└── README.md
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |  3 |
3 |
4 | Algorithms & Data Structures Guide
5 |
6 |
7 | #### A guide covering Data Structures and Algorithms such as Neural networks, MLPs, Arrays, Linked Lists, Trees, Hashtables, Stacks, Queues, Heaps, Graphs, Sorting & Searching, and Dynamic programming.
8 |
9 | **Note: You can easily convert this markdown file to a PDF in [VSCode](https://code.visualstudio.com/) using this handy extension [Markdown PDF](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=yzane.markdown-pdf).**
10 |
11 |
12 |  13 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 | # Table of Contents
17 |
18 | 1. [Algorithms & Data Structures Learning Resources](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Algorithms-and-Data-Structures#algorithms--data-structures-learning-resources)
19 |
20 | 2. [Algorithms](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Algorithms-and-Data-Structures#algorithms)
21 |
22 | 3. [Algorithmic Complexity Analysis](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Algorithms-and-Data-Structures#algorithmic-complexity-analysis)
23 |
24 | 4. [Data Structures](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Algorithms-and-Data-Structures#data-structures)
25 |
26 |
27 | ## Algorithms & Data Structures Learning Resources
28 | [Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Algorithms-and-Data-Structures#table-of-contents)
29 |
30 | [Algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Algorithm) is a procedure of well-defined, computer implementabled instructions, typically to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation task such as data processing, automated reasoning, and machine learning.
31 |
32 | [Data Structure](https://www.w3schools.in/data-structures-tutorial/intro/) is a specific way to store and organize data in a computer's memory so that these data can be used efficiently later. Data may be arranged in many different ways, such as the logical or mathematical model for a particular organization of data is termed as a data structure.
33 |
34 | [VisualGo: Visualising data structures and algorithms through animation](https://visualgo.net/en)
35 |
36 | [Data Structure & Algorithms Visualizations](https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/Algorithms.html)
37 |
38 | [Learning Data Structures and Algorithms courses on Coursera](https://www.coursera.org/specializations/data-structures-algorithms)
39 |
40 | [Learning Data Structures and Algorithms courses on Udemy](https://www.udemy.com/courses/search/?src=ukw&q=Data+Structures+and+Algorithms)
41 |
42 | [Learning Data Structures and Algorithms courses on edX](https://www.edx.org/search?q=Algorithms%20and%20Data%20Structures)
43 |
44 | [Intro to Data Structures and Algorithms courses on Udacity](https://www.udacity.com/course/data-structures-and-algorithms-in-python--ud513)
45 |
46 | [Learning Algorithms courses on Khan Academy](https://www.khanacademy.org/computing/computer-science/algorithms)
47 |
48 | [Data Structures and Algorithms course from Harvard University](https://online-learning.harvard.edu/course/data-structures-and-algorithms)
49 |
50 | [Data Structures and Algorithms course from Standford University(CS 166)](http://web.stanford.edu/class/cs166/)
51 |
52 | [Learning Data Structures and Algorithms on CodeChef](https://www.codechef.com/certification/data-structures-and-algorithms/prepare)
53 |
54 | [Learning Algorithms and Data Structures courses on Pluralsight](https://www.pluralsight.com/courses/algorithms-data-structures-part-one)
55 |
56 | [Data structure and algorithms online course on Learnbay.io](https://www.learnbay.io/data-structures-algorithms/)
57 |
58 | [Discrete Probability](https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/High_School_Mathematics_Extensions/Discrete_Probability)
59 |
60 | [Mathematical Proofs](https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/High_School_Mathematics_Extensions/Mathematical_Proofs)
61 |
62 |
63 | ## Algorithms
64 | [Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Algorithms-and-Data-Structures#table-of-contents)
65 |
66 | [Fuzzy logic](https://www.investopedia.com/terms/f/fuzzy-logic.asp) is a heuristic approach that allows for more advanced decision-tree processing and better integration with rules-based programming.
