├── .github
└── workflows
│ └── main.yml
├── .gitignore
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── efficientnet_pytorch
├── __init__.py
├── model.py
└── utils.py
├── examples
├── imagenet
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── data
│ │ └── README.md
│ └── main.py
└── simple
│ ├── check.ipynb
│ ├── example.ipynb
│ ├── img.jpg
│ ├── img2.jpg
│ └── labels_map.txt
├── hubconf.py
├── setup.py
├── sotabench.py
├── sotabench_setup.sh
├── tests
└── test_model.py
└── tf_to_pytorch
├── README.md
├── convert_tf_to_pt
├── download.sh
├── load_tf_weights.py
├── load_tf_weights_tf1.py
├── original_tf
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── efficientnet_builder.py
│ ├── efficientnet_model.py
│ ├── eval_ckpt_main.py
│ ├── eval_ckpt_main_tf1.py
│ ├── preprocessing.py
│ └── utils.py
├── rename.sh
└── run.sh
└── pretrained_tensorflow
└── download.sh
/.github/workflows/main.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: Workflow
2 |
3 | on:
4 | push:
5 | branches:
6 | - master
7 |
8 | jobs:
9 | pypi-job:
10 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
11 | steps:
12 | - uses: actions/checkout@v2
13 | - name: Install twine
14 | run: pip install twine
15 | - name: Build package
16 | run: python setup.py sdist
17 | - name: Publish a Python distribution to PyPI
18 | uses: pypa/gh-action-pypi-publish@release/v1
19 | with:
20 | user: __token__
21 | password: ${{ secrets.PYPI_API_TOKEN }}
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Custom
2 | tmp
3 | *.pkl
4 |
5 | # Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
6 | __pycache__/
7 | *.py[cod]
8 | *$py.class
9 |
10 | # C extensions
11 | *.so
12 |
13 | # Distribution / packaging
14 | .Python
15 | build/
16 | develop-eggs/
17 | dist/
18 | downloads/
19 | eggs/
20 | .eggs/
21 | lib/
22 | lib64/
23 | parts/
24 | sdist/
25 | var/
26 | wheels/
27 | *.egg-info/
28 | .installed.cfg
29 | *.egg
30 | MANIFEST
31 |
32 | # PyInstaller
33 | # Usually these files are written by a python script from a template
34 | # before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it.
35 | *.manifest
36 | *.spec
37 |
38 | # Installer logs
39 | pip-log.txt
40 | pip-delete-this-directory.txt
41 |
42 | # Unit test / coverage reports
43 | htmlcov/
44 | .tox/
45 | .coverage
46 | .coverage.*
47 | .cache
48 | nosetests.xml
49 | coverage.xml
50 | *.cover
51 | .hypothesis/
52 | .pytest_cache/
53 |
54 | # Translations
55 | *.mo
56 | *.pot
57 |
58 | # Django stuff:
59 | *.log
60 | local_settings.py
61 | db.sqlite3
62 |
63 | # Flask stuff:
64 | instance/
65 | .webassets-cache
66 |
67 | # Scrapy stuff:
68 | .scrapy
69 |
70 | # Sphinx documentation
71 | docs/_build/
72 |
73 | # PyBuilder
74 | target/
75 |
76 | # Jupyter Notebook
77 | .ipynb_checkpoints
78 |
79 | # pyenv
80 | .python-version
81 |
82 | # celery beat schedule file
83 | celerybeat-schedule
84 |
85 | # SageMath parsed files
86 | *.sage.py
87 |
88 | # Environments
89 | .env
90 | .venv
91 | env/
92 | venv/
93 | ENV/
94 | env.bak/
95 | venv.bak/
96 |
97 | # Spyder project settings
98 | .spyderproject
99 | .spyproject
100 |
101 | # Rope project settings
102 | .ropeproject
103 |
104 | # mkdocs documentation
105 | /site
106 |
107 | # mypy
108 | .mypy_cache/
109 | .DS_STORE
110 |
111 | # PyCharm
112 | .idea*
113 | *.xml
114 |
115 | # Custom
116 | tensorflow/
117 | example/test*
118 | *.pth*
119 | examples/imagenet/data/
120 | !examples/imagenet/data/README.md
121 | tmp
122 | tf_to_pytorch/pretrained_tensorflow
123 | !tf_to_pytorch/pretrained_tensorflow/download.sh
124 | examples/imagenet/run.sh
125 |
126 |
127 |
128 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | Apache License
3 | Version 2.0, January 2004
4 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/
5 |
6 | TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR USE, REPRODUCTION, AND DISTRIBUTION
7 |
8 | 1. Definitions.
9 |
10 | "License" shall mean the terms and conditions for use, reproduction,
11 | and distribution as defined by Sections 1 through 9 of this document.
12 |
13 | "Licensor" shall mean the copyright owner or entity authorized by
14 | the copyright owner that is granting the License.
15 |
16 | "Legal Entity" shall mean the union of the acting entity and all
17 | other entities that control, are controlled by, or are under common
18 | control with that entity. For the purposes of this definition,
19 | "control" means (i) the power, direct or indirect, to cause the
20 | direction or management of such entity, whether by contract or
21 | otherwise, or (ii) ownership of fifty percent (50%) or more of the
22 | outstanding shares, or (iii) beneficial ownership of such entity.
23 |
24 | "You" (or "Your") shall mean an individual or Legal Entity
25 | exercising permissions granted by this License.
26 |
27 | "Source" form shall mean the preferred form for making modifications,
28 | including but not limited to software source code, documentation
29 | source, and configuration files.
30 |
31 | "Object" form shall mean any form resulting from mechanical
32 | transformation or translation of a Source form, including but
33 | not limited to compiled object code, generated documentation,
34 | and conversions to other media types.
35 |
36 | "Work" shall mean the work of authorship, whether in Source or
37 | Object form, made available under the License, as indicated by a
38 | copyright notice that is included in or attached to the work
39 | (an example is provided in the Appendix below).
40 |
41 | "Derivative Works" shall mean any work, whether in Source or Object
42 | form, that is based on (or derived from) the Work and for which the
43 | editorial revisions, annotations, elaborations, or other modifications
44 | represent, as a whole, an original work of authorship. For the purposes
45 | of this License, Derivative Works shall not include works that remain
46 | separable from, or merely link (or bind by name) to the interfaces of,
47 | the Work and Derivative Works thereof.
48 |
49 | "Contribution" shall mean any work of authorship, including
50 | the original version of the Work and any modifications or additions
51 | to that Work or Derivative Works thereof, that is intentionally
52 | submitted to Licensor for inclusion in the Work by the copyright owner
53 | or by an individual or Legal Entity authorized to submit on behalf of
54 | the copyright owner. For the purposes of this definition, "submitted"
55 | means any form of electronic, verbal, or written communication sent
56 | to the Licensor or its representatives, including but not limited to
57 | communication on electronic mailing lists, source code control systems,
58 | and issue tracking systems that are managed by, or on behalf of, the
59 | Licensor for the purpose of discussing and improving the Work, but
60 | excluding communication that is conspicuously marked or otherwise
61 | designated in writing by the copyright owner as "Not a Contribution."
62 |
63 | "Contributor" shall mean Licensor and any individual or Legal Entity
64 | on behalf of whom a Contribution has been received by Licensor and
65 | subsequently incorporated within the Work.
66 |
67 | 2. Grant of Copyright License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
68 | this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
69 | worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
70 | copyright license to reproduce, prepare Derivative Works of,
71 | publicly display, publicly perform, sublicense, and distribute the
72 | Work and such Derivative Works in Source or Object form.
73 |
74 | 3. Grant of Patent License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
75 | this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
76 | worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
77 | (except as stated in this section) patent license to make, have made,
78 | use, offer to sell, sell, import, and otherwise transfer the Work,
79 | where such license applies only to those patent claims licensable
80 | by such Contributor that are necessarily infringed by their
81 | Contribution(s) alone or by combination of their Contribution(s)
82 | with the Work to which such Contribution(s) was submitted. If You
83 | institute patent litigation against any entity (including a
84 | cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that the Work
85 | or a Contribution incorporated within the Work constitutes direct
86 | or contributory patent infringement, then any patent licenses
87 | granted to You under this License for that Work shall terminate
88 | as of the date such litigation is filed.
89 |
90 | 4. Redistribution. You may reproduce and distribute copies of the
91 | Work or Derivative Works thereof in any medium, with or without
92 | modifications, and in Source or Object form, provided that You
93 | meet the following conditions:
94 |
95 | (a) You must give any other recipients of the Work or
96 | Derivative Works a copy of this License; and
97 |
98 | (b) You must cause any modified files to carry prominent notices
99 | stating that You changed the files; and
100 |
101 | (c) You must retain, in the Source form of any Derivative Works
102 | that You distribute, all copyright, patent, trademark, and
103 | attribution notices from the Source form of the Work,
104 | excluding those notices that do not pertain to any part of
105 | the Derivative Works; and
106 |
107 | (d) If the Work includes a "NOTICE" text file as part of its
108 | distribution, then any Derivative Works that You distribute must
109 | include a readable copy of the attribution notices contained
110 | within such NOTICE file, excluding those notices that do not
111 | pertain to any part of the Derivative Works, in at least one
112 | of the following places: within a NOTICE text file distributed
113 | as part of the Derivative Works; within the Source form or
114 | documentation, if provided along with the Derivative Works; or,
115 | within a display generated by the Derivative Works, if and
116 | wherever such third-party notices normally appear. The contents
117 | of the NOTICE file are for informational purposes only and
118 | do not modify the License. You may add Your own attribution
119 | notices within Derivative Works that You distribute, alongside
120 | or as an addendum to the NOTICE text from the Work, provided
121 | that such additional attribution notices cannot be construed
122 | as modifying the License.
123 |
124 | You may add Your own copyright statement to Your modifications and
125 | may provide additional or different license terms and conditions
126 | for use, reproduction, or distribution of Your modifications, or
127 | for any such Derivative Works as a whole, provided Your use,
128 | reproduction, and distribution of the Work otherwise complies with
129 | the conditions stated in this License.
130 |
131 | 5. Submission of Contributions. Unless You explicitly state otherwise,
132 | any Contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the Work
133 | by You to the Licensor shall be under the terms and conditions of
134 | this License, without any additional terms or conditions.
135 | Notwithstanding the above, nothing herein shall supersede or modify
136 | the terms of any separate license agreement you may have executed
137 | with Licensor regarding such Contributions.
138 |
139 | 6. Trademarks. This License does not grant permission to use the trade
140 | names, trademarks, service marks, or product names of the Licensor,
141 | except as required for reasonable and customary use in describing the
142 | origin of the Work and reproducing the content of the NOTICE file.
143 |
144 | 7. Disclaimer of Warranty. Unless required by applicable law or
145 | agreed to in writing, Licensor provides the Work (and each
146 | Contributor provides its Contributions) on an "AS IS" BASIS,
147 | WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or
148 | implied, including, without limitation, any warranties or conditions
149 | of TITLE, NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, or FITNESS FOR A
150 | PARTICULAR PURPOSE. You are solely responsible for determining the
151 | appropriateness of using or redistributing the Work and assume any
152 | risks associated with Your exercise of permissions under this License.
153 |
154 | 8. Limitation of Liability. In no event and under no legal theory,
155 | whether in tort (including negligence), contract, or otherwise,
156 | unless required by applicable law (such as deliberate and grossly
157 | negligent acts) or agreed to in writing, shall any Contributor be
158 | liable to You for damages, including any direct, indirect, special,
159 | incidental, or consequential damages of any character arising as a
160 | result of this License or out of the use or inability to use the
161 | Work (including but not limited to damages for loss of goodwill,
162 | work stoppage, computer failure or malfunction, or any and all
163 | other commercial damages or losses), even if such Contributor
164 | has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
165 |
166 | 9. Accepting Warranty or Additional Liability. While redistributing
167 | the Work or Derivative Works thereof, You may choose to offer,
168 | and charge a fee for, acceptance of support, warranty, indemnity,
169 | or other liability obligations and/or rights consistent with this
170 | License. However, in accepting such obligations, You may act only
171 | on Your own behalf and on Your sole responsibility, not on behalf
172 | of any other Contributor, and only if You agree to indemnify,
173 | defend, and hold each Contributor harmless for any liability
174 | incurred by, or claims asserted against, such Contributor by reason
175 | of your accepting any such warranty or additional liability.
176 |
177 | END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
178 |
179 | APPENDIX: How to apply the Apache License to your work.
180 |
181 | To apply the Apache License to your work, attach the following
182 | boilerplate notice, with the fields enclosed by brackets "[]"
183 | replaced with your own identifying information. (Don't include
184 | the brackets!) The text should be enclosed in the appropriate
185 | comment syntax for the file format. We also recommend that a
186 | file or class name and description of purpose be included on the
187 | same "printed page" as the copyright notice for easier
188 | identification within third-party archives.
189 |
190 | Copyright [yyyy] [name of copyright owner]
191 |
192 | Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
193 | you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
194 | You may obtain a copy of the License at
195 |
196 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
197 |
198 | Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
199 | distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
200 | WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
201 | See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
202 | limitations under the License.
203 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # EfficientNet PyTorch
2 |
3 | ### Quickstart
4 |
5 | Install with `pip install efficientnet_pytorch` and load a pretrained EfficientNet with:
6 | ```python
7 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet
8 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b0')
9 | ```
10 |
11 | ### Updates
12 |
13 | #### Update (April 2, 2021)
14 |
15 | The [EfficientNetV2 paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.00298) has been released! I am working on implementing it as you read this :)
16 |
17 | About EfficientNetV2:
18 | > EfficientNetV2 is a new family of convolutional networks that have faster training speed and better parameter efficiency than previous models. To develop this family of models, we use a combination of training-aware neural architecture search and scaling, to jointly optimize training speed and parameter efficiency. The models were searched from the search space enriched with new ops such as Fused-MBConv.
19 |
20 | Here is a comparison:
21 | >  22 |
23 |
24 | #### Update (Aug 25, 2020)
25 |
26 | This update adds:
27 | * A new `include_top` (default: `True`) option ([#208](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/208))
28 | * Continuous testing with [sotabench](https://sotabench.com/)
29 | * Code quality improvements and fixes ([#215](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/215) [#223](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/223))
30 |
31 | #### Update (May 14, 2020)
32 |
33 | This update adds comprehensive comments and documentation (thanks to @workingcoder).
34 |
35 | #### Update (January 23, 2020)
36 |
37 | This update adds a new category of pre-trained model based on adversarial training, called _advprop_. It is important to note that the preprocessing required for the advprop pretrained models is slightly different from normal ImageNet preprocessing. As a result, by default, advprop models are not used. To load a model with advprop, use:
38 | ```python
39 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained("efficientnet-b0", advprop=True)
40 | ```
41 | There is also a new, large `efficientnet-b8` pretrained model that is only available in advprop form. When using these models, replace ImageNet preprocessing code as follows:
42 | ```python
43 | if advprop: # for models using advprop pretrained weights
44 | normalize = transforms.Lambda(lambda img: img * 2.0 - 1.0)
45 | else:
46 | normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
47 | std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
48 | ```
49 | This update also addresses multiple other issues ([#115](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/115), [#128](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/128)).
50 |
51 | #### Update (October 15, 2019)
52 |
53 | This update allows you to choose whether to use a memory-efficient Swish activation. The memory-efficient version is chosen by default, but it cannot be used when exporting using PyTorch JIT. For this purpose, we have also included a standard (export-friendly) swish activation function. To switch to the export-friendly version, simply call `model.set_swish(memory_efficient=False)` after loading your desired model. This update addresses issues [#88](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/88) and [#89](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/89).
54 |
55 | #### Update (October 12, 2019)
56 |
57 | This update makes the Swish activation function more memory-efficient. It also addresses pull requests [#72](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/72), [#73](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/73), [#85](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/85), and [#86](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/86). Thanks to the authors of all the pull requests!
58 |
59 | #### Update (July 31, 2019)
60 |
61 | _Upgrade the pip package with_ `pip install --upgrade efficientnet-pytorch`
62 |
63 | The B6 and B7 models are now available. Additionally, _all_ pretrained models have been updated to use AutoAugment preprocessing, which translates to better performance across the board. Usage is the same as before:
64 | ```python
65 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet
66 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b7')
67 | ```
68 |
69 | #### Update (June 29, 2019)
70 |
71 | This update adds easy model exporting ([#20](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/20)) and feature extraction ([#38](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/38)).
72 |
73 | * [Example: Export to ONNX](#example-export)
74 | * [Example: Extract features](#example-feature-extraction)
75 | * Also: fixed a CUDA/CPU bug ([#32](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/32))
76 |
77 | It is also now incredibly simple to load a pretrained model with a new number of classes for transfer learning:
78 | ```python
79 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b1', num_classes=23)
80 | ```
81 |
82 |
83 | #### Update (June 23, 2019)
84 |
85 | The B4 and B5 models are now available. Their usage is identical to the other models:
86 | ```python
87 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet
88 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b4')
89 | ```
90 |
91 | ### Overview
92 | This repository contains an op-for-op PyTorch reimplementation of [EfficientNet](https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.11946), along with pre-trained models and examples.
93 |
94 | The goal of this implementation is to be simple, highly extensible, and easy to integrate into your own projects. This implementation is a work in progress -- new features are currently being implemented.
95 |
96 | At the moment, you can easily:
97 | * Load pretrained EfficientNet models
98 | * Use EfficientNet models for classification or feature extraction
99 | * Evaluate EfficientNet models on ImageNet or your own images
100 |
101 | _Upcoming features_: In the next few days, you will be able to:
102 | * Train new models from scratch on ImageNet with a simple command
103 | * Quickly finetune an EfficientNet on your own dataset
104 | * Export EfficientNet models for production
105 |
106 | ### Table of contents
107 | 1. [About EfficientNet](#about-efficientnet)
108 | 2. [About EfficientNet-PyTorch](#about-efficientnet-pytorch)
109 | 3. [Installation](#installation)
110 | 4. [Usage](#usage)
111 | * [Load pretrained models](#loading-pretrained-models)
112 | * [Example: Classify](#example-classification)
113 | * [Example: Extract features](#example-feature-extraction)
114 | * [Example: Export to ONNX](#example-export)
115 | 6. [Contributing](#contributing)
116 |
117 | ### About EfficientNet
118 |
119 | If you're new to EfficientNets, here is an explanation straight from the official TensorFlow implementation:
120 |
121 | EfficientNets are a family of image classification models, which achieve state-of-the-art accuracy, yet being an order-of-magnitude smaller and faster than previous models. We develop EfficientNets based on AutoML and Compound Scaling. In particular, we first use [AutoML Mobile framework](https://ai.googleblog.com/2018/08/mnasnet-towards-automating-design-of.html) to develop a mobile-size baseline network, named as EfficientNet-B0; Then, we use the compound scaling method to scale up this baseline to obtain EfficientNet-B1 to B7.
122 |
123 |
22 |
23 |
24 | #### Update (Aug 25, 2020)
25 |
26 | This update adds:
27 | * A new `include_top` (default: `True`) option ([#208](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/208))
28 | * Continuous testing with [sotabench](https://sotabench.com/)
29 | * Code quality improvements and fixes ([#215](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/215) [#223](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/223))
30 |
31 | #### Update (May 14, 2020)
32 |
33 | This update adds comprehensive comments and documentation (thanks to @workingcoder).
34 |
35 | #### Update (January 23, 2020)
36 |
37 | This update adds a new category of pre-trained model based on adversarial training, called _advprop_. It is important to note that the preprocessing required for the advprop pretrained models is slightly different from normal ImageNet preprocessing. As a result, by default, advprop models are not used. To load a model with advprop, use:
38 | ```python
39 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained("efficientnet-b0", advprop=True)
40 | ```
41 | There is also a new, large `efficientnet-b8` pretrained model that is only available in advprop form. When using these models, replace ImageNet preprocessing code as follows:
42 | ```python
43 | if advprop: # for models using advprop pretrained weights
44 | normalize = transforms.Lambda(lambda img: img * 2.0 - 1.0)
45 | else:
46 | normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
47 | std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
48 | ```
49 | This update also addresses multiple other issues ([#115](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/115), [#128](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/128)).
50 |
51 | #### Update (October 15, 2019)
52 |
53 | This update allows you to choose whether to use a memory-efficient Swish activation. The memory-efficient version is chosen by default, but it cannot be used when exporting using PyTorch JIT. For this purpose, we have also included a standard (export-friendly) swish activation function. To switch to the export-friendly version, simply call `model.set_swish(memory_efficient=False)` after loading your desired model. This update addresses issues [#88](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/88) and [#89](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/89).
54 |
55 | #### Update (October 12, 2019)
56 |
57 | This update makes the Swish activation function more memory-efficient. It also addresses pull requests [#72](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/72), [#73](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/73), [#85](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/85), and [#86](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/86). Thanks to the authors of all the pull requests!
58 |
59 | #### Update (July 31, 2019)
60 |
61 | _Upgrade the pip package with_ `pip install --upgrade efficientnet-pytorch`
62 |
63 | The B6 and B7 models are now available. Additionally, _all_ pretrained models have been updated to use AutoAugment preprocessing, which translates to better performance across the board. Usage is the same as before:
64 | ```python
65 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet
66 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b7')
67 | ```
68 |
69 | #### Update (June 29, 2019)
70 |
71 | This update adds easy model exporting ([#20](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/20)) and feature extraction ([#38](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/38)).
72 |
73 | * [Example: Export to ONNX](#example-export)
74 | * [Example: Extract features](#example-feature-extraction)
75 | * Also: fixed a CUDA/CPU bug ([#32](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/32))
76 |
77 | It is also now incredibly simple to load a pretrained model with a new number of classes for transfer learning:
78 | ```python
79 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b1', num_classes=23)
80 | ```
81 |
82 |
83 | #### Update (June 23, 2019)
84 |
85 | The B4 and B5 models are now available. Their usage is identical to the other models:
86 | ```python
87 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet
88 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b4')
89 | ```
90 |
91 | ### Overview
92 | This repository contains an op-for-op PyTorch reimplementation of [EfficientNet](https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.11946), along with pre-trained models and examples.
93 |
94 | The goal of this implementation is to be simple, highly extensible, and easy to integrate into your own projects. This implementation is a work in progress -- new features are currently being implemented.
95 |
96 | At the moment, you can easily:
97 | * Load pretrained EfficientNet models
98 | * Use EfficientNet models for classification or feature extraction
99 | * Evaluate EfficientNet models on ImageNet or your own images
100 |
101 | _Upcoming features_: In the next few days, you will be able to:
102 | * Train new models from scratch on ImageNet with a simple command
103 | * Quickly finetune an EfficientNet on your own dataset
104 | * Export EfficientNet models for production
105 |
106 | ### Table of contents
107 | 1. [About EfficientNet](#about-efficientnet)
108 | 2. [About EfficientNet-PyTorch](#about-efficientnet-pytorch)
109 | 3. [Installation](#installation)
110 | 4. [Usage](#usage)
111 | * [Load pretrained models](#loading-pretrained-models)
112 | * [Example: Classify](#example-classification)
113 | * [Example: Extract features](#example-feature-extraction)
114 | * [Example: Export to ONNX](#example-export)
115 | 6. [Contributing](#contributing)
116 |
117 | ### About EfficientNet
118 |
119 | If you're new to EfficientNets, here is an explanation straight from the official TensorFlow implementation:
120 |
121 | EfficientNets are a family of image classification models, which achieve state-of-the-art accuracy, yet being an order-of-magnitude smaller and faster than previous models. We develop EfficientNets based on AutoML and Compound Scaling. In particular, we first use [AutoML Mobile framework](https://ai.googleblog.com/2018/08/mnasnet-towards-automating-design-of.html) to develop a mobile-size baseline network, named as EfficientNet-B0; Then, we use the compound scaling method to scale up this baseline to obtain EfficientNet-B1 to B7.
122 |
123 |
124 |
125 |
126 | 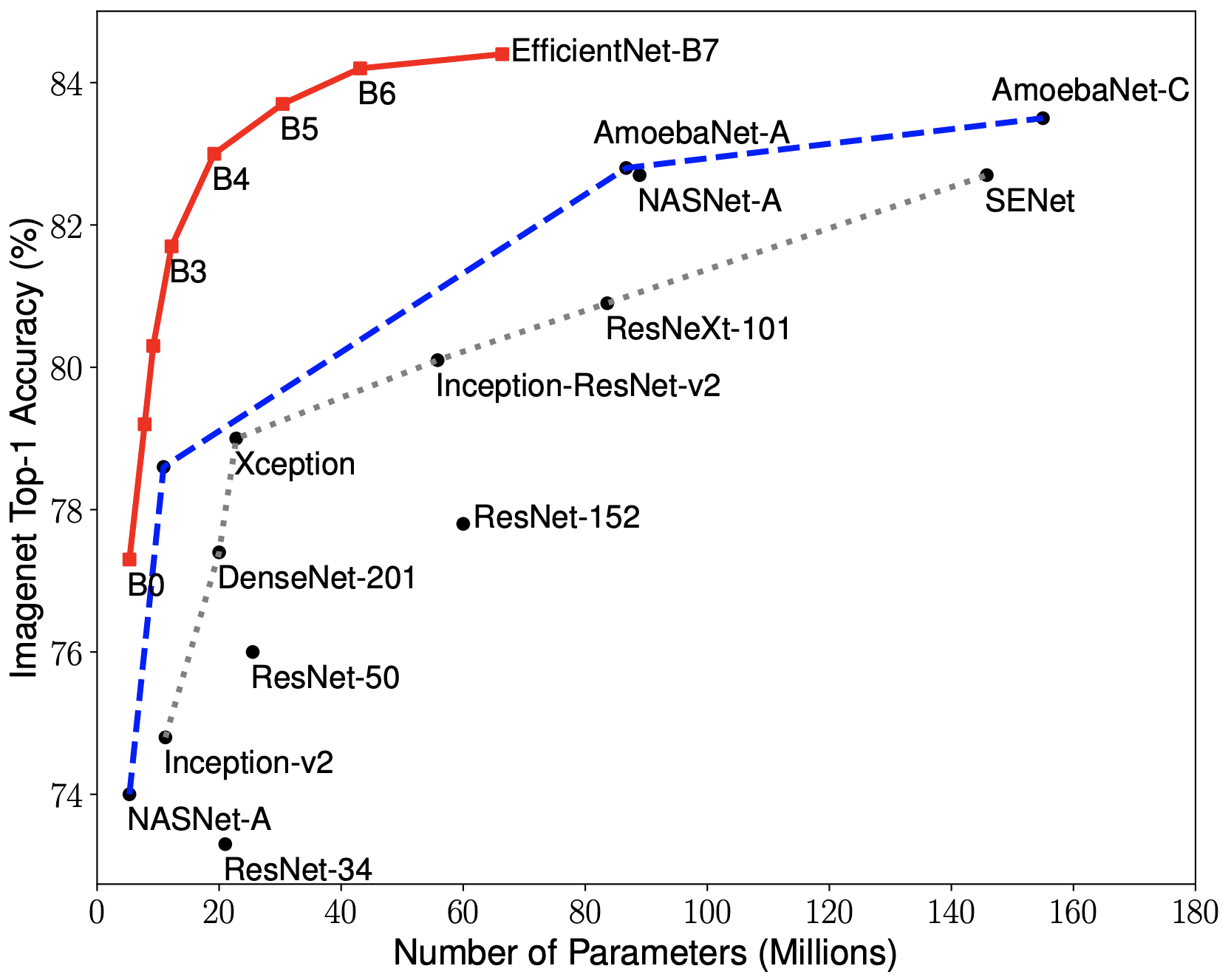 127 |
127 | |
128 |
129 | 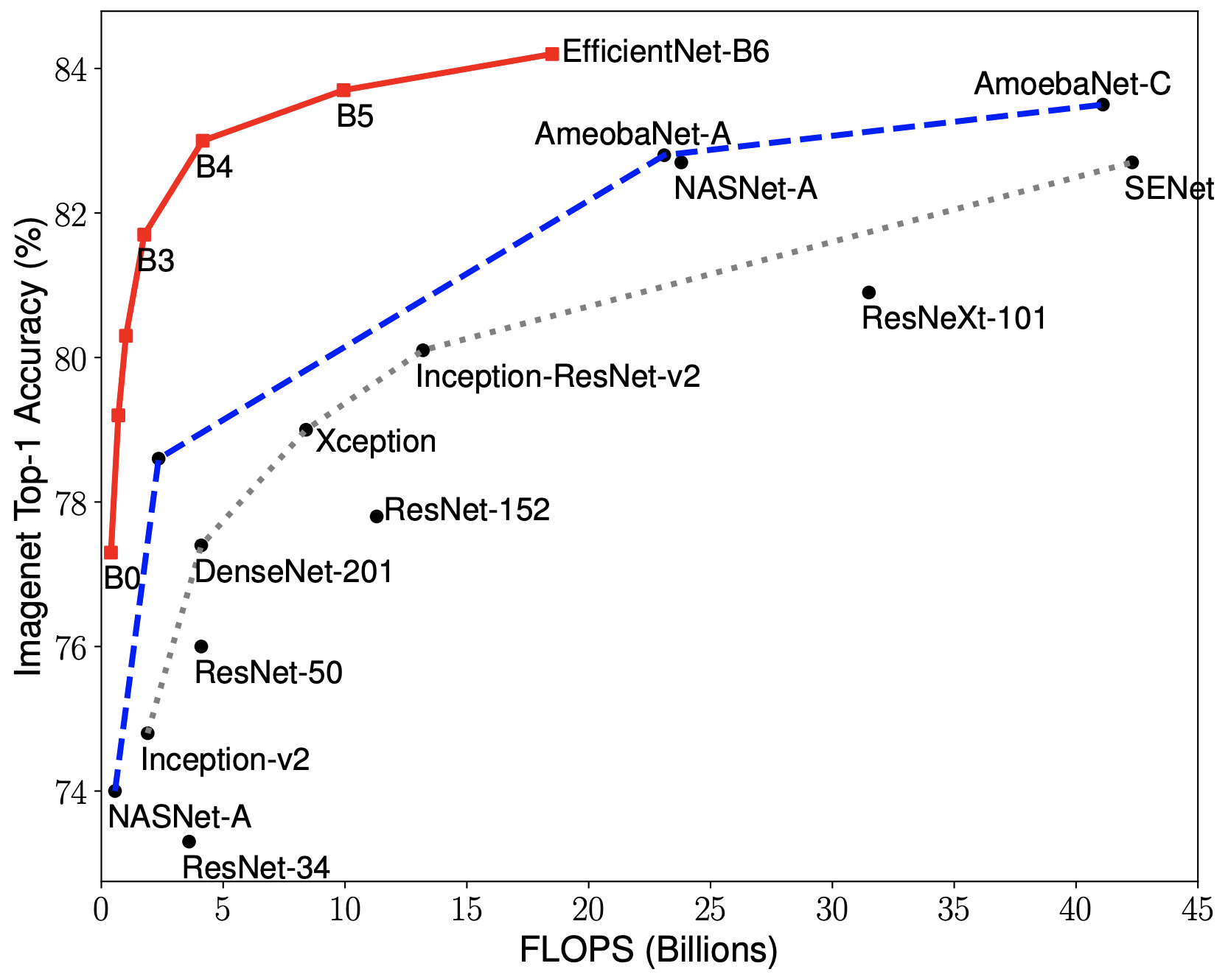 130 |
130 | |
131 |
132 |
133 |
134 | EfficientNets achieve state-of-the-art accuracy on ImageNet with an order of magnitude better efficiency:
135 |
136 |
137 | * In high-accuracy regime, our EfficientNet-B7 achieves state-of-the-art 84.4% top-1 / 97.1% top-5 accuracy on ImageNet with 66M parameters and 37B FLOPS, being 8.4x smaller and 6.1x faster on CPU inference than previous best [Gpipe](https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.06965).
