 | step_size = group['lr'] * math.sqrt(bias_correction2) / bias_correction1
301 |
302 | # Applies bounds on actual learning rate
303 | # lr_scheduler cannot affect final_lr, this is a workaround to apply lr decay
304 | final_lr = group['final_lr'] * group['lr'] / base_lr
305 | lower_bound = final_lr * (1 - 1 / (group['gamma'] * state['step'] + 1))
306 | upper_bound = final_lr * (1 + 1 / (group['gamma'] * state['step']))
307 | step_size = torch.full_like(denom, step_size)
308 | step_size.div_(denom).clamp_(lower_bound, upper_bound).mul_(exp_avg)
309 |
310 | p.data.add_(-step_size)
311 |
312 | return loss
313 |
314 |
315 | class Lookahead(Optimizer):
316 | '''
317 | a PyTorch implementation of the Lookahead Optimizer from th paper
318 | Lookahead Optimizer: k steps forward, 1 step back.
319 |
320 | https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.08610
321 |
322 | Example:
323 | >>> from optimizer import Lookahead
324 | >>> import torch.optim as optim
325 | >>> base_optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
326 | >>> optimizer = Lookahead(base_optimizer=base_optimizer,k=5,alpha=0.5)
327 | '''
328 |
329 | def __init__(self, base_optimizer, alpha=0.5, k=6):
330 | if not 0.0 <= alpha <= 1.0:
331 | raise ValueError(f'Invalid slow update rate: {alpha}')
332 | if not 1 <= k:
333 | raise ValueError(f'Invalid lookahead steps: {k}')
334 | self.optimizer = base_optimizer
335 | self.param_groups = self.optimizer.param_groups
336 | self.alpha = alpha
337 | self.k = k
338 | for group in self.param_groups:
339 | group["step_counter"] = 0
340 | self.slow_weights = [[p.clone().detach() for p in group['params']]
341 | for group in self.param_groups]
342 |
343 | for w in it.chain(*self.slow_weights):
344 | w.requires_grad = False
345 |
346 | def step(self, closure=None):
347 | loss = None
348 | if closure is not None:
349 | loss = closure()
350 | loss = self.optimizer.step()
351 | for group, slow_weights in zip(self.param_groups, self.slow_weights):
352 | group['step_counter'] += 1
353 | if group['step_counter'] % self.k != 0:
354 | continue
355 | for p, q in zip(group['params'], slow_weights):
356 | if p.grad is None:
357 | continue
358 | q.data.add_(self.alpha, p.data - q.data)
359 | p.data.copy_(q.data)
360 | return loss
361 |
362 |
363 | class RAdam(Optimizer):
364 | '''
365 | a PyTorch implementation of the RAdam Optimizer from th paper
366 | On the Variance of the Adaptive Learning Rate and Beyond.
367 |
368 | https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.03265
369 | Example:
370 | >>> from optimizer import RAdam
371 | >>> optimizer = RAdam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
372 | '''
373 |
374 | def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-3, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-8, weight_decay=0):
375 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, betas=betas, eps=eps, weight_decay=weight_decay)
376 | self.buffer = [[None, None, None] for ind in range(10)]
377 | super(RAdam, self).__init__(params, defaults)
378 |
379 | def __setstate__(self, state):
380 | super(RAdam, self).__setstate__(state)
381 |
382 | def step(self, closure=None):
383 |
384 | loss = None
385 | if closure is not None:
386 | loss = closure()
387 |
388 | for group in self.param_groups:
389 |
390 | for p in group['params']:
391 | if p.grad is None:
392 | continue
393 | grad = p.grad.data.float()
394 | if grad.is_sparse:
395 | raise RuntimeError('RAdam does not support sparse gradients')
396 |
397 | p_data_fp32 = p.data.float()
398 |
399 | state = self.state[p]
400 |
401 | if len(state) == 0:
402 | state['step'] = 0
403 | state['exp_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p_data_fp32)
404 | state['exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p_data_fp32)
405 | else:
406 | state['exp_avg'] = state['exp_avg'].type_as(p_data_fp32)
407 | state['exp_avg_sq'] = state['exp_avg_sq'].type_as(p_data_fp32)
408 |
409 | exp_avg, exp_avg_sq = state['exp_avg'], state['exp_avg_sq']
410 | beta1, beta2 = group['betas']
411 |
412 | exp_avg_sq.mul_(beta2).addcmul_(1 - beta2, grad, grad)
413 | exp_avg.mul_(beta1).add_(1 - beta1, grad)
414 |
415 | state['step'] += 1
416 | buffered = self.buffer[int(state['step'] % 10)]
417 | if state['step'] == buffered[0]:
418 | N_sma, step_size = buffered[1], buffered[2]
419 | else:
420 | buffered[0] = state['step']
421 | beta2_t = beta2 ** state['step']
422 | N_sma_max = 2 / (1 - beta2) - 1
423 | N_sma = N_sma_max - 2 * state['step'] * beta2_t / (1 - beta2_t)
424 | buffered[1] = N_sma
425 | if N_sma > 5:
426 | step_size = group['lr'] * math.sqrt(
427 | (1 - beta2_t) * (N_sma - 4) / (N_sma_max - 4) * (N_sma - 2) / N_sma * N_sma_max / (
428 | N_sma_max - 2)) / (1 - beta1 ** state['step'])
429 | else:
430 | step_size = group['lr'] / (1 - beta1 ** state['step'])
431 | buffered[2] = step_size
432 |
433 | if group['weight_decay'] != 0:
434 | p_data_fp32.add_(-group['weight_decay'] * group['lr'], p_data_fp32)
435 |
436 | if N_sma > 5:
437 | denom = exp_avg_sq.sqrt().add_(group['eps'])
438 | p_data_fp32.addcdiv_(-step_size, exp_avg, denom)
439 | else:
440 | p_data_fp32.add_(-step_size, exp_avg)
441 |
442 | p.data.copy_(p_data_fp32)
443 |
444 | return loss
445 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/progressbar.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import time
2 |
3 | class ProgressBar(object):
4 |
5 | def __init__(self, n_total,width=30):
6 | self.width = width
7 | self.n_total = n_total
8 | self.start_time = time.time()
9 |
10 | def batch_step(self, step, info, bar_type='Training'):
11 | now = time.time()
12 | current = step + 1
13 | recv_per = current / self.n_total
14 | bar = f'[{bar_type}] {current}/{self.n_total} ['
15 | if recv_per >= 1:
16 | recv_per = 1
17 | prog_width = int(self.width * recv_per)
18 | if prog_width > 0:
19 | bar += '=' * (prog_width - 1)
20 | if current< self.n_total:
21 | bar += ">"
22 | else:
23 | bar += '='
24 | bar += '.' * (self.width - prog_width)
25 | bar += ']'
26 | show_bar = f"\r{bar}"
27 | time_per_unit = (now - self.start_time) / current
28 | if current < self.n_total:
29 | eta = time_per_unit * (self.n_total - current)
30 | if eta > 3600:
31 | eta_format = ('%d:%02d:%02d' %
32 | (eta // 3600, (eta % 3600) // 60, eta % 60))
33 | elif eta > 60:
34 | eta_format = '%d:%02d' % (eta // 60, eta % 60)
35 | else:
36 | eta_format = '%ds' % eta
37 | time_info = f' - ETA: {eta_format}'
38 | else:
39 | if time_per_unit >= 1:
40 | time_info = f' {time_per_unit:.1f}s/step'
41 | elif time_per_unit >= 1e-3:
42 | time_info = f' {time_per_unit * 1e3:.1f}ms/step'
43 | else:
44 | time_info = f' {time_per_unit * 1e6:.1f}us/step'
45 |
46 | show_bar += time_info
47 | if len(info) != 0:
48 | show_info = f'{show_bar} ' + \
49 | "-".join([f' {key}: {value:.4f} ' for key, value in info.items()])
50 | print(show_info, end='')
51 | else:
52 | print(show_bar, end='')
53 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/trainingmonitor.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # encoding:utf-8
2 | import numpy as np
3 | from pathlib import Path
4 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
5 | from ..common.tools import load_json
6 | from ..common.tools import save_json
7 | plt.switch_backend('agg')
8 |
9 |
10 | class TrainingMonitor():
11 | def __init__(self, file_dir, arch, add_test=False):
12 | '''
13 | :param startAt: 重新开始训练的epoch点
14 | '''
15 | if isinstance(file_dir, Path):
16 | pass
17 | else:
18 | file_dir = Path(file_dir)
19 | file_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
20 |
21 | self.arch = arch
22 | self.file_dir = file_dir
23 | self.H = {}
24 | self.add_test = add_test
25 | self.json_path = file_dir / (arch + "_training_monitor.json")
