├── realworld_benchmark
├── models
├── configs
│ ├── molecules_graph_classification_PNA_HIV.json
│ ├── molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json
│ ├── superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json
│ └── superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json
├── environment_cpu.yml
├── nets
│ ├── mlp_readout_layer.py
│ ├── gru.py
│ ├── HIV_graph_classification
│ │ └── pna_net.py
│ ├── superpixels_graph_classification
│ │ └── pna_net.py
│ └── molecules_graph_regression
│ │ └── pna_net.py
├── data
│ ├── download_datasets.sh
│ ├── HIV.py
│ ├── molecules.py
│ └── superpixels.py
├── environment_gpu.yml
├── train
│ ├── train_HIV_graph_classification.py
│ ├── metrics.py
│ ├── train_molecules_graph_regression.py
│ └── train_superpixels_graph_classification.py
├── docs
│ └── setup.md
├── main_HIV.py
└── README.md
├── multitask_benchmark
├── requirements.txt
├── images
│ ├── results.png
│ ├── symbol.png
│ ├── architecture.png
│ ├── multitask_results.png
│ └── realworld_results.png
├── train
│ ├── gcn.py
│ ├── gin.py
│ ├── gat.py
│ ├── mpnn.py
│ └── pna.py
├── README.md
├── util
│ ├── util.py
│ └── train.py
└── datasets_generation
│ ├── multitask_dataset.py
│ ├── graph_generation.py
│ └── graph_algorithms.py
├── models
├── dgl
│ ├── scalers.py
│ ├── aggregators.py
│ └── pna_layer.py
├── pytorch_geometric
│ ├── scalers.py
│ ├── aggregators.py
│ ├── example.py
│ └── pna.py
├── pytorch
│ ├── pna
│ │ ├── scalers.py
│ │ ├── layer.py
│ │ └── aggregators.py
│ ├── gin
│ │ └── layer.py
│ ├── gcn
│ │ └── layer.py
│ ├── gat
│ │ └── layer.py
│ └── gnn_framework.py
└── layers.py
├── LICENSE
└── README.md
/realworld_benchmark/models:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ../models/
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/requirements.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | numpy
2 | networkx
3 | matplotlib
4 | torch
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/images/results.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lukecavabarrett/pna/HEAD/multitask_benchmark/images/results.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/images/symbol.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lukecavabarrett/pna/HEAD/multitask_benchmark/images/symbol.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/images/architecture.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lukecavabarrett/pna/HEAD/multitask_benchmark/images/architecture.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/images/multitask_results.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lukecavabarrett/pna/HEAD/multitask_benchmark/images/multitask_results.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/images/realworld_results.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lukecavabarrett/pna/HEAD/multitask_benchmark/images/realworld_results.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/dgl/scalers.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import numpy as np
3 |
4 |
5 | # each scaler is a function that takes as input X (B x N x Din), adj (B x N x N) and
6 | # avg_d (dictionary containing averages over training set) and returns X_scaled (B x N x Din) as output
7 |
8 | def scale_identity(h, D=None, avg_d=None):
9 | return h
10 |
11 |
12 | def scale_amplification(h, D, avg_d):
13 | # log(D + 1) / d * h where d is the average of the ``log(D + 1)`` in the training set
14 | return h * (np.log(D + 1) / avg_d["log"])
15 |
16 |
17 | def scale_attenuation(h, D, avg_d):
18 | # (log(D + 1))^-1 / d * X where d is the average of the ``log(D + 1))^-1`` in the training set
19 | return h * (avg_d["log"] / np.log(D + 1))
20 |
21 |
22 | SCALERS = {'identity': scale_identity, 'amplification': scale_amplification, 'attenuation': scale_attenuation}
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/configs/molecules_graph_classification_PNA_HIV.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "gpu": {
3 | "use": true,
4 | "id": 0
5 | },
6 | "model": "PNA",
7 | "dataset": "HIV",
8 |
9 | "params": {
10 | "seed": 41,
11 | "epochs": 200,
12 | "batch_size": 128,
13 | "init_lr": 0.01,
14 | "lr_reduce_factor": 0.5,
15 | "lr_schedule_patience": 20,
16 | "min_lr": 1e-4,
17 | "weight_decay": 3e-6,
18 | "print_epoch_interval": 5,
19 | "max_time": 48
20 | },
21 | "net_params": {
22 | "L": 4,
23 | "hidden_dim": 70,
24 | "out_dim": 70,
25 | "residual": true,
26 | "readout": "mean",
27 | "in_feat_dropout": 0.0,
28 | "dropout": 0.3,
29 | "batch_norm": true,
30 | "aggregators": "mean max min std",
31 | "scalers": "identity amplification attenuation",
32 | "posttrans_layers" : 1
33 | }
34 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/environment_cpu.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # MIT License
2 | # Copyright (c) 2020 Vijay Prakash Dwivedi, Chaitanya K. Joshi, Thomas Laurent, Yoshua Bengio, Xavier Bresson
3 |
4 |
5 | name: benchmark_gnn
6 | channels:
7 | - pytorch
8 | - dglteam
9 | - conda-forge
10 | dependencies:
11 | - python=3.7.4
12 | - python-dateutil=2.8.0
13 | - pytorch=1.3
14 | - torchvision==0.4.2
15 | - pillow==6.1
16 | - dgl=0.4.2
17 | - numpy=1.16.4
18 | - matplotlib=3.1.0
19 | - tensorboard=1.14.0
20 | - tensorboardx=1.8
21 | - absl-py
22 | - networkx=2.3
23 | - scikit-learn=0.21.2
24 | - scipy=1.3.0
25 | - notebook=6.0.0
26 | - h5py=2.9.0
27 | - mkl=2019.4
28 | - ipykernel=5.1.2
29 | - ipython=7.7.0
30 | - ipython_genutils=0.2.0
31 | - ipywidgets=7.5.1
32 | - jupyter=1.0.0
33 | - jupyter_client=5.3.1
34 | - jupyter_console=6.0.0
35 | - jupyter_core=4.5.0
36 | - plotly=4.1.1
37 | - scikit-image=0.15.0
38 | - requests==2.22.0
39 | - tqdm==4.43.0
40 | - pip:
41 | - ogb==1.2.2
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/nets/mlp_readout_layer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # MIT License
2 | # Copyright (c) 2020 Vijay Prakash Dwivedi, Chaitanya K. Joshi, Thomas Laurent, Yoshua Bengio, Xavier Bresson
3 |
4 |
5 | import torch
6 | import torch.nn as nn
7 | import torch.nn.functional as F
8 |
9 | """
10 | MLP Layer used after graph vector representation
11 | """
12 |
13 |
14 | class MLPReadout(nn.Module):
15 |
16 | def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim, L=2): # L=nb_hidden_layers
17 | super().__init__()
18 | list_FC_layers = [nn.Linear(input_dim // 2 ** l, input_dim // 2 ** (l + 1), bias=True) for l in range(L)]
19 | list_FC_layers.append(nn.Linear(input_dim // 2 ** L, output_dim, bias=True))
20 | self.FC_layers = nn.ModuleList(list_FC_layers)
21 | self.L = L
22 |
23 | def forward(self, x):
24 | y = x
25 | for l in range(self.L):
26 | y = self.FC_layers[l](y)
27 | y = F.relu(y)
28 | y = self.FC_layers[self.L](y)
29 | return y
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/data/download_datasets.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # MIT License
2 | # Copyright (c) 2020 Vijay Prakash Dwivedi, Chaitanya K. Joshi, Thomas Laurent, Yoshua Bengio, Xavier Bresson
3 |
4 |
5 | # Command to download dataset:
6 | # bash script_download_all_datasets.sh
7 |
8 |
9 | # ZINC
10 | FILE=ZINC.pkl
11 | if test -f "$FILE"; then
12 | echo -e "$FILE already downloaded."
13 | else
14 | echo -e "\ndownloading $FILE..."
15 | curl https://www.dropbox.com/s/bhimk9p1xst6dvo/ZINC.pkl?dl=1 -o ZINC.pkl -J -L -k
16 | fi
17 |
18 | # MNIST and CIFAR10
19 | FILE=MNIST.pkl
20 | if test -f "$FILE"; then
21 | echo -e "$FILE already downloaded."
22 | else
23 | echo -e "\ndownloading $FILE..."
24 | curl https://www.dropbox.com/s/wcfmo4yvnylceaz/MNIST.pkl?dl=1 -o MNIST.pkl -J -L -k
25 | fi
26 |
27 | FILE=CIFAR10.pkl
28 | if test -f "$FILE"; then
29 | echo -e "$FILE already downloaded."
30 | else
31 | echo -e "\ndownloading $FILE..."
32 | curl https://www.dropbox.com/s/agocm8pxg5u8yb5/CIFAR10.pkl?dl=1 -o CIFAR10.pkl -J -L -k
33 | fi
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/environment_gpu.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # MIT License
2 | # Copyright (c) 2020 Vijay Prakash Dwivedi, Chaitanya K. Joshi, Thomas Laurent, Yoshua Bengio, Xavier Bresson
3 |
4 |
5 | name: benchmark_gnn_gpu
6 | channels:
7 | - pytorch
8 | - dglteam
9 | - conda-forge
10 | - fragcolor
11 | dependencies:
12 | - cuda10.0
13 | - cudatoolkit=10.0
14 | - cudnn=7.6.5
15 | - python=3.7.4
16 | - python-dateutil=2.8.0
17 | - pytorch=1.3
18 | - torchvision==0.4.2
19 | - pillow==6.1
20 | - dgl-cuda10.0=0.4.2
21 | - numpy=1.16.4
22 | - matplotlib=3.1.0
23 | - tensorboard=1.14.0
24 | - tensorboardx=1.8
25 | - absl-py
26 | - networkx=2.3
27 | - scikit-learn=0.21.2
28 | - scipy=1.3.0
29 | - notebook=6.0.0
30 | - h5py=2.9.0
31 | - mkl=2019.4
32 | - ipykernel=5.1.2
33 | - ipython=7.7.0
34 | - ipython_genutils=0.2.0
35 | - ipywidgets=7.5.1
36 | - jupyter=1.0.0
37 | - jupyter_client=5.3.1
38 | - jupyter_console=6.0.0
39 | - jupyter_core=4.5.0
40 | - plotly=4.1.1
41 | - scikit-image=0.15.0
42 | - requests==2.22.0
43 | - tqdm==4.43.0
44 | - pip:
45 | - ogb==1.2.2
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/nets/gru.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | import torch.nn.functional as F
4 |
5 | class GRU(nn.Module):
6 | """
7 | Wrapper class for the GRU used by the GNN framework, nn.GRU is used for the Gated Recurrent Unit itself
8 | """
9 |
10 | def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, device):
11 | super(GRU, self).__init__()
12 | self.input_size = input_size
13 | self.hidden_size = hidden_size
14 | self.gru = nn.GRU(input_size=input_size, hidden_size=hidden_size).to(device)
15 |
16 | def forward(self, x, y):
17 | """
18 | :param x: shape: (B, N, Din) where Din <= input_size (difference is padded)
19 | :param y: shape: (B, N, Dh) where Dh <= hidden_size (difference is padded)
20 | :return: shape: (B, N, Dh)
21 | """
22 | assert (x.shape[-1] <= self.input_size and y.shape[-1] <= self.hidden_size)
23 | x = x.unsqueeze(0)
24 | y = y.unsqueeze(0)
25 | x = self.gru(x, y)[1]
26 | x = x.squeeze()
27 | return x
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/train/gcn.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import division
2 | from __future__ import print_function
3 |
4 | from models.pytorch.gcn.layer import GCNLayer
5 | from multitask_benchmark.util.train import execute_train, build_arg_parser
6 |
7 | # Training settings
8 | parser = build_arg_parser()
9 | args = parser.parse_args()
10 |
11 | execute_train(gnn_args=dict(nfeat=None,
12 | nhid=args.hidden,
13 | nodes_out=None,
14 | graph_out=None,
15 | dropout=args.dropout,
16 | device=None,
17 | first_conv_descr=dict(layer_type=GCNLayer, args=dict()),
18 | middle_conv_descr=dict(layer_type=GCNLayer, args=dict()),
19 | fc_layers=args.fc_layers,
20 | conv_layers=args.conv_layers,
21 | skip=args.skip,
22 | gru=args.gru,
23 | fixed=args.fixed,
24 | variable=args.variable), args=args)
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "gpu": {
3 | "use": true,
4 | "id": 0
5 | },
6 | "model": "PNA",
7 | "dataset": "ZINC",
8 | "out_dir": "out/molecules_graph_regression/",
9 | "params": {
10 | "seed": 41,
11 | "epochs": 1000,
12 | "batch_size": 128,
13 | "init_lr": 0.001,
14 | "lr_reduce_factor": 0.5,
15 | "lr_schedule_patience": 5,
16 | "min_lr": 1e-5,
17 | "weight_decay": 3e-6,
18 | "print_epoch_interval": 5,
19 | "max_time": 48
20 | },
21 | "net_params": {
22 | "L": 4,
23 | "hidden_dim": 75,
24 | "out_dim": 70,
25 | "residual": true,
26 | "edge_feat": false,
27 | "readout": "sum",
28 | "in_feat_dropout": 0.0,
29 | "dropout": 0.0,
30 | "graph_norm": true,
31 | "batch_norm": true,
32 | "aggregators": "mean max min std",
33 | "scalers": "identity amplification attenuation",
34 | "towers": 5,
35 | "divide_input_first": false,
36 | "divide_input_last": true,
37 | "gru": false,
38 | "edge_dim": 0,
39 | "pretrans_layers" : 1,
40 | "posttrans_layers" : 1
41 | }
42 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "gpu": {
3 | "use": true,
4 | "id": 0
5 | },
6 | "model": "PNA",
7 | "dataset": "MNIST",
8 | "out_dir": "out/superpixels_graph_classification/",
9 | "params": {
10 | "seed": 41,
11 | "epochs": 1000,
12 | "batch_size": 128,
13 | "init_lr": 0.001,
14 | "lr_reduce_factor": 0.5,
15 | "lr_schedule_patience": 5,
16 | "min_lr": 1e-5,
17 | "weight_decay": 3e-6,
18 | "print_epoch_interval": 5,
19 | "max_time": 48
20 | },
21 | "net_params": {
22 | "L": 4,
23 | "hidden_dim": 100,
24 | "out_dim": 70,
25 | "residual": true,
26 | "edge_feat": false,
27 | "readout": "sum",
28 | "in_feat_dropout": 0.0,
29 | "dropout": 0.0,
30 | "graph_norm": true,
31 | "batch_norm": true,
32 | "aggregators": "mean max min std",
33 | "scalers": "identity amplification attenuation",
34 | "towers": 5,
35 | "divide_input_first": true,
36 | "divide_input_last": false,
37 | "gru": false,
38 | "edge_dim": 0,
39 | "pretrans_layers" : 1,
40 | "posttrans_layers" : 1
41 | }
42 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "gpu": {
3 | "use": true,
4 | "id": 0
5 | },
6 | "model": "PNA",
7 | "dataset": "CIFAR10",
8 | "out_dir": "out/superpixels_graph_classification/",
9 | "params": {
10 | "seed": 41,
11 | "epochs": 1000,
12 | "batch_size": 128,
13 | "init_lr": 0.001,
14 | "lr_reduce_factor": 0.5,
15 | "lr_schedule_patience": 5,
16 | "min_lr": 1e-5,
17 | "weight_decay": 3e-6,
18 | "print_epoch_interval": 5,
19 | "max_time": 48
20 | },
21 | "net_params": {
22 | "L": 4,
23 | "hidden_dim": 75,
24 | "out_dim": 70,
25 | "residual": true,
26 | "edge_feat": false,
27 | "readout": "sum",
28 | "in_feat_dropout": 0.0,
29 | "dropout": 0.0,
30 | "graph_norm": true,
31 | "batch_norm": true,
32 | "aggregators": "mean max min std",
33 | "scalers": "identity amplification attenuation",
34 | "towers": 5,
35 | "divide_input_first": true,
36 | "divide_input_last": false,
37 | "gru": false,
38 | "edge_dim": 0,
39 | "pretrans_layers" : 1,
40 | "posttrans_layers" : 1
41 | }
42 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2020 Gabriele Corso, Luca Cavalleri
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/pytorch_geometric/scalers.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | from torch import Tensor
3 | from typing import Dict
4 |
5 | # Implemented with the help of Matthias Fey, author of PyTorch Geometric
6 | # For an example see https://github.com/rusty1s/pytorch_geometric/blob/master/examples/pna.py
7 |
8 | def scale_identity(src: Tensor, deg: Tensor, avg_deg: Dict[str, float]):
9 | return src
10 |
11 |
12 | def scale_amplification(src: Tensor, deg: Tensor, avg_deg: Dict[str, float]):
13 | return src * (torch.log(deg + 1) / avg_deg['log'])
14 |
15 |
16 | def scale_attenuation(src: Tensor, deg: Tensor, avg_deg: Dict[str, float]):
17 | scale = avg_deg['log'] / torch.log(deg + 1)
18 | scale[deg == 0] = 1
19 | return src * scale
20 |
21 |
22 | def scale_linear(src: Tensor, deg: Tensor, avg_deg: Dict[str, float]):
23 | return src * (deg / avg_deg['lin'])
24 |
25 |
26 | def scale_inverse_linear(src: Tensor, deg: Tensor, avg_deg: Dict[str, float]):
27 | scale = avg_deg['lin'] / deg
28 | scale[deg == 0] = 1
29 | return src * scale
30 |
31 |
32 | SCALERS = {
33 | 'identity': scale_identity,
34 | 'amplification': scale_amplification,
35 | 'attenuation': scale_attenuation,
36 | 'linear': scale_linear,
37 | 'inverse_linear': scale_inverse_linear
38 | }
39 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/train/gin.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import division
2 | from __future__ import print_function
3 |
4 | from models.pytorch.gin.layer import GINLayer
5 | from multitask_benchmark.util.train import execute_train, build_arg_parser
6 |
7 | # Training settings
8 | parser = build_arg_parser()
9 | parser.add_argument('--gin_fc_layers', type=int, default=2, help='Number of fully connected layers after the aggregation.')
10 | args = parser.parse_args()
11 |
12 | execute_train(gnn_args=dict(nfeat=None,
13 | nhid=args.hidden,
14 | nodes_out=None,
15 | graph_out=None,
16 | dropout=args.dropout,
17 | device=None,
18 | first_conv_descr=dict(layer_type=GINLayer, args=dict(fc_layers=args.gin_fc_layers)),
19 | middle_conv_descr=dict(layer_type=GINLayer, args=dict(fc_layers=args.gin_fc_layers)),
20 | fc_layers=args.fc_layers,
21 | conv_layers=args.conv_layers,
22 | skip=args.skip,
23 | gru=args.gru,
24 | fixed=args.fixed,
25 | variable=args.variable), args=args)
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/pytorch_geometric/aggregators.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | from torch import Tensor
3 | from torch_scatter import scatter
4 | from typing import Optional
5 |
6 | # Implemented with the help of Matthias Fey, author of PyTorch Geometric
7 | # For an example see https://github.com/rusty1s/pytorch_geometric/blob/master/examples/pna.py
8 |
9 | def aggregate_sum(src: Tensor, index: Tensor, dim_size: Optional[int]):
10 | return scatter(src, index, 0, None, dim_size, reduce='sum')
11 |
12 |
13 | def aggregate_mean(src: Tensor, index: Tensor, dim_size: Optional[int]):
14 | return scatter(src, index, 0, None, dim_size, reduce='mean')
15 |
16 |
17 | def aggregate_min(src: Tensor, index: Tensor, dim_size: Optional[int]):
18 | return scatter(src, index, 0, None, dim_size, reduce='min')
19 |
20 |
21 | def aggregate_max(src: Tensor, index: Tensor, dim_size: Optional[int]):
22 | return scatter(src, index, 0, None, dim_size, reduce='max')
23 |
24 |
25 | def aggregate_var(src, index, dim_size):
26 | mean = aggregate_mean(src, index, dim_size)
27 | mean_squares = aggregate_mean(src * src, index, dim_size)
28 | return mean_squares - mean * mean
29 |
30 |
31 | def aggregate_std(src, index, dim_size):
32 | return torch.sqrt(torch.relu(aggregate_var(src, index, dim_size)) + 1e-5)
33 |
34 |
35 | AGGREGATORS = {
36 | 'sum': aggregate_sum,
37 | 'mean': aggregate_mean,
38 | 'min': aggregate_min,
39 | 'max': aggregate_max,
40 | 'var': aggregate_var,
41 | 'std': aggregate_std,
42 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/dgl/aggregators.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 |
3 | EPS = 1e-5
4 |
5 |
6 | def aggregate_mean(h):
7 | return torch.mean(h, dim=1)
8 |
9 |
10 | def aggregate_max(h):
11 | return torch.max(h, dim=1)[0]
12 |
13 |
14 | def aggregate_min(h):
15 | return torch.min(h, dim=1)[0]
16 |
17 |
18 | def aggregate_std(h):
19 | return torch.sqrt(aggregate_var(h) + EPS)
20 |
21 |
22 | def aggregate_var(h):
23 | h_mean_squares = torch.mean(h * h, dim=-2)
24 | h_mean = torch.mean(h, dim=-2)
25 | var = torch.relu(h_mean_squares - h_mean * h_mean)
26 | return var
27 |
28 |
29 | def aggregate_moment(h, n=3):
30 | # for each node (E[(X-E[X])^n])^{1/n}
31 | # EPS is added to the absolute value of expectation before taking the nth root for stability
32 | h_mean = torch.mean(h, dim=1, keepdim=True)
33 | h_n = torch.mean(torch.pow(h - h_mean, n))
34 | rooted_h_n = torch.sign(h_n) * torch.pow(torch.abs(h_n) + EPS, 1. / n)
35 | return rooted_h_n
36 |
37 |
38 | def aggregate_moment_3(h):
39 | return aggregate_moment(h, n=3)
40 |
41 |
42 | def aggregate_moment_4(h):
43 | return aggregate_moment(h, n=4)
44 |
45 |
46 | def aggregate_moment_5(h):
47 | return aggregate_moment(h, n=5)
48 |
49 |
50 | def aggregate_sum(h):
51 | return torch.sum(h, dim=1)
52 |
53 |
54 | AGGREGATORS = {'mean': aggregate_mean, 'sum': aggregate_sum, 'max': aggregate_max, 'min': aggregate_min,
55 | 'std': aggregate_std, 'var': aggregate_var, 'moment3': aggregate_moment_3, 'moment4': aggregate_moment_4,
56 | 'moment5': aggregate_moment_5}
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/pytorch/pna/scalers.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 |
3 |
4 | # each scaler is a function that takes as input X (B x N x Din), adj (B x N x N) and
5 | # avg_d (dictionary containing averages over training set) and returns X_scaled (B x N x Din) as output
6 |
7 | def scale_identity(X, adj, avg_d=None):
8 | return X
9 |
10 |
11 | def scale_amplification(X, adj, avg_d=None):
12 | # log(D + 1) / d * X where d is the average of the ``log(D + 1)`` in the training set
13 | D = torch.sum(adj, -1)
14 | scale = (torch.log(D + 1) / avg_d["log"]).unsqueeze(-1)
15 | X_scaled = torch.mul(scale, X)
16 | return X_scaled
17 |
18 |
19 | def scale_attenuation(X, adj, avg_d=None):
20 | # (log(D + 1))^-1 / d * X where d is the average of the ``log(D + 1))^-1`` in the training set
21 | D = torch.sum(adj, -1)
22 | scale = (avg_d["log"] / torch.log(D + 1)).unsqueeze(-1)
23 | X_scaled = torch.mul(scale, X)
24 | return X_scaled
25 |
26 |
27 | def scale_linear(X, adj, avg_d=None):
28 | # d^{-1} D X where d is the average degree in the training set
29 | D = torch.sum(adj, -1, keepdim=True)
30 | X_scaled = D * X / avg_d["lin"]
31 | return X_scaled
32 |
33 |
34 | def scale_inverse_linear(X, adj, avg_d=None):
35 | # d D^{-1} X where d is the average degree in the training set
36 | D = torch.sum(adj, -1, keepdim=True)
37 | X_scaled = avg_d["lin"] * X / D
38 | return X_scaled
39 |
40 |
41 | SCALERS = {'identity': scale_identity, 'amplification': scale_amplification, 'attenuation': scale_attenuation,
42 | 'linear': scale_linear, 'inverse_linear': scale_inverse_linear}
43 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/train/gat.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import division
2 | from __future__ import print_function
3 |
4 | from models.pytorch.gat.layer import GATLayer
5 | from multitask_benchmark.util.train import execute_train, build_arg_parser
6 |
7 | # Training settings
8 | parser = build_arg_parser()
9 | parser.add_argument('--nheads', type=int, default=4, help='Number of attentions heads.')
10 | parser.add_argument('--alpha', type=float, default=0.2, help='Alpha for the leaky_relu.')
11 | args = parser.parse_args()
12 |
13 | execute_train(gnn_args=dict(nfeat=None,
14 | nhid=args.hidden,
15 | nodes_out=None,
16 | graph_out=None,
17 | dropout=args.dropout,
18 | device=None,
19 | first_conv_descr=dict(layer_type=GATLayer,
20 | args=dict(
21 | nheads=args.nheads,
22 | alpha=args.alpha
23 | )),
24 | middle_conv_descr=dict(layer_type=GATLayer,
25 | args=dict(
26 | nheads=args.nheads,
27 | alpha=args.alpha
28 | )),
29 | fc_layers=args.fc_layers,
30 | conv_layers=args.conv_layers,
31 | skip=args.skip,
32 | gru=args.gru,
33 | fixed=args.fixed,
34 | variable=args.variable), args=args)
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/pytorch/gin/layer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | from models.layers import MLP
4 |
5 |
6 | class GINLayer(nn.Module):
7 | """
8 | Graph Isomorphism Network layer, similar to https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.00826
9 | """
10 |
11 | def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, fc_layers=2, device='cpu'):
12 | """
13 | :param in_features: size of the input per node
14 | :param out_features: size of the output per node
15 | :param fc_layers: number of fully connected layers after the sum aggregator
16 | :param device: device used for computation
17 | """
18 | super(GINLayer, self).__init__()
19 |
20 | self.device = device
21 | self.in_features = in_features
22 | self.out_features = out_features
23 | self.epsilon = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(size=(1,), device=device))
24 | self.post_transformation = MLP(in_size=in_features, hidden_size=max(in_features, out_features),
25 | out_size=out_features, layers=fc_layers, mid_activation='relu',
26 | last_activation='relu', mid_b_norm=True, last_b_norm=False, device=device)
27 | self.reset_parameters()
28 |
29 | def reset_parameters(self):
30 | self.epsilon.data.fill_(0.1)
31 |
32 | def forward(self, input, adj):
33 | (B, N, _) = adj.shape
34 |
35 | # sum aggregation
36 | mod_adj = adj + torch.eye(N, device=self.device).unsqueeze(0) * (1 + self.epsilon)
37 | support = torch.matmul(mod_adj, input)
38 |
39 | # post-aggregation transformation
40 | return self.post_transformation(support)
41 |
42 | def __repr__(self):
43 | return self.__class__.__name__ + ' (' \
44 | + str(self.in_features) + ' -> ' \
45 | + str(self.out_features) + ')'
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/train/train_HIV_graph_classification.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | from ogb.graphproppred import Evaluator
3 |
4 | def train_epoch_sparse(model, optimizer, device, data_loader, epoch):
5 | model.train()
6 | epoch_loss = 0
7 | list_scores = []
8 | list_labels = []
9 | for iter, (batch_graphs, batch_labels) in enumerate(data_loader):
10 | batch_x = batch_graphs.ndata['feat'].to(device) # num x feat
11 | batch_labels = batch_labels.to(device)
12 | optimizer.zero_grad()
13 | batch_scores = model.forward(batch_graphs, batch_x)
14 | loss = model.loss(batch_scores, batch_labels)
15 | loss.backward()
16 | optimizer.step()
17 | epoch_loss += loss.detach().item()
18 | list_scores.append(batch_scores.detach())
19 | list_labels.append(batch_labels.detach().unsqueeze(-1))
20 |
21 | epoch_loss /= (iter + 1)
22 | evaluator = Evaluator(name='ogbg-molhiv')
23 | epoch_train_ROC = evaluator.eval({'y_pred': torch.cat(list_scores),
24 | 'y_true': torch.cat(list_labels)})['rocauc']
25 |
26 | return epoch_loss, epoch_train_ROC, optimizer
27 |
28 |
29 | def evaluate_network_sparse(model, device, data_loader, epoch):
30 | model.eval()
31 | epoch_test_loss = 0
32 | epoch_test_ROC = 0
33 | with torch.no_grad():
34 | list_scores = []
35 | list_labels = []
36 | for iter, (batch_graphs, batch_labels) in enumerate(data_loader):
37 | batch_x = batch_graphs.ndata['feat'].to(device)
38 | batch_labels = batch_labels.to(device)
39 | batch_scores = model.forward(batch_graphs, batch_x)
40 | loss = model.loss(batch_scores, batch_labels)
41 | epoch_test_loss += loss.detach().item()
42 | list_scores.append(batch_scores.detach())
43 | list_labels.append(batch_labels.detach().unsqueeze(-1))
44 |
45 | epoch_test_loss /= (iter + 1)
46 | evaluator = Evaluator(name='ogbg-molhiv')
47 | epoch_test_ROC = evaluator.eval({'y_pred': torch.cat(list_scores),
48 | 'y_true': torch.cat(list_labels)})['rocauc']
49 |
50 | return epoch_test_loss, epoch_test_ROC
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/pytorch/gcn/layer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | import torch
3 | import torch.nn as nn
4 | import torch.nn.functional as F
5 |
6 |
7 | class GCNLayer(nn.Module):
8 | """
9 | GCN layer, similar to https://arxiv.org/abs/1609.02907
10 | Implementation inspired by https://github.com/tkipf/pygcn
11 | """
12 |
13 | def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, bias=True, device='cpu'):
14 | """
15 | :param in_features: size of the input per node
16 | :param out_features: size of the output per node
17 | :param bias: whether to add a learnable bias before the activation
18 | :param device: device used for computation
19 | """
20 | super(GCNLayer, self).__init__()
21 | self.in_features = in_features
22 | self.out_features = out_features
23 | self.device = device
24 | self.W = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(size=(in_features, out_features), device=device))
25 | if bias:
26 | self.b = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(out_features, device=device))
27 | else:
28 | self.register_parameter('b', None)
29 | self.reset_parameters()
30 |
31 | def reset_parameters(self):
32 | stdv = 1. / math.sqrt(self.W.size(1))
33 | self.W.data.uniform_(-stdv, stdv)
34 | if self.b is not None:
35 | self.b.data.uniform_(-stdv, stdv)
36 |
37 | def forward(self, X, adj):
38 | (B, N, _) = adj.shape
39 |
40 | # linear transformation
41 | XW = torch.matmul(X, self.W)
42 |
43 | # normalised mean aggregation
44 | adj = adj + torch.eye(N, device=self.device).unsqueeze(0)
45 | rD = torch.mul(torch.pow(torch.sum(adj, -1, keepdim=True), -0.5),
46 | torch.eye(N, device=self.device).unsqueeze(0)) # D^{-1/2]
47 | adj = torch.matmul(torch.matmul(rD, adj), rD) # D^{-1/2] A' D^{-1/2]
48 | y = torch.bmm(adj, XW)
49 |
50 | if self.b is not None:
51 | y = y + self.b
52 | return F.leaky_relu(y)
53 |
54 | def __repr__(self):
55 | return self.__class__.__name__ + ' (' \
56 | + str(self.in_features) + ' -> ' \
57 | + str(self.out_features) + ')'
58 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/train/metrics.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # MIT License
2 | # Copyright (c) 2020 Vijay Prakash Dwivedi, Chaitanya K. Joshi, Thomas Laurent, Yoshua Bengio, Xavier Bresson
3 |
4 |
5 | import torch
6 | import torch.nn as nn
7 | import torch.nn.functional as F
8 |
9 | from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
10 | from sklearn.metrics import f1_score
11 | import numpy as np
12 |
13 |
14 | def MAE(scores, targets):
15 | MAE = F.l1_loss(scores, targets)
16 | return MAE
17 |
18 |
19 | def accuracy_TU(scores, targets):
20 | scores = scores.detach().argmax(dim=1)
21 | acc = (scores==targets).float().sum().item()
22 | return acc
23 |
24 |
25 | def accuracy_MNIST_CIFAR(scores, targets):
26 | scores = scores.detach().argmax(dim=1)
27 | acc = (scores==targets).float().sum().item()
28 | return acc
29 |
30 | def accuracy_CITATION_GRAPH(scores, targets):
31 | scores = scores.detach().argmax(dim=1)
32 | acc = (scores==targets).float().sum().item()
33 | acc = acc / len(targets)
34 | return acc
35 |
36 |
37 | def accuracy_SBM(scores, targets):
38 | S = targets.cpu().numpy()
39 | C = np.argmax( torch.nn.Softmax(dim=0)(scores).cpu().detach().numpy() , axis=1 )
40 | CM = confusion_matrix(S,C).astype(np.float32)
41 | nb_classes = CM.shape[0]
42 | targets = targets.cpu().detach().numpy()
43 | nb_non_empty_classes = 0
44 | pr_classes = np.zeros(nb_classes)
45 | for r in range(nb_classes):
46 | cluster = np.where(targets==r)[0]
47 | if cluster.shape[0] != 0:
48 | pr_classes[r] = CM[r,r]/ float(cluster.shape[0])
49 | if CM[r,r]>0:
50 | nb_non_empty_classes += 1
51 | else:
52 | pr_classes[r] = 0.0
53 | acc = 100.* np.sum(pr_classes)/ float(nb_non_empty_classes)
54 | return acc
55 |
56 |
57 | def binary_f1_score(scores, targets):
58 | """Computes the F1 score using scikit-learn for binary class labels.
59 |
60 | Returns the F1 score for the positive class, i.e. labelled '1'.
61 | """
62 | y_true = targets.cpu().numpy()
63 | y_pred = scores.argmax(dim=1).cpu().numpy()
64 | return f1_score(y_true, y_pred, average='binary')
65 |
66 |
67 | def accuracy_VOC(scores, targets):
68 | scores = scores.detach().argmax(dim=1).cpu()
69 | targets = targets.cpu().detach().numpy()
70 | acc = f1_score(scores, targets, average='weighted')
71 | return acc
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Multi-task benchmark
2 |
3 | 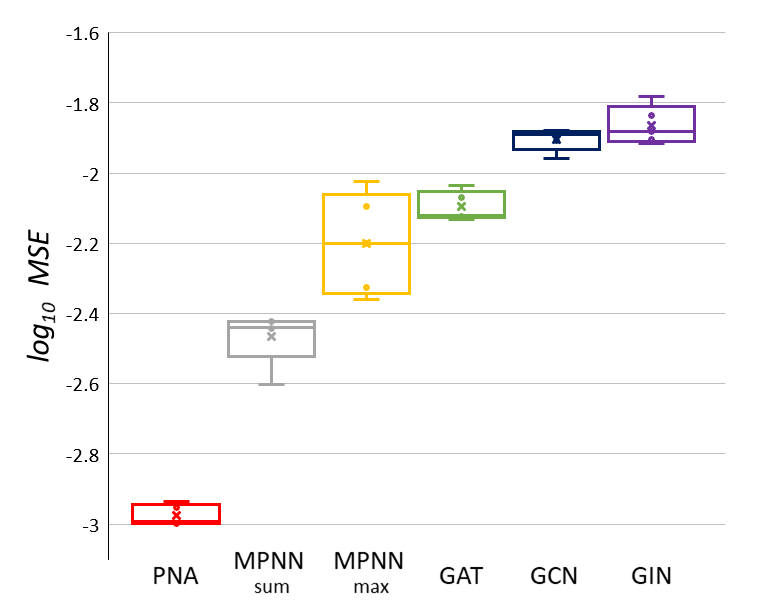 4 |
5 | ## Overview
6 |
7 | We provide the scripts for the generation and execution of the multi-task benchmark.
8 | - `dataset_generation` contains:
9 | - `graph_generation.py` with scripts to generate the various graphs and add randomness;
10 | - `graph_algorithms.py` with the implementation of many algorithms on graphs that can be used as labels;
11 | - `multitask_dataset.py` unifies the two files above generating and saving the benchmarks we used in the paper.
12 | - `util` contains:
13 | - preprocessing subroutines and loss functions (`util.py`);
14 | - general training and evaluation procedures (`train.py`).
15 | - `train` contains a script for each model which sets up the command line parameters and initiates the training procedure.
16 |
17 | This benchmark uses the PyTorch version of PNA (`../models/pytorch/pna`). Below you can find the instructions on how to create the dataset and run the models, these are also available in this [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/17NntHxoKQzpKmi8siMOLP9WfANlwbW8S?usp=sharing).
18 |
19 | ## Dependencies
20 | Install PyTorch from the [official website](https://pytorch.org/). The code was tested over PyTorch 1.4.
21 |
22 | Move to the source of the repository before running the following. Then install the other dependencies:
23 | ```
24 | pip3 install -r multitask_benchmark/requirements.txt
25 | ```
26 |
27 | ## Test run
28 |
29 | Generate the benchmark dataset (add `--extrapolation` for multiple test sets of different sizes):
30 | ```
31 | python3 -m multitask_benchmark.datasets_generation.multitask_dataset
32 | ```
33 |
34 | then run the training:
35 | ```
36 | python3 -m multitask_benchmark.train.pna --variable --fixed --gru --lr=0.003 --weight_decay=1e-6 --dropout=0.0 --epochs=10000 --patience=1000 --variable_conv_layers=N/2 --fc_layers=3 --hidden=16 --towers=4 --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --data=multitask_benchmark/data/multitask_dataset.pkl
37 | ```
38 |
39 | The command above uses the hyperparameters tuned for the non-extrapolating dataset and the architecture outlined in the diagram below. For more details on the architecture, how the hyperparameters were tuned and the results collected refer to our [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718).