67 |
68 |
69 | 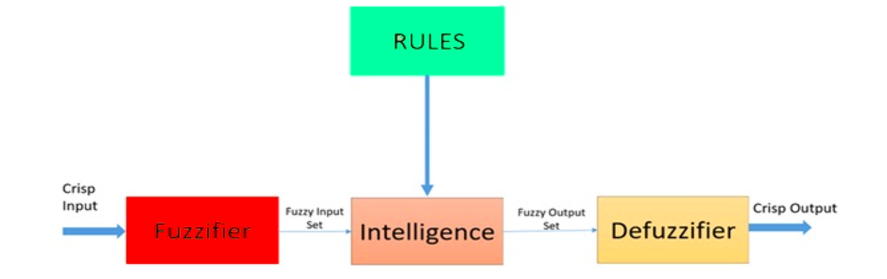 70 |
70 |
71 |
72 |
73 | **Architecture of a Fuzzy Logic System. Source: [ResearchGate](https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Architecture-of-a-fuzzy-logic-system_fig2_309452475)**
74 |
75 | [Support Vector Machine (SVM)](https://web.stanford.edu/~hastie/MOOC-Slides/svm.pdf) is a supervised machine learning model that uses classification algorithms for two-group classification problems.
76 |
77 |
78 | 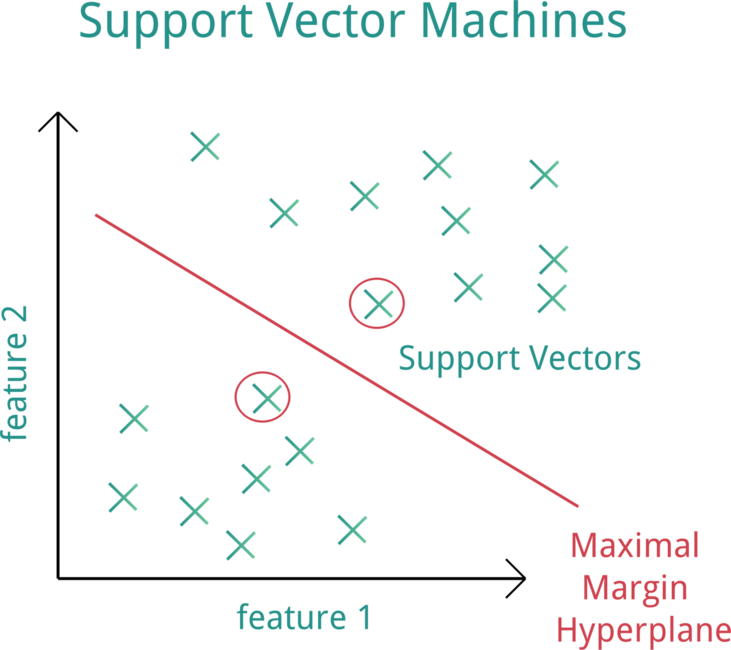 79 |
79 |
80 |
81 |
82 | **Support Vector Machine (SVM). Source:[OpenClipArt](https://openclipart.org/detail/182977/svm-support-vector-machines)**
83 |
84 | [Neural networks](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/neural-networks) are a subset of machine learning and are at the heart of deep learning algorithms. The name/structure is inspired by the human brain copying the process that biological neurons/nodes signal to one another.