138 |
139 | * In middle-accuracy regime, our EfficientNet-B1 is 7.6x smaller and 5.7x faster on CPU inference than [ResNet-152](https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385), with similar ImageNet accuracy.
140 |
141 | * Compared with the widely used [ResNet-50](https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385), our EfficientNet-B4 improves the top-1 accuracy from 76.3% of ResNet-50 to 82.6% (+6.3%), under similar FLOPS constraint.
142 |
143 | ### About EfficientNet PyTorch
144 |
145 | EfficientNet PyTorch is a PyTorch re-implementation of EfficientNet. It is consistent with the [original TensorFlow implementation](https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/tree/master/models/official/efficientnet), such that it is easy to load weights from a TensorFlow checkpoint. At the same time, we aim to make our PyTorch implementation as simple, flexible, and extensible as possible.
146 |
147 | If you have any feature requests or questions, feel free to leave them as GitHub issues!
148 |
149 | ### Installation
150 |
151 | Install via pip:
152 | ```bash
153 | pip install efficientnet_pytorch
154 | ```
155 |
156 | Or install from source:
157 | ```bash
158 | git clone https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch
159 | cd EfficientNet-Pytorch
160 | pip install -e .
161 | ```
162 |
163 | ### Usage
164 |
165 | #### Loading pretrained models
166 |
167 | Load an EfficientNet:
168 | ```python
169 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet
170 | model = EfficientNet.from_name('efficientnet-b0')
171 | ```
172 |
173 | Load a pretrained EfficientNet:
174 | ```python
175 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet
176 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b0')
177 | ```
178 |
179 | Details about the models are below:
180 |
181 | | *Name* |*# Params*|*Top-1 Acc.*|*Pretrained?*|
182 | |:-----------------:|:--------:|:----------:|:-----------:|
183 | | `efficientnet-b0` | 5.3M | 76.3 | ✓ |
184 | | `efficientnet-b1` | 7.8M | 78.8 | ✓ |
185 | | `efficientnet-b2` | 9.2M | 79.8 | ✓ |
186 | | `efficientnet-b3` | 12M | 81.1 | ✓ |
187 | | `efficientnet-b4` | 19M | 82.6 | ✓ |
188 | | `efficientnet-b5` | 30M | 83.3 | ✓ |
189 | | `efficientnet-b6` | 43M | 84.0 | ✓ |
190 | | `efficientnet-b7` | 66M | 84.4 | ✓ |
191 |
192 |
193 | #### Example: Classification
194 |
195 | Below is a simple, complete example. It may also be found as a jupyter notebook in `examples/simple` or as a [Colab Notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1Jw28xZ1NJq4Cja4jLe6tJ6_F5lCzElb4).
196 |
197 | We assume that in your current directory, there is a `img.jpg` file and a `labels_map.txt` file (ImageNet class names). These are both included in `examples/simple`.
198 |
199 | ```python
200 | import json
201 | from PIL import Image
202 | import torch
203 | from torchvision import transforms
204 |
205 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet
206 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b0')
207 |
208 | # Preprocess image
209 | tfms = transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize(224), transforms.ToTensor(),
210 | transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),])
211 | img = tfms(Image.open('img.jpg')).unsqueeze(0)
212 | print(img.shape) # torch.Size([1, 3, 224, 224])
213 |
214 | # Load ImageNet class names
215 | labels_map = json.load(open('labels_map.txt'))
216 | labels_map = [labels_map[str(i)] for i in range(1000)]
217 |
218 | # Classify
219 | model.eval()
220 | with torch.no_grad():
221 | outputs = model(img)
222 |
223 | # Print predictions
224 | print('-----')
225 | for idx in torch.topk(outputs, k=5).indices.squeeze(0).tolist():
226 | prob = torch.softmax(outputs, dim=1)[0, idx].item()
227 | print('{label:<75} ({p:.2f}%)'.format(label=labels_map[idx], p=prob*100))
228 | ```
229 |
230 | #### Example: Feature Extraction
231 |
232 | You can easily extract features with `model.extract_features`:
233 | ```python
234 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet
235 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b0')
236 |
237 | # ... image preprocessing as in the classification example ...
238 | print(img.shape) # torch.Size([1, 3, 224, 224])
239 |
240 | features = model.extract_features(img)
241 | print(features.shape) # torch.Size([1, 1280, 7, 7])
242 | ```
243 |
244 | #### Example: Export to ONNX
245 |
246 | Exporting to ONNX for deploying to production is now simple:
247 | ```python
248 | import torch
249 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet
250 |
251 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b1')
252 | dummy_input = torch.randn(10, 3, 240, 240)
253 |
254 | model.set_swish(memory_efficient=False)
255 | torch.onnx.export(model, dummy_input, "test-b1.onnx", verbose=True)
256 | ```
257 |
258 | [Here](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1rOAEXeXHaA8uo3aG2YcFDHItlRJMV0VP) is a Colab example.
259 |
260 |
261 | #### ImageNet
262 |
263 | See `examples/imagenet` for details about evaluating on ImageNet.
264 |
265 | ### Contributing
266 |
267 | If you find a bug, create a GitHub issue, or even better, submit a pull request. Similarly, if you have questions, simply post them as GitHub issues.
268 |
269 | I look forward to seeing what the community does with these models!
270 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/efficientnet_pytorch/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | __version__ = "0.7.1"
2 | from .model import EfficientNet, VALID_MODELS
3 | from .utils import (
4 | GlobalParams,
5 | BlockArgs,
6 | BlockDecoder,
7 | efficientnet,
8 | get_model_params,
9 | )
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/efficientnet_pytorch/model.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """model.py - Model and module class for EfficientNet.
2 | They are built to mirror those in the official TensorFlow implementation.
3 | """
4 |
5 | # Author: lukemelas (github username)
6 | # Github repo: https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch
7 | # With adjustments and added comments by workingcoder (github username).
8 |
9 | import torch
10 | from torch import nn
11 | from torch.nn import functional as F
12 | from .utils import (
13 | round_filters,
14 | round_repeats,
15 | drop_connect,
16 | get_same_padding_conv2d,
17 | get_model_params,
18 | efficientnet_params,
19 | load_pretrained_weights,
20 | Swish,
21 | MemoryEfficientSwish,
22 | calculate_output_image_size
23 | )
24 |
25 |
26 | VALID_MODELS = (
27 | 'efficientnet-b0', 'efficientnet-b1', 'efficientnet-b2', 'efficientnet-b3',
28 | 'efficientnet-b4', 'efficientnet-b5', 'efficientnet-b6', 'efficientnet-b7',
29 | 'efficientnet-b8',
30 |
31 | # Support the construction of 'efficientnet-l2' without pretrained weights
32 | 'efficientnet-l2'
33 | )
34 |
35 |
36 | class MBConvBlock(nn.Module):
37 | """Mobile Inverted Residual Bottleneck Block.
38 |
39 | Args:
40 | block_args (namedtuple): BlockArgs, defined in utils.py.
41 | global_params (namedtuple): GlobalParam, defined in utils.py.
42 | image_size (tuple or list): [image_height, image_width].
43 |
44 | References:
45 | [1] https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861 (MobileNet v1)
46 | [2] https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.04381 (MobileNet v2)
47 | [3] https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.02244 (MobileNet v3)
48 | """
49 |
50 | def __init__(self, block_args, global_params, image_size=None):
51 | super().__init__()
52 | self._block_args = block_args
53 | self._bn_mom = 1 - global_params.batch_norm_momentum # pytorch's difference from tensorflow
54 | self._bn_eps = global_params.batch_norm_epsilon
55 | self.has_se = (self._block_args.se_ratio is not None) and (0 < self._block_args.se_ratio <= 1)
56 | self.id_skip = block_args.id_skip # whether to use skip connection and drop connect
57 |
58 | # Expansion phase (Inverted Bottleneck)
59 | inp = self._block_args.input_filters # number of input channels
60 | oup = self._block_args.input_filters * self._block_args.expand_ratio # number of output channels
61 | if self._block_args.expand_ratio != 1:
62 | Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=image_size)
63 | self._expand_conv = Conv2d(in_channels=inp, out_channels=oup, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
64 | self._bn0 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=oup, momentum=self._bn_mom, eps=self._bn_eps)
65 | # image_size = calculate_output_image_size(image_size, 1) <-- this wouldn't modify image_size
66 |
67 | # Depthwise convolution phase
68 | k = self._block_args.kernel_size
69 | s = self._block_args.stride
70 | Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=image_size)
71 | self._depthwise_conv = Conv2d(
72 | in_channels=oup, out_channels=oup, groups=oup, # groups makes it depthwise
73 | kernel_size=k, stride=s, bias=False)
74 | self._bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=oup, momentum=self._bn_mom, eps=self._bn_eps)
75 | image_size = calculate_output_image_size(image_size, s)
76 |
77 | # Squeeze and Excitation layer, if desired
78 | if self.has_se:
79 | Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=(1, 1))
80 | num_squeezed_channels = max(1, int(self._block_args.input_filters * self._block_args.se_ratio))
81 | self._se_reduce = Conv2d(in_channels=oup, out_channels=num_squeezed_channels, kernel_size=1)
82 | self._se_expand = Conv2d(in_channels=num_squeezed_channels, out_channels=oup, kernel_size=1)
83 |
84 | # Pointwise convolution phase
85 | final_oup = self._block_args.output_filters
86 | Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=image_size)
87 | self._project_conv = Conv2d(in_channels=oup, out_channels=final_oup, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
88 | self._bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=final_oup, momentum=self._bn_mom, eps=self._bn_eps)
89 | self._swish = MemoryEfficientSwish()
90 |
91 | def forward(self, inputs, drop_connect_rate=None):
92 | """MBConvBlock's forward function.
93 |
94 | Args:
95 | inputs (tensor): Input tensor.
96 | drop_connect_rate (bool): Drop connect rate (float, between 0 and 1).
97 |
98 | Returns:
99 | Output of this block after processing.
100 | """
101 |
102 | # Expansion and Depthwise Convolution
103 | x = inputs
104 | if self._block_args.expand_ratio != 1:
105 | x = self._expand_conv(inputs)
106 | x = self._bn0(x)
107 | x = self._swish(x)
108 |
109 | x = self._depthwise_conv(x)
110 | x = self._bn1(x)
111 | x = self._swish(x)
112 |
113 | # Squeeze and Excitation
114 | if self.has_se:
115 | x_squeezed = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, 1)
116 | x_squeezed = self._se_reduce(x_squeezed)
117 | x_squeezed = self._swish(x_squeezed)
118 | x_squeezed = self._se_expand(x_squeezed)
119 | x = torch.sigmoid(x_squeezed) * x
120 |
121 | # Pointwise Convolution
122 | x = self._project_conv(x)
123 | x = self._bn2(x)
124 |
125 | # Skip connection and drop connect
126 | input_filters, output_filters = self._block_args.input_filters, self._block_args.output_filters
127 | if self.id_skip and self._block_args.stride == 1 and input_filters == output_filters:
128 | # The combination of skip connection and drop connect brings about stochastic depth.
129 | if drop_connect_rate:
130 | x = drop_connect(x, p=drop_connect_rate, training=self.training)
131 | x = x + inputs # skip connection
132 | return x
133 |
134 | def set_swish(self, memory_efficient=True):
135 | """Sets swish function as memory efficient (for training) or standard (for export).
136 |
137 | Args:
138 | memory_efficient (bool): Whether to use memory-efficient version of swish.
139 | """
140 | self._swish = MemoryEfficientSwish() if memory_efficient else Swish()
141 |
142 |
143 | class EfficientNet(nn.Module):
144 | """EfficientNet model.
145 | Most easily loaded with the .from_name or .from_pretrained methods.
146 |
147 | Args:
148 | blocks_args (list[namedtuple]): A list of BlockArgs to construct blocks.
149 | global_params (namedtuple): A set of GlobalParams shared between blocks.
150 |
151 | References:
152 | [1] https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.11946 (EfficientNet)
153 |
154 | Example:
155 | >>> import torch
156 | >>> from efficientnet.model import EfficientNet
157 | >>> inputs = torch.rand(1, 3, 224, 224)
158 | >>> model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b0')
159 | >>> model.eval()
160 | >>> outputs = model(inputs)
161 | """
162 |
163 | def __init__(self, blocks_args=None, global_params=None):
164 | super().__init__()
165 | assert isinstance(blocks_args, list), 'blocks_args should be a list'
166 | assert len(blocks_args) > 0, 'block args must be greater than 0'
167 | self._global_params = global_params
168 | self._blocks_args = blocks_args
169 |
170 | # Batch norm parameters
171 | bn_mom = 1 - self._global_params.batch_norm_momentum
172 | bn_eps = self._global_params.batch_norm_epsilon
173 |
174 | # Get stem static or dynamic convolution depending on image size
175 | image_size = global_params.image_size
176 | Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=image_size)
177 |
178 | # Stem
179 | in_channels = 3 # rgb
180 | out_channels = round_filters(32, self._global_params) # number of output channels
181 | self._conv_stem = Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=2, bias=False)
182 | self._bn0 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels, momentum=bn_mom, eps=bn_eps)
183 | image_size = calculate_output_image_size(image_size, 2)
184 |
185 | # Build blocks
186 | self._blocks = nn.ModuleList([])
187 | for block_args in self._blocks_args:
188 |
189 | # Update block input and output filters based on depth multiplier.
190 | block_args = block_args._replace(
191 | input_filters=round_filters(block_args.input_filters, self._global_params),
192 | output_filters=round_filters(block_args.output_filters, self._global_params),
193 | num_repeat=round_repeats(block_args.num_repeat, self._global_params)
194 | )
195 |
196 | # The first block needs to take care of stride and filter size increase.
197 | self._blocks.append(MBConvBlock(block_args, self._global_params, image_size=image_size))
198 | image_size = calculate_output_image_size(image_size, block_args.stride)
199 | if block_args.num_repeat > 1: # modify block_args to keep same output size
200 | block_args = block_args._replace(input_filters=block_args.output_filters, stride=1)
201 | for _ in range(block_args.num_repeat - 1):
202 | self._blocks.append(MBConvBlock(block_args, self._global_params, image_size=image_size))
203 | # image_size = calculate_output_image_size(image_size, block_args.stride) # stride = 1
204 |
205 | # Head
206 | in_channels = block_args.output_filters # output of final block
207 | out_channels = round_filters(1280, self._global_params)
208 | Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=image_size)
209 | self._conv_head = Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
210 | self._bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels, momentum=bn_mom, eps=bn_eps)
211 |
212 | # Final linear layer
213 | self._avg_pooling = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
214 | if self._global_params.include_top:
215 | self._dropout = nn.Dropout(self._global_params.dropout_rate)
216 | self._fc = nn.Linear(out_channels, self._global_params.num_classes)
217 |
218 | # set activation to memory efficient swish by default
219 | self._swish = MemoryEfficientSwish()
220 |
221 | def set_swish(self, memory_efficient=True):
222 | """Sets swish function as memory efficient (for training) or standard (for export).
223 |
224 | Args:
225 | memory_efficient (bool): Whether to use memory-efficient version of swish.
226 | """
227 | self._swish = MemoryEfficientSwish() if memory_efficient else Swish()
228 | for block in self._blocks:
229 | block.set_swish(memory_efficient)
230 |
231 | def extract_endpoints(self, inputs):
232 | """Use convolution layer to extract features
233 | from reduction levels i in [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].
234 |
235 | Args:
236 | inputs (tensor): Input tensor.
237 |
238 | Returns:
239 | Dictionary of last intermediate features
240 | with reduction levels i in [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].
241 | Example:
242 | >>> import torch
243 | >>> from efficientnet.model import EfficientNet
244 | >>> inputs = torch.rand(1, 3, 224, 224)
245 | >>> model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b0')
246 | >>> endpoints = model.extract_endpoints(inputs)
247 | >>> print(endpoints['reduction_1'].shape) # torch.Size([1, 16, 112, 112])
248 | >>> print(endpoints['reduction_2'].shape) # torch.Size([1, 24, 56, 56])
249 | >>> print(endpoints['reduction_3'].shape) # torch.Size([1, 40, 28, 28])
250 | >>> print(endpoints['reduction_4'].shape) # torch.Size([1, 112, 14, 14])
251 | >>> print(endpoints['reduction_5'].shape) # torch.Size([1, 320, 7, 7])
252 | >>> print(endpoints['reduction_6'].shape) # torch.Size([1, 1280, 7, 7])
253 | """
254 | endpoints = dict()
255 |
256 | # Stem
257 | x = self._swish(self._bn0(self._conv_stem(inputs)))
258 | prev_x = x
259 |
260 | # Blocks
261 | for idx, block in enumerate(self._blocks):
262 | drop_connect_rate = self._global_params.drop_connect_rate
263 | if drop_connect_rate:
264 | drop_connect_rate *= float(idx) / len(self._blocks) # scale drop connect_rate
265 | x = block(x, drop_connect_rate=drop_connect_rate)
266 | if prev_x.size(2) > x.size(2):
267 | endpoints['reduction_{}'.format(len(endpoints) + 1)] = prev_x
268 | elif idx == len(self._blocks) - 1:
269 | endpoints['reduction_{}'.format(len(endpoints) + 1)] = x
270 | prev_x = x
271 |
272 | # Head
273 | x = self._swish(self._bn1(self._conv_head(x)))
274 | endpoints['reduction_{}'.format(len(endpoints) + 1)] = x
275 |
276 | return endpoints
277 |
278 | def extract_features(self, inputs):
279 | """use convolution layer to extract feature .
280 |
281 | Args:
282 | inputs (tensor): Input tensor.
283 |
284 | Returns:
285 | Output of the final convolution
286 | layer in the efficientnet model.
287 | """
288 | # Stem
289 | x = self._swish(self._bn0(self._conv_stem(inputs)))
290 |
291 | # Blocks
292 | for idx, block in enumerate(self._blocks):
293 | drop_connect_rate = self._global_params.drop_connect_rate
294 | if drop_connect_rate:
295 | drop_connect_rate *= float(idx) / len(self._blocks) # scale drop connect_rate
296 | x = block(x, drop_connect_rate=drop_connect_rate)
297 |
298 | # Head
299 | x = self._swish(self._bn1(self._conv_head(x)))
300 |
301 | return x
302 |
303 | def forward(self, inputs):
304 | """EfficientNet's forward function.
305 | Calls extract_features to extract features, applies final linear layer, and returns logits.
306 |
307 | Args:
308 | inputs (tensor): Input tensor.
309 |
310 | Returns:
311 | Output of this model after processing.
312 | """
313 | # Convolution layers
314 | x = self.extract_features(inputs)
315 | # Pooling and final linear layer
316 | x = self._avg_pooling(x)
317 | if self._global_params.include_top:
318 | x = x.flatten(start_dim=1)
319 | x = self._dropout(x)
320 | x = self._fc(x)
321 | return x
322 |
323 | @classmethod
324 | def from_name(cls, model_name, in_channels=3, **override_params):
325 | """Create an efficientnet model according to name.
326 |
327 | Args:
328 | model_name (str): Name for efficientnet.
329 | in_channels (int): Input data's channel number.
330 | override_params (other key word params):
331 | Params to override model's global_params.
332 | Optional key:
333 | 'width_coefficient', 'depth_coefficient',
334 | 'image_size', 'dropout_rate',
335 | 'num_classes', 'batch_norm_momentum',
336 | 'batch_norm_epsilon', 'drop_connect_rate',
337 | 'depth_divisor', 'min_depth'
338 |
339 | Returns:
340 | An efficientnet model.
341 | """
342 | cls._check_model_name_is_valid(model_name)
343 | blocks_args, global_params = get_model_params(model_name, override_params)
344 | model = cls(blocks_args, global_params)
345 | model._change_in_channels(in_channels)
346 | return model
347 |
348 | @classmethod
349 | def from_pretrained(cls, model_name, weights_path=None, advprop=False,
350 | in_channels=3, num_classes=1000, **override_params):
351 | """Create an efficientnet model according to name.
352 |
353 | Args:
354 | model_name (str): Name for efficientnet.
355 | weights_path (None or str):
356 | str: path to pretrained weights file on the local disk.
357 | None: use pretrained weights downloaded from the Internet.
358 | advprop (bool):
359 | Whether to load pretrained weights
360 | trained with advprop (valid when weights_path is None).
361 | in_channels (int): Input data's channel number.
362 | num_classes (int):
363 | Number of categories for classification.
364 | It controls the output size for final linear layer.
365 | override_params (other key word params):
366 | Params to override model's global_params.
367 | Optional key:
368 | 'width_coefficient', 'depth_coefficient',
369 | 'image_size', 'dropout_rate',
370 | 'batch_norm_momentum',
371 | 'batch_norm_epsilon', 'drop_connect_rate',
372 | 'depth_divisor', 'min_depth'
373 |
374 | Returns:
375 | A pretrained efficientnet model.
376 | """
377 | model = cls.from_name(model_name, num_classes=num_classes, **override_params)
378 | load_pretrained_weights(model, model_name, weights_path=weights_path,
379 | load_fc=(num_classes == 1000), advprop=advprop)
380 | model._change_in_channels(in_channels)
381 | return model
382 |
383 | @classmethod
384 | def get_image_size(cls, model_name):
385 | """Get the input image size for a given efficientnet model.
386 |
387 | Args:
388 | model_name (str): Name for efficientnet.
389 |
390 | Returns:
391 | Input image size (resolution).
392 | """
393 | cls._check_model_name_is_valid(model_name)
394 | _, _, res, _ = efficientnet_params(model_name)
395 | return res
396 |
397 | @classmethod
398 | def _check_model_name_is_valid(cls, model_name):
399 | """Validates model name.
400 |
401 | Args:
402 | model_name (str): Name for efficientnet.
403 |
404 | Returns:
405 | bool: Is a valid name or not.
406 | """
407 | if model_name not in VALID_MODELS:
408 | raise ValueError('model_name should be one of: ' + ', '.join(VALID_MODELS))
409 |
410 | def _change_in_channels(self, in_channels):
411 | """Adjust model's first convolution layer to in_channels, if in_channels not equals 3.
412 |
413 | Args:
414 | in_channels (int): Input data's channel number.
415 | """
416 | if in_channels != 3:
417 | Conv2d = get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=self._global_params.image_size)
418 | out_channels = round_filters(32, self._global_params)
419 | self._conv_stem = Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=2, bias=False)
420 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/efficientnet_pytorch/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """utils.py - Helper functions for building the model and for loading model parameters.
2 | These helper functions are built to mirror those in the official TensorFlow implementation.
3 | """
4 |
5 | # Author: lukemelas (github username)
6 | # Github repo: https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch
7 | # With adjustments and added comments by workingcoder (github username).
8 |
9 | import re
10 | import math
11 | import collections
12 | from functools import partial
13 | import torch
14 | from torch import nn
15 | from torch.nn import functional as F
16 | from torch.utils import model_zoo
17 |
18 |
19 | ################################################################################
20 | # Help functions for model architecture
21 | ################################################################################
22 |
23 | # GlobalParams and BlockArgs: Two namedtuples
24 | # Swish and MemoryEfficientSwish: Two implementations of the method
25 | # round_filters and round_repeats:
26 | # Functions to calculate params for scaling model width and depth ! ! !
27 | # get_width_and_height_from_size and calculate_output_image_size
28 | # drop_connect: A structural design
29 | # get_same_padding_conv2d:
30 | # Conv2dDynamicSamePadding
31 | # Conv2dStaticSamePadding
32 | # get_same_padding_maxPool2d:
33 | # MaxPool2dDynamicSamePadding
34 | # MaxPool2dStaticSamePadding
35 | # It's an additional function, not used in EfficientNet,
36 | # but can be used in other model (such as EfficientDet).
37 |
38 | # Parameters for the entire model (stem, all blocks, and head)
39 | GlobalParams = collections.namedtuple('GlobalParams', [
40 | 'width_coefficient', 'depth_coefficient', 'image_size', 'dropout_rate',
41 | 'num_classes', 'batch_norm_momentum', 'batch_norm_epsilon',
42 | 'drop_connect_rate', 'depth_divisor', 'min_depth', 'include_top'])
43 |
44 | # Parameters for an individual model block
45 | BlockArgs = collections.namedtuple('BlockArgs', [
46 | 'num_repeat', 'kernel_size', 'stride', 'expand_ratio',
47 | 'input_filters', 'output_filters', 'se_ratio', 'id_skip'])
48 |
49 | # Set GlobalParams and BlockArgs's defaults
50 | GlobalParams.__new__.__defaults__ = (None,) * len(GlobalParams._fields)
51 | BlockArgs.__new__.__defaults__ = (None,) * len(BlockArgs._fields)
52 |
53 | # Swish activation function
54 | if hasattr(nn, 'SiLU'):
55 | Swish = nn.SiLU
56 | else:
57 | # For compatibility with old PyTorch versions
58 | class Swish(nn.Module):
59 | def forward(self, x):
60 | return x * torch.sigmoid(x)
61 |
62 |
63 | # A memory-efficient implementation of Swish function
64 | class SwishImplementation(torch.autograd.Function):
65 | @staticmethod
66 | def forward(ctx, i):
67 | result = i * torch.sigmoid(i)
68 | ctx.save_for_backward(i)
69 | return result
70 |
71 | @staticmethod
72 | def backward(ctx, grad_output):
73 | i = ctx.saved_tensors[0]
74 | sigmoid_i = torch.sigmoid(i)
75 | return grad_output * (sigmoid_i * (1 + i * (1 - sigmoid_i)))
76 |
77 |
78 | class MemoryEfficientSwish(nn.Module):
79 | def forward(self, x):
80 | return SwishImplementation.apply(x)
81 |
82 |
83 | def round_filters(filters, global_params):
84 | """Calculate and round number of filters based on width multiplier.
85 | Use width_coefficient, depth_divisor and min_depth of global_params.
86 |
87 | Args:
88 | filters (int): Filters number to be calculated.
89 | global_params (namedtuple): Global params of the model.
90 |
91 | Returns:
92 | new_filters: New filters number after calculating.
93 | """
94 | multiplier = global_params.width_coefficient
95 | if not multiplier:
96 | return filters
97 | # TODO: modify the params names.
98 | # maybe the names (width_divisor,min_width)
99 | # are more suitable than (depth_divisor,min_depth).
100 | divisor = global_params.depth_divisor
101 | min_depth = global_params.min_depth
102 | filters *= multiplier
103 | min_depth = min_depth or divisor # pay attention to this line when using min_depth
104 | # follow the formula transferred from official TensorFlow implementation
105 | new_filters = max(min_depth, int(filters + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)
106 | if new_filters < 0.9 * filters: # prevent rounding by more than 10%
107 | new_filters += divisor
108 | return int(new_filters)
109 |
110 |
111 | def round_repeats(repeats, global_params):
112 | """Calculate module's repeat number of a block based on depth multiplier.