40 |
41 | 
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/train/train_molecules_graph_regression.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # MIT License
2 | # Copyright (c) 2020 Vijay Prakash Dwivedi, Chaitanya K. Joshi, Thomas Laurent, Yoshua Bengio, Xavier Bresson
3 |
4 |
5 | """
6 | Utility functions for training one epoch
7 | and evaluating one epoch
8 | """
9 | import torch
10 | import torch.nn as nn
11 | import math
12 |
13 | from .metrics import MAE
14 |
15 | def train_epoch(model, optimizer, device, data_loader, epoch):
16 | model.train()
17 | epoch_loss = 0
18 | epoch_train_mae = 0
19 | nb_data = 0
20 | gpu_mem = 0
21 | for iter, (batch_graphs, batch_targets, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e) in enumerate(data_loader):
22 | batch_x = batch_graphs.ndata['feat'].to(device) # num x feat
23 | batch_e = batch_graphs.edata['feat'].to(device)
24 | batch_snorm_e = batch_snorm_e.to(device)
25 | batch_targets = batch_targets.to(device)
26 | batch_snorm_n = batch_snorm_n.to(device) # num x 1
27 | optimizer.zero_grad()
28 |
29 | batch_scores = model.forward(batch_graphs, batch_x, batch_e, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e)
30 | loss = model.loss(batch_scores, batch_targets)
31 | loss.backward()
32 | optimizer.step()
33 | epoch_loss += loss.detach().item()
34 | epoch_train_mae += MAE(batch_scores, batch_targets)
35 | nb_data += batch_targets.size(0)
36 | epoch_loss /= (iter + 1)
37 | epoch_train_mae /= (iter + 1)
38 |
39 | return epoch_loss, epoch_train_mae, optimizer
40 |
41 | def evaluate_network(model, device, data_loader, epoch):
42 | model.eval()
43 | epoch_test_loss = 0
44 | epoch_test_mae = 0
45 | nb_data = 0
46 | with torch.no_grad():
47 | for iter, (batch_graphs, batch_targets, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e) in enumerate(data_loader):
48 | batch_x = batch_graphs.ndata['feat'].to(device)
49 | batch_e = batch_graphs.edata['feat'].to(device)
50 | batch_snorm_e = batch_snorm_e.to(device)
51 | batch_targets = batch_targets.to(device)
52 | batch_snorm_n = batch_snorm_n.to(device)
53 |
54 | batch_scores = model.forward(batch_graphs, batch_x, batch_e, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e)
55 | loss = model.loss(batch_scores, batch_targets)
56 | epoch_test_loss += loss.detach().item()
57 | epoch_test_mae += MAE(batch_scores, batch_targets)
58 | nb_data += batch_targets.size(0)
59 | epoch_test_loss /= (iter + 1)
60 | epoch_test_mae /= (iter + 1)
61 |
62 | return epoch_test_loss, epoch_test_mae
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/train/train_superpixels_graph_classification.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # MIT License
2 | # Copyright (c) 2020 Vijay Prakash Dwivedi, Chaitanya K. Joshi, Thomas Laurent, Yoshua Bengio, Xavier Bresson
3 |
4 |
5 | """
6 | Utility functions for training one epoch
7 | and evaluating one epoch
8 | """
9 | import torch
10 | import torch.nn as nn
11 | import math
12 |
13 | from .metrics import accuracy_MNIST_CIFAR as accuracy
14 |
15 | def train_epoch(model, optimizer, device, data_loader, epoch):
16 | model.train()
17 | epoch_loss = 0
18 | epoch_train_acc = 0
19 | nb_data = 0
20 | gpu_mem = 0
21 | for iter, (batch_graphs, batch_labels, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e) in enumerate(data_loader):
22 | batch_x = batch_graphs.ndata['feat'].to(device) # num x feat
23 | batch_e = batch_graphs.edata['feat'].to(device)
24 | batch_snorm_e = batch_snorm_e.to(device)
25 | batch_labels = batch_labels.to(device)
26 | batch_snorm_n = batch_snorm_n.to(device) # num x 1
27 | optimizer.zero_grad()
28 |
29 | batch_scores = model.forward(batch_graphs, batch_x, batch_e, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e)
30 | loss = model.loss(batch_scores, batch_labels)
31 | loss.backward()
32 | optimizer.step()
33 | epoch_loss += loss.detach().item()
34 | epoch_train_acc += accuracy(batch_scores, batch_labels)
35 | nb_data += batch_labels.size(0)
36 | epoch_loss /= (iter + 1)
37 | epoch_train_acc /= nb_data
38 |
39 | return epoch_loss, epoch_train_acc, optimizer
40 |
41 | def evaluate_network(model, device, data_loader, epoch):
42 | model.eval()
43 | epoch_test_loss = 0
44 | epoch_test_acc = 0
45 | nb_data = 0
46 | with torch.no_grad():
47 | for iter, (batch_graphs, batch_labels, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e) in enumerate(data_loader):
48 | batch_x = batch_graphs.ndata['feat'].to(device)
49 | batch_e = batch_graphs.edata['feat'].to(device)
50 | batch_snorm_e = batch_snorm_e.to(device)
51 | batch_labels = batch_labels.to(device)
52 | batch_snorm_n = batch_snorm_n.to(device)
53 |
54 | batch_scores = model.forward(batch_graphs, batch_x, batch_e, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e)
55 | loss = model.loss(batch_scores, batch_labels)
56 | epoch_test_loss += loss.detach().item()
57 | epoch_test_acc += accuracy(batch_scores, batch_labels)
58 | nb_data += batch_labels.size(0)
59 | epoch_test_loss /= (iter + 1)
60 | epoch_test_acc /= nb_data
61 |
62 | return epoch_test_loss, epoch_test_acc
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/nets/HIV_graph_classification/pna_net.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | import dgl
3 | from models.dgl.pna_layer import PNASimpleLayer
4 | from nets.mlp_readout_layer import MLPReadout
5 | import torch
6 | from ogb.graphproppred.mol_encoder import AtomEncoder
7 |
8 |
9 | class PNANet(nn.Module):
10 | def __init__(self, net_params):
11 | super().__init__()
12 | hidden_dim = net_params['hidden_dim']
13 | out_dim = net_params['out_dim']
14 | in_feat_dropout = net_params['in_feat_dropout']
15 | dropout = net_params['dropout']
16 | n_layers = net_params['L']
17 | self.readout = net_params['readout']
18 | self.batch_norm = net_params['batch_norm']
19 | self.aggregators = net_params['aggregators']
20 | self.scalers = net_params['scalers']
21 | self.avg_d = net_params['avg_d']
22 | self.residual = net_params['residual']
23 | posttrans_layers = net_params['posttrans_layers']
24 | device = net_params['device']
25 | self.device = device
26 |
27 | self.in_feat_dropout = nn.Dropout(in_feat_dropout)
28 | self.embedding_h = AtomEncoder(emb_dim=hidden_dim)
29 |
30 | self.layers = nn.ModuleList(
31 | [PNASimpleLayer(in_dim=hidden_dim, out_dim=hidden_dim, dropout=dropout,
32 | batch_norm=self.batch_norm, residual=self.residual, aggregators=self.aggregators,
33 | scalers=self.scalers, avg_d=self.avg_d, posttrans_layers=posttrans_layers)
34 | for _ in range(n_layers - 1)])
35 | self.layers.append(PNASimpleLayer(in_dim=hidden_dim, out_dim=out_dim, dropout=dropout,
36 | batch_norm=self.batch_norm,
37 | residual=self.residual, aggregators=self.aggregators, scalers=self.scalers,
38 | avg_d=self.avg_d, posttrans_layers=posttrans_layers))
39 |
40 | self.MLP_layer = MLPReadout(out_dim, 1) # 1 out dim since regression problem
41 |
42 | def forward(self, g, h):
43 | h = self.embedding_h(h)
44 | h = self.in_feat_dropout(h)
45 |
46 | for i, conv in enumerate(self.layers):
47 | h = conv(g, h)
48 |
49 | g.ndata['h'] = h
50 |
51 | if self.readout == "sum":
52 | hg = dgl.sum_nodes(g, 'h')
53 | elif self.readout == "max":
54 | hg = dgl.max_nodes(g, 'h')
55 | elif self.readout == "mean":
56 | hg = dgl.mean_nodes(g, 'h')
57 | else:
58 | hg = dgl.mean_nodes(g, 'h') # default readout is mean nodes
59 |
60 | return self.MLP_layer(hg)
61 |
62 | def loss(self, scores, labels):
63 | loss = torch.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()(scores, labels.type(torch.FloatTensor).to('cuda').unsqueeze(-1))
64 | return loss
65 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation
2 |
3 | Implementation of Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation for Graph Nets [arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718) in PyTorch, DGL and PyTorch Geometric.
4 |
5 | *Update: now you can find PNA directly integrated in both [PyTorch Geometric](https://pytorch-geometric.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/nn.html#torch_geometric.nn.conv.PNAConv) and [DGL](https://docs.dgl.ai/generated/dgl.nn.pytorch.conv.PNAConv.html)!*
6 |
7 | 
8 |
9 | ## Overview
10 |
11 | We provide the implementation of the Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation (PNA) in PyTorch, DGL and PyTorch Geometric frameworks, along with scripts to generate and run the multitask benchmarks, scripts for running real-world benchmarks, a flexible PyTorch GNN framework and implementations of the other models used for comparison. The repository is organised as follows:
12 |
13 | - `models` contains:
14 | - `pytorch` contains the various GNN models implemented in PyTorch:
15 | - the implementation of the aggregators, the scalers and the PNA layer (`pna`)
16 | - the flexible GNN framework that can be used with any type of graph convolutions (`gnn_framework.py`)
17 | - implementations of the other GNN models used for comparison in the paper, namely GCN, GAT, GIN and MPNN
18 | - `dgl` contains the PNA model implemented via the [DGL library](https://www.dgl.ai/): aggregators, scalers, and layer.
19 | - `pytorch_geometric` contains the PNA model implemented via the [PyTorch Geometric library](https://pytorch-geometric.readthedocs.io/): aggregators, scalers, and layer.
20 | - `layers.py` contains general NN layers used by the various models
21 | - `multi_task` contains various scripts to recreate the multi_task benchmark along with the files used to train the various models. In `multi_task/README.md` we detail the instructions for the generation and training hyperparameters tuned.
22 | - `real_world` contains various scripts from [Benchmarking GNNs](https://github.com/graphdeeplearning/benchmarking-gnns) to download the real-world benchmarks and train the PNA on them. In `real_world/README.md` we provide instructions for the generation and training hyperparameters tuned.
23 |
24 | 
25 |
26 | ## Reference
27 | ```
28 | @inproceedings{corso2020pna,
29 | title = {Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation for Graph Nets},
30 | author = {Corso, Gabriele and Cavalleri, Luca and Beaini, Dominique and Li\`{o}, Pietro and Veli\v{c}kovi\'{c}, Petar},
31 | booktitle = {Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
32 | year = {2020}
33 | }
34 | ```
35 |
36 | ## License
37 | MIT
38 |
39 |
40 | ## Acknowledgements
41 |
42 | The authors would like to thank Saro Passaro for running some of the tests presented in this repository and
43 | Giorgos Bouritsas, Fabrizio Frasca, Leonardo Cotta, Zhanghao Wu, Zhanqiu Zhang and George Watkins for pointing out some issues with the code.
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/data/HIV.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import time
2 | import dgl
3 | import torch
4 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
5 | from ogb.graphproppred import DglGraphPropPredDataset
6 | from ogb.graphproppred import Evaluator
7 | import torch.utils.data
8 |
9 |
10 | class HIVDGL(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
11 | def __init__(self, data, split):
12 | self.split = split
13 | self.data = [g for g in data[self.split]]
14 | self.graph_lists = []
15 | self.graph_labels = []
16 | for g in self.data:
17 | if g[0].number_of_nodes() > 5:
18 | self.graph_lists.append(g[0])
19 | self.graph_labels.append(g[1])
20 | self.n_samples = len(self.graph_lists)
21 |
22 | def __len__(self):
23 | """Return the number of graphs in the dataset."""
24 | return self.n_samples
25 |
26 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
27 | """
28 | Get the idx^th sample.
29 | Parameters
30 | ---------
31 | idx : int
32 | The sample index.
33 | Returns
34 | -------
35 | (dgl.DGLGraph, int)
36 | DGLGraph with node feature stored in `feat` field
37 | And its label.
38 | """
39 | return self.graph_lists[idx], self.graph_labels[idx]
40 |
41 |
42 | class HIVDataset(Dataset):
43 | def __init__(self, name, verbose=True):
44 | start = time.time()
45 | if verbose:
46 | print("[I] Loading dataset %s..." % (name))
47 | self.name = name
48 | self.dataset = DglGraphPropPredDataset(name = 'ogbg-molhiv')
49 | self.split_idx = self.dataset.get_idx_split()
50 |
51 | self.train = HIVDGL(self.dataset, self.split_idx['train'])
52 | self.val = HIVDGL(self.dataset, self.split_idx['valid'])
53 | self.test = HIVDGL(self.dataset, self.split_idx['test'])
54 |
55 | self.evaluator = Evaluator(name='ogbg-molhiv')
56 |
57 | if verbose:
58 | print('train, test, val sizes :', len(self.train), len(self.test), len(self.val))
59 | print("[I] Finished loading.")
60 | print("[I] Data load time: {:.4f}s".format(time.time() - start))
61 |
62 | # form a mini batch from a given list of samples = [(graph, label) pairs]
63 | def collate(self, samples):
64 | # The input samples is a list of pairs (graph, label).
65 | graphs, labels = map(list, zip(*samples))
66 | labels = torch.cat(labels).long()
67 | batched_graph = dgl.batch(graphs)
68 |
69 | return batched_graph, labels
70 |
71 | def _add_self_loops(self):
72 | # function for adding self loops
73 | # this function will be called only if self_loop flag is True
74 |
75 | self.train.graph_lists = [self_loop(g) for g in self.train.graph_lists]
76 | self.val.graph_lists = [self_loop(g) for g in self.val.graph_lists]
77 | self.test.graph_lists = [self_loop(g) for g in self.test.graph_lists]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/docs/setup.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Benchmark setup
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
4 |
5 | ## Overview
6 |
7 | We provide the scripts for the generation and execution of the multi-task benchmark.
8 | - `dataset_generation` contains:
9 | - `graph_generation.py` with scripts to generate the various graphs and add randomness;
10 | - `graph_algorithms.py` with the implementation of many algorithms on graphs that can be used as labels;
11 | - `multitask_dataset.py` unifies the two files above generating and saving the benchmarks we used in the paper.
12 | - `util` contains:
13 | - preprocessing subroutines and loss functions (`util.py`);
14 | - general training and evaluation procedures (`train.py`).
15 | - `train` contains a script for each model which sets up the command line parameters and initiates the training procedure.
16 |
17 | This benchmark uses the PyTorch version of PNA (`../models/pytorch/pna`). Below you can find the instructions on how to create the dataset and run the models, these are also available in this [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/17NntHxoKQzpKmi8siMOLP9WfANlwbW8S?usp=sharing).
18 |
19 | ## Dependencies
20 | Install PyTorch from the [official website](https://pytorch.org/). The code was tested over PyTorch 1.4.
21 |
22 | Move to the source of the repository before running the following. Then install the other dependencies:
23 | ```
24 | pip3 install -r multitask_benchmark/requirements.txt
25 | ```
26 |
27 | ## Test run
28 |
29 | Generate the benchmark dataset (add `--extrapolation` for multiple test sets of different sizes):
30 | ```
31 | python3 -m multitask_benchmark.datasets_generation.multitask_dataset
32 | ```
33 |
34 | then run the training:
35 | ```
36 | python3 -m multitask_benchmark.train.pna --variable --fixed --gru --lr=0.003 --weight_decay=1e-6 --dropout=0.0 --epochs=10000 --patience=1000 --variable_conv_layers=N/2 --fc_layers=3 --hidden=16 --towers=4 --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --data=multitask_benchmark/data/multitask_dataset.pkl
37 | ```
38 |
39 | The command above uses the hyperparameters tuned for the non-extrapolating dataset and the architecture outlined in the diagram below. For more details on the architecture, how the hyperparameters were tuned and the results collected refer to our [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718).
40 |
41 | 
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/train/train_molecules_graph_regression.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # MIT License
2 | # Copyright (c) 2020 Vijay Prakash Dwivedi, Chaitanya K. Joshi, Thomas Laurent, Yoshua Bengio, Xavier Bresson
3 |
4 |
5 | """
6 | Utility functions for training one epoch
7 | and evaluating one epoch
8 | """
9 | import torch
10 | import torch.nn as nn
11 | import math
12 |
13 | from .metrics import MAE
14 |
15 | def train_epoch(model, optimizer, device, data_loader, epoch):
16 | model.train()
17 | epoch_loss = 0
18 | epoch_train_mae = 0
19 | nb_data = 0
20 | gpu_mem = 0
21 | for iter, (batch_graphs, batch_targets, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e) in enumerate(data_loader):
22 | batch_x = batch_graphs.ndata['feat'].to(device) # num x feat
23 | batch_e = batch_graphs.edata['feat'].to(device)
24 | batch_snorm_e = batch_snorm_e.to(device)
25 | batch_targets = batch_targets.to(device)
26 | batch_snorm_n = batch_snorm_n.to(device) # num x 1
27 | optimizer.zero_grad()
28 |
29 | batch_scores = model.forward(batch_graphs, batch_x, batch_e, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e)
30 | loss = model.loss(batch_scores, batch_targets)
31 | loss.backward()
32 | optimizer.step()
33 | epoch_loss += loss.detach().item()
34 | epoch_train_mae += MAE(batch_scores, batch_targets)
35 | nb_data += batch_targets.size(0)
36 | epoch_loss /= (iter + 1)
37 | epoch_train_mae /= (iter + 1)
38 |
39 | return epoch_loss, epoch_train_mae, optimizer
40 |
41 | def evaluate_network(model, device, data_loader, epoch):
42 | model.eval()
43 | epoch_test_loss = 0
44 | epoch_test_mae = 0
45 | nb_data = 0
46 | with torch.no_grad():
47 | for iter, (batch_graphs, batch_targets, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e) in enumerate(data_loader):
48 | batch_x = batch_graphs.ndata['feat'].to(device)
49 | batch_e = batch_graphs.edata['feat'].to(device)
50 | batch_snorm_e = batch_snorm_e.to(device)
51 | batch_targets = batch_targets.to(device)
52 | batch_snorm_n = batch_snorm_n.to(device)
53 |
54 | batch_scores = model.forward(batch_graphs, batch_x, batch_e, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e)
55 | loss = model.loss(batch_scores, batch_targets)
56 | epoch_test_loss += loss.detach().item()
57 | epoch_test_mae += MAE(batch_scores, batch_targets)
58 | nb_data += batch_targets.size(0)
59 | epoch_test_loss /= (iter + 1)
60 | epoch_test_mae /= (iter + 1)
61 |
62 | return epoch_test_loss, epoch_test_mae
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/train/train_superpixels_graph_classification.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # MIT License
2 | # Copyright (c) 2020 Vijay Prakash Dwivedi, Chaitanya K. Joshi, Thomas Laurent, Yoshua Bengio, Xavier Bresson
3 |
4 |
5 | """
6 | Utility functions for training one epoch
7 | and evaluating one epoch
8 | """
9 | import torch
10 | import torch.nn as nn
11 | import math
12 |
13 | from .metrics import accuracy_MNIST_CIFAR as accuracy
14 |
15 | def train_epoch(model, optimizer, device, data_loader, epoch):
16 | model.train()
17 | epoch_loss = 0
18 | epoch_train_acc = 0
19 | nb_data = 0
20 | gpu_mem = 0
21 | for iter, (batch_graphs, batch_labels, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e) in enumerate(data_loader):
22 | batch_x = batch_graphs.ndata['feat'].to(device) # num x feat
23 | batch_e = batch_graphs.edata['feat'].to(device)
24 | batch_snorm_e = batch_snorm_e.to(device)
25 | batch_labels = batch_labels.to(device)
26 | batch_snorm_n = batch_snorm_n.to(device) # num x 1
27 | optimizer.zero_grad()
28 |
29 | batch_scores = model.forward(batch_graphs, batch_x, batch_e, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e)
30 | loss = model.loss(batch_scores, batch_labels)
31 | loss.backward()
32 | optimizer.step()
33 | epoch_loss += loss.detach().item()
34 | epoch_train_acc += accuracy(batch_scores, batch_labels)
35 | nb_data += batch_labels.size(0)
36 | epoch_loss /= (iter + 1)
37 | epoch_train_acc /= nb_data
38 |
39 | return epoch_loss, epoch_train_acc, optimizer
40 |
41 | def evaluate_network(model, device, data_loader, epoch):
42 | model.eval()
43 | epoch_test_loss = 0
44 | epoch_test_acc = 0
45 | nb_data = 0
46 | with torch.no_grad():
47 | for iter, (batch_graphs, batch_labels, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e) in enumerate(data_loader):
48 | batch_x = batch_graphs.ndata['feat'].to(device)
49 | batch_e = batch_graphs.edata['feat'].to(device)
50 | batch_snorm_e = batch_snorm_e.to(device)
51 | batch_labels = batch_labels.to(device)
52 | batch_snorm_n = batch_snorm_n.to(device)
53 |
54 | batch_scores = model.forward(batch_graphs, batch_x, batch_e, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e)
55 | loss = model.loss(batch_scores, batch_labels)
56 | epoch_test_loss += loss.detach().item()
57 | epoch_test_acc += accuracy(batch_scores, batch_labels)
58 | nb_data += batch_labels.size(0)
59 | epoch_test_loss /= (iter + 1)
60 | epoch_test_acc /= nb_data
61 |
62 | return epoch_test_loss, epoch_test_acc
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/nets/HIV_graph_classification/pna_net.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | import dgl
3 | from models.dgl.pna_layer import PNASimpleLayer
4 | from nets.mlp_readout_layer import MLPReadout
5 | import torch
6 | from ogb.graphproppred.mol_encoder import AtomEncoder
7 |
8 |
9 | class PNANet(nn.Module):
10 | def __init__(self, net_params):
11 | super().__init__()
12 | hidden_dim = net_params['hidden_dim']
13 | out_dim = net_params['out_dim']
14 | in_feat_dropout = net_params['in_feat_dropout']
15 | dropout = net_params['dropout']
16 | n_layers = net_params['L']
17 | self.readout = net_params['readout']
18 | self.batch_norm = net_params['batch_norm']
19 | self.aggregators = net_params['aggregators']
20 | self.scalers = net_params['scalers']
21 | self.avg_d = net_params['avg_d']
22 | self.residual = net_params['residual']
23 | posttrans_layers = net_params['posttrans_layers']
24 | device = net_params['device']
25 | self.device = device
26 |
27 | self.in_feat_dropout = nn.Dropout(in_feat_dropout)
28 | self.embedding_h = AtomEncoder(emb_dim=hidden_dim)
29 |
30 | self.layers = nn.ModuleList(
31 | [PNASimpleLayer(in_dim=hidden_dim, out_dim=hidden_dim, dropout=dropout,
32 | batch_norm=self.batch_norm, residual=self.residual, aggregators=self.aggregators,
33 | scalers=self.scalers, avg_d=self.avg_d, posttrans_layers=posttrans_layers)
34 | for _ in range(n_layers - 1)])
35 | self.layers.append(PNASimpleLayer(in_dim=hidden_dim, out_dim=out_dim, dropout=dropout,
36 | batch_norm=self.batch_norm,
37 | residual=self.residual, aggregators=self.aggregators, scalers=self.scalers,
38 | avg_d=self.avg_d, posttrans_layers=posttrans_layers))
39 |
40 | self.MLP_layer = MLPReadout(out_dim, 1) # 1 out dim since regression problem
41 |
42 | def forward(self, g, h):
43 | h = self.embedding_h(h)
44 | h = self.in_feat_dropout(h)
45 |
46 | for i, conv in enumerate(self.layers):
47 | h = conv(g, h)
48 |
49 | g.ndata['h'] = h
50 |
51 | if self.readout == "sum":
52 | hg = dgl.sum_nodes(g, 'h')
53 | elif self.readout == "max":
54 | hg = dgl.max_nodes(g, 'h')
55 | elif self.readout == "mean":
56 | hg = dgl.mean_nodes(g, 'h')
57 | else:
58 | hg = dgl.mean_nodes(g, 'h') # default readout is mean nodes
59 |
60 | return self.MLP_layer(hg)
61 |
62 | def loss(self, scores, labels):
63 | loss = torch.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()(scores, labels.type(torch.FloatTensor).to('cuda').unsqueeze(-1))
64 | return loss
65 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation
2 |
3 | Implementation of Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation for Graph Nets [arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718) in PyTorch, DGL and PyTorch Geometric.
4 |
5 | *Update: now you can find PNA directly integrated in both [PyTorch Geometric](https://pytorch-geometric.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/nn.html#torch_geometric.nn.conv.PNAConv) and [DGL](https://docs.dgl.ai/generated/dgl.nn.pytorch.conv.PNAConv.html)!*
6 |
7 | 
8 |
9 | ## Overview
10 |
11 | We provide the implementation of the Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation (PNA) in PyTorch, DGL and PyTorch Geometric frameworks, along with scripts to generate and run the multitask benchmarks, scripts for running real-world benchmarks, a flexible PyTorch GNN framework and implementations of the other models used for comparison. The repository is organised as follows:
12 |
13 | - `models` contains:
14 | - `pytorch` contains the various GNN models implemented in PyTorch:
15 | - the implementation of the aggregators, the scalers and the PNA layer (`pna`)
16 | - the flexible GNN framework that can be used with any type of graph convolutions (`gnn_framework.py`)
17 | - implementations of the other GNN models used for comparison in the paper, namely GCN, GAT, GIN and MPNN
18 | - `dgl` contains the PNA model implemented via the [DGL library](https://www.dgl.ai/): aggregators, scalers, and layer.
19 | - `pytorch_geometric` contains the PNA model implemented via the [PyTorch Geometric library](https://pytorch-geometric.readthedocs.io/): aggregators, scalers, and layer.
20 | - `layers.py` contains general NN layers used by the various models
21 | - `multi_task` contains various scripts to recreate the multi_task benchmark along with the files used to train the various models. In `multi_task/README.md` we detail the instructions for the generation and training hyperparameters tuned.
22 | - `real_world` contains various scripts from [Benchmarking GNNs](https://github.com/graphdeeplearning/benchmarking-gnns) to download the real-world benchmarks and train the PNA on them. In `real_world/README.md` we provide instructions for the generation and training hyperparameters tuned.
23 |
24 | 
25 |
26 | ## Reference
27 | ```
28 | @inproceedings{corso2020pna,
29 | title = {Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation for Graph Nets},
30 | author = {Corso, Gabriele and Cavalleri, Luca and Beaini, Dominique and Li\`{o}, Pietro and Veli\v{c}kovi\'{c}, Petar},
31 | booktitle = {Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
32 | year = {2020}
33 | }
34 | ```
35 |
36 | ## License
37 | MIT
38 |
39 |
40 | ## Acknowledgements
41 |
42 | The authors would like to thank Saro Passaro for running some of the tests presented in this repository and
43 | Giorgos Bouritsas, Fabrizio Frasca, Leonardo Cotta, Zhanghao Wu, Zhanqiu Zhang and George Watkins for pointing out some issues with the code.
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/data/HIV.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import time
2 | import dgl
3 | import torch
4 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
5 | from ogb.graphproppred import DglGraphPropPredDataset
6 | from ogb.graphproppred import Evaluator
7 | import torch.utils.data
8 |
9 |
10 | class HIVDGL(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
11 | def __init__(self, data, split):
12 | self.split = split
13 | self.data = [g for g in data[self.split]]
14 | self.graph_lists = []
15 | self.graph_labels = []
16 | for g in self.data:
17 | if g[0].number_of_nodes() > 5:
18 | self.graph_lists.append(g[0])
19 | self.graph_labels.append(g[1])
20 | self.n_samples = len(self.graph_lists)
21 |
22 | def __len__(self):
23 | """Return the number of graphs in the dataset."""
24 | return self.n_samples
25 |
26 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
27 | """
28 | Get the idx^th sample.
29 | Parameters
30 | ---------
31 | idx : int
32 | The sample index.
33 | Returns
34 | -------
35 | (dgl.DGLGraph, int)
36 | DGLGraph with node feature stored in `feat` field
37 | And its label.
38 | """
39 | return self.graph_lists[idx], self.graph_labels[idx]
40 |
41 |
42 | class HIVDataset(Dataset):
43 | def __init__(self, name, verbose=True):
44 | start = time.time()
45 | if verbose:
46 | print("[I] Loading dataset %s..." % (name))
47 | self.name = name
48 | self.dataset = DglGraphPropPredDataset(name = 'ogbg-molhiv')
49 | self.split_idx = self.dataset.get_idx_split()
50 |
51 | self.train = HIVDGL(self.dataset, self.split_idx['train'])
52 | self.val = HIVDGL(self.dataset, self.split_idx['valid'])
53 | self.test = HIVDGL(self.dataset, self.split_idx['test'])
54 |
55 | self.evaluator = Evaluator(name='ogbg-molhiv')
56 |
57 | if verbose:
58 | print('train, test, val sizes :', len(self.train), len(self.test), len(self.val))
59 | print("[I] Finished loading.")
60 | print("[I] Data load time: {:.4f}s".format(time.time() - start))
61 |
62 | # form a mini batch from a given list of samples = [(graph, label) pairs]
63 | def collate(self, samples):
64 | # The input samples is a list of pairs (graph, label).
65 | graphs, labels = map(list, zip(*samples))
66 | labels = torch.cat(labels).long()
67 | batched_graph = dgl.batch(graphs)
68 |
69 | return batched_graph, labels
70 |
71 | def _add_self_loops(self):
72 | # function for adding self loops
73 | # this function will be called only if self_loop flag is True
74 |
75 | self.train.graph_lists = [self_loop(g) for g in self.train.graph_lists]
76 | self.val.graph_lists = [self_loop(g) for g in self.val.graph_lists]
77 | self.test.graph_lists = [self_loop(g) for g in self.test.graph_lists]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/docs/setup.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Benchmark setup
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 | ## 1. Setup Conda
8 |
9 | ```
10 | # Conda installation
11 |
12 | # For Linux
13 | curl -o ~/miniconda.sh -O https://repo.continuum.io/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
14 |
15 | # For OSX
16 | curl -o ~/miniconda.sh -O https://repo.continuum.io/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-MacOSX-x86_64.sh
17 |
18 | chmod +x ~/miniconda.sh
19 | ~/miniconda.sh
20 |
21 | source ~/.bashrc # For Linux
22 | source ~/.bash_profile # For OSX
23 | ```
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 | ## 2. Setup Python environment for CPU
29 |
30 | ```
31 | # Clone GitHub repo
32 | conda install git
33 | git clone https://github.com/lukecavabarrett/pna.git
34 | cd pna
35 |
36 | # Install python environment
37 | conda env create -f environment_cpu.yml
38 |
39 | # Activate environment
40 | conda activate benchmark_gnn
41 | ```
42 |
43 |
44 |
45 |
46 |
47 | ## 3. Setup Python environment for GPU
48 |
49 | DGL requires CUDA **10.0**.
50 |
51 | For Ubuntu **18.04**
52 |
53 | ```
54 | # Setup CUDA 10.0 on Ubuntu 18.04
55 | sudo apt-get --purge remove "*cublas*" "cuda*"
56 | sudo apt --purge remove "nvidia*"
57 | sudo apt autoremove
58 | wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/ubuntu1804/x86_64/cuda-repo-ubuntu1804_10.0.130-1_amd64.deb
59 | sudo dpkg -i cuda-repo-ubuntu1804_10.0.130-1_amd64.deb
60 | sudo apt-key adv --fetch-keys http://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/ubuntu1804/x86_64/7fa2af80.pub
61 | sudo apt update
62 | sudo apt install -y cuda-10-0
63 | sudo reboot
64 | cat /usr/local/cuda/version.txt # Check CUDA version is 10.0
65 |
66 | # Clone GitHub repo
67 | conda install git
68 | git clone https://github.com/lukecavabarrett/pna.git
69 | cd pna
70 |
71 | # Install python environment
72 | conda env create -f environment_gpu.yml
73 |
74 | # Activate environment
75 | conda activate benchmark_gnn
76 | ```
77 |
78 |
79 |
80 | For Ubuntu **16.04**
81 |
82 | ```
83 | # Setup CUDA 10.0 on Ubuntu 16.04
84 | sudo apt-get --purge remove "*cublas*" "cuda*"
85 | sudo apt --purge remove "nvidia*"
86 | sudo apt autoremove
87 | wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/ubuntu1604/x86_64/cuda-repo-ubuntu1604_10.0.130-1_amd64.deb
88 | sudo dpkg -i cuda-repo-ubuntu1604_10.0.130-1_amd64.deb
89 | sudo apt-key adv --fetch-keys http://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/ubuntu1604/x86_64/7fa2af80.pub
90 | sudo apt update
91 | sudo apt install -y cuda-10-0
92 | sudo reboot
93 | cat /usr/local/cuda/version.txt # Check CUDA version is 10.0
94 |
95 | # Clone GitHub repo
96 | conda install git
97 | git clone https://github.com/lukecavabarrett/pna.git
98 | cd pna
99 |
100 | # Install python environment
101 | conda env create -f environment_gpu.yml
102 |
103 | # Activate environment
104 | conda activate benchmark_gnn
105 | ```
106 |
107 | ## 4. Download Datasets
108 |
109 | ```
110 | # At the root of the repo
111 | cd realworld_benchmark/data/
112 | bash download_datasets.sh
113 | ```
114 |
115 |
116 |
117 |
118 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/train/mpnn.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import division
2 | from __future__ import print_function
3 |
4 | from models.pytorch.pna.layer import PNALayer
5 | from multitask_benchmark.util.train import execute_train, build_arg_parser
6 |
7 | # Training settings
8 | parser = build_arg_parser()
9 | parser.add_argument('--self_loop', action='store_true', default=False, help='Whether to add self loops in aggregators')
10 | parser.add_argument('--towers', type=int, default=4, help='Number of towers in MPNN layers')
11 | parser.add_argument('--aggregation', type=str, default='sum', help='Type of aggregation')
12 | parser.add_argument('--pretrans_layers', type=int, default=1, help='Number of MLP layers before aggregation')
13 | parser.add_argument('--posttrans_layers', type=int, default=1, help='Number of MLP layers after aggregation')
14 | args = parser.parse_args()
15 |
16 | # The MPNNs can be considered a particular case of PNA networks with a single aggregator and no scalers (identity)
17 |
18 | execute_train(gnn_args=dict(nfeat=None,
19 | nhid=args.hidden,
20 | nodes_out=None,
21 | graph_out=None,
22 | dropout=args.dropout,
23 | device=None,
24 | first_conv_descr=dict(layer_type=PNALayer,
25 | args=dict(
26 | aggregators=[args.aggregation],
27 | scalers=['identity'], avg_d=None,
28 | towers=args.towers,
29 | self_loop=args.self_loop,
30 | divide_input=False,
31 | pretrans_layers=args.pretrans_layers,
32 | posttrans_layers=args.posttrans_layers
33 | )),
34 | middle_conv_descr=dict(layer_type=PNALayer,
35 | args=dict(
36 | aggregators=[args.aggregation],
37 | scalers=['identity'],
38 | avg_d=None, towers=args.towers,
39 | self_loop=args.self_loop,
40 | divide_input=True,
41 | pretrans_layers=args.pretrans_layers,
42 | posttrans_layers=args.posttrans_layers
43 | )),
44 | fc_layers=args.fc_layers,
45 | conv_layers=args.conv_layers,
46 | skip=args.skip,
47 | gru=args.gru,
48 | fixed=args.fixed,
49 | variable=args.variable), args=args)
50 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/pytorch/gat/layer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | import torch.nn.functional as F
4 |
5 |
6 | class GATHead(nn.Module):
7 |
8 | def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, alpha, activation=True, device='cpu'):
9 | super(GATHead, self).__init__()
10 | self.in_features = in_features
11 | self.out_features = out_features
12 | self.activation = activation
13 |
14 | self.W = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(size=(in_features, out_features), device=device))
15 | self.a = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(size=(2 * out_features, 1), device=device))
16 | self.leakyrelu = nn.LeakyReLU(alpha)
17 |
18 | self.reset_parameters()
19 |
20 | def reset_parameters(self):
21 | nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.W.data, gain=0.1414)
22 | nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.a.data, gain=0.1414)
23 |
24 | def forward(self, input, adj):
25 |
26 | h = torch.matmul(input, self.W)
27 | (B, N, _) = adj.shape
28 | a_input = torch.cat([h.repeat(1, 1, N).view(B, N * N, -1), h.repeat(1, N, 1)], dim=1)\
29 | .view(B, N, -1, 2 * self.out_features)
30 | e = self.leakyrelu(torch.matmul(a_input, self.a).squeeze(3))
31 |
32 | zero_vec = -9e15 * torch.ones_like(e)
33 |
34 | attention = torch.where(adj > 0, e, zero_vec)
35 | attention = F.softmax(attention, dim=1)
36 | h_prime = torch.matmul(attention, h)
37 |
38 | if self.activation:
39 | return F.elu(h_prime)
40 | else:
41 | return h_prime
42 |
43 | def __repr__(self):
44 | return self.__class__.__name__ + ' (' + str(self.in_features) + ' -> ' + str(self.out_features) + ')'
45 |
46 |
47 | class GATLayer(nn.Module):
48 | """
49 | Graph Attention Layer, GAT paper at https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.10903
50 | Implementation inspired by https://github.com/Diego999/pyGAT
51 | """
52 |
53 | def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, alpha, nheads=1, activation=True, device='cpu'):
54 | """
55 | :param in_features: size of the input per node
56 | :param out_features: size of the output per node
57 | :param alpha: slope of the leaky relu
58 | :param nheads: number of attention heads
59 | :param activation: whether to apply a non-linearity
60 | :param device: device used for computation
61 | """
62 | super(GATLayer, self).__init__()
63 | assert (out_features % nheads == 0)
64 |
65 | self.input_head = in_features
66 | self.output_head = out_features // nheads
67 |
68 | self.heads = nn.ModuleList()
69 | for _ in range(nheads):
70 | self.heads.append(GATHead(in_features=self.input_head, out_features=self.output_head, alpha=alpha,
71 | activation=activation, device=device))
72 |
73 | def forward(self, input, adj):
74 | y = torch.cat([head(input, adj) for head in self.heads], dim=2)
75 | return y
76 |
77 | def __repr__(self):
78 | return self.__class__.__name__ + ' (' \
79 | + str(self.in_features) + ' -> ' \
80 | + str(self.out_features) + ')'
81 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/train/pna.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import division
2 | from __future__ import print_function
3 |
4 | from models.pytorch.pna.layer import PNALayer
5 | from multitask_benchmark.util.train import execute_train, build_arg_parser
6 |
7 | # Training settings
8 | parser = build_arg_parser()
9 | parser.add_argument('--self_loop', action='store_true', default=False, help='Whether to add self loops in aggregators')
10 | parser.add_argument('--aggregators', type=str, default='mean max min std', help='Aggregators to use')
11 | parser.add_argument('--scalers', type=str, default='identity amplification attenuation', help='Scalers to use')
12 | parser.add_argument('--towers', type=int, default=4, help='Number of towers in PNA layers')
13 | parser.add_argument('--pretrans_layers', type=int, default=1, help='Number of MLP layers before aggregation')
14 | parser.add_argument('--posttrans_layers', type=int, default=1, help='Number of MLP layers after aggregation')
15 | args = parser.parse_args()
16 |
17 | execute_train(gnn_args=dict(nfeat=None,
18 | nhid=args.hidden,
19 | nodes_out=None,
20 | graph_out=None,
21 | dropout=args.dropout,
22 | device=None,
23 | first_conv_descr=dict(layer_type=PNALayer,
24 | args=dict(
25 | aggregators=args.aggregators.split(),
26 | scalers=args.scalers.split(), avg_d=None,
27 | towers=args.towers,
28 | self_loop=args.self_loop,
29 | divide_input=False,
30 | pretrans_layers=args.pretrans_layers,
31 | posttrans_layers=args.posttrans_layers
32 | )),
33 | middle_conv_descr=dict(layer_type=PNALayer,
34 | args=dict(
35 | aggregators=args.aggregators.split(),
36 | scalers=args.scalers.split(),
37 | avg_d=None, towers=args.towers,
38 | self_loop=args.self_loop,
39 | divide_input=True,
40 | pretrans_layers=args.pretrans_layers,
41 | posttrans_layers=args.posttrans_layers
42 | )),
43 | fc_layers=args.fc_layers,
44 | conv_layers=args.conv_layers,
45 | skip=args.skip,
46 | gru=args.gru,
47 | fixed=args.fixed,
48 | variable=args.variable), args=args)
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/pytorch_geometric/example.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn.functional as F
3 | from torch.nn import ModuleList
4 | from torch.nn import Sequential, ReLU, Linear
5 | from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import ReduceLROnPlateau
6 | from torch_geometric.utils import degree
7 | from ogb.graphproppred import PygGraphPropPredDataset, Evaluator
8 | from ogb.graphproppred.mol_encoder import AtomEncoder
9 | from torch_geometric.data import DataLoader
10 | from torch_geometric.nn import BatchNorm, global_mean_pool
11 |
12 | from models.pytorch_geometric.pna import PNAConvSimple
13 |
14 | dataset = PygGraphPropPredDataset(name="ogbg-molhiv")
15 |
16 | split_idx = dataset.get_idx_split()
17 | train_loader = DataLoader(dataset[split_idx["train"]], batch_size=128, shuffle=True)
18 | val_loader = DataLoader(dataset[split_idx["valid"]], batch_size=128, shuffle=False)
19 | test_loader = DataLoader(dataset[split_idx["test"]], batch_size=128, shuffle=False)
20 |
21 | # Compute in-degree histogram over training data.