85 |
86 |
87 |  88 |
88 |
89 |
90 |
91 | **Neural Networks Toplogies. Source: [Fjodor van Veen](https://www.asimovinstitute.org/author/fjodorvanveen/) from [Asimov institute](https://www.asimovinstitute.org/).**
92 |
93 |
94 | 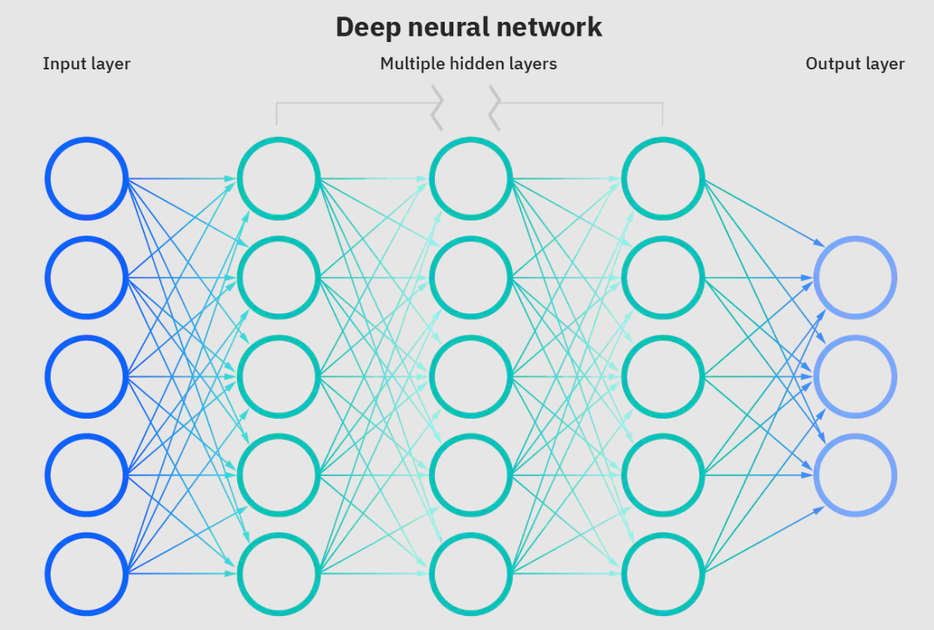 95 |
95 |
96 |
97 |
98 | **Deep neural network. Source: [IBM](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/neural-networks)**
99 |
100 | [Convolutional Neural Networks (R-CNN)](https://stanford.edu/~shervine/teaching/cs-230/cheatsheet-convolutional-neural-networks) is an object detection algorithm that first segments the image to find potential relevant bounding boxes and then run the detection algorithm to find most probable objects in those bounding boxes.
101 |
102 |
103 | 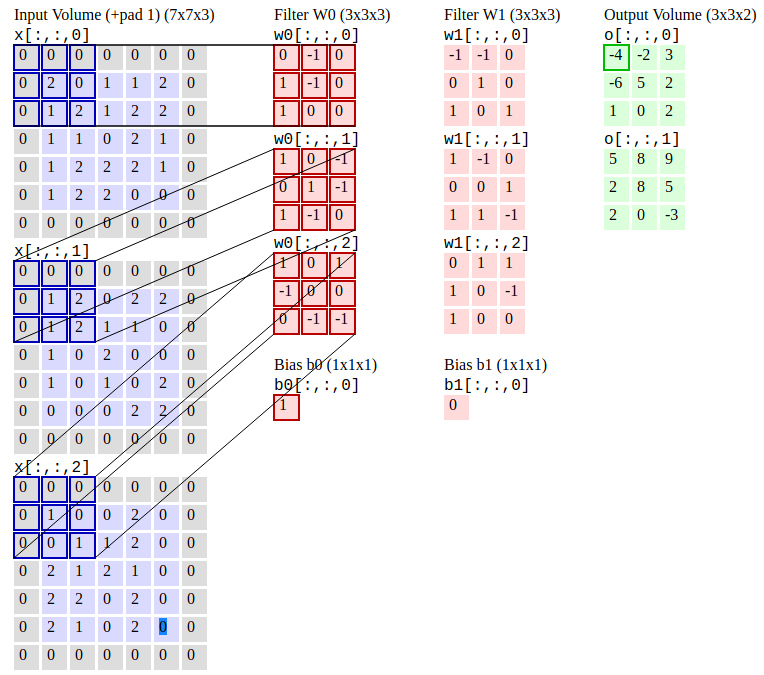 104 |
104 |
105 |
106 |
107 | **Convolutional Neural Networks. Source: [CS231n](https://cs231n.github.io/convolutional-networks/#conv)**
108 |
109 | [Recurrent neural networks (RNNs)](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/recurrent-neural-networks) is a type of artificial neural network which uses sequential data or time series data.
110 |
111 |
112 |  113 |
113 |
114 |
115 |
116 | **Recurrent Neural Networks. Source: [Slideteam](https://www.slideteam.net/recurrent-neural-networks-rnns-ppt-powerpoint-presentation-file-templates.html)**
117 |
118 | [Multilayer Perceptrons (MLPs)](https://deepai.org/machine-learning-glossary-and-terms/multilayer-perceptron) is multi-layer neural networks composed of multiple layers of [perceptrons](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Perceptron) with a threshold activation.