113 | Use depth_coefficient of global_params.
114 |
115 | Args:
116 | repeats (int): num_repeat to be calculated.
117 | global_params (namedtuple): Global params of the model.
118 |
119 | Returns:
120 | new repeat: New repeat number after calculating.
121 | """
122 | multiplier = global_params.depth_coefficient
123 | if not multiplier:
124 | return repeats
125 | # follow the formula transferred from official TensorFlow implementation
126 | return int(math.ceil(multiplier * repeats))
127 |
128 |
129 | def drop_connect(inputs, p, training):
130 | """Drop connect.
131 |
132 | Args:
133 | input (tensor: BCWH): Input of this structure.
134 | p (float: 0.0~1.0): Probability of drop connection.
135 | training (bool): The running mode.
136 |
137 | Returns:
138 | output: Output after drop connection.
139 | """
140 | assert 0 <= p <= 1, 'p must be in range of [0,1]'
141 |
142 | if not training:
143 | return inputs
144 |
145 | batch_size = inputs.shape[0]
146 | keep_prob = 1 - p
147 |
148 | # generate binary_tensor mask according to probability (p for 0, 1-p for 1)
149 | random_tensor = keep_prob
150 | random_tensor += torch.rand([batch_size, 1, 1, 1], dtype=inputs.dtype, device=inputs.device)
151 | binary_tensor = torch.floor(random_tensor)
152 |
153 | output = inputs / keep_prob * binary_tensor
154 | return output
155 |
156 |
157 | def get_width_and_height_from_size(x):
158 | """Obtain height and width from x.
159 |
160 | Args:
161 | x (int, tuple or list): Data size.
162 |
163 | Returns:
164 | size: A tuple or list (H,W).
165 | """
166 | if isinstance(x, int):
167 | return x, x
168 | if isinstance(x, list) or isinstance(x, tuple):
169 | return x
170 | else:
171 | raise TypeError()
172 |
173 |
174 | def calculate_output_image_size(input_image_size, stride):
175 | """Calculates the output image size when using Conv2dSamePadding with a stride.
176 | Necessary for static padding. Thanks to mannatsingh for pointing this out.
177 |
178 | Args:
179 | input_image_size (int, tuple or list): Size of input image.
180 | stride (int, tuple or list): Conv2d operation's stride.
181 |
182 | Returns:
183 | output_image_size: A list [H,W].
184 | """
185 | if input_image_size is None:
186 | return None
187 | image_height, image_width = get_width_and_height_from_size(input_image_size)
188 | stride = stride if isinstance(stride, int) else stride[0]
189 | image_height = int(math.ceil(image_height / stride))
190 | image_width = int(math.ceil(image_width / stride))
191 | return [image_height, image_width]
192 |
193 |
194 | # Note:
195 | # The following 'SamePadding' functions make output size equal ceil(input size/stride).
196 | # Only when stride equals 1, can the output size be the same as input size.
197 | # Don't be confused by their function names ! ! !
198 |
199 | def get_same_padding_conv2d(image_size=None):
200 | """Chooses static padding if you have specified an image size, and dynamic padding otherwise.
201 | Static padding is necessary for ONNX exporting of models.
202 |
203 | Args:
204 | image_size (int or tuple): Size of the image.
205 |
206 | Returns:
207 | Conv2dDynamicSamePadding or Conv2dStaticSamePadding.
208 | """
209 | if image_size is None:
210 | return Conv2dDynamicSamePadding
211 | else:
212 | return partial(Conv2dStaticSamePadding, image_size=image_size)
213 |
214 |
215 | class Conv2dDynamicSamePadding(nn.Conv2d):
216 | """2D Convolutions like TensorFlow, for a dynamic image size.
217 | The padding is operated in forward function by calculating dynamically.
218 | """
219 |
220 | # Tips for 'SAME' mode padding.
221 | # Given the following:
222 | # i: width or height
223 | # s: stride
224 | # k: kernel size
225 | # d: dilation
226 | # p: padding
227 | # Output after Conv2d:
228 | # o = floor((i+p-((k-1)*d+1))/s+1)
229 | # If o equals i, i = floor((i+p-((k-1)*d+1))/s+1),
230 | # => p = (i-1)*s+((k-1)*d+1)-i
231 |
232 | def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True):
233 | super().__init__(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, 0, dilation, groups, bias)
234 | self.stride = self.stride if len(self.stride) == 2 else [self.stride[0]] * 2
235 |
236 | def forward(self, x):
237 | ih, iw = x.size()[-2:]
238 | kh, kw = self.weight.size()[-2:]
239 | sh, sw = self.stride
240 | oh, ow = math.ceil(ih / sh), math.ceil(iw / sw) # change the output size according to stride ! ! !
241 | pad_h = max((oh - 1) * self.stride[0] + (kh - 1) * self.dilation[0] + 1 - ih, 0)
242 | pad_w = max((ow - 1) * self.stride[1] + (kw - 1) * self.dilation[1] + 1 - iw, 0)
243 | if pad_h > 0 or pad_w > 0:
244 | x = F.pad(x, [pad_w // 2, pad_w - pad_w // 2, pad_h // 2, pad_h - pad_h // 2])
245 | return F.conv2d(x, self.weight, self.bias, self.stride, self.padding, self.dilation, self.groups)
246 |
247 |
248 | class Conv2dStaticSamePadding(nn.Conv2d):
249 | """2D Convolutions like TensorFlow's 'SAME' mode, with the given input image size.
250 | The padding mudule is calculated in construction function, then used in forward.
251 | """
252 |
253 | # With the same calculation as Conv2dDynamicSamePadding
254 |
255 | def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, image_size=None, **kwargs):
256 | super().__init__(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, **kwargs)
257 | self.stride = self.stride if len(self.stride) == 2 else [self.stride[0]] * 2
258 |
259 | # Calculate padding based on image size and save it
260 | assert image_size is not None
261 | ih, iw = (image_size, image_size) if isinstance(image_size, int) else image_size
262 | kh, kw = self.weight.size()[-2:]
263 | sh, sw = self.stride
264 | oh, ow = math.ceil(ih / sh), math.ceil(iw / sw)
265 | pad_h = max((oh - 1) * self.stride[0] + (kh - 1) * self.dilation[0] + 1 - ih, 0)
266 | pad_w = max((ow - 1) * self.stride[1] + (kw - 1) * self.dilation[1] + 1 - iw, 0)
267 | if pad_h > 0 or pad_w > 0:
268 | self.static_padding = nn.ZeroPad2d((pad_w // 2, pad_w - pad_w // 2,
269 | pad_h // 2, pad_h - pad_h // 2))
270 | else:
271 | self.static_padding = nn.Identity()
272 |
273 | def forward(self, x):
274 | x = self.static_padding(x)
275 | x = F.conv2d(x, self.weight, self.bias, self.stride, self.padding, self.dilation, self.groups)
276 | return x
277 |
278 |
279 | def get_same_padding_maxPool2d(image_size=None):
280 | """Chooses static padding if you have specified an image size, and dynamic padding otherwise.
281 | Static padding is necessary for ONNX exporting of models.
282 |
283 | Args:
284 | image_size (int or tuple): Size of the image.
285 |
286 | Returns:
287 | MaxPool2dDynamicSamePadding or MaxPool2dStaticSamePadding.
288 | """
289 | if image_size is None:
290 | return MaxPool2dDynamicSamePadding
291 | else:
292 | return partial(MaxPool2dStaticSamePadding, image_size=image_size)
293 |
294 |
295 | class MaxPool2dDynamicSamePadding(nn.MaxPool2d):
296 | """2D MaxPooling like TensorFlow's 'SAME' mode, with a dynamic image size.
297 | The padding is operated in forward function by calculating dynamically.
298 | """
299 |
300 | def __init__(self, kernel_size, stride, padding=0, dilation=1, return_indices=False, ceil_mode=False):
301 | super().__init__(kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation, return_indices, ceil_mode)
302 | self.stride = [self.stride] * 2 if isinstance(self.stride, int) else self.stride
303 | self.kernel_size = [self.kernel_size] * 2 if isinstance(self.kernel_size, int) else self.kernel_size
304 | self.dilation = [self.dilation] * 2 if isinstance(self.dilation, int) else self.dilation
305 |
306 | def forward(self, x):
307 | ih, iw = x.size()[-2:]
308 | kh, kw = self.kernel_size
309 | sh, sw = self.stride
310 | oh, ow = math.ceil(ih / sh), math.ceil(iw / sw)
311 | pad_h = max((oh - 1) * self.stride[0] + (kh - 1) * self.dilation[0] + 1 - ih, 0)
312 | pad_w = max((ow - 1) * self.stride[1] + (kw - 1) * self.dilation[1] + 1 - iw, 0)
313 | if pad_h > 0 or pad_w > 0:
314 | x = F.pad(x, [pad_w // 2, pad_w - pad_w // 2, pad_h // 2, pad_h - pad_h // 2])
315 | return F.max_pool2d(x, self.kernel_size, self.stride, self.padding,
316 | self.dilation, self.ceil_mode, self.return_indices)
317 |
318 |
319 | class MaxPool2dStaticSamePadding(nn.MaxPool2d):
320 | """2D MaxPooling like TensorFlow's 'SAME' mode, with the given input image size.
321 | The padding mudule is calculated in construction function, then used in forward.
322 | """
323 |
324 | def __init__(self, kernel_size, stride, image_size=None, **kwargs):
325 | super().__init__(kernel_size, stride, **kwargs)
326 | self.stride = [self.stride] * 2 if isinstance(self.stride, int) else self.stride
327 | self.kernel_size = [self.kernel_size] * 2 if isinstance(self.kernel_size, int) else self.kernel_size
328 | self.dilation = [self.dilation] * 2 if isinstance(self.dilation, int) else self.dilation
329 |
330 | # Calculate padding based on image size and save it
331 | assert image_size is not None
332 | ih, iw = (image_size, image_size) if isinstance(image_size, int) else image_size
333 | kh, kw = self.kernel_size
334 | sh, sw = self.stride
335 | oh, ow = math.ceil(ih / sh), math.ceil(iw / sw)
336 | pad_h = max((oh - 1) * self.stride[0] + (kh - 1) * self.dilation[0] + 1 - ih, 0)
337 | pad_w = max((ow - 1) * self.stride[1] + (kw - 1) * self.dilation[1] + 1 - iw, 0)
338 | if pad_h > 0 or pad_w > 0:
339 | self.static_padding = nn.ZeroPad2d((pad_w // 2, pad_w - pad_w // 2, pad_h // 2, pad_h - pad_h // 2))
340 | else:
341 | self.static_padding = nn.Identity()
342 |
343 | def forward(self, x):
344 | x = self.static_padding(x)
345 | x = F.max_pool2d(x, self.kernel_size, self.stride, self.padding,
346 | self.dilation, self.ceil_mode, self.return_indices)
347 | return x
348 |
349 |
350 | ################################################################################
351 | # Helper functions for loading model params
352 | ################################################################################
353 |
354 | # BlockDecoder: A Class for encoding and decoding BlockArgs
355 | # efficientnet_params: A function to query compound coefficient
356 | # get_model_params and efficientnet:
357 | # Functions to get BlockArgs and GlobalParams for efficientnet
358 | # url_map and url_map_advprop: Dicts of url_map for pretrained weights
359 | # load_pretrained_weights: A function to load pretrained weights
360 |
361 | class BlockDecoder(object):
362 | """Block Decoder for readability,
363 | straight from the official TensorFlow repository.
364 | """
365 |
366 | @staticmethod
367 | def _decode_block_string(block_string):
368 | """Get a block through a string notation of arguments.
369 |
370 | Args:
371 | block_string (str): A string notation of arguments.
372 | Examples: 'r1_k3_s11_e1_i32_o16_se0.25_noskip'.
373 |
374 | Returns:
375 | BlockArgs: The namedtuple defined at the top of this file.
376 | """
377 | assert isinstance(block_string, str)
378 |
379 | ops = block_string.split('_')
380 | options = {}
381 | for op in ops:
382 | splits = re.split(r'(\d.*)', op)
383 | if len(splits) >= 2:
384 | key, value = splits[:2]
385 | options[key] = value
386 |
387 | # Check stride
388 | assert (('s' in options and len(options['s']) == 1) or
389 | (len(options['s']) == 2 and options['s'][0] == options['s'][1]))
390 |
391 | return BlockArgs(
392 | num_repeat=int(options['r']),
393 | kernel_size=int(options['k']),
394 | stride=[int(options['s'][0])],
395 | expand_ratio=int(options['e']),
396 | input_filters=int(options['i']),
397 | output_filters=int(options['o']),
398 | se_ratio=float(options['se']) if 'se' in options else None,
399 | id_skip=('noskip' not in block_string))
400 |
401 | @staticmethod
402 | def _encode_block_string(block):
403 | """Encode a block to a string.
404 |
405 | Args:
406 | block (namedtuple): A BlockArgs type argument.
407 |
408 | Returns:
409 | block_string: A String form of BlockArgs.
410 | """
411 | args = [
412 | 'r%d' % block.num_repeat,
413 | 'k%d' % block.kernel_size,
414 | 's%d%d' % (block.strides[0], block.strides[1]),
415 | 'e%s' % block.expand_ratio,
416 | 'i%d' % block.input_filters,
417 | 'o%d' % block.output_filters
418 | ]
419 | if 0 < block.se_ratio <= 1:
420 | args.append('se%s' % block.se_ratio)
421 | if block.id_skip is False:
422 | args.append('noskip')
423 | return '_'.join(args)
424 |
425 | @staticmethod
426 | def decode(string_list):
427 | """Decode a list of string notations to specify blocks inside the network.
428 |
429 | Args:
430 | string_list (list[str]): A list of strings, each string is a notation of block.
431 |
432 | Returns:
433 | blocks_args: A list of BlockArgs namedtuples of block args.
434 | """
435 | assert isinstance(string_list, list)
436 | blocks_args = []
437 | for block_string in string_list:
438 | blocks_args.append(BlockDecoder._decode_block_string(block_string))
439 | return blocks_args
440 |
441 | @staticmethod
442 | def encode(blocks_args):
443 | """Encode a list of BlockArgs to a list of strings.
444 |
445 | Args:
446 | blocks_args (list[namedtuples]): A list of BlockArgs namedtuples of block args.
447 |
448 | Returns:
449 | block_strings: A list of strings, each string is a notation of block.
450 | """
451 | block_strings = []
452 | for block in blocks_args:
453 | block_strings.append(BlockDecoder._encode_block_string(block))
454 | return block_strings
455 |
456 |
457 | def efficientnet_params(model_name):
458 | """Map EfficientNet model name to parameter coefficients.
459 |
460 | Args:
461 | model_name (str): Model name to be queried.
462 |
463 | Returns:
464 | params_dict[model_name]: A (width,depth,res,dropout) tuple.
465 | """
466 | params_dict = {
467 | # Coefficients: width,depth,res,dropout
468 | 'efficientnet-b0': (1.0, 1.0, 224, 0.2),
469 | 'efficientnet-b1': (1.0, 1.1, 240, 0.2),
470 | 'efficientnet-b2': (1.1, 1.2, 260, 0.3),
471 | 'efficientnet-b3': (1.2, 1.4, 300, 0.3),
472 | 'efficientnet-b4': (1.4, 1.8, 380, 0.4),
473 | 'efficientnet-b5': (1.6, 2.2, 456, 0.4),
474 | 'efficientnet-b6': (1.8, 2.6, 528, 0.5),
475 | 'efficientnet-b7': (2.0, 3.1, 600, 0.5),
476 | 'efficientnet-b8': (2.2, 3.6, 672, 0.5),
477 | 'efficientnet-l2': (4.3, 5.3, 800, 0.5),
478 | }
479 | return params_dict[model_name]
480 |
481 |
482 | def efficientnet(width_coefficient=None, depth_coefficient=None, image_size=None,
483 | dropout_rate=0.2, drop_connect_rate=0.2, num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
484 | """Create BlockArgs and GlobalParams for efficientnet model.
485 |
486 | Args:
487 | width_coefficient (float)
488 | depth_coefficient (float)
489 | image_size (int)
490 | dropout_rate (float)
491 | drop_connect_rate (float)
492 | num_classes (int)
493 |
494 | Meaning as the name suggests.
495 |
496 | Returns:
497 | blocks_args, global_params.
498 | """
499 |
500 | # Blocks args for the whole model(efficientnet-b0 by default)
501 | # It will be modified in the construction of EfficientNet Class according to model
502 | blocks_args = [
503 | 'r1_k3_s11_e1_i32_o16_se0.25',
504 | 'r2_k3_s22_e6_i16_o24_se0.25',
505 | 'r2_k5_s22_e6_i24_o40_se0.25',
506 | 'r3_k3_s22_e6_i40_o80_se0.25',
507 | 'r3_k5_s11_e6_i80_o112_se0.25',
508 | 'r4_k5_s22_e6_i112_o192_se0.25',
509 | 'r1_k3_s11_e6_i192_o320_se0.25',
510 | ]
511 | blocks_args = BlockDecoder.decode(blocks_args)
512 |
513 | global_params = GlobalParams(
514 | width_coefficient=width_coefficient,
515 | depth_coefficient=depth_coefficient,
516 | image_size=image_size,
517 | dropout_rate=dropout_rate,
518 |
519 | num_classes=num_classes,
520 | batch_norm_momentum=0.99,
521 | batch_norm_epsilon=1e-3,
522 | drop_connect_rate=drop_connect_rate,
523 | depth_divisor=8,
524 | min_depth=None,
525 | include_top=include_top,
526 | )
527 |
528 | return blocks_args, global_params
529 |
530 |
531 | def get_model_params(model_name, override_params):
532 | """Get the block args and global params for a given model name.
533 |
534 | Args:
535 | model_name (str): Model's name.
536 | override_params (dict): A dict to modify global_params.
537 |
538 | Returns:
539 | blocks_args, global_params
540 | """
541 | if model_name.startswith('efficientnet'):
542 | w, d, s, p = efficientnet_params(model_name)
543 | # note: all models have drop connect rate = 0.2
544 | blocks_args, global_params = efficientnet(
545 | width_coefficient=w, depth_coefficient=d, dropout_rate=p, image_size=s)
546 | else:
547 | raise NotImplementedError('model name is not pre-defined: {}'.format(model_name))
548 | if override_params:
549 | # ValueError will be raised here if override_params has fields not included in global_params.
550 | global_params = global_params._replace(**override_params)
551 | return blocks_args, global_params
552 |
553 |
554 | # train with Standard methods
555 | # check more details in paper(EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks)
556 | url_map = {
557 | 'efficientnet-b0': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b0-355c32eb.pth',
558 | 'efficientnet-b1': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b1-f1951068.pth',
559 | 'efficientnet-b2': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b2-8bb594d6.pth',
560 | 'efficientnet-b3': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b3-5fb5a3c3.pth',
561 | 'efficientnet-b4': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b4-6ed6700e.pth',
562 | 'efficientnet-b5': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b5-b6417697.pth',
563 | 'efficientnet-b6': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b6-c76e70fd.pth',
564 | 'efficientnet-b7': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/efficientnet-b7-dcc49843.pth',
565 | }
566 |
567 | # train with Adversarial Examples(AdvProp)
568 | # check more details in paper(Adversarial Examples Improve Image Recognition)
569 | url_map_advprop = {
570 | 'efficientnet-b0': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b0-b64d5a18.pth',
571 | 'efficientnet-b1': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b1-0f3ce85a.pth',
572 | 'efficientnet-b2': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b2-6e9d97e5.pth',
573 | 'efficientnet-b3': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b3-cdd7c0f4.pth',
574 | 'efficientnet-b4': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b4-44fb3a87.pth',
575 | 'efficientnet-b5': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b5-86493f6b.pth',
576 | 'efficientnet-b6': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b6-ac80338e.pth',
577 | 'efficientnet-b7': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b7-4652b6dd.pth',
578 | 'efficientnet-b8': 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/releases/download/1.0/adv-efficientnet-b8-22a8fe65.pth',
579 | }
580 |
581 | # TODO: add the petrained weights url map of 'efficientnet-l2'
582 |
583 |
584 | def load_pretrained_weights(model, model_name, weights_path=None, load_fc=True, advprop=False, verbose=True):
585 | """Loads pretrained weights from weights path or download using url.
586 |
587 | Args:
588 | model (Module): The whole model of efficientnet.
589 | model_name (str): Model name of efficientnet.
590 | weights_path (None or str):
591 | str: path to pretrained weights file on the local disk.
592 | None: use pretrained weights downloaded from the Internet.
593 | load_fc (bool): Whether to load pretrained weights for fc layer at the end of the model.
594 | advprop (bool): Whether to load pretrained weights
595 | trained with advprop (valid when weights_path is None).
596 | """
597 | if isinstance(weights_path, str):
598 | state_dict = torch.load(weights_path)
599 | else:
600 | # AutoAugment or Advprop (different preprocessing)
601 | url_map_ = url_map_advprop if advprop else url_map
602 | state_dict = model_zoo.load_url(url_map_[model_name])
603 |
604 | if load_fc:
605 | ret = model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=False)
606 | assert not ret.missing_keys, 'Missing keys when loading pretrained weights: {}'.format(ret.missing_keys)
607 | else:
608 | state_dict.pop('_fc.weight')
609 | state_dict.pop('_fc.bias')
610 | ret = model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=False)
611 | assert set(ret.missing_keys) == set(
612 | ['_fc.weight', '_fc.bias']), 'Missing keys when loading pretrained weights: {}'.format(ret.missing_keys)
613 | assert not ret.unexpected_keys, 'Missing keys when loading pretrained weights: {}'.format(ret.unexpected_keys)
614 |
615 | if verbose:
616 | print('Loaded pretrained weights for {}'.format(model_name))
617 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/imagenet/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ### Imagenet
2 |
3 | This is a preliminary directory for evaluating the model on ImageNet. It is adapted from the standard PyTorch Imagenet script.
4 |
5 | For now, only evaluation is supported, but I am currently building scripts to assist with training new models on Imagenet.
6 |
7 | The evaluation results are slightly different from the original TensorFlow repository, due to differences in data preprocessing. For example, with the current preprocessing, `efficientnet-b3` gives a top-1 accuracy of `80.8`, rather than `81.1` in the paper. I am working on porting the TensorFlow preprocessing into PyTorch to address this issue.
8 |
9 | To run on Imagenet, place your `train` and `val` directories in `data`.
10 |
11 | Example commands:
12 | ```bash
13 | # Evaluate small EfficientNet on CPU
14 | python main.py data -e -a 'efficientnet-b0' --pretrained
15 | ```
16 | ```bash
17 | # Evaluate medium EfficientNet on GPU
18 | python main.py data -e -a 'efficientnet-b3' --pretrained --gpu 0 --batch-size 128
19 | ```
20 | ```bash
21 | # Evaluate ResNet-50 for comparison
22 | python main.py data -e -a 'resnet50' --pretrained --gpu 0
23 | ```
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/imagenet/data/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ### ImageNet
2 |
3 | Download ImageNet and place it into `train` and `val` folders here.
4 |
5 | More details may be found with the official PyTorch ImageNet example [here](https://github.com/pytorch/examples/blob/master/imagenet).
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/imagenet/main.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Evaluate on ImageNet. Note that at the moment, training is not implemented (I am working on it).
3 | that being said, evaluation is working.
4 | """
5 |
6 | import argparse
7 | import os
8 | import random
9 | import shutil
10 | import time
11 | import warnings
12 | import PIL
13 |
14 | import torch
15 | import torch.nn as nn
16 | import torch.nn.parallel
17 | import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
18 | import torch.distributed as dist
19 | import torch.optim
20 | import torch.multiprocessing as mp
21 | import torch.utils.data
22 | import torch.utils.data.distributed
23 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
24 | import torchvision.datasets as datasets
25 | import torchvision.models as models
26 |
27 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet
28 |
29 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch ImageNet Training')
30 | parser.add_argument('data', metavar='DIR',
31 | help='path to dataset')
32 | parser.add_argument('-a', '--arch', metavar='ARCH', default='resnet18',
33 | help='model architecture (default: resnet18)')
34 | parser.add_argument('-j', '--workers', default=4, type=int, metavar='N',
35 | help='number of data loading workers (default: 4)')
36 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', default=90, type=int, metavar='N',
37 | help='number of total epochs to run')
38 | parser.add_argument('--start-epoch', default=0, type=int, metavar='N',
39 | help='manual epoch number (useful on restarts)')
40 | parser.add_argument('-b', '--batch-size', default=256, type=int,
41 | metavar='N',
42 | help='mini-batch size (default: 256), this is the total '
43 | 'batch size of all GPUs on the current node when '
44 | 'using Data Parallel or Distributed Data Parallel')
45 | parser.add_argument('--lr', '--learning-rate', default=0.1, type=float,
46 | metavar='LR', help='initial learning rate', dest='lr')
47 | parser.add_argument('--momentum', default=0.9, type=float, metavar='M',
48 | help='momentum')
49 | parser.add_argument('--wd', '--weight-decay', default=1e-4, type=float,
50 | metavar='W', help='weight decay (default: 1e-4)',
51 | dest='weight_decay')
52 | parser.add_argument('-p', '--print-freq', default=10, type=int,
53 | metavar='N', help='print frequency (default: 10)')
54 | parser.add_argument('--resume', default='', type=str, metavar='PATH',
55 | help='path to latest checkpoint (default: none)')
56 | parser.add_argument('-e', '--evaluate', dest='evaluate', action='store_true',
57 | help='evaluate model on validation set')
58 | parser.add_argument('--pretrained', dest='pretrained', action='store_true',
59 | help='use pre-trained model')
60 | parser.add_argument('--world-size', default=-1, type=int,
61 | help='number of nodes for distributed training')
62 | parser.add_argument('--rank', default=-1, type=int,
63 | help='node rank for distributed training')
64 | parser.add_argument('--dist-url', default='tcp://224.66.41.62:23456', type=str,
65 | help='url used to set up distributed training')
66 | parser.add_argument('--dist-backend', default='nccl', type=str,
67 | help='distributed backend')
68 | parser.add_argument('--seed', default=None, type=int,
69 | help='seed for initializing training. ')
70 | parser.add_argument('--gpu', default=None, type=int,
71 | help='GPU id to use.')
72 | parser.add_argument('--image_size', default=224, type=int,
73 | help='image size')
74 | parser.add_argument('--advprop', default=False, action='store_true',
75 | help='use advprop or not')
76 | parser.add_argument('--multiprocessing-distributed', action='store_true',
77 | help='Use multi-processing distributed training to launch '
78 | 'N processes per node, which has N GPUs. This is the '
79 | 'fastest way to use PyTorch for either single node or '
80 | 'multi node data parallel training')
81 |
82 | best_acc1 = 0
83 |
84 |
85 | def main():
86 | args = parser.parse_args()
87 |
88 | if args.seed is not None:
89 | random.seed(args.seed)
90 | torch.manual_seed(args.seed)
91 | cudnn.deterministic = True
92 | warnings.warn('You have chosen to seed training. '
93 | 'This will turn on the CUDNN deterministic setting, '
94 | 'which can slow down your training considerably! '
95 | 'You may see unexpected behavior when restarting '
96 | 'from checkpoints.')
97 |
98 | if args.gpu is not None:
99 | warnings.warn('You have chosen a specific GPU. This will completely '
100 | 'disable data parallelism.')
101 |
102 | if args.dist_url == "env://" and args.world_size == -1:
103 | args.world_size = int(os.environ["WORLD_SIZE"])
104 |
105 | args.distributed = args.world_size > 1 or args.multiprocessing_distributed
106 |
107 | ngpus_per_node = torch.cuda.device_count()
108 | if args.multiprocessing_distributed:
109 | # Since we have ngpus_per_node processes per node, the total world_size
110 | # needs to be adjusted accordingly
111 | args.world_size = ngpus_per_node * args.world_size
112 | # Use torch.multiprocessing.spawn to launch distributed processes: the
113 | # main_worker process function
114 | mp.spawn(main_worker, nprocs=ngpus_per_node, args=(ngpus_per_node, args))
115 | else:
116 | # Simply call main_worker function
117 | main_worker(args.gpu, ngpus_per_node, args)
118 |
119 |
120 | def main_worker(gpu, ngpus_per_node, args):
121 | global best_acc1
122 | args.gpu = gpu
123 |
124 | if args.gpu is not None:
125 | print("Use GPU: {} for training".format(args.gpu))
126 |
127 | if args.distributed:
128 | if args.dist_url == "env://" and args.rank == -1:
129 | args.rank = int(os.environ["RANK"])
130 | if args.multiprocessing_distributed:
131 | # For multiprocessing distributed training, rank needs to be the
132 | # global rank among all the processes
133 | args.rank = args.rank * ngpus_per_node + gpu
134 | dist.init_process_group(backend=args.dist_backend, init_method=args.dist_url,
135 | world_size=args.world_size, rank=args.rank)
136 | # create model
137 | if 'efficientnet' in args.arch: # NEW
138 | if args.pretrained:
139 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained(args.arch, advprop=args.advprop)
140 | print("=> using pre-trained model '{}'".format(args.arch))
141 | else:
142 | print("=> creating model '{}'".format(args.arch))
143 | model = EfficientNet.from_name(args.arch)
144 |
145 | else:
146 | if args.pretrained:
147 | print("=> using pre-trained model '{}'".format(args.arch))
148 | model = models.__dict__[args.arch](pretrained=True)
149 | else:
150 | print("=> creating model '{}'".format(args.arch))
151 | model = models.__dict__[args.arch]()
152 |
153 | if args.distributed:
154 | # For multiprocessing distributed, DistributedDataParallel constructor
155 | # should always set the single device scope, otherwise,
156 | # DistributedDataParallel will use all available devices.