22 | deg = torch.zeros(10, dtype=torch.long)
23 | for data in dataset[split_idx['train']]:
24 | d = degree(data.edge_index[1], num_nodes=data.num_nodes, dtype=torch.long)
25 | deg += torch.bincount(d, minlength=deg.numel())
26 |
27 | class Net(torch.nn.Module):
28 | def __init__(self):
29 | super(Net, self).__init__()
30 |
31 | self.node_emb = AtomEncoder(emb_dim=80)
32 |
33 | aggregators = ['mean', 'min', 'max', 'std']
34 | scalers = ['identity', 'amplification', 'attenuation']
35 |
36 | self.convs = ModuleList()
37 | self.batch_norms = ModuleList()
38 | for _ in range(4):
39 | conv = PNAConvSimple(in_channels=80, out_channels=80, aggregators=aggregators,
40 | scalers=scalers, deg=deg, post_layers=1)
41 | self.convs.append(conv)
42 | self.batch_norms.append(BatchNorm(80))
43 |
44 | self.mlp = Sequential(Linear(80, 40), ReLU(), Linear(40, 20), ReLU(), Linear(20, 1))
45 |
46 | def forward(self, x, edge_index, edge_attr, batch):
47 | x = self.node_emb(x)
48 |
49 | for conv, batch_norm in zip(self.convs, self.batch_norms):
50 | h = F.relu(batch_norm(conv(x, edge_index, edge_attr)))
51 | x = h + x # residual#
52 | x = F.dropout(x, 0.3, training=self.training)
53 |
54 | x = global_mean_pool(x, batch)
55 | return self.mlp(x)
56 |
57 |
58 | device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
59 | model = Net().to(device)
60 | optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, weight_decay=3e-6)
61 | scheduler = ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, mode='max', factor=0.5, patience=20, min_lr=0.0001)
62 |
63 |
64 | def train(epoch):
65 | model.train()
66 |
67 | total_loss = 0
68 | for data in train_loader:
69 | data = data.to(device)
70 | optimizer.zero_grad()
71 | out = model(data.x, data.edge_index, None, data.batch)
72 |
73 | loss = torch.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()(out.to(torch.float32), data.y.to(torch.float32))
74 | loss.backward()
75 | total_loss += loss.item() * data.num_graphs
76 | optimizer.step()
77 | return total_loss / len(train_loader.dataset)
78 |
79 |
80 | @torch.no_grad()
81 | def test(loader):
82 | model.eval()
83 | evaluator = Evaluator(name='ogbg-molhiv')
84 | list_pred = []
85 | list_labels = []
86 | for data in loader:
87 | data = data.to(device)
88 | out = model(data.x, data.edge_index, None, data.batch)
89 | list_pred.append(out)
90 | list_labels.append(data.y)
91 | epoch_test_ROC = evaluator.eval({'y_pred': torch.cat(list_pred),
92 | 'y_true': torch.cat(list_labels)})['rocauc']
93 | return epoch_test_ROC
94 |
95 |
96 | best = (0, 0)
97 |
98 | for epoch in range(1, 201):
99 | loss = train(epoch)
100 | val_roc = test(val_loader)
101 | test_roc = test(test_loader)
102 | scheduler.step(val_roc)
103 | print(f'Epoch: {epoch:02d}, Loss: {loss:.4f}, Val: {val_roc:.4f}, '
104 | f'Test: {test_roc:.4f}')
105 | if val_roc > best[0]:
106 | best = (val_roc, test_roc)
107 |
108 | print(f'Best epoch val: {best[0]:.4f}, test: {best[1]:.4f}')
109 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/nets/superpixels_graph_classification/pna_net.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 |
3 | import dgl
4 |
5 | from nets.gru import GRU
6 | from models.dgl.pna_layer import PNALayer
7 | from nets.mlp_readout_layer import MLPReadout
8 |
9 | """
10 | PNA: Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation
11 | Gabriele Corso, Luca Cavalleri, Dominique Beaini, Pietro Lio, Petar Velickovic
12 | https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718
13 | Architecture follows that in https://github.com/graphdeeplearning/benchmarking-gnns
14 | """
15 |
16 |
17 | class PNANet(nn.Module):
18 | def __init__(self, net_params):
19 | super().__init__()
20 | in_dim = net_params['in_dim']
21 | in_dim_edge = net_params['in_dim_edge']
22 | hidden_dim = net_params['hidden_dim']
23 | out_dim = net_params['out_dim']
24 | n_classes = net_params['n_classes']
25 | in_feat_dropout = net_params['in_feat_dropout']
26 | dropout = net_params['dropout']
27 | n_layers = net_params['L']
28 | self.readout = net_params['readout']
29 | self.graph_norm = net_params['graph_norm']
30 | self.batch_norm = net_params['batch_norm']
31 | self.residual = net_params['residual']
32 | self.aggregators = net_params['aggregators']
33 | self.scalers = net_params['scalers']
34 | self.avg_d = net_params['avg_d']
35 | self.towers = net_params['towers']
36 | self.divide_input_first = net_params['divide_input_first']
37 | self.divide_input_last = net_params['divide_input_last']
38 | self.edge_feat = net_params['edge_feat']
39 | edge_dim = net_params['edge_dim']
40 | pretrans_layers = net_params['pretrans_layers']
41 | posttrans_layers = net_params['posttrans_layers']
42 | self.gru_enable = net_params['gru']
43 | device = net_params['device']
44 |
45 | self.embedding_h = nn.Linear(in_dim, hidden_dim)
46 |
47 | if self.edge_feat:
48 | self.embedding_e = nn.Linear(in_dim_edge, edge_dim)
49 |
50 | self.layers = nn.ModuleList([PNALayer(in_dim=hidden_dim, out_dim=hidden_dim, dropout=dropout,
51 | graph_norm=self.graph_norm, batch_norm=self.batch_norm,
52 | residual=self.residual, aggregators=self.aggregators,
53 | scalers=self.scalers,
54 | avg_d=self.avg_d, towers=self.towers, edge_features=self.edge_feat,
55 | edge_dim=edge_dim, divide_input=self.divide_input_first,
56 | pretrans_layers=pretrans_layers, posttrans_layers=posttrans_layers) for _
57 | in range(n_layers - 1)])
58 | self.layers.append(PNALayer(in_dim=hidden_dim, out_dim=out_dim, dropout=dropout,
59 | graph_norm=self.graph_norm, batch_norm=self.batch_norm,
60 | residual=self.residual, aggregators=self.aggregators, scalers=self.scalers,
61 | avg_d=self.avg_d, towers=self.towers, divide_input=self.divide_input_last,
62 | edge_features=self.edge_feat, edge_dim=edge_dim,
63 | pretrans_layers=pretrans_layers, posttrans_layers=posttrans_layers))
64 |
65 | if self.gru_enable:
66 | self.gru = GRU(hidden_dim, hidden_dim, device)
67 |
68 | self.MLP_layer = MLPReadout(out_dim, n_classes)
69 |
70 | def forward(self, g, h, e, snorm_n, snorm_e):
71 | h = self.embedding_h(h)
72 | if self.edge_feat:
73 | e = self.embedding_e(e)
74 |
75 | for i, conv in enumerate(self.layers):
76 | h_t = conv(g, h, e, snorm_n)
77 | if self.gru_enable and i != len(self.layers) - 1:
78 | h_t = self.gru(h, h_t)
79 | h = h_t
80 |
81 | g.ndata['h'] = h
82 |
83 | if self.readout == "sum":
84 | hg = dgl.sum_nodes(g, 'h')
85 | elif self.readout == "max":
86 | hg = dgl.max_nodes(g, 'h')
87 | elif self.readout == "mean":
88 | hg = dgl.mean_nodes(g, 'h')
89 | else:
90 | hg = dgl.mean_nodes(g, 'h') # default readout is mean nodes
91 |
92 | return self.MLP_layer(hg)
93 |
94 | def loss(self, pred, label):
95 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
96 | loss = criterion(pred, label)
97 | return loss
98 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/nets/molecules_graph_regression/pna_net.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | import dgl
3 |
4 | from nets.gru import GRU
5 | from models.dgl.pna_layer import PNALayer
6 | from nets.mlp_readout_layer import MLPReadout
7 |
8 | """
9 | PNA: Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation
10 | Gabriele Corso, Luca Cavalleri, Dominique Beaini, Pietro Lio, Petar Velickovic
11 | https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718
12 | Architecture follows that in https://github.com/graphdeeplearning/benchmarking-gnns
13 | """
14 |
15 |
16 | class PNANet(nn.Module):
17 | def __init__(self, net_params):
18 | super().__init__()
19 | num_atom_type = net_params['num_atom_type']
20 | num_bond_type = net_params['num_bond_type']
21 | hidden_dim = net_params['hidden_dim']
22 | out_dim = net_params['out_dim']
23 | in_feat_dropout = net_params['in_feat_dropout']
24 | dropout = net_params['dropout']
25 | n_layers = net_params['L']
26 | self.readout = net_params['readout']
27 | self.graph_norm = net_params['graph_norm']
28 | self.batch_norm = net_params['batch_norm']
29 | self.residual = net_params['residual']
30 | self.aggregators = net_params['aggregators']
31 | self.scalers = net_params['scalers']
32 | self.avg_d = net_params['avg_d']
33 | self.towers = net_params['towers']
34 | self.divide_input_first = net_params['divide_input_first']
35 | self.divide_input_last = net_params['divide_input_last']
36 | self.edge_feat = net_params['edge_feat']
37 | edge_dim = net_params['edge_dim']
38 | pretrans_layers = net_params['pretrans_layers']
39 | posttrans_layers = net_params['posttrans_layers']
40 | self.gru_enable = net_params['gru']
41 | device = net_params['device']
42 |
43 | self.in_feat_dropout = nn.Dropout(in_feat_dropout)
44 |
45 | self.embedding_h = nn.Embedding(num_atom_type, hidden_dim)
46 |
47 | if self.edge_feat:
48 | self.embedding_e = nn.Embedding(num_bond_type, edge_dim)
49 |
50 | self.layers = nn.ModuleList([PNALayer(in_dim=hidden_dim, out_dim=hidden_dim, dropout=dropout,
51 | graph_norm=self.graph_norm, batch_norm=self.batch_norm,
52 | residual=self.residual, aggregators=self.aggregators, scalers=self.scalers,
53 | avg_d=self.avg_d, towers=self.towers, edge_features=self.edge_feat,
54 | edge_dim=edge_dim, divide_input=self.divide_input_first,
55 | pretrans_layers=pretrans_layers, posttrans_layers=posttrans_layers) for _
56 | in range(n_layers - 1)])
57 | self.layers.append(PNALayer(in_dim=hidden_dim, out_dim=out_dim, dropout=dropout,
58 | graph_norm=self.graph_norm, batch_norm=self.batch_norm,
59 | residual=self.residual, aggregators=self.aggregators, scalers=self.scalers,
60 | avg_d=self.avg_d, towers=self.towers, divide_input=self.divide_input_last,
61 | edge_features=self.edge_feat, edge_dim=edge_dim,
62 | pretrans_layers=pretrans_layers, posttrans_layers=posttrans_layers))
63 |
64 | if self.gru_enable:
65 | self.gru = GRU(hidden_dim, hidden_dim, device)
66 |
67 | self.MLP_layer = MLPReadout(out_dim, 1) # 1 out dim since regression problem
68 |
69 | def forward(self, g, h, e, snorm_n, snorm_e):
70 | h = self.embedding_h(h)
71 | h = self.in_feat_dropout(h)
72 | if self.edge_feat:
73 | e = self.embedding_e(e)
74 |
75 | for i, conv in enumerate(self.layers):
76 | h_t = conv(g, h, e, snorm_n)
77 | if self.gru_enable and i != len(self.layers) - 1:
78 | h_t = self.gru(h, h_t)
79 | h = h_t
80 |
81 | g.ndata['h'] = h
82 |
83 | if self.readout == "sum":
84 | hg = dgl.sum_nodes(g, 'h')
85 | elif self.readout == "max":
86 | hg = dgl.max_nodes(g, 'h')
87 | elif self.readout == "mean":
88 | hg = dgl.mean_nodes(g, 'h')
89 | else:
90 | hg = dgl.mean_nodes(g, 'h') # default readout is mean nodes
91 |
92 | return self.MLP_layer(hg)
93 |
94 | def loss(self, scores, targets):
95 | loss = nn.L1Loss()(scores, targets)
96 | return loss
97 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/util/util.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import division
2 | from __future__ import print_function
3 |
4 | import torch
5 | import torch.nn.functional as F
6 |
7 |
8 | def load_dataset(data_path, loss, only_nodes, only_graph, print_baseline=True):
9 | with open(data_path, 'rb') as f:
10 | (adj, features, node_labels, graph_labels) = torch.load(f)
11 |
12 | # normalize labels
13 | max_node_labels = torch.cat([nls.max(0)[0].max(0)[0].unsqueeze(0) for nls in node_labels['train']]).max(0)[0]
14 | max_graph_labels = torch.cat([gls.max(0)[0].unsqueeze(0) for gls in graph_labels['train']]).max(0)[0]
15 | for dset in node_labels.keys():
16 | node_labels[dset] = [nls / max_node_labels for nls in node_labels[dset]]
17 | graph_labels[dset] = [gls / max_graph_labels for gls in graph_labels[dset]]
18 |
19 | if print_baseline:
20 | # calculate baseline
21 | mean_node_labels = torch.cat([nls.mean(0).mean(0).unsqueeze(0) for nls in node_labels['train']]).mean(0)
22 | mean_graph_labels = torch.cat([gls.mean(0).unsqueeze(0) for gls in graph_labels['train']]).mean(0)
23 |
24 | for dset in node_labels.keys():
25 | if dset not in ['train', 'val']:
26 | baseline_nodes = [mean_node_labels.repeat(list(nls.shape[0:-1]) + [1]) for nls in node_labels[dset]]
27 | baseline_graph = [mean_graph_labels.repeat([gls.shape[0], 1]) for gls in graph_labels[dset]]
28 |
29 | print("Baseline loss ", dset,
30 | specific_loss_multiple_batches((baseline_nodes, baseline_graph),
31 | (node_labels[dset], graph_labels[dset]),
32 | loss=loss, only_nodes=only_nodes, only_graph=only_graph))
33 |
34 | return adj, features, node_labels, graph_labels
35 |
36 |
37 | def get_loss(loss, output, target):
38 | if loss == "mse":
39 | return F.mse_loss(output, target)
40 | elif loss == "cross_entropy":
41 | if len(output.shape) > 2:
42 | (B, N, _) = output.shape
43 | output = output.reshape((B * N, -1))
44 | target = target.reshape((B * N, -1))
45 | _, target = target.max(dim=1)
46 | return F.cross_entropy(output, target)
47 | else:
48 | print("Error: loss function not supported")
49 |
50 |
51 | def total_loss(output, target, loss='mse', only_nodes=False, only_graph=False):
52 | """ returns the average of the average losses of each task """
53 | assert not (only_nodes and only_graph)
54 |
55 | if only_nodes:
56 | nodes_loss = get_loss(loss, output[0], target[0])
57 | return nodes_loss
58 | elif only_graph:
59 | graph_loss = get_loss(loss, output[1], target[1])
60 | return graph_loss
61 |
62 | nodes_loss = get_loss(loss, output[0], target[0])
63 | graph_loss = get_loss(loss, output[1], target[1])
64 | weighted_average = (nodes_loss * output[0].shape[-1] + graph_loss * output[1].shape[-1]) / (
65 | output[0].shape[-1] + output[1].shape[-1])
66 | return weighted_average
67 |
68 |
69 | def total_loss_multiple_batches(output, target, loss='mse', only_nodes=False, only_graph=False):
70 | """ returns the average of the average losses of each task over all batches,
71 | batches are weighted equally regardless of their cardinality or graph size """
72 | n_batches = len(output[0])
73 | return sum([total_loss((output[0][batch], output[1][batch]), (target[0][batch], target[1][batch]),
74 | loss, only_nodes, only_graph).data.item()
75 | for batch in range(n_batches)]) / n_batches
76 |
77 |
78 | def specific_loss(output, target, loss='mse', only_nodes=False, only_graph=False):
79 | """ returns the average loss for each task """
80 | assert not (only_nodes and only_graph)
81 | n_nodes_labels = output[0].shape[-1] if not only_graph else 0
82 | n_graph_labels = output[1].shape[-1] if not only_nodes else 0
83 |
84 | if only_nodes:
85 | nodes_loss = [get_loss(loss, output[0][:, :, k], target[0][:, :, k]).item() for k in range(n_nodes_labels)]
86 | return nodes_loss
87 | elif only_graph:
88 | graph_loss = [get_loss(loss, output[1][:, k], target[1][:, k]).item() for k in range(n_graph_labels)]
89 | return graph_loss
90 |
91 | nodes_loss = [get_loss(loss, output[0][:, :, k], target[0][:, :, k]).item() for k in range(n_nodes_labels)]
92 | graph_loss = [get_loss(loss, output[1][:, k], target[1][:, k]).item() for k in range(n_graph_labels)]
93 | return nodes_loss + graph_loss
94 |
95 |
96 | def specific_loss_multiple_batches(output, target, loss='mse', only_nodes=False, only_graph=False):
97 | """ returns the average loss over all batches for each task,
98 | batches are weighted equally regardless of their cardinality or graph size """
99 | assert not (only_nodes and only_graph)
100 |
101 | n_batches = len(output[0])
102 | classes = (output[0][0].shape[-1] if not only_graph else 0) + (output[1][0].shape[-1] if not only_nodes else 0)
103 |
104 | sum_losses = [0] * classes
105 | for batch in range(n_batches):
106 | spec_loss = specific_loss((output[0][batch], output[1][batch]), (target[0][batch], target[1][batch]), loss,
107 | only_nodes, only_graph)
108 | for par in range(classes):
109 | sum_losses[par] += spec_loss[par]
110 |
111 | return [sum_loss / n_batches for sum_loss in sum_losses]
112 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/pytorch/pna/layer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 |
4 | from models.pytorch.pna.aggregators import AGGREGATORS
5 | from models.pytorch.pna.scalers import SCALERS
6 | from models.layers import FCLayer, MLP
7 |
8 |
9 | class PNATower(nn.Module):
10 | def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, aggregators, scalers, avg_d, self_loop, pretrans_layers,
11 | posttrans_layers, device):
12 | """
13 | :param in_features: size of the input per node of the tower
14 | :param out_features: size of the output per node of the tower
15 | :param aggregators: set of aggregation functions each taking as input X (B x N x N x Din), adj (B x N x N), self_loop and device
16 | :param scalers: set of scaling functions each taking as input X (B x N x Din), adj (B x N x N) and avg_d
17 | """
18 | super(PNATower, self).__init__()
19 |
20 | self.device = device
21 | self.in_features = in_features
22 | self.out_features = out_features
23 | self.aggregators = aggregators
24 | self.scalers = scalers
25 | self.self_loop = self_loop
26 | self.pretrans = MLP(in_size=2 * self.in_features, hidden_size=self.in_features, out_size=self.in_features,
27 | layers=pretrans_layers, mid_activation='relu', last_activation='none')
28 | self.posttrans = MLP(in_size=(len(aggregators) * len(scalers) + 1) * self.in_features,
29 | hidden_size=self.out_features, out_size=self.out_features, layers=posttrans_layers,
30 | mid_activation='relu', last_activation='none')
31 | self.avg_d = avg_d
32 |
33 | def forward(self, input, adj):
34 | (B, N, _) = adj.shape
35 |
36 | # pre-aggregation transformation
37 | h_i = input.unsqueeze(2).repeat(1, 1, N, 1)
38 | h_j = input.unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, N, 1, 1)
39 | h_cat = torch.cat([h_i, h_j], dim=3)
40 | h_mod = self.pretrans(h_cat)
41 |
42 | # aggregation
43 | m = torch.cat([aggregate(h_mod, adj, self_loop=self.self_loop, device=self.device) for aggregate in self.aggregators], dim=2)
44 | m = torch.cat([scale(m, adj, avg_d=self.avg_d) for scale in self.scalers], dim=2)
45 |
46 | # post-aggregation transformation
47 | m_cat = torch.cat([input, m], dim=2)
48 | out = self.posttrans(m_cat)
49 | return out
50 |
51 | def __repr__(self):
52 | return self.__class__.__name__ + ' (' \
53 | + str(self.in_features) + ' -> ' \
54 | + str(self.out_features) + ')'
55 |
56 |
57 | class PNALayer(nn.Module):
58 | """
59 | Implements a single convolutional layer of the Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation Networks
60 | as described in https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718
61 | """
62 |
63 | def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, aggregators, scalers, avg_d, towers=1, self_loop=False,
64 | pretrans_layers=1, posttrans_layers=1, divide_input=True, device='cpu'):
65 | """
66 | :param in_features: size of the input per node
67 | :param out_features: size of the output per node
68 | :param aggregators: set of aggregation function identifiers
69 | :param scalers: set of scaling functions identifiers
70 | :param avg_d: average degree of nodes in the training set, used by scalers to normalize
71 | :param self_loop: whether to add a self loop in the adjacency matrix when aggregating
72 | :param pretrans_layers: number of layers in the transformation before the aggregation
73 | :param posttrans_layers: number of layers in the transformation after the aggregation
74 | :param divide_input: whether the input features should be split between towers or not
75 | :param device: device used for computation
76 | """
77 | super(PNALayer, self).__init__()
78 | assert ((not divide_input) or in_features % towers == 0), "if divide_input is set the number of towers has to divide in_features"
79 | assert (out_features % towers == 0), "the number of towers has to divide the out_features"
80 |
81 | # retrieve the aggregators and scalers functions
82 | aggregators = [AGGREGATORS[aggr] for aggr in aggregators]
83 | scalers = [SCALERS[scale] for scale in scalers]
84 |
85 | self.divide_input = divide_input
86 | self.input_tower = in_features // towers if divide_input else in_features
87 | self.output_tower = out_features // towers
88 |
89 | # convolution
90 | self.towers = nn.ModuleList()
91 | for _ in range(towers):
92 | self.towers.append(
93 | PNATower(in_features=self.input_tower, out_features=self.output_tower, aggregators=aggregators,
94 | scalers=scalers, avg_d=avg_d, self_loop=self_loop, pretrans_layers=pretrans_layers,
95 | posttrans_layers=posttrans_layers, device=device))
96 | # mixing network
97 | self.mixing_network = FCLayer(out_features, out_features, activation='LeakyReLU')
98 |
99 | def forward(self, input, adj):
100 | # convolution
101 | if self.divide_input:
102 | y = torch.cat(
103 | [tower(input[:, :, n_tower * self.input_tower: (n_tower + 1) * self.input_tower], adj)
104 | for n_tower, tower in enumerate(self.towers)], dim=2)
105 | else:
106 | y = torch.cat([tower(input, adj) for tower in self.towers], dim=2)
107 |
108 | # mixing network
109 | return self.mixing_network(y)
110 |
111 | def __repr__(self):
112 | return self.__class__.__name__ + ' (' \
113 | + str(self.in_features) + ' -> ' \
114 | + str(self.out_features) + ')'
115 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/pytorch/gnn_framework.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import types
2 | import torch
3 | import torch.nn as nn
4 | import torch.nn.functional as F
5 | from models.layers import GRU, S2SReadout, MLP
6 |
7 |
8 | class GNN(nn.Module):
9 | def __init__(self, nfeat, nhid, nodes_out, graph_out, dropout, conv_layers=2, fc_layers=3, first_conv_descr=None,
10 | middle_conv_descr=None, final_activation='LeakyReLU', skip=False, gru=False, fixed=False,
11 | variable=False, device='cpu'):
12 | """
13 | :param nfeat: number of input features per node
14 | :param nhid: number of hidden features per node
15 | :param nodes_out: number of nodes' labels
16 | :param graph_out: number of graph labels
17 | :param dropout: dropout value
18 | :param conv_layers: if variable, conv_layers should be a function : adj -> int, otherwise an int
19 | :param fc_layers: number of fully connected layers before the labels
20 | :param first_conv_descr: dict or SimpleNamespace: "type"-> type of layer, "args" -> dict of calling args
21 | :param middle_conv_descr: dict or SimpleNamespace : "type"-> type of layer, "args" -> dict of calling args
22 | :param final_activation: activation to be used on the last fc layer before the labels
23 | :param skip: whether to use skip connections feeding to the readout
24 | :param gru: whether to use a shared GRU after each convolution
25 | :param fixed: whether to reuse the same middle convolutional layer multiple times
26 | :param variable: whether the number of convolutional layers is variable or fixed
27 | :param device: device used for computation
28 | """
29 | super(GNN, self).__init__()
30 | if variable:
31 | assert callable(conv_layers), "conv_layers should be a function from adjacency matrix to int"
32 | assert fixed, "With a variable number of layers they must be fixed"
33 | assert not skip, "cannot have skip and fixed at the same time"
34 | else:
35 | assert type(conv_layers) == int, "conv_layers should be an int"
36 | assert conv_layers > 0, "conv_layers should be greater than 0"
37 |
38 | if type(first_conv_descr) == dict:
39 | first_conv_descr = types.SimpleNamespace(**first_conv_descr)
40 | assert type(first_conv_descr) == types.SimpleNamespace, "first_conv_descr should be dict or SimpleNamespace"
41 | if type(first_conv_descr.args) == dict:
42 | first_conv_descr.args = types.SimpleNamespace(**first_conv_descr.args)
43 | assert type(first_conv_descr.args) == types.SimpleNamespace, \
44 | "first_conv_descr.args should be either a dict or a SimpleNamespace"
45 |
46 | if type(middle_conv_descr) == dict:
47 | middle_conv_descr = types.SimpleNamespace(**middle_conv_descr)
48 | assert type(middle_conv_descr) == types.SimpleNamespace, "middle_conv_descr should be dict or SimpleNamespace"
49 | if type(middle_conv_descr.args) == dict:
50 | middle_conv_descr.args = types.SimpleNamespace(**middle_conv_descr.args)
51 | assert type(middle_conv_descr.args) == types.SimpleNamespace, \
52 | "middle_conv_descr.args should be either a dict or a SimpleNamespace"
53 |
54 | self.dropout = dropout
55 | self.conv_layers = nn.ModuleList()
56 | self.skip = skip
57 | self.fixed = fixed
58 | self.variable = variable
59 | self.n_fixed_conv = conv_layers
60 | self.gru = GRU(input_size=nhid, hidden_size=nhid, device=device) if gru else None
61 |
62 | # first graph convolution
63 | first_conv_descr.args.in_features = nfeat
64 | first_conv_descr.args.out_features = nhid
65 | first_conv_descr.args.device = device
66 | self.conv_layers.append(first_conv_descr.layer_type(**vars(first_conv_descr.args)))
67 |
68 | # middle graph convolutions
69 | middle_conv_descr.args.in_features = nhid
70 | middle_conv_descr.args.out_features = nhid
71 | middle_conv_descr.args.device = device
72 | for l in range(1 if fixed else conv_layers - 1):
73 | self.conv_layers.append(
74 | middle_conv_descr.layer_type(**vars(middle_conv_descr.args)))
75 |
76 | n_conv_out = nfeat + conv_layers * nhid if skip else nhid
77 |
78 | # nodes output: fully connected layers
79 | self.nodes_read_out = MLP(in_size=n_conv_out, hidden_size=n_conv_out, out_size=nodes_out, layers=fc_layers,
80 | mid_activation="LeakyReLU", last_activation=final_activation, device=device)
81 |
82 | # graph output: S2S readout
83 | self.graph_read_out = S2SReadout(n_conv_out, n_conv_out, graph_out, fc_layers=fc_layers, device=device,
84 | final_activation=final_activation)
85 |
86 | def forward(self, x, adj):
87 | # graph convolutions
88 | skip_connections = [x] if self.skip else None
89 |
90 | n_layers = self.n_fixed_conv(adj) if self.variable else self.n_fixed_conv
91 | conv_layers = [self.conv_layers[0]] + ([self.conv_layers[1]] * (n_layers - 1)) if self.fixed else self.conv_layers
92 |
93 | for layer, conv in enumerate(conv_layers):
94 | y = conv(x, adj)
95 | x = y if self.gru is None else self.gru(x, y)
96 |
97 | if self.skip:
98 | skip_connections.append(x)
99 |
100 | # dropout at all layers but the last
101 | if layer != n_layers - 1:
102 | x = F.dropout(x, self.dropout, training=self.training)
103 |
104 | if self.skip:
105 | x = torch.cat(skip_connections, dim=2)
106 |
107 | # readout output
108 | return (self.nodes_read_out(x), self.graph_read_out(x))
109 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/pytorch/pna/aggregators.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | import torch
3 |
4 | EPS = 1e-5
5 |
6 |
7 | # each aggregator is a function taking as input X (B x N x N x Din), adj (B x N x N), self_loop and device and
8 | # returning the aggregated value of X (B x N x Din) for each dimension
9 |
10 | def aggregate_identity(X, adj, self_loop=False, device='cpu'):
11 | # Y is corresponds to the elements of the main diagonal of X
12 | (_, N, N, _) = X.shape
13 | Y = torch.sum(torch.mul(X, torch.eye(N).reshape(1, N, N, 1)), dim=2)
14 | return Y
15 |
16 |
17 | def aggregate_mean(X, adj, self_loop=False, device='cpu'):
18 | # D^{-1} A * X i.e. the mean of the neighbours
19 |
20 | if self_loop: # add self connections
21 | (B, N, _) = adj.shape
22 | adj = adj + torch.eye(N, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
23 |
24 | D = torch.sum(adj, -1, keepdim=True)
25 | X_sum = torch.sum(torch.mul(X, adj.unsqueeze(-1)), dim=2)
26 | X_mean = torch.div(X_sum, D)
27 | return X_mean
28 |
29 |
30 | def aggregate_max(X, adj, min_value=-math.inf, self_loop=False, device='cpu'):
31 | (B, N, N, Din) = X.shape
32 |
33 | if self_loop: # add self connections
34 | adj = adj + torch.eye(N, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
35 |
36 | adj = adj.unsqueeze(-1) # adding extra dimension
37 | M = torch.where(adj > 0.0, X, torch.tensor(min_value, device=device))
38 | max = torch.max(M, -3)[0]
39 | return max
40 |
41 |
42 | def aggregate_min(X, adj, max_value=math.inf, self_loop=False, device='cpu'):
43 | (B, N, N, Din) = X.shape
44 |
45 | if self_loop: # add self connections
46 | adj = adj + torch.eye(N, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
47 |
48 | adj = adj.unsqueeze(-1) # adding extra dimension
49 | M = torch.where(adj > 0.0, X, torch.tensor(max_value, device=device))
50 | min = torch.min(M, -3)[0]
51 | return min
52 |
53 |
54 | def aggregate_std(X, adj, self_loop=False, device='cpu'):
55 | # sqrt(relu(D^{-1} A X^2 - (D^{-1} A X)^2) + EPS) i.e. the standard deviation of the features of the neighbours
56 | # the EPS is added for the stability of the derivative of the square root
57 | std = torch.sqrt(aggregate_var(X, adj, self_loop, device) + EPS) # sqrt(mean_squares_X - mean_X^2)
58 | return std
59 |
60 |
61 | def aggregate_var(X, adj, self_loop=False, device='cpu'):
62 | # relu(D^{-1} A X^2 - (D^{-1} A X)^2) i.e. the variance of the features of the neighbours
63 |
64 | if self_loop: # add self connections
65 | (B, N, _) = adj.shape
66 | adj = adj + torch.eye(N, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
67 |
68 | D = torch.sum(adj, -1, keepdim=True)
69 | X_sum_squares = torch.sum(torch.mul(torch.mul(X, X), adj.unsqueeze(-1)), dim=2)
70 | X_mean_squares = torch.div(X_sum_squares, D) # D^{-1} A X^2
71 | X_mean = aggregate_mean(X, adj) # D^{-1} A X
72 | var = torch.relu(X_mean_squares - torch.mul(X_mean, X_mean)) # relu(mean_squares_X - mean_X^2)
73 | return var
74 |
75 |
76 | def aggregate_sum(X, adj, self_loop=False, device='cpu'):
77 | # A * X i.e. the mean of the neighbours
78 |
79 | if self_loop: # add self connections
80 | (B, N, _) = adj.shape
81 | adj = adj + torch.eye(N, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
82 |
83 | X_sum = torch.sum(torch.mul(X, adj.unsqueeze(-1)), dim=2)
84 | return X_sum
85 |
86 |
87 | def aggregate_normalised_mean(X, adj, self_loop=False, device='cpu'):
88 | # D^{-1/2] A D^{-1/2] X
89 | (B, N, N, _) = X.shape
90 |
91 | if self_loop: # add self connections
92 | adj = adj + torch.eye(N, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
93 |
94 | rD = torch.mul(torch.pow(torch.sum(adj, -1, keepdim=True), -0.5), torch.eye(N, device=device)
95 | .unsqueeze(0).repeat(B, 1, 1)) # D^{-1/2]
96 | adj = torch.matmul(torch.matmul(rD, adj), rD) # D^{-1/2] A' D^{-1/2]
97 |
98 | X_sum = torch.sum(torch.mul(X, adj.unsqueeze(-1)), dim=2)
99 | return X_sum
100 |
101 |
102 | def aggregate_softmax(X, adj, self_loop=False, device='cpu'):
103 | # for each node sum_i(x_i*exp(x_i)/sum_j(exp(x_j)) where x_i and x_j vary over the neighbourhood of the node
104 | (B, N, N, Din) = X.shape
105 |
106 | if self_loop: # add self connections
107 | adj = adj + torch.eye(N, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
108 |
109 | X_exp = torch.exp(X)
110 | adj = adj.unsqueeze(-1) # adding extra dimension
111 | X_exp = torch.mul(X_exp, adj)
112 | X_sum = torch.sum(X_exp, dim=2, keepdim=True)
113 | softmax = torch.sum(torch.mul(torch.div(X_exp, X_sum), X), dim=2)
114 | return softmax
115 |
116 |
117 | def aggregate_softmin(X, adj, self_loop=False, device='cpu'):
118 | # for each node sum_i(x_i*exp(-x_i)/sum_j(exp(-x_j)) where x_i and x_j vary over the neighbourhood of the node
119 | return -aggregate_softmax(-X, adj, self_loop=self_loop, device=device)
120 |
121 |
122 | def aggregate_moment(X, adj, self_loop=False, device='cpu', n=3):
123 | # for each node (E[(X-E[X])^n])^{1/n}
124 | # EPS is added to the absolute value of expectation before taking the nth root for stability
125 |
126 | if self_loop: # add self connections
127 | (B, N, _) = adj.shape
128 | adj = adj + torch.eye(N, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
129 |
130 | D = torch.sum(adj, -1, keepdim=True)
131 | X_mean = aggregate_mean(X, adj, self_loop=self_loop, device=device)
132 | X_n = torch.div(torch.sum(torch.mul(torch.pow(X - X_mean.unsqueeze(2), n), adj.unsqueeze(-1)), dim=2), D)
133 | rooted_X_n = torch.sign(X_n) * torch.pow(torch.abs(X_n) + EPS, 1. / n)
134 | return rooted_X_n
135 |
136 |
137 | def aggregate_moment_3(X, adj, self_loop=False, device='cpu'):
138 | return aggregate_moment(X, adj, self_loop=self_loop, device=device, n=3)
139 |
140 |
141 | def aggregate_moment_4(X, adj, self_loop=False, device='cpu'):
142 | return aggregate_moment(X, adj, self_loop=self_loop, device=device, n=4)
143 |
144 |
145 | def aggregate_moment_5(X, adj, self_loop=False, device='cpu'):
146 | return aggregate_moment(X, adj, self_loop=self_loop, device=device, n=5)
147 |
148 |
149 | AGGREGATORS = {'mean': aggregate_mean, 'sum': aggregate_sum, 'max': aggregate_max, 'min': aggregate_min,
150 | 'identity': aggregate_identity, 'std': aggregate_std, 'var': aggregate_var,
151 | 'normalised_mean': aggregate_normalised_mean, 'softmax': aggregate_softmax, 'softmin': aggregate_softmin,
152 | 'moment3': aggregate_moment_3, 'moment4': aggregate_moment_4, 'moment5': aggregate_moment_5}
153 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/datasets_generation/multitask_dataset.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import argparse
2 | import os
3 | import pickle
4 |
5 | import numpy as np
6 | import torch
7 | from inspect import signature
8 |
9 | from tqdm import tqdm
10 |
11 | from . import graph_algorithms
12 | from .graph_generation import GraphType, generate_graph
13 |
14 |
15 | class DatasetMultitask:
16 |
17 | def __init__(self, n_graphs, N, seed, graph_type, get_nodes_labels, get_graph_labels, print_every, sssp, filename):
18 | self.adj = {}
19 | self.features = {}
20 | self.nodes_labels = {}
21 | self.graph_labels = {}
22 |
23 | def to_categorical(x, N):
24 | v = np.zeros(N)
25 | v[x] = 1
26 | return v
27 |
28 | for dset in N.keys():
29 | if dset not in n_graphs:
30 | n_graphs[dset] = n_graphs['default']
31 |
32 | total_n_graphs = sum(n_graphs[dset])
33 |
34 | set_adj = [[] for _ in n_graphs[dset]]
35 | set_features = [[] for _ in n_graphs[dset]]
36 | set_nodes_labels = [[] for _ in n_graphs[dset]]
37 | set_graph_labels = [[] for _ in n_graphs[dset]]
38 |
39 | t = tqdm(total=np.sum(n_graphs[dset]), desc=dset, leave=True, unit=' graphs')
40 | for batch, batch_size in enumerate(n_graphs[dset]):
41 | for i in range(batch_size):
42 | # generate a random graph of type graph_type and size N
43 | seed += 1
44 | adj, features, type = generate_graph(N[dset][batch], graph_type, seed=seed)
45 |
46 | while np.min(np.max(adj, 0)) == 0.0:
47 | # remove graph with singleton nodes
48 | seed += 1
49 | adj, features, _ = generate_graph(N[dset][batch], type, seed=seed)
50 |
51 | t.update(1)
52 |
53 | # make sure there are no self connection
54 | assert np.all(
55 | np.multiply(adj, np.eye(N[dset][batch])) == np.zeros((N[dset][batch], N[dset][batch])))
56 |
57 | if sssp:
58 | # define the source node
59 | source_node = np.random.randint(0, N[dset][batch])
60 |
61 | # compute the labels with graph_algorithms; if sssp add the sssp
62 | node_labels = get_nodes_labels(adj, features,
63 | graph_algorithms.all_pairs_shortest_paths(adj, 0)[source_node]
64 | if sssp else None)
65 | graph_labels = get_graph_labels(adj, features)
66 | if sssp:
67 | # add the 1-hot feature determining the starting node
68 | features = np.stack([to_categorical(source_node, N[dset][batch]), features], axis=1)
69 |
70 | set_adj[batch].append(adj)
71 | set_features[batch].append(features)
72 | set_nodes_labels[batch].append(node_labels)
73 | set_graph_labels[batch].append(graph_labels)
74 |
75 | t.close()
76 | self.adj[dset] = [torch.from_numpy(np.asarray(adjs)).float() for adjs in set_adj]
77 | self.features[dset] = [torch.from_numpy(np.asarray(fs)).float() for fs in set_features]
78 | self.nodes_labels[dset] = [torch.from_numpy(np.asarray(nls)).float() for nls in set_nodes_labels]
79 | self.graph_labels[dset] = [torch.from_numpy(np.asarray(gls)).float() for gls in set_graph_labels]
80 |
81 | self.save_as_pickle(filename)
82 |
83 | def save_as_pickle(self, filename):
84 | """" Saves the data into a pickle file at filename """
85 | directory = os.path.dirname(filename)
86 | if not os.path.exists(directory):
87 | os.makedirs(directory)
88 |
89 | with open(filename, 'wb') as f:
90 | torch.save((self.adj, self.features, self.nodes_labels, self.graph_labels), f)
91 |
92 |
93 | if __name__ == '__main__':
94 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
95 | parser.add_argument('--out', type=str, default='./multitask_benchmark/data/multitask_dataset.pkl', help='Data path.')
96 | parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=1234, help='Random seed.')
97 | parser.add_argument('--graph_type', type=str, default='RANDOM', help='Type of graphs in train set')
98 | parser.add_argument('--nodes_labels', nargs='+', default=["eccentricity", "graph_laplacian_features", "sssp"])
99 | parser.add_argument('--graph_labels', nargs='+', default=["is_connected", "diameter", "spectral_radius"])
100 | parser.add_argument('--extrapolation', action='store_true', default=False,
101 | help='Generated various test sets of dimensions larger than train and validation.')