26 |
27 | def reset(self,start_at):
28 | if start_at > 0:
29 | if self.json_path is not None:
30 | if self.json_path.exists():
31 | self.H = load_json(self.json_path)
32 | for k in self.H.keys():
33 | self.H[k] = self.H[k][:start_at]
34 |
35 | def epoch_step(self, logs={}):
36 | for (k, v) in logs.items():
37 | l = self.H.get(k, [])
38 | # np.float32会报错
39 | if not isinstance(v, np.float):
40 | v = round(float(v), 4)
41 | l.append(v)
42 | self.H[k] = l
43 |
44 | # 写入文件
45 | if self.json_path is not None:
46 | save_json(data = self.H,file_path=self.json_path)
47 |
48 | # 保存train图像
49 | if len(self.H["loss"]) == 1:
50 | self.paths = {key: self.file_dir / (self.arch + f'_{key.upper()}') for key in self.H.keys()}
51 |
52 | if len(self.H["loss"]) > 1:
53 | # 指标变化
54 | # 曲线
55 | # 需要成对出现
56 | keys = [key for key, _ in self.H.items() if '_' not in key]
57 | for key in keys:
58 | N = np.arange(0, len(self.H[key]))
59 | plt.style.use("ggplot")
60 | plt.figure()
61 | plt.plot(N, self.H[key], label=f"train_{key}")
62 | plt.plot(N, self.H[f"valid_{key}"], label=f"valid_{key}")
63 | if self.add_test:
64 | plt.plot(N, self.H[f"test_{key}"], label=f"test_{key}")
65 | plt.legend()
66 | plt.xlabel("Epoch #")
67 | plt.ylabel(key)
68 | plt.title(f"Training {key} [Epoch {len(self.H[key])}]")
69 | plt.savefig(str(self.paths[key]))
70 | plt.close()
71 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/common/tools.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import random
3 | import torch
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import json
6 | import pickle
7 | import torch.nn as nn
8 | from collections import OrderedDict
9 | from pathlib import Path
10 | import logging
11 |
12 | logger = logging.getLogger()
13 |
14 |
15 | def print_config(config):
16 | info = "Running with the following configs:\n"
17 | for k, v in config.items():
18 | info += f"\t{k} : {str(v)}\n"
19 | print("\n" + info + "\n")
20 | return
21 |
22 |
23 | def init_logger(log_file=None, log_file_level=logging.NOTSET):
24 | '''
25 | logging
26 | Example:
27 | >>> from common.tools import init_logger,logger
28 | >>> init_logger(log_file)
29 | >>> logger.info("abc'")
30 | '''
31 | if isinstance(log_file, Path):
32 | log_file = str(log_file)
33 | # log_format = logging.Formatter("[%(asctime)s %(levelname)s] %(message)s")
34 | log_format = logging.Formatter("%(message)s")
35 | logger = logging.getLogger()
36 | logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
37 | console_handler = logging.StreamHandler()
38 | console_handler.setFormatter(log_format)
39 | logger.handlers = [console_handler]
40 | if log_file and log_file != '':
41 | file_handler = logging.FileHandler(log_file)
42 | file_handler.setLevel(log_file_level)
43 | file_handler.setFormatter(log_format)
44 | logger.addHandler(file_handler)
45 | return logger
46 |
47 |
48 | def seed_everything(seed=1029):
49 | '''
50 | 设置整个开发环境的seed
51 | :param seed:
52 | :param device:
53 | :return:
54 | '''
55 | random.seed(seed)
56 | os.environ['PYTHONHASHSEED'] = str(seed)
57 | np.random.seed(seed)
58 | torch.manual_seed(seed)
59 | torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed)
60 | torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)
61 | # some cudnn methods can be random even after fixing the seed
62 | # unless you tell it to be deterministic
63 | torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
64 |
65 |
66 | def prepare_device(use_gpu):
67 | """
68 | setup GPU device if available, move model into configured device
69 | # 如果n_gpu_use为数字,则使用range生成list
70 | # 如果输入的是一个list,则默认使用list[0]作为controller
71 | Example:
72 | use_gpu = '' : cpu
73 | use_gpu = '0': cuda:0
74 | use_gpu = '0,1' : cuda:0 and cuda:1
75 | """
76 | n_gpu_use = [int(x) for x in use_gpu.split(",")]
77 | if not use_gpu:
78 | device_type = 'cpu'
79 | else:
80 | device_type = f"cuda:{n_gpu_use[0]}"
81 | n_gpu = torch.cuda.device_count()
82 | if len(n_gpu_use) > 0 and n_gpu == 0:
83 | logger.warning("Warning: There\'s no GPU available on this machine, training will be performed on CPU.")
84 | device_type = 'cpu'
85 | if len(n_gpu_use) > n_gpu:
86 | msg = f"Warning: The number of GPU\'s configured to use is {n_gpu}, but only {n_gpu} are available on this machine."
87 | logger.warning(msg)
88 | n_gpu_use = range(n_gpu)
89 | device = torch.device(device_type)
90 | list_ids = n_gpu_use
91 | return device, list_ids
92 |
93 |
94 | def model_device(n_gpu, model):
95 | '''
96 | :param n_gpu:
97 | :param model:
98 | :return:
99 | '''
100 | device, device_ids = prepare_device(n_gpu)
101 | if len(device_ids) > 1:
102 | logger.info(f"current {len(device_ids)} GPUs")
103 | model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model, device_ids=device_ids)
104 | if len(device_ids) == 1:
105 | os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = str(device_ids[0])
106 | model = model.to(device)
107 | return model, device
108 |
109 |
110 | def restore_checkpoint(resume_path, model=None):
111 | '''
112 | 加载模型
113 | :param resume_path:
114 | :param model:
115 | :param optimizer:
116 | :return:
117 | 注意: 如果是加载Bert模型的话,需要调整,不能使用该模式
118 | 可以使用模块自带的Bert_model.from_pretrained(state_dict = your save state_dict)
119 | '''
120 | if isinstance(resume_path, Path):
121 | resume_path = str(resume_path)
122 | checkpoint = torch.load(resume_path)
123 | best = checkpoint['best']
124 | start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch'] + 1
125 | states = checkpoint['state_dict']
126 | if isinstance(model, nn.DataParallel):
127 | model.module.load_state_dict(states)
128 | else:
129 | model.load_state_dict(states)
130 | return [model, best, start_epoch]
131 |
132 |
133 | def save_pickle(data, file_path):
134 | '''
135 | 保存成pickle文件
136 | :param data:
137 | :param file_name:
138 | :param pickle_path:
139 | :return:
140 | '''
141 | if isinstance(file_path, Path):
142 | file_path = str(file_path)
143 | with open(file_path, 'wb') as f:
144 | pickle.dump(data, f)
145 |
146 |
147 | def load_pickle(input_file):
148 | '''
149 | 读取pickle文件
150 | :param pickle_path:
151 | :param file_name:
152 | :return:
153 | '''
154 | with open(str(input_file), 'rb') as f:
155 | data = pickle.load(f)
156 | return data
157 |
158 |
159 | def save_json(data, file_path):
160 | '''
161 | 保存成json文件
162 | :param data:
163 | :param json_path:
164 | :param file_name:
165 | :return:
166 | '''
167 | if not isinstance(file_path, Path):
168 | file_path = Path(file_path)
169 | # if isinstance(data,dict):
170 | # data = json.dumps(data)
171 | with open(str(file_path), 'w') as f:
172 | json.dump(data, f)
173 |
174 |
175 | def load_json(file_path):
176 | '''
177 | 加载json文件
178 | :param json_path:
179 | :param file_name:
180 | :return:
181 | '''
182 | if not isinstance(file_path, Path):
183 | file_path = Path(file_path)
184 | with open(str(file_path), 'r') as f:
185 | data = json.load(f)
186 | return data
187 |
188 |
189 | def save_model(model, model_path):
190 | """ 存储不含有显卡信息的state_dict或model
191 | :param model:
192 | :param model_name:
193 | :param only_param:
194 | :return:
195 | """
196 | if isinstance(model_path, Path):
197 | model_path = str(model_path)
198 | if isinstance(model, nn.DataParallel):
199 | model = model.module
200 | state_dict = model.state_dict()
201 | for key in state_dict:
202 | state_dict[key] = state_dict[key].cpu()
203 | torch.save(state_dict, model_path)
204 |
205 |
206 | def load_model(model, model_path):
207 | '''
208 | 加载模型
209 | :param model:
210 | :param model_name:
211 | :param model_path:
212 | :param only_param:
213 | :return:
214 | '''
215 | if isinstance(model_path, Path):
216 | model_path = str(model_path)
217 | logging.info(f"loading model from {str(model_path)} .")
