├── my_ADRC
├── td.m
├── adrc.m
├── eso.m
├── test_adrc.m
├── test_pid.slx
├── slprj
│ ├── sl_proj.tmw
│ └── grt
│ │ └── untitled
│ │ └── tmwinternal
│ │ └── minfo.mat
├── untitled_grt_rtw
│ └── build_exception.mat
├── leso3.m
├── nlsef3.m
├── td3.m
└── eso3.m
├── my_nnpid
├── rnn.m
├── bp_nn.m
├── pid_nn.m
├── test_nn.m
├── my_nn_pid.m
└── lstm.m
├── images
├── TD_i_d.PNG
├── TD_i_t.PNG
├── TD_i_d_e.PNG
├── TD_i_t_e.PNG
├── pid_test.PNG
├── adrc_test.PNG
├── adrc_test_s_e.PNG
├── pid_test_s_e.PNG
└── transfer_func.PNG
├── README.md
├── doc_2.md
├── .gitignore
├── LICENSE
└── doc_1.md
/my_ADRC/td.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/my_ADRC/td.m
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_ADRC/adrc.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/my_ADRC/adrc.m
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_ADRC/eso.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/my_ADRC/eso.m
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_nnpid/rnn.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/my_nnpid/rnn.m
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/TD_i_d.PNG:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/images/TD_i_d.PNG
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/TD_i_t.PNG:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/images/TD_i_t.PNG
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_nnpid/bp_nn.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/my_nnpid/bp_nn.m
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_nnpid/pid_nn.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/my_nnpid/pid_nn.m
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/TD_i_d_e.PNG:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/images/TD_i_d_e.PNG
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/TD_i_t_e.PNG:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/images/TD_i_t_e.PNG
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/pid_test.PNG:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/images/pid_test.PNG
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_ADRC/test_adrc.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/my_ADRC/test_adrc.m
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_nnpid/test_nn.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/my_nnpid/test_nn.m
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/adrc_test.PNG:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/images/adrc_test.PNG
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_ADRC/test_pid.slx:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/my_ADRC/test_pid.slx
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_nnpid/my_nn_pid.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/my_nnpid/my_nn_pid.m
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/adrc_test_s_e.PNG:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/images/adrc_test_s_e.PNG
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/pid_test_s_e.PNG:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/images/pid_test_s_e.PNG
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/transfer_func.PNG:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/images/transfer_func.PNG
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # ADRC-matlab
2 | 用matlab写的ADRC程序。
3 | 还有一些相关类似读书报告的文档。
4 | 例如
5 |
6 | ### [小白理解ADRC控制器](./doc_1.md)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_ADRC/slprj/sl_proj.tmw:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Simulink Coder project marker file. Please don't change it.
2 | slprjVersion: 8.7_029
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_ADRC/untitled_grt_rtw/build_exception.mat:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/my_ADRC/untitled_grt_rtw/build_exception.mat
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_ADRC/slprj/grt/untitled/tmwinternal/minfo.mat:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lvniqi/ADRC-matlab/HEAD/my_ADRC/slprj/grt/untitled/tmwinternal/minfo.mat
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc_2.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 小白理解神经网络PID
2 | ==========
3 | 整篇文章仅包含古董公式,新鲜的公式不知道在哪里,有知道的请告知:stuck_out_tongue_winking_eye:。
4 |
5 | ## 引入
6 | 如何将PID控制器挺好用,
7 | 但是如何加上点好玩~~玄学~~的东西让它看起来更高大上,
8 | 以期帮助我们更好地灌水呢?
9 | 这时候就要上神经网络这个大杀器了。
10 |
11 | 不过实际上PID神经网络是快20年前大佬们玩剩下的东西,我写这个就是想看看实际上效果和局限在哪里。
12 |
13 | ##
14 |
15 |  --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Prerequisites
2 | *.d
3 |
4 | # Compiled Object files
5 | *.slo
6 | *.lo
7 | *.o
8 | *.obj
9 |
10 | # Precompiled Headers
11 | *.gch
12 | *.pch
13 |
14 | # Compiled Dynamic libraries
15 | *.so
16 | *.dylib
17 | *.dll
18 |
19 | # Fortran module files
20 | *.mod
21 | *.smod
22 |
23 | # Compiled Static libraries
24 | *.lai
25 | *.la
26 | *.a
27 | *.lib
28 |
29 | # Executables
30 | *.exe
31 | *.out
32 | *.app
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_ADRC/leso3.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function [z1_new,z2_new,z3_new] = leso3(z1_last,z2_last,z3_last, ...
2 | w, ...