102 | parser.add_argument('--print_every', type=int, default=20, help='')
103 | args = parser.parse_args()
104 |
105 | if 'sssp' in args.nodes_labels:
106 | sssp = True
107 | args.nodes_labels.remove('sssp')
108 | else:
109 | sssp = False
110 |
111 | # gets the functions of graph_algorithms from the specified datasets
112 | nodes_labels_algs = list(map(lambda s: getattr(graph_algorithms, s), args.nodes_labels))
113 | graph_labels_algs = list(map(lambda s: getattr(graph_algorithms, s), args.graph_labels))
114 |
115 |
116 | def get_nodes_labels(A, F, initial=None):
117 | labels = [] if initial is None else [initial]
118 | for f in nodes_labels_algs:
119 | params = signature(f).parameters
120 | labels.append(f(A, F) if 'F' in params else f(A))
121 | return np.swapaxes(np.stack(labels), 0, 1)
122 |
123 |
124 | def get_graph_labels(A, F):
125 | labels = []
126 | for f in graph_labels_algs:
127 | params = signature(f).parameters
128 | labels.append(f(A, F) if 'F' in params else f(A))
129 | return np.asarray(labels).flatten()
130 |
131 |
132 | data = DatasetMultitask(n_graphs={'train': [512] * 10, 'val': [128] * 5, 'default': [256] * 5},
133 | N={**{'train': range(15, 25), 'val': range(15, 25)}, **(
134 | {'test-(20,25)': range(20, 25), 'test-(25,30)': range(25, 30),
135 | 'test-(30,35)': range(30, 35), 'test-(35,40)': range(35, 40),
136 | 'test-(40,45)': range(40, 45), 'test-(45,50)': range(45, 50),
137 | 'test-(60,65)': range(60, 65), 'test-(75,80)': range(75, 80),
138 | 'test-(95,100)': range(95, 100)} if args.extrapolation else
139 | {'test': range(15, 25)})},
140 | seed=args.seed, graph_type=getattr(GraphType, args.graph_type),
141 | get_nodes_labels=get_nodes_labels, get_graph_labels=get_graph_labels,
142 | print_every=args.print_every, sssp=sssp, filename=args.out)
143 |
144 | data.save_as_pickle(args.out)
145 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/data/molecules.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # MIT License
2 | # Copyright (c) 2020 Vijay Prakash Dwivedi, Chaitanya K. Joshi, Thomas Laurent, Yoshua Bengio, Xavier Bresson
3 |
4 |
5 | import torch
6 | import pickle
7 | import torch.utils.data
8 | import time
9 | import numpy as np
10 | import csv
11 | import dgl
12 |
13 |
14 | class MoleculeDGL(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
15 | def __init__(self, data_dir, split, num_graphs):
16 | self.data_dir = data_dir
17 | self.split = split
18 | self.num_graphs = num_graphs
19 |
20 | with open(data_dir + "/%s.pickle" % self.split, "rb") as f:
21 | self.data = pickle.load(f)
22 |
23 | # loading the sampled indices from file ./zinc_molecules/.index
24 | with open(data_dir + "/%s.index" % self.split, "r") as f:
25 | data_idx = [list(map(int, idx)) for idx in csv.reader(f)]
26 | self.data = [self.data[i] for i in data_idx[0]]
27 |
28 | assert len(self.data) == num_graphs, "Sample num_graphs again; available idx: train/val/test => 10k/1k/1k"
29 |
30 | """
31 | data is a list of Molecule dict objects with following attributes
32 |
33 | molecule = data[idx]
34 | ; molecule['num_atom'] : nb of atoms, an integer (N)
35 | ; molecule['atom_type'] : tensor of size N, each element is an atom type, an integer between 0 and num_atom_type
36 | ; molecule['bond_type'] : tensor of size N x N, each element is a bond type, an integer between 0 and num_bond_type
37 | ; molecule['logP_SA_cycle_normalized'] : the chemical property to regress, a float variable
38 | """
39 |
40 | self.graph_lists = []
41 | self.graph_labels = []
42 | self.n_samples = len(self.data)
43 | self._prepare()
44 |
45 | def _prepare(self):
46 | print("preparing %d graphs for the %s set..." % (self.num_graphs, self.split.upper()))
47 |
48 | for molecule in self.data:
49 | node_features = molecule['atom_type'].long()
50 |
51 | adj = molecule['bond_type']
52 | edge_list = (adj != 0).nonzero() # converting adj matrix to edge_list
53 |
54 | edge_idxs_in_adj = edge_list.split(1, dim=1)
55 | edge_features = adj[edge_idxs_in_adj].reshape(-1).long()
56 |
57 | # Create the DGL Graph
58 | g = dgl.DGLGraph()
59 | g.add_nodes(molecule['num_atom'])
60 | g.ndata['feat'] = node_features
61 |
62 | for src, dst in edge_list:
63 | g.add_edges(src.item(), dst.item())
64 | g.edata['feat'] = edge_features
65 |
66 | self.graph_lists.append(g)
67 | self.graph_labels.append(molecule['logP_SA_cycle_normalized'])
68 |
69 | def __len__(self):
70 | """Return the number of graphs in the dataset."""
71 | return self.n_samples
72 |
73 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
74 | """
75 | Get the idx^th sample.
76 | Parameters
77 | ---------
78 | idx : int
79 | The sample index.
80 | Returns
81 | -------
82 | (dgl.DGLGraph, int)
83 | DGLGraph with node feature stored in `feat` field
84 | And its label.
85 | """
86 | return self.graph_lists[idx], self.graph_labels[idx]
87 |
88 |
89 | class MoleculeDatasetDGL(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
90 | def __init__(self, name='Zinc'):
91 | t0 = time.time()
92 | self.name = name
93 |
94 | self.num_atom_type = 28 # known meta-info about the zinc dataset; can be calculated as well
95 | self.num_bond_type = 4 # known meta-info about the zinc dataset; can be calculated as well
96 |
97 | data_dir = './data/molecules'
98 |
99 | self.train = MoleculeDGL(data_dir, 'train', num_graphs=10000)
100 | self.val = MoleculeDGL(data_dir, 'val', num_graphs=1000)
101 | self.test = MoleculeDGL(data_dir, 'test', num_graphs=1000)
102 | print("Time taken: {:.4f}s".format(time.time() - t0))
103 |
104 |
105 | def self_loop(g):
106 | """
107 | Utility function only, to be used only when necessary as per user self_loop flag
108 | : Overwriting the function dgl.transform.add_self_loop() to not miss ndata['feat'] and edata['feat']
109 |
110 |
111 | This function is called inside a function in MoleculeDataset class.
112 | """
113 | new_g = dgl.DGLGraph()
114 | new_g.add_nodes(g.number_of_nodes())
115 | new_g.ndata['feat'] = g.ndata['feat']
116 |
117 | src, dst = g.all_edges(order="eid")
118 | src = dgl.backend.zerocopy_to_numpy(src)
119 | dst = dgl.backend.zerocopy_to_numpy(dst)
120 | non_self_edges_idx = src != dst
121 | nodes = np.arange(g.number_of_nodes())
122 | new_g.add_edges(src[non_self_edges_idx], dst[non_self_edges_idx])
123 | new_g.add_edges(nodes, nodes)
124 |
125 | # This new edata is not used since this function gets called only for GCN, GAT
126 | # However, we need this for the generic requirement of ndata and edata
127 | new_g.edata['feat'] = torch.zeros(new_g.number_of_edges())
128 | return new_g
129 |
130 |
131 | class MoleculeDataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
132 |
133 | def __init__(self, name):
134 | """
135 | Loading SBM datasets
136 | """
137 | start = time.time()
138 | print("[I] Loading dataset %s..." % (name))
139 | self.name = name
140 | data_dir = 'data/'
141 | with open(data_dir + name + '.pkl', "rb") as f:
142 | f = pickle.load(f)
143 | self.train = f[0]
144 | self.val = f[1]
145 | self.test = f[2]
146 | self.num_atom_type = f[3]
147 | self.num_bond_type = f[4]
148 | print('train, test, val sizes :', len(self.train), len(self.test), len(self.val))
149 | print("[I] Finished loading.")
150 | print("[I] Data load time: {:.4f}s".format(time.time() - start))
151 |
152 | # form a mini batch from a given list of samples = [(graph, label) pairs]
153 | def collate(self, samples):
154 | # The input samples is a list of pairs (graph, label).
155 | graphs, labels = map(list, zip(*samples))
156 | labels = torch.tensor(np.array(labels)).unsqueeze(1)
157 | tab_sizes_n = [graphs[i].number_of_nodes() for i in range(len(graphs))]
158 | tab_snorm_n = [torch.FloatTensor(size, 1).fill_(1. / float(size)) for size in tab_sizes_n]
159 | snorm_n = torch.cat(tab_snorm_n).sqrt()
160 | tab_sizes_e = [graphs[i].number_of_edges() for i in range(len(graphs))]
161 | tab_snorm_e = [torch.FloatTensor(size, 1).fill_(1. / float(size)) for size in tab_sizes_e]
162 | snorm_e = torch.cat(tab_snorm_e).sqrt()
163 | batched_graph = dgl.batch(graphs)
164 | return batched_graph, labels, snorm_n, snorm_e
165 |
166 | def _add_self_loops(self):
167 | # function for adding self loops
168 | # this function will be called only if self_loop flag is True
169 |
170 | self.train.graph_lists = [self_loop(g) for g in self.train.graph_lists]
171 | self.val.graph_lists = [self_loop(g) for g in self.val.graph_lists]
172 | self.test.graph_lists = [self_loop(g) for g in self.test.graph_lists]
173 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/datasets_generation/graph_generation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import random
3 | import networkx as nx
4 | import math
5 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # only required to plot
6 | from enum import Enum
7 |
8 | """
9 | Generates random graphs of different types of a given size.
10 | Some of the graph are created using the NetworkX library, for more info see
11 | https://networkx.github.io/documentation/networkx-1.10/reference/generators.html
12 | """
13 |
14 |
15 | class GraphType(Enum):
16 | RANDOM = 0
17 | ERDOS_RENYI = 1
18 | BARABASI_ALBERT = 2
19 | GRID = 3
20 | CAVEMAN = 5
21 | TREE = 6
22 | LADDER = 7
23 | LINE = 8
24 | STAR = 9
25 | CATERPILLAR = 10
26 | LOBSTER = 11
27 |
28 |
29 | # probabilities of each type in case of random type
30 | MIXTURE = [(GraphType.ERDOS_RENYI, 0.2), (GraphType.BARABASI_ALBERT, 0.2), (GraphType.GRID, 0.05),
31 | (GraphType.CAVEMAN, 0.05), (GraphType.TREE, 0.15), (GraphType.LADDER, 0.05),
32 | (GraphType.LINE, 0.05), (GraphType.STAR, 0.05), (GraphType.CATERPILLAR, 0.1), (GraphType.LOBSTER, 0.1)]
33 |
34 |
35 | def erdos_renyi(N, degree, seed):
36 | """ Creates an Erdős-Rényi or binomial graph of size N with degree/N probability of edge creation """
37 | return nx.fast_gnp_random_graph(N, degree / N, seed, directed=False)
38 |
39 |
40 | def barabasi_albert(N, degree, seed):
41 | """ Creates a random graph according to the Barabási–Albert preferential attachment model
42 | of size N and where nodes are atteched with degree edges """
43 | return nx.barabasi_albert_graph(N, degree, seed)
44 |
45 |
46 | def grid(N):
47 | """ Creates a m x k 2d grid graph with N = m*k and m and k as close as possible """
48 | m = 1
49 | for i in range(1, int(math.sqrt(N)) + 1):
50 | if N % i == 0:
51 | m = i
52 | return nx.grid_2d_graph(m, N // m)
53 |
54 |
55 | def caveman(N):
56 | """ Creates a caveman graph of m cliques of size k, with m and k as close as possible """
57 | m = 1
58 | for i in range(1, int(math.sqrt(N)) + 1):
59 | if N % i == 0:
60 | m = i
61 | return nx.caveman_graph(m, N // m)
62 |
63 |
64 | def tree(N, seed):
65 | """ Creates a tree of size N with a power law degree distribution """
66 | return nx.random_powerlaw_tree(N, seed=seed, tries=10000)
67 |
68 |
69 | def ladder(N):
70 | """ Creates a ladder graph of N nodes: two rows of N/2 nodes, with each pair connected by a single edge.
71 | In case N is odd another node is attached to the first one. """
72 | G = nx.ladder_graph(N // 2)
73 | if N % 2 != 0:
74 | G.add_node(N - 1)
75 | G.add_edge(0, N - 1)
76 | return G
77 |
78 |
79 | def line(N):
80 | """ Creates a graph composed of N nodes in a line """
81 | return nx.path_graph(N)
82 |
83 |
84 | def star(N):
85 | """ Creates a graph composed by one center node connected N-1 outer nodes """
86 | return nx.star_graph(N - 1)
87 |
88 |
89 | def caterpillar(N, seed):
90 | """ Creates a random caterpillar graph with a backbone of size b (drawn from U[1, N)), and N − b
91 | pendent vertices uniformly connected to the backbone. """
92 | np.random.seed(seed)
93 | B = np.random.randint(low=1, high=N)
94 | G = nx.empty_graph(N)
95 | for i in range(1, B):
96 | G.add_edge(i - 1, i)
97 | for i in range(B, N):
98 | G.add_edge(i, np.random.randint(B))
99 | return G
100 |
101 |
102 | def lobster(N, seed):
103 | """ Creates a random Lobster graph with a backbone of size b (drawn from U[1, N)), and p (drawn
104 | from U[1, N − b ]) pendent vertices uniformly connected to the backbone, and additional
105 | N − b − p pendent vertices uniformly connected to the previous pendent vertices """
106 | np.random.seed(seed)
107 | B = np.random.randint(low=1, high=N)
108 | F = np.random.randint(low=B + 1, high=N + 1)
109 | G = nx.empty_graph(N)
110 | for i in range(1, B):
111 | G.add_edge(i - 1, i)
112 | for i in range(B, F):
113 | G.add_edge(i, np.random.randint(B))
114 | for i in range(F, N):
115 | G.add_edge(i, np.random.randint(low=B, high=F))
116 | return G
117 |
118 |
119 | def randomize(A):
120 | """ Adds some randomness by toggling some edges without changing the expected number of edges of the graph """
121 | BASE_P = 0.9
122 |
123 | # e is the number of edges, r the number of missing edges
124 | N = A.shape[0]
125 | e = np.sum(A) / 2
126 | r = N * (N - 1) / 2 - e
127 |
128 | # ep chance of an existing edge to remain, rp chance of another edge to appear
129 | if e <= r:
130 | ep = BASE_P
131 | rp = (1 - BASE_P) * e / r
132 | else:
133 | ep = BASE_P + (1 - BASE_P) * (e - r) / e
134 | rp = 1 - BASE_P
135 |
136 | array = np.random.uniform(size=(N, N), low=0.0, high=0.5)
137 | array = array + array.transpose()
138 | remaining = np.multiply(np.where(array < ep, 1, 0), A)
139 | appearing = np.multiply(np.multiply(np.where(array < rp, 1, 0), 1 - A), 1 - np.eye(N))
140 | ans = np.add(remaining, appearing)
141 |
142 | # assert (np.all(np.multiply(ans, np.eye(N)) == np.zeros((N, N))))
143 | # assert (np.all(ans >= 0))
144 | # assert (np.all(ans <= 1))
145 | # assert (np.all(ans == ans.transpose()))
146 | return ans
147 |
148 |
149 | def generate_graph(N, type=GraphType.RANDOM, seed=None, degree=None):
150 | """
151 | Generates random graphs of different types of a given size. Note:
152 | - graph are undirected and without weights on edges
153 | - node values are sampled independently from U[0,1]
154 |
155 | :param N: number of nodes
156 | :param type: type chosen between the categories specified in GraphType enum
157 | :param seed: random seed
158 | :param degree: average degree of a node, only used in some graph types
159 | :return: adj_matrix: N*N numpy matrix
160 | node_values: numpy array of size N
161 | """
162 | random.seed(seed)
163 | np.random.seed(seed)
164 |
165 | # sample which random type to use
166 | if type == GraphType.RANDOM:
167 | type = np.random.choice([t for (t, _) in MIXTURE], 1, p=[pr for (_, pr) in MIXTURE])[0]
168 |
169 | # generate the graph structure depending on the type
170 | if type == GraphType.ERDOS_RENYI:
171 | if degree == None: degree = random.random() * N
172 | G = erdos_renyi(N, degree, seed)
173 | elif type == GraphType.BARABASI_ALBERT:
174 | if degree == None: degree = int(random.random() * (N - 1)) + 1
175 | G = barabasi_albert(N, degree, seed)
176 | elif type == GraphType.GRID:
177 | G = grid(N)
178 | elif type == GraphType.CAVEMAN:
179 | G = caveman(N)
180 | elif type == GraphType.TREE:
181 | G = tree(N, seed)
182 | elif type == GraphType.LADDER:
183 | G = ladder(N)
184 | elif type == GraphType.LINE:
185 | G = line(N)
186 | elif type == GraphType.STAR:
187 | G = star(N)
188 | elif type == GraphType.CATERPILLAR:
189 | G = caterpillar(N, seed)
190 | elif type == GraphType.LOBSTER:
191 | G = lobster(N, seed)
192 | else:
193 | print("Type not defined")
194 | return
195 |
196 | # generate adjacency matrix and nodes values
197 | nodes = list(G)
198 | random.shuffle(nodes)
199 | adj_matrix = nx.to_numpy_array(G, nodes)
200 | node_values = np.random.uniform(low=0, high=1, size=N)
201 |
202 | # randomization
203 | adj_matrix = randomize(adj_matrix)
204 |
205 | # draw the graph created
206 | # nx.draw(G, pos=nx.spring_layout(G))
207 | # plt.draw()
208 |
209 | return adj_matrix, node_values, type
210 |
211 |
212 | if __name__ == '__main__':
213 | for i in range(100):
214 | adj_matrix, node_values = generate_graph(10, GraphType.RANDOM, seed=i)
215 | print(adj_matrix)
216 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/dgl/pna_layer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | import torch.nn.functional as F
4 | import dgl.function as fn
5 |
6 | from .aggregators import AGGREGATORS
7 | from models.layers import MLP, FCLayer
8 | from .scalers import SCALERS
9 |
10 | """
11 | PNA: Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation
12 | Gabriele Corso, Luca Cavalleri, Dominique Beaini, Pietro Lio, Petar Velickovic
13 | https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718
14 | """
15 |
16 |
17 | class PNATower(nn.Module):
18 | def __init__(self, in_dim, out_dim, dropout, graph_norm, batch_norm, aggregators, scalers, avg_d,
19 | pretrans_layers, posttrans_layers, edge_features, edge_dim):
20 | super().__init__()
21 | self.dropout = dropout
22 | self.graph_norm = graph_norm
23 | self.batch_norm = batch_norm
24 | self.edge_features = edge_features
25 |
26 | self.batchnorm_h = nn.BatchNorm1d(out_dim)
27 | self.aggregators = aggregators
28 | self.scalers = scalers
29 | self.pretrans = MLP(in_size=2 * in_dim + (edge_dim if edge_features else 0), hidden_size=in_dim,
30 | out_size=in_dim, layers=pretrans_layers, mid_activation='relu', last_activation='none')
31 | self.posttrans = MLP(in_size=(len(aggregators) * len(scalers) + 1) * in_dim, hidden_size=out_dim,
32 | out_size=out_dim, layers=posttrans_layers, mid_activation='relu', last_activation='none')
33 | self.avg_d = avg_d
34 |
35 | def pretrans_edges(self, edges):
36 | if self.edge_features:
37 | z2 = torch.cat([edges.src['h'], edges.dst['h'], edges.data['ef']], dim=1)
38 | else:
39 | z2 = torch.cat([edges.src['h'], edges.dst['h']], dim=1)
40 | return {'e': self.pretrans(z2)}
41 |
42 | def message_func(self, edges):
43 | return {'e': edges.data['e']}
44 |
45 | def reduce_func(self, nodes):
46 | h = nodes.mailbox['e']
47 | D = h.shape[-2]
48 | h = torch.cat([aggregate(h) for aggregate in self.aggregators], dim=1)
49 | h = torch.cat([scale(h, D=D, avg_d=self.avg_d) for scale in self.scalers], dim=1)
50 | return {'h': h}
51 |
52 | def posttrans_nodes(self, nodes):
53 | return self.posttrans(nodes.data['h'])
54 |
55 | def forward(self, g, h, e, snorm_n):
56 | g.ndata['h'] = h
57 | if self.edge_features: # add the edges information only if edge_features = True
58 | g.edata['ef'] = e
59 |
60 | # pretransformation
61 | g.apply_edges(self.pretrans_edges)
62 |
63 | # aggregation
64 | g.update_all(self.message_func, self.reduce_func)
65 | h = torch.cat([h, g.ndata['h']], dim=1)
66 |
67 | # posttransformation
68 | h = self.posttrans(h)
69 |
70 | # graph and batch normalization
71 | if self.graph_norm:
72 | h = h * snorm_n
73 | if self.batch_norm:
74 | h = self.batchnorm_h(h)
75 | h = F.dropout(h, self.dropout, training=self.training)
76 | return h
77 |
78 |
79 | class PNALayer(nn.Module):
80 |
81 | def __init__(self, in_dim, out_dim, aggregators, scalers, avg_d, dropout, graph_norm, batch_norm, towers=1,
82 | pretrans_layers=1, posttrans_layers=1, divide_input=True, residual=False, edge_features=False,
83 | edge_dim=0):
84 | """
85 | :param in_dim: size of the input per node
86 | :param out_dim: size of the output per node
87 | :param aggregators: set of aggregation function identifiers
88 | :param scalers: set of scaling functions identifiers
89 | :param avg_d: average degree of nodes in the training set, used by scalers to normalize
90 | :param dropout: dropout used
91 | :param graph_norm: whether to use graph normalisation
92 | :param batch_norm: whether to use batch normalisation
93 | :param towers: number of towers to use
94 | :param pretrans_layers: number of layers in the transformation before the aggregation
95 | :param posttrans_layers: number of layers in the transformation after the aggregation
96 | :param divide_input: whether the input features should be split between towers or not
97 | :param residual: whether to add a residual connection
98 | :param edge_features: whether to use the edge features
99 | :param edge_dim: size of the edge features
100 | """
101 | super().__init__()
102 | assert ((not divide_input) or in_dim % towers == 0), "if divide_input is set the number of towers has to divide in_dim"
103 | assert (out_dim % towers == 0), "the number of towers has to divide the out_dim"
104 | assert avg_d is not None
105 |
106 | # retrieve the aggregators and scalers functions
107 | aggregators = [AGGREGATORS[aggr] for aggr in aggregators.split()]
108 | scalers = [SCALERS[scale] for scale in scalers.split()]
109 |
110 | self.divide_input = divide_input
111 | self.input_tower = in_dim // towers if divide_input else in_dim
112 | self.output_tower = out_dim // towers
113 | self.in_dim = in_dim
114 | self.out_dim = out_dim
115 | self.edge_features = edge_features
116 | self.residual = residual
117 | if in_dim != out_dim:
118 | self.residual = False
119 |
120 | # convolution
121 | self.towers = nn.ModuleList()
122 | for _ in range(towers):
123 | self.towers.append(PNATower(in_dim=self.input_tower, out_dim=self.output_tower, aggregators=aggregators,
124 | scalers=scalers, avg_d=avg_d, pretrans_layers=pretrans_layers,
125 | posttrans_layers=posttrans_layers, batch_norm=batch_norm, dropout=dropout,
126 | graph_norm=graph_norm, edge_features=edge_features, edge_dim=edge_dim))
127 | # mixing network
128 | self.mixing_network = FCLayer(out_dim, out_dim, activation='LeakyReLU')
129 |
130 | def forward(self, g, h, e, snorm_n):
131 | h_in = h # for residual connection
132 |
133 | if self.divide_input:
134 | h_cat = torch.cat(
135 | [tower(g, h[:, n_tower * self.input_tower: (n_tower + 1) * self.input_tower],
136 | e, snorm_n)
137 | for n_tower, tower in enumerate(self.towers)], dim=1)
138 | else:
139 | h_cat = torch.cat([tower(g, h, e, snorm_n) for tower in self.towers], dim=1)
140 |
141 | h_out = self.mixing_network(h_cat)
142 |
143 | if self.residual:
144 | h_out = h_in + h_out # residual connection
145 | return h_out
146 |
147 | def __repr__(self):
148 | return '{}(in_channels={}, out_channels={})'.format(self.__class__.__name__, self.in_dim, self.out_dim)
149 |
150 |
151 | class PNASimpleLayer(nn.Module):
152 |
153 | def __init__(self, in_dim, out_dim, aggregators, scalers, avg_d, dropout, batch_norm, residual,
154 | posttrans_layers=1):
155 | """
156 | A simpler version of PNA layer that simply aggregates the neighbourhood (similar to GCN and GIN),
157 | without using the pretransformation or the tower mechanisms of the MPNN. It does not support edge features.
158 |
159 | :param in_dim: size of the input per node
160 | :param out_dim: size of the output per node
161 | :param aggregators: set of aggregation function identifiers
162 | :param scalers: set of scaling functions identifiers
163 | :param avg_d: average degree of nodes in the training set, used by scalers to normalize
164 | :param dropout: dropout used
165 | :param batch_norm: whether to use batch normalisation
166 | :param posttrans_layers: number of layers in the transformation after the aggregation
167 | """
168 | super().__init__()
169 |
170 | # retrieve the aggregators and scalers functions
171 | aggregators = [AGGREGATORS[aggr] for aggr in aggregators.split()]
172 | scalers = [SCALERS[scale] for scale in scalers.split()]
173 |
174 | self.aggregators = aggregators
175 | self.scalers = scalers
176 | self.in_dim = in_dim
177 | self.out_dim = out_dim
178 | self.dropout = dropout
179 | self.batch_norm = batch_norm
180 | self.residual = residual
181 |
182 | self.batchnorm_h = nn.BatchNorm1d(out_dim)
183 | self.posttrans = MLP(in_size=(len(aggregators) * len(scalers)) * in_dim, hidden_size=out_dim,
184 | out_size=out_dim, layers=posttrans_layers, mid_activation='relu',
185 | last_activation='none')
186 | self.avg_d = avg_d
187 |
188 |
189 | def reduce_func(self, nodes):
190 | h = nodes.mailbox['m']
191 | D = h.shape[-2]
192 | h = torch.cat([aggregate(h) for aggregate in self.aggregators], dim=1)
193 | h = torch.cat([scale(h, D=D, avg_d=self.avg_d) for scale in self.scalers], dim=1)
194 | return {'h': h}
195 |
196 |
197 | def forward(self, g, h):
198 | h_in = h
199 | g.ndata['h'] = h
200 |
201 | # aggregation
202 | g.update_all(fn.copy_u('h', 'm'), self.reduce_func)
203 | h = g.ndata['h']
204 |
205 | # posttransformation
206 | h = self.posttrans(h)
207 |
208 | # batch normalization and residual
209 | if self.batch_norm:
210 | h = self.batchnorm_h(h)
211 | h = F.relu(h)
212 | if self.residual:
213 | h = h_in + h
214 |
215 | h = F.dropout(h, self.dropout, training=self.training)
216 | return h
217 |
218 | def __repr__(self):
219 | return '{}(in_channels={}, out_channels={})'.format(self.__class__.__name__, self.in_dim, self.out_dim)
220 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/util/train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import division
2 | from __future__ import print_function
3 |
4 | import argparse
5 | import os
6 | import sys
7 | import time
8 | from types import SimpleNamespace
9 |
10 | import math
11 | import numpy as np
12 | import torch
13 | import torch.optim as optim
14 | from tqdm import tqdm
15 |
16 | from models.pytorch.gnn_framework import GNN
17 | from multitask_benchmark.util.util import load_dataset, total_loss, total_loss_multiple_batches, \
18 | specific_loss_multiple_batches
19 |
20 |
21 | def build_arg_parser():
22 | """
23 | :return: argparse.ArgumentParser() filled with the standard arguments for a training session.
24 | Might need to be enhanced for some train_scripts.
25 | """
26 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
27 |
28 | parser.add_argument('--data', type=str, default='../../data/multitask_dataset.pkl', help='Data path.')
29 | parser.add_argument('--no-cuda', action='store_true', default=False, help='Disables CUDA training.')
30 | parser.add_argument('--only_nodes', action='store_true', default=False, help='Evaluate only nodes labels.')
31 | parser.add_argument('--only_graph', action='store_true', default=False, help='Evaluate only graph labels.')
32 | parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=42, help='Random seed.')
33 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=10000, help='Number of epochs to train.')
34 | parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=0.003, help='Initial learning rate.')
35 | parser.add_argument('--weight_decay', type=float, default=1e-6, help='Weight decay (L2 loss on parameters).')
36 | parser.add_argument('--hidden', type=int, default=16, help='Number of hidden units.')
37 | parser.add_argument('--dropout', type=float, default=0.0, help='Dropout rate (1 - keep probability).')
38 | parser.add_argument('--patience', type=int, default=1000, help='Patience')
39 | parser.add_argument('--conv_layers', type=int, default=None, help='Graph convolutions')
40 | parser.add_argument('--variable_conv_layers', type=str, default='N', help='Graph convolutions function name')
41 | parser.add_argument('--fc_layers', type=int, default=3, help='Fully connected layers in readout')
42 | parser.add_argument('--loss', type=str, default='mse', help='Loss function to use.')
43 | parser.add_argument('--print_every', type=int, default=50, help='Print training results every')
44 | parser.add_argument('--final_activation', type=str, default='LeakyReLu',
45 | help='final activation in both FC layers for nodes and S2S for Graph')
46 | parser.add_argument('--skip', action='store_true', default=False,
47 | help='Whether to use the model with skip connections.')
48 | parser.add_argument('--gru', action='store_true', default=False,
49 | help='Whether to use a GRU in the update function of the layers.')
50 | parser.add_argument('--fixed', action='store_true', default=False,
51 | help='Whether to use the model with fixed middle convolutions.')
52 | parser.add_argument('--variable', action='store_true', default=False,
53 | help='Whether to have a variable number of comvolutional layers.')
54 | return parser
55 |
56 |
57 | # map from names (as passed as parameters) to function determining number of convolutional layers at runtime
58 | VARIABLE_LAYERS_FUNCTIONS = {
59 | 'N': lambda adj: adj.shape[1],
60 | 'N/2': lambda adj: adj.shape[1] // 2,
61 | '4log2N': lambda adj: int(4 * math.log2(adj.shape[1])),
62 | '2log2N': lambda adj: int(2 * math.log2(adj.shape[1])),
63 | '3sqrtN': lambda adj: int(3 * math.sqrt(adj.shape[1]))
64 | }
65 |
66 |
67 | def execute_train(gnn_args, args):
68 | """
69 | :param gnn_args: the description of the model to be trained (expressed as arguments for GNN.__init__)
70 | :param args: the parameters of the training session
71 | """
72 | args.cuda = not args.no_cuda and torch.cuda.is_available()
73 |
74 | np.random.seed(args.seed)
75 | torch.manual_seed(args.seed)
76 | if args.cuda:
77 | torch.cuda.manual_seed(args.seed)
78 |
79 | device = 'cuda' if args.cuda else 'cpu'
80 | print('Using device:', device)
81 |
82 | # load data
83 | adj, features, node_labels, graph_labels = load_dataset(args.data, args.loss, args.only_nodes, args.only_graph,
84 | print_baseline=True)
85 |
86 | # model and optimizer
87 | gnn_args = SimpleNamespace(**gnn_args)
88 |
89 | # compute avg_d on the training set
90 | if 'avg_d' in gnn_args.first_conv_descr['args'] or 'avg_d' in gnn_args.middle_conv_descr['args']:
91 | dlist = [torch.sum(A, dim=-1) for A in adj['train']]
92 | avg_d = dict(lin=sum([torch.mean(D) for D in dlist]) / len(dlist),
93 | exp=sum([torch.mean(torch.exp(torch.div(1, D)) - 1) for D in dlist]) / len(dlist),
94 | log=sum([torch.mean(torch.log(D + 1)) for D in dlist]) / len(dlist))
95 | if 'avg_d' in gnn_args.first_conv_descr['args']:
96 | gnn_args.first_conv_descr['args']['avg_d'] = avg_d
97 | if 'avg_d' in gnn_args.middle_conv_descr['args']:
98 | gnn_args.middle_conv_descr['args']['avg_d'] = avg_d
99 |
100 | gnn_args.device = device
101 | gnn_args.nfeat = features['train'][0].shape[2]
102 | gnn_args.nodes_out = node_labels['train'][0].shape[-1]
103 | gnn_args.graph_out = graph_labels['train'][0].shape[-1]
104 | if gnn_args.variable:
105 | assert gnn_args.conv_layers is None, "If model is variable, you shouldn't specify conv_layers (maybe you " \
106 | "meant variable_conv_layers?) "
107 | else:
108 | assert gnn_args.conv_layers is not None, "If the model is not variable, you should specify conv_layers"
109 | gnn_args.conv_layers = VARIABLE_LAYERS_FUNCTIONS[
110 | args.variable_conv_layers] if gnn_args.variable else args.conv_layers
111 | model = GNN(**vars(gnn_args))
112 | optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=args.lr, weight_decay=args.weight_decay)
113 |
114 | pytorch_total_params = sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad)
115 | print("Total params", pytorch_total_params)
116 |
117 | def move_cuda(dset):
118 | assert args.cuda, "Cannot move dataset on CUDA, running on cpu"
119 | if features[dset][0].is_cuda:
120 | # already on CUDA
121 | return
122 | features[dset] = [x.cuda() for x in features[dset]]
123 | adj[dset] = [x.cuda() for x in adj[dset]]
124 | node_labels[dset] = [x.cuda() for x in node_labels[dset]]
125 | graph_labels[dset] = [x.cuda() for x in graph_labels[dset]]
126 |
127 | if args.cuda:
128 | model.cuda()
129 | # move train, val to CUDA (delay moving test until needed)
130 | move_cuda('train')
131 | move_cuda('val')
132 |
133 | def train(epoch):
134 | """
135 | Execute a single epoch of the training loop
136 |
137 | :param epoch:int the number of the epoch being performed (0-indexed)
138 | """
139 | t = time.time()
140 |
141 | # train step
142 | model.train()
143 | for batch in range(len(adj['train'])):
144 | optimizer.zero_grad()
145 | output = model(features['train'][batch], adj['train'][batch])
146 | loss_train = total_loss(output, (node_labels['train'][batch], graph_labels['train'][batch]), loss=args.loss,
147 | only_nodes=args.only_nodes, only_graph=args.only_graph)
148 | loss_train.backward()
149 | optimizer.step()
150 |
151 | # validation epoch
152 | model.eval()
153 | output_zip = [model(features['val'][batch], adj['val'][batch]) for batch in range(len(adj['val']))]
154 | output = ([x[0] for x in output_zip], [x[1] for x in output_zip])
155 |
156 | loss_val = total_loss_multiple_batches(output, (node_labels['val'], graph_labels['val']), loss=args.loss,
157 | only_nodes=args.only_nodes, only_graph=args.only_graph)
158 |
159 | return loss_train.data.item(), loss_val
160 |
161 | def compute_test():
162 | """
163 | Evaluate the current model on all the sets of the dataset, printing results.
164 | This procedure is destructive on datasets.
165 | """
166 | model.eval()
167 |
168 | sets = list(features.keys())
169 | for dset in sets:
170 | # move data on CUDA if not already on it
171 | if args.cuda:
172 | move_cuda(dset)
173 |
174 | output_zip = [model(features[dset][batch], adj[dset][batch]) for batch in range(len(adj[dset]))]
175 | output = ([x[0] for x in output_zip], [x[1] for x in output_zip])
176 | loss_test = total_loss_multiple_batches(output, (node_labels[dset], graph_labels[dset]), loss=args.loss,
177 | only_nodes=args.only_nodes, only_graph=args.only_graph)
178 | print("Test set results ", dset, ": loss= {:.4f}".format(loss_test))
179 | print(dset, ": ",
180 | specific_loss_multiple_batches(output, (node_labels[dset], graph_labels[dset]), loss=args.loss,
181 | only_nodes=args.only_nodes, only_graph=args.only_graph))
182 |
183 | # free unnecessary data
184 | del output_zip
185 | del output
186 | del loss_test
187 | del features[dset]
188 | del adj[dset]
189 | del node_labels[dset]
190 | del graph_labels[dset]
191 | torch.cuda.empty_cache()
192 |
193 | sys.stdout.flush()
194 | # Train model
195 | t_total = time.time()
196 | loss_values = []
197 | bad_counter = 0
198 | best = args.epochs + 1
199 | best_epoch = -1
200 |
201 | sys.stdout.flush()
202 | with tqdm(range(args.epochs), leave=True, unit='epoch') as t:
203 | for epoch in t:
204 | loss_train, loss_val = train(epoch)
205 | loss_values.append(loss_val)
206 | t.set_description('loss.train: {:.4f}, loss.val: {:.4f}'.format(loss_train, loss_val))
207 | if loss_values[-1] < best:
208 | # save current model
209 | torch.save(model.state_dict(), '{}.pkl'.format(epoch))
210 | # remove previous model
211 | if best_epoch >= 0:
212 | os.remove('{}.pkl'.format(best_epoch))
213 | # update training variables
214 | best = loss_values[-1]
215 | best_epoch = epoch
216 | bad_counter = 0
217 | else:
218 | bad_counter += 1
219 |
220 | if bad_counter == args.patience:
221 | print('Early stop at epoch {} (no improvement in last {} epochs)'.format(epoch + 1, bad_counter))
222 | break
223 |
224 | print("Optimization Finished!")
225 | print("Total time elapsed: {:.4f}s".format(time.time() - t_total))
226 |
227 | # Restore best model
228 | print('Loading {}th epoch'.format(best_epoch + 1))
229 | model.load_state_dict(torch.load('{}.pkl'.format(best_epoch)))
230 |
231 | # Testing
232 | with torch.no_grad():
233 | compute_test()
234 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/main_HIV.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import os
3 | import time
4 | import random
5 | import argparse, json
6 | import torch
7 | import torch.optim as optim
8 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
9 | from tqdm import tqdm
10 |
11 | from nets.HIV_graph_classification.pna_net import PNANet
12 | from data.HIV import HIVDataset # import dataset
13 | from train.train_HIV_graph_classification import train_epoch_sparse as train_epoch, \
14 | evaluate_network_sparse as evaluate_network
15 |
16 |
17 | def gpu_setup(use_gpu, gpu_id):
18 | os.environ["CUDA_DEVICE_ORDER"] = "PCI_BUS_ID"
19 | os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = str(gpu_id)
20 |
21 | if torch.cuda.is_available() and use_gpu:
22 | print('cuda available with GPU:', torch.cuda.get_device_name(0))
23 | device = torch.device("cuda")
24 | else:
25 | print('cuda not available')
26 | device = torch.device("cpu")
27 | return device
28 |
29 |
30 | def view_model_param(net_params):
31 | model = PNANet(net_params)
32 | total_param = 0
33 | print("MODEL DETAILS:\n")
34 | # print(model)
35 | for param in model.parameters():
36 | # print(param.data.size())
37 | total_param += np.prod(list(param.data.size()))
38 | print('PNA Total parameters:', total_param)
39 | return total_param
40 |
41 |
42 | def train_val_pipeline(dataset, params, net_params):
43 | t0 = time.time()
44 | per_epoch_time = []
45 |
46 | trainset, valset, testset = dataset.train, dataset.val, dataset.test
47 | device = net_params['device']
48 |
49 | # setting seeds
50 | random.seed(params['seed'])
51 | np.random.seed(params['seed'])
52 | torch.manual_seed(params['seed'])
53 | if device.type == 'cuda':
54 | torch.cuda.manual_seed(params['seed'])
55 |
56 | print("Training Graphs: ", len(trainset))
57 | print("Validation Graphs: ", len(valset))
58 | print("Test Graphs: ", len(testset))
59 |
60 | model = PNANet(net_params)
61 | model = model.to(device)
62 |
63 | optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=params['init_lr'], weight_decay=params['weight_decay'])
64 | scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, mode='min',
65 | factor=params['lr_reduce_factor'],
66 | patience=params['lr_schedule_patience'],
67 | verbose=True)
68 |
69 | epoch_train_losses, epoch_val_losses = [], []
70 | epoch_train_ROCs, epoch_val_ROCs, epoch_test_ROCs = [], [], []
71 |
72 | train_loader = DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=params['batch_size'], shuffle=True, collate_fn=dataset.collate,
73 | pin_memory=True)
74 | val_loader = DataLoader(valset, batch_size=params['batch_size'], shuffle=False, collate_fn=dataset.collate,
75 | pin_memory=True)
76 | test_loader = DataLoader(testset, batch_size=params['batch_size'], shuffle=False, collate_fn=dataset.collate,
77 | pin_memory=True)
78 |
79 | # At any point you can hit Ctrl + C to break out of training early.