157 | if args.gpu is not None:
158 | torch.cuda.set_device(args.gpu)
159 | model.cuda(args.gpu)
160 | # When using a single GPU per process and per
161 | # DistributedDataParallel, we need to divide the batch size
162 | # ourselves based on the total number of GPUs we have
163 | args.batch_size = int(args.batch_size / ngpus_per_node)
164 | args.workers = int(args.workers / ngpus_per_node)
165 | model = torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel(model, device_ids=[args.gpu])
166 | else:
167 | model.cuda()
168 | # DistributedDataParallel will divide and allocate batch_size to all
169 | # available GPUs if device_ids are not set
170 | model = torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel(model)
171 | elif args.gpu is not None:
172 | torch.cuda.set_device(args.gpu)
173 | model = model.cuda(args.gpu)
174 | else:
175 | # DataParallel will divide and allocate batch_size to all available GPUs
176 | if args.arch.startswith('alexnet') or args.arch.startswith('vgg'):
177 | model.features = torch.nn.DataParallel(model.features)
178 | model.cuda()
179 | else:
180 | model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model).cuda()
181 |
182 | # define loss function (criterion) and optimizer
183 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda(args.gpu)
184 |
185 | optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), args.lr,
186 | momentum=args.momentum,
187 | weight_decay=args.weight_decay)
188 |
189 | # optionally resume from a checkpoint
190 | if args.resume:
191 | if os.path.isfile(args.resume):
192 | print("=> loading checkpoint '{}'".format(args.resume))
193 | checkpoint = torch.load(args.resume)
194 | args.start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch']
195 | best_acc1 = checkpoint['best_acc1']
196 | if args.gpu is not None:
197 | # best_acc1 may be from a checkpoint from a different GPU
198 | best_acc1 = best_acc1.to(args.gpu)
199 | model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
200 | optimizer.load_state_dict(checkpoint['optimizer'])
201 | print("=> loaded checkpoint '{}' (epoch {})"
202 | .format(args.resume, checkpoint['epoch']))
203 | else:
204 | print("=> no checkpoint found at '{}'".format(args.resume))
205 |
206 | cudnn.benchmark = True
207 |
208 | # Data loading code
209 | traindir = os.path.join(args.data, 'train')
210 | valdir = os.path.join(args.data, 'val')
211 | if args.advprop:
212 | normalize = transforms.Lambda(lambda img: img * 2.0 - 1.0)
213 | else:
214 | normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
215 | std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
216 |
217 | if 'efficientnet' in args.arch:
218 | image_size = EfficientNet.get_image_size(args.arch)
219 | else:
220 | image_size = args.image_size
221 |
222 | train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(
223 | traindir,
224 | transforms.Compose([
225 | transforms.RandomResizedCrop(image_size),
226 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
227 | transforms.ToTensor(),
228 | normalize,
229 | ]))
230 |
231 | if args.distributed:
232 | train_sampler = torch.utils.data.distributed.DistributedSampler(train_dataset)
233 | else:
234 | train_sampler = None
235 |
236 | train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
237 | train_dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=(train_sampler is None),
238 | num_workers=args.workers, pin_memory=True, sampler=train_sampler)
239 |
240 | val_transforms = transforms.Compose([
241 | transforms.Resize(image_size, interpolation=PIL.Image.BICUBIC),
242 | transforms.CenterCrop(image_size),
243 | transforms.ToTensor(),
244 | normalize,
245 | ])
246 | print('Using image size', image_size)
247 |
248 | val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
249 | datasets.ImageFolder(valdir, val_transforms),
250 | batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=False,
251 | num_workers=args.workers, pin_memory=True)
252 |
253 | if args.evaluate:
254 | res = validate(val_loader, model, criterion, args)
255 | with open('res.txt', 'w') as f:
256 | print(res, file=f)
257 | return
258 |
259 | for epoch in range(args.start_epoch, args.epochs):
260 | if args.distributed:
261 | train_sampler.set_epoch(epoch)
262 | adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch, args)
263 |
264 | # train for one epoch
265 | train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch, args)
266 |
267 | # evaluate on validation set
268 | acc1 = validate(val_loader, model, criterion, args)
269 |
270 | # remember best acc@1 and save checkpoint
271 | is_best = acc1 > best_acc1
272 | best_acc1 = max(acc1, best_acc1)
273 |
274 | if not args.multiprocessing_distributed or (args.multiprocessing_distributed
275 | and args.rank % ngpus_per_node == 0):
276 | save_checkpoint({
277 | 'epoch': epoch + 1,
278 | 'arch': args.arch,
279 | 'state_dict': model.state_dict(),
280 | 'best_acc1': best_acc1,
281 | 'optimizer' : optimizer.state_dict(),
282 | }, is_best)
283 |
284 |
285 | def train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch, args):
286 | batch_time = AverageMeter('Time', ':6.3f')
287 | data_time = AverageMeter('Data', ':6.3f')
288 | losses = AverageMeter('Loss', ':.4e')
289 | top1 = AverageMeter('Acc@1', ':6.2f')
290 | top5 = AverageMeter('Acc@5', ':6.2f')
291 | progress = ProgressMeter(len(train_loader), batch_time, data_time, losses, top1,
292 | top5, prefix="Epoch: [{}]".format(epoch))
293 |
294 | # switch to train mode
295 | model.train()
296 |
297 | end = time.time()
298 | for i, (images, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
299 | # measure data loading time
300 | data_time.update(time.time() - end)
301 |
302 | if args.gpu is not None:
303 | images = images.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
304 | target = target.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
305 |
306 | # compute output
307 | output = model(images)
308 | loss = criterion(output, target)
309 |
310 | # measure accuracy and record loss
311 | acc1, acc5 = accuracy(output, target, topk=(1, 5))
312 | losses.update(loss.item(), images.size(0))
313 | top1.update(acc1[0], images.size(0))
314 | top5.update(acc5[0], images.size(0))
315 |
316 | # compute gradient and do SGD step
317 | optimizer.zero_grad()
318 | loss.backward()
319 | optimizer.step()
320 |
321 | # measure elapsed time
322 | batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
323 | end = time.time()
324 |
325 | if i % args.print_freq == 0:
326 | progress.print(i)
327 |
328 |
329 | def validate(val_loader, model, criterion, args):
330 | batch_time = AverageMeter('Time', ':6.3f')
331 | losses = AverageMeter('Loss', ':.4e')
332 | top1 = AverageMeter('Acc@1', ':6.2f')
333 | top5 = AverageMeter('Acc@5', ':6.2f')
334 | progress = ProgressMeter(len(val_loader), batch_time, losses, top1, top5,
335 | prefix='Test: ')
336 |
337 | # switch to evaluate mode
338 | model.eval()
339 |
340 | with torch.no_grad():
341 | end = time.time()
342 | for i, (images, target) in enumerate(val_loader):
343 | if args.gpu is not None:
344 | images = images.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
345 | target = target.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
346 |
347 | # compute output
348 | output = model(images)
349 | loss = criterion(output, target)
350 |
351 | # measure accuracy and record loss
352 | acc1, acc5 = accuracy(output, target, topk=(1, 5))
353 | losses.update(loss.item(), images.size(0))
354 | top1.update(acc1[0], images.size(0))
355 | top5.update(acc5[0], images.size(0))
356 |
357 | # measure elapsed time
358 | batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
359 | end = time.time()
360 |
361 | if i % args.print_freq == 0:
362 | progress.print(i)
363 |
364 | # TODO: this should also be done with the ProgressMeter
365 | print(' * Acc@1 {top1.avg:.3f} Acc@5 {top5.avg:.3f}'
366 | .format(top1=top1, top5=top5))
367 |
368 | return top1.avg
369 |
370 |
371 | def save_checkpoint(state, is_best, filename='checkpoint.pth.tar'):
372 | torch.save(state, filename)
373 | if is_best:
374 | shutil.copyfile(filename, 'model_best.pth.tar')
375 |
376 |
377 | class AverageMeter(object):
378 | """Computes and stores the average and current value"""
379 | def __init__(self, name, fmt=':f'):
380 | self.name = name
381 | self.fmt = fmt
382 | self.reset()
383 |
384 | def reset(self):
385 | self.val = 0
386 | self.avg = 0
387 | self.sum = 0
388 | self.count = 0
389 |
390 | def update(self, val, n=1):
391 | self.val = val
392 | self.sum += val * n
393 | self.count += n
394 | self.avg = self.sum / self.count
395 |
396 | def __str__(self):
397 | fmtstr = '{name} {val' + self.fmt + '} ({avg' + self.fmt + '})'
398 | return fmtstr.format(**self.__dict__)
399 |
400 |
401 | class ProgressMeter(object):
402 | def __init__(self, num_batches, *meters, prefix=""):
403 | self.batch_fmtstr = self._get_batch_fmtstr(num_batches)
404 | self.meters = meters
405 | self.prefix = prefix
406 |
407 | def print(self, batch):
408 | entries = [self.prefix + self.batch_fmtstr.format(batch)]
409 | entries += [str(meter) for meter in self.meters]
410 | print('\t'.join(entries))
411 |
412 | def _get_batch_fmtstr(self, num_batches):
413 | num_digits = len(str(num_batches // 1))
414 | fmt = '{:' + str(num_digits) + 'd}'
415 | return '[' + fmt + '/' + fmt.format(num_batches) + ']'
416 |
417 |
418 | def adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch, args):
419 | """Sets the learning rate to the initial LR decayed by 10 every 30 epochs"""
420 | lr = args.lr * (0.1 ** (epoch // 30))
421 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
422 | param_group['lr'] = lr
423 |
424 |
425 | def accuracy(output, target, topk=(1,)):
426 | """Computes the accuracy over the k top predictions for the specified values of k"""
427 | with torch.no_grad():
428 | maxk = max(topk)
429 | batch_size = target.size(0)
430 |
431 | _, pred = output.topk(maxk, 1, True, True)
432 | pred = pred.t()
433 | correct = pred.eq(target.view(1, -1).expand_as(pred))
434 |
435 | res = []
436 | for k in topk:
437 | correct_k = correct[:k].reshape(-1).float().sum(0, keepdim=True)
438 | res.append(correct_k.mul_(100.0 / batch_size))
439 | return res
440 |
441 |
442 | if __name__ == '__main__':
443 | main()
444 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/simple/img.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/7e8b0d312162f335785fb5dcfa1df29a75a1783a/examples/simple/img.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/simple/img2.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/7e8b0d312162f335785fb5dcfa1df29a75a1783a/examples/simple/img2.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/hubconf.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet as _EfficientNet
2 |
3 | dependencies = ['torch']
4 |
5 |
6 | def _create_model_fn(model_name):
7 | def _model_fn(num_classes=1000, in_channels=3, pretrained='imagenet'):
8 | """Create Efficient Net.
9 |
10 | Described in detail here: https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.11946
11 |
12 | Args:
13 | num_classes (int, optional): Number of classes, default is 1000.
14 | in_channels (int, optional): Number of input channels, default
15 | is 3.
16 | pretrained (str, optional): One of [None, 'imagenet', 'advprop']
17 | If None, no pretrained model is loaded.
18 | If 'imagenet', models trained on imagenet dataset are loaded.
19 | If 'advprop', models trained using adversarial training called
20 | advprop are loaded. It is important to note that the
21 | preprocessing required for the advprop pretrained models is
22 | slightly different from normal ImageNet preprocessing
23 | """
24 | model_name_ = model_name.replace('_', '-')
25 | if pretrained is not None:
26 | model = _EfficientNet.from_pretrained(
27 | model_name=model_name_,
28 | advprop=(pretrained == 'advprop'),
29 | num_classes=num_classes,
30 | in_channels=in_channels)
31 | else:
32 | model = _EfficientNet.from_name(
33 | model_name=model_name_,
34 | override_params={'num_classes': num_classes},
35 | )
36 | model._change_in_channels(in_channels)
37 |
38 | return model
39 |
40 | return _model_fn
41 |
42 | for model_name in ['efficientnet_b' + str(i) for i in range(9)]:
43 | locals()[model_name] = _create_model_fn(model_name)
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python
2 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
3 |
4 | # Note: To use the 'upload' functionality of this file, you must:
5 | # $ pipenv install twine --dev
6 |
7 | import io
8 | import os
9 | import sys
10 | from shutil import rmtree
11 |
12 | from setuptools import find_packages, setup, Command
13 |
14 | # Package meta-data.
15 | NAME = 'efficientnet_pytorch'
16 | DESCRIPTION = 'EfficientNet implemented in PyTorch.'
17 | URL = 'https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch'
18 | EMAIL = 'lmelaskyriazi@college.harvard.edu'
19 | AUTHOR = 'Luke'
20 | REQUIRES_PYTHON = '>=3.5.0'
21 | VERSION = '0.7.1'
22 |
23 | # What packages are required for this module to be executed?
24 | REQUIRED = [
25 | 'torch'
26 | ]
27 |
28 | # What packages are optional?
29 | EXTRAS = {
30 | # 'fancy feature': ['django'],
31 | }
32 |
33 | # The rest you shouldn't have to touch too much :)
34 | # ------------------------------------------------
35 | # Except, perhaps the License and Trove Classifiers!
36 | # If you do change the License, remember to change the Trove Classifier for that!
37 |
38 | here = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__))
39 |
40 | # Import the README and use it as the long-description.
41 | # Note: this will only work if 'README.md' is present in your MANIFEST.in file!
42 | try:
43 | with io.open(os.path.join(here, 'README.md'), encoding='utf-8') as f:
44 | long_description = '\n' + f.read()
45 | except FileNotFoundError:
46 | long_description = DESCRIPTION
47 |
48 | # Load the package's __version__.py module as a dictionary.
49 | about = {}
50 | if not VERSION:
51 | project_slug = NAME.lower().replace("-", "_").replace(" ", "_")
52 | with open(os.path.join(here, project_slug, '__version__.py')) as f:
53 | exec(f.read(), about)
54 | else:
55 | about['__version__'] = VERSION
56 |
57 |
58 | class UploadCommand(Command):
59 | """Support setup.py upload."""
60 |
61 | description = 'Build and publish the package.'
62 | user_options = []
63 |
64 | @staticmethod
65 | def status(s):
66 | """Prints things in bold."""
67 | print('\033[1m{0}\033[0m'.format(s))
68 |
69 | def initialize_options(self):
70 | pass
71 |
72 | def finalize_options(self):
73 | pass
74 |
75 | def run(self):
76 | try:
77 | self.status('Removing previous builds…')
78 | rmtree(os.path.join(here, 'dist'))
79 | except OSError:
80 | pass
81 |
82 | self.status('Building Source and Wheel (universal) distribution…')
83 | os.system('{0} setup.py sdist bdist_wheel --universal'.format(sys.executable))
84 |
85 | self.status('Uploading the package to PyPI via Twine…')
86 | os.system('twine upload dist/*')
87 |
88 | self.status('Pushing git tags…')
89 | os.system('git tag v{0}'.format(about['__version__']))
90 | os.system('git push --tags')
91 |
92 | sys.exit()
93 |
94 |
95 | # Where the magic happens:
96 | setup(
97 | name=NAME,
98 | version=about['__version__'],
99 | description=DESCRIPTION,
100 | long_description=long_description,
101 | long_description_content_type='text/markdown',
102 | author=AUTHOR,
103 | author_email=EMAIL,
104 | python_requires=REQUIRES_PYTHON,
105 | url=URL,
106 | packages=find_packages(exclude=["tests", "*.tests", "*.tests.*", "tests.*"]),
107 | # py_modules=['model'], # If your package is a single module, use this instead of 'packages'
108 | install_requires=REQUIRED,
109 | extras_require=EXTRAS,
110 | include_package_data=True,
111 | license='Apache',
112 | classifiers=[
113 | # Full list: https://pypi.python.org/pypi?%3Aaction=list_classifiers
114 | 'License :: OSI Approved :: Apache Software License',
115 | 'Programming Language :: Python',
116 | 'Programming Language :: Python :: 3',
117 | 'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.6',
118 | ],
119 | # $ setup.py publish support.
120 | cmdclass={
121 | 'upload': UploadCommand,
122 | },
123 | )
124 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sotabench.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import PIL
4 | import torch
5 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
6 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
7 | from torchvision.datasets import ImageNet
8 |
9 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet
10 |
11 | from sotabencheval.image_classification import ImageNetEvaluator
12 | from sotabencheval.utils import is_server
13 |
14 | if is_server():
15 | DATA_ROOT = DATA_ROOT = os.environ.get('IMAGENET_DIR', './imagenet') # './.data/vision/imagenet'
16 | else: # local settings
17 | DATA_ROOT = os.environ['IMAGENET_DIR']
18 | assert bool(DATA_ROOT), 'please set IMAGENET_DIR environment variable'
19 | print('Local data root: ', DATA_ROOT)
20 |
21 | model_name = 'EfficientNet-B5'
22 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained(model_name.lower())
23 | image_size = EfficientNet.get_image_size(model_name.lower())
24 |
25 | input_transform = transforms.Compose([
26 | transforms.Resize(image_size, PIL.Image.BICUBIC),
27 | transforms.CenterCrop(image_size),
28 | transforms.ToTensor(),
29 | transforms.Normalize(
30 | mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),
31 | ])
32 |
33 | test_dataset = ImageNet(
34 | DATA_ROOT,
35 | split="val",
36 | transform=input_transform,
37 | target_transform=None,
38 | )
39 |
40 | test_loader = DataLoader(
41 | test_dataset,
42 | batch_size=128,
43 | shuffle=False,
44 | num_workers=4,
45 | pin_memory=True,
46 | )
47 |
48 | model = model.cuda()
49 | model.eval()
50 |
51 | evaluator = ImageNetEvaluator(model_name=model_name,
52 | paper_arxiv_id='1905.11946')
53 |
54 | def get_img_id(image_name):
55 | return image_name.split('/')[-1].replace('.JPEG', '')
56 |
57 | with torch.no_grad():
58 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(test_loader):
59 | input = input.to(device='cuda', non_blocking=True)
60 | target = target.to(device='cuda', non_blocking=True)
61 | output = model(input)
62 | image_ids = [get_img_id(img[0]) for img in test_loader.dataset.imgs[i*test_loader.batch_size:(i+1)*test_loader.batch_size]]
63 | evaluator.add(dict(zip(image_ids, list(output.cpu().numpy()))))
64 | if evaluator.cache_exists:
65 | break
66 |
67 | if not is_server():
68 | print("Results:")
69 | print(evaluator.get_results())
70 |
71 | evaluator.save()
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sotabench_setup.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env bash -x
2 | source /workspace/venv/bin/activate
3 | PYTHON=${PYTHON:-"python"}
4 | $PYTHON -m pip install torch
5 | $PYTHON -m pip install torchvision
6 | $PYTHON -m pip install scipy
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_model.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from collections import OrderedDict
2 |
3 | import pytest
4 | import torch
5 | import torch.nn as nn
6 |
7 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet
8 |
9 |
10 | # -- fixtures -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
11 |
12 | @pytest.fixture(scope='module', params=[x for x in range(4)])
13 | def model(request):
14 | return 'efficientnet-b{}'.format(request.param)
15 |
16 |
17 | @pytest.fixture(scope='module', params=[True, False])
18 | def pretrained(request):
19 | return request.param
20 |
21 |
22 | @pytest.fixture(scope='function')
23 | def net(model, pretrained):
24 | return EfficientNet.from_pretrained(model) if pretrained else EfficientNet.from_name(model)
25 |
26 |
27 | # -- tests ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
28 |
29 | @pytest.mark.parametrize('img_size', [224, 256, 512])
30 | def test_forward(net, img_size):
31 | """Test `.forward()` doesn't throw an error"""
32 | data = torch.zeros((1, 3, img_size, img_size))
33 | output = net(data)
34 | assert not torch.isnan(output).any()
35 |
36 |
37 | def test_dropout_training(net):
38 | """Test dropout `.training` is set by `.train()` on parent `nn.module`"""
39 | net.train()
40 | assert net._dropout.training == True
41 |
42 |
43 | def test_dropout_eval(net):
44 | """Test dropout `.training` is set by `.eval()` on parent `nn.module`"""
45 | net.eval()
46 | assert net._dropout.training == False
47 |
48 |
49 | def test_dropout_update(net):
50 | """Test dropout `.training` is updated by `.train()` and `.eval()` on parent `nn.module`"""
51 | net.train()
52 | assert net._dropout.training == True
53 | net.eval()
54 | assert net._dropout.training == False
55 | net.train()
56 | assert net._dropout.training == True
57 | net.eval()
58 | assert net._dropout.training == False
59 |
60 |
61 | @pytest.mark.parametrize('img_size', [224, 256, 512])
62 | def test_modify_dropout(net, img_size):
63 | """Test ability to modify dropout and fc modules of network"""
64 | dropout = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
65 | ('_bn2', nn.BatchNorm1d(net._bn1.num_features)),
66 | ('_drop1', nn.Dropout(p=net._global_params.dropout_rate)),
67 | ('_linear1', nn.Linear(net._bn1.num_features, 512)),
68 | ('_relu', nn.ReLU()),
69 | ('_bn3', nn.BatchNorm1d(512)),
70 | ('_drop2', nn.Dropout(p=net._global_params.dropout_rate / 2))
71 | ]))
72 | fc = nn.Linear(512, net._global_params.num_classes)
73 |
74 | net._dropout = dropout
75 | net._fc = fc
76 |
77 | data = torch.zeros((2, 3, img_size, img_size))
78 | output = net(data)
79 | assert not torch.isnan(output).any()
80 |
81 |
82 | @pytest.mark.parametrize('img_size', [224, 256, 512])
83 | def test_modify_pool(net, img_size):
84 | """Test ability to modify pooling module of network"""
85 |
86 | class AdaptiveMaxAvgPool(nn.Module):
87 |
88 | def __init__(self):
89 | super().__init__()
90 | self.ada_avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
91 | self.ada_maxpool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d(1)
92 |
93 | def forward(self, x):
94 | avg_x = self.ada_avgpool(x)
95 | max_x = self.ada_maxpool(x)
96 | x = torch.cat((avg_x, max_x), dim=1)
97 | return x
98 |
99 | avg_pooling = AdaptiveMaxAvgPool()
100 | fc = nn.Linear(net._fc.in_features * 2, net._global_params.num_classes)
101 |
102 | net._avg_pooling = avg_pooling
103 | net._fc = fc
104 |
105 | data = torch.zeros((2, 3, img_size, img_size))
106 | output = net(data)
107 | assert not torch.isnan(output).any()
108 |
109 |
110 | @pytest.mark.parametrize('img_size', [224, 256, 512])
111 | def test_extract_endpoints(net, img_size):
112 | """Test `.extract_endpoints()` doesn't throw an error"""
113 | data = torch.zeros((1, 3, img_size, img_size))
114 | endpoints = net.extract_endpoints(data)
115 | assert not torch.isnan(endpoints['reduction_1']).any()
116 | assert not torch.isnan(endpoints['reduction_2']).any()
117 | assert not torch.isnan(endpoints['reduction_3']).any()
118 | assert not torch.isnan(endpoints['reduction_4']).any()
119 | assert not torch.isnan(endpoints['reduction_5']).any()
120 | assert endpoints['reduction_1'].size(2) == img_size // 2
121 | assert endpoints['reduction_2'].size(2) == img_size // 4
122 | assert endpoints['reduction_3'].size(2) == img_size // 8
123 | assert endpoints['reduction_4'].size(2) == img_size // 16
124 | assert endpoints['reduction_5'].size(2) == img_size // 32
125 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tf_to_pytorch/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ### TensorFlow to PyTorch Conversion
2 |
3 | This directory is used to convert TensorFlow weights to PyTorch. It was hacked together fairly quickly, so the code is not the most beautiful (just a warning!), but it does the job. I will be refactoring it soon.
4 |
5 | I should also emphasize that you do *not* need to run any of this code to load pretrained weights. Simply use `EfficientNet.from_pretrained(...)`.
6 |
7 | That being said, the main script here is `convert_to_tf/load_tf_weights.py`. In order to use it, you should first download the pretrained TensorFlow weights:
8 | ```bash
9 | cd pretrained_tensorflow
10 | ./download.sh efficientnet-b0
11 | cd ..
12 | ```
13 | Then
14 | ```bash
15 | mkdir -p pretrained_pytorch
16 | cd convert_tf_to_pt
17 | python load_tf_weights.py \
18 | --model_name efficientnet-b0 \
19 | --tf_checkpoint ../pretrained_tensorflow/efficientnet-b0/ \
20 | --output_file ../pretrained_pytorch/efficientnet-b0.pth
21 | ```
22 |
23 |
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tf_to_pytorch/convert_tf_to_pt/download.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env bash
2 |
3 | mkdir original_tf
4 | cd original_tf
5 | touch __init__.py
6 | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tensorflow/tpu/master/models/official/efficientnet/efficientnet_builder.py
7 | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tensorflow/tpu/master/models/official/efficientnet/efficientnet_model.py
8 | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tensorflow/tpu/master/models/official/efficientnet/eval_ckpt_main.py
9 | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tensorflow/tpu/master/models/official/efficientnet/utils.py
10 | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tensorflow/tpu/master/models/official/efficientnet/preprocessing.py
11 | cd ..
12 | mkdir -p tmp
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tf_to_pytorch/convert_tf_to_pt/load_tf_weights.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import tensorflow as tf
3 | import torch
4 |
5 | tf.compat.v1.disable_v2_behavior()
6 |
7 | def load_param(checkpoint_file, conversion_table, model_name):
8 | """
9 | Load parameters according to conversion_table.