218 | states = torch.load(model_path)
219 | state = states['state_dict']
220 | if isinstance(model, nn.DataParallel):
221 | model.module.load_state_dict(state)
222 | else:
223 | model.load_state_dict(state)
224 | return model
225 |
226 |
227 | class AverageMeter(object):
228 | '''
229 | computes and stores the average and current value
230 | Example:
231 | >>> loss = AverageMeter()
232 | >>> for step,batch in enumerate(train_data):
233 | >>> pred = self.model(batch)
234 | >>> raw_loss = self.metrics(pred,target)
235 | >>> loss.update(raw_loss.item(),n = 1)
236 | >>> cur_loss = loss.avg
237 | '''
238 |
239 | def __init__(self):
240 | self.reset()
241 |
242 | def reset(self):
243 | self.val = 0
244 | self.avg = 0
245 | self.sum = 0
246 | self.count = 0
247 |
248 | def update(self, val, n=1):
249 | self.val = val
250 | self.sum += val * n
251 | self.count += n
252 | self.avg = self.sum / self.count
253 |
254 |
255 | def summary(model, *inputs, batch_size=-1, show_input=True):
256 | '''
257 | 打印模型结构信息
258 | :param model:
259 | :param inputs:
260 | :param batch_size:
261 | :param show_input:
262 | :return:
263 | Example:
264 | >>> print("model summary info: ")
265 | >>> for step,batch in enumerate(train_data):
266 | >>> summary(self.model,*batch,show_input=True)
267 | >>> break
268 | '''
269 |
270 | def register_hook(module):
271 | def hook(module, input, output=None):
272 | class_name = str(module.__class__).split(".")[-1].split("'")[0]
273 | module_idx = len(summary)
274 |
275 | m_key = f"{class_name}-{module_idx + 1}"
276 | summary[m_key] = OrderedDict()
277 | summary[m_key]["input_shape"] = list(input[0].size())
278 | summary[m_key]["input_shape"][0] = batch_size
279 |
280 | if show_input is False and output is not None:
281 | if isinstance(output, (list, tuple)):
282 | for out in output:
283 | if isinstance(out, torch.Tensor):
284 | summary[m_key]["output_shape"] = [
285 | [-1] + list(out.size())[1:]
286 | ][0]
287 | else:
288 | summary[m_key]["output_shape"] = [
289 | [-1] + list(out[0].size())[1:]
290 | ][0]
291 | else:
292 | summary[m_key]["output_shape"] = list(output.size())
293 | summary[m_key]["output_shape"][0] = batch_size
294 |
295 | params = 0
296 | if hasattr(module, "weight") and hasattr(module.weight, "size"):
297 | params += torch.prod(torch.LongTensor(list(module.weight.size())))
298 | summary[m_key]["trainable"] = module.weight.requires_grad
299 | if hasattr(module, "bias") and hasattr(module.bias, "size"):
300 | params += torch.prod(torch.LongTensor(list(module.bias.size())))
301 | summary[m_key]["nb_params"] = params
302 |
303 | if (not isinstance(module, nn.Sequential) and not isinstance(module, nn.ModuleList) and not (module == model)):
304 | if show_input is True:
305 | hooks.append(module.register_forward_pre_hook(hook))
306 | else:
307 | hooks.append(module.register_forward_hook(hook))
308 |
309 | # create properties
310 | summary = OrderedDict()
311 | hooks = []
312 |
313 | # register hook
314 | model.apply(register_hook)
315 | model(*inputs)
316 |
317 | # remove these hooks
318 | for h in hooks:
319 | h.remove()
320 |
321 | print("-----------------------------------------------------------------------")
322 | if show_input is True:
323 | line_new = f"{'Layer (type)':>25} {'Input Shape':>25} {'Param #':>15}"
324 | else:
325 | line_new = f"{'Layer (type)':>25} {'Output Shape':>25} {'Param #':>15}"
326 | print(line_new)
327 | print("=======================================================================")
328 |
329 | total_params = 0
330 | total_output = 0
331 | trainable_params = 0
332 | for layer in summary:
333 | # input_shape, output_shape, trainable, nb_params
334 | if show_input is True:
335 | line_new = "{:>25} {:>25} {:>15}".format(
336 | layer,
337 | str(summary[layer]["input_shape"]),
338 | "{0:,}".format(summary[layer]["nb_params"]),
339 | )
340 | else:
341 | line_new = "{:>25} {:>25} {:>15}".format(
342 | layer,
343 | str(summary[layer]["output_shape"]),
344 | "{0:,}".format(summary[layer]["nb_params"]),
345 | )
346 |
347 | total_params += summary[layer]["nb_params"]
348 | if show_input is True:
349 | total_output += np.prod(summary[layer]["input_shape"])
350 | else:
351 | total_output += np.prod(summary[layer]["output_shape"])
352 | if "trainable" in summary[layer]:
353 | if summary[layer]["trainable"] == True:
354 | trainable_params += summary[layer]["nb_params"]
355 |
356 | print(line_new)
357 |
358 | print("=======================================================================")
359 | print(f"Total params: {total_params:0,}")
360 | print(f"Trainable params: {trainable_params:0,}")
361 | print(f"Non-trainable params: {(total_params - trainable_params):0,}")
362 | print("-----------------------------------------------------------------------")
363 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/configs/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/configs/base.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from pathlib import Path
2 |
3 | BASE_DIR = Path('pybert')
4 | config = {
5 | 'raw_data_path': BASE_DIR / 'dataset/cnews.txt',
6 | 'test_path': BASE_DIR / 'dataset/test.txt',
7 |
8 | 'data_dir': BASE_DIR / 'dataset',
9 | 'log_dir': BASE_DIR / 'output/log',
10 | 'writer_dir': BASE_DIR / "output/TSboard",
11 | 'figure_dir': BASE_DIR / "output/figure",
12 | 'checkpoint_dir': BASE_DIR / "output/checkpoints",
13 | 'cache_dir': BASE_DIR / 'model/',
14 | 'result': BASE_DIR / "output/result",
15 |
16 | 'bert_vocab_path': BASE_DIR / 'pretrain/bert/base-chinese/vocab.txt',
17 | 'bert_config_file': BASE_DIR / 'pretrain/bert/base-chinese/config.json',
18 | 'bert_model_dir': BASE_DIR / 'pretrain/bert/base-chinese',
19 |
20 | 'xlnet_vocab_path': BASE_DIR / 'pretrain/xlnet/base-cased/spiece.model',
21 | 'xlnet_config_file': BASE_DIR / 'pretrain/xlnet/base-cased/config.json',
22 | 'xlnet_model_dir': BASE_DIR / 'pretrain/xlnet/base-cased'
23 | }
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/dataset/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/io/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/io/bert_processor.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import csv
2 | import torch
3 | import numpy as np
4 | from ..common.tools import load_pickle
5 | from ..common.tools import logger
6 | from ..callback.progressbar import ProgressBar
7 | from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset
8 | from pytorch_transformers import BertTokenizer
9 |
10 |
11 | class InputExample(object):
12 | def __init__(self, guid, text_a, text_b=None, label=None):
13 | """Constructs a InputExample.