3 | input,b0,output,h)
4 | beta_01 = 3*w;
5 | beta_02 = 3*w^2;
6 | beta_03 = w^3;
7 | e = z1_last-output;
8 | z1_new = z1_last+h*(z2_last-beta_01*e);
9 | z2_new = z2_last + h*(z3_last-beta_02*e+b0*input);
10 | z3_new = z3_last + h*(-beta_03*e);
11 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_ADRC/nlsef3.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function u0 = nlsef3(e1,e2,c,r,h1)
2 | u0 = -fhan(e1,c*e2,r,h1);
3 | end
4 |
5 | function fh = fhan(x1_last,x2_last,r,h0)
6 | d = r*h0;
7 | d0 = h0*d;
8 | x1_new = x1_last+h0*x2_last;
9 | a0 = sqrt(d^2+8*r*abs(x1_new));
10 | if abs(x1_new)>d0
11 | a=x2_last+(a0-d)/2*sign(x1_new);
12 | else
13 | a = x2_last+x1_new/h0;
14 | end
15 | fh = -r*sat(a,d);
16 | end
17 |
18 | function M=sat(x,delta)
19 | if abs(x)<=delta
20 | M=x/delta;
21 | else
22 | M=sign(x);
23 | end
24 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_ADRC/td3.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function [x1_new,x2_new] = td3(x1_last,x2_last,input,r,h,h0)
2 | x1_new = x1_last+h*x2_last;
3 | x2_new = x2_last+h*fhan(x1_last-input,x2_last,r,h0);
4 | end
5 |
6 | function fh = fhan(x1_last,x2_last,r,h0)
7 | d = r*h0;
8 | d0 = h0*d;
9 | x1_new = x1_last+h0*x2_last;
10 | a0 = sqrt(d^2+8*r*abs(x1_new));
11 | if abs(x1_new)>d0
12 | a=x2_last+(a0-d)/2*sign(x1_new);
13 | else
14 | a = x2_last+x1_new/h0;
15 | end
16 | fh = -r*sat(a,d);
17 | end
18 |
19 | function M=sat(x,delta)
20 | if abs(x)<=delta
21 | M=x/delta;
22 | else
23 | M=sign(x);
24 | end
25 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_ADRC/eso3.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function [z1_new,z2_new,z3_new] = eso3(z1_last,z2_last,z3_last, ...
2 | beta_01,beta_02,beta_03, ...
3 | input,b0,output,h,threshold)
4 | e = z1_last-output;
5 | fe = fal(e,0.5,threshold);
6 | fe1 = fal(e,0.25,threshold);
7 | z1_new = z1_last+h*(z2_last-beta_01*e);
8 | z2_new = z2_last + h*(z3_last-beta_02*fe+b0*input);
9 | z3_new = z3_last + h*(-beta_03*fe1);
10 | end
11 |
12 | function fe = fal(error,pow,threshold)
13 | if abs(error) > threshold
14 | fe = abs(error)^pow*sign(error);
15 | else
16 | fe = error/threshold^pow;
17 | end
18 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2017 lvniqi
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc_1.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 小白理解ADRC控制器
2 | ==========
3 | 整篇文章仅包含毫无意义的公式,有意义的公式都在书里,小白请放心食用:stuck_out_tongue_winking_eye:
4 |
5 | ## 引入
6 | ### 传统PID存在的问题
7 | 传统上,对于模型不确定的系统我们(或者仅仅是我?)都喜欢用PID控制。
8 | 即使在模型清楚的情况下,有时我们也很难获得模型的部分参数,所以继续沿用PID控制器。
9 |
10 | 一般我们看到的的pid控制是长这样的:
11 |
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Prerequisites
2 | *.d
3 |
4 | # Compiled Object files
5 | *.slo
6 | *.lo
7 | *.o
8 | *.obj
9 |
10 | # Precompiled Headers
11 | *.gch
12 | *.pch
13 |
14 | # Compiled Dynamic libraries
15 | *.so
16 | *.dylib
17 | *.dll
18 |
19 | # Fortran module files
20 | *.mod
21 | *.smod
22 |
23 | # Compiled Static libraries
24 | *.lai
25 | *.la
26 | *.a
27 | *.lib
28 |
29 | # Executables
30 | *.exe
31 | *.out
32 | *.app
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_ADRC/leso3.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function [z1_new,z2_new,z3_new] = leso3(z1_last,z2_last,z3_last, ...
2 | w, ...