10 |
11 | Args:
12 | checkpoint_file (string): pretrained checkpoint model file in tensorflow
13 | conversion_table (dict): { pytorch tensor in a model : checkpoint variable name }
14 | """
15 | for pyt_param, tf_param_name in conversion_table.items():
16 | tf_param_name = str(model_name) + '/' + tf_param_name
17 | tf_param = tf.train.load_variable(checkpoint_file, tf_param_name)
18 | if 'conv' in tf_param_name and 'kernel' in tf_param_name:
19 | tf_param = np.transpose(tf_param, (3, 2, 0, 1))
20 | if 'depthwise' in tf_param_name:
21 | tf_param = np.transpose(tf_param, (1, 0, 2, 3))
22 | elif tf_param_name.endswith('kernel'): # for weight(kernel), we should do transpose
23 | tf_param = np.transpose(tf_param)
24 | assert pyt_param.size() == tf_param.shape, \
25 | 'Dim Mismatch: %s vs %s ; %s' % (tuple(pyt_param.size()), tf_param.shape, tf_param_name)
26 | pyt_param.data = torch.from_numpy(tf_param)
27 |
28 |
29 | def load_efficientnet(model, checkpoint_file, model_name):
30 | """
31 | Load PyTorch EfficientNet from TensorFlow checkpoint file
32 | """
33 |
34 | # This will store the enire conversion table
35 | conversion_table = {}
36 | merge = lambda dict1, dict2: {**dict1, **dict2}
37 |
38 | # All the weights not in the conv blocks
39 | conversion_table_for_weights_outside_blocks = {
40 | model._conv_stem.weight: 'stem/conv2d/kernel', # [3, 3, 3, 32]),
41 | model._bn0.bias: 'stem/tpu_batch_normalization/beta', # [32]),
42 | model._bn0.weight: 'stem/tpu_batch_normalization/gamma', # [32]),
43 | model._bn0.running_mean: 'stem/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_mean', # [32]),
44 | model._bn0.running_var: 'stem/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_variance', # [32]),
45 | model._conv_head.weight: 'head/conv2d/kernel', # [1, 1, 320, 1280]),
46 | model._bn1.bias: 'head/tpu_batch_normalization/beta', # [1280]),
47 | model._bn1.weight: 'head/tpu_batch_normalization/gamma', # [1280]),
48 | model._bn1.running_mean: 'head/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_mean', # [32]),
49 | model._bn1.running_var: 'head/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_variance', # [32]),
50 | model._fc.bias: 'head/dense/bias', # [1000]),
51 | model._fc.weight: 'head/dense/kernel', # [1280, 1000]),
52 | }
53 | conversion_table = merge(conversion_table, conversion_table_for_weights_outside_blocks)
54 |
55 | # The first conv block is special because it does not have _expand_conv
56 | conversion_table_for_first_block = {
57 | model._blocks[0]._project_conv.weight: 'blocks_0/conv2d/kernel', # 1, 1, 32, 16]),
58 | model._blocks[0]._depthwise_conv.weight: 'blocks_0/depthwise_conv2d/depthwise_kernel', # [3, 3, 32, 1]),
59 | model._blocks[0]._se_reduce.bias: 'blocks_0/se/conv2d/bias', # , [8]),
60 | model._blocks[0]._se_reduce.weight: 'blocks_0/se/conv2d/kernel', # , [1, 1, 32, 8]),
61 | model._blocks[0]._se_expand.bias: 'blocks_0/se/conv2d_1/bias', # , [32]),
62 | model._blocks[0]._se_expand.weight: 'blocks_0/se/conv2d_1/kernel', # , [1, 1, 8, 32]),
63 | model._blocks[0]._bn1.bias: 'blocks_0/tpu_batch_normalization/beta', # [32]),
64 | model._blocks[0]._bn1.weight: 'blocks_0/tpu_batch_normalization/gamma', # [32]),
65 | model._blocks[0]._bn1.running_mean: 'blocks_0/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_mean',
66 | model._blocks[0]._bn1.running_var: 'blocks_0/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_variance',
67 | model._blocks[0]._bn2.bias: 'blocks_0/tpu_batch_normalization_1/beta', # [16]),
68 | model._blocks[0]._bn2.weight: 'blocks_0/tpu_batch_normalization_1/gamma', # [16]),
69 | model._blocks[0]._bn2.running_mean: 'blocks_0/tpu_batch_normalization_1/moving_mean',
70 | model._blocks[0]._bn2.running_var: 'blocks_0/tpu_batch_normalization_1/moving_variance',
71 | }
72 | conversion_table = merge(conversion_table, conversion_table_for_first_block)
73 |
74 | # Conv blocks
75 | for i in range(len(model._blocks)):
76 |
77 | is_first_block = '_expand_conv.weight' not in [n for n, p in model._blocks[i].named_parameters()]
78 |
79 | if is_first_block:
80 | conversion_table_block = {
81 | model._blocks[i]._project_conv.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/conv2d/kernel', # 1, 1, 32, 16]),
82 | model._blocks[i]._depthwise_conv.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/depthwise_conv2d/depthwise_kernel',
83 | # [3, 3, 32, 1]),
84 | model._blocks[i]._se_reduce.bias: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/se/conv2d/bias', # , [8]),
85 | model._blocks[i]._se_reduce.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/se/conv2d/kernel', # , [1, 1, 32, 8]),
86 | model._blocks[i]._se_expand.bias: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/se/conv2d_1/bias', # , [32]),
87 | model._blocks[i]._se_expand.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/se/conv2d_1/kernel', # , [1, 1, 8, 32]),
88 | model._blocks[i]._bn1.bias: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization/beta', # [32]),
89 | model._blocks[i]._bn1.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization/gamma', # [32]),
90 | model._blocks[i]._bn1.running_mean: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_mean',
91 | model._blocks[i]._bn1.running_var: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_variance',
92 | model._blocks[i]._bn2.bias: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_1/beta', # [16]),
93 | model._blocks[i]._bn2.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_1/gamma', # [16]),
94 | model._blocks[i]._bn2.running_mean: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_1/moving_mean',
95 | model._blocks[i]._bn2.running_var: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_1/moving_variance',
96 | }
97 |
98 | else:
99 | conversion_table_block = {
100 | model._blocks[i]._expand_conv.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/conv2d/kernel',
101 | model._blocks[i]._project_conv.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/conv2d_1/kernel',
102 | model._blocks[i]._depthwise_conv.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/depthwise_conv2d/depthwise_kernel',
103 | model._blocks[i]._se_reduce.bias: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/se/conv2d/bias',
104 | model._blocks[i]._se_reduce.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/se/conv2d/kernel',
105 | model._blocks[i]._se_expand.bias: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/se/conv2d_1/bias',
106 | model._blocks[i]._se_expand.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/se/conv2d_1/kernel',
107 | model._blocks[i]._bn0.bias: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization/beta',
108 | model._blocks[i]._bn0.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization/gamma',
109 | model._blocks[i]._bn0.running_mean: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_mean',
110 | model._blocks[i]._bn0.running_var: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_variance',
111 | model._blocks[i]._bn1.bias: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_1/beta',
112 | model._blocks[i]._bn1.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_1/gamma',
113 | model._blocks[i]._bn1.running_mean: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_1/moving_mean',
114 | model._blocks[i]._bn1.running_var: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_1/moving_variance',
115 | model._blocks[i]._bn2.bias: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_2/beta',
116 | model._blocks[i]._bn2.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_2/gamma',
117 | model._blocks[i]._bn2.running_mean: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_2/moving_mean',
118 | model._blocks[i]._bn2.running_var: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_2/moving_variance',
119 | }
120 |
121 | conversion_table = merge(conversion_table, conversion_table_block)
122 |
123 | # Load TensorFlow parameters into PyTorch model
124 | load_param(checkpoint_file, conversion_table, model_name)
125 | return conversion_table
126 |
127 |
128 | def load_and_save_temporary_tensorflow_model(model_name, model_ckpt, example_img= '../../example/img.jpg'):
129 | """ Loads and saves a TensorFlow model. """
130 | image_files = [example_img]
131 | eval_ckpt_driver = eval_ckpt_main.EvalCkptDriver(model_name)
132 | with tf.Graph().as_default(), tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess:
133 | images, labels = eval_ckpt_driver.build_dataset(image_files, [0] * len(image_files), False)
134 | probs = eval_ckpt_driver.build_model(images, is_training=False)
135 | sess.run(tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer())
136 | print(model_ckpt)
137 | eval_ckpt_driver.restore_model(sess, model_ckpt)
138 | tf.compat.v1.train.Saver().save(sess, 'tmp/model.ckpt')
139 |
140 |
141 | if __name__ == '__main__':
142 |
143 | import sys
144 | import argparse
145 |
146 | sys.path.append('original_tf')
147 | import eval_ckpt_main
148 |
149 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet
150 |
151 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
152 | description='Convert TF model to PyTorch model and save for easier future loading')
153 | parser.add_argument('--model_name', type=str, default='efficientnet-b0',
154 | help='efficientnet-b{N}, where N is an integer 0 <= N <= 8')
155 | parser.add_argument('--tf_checkpoint', type=str, default='pretrained_tensorflow/efficientnet-b0/',
156 | help='checkpoint file path')
157 | parser.add_argument('--output_file', type=str, default='pretrained_pytorch/efficientnet-b0.pth',
158 | help='output PyTorch model file name')
159 | args = parser.parse_args()
160 |
161 | # Build model
162 | model = EfficientNet.from_name(args.model_name)
163 |
164 | # Load and save temporary TensorFlow file due to TF nuances
165 | print(args.tf_checkpoint)
166 | load_and_save_temporary_tensorflow_model(args.model_name, args.tf_checkpoint)
167 |
168 | # Load weights
169 | load_efficientnet(model, 'tmp/model.ckpt', model_name=args.model_name)
170 | print('Loaded TF checkpoint weights')
171 |
172 | # Save PyTorch file
173 | torch.save(model.state_dict(), args.output_file)
174 | print('Saved model to', args.output_file)
175 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tf_to_pytorch/convert_tf_to_pt/load_tf_weights_tf1.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import tensorflow as tf
3 | import torch
4 |
5 | def load_param(checkpoint_file, conversion_table, model_name):
6 | """
7 | Load parameters according to conversion_table.
8 |
9 | Args:
10 | checkpoint_file (string): pretrained checkpoint model file in tensorflow
11 | conversion_table (dict): { pytorch tensor in a model : checkpoint variable name }
12 | """
13 | for pyt_param, tf_param_name in conversion_table.items():
14 | tf_param_name = str(model_name) + '/' + tf_param_name
15 | tf_param = tf.train.load_variable(checkpoint_file, tf_param_name)
16 | if 'conv' in tf_param_name and 'kernel' in tf_param_name:
17 | tf_param = np.transpose(tf_param, (3, 2, 0, 1))
18 | if 'depthwise' in tf_param_name:
19 | tf_param = np.transpose(tf_param, (1, 0, 2, 3))
20 | elif tf_param_name.endswith('kernel'): # for weight(kernel), we should do transpose
21 | tf_param = np.transpose(tf_param)
22 | assert pyt_param.size() == tf_param.shape, \
23 | 'Dim Mismatch: %s vs %s ; %s' % (tuple(pyt_param.size()), tf_param.shape, tf_param_name)
24 | pyt_param.data = torch.from_numpy(tf_param)
25 |
26 |
27 | def load_efficientnet(model, checkpoint_file, model_name):
28 | """
29 | Load PyTorch EfficientNet from TensorFlow checkpoint file
30 | """
31 |
32 | # This will store the enire conversion table
33 | conversion_table = {}
34 | merge = lambda dict1, dict2: {**dict1, **dict2}
35 |
36 | # All the weights not in the conv blocks
37 | conversion_table_for_weights_outside_blocks = {
38 | model._conv_stem.weight: 'stem/conv2d/kernel', # [3, 3, 3, 32]),
39 | model._bn0.bias: 'stem/tpu_batch_normalization/beta', # [32]),
40 | model._bn0.weight: 'stem/tpu_batch_normalization/gamma', # [32]),
41 | model._bn0.running_mean: 'stem/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_mean', # [32]),
42 | model._bn0.running_var: 'stem/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_variance', # [32]),
43 | model._conv_head.weight: 'head/conv2d/kernel', # [1, 1, 320, 1280]),
44 | model._bn1.bias: 'head/tpu_batch_normalization/beta', # [1280]),
45 | model._bn1.weight: 'head/tpu_batch_normalization/gamma', # [1280]),
46 | model._bn1.running_mean: 'head/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_mean', # [32]),
47 | model._bn1.running_var: 'head/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_variance', # [32]),
48 | model._fc.bias: 'head/dense/bias', # [1000]),
49 | model._fc.weight: 'head/dense/kernel', # [1280, 1000]),
50 | }
51 | conversion_table = merge(conversion_table, conversion_table_for_weights_outside_blocks)
52 |
53 | # The first conv block is special because it does not have _expand_conv
54 | conversion_table_for_first_block = {
55 | model._blocks[0]._project_conv.weight: 'blocks_0/conv2d/kernel', # 1, 1, 32, 16]),
56 | model._blocks[0]._depthwise_conv.weight: 'blocks_0/depthwise_conv2d/depthwise_kernel', # [3, 3, 32, 1]),
57 | model._blocks[0]._se_reduce.bias: 'blocks_0/se/conv2d/bias', # , [8]),
58 | model._blocks[0]._se_reduce.weight: 'blocks_0/se/conv2d/kernel', # , [1, 1, 32, 8]),
59 | model._blocks[0]._se_expand.bias: 'blocks_0/se/conv2d_1/bias', # , [32]),
60 | model._blocks[0]._se_expand.weight: 'blocks_0/se/conv2d_1/kernel', # , [1, 1, 8, 32]),
61 | model._blocks[0]._bn1.bias: 'blocks_0/tpu_batch_normalization/beta', # [32]),
62 | model._blocks[0]._bn1.weight: 'blocks_0/tpu_batch_normalization/gamma', # [32]),
63 | model._blocks[0]._bn1.running_mean: 'blocks_0/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_mean',
64 | model._blocks[0]._bn1.running_var: 'blocks_0/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_variance',
65 | model._blocks[0]._bn2.bias: 'blocks_0/tpu_batch_normalization_1/beta', # [16]),
66 | model._blocks[0]._bn2.weight: 'blocks_0/tpu_batch_normalization_1/gamma', # [16]),
67 | model._blocks[0]._bn2.running_mean: 'blocks_0/tpu_batch_normalization_1/moving_mean',
68 | model._blocks[0]._bn2.running_var: 'blocks_0/tpu_batch_normalization_1/moving_variance',
69 | }
70 | conversion_table = merge(conversion_table, conversion_table_for_first_block)
71 |
72 | # Conv blocks
73 | for i in range(len(model._blocks)):
74 |
75 | is_first_block = '_expand_conv.weight' not in [n for n, p in model._blocks[i].named_parameters()]
76 |
77 | if is_first_block:
78 | conversion_table_block = {
79 | model._blocks[i]._project_conv.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/conv2d/kernel', # 1, 1, 32, 16]),
80 | model._blocks[i]._depthwise_conv.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/depthwise_conv2d/depthwise_kernel',
81 | # [3, 3, 32, 1]),
82 | model._blocks[i]._se_reduce.bias: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/se/conv2d/bias', # , [8]),
83 | model._blocks[i]._se_reduce.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/se/conv2d/kernel', # , [1, 1, 32, 8]),
84 | model._blocks[i]._se_expand.bias: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/se/conv2d_1/bias', # , [32]),
85 | model._blocks[i]._se_expand.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/se/conv2d_1/kernel', # , [1, 1, 8, 32]),
86 | model._blocks[i]._bn1.bias: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization/beta', # [32]),
87 | model._blocks[i]._bn1.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization/gamma', # [32]),
88 | model._blocks[i]._bn1.running_mean: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_mean',
89 | model._blocks[i]._bn1.running_var: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_variance',
90 | model._blocks[i]._bn2.bias: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_1/beta', # [16]),
91 | model._blocks[i]._bn2.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_1/gamma', # [16]),
92 | model._blocks[i]._bn2.running_mean: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_1/moving_mean',
93 | model._blocks[i]._bn2.running_var: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_1/moving_variance',
94 | }
95 |
96 | else:
97 | conversion_table_block = {
98 | model._blocks[i]._expand_conv.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/conv2d/kernel',
99 | model._blocks[i]._project_conv.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/conv2d_1/kernel',
100 | model._blocks[i]._depthwise_conv.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/depthwise_conv2d/depthwise_kernel',
101 | model._blocks[i]._se_reduce.bias: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/se/conv2d/bias',
102 | model._blocks[i]._se_reduce.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/se/conv2d/kernel',
103 | model._blocks[i]._se_expand.bias: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/se/conv2d_1/bias',
104 | model._blocks[i]._se_expand.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/se/conv2d_1/kernel',
105 | model._blocks[i]._bn0.bias: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization/beta',
106 | model._blocks[i]._bn0.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization/gamma',
107 | model._blocks[i]._bn0.running_mean: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_mean',
108 | model._blocks[i]._bn0.running_var: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization/moving_variance',
109 | model._blocks[i]._bn1.bias: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_1/beta',
110 | model._blocks[i]._bn1.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_1/gamma',
111 | model._blocks[i]._bn1.running_mean: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_1/moving_mean',
112 | model._blocks[i]._bn1.running_var: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_1/moving_variance',
113 | model._blocks[i]._bn2.bias: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_2/beta',
114 | model._blocks[i]._bn2.weight: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_2/gamma',
115 | model._blocks[i]._bn2.running_mean: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_2/moving_mean',
116 | model._blocks[i]._bn2.running_var: 'blocks_' + str(i) + '/tpu_batch_normalization_2/moving_variance',
117 | }
118 |
119 | conversion_table = merge(conversion_table, conversion_table_block)
120 |
121 | # Load TensorFlow parameters into PyTorch model
122 | load_param(checkpoint_file, conversion_table, model_name)
123 | return conversion_table
124 |
125 |
126 | def load_and_save_temporary_tensorflow_model(model_name, model_ckpt, example_img= '../../example/img.jpg'):
127 | """ Loads and saves a TensorFlow model. """
128 | image_files = [example_img]
129 | eval_ckpt_driver = eval_ckpt_main.EvalCkptDriver(model_name)
130 | with tf.Graph().as_default(), tf.Session() as sess:
131 | images, labels = eval_ckpt_driver.build_dataset(image_files, [0] * len(image_files), False)
132 | probs = eval_ckpt_driver.build_model(images, is_training=False)
133 | sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
134 | print(model_ckpt)
135 | eval_ckpt_driver.restore_model(sess, model_ckpt)
136 | tf.train.Saver().save(sess, 'tmp/model.ckpt')
137 |
138 |
139 | if __name__ == '__main__':
140 |
141 | import sys
142 | import argparse
143 |
144 | sys.path.append('original_tf')
145 | import eval_ckpt_main
146 |
147 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet
148 |
149 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
150 | description='Convert TF model to PyTorch model and save for easier future loading')
151 | parser.add_argument('--model_name', type=str, default='efficientnet-b0',
152 | help='efficientnet-b{N}, where N is an integer 0 <= N <= 8')
153 | parser.add_argument('--tf_checkpoint', type=str, default='pretrained_tensorflow/efficientnet-b0/',
154 | help='checkpoint file path')
155 | parser.add_argument('--output_file', type=str, default='pretrained_pytorch/efficientnet-b0.pth',
156 | help='output PyTorch model file name')
157 | args = parser.parse_args()
158 |
159 | # Build model
160 | model = EfficientNet.from_name(args.model_name)
161 |
162 | # Load and save temporary TensorFlow file due to TF nuances
163 | print(args.tf_checkpoint)
164 | load_and_save_temporary_tensorflow_model(args.model_name, args.tf_checkpoint)
165 |
166 | # Load weights
167 | load_efficientnet(model, 'tmp/model.ckpt', model_name=args.model_name)
168 | print('Loaded TF checkpoint weights')
169 |
170 | # Save PyTorch file
171 | torch.save(model.state_dict(), args.output_file)
172 | print('Saved model to', args.output_file)
173 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tf_to_pytorch/convert_tf_to_pt/original_tf/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/7e8b0d312162f335785fb5dcfa1df29a75a1783a/tf_to_pytorch/convert_tf_to_pt/original_tf/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tf_to_pytorch/convert_tf_to_pt/original_tf/efficientnet_builder.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2019 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 | """Model Builder for EfficientNet."""
16 |
17 | from __future__ import absolute_import
18 | from __future__ import division
19 | from __future__ import print_function
20 |
21 | import functools
22 | import os
23 | import re
24 | from absl import logging
25 | import numpy as np
26 | import six
27 | import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
28 |
29 | import efficientnet_model
30 | import utils
31 | MEAN_RGB = [0.485 * 255, 0.456 * 255, 0.406 * 255]
32 | STDDEV_RGB = [0.229 * 255, 0.224 * 255, 0.225 * 255]
33 |
34 |
35 | def efficientnet_params(model_name):
36 | """Get efficientnet params based on model name."""
37 | params_dict = {
38 | # (width_coefficient, depth_coefficient, resolution, dropout_rate)
39 | 'efficientnet-b0': (1.0, 1.0, 224, 0.2),
40 | 'efficientnet-b1': (1.0, 1.1, 240, 0.2),
41 | 'efficientnet-b2': (1.1, 1.2, 260, 0.3),
42 | 'efficientnet-b3': (1.2, 1.4, 300, 0.3),
43 | 'efficientnet-b4': (1.4, 1.8, 380, 0.4),
44 | 'efficientnet-b5': (1.6, 2.2, 456, 0.4),
45 | 'efficientnet-b6': (1.8, 2.6, 528, 0.5),
46 | 'efficientnet-b7': (2.0, 3.1, 600, 0.5),
47 | 'efficientnet-b8': (2.2, 3.6, 672, 0.5),
48 | 'efficientnet-l2': (4.3, 5.3, 800, 0.5),
49 | }
50 | return params_dict[model_name]
51 |
52 |
53 | class BlockDecoder(object):
54 | """Block Decoder for readability."""
55 |
56 | def _decode_block_string(self, block_string):
57 | """Gets a block through a string notation of arguments."""
58 | if six.PY2:
59 | assert isinstance(block_string, (str, unicode))
60 | else:
61 | assert isinstance(block_string, str)
62 | ops = block_string.split('_')
63 | options = {}
64 | for op in ops:
65 | splits = re.split(r'(\d.*)', op)
66 | if len(splits) >= 2:
67 | key, value = splits[:2]
68 | options[key] = value
69 |
70 | if 's' not in options or len(options['s']) != 2:
71 | raise ValueError('Strides options should be a pair of integers.')
72 |
73 | return efficientnet_model.BlockArgs(
74 | kernel_size=int(options['k']),
75 | num_repeat=int(options['r']),
76 | input_filters=int(options['i']),
77 | output_filters=int(options['o']),
78 | expand_ratio=int(options['e']),
79 | id_skip=('noskip' not in block_string),
80 | se_ratio=float(options['se']) if 'se' in options else None,
81 | strides=[int(options['s'][0]),
82 | int(options['s'][1])],
83 | conv_type=int(options['c']) if 'c' in options else 0,
84 | fused_conv=int(options['f']) if 'f' in options else 0,
85 | super_pixel=int(options['p']) if 'p' in options else 0,
86 | condconv=('cc' in block_string))
87 |
88 | def _encode_block_string(self, block):
89 | """Encodes a block to a string."""
90 | args = [
91 | 'r%d' % block.num_repeat,
92 | 'k%d' % block.kernel_size,
93 | 's%d%d' % (block.strides[0], block.strides[1]),
94 | 'e%s' % block.expand_ratio,
95 | 'i%d' % block.input_filters,
96 | 'o%d' % block.output_filters,
97 | 'c%d' % block.conv_type,
98 | 'f%d' % block.fused_conv,
99 | 'p%d' % block.super_pixel,
100 | ]
101 | if block.se_ratio > 0 and block.se_ratio <= 1:
102 | args.append('se%s' % block.se_ratio)
103 | if block.id_skip is False: # pylint: disable=g-bool-id-comparison
104 | args.append('noskip')
105 | if block.condconv:
106 | args.append('cc')
107 | return '_'.join(args)
108 |
109 | def decode(self, string_list):
110 | """Decodes a list of string notations to specify blocks inside the network.
111 |
112 | Args:
113 | string_list: a list of strings, each string is a notation of block.
114 |
115 | Returns:
116 | A list of namedtuples to represent blocks arguments.
117 | """
118 | assert isinstance(string_list, list)
119 | blocks_args = []
120 | for block_string in string_list:
121 | blocks_args.append(self._decode_block_string(block_string))
122 | return blocks_args
123 |
124 | def encode(self, blocks_args):
125 | """Encodes a list of Blocks to a list of strings.
126 |
127 | Args:
128 | blocks_args: A list of namedtuples to represent blocks arguments.
129 | Returns:
130 | a list of strings, each string is a notation of block.
131 | """
132 | block_strings = []
133 | for block in blocks_args:
134 | block_strings.append(self._encode_block_string(block))
135 | return block_strings
136 |
137 |
138 | def swish(features, use_native=True, use_hard=False):
139 | """Computes the Swish activation function.
140 |
141 | We provide three alternnatives:
142 | - Native tf.nn.swish, use less memory during training than composable swish.
143 | - Quantization friendly hard swish.
144 | - A composable swish, equivalant to tf.nn.swish, but more general for
145 | finetuning and TF-Hub.
146 |
147 | Args:
148 | features: A `Tensor` representing preactivation values.
149 | use_native: Whether to use the native swish from tf.nn that uses a custom
150 | gradient to reduce memory usage, or to use customized swish that uses
151 | default TensorFlow gradient computation.
152 | use_hard: Whether to use quantization-friendly hard swish.
153 |
154 | Returns:
155 | The activation value.
156 | """
157 | if use_native and use_hard:
158 | raise ValueError('Cannot specify both use_native and use_hard.')
159 |
160 | if use_native:
161 | return tf.nn.swish(features)
162 |
163 | if use_hard:
164 | return features * tf.nn.relu6(features + np.float32(3)) * (1. / 6.)
165 |
166 | features = tf.convert_to_tensor(features, name='features')
167 | return features * tf.nn.sigmoid(features)
168 |
169 |
170 | _DEFAULT_BLOCKS_ARGS = [
171 | 'r1_k3_s11_e1_i32_o16_se0.25', 'r2_k3_s22_e6_i16_o24_se0.25',
172 | 'r2_k5_s22_e6_i24_o40_se0.25', 'r3_k3_s22_e6_i40_o80_se0.25',
173 | 'r3_k5_s11_e6_i80_o112_se0.25', 'r4_k5_s22_e6_i112_o192_se0.25',
174 | 'r1_k3_s11_e6_i192_o320_se0.25',
175 | ]
176 |
177 |
178 | def efficientnet(width_coefficient=None,
179 | depth_coefficient=None,
180 | dropout_rate=0.2,
181 | survival_prob=0.8):
182 | """Creates a efficientnet model."""
183 | global_params = efficientnet_model.GlobalParams(
184 | blocks_args=_DEFAULT_BLOCKS_ARGS,
185 | batch_norm_momentum=0.99,
186 | batch_norm_epsilon=1e-3,
187 | dropout_rate=dropout_rate,
188 | survival_prob=survival_prob,
189 | data_format='channels_last',
190 | num_classes=1000,
191 | width_coefficient=width_coefficient,
192 | depth_coefficient=depth_coefficient,
193 | depth_divisor=8,
194 | min_depth=None,
195 | relu_fn=tf.nn.swish,
196 | # The default is TPU-specific batch norm.
197 | # The alternative is tf.layers.BatchNormalization.
198 | batch_norm=utils.TpuBatchNormalization, # TPU-specific requirement.
199 | use_se=True,
200 | clip_projection_output=False)
201 | return global_params
202 |
203 |
204 | def get_model_params(model_name, override_params):
205 | """Get the block args and global params for a given model."""
206 | if model_name.startswith('efficientnet'):
207 | width_coefficient, depth_coefficient, _, dropout_rate = (
208 | efficientnet_params(model_name))
209 | global_params = efficientnet(
210 | width_coefficient, depth_coefficient, dropout_rate)
211 | else:
212 | raise NotImplementedError('model name is not pre-defined: %s' % model_name)
213 |
214 | if override_params:
215 | # ValueError will be raised here if override_params has fields not included
216 | # in global_params.
217 | global_params = global_params._replace(**override_params)
218 |
219 | decoder = BlockDecoder()
220 | blocks_args = decoder.decode(global_params.blocks_args)
221 |
222 | logging.info('global_params= %s', global_params)
223 | return blocks_args, global_params
224 |
225 |
226 | def build_model(images,
227 | model_name,
228 | training,
229 | override_params=None,
230 | model_dir=None,
231 | fine_tuning=False,
232 | features_only=False,
233 | pooled_features_only=False):
234 | """A helper functiion to creates a model and returns predicted logits.
235 |
236 | Args:
237 | images: input images tensor.
238 | model_name: string, the predefined model name.
239 | training: boolean, whether the model is constructed for training.
240 | override_params: A dictionary of params for overriding. Fields must exist in
241 | efficientnet_model.GlobalParams.
242 | model_dir: string, optional model dir for saving configs.
243 | fine_tuning: boolean, whether the model is used for finetuning.
244 | features_only: build the base feature network only (excluding final
245 | 1x1 conv layer, global pooling, dropout and fc head).
246 | pooled_features_only: build the base network for features extraction (after
247 | 1x1 conv layer and global pooling, but before dropout and fc head).
248 |
249 | Returns:
250 | logits: the logits tensor of classes.
251 | endpoints: the endpoints for each layer.
252 |
253 | Raises:
254 | When model_name specified an undefined model, raises NotImplementedError.
255 | When override_params has invalid fields, raises ValueError.
256 | """
257 | assert isinstance(images, tf.Tensor)
258 | assert not (features_only and pooled_features_only)
259 |
260 | # For backward compatibility.
261 | if override_params and override_params.get('drop_connect_rate', None):
262 | override_params['survival_prob'] = 1 - override_params['drop_connect_rate']
263 |
264 | if not training or fine_tuning:
265 | if not override_params:
266 | override_params = {}
267 | override_params['batch_norm'] = utils.BatchNormalization
268 | if fine_tuning:
269 | override_params['relu_fn'] = functools.partial(swish, use_native=False)
270 | blocks_args, global_params = get_model_params(model_name, override_params)
271 |
272 | if model_dir:
273 | param_file = os.path.join(model_dir, 'model_params.txt')
274 | if not tf.gfile.Exists(param_file):
275 | if not tf.gfile.Exists(model_dir):
276 | tf.gfile.MakeDirs(model_dir)
277 | with tf.gfile.GFile(param_file, 'w') as f:
278 | logging.info('writing to %s', param_file)
279 | f.write('model_name= %s\n\n' % model_name)
280 | f.write('global_params= %s\n\n' % str(global_params))
281 | f.write('blocks_args= %s\n\n' % str(blocks_args))
282 |
283 | with tf.variable_scope(model_name):
284 | model = efficientnet_model.Model(blocks_args, global_params)
285 | outputs = model(
286 | images,
287 | training=training,
288 | features_only=features_only,
289 | pooled_features_only=pooled_features_only)
290 | if features_only:
291 | outputs = tf.identity(outputs, 'features')
292 | elif pooled_features_only:
293 | outputs = tf.identity(outputs, 'pooled_features')
294 | else:
295 | outputs = tf.identity(outputs, 'logits')
296 | return outputs, model.endpoints
297 |
298 |
299 | def build_model_base(images, model_name, training, override_params=None):
300 | """A helper functiion to create a base model and return global_pool.
301 |
302 | Args:
303 | images: input images tensor.
304 | model_name: string, the predefined model name.
305 | training: boolean, whether the model is constructed for training.
306 | override_params: A dictionary of params for overriding. Fields must exist in
307 | efficientnet_model.GlobalParams.
308 |
309 | Returns:
310 | features: global pool features.
311 | endpoints: the endpoints for each layer.
312 |
313 | Raises:
314 | When model_name specified an undefined model, raises NotImplementedError.