14 | Args:
15 | guid: Unique id for the example.
16 | text_a: string. The untokenized text of the first sequence. For single
17 | sequence tasks, only this sequence must be specified.
18 | text_b: (Optional) string. The untokenized text of the second sequence.
19 | Only must be specified for sequence pair tasks.
20 | label: (Optional) string. The label of the example. This should be
21 | specified for train and dev examples, but not for test examples.
22 | """
23 | self.guid = guid
24 | self.text_a = text_a
25 | self.text_b = text_b
26 | self.label = label
27 |
28 |
29 | class InputFeature(object):
30 | '''
31 | A single set of features of data.
32 | '''
33 |
34 | def __init__(self, input_ids, input_mask, segment_ids, label_id, input_len):
35 | self.input_ids = input_ids
36 | self.input_mask = input_mask
37 | self.segment_ids = segment_ids
38 | self.label_id = label_id
39 | self.input_len = input_len
40 |
41 |
42 | class BertProcessor(object):
43 | """Base class for data converters for sequence classification data sets."""
44 |
45 | def __init__(self, vocab_path, do_lower_case):
46 | self.tokenizer = BertTokenizer(vocab_path, do_lower_case)
47 |
48 | def get_train(self, data_file):
49 | """Gets a collection of `InputExample`s for the train set."""
50 | return self.read_data(data_file)
51 |
52 | def get_dev(self, data_file):
53 | """Gets a collection of `InputExample`s for the dev set."""
54 | return self.read_data(data_file)
55 |
56 | def get_test(self, lines):
57 | return lines
58 |
59 | def get_labels(self):
60 | """Gets the list of labels for this data set."""
61 | return ["财经", "体育", "娱乐", "家居", "房产", "教育", "时尚", "时政", "游戏", "科技"]
62 |
63 | @classmethod
64 | def read_data(cls, input_file, quotechar=None):
65 | """Reads a tab separated value file."""
66 | if 'pkl' in str(input_file):
67 | lines = load_pickle(input_file)
68 | else:
69 | lines = input_file
70 | return lines
71 |
72 | def truncate_seq_pair(self, tokens_a, tokens_b, max_length):
73 | # This is a simple heuristic which will always truncate the longer sequence
74 | # one token at a time. This makes more sense than truncating an equal percent
75 | # of tokens from each, since if one sequence is very short then each token
76 | # that's truncated likely contains more information than a longer sequence.
77 | while True:
78 | total_length = len(tokens_a) + len(tokens_b)
79 | if total_length <= max_length:
80 | break
81 | if len(tokens_a) > len(tokens_b):
82 | tokens_a.pop()
83 | else:
84 | tokens_b.pop()
85 |
86 | def create_examples(self, lines, example_type, cached_examples_file):
87 | '''
88 | Creates examples for data
89 | '''
90 | pbar = ProgressBar(n_total=len(lines))
91 | if cached_examples_file.exists():
92 | logger.info("Loading examples from cached file %s", cached_examples_file)
93 | examples = torch.load(cached_examples_file)
94 | else:
95 | examples = []
96 | for i, line in enumerate(lines):
97 | guid = '%s-%d' % (example_type, i)
98 | text_a = line[0]
99 | label = line[1]
100 | text_b = None
101 | example = InputExample(guid=guid, text_a=text_a, text_b=text_b, label=label)
102 | examples.append(example)
103 | pbar.batch_step(step=i, info={}, bar_type='create examples')
104 | logger.info("Saving examples into cached file %s", cached_examples_file)
105 | torch.save(examples, cached_examples_file)
106 | return examples
107 |
108 | def create_features(self, examples, max_seq_len, cached_features_file):
109 | '''
110 | # The convention in BERT is:
111 | # (a) For sequence pairs:
112 | # tokens: [CLS] is this jack ##son ##ville ? [SEP] no it is not . [SEP]
113 | # type_ids: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
114 | # (b) For single sequences:
115 | # tokens: [CLS] the dog is hairy . [SEP]
116 | # type_ids: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
117 | '''
118 | pbar = ProgressBar(n_total=len(examples))
119 | if cached_features_file.exists():
120 | logger.info("Loading features from cached file %s", cached_features_file)
121 | features = torch.load(cached_features_file)
122 | else:
123 | features = []
124 | for ex_id, example in enumerate(examples):
125 | tokens_a = self.tokenizer.tokenize(example.text_a)
126 | tokens_b = None
127 | label_id = int(example.label)
128 |
129 | if example.text_b:
130 | tokens_b = self.tokenizer.tokenize(example.text_b)
131 | # Modifies `tokens_a` and `tokens_b` in place so that the total
132 | # length is less than the specified length.