119 |
120 |
121 |  122 |
122 |
123 |
124 |
125 | **Multilayer Perceptrons. Source: [DeepAI](https://deepai.org/machine-learning-glossary-and-terms/multilayer-perceptron)**
126 |
127 | [Random forest](https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/random-forest) is a commonly-used machine learning algorithm, which combines the output of multiple decision trees to reach a single result. A decision tree in a forest cannot be pruned for sampling and therefore, prediction selection. Its ease of use and flexibility have fueled its adoption, as it handles both classification and regression problems.
128 |
129 |
130 |  131 |
131 |
132 |
133 |
134 | **Random forest. Source: [wikimedia](https://community.tibco.com/wiki/random-forest-template-tibco-spotfirer-wiki-page)**
135 |
136 | [Decision trees](https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~bhiksha/courses/10-601/decisiontrees/) are tree-structured models for classification and regression.
137 |
138 |
139 |  140 |
140 |
141 |
142 |
143 | ***Decision Trees. Source: [CMU](http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~bhiksha/courses/10-601/decisiontrees/)**
144 |
145 | [Naive Bayes](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Naive_Bayes_classifier) is a machine learning algorithm that is used solved calssification problems. It's based on applying [Bayes' theorem](https://www.mathsisfun.com/data/bayes-theorem.html) with strong independence assumptions between the features.
146 |
147 |
148 |  149 |
149 |
150 |
151 |
152 | **Bayes' theorem. Source: [mathisfun](https://www.mathsisfun.com/data/bayes-theorem.html)**
153 |
154 | **Graph Algorithms**
155 |
156 | - Breadth First Search (BFS)
157 | - Depth First Search (DFS)
158 | - Shortest Path from source to all vertices **Dijkstra**
159 | - Shortest Path from every vertex to every other vertex **Floyd Warshall**
160 | - Minimum Spanning tree **Prim**
161 | - Minimum Spanning tree **Kruskal**
162 | - Topological Sort
163 | - Articulation Points (Cut Vertices) in a Graph
164 | - Bridges in a graph
165 |
166 |
167 | **Searching And Sorting**
168 |
169 | - Binary Search
170 | - Quick Sort
171 | - Merge Sort
172 | - Order Statistics
173 | - KMP algorithm
174 | - Rabin karp
175 | - Z’s algorithm
176 | - String Matching/String Parsing
177 | - Counting Sort
178 |
179 |
180 | **Dynamic Programming**
181 |
182 | - Longest Common Subsequence
183 | - Longest Increasing Subsequence
184 | - Edit Distance
185 | - Minimum Partition
186 | - Ways to Cover a Distance
187 | - Longest Path In Matrix
188 | - Subset Sum Problem
189 | - Optimal Strategy for a Game
190 | - 0-1 Knapsack Problem
191 | - Assembly Line Scheduling
192 |
193 |
194 | ## Algorithmic Complexity Analysis
195 | [Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Algorithms-and-Data-Structures#table-of-contents)
196 |
197 | - Big O Notation
198 | - Time Complexity
199 | - Space Complexity
200 |
201 |  202 |
203 | **Order of growth of algorithms specified in Big-O notation. Source: Big-O Cheat Sheet**
204 |
205 |
202 |
203 | **Order of growth of algorithms specified in Big-O notation. Source: Big-O Cheat Sheet**
204 |
205 |  206 |
207 | **Complexity of operations on Data Structures. Source: Big-O Cheat Sheet**
208 |
209 |
210 |
206 |
207 | **Complexity of operations on Data Structures. Source: Big-O Cheat Sheet**
208 |
209 |
210 |  211 |
212 | **Complexity of Sorting algorithms. Source: Big-O Cheat Sheet**
213 |
214 |
215 | ## Data Structures
216 | [Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Algorithms-and-Data-Structures#table-of-contents)
217 |
218 | [Arrays](https://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/arrays/) are a series of elements(numbers, booleans, or strings) of the same type placed in phyiscal memory locations that can be individually referenced by adding an index to a unique identifier.
219 |
220 | - [Vector](https://www.cplusplus.com/reference/vector/vector/) is a dynamic array, where the size can be increased when an element is inserted or deleted, with the storage being handled automatically by the container.