3 | input,b0,output,h)
4 | beta_01 = 3*w;
5 | beta_02 = 3*w^2;
6 | beta_03 = w^3;
7 | e = z1_last-output;
8 | z1_new = z1_last+h*(z2_last-beta_01*e);
9 | z2_new = z2_last + h*(z3_last-beta_02*e+b0*input);
10 | z3_new = z3_last + h*(-beta_03*e);
11 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_ADRC/nlsef3.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function u0 = nlsef3(e1,e2,c,r,h1)
2 | u0 = -fhan(e1,c*e2,r,h1);
3 | end
4 |
5 | function fh = fhan(x1_last,x2_last,r,h0)
6 | d = r*h0;
7 | d0 = h0*d;
8 | x1_new = x1_last+h0*x2_last;
9 | a0 = sqrt(d^2+8*r*abs(x1_new));
10 | if abs(x1_new)>d0
11 | a=x2_last+(a0-d)/2*sign(x1_new);
12 | else
13 | a = x2_last+x1_new/h0;
14 | end
15 | fh = -r*sat(a,d);
16 | end
17 |
18 | function M=sat(x,delta)
19 | if abs(x)<=delta
20 | M=x/delta;
21 | else
22 | M=sign(x);
23 | end
24 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_ADRC/td3.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function [x1_new,x2_new] = td3(x1_last,x2_last,input,r,h,h0)
2 | x1_new = x1_last+h*x2_last;
3 | x2_new = x2_last+h*fhan(x1_last-input,x2_last,r,h0);
4 | end
5 |
6 | function fh = fhan(x1_last,x2_last,r,h0)
7 | d = r*h0;
8 | d0 = h0*d;
9 | x1_new = x1_last+h0*x2_last;
10 | a0 = sqrt(d^2+8*r*abs(x1_new));
11 | if abs(x1_new)>d0
12 | a=x2_last+(a0-d)/2*sign(x1_new);
13 | else
14 | a = x2_last+x1_new/h0;
15 | end
16 | fh = -r*sat(a,d);
17 | end
18 |
19 | function M=sat(x,delta)
20 | if abs(x)<=delta
21 | M=x/delta;
22 | else
23 | M=sign(x);
24 | end
25 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/my_ADRC/eso3.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function [z1_new,z2_new,z3_new] = eso3(z1_last,z2_last,z3_last, ...
2 | beta_01,beta_02,beta_03, ...
3 | input,b0,output,h,threshold)
4 | e = z1_last-output;
5 | fe = fal(e,0.5,threshold);
6 | fe1 = fal(e,0.25,threshold);
7 | z1_new = z1_last+h*(z2_last-beta_01*e);
8 | z2_new = z2_last + h*(z3_last-beta_02*fe+b0*input);
9 | z3_new = z3_last + h*(-beta_03*fe1);
10 | end
11 |
12 | function fe = fal(error,pow,threshold)
13 | if abs(error) > threshold
14 | fe = abs(error)^pow*sign(error);
15 | else
16 | fe = error/threshold^pow;
17 | end
18 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2017 lvniqi
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc_1.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 小白理解ADRC控制器
2 | ==========
3 | 整篇文章仅包含毫无意义的公式,有意义的公式都在书里,小白请放心食用:stuck_out_tongue_winking_eye:
4 |
5 | ## 引入
6 | ### 传统PID存在的问题
7 | 传统上,对于模型不确定的系统我们(或者仅仅是我?)都喜欢用PID控制。
8 | 即使在模型清楚的情况下,有时我们也很难获得模型的部分参数,所以继续沿用PID控制器。
9 |
10 | 一般我们看到的的pid控制是长这样的:
11 |
12 |
13 |

14 |
 59 |
60 | 是不是看着很乱?哈哈~我只是想安利一下这个
61 | [画图工具](https://yuml.me/diagram/scruffy/class/samples)。
62 |
63 | 正常的画风是这样的:
64 |
65 |
59 |
60 | 是不是看着很乱?哈哈~我只是想安利一下这个