133 | # Account for [CLS], [SEP], [SEP] with "- 3"
134 | self.truncate_seq_pair(tokens_a, tokens_b, max_length=max_seq_len - 3)
135 | else:
136 | # Account for [CLS] and [SEP] with '-2'
137 | if len(tokens_a) > max_seq_len - 2:
138 | tokens_a = tokens_a[:max_seq_len - 2]
139 | tokens = ['[CLS]'] + tokens_a + ['[SEP]']
140 | segment_ids = [0] * len(tokens)
141 | if tokens_b:
142 | tokens += tokens_b + ['[SEP]']
143 | segment_ids += [1] * (len(tokens_b) + 1)
144 |
145 | input_ids = self.tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens)
146 | input_mask = [1] * len(input_ids)
147 | padding = [0] * (max_seq_len - len(input_ids))
148 | input_len = len(input_ids)
149 |
150 | input_ids += padding
151 | input_mask += padding
152 | segment_ids += padding
153 |
154 | assert len(input_ids) == max_seq_len
155 | assert len(input_mask) == max_seq_len
156 | assert len(segment_ids) == max_seq_len
157 |
158 | if ex_id < 2:
159 | logger.info("*** Example ***")
160 | logger.info(f"guid: {example.guid}" % ())
161 | logger.info(f"tokens: {' '.join([str(x) for x in tokens])}")
162 | logger.info(f"input_ids: {' '.join([str(x) for x in input_ids])}")
163 | logger.info(f"input_mask: {' '.join([str(x) for x in input_mask])}")
164 | logger.info(f"segment_ids: {' '.join([str(x) for x in segment_ids])}")
165 |
166 | feature = InputFeature(input_ids=input_ids,
167 | input_mask=input_mask,
168 | segment_ids=segment_ids,
169 | label_id=label_id,
170 | input_len=input_len)
171 | features.append(feature)
172 | pbar.batch_step(step=ex_id, info={}, bar_type='create features')
173 | logger.info("Saving features into cached file %s", cached_features_file)
174 | torch.save(features, cached_features_file)
175 | return features
176 |
177 | def create_dataset(self, features, is_sorted=False):
178 | # Convert to Tensors and build dataset
179 | if is_sorted:
180 | logger.info("sorted data by th length of input")
181 | features = sorted(features, key=lambda x: x.input_len, reverse=True)
182 | all_input_ids = torch.tensor([f.input_ids for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
183 | all_input_mask = torch.tensor([f.input_mask for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
184 | all_segment_ids = torch.tensor([f.segment_ids for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
185 | all_label_ids = torch.tensor([f.label_id for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
186 | dataset = TensorDataset(all_input_ids, all_input_mask, all_segment_ids, all_label_ids)
187 | return dataset
188 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/io/task_data.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import random
2 | import pandas as pd
3 | from tqdm import tqdm
4 | from ..common.tools import save_pickle
5 | from ..common.tools import logger
6 | from ..callback.progressbar import ProgressBar
7 |
8 | class TaskData(object):
9 | def __init__(self):
10 | pass
11 | def train_val_split(self,X, y,valid_size,stratify=False,shuffle=True,save = True,
12 | seed = None,data_name = None,data_dir = None):
13 | pbar = ProgressBar(n_total=len(X))
14 | logger.info('split raw data into train and valid')
15 | if stratify:
16 | num_classes = len(list(set(y)))
17 | train, valid = [], []
18 | bucket = [[] for _ in range(num_classes)]
19 | for step,(data_x, data_y) in enumerate(zip(X, y)):
20 | bucket[int(data_y)].append((data_x, data_y))
21 | pbar.batch_step(step=step,info = {},bar_type='bucket')
22 | del X, y
23 | for bt in tqdm(bucket, desc='split'):
24 | N = len(bt)
25 | if N == 0:
26 | continue
27 | test_size = int(N * valid_size)
28 | if shuffle:
29 | random.seed(seed)
30 | random.shuffle(bt)
31 | valid.extend(bt[:test_size])
32 | train.extend(bt[test_size:])
33 | if shuffle:
34 | random.seed(seed)
35 | random.shuffle(train)
36 | else:
37 | data = []
38 | for step,(data_x, data_y) in enumerate(zip(X, y)):
39 | data.append((data_x, data_y))
40 | pbar.batch_step(step=step, info={}, bar_type='merge')
41 | del X, y
42 | N = len(data)
43 | test_size = int(N * valid_size)
44 | if shuffle:
45 | random.seed(seed)
46 | random.shuffle(data)
47 | valid = data[:test_size]
48 | train = data[test_size:]
49 | # 混洗train数据集
50 | if shuffle:
51 | random.seed(seed)
52 | random.shuffle(train)
53 | if save:
54 | train_path = data_dir / f"{data_name}.train.pkl"
55 | valid_path = data_dir / f"{data_name}.valid.pkl"
56 | save_pickle(data=train,file_path=train_path)
57 | save_pickle(data = valid,file_path=valid_path)
58 | return train, valid
59 |
60 | def read_data(self,raw_data_path,preprocessor = None,is_train=True,label2id=None):
61 | '''
62 | :param raw_data_path:
63 | :param skip_header:
64 | :param preprocessor:
65 | :return:
66 | '''
67 | targets,sentences = [],[]
68 | with open(raw_data_path,'r') as fr:
69 | for i,line in enumerate(fr):
70 | # 如果首行为列名,则skip_header=True
71 | if i == 0:
72 | continue
73 | if is_train:
74 | lines = line.strip().split('\t')
75 | target = label2id[lines[0]]
76 | sentence = str(lines[1])
77 | else:
78 | lines = line.strip('\n')
79 | target = -1
80 | sentence = str(lines)
81 | if preprocessor:
82 | sentence = preprocessor(sentence)
83 | if sentence:
84 | targets.append(target)
85 | sentences.append(sentence)
86 | return targets,sentences
87 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/model/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lonePatient/BERT-chinese-text-classification-pytorch/2f9ae40abd64b8680c703c212852b32ca2bfe310/pybert/model/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/model/nn/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/model/nn/bert_for_multi_class.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | from pytorch_transformers.modeling_bert import BertPreTrainedModel, BertModel
3 |
4 |
5 | class BertForMultiClass(BertPreTrainedModel):
6 | def __init__(self, config):
7 | super(BertForMultiClass, self).__init__(config)
8 | self.bert = BertModel(config)
9 | self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.hidden_dropout_prob)
10 | self.classifier = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.num_labels)
11 | self.apply(self.init_weights)
12 |
13 | def forward(self, input_ids, token_type_ids=None, attention_mask=None, head_mask=None):
14 | outputs = self.bert(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask,
15 | head_mask=head_mask)
16 | pooled_output = outputs[1]
17 | pooled_output = self.dropout(pooled_output)
18 | logits = self.classifier(pooled_output)
19 | return logits
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/output/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/output/checkpoints/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/output/embedding/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/output/feature/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/output/figure/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/output/log/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/output/result/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/preprocessing/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/preprocessing/augmentation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # encoding:utf-8
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import random
4 |
5 |
6 | class Augmentator(object):
7 | def __init__(self, is_train_mode=True, proba=0.5):
8 | self.mode = is_train_mode
9 | self.proba = proba
10 | self.augs = []
11 | self._reset()
12 |
13 | # 总的增强列表
14 | def _reset(self):
15 | self.augs.append(lambda text: self._shuffle(text))
16 | self.augs.append(lambda text: self._dropout(text, p=0.5))
17 |
18 | # 打乱
19 | def _shuffle(self, text):
20 | text = np.random.permutation(text.strip().split())
21 | return ' '.join(text)