315 | When override_params has invalid fields, raises ValueError.
316 | """
317 | assert isinstance(images, tf.Tensor)
318 | # For backward compatibility.
319 | if override_params and override_params.get('drop_connect_rate', None):
320 | override_params['survival_prob'] = 1 - override_params['drop_connect_rate']
321 |
322 | blocks_args, global_params = get_model_params(model_name, override_params)
323 |
324 | with tf.variable_scope(model_name):
325 | model = efficientnet_model.Model(blocks_args, global_params)
326 | features = model(images, training=training, features_only=True)
327 |
328 | features = tf.identity(features, 'features')
329 | return features, model.endpoints
330 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tf_to_pytorch/convert_tf_to_pt/original_tf/efficientnet_model.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2019 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 | """Contains definitions for EfficientNet model.
16 |
17 | [1] Mingxing Tan, Quoc V. Le
18 | EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks.
19 | ICML'19, https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.11946
20 | """
21 |
22 | from __future__ import absolute_import
23 | from __future__ import division
24 | from __future__ import print_function
25 |
26 | import collections
27 | import functools
28 | import math
29 |
30 | from absl import logging
31 | import numpy as np
32 | import six
33 | from six.moves import xrange
34 | import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
35 |
36 | import utils
37 | # from condconv import condconv_layers
38 |
39 | GlobalParams = collections.namedtuple('GlobalParams', [
40 | 'batch_norm_momentum', 'batch_norm_epsilon', 'dropout_rate', 'data_format',
41 | 'num_classes', 'width_coefficient', 'depth_coefficient', 'depth_divisor',
42 | 'min_depth', 'survival_prob', 'relu_fn', 'batch_norm', 'use_se',
43 | 'local_pooling', 'condconv_num_experts', 'clip_projection_output',
44 | 'blocks_args'
45 | ])
46 | GlobalParams.__new__.__defaults__ = (None,) * len(GlobalParams._fields)
47 |
48 | BlockArgs = collections.namedtuple('BlockArgs', [
49 | 'kernel_size', 'num_repeat', 'input_filters', 'output_filters',
50 | 'expand_ratio', 'id_skip', 'strides', 'se_ratio', 'conv_type', 'fused_conv',
51 | 'super_pixel', 'condconv'
52 | ])
53 | # defaults will be a public argument for namedtuple in Python 3.7
54 | # https://docs.python.org/3/library/collections.html#collections.namedtuple
55 | BlockArgs.__new__.__defaults__ = (None,) * len(BlockArgs._fields)
56 |
57 |
58 | def conv_kernel_initializer(shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None):
59 | """Initialization for convolutional kernels.
60 |
61 | The main difference with tf.variance_scaling_initializer is that
62 | tf.variance_scaling_initializer uses a truncated normal with an uncorrected
63 | standard deviation, whereas here we use a normal distribution. Similarly,
64 | tf.initializers.variance_scaling uses a truncated normal with
65 | a corrected standard deviation.
66 |
67 | Args:
68 | shape: shape of variable
69 | dtype: dtype of variable
70 | partition_info: unused
71 |
72 | Returns:
73 | an initialization for the variable
74 | """
75 | del partition_info
76 | kernel_height, kernel_width, _, out_filters = shape
77 | fan_out = int(kernel_height * kernel_width * out_filters)
78 | return tf.random_normal(
79 | shape, mean=0.0, stddev=np.sqrt(2.0 / fan_out), dtype=dtype)
80 |
81 |
82 | def dense_kernel_initializer(shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None):
83 | """Initialization for dense kernels.
84 |
85 | This initialization is equal to
86 | tf.variance_scaling_initializer(scale=1.0/3.0, mode='fan_out',
87 | distribution='uniform').
88 | It is written out explicitly here for clarity.
89 |
90 | Args:
91 | shape: shape of variable
92 | dtype: dtype of variable
93 | partition_info: unused
94 |
95 | Returns:
96 | an initialization for the variable
97 | """
98 | del partition_info
99 | init_range = 1.0 / np.sqrt(shape[1])
100 | return tf.random_uniform(shape, -init_range, init_range, dtype=dtype)
101 |
102 |
103 | def superpixel_kernel_initializer(shape, dtype='float32', partition_info=None):
104 | """Initializes superpixel kernels.
105 |
106 | This is inspired by space-to-depth transformation that is mathematically
107 | equivalent before and after the transformation. But we do the space-to-depth
108 | via a convolution. Moreover, we make the layer trainable instead of direct
109 | transform, we can initialization it this way so that the model can learn not
110 | to do anything but keep it mathematically equivalent, when improving
111 | performance.
112 |
113 |
114 | Args:
115 | shape: shape of variable
116 | dtype: dtype of variable
117 | partition_info: unused
118 |
119 | Returns:
120 | an initialization for the variable
121 | """
122 | del partition_info
123 | # use input depth to make superpixel kernel.
124 | depth = shape[-2]
125 | filters = np.zeros([2, 2, depth, 4 * depth], dtype=dtype)
126 | i = np.arange(2)
127 | j = np.arange(2)
128 | k = np.arange(depth)
129 | mesh = np.array(np.meshgrid(i, j, k)).T.reshape(-1, 3).T
130 | filters[
131 | mesh[0],
132 | mesh[1],
133 | mesh[2],
134 | 4 * mesh[2] + 2 * mesh[0] + mesh[1]] = 1
135 | return filters
136 |
137 |
138 | def round_filters(filters, global_params):
139 | """Round number of filters based on depth multiplier."""
140 | orig_f = filters
141 | multiplier = global_params.width_coefficient
142 | divisor = global_params.depth_divisor
143 | min_depth = global_params.min_depth
144 | if not multiplier:
145 | return filters
146 |
147 | filters *= multiplier
148 | min_depth = min_depth or divisor
149 | new_filters = max(min_depth, int(filters + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)
150 | # Make sure that round down does not go down by more than 10%.
151 | if new_filters < 0.9 * filters:
152 | new_filters += divisor
153 | logging.info('round_filter input=%s output=%s', orig_f, new_filters)
154 | return int(new_filters)
155 |
156 |
157 | def round_repeats(repeats, global_params):
158 | """Round number of filters based on depth multiplier."""
159 | multiplier = global_params.depth_coefficient
160 | if not multiplier:
161 | return repeats
162 | return int(math.ceil(multiplier * repeats))
163 |
164 |
165 | class MBConvBlock(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
166 | """A class of MBConv: Mobile Inverted Residual Bottleneck.
167 |
168 | Attributes:
169 | endpoints: dict. A list of internal tensors.
170 | """
171 |
172 | def __init__(self, block_args, global_params):
173 | """Initializes a MBConv block.
174 |
175 | Args:
176 | block_args: BlockArgs, arguments to create a Block.
177 | global_params: GlobalParams, a set of global parameters.
178 | """
179 | super(MBConvBlock, self).__init__()
180 | self._block_args = block_args
181 | self._batch_norm_momentum = global_params.batch_norm_momentum
182 | self._batch_norm_epsilon = global_params.batch_norm_epsilon
183 | self._batch_norm = global_params.batch_norm
184 | self._condconv_num_experts = global_params.condconv_num_experts
185 | self._data_format = global_params.data_format
186 | if self._data_format == 'channels_first':
187 | self._channel_axis = 1
188 | self._spatial_dims = [2, 3]
189 | else:
190 | self._channel_axis = -1
191 | self._spatial_dims = [1, 2]
192 |
193 | self._relu_fn = global_params.relu_fn or tf.nn.swish
194 | self._has_se = (
195 | global_params.use_se and self._block_args.se_ratio is not None and
196 | 0 < self._block_args.se_ratio <= 1)
197 |
198 | self._clip_projection_output = global_params.clip_projection_output
199 |
200 | self.endpoints = None
201 |
202 | self.conv_cls = tf.layers.Conv2D
203 | self.depthwise_conv_cls = utils.DepthwiseConv2D
204 | if self._block_args.condconv:
205 | self.conv_cls = functools.partial(
206 | condconv_layers.CondConv2D, num_experts=self._condconv_num_experts)
207 | self.depthwise_conv_cls = functools.partial(
208 | condconv_layers.DepthwiseCondConv2D,
209 | num_experts=self._condconv_num_experts)
210 |
211 | # Builds the block accordings to arguments.
212 | self._build()
213 |
214 | def block_args(self):
215 | return self._block_args
216 |
217 | def _build(self):
218 | """Builds block according to the arguments."""
219 | if self._block_args.super_pixel == 1:
220 | self._superpixel = tf.layers.Conv2D(
221 | self._block_args.input_filters,
222 | kernel_size=[2, 2],
223 | strides=[2, 2],
224 | kernel_initializer=conv_kernel_initializer,
225 | padding='same',
226 | data_format=self._data_format,
227 | use_bias=False)
228 | self._bnsp = self._batch_norm(
229 | axis=self._channel_axis,
230 | momentum=self._batch_norm_momentum,
231 | epsilon=self._batch_norm_epsilon)
232 |
233 | if self._block_args.condconv:
234 | # Add the example-dependent routing function
235 | self._avg_pooling = tf.keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D(
236 | data_format=self._data_format)
237 | self._routing_fn = tf.layers.Dense(
238 | self._condconv_num_experts, activation=tf.nn.sigmoid)
239 |
240 | filters = self._block_args.input_filters * self._block_args.expand_ratio
241 | kernel_size = self._block_args.kernel_size
242 |
243 | # Fused expansion phase. Called if using fused convolutions.
244 | self._fused_conv = self.conv_cls(
245 | filters=filters,
246 | kernel_size=[kernel_size, kernel_size],
247 | strides=self._block_args.strides,
248 | kernel_initializer=conv_kernel_initializer,
249 | padding='same',
250 | data_format=self._data_format,
251 | use_bias=False)
252 |
253 | # Expansion phase. Called if not using fused convolutions and expansion
254 | # phase is necessary.
255 | self._expand_conv = self.conv_cls(
256 | filters=filters,
257 | kernel_size=[1, 1],
258 | strides=[1, 1],
259 | kernel_initializer=conv_kernel_initializer,
260 | padding='same',
261 | data_format=self._data_format,
262 | use_bias=False)
263 | self._bn0 = self._batch_norm(
264 | axis=self._channel_axis,
265 | momentum=self._batch_norm_momentum,
266 | epsilon=self._batch_norm_epsilon)
267 |
268 | # Depth-wise convolution phase. Called if not using fused convolutions.
269 | self._depthwise_conv = self.depthwise_conv_cls(
270 | kernel_size=[kernel_size, kernel_size],
271 | strides=self._block_args.strides,
272 | depthwise_initializer=conv_kernel_initializer,
273 | padding='same',
274 | data_format=self._data_format,
275 | use_bias=False)
276 |
277 | self._bn1 = self._batch_norm(
278 | axis=self._channel_axis,
279 | momentum=self._batch_norm_momentum,
280 | epsilon=self._batch_norm_epsilon)
281 |
282 | if self._has_se:
283 | num_reduced_filters = max(
284 | 1, int(self._block_args.input_filters * self._block_args.se_ratio))
285 | # Squeeze and Excitation layer.
286 | self._se_reduce = tf.layers.Conv2D(
287 | num_reduced_filters,
288 | kernel_size=[1, 1],
289 | strides=[1, 1],
290 | kernel_initializer=conv_kernel_initializer,
291 | padding='same',
292 | data_format=self._data_format,
293 | use_bias=True)
294 | self._se_expand = tf.layers.Conv2D(
295 | filters,
296 | kernel_size=[1, 1],
297 | strides=[1, 1],
298 | kernel_initializer=conv_kernel_initializer,
299 | padding='same',
300 | data_format=self._data_format,
301 | use_bias=True)
302 |
303 | # Output phase.
304 | filters = self._block_args.output_filters
305 | self._project_conv = self.conv_cls(
306 | filters=filters,
307 | kernel_size=[1, 1],
308 | strides=[1, 1],
309 | kernel_initializer=conv_kernel_initializer,
310 | padding='same',
311 | data_format=self._data_format,
312 | use_bias=False)
313 | self._bn2 = self._batch_norm(
314 | axis=self._channel_axis,
315 | momentum=self._batch_norm_momentum,
316 | epsilon=self._batch_norm_epsilon)
317 |
318 | def _call_se(self, input_tensor):
319 | """Call Squeeze and Excitation layer.
320 |
321 | Args:
322 | input_tensor: Tensor, a single input tensor for Squeeze/Excitation layer.
323 |
324 | Returns:
325 | A output tensor, which should have the same shape as input.
326 | """
327 | se_tensor = tf.reduce_mean(input_tensor, self._spatial_dims, keepdims=True)
328 | se_tensor = self._se_expand(self._relu_fn(self._se_reduce(se_tensor)))
329 | logging.info('Built Squeeze and Excitation with tensor shape: %s',
330 | (se_tensor.shape))
331 | return tf.sigmoid(se_tensor) * input_tensor
332 |
333 | def call(self, inputs, training=True, survival_prob=None):
334 | """Implementation of call().
335 |
336 | Args:
337 | inputs: the inputs tensor.
338 | training: boolean, whether the model is constructed for training.
339 | survival_prob: float, between 0 to 1, drop connect rate.
340 |
341 | Returns:
342 | A output tensor.
343 | """
344 | logging.info('Block input: %s shape: %s', inputs.name, inputs.shape)
345 | logging.info('Block input depth: %s output depth: %s',
346 | self._block_args.input_filters,
347 | self._block_args.output_filters)
348 |
349 | x = inputs
350 |
351 | fused_conv_fn = self._fused_conv
352 | expand_conv_fn = self._expand_conv
353 | depthwise_conv_fn = self._depthwise_conv
354 | project_conv_fn = self._project_conv
355 |
356 | if self._block_args.condconv:
357 | pooled_inputs = self._avg_pooling(inputs)
358 | routing_weights = self._routing_fn(pooled_inputs)
359 | # Capture routing weights as additional input to CondConv layers
360 | fused_conv_fn = functools.partial(
361 | self._fused_conv, routing_weights=routing_weights)
362 | expand_conv_fn = functools.partial(
363 | self._expand_conv, routing_weights=routing_weights)
364 | depthwise_conv_fn = functools.partial(
365 | self._depthwise_conv, routing_weights=routing_weights)
366 | project_conv_fn = functools.partial(
367 | self._project_conv, routing_weights=routing_weights)
368 |
369 | # creates conv 2x2 kernel
370 | if self._block_args.super_pixel == 1:
371 | with tf.variable_scope('super_pixel'):
372 | x = self._relu_fn(
373 | self._bnsp(self._superpixel(x), training=training))
374 | logging.info(
375 | 'Block start with SuperPixel: %s shape: %s', x.name, x.shape)
376 |
377 | if self._block_args.fused_conv:
378 | # If use fused mbconv, skip expansion and use regular conv.
379 | x = self._relu_fn(self._bn1(fused_conv_fn(x), training=training))
380 | logging.info('Conv2D: %s shape: %s', x.name, x.shape)
381 | else:
382 | # Otherwise, first apply expansion and then apply depthwise conv.
383 | if self._block_args.expand_ratio != 1:
384 | x = self._relu_fn(self._bn0(expand_conv_fn(x), training=training))
385 | logging.info('Expand: %s shape: %s', x.name, x.shape)
386 |
387 | x = self._relu_fn(self._bn1(depthwise_conv_fn(x), training=training))
388 | logging.info('DWConv: %s shape: %s', x.name, x.shape)
389 |
390 | if self._has_se:
391 | with tf.variable_scope('se'):
392 | x = self._call_se(x)
393 |
394 | self.endpoints = {'expansion_output': x}
395 |
396 | x = self._bn2(project_conv_fn(x), training=training)
397 | # Add identity so that quantization-aware training can insert quantization
398 | # ops correctly.
399 | x = tf.identity(x)
400 | if self._clip_projection_output:
401 | x = tf.clip_by_value(x, -6, 6)
402 | if self._block_args.id_skip:
403 | if all(
404 | s == 1 for s in self._block_args.strides
405 | ) and self._block_args.input_filters == self._block_args.output_filters:
406 | # Apply only if skip connection presents.
407 | if survival_prob:
408 | x = utils.drop_connect(x, training, survival_prob)
409 | x = tf.add(x, inputs)
410 | logging.info('Project: %s shape: %s', x.name, x.shape)
411 | return x
412 |
413 |
414 | class MBConvBlockWithoutDepthwise(MBConvBlock):
415 | """MBConv-like block without depthwise convolution and squeeze-and-excite."""
416 |
417 | def _build(self):
418 | """Builds block according to the arguments."""
419 | filters = self._block_args.input_filters * self._block_args.expand_ratio
420 | if self._block_args.expand_ratio != 1:
421 | # Expansion phase:
422 | self._expand_conv = tf.layers.Conv2D(
423 | filters,
424 | kernel_size=[3, 3],
425 | strides=[1, 1],
426 | kernel_initializer=conv_kernel_initializer,
427 | padding='same',
428 | use_bias=False)
429 | self._bn0 = self._batch_norm(
430 | axis=self._channel_axis,
431 | momentum=self._batch_norm_momentum,
432 | epsilon=self._batch_norm_epsilon)
433 |
434 | # Output phase:
435 | filters = self._block_args.output_filters
436 | self._project_conv = tf.layers.Conv2D(
437 | filters,
438 | kernel_size=[1, 1],
439 | strides=self._block_args.strides,
440 | kernel_initializer=conv_kernel_initializer,
441 | padding='same',
442 | use_bias=False)
443 | self._bn1 = self._batch_norm(
444 | axis=self._channel_axis,
445 | momentum=self._batch_norm_momentum,
446 | epsilon=self._batch_norm_epsilon)
447 |
448 | def call(self, inputs, training=True, survival_prob=None):
449 | """Implementation of call().
450 |
451 | Args:
452 | inputs: the inputs tensor.
453 | training: boolean, whether the model is constructed for training.
454 | survival_prob: float, between 0 to 1, drop connect rate.
455 |
456 | Returns:
457 | A output tensor.
458 | """
459 | logging.info('Block input: %s shape: %s', inputs.name, inputs.shape)
460 | if self._block_args.expand_ratio != 1:
461 | x = self._relu_fn(self._bn0(self._expand_conv(inputs), training=training))
462 | else:
463 | x = inputs
464 | logging.info('Expand: %s shape: %s', x.name, x.shape)
465 |
466 | self.endpoints = {'expansion_output': x}
467 |
468 | x = self._bn1(self._project_conv(x), training=training)
469 | # Add identity so that quantization-aware training can insert quantization
470 | # ops correctly.
471 | x = tf.identity(x)
472 | if self._clip_projection_output:
473 | x = tf.clip_by_value(x, -6, 6)
474 |
475 | if self._block_args.id_skip:
476 | if all(
477 | s == 1 for s in self._block_args.strides
478 | ) and self._block_args.input_filters == self._block_args.output_filters:
479 | # Apply only if skip connection presents.
480 | if survival_prob:
481 | x = utils.drop_connect(x, training, survival_prob)
482 | x = tf.add(x, inputs)
483 | logging.info('Project: %s shape: %s', x.name, x.shape)
484 | return x
485 |
486 |
487 | class Model(tf.keras.Model):
488 | """A class implements tf.keras.Model for MNAS-like model.
489 |
490 | Reference: https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.11626
491 | """
492 |
493 | def __init__(self, blocks_args=None, global_params=None):
494 | """Initializes an `Model` instance.
495 |
496 | Args:
497 | blocks_args: A list of BlockArgs to construct block modules.
498 | global_params: GlobalParams, a set of global parameters.
499 |
500 | Raises:
501 | ValueError: when blocks_args is not specified as a list.
502 | """
503 | super(Model, self).__init__()
504 | if not isinstance(blocks_args, list):
505 | raise ValueError('blocks_args should be a list.')
506 | self._global_params = global_params
507 | self._blocks_args = blocks_args
508 | self._relu_fn = global_params.relu_fn or tf.nn.swish
509 | self._batch_norm = global_params.batch_norm
510 |
511 | self.endpoints = None
512 |
513 | self._build()
514 |
515 | def _get_conv_block(self, conv_type):
516 | conv_block_map = {0: MBConvBlock, 1: MBConvBlockWithoutDepthwise}
517 | return conv_block_map[conv_type]
518 |
519 | def _build(self):
520 | """Builds a model."""
521 | self._blocks = []
522 | batch_norm_momentum = self._global_params.batch_norm_momentum
523 | batch_norm_epsilon = self._global_params.batch_norm_epsilon
524 | if self._global_params.data_format == 'channels_first':
525 | channel_axis = 1
526 | self._spatial_dims = [2, 3]
527 | else:
528 | channel_axis = -1
529 | self._spatial_dims = [1, 2]
530 |
531 | # Stem part.
532 | self._conv_stem = tf.layers.Conv2D(
533 | filters=round_filters(32, self._global_params),
534 | kernel_size=[3, 3],
535 | strides=[2, 2],
536 | kernel_initializer=conv_kernel_initializer,
537 | padding='same',
538 | data_format=self._global_params.data_format,
539 | use_bias=False)
540 | self._bn0 = self._batch_norm(
541 | axis=channel_axis,
542 | momentum=batch_norm_momentum,
543 | epsilon=batch_norm_epsilon)
544 |
545 | # Builds blocks.
546 | for block_args in self._blocks_args:
547 | assert block_args.num_repeat > 0
548 | assert block_args.super_pixel in [0, 1, 2]
549 | # Update block input and output filters based on depth multiplier.
550 | input_filters = round_filters(block_args.input_filters,
551 | self._global_params)
552 | output_filters = round_filters(block_args.output_filters,
553 | self._global_params)
554 | kernel_size = block_args.kernel_size
555 | block_args = block_args._replace(
556 | input_filters=input_filters,
557 | output_filters=output_filters,
558 | num_repeat=round_repeats(block_args.num_repeat, self._global_params))
559 |
560 | # The first block needs to take care of stride and filter size increase.
561 | conv_block = self._get_conv_block(block_args.conv_type)
562 | if not block_args.super_pixel: # no super_pixel at all
563 | self._blocks.append(conv_block(block_args, self._global_params))
564 | else:
565 | # if superpixel, adjust filters, kernels, and strides.
566 | depth_factor = int(4 / block_args.strides[0] / block_args.strides[1])
567 | block_args = block_args._replace(
568 | input_filters=block_args.input_filters * depth_factor,
569 | output_filters=block_args.output_filters * depth_factor,
570 | kernel_size=((block_args.kernel_size + 1) // 2 if depth_factor > 1
571 | else block_args.kernel_size))
572 | # if the first block has stride-2 and super_pixel trandformation
573 | if (block_args.strides[0] == 2 and block_args.strides[1] == 2):
574 | block_args = block_args._replace(strides=[1, 1])
575 | self._blocks.append(conv_block(block_args, self._global_params))
576 | block_args = block_args._replace( # sp stops at stride-2
577 | super_pixel=0,
578 | input_filters=input_filters,
579 | output_filters=output_filters,
580 | kernel_size=kernel_size)
581 | elif block_args.super_pixel == 1:
582 | self._blocks.append(conv_block(block_args, self._global_params))
583 | block_args = block_args._replace(super_pixel=2)
584 | else:
585 | self._blocks.append(conv_block(block_args, self._global_params))
586 | if block_args.num_repeat > 1: # rest of blocks with the same block_arg
587 | # pylint: disable=protected-access
588 | block_args = block_args._replace(
589 | input_filters=block_args.output_filters, strides=[1, 1])
590 | # pylint: enable=protected-access
591 | for _ in xrange(block_args.num_repeat - 1):
592 | self._blocks.append(conv_block(block_args, self._global_params))
593 |
594 | # Head part.
595 | self._conv_head = tf.layers.Conv2D(
596 | filters=round_filters(1280, self._global_params),
597 | kernel_size=[1, 1],
598 | strides=[1, 1],
599 | kernel_initializer=conv_kernel_initializer,
600 | padding='same',
601 | use_bias=False)
602 | self._bn1 = self._batch_norm(
603 | axis=channel_axis,
604 | momentum=batch_norm_momentum,
605 | epsilon=batch_norm_epsilon)
606 |
607 | self._avg_pooling = tf.keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D(
608 | data_format=self._global_params.data_format)
609 | if self._global_params.num_classes:
610 | self._fc = tf.layers.Dense(
611 | self._global_params.num_classes,
612 | kernel_initializer=dense_kernel_initializer)
613 | else:
614 | self._fc = None
615 |
616 | if self._global_params.dropout_rate > 0:
617 | self._dropout = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(self._global_params.dropout_rate)
618 | else:
619 | self._dropout = None
620 |
621 | def call(self,
622 | inputs,
623 | training=True,
624 | features_only=None,
625 | pooled_features_only=False):
626 | """Implementation of call().
627 |
628 | Args:
629 | inputs: input tensors.
630 | training: boolean, whether the model is constructed for training.
631 | features_only: build the base feature network only.
632 | pooled_features_only: build the base network for features extraction
633 | (after 1x1 conv layer and global pooling, but before dropout and fc
634 | head).
635 |
636 | Returns:
637 | output tensors.
638 | """
639 | outputs = None
640 | self.endpoints = {}
641 | reduction_idx = 0
642 | # Calls Stem layers
643 | with tf.variable_scope('stem'):
644 | outputs = self._relu_fn(
645 | self._bn0(self._conv_stem(inputs), training=training))
646 | logging.info('Built stem layers with output shape: %s', outputs.shape)
647 | self.endpoints['stem'] = outputs
648 |
649 | # Calls blocks.
650 | for idx, block in enumerate(self._blocks):
651 | is_reduction = False # reduction flag for blocks after the stem layer
652 | # If the first block has super-pixel (space-to-depth) layer, then stem is
653 | # the first reduction point.
654 | if (block.block_args().super_pixel == 1 and idx == 0):
655 | reduction_idx += 1
656 | self.endpoints['reduction_%s' % reduction_idx] = outputs
657 |
658 | elif ((idx == len(self._blocks) - 1) or
659 | self._blocks[idx + 1].block_args().strides[0] > 1):
660 | is_reduction = True
661 | reduction_idx += 1
662 |
663 | with tf.variable_scope('blocks_%s' % idx):
664 | survival_prob = self._global_params.survival_prob
665 | if survival_prob:
666 | drop_rate = 1.0 - survival_prob
667 | survival_prob = 1.0 - drop_rate * float(idx) / len(self._blocks)
668 | logging.info('block_%s survival_prob: %s', idx, survival_prob)
669 | outputs = block.call(
670 | outputs, training=training, survival_prob=survival_prob)
671 | self.endpoints['block_%s' % idx] = outputs
672 | if is_reduction:
673 | self.endpoints['reduction_%s' % reduction_idx] = outputs
674 | if block.endpoints:
675 | for k, v in six.iteritems(block.endpoints):
676 | self.endpoints['block_%s/%s' % (idx, k)] = v
677 | if is_reduction:
678 | self.endpoints['reduction_%s/%s' % (reduction_idx, k)] = v
679 | self.endpoints['features'] = outputs
680 |
681 | if not features_only:
682 | # Calls final layers and returns logits.
683 | with tf.variable_scope('head'):
684 | outputs = self._relu_fn(
685 | self._bn1(self._conv_head(outputs), training=training))
686 | self.endpoints['head_1x1'] = outputs
687 |
688 | if self._global_params.local_pooling:
689 | shape = outputs.get_shape().as_list()
690 | kernel_size = [
691 | 1, shape[self._spatial_dims[0]], shape[self._spatial_dims[1]], 1]
692 | outputs = tf.nn.avg_pool(
693 | outputs, ksize=kernel_size, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='VALID')
694 | self.endpoints['pooled_features'] = outputs
695 | if not pooled_features_only:
696 | if self._dropout:
697 | outputs = self._dropout(outputs, training=training)
698 | self.endpoints['global_pool'] = outputs
699 | if self._fc:
700 | outputs = tf.squeeze(outputs, self._spatial_dims)
701 | outputs = self._fc(outputs)
702 | self.endpoints['head'] = outputs
703 | else:
704 | outputs = self._avg_pooling(outputs)
705 | self.endpoints['pooled_features'] = outputs
706 | if not pooled_features_only:
707 | if self._dropout:
708 | outputs = self._dropout(outputs, training=training)
709 | self.endpoints['global_pool'] = outputs
710 | if self._fc:
711 | outputs = self._fc(outputs)
712 | self.endpoints['head'] = outputs
713 | return outputs
714 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tf_to_pytorch/convert_tf_to_pt/original_tf/eval_ckpt_main.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2019 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 | """Eval checkpoint driver.
16 |
17 | This is an example evaluation script for users to understand the EfficientNet
18 | model checkpoints on CPU. To serve EfficientNet, please consider to export a
19 | `SavedModel` from checkpoints and use tf-serving to serve.
20 | """
21 |
22 | from __future__ import absolute_import
23 | from __future__ import division
24 | from __future__ import print_function
25 |
26 | import json
27 | import sys
28 | from absl import app
29 | from absl import flags
30 | import numpy as np
31 | import tensorflow as tf
32 |
33 |
34 | import efficientnet_builder
35 | import preprocessing
36 |
37 |
38 | tf.compat.v1.disable_v2_behavior()
39 |
40 | flags.DEFINE_string('model_name', 'efficientnet-b0', 'Model name to eval.')