221 |
222 | [Linked Lists](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linked_list) is a linear collection of data elements whose order is not given by their physical placement in memory. Instead, elements in a linked list are linked using pointers.
223 |
224 | - [Singly Linked List](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/data-structures/linked-list/singly-linked-list/) is a type of linked data structure where each node points to the next node in the sequence. It does not have any pointer that points to the previous node.
225 |
226 | - [Doubly-Linked List](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Doubly_linked_list) is a type of linked data structure in which each node apart from storing its data has two links. A node consists of three parts: node data, a pointer to the next node in sequence (next pointer), pointer to the previous node (previous pointer).
227 |
228 | [Trees](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_(data_structure)) is a nonlinear data structure unlike arrays, linked lists, stacks and queues which are linear data structures. A tree can be empty with no nodes or in other instances a tree's structure consists of one node called the root and 0 or 1 or more subtrees.
229 |
230 | - Basic Tree
231 | - Binary Tree
232 | - Binary Search Tree
233 | - AVL Tree
234 | - Red-Black Tree
235 | - N-ary Tree
236 |
237 | [Hash Tables](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/scripting/learn/deep-dives/everything-about-hashtable?view=powershell-7.1) are a data structure, much like an array, except you store each value (object) using a key. It is a basic key/value store for mapping known as a hash function.
238 |
239 | [Stacks](https://www.thedshandbook.com/stacks/) is a linear data structure that store data in an order known as the Last In First Out (LIFO) order.
240 |
241 | - LIFO (Last In First Out)
242 | - FILO (First In Last Out)
243 |
244 | [Queues](https://www.thedshandbook.com/queues/) is a linear data structure that stores data in an order known as the First In First Out(FIFO) order.
245 |
246 | [Heaps](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heap_(data_structure)) is a specialized tree-based data structure which is essentially an almost complete tree that satisfies the heap property.
247 |
248 | - Max Heap
249 | - Min-Heap
250 | - Binary Heap
251 |
252 | [Graphs](https://www.thedshandbook.com/graphs/) is a data structure that represent relations between pairs of objects. It consists of nodes (known as vertices) that are connected through links (known as edges).
253 |
254 | ## Contribute
255 |
256 | - [x] If would you like to contribute to this guide simply make a [Pull Request](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Algorithms-and-Data-Structures-Guide/pulls).
257 |
258 |
259 | ## License
260 | [Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Algorithms-and-Data-Structures#table-of-contents)
261 |
262 | Distributed under the [Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) Public License](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
263 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
211 |
212 | **Complexity of Sorting algorithms. Source: Big-O Cheat Sheet**
213 |
214 |
215 | ## Data Structures
216 | [Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Algorithms-and-Data-Structures#table-of-contents)
217 |
218 | [Arrays](https://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/arrays/) are a series of elements(numbers, booleans, or strings) of the same type placed in phyiscal memory locations that can be individually referenced by adding an index to a unique identifier.
219 |
220 | - [Vector](https://www.cplusplus.com/reference/vector/vector/) is a dynamic array, where the size can be increased when an element is inserted or deleted, with the storage being handled automatically by the container.
221 |
222 | [Linked Lists](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linked_list) is a linear collection of data elements whose order is not given by their physical placement in memory. Instead, elements in a linked list are linked using pointers.
223 |
224 | - [Singly Linked List](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/data-structures/linked-list/singly-linked-list/) is a type of linked data structure where each node points to the next node in the sequence. It does not have any pointer that points to the previous node.
225 |
226 | - [Doubly-Linked List](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Doubly_linked_list) is a type of linked data structure in which each node apart from storing its data has two links. A node consists of three parts: node data, a pointer to the next node in sequence (next pointer), pointer to the previous node (previous pointer).
227 |
228 | [Trees](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_(data_structure)) is a nonlinear data structure unlike arrays, linked lists, stacks and queues which are linear data structures. A tree can be empty with no nodes or in other instances a tree's structure consists of one node called the root and 0 or 1 or more subtrees.
229 |
230 | - Basic Tree
231 | - Binary Tree
232 | - Binary Search Tree
233 | - AVL Tree
234 | - Red-Black Tree
235 | - N-ary Tree
236 |
237 | [Hash Tables](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/scripting/learn/deep-dives/everything-about-hashtable?view=powershell-7.1) are a data structure, much like an array, except you store each value (object) using a key. It is a basic key/value store for mapping known as a hash function.