22 |
23 | # 随机删除一些
24 | def _dropout(self, text, p=0.5):
25 | # random delete some text
26 | text = text.strip().split()
27 | len_ = len(text)
28 | indexs = np.random.choice(len_, int(len_ * p))
29 | for i in indexs:
30 | text[i] = ''
31 | return ' '.join(text)
32 |
33 | def __call__(self, text, aug_type):
34 | '''
35 | 用aug_type区分数据
36 | '''
37 | # TTA模式
38 | if 0 <= aug_type <= 2:
39 | pass
40 | # 训练模式
41 | if self.mode and random.random() < self.proba:
42 | aug = random.choice(self.augs)
43 | text = aug(text)
44 | return text
45 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/preprocessing/preprocessor.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # encoding:utf-8
2 | import re
3 | import jieba
4 |
5 |
6 | class Preprocessor(object):
7 | def __init__(self, min_len=2, stopwords_path=None):
8 | self.min_len = min_len
9 | self.stopwords_path = stopwords_path
10 | self.reset()
11 |
12 | # jieba分词
13 | def jieba_cut(self, sentence):
14 | seg_list = jieba.cut(sentence, cut_all=False)
15 | return ' '.join(seg_list)
16 |
17 | # 加载停用词
18 | def reset(self):
19 | if self.stopwords_path:
20 | with open(self.stopwords_path, 'r') as fr:
21 | self.stopwords = {}
22 | for line in fr:
23 | word = line.strip(' ').strip('\n')
24 | self.stopwords[word] = 1
25 |
26 | # 去除长度小于min_len的文本
27 | def clean_length(self, sentence):
28 | if len([x for x in sentence]) >= self.min_len:
29 | return sentence
30 |
31 | # 全角转化为半角
32 | def full2half(self, sentence):
33 | ret_str = ''
34 | for i in sentence:
35 | if ord(i) >= 33 + 65248 and ord(i) <= 126 + 65248:
36 | ret_str += chr(ord(i) - 65248)
37 | else:
38 | ret_str += i
39 | return ret_str
40 |
41 | # 去除停用词
42 | def remove_stopword(self, sentence):
43 | words = sentence.split()
44 | x = [word for word in words if word not in self.stopwords]
45 | return " ".join(x)
46 |
47 | # 提取中文
48 | def get_china(self, sentence):
49 | zhmodel = re.compile("[\u4e00-\u9fa5]")
50 | words = [x for x in sentence if zhmodel.search(x)]
51 | return ''.join(words)
52 |
53 | # 移除数字
54 | def remove_numbers(self, sentence):
55 | words = sentence.split()
56 | x = [re.sub('\d+', '', word) for word in words]
57 | return ' '.join([w for w in x if w != ''])
58 |
59 | def remove_whitespace(self, sentence):
60 | x = ''.join([x for x in sentence if x != ' ' or x != '' or x != ' '])
61 | return x
62 |
63 | # 主函数
64 | def __call__(self, sentence):
65 | x = sentence.strip('\n')
66 | x = self.full2half(x)
67 | # x = self.jieba_cut(x)
68 | # if self.stopwords_path:
69 | # x = self.remove_stopword(x)
70 | x = self.remove_whitespace(x)
71 | x = self.get_china(x)
72 | x = self.clean_length(x)
73 |
74 | return x
75 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/pretrain/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/pretrain/bert/base-chinese/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/test/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/test/predictor.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # encoding:utf-8
2 | import torch
3 | import numpy as np
4 | from ..common.tools import model_device
5 | from ..callback.progressbar import ProgressBar
6 |
7 |
8 | class Predictor(object):
9 | def __init__(self, model, logger, n_gpu):
10 | self.model = model
11 | self.logger = logger
12 | self.model, self.device = model_device(n_gpu=n_gpu, model=self.model)
13 |
14 | def predict(self, data):
15 | pbar = ProgressBar(n_total=len(data))
16 | all_logits = None
17 | self.model.eval()
18 | with torch.no_grad():
19 | for step, batch in enumerate(data):
20 | batch = tuple(t.to(self.device) for t in batch)
21 | input_ids, input_mask, segment_ids, label_ids = batch
22 | logits = self.model(input_ids, segment_ids, input_mask)
23 | logits = logits.softmax(-1)
24 | if all_logits is None:
25 | all_logits = logits.detach().cpu().numpy()
26 | else:
27 | all_logits = np.concatenate([all_logits, logits.detach().cpu().numpy()], axis=0)
28 | pbar.batch_step(step=step, info={}, bar_type='Testing')
29 | if 'cuda' in str(self.device):
30 | torch.cuda.empty_cache()
31 | return all_logits
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/train/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/train/losses.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
2 | from torch.nn import CrossEntropyLoss
3 |
4 | class CrossEntropy(object):
5 | def __init__(self):
6 | self.loss_f = CrossEntropyLoss()
7 | def __call__(self, output, target):
8 | loss = self.loss_f(input=output, target=target)
9 | return loss
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/train/metrics.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # encoding:utf-8
2 | import torch
3 | import numpy as np
4 | from sklearn.metrics import f1_score, classification_report
5 |
6 |
7 | class Accuracy(object):
8 |
9 | def __init__(self, topK):
10 | super(Accuracy, self).__init__()
11 | self.topK = topK
12 |
13 | def __call__(self, output, target):
14 | batch_size = target.size(0)
15 | _, pred = output.topk(self.topK, 1, True, True)
16 | pred = pred.t()
17 | correct = pred.eq(target.view(1, -1).expand_as(pred))
18 | correct_k = correct[:self.topK].view(-1).float().sum(0)
19 | result = correct_k / batch_size
20 | return result
21 |
22 |
23 | class F1Score(object):
24 | def __init__(self):
25 | pass
26 |
27 | def __call__(self, output, target):
28 | _, y_pred = torch.max(output.data, 1)
29 | y_pred = y_pred.cpu().numpy()
30 | y_true = target.cpu().numpy()
31 | f1 = f1_score(y_true, y_pred, average="macro")
32 | correct = np.sum((y_true == y_pred).astype(int))
33 | acc = correct / y_pred.shape[0]
34 | return (acc, f1)
35 |
36 |
37 | class ClassReport(object):
38 | def __init__(self, target_names=None):
39 | self.target_names = target_names
40 |
41 | def __call__(self, output, target):
42 | _, y_pred = torch.max(output.data, 1)
43 | y_pred = y_pred.cpu().numpy()
44 | y_true = target.cpu().numpy()
45 | classify_report = classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=self.target_names)
46 | print('\n\nclassify_report:\n', classify_report)
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/train/trainer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | from ..callback.progressbar import ProgressBar
3 | from ..common.tools import restore_checkpoint, model_device
4 | from ..common.tools import summary
5 | from ..common.tools import seed_everything
6 | from ..common.tools import AverageMeter
7 | from torch.nn.utils import clip_grad_norm_
8 |
9 |
10 | class Trainer(object):
11 | def __init__(self, n_gpu,
12 | model,
13 | epochs,
14 | logger,
15 | criterion,
16 | evaluate,
17 | optimizer,
18 | lr_scheduler,
19 | early_stopping,
20 | gradient_accumulation_steps,
21 | class_report=None,
22 | grad_clip=0.0,
23 | verbose=1,
24 | fp16=None,
25 | resume_path=None,
26 | training_monitor=None,
27 | model_checkpoint=None
28 | ):
29 | self.start_epoch = 1
30 | self.global_step = 0
31 | self.n_gpu = n_gpu
32 | self.model = model
33 | self.epochs = epochs
34 | self.logger = logger
35 | self.fp16 = fp16
36 | self.grad_clip = grad_clip
37 | self.verbose = verbose
38 | self.criterion = criterion
39 | self.optimizer = optimizer
40 | self.evaluate = evaluate
41 | self.class_report = class_report
42 | self.lr_scheduler = lr_scheduler
43 | self.early_stopping = early_stopping
44 | self.model_checkpoint = model_checkpoint
45 | self.training_monitor = training_monitor
46 | self.gradient_accumulation_steps = gradient_accumulation_steps
47 | self.model, self.device = model_device(n_gpu=self.n_gpu, model=self.model)
48 | if self.fp16:
49 | try:
50 | from apex import amp
51 | except ImportError:
52 | raise ImportError("Please install apex from https://www.github.com/nvidia/apex to use fp16 training.")