80 | try:
81 | with tqdm(range(params['epochs']), unit='epoch') as t:
82 | for epoch in t:
83 | if epoch == -1:
84 | model.reset_params()
85 |
86 | t.set_description('Epoch %d' % epoch)
87 | start = time.time()
88 |
89 | epoch_train_loss, epoch_train_roc, optimizer = train_epoch(model, optimizer, device, train_loader, epoch)
90 | epoch_val_loss, epoch_val_roc = evaluate_network(model, device, val_loader, epoch)
91 |
92 | epoch_train_losses.append(epoch_train_loss)
93 | epoch_val_losses.append(epoch_val_loss)
94 | epoch_train_ROCs.append(epoch_train_roc.item())
95 | epoch_val_ROCs.append(epoch_val_roc.item())
96 |
97 | _, epoch_test_roc = evaluate_network(model, device, test_loader, epoch)
98 | epoch_test_ROCs.append(epoch_test_roc.item())
99 |
100 | t.set_postfix(time=time.time() - start, lr=optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr'],
101 | train_loss=epoch_train_loss, val_loss=epoch_val_loss,
102 | train_ROC=epoch_train_roc.item(), val_ROC=epoch_val_roc.item(),
103 | test_ROC=epoch_test_roc.item(), refresh=False)
104 |
105 | per_epoch_time.append(time.time() - start)
106 | scheduler.step(-epoch_val_roc.item())
107 |
108 | if optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr'] < params['min_lr']:
109 | print("\n!! LR EQUAL TO MIN LR SET.")
110 | break
111 |
112 | # Stop training after params['max_time'] hours
113 | if time.time() - t0 > params['max_time'] * 3600:
114 | print('-' * 89)
115 | print("Max_time for training elapsed {:.2f} hours, so stopping".format(params['max_time']))
116 | break
117 |
118 | print('')
119 |
120 | except KeyboardInterrupt:
121 | print('-' * 89)
122 | print('Exiting from training early because of KeyboardInterrupt')
123 |
124 | best_val_epoch = np.argmax(np.array(epoch_val_ROCs))
125 | best_train_epoch = np.argmax(np.array(epoch_train_ROCs))
126 | best_val_roc = epoch_val_ROCs[best_val_epoch]
127 | best_val_test_roc = epoch_test_ROCs[best_val_epoch]
128 | best_val_train_roc = epoch_train_ROCs[best_val_epoch]
129 | best_train_roc = epoch_train_ROCs[best_train_epoch]
130 |
131 | print("Best Train ROC: {:.4f}".format(best_train_roc))
132 | print("Best Val ROC: {:.4f}".format(best_val_roc))
133 | print("Test ROC of Best Val: {:.4f}".format(best_val_test_roc))
134 | print("Train ROC of Best Val: {:.4f}".format(best_val_train_roc))
135 | print("TOTAL TIME TAKEN: {:.4f}s".format(time.time() - t0))
136 | print("AVG TIME PER EPOCH: {:.4f}s".format(np.mean(per_epoch_time)))
137 |
138 |
139 | def main():
140 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
141 | parser.add_argument('--config', help="Please give a config.json file with training/model/data/param details")
142 | parser.add_argument('--gpu_id', help="Please give a value for gpu id")
143 | parser.add_argument('--dataset', help="Please give a value for dataset name")
144 | parser.add_argument('--seed', help="Please give a value for seed")
145 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, help="Please give a value for epochs")
146 | parser.add_argument('--batch_size', help="Please give a value for batch_size")
147 | parser.add_argument('--init_lr', help="Please give a value for init_lr")
148 | parser.add_argument('--lr_reduce_factor', help="Please give a value for lr_reduce_factor")
149 | parser.add_argument('--lr_schedule_patience', help="Please give a value for lr_schedule_patience")
150 | parser.add_argument('--min_lr', help="Please give a value for min_lr")
151 | parser.add_argument('--weight_decay', help="Please give a value for weight_decay")
152 | parser.add_argument('--print_epoch_interval', help="Please give a value for print_epoch_interval")
153 | parser.add_argument('--L', help="Please give a value for L")
154 | parser.add_argument('--hidden_dim', help="Please give a value for hidden_dim")
155 | parser.add_argument('--out_dim', help="Please give a value for out_dim")
156 | parser.add_argument('--residual', help="Please give a value for residual")
157 | parser.add_argument('--edge_feat', help="Please give a value for edge_feat")
158 | parser.add_argument('--readout', help="Please give a value for readout")
159 | parser.add_argument('--in_feat_dropout', help="Please give a value for in_feat_dropout")
160 | parser.add_argument('--dropout', help="Please give a value for dropout")
161 | parser.add_argument('--batch_norm', help="Please give a value for batch_norm")
162 | parser.add_argument('--max_time', help="Please give a value for max_time")
163 | parser.add_argument('--expid', help='Experiment id.')
164 | parser.add_argument('--aggregators', type=str, help='Aggregators to use.')
165 | parser.add_argument('--scalers', type=str, help='Scalers to use.')
166 | parser.add_argument('--posttrans_layers', type=int, help='posttrans_layers.')
167 |
168 | args = parser.parse_args()
169 | print(args.config)
170 |
171 | with open(args.config) as f:
172 | config = json.load(f)
173 |
174 | # device
175 | if args.gpu_id is not None:
176 | config['gpu']['id'] = int(args.gpu_id)
177 | config['gpu']['use'] = True
178 | device = gpu_setup(config['gpu']['use'], config['gpu']['id'])
179 |
180 | # dataset, out_dir
181 | if args.dataset is not None:
182 | DATASET_NAME = args.dataset
183 | else:
184 | DATASET_NAME = config['dataset']
185 | dataset = HIVDataset(DATASET_NAME)
186 |
187 | # parameters
188 | params = config['params']
189 | if args.seed is not None:
190 | params['seed'] = int(args.seed)
191 | if args.epochs is not None:
192 | params['epochs'] = int(args.epochs)
193 | if args.batch_size is not None:
194 | params['batch_size'] = int(args.batch_size)
195 | if args.init_lr is not None:
196 | params['init_lr'] = float(args.init_lr)
197 | if args.lr_reduce_factor is not None:
198 | params['lr_reduce_factor'] = float(args.lr_reduce_factor)
199 | if args.lr_schedule_patience is not None:
200 | params['lr_schedule_patience'] = int(args.lr_schedule_patience)
201 | if args.min_lr is not None:
202 | params['min_lr'] = float(args.min_lr)
203 | if args.weight_decay is not None:
204 | params['weight_decay'] = float(args.weight_decay)
205 | if args.print_epoch_interval is not None:
206 | params['print_epoch_interval'] = int(args.print_epoch_interval)
207 | if args.max_time is not None:
208 | params['max_time'] = float(args.max_time)
209 |
210 | # network parameters
211 | net_params = config['net_params']
212 | net_params['device'] = device
213 | net_params['gpu_id'] = config['gpu']['id']
214 | net_params['batch_size'] = params['batch_size']
215 | if args.L is not None:
216 | net_params['L'] = int(args.L)
217 | if args.hidden_dim is not None:
218 | net_params['hidden_dim'] = int(args.hidden_dim)
219 | if args.out_dim is not None:
220 | net_params['out_dim'] = int(args.out_dim)
221 | if args.residual is not None:
222 | net_params['residual'] = True if args.residual == 'True' else False
223 | if args.edge_feat is not None:
224 | net_params['edge_feat'] = True if args.edge_feat == 'True' else False
225 | if args.readout is not None:
226 | net_params['readout'] = args.readout
227 | if args.in_feat_dropout is not None:
228 | net_params['in_feat_dropout'] = float(args.in_feat_dropout)
229 | if args.dropout is not None:
230 | net_params['dropout'] = float(args.dropout)
231 | if args.batch_norm is not None:
232 | net_params['batch_norm'] = True if args.batch_norm == 'True' else False
233 | if args.aggregators is not None:
234 | net_params['aggregators'] = args.aggregators
235 | if args.scalers is not None:
236 | net_params['scalers'] = args.scalers
237 | if args.posttrans_layers is not None:
238 | net_params['posttrans_layers'] = args.posttrans_layers
239 |
240 | D = torch.cat([torch.sparse.sum(g.adjacency_matrix(transpose=True), dim=-1).to_dense() for g in
241 | dataset.train.graph_lists])
242 | net_params['avg_d'] = dict(lin=torch.mean(D),
243 | exp=torch.mean(torch.exp(torch.div(1, D)) - 1),
244 | log=torch.mean(torch.log(D + 1)))
245 |
246 | net_params['total_param'] = view_model_param(net_params)
247 | train_val_pipeline(dataset, params, net_params)
248 |
249 |
250 | main()
251 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/pytorch_geometric/pna.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from typing import Optional, List, Dict
2 | from torch_geometric.typing import Adj, OptTensor
3 |
4 | import torch
5 | from torch import Tensor
6 | from torch.nn import ModuleList, Sequential, Linear, ReLU
7 | from torch_geometric.nn.conv import MessagePassing
8 | from torch_geometric.nn.inits import reset
9 | from torch_geometric.utils import degree
10 |
11 | from models.pytorch_geometric.aggregators import AGGREGATORS
12 | from models.pytorch_geometric.scalers import SCALERS
13 |
14 | # Implemented with the help of Matthias Fey, author of PyTorch Geometric
15 | # For an example see https://github.com/rusty1s/pytorch_geometric/blob/master/examples/pna.py
16 |
17 | class PNAConv(MessagePassing):
18 | r"""The Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation graph convolution operator
19 | from the `"Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation for Graph Nets"
20 | `_ paper
21 | .. math::
22 | \bigoplus = \underbrace{\begin{bmatrix}I \\ S(D, \alpha=1) \\
23 | S(D, \alpha=-1) \end{bmatrix} }_{\text{scalers}}
24 | \otimes \underbrace{\begin{bmatrix} \mu \\ \sigma \\ \max \\ \min
25 | \end{bmatrix}}_{\text{aggregators}},
26 | in:
27 | .. math::
28 | X_i^{(t+1)} = U \left( X_i^{(t)}, \underset{(j,i) \in E}{\bigoplus}
29 | M \left( X_i^{(t)}, X_j^{(t)} \right) \right)
30 | where :math:`M` and :math:`U` denote the MLP referred to with pretrans
31 | and posttrans respectively.
32 | Args:
33 | in_channels (int): Size of each input sample.
34 | out_channels (int): Size of each output sample.
35 | aggregators (list of str): Set of aggregation function identifiers,
36 | namely :obj:`"sum"`, :obj:`"mean"`, :obj:`"min"`, :obj:`"max"`,
37 | :obj:`"var"` and :obj:`"std"`.
38 | scalers: (list of str): Set of scaling function identifiers, namely
39 | :obj:`"identity"`, :obj:`"amplification"`,
40 | :obj:`"attenuation"`, :obj:`"linear"` and
41 | :obj:`"inverse_linear"`.
42 | deg (Tensor): Histogram of in-degrees of nodes in the training set,
43 | used by scalers to normalize.
44 | edge_dim (int, optional): Edge feature dimensionality (in case
45 | there are any). (default :obj:`None`)
46 | towers (int, optional): Number of towers (default: :obj:`1`).
47 | pre_layers (int, optional): Number of transformation layers before
48 | aggregation (default: :obj:`1`).
49 | post_layers (int, optional): Number of transformation layers after
50 | aggregation (default: :obj:`1`).
51 | divide_input (bool, optional): Whether the input features should
52 | be split between towers or not (default: :obj:`False`).
53 | **kwargs (optional): Additional arguments of
54 | :class:`torch_geometric.nn.conv.MessagePassing`.
55 | """
56 | def __init__(self, in_channels: int, out_channels: int,
57 | aggregators: List[str], scalers: List[str], deg: Tensor,
58 | edge_dim: Optional[int] = None, towers: int = 1,
59 | pre_layers: int = 1, post_layers: int = 1,
60 | divide_input: bool = False, **kwargs):
61 |
62 | super(PNAConv, self).__init__(aggr=None, node_dim=0, **kwargs)
63 |
64 | if divide_input:
65 | assert in_channels % towers == 0
66 | assert out_channels % towers == 0
67 |
68 | self.in_channels = in_channels
69 | self.out_channels = out_channels
70 | self.aggregators = [AGGREGATORS[aggr] for aggr in aggregators]
71 | self.scalers = [SCALERS[scale] for scale in scalers]
72 | self.edge_dim = edge_dim
73 | self.towers = towers
74 | self.divide_input = divide_input
75 |
76 | self.F_in = in_channels // towers if divide_input else in_channels
77 | self.F_out = self.out_channels // towers
78 |
79 | deg = deg.to(torch.float)
80 | total_no_vertices = deg.sum()
81 | bin_degrees = torch.arange(len(deg))
82 | self.avg_deg: Dict[str, float] = {
83 | 'lin': ((bin_degrees * deg).sum() / total_no_vertices).item(),
84 | 'log': (((bin_degrees + 1).log() * deg).sum() / total_no_vertices).item(),
85 | 'exp': ((bin_degrees.exp() * deg).sum() / total_no_vertices).item(),
86 | }
87 |
88 | if self.edge_dim is not None:
89 | self.edge_encoder = Linear(edge_dim, self.F_in)
90 |
91 | self.pre_nns = ModuleList()
92 | self.post_nns = ModuleList()
93 | for _ in range(towers):
94 | modules = [Linear((3 if edge_dim else 2) * self.F_in, self.F_in)]
95 | for _ in range(pre_layers - 1):
96 | modules += [ReLU()]
97 | modules += [Linear(self.F_in, self.F_in)]
98 | self.pre_nns.append(Sequential(*modules))
99 |
100 | in_channels = (len(aggregators) * len(scalers) + 1) * self.F_in
101 | modules = [Linear(in_channels, self.F_out)]
102 | for _ in range(post_layers - 1):
103 | modules += [ReLU()]
104 | modules += [Linear(self.F_out, self.F_out)]
105 | self.post_nns.append(Sequential(*modules))
106 |
107 | self.lin = Linear(out_channels, out_channels)
108 |
109 | self.reset_parameters()
110 |
111 | def reset_parameters(self):
112 | if self.edge_dim is not None:
113 | self.edge_encoder.reset_parameters()
114 | for nn in self.pre_nns:
115 | reset(nn)
116 | for nn in self.post_nns:
117 | reset(nn)
118 | self.lin.reset_parameters()
119 |
120 | def forward(self, x: Tensor, edge_index: Adj,
121 | edge_attr: OptTensor = None) -> Tensor:
122 |
123 | if self.divide_input:
124 | x = x.view(-1, self.towers, self.F_in)
125 | else:
126 | x = x.view(-1, 1, self.F_in).repeat(1, self.towers, 1)
127 |
128 | # propagate_type: (x: Tensor, edge_attr: OptTensor)
129 | out = self.propagate(edge_index, x=x, edge_attr=edge_attr, size=None)
130 |
131 | out = torch.cat([x, out], dim=-1)
132 | outs = [nn(out[:, i]) for i, nn in enumerate(self.post_nns)]
133 | out = torch.cat(outs, dim=1)
134 |
135 | return self.lin(out)
136 |
137 | def message(self, x_i: Tensor, x_j: Tensor,
138 | edge_attr: OptTensor) -> Tensor:
139 |
140 | h: Tensor = x_i # Dummy.
141 | if edge_attr is not None:
142 | edge_attr = self.edge_encoder(edge_attr)
143 | edge_attr = edge_attr.view(-1, 1, self.F_in)
144 | edge_attr = edge_attr.repeat(1, self.towers, 1)
145 | h = torch.cat([x_i, x_j, edge_attr], dim=-1)
146 | else:
147 | h = torch.cat([x_i, x_j], dim=-1)
148 |
149 | hs = [nn(h[:, i]) for i, nn in enumerate(self.pre_nns)]
150 | return torch.stack(hs, dim=1)
151 |
152 | def aggregate(self, inputs: Tensor, index: Tensor,
153 | dim_size: Optional[int] = None) -> Tensor:
154 | outs = [aggr(inputs, index, dim_size) for aggr in self.aggregators]
155 | out = torch.cat(outs, dim=-1)
156 |
157 | deg = degree(index, dim_size, dtype=inputs.dtype).view(-1, 1, 1)
158 | outs = [scaler(out, deg, self.avg_deg) for scaler in self.scalers]
159 | return torch.cat(outs, dim=-1)
160 |
161 | def __repr__(self):
162 | return (f'{self.__class__.__name__}({self.in_channels}, '
163 | f'{self.out_channels}, towers={self.towers}, dim={self.dim})')
164 | raise NotImplementedError
165 |
166 |
167 | class PNAConvSimple(MessagePassing):
168 | r"""The Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation graph convolution operator
169 | from the `"Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation for Graph Nets"
170 | `_ paper
171 | .. math::
172 | \bigoplus = \underbrace{\begin{bmatrix}I \\ S(D, \alpha=1) \\
173 | S(D, \alpha=-1) \end{bmatrix} }_{\text{scalers}}
174 | \otimes \underbrace{\begin{bmatrix} \mu \\ \sigma \\ \max \\ \min
175 | \end{bmatrix}}_{\text{aggregators}},
176 | in:
177 | .. math::
178 | X_i^{(t+1)} = U \left( \underset{(j,i) \in E}{\bigoplus}
179 | M \left(X_j^{(t)} \right) \right)
180 | where :math:`U` denote the MLP referred to with posttrans.
181 | Args:
182 | in_channels (int): Size of each input sample.
183 | out_channels (int): Size of each output sample.
184 | aggregators (list of str): Set of aggregation function identifiers,
185 | namely :obj:`"sum"`, :obj:`"mean"`, :obj:`"min"`, :obj:`"max"`,
186 | :obj:`"var"` and :obj:`"std"`.
187 | scalers: (list of str): Set of scaling function identifiers, namely
188 | :obj:`"identity"`, :obj:`"amplification"`,
189 | :obj:`"attenuation"`, :obj:`"linear"` and
190 | :obj:`"inverse_linear"`.
191 | deg (Tensor): Histogram of in-degrees of nodes in the training set,
192 | used by scalers to normalize.
193 | post_layers (int, optional): Number of transformation layers after
194 | aggregation (default: :obj:`1`).
195 | **kwargs (optional): Additional arguments of
196 | :class:`torch_geometric.nn.conv.MessagePassing`.
197 | """
198 | def __init__(self, in_channels: int, out_channels: int,
199 | aggregators: List[str], scalers: List[str], deg: Tensor,
200 | post_layers: int = 1, **kwargs):
201 |
202 | super(PNAConvSimple, self).__init__(aggr=None, node_dim=0, **kwargs)
203 |
204 | self.in_channels = in_channels
205 | self.out_channels = out_channels
206 | self.aggregators = [AGGREGATORS[aggr] for aggr in aggregators]
207 | self.scalers = [SCALERS[scale] for scale in scalers]
208 |
209 | self.F_in = in_channels
210 | self.F_out = self.out_channels
211 |
212 | deg = deg.to(torch.float)
213 | total_no_vertices = deg.sum()
214 | bin_degrees = torch.arange(len(deg))
215 | self.avg_deg: Dict[str, float] = {
216 | 'lin': ((bin_degrees * deg).sum() / total_no_vertices).item(),
217 | 'log': (((bin_degrees + 1).log() * deg).sum() / total_no_vertices).item(),
218 | 'exp': ((bin_degrees.exp() * deg).sum() / total_no_vertices).item(),
219 | }
220 |
221 | in_channels = (len(aggregators) * len(scalers)) * self.F_in
222 | modules = [Linear(in_channels, self.F_out)]
223 | for _ in range(post_layers - 1):
224 | modules += [ReLU()]
225 | modules += [Linear(self.F_out, self.F_out)]
226 | self.post_nn = Sequential(*modules)
227 |
228 | self.reset_parameters()
229 |
230 | def reset_parameters(self):
231 | reset(self.post_nn)
232 |
233 | def forward(self, x: Tensor, edge_index: Adj, edge_attr: OptTensor = None) -> Tensor:
234 |
235 | # propagate_type: (x: Tensor)
236 | out = self.propagate(edge_index, x=x, size=None)
237 | return self.post_nn(out)
238 |
239 | def message(self, x_j: Tensor) -> Tensor:
240 | return x_j
241 |
242 | def aggregate(self, inputs: Tensor, index: Tensor,
243 | dim_size: Optional[int] = None) -> Tensor:
244 | outs = [aggr(inputs, index, dim_size) for aggr in self.aggregators]
245 | out = torch.cat(outs, dim=-1)
246 |
247 | deg = degree(index, dim_size, dtype=inputs.dtype).view(-1, 1)
248 | outs = [scaler(out, deg, self.avg_deg) for scaler in self.scalers]
249 | return torch.cat(outs, dim=-1)
250 |
251 | def __repr__(self):
252 | return (f'{self.__class__.__name__}({self.in_channels}, '
253 | f'{self.out_channels}')
254 | raise NotImplementedError
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/layers.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | import torch.nn.functional as F
4 |
5 | SUPPORTED_ACTIVATION_MAP = {'ReLU', 'Sigmoid', 'Tanh', 'ELU', 'SELU', 'GLU', 'LeakyReLU', 'Softplus', 'None'}
6 |
7 |
8 | def get_activation(activation):
9 | """ returns the activation function represented by the input string """
10 | if activation and callable(activation):
11 | # activation is already a function
12 | return activation
13 | # search in SUPPORTED_ACTIVATION_MAP a torch.nn.modules.activation
14 | activation = [x for x in SUPPORTED_ACTIVATION_MAP if activation.lower() == x.lower()]
15 | assert len(activation) == 1 and isinstance(activation[0], str), 'Unhandled activation function'
16 | activation = activation[0]
17 | if activation.lower() == 'none':
18 | return None
19 | return vars(torch.nn.modules.activation)[activation]()
20 |
21 |
22 | class Set2Set(torch.nn.Module):
23 | r"""
24 | Set2Set global pooling operator from the `"Order Matters: Sequence to sequence for sets"
25 | `_ paper. This pooling layer performs the following operation
26 |
27 | .. math::
28 | \mathbf{q}_t &= \mathrm{LSTM}(\mathbf{q}^{*}_{t-1})
29 |
30 | \alpha_{i,t} &= \mathrm{softmax}(\mathbf{x}_i \cdot \mathbf{q}_t)
31 |
32 | \mathbf{r}_t &= \sum_{i=1}^N \alpha_{i,t} \mathbf{x}_i
33 |
34 | \mathbf{q}^{*}_t &= \mathbf{q}_t \, \Vert \, \mathbf{r}_t,
35 |
36 | where :math:`\mathbf{q}^{*}_T` defines the output of the layer with twice
37 | the dimensionality as the input.
38 |
39 | Arguments
40 | ---------
41 | input_dim: int
42 | Size of each input sample.
43 | hidden_dim: int, optional
44 | the dim of set representation which corresponds to the input dim of the LSTM in Set2Set.
45 | This is typically the sum of the input dim and the lstm output dim. If not provided, it will be set to :obj:`input_dim*2`
46 | steps: int, optional
47 | Number of iterations :math:`T`. If not provided, the number of nodes will be used.
48 | num_layers : int, optional
49 | Number of recurrent layers (e.g., :obj:`num_layers=2` would mean stacking two LSTMs together)
50 | (Default, value = 1)
51 | """
52 |
53 | def __init__(self, nin, nhid=None, steps=None, num_layers=1, activation=None, device='cpu'):
54 | super(Set2Set, self).__init__()
55 | self.steps = steps
56 | self.nin = nin
57 | self.nhid = nin * 2 if nhid is None else nhid
58 | if self.nhid <= self.nin:
59 | raise ValueError('Set2Set hidden_dim should be larger than input_dim')
60 | # the hidden is a concatenation of weighted sum of embedding and LSTM output
61 | self.lstm_output_dim = self.nhid - self.nin
62 | self.num_layers = num_layers
63 | self.lstm = nn.LSTM(self.nhid, self.nin, num_layers=num_layers, batch_first=True).to(device)
64 | self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
65 |
66 | def forward(self, x):
67 | r"""
68 | Applies the pooling on input tensor x
69 |
70 | Arguments
71 | ----------
72 | x: torch.FloatTensor
73 | Input tensor of size (B, N, D)
74 |
75 | Returns
76 | -------
77 | x: `torch.FloatTensor`
78 | Tensor resulting from the set2set pooling operation.
79 | """
80 |
81 | batch_size = x.shape[0]
82 | n = self.steps or x.shape[1]
83 |
84 | h = (x.new_zeros((self.num_layers, batch_size, self.nin)),
85 | x.new_zeros((self.num_layers, batch_size, self.nin)))
86 |
87 | q_star = x.new_zeros(batch_size, 1, self.nhid)
88 |
89 | for i in range(n):
90 | # q: batch_size x 1 x input_dim
91 | q, h = self.lstm(q_star, h)
92 | # e: batch_size x n x 1
93 | e = torch.matmul(x, torch.transpose(q, 1, 2))
94 | a = self.softmax(e)
95 | r = torch.sum(a * x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
96 | q_star = torch.cat([q, r], dim=-1)
97 |
98 | return torch.squeeze(q_star, dim=1)
99 |
100 |
101 | class FCLayer(nn.Module):
102 | r"""
103 | A simple fully connected and customizable layer. This layer is centered around a torch.nn.Linear module.
104 | The order in which transformations are applied is:
105 |
106 | #. Dense Layer
107 | #. Activation
108 | #. Dropout (if applicable)
109 | #. Batch Normalization (if applicable)
110 |
111 | Arguments
112 | ----------
113 | in_size: int
114 | Input dimension of the layer (the torch.nn.Linear)
115 | out_size: int
116 | Output dimension of the layer.
117 | dropout: float, optional
118 | The ratio of units to dropout. No dropout by default.
119 | (Default value = 0.)
120 | activation: str or callable, optional
121 | Activation function to use.
122 | (Default value = relu)
123 | b_norm: bool, optional
124 | Whether to use batch normalization
125 | (Default value = False)
126 | bias: bool, optional
127 | Whether to enable bias in for the linear layer.
128 | (Default value = True)
129 | init_fn: callable, optional
130 | Initialization function to use for the weight of the layer. Default is
131 | :math:`\mathcal{U}(-\sqrt{k}, \sqrt{k})` with :math:`k=\frac{1}{ \text{in_size}}`
132 | (Default value = None)
133 |
134 | Attributes
135 | ----------
136 | dropout: int
137 | The ratio of units to dropout.
138 | b_norm: int
139 | Whether to use batch normalization
140 | linear: torch.nn.Linear
141 | The linear layer
142 | activation: the torch.nn.Module
143 | The activation layer
144 | init_fn: function
145 | Initialization function used for the weight of the layer
146 | in_size: int
147 | Input dimension of the linear layer
148 | out_size: int
149 | Output dimension of the linear layer
150 | """
151 |
152 | def __init__(self, in_size, out_size, activation='relu', dropout=0., b_norm=False, bias=True, init_fn=None,
153 | device='cpu'):
154 | super(FCLayer, self).__init__()
155 |
156 | self.__params = locals()
157 | del self.__params['__class__']
158 | del self.__params['self']
159 | self.in_size = in_size
160 | self.out_size = out_size
161 | self.bias = bias
162 | self.linear = nn.Linear(in_size, out_size, bias=bias).to(device)
163 | self.dropout = None
164 | self.b_norm = None
165 | if dropout:
166 | self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=dropout)
167 | if b_norm:
168 | self.b_norm = nn.BatchNorm1d(out_size).to(device)
169 | self.activation = get_activation(activation)
170 | self.init_fn = nn.init.xavier_uniform_
171 |
172 | self.reset_parameters()
173 |
174 | def reset_parameters(self, init_fn=None):
175 | init_fn = init_fn or self.init_fn
176 | if init_fn is not None:
177 | init_fn(self.linear.weight, 1 / self.in_size)
178 | if self.bias:
179 | self.linear.bias.data.zero_()
180 |
181 | def forward(self, x):
182 | h = self.linear(x)
183 | if self.activation is not None:
184 | h = self.activation(h)
185 | if self.dropout is not None:
186 | h = self.dropout(h)
187 | if self.b_norm is not None:
188 | if h.shape[1] != self.out_size:
189 | h = self.b_norm(h.transpose(1, 2)).transpose(1, 2)
190 | else:
191 | h = self.b_norm(h)
192 | return h
193 |
194 | def __repr__(self):
195 | return self.__class__.__name__ + ' (' \
196 | + str(self.in_size) + ' -> ' \
197 | + str(self.out_size) + ')'
198 |
199 |
200 | class MLP(nn.Module):
201 | """
202 | Simple multi-layer perceptron, built of a series of FCLayers
203 | """
204 |
205 | def __init__(self, in_size, hidden_size, out_size, layers, mid_activation='relu', last_activation='none',
206 | dropout=0., mid_b_norm=False, last_b_norm=False, device='cpu'):
207 | super(MLP, self).__init__()
208 |
209 | self.in_size = in_size
210 | self.hidden_size = hidden_size
211 | self.out_size = out_size
212 |
213 | self.fully_connected = nn.ModuleList()
214 | if layers <= 1:
215 | self.fully_connected.append(FCLayer(in_size, out_size, activation=last_activation, b_norm=last_b_norm,
216 | device=device, dropout=dropout))
217 | else:
218 | self.fully_connected.append(FCLayer(in_size, hidden_size, activation=mid_activation, b_norm=mid_b_norm,
219 | device=device, dropout=dropout))
220 | for _ in range(layers - 2):
221 | self.fully_connected.append(FCLayer(hidden_size, hidden_size, activation=mid_activation,
222 | b_norm=mid_b_norm, device=device, dropout=dropout))
223 | self.fully_connected.append(FCLayer(hidden_size, out_size, activation=last_activation, b_norm=last_b_norm,
224 | device=device, dropout=dropout))
225 |
226 | def forward(self, x):
227 | for fc in self.fully_connected:
228 | x = fc(x)
229 | return x
230 |
231 | def __repr__(self):
232 | return self.__class__.__name__ + ' (' \
233 | + str(self.in_size) + ' -> ' \
234 | + str(self.out_size) + ')'
235 |
236 |
237 | class GRU(nn.Module):
238 | """
239 | Wrapper class for the GRU used by the GNN framework, nn.GRU is used for the Gated Recurrent Unit itself
240 | """
241 |
242 | def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, device):
243 | super(GRU, self).__init__()
244 | self.input_size = input_size
245 | self.hidden_size = hidden_size
246 | self.gru = nn.GRU(input_size=input_size, hidden_size=hidden_size).to(device)
247 |
248 | def forward(self, x, y):
249 | """
250 | :param x: shape: (B, N, Din) where Din <= input_size (difference is padded)
251 | :param y: shape: (B, N, Dh) where Dh <= hidden_size (difference is padded)
252 | :return: shape: (B, N, Dh)
253 | """
254 | assert (x.shape[-1] <= self.input_size and y.shape[-1] <= self.hidden_size)
255 |
256 | (B, N, _) = x.shape
257 | x = x.reshape(1, B * N, -1).contiguous()
258 | y = y.reshape(1, B * N, -1).contiguous()
259 |
260 | # padding if necessary
261 | if x.shape[-1] < self.input_size:
262 | x = F.pad(input=x, pad=[0, self.input_size - x.shape[-1]], mode='constant', value=0)
263 | if y.shape[-1] < self.hidden_size:
264 | y = F.pad(input=y, pad=[0, self.hidden_size - y.shape[-1]], mode='constant', value=0)
265 |
266 | x = self.gru(x, y)[1]
267 | x = x.reshape(B, N, -1)
268 | return x
269 |
270 |
271 | class S2SReadout(nn.Module):
272 | """
273 | Performs a Set2Set aggregation of all the graph nodes' features followed by a series of fully connected layers
274 | """
275 |
276 | def __init__(self, in_size, hidden_size, out_size, fc_layers=3, device='cpu', final_activation='relu'):
277 | super(S2SReadout, self).__init__()
278 |
279 | # set2set aggregation
280 | self.set2set = Set2Set(in_size, device=device)
281 |
282 | # fully connected layers
283 | self.mlp = MLP(in_size=2 * in_size, hidden_size=hidden_size, out_size=out_size, layers=fc_layers,
284 | mid_activation="relu", last_activation=final_activation, mid_b_norm=True, last_b_norm=False,
285 | device=device)
286 |
287 | def forward(self, x):
288 | x = self.set2set(x)
289 | return self.mlp(x)
290 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/data/superpixels.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # MIT License
2 | # Copyright (c) 2020 Vijay Prakash Dwivedi, Chaitanya K. Joshi, Thomas Laurent, Yoshua Bengio, Xavier Bresson
3 |
4 |
5 | import os
6 | import pickle
7 | from scipy.spatial.distance import cdist
8 | import numpy as np
9 | import itertools
10 |
11 | import dgl
12 | import torch
13 | import torch.utils.data
14 |
15 | import time
16 |
17 | import csv
18 | from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedShuffleSplit
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 | def sigma(dists, kth=8):
24 | # Compute sigma and reshape
25 | try:
26 | # Get k-nearest neighbors for each node
27 | knns = np.partition(dists, kth, axis=-1)[:, kth::-1]
28 | sigma = knns.sum(axis=1).reshape((knns.shape[0], 1))/kth
29 | except ValueError: # handling for graphs with num_nodes less than kth
30 | num_nodes = dists.shape[0]
31 | # this sigma value is irrelevant since not used for final compute_edge_list
32 | sigma = np.array([1]*num_nodes).reshape(num_nodes,1)
33 |
34 | return sigma + 1e-8 # adding epsilon to avoid zero value of sigma
35 |
36 |
37 | def compute_adjacency_matrix_images(coord, feat, use_feat=True, kth=8):
38 | coord = coord.reshape(-1, 2)
39 | # Compute coordinate distance
40 | c_dist = cdist(coord, coord)
41 |
42 | if use_feat:
43 | # Compute feature distance
44 | f_dist = cdist(feat, feat)
45 | # Compute adjacency
46 | A = np.exp(- (c_dist/sigma(c_dist))**2 - (f_dist/sigma(f_dist))**2 )
47 | else:
48 | A = np.exp(- (c_dist/sigma(c_dist))**2)
49 |
50 | # Convert to symmetric matrix
51 | A = 0.5 * (A + A.T)
52 | A[np.diag_indices_from(A)] = 0
53 | return A
54 |
55 |
56 | def compute_edges_list(A, kth=8+1):
57 | # Get k-similar neighbor indices for each node
58 |
59 | num_nodes = A.shape[0]
60 | new_kth = num_nodes - kth
61 |
62 | if num_nodes > 9:
63 | knns = np.argpartition(A, new_kth-1, axis=-1)[:, new_kth:-1]
64 | knn_values = np.partition(A, new_kth-1, axis=-1)[:, new_kth:-1] # NEW
65 | else:
66 | # handling for graphs with less than kth nodes
67 | # in such cases, the resulting graph will be fully connected
68 | knns = np.tile(np.arange(num_nodes), num_nodes).reshape(num_nodes, num_nodes)
69 | knn_values = A # NEW
70 |
71 | # removing self loop
72 | if num_nodes != 1:
73 | knn_values = A[knns != np.arange(num_nodes)[:,None]].reshape(num_nodes,-1) # NEW
74 | knns = knns[knns != np.arange(num_nodes)[:,None]].reshape(num_nodes,-1)
75 | return knns, knn_values # NEW
76 |
77 |
78 | class SuperPixDGL(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
79 | def __init__(self,
80 | data_dir,
81 | dataset,
82 | split,
83 | use_mean_px=True,
84 | use_coord=True):
85 |
86 | self.split = split
87 |
88 | self.graph_lists = []
89 |
90 | if dataset == 'MNIST':
91 | self.img_size = 28
92 | with open(os.path.join(data_dir, 'mnist_75sp_%s.pkl' % split), 'rb') as f:
93 | self.labels, self.sp_data = pickle.load(f)
94 | self.graph_labels = torch.LongTensor(self.labels)
95 | elif dataset == 'CIFAR10':
96 | self.img_size = 32
97 | with open(os.path.join(data_dir, 'cifar10_150sp_%s.pkl' % split), 'rb') as f:
98 | self.labels, self.sp_data = pickle.load(f)
99 | self.graph_labels = torch.LongTensor(self.labels)
100 |
101 | self.use_mean_px = use_mean_px
102 | self.use_coord = use_coord
103 | self.n_samples = len(self.labels)
104 |
105 | self._prepare()
106 |
107 | def _prepare(self):
108 | print("preparing %d graphs for the %s set..." % (self.n_samples, self.split.upper()))
109 | self.Adj_matrices, self.node_features, self.edges_lists, self.edge_features = [], [], [], []
110 | for index, sample in enumerate(self.sp_data):
111 | mean_px, coord = sample[:2]
112 |
113 | try:
114 | coord = coord / self.img_size
115 | except AttributeError:
116 | VOC_has_variable_image_sizes = True
117 |
118 | if self.use_mean_px:
119 | A = compute_adjacency_matrix_images(coord, mean_px) # using super-pixel locations + features
120 | else:
121 | A = compute_adjacency_matrix_images(coord, mean_px, False) # using only super-pixel locations
122 | edges_list, edge_values_list = compute_edges_list(A) # NEW
123 |
124 | N_nodes = A.shape[0]
125 |
126 | mean_px = mean_px.reshape(N_nodes, -1)
127 | coord = coord.reshape(N_nodes, 2)
128 | x = np.concatenate((mean_px, coord), axis=1)
129 |
130 | edge_values_list = edge_values_list.reshape(-1) # NEW # TO DOUBLE-CHECK !
131 |
132 | self.node_features.append(x)
133 | self.edge_features.append(edge_values_list) # NEW
134 | self.Adj_matrices.append(A)
135 | self.edges_lists.append(edges_list)
136 |
137 | for index in range(len(self.sp_data)):
138 | g = dgl.DGLGraph()
139 | g.add_nodes(self.node_features[index].shape[0])
140 | g.ndata['feat'] = torch.Tensor(self.node_features[index]).half()
141 |
142 | for src, dsts in enumerate(self.edges_lists[index]):
143 | # handling for 1 node where the self loop would be the only edge
144 | # since, VOC Superpixels has few samples (5 samples) with only 1 node
145 | if self.node_features[index].shape[0] == 1:
146 | g.add_edges(src, dsts)
147 | else:
148 | g.add_edges(src, dsts[dsts!=src])
149 |
150 | # adding edge features for Residual Gated ConvNet
151 | edge_feat_dim = g.ndata['feat'].shape[1] # dim same as node feature dim
152 | #g.edata['feat'] = torch.ones(g.number_of_edges(), edge_feat_dim).half()
153 | g.edata['feat'] = torch.Tensor(self.edge_features[index]).unsqueeze(1).half() # NEW
154 |
155 | self.graph_lists.append(g)
156 |
157 | def __len__(self):
158 | """Return the number of graphs in the dataset."""
159 | return self.n_samples
160 |
161 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
162 | """
163 | Get the idx^th sample.
164 | Parameters
165 | ---------
166 | idx : int
167 | The sample index.
168 | Returns
169 | -------
170 | (dgl.DGLGraph, int)
171 | DGLGraph with node feature stored in `feat` field
172 | And its label.
173 | """
174 | return self.graph_lists[idx], self.graph_labels[idx]
175 |
176 |
177 | class DGLFormDataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
178 | """
179 | DGLFormDataset wrapping graph list and label list as per pytorch Dataset.
180 | *lists (list): lists of 'graphs' and 'labels' with same len().