41 | flags.DEFINE_string('runmode', 'examples', 'Running mode: examples or imagenet')
42 | flags.DEFINE_string('imagenet_eval_glob', None,
43 | 'Imagenet eval image glob, '
44 | 'such as /imagenet/ILSVRC2012*.JPEG')
45 | flags.DEFINE_string('imagenet_eval_label', None,
46 | 'Imagenet eval label file path, '
47 | 'such as /imagenet/ILSVRC2012_validation_ground_truth.txt')
48 | flags.DEFINE_string('ckpt_dir', '/tmp/ckpt/', 'Checkpoint folders')
49 | flags.DEFINE_string('example_img', '/tmp/panda.jpg',
50 | 'Filepath for a single example image.')
51 | flags.DEFINE_string('labels_map_file', '/tmp/labels_map.txt',
52 | 'Labels map from label id to its meaning.')
53 | flags.DEFINE_integer('num_images', 5000,
54 | 'Number of images to eval. Use -1 to eval all images.')
55 | FLAGS = flags.FLAGS
56 |
57 | MEAN_RGB = [0.485 * 255, 0.456 * 255, 0.406 * 255]
58 | STDDEV_RGB = [0.229 * 255, 0.224 * 255, 0.225 * 255]
59 |
60 |
61 | class EvalCkptDriver(object):
62 | """A driver for running eval inference.
63 |
64 | Attributes:
65 | model_name: str. Model name to eval.
66 | batch_size: int. Eval batch size.
67 | num_classes: int. Number of classes, default to 1000 for ImageNet.
68 | image_size: int. Input image size, determined by model name.
69 | """
70 |
71 | def __init__(self, model_name='efficientnet-b0', batch_size=1):
72 | """Initialize internal variables."""
73 | self.model_name = model_name
74 | self.batch_size = batch_size
75 | self.num_classes = 1000
76 | # Model Scaling parameters
77 | _, _, self.image_size, _ = efficientnet_builder.efficientnet_params(
78 | model_name)
79 |
80 | def restore_model(self, sess, ckpt_dir):
81 | """Restore variables from checkpoint dir."""
82 | checkpoint = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(ckpt_dir)
83 | ema = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(decay=0.9999)
84 | ema_vars = tf.compat.v1.trainable_variables() + tf.compat.v1.get_collection('moving_vars')
85 | for v in tf.compat.v1.global_variables():
86 | if 'moving_mean' in v.name or 'moving_variance' in v.name:
87 | ema_vars.append(v)
88 | ema_vars = list(set(ema_vars))
89 | var_dict = ema.variables_to_restore(ema_vars)
90 | saver = tf.compat.v1.train.Saver(var_dict, max_to_keep=1)
91 | saver.restore(sess, checkpoint)
92 |
93 | def build_model(self, features, is_training):
94 | """Build model with input features."""
95 | features -= tf.constant(MEAN_RGB, shape=[1, 1, 3], dtype=features.dtype)
96 | features /= tf.constant(STDDEV_RGB, shape=[1, 1, 3], dtype=features.dtype)
97 | logits, _ = efficientnet_builder.build_model(
98 | features, self.model_name, is_training)
99 | probs = tf.nn.softmax(logits)
100 | probs = tf.squeeze(probs)
101 | return probs
102 |
103 | def build_dataset(self, filenames, labels, is_training):
104 | """Build input dataset."""
105 | filenames = tf.constant(filenames)
106 | labels = tf.constant(labels)
107 |
108 | dataset = tf.compat.v1.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((filenames, labels))
109 |
110 | def _parse_function(filename, label):
111 | image_string = tf.io.read_file(filename)
112 | image_decoded = preprocessing.preprocess_image(
113 | image_string, is_training, self.image_size)
114 | image = tf.cast(image_decoded, tf.float32)
115 | return image, label
116 |
117 | dataset = dataset.map(_parse_function)
118 | dataset = dataset.batch(self.batch_size)
119 |
120 | iterator = dataset.make_one_shot_iterator()
121 | #iterator = iter(dataset)
122 | images, labels = iterator.get_next()
123 | return images, labels
124 |
125 | def run_inference(self, ckpt_dir, image_files, labels):
126 | """Build and run inference on the target images and labels."""
127 | with tf.Graph().as_default(), tf.Session() as sess:
128 | images, labels = self.build_dataset(image_files, labels, False)
129 | probs = self.build_model(images, is_training=False)
130 |
131 | sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
132 | self.restore_model(sess, ckpt_dir)
133 |
134 | prediction_idx = []
135 | prediction_prob = []
136 | for _ in range(len(image_files) // self.batch_size):
137 | out_probs = sess.run(probs)
138 | idx = np.argsort(out_probs)[::-1]
139 | prediction_idx.append(idx[:5])
140 | prediction_prob.append([out_probs[pid] for pid in idx[:5]])
141 |
142 | # Return the top 5 predictions (idx and prob) for each image.
143 | return prediction_idx, prediction_prob
144 |
145 |
146 | def eval_example_images(model_name, ckpt_dir, image_files, labels_map_file):
147 | """Eval a list of example images.
148 |
149 | Args:
150 | model_name: str. The name of model to eval.
151 | ckpt_dir: str. Checkpoint directory path.
152 | image_files: List[str]. A list of image file paths.
153 | labels_map_file: str. The labels map file path.
154 |
155 | Returns:
156 | A tuple (pred_idx, and pred_prob), where pred_idx is the top 5 prediction
157 | index and pred_prob is the top 5 prediction probability.
158 | """
159 | eval_ckpt_driver = EvalCkptDriver(model_name)
160 | classes = json.loads(tf.gfile.Open(labels_map_file).read())
161 | pred_idx, pred_prob = eval_ckpt_driver.run_inference(
162 | ckpt_dir, image_files, [0] * len(image_files))
163 | for i in range(len(image_files)):
164 | print('predicted class for image {}: '.format(image_files[i]))
165 | for j, idx in enumerate(pred_idx[i]):
166 | print(' -> top_{} ({:4.2f}%): {} '.format(
167 | j, pred_prob[i][j] * 100, classes[str(idx)]))
168 | return pred_idx, pred_prob
169 |
170 |
171 | def eval_imagenet(model_name,
172 | ckpt_dir,
173 | imagenet_eval_glob,
174 | imagenet_eval_label,
175 | num_images):
176 | """Eval ImageNet images and report top1/top5 accuracy.
177 |
178 | Args:
179 | model_name: str. The name of model to eval.
180 | ckpt_dir: str. Checkpoint directory path.
181 | imagenet_eval_glob: str. File path glob for all eval images.
182 | imagenet_eval_label: str. File path for eval label.
183 | num_images: int. Number of images to eval: -1 means eval the whole dataset.
184 |
185 | Returns:
186 | A tuple (top1, top5) for top1 and top5 accuracy.
187 | """
188 | eval_ckpt_driver = EvalCkptDriver(model_name)
189 | imagenet_val_labels = [int(i) for i in tf.gfile.GFile(imagenet_eval_label)]
190 | imagenet_filenames = sorted(tf.gfile.Glob(imagenet_eval_glob))
191 | if num_images < 0:
192 | num_images = len(imagenet_filenames)
193 | image_files = imagenet_filenames[:num_images]
194 | labels = imagenet_val_labels[:num_images]
195 |
196 | pred_idx, _ = eval_ckpt_driver.run_inference(ckpt_dir, image_files, labels)
197 | top1_cnt, top5_cnt = 0.0, 0.0
198 | for i, label in enumerate(labels):
199 | top1_cnt += label in pred_idx[i][:1]
200 | top5_cnt += label in pred_idx[i][:5]
201 | if i % 100 == 0:
202 | print('Step {}: top1_acc = {:4.2f}% top5_acc = {:4.2f}%'.format(
203 | i, 100 * top1_cnt / (i + 1), 100 * top5_cnt / (i + 1)))
204 | sys.stdout.flush()
205 | top1, top5 = 100 * top1_cnt / num_images, 100 * top5_cnt / num_images
206 | print('Final: top1_acc = {:4.2f}% top5_acc = {:4.2f}%'.format(top1, top5))
207 | return top1, top5
208 |
209 |
210 | def main(unused_argv):
211 | tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.ERROR)
212 | if FLAGS.runmode == 'examples':
213 | # Run inference for an example image.
214 | eval_example_images(FLAGS.model_name, FLAGS.ckpt_dir, [FLAGS.example_img],
215 | FLAGS.labels_map_file)
216 | elif FLAGS.runmode == 'imagenet':
217 | # Run inference for imagenet.
218 | eval_imagenet(FLAGS.model_name, FLAGS.ckpt_dir, FLAGS.imagenet_eval_glob,
219 | FLAGS.imagenet_eval_label, FLAGS.num_images)
220 | else:
221 | print('must specify runmode: examples or imagenet')
222 |
223 |
224 | if __name__ == '__main__':
225 | app.run(main)
226 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tf_to_pytorch/convert_tf_to_pt/original_tf/eval_ckpt_main_tf1.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2019 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 | """Eval checkpoint driver.
16 |
17 | This is an example evaluation script for users to understand the EfficientNet
18 | model checkpoints on CPU. To serve EfficientNet, please consider to export a
19 | `SavedModel` from checkpoints and use tf-serving to serve.
20 | """
21 |
22 | from __future__ import absolute_import
23 | from __future__ import division
24 | from __future__ import print_function
25 |
26 | import json
27 | import sys
28 | from absl import app
29 | from absl import flags
30 | import numpy as np
31 | import tensorflow as tf
32 |
33 |
34 | import efficientnet_builder
35 | import preprocessing
36 |
37 |
38 | flags.DEFINE_string('model_name', 'efficientnet-b0', 'Model name to eval.')
39 | flags.DEFINE_string('runmode', 'examples', 'Running mode: examples or imagenet')
40 | flags.DEFINE_string('imagenet_eval_glob', None,
41 | 'Imagenet eval image glob, '
42 | 'such as /imagenet/ILSVRC2012*.JPEG')
43 | flags.DEFINE_string('imagenet_eval_label', None,
44 | 'Imagenet eval label file path, '
45 | 'such as /imagenet/ILSVRC2012_validation_ground_truth.txt')
46 | flags.DEFINE_string('ckpt_dir', '/tmp/ckpt/', 'Checkpoint folders')
47 | flags.DEFINE_string('example_img', '/tmp/panda.jpg',
48 | 'Filepath for a single example image.')
49 | flags.DEFINE_string('labels_map_file', '/tmp/labels_map.txt',
50 | 'Labels map from label id to its meaning.')
51 | flags.DEFINE_integer('num_images', 5000,
52 | 'Number of images to eval. Use -1 to eval all images.')
53 | FLAGS = flags.FLAGS
54 |
55 | MEAN_RGB = [0.485 * 255, 0.456 * 255, 0.406 * 255]
56 | STDDEV_RGB = [0.229 * 255, 0.224 * 255, 0.225 * 255]
57 |
58 |
59 | class EvalCkptDriver(object):
60 | """A driver for running eval inference.
61 |
62 | Attributes:
63 | model_name: str. Model name to eval.
64 | batch_size: int. Eval batch size.
65 | num_classes: int. Number of classes, default to 1000 for ImageNet.
66 | image_size: int. Input image size, determined by model name.
67 | """
68 |
69 | def __init__(self, model_name='efficientnet-b0', batch_size=1):
70 | """Initialize internal variables."""
71 | self.model_name = model_name
72 | self.batch_size = batch_size
73 | self.num_classes = 1000
74 | # Model Scaling parameters
75 | _, _, self.image_size, _ = efficientnet_builder.efficientnet_params(
76 | model_name)
77 |
78 | def restore_model(self, sess, ckpt_dir):
79 | """Restore variables from checkpoint dir."""
80 | checkpoint = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(ckpt_dir)
81 | ema = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(decay=0.9999)
82 | ema_vars = tf.trainable_variables() + tf.get_collection('moving_vars')
83 | for v in tf.global_variables():
84 | if 'moving_mean' in v.name or 'moving_variance' in v.name:
85 | ema_vars.append(v)
86 | ema_vars = list(set(ema_vars))
87 | var_dict = ema.variables_to_restore(ema_vars)
88 | saver = tf.train.Saver(var_dict, max_to_keep=1)
89 | saver.restore(sess, checkpoint)
90 |
91 | def build_model(self, features, is_training):
92 | """Build model with input features."""
93 | features -= tf.constant(MEAN_RGB, shape=[1, 1, 3], dtype=features.dtype)
94 | features /= tf.constant(STDDEV_RGB, shape=[1, 1, 3], dtype=features.dtype)
95 | logits, _ = efficientnet_builder.build_model(
96 | features, self.model_name, is_training)
97 | probs = tf.nn.softmax(logits)
98 | probs = tf.squeeze(probs)
99 | return probs
100 |
101 | def build_dataset(self, filenames, labels, is_training):
102 | """Build input dataset."""
103 | filenames = tf.constant(filenames)
104 | labels = tf.constant(labels)
105 | dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((filenames, labels))
106 |
107 | def _parse_function(filename, label):
108 | image_string = tf.read_file(filename)
109 | image_decoded = preprocessing.preprocess_image(
110 | image_string, is_training, self.image_size)
111 | image = tf.cast(image_decoded, tf.float32)
112 | return image, label
113 |
114 | dataset = dataset.map(_parse_function)
115 | dataset = dataset.batch(self.batch_size)
116 |
117 | iterator = dataset.make_one_shot_iterator()
118 | images, labels = iterator.get_next()
119 | return images, labels
120 |
121 | def run_inference(self, ckpt_dir, image_files, labels):
122 | """Build and run inference on the target images and labels."""
123 | with tf.Graph().as_default(), tf.Session() as sess:
124 | images, labels = self.build_dataset(image_files, labels, False)
125 | probs = self.build_model(images, is_training=False)
126 |
127 | sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
128 | self.restore_model(sess, ckpt_dir)
129 |
130 | prediction_idx = []
131 | prediction_prob = []
132 | for _ in range(len(image_files) // self.batch_size):
133 | out_probs = sess.run(probs)
134 | idx = np.argsort(out_probs)[::-1]
135 | prediction_idx.append(idx[:5])
136 | prediction_prob.append([out_probs[pid] for pid in idx[:5]])
137 |
138 | # Return the top 5 predictions (idx and prob) for each image.
139 | return prediction_idx, prediction_prob
140 |
141 |
142 | def eval_example_images(model_name, ckpt_dir, image_files, labels_map_file):
143 | """Eval a list of example images.
144 |
145 | Args:
146 | model_name: str. The name of model to eval.
147 | ckpt_dir: str. Checkpoint directory path.
148 | image_files: List[str]. A list of image file paths.
149 | labels_map_file: str. The labels map file path.
150 |
151 | Returns:
152 | A tuple (pred_idx, and pred_prob), where pred_idx is the top 5 prediction
153 | index and pred_prob is the top 5 prediction probability.
154 | """
155 | eval_ckpt_driver = EvalCkptDriver(model_name)
156 | classes = json.loads(tf.gfile.Open(labels_map_file).read())
157 | pred_idx, pred_prob = eval_ckpt_driver.run_inference(
158 | ckpt_dir, image_files, [0] * len(image_files))
159 | for i in range(len(image_files)):
160 | print('predicted class for image {}: '.format(image_files[i]))
161 | for j, idx in enumerate(pred_idx[i]):
162 | print(' -> top_{} ({:4.2f}%): {} '.format(
163 | j, pred_prob[i][j] * 100, classes[str(idx)]))
164 | return pred_idx, pred_prob
165 |
166 |
167 | def eval_imagenet(model_name,
168 | ckpt_dir,
169 | imagenet_eval_glob,
170 | imagenet_eval_label,
171 | num_images):
172 | """Eval ImageNet images and report top1/top5 accuracy.
173 |
174 | Args:
175 | model_name: str. The name of model to eval.
176 | ckpt_dir: str. Checkpoint directory path.
177 | imagenet_eval_glob: str. File path glob for all eval images.
178 | imagenet_eval_label: str. File path for eval label.
179 | num_images: int. Number of images to eval: -1 means eval the whole dataset.
180 |
181 | Returns:
182 | A tuple (top1, top5) for top1 and top5 accuracy.
183 | """
184 | eval_ckpt_driver = EvalCkptDriver(model_name)
185 | imagenet_val_labels = [int(i) for i in tf.gfile.GFile(imagenet_eval_label)]
186 | imagenet_filenames = sorted(tf.gfile.Glob(imagenet_eval_glob))
187 | if num_images < 0:
188 | num_images = len(imagenet_filenames)
189 | image_files = imagenet_filenames[:num_images]
190 | labels = imagenet_val_labels[:num_images]
191 |
192 | pred_idx, _ = eval_ckpt_driver.run_inference(ckpt_dir, image_files, labels)
193 | top1_cnt, top5_cnt = 0.0, 0.0
194 | for i, label in enumerate(labels):
195 | top1_cnt += label in pred_idx[i][:1]
196 | top5_cnt += label in pred_idx[i][:5]
197 | if i % 100 == 0:
198 | print('Step {}: top1_acc = {:4.2f}% top5_acc = {:4.2f}%'.format(
199 | i, 100 * top1_cnt / (i + 1), 100 * top5_cnt / (i + 1)))
200 | sys.stdout.flush()
201 | top1, top5 = 100 * top1_cnt / num_images, 100 * top5_cnt / num_images
202 | print('Final: top1_acc = {:4.2f}% top5_acc = {:4.2f}%'.format(top1, top5))
203 | return top1, top5
204 |
205 |
206 | def main(unused_argv):
207 | tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.ERROR)
208 | if FLAGS.runmode == 'examples':
209 | # Run inference for an example image.
210 | eval_example_images(FLAGS.model_name, FLAGS.ckpt_dir, [FLAGS.example_img],
211 | FLAGS.labels_map_file)
212 | elif FLAGS.runmode == 'imagenet':
213 | # Run inference for imagenet.
214 | eval_imagenet(FLAGS.model_name, FLAGS.ckpt_dir, FLAGS.imagenet_eval_glob,
215 | FLAGS.imagenet_eval_label, FLAGS.num_images)
216 | else:
217 | print('must specify runmode: examples or imagenet')
218 |
219 |
220 | if __name__ == '__main__':
221 | app.run(main)
222 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tf_to_pytorch/convert_tf_to_pt/original_tf/preprocessing.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2019 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 | """ImageNet preprocessing."""
16 | from __future__ import absolute_import
17 | from __future__ import division
18 | from __future__ import print_function
19 |
20 | from absl import logging
21 |
22 | import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
23 |
24 |
25 | IMAGE_SIZE = 224
26 | CROP_PADDING = 32
27 |
28 |
29 | def distorted_bounding_box_crop(image_bytes,
30 | bbox,
31 | min_object_covered=0.1,
32 | aspect_ratio_range=(0.75, 1.33),
33 | area_range=(0.05, 1.0),
34 | max_attempts=100,
35 | scope=None):
36 | """Generates cropped_image using one of the bboxes randomly distorted.
37 |
38 | See `tf.image.sample_distorted_bounding_box` for more documentation.
39 |
40 | Args:
41 | image_bytes: `Tensor` of binary image data.
42 | bbox: `Tensor` of bounding boxes arranged `[1, num_boxes, coords]`
43 | where each coordinate is [0, 1) and the coordinates are arranged
44 | as `[ymin, xmin, ymax, xmax]`. If num_boxes is 0 then use the whole
45 | image.
46 | min_object_covered: An optional `float`. Defaults to `0.1`. The cropped
47 | area of the image must contain at least this fraction of any bounding
48 | box supplied.
49 | aspect_ratio_range: An optional list of `float`s. The cropped area of the
50 | image must have an aspect ratio = width / height within this range.
51 | area_range: An optional list of `float`s. The cropped area of the image
52 | must contain a fraction of the supplied image within in this range.
53 | max_attempts: An optional `int`. Number of attempts at generating a cropped
54 | region of the image of the specified constraints. After `max_attempts`
55 | failures, return the entire image.
56 | scope: Optional `str` for name scope.
57 | Returns:
58 | cropped image `Tensor`
59 | """
60 | with tf.name_scope(scope, 'distorted_bounding_box_crop', [image_bytes, bbox]):
61 | shape = tf.image.extract_jpeg_shape(image_bytes)
62 | sample_distorted_bounding_box = tf.image.sample_distorted_bounding_box(
63 | shape,
64 | bounding_boxes=bbox,
65 | min_object_covered=min_object_covered,
66 | aspect_ratio_range=aspect_ratio_range,
67 | area_range=area_range,
68 | max_attempts=max_attempts,
69 | use_image_if_no_bounding_boxes=True)
70 | bbox_begin, bbox_size, _ = sample_distorted_bounding_box
71 |
72 | # Crop the image to the specified bounding box.
73 | offset_y, offset_x, _ = tf.unstack(bbox_begin)
74 | target_height, target_width, _ = tf.unstack(bbox_size)
75 | crop_window = tf.stack([offset_y, offset_x, target_height, target_width])
76 | image = tf.image.decode_and_crop_jpeg(image_bytes, crop_window, channels=3)
77 |
78 | return image
79 |
80 |
81 | def _at_least_x_are_equal(a, b, x):
82 | """At least `x` of `a` and `b` `Tensors` are equal."""
83 | match = tf.equal(a, b)
84 | match = tf.cast(match, tf.int32)
85 | return tf.greater_equal(tf.reduce_sum(match), x)
86 |
87 |
88 | def _decode_and_random_crop(image_bytes, image_size):
89 | """Make a random crop of image_size."""
90 | bbox = tf.constant([0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0], dtype=tf.float32, shape=[1, 1, 4])
91 | image = distorted_bounding_box_crop(
92 | image_bytes,
93 | bbox,
94 | min_object_covered=0.1,
95 | aspect_ratio_range=(3. / 4, 4. / 3.),
96 | area_range=(0.08, 1.0),
97 | max_attempts=10,
98 | scope=None)
99 | original_shape = tf.image.extract_jpeg_shape(image_bytes)
100 | bad = _at_least_x_are_equal(original_shape, tf.shape(image), 3)
101 |
102 | image = tf.cond(
103 | bad,
104 | lambda: _decode_and_center_crop(image_bytes, image_size),
105 | lambda: tf.image.resize_bicubic([image], # pylint: disable=g-long-lambda
106 | [image_size, image_size])[0])
107 |
108 | return image
109 |
110 |
111 | def _decode_and_center_crop(image_bytes, image_size):
112 | """Crops to center of image with padding then scales image_size."""
113 | shape = tf.image.extract_jpeg_shape(image_bytes)
114 | image_height = shape[0]
115 | image_width = shape[1]
116 |
117 | padded_center_crop_size = tf.cast(
118 | ((image_size / (image_size + CROP_PADDING)) *
119 | tf.cast(tf.minimum(image_height, image_width), tf.float32)),
120 | tf.int32)
121 |
122 | offset_height = ((image_height - padded_center_crop_size) + 1) // 2
123 | offset_width = ((image_width - padded_center_crop_size) + 1) // 2
124 | crop_window = tf.stack([offset_height, offset_width,
125 | padded_center_crop_size, padded_center_crop_size])
126 | image = tf.image.decode_and_crop_jpeg(image_bytes, crop_window, channels=3)
127 | image = tf.image.resize_bicubic([image], [image_size, image_size])[0]
128 | return image
129 |
130 |
131 | def _flip(image):
132 | """Random horizontal image flip."""
133 | image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(image)
134 | return image
135 |
136 |
137 | def preprocess_for_train(image_bytes, use_bfloat16, image_size=IMAGE_SIZE,
138 | augment_name=None,
139 | randaug_num_layers=None, randaug_magnitude=None):
140 | """Preprocesses the given image for evaluation.
141 |
142 | Args:
143 | image_bytes: `Tensor` representing an image binary of arbitrary size.
144 | use_bfloat16: `bool` for whether to use bfloat16.
145 | image_size: image size.
146 | augment_name: `string` that is the name of the augmentation method
147 | to apply to the image. `autoaugment` if AutoAugment is to be used or
148 | `randaugment` if RandAugment is to be used. If the value is `None` no
149 | augmentation method will be applied applied. See autoaugment.py for more
150 | details.
151 | randaug_num_layers: 'int', if RandAug is used, what should the number of
152 | layers be. See autoaugment.py for detailed description.
153 | randaug_magnitude: 'int', if RandAug is used, what should the magnitude
154 | be. See autoaugment.py for detailed description.
155 |
156 | Returns:
157 | A preprocessed image `Tensor`.
158 | """
159 | image = _decode_and_random_crop(image_bytes, image_size)
160 | image = _flip(image)
161 | image = tf.reshape(image, [image_size, image_size, 3])
162 |
163 | image = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(
164 | image, dtype=tf.bfloat16 if use_bfloat16 else tf.float32)
165 |
166 | if augment_name:
167 | try:
168 | import autoaugment # pylint: disable=g-import-not-at-top
169 | except ImportError as e:
170 | logging.exception('Autoaugment is not supported in TF 2.x.')
171 | raise e
172 |
173 | logging.info('Apply AutoAugment policy %s', augment_name)
174 | input_image_type = image.dtype
175 | image = tf.clip_by_value(image, 0.0, 255.0)
176 | image = tf.cast(image, dtype=tf.uint8)
177 |
178 | if augment_name == 'autoaugment':
179 | logging.info('Apply AutoAugment policy %s', augment_name)
180 | image = autoaugment.distort_image_with_autoaugment(image, 'v0')
181 | elif augment_name == 'randaugment':
182 | image = autoaugment.distort_image_with_randaugment(
183 | image, randaug_num_layers, randaug_magnitude)
184 | else:
185 | raise ValueError('Invalid value for augment_name: %s' % (augment_name))
186 |
187 | image = tf.cast(image, dtype=input_image_type)
188 | return image
189 |
190 |
191 | def preprocess_for_eval(image_bytes, use_bfloat16, image_size=IMAGE_SIZE):
192 | """Preprocesses the given image for evaluation.
193 |
194 | Args:
195 | image_bytes: `Tensor` representing an image binary of arbitrary size.
196 | use_bfloat16: `bool` for whether to use bfloat16.
197 | image_size: image size.
198 |
199 | Returns:
200 | A preprocessed image `Tensor`.
201 | """
202 | image = _decode_and_center_crop(image_bytes, image_size)
203 | image = tf.reshape(image, [image_size, image_size, 3])
204 | image = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(
205 | image, dtype=tf.bfloat16 if use_bfloat16 else tf.float32)
206 | return image
207 |
208 |
209 | def preprocess_image(image_bytes,
210 | is_training=False,
211 | use_bfloat16=False,
212 | image_size=IMAGE_SIZE,
213 | augment_name=None,
214 | randaug_num_layers=None,
215 | randaug_magnitude=None):
216 | """Preprocesses the given image.
217 |
218 | Args:
219 | image_bytes: `Tensor` representing an image binary of arbitrary size.
220 | is_training: `bool` for whether the preprocessing is for training.
221 | use_bfloat16: `bool` for whether to use bfloat16.
222 | image_size: image size.
223 | augment_name: `string` that is the name of the augmentation method
224 | to apply to the image. `autoaugment` if AutoAugment is to be used or
225 | `randaugment` if RandAugment is to be used. If the value is `None` no
226 | augmentation method will be applied applied. See autoaugment.py for more
227 | details.
228 | randaug_num_layers: 'int', if RandAug is used, what should the number of
229 | layers be. See autoaugment.py for detailed description.
230 | randaug_magnitude: 'int', if RandAug is used, what should the magnitude
231 | be. See autoaugment.py for detailed description.
232 |
233 | Returns:
234 | A preprocessed image `Tensor` with value range of [0, 255].
235 | """
236 | if is_training:
237 | return preprocess_for_train(
238 | image_bytes, use_bfloat16, image_size, augment_name,
239 | randaug_num_layers, randaug_magnitude)
240 | else:
241 | return preprocess_for_eval(image_bytes, use_bfloat16, image_size)
242 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tf_to_pytorch/convert_tf_to_pt/original_tf/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2019 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 | """Model utilities."""
16 |
17 | from __future__ import absolute_import
18 | from __future__ import division
19 | from __future__ import print_function
20 |
21 | import json
22 | import os
23 | import sys
24 |
25 | from absl import logging
26 | import numpy as np
27 | import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
28 |
29 | from tensorflow.python.tpu import tpu_function # pylint:disable=g-direct-tensorflow-import
30 |
31 |
32 | def build_learning_rate(initial_lr,
33 | global_step,
34 | steps_per_epoch=None,
35 | lr_decay_type='exponential',
36 | decay_factor=0.97,
37 | decay_epochs=2.4,
38 | total_steps=None,
39 | warmup_epochs=5):
40 | """Build learning rate."""