53 |
54 | if resume_path:
55 | self.logger.info(f"\nLoading checkpoint: {resume_path}")
56 | resume_dict = torch.load(resume_path / 'checkpoint_info.bin')
57 | best = resume_dict['epoch']
58 | self.start_epoch = resume_dict['epoch']
59 | if self.model_checkpoint:
60 | self.model_checkpoint.best = best
61 | self.logger.info(f"\nCheckpoint '{resume_path}' and epoch {self.start_epoch} loaded")
62 |
63 | def save_info(self, epoch, best):
64 | model_save = self.model.module if hasattr(self.model, 'module') else self.model
65 | state = {"model": model_save,
66 | 'epoch': epoch,
67 | 'best': best}
68 | return state
69 |
70 | def valid_epoch(self, data):
71 | pbar = ProgressBar(n_total=len(data))
72 | outputs = []
73 | targets = []
74 | info = {}
75 | self.model.eval()
76 | with torch.no_grad():
77 | for step, batch in enumerate(data):
78 | batch = tuple(t.to(self.device) for t in batch)
79 | input_ids, input_mask, segment_ids, label_ids = batch
80 | logits = self.model(input_ids, segment_ids, input_mask)
81 | outputs.append(logits.cpu().detach())
82 | targets.append(label_ids.cpu().detach())
83 | pbar.batch_step(step=step, info={}, bar_type='Evaluating')
84 | outputs = torch.cat(outputs, dim=0).cpu().detach()
85 | targets = torch.cat(targets, dim=0).cpu().detach()
86 | loss = self.criterion(target=targets, output=outputs)
87 | info['valid_loss'] = loss.item()
88 | val_acc, val_f1 = self.evaluate(output=outputs, target=targets)
89 | info['valid_acc'] = val_acc
90 | info['valid_f1'] = val_f1
91 | self.class_report(outputs, targets)
92 | if 'cuda' in str(self.device):
93 | torch.cuda.empty_cache()
94 | return info
95 |
96 | def train_epoch(self, data):
97 | pbar = ProgressBar(n_total=len(data))
98 | tr_loss = AverageMeter()
99 | outputs = []
100 | targets = []
101 | info = {}
102 | for step, batch in enumerate(data):
103 | self.model.train()
104 | batch = tuple(t.to(self.device) for t in batch)
105 | input_ids, input_mask, segment_ids, label_ids = batch
106 | logits = self.model(input_ids, segment_ids, input_mask)
107 | loss = self.criterion(output=logits, target=label_ids)
108 | if len(self.n_gpu) >= 2:
109 | loss = loss.mean()
110 | if self.gradient_accumulation_steps > 1:
111 | loss = loss / self.gradient_accumulation_steps
112 | if self.fp16:
113 | with amp.scale_loss(loss, self.optimizer) as scaled_loss:
114 | scaled_loss.backward()
115 | clip_grad_norm_(amp.master_params(self.optimizer), self.grad_clip)
116 | else:
117 | loss.backward()
118 | clip_grad_norm_(self.model.parameters(), self.grad_clip)
119 | if (step + 1) % self.gradient_accumulation_steps == 0:
120 | self.lr_scheduler.step()
121 | self.optimizer.step()
122 | self.optimizer.zero_grad()
123 | self.global_step += 1
124 | tr_loss.update(loss.item(), n=1)
125 | if self.verbose >= 1:
126 | pbar.batch_step(step=step, info={'loss': loss.item()}, bar_type='Training')
127 | outputs.append(logits.cpu().detach())
128 | targets.append(label_ids.cpu().detach())
129 | outputs = torch.cat(outputs, dim=0).cpu().detach()
130 | targets = torch.cat(targets, dim=0).cpu().detach()
131 | acc, f1 = self.evaluate(output=outputs, target=targets)
132 | info['loss'] = tr_loss.avg
133 | info['acc'] = acc
134 | info['f1'] = f1
135 | if "cuda" in str(self.device):
136 | torch.cuda.empty_cache()
137 | return info
138 |
139 | def train(self, train_data, valid_data, seed):
140 | seed_everything(seed)
141 | print("model summary info: ")
142 | for step, (input_ids, input_mask, segment_ids, label_ids) in enumerate(train_data):
143 | input_ids = input_ids.to(self.device)
144 | input_mask = input_mask.to(self.device)
145 | segment_ids = segment_ids.to(self.device)
146 | summary(self.model, *(input_ids, segment_ids, input_mask), show_input=True)
147 | break
148 |
149 | # ***************************************************************
150 | for epoch in range(self.start_epoch, self.start_epoch + self.epochs):
151 | self.logger.info(f"Epoch {epoch}/{self.epochs}")
152 | train_log = self.train_epoch(train_data)
153 | valid_log = self.valid_epoch(valid_data)
154 |
155 | logs = dict(train_log, **valid_log)
156 | show_info = f'\nEpoch: {epoch} - ' + "-".join([f' {key}: {value:.4f} ' for key, value in logs.items()])
157 | self.logger.info(show_info)
158 |
159 | # save
160 | if self.training_monitor:
161 | self.training_monitor.epoch_step(logs)
162 |
163 | # save model
164 | if self.model_checkpoint:
165 | state = self.save_info(epoch, best=logs['valid_loss'])
166 | self.model_checkpoint.bert_epoch_step(current=logs[self.model_checkpoint.monitor], state=state)
167 |
168 | # early_stopping
169 | if self.early_stopping:
170 | self.early_stopping.epoch_step(epoch=epoch, current=logs[self.early_stopping.monitor])
171 | if self.early_stopping.stop_training:
172 | break
173 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/run_bert.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # encoding:utf-8
2 | import torch
3 | import warnings
4 | from pathlib import Path
5 | from argparse import ArgumentParser
6 | from pybert.train.trainer import Trainer
7 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
8 | from pybert.io.bert_processor import BertProcessor
9 | from pybert.common.tools import init_logger, logger
10 | from pybert.common.tools import seed_everything
11 | from pybert.configs.base import config
12 | from pybert.train.losses import CrossEntropy
13 | from pybert.model.nn.bert_for_multi_class import BertForMultiClass
14 | from pybert.callback.modelcheckpoint import ModelCheckpoint
15 | from pybert.callback.trainingmonitor import TrainingMonitor
16 | from pybert.train.metrics import F1Score, ClassReport
17 | from pytorch_transformers import AdamW, WarmupLinearSchedule
18 | from torch.utils.data import RandomSampler, SequentialSampler
19 |
20 | warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
21 |
22 |
23 | def run_train(args):
24 | # --------- data
25 | processor = BertProcessor(vocab_path=config['bert_vocab_path'], do_lower_case=args.do_lower_case)
26 | label_list = processor.get_labels()
27 | label2id = {label: i for i, label in enumerate(label_list)}
28 | id2label = {i: label for i, label in enumerate(label_list)}
29 |
30 | train_data = processor.get_train(config['data_dir'] / f"{args.data_name}.train.pkl")
31 | train_examples = processor.create_examples(lines=train_data,
32 | example_type='train',
33 | cached_examples_file=config[
34 | 'data_dir'] / f"cached_train_examples_{args.arch}")
35 | train_features = processor.create_features(examples=train_examples,
36 | max_seq_len=args.train_max_seq_len,
37 | cached_features_file=config[
38 | 'data_dir'] / "cached_train_features_{}_{}".format(
39 | args.train_max_seq_len, args.arch
40 | ))
41 | train_dataset = processor.create_dataset(train_features, is_sorted=args.sorted)
42 | if args.sorted:
43 | train_sampler = SequentialSampler(train_dataset)
44 | else:
45 | train_sampler = RandomSampler(train_dataset)
46 | train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_dataset, sampler=train_sampler, batch_size=args.train_batch_size)
47 |
48 | valid_data = processor.get_dev(config['data_dir'] / f"{args.data_name}.valid.pkl")
49 | valid_examples = processor.create_examples(lines=valid_data,
50 | example_type='valid',
51 | cached_examples_file=config[
52 | 'data_dir'] / f"cached_valid_examples_{args.arch}")
53 |
54 | valid_features = processor.create_features(examples=valid_examples,
55 | max_seq_len=args.eval_max_seq_len,
56 | cached_features_file=config[
57 | 'data_dir'] / "cached_valid_features_{}_{}".format(
58 | args.eval_max_seq_len, args.arch
59 | ))
60 | valid_dataset = processor.create_dataset(valid_features)
61 | valid_sampler = SequentialSampler(valid_dataset)
62 | valid_dataloader = DataLoader(valid_dataset, sampler=valid_sampler, batch_size=args.eval_batch_size)
63 |
64 | # ------- model
65 | logger.info("initializing model")
66 | if args.resume_path:
67 | args.resume_path = Path(args.resume_path)
68 | model = BertForMultiClass.from_pretrained(args.resume_path, num_labels=len(label_list))
69 | else:
70 | model = BertForMultiClass.from_pretrained(config['bert_model_dir'], num_labels=len(label_list))
71 | t_total = int(len(train_dataloader) / args.gradient_accumulation_steps * args.epochs)
72 |
73 | param_optimizer = list(model.named_parameters())
74 | no_decay = ['bias', 'LayerNorm.weight']
75 | optimizer_grouped_parameters = [
76 | {'params': [p for n, p in param_optimizer if not any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)],
77 | 'weight_decay': args.weight_decay},
78 | {'params': [p for n, p in param_optimizer if any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)], 'weight_decay': 0.0}
79 | ]
80 | warmup_steps = int(t_total * args.warmup_proportion)
81 | optimizer = AdamW(optimizer_grouped_parameters, lr=args.learning_rate, eps=args.adam_epsilon)
82 | lr_scheduler = WarmupLinearSchedule(optimizer, warmup_steps=warmup_steps, t_total=t_total)
83 |
84 | if args.fp16:
85 | try:
86 | from apex import amp
87 | except ImportError:
88 | raise ImportError("Please install apex from https://www.github.com/nvidia/apex to use fp16 training.")