181 | """
182 | def __init__(self, *lists):
183 | assert all(len(lists[0]) == len(li) for li in lists)
184 | self.lists = lists
185 | self.graph_lists = lists[0]
186 | self.graph_labels = lists[1]
187 |
188 | def __getitem__(self, index):
189 | return tuple(li[index] for li in self.lists)
190 |
191 | def __len__(self):
192 | return len(self.lists[0])
193 |
194 |
195 | class SuperPixDatasetDGL(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
196 | def __init__(self, name, num_val=5000):
197 | """
198 | Takes input standard image dataset name (MNIST/CIFAR10)
199 | and returns the superpixels graph.
200 |
201 | This class uses results from the above SuperPix class.
202 | which contains the steps for the generation of the Superpixels
203 | graph from a superpixel .pkl file that has been given by
204 | https://github.com/bknyaz/graph_attention_pool
205 |
206 | Please refer the SuperPix class for details.
207 | """
208 | t_data = time.time()
209 | self.name = name
210 |
211 | use_mean_px = True # using super-pixel locations + features
212 | use_mean_px = False # using only super-pixel locations
213 | if use_mean_px:
214 | print('Adj matrix defined from super-pixel locations + features')
215 | else:
216 | print('Adj matrix defined from super-pixel locations (only)')
217 | use_coord = True
218 | self.test = SuperPixDGL("./data/superpixels", dataset=self.name, split='test',
219 | use_mean_px=use_mean_px,
220 | use_coord=use_coord)
221 |
222 | self.train_ = SuperPixDGL("./data/superpixels", dataset=self.name, split='train',
223 | use_mean_px=use_mean_px,
224 | use_coord=use_coord)
225 |
226 | _val_graphs, _val_labels = self.train_[:num_val]
227 | _train_graphs, _train_labels = self.train_[num_val:]
228 |
229 | self.val = DGLFormDataset(_val_graphs, _val_labels)
230 | self.train = DGLFormDataset(_train_graphs, _train_labels)
231 |
232 | print("[I] Data load time: {:.4f}s".format(time.time()-t_data))
233 |
234 |
235 |
236 | def self_loop(g):
237 | """
238 | Utility function only, to be used only when necessary as per user self_loop flag
239 | : Overwriting the function dgl.transform.add_self_loop() to not miss ndata['feat'] and edata['feat']
240 |
241 |
242 | This function is called inside a function in SuperPixDataset class.
243 | """
244 | new_g = dgl.DGLGraph()
245 | new_g.add_nodes(g.number_of_nodes())
246 | new_g.ndata['feat'] = g.ndata['feat']
247 |
248 | src, dst = g.all_edges(order="eid")
249 | src = dgl.backend.zerocopy_to_numpy(src)
250 | dst = dgl.backend.zerocopy_to_numpy(dst)
251 | non_self_edges_idx = src != dst
252 | nodes = np.arange(g.number_of_nodes())
253 | new_g.add_edges(src[non_self_edges_idx], dst[non_self_edges_idx])
254 | new_g.add_edges(nodes, nodes)
255 |
256 | # This new edata is not used since this function gets called only for GCN, GAT
257 | # However, we need this for the generic requirement of ndata and edata
258 | new_g.edata['feat'] = torch.zeros(new_g.number_of_edges())
259 | return new_g
260 |
261 |
262 |
263 | class SuperPixDataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
264 |
265 | def __init__(self, name):
266 | """
267 | Loading Superpixels datasets
268 | """
269 | start = time.time()
270 | print("[I] Loading dataset %s..." % (name))
271 | self.name = name
272 | data_dir = 'data/'
273 | with open(data_dir+name+'.pkl',"rb") as f:
274 | f = pickle.load(f)
275 | self.train = f[0]
276 | self.val = f[1]
277 | self.test = f[2]
278 | print('train, test, val sizes :',len(self.train),len(self.test),len(self.val))
279 | print("[I] Finished loading.")
280 | print("[I] Data load time: {:.4f}s".format(time.time()-start))
281 |
282 |
283 | # form a mini batch from a given list of samples = [(graph, label) pairs]
284 | def collate(self, samples):
285 | # The input samples is a list of pairs (graph, label).
286 | graphs, labels = map(list, zip(*samples))
287 | labels = torch.tensor(np.array(labels))
288 | tab_sizes_n = [ graphs[i].number_of_nodes() for i in range(len(graphs))]
289 | tab_snorm_n = [ torch.FloatTensor(size,1).fill_(1./float(size)) for size in tab_sizes_n ]
290 | snorm_n = torch.cat(tab_snorm_n).sqrt()
291 | tab_sizes_e = [ graphs[i].number_of_edges() for i in range(len(graphs))]
292 | tab_snorm_e = [ torch.FloatTensor(size,1).fill_(1./float(size)) for size in tab_sizes_e ]
293 | snorm_e = torch.cat(tab_snorm_e).sqrt()
294 | for idx, graph in enumerate(graphs):
295 | graphs[idx].ndata['feat'] = graph.ndata['feat'].float()
296 | graphs[idx].edata['feat'] = graph.edata['feat'].float()
297 | batched_graph = dgl.batch(graphs)
298 | return batched_graph, labels, snorm_n, snorm_e
299 |
300 | def _add_self_loops(self):
301 |
302 | # function for adding self loops
303 | # this function will be called only if self_loop flag is True
304 |
305 | self.train.graph_lists = [self_loop(g) for g in self.train.graph_lists]
306 | self.val.graph_lists = [self_loop(g) for g in self.val.graph_lists]
307 | self.test.graph_lists = [self_loop(g) for g in self.test.graph_lists]
308 |
309 | self.train = DGLFormDataset(self.train.graph_lists, self.train.graph_labels)
310 | self.val = DGLFormDataset(self.val.graph_lists, self.val.graph_labels)
311 | self.test = DGLFormDataset(self.test.graph_lists, self.test.graph_labels)
312 |
313 |
314 |
315 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Real-world benchmarks
2 |
3 | 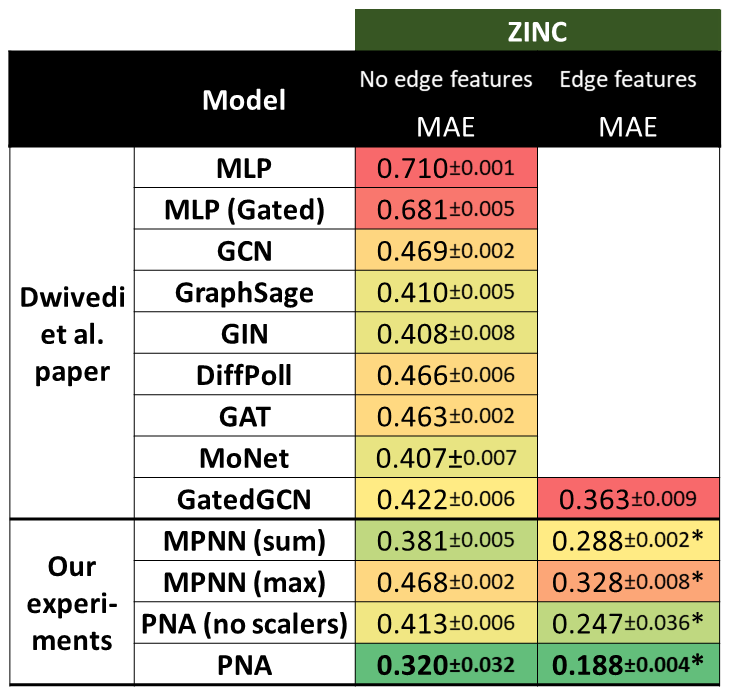 4 |
5 | ## Overview
6 |
7 | We provide the scripts for the download and execution of the real-world benchmarks we used.
8 | Many scripts in this directory were taken directly from or inspired by "Benchmarking GNNs"
9 | by Dwivedi _et al._ refer to their [code](https://github.com/graphdeeplearning/benchmarking-gnns)
10 | and [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.00982) for more details on their work. The graph classification
11 | benchmark MolHIV comes from the [Open Graph Benchmark](https://ogb.stanford.edu/).
12 |
13 | - `configs` contains .json configuration files for the various datasets;
14 | - `data` contains scripts to download the datasets;
15 | - `nets` contains the architectures that were used with the PNA in the benchmarks;
16 | - `train` contains the training scripts.
17 |
18 | These benchmarks use the DGL version of PNA (`../models/dgl`) with the MolHIV model using the *simple* layer architecture.
19 | Below you can find the instructions on how to download the datasets and run the models.
20 | You can run these scripts directly in this [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1RnV4MBjCl98eubAGpEF-eXdAW5mTP3h3?usp=sharing).
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 | ## Test run
25 |
26 | ### Benchmark Setup
27 |
28 | [Follow these instructions](./docs/setup.md) to install the benchmark and setup the environment.
29 |
30 | ### Run model training
31 | ```
32 | # at the root of the repo
33 | cd realworld_benchmark
34 | python { main_molecules.py | main_superpixels.py } [--param=value ...] --dataset { ZINC | MNIST | CIFAR10 } --gpu_id gpu_id --config config_file
35 | ```
36 |
37 |
38 | ## Tuned hyperparameters
39 |
40 | You can find below the hyperparameters we used for our experiments. In general, the depth of the architectures was not changed while the width was adjusted to keep the total number of parameters of the model between 100k and 110k as done in "Benchmarking GNNs" to ensure a fair comparison of the architectures. Refer to our [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718) for an interpretation of the results.
41 |
42 | ```
43 | For OGB leaderboard (hyperparameters taken from the DGN model - 300k parameters):
44 |
45 | python -m main_HIV --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=80 --out_dim=80 --residual=True --readout=mean --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --dataset HIV --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_classification_PNA_HIV.json" --epochs=200 --init_lr=0.01 --lr_reduce_factor=0.5 --lr_schedule_patience=20 --min_lr=0.0001
46 |
47 |
48 | For the leaderboard (2nd version of the datasets - 400/500k parameters)
49 |
50 | # ZINC
51 | PNA:
52 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=16 --hidden_dim=70 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=40 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --pretrans_layers=1 --posttrans_layers=1 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
53 | MPNN (sum/max):
54 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=16 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=110 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=40 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --pretrans_layers=1 --posttrans_layers=1 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
55 |
56 |
57 | For the paper (1st version of the datasets - 100k parameters)
58 | --- PNA ---
59 |
60 | # ZINC
61 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=False --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
62 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=70 --out_dim=60 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --pretrans_layers=1 --posttrans_layers=1 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
63 |
64 | # CIFAR10
65 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.1 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
66 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
67 |
68 | # MNIST
69 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.1 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
70 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
71 |
72 |
73 | --- PNA (no scalers) ---
74 |
75 | # ZINC
76 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
77 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=90 --out_dim=80 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --pretrans_layers=1 --posttrans_layers=1 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
78 |
79 | # CIFAR10
80 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.1 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
81 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
82 |
83 | # MNIST
84 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.1 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
85 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
86 |
87 |
88 | --- MPNN (sum/max) ---
89 |
90 | # ZINC
91 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=1e-5 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=80 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
92 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=100 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_dim=50 --edge_feat=True --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
93 |
94 | # CIFAR10
95 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.2 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
96 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=20 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.2 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
97 |
98 | # MNIST
99 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.2 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
100 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=20 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.2 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
101 |
102 | ```
103 |
104 | alternatively, for OGB leaderboard, run the following scripts in the [DGN](https://github.com/Saro00/DGN) repository:
105 |
106 | ```
107 | # MolHIV
108 |
109 | python -m main_HIV --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=80 --out_dim=80 --residual=True --readout=mean --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --dataset HIV --config "configs/molecules_graph_classification_DGN_HIV.json" --epochs=200 --init_lr=0.01 --lr_reduce_factor=0.5 --lr_schedule_patience=20 --min_lr=0.0001
110 |
111 | # MolPCBA
112 |
113 | python main_PCBA.py --type_net="complex" --batch_size=512 --lap_norm="none" --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=510 --out_dim=510 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --readout=sum --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean sum max" --scalers="identity" --config "configs/molecules_graph_classification_DGN_PCBA.json" --lr_schedule_patience=4 --towers=5 --dropout=0.2 --init_lr=0.0005 --min_lr=0.00002 --edge_dim=16 --lr_reduce_factor=0.8
114 | ```
115 |
116 |
117 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/datasets_generation/graph_algorithms.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | from queue import Queue
3 |
4 | import numpy as np
5 |
6 |
7 | def is_connected(A):
8 | """
9 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
10 | :return:bool whether the graph is connected or not
11 | """
12 | for _ in range(int(1 + math.ceil(math.log2(A.shape[0])))):
13 | A = np.dot(A, A)
14 | return np.min(A) > 0
15 |
16 |
17 | def identity(A, F):
18 | """
19 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
20 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
21 | :return:F
22 | """
23 | return F
24 |
25 |
26 | def first_neighbours(A):
27 | """
28 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
29 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
30 | :return: for each node, the number of nodes reachable in 1 hop
31 | """
32 | return np.sum(A > 0, axis=0)
33 |
34 |
35 | def second_neighbours(A):
36 | """
37 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
38 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
39 | :return: for each node, the number of nodes reachable in no more than 2 hops
40 | """
41 | A = A > 0.0
42 | A = A + np.dot(A, A)
43 | np.fill_diagonal(A, 0)
44 | return np.sum(A > 0, axis=0)
45 |
46 |
47 | def kth_neighbours(A, k):
48 | """
49 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
50 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
51 | :return: for each node, the number of nodes reachable in k hops
52 | """
53 | A = A > 0.0
54 | R = np.zeros(A.shape)
55 | for _ in range(k):
56 | R = np.dot(R, A) + A
57 | np.fill_diagonal(R, 0)
58 | return np.sum(R > 0, axis=0)
59 |
60 |
61 | def map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, f_reduce, f_map=None, hops=1, consider_itself=False):
62 | """
63 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
64 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
65 | :return: for each node, map its neighbourhood with f_map, and reduce it with f_reduce
66 | """
67 | if f_map is not None:
68 | F = f_map(F)
69 | A = np.array(A)
70 |
71 | A = A > 0
72 | R = np.zeros(A.shape)
73 | for _ in range(hops):
74 | R = np.dot(R, A) + A
75 | np.fill_diagonal(R, 1 if consider_itself else 0)
76 | R = R > 0
77 |
78 | return np.array([f_reduce(F[R[i]]) for i in range(A.shape[0])])
79 |
80 |
81 | def max_neighbourhood(A, F):
82 | """
83 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
84 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
85 | :return: for each node, the maximum in its neighbourhood
86 | """
87 | return map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.max, consider_itself=True)
88 |
89 |
90 | def min_neighbourhood(A, F):
91 | """
92 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
93 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
94 | :return: for each node, the minimum in its neighbourhood
95 | """
96 | return map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.min, consider_itself=True)
97 |
98 |
99 | def std_neighbourhood(A, F):
100 | """
101 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
102 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
103 | :return: for each node, the standard deviation of its neighbourhood
104 | """
105 | return map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.std, consider_itself=True)
106 |
107 |
108 | def mean_neighbourhood(A, F):
109 | """
110 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
111 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
112 | :return: for each node, the mean of its neighbourhood
113 | """
114 | return map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.mean, consider_itself=True)
115 |
116 |
117 | def local_maxima(A, F):
118 | """
119 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
120 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
121 | :return: for each node, whether it is the maximum in its neighbourhood
122 | """
123 | return F == map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.max, consider_itself=True)
124 |
125 |
126 | def graph_laplacian(A):
127 | """
128 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
129 | :return: the laplacian of the adjacency matrix
130 | """
131 | L = (A > 0) * -1
132 | np.fill_diagonal(L, np.sum(A > 0, axis=0))
133 | return L
134 |
135 |
136 | def graph_laplacian_features(A, F):
137 | """
138 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
139 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
140 | :return: the laplacian of the adjacency matrix multiplied by the features
141 | """
142 | return np.matmul(graph_laplacian(A), F)
143 |
144 |
145 | def isomorphism(A1, A2, F1=None, F2=None):
146 | """
147 | Takes two adjacency matrices (A1,A2) and (optionally) two lists of features. It uses Weisfeiler-Lehman algorithms, so false positives might arise
148 | :param A1: adj_matrix, N*N numpy matrix
149 | :param A2: adj_matrix, N*N numpy matrix
150 | :param F1: node_values, numpy array of size N
151 | :param F1: node_values, numpy array of size N
152 | :return: isomorphic: boolean which is false when the two graphs are not isomorphic, true when they probably are.
153 | """
154 | N = A1.shape[0]
155 | if (F1 is None) ^ (F2 is None):
156 | raise ValueError("either both or none between F1,F2 must be defined.")
157 | if F1 is None:
158 | # Assign same initial value to each node
159 | F1 = np.ones(N, int)
160 | F2 = np.ones(N, int)
161 | else:
162 | if not np.array_equal(np.sort(F1), np.sort(F2)):
163 | return False
164 | if F1.dtype() != int:
165 | raise NotImplementedError('Still have to implement this')
166 |
167 | p = 1000000007
168 |
169 | def mapping(F):
170 | return (F * 234 + 133) % 1000000007
171 |
172 | def adjacency_hash(F):
173 | F = np.sort(F)
174 | b = 257
175 |
176 | h = 0
177 | for f in F:
178 | h = (b * h + f) % 1000000007
179 | return h
180 |
181 | for i in range(N):
182 | F1 = map_reduce_neighbourhood(A1, F1, adjacency_hash, f_map=mapping, consider_itself=True, hops=1)
183 | F2 = map_reduce_neighbourhood(A2, F2, adjacency_hash, f_map=mapping, consider_itself=True, hops=1)
184 | if not np.array_equal(np.sort(F1), np.sort(F2)):
185 | return False
186 | return True
187 |
188 |
189 | def count_edges(A):
190 | """
191 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
192 | :return: the number of edges in the graph
193 | """
194 | return np.sum(A) / 2
195 |
196 |
197 | def is_eulerian_cyclable(A):
198 | """
199 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
200 | :return: whether the graph has an eulerian cycle
201 | """
202 | return is_connected(A) and np.count_nonzero(first_neighbours(A) % 2 == 1) == 0
203 |
204 |
205 | def is_eulerian_percorrible(A):
206 | """
207 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
208 | :return: whether the graph has an eulerian path
209 | """
210 | return is_connected(A) and np.count_nonzero(first_neighbours(A) % 2 == 1) in [0, 2]
211 |
212 |
213 | def map_reduce_graph(A, F, f_reduce):
214 | """
215 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
216 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
217 | :return: the features of the nodes reduced by f_reduce
218 | """
219 | return f_reduce(F)
220 |
221 |
222 | def mean_graph(A, F):
223 | """
224 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
225 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
226 | :return: the mean of the features
227 | """
228 | return map_reduce_graph(A, F, np.mean)
229 |
230 |
231 | def max_graph(A, F):
232 | """
233 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
234 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
235 | :return: the maximum of the features
236 | """
237 | return map_reduce_graph(A, F, np.max)
238 |
239 |
240 | def min_graph(A, F):
241 | """
242 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
243 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
244 | :return: the minimum of the features
245 | """
246 | return map_reduce_graph(A, F, np.min)
247 |
248 |
249 | def std_graph(A, F):
250 | """
251 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
252 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
253 | :return: the standard deviation of the features
254 | """
255 | return map_reduce_graph(A, F, np.std)
256 |
257 |
258 | def has_hamiltonian_cycle(A):
259 | """
260 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
261 | :return:bool whether the graph has an hamiltonian cycle
262 | """
263 | A += np.transpose(A)
264 | A = A > 0
265 | V = A.shape[0]
266 |
267 | def ham_cycle_loop(pos):
268 | if pos == V:
269 | if A[path[pos - 1]][path[0]]:
270 | return True
271 | else:
272 | return False
273 | for v in range(1, V):
274 | if A[path[pos - 1]][v] and not used[v]:
275 | path[pos] = v
276 | used[v] = True
277 | if ham_cycle_loop(pos + 1):
278 | return True
279 | path[pos] = -1
280 | used[v] = False
281 | return False
282 |
283 | used = [False] * V
284 | path = [-1] * V
285 | path[0] = 0
286 |
287 | return ham_cycle_loop(1)
288 |
289 |
290 | def all_pairs_shortest_paths(A, inf_sub=math.inf):
291 | """
292 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
293 | :param inf_sub: the placeholder value to use for pairs which are not connected
294 | :return:np.array all pairs shortest paths
295 | """
296 | A = np.array(A)
297 | N = A.shape[0]
298 | for i in range(N):
299 | for j in range(N):
300 | if A[i][j] == 0:
301 | A[i][j] = math.inf
302 | if i == j:
303 | A[i][j] = 0
304 |
305 | for k in range(N):
306 | for i in range(N):
307 | for j in range(N):
308 | A[i][j] = min(A[i][j], A[i][k] + A[k][j])
309 |
310 | A = np.where(A == math.inf, inf_sub, A)
311 | return A
312 |
313 |
314 | def diameter(A):
315 | """
316 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
317 | :return: the diameter of the gra[h
318 | """
319 | sum = np.sum(A)
320 | apsp = all_pairs_shortest_paths(A)
321 | apsp = np.where(apsp < sum + 1, apsp, -1)
322 | return np.max(apsp)
323 |
324 |
325 | def eccentricity(A):
326 | """
327 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
328 | :return: the eccentricity of the gra[h
329 | """
330 | sum = np.sum(A)
331 | apsp = all_pairs_shortest_paths(A)
332 | apsp = np.where(apsp < sum + 1, apsp, -1)
333 | return np.max(apsp, axis=0)
334 |
335 |
336 | def sssp_predecessor(A, F):
337 | """
338 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
339 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
340 | :return: for each node, the best next step to reach the designated source
341 | """
342 | assert (np.sum(F) == 1)
343 | assert (np.max(F) == 1)
344 | s = np.argmax(F)
345 | N = A.shape[0]
346 | P = np.zeros(A.shape)
347 | V = np.zeros(N)
348 | bfs = Queue()
349 | bfs.put(s)
350 | V[s] = 1
351 | while not bfs.empty():
352 | u = bfs.get()
353 | for v in range(N):
354 | if A[u][v] > 0 and V[v] == 0:
355 | V[v] = 1
356 | P[v][u] = 1
357 | bfs.put(v)
358 | return P
359 |
360 |
361 | def max_eigenvalue(A):
362 | """
363 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
364 | :return: the maximum eigenvalue of A
365 | since A is positive symmetric, all the eigenvalues are guaranteed to be real
366 | """
367 | [W, _] = np.linalg.eig(A)
368 | return W[np.argmax(np.absolute(W))].real
369 |
370 |
371 | def max_eigenvalues(A, k):
372 | """
373 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
374 | :param k:int the number of eigenvalues to be selected
375 | :return: the k greatest (by absolute value) eigenvalues of A
376 | """
377 | [W, _] = np.linalg.eig(A)
378 | values = W[sorted(range(len(W)), key=lambda x: -np.absolute(W[x]))[:k]]
379 | return values.real
380 |
381 |
382 | def max_absolute_eigenvalues(A, k):
383 | """
384 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
385 | :param k:int the number of eigenvalues to be selected
386 | :return: the absolute value of the k greatest (by absolute value) eigenvalues of A
387 | """
388 | return np.absolute(max_eigenvalues(A, k))
389 |
390 |
391 | def max_absolute_eigenvalues_laplacian(A, n):
392 | """
393 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
394 | :param k:int the number of eigenvalues to be selected
395 | :return: the absolute value of the k greatest (by absolute value) eigenvalues of the laplacian of A
396 | """
397 | A = graph_laplacian(A)
398 | return np.absolute(max_eigenvalues(A, n))
399 |
400 |
401 | def max_eigenvector(A):
402 | """
403 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
404 | :return: the maximum (by absolute value) eigenvector of A
405 | since A is positive symmetric, all the eigenvectors are guaranteed to be real
406 | """
407 | [W, V] = np.linalg.eig(A)
408 | return V[:, np.argmax(np.absolute(W))].real
409 |
410 |
411 | def spectral_radius(A):
412 | """
413 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
414 | :return: the maximum (by absolute value) eigenvector of A
415 | since A is positive symmetric, all the eigenvectors are guaranteed to be real
416 | """
417 | return np.abs(max_eigenvalue(A))
418 |
419 |
420 | def page_rank(A, F=None, iter=64):
421 | """
422 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
423 | :param F:np.array with initial weights. If None, uniform initialization will happen.
424 | :param iter: log2 of length of power iteration
425 | :return: for each node, its pagerank
426 | """
427 |
428 | # normalize A rows
429 | A = np.array(A)
430 | A /= A.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]
431 |
432 | # power iteration
433 | for _ in range(iter):
434 | A = np.matmul(A, A)
435 |
436 | # generate prior distribution
437 | if F is None:
438 | F = np.ones(A.shape[-1])
439 | else:
440 | F = np.array(F)
441 |
442 | # normalize prior
443 | F /= np.sum(F)
444 |
445 | # compute limit distribution
446 | return np.matmul(F, A)
447 |
448 |
449 | def tsp_length(A, F=None):
450 | """
451 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
452 | :param F:np.array determining which nodes are to be visited. If None, all of them are.
453 | :return: the length of the Traveling Salesman Problem shortest solution
454 | """
455 |
456 | A = all_pairs_shortest_paths(A)
457 | N = A.shape[0]
458 | if F is None:
459 | F = np.ones(N)
460 | targets = np.nonzero(F)[0]
461 | T = targets.shape[0]
462 | S = (1 << T)
463 | dp = np.zeros((S, T))
464 |
465 | def popcount(x):
466 | b = 0
467 | while x > 0:
468 | x &= x - 1
469 | b += 1
470 | return b
471 |
472 | msks = np.argsort(np.vectorize(popcount)(np.arange(S)))
473 | for i in range(T + 1):
474 | for j in range(T):
475 | if (1 << j) & msks[i] == 0:
476 | dp[msks[i]][j] = math.inf
477 |
478 | for i in range(T + 1, S):
479 | msk = msks[i]
480 | for u in range(T):
481 | if (1 << u) & msk == 0:
482 | dp[msk][u] = math.inf
483 | continue
484 | cost = math.inf
485 | for v in range(T):
486 | if v == u or (1 << v) & msk == 0:
487 | continue
488 | cost = min(cost, dp[msk ^ (1 << u)][v] + A[targets[v]][targets[u]])
489 | dp[msk][u] = cost
490 | return np.min(dp[S - 1])
491 |
492 |
493 | def get_nodes_labels(A, F):
494 | """
495 | Takes the adjacency matrix and the list of nodes features (and a list of algorithms) and returns
496 | a set of labels for each node
497 | :param A: adj_matrix, N*N numpy matrix
498 | :param F: node_values, numpy array of size N
499 | :return: labels: KxN numpy matrix where K is the number of labels for each node
500 | """
501 | labels = [identity(A, F), map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.mean, consider_itself=True),
502 | map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.max, consider_itself=True),
503 | map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.std, consider_itself=True), first_neighbours(A), second_neighbours(A),
504 | eccentricity(A)]
505 | return np.swapaxes(np.stack(labels), 0, 1)
506 |
507 |
508 | def get_graph_labels(A, F):
509 | """
510 | Takes the adjacency matrix and the list of nodes features (and a list of algorithms) and returns
511 | a set of labels for the whole graph
512 | :param A: adj_matrix, N*N numpy matrix
513 | :param F: node_values, numpy array of size N
514 | :return: labels: numpy array of size K where K is the number of labels for the graph
515 | """
516 | labels = [diameter(A)]
517 | return np.asarray(labels)
518 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4 |
5 | ## Overview
6 |
7 | We provide the scripts for the download and execution of the real-world benchmarks we used.
8 | Many scripts in this directory were taken directly from or inspired by "Benchmarking GNNs"
9 | by Dwivedi _et al._ refer to their [code](https://github.com/graphdeeplearning/benchmarking-gnns)
10 | and [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.00982) for more details on their work. The graph classification
11 | benchmark MolHIV comes from the [Open Graph Benchmark](https://ogb.stanford.edu/).
12 |
13 | - `configs` contains .json configuration files for the various datasets;
14 | - `data` contains scripts to download the datasets;
15 | - `nets` contains the architectures that were used with the PNA in the benchmarks;
16 | - `train` contains the training scripts.
17 |
18 | These benchmarks use the DGL version of PNA (`../models/dgl`) with the MolHIV model using the *simple* layer architecture.
19 | Below you can find the instructions on how to download the datasets and run the models.
20 | You can run these scripts directly in this [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1RnV4MBjCl98eubAGpEF-eXdAW5mTP3h3?usp=sharing).
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 | ## Test run
25 |
26 | ### Benchmark Setup
27 |
28 | [Follow these instructions](./docs/setup.md) to install the benchmark and setup the environment.
29 |
30 | ### Run model training
31 | ```
32 | # at the root of the repo
33 | cd realworld_benchmark
34 | python { main_molecules.py | main_superpixels.py } [--param=value ...] --dataset { ZINC | MNIST | CIFAR10 } --gpu_id gpu_id --config config_file
35 | ```
36 |
37 |
38 | ## Tuned hyperparameters
39 |
40 | You can find below the hyperparameters we used for our experiments. In general, the depth of the architectures was not changed while the width was adjusted to keep the total number of parameters of the model between 100k and 110k as done in "Benchmarking GNNs" to ensure a fair comparison of the architectures. Refer to our [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718) for an interpretation of the results.
41 |
42 | ```
43 | For OGB leaderboard (hyperparameters taken from the DGN model - 300k parameters):
44 |
45 | python -m main_HIV --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=80 --out_dim=80 --residual=True --readout=mean --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --dataset HIV --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_classification_PNA_HIV.json" --epochs=200 --init_lr=0.01 --lr_reduce_factor=0.5 --lr_schedule_patience=20 --min_lr=0.0001
46 |
47 |
48 | For the leaderboard (2nd version of the datasets - 400/500k parameters)
49 |
50 | # ZINC
51 | PNA:
52 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=16 --hidden_dim=70 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=40 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --pretrans_layers=1 --posttrans_layers=1 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
53 | MPNN (sum/max):
54 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=16 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=110 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=40 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --pretrans_layers=1 --posttrans_layers=1 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
55 |
56 |
57 | For the paper (1st version of the datasets - 100k parameters)
58 | --- PNA ---
59 |
60 | # ZINC
61 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=False --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
62 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=70 --out_dim=60 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --pretrans_layers=1 --posttrans_layers=1 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
63 |
64 | # CIFAR10
65 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.1 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
66 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
67 |
68 | # MNIST
69 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.1 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
70 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
71 |
72 |
73 | --- PNA (no scalers) ---
74 |
75 | # ZINC
76 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
77 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=90 --out_dim=80 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --pretrans_layers=1 --posttrans_layers=1 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
78 |
79 | # CIFAR10
80 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.1 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
81 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
82 |
83 | # MNIST
84 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.1 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
85 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
86 |
87 |
88 | --- MPNN (sum/max) ---
89 |
90 | # ZINC
91 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=1e-5 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=80 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
92 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=100 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_dim=50 --edge_feat=True --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
93 |
94 | # CIFAR10
95 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.2 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
96 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=20 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.2 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
97 |
98 | # MNIST
99 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.2 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
100 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=20 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.2 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
101 |
102 | ```
103 |
104 | alternatively, for OGB leaderboard, run the following scripts in the [DGN](https://github.com/Saro00/DGN) repository:
105 |
106 | ```
107 | # MolHIV
108 |
109 | python -m main_HIV --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=80 --out_dim=80 --residual=True --readout=mean --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --dataset HIV --config "configs/molecules_graph_classification_DGN_HIV.json" --epochs=200 --init_lr=0.01 --lr_reduce_factor=0.5 --lr_schedule_patience=20 --min_lr=0.0001
110 |
111 | # MolPCBA
112 |
113 | python main_PCBA.py --type_net="complex" --batch_size=512 --lap_norm="none" --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=510 --out_dim=510 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --readout=sum --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean sum max" --scalers="identity" --config "configs/molecules_graph_classification_DGN_PCBA.json" --lr_schedule_patience=4 --towers=5 --dropout=0.2 --init_lr=0.0005 --min_lr=0.00002 --edge_dim=16 --lr_reduce_factor=0.8
114 | ```
115 |
116 |
117 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/datasets_generation/graph_algorithms.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | from queue import Queue
3 |
4 | import numpy as np
5 |
6 |
7 | def is_connected(A):
8 | """
9 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
10 | :return:bool whether the graph is connected or not
11 | """
12 | for _ in range(int(1 + math.ceil(math.log2(A.shape[0])))):
13 | A = np.dot(A, A)
14 | return np.min(A) > 0
15 |
16 |
17 | def identity(A, F):
18 | """
19 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
20 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
21 | :return:F
22 | """
23 | return F
24 |
25 |
26 | def first_neighbours(A):
27 | """
28 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
29 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
30 | :return: for each node, the number of nodes reachable in 1 hop
31 | """
32 | return np.sum(A > 0, axis=0)
33 |
34 |
35 | def second_neighbours(A):
36 | """
37 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
38 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
39 | :return: for each node, the number of nodes reachable in no more than 2 hops
40 | """
41 | A = A > 0.0
42 | A = A + np.dot(A, A)
43 | np.fill_diagonal(A, 0)
44 | return np.sum(A > 0, axis=0)
45 |
46 |
47 | def kth_neighbours(A, k):
48 | """
49 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
50 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
51 | :return: for each node, the number of nodes reachable in k hops
52 | """
53 | A = A > 0.0
54 | R = np.zeros(A.shape)
55 | for _ in range(k):
56 | R = np.dot(R, A) + A
57 | np.fill_diagonal(R, 0)
58 | return np.sum(R > 0, axis=0)
59 |
60 |
61 | def map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, f_reduce, f_map=None, hops=1, consider_itself=False):
62 | """
63 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
64 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
65 | :return: for each node, map its neighbourhood with f_map, and reduce it with f_reduce
66 | """
67 | if f_map is not None:
68 | F = f_map(F)
69 | A = np.array(A)
70 |
71 | A = A > 0
72 | R = np.zeros(A.shape)
73 | for _ in range(hops):
74 | R = np.dot(R, A) + A
75 | np.fill_diagonal(R, 1 if consider_itself else 0)
76 | R = R > 0
77 |
78 | return np.array([f_reduce(F[R[i]]) for i in range(A.shape[0])])
79 |
80 |
81 | def max_neighbourhood(A, F):
82 | """
83 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
84 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
85 | :return: for each node, the maximum in its neighbourhood
86 | """
87 | return map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.max, consider_itself=True)
88 |
89 |
90 | def min_neighbourhood(A, F):
91 | """
92 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
93 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
94 | :return: for each node, the minimum in its neighbourhood
95 | """
96 | return map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.min, consider_itself=True)
97 |
98 |
99 | def std_neighbourhood(A, F):
100 | """
101 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
102 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
103 | :return: for each node, the standard deviation of its neighbourhood
104 | """
105 | return map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.std, consider_itself=True)
106 |
107 |
108 | def mean_neighbourhood(A, F):
109 | """
110 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
111 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
112 | :return: for each node, the mean of its neighbourhood
113 | """
114 | return map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.mean, consider_itself=True)
115 |
116 |
117 | def local_maxima(A, F):
118 | """
119 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
120 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
121 | :return: for each node, whether it is the maximum in its neighbourhood
122 | """
123 | return F == map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.max, consider_itself=True)
124 |
125 |
126 | def graph_laplacian(A):
127 | """
128 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
129 | :return: the laplacian of the adjacency matrix
130 | """
131 | L = (A > 0) * -1
132 | np.fill_diagonal(L, np.sum(A > 0, axis=0))
133 | return L
134 |
135 |
136 | def graph_laplacian_features(A, F):
137 | """
138 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
139 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
140 | :return: the laplacian of the adjacency matrix multiplied by the features
141 | """
142 | return np.matmul(graph_laplacian(A), F)
143 |
144 |
145 | def isomorphism(A1, A2, F1=None, F2=None):
146 | """
147 | Takes two adjacency matrices (A1,A2) and (optionally) two lists of features. It uses Weisfeiler-Lehman algorithms, so false positives might arise
148 | :param A1: adj_matrix, N*N numpy matrix
149 | :param A2: adj_matrix, N*N numpy matrix
150 | :param F1: node_values, numpy array of size N
151 | :param F1: node_values, numpy array of size N
152 | :return: isomorphic: boolean which is false when the two graphs are not isomorphic, true when they probably are.
153 | """
154 | N = A1.shape[0]
155 | if (F1 is None) ^ (F2 is None):
156 | raise ValueError("either both or none between F1,F2 must be defined.")