41 | if lr_decay_type == 'exponential':
42 | assert steps_per_epoch is not None
43 | decay_steps = steps_per_epoch * decay_epochs
44 | lr = tf.train.exponential_decay(
45 | initial_lr, global_step, decay_steps, decay_factor, staircase=True)
46 | elif lr_decay_type == 'cosine':
47 | assert total_steps is not None
48 | lr = 0.5 * initial_lr * (
49 | 1 + tf.cos(np.pi * tf.cast(global_step, tf.float32) / total_steps))
50 | elif lr_decay_type == 'constant':
51 | lr = initial_lr
52 | else:
53 | assert False, 'Unknown lr_decay_type : %s' % lr_decay_type
54 |
55 | if warmup_epochs:
56 | logging.info('Learning rate warmup_epochs: %d', warmup_epochs)
57 | warmup_steps = int(warmup_epochs * steps_per_epoch)
58 | warmup_lr = (
59 | initial_lr * tf.cast(global_step, tf.float32) / tf.cast(
60 | warmup_steps, tf.float32))
61 | lr = tf.cond(global_step < warmup_steps, lambda: warmup_lr, lambda: lr)
62 |
63 | return lr
64 |
65 |
66 | def build_optimizer(learning_rate,
67 | optimizer_name='rmsprop',
68 | decay=0.9,
69 | epsilon=0.001,
70 | momentum=0.9):
71 | """Build optimizer."""
72 | if optimizer_name == 'sgd':
73 | logging.info('Using SGD optimizer')
74 | optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate)
75 | elif optimizer_name == 'momentum':
76 | logging.info('Using Momentum optimizer')
77 | optimizer = tf.train.MomentumOptimizer(
78 | learning_rate=learning_rate, momentum=momentum)
79 | elif optimizer_name == 'rmsprop':
80 | logging.info('Using RMSProp optimizer')
81 | optimizer = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(learning_rate, decay, momentum,
82 | epsilon)
83 | else:
84 | logging.fatal('Unknown optimizer: %s', optimizer_name)
85 |
86 | return optimizer
87 |
88 |
89 | class TpuBatchNormalization(tf.layers.BatchNormalization):
90 | # class TpuBatchNormalization(tf.layers.BatchNormalization):
91 | """Cross replica batch normalization."""
92 |
93 | def __init__(self, fused=False, **kwargs):
94 | if fused in (True, None):
95 | raise ValueError('TpuBatchNormalization does not support fused=True.')
96 | super(TpuBatchNormalization, self).__init__(fused=fused, **kwargs)
97 |
98 | def _cross_replica_average(self, t, num_shards_per_group):
99 | """Calculates the average value of input tensor across TPU replicas."""
100 | num_shards = tpu_function.get_tpu_context().number_of_shards
101 | group_assignment = None
102 | if num_shards_per_group > 1:
103 | if num_shards % num_shards_per_group != 0:
104 | raise ValueError('num_shards: %d mod shards_per_group: %d, should be 0'
105 | % (num_shards, num_shards_per_group))
106 | num_groups = num_shards // num_shards_per_group
107 | group_assignment = [[
108 | x for x in range(num_shards) if x // num_shards_per_group == y
109 | ] for y in range(num_groups)]
110 | return tf.tpu.cross_replica_sum(t, group_assignment) / tf.cast(
111 | num_shards_per_group, t.dtype)
112 |
113 | def _moments(self, inputs, reduction_axes, keep_dims):
114 | """Compute the mean and variance: it overrides the original _moments."""
115 | shard_mean, shard_variance = super(TpuBatchNormalization, self)._moments(
116 | inputs, reduction_axes, keep_dims=keep_dims)
117 |
118 | num_shards = tpu_function.get_tpu_context().number_of_shards or 1
119 | if num_shards <= 8: # Skip cross_replica for 2x2 or smaller slices.
120 | num_shards_per_group = 1
121 | else:
122 | num_shards_per_group = max(8, num_shards // 8)
123 | logging.info('TpuBatchNormalization with num_shards_per_group %s',
124 | num_shards_per_group)
125 | if num_shards_per_group > 1:
126 | # Compute variance using: Var[X]= E[X^2] - E[X]^2.
127 | shard_square_of_mean = tf.math.square(shard_mean)
128 | shard_mean_of_square = shard_variance + shard_square_of_mean
129 | group_mean = self._cross_replica_average(
130 | shard_mean, num_shards_per_group)
131 | group_mean_of_square = self._cross_replica_average(
132 | shard_mean_of_square, num_shards_per_group)
133 | group_variance = group_mean_of_square - tf.math.square(group_mean)
134 | return (group_mean, group_variance)
135 | else:
136 | return (shard_mean, shard_variance)
137 |
138 |
139 | class BatchNormalization(tf.layers.BatchNormalization):
140 | """Fixed default name of BatchNormalization to match TpuBatchNormalization."""
141 |
142 | def __init__(self, name='tpu_batch_normalization', **kwargs):
143 | super(BatchNormalization, self).__init__(name=name, **kwargs)
144 |
145 |
146 | def drop_connect(inputs, is_training, survival_prob):
147 | """Drop the entire conv with given survival probability."""
148 | # "Deep Networks with Stochastic Depth", https://arxiv.org/pdf/1603.09382.pdf
149 | if not is_training:
150 | return inputs
151 |
152 | # Compute tensor.
153 | batch_size = tf.shape(inputs)[0]
154 | random_tensor = survival_prob
155 | random_tensor += tf.random_uniform([batch_size, 1, 1, 1], dtype=inputs.dtype)
156 | binary_tensor = tf.floor(random_tensor)
157 | # Unlike conventional way that multiply survival_prob at test time, here we
158 | # divide survival_prob at training time, such that no addition compute is
159 | # needed at test time.
160 | output = tf.div(inputs, survival_prob) * binary_tensor
161 | return output
162 |
163 |
164 | def archive_ckpt(ckpt_eval, ckpt_objective, ckpt_path):
165 | """Archive a checkpoint if the metric is better."""
166 | ckpt_dir, ckpt_name = os.path.split(ckpt_path)
167 |
168 | saved_objective_path = os.path.join(ckpt_dir, 'best_objective.txt')
169 | saved_objective = float('-inf')
170 | if tf.gfile.Exists(saved_objective_path):
171 | with tf.gfile.GFile(saved_objective_path, 'r') as f:
172 | saved_objective = float(f.read())
173 | if saved_objective > ckpt_objective:
174 | logging.info('Ckpt %s is worse than %s', ckpt_objective, saved_objective)
175 | return False
176 |
177 | filenames = tf.gfile.Glob(ckpt_path + '.*')
178 | if filenames is None:
179 | logging.info('No files to copy for checkpoint %s', ckpt_path)
180 | return False
181 |
182 | # Clear the old folder.
183 | dst_dir = os.path.join(ckpt_dir, 'archive')
184 | if tf.gfile.Exists(dst_dir):
185 | tf.gfile.DeleteRecursively(dst_dir)
186 | tf.gfile.MakeDirs(dst_dir)
187 |
188 | # Write checkpoints.
189 | for f in filenames:
190 | dest = os.path.join(dst_dir, os.path.basename(f))
191 | tf.gfile.Copy(f, dest, overwrite=True)
192 | ckpt_state = tf.train.generate_checkpoint_state_proto(
193 | dst_dir,
194 | model_checkpoint_path=ckpt_name,
195 | all_model_checkpoint_paths=[ckpt_name])
196 | with tf.gfile.GFile(os.path.join(dst_dir, 'checkpoint'), 'w') as f:
197 | f.write(str(ckpt_state))
198 | with tf.gfile.GFile(os.path.join(dst_dir, 'best_eval.txt'), 'w') as f:
199 | f.write('%s' % ckpt_eval)
200 |
201 | # Update the best objective.
202 | with tf.gfile.GFile(saved_objective_path, 'w') as f:
203 | f.write('%f' % ckpt_objective)
204 |
205 | logging.info('Copying checkpoint %s to %s', ckpt_path, dst_dir)
206 | return True
207 |
208 |
209 | def get_ema_vars():
210 | """Get all exponential moving average (ema) variables."""
211 | ema_vars = tf.trainable_variables() + tf.get_collection('moving_vars')
212 | for v in tf.global_variables():
213 | # We maintain mva for batch norm moving mean and variance as well.
214 | if 'moving_mean' in v.name or 'moving_variance' in v.name:
215 | ema_vars.append(v)
216 | return list(set(ema_vars))
217 |
218 |
219 | class DepthwiseConv2D(tf.keras.layers.DepthwiseConv2D, tf.layers.Layer):
220 | """Wrap keras DepthwiseConv2D to tf.layers."""
221 |
222 | pass
223 |
224 |
225 | class EvalCkptDriver(object):
226 | """A driver for running eval inference.
227 |
228 | Attributes:
229 | model_name: str. Model name to eval.
230 | batch_size: int. Eval batch size.
231 | image_size: int. Input image size, determined by model name.
232 | num_classes: int. Number of classes, default to 1000 for ImageNet.
233 | include_background_label: whether to include extra background label.
234 | """
235 |
236 | def __init__(self,
237 | model_name,
238 | batch_size=1,
239 | image_size=224,
240 | num_classes=1000,
241 | include_background_label=False):
242 | """Initialize internal variables."""
243 | self.model_name = model_name
244 | self.batch_size = batch_size
245 | self.num_classes = num_classes
246 | self.include_background_label = include_background_label
247 | self.image_size = image_size
248 |
249 | def restore_model(self, sess, ckpt_dir, enable_ema=True, export_ckpt=None):
250 | """Restore variables from checkpoint dir."""
251 | sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
252 | checkpoint = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(ckpt_dir)
253 | if enable_ema:
254 | ema = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(decay=0.0)
255 | ema_vars = get_ema_vars()
256 | var_dict = ema.variables_to_restore(ema_vars)
257 | ema_assign_op = ema.apply(ema_vars)
258 | else:
259 | var_dict = get_ema_vars()
260 | ema_assign_op = None
261 |
262 | tf.train.get_or_create_global_step()
263 | sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
264 | saver = tf.train.Saver(var_dict, max_to_keep=1)
265 | saver.restore(sess, checkpoint)
266 |
267 | if export_ckpt:
268 | if ema_assign_op is not None:
269 | sess.run(ema_assign_op)
270 | saver = tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=1, save_relative_paths=True)
271 | saver.save(sess, export_ckpt)
272 |
273 | def build_model(self, features, is_training):
274 | """Build model with input features."""
275 | del features, is_training
276 | raise ValueError('Must be implemented by subclasses.')
277 |
278 | def get_preprocess_fn(self):
279 | raise ValueError('Must be implemented by subclsses.')
280 |
281 | def build_dataset(self, filenames, labels, is_training):
282 | """Build input dataset."""
283 | batch_drop_remainder = False
284 | if 'condconv' in self.model_name and not is_training:
285 | # CondConv layers can only be called with known batch dimension. Thus, we
286 | # must drop all remaining examples that do not make up one full batch.
287 | # To ensure all examples are evaluated, use a batch size that evenly
288 | # divides the number of files.
289 | batch_drop_remainder = True
290 | num_files = len(filenames)
291 | if num_files % self.batch_size != 0:
292 | tf.logging.warn('Remaining examples in last batch are not being '
293 | 'evaluated.')
294 | filenames = tf.constant(filenames)
295 | labels = tf.constant(labels)
296 | dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((filenames, labels))
297 |
298 | def _parse_function(filename, label):
299 | image_string = tf.read_file(filename)
300 | preprocess_fn = self.get_preprocess_fn()
301 | image_decoded = preprocess_fn(
302 | image_string, is_training, image_size=self.image_size)
303 | image = tf.cast(image_decoded, tf.float32)
304 | return image, label
305 |
306 | dataset = dataset.map(_parse_function)
307 | dataset = dataset.batch(self.batch_size,
308 | drop_remainder=batch_drop_remainder)
309 |
310 | iterator = dataset.make_one_shot_iterator()
311 | images, labels = iterator.get_next()
312 | return images, labels
313 |
314 | def run_inference(self,
315 | ckpt_dir,
316 | image_files,
317 | labels,
318 | enable_ema=True,
319 | export_ckpt=None):
320 | """Build and run inference on the target images and labels."""
321 | label_offset = 1 if self.include_background_label else 0
322 | with tf.Graph().as_default(), tf.Session() as sess:
323 | images, labels = self.build_dataset(image_files, labels, False)
324 | probs = self.build_model(images, is_training=False)
325 | if isinstance(probs, tuple):
326 | probs = probs[0]
327 |
328 | self.restore_model(sess, ckpt_dir, enable_ema, export_ckpt)
329 |
330 | prediction_idx = []
331 | prediction_prob = []
332 | for _ in range(len(image_files) // self.batch_size):
333 | out_probs = sess.run(probs)
334 | idx = np.argsort(out_probs)[::-1]
335 | prediction_idx.append(idx[:5] - label_offset)
336 | prediction_prob.append([out_probs[pid] for pid in idx[:5]])
337 |
338 | # Return the top 5 predictions (idx and prob) for each image.
339 | return prediction_idx, prediction_prob
340 |
341 | def eval_example_images(self,
342 | ckpt_dir,
343 | image_files,
344 | labels_map_file,
345 | enable_ema=True,
346 | export_ckpt=None):
347 | """Eval a list of example images.
348 |
349 | Args:
350 | ckpt_dir: str. Checkpoint directory path.
351 | image_files: List[str]. A list of image file paths.
352 | labels_map_file: str. The labels map file path.
353 | enable_ema: enable expotential moving average.
354 | export_ckpt: export ckpt folder.
355 |
356 | Returns:
357 | A tuple (pred_idx, and pred_prob), where pred_idx is the top 5 prediction
358 | index and pred_prob is the top 5 prediction probability.
359 | """
360 | classes = json.loads(tf.gfile.Open(labels_map_file).read())
361 | pred_idx, pred_prob = self.run_inference(
362 | ckpt_dir, image_files, [0] * len(image_files), enable_ema, export_ckpt)
363 | for i in range(len(image_files)):
364 | print('predicted class for image {}: '.format(image_files[i]))
365 | for j, idx in enumerate(pred_idx[i]):
366 | print(' -> top_{} ({:4.2f}%): {} '.format(j, pred_prob[i][j] * 100,
367 | classes[str(idx)]))
368 | return pred_idx, pred_prob
369 |
370 | def eval_imagenet(self, ckpt_dir, imagenet_eval_glob,
371 | imagenet_eval_label, num_images, enable_ema, export_ckpt):
372 | """Eval ImageNet images and report top1/top5 accuracy.
373 |
374 | Args:
375 | ckpt_dir: str. Checkpoint directory path.
376 | imagenet_eval_glob: str. File path glob for all eval images.
377 | imagenet_eval_label: str. File path for eval label.
378 | num_images: int. Number of images to eval: -1 means eval the whole
379 | dataset.
380 | enable_ema: enable expotential moving average.
381 | export_ckpt: export checkpoint folder.
382 |
383 | Returns:
384 | A tuple (top1, top5) for top1 and top5 accuracy.
385 | """
386 | imagenet_val_labels = [int(i) for i in tf.gfile.GFile(imagenet_eval_label)]
387 | imagenet_filenames = sorted(tf.gfile.Glob(imagenet_eval_glob))
388 | if num_images < 0:
389 | num_images = len(imagenet_filenames)
390 | image_files = imagenet_filenames[:num_images]
391 | labels = imagenet_val_labels[:num_images]
392 |
393 | pred_idx, _ = self.run_inference(
394 | ckpt_dir, image_files, labels, enable_ema, export_ckpt)
395 | top1_cnt, top5_cnt = 0.0, 0.0
396 | for i, label in enumerate(labels):
397 | top1_cnt += label in pred_idx[i][:1]
398 | top5_cnt += label in pred_idx[i][:5]
399 | if i % 100 == 0:
400 | print('Step {}: top1_acc = {:4.2f}% top5_acc = {:4.2f}%'.format(
401 | i, 100 * top1_cnt / (i + 1), 100 * top5_cnt / (i + 1)))
402 | sys.stdout.flush()
403 | top1, top5 = 100 * top1_cnt / num_images, 100 * top5_cnt / num_images
404 | print('Final: top1_acc = {:4.2f}% top5_acc = {:4.2f}%'.format(top1, top5))
405 | return top1, top5
406 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tf_to_pytorch/convert_tf_to_pt/rename.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | for i in 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
2 | do
3 | X=$(sha256sum efficientnet-b${i}.pth | head -c 8)
4 | mv efficientnet-b${i}.pth efficientnet-b${i}-${X}.pth
5 | done
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tf_to_pytorch/convert_tf_to_pt/run.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | python ../convert_tf_to_pt/load_tf_weights.py --model_name efficientnet-b0 --tf_checkpoint ../pretrained_tensorflow/efficientnet-b0/ --output_file ../pretrained_pytorch/efficientnet-b0.pth
2 |
3 | # python ../convert_tf_to_pt/load_tf_weights.py --model_name efficientnet-b1 --tf_checkpoint ../pretrained_tensorflow/efficientnet-b1/ --output_file ../pretrained_pytorch/efficientnet-b1.pth
4 |
5 | # python ../convert_tf_to_pt/load_tf_weights.py --model_name efficientnet-b2 --tf_checkpoint ../pretrained_tensorflow/efficientnet-b2/ --output_file ../pretrained_pytorch/efficientnet-b2.pth
6 |
7 | # python ../convert_tf_to_pt/load_tf_weights.py --model_name efficientnet-b3 --tf_checkpoint ../pretrained_tensorflow/efficientnet-b3/ --output_file ../pretrained_pytorch/efficientnet-b3.pth
8 |
9 | # python ../convert_tf_to_pt/load_tf_weights.py --model_name efficientnet-b4 --tf_checkpoint ../pretrained_tensorflow/efficientnet-b4/ --output_file ../pretrained_pytorch/efficientnet-b4.pth
10 |
11 | # python ../convert_tf_to_pt/load_tf_weights.py --model_name efficientnet-b5 --tf_checkpoint ../pretrained_tensorflow/efficientnet-b5/ --output_file ../pretrained_pytorch/efficientnet-b5.pth
12 |
13 | # python ../convert_tf_to_pt/load_tf_weights.py --model_name efficientnet-b6 --tf_checkpoint ../pretrained_tensorflow/efficientnet-b6/ --output_file ../pretrained_pytorch/efficientnet-b6.pth
14 |
15 | # python ../convert_tf_to_pt/load_tf_weights.py --model_name efficientnet-b7 --tf_checkpoint ../pretrained_tensorflow/efficientnet-b7/ --output_file ../pretrained_pytorch/efficientnet-b7.pth
16 |
17 | # python ../convert_tf_to_pt/load_tf_weights.py --model_name efficientnet-b8 --tf_checkpoint ../pretrained_tensorflow/efficientnet-b8/ --output_file ../pretrained_pytorch/efficientnet-b8.pth
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tf_to_pytorch/pretrained_tensorflow/download.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env bash
2 |
3 |
4 | # This script accepts a single command-line argument, which specifies which model to download.
5 | # Only the b0, b1, b2, and b3 models have been released, so your command must be one of them.
6 |
7 | # For example, to download efficientnet-b0, run:
8 | # ./download.sh efficientnet-b0
9 | # And to download efficientnet-b3, run:
10 | # ./download.sh efficientnet-b3
11 |
12 | MODEL=$1
13 | wget https://storage.googleapis.com/cloud-tpu-checkpoints/efficientnet/advprop/${MODEL}.tar.gz
14 | tar xvf ${MODEL}.tar.gz
15 | rm ${MODEL}.tar.gz
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 127 |
127 |  130 |
130 |  22 |
23 |
24 | #### Update (Aug 25, 2020)
25 |
26 | This update adds:
27 | * A new `include_top` (default: `True`) option ([#208](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/208))
28 | * Continuous testing with [sotabench](https://sotabench.com/)
29 | * Code quality improvements and fixes ([#215](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/215) [#223](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/223))
30 |
31 | #### Update (May 14, 2020)
32 |
33 | This update adds comprehensive comments and documentation (thanks to @workingcoder).
34 |
35 | #### Update (January 23, 2020)
36 |
37 | This update adds a new category of pre-trained model based on adversarial training, called _advprop_. It is important to note that the preprocessing required for the advprop pretrained models is slightly different from normal ImageNet preprocessing. As a result, by default, advprop models are not used. To load a model with advprop, use:
38 | ```python
39 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained("efficientnet-b0", advprop=True)
40 | ```
41 | There is also a new, large `efficientnet-b8` pretrained model that is only available in advprop form. When using these models, replace ImageNet preprocessing code as follows:
42 | ```python
43 | if advprop: # for models using advprop pretrained weights
44 | normalize = transforms.Lambda(lambda img: img * 2.0 - 1.0)
45 | else:
46 | normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
47 | std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
48 | ```
49 | This update also addresses multiple other issues ([#115](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/115), [#128](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/128)).
50 |
51 | #### Update (October 15, 2019)
52 |
53 | This update allows you to choose whether to use a memory-efficient Swish activation. The memory-efficient version is chosen by default, but it cannot be used when exporting using PyTorch JIT. For this purpose, we have also included a standard (export-friendly) swish activation function. To switch to the export-friendly version, simply call `model.set_swish(memory_efficient=False)` after loading your desired model. This update addresses issues [#88](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/88) and [#89](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/89).
54 |
55 | #### Update (October 12, 2019)
56 |
57 | This update makes the Swish activation function more memory-efficient. It also addresses pull requests [#72](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/72), [#73](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/73), [#85](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/85), and [#86](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/86). Thanks to the authors of all the pull requests!
58 |
59 | #### Update (July 31, 2019)
60 |
61 | _Upgrade the pip package with_ `pip install --upgrade efficientnet-pytorch`
62 |
63 | The B6 and B7 models are now available. Additionally, _all_ pretrained models have been updated to use AutoAugment preprocessing, which translates to better performance across the board. Usage is the same as before:
64 | ```python
65 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet
66 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b7')
67 | ```
68 |
69 | #### Update (June 29, 2019)
70 |
71 | This update adds easy model exporting ([#20](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/20)) and feature extraction ([#38](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/38)).
72 |
73 | * [Example: Export to ONNX](#example-export)
74 | * [Example: Extract features](#example-feature-extraction)
75 | * Also: fixed a CUDA/CPU bug ([#32](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/32))
76 |
77 | It is also now incredibly simple to load a pretrained model with a new number of classes for transfer learning:
78 | ```python
79 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b1', num_classes=23)
80 | ```
81 |
82 |
83 | #### Update (June 23, 2019)
84 |
85 | The B4 and B5 models are now available. Their usage is identical to the other models:
86 | ```python
87 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet
88 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b4')
89 | ```
90 |
91 | ### Overview
92 | This repository contains an op-for-op PyTorch reimplementation of [EfficientNet](https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.11946), along with pre-trained models and examples.
93 |
94 | The goal of this implementation is to be simple, highly extensible, and easy to integrate into your own projects. This implementation is a work in progress -- new features are currently being implemented.
95 |
96 | At the moment, you can easily:
97 | * Load pretrained EfficientNet models
98 | * Use EfficientNet models for classification or feature extraction
99 | * Evaluate EfficientNet models on ImageNet or your own images
100 |
101 | _Upcoming features_: In the next few days, you will be able to:
102 | * Train new models from scratch on ImageNet with a simple command
103 | * Quickly finetune an EfficientNet on your own dataset
104 | * Export EfficientNet models for production
105 |
106 | ### Table of contents
107 | 1. [About EfficientNet](#about-efficientnet)
108 | 2. [About EfficientNet-PyTorch](#about-efficientnet-pytorch)
109 | 3. [Installation](#installation)
110 | 4. [Usage](#usage)
111 | * [Load pretrained models](#loading-pretrained-models)
112 | * [Example: Classify](#example-classification)
113 | * [Example: Extract features](#example-feature-extraction)
114 | * [Example: Export to ONNX](#example-export)
115 | 6. [Contributing](#contributing)
116 |
117 | ### About EfficientNet
118 |
119 | If you're new to EfficientNets, here is an explanation straight from the official TensorFlow implementation:
120 |
121 | EfficientNets are a family of image classification models, which achieve state-of-the-art accuracy, yet being an order-of-magnitude smaller and faster than previous models. We develop EfficientNets based on AutoML and Compound Scaling. In particular, we first use [AutoML Mobile framework](https://ai.googleblog.com/2018/08/mnasnet-towards-automating-design-of.html) to develop a mobile-size baseline network, named as EfficientNet-B0; Then, we use the compound scaling method to scale up this baseline to obtain EfficientNet-B1 to B7.
122 |
123 |
22 |
23 |
24 | #### Update (Aug 25, 2020)
25 |
26 | This update adds:
27 | * A new `include_top` (default: `True`) option ([#208](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/208))
28 | * Continuous testing with [sotabench](https://sotabench.com/)
29 | * Code quality improvements and fixes ([#215](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/215) [#223](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/223))
30 |
31 | #### Update (May 14, 2020)
32 |
33 | This update adds comprehensive comments and documentation (thanks to @workingcoder).
34 |
35 | #### Update (January 23, 2020)
36 |
37 | This update adds a new category of pre-trained model based on adversarial training, called _advprop_. It is important to note that the preprocessing required for the advprop pretrained models is slightly different from normal ImageNet preprocessing. As a result, by default, advprop models are not used. To load a model with advprop, use:
38 | ```python
39 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained("efficientnet-b0", advprop=True)
40 | ```
41 | There is also a new, large `efficientnet-b8` pretrained model that is only available in advprop form. When using these models, replace ImageNet preprocessing code as follows:
42 | ```python
43 | if advprop: # for models using advprop pretrained weights
44 | normalize = transforms.Lambda(lambda img: img * 2.0 - 1.0)
45 | else:
46 | normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
47 | std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
48 | ```
49 | This update also addresses multiple other issues ([#115](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/115), [#128](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/128)).
50 |
51 | #### Update (October 15, 2019)
52 |
53 | This update allows you to choose whether to use a memory-efficient Swish activation. The memory-efficient version is chosen by default, but it cannot be used when exporting using PyTorch JIT. For this purpose, we have also included a standard (export-friendly) swish activation function. To switch to the export-friendly version, simply call `model.set_swish(memory_efficient=False)` after loading your desired model. This update addresses issues [#88](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/88) and [#89](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/89).
54 |
55 | #### Update (October 12, 2019)
56 |
57 | This update makes the Swish activation function more memory-efficient. It also addresses pull requests [#72](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/72), [#73](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/73), [#85](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/85), and [#86](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/pull/86). Thanks to the authors of all the pull requests!
58 |
59 | #### Update (July 31, 2019)
60 |
61 | _Upgrade the pip package with_ `pip install --upgrade efficientnet-pytorch`
62 |
63 | The B6 and B7 models are now available. Additionally, _all_ pretrained models have been updated to use AutoAugment preprocessing, which translates to better performance across the board. Usage is the same as before:
64 | ```python
65 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet
66 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b7')
67 | ```
68 |
69 | #### Update (June 29, 2019)
70 |
71 | This update adds easy model exporting ([#20](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/20)) and feature extraction ([#38](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/38)).
72 |
73 | * [Example: Export to ONNX](#example-export)
74 | * [Example: Extract features](#example-feature-extraction)
75 | * Also: fixed a CUDA/CPU bug ([#32](https://github.com/lukemelas/EfficientNet-PyTorch/issues/32))
76 |
77 | It is also now incredibly simple to load a pretrained model with a new number of classes for transfer learning:
78 | ```python
79 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b1', num_classes=23)
80 | ```
81 |
82 |
83 | #### Update (June 23, 2019)
84 |
85 | The B4 and B5 models are now available. Their usage is identical to the other models:
86 | ```python
87 | from efficientnet_pytorch import EfficientNet
88 | model = EfficientNet.from_pretrained('efficientnet-b4')
89 | ```
90 |
91 | ### Overview
92 | This repository contains an op-for-op PyTorch reimplementation of [EfficientNet](https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.11946), along with pre-trained models and examples.
93 |
94 | The goal of this implementation is to be simple, highly extensible, and easy to integrate into your own projects. This implementation is a work in progress -- new features are currently being implemented.
95 |
96 | At the moment, you can easily:
97 | * Load pretrained EfficientNet models
98 | * Use EfficientNet models for classification or feature extraction
99 | * Evaluate EfficientNet models on ImageNet or your own images
100 |
101 | _Upcoming features_: In the next few days, you will be able to:
102 | * Train new models from scratch on ImageNet with a simple command
103 | * Quickly finetune an EfficientNet on your own dataset
104 | * Export EfficientNet models for production
105 |
106 | ### Table of contents
107 | 1. [About EfficientNet](#about-efficientnet)
108 | 2. [About EfficientNet-PyTorch](#about-efficientnet-pytorch)
109 | 3. [Installation](#installation)
110 | 4. [Usage](#usage)
111 | * [Load pretrained models](#loading-pretrained-models)
112 | * [Example: Classify](#example-classification)
113 | * [Example: Extract features](#example-feature-extraction)
114 | * [Example: Export to ONNX](#example-export)
115 | 6. [Contributing](#contributing)
116 |
117 | ### About EfficientNet
118 |
119 | If you're new to EfficientNets, here is an explanation straight from the official TensorFlow implementation:
120 |
121 | EfficientNets are a family of image classification models, which achieve state-of-the-art accuracy, yet being an order-of-magnitude smaller and faster than previous models. We develop EfficientNets based on AutoML and Compound Scaling. In particular, we first use [AutoML Mobile framework](https://ai.googleblog.com/2018/08/mnasnet-towards-automating-design-of.html) to develop a mobile-size baseline network, named as EfficientNet-B0; Then, we use the compound scaling method to scale up this baseline to obtain EfficientNet-B1 to B7.
122 |
123 |  127 |
127 |  130 |
130 |