89 | model, optimizer = amp.initialize(model, optimizer, opt_level=args.fp16_opt_level)
90 |
91 | # ---- callbacks
92 | logger.info("initializing callbacks")
93 | train_monitor = TrainingMonitor(file_dir=config['figure_dir'], arch=args.arch)
94 | model_checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(checkpoint_dir=config['checkpoint_dir'], mode=args.mode,
95 | monitor=args.monitor, arch=args.arch,
96 | save_best_only=args.save_best)
97 |
98 | # **************************** training model ***********************
99 | logger.info("***** Running training *****")
100 | logger.info(" Num examples = %d", len(train_examples))
101 | logger.info(" Num Epochs = %d", args.epochs)
102 | logger.info(" Total train batch size (w. parallel, distributed & accumulation) = %d",
103 | args.train_batch_size * args.gradient_accumulation_steps * (
104 | torch.distributed.get_world_size() if args.local_rank != -1 else 1))
105 | logger.info(" Gradient Accumulation steps = %d", args.gradient_accumulation_steps)
106 | logger.info(" Total optimization steps = %d", t_total)
107 |
108 | trainer = Trainer(n_gpu=args.n_gpu,
109 | model=model,
110 | epochs=args.epochs,
111 | logger=logger,
112 | criterion=CrossEntropy(),
113 | optimizer=optimizer,
114 | lr_scheduler=lr_scheduler,
115 | early_stopping=None,
116 | training_monitor=train_monitor,
117 | fp16=args.fp16,
118 | resume_path=args.resume_path,
119 | grad_clip=args.grad_clip,
120 | model_checkpoint=model_checkpoint,
121 | gradient_accumulation_steps=args.gradient_accumulation_steps,
122 | evaluate=F1Score(),
123 | class_report=ClassReport(target_names=[id2label[x] for x in range(len(label2id))]))
124 | trainer.train(train_data=train_dataloader, valid_data=valid_dataloader, seed=args.seed)
125 |
126 |
127 | def run_test(args):
128 | from pybert.io.task_data import TaskData
129 | from pybert.test.predictor import Predictor
130 | data = TaskData()
131 | targets, sentences = data.read_data(raw_data_path=config['test_path'],
132 | preprocessor=None,
133 | is_train=False)
134 | lines = list(zip(sentences, targets))
135 | processor = BertProcessor(vocab_path=config['bert_vocab_path'], do_lower_case=args.do_lower_case)
136 | label_list = processor.get_labels()
137 | id2label = {i: label for i, label in enumerate(label_list)}
138 |
139 | test_data = processor.get_test(lines=lines)
140 | test_examples = processor.create_examples(lines=test_data,
141 | example_type='test',
142 | cached_examples_file=config[
143 | 'data_dir'] / f"cached_test_examples_{args.arch}")
144 | test_features = processor.create_features(examples=test_examples,
145 | max_seq_len=args.eval_max_seq_len,
146 | cached_features_file=config[
147 | 'data_dir'] / "cached_test_features_{}_{}".format(
148 | args.eval_max_seq_len, args.arch
149 | ))
150 | test_dataset = processor.create_dataset(test_features)
151 | test_sampler = SequentialSampler(test_dataset)
152 | test_dataloader = DataLoader(test_dataset, sampler=test_sampler, batch_size=args.train_batch_size)
153 | model = BertForMultiClass.from_pretrained(config['checkpoint_dir'], num_labels=len(label_list))
154 |
155 | # ----------- predicting
156 | logger.info('model predicting....')
157 | predictor = Predictor(model=model, logger=logger, n_gpu=args.n_gpu)
158 | result = predictor.predict(data=test_dataloader)
159 | print(result)
160 |
161 |
162 | def main():
163 | parser = ArgumentParser()
164 | parser.add_argument("--arch", default='bert', type=str)
165 | parser.add_argument("--do_data", action='store_true')
166 | parser.add_argument("--do_train", action='store_true')
167 | parser.add_argument("--do_test", action='store_true')
168 | parser.add_argument("--save_best", action='store_true')
169 | parser.add_argument("--do_lower_case", action='store_true')
170 | parser.add_argument('--data_name', default='cnews', type=str)
171 | parser.add_argument("--epochs", default=6, type=int)
172 | parser.add_argument("--resume_path", default='', type=str)
173 | parser.add_argument("--mode", default='max', type=str)
174 | parser.add_argument("--monitor", default='valid_f1', type=str)
175 | parser.add_argument("--valid_size", default=0.2, type=float)
176 | parser.add_argument("--local_rank", type=int, default=-1)
177 | parser.add_argument("--sorted", default=1, type=int, help='1 : True 0:False ')
178 | parser.add_argument("--n_gpu", type=str, default='0', help='"0,1,.." or "0" or "" ')
179 | parser.add_argument('--gradient_accumulation_steps', type=int, default=1)
180 | parser.add_argument("--train_batch_size", default=8, type=int)
181 | parser.add_argument('--eval_batch_size', default=8, type=int)
182 | parser.add_argument("--train_max_seq_len", default=256, type=int)
183 | parser.add_argument("--eval_max_seq_len", default=256, type=int)
184 | parser.add_argument('--loss_scale', type=float, default=0)
185 | parser.add_argument("--warmup_proportion", default=0.1, type=int, )
186 | parser.add_argument("--weight_decay", default=0.01, type=float)
187 | parser.add_argument("--adam_epsilon", default=1e-8, type=float)
188 | parser.add_argument("--grad_clip", default=1.0, type=float)
189 | parser.add_argument("--learning_rate", default=2e-5, type=float)
190 | parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=42)
191 | parser.add_argument('--fp16', action='store_true')
192 | parser.add_argument('--fp16_opt_level', type=str, default='O1')
193 |
194 | args = parser.parse_args()
195 | config['checkpoint_dir'] = config['checkpoint_dir'] / args.arch
196 | config['checkpoint_dir'].mkdir(exist_ok=True)
197 | # Good practice: save your training arguments together with the trained model
198 | torch.save(args, config['checkpoint_dir'] / 'training_args.bin')
199 | seed_everything(args.seed)
200 | init_logger(log_file=config['log_dir'] / f"{args.arch}.log")
201 |
202 | logger.info("Training/evaluation parameters %s", args)
203 |
204 | if args.do_data:
205 | from pybert.io.task_data import TaskData
206 | processor = BertProcessor(vocab_path=config['bert_vocab_path'], do_lower_case=args.do_lower_case)
207 | label_list = processor.get_labels()
208 | label2id = {label: i for i, label in enumerate(label_list)}
209 | data = TaskData()
210 | targets, sentences = data.read_data(raw_data_path=config['raw_data_path'],
211 | preprocessor=None, is_train=True,label2id=label2id)
212 | data.train_val_split(X=sentences, y=targets, shuffle=True, stratify=targets,
213 | valid_size=args.valid_size, data_dir=config['data_dir'],
214 | data_name=args.data_name)
215 | if args.do_train:
216 | run_train(args)
217 |
218 | if args.do_test:
219 | run_test(args)
220 |
221 | if __name__ == '__main__':
222 | main()
223 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------