238 |
239 | [Stacks](https://www.thedshandbook.com/stacks/) is a linear data structure that store data in an order known as the Last In First Out (LIFO) order.
240 |
241 | - LIFO (Last In First Out)
242 | - FILO (First In Last Out)
243 |
244 | [Queues](https://www.thedshandbook.com/queues/) is a linear data structure that stores data in an order known as the First In First Out(FIFO) order.
245 |
246 | [Heaps](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heap_(data_structure)) is a specialized tree-based data structure which is essentially an almost complete tree that satisfies the heap property.
247 |
248 | - Max Heap
249 | - Min-Heap
250 | - Binary Heap
251 |
252 | [Graphs](https://www.thedshandbook.com/graphs/) is a data structure that represent relations between pairs of objects. It consists of nodes (known as vertices) that are connected through links (known as edges).
253 |
254 | ## Contribute
255 |
256 | - [x] If would you like to contribute to this guide simply make a [Pull Request](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Algorithms-and-Data-Structures-Guide/pulls).
257 |
258 |
259 | ## License
260 | [Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Algorithms-and-Data-Structures#table-of-contents)
261 |
262 | Distributed under the [Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) Public License](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
263 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 3 |
3 |  3 |
3 |  13 |
13 |  70 |
70 |  79 |
79 |  88 |
88 |  95 |
95 |  104 |
104 |  113 |
113 |  122 |
122 |  131 |
131 |  140 |
140 |  149 |
149 |  202 |
203 | **Order of growth of algorithms specified in Big-O notation. Source: Big-O Cheat Sheet**
204 |
205 |
202 |
203 | **Order of growth of algorithms specified in Big-O notation. Source: Big-O Cheat Sheet**
204 |
205 |  206 |
207 | **Complexity of operations on Data Structures. Source: Big-O Cheat Sheet**
208 |
209 |
210 |
206 |
207 | **Complexity of operations on Data Structures. Source: Big-O Cheat Sheet**
208 |
209 |
210 |  211 |
212 | **Complexity of Sorting algorithms. Source: Big-O Cheat Sheet**
213 |
214 |
215 | ## Data Structures
216 | [Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Algorithms-and-Data-Structures#table-of-contents)
217 |
218 | [Arrays](https://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/arrays/) are a series of elements(numbers, booleans, or strings) of the same type placed in phyiscal memory locations that can be individually referenced by adding an index to a unique identifier.
219 |
220 | - [Vector](https://www.cplusplus.com/reference/vector/vector/) is a dynamic array, where the size can be increased when an element is inserted or deleted, with the storage being handled automatically by the container.
221 |
222 | [Linked Lists](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linked_list) is a linear collection of data elements whose order is not given by their physical placement in memory. Instead, elements in a linked list are linked using pointers.
223 |
224 | - [Singly Linked List](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/data-structures/linked-list/singly-linked-list/) is a type of linked data structure where each node points to the next node in the sequence. It does not have any pointer that points to the previous node.
225 |
226 | - [Doubly-Linked List](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Doubly_linked_list) is a type of linked data structure in which each node apart from storing its data has two links. A node consists of three parts: node data, a pointer to the next node in sequence (next pointer), pointer to the previous node (previous pointer).
227 |
228 | [Trees](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_(data_structure)) is a nonlinear data structure unlike arrays, linked lists, stacks and queues which are linear data structures. A tree can be empty with no nodes or in other instances a tree's structure consists of one node called the root and 0 or 1 or more subtrees.
229 |
230 | - Basic Tree
231 | - Binary Tree
232 | - Binary Search Tree
233 | - AVL Tree
234 | - Red-Black Tree
235 | - N-ary Tree
236 |
237 | [Hash Tables](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/scripting/learn/deep-dives/everything-about-hashtable?view=powershell-7.1) are a data structure, much like an array, except you store each value (object) using a key. It is a basic key/value store for mapping known as a hash function.
238 |
239 | [Stacks](https://www.thedshandbook.com/stacks/) is a linear data structure that store data in an order known as the Last In First Out (LIFO) order.