157 | if F1 is None:
158 | # Assign same initial value to each node
159 | F1 = np.ones(N, int)
160 | F2 = np.ones(N, int)
161 | else:
162 | if not np.array_equal(np.sort(F1), np.sort(F2)):
163 | return False
164 | if F1.dtype() != int:
165 | raise NotImplementedError('Still have to implement this')
166 |
167 | p = 1000000007
168 |
169 | def mapping(F):
170 | return (F * 234 + 133) % 1000000007
171 |
172 | def adjacency_hash(F):
173 | F = np.sort(F)
174 | b = 257
175 |
176 | h = 0
177 | for f in F:
178 | h = (b * h + f) % 1000000007
179 | return h
180 |
181 | for i in range(N):
182 | F1 = map_reduce_neighbourhood(A1, F1, adjacency_hash, f_map=mapping, consider_itself=True, hops=1)
183 | F2 = map_reduce_neighbourhood(A2, F2, adjacency_hash, f_map=mapping, consider_itself=True, hops=1)
184 | if not np.array_equal(np.sort(F1), np.sort(F2)):
185 | return False
186 | return True
187 |
188 |
189 | def count_edges(A):
190 | """
191 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
192 | :return: the number of edges in the graph
193 | """
194 | return np.sum(A) / 2
195 |
196 |
197 | def is_eulerian_cyclable(A):
198 | """
199 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
200 | :return: whether the graph has an eulerian cycle
201 | """
202 | return is_connected(A) and np.count_nonzero(first_neighbours(A) % 2 == 1) == 0
203 |
204 |
205 | def is_eulerian_percorrible(A):
206 | """
207 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
208 | :return: whether the graph has an eulerian path
209 | """
210 | return is_connected(A) and np.count_nonzero(first_neighbours(A) % 2 == 1) in [0, 2]
211 |
212 |
213 | def map_reduce_graph(A, F, f_reduce):
214 | """
215 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
216 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
217 | :return: the features of the nodes reduced by f_reduce
218 | """
219 | return f_reduce(F)
220 |
221 |
222 | def mean_graph(A, F):
223 | """
224 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
225 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
226 | :return: the mean of the features
227 | """
228 | return map_reduce_graph(A, F, np.mean)
229 |
230 |
231 | def max_graph(A, F):
232 | """
233 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
234 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
235 | :return: the maximum of the features
236 | """
237 | return map_reduce_graph(A, F, np.max)
238 |
239 |
240 | def min_graph(A, F):
241 | """
242 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
243 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
244 | :return: the minimum of the features
245 | """
246 | return map_reduce_graph(A, F, np.min)
247 |
248 |
249 | def std_graph(A, F):
250 | """
251 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
252 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
253 | :return: the standard deviation of the features
254 | """
255 | return map_reduce_graph(A, F, np.std)
256 |
257 |
258 | def has_hamiltonian_cycle(A):
259 | """
260 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
261 | :return:bool whether the graph has an hamiltonian cycle
262 | """
263 | A += np.transpose(A)
264 | A = A > 0
265 | V = A.shape[0]
266 |
267 | def ham_cycle_loop(pos):
268 | if pos == V:
269 | if A[path[pos - 1]][path[0]]:
270 | return True
271 | else:
272 | return False
273 | for v in range(1, V):
274 | if A[path[pos - 1]][v] and not used[v]:
275 | path[pos] = v
276 | used[v] = True
277 | if ham_cycle_loop(pos + 1):
278 | return True
279 | path[pos] = -1
280 | used[v] = False
281 | return False
282 |
283 | used = [False] * V
284 | path = [-1] * V
285 | path[0] = 0
286 |
287 | return ham_cycle_loop(1)
288 |
289 |
290 | def all_pairs_shortest_paths(A, inf_sub=math.inf):
291 | """
292 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
293 | :param inf_sub: the placeholder value to use for pairs which are not connected
294 | :return:np.array all pairs shortest paths
295 | """
296 | A = np.array(A)
297 | N = A.shape[0]
298 | for i in range(N):
299 | for j in range(N):
300 | if A[i][j] == 0:
301 | A[i][j] = math.inf
302 | if i == j:
303 | A[i][j] = 0
304 |
305 | for k in range(N):
306 | for i in range(N):
307 | for j in range(N):
308 | A[i][j] = min(A[i][j], A[i][k] + A[k][j])
309 |
310 | A = np.where(A == math.inf, inf_sub, A)
311 | return A
312 |
313 |
314 | def diameter(A):
315 | """
316 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
317 | :return: the diameter of the gra[h
318 | """
319 | sum = np.sum(A)
320 | apsp = all_pairs_shortest_paths(A)
321 | apsp = np.where(apsp < sum + 1, apsp, -1)
322 | return np.max(apsp)
323 |
324 |
325 | def eccentricity(A):
326 | """
327 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
328 | :return: the eccentricity of the gra[h
329 | """
330 | sum = np.sum(A)
331 | apsp = all_pairs_shortest_paths(A)
332 | apsp = np.where(apsp < sum + 1, apsp, -1)
333 | return np.max(apsp, axis=0)
334 |
335 |
336 | def sssp_predecessor(A, F):
337 | """
338 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
339 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
340 | :return: for each node, the best next step to reach the designated source
341 | """
342 | assert (np.sum(F) == 1)
343 | assert (np.max(F) == 1)
344 | s = np.argmax(F)
345 | N = A.shape[0]
346 | P = np.zeros(A.shape)
347 | V = np.zeros(N)
348 | bfs = Queue()
349 | bfs.put(s)
350 | V[s] = 1
351 | while not bfs.empty():
352 | u = bfs.get()
353 | for v in range(N):
354 | if A[u][v] > 0 and V[v] == 0:
355 | V[v] = 1
356 | P[v][u] = 1
357 | bfs.put(v)
358 | return P
359 |
360 |
361 | def max_eigenvalue(A):
362 | """
363 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
364 | :return: the maximum eigenvalue of A
365 | since A is positive symmetric, all the eigenvalues are guaranteed to be real
366 | """
367 | [W, _] = np.linalg.eig(A)
368 | return W[np.argmax(np.absolute(W))].real
369 |
370 |
371 | def max_eigenvalues(A, k):
372 | """
373 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
374 | :param k:int the number of eigenvalues to be selected
375 | :return: the k greatest (by absolute value) eigenvalues of A
376 | """
377 | [W, _] = np.linalg.eig(A)
378 | values = W[sorted(range(len(W)), key=lambda x: -np.absolute(W[x]))[:k]]
379 | return values.real
380 |
381 |
382 | def max_absolute_eigenvalues(A, k):
383 | """
384 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
385 | :param k:int the number of eigenvalues to be selected
386 | :return: the absolute value of the k greatest (by absolute value) eigenvalues of A
387 | """
388 | return np.absolute(max_eigenvalues(A, k))
389 |
390 |
391 | def max_absolute_eigenvalues_laplacian(A, n):
392 | """
393 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
394 | :param k:int the number of eigenvalues to be selected
395 | :return: the absolute value of the k greatest (by absolute value) eigenvalues of the laplacian of A
396 | """
397 | A = graph_laplacian(A)
398 | return np.absolute(max_eigenvalues(A, n))
399 |
400 |
401 | def max_eigenvector(A):
402 | """
403 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
404 | :return: the maximum (by absolute value) eigenvector of A
405 | since A is positive symmetric, all the eigenvectors are guaranteed to be real
406 | """
407 | [W, V] = np.linalg.eig(A)
408 | return V[:, np.argmax(np.absolute(W))].real
409 |
410 |
411 | def spectral_radius(A):
412 | """
413 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
414 | :return: the maximum (by absolute value) eigenvector of A
415 | since A is positive symmetric, all the eigenvectors are guaranteed to be real
416 | """
417 | return np.abs(max_eigenvalue(A))
418 |
419 |
420 | def page_rank(A, F=None, iter=64):
421 | """
422 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
423 | :param F:np.array with initial weights. If None, uniform initialization will happen.
424 | :param iter: log2 of length of power iteration
425 | :return: for each node, its pagerank
426 | """
427 |
428 | # normalize A rows
429 | A = np.array(A)
430 | A /= A.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]
431 |
432 | # power iteration
433 | for _ in range(iter):
434 | A = np.matmul(A, A)
435 |
436 | # generate prior distribution
437 | if F is None:
438 | F = np.ones(A.shape[-1])
439 | else:
440 | F = np.array(F)
441 |
442 | # normalize prior
443 | F /= np.sum(F)
444 |
445 | # compute limit distribution
446 | return np.matmul(F, A)
447 |
448 |
449 | def tsp_length(A, F=None):
450 | """
451 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
452 | :param F:np.array determining which nodes are to be visited. If None, all of them are.
453 | :return: the length of the Traveling Salesman Problem shortest solution
454 | """
455 |
456 | A = all_pairs_shortest_paths(A)
457 | N = A.shape[0]
458 | if F is None:
459 | F = np.ones(N)
460 | targets = np.nonzero(F)[0]
461 | T = targets.shape[0]
462 | S = (1 << T)
463 | dp = np.zeros((S, T))
464 |
465 | def popcount(x):
466 | b = 0
467 | while x > 0:
468 | x &= x - 1
469 | b += 1
470 | return b
471 |
472 | msks = np.argsort(np.vectorize(popcount)(np.arange(S)))
473 | for i in range(T + 1):
474 | for j in range(T):
475 | if (1 << j) & msks[i] == 0:
476 | dp[msks[i]][j] = math.inf
477 |
478 | for i in range(T + 1, S):
479 | msk = msks[i]
480 | for u in range(T):
481 | if (1 << u) & msk == 0:
482 | dp[msk][u] = math.inf
483 | continue
484 | cost = math.inf
485 | for v in range(T):
486 | if v == u or (1 << v) & msk == 0:
487 | continue
488 | cost = min(cost, dp[msk ^ (1 << u)][v] + A[targets[v]][targets[u]])
489 | dp[msk][u] = cost
490 | return np.min(dp[S - 1])
491 |
492 |
493 | def get_nodes_labels(A, F):
494 | """
495 | Takes the adjacency matrix and the list of nodes features (and a list of algorithms) and returns
496 | a set of labels for each node
497 | :param A: adj_matrix, N*N numpy matrix
498 | :param F: node_values, numpy array of size N
499 | :return: labels: KxN numpy matrix where K is the number of labels for each node
500 | """
501 | labels = [identity(A, F), map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.mean, consider_itself=True),
502 | map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.max, consider_itself=True),
503 | map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.std, consider_itself=True), first_neighbours(A), second_neighbours(A),
504 | eccentricity(A)]
505 | return np.swapaxes(np.stack(labels), 0, 1)
506 |
507 |
508 | def get_graph_labels(A, F):
509 | """
510 | Takes the adjacency matrix and the list of nodes features (and a list of algorithms) and returns
511 | a set of labels for the whole graph
512 | :param A: adj_matrix, N*N numpy matrix
513 | :param F: node_values, numpy array of size N
514 | :return: labels: numpy array of size K where K is the number of labels for the graph
515 | """
516 | labels = [diameter(A)]
517 | return np.asarray(labels)
518 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 4 |
5 | ## Overview
6 |
7 | We provide the scripts for the download and execution of the real-world benchmarks we used.
8 | Many scripts in this directory were taken directly from or inspired by "Benchmarking GNNs"
9 | by Dwivedi _et al._ refer to their [code](https://github.com/graphdeeplearning/benchmarking-gnns)
10 | and [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.00982) for more details on their work. The graph classification
11 | benchmark MolHIV comes from the [Open Graph Benchmark](https://ogb.stanford.edu/).
12 |
13 | - `configs` contains .json configuration files for the various datasets;
14 | - `data` contains scripts to download the datasets;
15 | - `nets` contains the architectures that were used with the PNA in the benchmarks;
16 | - `train` contains the training scripts.
17 |
18 | These benchmarks use the DGL version of PNA (`../models/dgl`) with the MolHIV model using the *simple* layer architecture.
19 | Below you can find the instructions on how to download the datasets and run the models.
20 | You can run these scripts directly in this [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1RnV4MBjCl98eubAGpEF-eXdAW5mTP3h3?usp=sharing).
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 | ## Test run
25 |
26 | ### Benchmark Setup
27 |
28 | [Follow these instructions](./docs/setup.md) to install the benchmark and setup the environment.
29 |
30 | ### Run model training
31 | ```
32 | # at the root of the repo
33 | cd realworld_benchmark
34 | python { main_molecules.py | main_superpixels.py } [--param=value ...] --dataset { ZINC | MNIST | CIFAR10 } --gpu_id gpu_id --config config_file
35 | ```
36 |
37 |
38 | ## Tuned hyperparameters
39 |
40 | You can find below the hyperparameters we used for our experiments. In general, the depth of the architectures was not changed while the width was adjusted to keep the total number of parameters of the model between 100k and 110k as done in "Benchmarking GNNs" to ensure a fair comparison of the architectures. Refer to our [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718) for an interpretation of the results.
41 |
42 | ```
43 | For OGB leaderboard (hyperparameters taken from the DGN model - 300k parameters):
44 |
45 | python -m main_HIV --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=80 --out_dim=80 --residual=True --readout=mean --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --dataset HIV --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_classification_PNA_HIV.json" --epochs=200 --init_lr=0.01 --lr_reduce_factor=0.5 --lr_schedule_patience=20 --min_lr=0.0001
46 |
47 |
48 | For the leaderboard (2nd version of the datasets - 400/500k parameters)
49 |
50 | # ZINC
51 | PNA:
52 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=16 --hidden_dim=70 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=40 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --pretrans_layers=1 --posttrans_layers=1 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
53 | MPNN (sum/max):
54 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=16 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=110 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=40 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --pretrans_layers=1 --posttrans_layers=1 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
55 |
56 |
57 | For the paper (1st version of the datasets - 100k parameters)
58 | --- PNA ---
59 |
60 | # ZINC
61 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=False --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
62 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=70 --out_dim=60 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --pretrans_layers=1 --posttrans_layers=1 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
63 |
64 | # CIFAR10
65 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.1 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
66 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
67 |
68 | # MNIST
69 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.1 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
70 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
71 |
72 |
73 | --- PNA (no scalers) ---
74 |
75 | # ZINC
76 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
77 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=90 --out_dim=80 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --pretrans_layers=1 --posttrans_layers=1 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
78 |
79 | # CIFAR10
80 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.1 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
81 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
82 |
83 | # MNIST
84 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.1 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
85 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
86 |
87 |
88 | --- MPNN (sum/max) ---
89 |
90 | # ZINC
91 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=1e-5 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=80 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
92 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=100 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_dim=50 --edge_feat=True --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
93 |
94 | # CIFAR10
95 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.2 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
96 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=20 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.2 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
97 |
98 | # MNIST
99 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.2 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
100 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=20 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.2 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
101 |
102 | ```
103 |
104 | alternatively, for OGB leaderboard, run the following scripts in the [DGN](https://github.com/Saro00/DGN) repository:
105 |
106 | ```
107 | # MolHIV
108 |
109 | python -m main_HIV --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=80 --out_dim=80 --residual=True --readout=mean --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --dataset HIV --config "configs/molecules_graph_classification_DGN_HIV.json" --epochs=200 --init_lr=0.01 --lr_reduce_factor=0.5 --lr_schedule_patience=20 --min_lr=0.0001
110 |
111 | # MolPCBA
112 |
113 | python main_PCBA.py --type_net="complex" --batch_size=512 --lap_norm="none" --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=510 --out_dim=510 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --readout=sum --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean sum max" --scalers="identity" --config "configs/molecules_graph_classification_DGN_PCBA.json" --lr_schedule_patience=4 --towers=5 --dropout=0.2 --init_lr=0.0005 --min_lr=0.00002 --edge_dim=16 --lr_reduce_factor=0.8
114 | ```
115 |
116 |
117 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/datasets_generation/graph_algorithms.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | from queue import Queue
3 |
4 | import numpy as np
5 |
6 |
7 | def is_connected(A):
8 | """
9 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
10 | :return:bool whether the graph is connected or not
11 | """
12 | for _ in range(int(1 + math.ceil(math.log2(A.shape[0])))):
13 | A = np.dot(A, A)
14 | return np.min(A) > 0
15 |
16 |
17 | def identity(A, F):
18 | """
19 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
20 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
21 | :return:F
22 | """
23 | return F
24 |
25 |
26 | def first_neighbours(A):
27 | """
28 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
29 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
30 | :return: for each node, the number of nodes reachable in 1 hop
31 | """
32 | return np.sum(A > 0, axis=0)
33 |
34 |
35 | def second_neighbours(A):
36 | """
37 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
38 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
39 | :return: for each node, the number of nodes reachable in no more than 2 hops
40 | """
41 | A = A > 0.0
42 | A = A + np.dot(A, A)
43 | np.fill_diagonal(A, 0)
44 | return np.sum(A > 0, axis=0)
45 |
46 |
47 | def kth_neighbours(A, k):
48 | """
49 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
50 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
51 | :return: for each node, the number of nodes reachable in k hops
52 | """
53 | A = A > 0.0
54 | R = np.zeros(A.shape)
55 | for _ in range(k):
56 | R = np.dot(R, A) + A
57 | np.fill_diagonal(R, 0)
58 | return np.sum(R > 0, axis=0)
59 |
60 |
61 | def map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, f_reduce, f_map=None, hops=1, consider_itself=False):
62 | """
63 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
64 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
65 | :return: for each node, map its neighbourhood with f_map, and reduce it with f_reduce
66 | """
67 | if f_map is not None:
68 | F = f_map(F)
69 | A = np.array(A)
70 |
71 | A = A > 0
72 | R = np.zeros(A.shape)
73 | for _ in range(hops):
74 | R = np.dot(R, A) + A
75 | np.fill_diagonal(R, 1 if consider_itself else 0)
76 | R = R > 0
77 |
78 | return np.array([f_reduce(F[R[i]]) for i in range(A.shape[0])])
79 |
80 |
81 | def max_neighbourhood(A, F):
82 | """
83 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
84 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
85 | :return: for each node, the maximum in its neighbourhood
86 | """
87 | return map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.max, consider_itself=True)
88 |
89 |
90 | def min_neighbourhood(A, F):
91 | """
92 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
93 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
94 | :return: for each node, the minimum in its neighbourhood
95 | """
96 | return map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.min, consider_itself=True)
97 |
98 |
99 | def std_neighbourhood(A, F):
100 | """
101 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
102 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
103 | :return: for each node, the standard deviation of its neighbourhood
104 | """
105 | return map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.std, consider_itself=True)
106 |
107 |
108 | def mean_neighbourhood(A, F):
109 | """
110 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
111 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
112 | :return: for each node, the mean of its neighbourhood
113 | """
114 | return map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.mean, consider_itself=True)
115 |
116 |
117 | def local_maxima(A, F):
118 | """
119 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
120 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
121 | :return: for each node, whether it is the maximum in its neighbourhood
122 | """
123 | return F == map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.max, consider_itself=True)
124 |
125 |
126 | def graph_laplacian(A):
127 | """
128 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
129 | :return: the laplacian of the adjacency matrix
130 | """
131 | L = (A > 0) * -1
132 | np.fill_diagonal(L, np.sum(A > 0, axis=0))
133 | return L
134 |
135 |
136 | def graph_laplacian_features(A, F):
137 | """
138 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
139 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
140 | :return: the laplacian of the adjacency matrix multiplied by the features
141 | """
142 | return np.matmul(graph_laplacian(A), F)
143 |
144 |
145 | def isomorphism(A1, A2, F1=None, F2=None):
146 | """
147 | Takes two adjacency matrices (A1,A2) and (optionally) two lists of features. It uses Weisfeiler-Lehman algorithms, so false positives might arise
148 | :param A1: adj_matrix, N*N numpy matrix
149 | :param A2: adj_matrix, N*N numpy matrix
150 | :param F1: node_values, numpy array of size N
151 | :param F1: node_values, numpy array of size N
152 | :return: isomorphic: boolean which is false when the two graphs are not isomorphic, true when they probably are.
153 | """
154 | N = A1.shape[0]
155 | if (F1 is None) ^ (F2 is None):
156 | raise ValueError("either both or none between F1,F2 must be defined.")
157 | if F1 is None:
158 | # Assign same initial value to each node
159 | F1 = np.ones(N, int)
160 | F2 = np.ones(N, int)
161 | else:
162 | if not np.array_equal(np.sort(F1), np.sort(F2)):
163 | return False
164 | if F1.dtype() != int:
165 | raise NotImplementedError('Still have to implement this')
166 |
167 | p = 1000000007
168 |
169 | def mapping(F):
170 | return (F * 234 + 133) % 1000000007
171 |
172 | def adjacency_hash(F):
173 | F = np.sort(F)
174 | b = 257
175 |
176 | h = 0
177 | for f in F:
178 | h = (b * h + f) % 1000000007
179 | return h
180 |
181 | for i in range(N):
182 | F1 = map_reduce_neighbourhood(A1, F1, adjacency_hash, f_map=mapping, consider_itself=True, hops=1)
183 | F2 = map_reduce_neighbourhood(A2, F2, adjacency_hash, f_map=mapping, consider_itself=True, hops=1)
184 | if not np.array_equal(np.sort(F1), np.sort(F2)):
185 | return False
186 | return True
187 |
188 |
189 | def count_edges(A):
190 | """
191 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
192 | :return: the number of edges in the graph
193 | """
194 | return np.sum(A) / 2
195 |
196 |
197 | def is_eulerian_cyclable(A):
198 | """
199 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
200 | :return: whether the graph has an eulerian cycle
201 | """
202 | return is_connected(A) and np.count_nonzero(first_neighbours(A) % 2 == 1) == 0
203 |
204 |
205 | def is_eulerian_percorrible(A):
206 | """
207 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
208 | :return: whether the graph has an eulerian path
209 | """
210 | return is_connected(A) and np.count_nonzero(first_neighbours(A) % 2 == 1) in [0, 2]
211 |
212 |
213 | def map_reduce_graph(A, F, f_reduce):
214 | """
215 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
216 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
217 | :return: the features of the nodes reduced by f_reduce
218 | """
219 | return f_reduce(F)
220 |
221 |
222 | def mean_graph(A, F):
223 | """
224 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
225 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
226 | :return: the mean of the features
227 | """
228 | return map_reduce_graph(A, F, np.mean)
229 |
230 |
231 | def max_graph(A, F):
232 | """
233 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
234 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
235 | :return: the maximum of the features
236 | """
237 | return map_reduce_graph(A, F, np.max)
238 |
239 |
240 | def min_graph(A, F):
241 | """
242 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
243 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
244 | :return: the minimum of the features
245 | """
246 | return map_reduce_graph(A, F, np.min)
247 |
248 |
249 | def std_graph(A, F):
250 | """
251 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
252 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
253 | :return: the standard deviation of the features
254 | """
255 | return map_reduce_graph(A, F, np.std)
256 |
257 |
258 | def has_hamiltonian_cycle(A):
259 | """
260 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
261 | :return:bool whether the graph has an hamiltonian cycle
262 | """
263 | A += np.transpose(A)
264 | A = A > 0
265 | V = A.shape[0]
266 |
267 | def ham_cycle_loop(pos):
268 | if pos == V:
269 | if A[path[pos - 1]][path[0]]:
270 | return True
271 | else:
272 | return False
273 | for v in range(1, V):
274 | if A[path[pos - 1]][v] and not used[v]:
275 | path[pos] = v
276 | used[v] = True
277 | if ham_cycle_loop(pos + 1):
278 | return True
279 | path[pos] = -1
280 | used[v] = False
281 | return False
282 |
283 | used = [False] * V
284 | path = [-1] * V
285 | path[0] = 0
286 |
287 | return ham_cycle_loop(1)
288 |
289 |
290 | def all_pairs_shortest_paths(A, inf_sub=math.inf):
291 | """
292 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
293 | :param inf_sub: the placeholder value to use for pairs which are not connected
294 | :return:np.array all pairs shortest paths
295 | """
296 | A = np.array(A)
297 | N = A.shape[0]
298 | for i in range(N):
299 | for j in range(N):
300 | if A[i][j] == 0:
301 | A[i][j] = math.inf
302 | if i == j:
303 | A[i][j] = 0
304 |
305 | for k in range(N):
306 | for i in range(N):
307 | for j in range(N):
308 | A[i][j] = min(A[i][j], A[i][k] + A[k][j])
309 |
310 | A = np.where(A == math.inf, inf_sub, A)
311 | return A
312 |
313 |
314 | def diameter(A):
315 | """
316 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
317 | :return: the diameter of the gra[h
318 | """
319 | sum = np.sum(A)
320 | apsp = all_pairs_shortest_paths(A)
321 | apsp = np.where(apsp < sum + 1, apsp, -1)
322 | return np.max(apsp)
323 |
324 |
325 | def eccentricity(A):
326 | """
327 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
328 | :return: the eccentricity of the gra[h
329 | """
330 | sum = np.sum(A)
331 | apsp = all_pairs_shortest_paths(A)
332 | apsp = np.where(apsp < sum + 1, apsp, -1)
333 | return np.max(apsp, axis=0)
334 |
335 |
336 | def sssp_predecessor(A, F):
337 | """
338 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
339 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
340 | :return: for each node, the best next step to reach the designated source
341 | """
342 | assert (np.sum(F) == 1)
343 | assert (np.max(F) == 1)
344 | s = np.argmax(F)
345 | N = A.shape[0]
346 | P = np.zeros(A.shape)
347 | V = np.zeros(N)
348 | bfs = Queue()
349 | bfs.put(s)
350 | V[s] = 1
351 | while not bfs.empty():
352 | u = bfs.get()
353 | for v in range(N):
354 | if A[u][v] > 0 and V[v] == 0:
355 | V[v] = 1
356 | P[v][u] = 1
357 | bfs.put(v)
358 | return P
359 |
360 |
361 | def max_eigenvalue(A):
362 | """
363 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
364 | :return: the maximum eigenvalue of A
365 | since A is positive symmetric, all the eigenvalues are guaranteed to be real
366 | """
367 | [W, _] = np.linalg.eig(A)
368 | return W[np.argmax(np.absolute(W))].real
369 |
370 |
371 | def max_eigenvalues(A, k):
372 | """
373 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
374 | :param k:int the number of eigenvalues to be selected
375 | :return: the k greatest (by absolute value) eigenvalues of A
376 | """
377 | [W, _] = np.linalg.eig(A)
378 | values = W[sorted(range(len(W)), key=lambda x: -np.absolute(W[x]))[:k]]
379 | return values.real
380 |
381 |
382 | def max_absolute_eigenvalues(A, k):
383 | """
384 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
385 | :param k:int the number of eigenvalues to be selected
386 | :return: the absolute value of the k greatest (by absolute value) eigenvalues of A
387 | """
388 | return np.absolute(max_eigenvalues(A, k))
389 |
390 |
391 | def max_absolute_eigenvalues_laplacian(A, n):
392 | """
393 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
394 | :param k:int the number of eigenvalues to be selected
395 | :return: the absolute value of the k greatest (by absolute value) eigenvalues of the laplacian of A
396 | """
397 | A = graph_laplacian(A)
398 | return np.absolute(max_eigenvalues(A, n))
399 |
400 |
401 | def max_eigenvector(A):
402 | """
403 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
404 | :return: the maximum (by absolute value) eigenvector of A
405 | since A is positive symmetric, all the eigenvectors are guaranteed to be real
406 | """
407 | [W, V] = np.linalg.eig(A)
408 | return V[:, np.argmax(np.absolute(W))].real
409 |
410 |
411 | def spectral_radius(A):
412 | """
413 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
414 | :return: the maximum (by absolute value) eigenvector of A
415 | since A is positive symmetric, all the eigenvectors are guaranteed to be real
416 | """
417 | return np.abs(max_eigenvalue(A))
418 |
419 |
420 | def page_rank(A, F=None, iter=64):
421 | """
422 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
423 | :param F:np.array with initial weights. If None, uniform initialization will happen.
424 | :param iter: log2 of length of power iteration
425 | :return: for each node, its pagerank
426 | """
427 |
428 | # normalize A rows
429 | A = np.array(A)
430 | A /= A.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]
431 |
432 | # power iteration
433 | for _ in range(iter):
434 | A = np.matmul(A, A)
435 |
436 | # generate prior distribution
437 | if F is None:
438 | F = np.ones(A.shape[-1])
439 | else:
440 | F = np.array(F)
441 |
442 | # normalize prior
443 | F /= np.sum(F)
444 |
445 | # compute limit distribution
446 | return np.matmul(F, A)
447 |
448 |
449 | def tsp_length(A, F=None):
450 | """
451 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
452 | :param F:np.array determining which nodes are to be visited. If None, all of them are.
453 | :return: the length of the Traveling Salesman Problem shortest solution
454 | """
455 |
456 | A = all_pairs_shortest_paths(A)
457 | N = A.shape[0]
458 | if F is None:
459 | F = np.ones(N)
460 | targets = np.nonzero(F)[0]
461 | T = targets.shape[0]
462 | S = (1 << T)
463 | dp = np.zeros((S, T))
464 |
465 | def popcount(x):
466 | b = 0
467 | while x > 0:
468 | x &= x - 1
469 | b += 1
470 | return b
471 |
472 | msks = np.argsort(np.vectorize(popcount)(np.arange(S)))
473 | for i in range(T + 1):
474 | for j in range(T):
475 | if (1 << j) & msks[i] == 0:
476 | dp[msks[i]][j] = math.inf
477 |
478 | for i in range(T + 1, S):
479 | msk = msks[i]
480 | for u in range(T):
481 | if (1 << u) & msk == 0:
482 | dp[msk][u] = math.inf
483 | continue
484 | cost = math.inf
485 | for v in range(T):
486 | if v == u or (1 << v) & msk == 0:
487 | continue
488 | cost = min(cost, dp[msk ^ (1 << u)][v] + A[targets[v]][targets[u]])
489 | dp[msk][u] = cost
490 | return np.min(dp[S - 1])
491 |
492 |
493 | def get_nodes_labels(A, F):
494 | """
495 | Takes the adjacency matrix and the list of nodes features (and a list of algorithms) and returns
496 | a set of labels for each node
497 | :param A: adj_matrix, N*N numpy matrix
498 | :param F: node_values, numpy array of size N
499 | :return: labels: KxN numpy matrix where K is the number of labels for each node
500 | """
501 | labels = [identity(A, F), map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.mean, consider_itself=True),
502 | map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.max, consider_itself=True),
503 | map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.std, consider_itself=True), first_neighbours(A), second_neighbours(A),
504 | eccentricity(A)]
505 | return np.swapaxes(np.stack(labels), 0, 1)
506 |
507 |
508 | def get_graph_labels(A, F):
509 | """
510 | Takes the adjacency matrix and the list of nodes features (and a list of algorithms) and returns
511 | a set of labels for the whole graph
512 | :param A: adj_matrix, N*N numpy matrix
513 | :param F: node_values, numpy array of size N
514 | :return: labels: numpy array of size K where K is the number of labels for the graph
515 | """
516 | labels = [diameter(A)]
517 | return np.asarray(labels)
518 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4 |
5 | ## Overview
6 |
7 | We provide the scripts for the download and execution of the real-world benchmarks we used.
8 | Many scripts in this directory were taken directly from or inspired by "Benchmarking GNNs"
9 | by Dwivedi _et al._ refer to their [code](https://github.com/graphdeeplearning/benchmarking-gnns)
10 | and [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.00982) for more details on their work. The graph classification
11 | benchmark MolHIV comes from the [Open Graph Benchmark](https://ogb.stanford.edu/).
12 |
13 | - `configs` contains .json configuration files for the various datasets;
14 | - `data` contains scripts to download the datasets;
15 | - `nets` contains the architectures that were used with the PNA in the benchmarks;
16 | - `train` contains the training scripts.
17 |
18 | These benchmarks use the DGL version of PNA (`../models/dgl`) with the MolHIV model using the *simple* layer architecture.
19 | Below you can find the instructions on how to download the datasets and run the models.
20 | You can run these scripts directly in this [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1RnV4MBjCl98eubAGpEF-eXdAW5mTP3h3?usp=sharing).
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 | ## Test run
25 |
26 | ### Benchmark Setup
27 |
28 | [Follow these instructions](./docs/setup.md) to install the benchmark and setup the environment.
29 |
30 | ### Run model training
31 | ```
32 | # at the root of the repo
33 | cd realworld_benchmark
34 | python { main_molecules.py | main_superpixels.py } [--param=value ...] --dataset { ZINC | MNIST | CIFAR10 } --gpu_id gpu_id --config config_file
35 | ```
36 |
37 |
38 | ## Tuned hyperparameters
39 |
40 | You can find below the hyperparameters we used for our experiments. In general, the depth of the architectures was not changed while the width was adjusted to keep the total number of parameters of the model between 100k and 110k as done in "Benchmarking GNNs" to ensure a fair comparison of the architectures. Refer to our [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718) for an interpretation of the results.
41 |
42 | ```
43 | For OGB leaderboard (hyperparameters taken from the DGN model - 300k parameters):
44 |
45 | python -m main_HIV --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=80 --out_dim=80 --residual=True --readout=mean --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --dataset HIV --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_classification_PNA_HIV.json" --epochs=200 --init_lr=0.01 --lr_reduce_factor=0.5 --lr_schedule_patience=20 --min_lr=0.0001
46 |
47 |
48 | For the leaderboard (2nd version of the datasets - 400/500k parameters)
49 |
50 | # ZINC
51 | PNA:
52 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=16 --hidden_dim=70 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=40 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --pretrans_layers=1 --posttrans_layers=1 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
53 | MPNN (sum/max):
54 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=16 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=110 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=40 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --pretrans_layers=1 --posttrans_layers=1 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
55 |
56 |
57 | For the paper (1st version of the datasets - 100k parameters)
58 | --- PNA ---
59 |
60 | # ZINC
61 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=False --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
62 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=70 --out_dim=60 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --pretrans_layers=1 --posttrans_layers=1 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
63 |
64 | # CIFAR10
65 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.1 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
66 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
67 |
68 | # MNIST
69 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.1 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
70 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=75 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
71 |
72 |
73 | --- PNA (no scalers) ---
74 |
75 | # ZINC
76 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
77 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=90 --out_dim=80 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --pretrans_layers=1 --posttrans_layers=1 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
78 |
79 | # CIFAR10
80 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.1 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
81 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
82 |
83 | # MNIST
84 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.1 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
85 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=95 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=50 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
86 |
87 |
88 | --- MPNN (sum/max) ---
89 |
90 | # ZINC
91 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=1e-5 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=80 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
92 | python main_molecules.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=100 --out_dim=70 --residual=True --edge_dim=50 --edge_feat=True --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.0 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset ZINC --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/molecules_graph_regression_pna_ZINC.json" --lr_schedule_patience=20
93 |
94 | # CIFAR10
95 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.2 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
96 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=20 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.2 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset CIFAR10 --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_CIFAR10.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
97 |
98 | # MNIST
99 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=False --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.2 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
100 | python main_superpixels.py --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=110 --out_dim=90 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --edge_dim=20 --readout=sum --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.2 --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="sum"/"max" --scalers="identity" --towers=5 --divide_input_first=True --divide_input_last=True --dataset MNIST --gpu_id 0 --config "configs/superpixels_graph_classification_pna_MNIST.json" --lr_schedule_patience=5
101 |
102 | ```
103 |
104 | alternatively, for OGB leaderboard, run the following scripts in the [DGN](https://github.com/Saro00/DGN) repository:
105 |
106 | ```
107 | # MolHIV
108 |
109 | python -m main_HIV --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=80 --out_dim=80 --residual=True --readout=mean --in_feat_dropout=0.0 --dropout=0.3 --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --dataset HIV --config "configs/molecules_graph_classification_DGN_HIV.json" --epochs=200 --init_lr=0.01 --lr_reduce_factor=0.5 --lr_schedule_patience=20 --min_lr=0.0001
110 |
111 | # MolPCBA
112 |
113 | python main_PCBA.py --type_net="complex" --batch_size=512 --lap_norm="none" --weight_decay=3e-6 --L=4 --hidden_dim=510 --out_dim=510 --residual=True --edge_feat=True --readout=sum --graph_norm=True --batch_norm=True --aggregators="mean sum max" --scalers="identity" --config "configs/molecules_graph_classification_DGN_PCBA.json" --lr_schedule_patience=4 --towers=5 --dropout=0.2 --init_lr=0.0005 --min_lr=0.00002 --edge_dim=16 --lr_reduce_factor=0.8
114 | ```
115 |
116 |
117 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multitask_benchmark/datasets_generation/graph_algorithms.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | from queue import Queue
3 |
4 | import numpy as np
5 |
6 |
7 | def is_connected(A):
8 | """
9 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
10 | :return:bool whether the graph is connected or not
11 | """
12 | for _ in range(int(1 + math.ceil(math.log2(A.shape[0])))):
13 | A = np.dot(A, A)
14 | return np.min(A) > 0
15 |
16 |
17 | def identity(A, F):
18 | """
19 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
20 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
21 | :return:F
22 | """
23 | return F
24 |
25 |
26 | def first_neighbours(A):
27 | """
28 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
29 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
30 | :return: for each node, the number of nodes reachable in 1 hop
31 | """
32 | return np.sum(A > 0, axis=0)
33 |
34 |
35 | def second_neighbours(A):
36 | """
37 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
38 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
39 | :return: for each node, the number of nodes reachable in no more than 2 hops
40 | """
41 | A = A > 0.0
42 | A = A + np.dot(A, A)
43 | np.fill_diagonal(A, 0)
44 | return np.sum(A > 0, axis=0)
45 |
46 |
47 | def kth_neighbours(A, k):
48 | """
49 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
50 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
51 | :return: for each node, the number of nodes reachable in k hops
52 | """
53 | A = A > 0.0
54 | R = np.zeros(A.shape)
55 | for _ in range(k):
56 | R = np.dot(R, A) + A
57 | np.fill_diagonal(R, 0)
58 | return np.sum(R > 0, axis=0)
59 |
60 |
61 | def map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, f_reduce, f_map=None, hops=1, consider_itself=False):
62 | """
63 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
64 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
65 | :return: for each node, map its neighbourhood with f_map, and reduce it with f_reduce
66 | """
67 | if f_map is not None:
68 | F = f_map(F)
69 | A = np.array(A)
70 |
71 | A = A > 0
72 | R = np.zeros(A.shape)
73 | for _ in range(hops):
74 | R = np.dot(R, A) + A
75 | np.fill_diagonal(R, 1 if consider_itself else 0)
76 | R = R > 0
77 |
78 | return np.array([f_reduce(F[R[i]]) for i in range(A.shape[0])])
79 |
80 |
81 | def max_neighbourhood(A, F):
82 | """
83 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
84 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
85 | :return: for each node, the maximum in its neighbourhood
86 | """
87 | return map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.max, consider_itself=True)
88 |
89 |
90 | def min_neighbourhood(A, F):
91 | """
92 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
93 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
94 | :return: for each node, the minimum in its neighbourhood
95 | """
96 | return map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.min, consider_itself=True)
97 |
98 |
99 | def std_neighbourhood(A, F):
100 | """
101 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
102 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
103 | :return: for each node, the standard deviation of its neighbourhood
104 | """
105 | return map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.std, consider_itself=True)
106 |
107 |
108 | def mean_neighbourhood(A, F):
109 | """
110 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
111 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
112 | :return: for each node, the mean of its neighbourhood
113 | """
114 | return map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.mean, consider_itself=True)
115 |
116 |
117 | def local_maxima(A, F):
118 | """
119 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
120 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
121 | :return: for each node, whether it is the maximum in its neighbourhood
122 | """
123 | return F == map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.max, consider_itself=True)
124 |
125 |
126 | def graph_laplacian(A):
127 | """
128 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
129 | :return: the laplacian of the adjacency matrix
130 | """
131 | L = (A > 0) * -1
132 | np.fill_diagonal(L, np.sum(A > 0, axis=0))
133 | return L
134 |
135 |
136 | def graph_laplacian_features(A, F):
137 | """
138 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
139 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
140 | :return: the laplacian of the adjacency matrix multiplied by the features
141 | """
142 | return np.matmul(graph_laplacian(A), F)
143 |
144 |
145 | def isomorphism(A1, A2, F1=None, F2=None):
146 | """
147 | Takes two adjacency matrices (A1,A2) and (optionally) two lists of features. It uses Weisfeiler-Lehman algorithms, so false positives might arise
148 | :param A1: adj_matrix, N*N numpy matrix
149 | :param A2: adj_matrix, N*N numpy matrix
150 | :param F1: node_values, numpy array of size N
151 | :param F1: node_values, numpy array of size N
152 | :return: isomorphic: boolean which is false when the two graphs are not isomorphic, true when they probably are.
153 | """
154 | N = A1.shape[0]
155 | if (F1 is None) ^ (F2 is None):
156 | raise ValueError("either both or none between F1,F2 must be defined.")