61 | [画图工具](https://yuml.me/diagram/scruffy/class/samples)。
62 |
63 | 正常的画风是这样的:
64 |
65 |
66 |
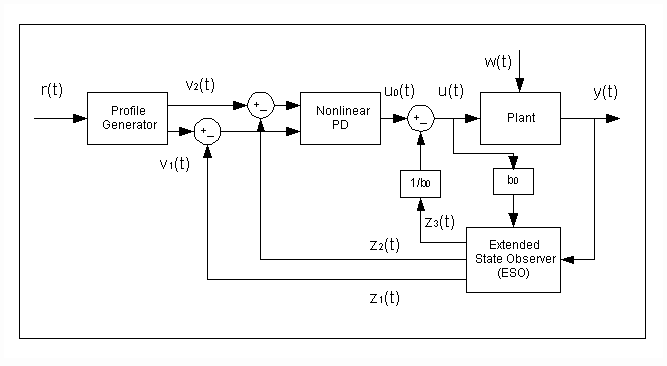
67 |
&space;\\&space;y&space;=&space;x_2&space;\end{matrix}\right.) 106 |
107 | 写成离散方程的样子,就变成一个实际可用的跟踪微分器,即
108 |
109 |
106 |
107 | 写成离散方程的样子,就变成一个实际可用的跟踪微分器,即
108 |
109 | &space;=&space;x1(k)+hx2(k)&space;\\&space;x_2(k+1)&space;=&space;x2(k)+h(-r^2(x_1(k)-v(k))-2rx_2(k))&space;\end{matrix}&space;\right.) 110 |
111 | x1为跟踪输出,x2为微分输出,h为采样周期
112 | 差分效果如下所示
113 |
114 | 
115 |
116 | 跟踪效果如下所示
117 |
118 | 
119 |
120 | 看起来不错,那么这么做的代价是什么。
121 | 眼尖的同学可能已经看出来了,跟踪有滞后。其实这么做,微分和跟踪都会有滞后。
122 | 我们将r的值改小一点看看。
123 |
110 |
111 | x1为跟踪输出,x2为微分输出,h为采样周期
112 | 差分效果如下所示
113 |
114 | 
115 |
116 | 跟踪效果如下所示
117 |
118 | 
119 |
120 | 看起来不错,那么这么做的代价是什么。
121 | 眼尖的同学可能已经看出来了,跟踪有滞后。其实这么做,微分和跟踪都会有滞后。
122 | 我们将r的值改小一点看看。
123 |
124 |

125 |

126 |
 143 |
144 | 由于a1,a2未知,我们只能根据输出y和输入u估计整个状态变量z。
145 | 一个全维状态观测器是这样的,通过引入l1、l2进行修正。
146 |
147 |
143 |
144 | 由于a1,a2未知,我们只能根据输出y和输入u估计整个状态变量z。
145 | 一个全维状态观测器是这样的,通过引入l1、l2进行修正。
146 |
147 | &space;\\&space;\dot{z_2}&space;=&space;a_1z_1+a_2z_2+u&space;+l_2(y_z-y)&space;\\&space;y_z&space;=&space;z_1&space;\end{matrix}&space;\right.) 148 |
149 | 令e = z1-x1那么
150 |
151 | 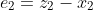
152 |
153 | 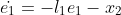
154 |
155 | e_1+a_2e_2)
156 |
157 | 因此只要l1、l2选取得当,e->0,观测器输出z逼近真实的状态变量x。
158 | 当然,你要是开心的话可以给e们过一个函数提高性能。
159 |
160 |
161 | ##### 扩张状态观测器(ESO)
162 |
163 | 那么**扩张状态观测器**究竟**扩张**在哪儿了呢?
164 | 对于一个二阶系统,假设其
165 |
166 | 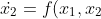+u)
167 |
168 | 中的f(x1,x2)进行扩张,使得
169 |
170 | 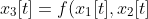)
171 |
172 | =w(t))
173 |
174 | 对,这个扩张出来的x3就是所谓的扩张状态,构建包含x3,输出z={z1,z2,z3}的观测器就是扩张状态观测器。
175 |
176 | ### 细枝末节
177 |
178 | 其他细枝末节的东西不高兴写了,TD、控制组合、ESO都可以有线性的,也可以有非线性的(~~类比激活函数:joy:大误~~)。
179 |
180 |
181 | ## 测试一下
182 | 看如下一个二阶含噪系统
183 |
184 | 
185 |
186 | 使用PID以及简单自动tune以后,输出是这样的。
187 |
148 |
149 | 令e = z1-x1那么
150 |
151 | 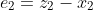
152 |
153 | 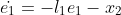
154 |
155 | e_1+a_2e_2)
156 |
157 | 因此只要l1、l2选取得当,e->0,观测器输出z逼近真实的状态变量x。
158 | 当然,你要是开心的话可以给e们过一个函数提高性能。
159 |
160 |
161 | ##### 扩张状态观测器(ESO)
162 |
163 | 那么**扩张状态观测器**究竟**扩张**在哪儿了呢?
164 | 对于一个二阶系统,假设其
165 |
166 | 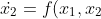+u)
167 |
168 | 中的f(x1,x2)进行扩张,使得
169 |
170 | 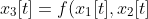)
171 |
172 | =w(t))
173 |
174 | 对,这个扩张出来的x3就是所谓的扩张状态,构建包含x3,输出z={z1,z2,z3}的观测器就是扩张状态观测器。
175 |
176 | ### 细枝末节
177 |
178 | 其他细枝末节的东西不高兴写了,TD、控制组合、ESO都可以有线性的,也可以有非线性的(~~类比激活函数:joy:大误~~)。
179 |
180 |
181 | ## 测试一下
182 | 看如下一个二阶含噪系统
183 |
184 | 
185 |
186 | 使用PID以及简单自动tune以后,输出是这样的。
187 |
188 |

189 |
194 |

195 |
 14 |
14 |  14 |
14 |  67 |
67 |  125 |
125 |  126 |
126 |  189 |
189 |  195 |
195 |