240 |
241 | - LIFO (Last In First Out)
242 | - FILO (First In Last Out)
243 |
244 | [Queues](https://www.thedshandbook.com/queues/) is a linear data structure that stores data in an order known as the First In First Out(FIFO) order.
245 |
246 | [Heaps](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heap_(data_structure)) is a specialized tree-based data structure which is essentially an almost complete tree that satisfies the heap property.
247 |
248 | - Max Heap
249 | - Min-Heap
250 | - Binary Heap
251 |
252 | [Graphs](https://www.thedshandbook.com/graphs/) is a data structure that represent relations between pairs of objects. It consists of nodes (known as vertices) that are connected through links (known as edges).
253 |
254 | ## Contribute
255 |
256 | - [x] If would you like to contribute to this guide simply make a [Pull Request](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Algorithms-and-Data-Structures-Guide/pulls).
257 |
258 |
259 | ## License
260 | [Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Algorithms-and-Data-Structures#table-of-contents)
261 |
262 | Distributed under the [Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) Public License](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
263 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
211 |
212 | **Complexity of Sorting algorithms. Source: Big-O Cheat Sheet**
213 |
214 |
215 | ## Data Structures
216 | [Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Algorithms-and-Data-Structures#table-of-contents)
217 |
218 | [Arrays](https://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/arrays/) are a series of elements(numbers, booleans, or strings) of the same type placed in phyiscal memory locations that can be individually referenced by adding an index to a unique identifier.
219 |
220 | - [Vector](https://www.cplusplus.com/reference/vector/vector/) is a dynamic array, where the size can be increased when an element is inserted or deleted, with the storage being handled automatically by the container.
221 |
222 | [Linked Lists](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linked_list) is a linear collection of data elements whose order is not given by their physical placement in memory. Instead, elements in a linked list are linked using pointers.
223 |
224 | - [Singly Linked List](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/data-structures/linked-list/singly-linked-list/) is a type of linked data structure where each node points to the next node in the sequence. It does not have any pointer that points to the previous node.
225 |
226 | - [Doubly-Linked List](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Doubly_linked_list) is a type of linked data structure in which each node apart from storing its data has two links. A node consists of three parts: node data, a pointer to the next node in sequence (next pointer), pointer to the previous node (previous pointer).
227 |
228 | [Trees](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_(data_structure)) is a nonlinear data structure unlike arrays, linked lists, stacks and queues which are linear data structures. A tree can be empty with no nodes or in other instances a tree's structure consists of one node called the root and 0 or 1 or more subtrees.
229 |
230 | - Basic Tree
231 | - Binary Tree
232 | - Binary Search Tree
233 | - AVL Tree
234 | - Red-Black Tree
235 | - N-ary Tree
236 |
237 | [Hash Tables](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/scripting/learn/deep-dives/everything-about-hashtable?view=powershell-7.1) are a data structure, much like an array, except you store each value (object) using a key. It is a basic key/value store for mapping known as a hash function.
238 |
239 | [Stacks](https://www.thedshandbook.com/stacks/) is a linear data structure that store data in an order known as the Last In First Out (LIFO) order.
240 |
241 | - LIFO (Last In First Out)
242 | - FILO (First In Last Out)
243 |
244 | [Queues](https://www.thedshandbook.com/queues/) is a linear data structure that stores data in an order known as the First In First Out(FIFO) order.
245 |
246 | [Heaps](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heap_(data_structure)) is a specialized tree-based data structure which is essentially an almost complete tree that satisfies the heap property.
247 |
248 | - Max Heap
249 | - Min-Heap
250 | - Binary Heap
251 |
252 | [Graphs](https://www.thedshandbook.com/graphs/) is a data structure that represent relations between pairs of objects. It consists of nodes (known as vertices) that are connected through links (known as edges).
253 |
254 | ## Contribute
255 |
256 | - [x] If would you like to contribute to this guide simply make a [Pull Request](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Algorithms-and-Data-Structures-Guide/pulls).
257 |
258 |
259 | ## License
260 | [Back to the Top](https://github.com/mikeroyal/Algorithms-and-Data-Structures#table-of-contents)
261 |
262 | Distributed under the [Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) Public License](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
263 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------