157 | if F1 is None:
158 | # Assign same initial value to each node
159 | F1 = np.ones(N, int)
160 | F2 = np.ones(N, int)
161 | else:
162 | if not np.array_equal(np.sort(F1), np.sort(F2)):
163 | return False
164 | if F1.dtype() != int:
165 | raise NotImplementedError('Still have to implement this')
166 |
167 | p = 1000000007
168 |
169 | def mapping(F):
170 | return (F * 234 + 133) % 1000000007
171 |
172 | def adjacency_hash(F):
173 | F = np.sort(F)
174 | b = 257
175 |
176 | h = 0
177 | for f in F:
178 | h = (b * h + f) % 1000000007
179 | return h
180 |
181 | for i in range(N):
182 | F1 = map_reduce_neighbourhood(A1, F1, adjacency_hash, f_map=mapping, consider_itself=True, hops=1)
183 | F2 = map_reduce_neighbourhood(A2, F2, adjacency_hash, f_map=mapping, consider_itself=True, hops=1)
184 | if not np.array_equal(np.sort(F1), np.sort(F2)):
185 | return False
186 | return True
187 |
188 |
189 | def count_edges(A):
190 | """
191 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
192 | :return: the number of edges in the graph
193 | """
194 | return np.sum(A) / 2
195 |
196 |
197 | def is_eulerian_cyclable(A):
198 | """
199 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
200 | :return: whether the graph has an eulerian cycle
201 | """
202 | return is_connected(A) and np.count_nonzero(first_neighbours(A) % 2 == 1) == 0
203 |
204 |
205 | def is_eulerian_percorrible(A):
206 | """
207 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
208 | :return: whether the graph has an eulerian path
209 | """
210 | return is_connected(A) and np.count_nonzero(first_neighbours(A) % 2 == 1) in [0, 2]
211 |
212 |
213 | def map_reduce_graph(A, F, f_reduce):
214 | """
215 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
216 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
217 | :return: the features of the nodes reduced by f_reduce
218 | """
219 | return f_reduce(F)
220 |
221 |
222 | def mean_graph(A, F):
223 | """
224 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
225 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
226 | :return: the mean of the features
227 | """
228 | return map_reduce_graph(A, F, np.mean)
229 |
230 |
231 | def max_graph(A, F):
232 | """
233 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
234 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
235 | :return: the maximum of the features
236 | """
237 | return map_reduce_graph(A, F, np.max)
238 |
239 |
240 | def min_graph(A, F):
241 | """
242 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
243 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
244 | :return: the minimum of the features
245 | """
246 | return map_reduce_graph(A, F, np.min)
247 |
248 |
249 | def std_graph(A, F):
250 | """
251 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
252 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
253 | :return: the standard deviation of the features
254 | """
255 | return map_reduce_graph(A, F, np.std)
256 |
257 |
258 | def has_hamiltonian_cycle(A):
259 | """
260 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
261 | :return:bool whether the graph has an hamiltonian cycle
262 | """
263 | A += np.transpose(A)
264 | A = A > 0
265 | V = A.shape[0]
266 |
267 | def ham_cycle_loop(pos):
268 | if pos == V:
269 | if A[path[pos - 1]][path[0]]:
270 | return True
271 | else:
272 | return False
273 | for v in range(1, V):
274 | if A[path[pos - 1]][v] and not used[v]:
275 | path[pos] = v
276 | used[v] = True
277 | if ham_cycle_loop(pos + 1):
278 | return True
279 | path[pos] = -1
280 | used[v] = False
281 | return False
282 |
283 | used = [False] * V
284 | path = [-1] * V
285 | path[0] = 0
286 |
287 | return ham_cycle_loop(1)
288 |
289 |
290 | def all_pairs_shortest_paths(A, inf_sub=math.inf):
291 | """
292 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
293 | :param inf_sub: the placeholder value to use for pairs which are not connected
294 | :return:np.array all pairs shortest paths
295 | """
296 | A = np.array(A)
297 | N = A.shape[0]
298 | for i in range(N):
299 | for j in range(N):
300 | if A[i][j] == 0:
301 | A[i][j] = math.inf
302 | if i == j:
303 | A[i][j] = 0
304 |
305 | for k in range(N):
306 | for i in range(N):
307 | for j in range(N):
308 | A[i][j] = min(A[i][j], A[i][k] + A[k][j])
309 |
310 | A = np.where(A == math.inf, inf_sub, A)
311 | return A
312 |
313 |
314 | def diameter(A):
315 | """
316 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
317 | :return: the diameter of the gra[h
318 | """
319 | sum = np.sum(A)
320 | apsp = all_pairs_shortest_paths(A)
321 | apsp = np.where(apsp < sum + 1, apsp, -1)
322 | return np.max(apsp)
323 |
324 |
325 | def eccentricity(A):
326 | """
327 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
328 | :return: the eccentricity of the gra[h
329 | """
330 | sum = np.sum(A)
331 | apsp = all_pairs_shortest_paths(A)
332 | apsp = np.where(apsp < sum + 1, apsp, -1)
333 | return np.max(apsp, axis=0)
334 |
335 |
336 | def sssp_predecessor(A, F):
337 | """
338 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
339 | :param F:np.array the nodes features
340 | :return: for each node, the best next step to reach the designated source
341 | """
342 | assert (np.sum(F) == 1)
343 | assert (np.max(F) == 1)
344 | s = np.argmax(F)
345 | N = A.shape[0]
346 | P = np.zeros(A.shape)
347 | V = np.zeros(N)
348 | bfs = Queue()
349 | bfs.put(s)
350 | V[s] = 1
351 | while not bfs.empty():
352 | u = bfs.get()
353 | for v in range(N):
354 | if A[u][v] > 0 and V[v] == 0:
355 | V[v] = 1
356 | P[v][u] = 1
357 | bfs.put(v)
358 | return P
359 |
360 |
361 | def max_eigenvalue(A):
362 | """
363 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
364 | :return: the maximum eigenvalue of A
365 | since A is positive symmetric, all the eigenvalues are guaranteed to be real
366 | """
367 | [W, _] = np.linalg.eig(A)
368 | return W[np.argmax(np.absolute(W))].real
369 |
370 |
371 | def max_eigenvalues(A, k):
372 | """
373 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
374 | :param k:int the number of eigenvalues to be selected
375 | :return: the k greatest (by absolute value) eigenvalues of A
376 | """
377 | [W, _] = np.linalg.eig(A)
378 | values = W[sorted(range(len(W)), key=lambda x: -np.absolute(W[x]))[:k]]
379 | return values.real
380 |
381 |
382 | def max_absolute_eigenvalues(A, k):
383 | """
384 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
385 | :param k:int the number of eigenvalues to be selected
386 | :return: the absolute value of the k greatest (by absolute value) eigenvalues of A
387 | """
388 | return np.absolute(max_eigenvalues(A, k))
389 |
390 |
391 | def max_absolute_eigenvalues_laplacian(A, n):
392 | """
393 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
394 | :param k:int the number of eigenvalues to be selected
395 | :return: the absolute value of the k greatest (by absolute value) eigenvalues of the laplacian of A
396 | """
397 | A = graph_laplacian(A)
398 | return np.absolute(max_eigenvalues(A, n))
399 |
400 |
401 | def max_eigenvector(A):
402 | """
403 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
404 | :return: the maximum (by absolute value) eigenvector of A
405 | since A is positive symmetric, all the eigenvectors are guaranteed to be real
406 | """
407 | [W, V] = np.linalg.eig(A)
408 | return V[:, np.argmax(np.absolute(W))].real
409 |
410 |
411 | def spectral_radius(A):
412 | """
413 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
414 | :return: the maximum (by absolute value) eigenvector of A
415 | since A is positive symmetric, all the eigenvectors are guaranteed to be real
416 | """
417 | return np.abs(max_eigenvalue(A))
418 |
419 |
420 | def page_rank(A, F=None, iter=64):
421 | """
422 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
423 | :param F:np.array with initial weights. If None, uniform initialization will happen.
424 | :param iter: log2 of length of power iteration
425 | :return: for each node, its pagerank
426 | """
427 |
428 | # normalize A rows
429 | A = np.array(A)
430 | A /= A.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]
431 |
432 | # power iteration
433 | for _ in range(iter):
434 | A = np.matmul(A, A)
435 |
436 | # generate prior distribution
437 | if F is None:
438 | F = np.ones(A.shape[-1])
439 | else:
440 | F = np.array(F)
441 |
442 | # normalize prior
443 | F /= np.sum(F)
444 |
445 | # compute limit distribution
446 | return np.matmul(F, A)
447 |
448 |
449 | def tsp_length(A, F=None):
450 | """
451 | :param A:np.array the adjacency matrix
452 | :param F:np.array determining which nodes are to be visited. If None, all of them are.
453 | :return: the length of the Traveling Salesman Problem shortest solution
454 | """
455 |
456 | A = all_pairs_shortest_paths(A)
457 | N = A.shape[0]
458 | if F is None:
459 | F = np.ones(N)
460 | targets = np.nonzero(F)[0]
461 | T = targets.shape[0]
462 | S = (1 << T)
463 | dp = np.zeros((S, T))
464 |
465 | def popcount(x):
466 | b = 0
467 | while x > 0:
468 | x &= x - 1
469 | b += 1
470 | return b
471 |
472 | msks = np.argsort(np.vectorize(popcount)(np.arange(S)))
473 | for i in range(T + 1):
474 | for j in range(T):
475 | if (1 << j) & msks[i] == 0:
476 | dp[msks[i]][j] = math.inf
477 |
478 | for i in range(T + 1, S):
479 | msk = msks[i]
480 | for u in range(T):
481 | if (1 << u) & msk == 0:
482 | dp[msk][u] = math.inf
483 | continue
484 | cost = math.inf
485 | for v in range(T):
486 | if v == u or (1 << v) & msk == 0:
487 | continue
488 | cost = min(cost, dp[msk ^ (1 << u)][v] + A[targets[v]][targets[u]])
489 | dp[msk][u] = cost
490 | return np.min(dp[S - 1])
491 |
492 |
493 | def get_nodes_labels(A, F):
494 | """
495 | Takes the adjacency matrix and the list of nodes features (and a list of algorithms) and returns
496 | a set of labels for each node
497 | :param A: adj_matrix, N*N numpy matrix
498 | :param F: node_values, numpy array of size N
499 | :return: labels: KxN numpy matrix where K is the number of labels for each node
500 | """
501 | labels = [identity(A, F), map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.mean, consider_itself=True),
502 | map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.max, consider_itself=True),
503 | map_reduce_neighbourhood(A, F, np.std, consider_itself=True), first_neighbours(A), second_neighbours(A),
504 | eccentricity(A)]
505 | return np.swapaxes(np.stack(labels), 0, 1)
506 |
507 |
508 | def get_graph_labels(A, F):
509 | """
510 | Takes the adjacency matrix and the list of nodes features (and a list of algorithms) and returns
511 | a set of labels for the whole graph
512 | :param A: adj_matrix, N*N numpy matrix
513 | :param F: node_values, numpy array of size N
514 | :return: labels: numpy array of size K where K is the number of labels for the graph
515 | """
516 | labels = [diameter(A)]
517 | return np.asarray(labels)
518 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 4 |
5 | ## Overview
6 |
7 | We provide the scripts for the generation and execution of the multi-task benchmark.
8 | - `dataset_generation` contains:
9 | - `graph_generation.py` with scripts to generate the various graphs and add randomness;
10 | - `graph_algorithms.py` with the implementation of many algorithms on graphs that can be used as labels;
11 | - `multitask_dataset.py` unifies the two files above generating and saving the benchmarks we used in the paper.
12 | - `util` contains:
13 | - preprocessing subroutines and loss functions (`util.py`);
14 | - general training and evaluation procedures (`train.py`).
15 | - `train` contains a script for each model which sets up the command line parameters and initiates the training procedure.
16 |
17 | This benchmark uses the PyTorch version of PNA (`../models/pytorch/pna`). Below you can find the instructions on how to create the dataset and run the models, these are also available in this [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/17NntHxoKQzpKmi8siMOLP9WfANlwbW8S?usp=sharing).
18 |
19 | ## Dependencies
20 | Install PyTorch from the [official website](https://pytorch.org/). The code was tested over PyTorch 1.4.
21 |
22 | Move to the source of the repository before running the following. Then install the other dependencies:
23 | ```
24 | pip3 install -r multitask_benchmark/requirements.txt
25 | ```
26 |
27 | ## Test run
28 |
29 | Generate the benchmark dataset (add `--extrapolation` for multiple test sets of different sizes):
30 | ```
31 | python3 -m multitask_benchmark.datasets_generation.multitask_dataset
32 | ```
33 |
34 | then run the training:
35 | ```
36 | python3 -m multitask_benchmark.train.pna --variable --fixed --gru --lr=0.003 --weight_decay=1e-6 --dropout=0.0 --epochs=10000 --patience=1000 --variable_conv_layers=N/2 --fc_layers=3 --hidden=16 --towers=4 --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --data=multitask_benchmark/data/multitask_dataset.pkl
37 | ```
38 |
39 | The command above uses the hyperparameters tuned for the non-extrapolating dataset and the architecture outlined in the diagram below. For more details on the architecture, how the hyperparameters were tuned and the results collected refer to our [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718).
40 |
41 | 
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/train/train_molecules_graph_regression.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # MIT License
2 | # Copyright (c) 2020 Vijay Prakash Dwivedi, Chaitanya K. Joshi, Thomas Laurent, Yoshua Bengio, Xavier Bresson
3 |
4 |
5 | """
6 | Utility functions for training one epoch
7 | and evaluating one epoch
8 | """
9 | import torch
10 | import torch.nn as nn
11 | import math
12 |
13 | from .metrics import MAE
14 |
15 | def train_epoch(model, optimizer, device, data_loader, epoch):
16 | model.train()
17 | epoch_loss = 0
18 | epoch_train_mae = 0
19 | nb_data = 0
20 | gpu_mem = 0
21 | for iter, (batch_graphs, batch_targets, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e) in enumerate(data_loader):
22 | batch_x = batch_graphs.ndata['feat'].to(device) # num x feat
23 | batch_e = batch_graphs.edata['feat'].to(device)
24 | batch_snorm_e = batch_snorm_e.to(device)
25 | batch_targets = batch_targets.to(device)
26 | batch_snorm_n = batch_snorm_n.to(device) # num x 1
27 | optimizer.zero_grad()
28 |
29 | batch_scores = model.forward(batch_graphs, batch_x, batch_e, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e)
30 | loss = model.loss(batch_scores, batch_targets)
31 | loss.backward()
32 | optimizer.step()
33 | epoch_loss += loss.detach().item()
34 | epoch_train_mae += MAE(batch_scores, batch_targets)
35 | nb_data += batch_targets.size(0)
36 | epoch_loss /= (iter + 1)
37 | epoch_train_mae /= (iter + 1)
38 |
39 | return epoch_loss, epoch_train_mae, optimizer
40 |
41 | def evaluate_network(model, device, data_loader, epoch):
42 | model.eval()
43 | epoch_test_loss = 0
44 | epoch_test_mae = 0
45 | nb_data = 0
46 | with torch.no_grad():
47 | for iter, (batch_graphs, batch_targets, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e) in enumerate(data_loader):
48 | batch_x = batch_graphs.ndata['feat'].to(device)
49 | batch_e = batch_graphs.edata['feat'].to(device)
50 | batch_snorm_e = batch_snorm_e.to(device)
51 | batch_targets = batch_targets.to(device)
52 | batch_snorm_n = batch_snorm_n.to(device)
53 |
54 | batch_scores = model.forward(batch_graphs, batch_x, batch_e, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e)
55 | loss = model.loss(batch_scores, batch_targets)
56 | epoch_test_loss += loss.detach().item()
57 | epoch_test_mae += MAE(batch_scores, batch_targets)
58 | nb_data += batch_targets.size(0)
59 | epoch_test_loss /= (iter + 1)
60 | epoch_test_mae /= (iter + 1)
61 |
62 | return epoch_test_loss, epoch_test_mae
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/train/train_superpixels_graph_classification.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # MIT License
2 | # Copyright (c) 2020 Vijay Prakash Dwivedi, Chaitanya K. Joshi, Thomas Laurent, Yoshua Bengio, Xavier Bresson
3 |
4 |
5 | """
6 | Utility functions for training one epoch
7 | and evaluating one epoch
8 | """
9 | import torch
10 | import torch.nn as nn
11 | import math
12 |
13 | from .metrics import accuracy_MNIST_CIFAR as accuracy
14 |
15 | def train_epoch(model, optimizer, device, data_loader, epoch):
16 | model.train()
17 | epoch_loss = 0
18 | epoch_train_acc = 0
19 | nb_data = 0
20 | gpu_mem = 0
21 | for iter, (batch_graphs, batch_labels, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e) in enumerate(data_loader):
22 | batch_x = batch_graphs.ndata['feat'].to(device) # num x feat
23 | batch_e = batch_graphs.edata['feat'].to(device)
24 | batch_snorm_e = batch_snorm_e.to(device)
25 | batch_labels = batch_labels.to(device)
26 | batch_snorm_n = batch_snorm_n.to(device) # num x 1
27 | optimizer.zero_grad()
28 |
29 | batch_scores = model.forward(batch_graphs, batch_x, batch_e, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e)
30 | loss = model.loss(batch_scores, batch_labels)
31 | loss.backward()
32 | optimizer.step()
33 | epoch_loss += loss.detach().item()
34 | epoch_train_acc += accuracy(batch_scores, batch_labels)
35 | nb_data += batch_labels.size(0)
36 | epoch_loss /= (iter + 1)
37 | epoch_train_acc /= nb_data
38 |
39 | return epoch_loss, epoch_train_acc, optimizer
40 |
41 | def evaluate_network(model, device, data_loader, epoch):
42 | model.eval()
43 | epoch_test_loss = 0
44 | epoch_test_acc = 0
45 | nb_data = 0
46 | with torch.no_grad():
47 | for iter, (batch_graphs, batch_labels, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e) in enumerate(data_loader):
48 | batch_x = batch_graphs.ndata['feat'].to(device)
49 | batch_e = batch_graphs.edata['feat'].to(device)
50 | batch_snorm_e = batch_snorm_e.to(device)
51 | batch_labels = batch_labels.to(device)
52 | batch_snorm_n = batch_snorm_n.to(device)
53 |
54 | batch_scores = model.forward(batch_graphs, batch_x, batch_e, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e)
55 | loss = model.loss(batch_scores, batch_labels)
56 | epoch_test_loss += loss.detach().item()
57 | epoch_test_acc += accuracy(batch_scores, batch_labels)
58 | nb_data += batch_labels.size(0)
59 | epoch_test_loss /= (iter + 1)
60 | epoch_test_acc /= nb_data
61 |
62 | return epoch_test_loss, epoch_test_acc
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/nets/HIV_graph_classification/pna_net.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | import dgl
3 | from models.dgl.pna_layer import PNASimpleLayer
4 | from nets.mlp_readout_layer import MLPReadout
5 | import torch
6 | from ogb.graphproppred.mol_encoder import AtomEncoder
7 |
8 |
9 | class PNANet(nn.Module):
10 | def __init__(self, net_params):
11 | super().__init__()
12 | hidden_dim = net_params['hidden_dim']
13 | out_dim = net_params['out_dim']
14 | in_feat_dropout = net_params['in_feat_dropout']
15 | dropout = net_params['dropout']
16 | n_layers = net_params['L']
17 | self.readout = net_params['readout']
18 | self.batch_norm = net_params['batch_norm']
19 | self.aggregators = net_params['aggregators']
20 | self.scalers = net_params['scalers']
21 | self.avg_d = net_params['avg_d']
22 | self.residual = net_params['residual']
23 | posttrans_layers = net_params['posttrans_layers']
24 | device = net_params['device']
25 | self.device = device
26 |
27 | self.in_feat_dropout = nn.Dropout(in_feat_dropout)
28 | self.embedding_h = AtomEncoder(emb_dim=hidden_dim)
29 |
30 | self.layers = nn.ModuleList(
31 | [PNASimpleLayer(in_dim=hidden_dim, out_dim=hidden_dim, dropout=dropout,
32 | batch_norm=self.batch_norm, residual=self.residual, aggregators=self.aggregators,
33 | scalers=self.scalers, avg_d=self.avg_d, posttrans_layers=posttrans_layers)
34 | for _ in range(n_layers - 1)])
35 | self.layers.append(PNASimpleLayer(in_dim=hidden_dim, out_dim=out_dim, dropout=dropout,
36 | batch_norm=self.batch_norm,
37 | residual=self.residual, aggregators=self.aggregators, scalers=self.scalers,
38 | avg_d=self.avg_d, posttrans_layers=posttrans_layers))
39 |
40 | self.MLP_layer = MLPReadout(out_dim, 1) # 1 out dim since regression problem
41 |
42 | def forward(self, g, h):
43 | h = self.embedding_h(h)
44 | h = self.in_feat_dropout(h)
45 |
46 | for i, conv in enumerate(self.layers):
47 | h = conv(g, h)
48 |
49 | g.ndata['h'] = h
50 |
51 | if self.readout == "sum":
52 | hg = dgl.sum_nodes(g, 'h')
53 | elif self.readout == "max":
54 | hg = dgl.max_nodes(g, 'h')
55 | elif self.readout == "mean":
56 | hg = dgl.mean_nodes(g, 'h')
57 | else:
58 | hg = dgl.mean_nodes(g, 'h') # default readout is mean nodes
59 |
60 | return self.MLP_layer(hg)
61 |
62 | def loss(self, scores, labels):
63 | loss = torch.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()(scores, labels.type(torch.FloatTensor).to('cuda').unsqueeze(-1))
64 | return loss
65 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation
2 |
3 | Implementation of Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation for Graph Nets [arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718) in PyTorch, DGL and PyTorch Geometric.
4 |
5 | *Update: now you can find PNA directly integrated in both [PyTorch Geometric](https://pytorch-geometric.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/nn.html#torch_geometric.nn.conv.PNAConv) and [DGL](https://docs.dgl.ai/generated/dgl.nn.pytorch.conv.PNAConv.html)!*
6 |
7 | 
8 |
9 | ## Overview
10 |
11 | We provide the implementation of the Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation (PNA) in PyTorch, DGL and PyTorch Geometric frameworks, along with scripts to generate and run the multitask benchmarks, scripts for running real-world benchmarks, a flexible PyTorch GNN framework and implementations of the other models used for comparison. The repository is organised as follows:
12 |
13 | - `models` contains:
14 | - `pytorch` contains the various GNN models implemented in PyTorch:
15 | - the implementation of the aggregators, the scalers and the PNA layer (`pna`)
16 | - the flexible GNN framework that can be used with any type of graph convolutions (`gnn_framework.py`)
17 | - implementations of the other GNN models used for comparison in the paper, namely GCN, GAT, GIN and MPNN
18 | - `dgl` contains the PNA model implemented via the [DGL library](https://www.dgl.ai/): aggregators, scalers, and layer.
19 | - `pytorch_geometric` contains the PNA model implemented via the [PyTorch Geometric library](https://pytorch-geometric.readthedocs.io/): aggregators, scalers, and layer.
20 | - `layers.py` contains general NN layers used by the various models
21 | - `multi_task` contains various scripts to recreate the multi_task benchmark along with the files used to train the various models. In `multi_task/README.md` we detail the instructions for the generation and training hyperparameters tuned.
22 | - `real_world` contains various scripts from [Benchmarking GNNs](https://github.com/graphdeeplearning/benchmarking-gnns) to download the real-world benchmarks and train the PNA on them. In `real_world/README.md` we provide instructions for the generation and training hyperparameters tuned.
23 |
24 | 
25 |
26 | ## Reference
27 | ```
28 | @inproceedings{corso2020pna,
29 | title = {Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation for Graph Nets},
30 | author = {Corso, Gabriele and Cavalleri, Luca and Beaini, Dominique and Li\`{o}, Pietro and Veli\v{c}kovi\'{c}, Petar},
31 | booktitle = {Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
32 | year = {2020}
33 | }
34 | ```
35 |
36 | ## License
37 | MIT
38 |
39 |
40 | ## Acknowledgements
41 |
42 | The authors would like to thank Saro Passaro for running some of the tests presented in this repository and
43 | Giorgos Bouritsas, Fabrizio Frasca, Leonardo Cotta, Zhanghao Wu, Zhanqiu Zhang and George Watkins for pointing out some issues with the code.
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/data/HIV.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import time
2 | import dgl
3 | import torch
4 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
5 | from ogb.graphproppred import DglGraphPropPredDataset
6 | from ogb.graphproppred import Evaluator
7 | import torch.utils.data
8 |
9 |
10 | class HIVDGL(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
11 | def __init__(self, data, split):
12 | self.split = split
13 | self.data = [g for g in data[self.split]]
14 | self.graph_lists = []
15 | self.graph_labels = []
16 | for g in self.data:
17 | if g[0].number_of_nodes() > 5:
18 | self.graph_lists.append(g[0])
19 | self.graph_labels.append(g[1])
20 | self.n_samples = len(self.graph_lists)
21 |
22 | def __len__(self):
23 | """Return the number of graphs in the dataset."""
24 | return self.n_samples
25 |
26 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
27 | """
28 | Get the idx^th sample.
29 | Parameters
30 | ---------
31 | idx : int
32 | The sample index.
33 | Returns
34 | -------
35 | (dgl.DGLGraph, int)
36 | DGLGraph with node feature stored in `feat` field
37 | And its label.
38 | """
39 | return self.graph_lists[idx], self.graph_labels[idx]
40 |
41 |
42 | class HIVDataset(Dataset):
43 | def __init__(self, name, verbose=True):
44 | start = time.time()
45 | if verbose:
46 | print("[I] Loading dataset %s..." % (name))
47 | self.name = name
48 | self.dataset = DglGraphPropPredDataset(name = 'ogbg-molhiv')
49 | self.split_idx = self.dataset.get_idx_split()
50 |
51 | self.train = HIVDGL(self.dataset, self.split_idx['train'])
52 | self.val = HIVDGL(self.dataset, self.split_idx['valid'])
53 | self.test = HIVDGL(self.dataset, self.split_idx['test'])
54 |
55 | self.evaluator = Evaluator(name='ogbg-molhiv')
56 |
57 | if verbose:
58 | print('train, test, val sizes :', len(self.train), len(self.test), len(self.val))
59 | print("[I] Finished loading.")
60 | print("[I] Data load time: {:.4f}s".format(time.time() - start))
61 |
62 | # form a mini batch from a given list of samples = [(graph, label) pairs]
63 | def collate(self, samples):
64 | # The input samples is a list of pairs (graph, label).
65 | graphs, labels = map(list, zip(*samples))
66 | labels = torch.cat(labels).long()
67 | batched_graph = dgl.batch(graphs)
68 |
69 | return batched_graph, labels
70 |
71 | def _add_self_loops(self):
72 | # function for adding self loops
73 | # this function will be called only if self_loop flag is True
74 |
75 | self.train.graph_lists = [self_loop(g) for g in self.train.graph_lists]
76 | self.val.graph_lists = [self_loop(g) for g in self.val.graph_lists]
77 | self.test.graph_lists = [self_loop(g) for g in self.test.graph_lists]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/docs/setup.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Benchmark setup
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
4 |
5 | ## Overview
6 |
7 | We provide the scripts for the generation and execution of the multi-task benchmark.
8 | - `dataset_generation` contains:
9 | - `graph_generation.py` with scripts to generate the various graphs and add randomness;
10 | - `graph_algorithms.py` with the implementation of many algorithms on graphs that can be used as labels;
11 | - `multitask_dataset.py` unifies the two files above generating and saving the benchmarks we used in the paper.
12 | - `util` contains:
13 | - preprocessing subroutines and loss functions (`util.py`);
14 | - general training and evaluation procedures (`train.py`).
15 | - `train` contains a script for each model which sets up the command line parameters and initiates the training procedure.
16 |
17 | This benchmark uses the PyTorch version of PNA (`../models/pytorch/pna`). Below you can find the instructions on how to create the dataset and run the models, these are also available in this [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/17NntHxoKQzpKmi8siMOLP9WfANlwbW8S?usp=sharing).
18 |
19 | ## Dependencies
20 | Install PyTorch from the [official website](https://pytorch.org/). The code was tested over PyTorch 1.4.
21 |
22 | Move to the source of the repository before running the following. Then install the other dependencies:
23 | ```
24 | pip3 install -r multitask_benchmark/requirements.txt
25 | ```
26 |
27 | ## Test run
28 |
29 | Generate the benchmark dataset (add `--extrapolation` for multiple test sets of different sizes):
30 | ```
31 | python3 -m multitask_benchmark.datasets_generation.multitask_dataset
32 | ```
33 |
34 | then run the training:
35 | ```
36 | python3 -m multitask_benchmark.train.pna --variable --fixed --gru --lr=0.003 --weight_decay=1e-6 --dropout=0.0 --epochs=10000 --patience=1000 --variable_conv_layers=N/2 --fc_layers=3 --hidden=16 --towers=4 --aggregators="mean max min std" --scalers="identity amplification attenuation" --data=multitask_benchmark/data/multitask_dataset.pkl
37 | ```
38 |
39 | The command above uses the hyperparameters tuned for the non-extrapolating dataset and the architecture outlined in the diagram below. For more details on the architecture, how the hyperparameters were tuned and the results collected refer to our [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718).
40 |
41 | 
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/train/train_molecules_graph_regression.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # MIT License
2 | # Copyright (c) 2020 Vijay Prakash Dwivedi, Chaitanya K. Joshi, Thomas Laurent, Yoshua Bengio, Xavier Bresson
3 |
4 |
5 | """
6 | Utility functions for training one epoch
7 | and evaluating one epoch
8 | """
9 | import torch
10 | import torch.nn as nn
11 | import math
12 |
13 | from .metrics import MAE
14 |
15 | def train_epoch(model, optimizer, device, data_loader, epoch):
16 | model.train()
17 | epoch_loss = 0
18 | epoch_train_mae = 0
19 | nb_data = 0
20 | gpu_mem = 0
21 | for iter, (batch_graphs, batch_targets, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e) in enumerate(data_loader):
22 | batch_x = batch_graphs.ndata['feat'].to(device) # num x feat
23 | batch_e = batch_graphs.edata['feat'].to(device)
24 | batch_snorm_e = batch_snorm_e.to(device)
25 | batch_targets = batch_targets.to(device)
26 | batch_snorm_n = batch_snorm_n.to(device) # num x 1
27 | optimizer.zero_grad()
28 |
29 | batch_scores = model.forward(batch_graphs, batch_x, batch_e, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e)
30 | loss = model.loss(batch_scores, batch_targets)
31 | loss.backward()
32 | optimizer.step()
33 | epoch_loss += loss.detach().item()
34 | epoch_train_mae += MAE(batch_scores, batch_targets)
35 | nb_data += batch_targets.size(0)
36 | epoch_loss /= (iter + 1)
37 | epoch_train_mae /= (iter + 1)
38 |
39 | return epoch_loss, epoch_train_mae, optimizer
40 |
41 | def evaluate_network(model, device, data_loader, epoch):
42 | model.eval()
43 | epoch_test_loss = 0
44 | epoch_test_mae = 0
45 | nb_data = 0
46 | with torch.no_grad():
47 | for iter, (batch_graphs, batch_targets, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e) in enumerate(data_loader):
48 | batch_x = batch_graphs.ndata['feat'].to(device)
49 | batch_e = batch_graphs.edata['feat'].to(device)
50 | batch_snorm_e = batch_snorm_e.to(device)
51 | batch_targets = batch_targets.to(device)
52 | batch_snorm_n = batch_snorm_n.to(device)
53 |
54 | batch_scores = model.forward(batch_graphs, batch_x, batch_e, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e)
55 | loss = model.loss(batch_scores, batch_targets)
56 | epoch_test_loss += loss.detach().item()
57 | epoch_test_mae += MAE(batch_scores, batch_targets)
58 | nb_data += batch_targets.size(0)
59 | epoch_test_loss /= (iter + 1)
60 | epoch_test_mae /= (iter + 1)
61 |
62 | return epoch_test_loss, epoch_test_mae
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/train/train_superpixels_graph_classification.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # MIT License
2 | # Copyright (c) 2020 Vijay Prakash Dwivedi, Chaitanya K. Joshi, Thomas Laurent, Yoshua Bengio, Xavier Bresson
3 |
4 |
5 | """
6 | Utility functions for training one epoch
7 | and evaluating one epoch
8 | """
9 | import torch
10 | import torch.nn as nn
11 | import math
12 |
13 | from .metrics import accuracy_MNIST_CIFAR as accuracy
14 |
15 | def train_epoch(model, optimizer, device, data_loader, epoch):
16 | model.train()
17 | epoch_loss = 0
18 | epoch_train_acc = 0
19 | nb_data = 0
20 | gpu_mem = 0
21 | for iter, (batch_graphs, batch_labels, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e) in enumerate(data_loader):
22 | batch_x = batch_graphs.ndata['feat'].to(device) # num x feat
23 | batch_e = batch_graphs.edata['feat'].to(device)
24 | batch_snorm_e = batch_snorm_e.to(device)
25 | batch_labels = batch_labels.to(device)
26 | batch_snorm_n = batch_snorm_n.to(device) # num x 1
27 | optimizer.zero_grad()
28 |
29 | batch_scores = model.forward(batch_graphs, batch_x, batch_e, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e)
30 | loss = model.loss(batch_scores, batch_labels)
31 | loss.backward()
32 | optimizer.step()
33 | epoch_loss += loss.detach().item()
34 | epoch_train_acc += accuracy(batch_scores, batch_labels)
35 | nb_data += batch_labels.size(0)
36 | epoch_loss /= (iter + 1)
37 | epoch_train_acc /= nb_data
38 |
39 | return epoch_loss, epoch_train_acc, optimizer
40 |
41 | def evaluate_network(model, device, data_loader, epoch):
42 | model.eval()
43 | epoch_test_loss = 0
44 | epoch_test_acc = 0
45 | nb_data = 0
46 | with torch.no_grad():
47 | for iter, (batch_graphs, batch_labels, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e) in enumerate(data_loader):
48 | batch_x = batch_graphs.ndata['feat'].to(device)
49 | batch_e = batch_graphs.edata['feat'].to(device)
50 | batch_snorm_e = batch_snorm_e.to(device)
51 | batch_labels = batch_labels.to(device)
52 | batch_snorm_n = batch_snorm_n.to(device)
53 |
54 | batch_scores = model.forward(batch_graphs, batch_x, batch_e, batch_snorm_n, batch_snorm_e)
55 | loss = model.loss(batch_scores, batch_labels)
56 | epoch_test_loss += loss.detach().item()
57 | epoch_test_acc += accuracy(batch_scores, batch_labels)
58 | nb_data += batch_labels.size(0)
59 | epoch_test_loss /= (iter + 1)
60 | epoch_test_acc /= nb_data
61 |
62 | return epoch_test_loss, epoch_test_acc
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/nets/HIV_graph_classification/pna_net.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | import dgl
3 | from models.dgl.pna_layer import PNASimpleLayer
4 | from nets.mlp_readout_layer import MLPReadout
5 | import torch
6 | from ogb.graphproppred.mol_encoder import AtomEncoder
7 |
8 |
9 | class PNANet(nn.Module):
10 | def __init__(self, net_params):
11 | super().__init__()
12 | hidden_dim = net_params['hidden_dim']
13 | out_dim = net_params['out_dim']
14 | in_feat_dropout = net_params['in_feat_dropout']
15 | dropout = net_params['dropout']
16 | n_layers = net_params['L']
17 | self.readout = net_params['readout']
18 | self.batch_norm = net_params['batch_norm']
19 | self.aggregators = net_params['aggregators']
20 | self.scalers = net_params['scalers']
21 | self.avg_d = net_params['avg_d']
22 | self.residual = net_params['residual']
23 | posttrans_layers = net_params['posttrans_layers']
24 | device = net_params['device']
25 | self.device = device
26 |
27 | self.in_feat_dropout = nn.Dropout(in_feat_dropout)
28 | self.embedding_h = AtomEncoder(emb_dim=hidden_dim)
29 |
30 | self.layers = nn.ModuleList(
31 | [PNASimpleLayer(in_dim=hidden_dim, out_dim=hidden_dim, dropout=dropout,
32 | batch_norm=self.batch_norm, residual=self.residual, aggregators=self.aggregators,
33 | scalers=self.scalers, avg_d=self.avg_d, posttrans_layers=posttrans_layers)
34 | for _ in range(n_layers - 1)])
35 | self.layers.append(PNASimpleLayer(in_dim=hidden_dim, out_dim=out_dim, dropout=dropout,
36 | batch_norm=self.batch_norm,
37 | residual=self.residual, aggregators=self.aggregators, scalers=self.scalers,
38 | avg_d=self.avg_d, posttrans_layers=posttrans_layers))
39 |
40 | self.MLP_layer = MLPReadout(out_dim, 1) # 1 out dim since regression problem
41 |
42 | def forward(self, g, h):
43 | h = self.embedding_h(h)
44 | h = self.in_feat_dropout(h)
45 |
46 | for i, conv in enumerate(self.layers):
47 | h = conv(g, h)
48 |
49 | g.ndata['h'] = h
50 |
51 | if self.readout == "sum":
52 | hg = dgl.sum_nodes(g, 'h')
53 | elif self.readout == "max":
54 | hg = dgl.max_nodes(g, 'h')
55 | elif self.readout == "mean":
56 | hg = dgl.mean_nodes(g, 'h')
57 | else:
58 | hg = dgl.mean_nodes(g, 'h') # default readout is mean nodes
59 |
60 | return self.MLP_layer(hg)
61 |
62 | def loss(self, scores, labels):
63 | loss = torch.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()(scores, labels.type(torch.FloatTensor).to('cuda').unsqueeze(-1))
64 | return loss
65 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation
2 |
3 | Implementation of Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation for Graph Nets [arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05718) in PyTorch, DGL and PyTorch Geometric.
4 |
5 | *Update: now you can find PNA directly integrated in both [PyTorch Geometric](https://pytorch-geometric.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/nn.html#torch_geometric.nn.conv.PNAConv) and [DGL](https://docs.dgl.ai/generated/dgl.nn.pytorch.conv.PNAConv.html)!*
6 |
7 | 
8 |
9 | ## Overview
10 |
11 | We provide the implementation of the Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation (PNA) in PyTorch, DGL and PyTorch Geometric frameworks, along with scripts to generate and run the multitask benchmarks, scripts for running real-world benchmarks, a flexible PyTorch GNN framework and implementations of the other models used for comparison. The repository is organised as follows:
12 |
13 | - `models` contains:
14 | - `pytorch` contains the various GNN models implemented in PyTorch:
15 | - the implementation of the aggregators, the scalers and the PNA layer (`pna`)
16 | - the flexible GNN framework that can be used with any type of graph convolutions (`gnn_framework.py`)
17 | - implementations of the other GNN models used for comparison in the paper, namely GCN, GAT, GIN and MPNN
18 | - `dgl` contains the PNA model implemented via the [DGL library](https://www.dgl.ai/): aggregators, scalers, and layer.
19 | - `pytorch_geometric` contains the PNA model implemented via the [PyTorch Geometric library](https://pytorch-geometric.readthedocs.io/): aggregators, scalers, and layer.
20 | - `layers.py` contains general NN layers used by the various models
21 | - `multi_task` contains various scripts to recreate the multi_task benchmark along with the files used to train the various models. In `multi_task/README.md` we detail the instructions for the generation and training hyperparameters tuned.
22 | - `real_world` contains various scripts from [Benchmarking GNNs](https://github.com/graphdeeplearning/benchmarking-gnns) to download the real-world benchmarks and train the PNA on them. In `real_world/README.md` we provide instructions for the generation and training hyperparameters tuned.
23 |
24 | 
25 |
26 | ## Reference
27 | ```
28 | @inproceedings{corso2020pna,
29 | title = {Principal Neighbourhood Aggregation for Graph Nets},
30 | author = {Corso, Gabriele and Cavalleri, Luca and Beaini, Dominique and Li\`{o}, Pietro and Veli\v{c}kovi\'{c}, Petar},
31 | booktitle = {Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
32 | year = {2020}
33 | }
34 | ```
35 |
36 | ## License
37 | MIT
38 |
39 |
40 | ## Acknowledgements
41 |
42 | The authors would like to thank Saro Passaro for running some of the tests presented in this repository and
43 | Giorgos Bouritsas, Fabrizio Frasca, Leonardo Cotta, Zhanghao Wu, Zhanqiu Zhang and George Watkins for pointing out some issues with the code.
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/data/HIV.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import time
2 | import dgl
3 | import torch
4 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
5 | from ogb.graphproppred import DglGraphPropPredDataset
6 | from ogb.graphproppred import Evaluator
7 | import torch.utils.data
8 |
9 |
10 | class HIVDGL(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
11 | def __init__(self, data, split):
12 | self.split = split
13 | self.data = [g for g in data[self.split]]
14 | self.graph_lists = []
15 | self.graph_labels = []
16 | for g in self.data:
17 | if g[0].number_of_nodes() > 5:
18 | self.graph_lists.append(g[0])
19 | self.graph_labels.append(g[1])
20 | self.n_samples = len(self.graph_lists)
21 |
22 | def __len__(self):
23 | """Return the number of graphs in the dataset."""
24 | return self.n_samples
25 |
26 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
27 | """
28 | Get the idx^th sample.
29 | Parameters
30 | ---------
31 | idx : int
32 | The sample index.
33 | Returns
34 | -------
35 | (dgl.DGLGraph, int)
36 | DGLGraph with node feature stored in `feat` field
37 | And its label.
38 | """
39 | return self.graph_lists[idx], self.graph_labels[idx]
40 |
41 |
42 | class HIVDataset(Dataset):
43 | def __init__(self, name, verbose=True):
44 | start = time.time()
45 | if verbose:
46 | print("[I] Loading dataset %s..." % (name))
47 | self.name = name
48 | self.dataset = DglGraphPropPredDataset(name = 'ogbg-molhiv')
49 | self.split_idx = self.dataset.get_idx_split()
50 |
51 | self.train = HIVDGL(self.dataset, self.split_idx['train'])
52 | self.val = HIVDGL(self.dataset, self.split_idx['valid'])
53 | self.test = HIVDGL(self.dataset, self.split_idx['test'])
54 |
55 | self.evaluator = Evaluator(name='ogbg-molhiv')
56 |
57 | if verbose:
58 | print('train, test, val sizes :', len(self.train), len(self.test), len(self.val))
59 | print("[I] Finished loading.")
60 | print("[I] Data load time: {:.4f}s".format(time.time() - start))
61 |
62 | # form a mini batch from a given list of samples = [(graph, label) pairs]
63 | def collate(self, samples):
64 | # The input samples is a list of pairs (graph, label).
65 | graphs, labels = map(list, zip(*samples))
66 | labels = torch.cat(labels).long()
67 | batched_graph = dgl.batch(graphs)
68 |
69 | return batched_graph, labels
70 |
71 | def _add_self_loops(self):
72 | # function for adding self loops
73 | # this function will be called only if self_loop flag is True
74 |
75 | self.train.graph_lists = [self_loop(g) for g in self.train.graph_lists]
76 | self.val.graph_lists = [self_loop(g) for g in self.val.graph_lists]
77 | self.test.graph_lists = [self_loop(g) for g in self.test.graph_lists]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/realworld_benchmark/docs/setup.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Benchmark setup
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |