├── .gitignore
├── .travis.yml
├── HOWTO_RELEASE.md
├── LICENSE
├── MANIFEST.in
├── Makefile
├── README.md
├── conda_recipes
├── README.md
├── build_all.sh
├── flann
│ ├── .binstar.yml
│ ├── build.sh
│ └── meta.yaml
├── megaman
│ ├── .binstar.yml
│ ├── build.sh
│ ├── meta.yaml
│ └── run_test.sh
├── pyamg
│ ├── .binstar.yml
│ ├── build.sh
│ ├── meta.yaml
│ └── run_test.sh
└── pyflann
│ ├── .binstar.yml
│ ├── build.sh
│ └── meta.yaml
├── doc
├── .gitignore
├── Makefile
├── conf.py
├── embedding
│ ├── API.rst
│ ├── index.rst
│ ├── isomap.rst
│ ├── locally_linear.rst
│ ├── ltsa.rst
│ └── spectral_embedding.rst
├── geometry
│ ├── API.rst
│ ├── geometry.rst
│ └── index.rst
├── images
│ ├── circle_to_ellipse_embedding.png
│ ├── index.rst
│ ├── spectra_D4000.png
│ ├── spectra_Halpha.png
│ ├── spectra_Halpha.rst
│ ├── word2vec.rst
│ └── word2vec_rmetric_plot_no_digits.png
├── index.rst
├── installation.rst
├── sphinxext
│ └── numpy_ext
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── astropyautosummary.py
│ │ ├── autodoc_enhancements.py
│ │ ├── automodapi.py
│ │ ├── automodsumm.py
│ │ ├── changelog_links.py
│ │ ├── comment_eater.py
│ │ ├── compiler_unparse.py
│ │ ├── docscrape.py
│ │ ├── docscrape_sphinx.py
│ │ ├── doctest.py
│ │ ├── edit_on_github.py
│ │ ├── numpydoc.py
│ │ ├── phantom_import.py
│ │ ├── smart_resolver.py
│ │ ├── tocdepthfix.py
│ │ ├── traitsdoc.py
│ │ ├── utils.py
│ │ └── viewcode.py
└── utils
│ ├── API.rst
│ └── index.rst
├── examples
├── example.py
├── examples_index.ipynb
├── manifold_intro.ipynb
├── megaman_install_usage_colab.ipynb
├── megaman_tutorial.ipynb
├── megaman_tutorial.py
├── rad_est_utils.py
├── radius_estimation_tutorial.ipynb
├── tutorial_data_plot.png
├── tutorial_embeddings.png
├── tutorial_isomap_plot.png
└── tutorial_spectral_plot.png
├── megaman
├── __check_build
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── _check_build.pyx
│ └── setup.py
├── __init__.py
├── datasets
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── datasets.py
│ └── megaman.png
├── embedding
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── base.py
│ ├── isomap.py
│ ├── locally_linear.py
│ ├── ltsa.py
│ ├── spectral_embedding.py
│ └── tests
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── test_base.py
│ │ ├── test_embeddings.py
│ │ ├── test_isomap.py
│ │ ├── test_lle.py
│ │ ├── test_ltsa.py
│ │ └── test_spectral_embedding.py
├── geometry
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── adjacency.py
│ ├── affinity.py
│ ├── complete_adjacency_matrix.py
│ ├── cyflann
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── cyflann_index.cc
│ │ ├── cyflann_index.h
│ │ ├── index.pxd
│ │ ├── index.pyx
│ │ └── setup.py
│ ├── geometry.py
│ ├── laplacian.py
│ ├── rmetric.py
│ ├── tests
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── test_adjacency.py
│ │ ├── test_affinity.py
│ │ ├── test_complete_adjacency_matrix.py
│ │ ├── test_geometry.py
│ │ ├── test_laplacian.m
│ │ ├── test_laplacian.py
│ │ ├── test_rmetric.py
│ │ └── testmegaman_laplacian_rad0_2_lam1_5_n200.mat
│ └── utils.py
├── plotter
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── covar_plotter3.py
│ ├── plotter.py
│ ├── scatter_3d.py
│ └── utils.py
├── relaxation
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── optimizer.py
│ ├── precomputed.py
│ ├── riemannian_relaxation.py
│ ├── tests
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── eps_halfdome.mat
│ │ ├── rloss_halfdome.mat
│ │ ├── test_precomputed_S.py
│ │ ├── test_precomputed_Y.py
│ │ ├── test_regression_test.py
│ │ ├── test_relaxation_keywords.py
│ │ ├── test_tracing_var.py
│ │ └── utils.py
│ ├── trace_variable.py
│ └── utils.py
├── setup.py
└── utils
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── analyze_dimension_and_radius.py
│ ├── covar_plotter.py
│ ├── eigendecomp.py
│ ├── estimate_radius.py
│ ├── k_means_clustering.py
│ ├── large_sparse_functions.py
│ ├── nystrom_extension.py
│ ├── spectral_clustering.py
│ ├── testing.py
│ ├── tests
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── test_analyze_dimension_and_radius.py
│ ├── test_eigendecomp.py
│ ├── test_estimate_radius.py
│ ├── test_nystrom.py
│ ├── test_spectral_clustering.py
│ ├── test_testing.py
│ └── test_validation.py
│ └── validation.py
├── setup.py
└── tools
└── cythonize.py
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | *~
2 | *.pyc
3 | junk*
4 | *.cxx
5 | *.c
6 | cythonize.dat
7 |
8 | cover
9 |
10 | MANIFEST
11 |
12 | # Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
13 | __pycache__/
14 | *.py[cod]
15 | *$py.class
16 |
17 | # C extensions
18 | *.so
19 |
20 | # Distribution / packaging
21 | .Python
22 | env/
23 | build/
24 | develop-eggs/
25 | dist/
26 | downloads/
27 | eggs/
28 | .eggs/
29 | lib/
30 | lib64/
31 | parts/
32 | sdist/
33 | var/
34 | *.egg-info/
35 | .installed.cfg
36 | *.egg
37 |
38 | # PyInstaller
39 | # Usually these files are written by a python script from a template
40 | # before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it.
41 | *.manifest
42 | *.spec
43 |
44 | # Installer logs
45 | pip-log.txt
46 | pip-delete-this-directory.txt
47 |
48 | # Unit test / coverage reports
49 | htmlcov/
50 | .tox/
51 | .coverage
52 | .coverage.*
53 | .cache
54 | nosetests.xml
55 | coverage.xml
56 | *,cover
57 | .hypothesis/
58 |
59 | # Translations
60 | *.mo
61 | *.pot
62 |
63 | # Django stuff:
64 | *.log
65 | local_settings.py
66 |
67 | # Flask instance folder
68 | instance/
69 |
70 | # Sphinx documentation
71 | docs/_build/
72 |
73 | # PyBuilder
74 | target/
75 |
76 | # IPython Notebook
77 | .ipynb_checkpoints
78 | Untitled*.ipynb
79 |
80 | # pyenv
81 | .python-version
82 |
83 | # macos DS_Store
84 | .DS_Store
85 | **/*/.DS_Store
86 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.travis.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | language: python
2 |
3 | # sudo false implies containerized builds
4 | sudo: false
5 |
6 | python:
7 | - 2.7
8 | - 3.4
9 | - 3.5
10 |
11 | env:
12 | global:
13 | # Directory where tests are run from
14 | - TEST_DIR=/tmp/megaman
15 | - CONDA_CHANNEL="conda-forge"
16 | - CONDA_DEPS="pip nose coverage cython scikit-learn flann h5py"
17 | - PIP_DEPS="coveralls"
18 | matrix:
19 | - EXTRA_DEPS="pyflann pyamg"
20 | - EXTRA_DEPS=""
21 |
22 | before_install:
23 | - export MINICONDA=$HOME/miniconda
24 | - export PATH="$MINICONDA/bin:$PATH"
25 | - hash -r
26 | - wget http://repo.continuum.io/miniconda/Miniconda-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh -O miniconda.sh
27 | - bash miniconda.sh -b -f -p $MINICONDA
28 | - conda config --set always_yes yes
29 | - conda update conda
30 | - conda info -a
31 | - conda create -n testenv python=$TRAVIS_PYTHON_VERSION
32 | - source activate testenv
33 | - conda install -c $CONDA_CHANNEL $CONDA_DEPS $EXTRA_DEPS
34 | - travis_retry pip install $PIP_DEPS
35 |
36 | install:
37 | - python setup.py install
38 |
39 | script:
40 | - mkdir -p $TEST_DIR
41 | - cd $TEST_DIR && nosetests -v --with-coverage --cover-package=megaman megaman
42 |
43 | after_success:
44 | - coveralls
45 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/HOWTO_RELEASE.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # How to Release
2 |
3 | Here's a quick step-by-step for cutting a new release of megaman.
4 |
5 | ## Pre-release
6 |
7 | 1. update version in ``megaman/__init__.py`` to, e.g. "0.1"
8 |
9 | 2. update version in **two places** in ``doc/conf.py`` to the same
10 |
11 | 3. create a release tag; e.g.
12 | ```
13 | $ git tag -a v0.1 -m 'version 0.1 release'
14 | ```
15 |
16 | 4. push the commits and tag to github
17 |
18 | 5. confirm that CI tests pass on github
19 |
20 | 6. under "tags" on github, update the release notes
21 |
22 |
23 | ## Publishing the Release
24 |
25 | 1. push the new release to PyPI (requires jakevdp's permissions)
26 | ```
27 | $ python setup.py sdist upload
28 | ```
29 |
30 | 2. change directories to ``doc`` and build the documentation:
31 | ```
32 | $ cd doc/
33 | $ make html # build documentation
34 | $ make publish # publish to github pages
35 | ```
36 |
37 | 3. Publish the conda build:
38 | submit a PR to http://github.com/conda-forge/megaman-feedstock
39 | updating recipe/meta.yaml with the appropriate version. Once merged,
40 | then the conda install command will point to the new version.
41 |
42 | ## Post-release
43 |
44 | 1. update version in ``megaman/__init__.py`` to next version; e.g. '0.2.dev0'
45 |
46 | 2. update version in ``doc/conf.py`` to the same (in two places)
47 |
48 | 3. push changes to github
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Copyright (c) 2016
2 | All rights reserved.
3 |
4 | Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
5 | modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
6 |
7 | * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this
8 | list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
9 |
10 | * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
11 | this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
12 | and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
13 |
14 | THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"
15 | AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
16 | IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
17 | DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE
18 | FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
19 | DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
20 | SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
21 | CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY,
22 | OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
23 | OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
24 |
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MANIFEST.in:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | include *.md
2 | include *.py
3 | recursive-include megaman *.py *.pyx *.pxd *.cc *.h *.mat *.png
4 | recursive-include doc *
5 | recursive-include tools *.py
6 | recursive-include examples *.py *.ipynb
7 | include Makefile
8 | include LICENSE
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Makefile:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | CURRENT_DIR = $(shell pwd)
2 | TEST_DIR = /tmp/megaman
3 | PKG = megaman
4 |
5 | install:
6 | python setup.py install
7 |
8 | clean:
9 | rm -r build/
10 |
11 | test-dir:
12 | mkdir -p $(TEST_DIR)
13 |
14 | test: test-dir install
15 | cd $(TEST_DIR) && nosetests $(PKG)
16 |
17 | doctest: test-dir install
18 | cd $(TEST_DIR) && nosetests --with-doctest $(PKG)
19 |
20 | test-coverage: test-dir install
21 | cd $(TEST_DIR) && nosetests --with-coverage --cover-package=$(PKG) $(PKG)
22 |
23 | test-coverage-html: test-dir install
24 | cd $(TEST_DIR) && nosetests --with-coverage --cover-html --cover-package=$(PKG) $(PKG)
25 | rsync -r $(TEST_DIR)/cover $(CURRENT_DIR)/
26 | echo "open ./cover/index.html with a web browser to see coverage report"
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # megaman: Manifold Learning for Millions of Points
2 |
3 | 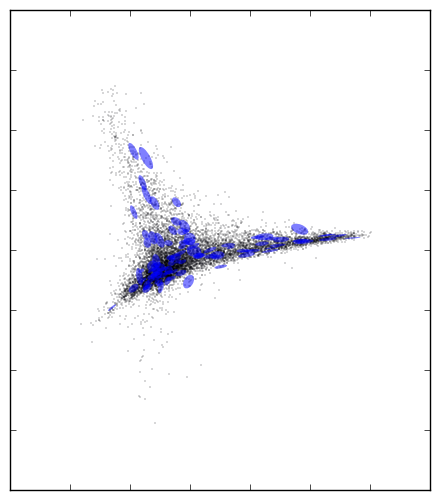
 4 |
5 | [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/megaman)
6 | [](https://travis-ci.org/mmp2/megaman)
7 | [](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/megaman)
8 | [](https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE)
9 |
10 | ``megaman`` is a scalable manifold learning package implemented in
11 | python. It has a front-end API designed to be familiar
12 | to [scikit-learn](http://scikit-learn.org/) but harnesses
13 | the C++ Fast Library for Approximate Nearest Neighbors (FLANN)
14 | and the Sparse Symmetric Positive Definite (SSPD) solver
15 | Locally Optimal Block Precodition Gradient (LOBPCG) method
16 | to scale manifold learning algorithms to large data sets.
17 | On a personal computer megaman can embed 1 million data points
18 | with hundreds of dimensions in 10 minutes.
19 | megaman is designed for researchers and as such caches intermediary
20 | steps and indices to allow for fast re-computation with new parameters.
21 |
22 | Package documentation can be found at http://mmp2.github.io/megaman/
23 |
24 | If you use our software please cite the following JMLR paper:
25 |
26 | McQueen, Meila, VanderPlas, & Zhang, "Megaman: Scalable Manifold Learning in Python",
27 | Journal of Machine Learning Research, Vol 17 no. 14, 2016.
28 | http://jmlr.org/papers/v17/16-109.html
29 |
30 | You can also find our arXiv paper at http://arxiv.org/abs/1603.02763
31 |
32 | ## Examples
33 |
34 | - [Tutorial Notebook]( https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/examples/megaman_tutorial.ipynb)
35 |
36 | ## Installation and Examples in Google Colab
37 |
38 | Below it's a tutorial to install megaman on Google Colab, through Conda environment.
39 |
40 | It also provides tutorial of using megaman to build spectral embedding on uniform swiss roll dataset.
41 |
42 | - [Install & Example script]( https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1ms22YK3TvrIx0gji6UZqG0zoSNRCWtXj?usp=sharing)
43 | - [You can download the Jupyter Notebook version here]( https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/examples/megaman_install_usage_colab.ipynb)
44 |
45 | ## ~~Installation with Conda~~
46 |
47 |
59 |
60 | Due to the change of API,
61 | `$ conda install -c conda-forge megaman`
62 | is no longer supported.
63 | We are currently working on fixing the bug.
64 |
65 | Please see the full install instructions below to build `megaman` from source.
66 |
67 | ## Installation from source
68 |
69 | To install megaman from source requires the following:
70 |
71 | - [python](http://python.org) tested with versions 2.7, 3.5 and 3.6
72 | - [numpy](http://numpy.org) version 1.8 or higher
73 | - [scipy](http://scipy.org) version 0.16.0 or higher
74 | - [scikit-learn](http://scikit-learn.org)
75 | - [FLANN](http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/)
76 | - [pyflann](http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/) which offers another method of computing distance matrices (this is bundled with the FLANN source code)
77 | - [cython](http://cython.org/)
78 | - a C++ compiler such as ``gcc``/``g++``
79 |
80 | Optional requirements include
81 |
82 | - [pyamg](http://pyamg.org/), which allows for faster decompositions of large matrices
83 | - [nose](https://nose.readthedocs.org/) for running the unit tests
84 | - [h5py](http://www.h5py.org) for reading testing .mat files
85 | - [plotly](https://plot.ly) an graphing library for interactive plot
86 |
87 |
88 | These requirements can be installed on Linux and MacOSX using the following conda command:
89 |
90 | ```shell
91 | $ conda create -n manifold_env python=3.5 -y
92 | # can also use python=2.7 or python=3.6
93 |
94 | $ source activate manifold_env
95 | $ conda install --channel=conda-forge -y pip nose coverage cython numpy scipy \
96 | scikit-learn pyflann pyamg h5py plotly
97 | ```
98 |
99 | Clone this repository and `cd` into source repository
100 |
101 | ```shell
102 | $ cd /tmp/
103 | $ git clone https://github.com/mmp2/megaman.git
104 | $ cd megaman
105 | ```
106 |
107 | Finally, within the source repository, run this command to install the ``megaman`` package itself:
108 | ```shell
109 | $ python setup.py install
110 | ```
111 |
112 | ## Unit Tests
113 | megaman uses ``nose`` for unit tests. With ``nose`` installed, type
114 | ```
115 | $ make test
116 | ```
117 | to run the unit tests. ``megaman`` is tested on Python versions 2.7, 3.4, and 3.5.
118 |
119 | ## Authors
120 | - [James McQueen](http://www.stat.washington.edu/people/jmcq/)
121 | - [Marina Meila](http://www.stat.washington.edu/mmp/)
122 | - [Zhongyue Zhang](https://github.com/Jerryzcn)
123 | - [Jake VanderPlas](http://www.vanderplas.com)
124 | - [Yu-Chia Chen](https://github.com/yuchaz)
125 |
126 | ## Other Contributors
127 |
128 | - Xiao Wang: lazy rmetric, Nystrom Extension
129 | - [Hangliang Ren (Harry)](https://github.com/Harryahh): Installation tutorials, Spectral Embedding
130 |
131 | ## Future Work
132 |
133 | See this issues list for what we have planned for upcoming releases:
134 |
135 | [Future Work](https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/issues/47)
136 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Conda recipes
2 |
3 | This directory contains conda build recipes for megaman and its dependencies.
4 | For more information see the
5 | [Conda Build documentation](http://conda.pydata.org/docs/build_tutorials/pkgs2.html)
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/build_all.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | conda config --set anaconda_upload yes
2 | conda build flann
3 | conda build --py all pyflann
4 | conda build --python 2.7 --python 3.4 --python 3.5 --numpy 1.9 --numpy 1.10 pyamg
5 | conda build --python 2.7 --python 3.4 --python 3.5 --numpy 1.10 megaman
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/flann/.binstar.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package: flann
2 | platform:
3 | - osx-64
4 | - osx-32
5 | - linux-64
6 | - linux-32
7 | script:
8 | - conda build .
9 | build_targets:
10 | - conda
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/flann/build.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | # cannot build flann from within the source directory
4 | mkdir build
5 | cd build
6 |
7 | # On OSX, we need to ensure we're using conda's gcc/g++
8 | if [[ `uname` == Darwin ]]; then
9 | export CC=gcc
10 | export CXX=g++
11 | fi
12 |
13 | cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=$PREFIX -DBUILD_MATLAB_BINDINGS:BOOL=OFF -DBUILD_PYTHON_BINDINGS:BOOL=OFF -DBUILD_EXAMPLES:BOOL=OFF
14 |
15 | make -j$CPU_COUNT install
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/flann/meta.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package:
2 | name: flann
3 | version: "1.8.5dev"
4 |
5 | source:
6 | git_url: https://github.com/mariusmuja/flann.git
7 | git_tag: b8a442fd98f8ce32ae3465bfd3427b5cbc36f6a5
8 |
9 | build:
10 | number: 2
11 | string: {{PKG_BUILDNUM}}_g{{GIT_FULL_HASH[:7]}}
12 |
13 | requirements:
14 | build:
15 | - gcc 4.8* # [osx]
16 | - hdf5
17 | - cmake
18 | run:
19 | - libgcc 4.8* #[osx]
20 | - hdf5
21 |
22 | about:
23 | home: http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/
24 | license: BSD
25 | license_file: COPYING
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/megaman/.binstar.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package: megaman
2 | platform:
3 | - osx-64
4 | - osx-32
5 | - linux-64
6 | - linux-32
7 | script:
8 | - conda build .
9 | build_targets:
10 | - conda
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/megaman/build.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | # On OSX, we need to ensure we're using conda's gcc/g++
4 | if [[ `uname` == Darwin ]]; then
5 | export CC=gcc
6 | export CXX=g++
7 | fi
8 |
9 | $PYTHON setup.py install
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/megaman/meta.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package:
2 | name: megaman
3 | version: 0.1.1
4 |
5 | source:
6 | git_url: https://github.com/mmp2/megaman.git
7 | git_tag: v0.1.1
8 |
9 | build:
10 | number: 2
11 | string: np{{CONDA_NPY}}py{{CONDA_PY}}_{{PKG_BUILDNUM}}
12 |
13 | requirements:
14 | build:
15 | - python >=2.7,<3|>=3.4,{{PY_VER}}*
16 | - numpy {{NPY_VER}}*
17 | - cython
18 | - flann
19 | - gcc 4.8* # [osx]
20 | run:
21 | - python {{PY_VER}}*
22 | - numpy {{NPY_VER}}*
23 | - scipy >=0.16
24 | - scikit-learn >=0.17
25 | - pyamg
26 | - pyflann
27 | - libgcc 4.8* # [osx]
28 |
29 | test:
30 | requires:
31 | - nose
32 | imports:
33 | - megaman
34 | - megaman.geometry
35 | - megaman.embedding
36 | - megaman.utils
37 |
38 | about:
39 | home: http://mmp2.github.io/megaman
40 | license: BSD
41 | license_file: LICENSE
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/megaman/run_test.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | nosetests -v megaman
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyamg/.binstar.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package: pyamg
2 | platform:
3 | - osx-64
4 | - osx-32
5 | - linux-64
6 | - linux-32
7 | script:
8 | - conda build .
9 | build_targets:
10 | - conda
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyamg/build.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | # On OSX, we need to ensure we're using conda's gcc/g++
4 | if [[ `uname` == Darwin ]]; then
5 | export CC=gcc
6 | export CXX=g++
7 | fi
8 |
9 | $PYTHON setup.py install
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyamg/meta.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package:
2 | name: pyamg
3 | version: "3.0.2"
4 |
5 | source:
6 | git_url: https://github.com/pyamg/pyamg.git
7 | git_tag: v3.0.2
8 |
9 | build:
10 | number: 2
11 | string: np{{CONDA_NPY}}py{{CONDA_PY}}_{{PKG_BUILDNUM}}
12 |
13 | requirements:
14 | build:
15 | - python >=2.7,<3|>=3.4,{{PY_VER}}*
16 | - numpy {{NPY_VER}}*
17 | - scipy
18 | - nose
19 | - zlib # [linux]
20 | - gcc 4.8* # [osx]
21 | run:
22 | - python {{PY_VER}}*
23 | - numpy {{NPY_VER}}*
24 | - scipy
25 | - zlib # [linux]
26 |
27 | test:
28 | requires:
29 | - nose
30 | imports:
31 | - pyamg
32 |
33 | about:
34 | home: http://www.pyamg.org/
35 | license: MIT
36 | license_file: LICENSE.txt
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyamg/run_test.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | if [[ `uname` == Darwin ]] && [ $PY_VER == "2.7" ]; then
4 | echo "skipping tests; see https://github.com/pyamg/pyamg/issues/165"
5 | else
6 | nosetests -v pyamg
7 | fi
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyflann/.binstar.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package: pyflann
2 | platform:
3 | - osx-64
4 | - osx-32
5 | - linux-64
6 | - linux-32
7 | script:
8 | - conda build .
9 | build_targets:
10 | - conda
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyflann/build.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | cd src/python
4 | cmake . -DLIBRARY_OUTPUT_PATH=$PREFIX/lib -DFLANN_VERSION="$PKG_VERSION"
5 | $PYTHON setup.py install
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyflann/meta.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package:
2 | name: pyflann
3 | version: "1.8.5dev"
4 |
5 | source:
6 | git_url: https://github.com/mariusmuja/flann.git
7 | git_tag: b8a442fd98f8ce32ae3465bfd3427b5cbc36f6a5
8 |
9 | build:
10 | number: 2
11 | string: py{{CONDA_PY}}_{{PKG_BUILDNUM}}_g{{GIT_FULL_HASH[:7]}}
12 |
13 | requirements:
14 | build:
15 | - python {{PY_VER}}*
16 | - setuptools
17 | - flann 1.8.5dev
18 | - cmake
19 | run:
20 | - python {{PY_VER}}*
21 | - flann 1.8.5dev
22 | - numpy
23 |
24 | test:
25 | imports:
26 | - pyflann
27 |
28 | about:
29 | home: http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/
30 | license: BSD
31 | license_file: COPYING
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | _build
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/embedding/API.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _embedding_API:
2 |
3 | .. testsetup:: *
4 |
5 | from megaman.embedding import *
6 |
7 | API Documentation
8 | =================
9 |
10 | .. automodule:: megaman.embedding.spectral_embedding
11 | :members:
12 |
13 | .. automodule:: megaman.embedding.isomap
14 | :members:
15 |
16 | .. automodule:: megaman.embedding.locally_linear
17 | :members:
18 |
19 | .. automodule:: megaman.embedding.ltsa
20 | :members:
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/embedding/index.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _embedding:
2 |
3 | ***************************************************
4 | Tools for Embedding (``megaman.embedding``)
5 | ***************************************************
6 |
7 | This module contains tools for nonlinear embedding data sets.
8 | These tools include Isomap, Spectral Embedding & Diffusion
9 | Maps, Local Tangent Space Alignment, and Locally Linear
10 | Embedding
11 |
12 | .. toctree::
13 | :maxdepth: 2
14 |
15 | isomap.rst
16 | locally_linear.rst
17 | ltsa.rst
18 | spectral_embedding.rst
19 | API
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/embedding/isomap.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _isomap:
2 |
3 | Isomap
4 | ======
5 |
6 | Isomap is one of the embeddings implemented in the megaman package.
7 | Isomap uses Multidimensional Scaling (MDS) to preserve pairwsise
8 | graph shortest distance computed using a sparse neighborhood graph.
9 |
10 | For more information see:
11 |
12 | * Tenenbaum, J.B.; De Silva, V.; & Langford, J.C.
13 | A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction.
14 | Science 290 (5500)
15 |
16 | :class:'~megaman.embedding.Isomap'
17 | This class is used to interface with isomap embedding function.
18 | Like all embedding functions in megaman it operates using a
19 | Geometry object. The Isomap class allows you to optionally
20 | pass an exiting Geometry object, otherwise it creates one.
21 |
22 | API of Isomap
23 | -------------
24 |
25 | The Isomap model, along with all the other models in megaman, have an API
26 | designed to follow in the same vein of
27 | `scikit-learn `_ API.
28 |
29 | Consequentially, the Isomap class functions as follows
30 |
31 | 1. At class instantiation `.Isomap()` parameters are passed. See API
32 | documementation for more information. An existing Geometry object
33 | can be passed to `.Isomap()`.
34 | 2. The `.fit()` method creates a Geometry object if one was not
35 | already passed and then calculates th embedding.
36 | The number of components and eigen solver can also be passed to the
37 | `.fit()` function. Since Isomap caches important quantities
38 | (like the graph distance matrix) which do not change by selecting
39 | different eigen solvers and embeding dimension these can be passed
40 | and a new embedding computed without re-computing existing quantities.
41 | the `.fit()` function does not return anything but it does create
42 | the attribute `self.embedding_` only one `self.embedding_` exists
43 | at a given time. If a new embedding is computed the old one is overwritten.
44 | 3. The `.fit_transform()` function calls the `fit()` function and returns
45 | the embedding. It does not allow for changing parameters.
46 |
47 | See the API documentation for further information.
48 |
49 | Example Usage
50 | -------------
51 |
52 | Here is an example using the function on a random data set::
53 |
54 | import numpy as np
55 | from megaman.geometry import Geometry
56 | from megaman.embedding import Isomap
57 |
58 | X = np.random.randn(100, 10)
59 | radius = 5
60 | adjacency_method = 'cyflann'
61 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':radius} # ignore distances above this radius
62 |
63 | geom = Geometry(adjacency_method=adjacency_method, adjacency_kwds=adjacency_kwds)
64 |
65 | isomap = Isomap(n_components=n_components, eigen_solver='arpack', geom=geom)
66 | embed_isomap = isomap.fit_transform(X)
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/embedding/locally_linear.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _locally_linear:
2 |
3 | Locally Linear Embedding
4 | ========================
5 |
6 | Locally linear embedding is one of the methods implemented in the megaman package.
7 | Locally Linear Embedding uses reconstruction weights estiamted on the original
8 | data set to produce an embedding that preserved the original reconstruction
9 | weights.
10 |
11 | For more information see:
12 |
13 | * Roweis, S. & Saul, L. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction
14 | by locally linear embedding. Science 290:2323 (2000).
15 |
16 | :class:'~megaman.embedding.LocallyLinearEmbedding'
17 | This class is used to interface with locally linear embedding function.
18 | Like all embedding functions in megaman it operates using a
19 | Geometry object. The Locally Linear class allows you to optionally
20 | pass an exiting Geometry object, otherwise it creates one.
21 |
22 |
23 | API of Locally Linear Embedding
24 | -------------------------------
25 |
26 | The Locally Linear model, along with all the other models in megaman, have an API
27 | designed to follow in the same vein of
28 | `scikit-learn `_ API.
29 |
30 | Consequentially, the Locally Linear class functions as follows
31 |
32 | 1. At class instantiation `.LocallyLinear()` parameters are passed. See API
33 | documementation for more information. An existing Geometry object
34 | can be passed to `.LocallyLinear()`.
35 | 2. The `.fit()` method creates a Geometry object if one was not
36 | already passed and then calculates th embedding.
37 | The number of components and eigen solver can also be passed to the
38 | `.fit()` function. WARNING: NOT COMPLETED
39 | Since LocallyLinear caches important quantities
40 | (like the barycenter weight matrix) which do not change by selecting
41 | different eigen solvers and embeding dimension these can be passed
42 | and a new embedding computed without re-computing existing quantities.
43 | the `.fit()` function does not return anything but it does create
44 | the attribute `self.embedding_` only one `self.embedding_` exists
45 | at a given time. If a new embedding is computed the old one is overwritten.
46 | 3. The `.fit_transform()` function calls the `fit()` function and returns
47 | the embedding. It does not allow for changing parameters.
48 |
49 | See the API documentation for further information.
50 |
51 | Example Usage
52 | -------------
53 |
54 | Here is an example using the function on a random data set::
55 |
56 | import numpy as np
57 | from megaman.geometry import Geometry
58 | from megaman.embedding import (Isomap, LocallyLinearEmbedding, LTSA, SpectralEmbedding)
59 |
60 | X = np.random.randn(100, 10)
61 | radius = 5
62 | adjacency_method = 'cyflann'
63 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':radius} # ignore distances above this radius
64 |
65 | geom = Geometry(adjacency_method=adjacency_method, adjacency_kwds=adjacency_kwds)
66 | lle = LocallyLinearEmbedding(n_components=n_components, eigen_solver='arpack', geom=geom)
67 | embed_lle = lle.fit_transform(X)
68 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/embedding/ltsa.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _ltsa:
2 |
3 | Local Tangent Space Alignment
4 | =============================
5 |
6 | Local Tangent Space Alignment is one of the methods implemented in the megaman package.
7 | Local Tangent Space Alighment uses independent estimates of the local tangent
8 | space at each point and then uses a global alignment procedure with a
9 | unit-scale condition to create a single embedding from each local tangent
10 | space.
11 |
12 | For more information see:
13 |
14 | * Zhang, Z. & Zha, H. Principal manifolds and nonlinear
15 | dimensionality reduction via tangent space alignment.
16 | Journal of Shanghai Univ. 8:406 (2004)
17 |
18 | :class:'~megaman.embedding.LTSA'
19 | This class is used to interface with local tangent space
20 | alignment embedding function.
21 | Like all embedding functions in megaman it operates using a
22 | Geometry object. The Locally Linear class allows you to optionally
23 | pass an exiting Geometry object, otherwise it creates one.
24 |
25 |
26 | API of Local Tangent Space Alignment
27 | ------------------------------------
28 |
29 | The Locally Tangent Space Alignment model, along with all the other models in megaman,
30 | have an API designed to follow in the same vein of
31 | `scikit-learn `_ API.
32 |
33 | Consequentially, the LTSA class functions as follows
34 |
35 | 1. At class instantiation `.LTSA()` parameters are passed. See API
36 | documementation for more information. An existing Geometry object
37 | can be passed to `.LTSA()`.
38 | 2. The `.fit()` method creates a Geometry object if one was not
39 | already passed and then calculates th embedding.
40 | The eigen solver can also be passed to the
41 | `.fit()` function. WARNING: NOT COMPLETED
42 | Since LTSA caches important quantities
43 | (like the local tangent spaces) which do not change by selecting
44 | different eigen solvers and this can be passed
45 | and a new embedding computed without re-computing existing quantities.
46 | the `.fit()` function does not return anything but it does create
47 | the attribute `self.embedding_` only one `self.embedding_` exists
48 | at a given time. If a new embedding is computed the old one is overwritten.
49 | 3. The `.fit_transform()` function calls the `fit()` function and returns
50 | the embedding. It does not allow for changing parameters.
51 |
52 | See the API documentation for further information.
53 |
54 | Example Usage
55 | -------------
56 |
57 | Here is an example using the function on a random data set::
58 |
59 | import numpy as np
60 | from megaman.geometry import Geometry
61 | from megaman.embedding import (Isomap, LocallyLinearEmbedding, LTSA, SpectralEmbedding)
62 |
63 | X = np.random.randn(100, 10)
64 | radius = 5
65 | adjacency_method = 'cyflann'
66 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':radius} # ignore distances above this radius
67 |
68 | geom = Geometry(adjacency_method=adjacency_method, adjacency_kwds=adjacency_kwds)
69 |
70 | ltsa =LTSA(n_components=n_components, eigen_solver='arpack', geom=geom)
71 | embed_ltsa = ltsa.fit_transform(X)
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/embedding/spectral_embedding.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _spectral_embedding:
2 |
3 | Spectral Embedding
4 | ==================
5 |
6 | Spectral Embedding is on of the methods implemented in the megaman package.
7 | Spectral embedding (and diffusion maps) uses the spectrum (eigen vectors
8 | and eigen values) of a graph Laplacian estimated from the data set. There
9 | are a number of different graph Laplacians that can be used.
10 |
11 | For more information see:
12 |
13 | * A Tutorial on Spectral Clustering, 2007
14 | Ulrike von Luxburg
15 | http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.165.9323
16 |
17 | :class:'~megaman.embedding.SpectralEmbedding'
18 | This class is used to interface with spectral embedding function.
19 | Like all embedding functions in megaman it operates using a
20 | Geometry object. The Isomap class allows you to optionally
21 | pass an exiting Geometry object, otherwise it creates one.
22 |
23 | API of Spectral Embedding
24 | -------------------------
25 |
26 | The Spectral Embedding model, along with all the other models in megaman,
27 | have an API designed to follow in the same vein of
28 | `scikit-learn `_ API.
29 |
30 | Consequentially, the LTSA class functions as follows
31 |
32 | 1. At class instantiation `.SpectralEmbedding()` parameters are passed. See API
33 | documementation for more information. An existing Geometry object
34 | can be passed to `.SpectralEmbedding()`. Here is also where
35 | you have the option to use diffusion maps.
36 | 2. The `.fit()` method creates a Geometry object if one was not
37 | already passed and then calculates th embedding.
38 | The eigen solver can also be passed to the
39 | `.fit()` function. WARNING: NOT COMPLETED
40 | Since Geometry caches important quantities
41 | (like the graph Laplacian) which do not change by selecting
42 | different eigen solvers and this can be passed
43 | and a new embedding computed without re-computing existing quantities.
44 | the `.fit()` function does not return anything but it does create
45 | the attribute `self.embedding_` only one `self.embedding_` exists
46 | at a given time. If a new embedding is computed the old one is overwritten.
47 | 3. The `.fit_transform()` function calls the `fit()` function and returns
48 | the embedding. It does not allow for changing parameters.
49 |
50 | See the API documentation for further information.
51 |
52 | Example Usage
53 | -------------
54 |
55 | Here is an example using the function on a random data set::
56 |
57 | import numpy as np
58 | from megaman.geometry import Geometry
59 | from megaman.embedding import SpectralEmbedding
60 |
61 | X = np.random.randn(100, 10)
62 | radius = 5
63 | adjacency_method = 'cyflann'
64 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':radius} # ignore distances above this radius
65 | affinity_method = 'gaussian'
66 | affinity_kwds = {'radius':radius} # A = exp(-||x - y||/radius^2)
67 | laplacian_method = 'geometric'
68 | laplacian_kwds = {'scaling_epps':radius} # scaling ensures convergence to Laplace-Beltrami operator
69 |
70 | geom = Geometry(adjacency_method=adjacency_method, adjacency_kwds=adjacency_kwds,
71 | affinity_method=affinity_method, affinity_kwds=affinity_kwds,
72 | laplacian_method=laplacian_method, laplacian_kwds=laplacian_kwds)
73 |
74 | spectral = SpectralEmbedding(n_components=n_components, eigen_solver='arpack',
75 | geom=geom)
76 | embed_spectral = spectral.fit_transform(X)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/geometry/API.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _geometry_API:
2 |
3 | .. testsetup:: *
4 |
5 | from megaman.geometry import *
6 |
7 | API Documentation
8 | =================
9 |
10 | .. automodule:: megaman.geometry.geometry
11 | :members:
12 |
13 | .. automodule:: megaman.geometry.rmetric
14 | :members:
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/geometry/geometry.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _geom:
2 |
3 | Geometry
4 | ========
5 |
6 | One of the fundamental objectives of manifold learning is to understand
7 | the geometry of the data. As such the primary class of this package
8 | is the geometry class:
9 |
10 | :class:'~megaman.geometry.Geometry'
11 | This class is used as the interface to compute various quantities
12 | on the original data set including: pairwise distance graphs,
13 | affinity matrices, and laplacian matrices. It also caches these
14 | quantities and allows for fast re-computation with new parameters.
15 |
16 | API of Geometry
17 | ---------------
18 |
19 | The Geometry class is used to interface with functions that compute various
20 | geometric quantities with respect to the original data set. This is the object
21 | that is passed (or computed) within each embedding function. It is how
22 | megaman caches important quantities allowing for fast re-computation with
23 | various new parameters. Beyond instantiation, the Geometry class offers
24 | three types of functions: compute, set & delete that work with the four
25 | primary data matrices: (raw) data, adjacency matrix, affinity matrix,
26 | and Laplacian Matrix.
27 |
28 | 1. Class instantiation : during class instantiation you input the parameters
29 | concerning the original data matrix such as the distance calculation method,
30 | neighborhood and affinity radius, laplacian type. Each of the three
31 | computed matrices (adjacency, affinity, laplacian) have their
32 | own keyword dictionaries which permit these methods to easily be extended.
33 | 2. `set_[some]_matrix` : these functions allow you to assign a matrix of data
34 | to the geometry object. In particular these are used to fit the geometry
35 | to your input data (which may be of the form data_matrix, adjacency_matrix,
36 | or affinity_matrix). You can also set a Laplacian matrix.
37 | 3. `compute_[some]_matrix` : these functions are designed to compute the
38 | selected matrix (e.g. adjacency). Additional keyword arguments can be
39 | passed which override the ones passed at instantiation. NB: this method
40 | will always re-compute a matrix.
41 | 4. Geometry Attributes. Other than the parameters passed at instantiation each
42 | matrix that is computed is stored as an attribute e.g. geom.adjacency_matrix,
43 | geom.adjacency_matrix, geom.laplacian_matrix. Raw data is stored as geom.X.
44 | If you want to query for these matrices without recomputing you should use
45 | these attributes e.g. my_affinity = geom.affinity_matrix.
46 | 5. `delete_[some]_matrix` : if you are working with large data sets and choose
47 | an algorithm (e.g. Isomap or Spectral Embedding) that do not require the
48 | original data_matrix, these methods can be used to clear memory.
49 |
50 | See the API documentation for further information.
51 |
52 | Example Usage
53 | -------------
54 |
55 | Here is an example using the function on a random data set::
56 |
57 | import numpy as np
58 | from megaman.geometry import Geometry
59 |
60 | X = np.random.randn(100, 10)
61 | radius = 5
62 | adjacency_method = 'cyflann'
63 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':radius} # ignore distances above this radius
64 | affinity_method = 'gaussian'
65 | affinity_kwds = {'radius':radius} # A = exp(-||x - y||/radius^2)
66 | laplacian_method = 'geometric'
67 | laplacian_kwds = {'scaling_epps':radius} # scaling ensures convergence to Laplace-Beltrami operator
68 |
69 | geom = Geometry(adjacency_method=adjacency_method, adjacency_kwds=adjacency_kwds,
70 | affinity_method=affinity_method, affinity_kwds=affinity_kwds,
71 | laplacian_method=laplacian_method, laplacian_kwds=laplacian_kwds)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/geometry/index.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _geometry:
2 |
3 | ***************************************************
4 | Tools for Geometric Analysis (``megaman.geometry``)
5 | ***************************************************
6 |
7 | This module contains tools for analyzing inherent geometry of a data set.
8 | These tools include pairwise distance calculation, as well as affinity and
9 | Laplacian construction (e.g. :class:`~megaman.geometry.Geometry`).
10 |
11 | .. toctree::
12 | :maxdepth: 2
13 |
14 | geometry.rst
15 | API
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/images/circle_to_ellipse_embedding.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/doc/images/circle_to_ellipse_embedding.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/images/index.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _images:
2 |
3 | *********************
4 | Figures from Megaman
5 | *********************
6 |
7 | This section contains some experimental results from using the
8 | megaman package.
9 |
10 | .. toctree::
11 | :maxdepth: 2
12 |
13 | spectra_Halpha.rst
14 | word2vec.rst
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/images/spectra_D4000.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/doc/images/spectra_D4000.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/images/spectra_Halpha.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/doc/images/spectra_Halpha.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/images/spectra_Halpha.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
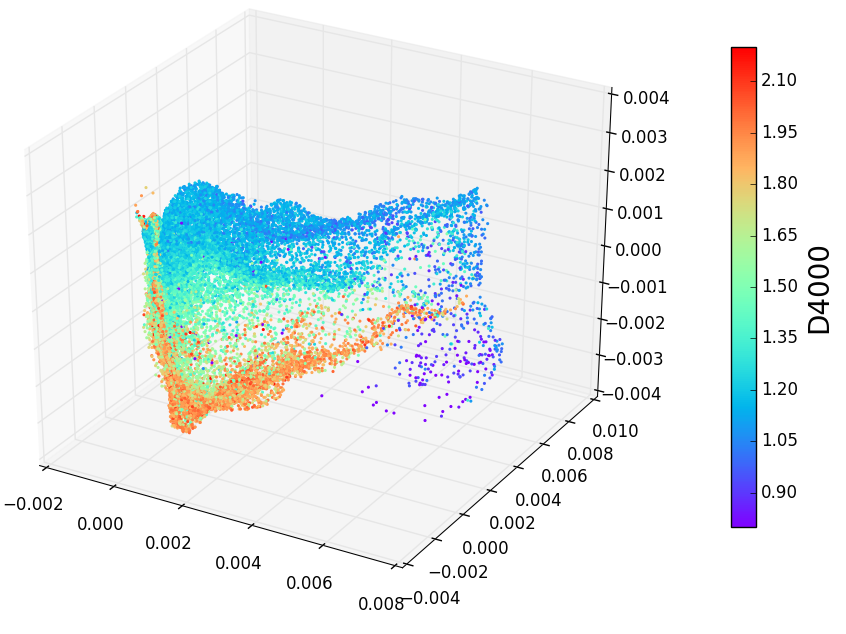
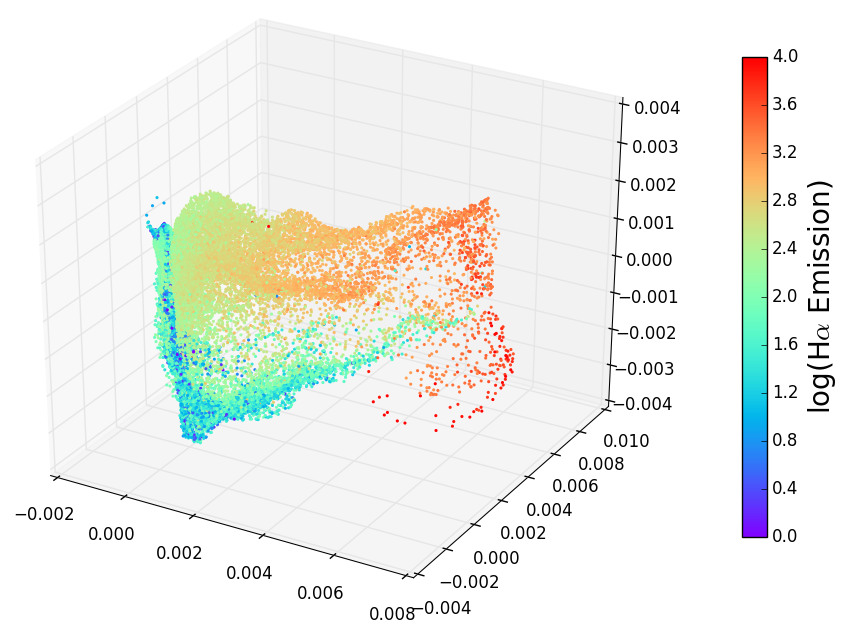
1 | .. _spectrum_Halpha:
2 |
3 | Spectrum Halpha Plot
4 | ====================
5 |
6 | .. figure:: spectra_Halpha.png
7 | :scale: 50 %
8 | :alt: spectrm Halpha
9 |
10 | A three-dimensional embedding of the main sample of galaxy spectra
11 | from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (approximately 675,000 spectra
12 | observed in 3750 dimensions). Colors in the above figure indicate
13 | the strength of Hydrogen alpha emission, a very nonlinear feature
14 | which requires dozens of dimensions to be captured in a linear embedding.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/images/word2vec.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _word2vec:
2 |
3 | Word2Vec Plot
4 | ====================
5 |
6 | .. figure:: word2vec_rmetric_plot_no_digits.png
7 | :scale: 50 %
8 | :alt: word2vec embedding with R. metric
9 |
10 | 3,000,000 words and phrases mapped by word2vec using Google News into 300
11 | dimensions. The data was then embedded into 2 dimensions using Spectral
12 | Embedding. The plot shows a sample of 10,000 points displaying the overall
13 | shape of the embedding as well as the estimated "stretch"
14 | (i.e. dual push-forward Riemannian metric) at various locations in the embedding.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/images/word2vec_rmetric_plot_no_digits.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/doc/images/word2vec_rmetric_plot_no_digits.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/index.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. image:: images/spectra_Halpha.png
2 | :height: 238 px
3 | :width: 318 px
4 | :align: left
5 | :target: /megaman/images/spectra_Halpha
6 | .. image:: images/word2vec_rmetric_plot_no_digits.png
7 | :height: 250 px
8 | :width: 220 px
9 | :align: right
10 | :target: /megaman/images/word2vec
11 |
12 |
13 | megaman: Manifold Learning for Millions of Points
14 | =================================================
15 |
16 | megaman is a scalable manifold learning package implemented in
17 | python. It has a front-end API designed to be familiar
18 | to `scikit-learn `_ but harnesses
19 | the C++ Fast Library for Approximate Nearest Neighbors (FLANN)
20 | and the Sparse Symmetric Positive Definite (SSPD) solver
21 | Locally Optimal Block Precodition Gradient (LOBPCG) method
22 | to scale manifold learning algorithms to large data sets.
23 | It is designed for researchers and as such caches intermediary
24 | steps and indices to allow for fast re-computation with new parameters.
25 |
26 | For issues & contributions, see the source
27 | `repository on github `_.
28 |
29 | For example notebooks see the
30 | `index on github `_.
31 |
32 | You can also read our
33 | `arXiv paper `_.
34 |
35 | Documentation
36 | =============
37 |
38 | .. toctree::
39 | :maxdepth: 2
40 |
41 | installation
42 | geometry/index
43 | embedding/index
44 | utils/index
45 | images/index
46 |
47 |
48 | Indices and tables
49 | ==================
50 |
51 | * :ref:`genindex`
52 | * :ref:`modindex`
53 | * :ref:`search`
54 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/installation.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Installation
2 | ============
3 |
4 | Though ``megaman`` has a fair number of compiled dependencies, it is
5 | straightforward to install using the cross-platform conda_ package manager.
6 |
7 | Installation with Conda
8 | -----------------------
9 |
10 | To install ``megaman`` and all its dependencies using conda_, run::
11 |
12 | $ conda install megaman --channel=conda-forge
13 |
14 | Currently builds are available for OSX and Linux, on Python 2.7, 3.4, and 3.5.
15 | For other operating systems, see the full install instructions below.
16 |
17 | Installation from Source
18 | ------------------------
19 |
20 | To install ``megaman`` from source requires the following:
21 |
22 | - python_: tested with versions 2.7, 3.4, and 3.5
23 | - numpy_: version 1.8 or higher
24 | - scipy_: version 0.16.0 or higher
25 | - scikit-learn_: version 0.16.0 or higher
26 | - FLANN_: version 1.8 or higher
27 | - cython_: version 0.23 or higher
28 | - a C++ compiler such as ``gcc``/``g++`` (we recommend version 4.8.*)
29 |
30 | Optional requirements include:
31 |
32 | - pyamg_, which provides fast decompositions of large sparse matrices
33 | - pyflann_, which offers an alternative FLANN interface for computing distance matrices (this is bundled with the FLANN source code)
34 | - nose_ for running the unit tests
35 |
36 | These requirements can be installed on Linux and MacOSX using the following conda command::
37 |
38 | $ conda install --channel=jakevdp pip nose coverage gcc cython numpy scipy scikit-learn pyflann pyamg
39 |
40 | Finally, within the source repository, run this command to install the ``megaman`` package itself::
41 |
42 | $ python setup.py install
43 |
44 | Unit Tests
45 | ----------
46 | ``megaman`` uses nose_ for unit tests. To run the unit tests once ``nose`` is installed, type in the source directory::
47 |
48 | $ make test
49 |
50 | or, outside the source directory once ``megaman`` is installed::
51 |
52 | $ nosetests megaman
53 |
54 | ``megaman`` is tested on Python versions 2.7, 3.4, and 3.5.
55 |
56 | .. _conda: http://conda.pydata.org/miniconda.html
57 | .. _python: http://python.org
58 | .. _numpy: http://numpy.org
59 | .. _scipy: http://scipy.org
60 | .. _scikit-learn: http://scikit-learn.org
61 | .. _FLANN: http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/
62 | .. _pyamg: http://pyamg.org/
63 | .. _pyflann: http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/
64 | .. _nose: https://nose.readthedocs.org/
65 | .. _cython: http://cython.org/
66 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import division, absolute_import, print_function
2 |
3 | from .numpydoc import setup
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/astropyautosummary.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Licensed under a 3-clause BSD style license - see LICENSE.rst
2 | """
3 | This sphinx extension builds off of `sphinx.ext.autosummary` to
4 | clean up some issues it presents in the Astropy docs.
5 |
6 | The main issue this fixes is the summary tables getting cut off before the
7 | end of the sentence in some cases.
8 |
9 | Note: Sphinx 1.2 appears to have fixed the the main issues in the stock
10 | autosummary extension that are addressed by this extension. So use of this
11 | extension with newer versions of Sphinx is deprecated.
12 | """
13 |
14 | import re
15 |
16 | from distutils.version import LooseVersion
17 |
18 | import sphinx
19 |
20 | from sphinx.ext.autosummary import Autosummary
21 |
22 | from ...utils import deprecated
23 |
24 | # used in AstropyAutosummary.get_items
25 | _itemsummrex = re.compile(r'^([A-Z].*?\.(?:\s|$))')
26 |
27 |
28 | @deprecated('1.0', message='AstropyAutosummary is only needed when used '
29 | 'with Sphinx versions less than 1.2')
30 | class AstropyAutosummary(Autosummary):
31 | def get_items(self, names):
32 | """Try to import the given names, and return a list of
33 | ``[(name, signature, summary_string, real_name), ...]``.
34 | """
35 | from sphinx.ext.autosummary import (get_import_prefixes_from_env,
36 | import_by_name, get_documenter, mangle_signature)
37 |
38 | env = self.state.document.settings.env
39 |
40 | prefixes = get_import_prefixes_from_env(env)
41 |
42 | items = []
43 |
44 | max_item_chars = 50
45 |
46 | for name in names:
47 | display_name = name
48 | if name.startswith('~'):
49 | name = name[1:]
50 | display_name = name.split('.')[-1]
51 |
52 | try:
53 | import_by_name_values = import_by_name(name, prefixes=prefixes)
54 | except ImportError:
55 | self.warn('[astropyautosummary] failed to import %s' % name)
56 | items.append((name, '', '', name))
57 | continue
58 |
59 | # to accommodate Sphinx v1.2.2 and v1.2.3
60 | if len(import_by_name_values) == 3:
61 | real_name, obj, parent = import_by_name_values
62 | elif len(import_by_name_values) == 4:
63 | real_name, obj, parent, module_name = import_by_name_values
64 |
65 | # NB. using real_name here is important, since Documenters
66 | # handle module prefixes slightly differently
67 | documenter = get_documenter(obj, parent)(self, real_name)
68 | if not documenter.parse_name():
69 | self.warn('[astropyautosummary] failed to parse name %s' % real_name)
70 | items.append((display_name, '', '', real_name))
71 | continue
72 | if not documenter.import_object():
73 | self.warn('[astropyautosummary] failed to import object %s' % real_name)
74 | items.append((display_name, '', '', real_name))
75 | continue
76 |
77 | # -- Grab the signature
78 |
79 | sig = documenter.format_signature()
80 | if not sig:
81 | sig = ''
82 | else:
83 | max_chars = max(10, max_item_chars - len(display_name))
84 | sig = mangle_signature(sig, max_chars=max_chars)
85 | sig = sig.replace('*', r'\*')
86 |
87 | # -- Grab the summary
88 |
89 | doc = list(documenter.process_doc(documenter.get_doc()))
90 |
91 | while doc and not doc[0].strip():
92 | doc.pop(0)
93 | m = _itemsummrex.search(" ".join(doc).strip())
94 | if m:
95 | summary = m.group(1).strip()
96 | elif doc:
97 | summary = doc[0].strip()
98 | else:
99 | summary = ''
100 |
101 | items.append((display_name, sig, summary, real_name))
102 |
103 | return items
104 |
105 |
106 | def setup(app):
107 | # need autosummary, of course
108 | app.setup_extension('sphinx.ext.autosummary')
109 |
110 | # Don't make the replacement if Sphinx is at least 1.2
111 | if LooseVersion(sphinx.__version__) < LooseVersion('1.2.0'):
112 | # this replaces the default autosummary with the astropy one
113 | app.add_directive('autosummary', AstropyAutosummary)
114 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/autodoc_enhancements.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Miscellaneous enhancements to help autodoc along.
3 | """
4 |
5 |
6 | # See
7 | # https://github.com/astropy/astropy-helpers/issues/116#issuecomment-71254836
8 | # for further background on this.
9 | def type_object_attrgetter(obj, attr, *defargs):
10 | """
11 | This implements an improved attrgetter for type objects (i.e. classes)
12 | that can handle class attributes that are implemented as properties on
13 | a metaclass.
14 |
15 | Normally `getattr` on a class with a `property` (say, "foo"), would return
16 | the `property` object itself. However, if the class has a metaclass which
17 | *also* defines a `property` named "foo", ``getattr(cls, 'foo')`` will find
18 | the "foo" property on the metaclass and resolve it. For the purposes of
19 | autodoc we just want to document the "foo" property defined on the class,
20 | not on the metaclass.
21 |
22 | For example::
23 |
24 | >>> class Meta(type):
25 | ... @property
26 | ... def foo(cls):
27 | ... return 'foo'
28 | ...
29 | >>> class MyClass(metaclass=Meta):
30 | ... @property
31 | ... def foo(self):
32 | ... \"\"\"Docstring for MyClass.foo property.\"\"\"
33 | ... return 'myfoo'
34 | ...
35 | >>> getattr(MyClass, 'foo')
36 | 'foo'
37 | >>> type_object_attrgetter(MyClass, 'foo')
38 |
39 | >>> type_object_attrgetter(MyClass, 'foo').__doc__
40 | 'Docstring for MyClass.foo property.'
41 |
42 | The last line of the example shows the desired behavior for the purposes
43 | of autodoc.
44 | """
45 |
46 | for base in obj.__mro__:
47 | if attr in base.__dict__:
48 | if isinstance(base.__dict__[attr], property):
49 | # Note, this should only be used for properties--for any other
50 | # type of descriptor (classmethod, for example) this can mess
51 | # up existing expectations of what getattr(cls, ...) returns
52 | return base.__dict__[attr]
53 | break
54 |
55 | return getattr(obj, attr, *defargs)
56 |
57 |
58 | def setup(app):
59 | app.add_autodoc_attrgetter(type, type_object_attrgetter)
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/changelog_links.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Licensed under a 3-clause BSD style license - see LICENSE.rst
2 | """
3 | This sphinx extension makes the issue numbers in the changelog into links to
4 | GitHub issues.
5 | """
6 |
7 | from __future__ import print_function
8 |
9 | import re
10 |
11 | from docutils.nodes import Text, reference
12 |
13 | BLOCK_PATTERN = re.compile('\[#.+\]', flags=re.DOTALL)
14 | ISSUE_PATTERN = re.compile('#[0-9]+')
15 |
16 |
17 | def process_changelog_links(app, doctree, docname):
18 | for rex in app.changelog_links_rexes:
19 | if rex.match(docname):
20 | break
21 | else:
22 | # if the doc doesn't match any of the changelog regexes, don't process
23 | return
24 |
25 | app.info('[changelog_links] Adding changelog links to "{0}"'.format(docname))
26 |
27 | for item in doctree.traverse():
28 |
29 | if not isinstance(item, Text):
30 | continue
31 |
32 | # We build a new list of items to replace the current item. If
33 | # a link is found, we need to use a 'reference' item.
34 | children = []
35 |
36 | # First cycle through blocks of issues (delimited by []) then
37 | # iterate inside each one to find the individual issues.
38 | prev_block_end = 0
39 | for block in BLOCK_PATTERN.finditer(item):
40 | block_start, block_end = block.start(), block.end()
41 | children.append(Text(item[prev_block_end:block_start]))
42 | block = item[block_start:block_end]
43 | prev_end = 0
44 | for m in ISSUE_PATTERN.finditer(block):
45 | start, end = m.start(), m.end()
46 | children.append(Text(block[prev_end:start]))
47 | issue_number = block[start:end]
48 | refuri = app.config.github_issues_url + issue_number[1:]
49 | children.append(reference(text=issue_number,
50 | name=issue_number,
51 | refuri=refuri))
52 | prev_end = end
53 |
54 | prev_block_end = block_end
55 |
56 | # If no issues were found, this adds the whole item,
57 | # otherwise it adds the remaining text.
58 | children.append(Text(block[prev_end:block_end]))
59 |
60 | # If no blocks were found, this adds the whole item, otherwise
61 | # it adds the remaining text.
62 | children.append(Text(item[prev_block_end:]))
63 |
64 | # Replace item by the new list of items we have generated,
65 | # which may contain links.
66 | item.parent.replace(item, children)
67 |
68 |
69 | def setup_patterns_rexes(app):
70 | app.changelog_links_rexes = [re.compile(pat) for pat in
71 | app.config.changelog_links_docpattern]
72 |
73 |
74 | def setup(app):
75 | app.connect('doctree-resolved', process_changelog_links)
76 | app.connect('builder-inited', setup_patterns_rexes)
77 | app.add_config_value('github_issues_url', None, True)
78 | app.add_config_value('changelog_links_docpattern', ['.*changelog.*', 'whatsnew/.*'], True)
79 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/comment_eater.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import division, absolute_import, print_function
2 |
3 | import sys
4 | if sys.version_info[0] >= 3:
5 | from io import StringIO
6 | else:
7 | from io import StringIO
8 |
9 | import compiler
10 | import inspect
11 | import textwrap
12 | import tokenize
13 |
14 | from .compiler_unparse import unparse
15 |
16 |
17 | class Comment(object):
18 | """ A comment block.
19 | """
20 | is_comment = True
21 | def __init__(self, start_lineno, end_lineno, text):
22 | # int : The first line number in the block. 1-indexed.
23 | self.start_lineno = start_lineno
24 | # int : The last line number. Inclusive!
25 | self.end_lineno = end_lineno
26 | # str : The text block including '#' character but not any leading spaces.
27 | self.text = text
28 |
29 | def add(self, string, start, end, line):
30 | """ Add a new comment line.
31 | """
32 | self.start_lineno = min(self.start_lineno, start[0])
33 | self.end_lineno = max(self.end_lineno, end[0])
34 | self.text += string
35 |
36 | def __repr__(self):
37 | return '%s(%r, %r, %r)' % (self.__class__.__name__, self.start_lineno,
38 | self.end_lineno, self.text)
39 |
40 |
41 | class NonComment(object):
42 | """ A non-comment block of code.
43 | """
44 | is_comment = False
45 | def __init__(self, start_lineno, end_lineno):
46 | self.start_lineno = start_lineno
47 | self.end_lineno = end_lineno
48 |
49 | def add(self, string, start, end, line):
50 | """ Add lines to the block.
51 | """
52 | if string.strip():
53 | # Only add if not entirely whitespace.
54 | self.start_lineno = min(self.start_lineno, start[0])
55 | self.end_lineno = max(self.end_lineno, end[0])
56 |
57 | def __repr__(self):
58 | return '%s(%r, %r)' % (self.__class__.__name__, self.start_lineno,
59 | self.end_lineno)
60 |
61 |
62 | class CommentBlocker(object):
63 | """ Pull out contiguous comment blocks.
64 | """
65 | def __init__(self):
66 | # Start with a dummy.
67 | self.current_block = NonComment(0, 0)
68 |
69 | # All of the blocks seen so far.
70 | self.blocks = []
71 |
72 | # The index mapping lines of code to their associated comment blocks.
73 | self.index = {}
74 |
75 | def process_file(self, file):
76 | """ Process a file object.
77 | """
78 | if sys.version_info[0] >= 3:
79 | nxt = file.__next__
80 | else:
81 | nxt = file.next
82 | for token in tokenize.generate_tokens(nxt):
83 | self.process_token(*token)
84 | self.make_index()
85 |
86 | def process_token(self, kind, string, start, end, line):
87 | """ Process a single token.
88 | """
89 | if self.current_block.is_comment:
90 | if kind == tokenize.COMMENT:
91 | self.current_block.add(string, start, end, line)
92 | else:
93 | self.new_noncomment(start[0], end[0])
94 | else:
95 | if kind == tokenize.COMMENT:
96 | self.new_comment(string, start, end, line)
97 | else:
98 | self.current_block.add(string, start, end, line)
99 |
100 | def new_noncomment(self, start_lineno, end_lineno):
101 | """ We are transitioning from a noncomment to a comment.
102 | """
103 | block = NonComment(start_lineno, end_lineno)
104 | self.blocks.append(block)
105 | self.current_block = block
106 |
107 | def new_comment(self, string, start, end, line):
108 | """ Possibly add a new comment.
109 |
110 | Only adds a new comment if this comment is the only thing on the line.
111 | Otherwise, it extends the noncomment block.
112 | """
113 | prefix = line[:start[1]]
114 | if prefix.strip():
115 | # Oops! Trailing comment, not a comment block.
116 | self.current_block.add(string, start, end, line)
117 | else:
118 | # A comment block.
119 | block = Comment(start[0], end[0], string)
120 | self.blocks.append(block)
121 | self.current_block = block
122 |
123 | def make_index(self):
124 | """ Make the index mapping lines of actual code to their associated
125 | prefix comments.
126 | """
127 | for prev, block in zip(self.blocks[:-1], self.blocks[1:]):
128 | if not block.is_comment:
129 | self.index[block.start_lineno] = prev
130 |
131 | def search_for_comment(self, lineno, default=None):
132 | """ Find the comment block just before the given line number.
133 |
134 | Returns None (or the specified default) if there is no such block.
135 | """
136 | if not self.index:
137 | self.make_index()
138 | block = self.index.get(lineno, None)
139 | text = getattr(block, 'text', default)
140 | return text
141 |
142 |
143 | def strip_comment_marker(text):
144 | """ Strip # markers at the front of a block of comment text.
145 | """
146 | lines = []
147 | for line in text.splitlines():
148 | lines.append(line.lstrip('#'))
149 | text = textwrap.dedent('\n'.join(lines))
150 | return text
151 |
152 |
153 | def get_class_traits(klass):
154 | """ Yield all of the documentation for trait definitions on a class object.
155 | """
156 | # FIXME: gracefully handle errors here or in the caller?
157 | source = inspect.getsource(klass)
158 | cb = CommentBlocker()
159 | cb.process_file(StringIO(source))
160 | mod_ast = compiler.parse(source)
161 | class_ast = mod_ast.node.nodes[0]
162 | for node in class_ast.code.nodes:
163 | # FIXME: handle other kinds of assignments?
164 | if isinstance(node, compiler.ast.Assign):
165 | name = node.nodes[0].name
166 | rhs = unparse(node.expr).strip()
167 | doc = strip_comment_marker(cb.search_for_comment(node.lineno, default=''))
168 | yield name, rhs, doc
169 |
170 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/doctest.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Licensed under a 3-clause BSD style license - see LICENSE.rst
2 | """
3 | This is a set of three directives that allow us to insert metadata
4 | about doctests into the .rst files so the testing framework knows
5 | which tests to skip.
6 |
7 | This is quite different from the doctest extension in Sphinx itself,
8 | which actually does something. For astropy, all of the testing is
9 | centrally managed from py.test and Sphinx is not used for running
10 | tests.
11 | """
12 | import re
13 | from docutils.nodes import literal_block
14 | from sphinx.util.compat import Directive
15 |
16 |
17 | class DoctestSkipDirective(Directive):
18 | has_content = True
19 |
20 | def run(self):
21 | # Check if there is any valid argument, and skip it. Currently only
22 | # 'win32' is supported in astropy.tests.pytest_plugins.
23 | if re.match('win32', self.content[0]):
24 | self.content = self.content[2:]
25 | code = '\n'.join(self.content)
26 | return [literal_block(code, code)]
27 |
28 |
29 | class DoctestRequiresDirective(DoctestSkipDirective):
30 | # This is silly, but we really support an unbounded number of
31 | # optional arguments
32 | optional_arguments = 64
33 |
34 |
35 | def setup(app):
36 | app.add_directive('doctest-requires', DoctestRequiresDirective)
37 | app.add_directive('doctest-skip', DoctestSkipDirective)
38 | app.add_directive('doctest-skip-all', DoctestSkipDirective)
39 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/smart_resolver.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Licensed under a 3-clause BSD style license - see LICENSE.rst
2 | """
3 | The classes in the astropy docs are documented by their API location,
4 | which is not necessarily where they are defined in the source. This
5 | causes a problem when certain automated features of the doc build,
6 | such as the inheritance diagrams or the `Bases` list of a class
7 | reference a class by its canonical location rather than its "user"
8 | location.
9 |
10 | In the `autodoc-process-docstring` event, a mapping from the actual
11 | name to the API name is maintained. Later, in the `missing-reference`
12 | event, unresolved references are looked up in this dictionary and
13 | corrected if possible.
14 | """
15 |
16 | from docutils.nodes import literal, reference
17 |
18 |
19 | def process_docstring(app, what, name, obj, options, lines):
20 | if isinstance(obj, type):
21 | env = app.env
22 | if not hasattr(env, 'class_name_mapping'):
23 | env.class_name_mapping = {}
24 | mapping = env.class_name_mapping
25 | mapping[obj.__module__ + '.' + obj.__name__] = name
26 |
27 |
28 | def missing_reference_handler(app, env, node, contnode):
29 | if not hasattr(env, 'class_name_mapping'):
30 | env.class_name_mapping = {}
31 | mapping = env.class_name_mapping
32 | reftype = node['reftype']
33 | reftarget = node['reftarget']
34 | if reftype in ('obj', 'class', 'exc', 'meth'):
35 | reftarget = node['reftarget']
36 | suffix = ''
37 | if reftarget not in mapping:
38 | if '.' in reftarget:
39 | front, suffix = reftarget.rsplit('.', 1)
40 | else:
41 | suffix = reftarget
42 |
43 | if suffix.startswith('_') and not suffix.startswith('__'):
44 | # If this is a reference to a hidden class or method,
45 | # we can't link to it, but we don't want to have a
46 | # nitpick warning.
47 | return node[0].deepcopy()
48 |
49 | if reftype in ('obj', 'meth') and '.' in reftarget:
50 | if front in mapping:
51 | reftarget = front
52 | suffix = '.' + suffix
53 |
54 | if (reftype in ('class', ) and '.' in reftarget
55 | and reftarget not in mapping):
56 |
57 | if '.' in front:
58 | reftarget, _ = front.rsplit('.', 1)
59 | suffix = '.' + suffix
60 | reftarget = reftarget + suffix
61 | prefix = reftarget.rsplit('.')[0]
62 | if (reftarget not in mapping and
63 | prefix in env.intersphinx_named_inventory):
64 |
65 | if reftarget in env.intersphinx_named_inventory[prefix]['py:class']:
66 | newtarget = env.intersphinx_named_inventory[prefix]['py:class'][reftarget][2]
67 | if not node['refexplicit'] and \
68 | '~' not in node.rawsource:
69 | contnode = literal(text=reftarget)
70 | newnode = reference('', '', internal=True)
71 | newnode['reftitle'] = reftarget
72 | newnode['refuri'] = newtarget
73 | newnode.append(contnode)
74 |
75 | return newnode
76 |
77 | if reftarget in mapping:
78 | newtarget = mapping[reftarget] + suffix
79 | if not node['refexplicit'] and not '~' in node.rawsource:
80 | contnode = literal(text=newtarget)
81 | newnode = env.domains['py'].resolve_xref(
82 | env, node['refdoc'], app.builder, 'class', newtarget,
83 | node, contnode)
84 | if newnode is not None:
85 | newnode['reftitle'] = reftarget
86 | return newnode
87 |
88 |
89 | def setup(app):
90 | app.connect('autodoc-process-docstring', process_docstring)
91 |
92 | app.connect('missing-reference', missing_reference_handler)
93 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/tocdepthfix.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from sphinx import addnodes
2 |
3 |
4 | def fix_toc_entries(app, doctree):
5 | # Get the docname; I don't know why this isn't just passed in to the
6 | # callback
7 | # This seems a bit unreliable as it's undocumented, but it's not "private"
8 | # either:
9 | docname = app.builder.env.temp_data['docname']
10 | if app.builder.env.metadata[docname].get('tocdepth', 0) != 0:
11 | # We need to reprocess any TOC nodes in the doctree and make sure all
12 | # the files listed in any TOCs are noted
13 | for treenode in doctree.traverse(addnodes.toctree):
14 | app.builder.env.note_toctree(docname, treenode)
15 |
16 |
17 | def setup(app):
18 | app.connect('doctree-read', fix_toc_entries)
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/traitsdoc.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | =========
3 | traitsdoc
4 | =========
5 |
6 | Sphinx extension that handles docstrings in the Numpy standard format, [1]
7 | and support Traits [2].
8 |
9 | This extension can be used as a replacement for ``numpydoc`` when support
10 | for Traits is required.
11 |
12 | .. [1] http://projects.scipy.org/numpy/wiki/CodingStyleGuidelines#docstring-standard
13 | .. [2] http://code.enthought.com/projects/traits/
14 |
15 | """
16 | from __future__ import division, absolute_import, print_function
17 |
18 | import inspect
19 | import os
20 | import pydoc
21 | import collections
22 |
23 | from . import docscrape
24 | from . import docscrape_sphinx
25 | from .docscrape_sphinx import SphinxClassDoc, SphinxFunctionDoc, SphinxDocString
26 |
27 | from . import numpydoc
28 |
29 | from . import comment_eater
30 |
31 | class SphinxTraitsDoc(SphinxClassDoc):
32 | def __init__(self, cls, modulename='', func_doc=SphinxFunctionDoc):
33 | if not inspect.isclass(cls):
34 | raise ValueError("Initialise using a class. Got %r" % cls)
35 | self._cls = cls
36 |
37 | if modulename and not modulename.endswith('.'):
38 | modulename += '.'
39 | self._mod = modulename
40 | self._name = cls.__name__
41 | self._func_doc = func_doc
42 |
43 | docstring = pydoc.getdoc(cls)
44 | docstring = docstring.split('\n')
45 |
46 | # De-indent paragraph
47 | try:
48 | indent = min(len(s) - len(s.lstrip()) for s in docstring
49 | if s.strip())
50 | except ValueError:
51 | indent = 0
52 |
53 | for n,line in enumerate(docstring):
54 | docstring[n] = docstring[n][indent:]
55 |
56 | self._doc = docscrape.Reader(docstring)
57 | self._parsed_data = {
58 | 'Signature': '',
59 | 'Summary': '',
60 | 'Description': [],
61 | 'Extended Summary': [],
62 | 'Parameters': [],
63 | 'Returns': [],
64 | 'Raises': [],
65 | 'Warns': [],
66 | 'Other Parameters': [],
67 | 'Traits': [],
68 | 'Methods': [],
69 | 'See Also': [],
70 | 'Notes': [],
71 | 'References': '',
72 | 'Example': '',
73 | 'Examples': '',
74 | 'index': {}
75 | }
76 |
77 | self._parse()
78 |
79 | def _str_summary(self):
80 | return self['Summary'] + ['']
81 |
82 | def _str_extended_summary(self):
83 | return self['Description'] + self['Extended Summary'] + ['']
84 |
85 | def __str__(self, indent=0, func_role="func"):
86 | out = []
87 | out += self._str_signature()
88 | out += self._str_index() + ['']
89 | out += self._str_summary()
90 | out += self._str_extended_summary()
91 | for param_list in ('Parameters', 'Traits', 'Methods',
92 | 'Returns','Raises'):
93 | out += self._str_param_list(param_list)
94 | out += self._str_see_also("obj")
95 | out += self._str_section('Notes')
96 | out += self._str_references()
97 | out += self._str_section('Example')
98 | out += self._str_section('Examples')
99 | out = self._str_indent(out,indent)
100 | return '\n'.join(out)
101 |
102 | def looks_like_issubclass(obj, classname):
103 | """ Return True if the object has a class or superclass with the given class
104 | name.
105 |
106 | Ignores old-style classes.
107 | """
108 | t = obj
109 | if t.__name__ == classname:
110 | return True
111 | for klass in t.__mro__:
112 | if klass.__name__ == classname:
113 | return True
114 | return False
115 |
116 | def get_doc_object(obj, what=None, config=None):
117 | if what is None:
118 | if inspect.isclass(obj):
119 | what = 'class'
120 | elif inspect.ismodule(obj):
121 | what = 'module'
122 | elif isinstance(obj, collections.Callable):
123 | what = 'function'
124 | else:
125 | what = 'object'
126 | if what == 'class':
127 | doc = SphinxTraitsDoc(obj, '', func_doc=SphinxFunctionDoc, config=config)
128 | if looks_like_issubclass(obj, 'HasTraits'):
129 | for name, trait, comment in comment_eater.get_class_traits(obj):
130 | # Exclude private traits.
131 | if not name.startswith('_'):
132 | doc['Traits'].append((name, trait, comment.splitlines()))
133 | return doc
134 | elif what in ('function', 'method'):
135 | return SphinxFunctionDoc(obj, '', config=config)
136 | else:
137 | return SphinxDocString(pydoc.getdoc(obj), config=config)
138 |
139 | def setup(app):
140 | # init numpydoc
141 | numpydoc.setup(app, get_doc_object)
142 |
143 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import inspect
2 | import sys
3 |
4 |
5 | def find_mod_objs(modname, onlylocals=False):
6 | """ Returns all the public attributes of a module referenced by name.
7 |
8 | .. note::
9 | The returned list *not* include subpackages or modules of
10 | `modname`,nor does it include private attributes (those that
11 | beginwith '_' or are not in `__all__`).
12 |
13 | Parameters
14 | ----------
15 | modname : str
16 | The name of the module to search.
17 | onlylocals : bool
18 | If True, only attributes that are either members of `modname` OR one of
19 | its modules or subpackages will be included.
20 |
21 | Returns
22 | -------
23 | localnames : list of str
24 | A list of the names of the attributes as they are named in the
25 | module `modname` .
26 | fqnames : list of str
27 | A list of the full qualified names of the attributes (e.g.,
28 | ``astropy.utils.misc.find_mod_objs``). For attributes that are
29 | simple variables, this is based on the local name, but for
30 | functions or classes it can be different if they are actually
31 | defined elsewhere and just referenced in `modname`.
32 | objs : list of objects
33 | A list of the actual attributes themselves (in the same order as
34 | the other arguments)
35 |
36 | """
37 |
38 | __import__(modname)
39 | mod = sys.modules[modname]
40 |
41 | if hasattr(mod, '__all__'):
42 | pkgitems = [(k, mod.__dict__[k]) for k in mod.__all__]
43 | else:
44 | pkgitems = [(k, mod.__dict__[k]) for k in dir(mod) if k[0] != '_']
45 |
46 | # filter out modules and pull the names and objs out
47 | ismodule = inspect.ismodule
48 | localnames = [k for k, v in pkgitems if not ismodule(v)]
49 | objs = [v for k, v in pkgitems if not ismodule(v)]
50 |
51 | # fully qualified names can be determined from the object's module
52 | fqnames = []
53 | for obj, lnm in zip(objs, localnames):
54 | if hasattr(obj, '__module__') and hasattr(obj, '__name__'):
55 | fqnames.append(obj.__module__ + '.' + obj.__name__)
56 | else:
57 | fqnames.append(modname + '.' + lnm)
58 |
59 | if onlylocals:
60 | valids = [fqn.startswith(modname) for fqn in fqnames]
61 | localnames = [e for i, e in enumerate(localnames) if valids[i]]
62 | fqnames = [e for i, e in enumerate(fqnames) if valids[i]]
63 | objs = [e for i, e in enumerate(objs) if valids[i]]
64 |
65 | return localnames, fqnames, objs
66 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/utils/API.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _utils_API:
2 |
3 | .. testsetup:: *
4 |
5 | from megaman.utils import *
6 |
7 | API Documentation
8 | =================
9 |
10 | .. automodule:: megaman.utils.eigendecomp
11 | :members:
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/utils/index.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _utils:
2 |
3 | ***************************************************
4 | Utility tools for megaman (``megaman.utils``)
5 | ***************************************************
6 |
7 | This module contains utility functions used inside
8 | megaman. In particular the eigendecomposition.
9 |
10 | .. toctree::
11 | :maxdepth: 2
12 |
13 | API
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/example.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import sys
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import scipy as sp
4 | import scipy.sparse as sparse
5 | from megaman.geometry import Geometry
6 | from sklearn import datasets
7 | from megaman.embedding import (Isomap, LocallyLinearEmbedding,
8 | LTSA, SpectralEmbedding)
9 |
10 | # Generate an example data set
11 | N = 10
12 | X, color = datasets.samples_generator.make_s_curve(N, random_state=0)
13 |
14 | # Geometry is the main class that will Cache things like distance, affinity, and laplacian.
15 | # you instantiate the Geometry class with the parameters & methods for the three main components:
16 | # Adjacency: an NxN (sparse) pairwise matrix indicating neighborhood regions
17 | # Affinity an NxN (sparse) pairwise matrix insicated similarity between points
18 | # Laplacian an NxN (sparse) pairwsie matrix containing geometric manifold information
19 |
20 | radius = 5
21 | adjacency_method = 'cyflann'
22 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':radius} # ignore distances above this radius
23 | affinity_method = 'gaussian'
24 | affinity_kwds = {'radius':radius} # A = exp(-||x - y||/radius^2)
25 | laplacian_method = 'geometric'
26 | laplacian_kwds = {'scaling_epps':radius} # scaling ensures convergence to Laplace-Beltrami operator
27 |
28 | geom = Geometry(adjacency_method=adjacency_method, adjacency_kwds=adjacency_kwds,
29 | affinity_method=affinity_method, affinity_kwds=affinity_kwds,
30 | laplacian_method=laplacian_method, laplacian_kwds=laplacian_kwds)
31 |
32 | # You can/should also use the set_data_matrix, set_adjacency_matrix, set_affinity_matrix
33 | # to send your data set (in whichever form it takes) this way.
34 | geom.set_data_matrix(X)
35 |
36 | # You can get the distance, affinity etc with e.g: Geometry.get_distance_matrix()
37 | # you can update the keyword arguments passed inially using these functions
38 | adjacency_matrix = geom.compute_adjacency_matrix()
39 | # by defualt this is pass-by-reference. Use copy=True to get a copied version.
40 |
41 | # If you don't want to pre-compute a Geometry you can pass a dictionary or geometry
42 | # arguments to one of the embedding classes.
43 | geom = {'adjacency_method':adjacency_method, 'adjacency_kwds':adjacency_kwds,
44 | 'affinity_method':affinity_method, 'affinity_kwds':affinity_kwds,
45 | 'laplacian_method':laplacian_method, 'laplacian_kwds':laplacian_kwds}
46 |
47 |
48 | # an example follows for creating each embedding into 2 dimensions.
49 | n_components = 2
50 |
51 | # LTSA
52 | ltsa =LTSA(n_components=n_components, eigen_solver='arpack',
53 | geom=geom)
54 | embed_ltsa = ltsa.fit_transform(X)
55 |
56 | # LLE
57 | lle = LocallyLinearEmbedding(n_components=n_components, eigen_solver='arpack',
58 | geom=geom)
59 | embed_lle = lle.fit_transform(X)
60 |
61 | # Isomap
62 | isomap = Isomap(n_components=n_components, eigen_solver='arpack',
63 | geom=geom)
64 | embed_isomap = isomap.fit_transform(X)
65 |
66 | # Spectral Embedding
67 | spectral = SpectralEmbedding(n_components=n_components, eigen_solver='arpack',
68 | geom=geom)
69 | embed_spectral = spectral.fit_transform(X)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/examples_index.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "markdown",
5 | "metadata": {},
6 | "source": [
7 | "# `megaman`: Manifold Learning for Millions of Points "
8 | ]
9 | },
10 | {
11 | "cell_type": "markdown",
12 | "metadata": {},
13 | "source": [
14 | "This noteook contains links to examples of using `megaman` to perform manifold learning on data. \n",
15 | "\n",
16 | "See also the [megaman documentation](http://mmp2.github.io/megaman/)."
17 | ]
18 | },
19 | {
20 | "cell_type": "markdown",
21 | "metadata": {},
22 | "source": [
23 | "* [megaman_tutorial.ipynb](https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/examples/megaman_tutorial.ipynb)\n",
24 | "* [manifold_intro.ipynb](https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/examples/manifold_intro.ipynb)"
25 | ]
26 | },
27 | {
28 | "cell_type": "code",
29 | "execution_count": null,
30 | "metadata": {
31 | "collapsed": true
32 | },
33 | "outputs": [],
34 | "source": []
35 | }
36 | ],
37 | "metadata": {
38 | "kernelspec": {
39 | "display_name": "Python 2",
40 | "language": "python",
41 | "name": "python2"
42 | },
43 | "language_info": {
44 | "codemirror_mode": {
45 | "name": "ipython",
46 | "version": 2
47 | },
48 | "file_extension": ".py",
49 | "mimetype": "text/x-python",
50 | "name": "python",
51 | "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
52 | "pygments_lexer": "ipython2",
53 | "version": "2.7.11"
54 | }
55 | },
56 | "nbformat": 4,
57 | "nbformat_minor": 0
58 | }
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/rad_est_utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import scipy
3 | import scipy.linalg
4 | import os
5 | import plotly.graph_objs as go
6 |
7 | try:
8 | from tqdm import *
9 | tqdm_installed = True
10 | except ImportError as e:
11 | tqdm_installed = False
12 | print('tqdm not installed, will not show the progress bar')
13 |
14 | def find_neighbors(idx, dist):
15 | nbr = dist[idx, :].nonzero()[1]
16 | if idx not in nbr:
17 | return np.append(nbr, idx)
18 | else:
19 | return nbr
20 |
21 |
22 | def find_local_singular_values(data, idx, dist, dim=15):
23 | nbr = find_neighbors(idx, dist)
24 | if nbr.shape[0] == 1:
25 | return np.zeros(dim)
26 | else:
27 | local_pca_data = data[nbr, :]
28 | local_center = np.mean(local_pca_data, axis=0)
29 | local_pca_data -= local_center[None, :]
30 |
31 | sing = scipy.linalg.svd(local_pca_data, compute_uv=False)
32 | sing_return = sing[:dim]
33 | return np.pad(sing_return, (0, dim - sing_return.shape[0]), 'constant')
34 |
35 |
36 | def find_all_singular_values(data, rad, dist):
37 | dist_copy = dist.copy()
38 | dist_copy[dist_copy > rad] = 0.0
39 | dist_copy.eliminate_zeros()
40 | dim = data.shape[1]
41 | singular_list = np.array([find_local_singular_values(data, idx, dist_copy, dim)
42 | for idx in range(data.shape[0])])
43 | return singular_list
44 |
45 |
46 | def find_mean_singular_values(data, rad, dist):
47 | singular_list = find_all_singular_values(data, rad, dist)
48 | return np.mean(singular_list, axis=0)
49 |
50 |
51 | def find_argmax_dimension(data, dist, optimal_rad):
52 | singular_list = find_all_singular_values(data, optimal_rad, dist)
53 | singular_gap = np.hstack(
54 | (-1 * np.diff(singular_list, axis=1), singular_list[:, -1, None]))
55 | return np.argmax(singular_gap, axis=1) + 1
56 |
57 |
58 | def ordinal (n):
59 | return "%d%s" % (n,"tsnrhtdd"[(n//10%10!=1)*(n%10<4)*n%10::4])
60 |
61 |
62 | def estimate_dimension(data, dist, rad_search_space=None):
63 | if rad_search_space is None:
64 | rad_search_space = np.logspace(np.log10(1e-1), np.log10(5), 50)
65 |
66 | rad_iterator = rad_search_space if not tqdm_installed else tqdm(
67 | rad_search_space)
68 | sgv = np.array([find_mean_singular_values(data, rad, dist)
69 | for rad in rad_iterator])
70 |
71 | return rad_search_space, sgv
72 |
73 |
74 | def plot_singular_values_versus_radius(singular_values, rad_search_space, start_idx, end_idx):
75 | all_trace = []
76 | singular_gap = -np.diff(singular_values,axis=1)
77 | for idx, sing in enumerate(singular_values.T):
78 | singular_line = go.Scatter(
79 | x=rad_search_space, y=sing, name='{} singular value'.format(ordinal(idx+1))
80 | )
81 | if idx <= 2:
82 | singular_line['text'] = [ 'Singular gap: {:.2f}'.format(singular_gap[rid, idx]) for rid in range(50) ]
83 | if idx > 3:
84 | singular_line['hoverinfo'] = 'none'
85 | all_trace.append(singular_line)
86 | if idx == 2:
87 | # HACK: just specify the color manually, need to generate each later.
88 | all_trace.append(go.Scatter(
89 | x=rad_search_space[start_idx:end_idx], y=singular_values[start_idx:end_idx,2],
90 | mode='lines',marker=dict(color='green'),
91 | showlegend=False, hoverinfo='none'
92 | ))
93 | all_trace.append(go.Scatter(
94 | x=rad_search_space[start_idx:end_idx], y=singular_values[start_idx:end_idx,1],
95 | fill='tonexty', mode='none', showlegend=False, hoverinfo='none'
96 | ))
97 | return all_trace
98 |
99 | def generate_layouts(start_idx, end_idx, est_rad_dim1, est_rad_dim2, rad_search_space):
100 | return go.Layout(
101 | title='Singular values - radii plot',
102 | xaxis=dict(
103 | title='$\\text{Radius } r $',
104 | # type='log',
105 | autorange=True
106 | ),
107 | yaxis=dict(title='$\\text{Singular value } \\sigma$'),
108 | shapes=[{
109 | 'type': 'rect',
110 | 'xref': 'x',
111 | 'yref': 'paper',
112 | 'x0': rad_search_space[start_idx],
113 | 'y0': 0,
114 | 'x1': rad_search_space[end_idx-1],
115 | 'y1': 1,
116 | 'fillcolor': '#d3d3d3',
117 | 'opacity': 0.4,
118 | 'line': {
119 | 'width': 0,
120 | }
121 | }],
122 | annotations=[
123 | dict(
124 | x=est_rad_dim1,
125 | y=0,
126 | xref='x',
127 | yref='y',
128 | text='$\\hat{r}_{d=1}$',
129 | font = dict(size = 30),
130 | showarrow=True,
131 | arrowhead=7,
132 | ax=20,
133 | ay=30
134 | ),
135 | dict(
136 | x=est_rad_dim2,
137 | y=0,
138 | xref='x',
139 | yref='y',
140 | text='$\\hat{r}_{d=2}$',
141 | font = dict(size = 30),
142 | showarrow=True,
143 | arrowhead=7,
144 | ax=-20,
145 | ay=30
146 | )
147 | ])
148 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/tutorial_data_plot.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/examples/tutorial_data_plot.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/tutorial_embeddings.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/examples/tutorial_embeddings.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/tutorial_isomap_plot.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/examples/tutorial_isomap_plot.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/tutorial_spectral_plot.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/examples/tutorial_spectral_plot.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/__check_build/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Author: Jake VanderPlas
2 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
3 | #
4 | # Adapted from scikit-learn's similar utility
5 |
6 | """ Module to give helpful messages to the user that did not
7 | compile megaman properly (adapted from scikit-learn's check_build utility)
8 | """
9 | import os
10 |
11 | INPLACE_MSG = """
12 | It appears that you are importing a local megaman source tree.
13 | Please either use an inplace install or try from another location."""
14 |
15 | STANDARD_MSG = """
16 | If you have used an installer, please check that it is suited for your
17 | Python version, your operating system and your platform."""
18 |
19 | ERROR_TEMPLATE = """{error}
20 | ___________________________________________________________________________
21 | Contents of {local_dir}:
22 | {contents}
23 | ___________________________________________________________________________
24 | It seems that megaman has not been built correctly.
25 |
26 | If you have installed megaman from source, please do not forget
27 | to build the package before using it: run `python setup.py install`
28 | in the source directory.
29 | {msg}"""
30 |
31 |
32 | def raise_build_error(e):
33 | # Raise a comprehensible error and list the contents of the
34 | # directory to help debugging on the mailing list.
35 | local_dir = os.path.split(__file__)[0]
36 | msg = STANDARD_MSG
37 | if local_dir == "megaman/__check_build":
38 | # Picking up the local install: this will work only if the
39 | # install is an 'inplace build'
40 | msg = INPLACE_MSG
41 | dir_content = list()
42 | for i, filename in enumerate(os.listdir(local_dir)):
43 | if ((i + 1) % 3):
44 | dir_content.append(filename.ljust(26))
45 | else:
46 | dir_content.append(filename + '\n')
47 | contents = ''.join(dir_content).strip()
48 | raise ImportError(ERROR_TEMPLATE.format(error=e,
49 | local_dir=local_dir,
50 | contents=contents,
51 | msg=msg))
52 |
53 | try:
54 | from ._check_build import check_build
55 | except ImportError as e:
56 | raise_build_error(e)
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/__check_build/_check_build.pyx:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | def check_build():
4 | return
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/__check_build/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import numpy
4 |
5 |
6 | def configuration(parent_package='', top_path=None):
7 | from numpy.distutils.misc_util import Configuration
8 | config = Configuration('__check_build', parent_package, top_path)
9 | config.add_extension('_check_build',
10 | sources=['_check_build.c'])
11 |
12 | return config
13 |
14 | if __name__ == '__main__':
15 | from numpy.distutils.core import setup
16 | setup(**configuration(top_path='').todict())
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """megaman: Scalable Manifold Learning"""
2 |
3 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
4 |
5 | __version__ = "0.3.dev0"
6 |
7 | from . import __check_build
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/datasets/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .datasets import (get_megaman_image, generate_megaman_data,
2 | generate_megaman_manifold, generate_noisefree_hourglass,
3 | generate_noisy_hourglass)
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/datasets/datasets.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Some sample datasets"""
2 | from __future__ import division
3 |
4 | import os
5 |
6 | import numpy as np
7 | from scipy import ndimage
8 | from sklearn.utils import check_random_state
9 |
10 | import collections
11 |
12 | def get_megaman_image(factor=1):
13 | """Return an RGBA representation of the megaman icon"""
14 | imfile = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'megaman.png')
15 | data = ndimage.imread(imfile) / 255
16 | if factor > 1:
17 | data = data.repeat(factor, axis=0).repeat(factor, axis=1)
18 | return data
19 |
20 |
21 | def generate_megaman_data(sampling=2):
22 | """Generate 2D point data of the megaman image"""
23 | data = get_megaman_image()
24 | x = np.arange(sampling * data.shape[1]) / float(sampling)
25 | y = np.arange(sampling * data.shape[0]) / float(sampling)
26 | X, Y = map(np.ravel, np.meshgrid(x, y))
27 | C = data[np.floor(Y.max() - Y).astype(int),
28 | np.floor(X).astype(int)]
29 | return np.vstack([X, Y]).T, C
30 |
31 |
32 | def _make_S_curve(x, range=(-0.75, 0.75)):
33 | """Make a 2D S-curve from a 1D vector"""
34 | assert x.ndim == 1
35 | x = x - x.min()
36 | theta = 2 * np.pi * (range[0] + (range[1] - range[0]) * x / x.max())
37 | X = np.empty((x.shape[0], 2), dtype=float)
38 | X[:, 0] = np.sign(theta) * (1 - np.cos(theta))
39 | X[:, 1] = np.sin(theta)
40 | X *= x.max() / (2 * np.pi * (range[1] - range[0]))
41 | return X
42 |
43 |
44 | def generate_megaman_manifold(sampling=2, nfolds=2,
45 | rotate=True, random_state=None):
46 | """Generate a manifold of the megaman data"""
47 | X, c = generate_megaman_data(sampling)
48 | for i in range(nfolds):
49 | X = np.hstack([_make_S_curve(x) for x in X.T])
50 |
51 | if rotate:
52 | rand = check_random_state(random_state)
53 | R = rand.randn(X.shape[1], X.shape[1])
54 | U, s, VT = np.linalg.svd(R)
55 | X = np.dot(X, U)
56 |
57 | return X, c
58 |
59 | def generate_noisefree_hourglass(n_size, scaling_factor=1.75, seed=None):
60 | if seed is not None:
61 | np.random.seed(seed)
62 | fz = lambda z: -4*z**4 + 4*z**2 + 1
63 | X = np.random.normal(0,1,[n_size,3])
64 | sphere = X / np.linalg.norm(X,axis=1)[:,None]
65 | r = np.linalg.norm(sphere,axis=1)
66 |
67 | x,y,z = sphere.T
68 | theta = np.arctan2(y,x)
69 | phi = np.arccos(z/r)
70 |
71 | r_hour = fz(z)
72 | theta_hour = theta
73 | z_hour = z
74 | phi_hour = np.arccos(z_hour/r_hour)
75 |
76 | x_hour = r_hour*np.cos(theta_hour)*np.sin(phi_hour)
77 | y_hour = r_hour*np.sin(theta_hour)*np.sin(phi_hour)
78 | z_hour = r_hour*np.cos(phi_hour)
79 |
80 | x_hour *= 0.5
81 | y_hour *= 0.5
82 |
83 | hourglass = np.vstack((x_hour,y_hour,z_hour)).T
84 | hourglass *= scaling_factor
85 |
86 | return hourglass
87 |
88 | def _genereate_noises(sigmas, size, dimensions, seed=None):
89 | if seed is not None:
90 | np.random.seed(seed)
91 | if isinstance(sigmas, (collections.Sequence, np.ndarray)):
92 | assert len(sigmas) == dimensions, \
93 | 'The size of sigmas should be the same as noises dimensions'
94 | return np.random.multivariate_normal(np.zeros(dimensions),
95 | np.diag(sigmas), size)
96 | else:
97 | return np.random.normal(0,sigmas,[size,dimensions])
98 |
99 | def _add_noises_on_primary_dimensions(data,sigmas=0.1,seed=None):
100 | size,dim = data.shape
101 | noises = _genereate_noises(sigmas,size,dim)
102 | return data + noises
103 |
104 | def _add_noises_on_additional_dimensions(data,addition_dims,sigmas=1,seed=None):
105 | if addition_dims == 0:
106 | return data
107 | else:
108 | noises = _genereate_noises(sigmas,data.shape[0],addition_dims,seed)
109 | return np.hstack((data,noises))
110 |
111 | def generate_noisy_hourglass(size, sigma_primary=0.05, addition_dims=0,
112 | sigma_additional=0.1, scaling_factor=1.75, seed=None):
113 | hourglass = generate_noisefree_hourglass(size, scaling_factor, seed)
114 | hourglass = _add_noises_on_primary_dimensions(hourglass, sigma_primary)
115 | hourglass = _add_noises_on_additional_dimensions(hourglass, addition_dims,
116 | sigma_additional)
117 | return hourglass
118 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/datasets/megaman.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/datasets/megaman.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/embedding/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | The :mod:`sklearn.megaman` module implements data embedding techniques.
3 | """
4 |
5 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
6 |
7 | from .locally_linear import LocallyLinearEmbedding
8 | from .isomap import Isomap
9 | from .ltsa import LTSA
10 | from .spectral_embedding import SpectralEmbedding
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/embedding/base.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """ base estimator class for megaman """
2 |
3 | # Author: James McQueen --
4 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
5 |
6 | import numpy as np
7 | from scipy.sparse import isspmatrix
8 |
9 | from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin
10 | from sklearn.utils.validation import check_array
11 |
12 | from ..geometry.geometry import Geometry
13 |
14 | # from sklearn.utils.validation import FLOAT_DTYPES
15 | FLOAT_DTYPES = (np.float64, np.float32, np.float16)
16 |
17 |
18 | class BaseEmbedding(BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin):
19 | """ Base Class for all megaman embeddings.
20 |
21 | Inherits BaseEstimator and TransformerMixin from sklearn.
22 |
23 | BaseEmbedding creates the common interface to the geometry
24 | class for all embeddings as well as providing a common
25 | .fit_transform().
26 |
27 | Parameters
28 | ----------
29 | n_components : integer
30 | number of coordinates for the manifold.
31 | radius : float (optional)
32 | radius for adjacency and affinity calculations. Will be overridden if
33 | either is set in `geom`
34 | geom : dict or megaman.geometry.Geometry object
35 | specification of geometry parameters: keys are
36 | ["adjacency_method", "adjacency_kwds", "affinity_method",
37 | "affinity_kwds", "laplacian_method", "laplacian_kwds"]
38 |
39 | Attributes
40 | ----------
41 | geom_ : a fitted megaman.geometry.Geometry object.
42 | """
43 | def __init__(self, n_components=2, radius=None, geom=None):
44 | self.n_components = n_components
45 | self.radius = radius
46 | self.geom = geom
47 |
48 | def _validate_input(self, X, input_type):
49 | if input_type == 'data':
50 | sparse_formats = None
51 | elif input_type in ['adjacency', 'affinity']:
52 | sparse_formats = ['csr', 'coo', 'lil', 'bsr', 'dok', 'dia']
53 | else:
54 | raise ValueError("unrecognized input_type: {0}".format(input_type))
55 | return check_array(X, dtype=FLOAT_DTYPES, accept_sparse=sparse_formats)
56 |
57 | # # The world is not ready for this...
58 | # def estimate_radius(self, X, input_type='data', intrinsic_dim=None):
59 | # """Estimate a radius based on the data and intrinsic dimensionality
60 | #
61 | # Parameters
62 | # ----------
63 | # X : array_like, [n_samples, n_features]
64 | # dataset for which radius is estimated
65 | # intrinsic_dim : int (optional)
66 | # estimated intrinsic dimensionality of the manifold. If not
67 | # specified, then intrinsic_dim = self.n_components
68 | #
69 | # Returns
70 | # -------
71 | # radius : float
72 | # The estimated radius for the fit
73 | # """
74 | # if input_type == 'affinity':
75 | # return None
76 | # elif input_type == 'adjacency':
77 | # return X.max()
78 | # elif input_type == 'data':
79 | # if intrinsic_dim is None:
80 | # intrinsic_dim = self.n_components
81 | # mean_std = np.std(X, axis=0).mean()
82 | # n_features = X.shape[1]
83 | # return 0.5 * mean_std / n_features ** (1. / (intrinsic_dim + 6))
84 | # else:
85 | # raise ValueError("Unrecognized input_type: {0}".format(input_type))
86 |
87 | def fit_geometry(self, X=None, input_type='data'):
88 | """Inputs self.geom, and produces the fitted geometry self.geom_"""
89 | if self.geom is None:
90 | self.geom_ = Geometry()
91 | elif isinstance(self.geom, Geometry):
92 | self.geom_ = self.geom
93 | else:
94 | try:
95 | kwds = dict(**self.geom)
96 | except TypeError:
97 | raise ValueError("geom must be a Geometry instance or "
98 | "a mappable/dictionary")
99 | self.geom_ = Geometry(**kwds)
100 |
101 | if self.radius is not None:
102 | self.geom_.set_radius(self.radius, override=False)
103 |
104 | # if self.radius == 'auto':
105 | # if X is not None and input_type != 'affinity':
106 | # self.geom_.set_radius(self.estimate_radius(X, input_type),
107 | # override=False)
108 | # else:
109 | # self.geom_.set_radius(self.radius,
110 | # override=False)
111 |
112 | if X is not None:
113 | self.geom_.set_matrix(X, input_type)
114 |
115 | return self
116 |
117 | def fit_transform(self, X, y=None, input_type='data'):
118 | """Fit the model from data in X and transform X.
119 |
120 | Parameters
121 | ----------
122 | input_type : string, one of: 'data', 'distance' or 'affinity'.
123 | The values of input data X. (default = 'data')
124 | X: array-like, shape (n_samples, n_features)
125 | Training vector, where n_samples in the number of samples
126 | and n_features is the number of features.
127 |
128 | If self.input_type is 'distance':
129 |
130 | X : array-like, shape (n_samples, n_samples),
131 | Interpret X as precomputed distance or adjacency graph
132 | computed from samples.
133 |
134 | Returns
135 | -------
136 | X_new: array-like, shape (n_samples, n_components)
137 | """
138 | self.fit(X, y=y, input_type=input_type)
139 | return self.embedding_
140 |
141 | def transform(self, X, y=None, input_type='data'):
142 | raise NotImplementedError("transform() not implemented. "
143 | "Try fit_transform()")
144 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/embedding/tests/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/embedding/tests/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/embedding/tests/test_base.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 | from numpy.testing import assert_allclose
5 |
6 | from megaman.utils.testing import assert_raise_message
7 | from megaman.geometry.geometry import Geometry
8 | from megaman.embedding.base import BaseEmbedding
9 |
10 |
11 | def test_geometry_dict():
12 | """ Test passing a dictionary and confirm the output """
13 | geom_dict = dict(adjacency_method = 'auto',
14 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':4},
15 | affinity_method = 'auto',
16 | affinity_kwds = {'radius':4},
17 | laplacian_method = 'geometric',
18 | laplacian_kwds = {'scaling_eps':4})
19 | g1 = Geometry(**geom_dict)
20 | base_embedding = BaseEmbedding(geom=geom_dict).fit_geometry()
21 | assert(g1.__dict__ == base_embedding.geom_.__dict__)
22 |
23 |
24 | def test_geometry_object():
25 | """ Test passing a geometry object and confirm the output """
26 | g1 = Geometry(adjacency_method = 'auto',
27 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':4},
28 | affinity_method = 'auto',
29 | affinity_kwds = {'radius':4},
30 | laplacian_method = 'geometric',
31 | laplacian_kwds = {'scaling_eps':4})
32 | base_embedding = BaseEmbedding(geom=g1).fit_geometry()
33 | assert(g1.__dict__ == base_embedding.geom_.__dict__)
34 |
35 |
36 | def test_geometry_update():
37 | """ Test passing geometry object then independently update a parameter and confirm that the embedding
38 | geometry is also updated """
39 | g1 = Geometry(adjacency_method = 'auto',
40 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':4},
41 | affinity_method = 'auto',
42 | affinity_kwds = {'radius':4},
43 | laplacian_method = 'geometric',
44 | laplacian_kwds = {'scaling_eps':4})
45 | base_embedding = BaseEmbedding(geom=g1)
46 | X = np.random.rand(10, 2)
47 | # Now update g1 -- object that was passed
48 | g1.set_data_matrix(X)
49 | # confirm internal object is updated
50 | assert_allclose(g1.X, base_embedding.geom.X)
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/embedding/tests/test_embeddings.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """General tests for embeddings"""
2 |
3 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
4 |
5 | from itertools import product
6 |
7 | import numpy as np
8 | from numpy.testing import assert_raises, assert_allclose
9 |
10 | from megaman.embedding import (Isomap, LocallyLinearEmbedding,
11 | LTSA, SpectralEmbedding)
12 | from megaman.geometry.geometry import Geometry
13 |
14 | EMBEDDINGS = [Isomap, LocallyLinearEmbedding, LTSA, SpectralEmbedding]
15 |
16 | # # TODO: make estimator_checks pass!
17 | # def test_estimator_checks():
18 | # from sklearn.utils.estimator_checks import check_estimator
19 | # for Embedding in EMBEDDINGS:
20 | # yield check_estimator, Embedding
21 |
22 |
23 | def test_embeddings_fit_vs_transform():
24 | rand = np.random.RandomState(42)
25 | X = rand.rand(100, 5)
26 | geom = Geometry(adjacency_kwds = {'radius':1.0},
27 | affinity_kwds = {'radius':1.0})
28 |
29 | def check_embedding(Embedding, n_components):
30 | model = Embedding(n_components=n_components,
31 | geom=geom, random_state=rand)
32 | embedding = model.fit_transform(X)
33 | assert model.embedding_.shape == (X.shape[0], n_components)
34 | assert_allclose(embedding, model.embedding_)
35 |
36 | for Embedding in EMBEDDINGS:
37 | for n_components in [1, 2, 3]:
38 | yield check_embedding, Embedding, n_components
39 |
40 |
41 | def test_embeddings_bad_arguments():
42 | rand = np.random.RandomState(32)
43 | X = rand.rand(100, 3)
44 |
45 | def check_bad_args(Embedding):
46 | # no radius set
47 | embedding = Embedding()
48 | assert_raises(ValueError, embedding.fit, X)
49 |
50 | # unrecognized geometry
51 | embedding = Embedding(radius=2, geom='blah')
52 | assert_raises(ValueError, embedding.fit, X)
53 |
54 | for Embedding in EMBEDDINGS:
55 | yield check_bad_args, Embedding
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/embedding/tests/test_isomap.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import sys
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import scipy as sp
6 | import scipy.sparse as sparse
7 | from scipy.spatial.distance import squareform, pdist
8 | from itertools import product
9 | from sklearn import manifold, datasets
10 | from sklearn.neighbors import NearestNeighbors
11 |
12 | from numpy.testing import assert_array_almost_equal
13 |
14 | import megaman.embedding.isomap as iso
15 | import megaman.geometry.geometry as geom
16 | from megaman.utils.eigendecomp import EIGEN_SOLVERS
17 |
18 |
19 | def _check_with_col_sign_flipping(A, B, tol=0.0):
20 | """ Check array A and B are equal with possible sign flipping on
21 | each columns"""
22 | sign = True
23 | for column_idx in range(A.shape[1]):
24 | sign = sign and ((((A[:, column_idx] -
25 | B[:, column_idx]) ** 2).mean() <= tol ** 2) or
26 | (((A[:, column_idx] +
27 | B[:, column_idx]) ** 2).mean() <= tol ** 2))
28 | if not sign:
29 | return False
30 | return True
31 |
32 | def test_isomap_with_sklearn():
33 | N = 10
34 | X, color = datasets.samples_generator.make_s_curve(N, random_state=0)
35 | n_components = 2
36 | n_neighbors = 3
37 | knn = NearestNeighbors(n_neighbors + 1).fit(X)
38 | # Assign the geometry matrix to get the same answer since sklearn using k-neighbors instead of radius-neighbors
39 | g = geom.Geometry(X)
40 | g.set_adjacency_matrix(knn.kneighbors_graph(X, mode = 'distance'))
41 | # test Isomap with sklearn
42 | sk_Y_iso = manifold.Isomap(n_neighbors, n_components, eigen_solver = 'arpack').fit_transform(X)
43 | mm_Y_iso = iso.isomap(g, n_components)
44 | assert(_check_with_col_sign_flipping(sk_Y_iso, mm_Y_iso, 0.05))
45 |
46 | def test_isomap_simple_grid():
47 | # Isomap should preserve distances when all neighbors are used
48 | N_per_side = 5
49 | Npts = N_per_side ** 2
50 | radius = 10
51 | # grid of equidistant points in 2D, n_components = n_dim
52 | X = np.array(list(product(range(N_per_side), repeat=2)))
53 | # distances from each point to all others
54 | G = squareform(pdist(X))
55 | g = geom.Geometry(adjacency_kwds = {'radius':radius})
56 | for eigen_solver in EIGEN_SOLVERS:
57 | clf = iso.Isomap(n_components = 2, eigen_solver = eigen_solver, geom=g)
58 | clf.fit(X)
59 | G_iso = squareform(pdist(clf.embedding_))
60 | assert_array_almost_equal(G, G_iso)
61 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/embedding/tests/test_lle.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import sys
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import scipy as sp
6 | import scipy.sparse as sparse
7 | from scipy.spatial.distance import squareform, pdist
8 | from itertools import product
9 | from numpy.testing import assert_array_almost_equal
10 |
11 | from sklearn import manifold, datasets
12 | from sklearn.neighbors import NearestNeighbors
13 |
14 | import megaman.embedding.locally_linear as lle
15 | import megaman.geometry.geometry as geom
16 | from megaman.utils.eigendecomp import EIGEN_SOLVERS
17 |
18 |
19 | def _check_with_col_sign_flipping(A, B, tol=0.0):
20 | """ Check array A and B are equal with possible sign flipping on
21 | each columns"""
22 | sign = True
23 | for column_idx in range(A.shape[1]):
24 | sign = sign and ((((A[:, column_idx] -
25 | B[:, column_idx]) ** 2).mean() <= tol ** 2) or
26 | (((A[:, column_idx] +
27 | B[:, column_idx]) ** 2).mean() <= tol ** 2))
28 | if not sign:
29 | return False
30 | return True
31 |
32 | def test_lle_with_sklearn():
33 | N = 10
34 | X, color = datasets.samples_generator.make_s_curve(N, random_state=0)
35 | n_components = 2
36 | n_neighbors = 3
37 | knn = NearestNeighbors(n_neighbors + 1).fit(X)
38 | G = geom.Geometry()
39 | G.set_data_matrix(X)
40 | G.set_adjacency_matrix(knn.kneighbors_graph(X, mode = 'distance'))
41 | sk_Y_lle = manifold.LocallyLinearEmbedding(n_neighbors, n_components, method = 'standard').fit_transform(X)
42 | (mm_Y_lle, err) = lle.locally_linear_embedding(G, n_components)
43 | assert(_check_with_col_sign_flipping(sk_Y_lle, mm_Y_lle, 0.05))
44 |
45 | def test_barycenter_kneighbors_graph():
46 | X = np.array([[0, 1], [1.01, 1.], [2, 0]])
47 | distance_matrix = squareform(pdist(X))
48 | A = lle.barycenter_graph(distance_matrix, X)
49 | # check that columns sum to one
50 | assert_array_almost_equal(np.sum(A.toarray(), 1), np.ones(3))
51 | pred = np.dot(A.toarray(), X)
52 | assert(np.linalg.norm(pred - X) / X.shape[0] < 1)
53 |
54 | def test_lle_simple_grid():
55 | # note: ARPACK is numerically unstable, so this test will fail for
56 | # some random seeds. We choose 20 because the tests pass.
57 | rng = np.random.RandomState(20)
58 | tol = 0.1
59 | # grid of equidistant points in 2D, n_components = n_dim
60 | X = np.array(list(product(range(5), repeat=2)))
61 | X = X + 1e-10 * rng.uniform(size=X.shape)
62 | n_components = 2
63 | G = geom.Geometry(adjacency_kwds = {'radius':3})
64 | G.set_data_matrix(X)
65 | tol = 0.1
66 | distance_matrix = G.compute_adjacency_matrix()
67 | N = lle.barycenter_graph(distance_matrix, X).todense()
68 | reconstruction_error = np.linalg.norm(np.dot(N, X) - X, 'fro')
69 | assert(reconstruction_error < tol)
70 | for eigen_solver in EIGEN_SOLVERS:
71 | clf = lle.LocallyLinearEmbedding(n_components = n_components, geom = G,
72 | eigen_solver = eigen_solver, random_state = rng)
73 | clf.fit(X)
74 | assert(clf.embedding_.shape[1] == n_components)
75 | reconstruction_error = np.linalg.norm(
76 | np.dot(N, clf.embedding_) - clf.embedding_, 'fro') ** 2
77 | assert(reconstruction_error < tol)
78 |
79 | def test_lle_manifold():
80 | rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
81 | # similar test on a slightly more complex manifold
82 | X = np.array(list(product(np.arange(18), repeat=2)))
83 | X = np.c_[X, X[:, 0] ** 2 / 18]
84 | X = X + 1e-10 * rng.uniform(size=X.shape)
85 | n_components = 2
86 | G = geom.Geometry(adjacency_kwds = {'radius':3})
87 | G.set_data_matrix(X)
88 | distance_matrix = G.compute_adjacency_matrix()
89 | tol = 1.5
90 | N = lle.barycenter_graph(distance_matrix, X).todense()
91 | reconstruction_error = np.linalg.norm(np.dot(N, X) - X)
92 | assert(reconstruction_error < tol)
93 | for eigen_solver in EIGEN_SOLVERS:
94 | clf = lle.LocallyLinearEmbedding(n_components = n_components, geom = G,
95 | eigen_solver = eigen_solver, random_state = rng)
96 | clf.fit(X)
97 | assert(clf.embedding_.shape[1] == n_components)
98 | reconstruction_error = np.linalg.norm(
99 | np.dot(N, clf.embedding_) - clf.embedding_, 'fro') ** 2
100 | assert(reconstruction_error < tol)
101 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/embedding/tests/test_ltsa.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import sys
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import scipy as sp
6 | import scipy.sparse as sparse
7 | from itertools import product
8 |
9 | from sklearn import manifold, datasets
10 | from sklearn.neighbors import NearestNeighbors
11 |
12 | from numpy.testing import assert_array_almost_equal
13 | import megaman.embedding.ltsa as ltsa
14 | from megaman.embedding.locally_linear import barycenter_graph
15 | import megaman.geometry.geometry as geom
16 | from megaman.utils.eigendecomp import EIGEN_SOLVERS
17 |
18 |
19 | def _check_with_col_sign_flipping(A, B, tol=0.0):
20 | """ Check array A and B are equal with possible sign flipping on
21 | each columns"""
22 | sign = True
23 | for column_idx in range(A.shape[1]):
24 | sign = sign and ((((A[:, column_idx] -
25 | B[:, column_idx]) ** 2).mean() <= tol ** 2) or
26 | (((A[:, column_idx] +
27 | B[:, column_idx]) ** 2).mean() <= tol ** 2))
28 | if not sign:
29 | return False
30 | return True
31 |
32 |
33 | def test_ltsa_with_sklearn():
34 | N = 10
35 | X, color = datasets.samples_generator.make_s_curve(N, random_state=0)
36 | n_components = 2
37 | n_neighbors = 3
38 | knn = NearestNeighbors(n_neighbors + 1).fit(X)
39 | G = geom.Geometry()
40 | G.set_data_matrix(X)
41 | G.set_adjacency_matrix(knn.kneighbors_graph(X, mode = 'distance'))
42 | sk_Y_ltsa = manifold.LocallyLinearEmbedding(n_neighbors, n_components,
43 | method = 'ltsa',
44 | eigen_solver = 'arpack').fit_transform(X)
45 | (mm_Y_ltsa, err) = ltsa.ltsa(G, n_components, eigen_solver = 'arpack')
46 | assert(_check_with_col_sign_flipping(sk_Y_ltsa, mm_Y_ltsa, 0.05))
47 |
48 |
49 | def test_ltsa_eigendecomps():
50 | N = 10
51 | X, color = datasets.samples_generator.make_s_curve(N, random_state=0)
52 | n_components = 2
53 | G = geom.Geometry(adjacency_method = 'brute', adjacency_kwds = {'radius':2})
54 | G.set_data_matrix(X)
55 | mm_ltsa_ref, err_ref = ltsa.ltsa(G, n_components,
56 | eigen_solver=EIGEN_SOLVERS[0])
57 | for eigen_solver in EIGEN_SOLVERS[1:]:
58 | mm_ltsa, err = ltsa.ltsa(G, n_components, eigen_solver=eigen_solver)
59 | assert(_check_with_col_sign_flipping(mm_ltsa, mm_ltsa_ref, 0.05))
60 |
61 |
62 | def test_ltsa_manifold():
63 | rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
64 | # similar test on a slightly more complex manifold
65 | X = np.array(list(product(np.arange(18), repeat=2)))
66 | X = np.c_[X, X[:, 0] ** 2 / 18]
67 | X = X + 1e-10 * rng.uniform(size=X.shape)
68 | n_components = 2
69 | G = geom.Geometry(adjacency_kwds = {'radius':3})
70 | G.set_data_matrix(X)
71 | distance_matrix = G.compute_adjacency_matrix()
72 | tol = 1.5
73 | N = barycenter_graph(distance_matrix, X).todense()
74 | reconstruction_error = np.linalg.norm(np.dot(N, X) - X)
75 | assert(reconstruction_error < tol)
76 | for eigen_solver in EIGEN_SOLVERS:
77 | clf = ltsa.LTSA(n_components = n_components, geom = G,
78 | eigen_solver = eigen_solver, random_state = rng)
79 | clf.fit(X)
80 | assert(clf.embedding_.shape[1] == n_components)
81 | reconstruction_error = np.linalg.norm(
82 | np.dot(N, clf.embedding_) - clf.embedding_, 'fro') ** 2
83 | assert(reconstruction_error < tol)
84 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | from .rmetric import RiemannMetric
4 | from .geometry import Geometry
5 | from .adjacency import Adjacency, compute_adjacency_matrix, adjacency_methods
6 | from .affinity import Affinity, compute_affinity_matrix, affinity_methods
7 | from .laplacian import Laplacian, compute_laplacian_matrix, laplacian_methods
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/affinity.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | from __future__ import division
4 | import numpy as np
5 | from scipy.sparse import isspmatrix
6 | from sklearn.utils.validation import check_array
7 |
8 | from .utils import RegisterSubclasses
9 |
10 |
11 | def compute_affinity_matrix(adjacency_matrix, method='auto', **kwargs):
12 | """Compute the affinity matrix with the given method"""
13 | if method == 'auto':
14 | method = 'gaussian'
15 | return Affinity.init(method, **kwargs).affinity_matrix(adjacency_matrix)
16 |
17 |
18 | def affinity_methods():
19 | """Return the list of valid affinity methods"""
20 | return ['auto'] + list(Affinity.methods())
21 |
22 |
23 | class Affinity(RegisterSubclasses):
24 | """Base class for computing affinity matrices"""
25 | def __init__(self, radius=None, symmetrize=True):
26 | if radius is None:
27 | raise ValueError("must specify radius for affinity matrix")
28 | self.radius = radius
29 | self.symmetrize = symmetrize
30 |
31 | def affinity_matrix(self, adjacency_matrix):
32 | raise NotImplementedError()
33 |
34 |
35 | class GaussianAffinity(Affinity):
36 | name = "gaussian"
37 |
38 | @staticmethod
39 | def _symmetrize(A):
40 | # TODO: make this more efficient?
41 | # Also, need to maintain explicit zeros!
42 | return 0.5 * (A + A.T)
43 |
44 | def affinity_matrix(self, adjacency_matrix):
45 | A = check_array(adjacency_matrix, dtype=float, copy=True,
46 | accept_sparse=['csr', 'csc', 'coo'])
47 |
48 | if isspmatrix(A):
49 | data = A.data
50 | else:
51 | data = A
52 |
53 | # in-place computation of
54 | # data = np.exp(-(data / radius) ** 2)
55 | data **= 2
56 | data /= -self.radius ** 2
57 | np.exp(data, out=data)
58 |
59 | if self.symmetrize:
60 | A = self._symmetrize(A)
61 |
62 | # for sparse, need a true zero on the diagonal
63 | # TODO: make this more efficient?
64 | if isspmatrix(A):
65 | A.setdiag(1)
66 |
67 | return A
68 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/complete_adjacency_matrix.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 | from .adjacency import CyFLANNAdjacency, compute_adjacency_matrix
3 | from scipy.sparse import vstack, hstack
4 |
5 | def complete_adjacency_matrix(Dtrain, Xtrain, Xtest, adjacency_kwds):
6 | if 'cyflann_kwds' in adjacency_kwds.keys():
7 | cyflann_kwds = adjacency_kwds['cyflann_kwds']
8 | else:
9 | cyflann_kwds = {}
10 | radius = adjacency_kwds['radius']
11 | Cyflann = CyFLANNAdjacency(radius=radius, **cyflann_kwds)
12 | train_index = Cyflann.build_index(Xtrain)
13 | test_train_adjacency = train_index.radius_neighbors_graph(Xtest, radius)
14 | test_test_adjacency = compute_adjacency_matrix(Xtest, method='cyflann', **adjacency_kwds)
15 | train_adjacency = hstack([Dtrain, test_train_adjacency.transpose()])
16 | test_adjacency = hstack([test_train_adjacency, test_test_adjacency])
17 | return vstack([train_adjacency, test_adjacency])
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/cyflann/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/geometry/cyflann/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/cyflann/cyflann_index.cc:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /* Authors: Zhongyue Zhang
2 |
3 | LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
4 | ================================================= */
5 |
6 | #include "cyflann_index.h"
7 |
8 | CyflannIndex::CyflannIndex(const std::vector& dataset, int num_dims) {
9 | int num_pts = dataset.size() / num_dims;
10 | dataset_ = new float[dataset.size()];
11 | std::copy(dataset.begin(), dataset.end(), dataset_);
12 | Matrix data(dataset_, num_pts, num_dims);
13 | // TODO: add support for different distance metric.
14 | index_ = new Index< L2 >(data, KMeansIndexParams());
15 | }
16 |
17 | CyflannIndex::CyflannIndex(const std::vector& dataset, int num_dims,
18 | std::string index_type, int num_trees, int branching, int iterations,
19 | float cb_index) {
20 | int num_pts = dataset.size() / num_dims;
21 | dataset_ = new float[dataset.size()];
22 | std::copy(dataset.begin(), dataset.end(), dataset_);
23 | Matrix data(dataset_, num_pts, num_dims);
24 | // TODO: wrap all info into a class in the future.
25 | if (index_type == "kdtrees") {
26 | index_ = new Index< L2 >(data, KDTreeIndexParams(num_trees));
27 | } else if (index_type == "kmeans") {
28 | index_ = new Index< L2 >(data, KMeansIndexParams(branching,
29 | iterations, FLANN_CENTERS_RANDOM, cb_index));
30 | } else {
31 | index_ = new Index< L2 >(data, CompositeIndexParams(num_trees,
32 | branching, iterations, FLANN_CENTERS_RANDOM, cb_index));
33 | }
34 | }
35 |
36 | CyflannIndex::CyflannIndex(const std::vector& dataset, int num_dims,
37 | float target_precision, float build_weight, float memory_weight,
38 | float sample_fraction) {
39 | int num_pts = dataset.size() / num_dims;
40 | dataset_ = new float[dataset.size()];
41 | std::copy(dataset.begin(), dataset.end(), dataset_);
42 | Matrix data(dataset_, num_pts, num_dims);
43 | // TODO: add support for different distance metric.
44 | index_ = new Index< L2 >(data, AutotunedIndexParams(
45 | target_precision, build_weight, memory_weight, sample_fraction));
46 | }
47 |
48 | CyflannIndex::CyflannIndex(const std::vector& dataset, int num_dims,
49 | std::string filename) {
50 | int num_pts = dataset.size() / num_dims;
51 | dataset_ = new float[dataset.size()];
52 | std::copy(dataset.begin(), dataset.end(), dataset_);
53 | Matrix data(dataset_, num_pts, num_dims);
54 | // TODO: add support for different distance metric.
55 | index_ = new Index< L2 >(data, SavedIndexParams(filename));
56 | }
57 |
58 | CyflannIndex::~CyflannIndex() {
59 | delete index_;
60 | delete[] dataset_;
61 | }
62 |
63 | void CyflannIndex::buildIndex(){
64 | index_->buildIndex();
65 | }
66 |
67 | int CyflannIndex::knnSearch(const std::vector& queries,
68 | std::vector< std::vector >& indices,
69 | std::vector< std::vector >& dists,
70 | int knn, int num_dims, int num_checks) {
71 | int num_pts = queries.size() / num_dims;
72 | float* array = new float[queries.size()];
73 | std::copy(queries.begin(), queries.end(), array);
74 | Matrix qpts(array, num_pts, num_dims);
75 | int res = index_->knnSearch(qpts, indices, dists, knn,
76 | SearchParams(num_checks));
77 | delete[] array;
78 | return res;
79 | }
80 |
81 | int CyflannIndex::radiusSearch(const std::vector& queries,
82 | std::vector< std::vector >& indices,
83 | std::vector< std::vector >& dists,
84 | float radius, int num_dims, int num_checks) {
85 | int num_pts = queries.size() / num_dims;
86 | float* array = new float[queries.size()];
87 | std::copy(queries.begin(), queries.end(), array);
88 | Matrix dataset(array, num_pts, num_dims);
89 | int res = index_->radiusSearch(dataset, indices, dists, radius,
90 | SearchParams(num_checks));
91 | delete[] array;
92 | return res;
93 | }
94 |
95 | void CyflannIndex::save(std::string filename) {
96 | index_->save(filename);
97 | }
98 |
99 | int CyflannIndex::veclen() { return index_->veclen(); }
100 |
101 | int CyflannIndex::size() { return index_->size(); }
102 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/cyflann/cyflann_index.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /* Authors: Zhongyue Zhang
2 |
3 | LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
4 | ================================================= */
5 | #ifndef CYFLANN_INDEX_H_
6 | #define CYFLANN_INDEX_H_
7 |
8 | #include
9 | #include
10 | using namespace flann;
11 |
12 | class CyflannIndex {
13 | public:
14 |
15 | CyflannIndex(const std::vector& dataset, int num_dims);
16 |
17 | CyflannIndex(const std::vector& dataset, int num_dims,
18 | std::string index_type, int num_trees, int branching, int iterations,
19 | float cb_index);
20 |
21 | CyflannIndex(const std::vector& dataset, int num_dims,
22 | float target_precision, float build_weight, float memory_weight,
23 | float sample_fraction);
24 |
25 | CyflannIndex(const std::vector& dataset, int num_dims,
26 | std::string filename);
27 |
28 | ~CyflannIndex();
29 |
30 | void buildIndex();
31 |
32 | int knnSearch(const std::vector& queries,
33 | std::vector< std::vector >& indices,
34 | std::vector< std::vector >& dists,
35 | int knn, int num_dims, int num_checks);
36 |
37 | int radiusSearch(const std::vector& queries,
38 | std::vector< std::vector >& indices,
39 | std::vector< std::vector >& dists,
40 | float radius, int num_dims, int num_checks);
41 |
42 | void save(std::string filename);
43 |
44 | int veclen();
45 |
46 | int size();
47 |
48 | private:
49 | float* dataset_;
50 | Index< L2 >* index_;
51 | };
52 |
53 | // Takes a flattened matrix queries, with dimension num_dims.
54 | // For each data point in queries, search for neighbors within the radius.
55 | int radiusSearch(const std::vector& queries,
56 | std::vector< std::vector >& indices,
57 | std::vector< std::vector >& dists,
58 | float radius, int num_dims);
59 |
60 | #endif // CYFLANN_INDEX_H_
61 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/cyflann/index.pxd:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Authors: Zhongyue Zhang
2 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
3 |
4 | from __future__ import division
5 | import cython
6 | import numpy as np
7 | cimport numpy as np
8 | from libcpp.vector cimport vector
9 | from libcpp.string cimport string
10 |
11 | ctypedef np.float32_t dtype_t
12 | ctypedef np.int32_t dtypei_t
13 |
14 | cdef extern from "cyflann_index.h":
15 | cdef cppclass CyflannIndex:
16 | CyflannIndex(const vector[dtype_t]& dataset, dtypei_t ndim) except +
17 | CyflannIndex(const vector[dtype_t]& dataset, dtypei_t num_dims,
18 | string index_type, dtypei_t num_trees, dtypei_t branching,
19 | dtypei_t iterations, dtype_t cb_index)
20 | CyflannIndex(const vector[dtype_t]& dataset, dtypei_t ndim,
21 | dtype_t target_precision, dtype_t build_weight,
22 | dtype_t memory_weight, dtype_t sample_fraction)
23 | CyflannIndex(const vector[dtype_t]& dataset, dtypei_t ndim,
24 | string filename)
25 | void buildIndex()
26 | int knnSearch(const vector[dtype_t]& queries,
27 | vector[vector[dtypei_t]]& indices,
28 | vector[vector[dtype_t]]& dists,
29 | dtypei_t knn, dtypei_t num_dims, dtypei_t num_checks)
30 | int radiusSearch(const vector[dtype_t]& queries,
31 | vector[vector[dtypei_t]]& indices,
32 | vector[vector[dtype_t]]& dists,
33 | dtype_t radius, dtypei_t num_dims, dtypei_t num_checks)
34 | void save(string filename)
35 | int veclen()
36 | int size()
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/cyflann/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import os
4 | import sys
5 | import platform
6 |
7 | FLANN_ROOT = os.environ.get('FLANN_ROOT', sys.exec_prefix)
8 | CONDA_BUILD = os.environ.get('CONDA_BUILD', 0)
9 |
10 | def configuration(parent_package='', top_path=None):
11 | import numpy
12 | from numpy.distutils.misc_util import Configuration
13 |
14 | config = Configuration('geometry/cyflann', parent_package, top_path)
15 | libraries = ['flann', 'flann_cpp']
16 | if os.name == 'posix':
17 | libraries.append('m')
18 |
19 | kwds = {}
20 | flann_include = os.path.join(FLANN_ROOT, 'include')
21 | flann_lib = os.path.join(FLANN_ROOT, 'lib')
22 |
23 | if CONDA_BUILD:
24 | # conda uses relative dynamic library paths
25 | pass
26 | else:
27 | # direct installations use absolute library paths
28 | print("Compiling FLANN with FLANN_ROOT={0}".format(FLANN_ROOT))
29 |
30 | # from http://stackoverflow.com/questions/19123623/python-runtime-library-dirs-doesnt-work-on-mac
31 | if platform.system() == 'Darwin':
32 | kwds['extra_link_args'] = ['-Wl,-rpath,'+flann_lib]
33 | kwds['runtime_library_dirs'] = [flann_lib]
34 |
35 | config.add_extension("index",
36 | sources=["index.cxx", "cyflann_index.cc"],
37 | include_dirs=[numpy.get_include(), flann_include],
38 | libraries=libraries,
39 | library_dirs=[flann_lib],
40 | extra_compile_args=["-O3"],
41 | **kwds)
42 |
43 | return config
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/tests/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/geometry/tests/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/tests/test_adjacency.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | from nose import SkipTest
4 |
5 | import numpy as np
6 | from numpy.testing import assert_allclose, assert_raises, assert_equal
7 | from scipy.sparse import isspmatrix
8 | from scipy.spatial.distance import cdist, pdist, squareform
9 |
10 | from megaman.geometry import (Geometry, compute_adjacency_matrix, Adjacency,
11 | adjacency_methods)
12 |
13 |
14 | try:
15 | import pyflann as pyf
16 | NO_PYFLANN = False
17 | except ImportError:
18 | NO_PYFLANN = True
19 |
20 |
21 | def test_adjacency_methods():
22 | assert_equal(set(adjacency_methods()),
23 | {'auto', 'pyflann', 'ball_tree',
24 | 'cyflann', 'brute', 'kd_tree'})
25 |
26 |
27 | def test_adjacency_input_validation():
28 | X = np.random.rand(20, 3)
29 | # need to specify radius or n_neighbors
30 | assert_raises(ValueError, compute_adjacency_matrix, X)
31 | # cannot specify both radius and n_neighbors
32 | assert_raises(ValueError, compute_adjacency_matrix, X,
33 | radius=1, n_neighbors=10)
34 |
35 |
36 | def test_adjacency():
37 | rng = np.random.RandomState(36)
38 | X = rng.rand(100, 3)
39 | Gtrue = {}
40 |
41 | exact_methods = [m for m in Adjacency.methods()
42 | if not m.endswith('flann')]
43 |
44 | def check_kneighbors(n_neighbors, method):
45 | if method == 'pyflann' and NO_PYFLANN:
46 | raise SkipTest("pyflann not installed")
47 |
48 | G = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, method=method,
49 | n_neighbors=n_neighbors)
50 | assert isspmatrix(G)
51 | assert G.shape == (X.shape[0], X.shape[0])
52 | if method in exact_methods:
53 | assert_allclose(G.toarray(), Gtrue[n_neighbors].toarray())
54 |
55 | def check_radius(radius, method):
56 | if method == 'pyflann' and NO_PYFLANN:
57 | raise SkipTest("pyflann not installed")
58 |
59 | G = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, method=method,
60 | radius=radius)
61 | assert isspmatrix(G)
62 | assert G.shape == (X.shape[0], X.shape[0])
63 | if method in exact_methods:
64 | assert_allclose(G.toarray(), Gtrue[radius].toarray())
65 |
66 | for n_neighbors in [5, 10, 15]:
67 | Gtrue[n_neighbors] = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, method='brute',
68 | n_neighbors=n_neighbors)
69 | for method in Adjacency.methods():
70 | yield check_kneighbors, n_neighbors, method
71 |
72 | for radius in [0.1, 0.5, 1.0]:
73 | Gtrue[radius] = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, method='brute',
74 | radius=radius)
75 | for method in Adjacency.methods():
76 | yield check_radius, radius, method
77 |
78 |
79 | def test_unknown_method():
80 | X = np.arange(20).reshape((10, 2))
81 | assert_raises(ValueError, compute_adjacency_matrix, X, 'foo')
82 |
83 |
84 | def test_all_methods_close():
85 | rand = np.random.RandomState(36)
86 | X = rand.randn(10, 2)
87 | D_true = squareform(pdist(X))
88 | D_true[D_true > 0.5] = 0
89 |
90 | def check_method(method):
91 | kwargs = {}
92 | if method == 'pyflann':
93 | try:
94 | import pyflann as pyf
95 | except ImportError:
96 | raise SkipTest("pyflann not installed.")
97 | flindex = pyf.FLANN()
98 | flindex.build_index(X, algorithm='kmeans',
99 | target_precision=0.9)
100 | kwargs['flann_index'] = flindex
101 | this_D = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, method=method, radius=0.5,
102 | **kwargs)
103 | assert_allclose(this_D.toarray(), D_true, rtol=1E-5)
104 |
105 | for method in ['auto', 'cyflann', 'pyflann', 'brute']:
106 | yield check_method, method
107 |
108 |
109 | def test_custom_adjacency():
110 | class CustomAdjacency(Adjacency):
111 | name = "custom"
112 | def adjacency_graph(self, X):
113 | return squareform(pdist(X))
114 |
115 | rand = np.random.RandomState(42)
116 | X = rand.rand(10, 2)
117 | D = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, method='custom', radius=1)
118 | assert_allclose(D, cdist(X, X))
119 |
120 | Adjacency._remove_from_registry("custom")
121 |
122 | def test_cyflann_index_type():
123 | rand = np.random.RandomState(36)
124 | X = rand.randn(10, 2)
125 | D_true = squareform(pdist(X))
126 | D_true[D_true > 1.5] = 0
127 |
128 | def check_index_type(index_type):
129 | method = 'cyflann'
130 | radius = 1.5
131 | cyflann_kwds = {'index_type':index_type}
132 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':radius, 'cyflann_kwds':cyflann_kwds}
133 | this_D = compute_adjacency_matrix(X=X, method = 'cyflann', **adjacency_kwds)
134 | assert_allclose(this_D.toarray(), D_true, rtol=1E-5, atol=1E-5)
135 |
136 | for index_type in ['kmeans', 'kdtrees']:
137 | yield check_index_type, index_type
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/tests/test_affinity.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | from __future__ import division ## removes integer division
4 |
5 | import os
6 |
7 | import numpy as np
8 | from numpy.testing import assert_allclose, assert_equal, assert_raises
9 |
10 | from scipy.spatial.distance import cdist, pdist, squareform
11 | from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
12 | from scipy import io
13 |
14 | from megaman.geometry import (compute_adjacency_matrix,
15 | compute_affinity_matrix, Affinity,
16 | affinity_methods)
17 |
18 | random_state = np.random.RandomState(36)
19 | n_sample = 10
20 | d = 2
21 | X = random_state.randn(n_sample, d)
22 | D = squareform(pdist(X))
23 | D[D > 1/d] = 0
24 |
25 |
26 | TEST_DATA = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__),
27 | 'testmegaman_laplacian_rad0_2_lam1_5_n200.mat')
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 | def test_affinity_methods():
32 | assert_equal(set(affinity_methods()), {'auto', 'gaussian'})
33 |
34 |
35 | def test_affinity_input_validation():
36 | X = np.random.rand(20, 3)
37 | D = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, radius=1)
38 | assert_raises(ValueError, compute_affinity_matrix, X)
39 |
40 |
41 | def test_affinity_sparse_vs_dense():
42 | """
43 | Test that A_sparse is the same as A_dense for a small A matrix
44 | """
45 | rad = 2.
46 | n_samples = 6
47 | X = np.arange(n_samples)
48 | X = X[ :,np.newaxis]
49 | X = np.concatenate((X,np.zeros((n_samples,1),dtype=float)),axis=1)
50 | X = np.asarray( X, order="C" )
51 | test_dist_matrix = compute_adjacency_matrix( X, method = 'auto', radius = rad )
52 | A_dense = compute_affinity_matrix(test_dist_matrix.toarray(), method = 'auto',
53 | radius = rad, symmetrize = False )
54 | A_sparse = compute_affinity_matrix(csr_matrix(test_dist_matrix),
55 | method = 'auto', radius = rad, symmetrize = False)
56 | A_spdense = A_sparse.toarray()
57 | A_spdense[ A_spdense == 0 ] = 1.
58 | assert_allclose(A_dense, A_spdense)
59 |
60 |
61 | def test_affinity_vs_matlab():
62 | """Test that the affinity calculation matches the matlab result"""
63 | matlab = io.loadmat(TEST_DATA)
64 |
65 | D = np.sqrt(matlab['S']) # matlab outputs squared distances
66 | A_matlab = matlab['A']
67 | radius = matlab['rad'][0]
68 |
69 | # check dense affinity computation
70 | A_dense = compute_affinity_matrix(D, radius=radius)
71 | assert_allclose(A_dense, A_matlab)
72 |
73 | # check sparse affinity computation
74 | A_sparse = compute_affinity_matrix(csr_matrix(D), radius=radius)
75 | assert_allclose(A_sparse.toarray(), A_matlab)
76 |
77 |
78 | def test_affinity():
79 | rand = np.random.RandomState(42)
80 | X = np.random.rand(20, 3)
81 | D = cdist(X, X)
82 |
83 | def check_affinity(adjacency_radius, affinity_radius, symmetrize):
84 | adj = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, radius=adjacency_radius)
85 | aff = compute_affinity_matrix(adj, radius=affinity_radius,
86 | symmetrize=True)
87 |
88 | A = np.exp(-(D / affinity_radius) ** 2)
89 | A[D > adjacency_radius] = 0
90 | assert_allclose(aff.toarray(), A)
91 |
92 | for adjacency_radius in [0.5, 1.0, 5.0]:
93 | for affinity_radius in [0.1, 0.5, 1.0]:
94 | for symmetrize in [True, False]:
95 | yield (check_affinity, adjacency_radius,
96 | affinity_radius, symmetrize)
97 |
98 |
99 | def test_custom_affinity():
100 | class CustomAffinity(Affinity):
101 | name = "custom"
102 | def affinity_matrix(self, adjacency_matrix):
103 | return np.exp(-abs(adjacency_matrix.toarray()))
104 |
105 | rand = np.random.RandomState(42)
106 | X = rand.rand(10, 2)
107 | D = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, radius=10)
108 | A = compute_affinity_matrix(D, method='custom', radius=1)
109 | assert_allclose(A, np.exp(-abs(D.toarray())))
110 |
111 | Affinity._remove_from_registry("custom")
112 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/tests/test_complete_adjacency_matrix.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from scipy.spatial.distance import cdist, pdist, squareform
2 | from megaman.geometry.adjacency import compute_adjacency_matrix
3 | from megaman.geometry.complete_adjacency_matrix import complete_adjacency_matrix
4 | import numpy as np
5 | from numpy.testing import assert_allclose
6 |
7 | def test_complete_adjacency():
8 | rand = np.random.RandomState(36)
9 | radius = 1.5
10 | X = rand.randn(10, 2)
11 | Xtest = rand.randn(4, 2)
12 |
13 | Xtotal = np.vstack([X, Xtest])
14 | D_true = squareform(pdist(Xtotal))
15 | D_true[D_true > radius] = 0
16 |
17 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':radius}
18 | Dtrain = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, method='cyflann', radius = radius)
19 | this_D = complete_adjacency_matrix(Dtrain, X, Xtest, adjacency_kwds)
20 |
21 | assert_allclose(this_D.toarray(), D_true, rtol=1E-4)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/tests/test_laplacian.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | % generates the test data used by test_laplacian.py
2 | % LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
3 | %
4 |
5 | %addpath /mnt/costila/speclust/code-dominique-rmetric/
6 | addpath /mnt/costila/mmp/research/spectral/dominique-epsilon/EpsilonDemo/
7 |
8 | outfroot = 'testmegaman_laplacian'
9 | rad = 0.2;
10 | renormlam = 1.5; % renormalization exponent
11 | opts.lam = renormlam;
12 | n = 200;
13 | seed = 36;
14 | rand( 'seed', seed );
15 | xx1 = rand( 1, n );
16 | xx2 = rand( 1, n );
17 | xx3 = sin( 2*pi*xx1).*sqrt(xx2);
18 |
19 | xx = [ xx1; xx2; xx3 ];
20 |
21 | epps = rad*rad;
22 | [ A, S ] = similarity( xx', epps );
23 | norms = {'geometric', 'unormalized', 'randomwalk', 'symmetricnormalized', 'renormalized' };
24 | names = {'geom', 'unnorm', 'rw', 'symnorm', 'reno1_5' };
25 |
26 | for ii = 1:length( norms );
27 | disp( norms{ ii } )
28 | opts.lapType = norms{ ii };
29 | [ L, phi, lam, flag ] = laplacian( A, 2, epps, opts );
30 | eval( [ 'L' names{ ii } '=L;']);
31 | eval( [ 'phi' names{ ii } '=phi;']);
32 | eval( [ 'lam' names{ ii } '=lam;']);
33 | end;
34 |
35 | [G, VV, LL, Ginv ] = rmetric( Lgeom, phigeom, 2, 0 );
36 |
37 | rad
38 | num2str_(rad)
39 | renormlam
40 | num2str_(renormlam)
41 | outfname = [ outfroot '_rad' num2str_(rad) '_lam' num2str_(renormlam) '_n' num2str( n ) '.mat' ]
42 |
43 | save( outfname )
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/tests/test_laplacian.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import os
4 |
5 | import numpy as np
6 | from numpy.testing import assert_allclose, assert_equal, assert_raises
7 |
8 | from scipy.sparse import isspmatrix, csr_matrix
9 | from scipy import io
10 |
11 | from megaman.geometry import (compute_adjacency_matrix,
12 | compute_affinity_matrix,
13 | Laplacian, compute_laplacian_matrix,
14 | laplacian_methods)
15 |
16 |
17 | TEST_DATA = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__),
18 | 'testmegaman_laplacian_rad0_2_lam1_5_n200.mat')
19 |
20 |
21 | def test_laplacian_methods():
22 | assert_equal(set(laplacian_methods()),
23 | {'auto', 'renormalized', 'symmetricnormalized',
24 | 'geometric', 'randomwalk', 'unnormalized'})
25 |
26 |
27 | def test_laplacian_vs_matlab():
28 | # Test that the laplacian calculation matches the matlab result
29 | matlab = io.loadmat(TEST_DATA)
30 |
31 | laplacians = {'unnormalized': matlab['Lunnorm'],
32 | 'symmetricnormalized': matlab['Lsymnorm'],
33 | 'geometric': matlab['Lgeom'],
34 | 'randomwalk': matlab['Lrw'],
35 | 'renormalized': matlab['Lreno1_5']}
36 |
37 | radius = matlab['rad'][0]
38 |
39 | def check_laplacian(input_type, laplacian_method):
40 | kwargs = {'scaling_epps': radius}
41 | if laplacian_method == 'renormalized':
42 | kwargs['renormalization_exponent'] = 1.5
43 | adjacency = input_type(np.sqrt(matlab['S']))
44 | affinity = compute_affinity_matrix(adjacency, radius=radius)
45 | laplacian = compute_laplacian_matrix(affinity,
46 | method=laplacian_method,
47 | **kwargs)
48 | if input_type is csr_matrix:
49 | laplacian = laplacian.toarray()
50 | assert_allclose(laplacian, laplacians[laplacian_method])
51 |
52 | for input_type in [np.array, csr_matrix]:
53 | for laplacian_method in laplacians:
54 | yield check_laplacian, input_type, laplacian_method
55 |
56 |
57 | def test_laplacian_smoketest():
58 | rand = np.random.RandomState(42)
59 | X = rand.rand(20, 2)
60 | adj = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, radius=0.5)
61 | aff = compute_affinity_matrix(adj, radius=0.1)
62 |
63 | def check_laplacian(method):
64 | lap = compute_laplacian_matrix(aff, method=method)
65 |
66 | assert isspmatrix(lap)
67 | assert_equal(lap.shape, (X.shape[0], X.shape[0]))
68 |
69 | for method in Laplacian.asymmetric_methods():
70 | yield check_laplacian, method
71 |
72 |
73 | def test_laplacian_unknown_method():
74 | """Test that laplacian fails with an unknown method type"""
75 | A = np.array([[ 5, 2, 1 ], [ 2, 3, 2 ],[1,2,5]])
76 | assert_raises(ValueError, compute_laplacian_matrix, A, method='')
77 |
78 |
79 | def test_laplacian_full_output():
80 | # Test that full_output symmetrized laplacians have the right form
81 | rand = np.random.RandomState(42)
82 | X = rand.rand(20, 2)
83 |
84 | def check_symmetric(method, adjacency_radius, affinity_radius):
85 | adj = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, radius=adjacency_radius)
86 | aff = compute_affinity_matrix(adj, radius=affinity_radius)
87 | lap, lapsym, w = compute_laplacian_matrix(aff, method=method,
88 | full_output=True)
89 |
90 | sym = w[:, np.newaxis] * (lap.toarray() + np.eye(*lap.shape))
91 |
92 | assert_allclose(lapsym.toarray(), sym)
93 |
94 | for method in Laplacian.asymmetric_methods():
95 | for adjacency_radius in [0.5, 1.0]:
96 | for affinity_radius in [0.1, 0.3]:
97 | yield check_symmetric, method, adjacency_radius, affinity_radius
98 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/tests/test_rmetric.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import os
4 |
5 | from nose.tools import assert_true
6 | from nose.tools import assert_equal
7 | import scipy.io
8 | from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
9 | from scipy.sparse import csc_matrix
10 | from scipy.sparse import isspmatrix
11 | import numpy as np
12 | from numpy.testing import assert_array_almost_equal, assert_array_equal, assert_allclose
13 |
14 | from nose.tools import assert_raises
15 | from nose.plugins.skip import SkipTest
16 |
17 | from megaman.geometry.rmetric import *
18 | from megaman.embedding.spectral_embedding import _graph_is_connected
19 |
20 | TEST_DATA = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__),
21 | 'testmegaman_laplacian_rad0_2_lam1_5_n200.mat')
22 |
23 | def _load_test_data():
24 | """ Loads a .mat file from . and extract the following dense matrices
25 | test_dist_matrix = matrix of distances
26 | L = the geometric Laplacian
27 | Ginv = the dual Riemann metric [n,2,2] array
28 | G = the Riemann metric [n,2,2] array
29 | phi = embedding in 2 dimensions [n, 2] array
30 | rad = scalar, radius used in affinity calculations, Laplacians
31 | Note: rad is returned as an array of dimension 1. Outside one must
32 | make it a scalar by rad = rad[0]
33 |
34 | """
35 | xdict = scipy.io.loadmat(TEST_DATA)
36 | rad = xdict[ 'rad' ]
37 | test_dist_matrix = xdict[ 'S' ] # S contains squared distances
38 | test_dist_matrix = np.sqrt( test_dist_matrix ) #unused
39 | A = xdict[ 'A' ] #unused
40 | L = xdict[ 'Lgeom' ]
41 | G = xdict[ 'G' ]
42 | H = xdict[ 'Ginv' ]
43 | H = np.transpose( H, ( 2, 0, 1 ))
44 | G = np.transpose( G, ( 2, 0, 1 ))
45 | phi = xdict[ 'phigeom' ]
46 |
47 | print( 'phi.shape = ', phi.shape )
48 | print( 'G.shape = ', G.shape )
49 | print( 'H.shape = ', H.shape )
50 | print( 'L.shape = ', L.shape )
51 | return rad, L, G, H, phi
52 |
53 | def test_equal_original(almost_equal_decimals = 5):
54 | """ Loads the results from a matlab run and checks that our results
55 | are the same. The results loaded are the Laplacian, embedding phi,
56 | Riemannian metric G[2,2,200], and dual Riemannian metric H[2,2,200]
57 |
58 | Currently, this tests the riemann_metric() function only.
59 | TODO: to test the class RiemannMetric
60 |
61 | Only riemann_metric with given L is tested. For other inputs, to test
62 | later after the structure of the code is stabilized. (I.e I may remove
63 | the computation of the L to another function.
64 | """
65 | rad, L, Gtest, Htest, phi = _load_test_data()
66 |
67 | H = riemann_metric( phi, laplacian = L, n_dim = 2, invert_h = False )[0]
68 | n = phi.shape[ 0 ]
69 | assert_array_almost_equal( Htest, H, almost_equal_decimals )
70 |
71 | # To prevent the accumulation of small numerical errors, change the
72 | # generation process of G from invert H to invertion of Htest
73 | G = compute_G_from_H(Htest)[0]
74 | tol = np.mean( Gtest[:,0,0])*10**(-almost_equal_decimals )
75 | assert_allclose( Gtest, G, tol)
76 | # assert_array_max_ulp( Gtest, G, almost_equal_decimals )
77 | # this assertion fails because Gtest is generally asymmetric. G is
78 | # mostly symmetric but not always. I suspect this is due to the
79 | # numerical errors, as many of these 2x2 matrices are very poorly
80 | # conditioned. What to do? Perhaps generate another matlab test set
81 | # with better condition numbers...
82 |
83 | def test_lazy_rmetric(almost_equal_decimals=5):
84 | """ Load results from matlab and check lazy rmetric gets the
85 | same value as the full rmetric on a subset
86 | """
87 | rad, L, Gtest, Htest, phi = _load_test_data()
88 | n = phi.shape[0]
89 | sample = np.random.choice(range(n), min(50, n), replace=False)
90 | H = riemann_metric(phi, laplacian = L, n_dim = 2)[0]
91 | Hlazy = riemann_metric_lazy(phi, sample=sample, laplacian=L, n_dim=2)[0]
92 | assert_array_almost_equal( Hlazy, H[sample, :,:], almost_equal_decimals)
93 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/tests/testmegaman_laplacian_rad0_2_lam1_5_n200.mat:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/geometry/tests/testmegaman_laplacian_rad0_2_lam1_5_n200.mat
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | __all__ = ["RegisterSubclasses"]
4 |
5 |
6 | # From six.py
7 | def with_metaclass(meta, *bases):
8 | """Create a base class with a metaclass."""
9 | # Use a dummy metaclass that replaces itself with the actual metaclass.
10 | class metaclass(type):
11 | def __new__(cls, name, this_bases, d):
12 | return meta(name, bases, d)
13 | return type.__new__(metaclass, '_TemporaryClass', (), {})
14 |
15 |
16 | class RegistryMeta(type):
17 | """Metaclass for object type which registers subclasses"""
18 | def __init__(cls, name, bases, dct):
19 | if name in ['_TemporaryClass', 'RegisterSubclasses']:
20 | # these are hidden baseclasses. Do nothing
21 | pass
22 | elif not hasattr(cls, '_method_registry'):
23 | # this is a registry class. Create an empty registry
24 | cls._method_registry = {}
25 | elif hasattr(cls, 'name'):
26 | # this is a labeled derived class. Add cls to the registry
27 | cls._method_registry[cls.name] = cls
28 |
29 | super(RegistryMeta, cls).__init__(name, bases, dct)
30 |
31 |
32 | class RegisterSubclasses(with_metaclass(RegistryMeta)):
33 | @classmethod
34 | def get_method(cls, method):
35 | if method not in cls._method_registry:
36 | raise ValueError("method={0} not valid. Must be one of "
37 | "{1}".format(method, list(cls.methods())))
38 | return cls._method_registry[method]
39 |
40 | @classmethod
41 | def init(cls, method, *args, **kwargs):
42 | Method = cls.get_method(method)
43 | return Method(*args, **kwargs)
44 |
45 | @classmethod
46 | def _remove_from_registry(cls, method):
47 | cls._method_registry.pop(method, None)
48 |
49 | @classmethod
50 | def methods(cls):
51 | return cls._method_registry.keys()
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/plotter/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | from .plotter import (plot_with_plotly, plot_embedding_with_plotly,
4 | plot_with_matplotlib, plot_embedding_with_matplotlib)
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/plotter/plotter.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Author: Yu-Chia Chen
2 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
3 |
4 | import numpy as np
5 | from .utils import *
6 | from .utils import _check_backend
7 | from .scatter_3d import scatter_plot3d_plotly, scatter_plot3d_matplotlib
8 | from .covar_plotter3 import covar_plotter3d_plotly, covar_plotter3d_matplotlib
9 |
10 | @_check_backend('plotly')
11 | def plot_with_plotly( embedding, rieman_metric, nstd=2,
12 | color_by_ratio=True, if_ellipse=False ):
13 | from plotly.offline import iplot
14 | import plotly.graph_objs as go
15 | sigma_norms = get_top_two_sigma_norm(rieman_metric, color_by_ratio)
16 | colors, colorscale = generate_colors_and_colorscale('gist_rainbow',
17 | sigma_norms)
18 | scatter_pt = scatter_plot3d_plotly(embedding, coloring=sigma_norms,
19 | colorscale=colorscale)
20 | index = generate_grid(embedding.shape[0])
21 |
22 | if if_ellipse:
23 | ellipses_pt = covar_plotter3d_plotly(embedding,
24 | rieman_metric, index, colors)
25 | scatter_pt = ellipses_pt + scatter_pt
26 |
27 | layout = plotly_layout(embedding)
28 | fig = go.Figure(data=scatter_pt,layout=layout)
29 | iplot(fig,filename='scatter-3d-plotly')
30 |
31 | def plot_embedding_with_plotly(trace_var,idx,if_ellipse=False):
32 | plot_with_plotly(trace_var.Y[idx],trace_var.H[idx]/30,if_ellipse=if_ellipse)
33 |
34 | @_check_backend('matplotlib')
35 | def plot_with_matplotlib(embedding, rieman_metric, nstd=2,
36 | color_by_ratio=True, if_ellipse=False):
37 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
38 | sigma_norms = get_top_two_sigma_norm(rieman_metric, color_by_ratio)
39 | colors, _ncor = get_colors_array('gist_rainbow', sigma_norms, base255=False)
40 | fig,ax = scatter_plot3d_matplotlib(embedding, sigma_norms)
41 |
42 | index = generate_grid(embedding.shape[0])
43 | if if_ellipse:
44 | ax = covar_plotter3d_matplotlib(embedding, rieman_metric,
45 | index, ax, colors)
46 | plt.show()
47 |
48 | def plot_embedding_with_matplotlib(trace_var,idx,if_ellipse=False):
49 | plot_with_matplotlib(trace_var.Y[idx],trace_var.H[idx]/30,if_ellipse=if_ellipse)
50 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/plotter/scatter_3d.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Author: Yu-Chia Chen
2 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
3 |
4 | import numpy as np
5 | from .utils import _check_backend
6 |
7 | @_check_backend('matplotlib')
8 | def scatter_plot3d_matplotlib(embedding, coloring=None, fig=None,
9 | subplot=False, subplot_grid=None, **kwargs):
10 | from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import art3d, Axes3D
11 | if fig is None:
12 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
13 | fig = plt.figure()
14 | if subplot and subplot_grid is not None:
15 | sx,sy,sz = subplot_grid
16 | ax = fig.add_subplot(sx,sy,sz,projection='3d')
17 | else:
18 | if subplot is None and subplot:
19 | import warnings
20 | warnings.warn(
21 | 'Subplot grid is not provided, switching to non-subplot mode')
22 | ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
23 |
24 | ax.set_aspect('equal')
25 | s = [2 for i in range(embedding.shape[0])]
26 | x,y,z = embedding[:,:3].T
27 |
28 | if isinstance(coloring, str) and coloring.lower() in 'xyz':
29 | color_idx = 'xyz'.find(coloring)
30 | coloring = embedding[:,color_idx].flatten()
31 |
32 | if coloring is None:
33 | ax.scatter(x,y,z,s=s,**kwargs)
34 | else:
35 | sc = ax.scatter(x,y,z,c=coloring,cmap='gist_rainbow',s=s,**kwargs)
36 | fig.colorbar(sc)
37 |
38 | max_range = np.array(
39 | [x.max()-x.min(), y.max()-y.min(), z.max()-z.min()]).max() / 2.0
40 |
41 | mid_x = (x.max()+x.min()) * 0.5
42 | mid_y = (y.max()+y.min()) * 0.5
43 | mid_z = (z.max()+z.min()) * 0.5
44 | ax.set_xlim(mid_x - max_range, mid_x + max_range)
45 | ax.set_ylim(mid_y - max_range, mid_y + max_range)
46 | ax.set_zlim(mid_z - max_range, mid_z + max_range)
47 |
48 | return fig, ax
49 |
50 | @_check_backend('plotly')
51 | def scatter_plot3d_plotly(embedding, coloring=None,
52 | colorscale='Rainbow', **kwargs):
53 | import plotly.graph_objs as go
54 | x,y,z = embedding[:,:3].T
55 | if isinstance(coloring, str) and coloring.lower() in 'xyz':
56 | color_idx = 'xyz'.find(coloring)
57 | coloring = embedding[:,color_idx].flatten()
58 |
59 | marker = kwargs.pop('marker',None)
60 | name = kwargs.pop('name','Embedding')
61 | scatter_plot = go.Scatter3d(
62 | x=x,
63 | y=y,
64 | z=z,
65 | mode='markers',
66 | marker=dict(
67 | size=2,
68 | opacity=0.8,
69 | ),
70 | name=name,
71 | **kwargs
72 | )
73 | if coloring is not None:
74 | scatter_plot['marker'].update(dict(
75 | color=coloring,
76 | colorscale=colorscale,
77 | showscale=True,
78 | ))
79 | elif marker is not None:
80 | scatter_plot['marker'].update(marker)
81 |
82 | return [scatter_plot]
83 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/plotter/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Author: Yu-Chia Chen
2 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
3 |
4 | import numpy as np
5 |
6 | def _check_backend(backend):
7 | def decorator(func):
8 | def wrapper(*args,**kwargs):
9 | import warnings
10 | warnings.warn(
11 | 'Be careful in using megaman.plotter modules'
12 | ' API will change in the next release.',
13 | FutureWarning
14 | )
15 | import pkgutil
16 | package = pkgutil.find_loader(backend)
17 | if package is not None:
18 | return func(*args,**kwargs)
19 | else:
20 | raise ImportError('plotting backend {} not installed'.format(backend))
21 | return wrapper
22 | return decorator
23 |
24 | @_check_backend('matplotlib')
25 | def get_colors_array(name,coloring,base255=True):
26 | from matplotlib import colors, cm
27 | cmap = cm.get_cmap(name=name)
28 | norm = colors.Normalize()
29 | normalized_coloring = norm(coloring)
30 | colors_array = (cmap(normalized_coloring)[:,:3]*255).astype(np.uint8) \
31 | if base255 else cmap(normalized_coloring)
32 | return colors_array, normalized_coloring
33 |
34 | def generate_plotly_colorscale(name,num=256):
35 | colormap, normalized_coloring = get_colors_array(name,np.arange(num))
36 | return [ [n_coloring, 'rgb({},{},{})'.format(*colormap[idx])] \
37 | for idx, n_coloring in enumerate(normalized_coloring) ]
38 |
39 | def generate_colors_and_colorscale(name,coloring,**kwargs):
40 | colors_array, _ncor = get_colors_array(name,coloring)
41 | colorscale = generate_plotly_colorscale(name,**kwargs)
42 | return colors_array, colorscale
43 |
44 | def generate_grid(size,num_groups=100):
45 | return np.arange(0,size,num_groups)
46 |
47 | @_check_backend('plotly')
48 | def plotly_layout(embedding):
49 | import plotly.graph_objs as go
50 | max_value = 1.2*np.max(np.absolute(embedding[:,:3]))
51 | axis_range = [-max_value,max_value]
52 | layout = go.Layout(
53 | title='Plot with ellipse',
54 | height=600,
55 | width=600,
56 | scene=dict(
57 | xaxis=dict(
58 | gridcolor='rgb(255, 255, 255)',
59 | zerolinecolor='rgb(255, 255, 255)',
60 | showbackground=True,
61 | backgroundcolor='rgb(230, 230,230)',
62 | range=axis_range,
63 | ),
64 | yaxis=dict(
65 | gridcolor='rgb(255, 255, 255)',
66 | zerolinecolor='rgb(255, 255, 255)',
67 | showbackground=True,
68 | backgroundcolor='rgb(230, 230,230)',
69 | range=axis_range,
70 | ),
71 | zaxis=dict(
72 | gridcolor='rgb(255, 255, 255)',
73 | zerolinecolor='rgb(255, 255, 255)',
74 | showbackground=True,
75 | backgroundcolor='rgb(230, 230,230)',
76 | range=axis_range,
77 | ),
78 | )
79 | )
80 | return layout
81 |
82 | def get_top_two_sigma_norm(H,color_by_ratio=True):
83 | eigen_vals = np.array([ sorted_eigh(Hk)[0][:2] for Hk in H ])
84 | if color_by_ratio == True:
85 | toptwo_eigen_vals_norm = eigen_vals[:,1] / eigen_vals[:,0]
86 | else:
87 | toptwo_eigen_vals_norm = eigen_vals[:,0]
88 | return toptwo_eigen_vals_norm
89 |
90 | def sorted_eigh(M):
91 | vals, vecs = np.linalg.eigh(M)
92 | return vals[::-1], vecs[:,::-1]
93 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | from .riemannian_relaxation import *
4 | from .trace_variable import TracingVariable
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/optimizer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Author: Yu-Chia Chen
2 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
3 |
4 | from __future__ import division
5 | from megaman.geometry.utils import RegisterSubclasses
6 |
7 | def init_optimizer(**kwargs):
8 | optimizer = kwargs.get('step_method', 'fixed')
9 | return BaseOptimizer.init(optimizer, **kwargs)
10 |
11 | class BaseOptimizer(RegisterSubclasses):
12 | """
13 | Base class for the optimizer.
14 |
15 | BaseOptimizer creates the common interface to the optimzer class
16 | as well as providing a common apply_optimization() which can be used
17 | in RiemannianRelaxation class to update the embeddings.
18 |
19 | Parameters
20 | ----------
21 | linesearch : bool
22 | If use linesearch to search for optima eta.
23 | eta_max : float
24 | (Linesearch mode) The maximum learning rate (eta) to start search with.
25 | eta : float
26 | (Non linesearch mode) The fixed learning rate (eta) to use.
27 | linesearch_first : bool
28 | (Linesearch mode) If do linesearch at first iteration.
29 | """
30 | def __init__(self, linesearch=False, eta_max=None, eta=None,
31 | linesearch_first=False, **kwargs):
32 | self.linesearch = linesearch
33 | if self.linesearch:
34 | self.linesearch_first = linesearch_first
35 | if eta_max is not None:
36 | self.eta_max = eta_max
37 | self.eta_min = 2**-10
38 | else:
39 | raise ValueError('Should provide eta_max keyword '
40 | 'when linesearch method is used.')
41 | else:
42 | if eta is not None:
43 | self.eta = eta
44 | else:
45 | raise ValueError('Should provide eta keyword '
46 | 'when fixed method is used.')
47 |
48 | def apply_optimization(self, update_embedding_with, grad, **kwargs):
49 | """
50 | Calculating (Obtaining) the learning rate (eta) and apply optimizations
51 | on the embedding states by the specified method.
52 |
53 | Parameters
54 | ----------
55 | update_embedding_with : function
56 | Function used to update the state of RiemannianRelaxation
57 | class (Y or S).
58 |
59 | grad : (n x s) array
60 | Gradients used in updating the embedding.
61 |
62 | calc_loss : function (used by its child function)
63 | Function used to calculated the loss from the temperary state of
64 | RiemannianRelaxation instance. (YT or ST)
65 |
66 | loss : float (used by its child function)
67 | Loss of the current state of RiemannianRelaxation instance.
68 | """
69 | if self.linesearch:
70 | return self._apply_linesearch_optimzation(update_embedding_with,
71 | grad, **kwargs)
72 | else:
73 | return self._apply_fixed_optimization(update_embedding_with,
74 | grad, **kwargs)
75 |
76 | def _apply_linesearch_optimzation(self, update_embedding_with, grad,
77 | calc_loss, loss, **kwargs):
78 | self.eta = self.eta_max
79 | if kwargs.get('first_iter',False) and not self.linesearch_first:
80 | self.eta = kwargs.get('eta_first',1)
81 | loss_diff = 1
82 | while loss_diff > 0:
83 | loss_diff, temp_embedding, delta = self._linesearch_once(
84 | update_embedding_with,grad,calc_loss,loss,**kwargs)
85 | if self.eta <= self.eta_min and loss_diff > 0:
86 | loss_diff, temp_embedding, delta = self._linesearch_once(
87 | update_embedding_with,grad,calc_loss,loss,**kwargs)
88 | loss_diff = -1
89 | self.eta *= 2
90 | update_embedding_with(new_embedding=temp_embedding)
91 | return delta
92 |
93 | def _linesearch_once(self, update_embedding_with, grad,
94 | calc_loss, loss, **kwargs):
95 | delta = self._calc_delta(grad)
96 | temp_embedding = update_embedding_with(delta=delta,copy=True)
97 | loss_diff = calc_loss(temp_embedding) - loss
98 | self.eta /= 2
99 | return loss_diff, temp_embedding, delta
100 |
101 | def _apply_fixed_optimization(self,update_embedding_with,grad,**kwargs):
102 | delta = self._calc_delta(grad)
103 | update_embedding_with(delta=delta)
104 | return delta
105 |
106 | def _calc_delta(self,grad,**kwargs):
107 | raise NotImplementedError()
108 |
109 | class FixedOptimizer(BaseOptimizer):
110 | """Optimizer for fixed (non-momentum) method."""
111 | name='fixed'
112 | def _calc_delta(self,grad,**kwargs):
113 | return -self.eta*grad
114 |
115 | class MomentumOptimizer(BaseOptimizer):
116 | """Optimizer for momentum method."""
117 | name='momentum'
118 | def __init__(self,momentum,**kwargs):
119 | BaseOptimizer.__init__(**kwargs)
120 | self.momentum = momentum
121 | self.last_delta = 0
122 |
123 | def _calc_delta(self,grad,**kwargs):
124 | return -self.eta * grad + self.momentum * self.last_delta
125 |
126 | def apply_optimization(self,update_embedding_with,grad,**kwargs):
127 | self.last_delta = BaseOptimizer.apply_optimization(
128 | self,update_embedding_with,grad,**kwargs)
129 | return self.last_delta
130 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/tests/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/relaxation/tests/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/tests/eps_halfdome.mat:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/relaxation/tests/eps_halfdome.mat
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/tests/rloss_halfdome.mat:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/relaxation/tests/rloss_halfdome.mat
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/tests/test_precomputed_S.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from megaman.relaxation.precomputed import *
2 | from .utils import generate_toy_laplacian
3 |
4 | class BaseTestARkNeighbors(object):
5 | def generate_laplacian(self):
6 | raise NotImplementedError()
7 | def setup_message(self):
8 | raise NotImplementedError()
9 |
10 | def setUp(self):
11 | self.generate_laplacian_and_range()
12 | self.setup_message()
13 | self.A, self.pairs = makeA(self.laplacian)
14 |
15 | # HACK: A is somehow sorted by column, so here I'll change it manually.
16 | sortbyrow = np.lexsort((self.pairs[:,1],self.pairs[:,0]))
17 | self.A = self.A[sortbyrow]
18 | self.pairs = self.pairs[sortbyrow]
19 |
20 | # self.Rk_tensor, self.nbk = compute_Rk(self.laplacian,self.A,self.n)
21 | self.correct_S, self.correct_pairs = self.project_S_from_laplacian()
22 |
23 | def generate_laplacian_and_range(self):
24 | self.laplacian = self.generate_laplacian()
25 | self.n = self.laplacian.shape[0]
26 | self.range = np.arange(self.n)
27 | self.Y = self.generate_toy_Y()
28 |
29 | def generate_toy_Y(self):
30 | return np.random.uniform(size=self.n)
31 |
32 | def ij_is_neighbors(self,i,j):
33 | return self.laplacian[i,j] != 0
34 |
35 | def project_S_from_laplacian(self):
36 | # TODO: make the test process faster!
37 | S = [ self.Y[i]-self.Y[j] for i in np.arange(self.n) \
38 | for j in np.arange(i+1,self.n) \
39 | if self.ij_is_neighbors(i,j) ]
40 | pairs = [ [i,j] for i in np.arange(self.n) \
41 | for j in np.arange(i+1,self.n) \
42 | if self.ij_is_neighbors(i,j) ]
43 | return np.array(S), np.array(pairs)
44 |
45 | def test_A_length_equality(self):
46 | A_length = self.A.shape[0]
47 | correct_A_length = self.correct_S.shape[0]
48 | assert A_length == correct_A_length, 'The first dimension of A is calculated wrong.'
49 |
50 | def test_pairs(self):
51 | np.testing.assert_array_equal(
52 | self.pairs, self.correct_pairs,
53 | err_msg='Sorted pairs should be the same.'
54 | )
55 |
56 | def test_A(self):
57 | testing_S = self.A.dot(self.Y)
58 | np.testing.assert_allclose(
59 | testing_S, self.correct_S,
60 | err_msg='A*y should be the same as yj-yi for all j>i'
61 | )
62 |
63 | def _test_ATAinv(self):
64 | # TODO: why this test will running out of the memory?
65 | ATAinv = np.linalg.pinv(self.A.T.dot(self.A).todense())
66 | S = self.A.dot(self.Y)
67 | testing_Y = ATAinv.dot(self.A.T).dot(S)
68 | np.testing.assert_allclose(
69 | testing_Y, self.Y,
70 | err_msg='ATAinv * AT * S should be the same as original Y'
71 | )
72 |
73 | def _test_Rk(self):
74 | # TODO: Need to understand what Rk means.
75 | pass
76 |
77 | class TestAkRkNbkFromToyLaplacian(BaseTestARkNeighbors):
78 | def generate_laplacian(self):
79 | return generate_toy_laplacian(n=200)
80 | def setup_message(self):
81 | print ('Tesking Rk properties for toy laplacian.')
82 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/tests/test_regression_test.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from megaman.relaxation import *
2 | from functools import wraps
3 |
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import numpy.testing
6 |
7 | from .utils import gen_data, Bunch
8 | import shutil
9 |
10 | def _regression_test(if_epsilon):
11 | def _test_deco(func):
12 | @wraps(func)
13 | def wrapper():
14 | test_dict = func()
15 | var = Bunch(test_dict)
16 |
17 | rr = run_riemannian_relaxation(var.laplacian, var.Y_list[0], var.d, var.relaxation_kwds)
18 |
19 | calculated_loss_list = []
20 | calculated_DL_list = []
21 | calculated_Y_list = []
22 |
23 | for idx,Y in enumerate(var.Y_list):
24 | rr.Y = Y
25 | rr.H = np.copy(var.H_list[idx])
26 | if if_epsilon and idx >= 1:
27 | rr.UU, rr.IUUEPS = compute_principal_plane(var.H_list[idx-1],rr.epsI,var.d)
28 | calculated_loss_list.append(rr.rieman_loss())
29 |
30 | for idx,H in enumerate(var.H_list):
31 | rr.H = H
32 | rr.Y = np.copy(var.Y_list[idx])
33 | calculated_DL_list.append(rr.compute_gradient())
34 |
35 | for idx,grad in enumerate(var.grad_list):
36 | rr.grad = grad
37 | rr.Y = np.copy(var.Y_list[idx])
38 | rr.loss = var.loss_list[idx]
39 | if if_epsilon:
40 | rr.H = rr.compute_dual_rmetric()
41 | rr.UU, rr.IUUEPS = compute_principal_plane(rr.H,rr.epsI,var.d)
42 | rr.make_optimization_step(first_iter=(idx == 0))
43 | calculated_Y_list.append(rr.Y)
44 |
45 | np.testing.assert_allclose(
46 | calculated_loss_list, var.loss_list,
47 | err_msg='Loss calculated from matlab should be similar to that calculated from python, in {}'.format(__name__)
48 | )
49 | np.testing.assert_allclose(
50 | calculated_DL_list[:-1], var.DL_list,
51 | err_msg='gradient difference calculated from matlab should be similar to that calculated from python, in {}'.format(__name__)
52 | )
53 | np.testing.assert_allclose(
54 | calculated_Y_list, var.Y_list[1:],
55 | err_msg='Y calculated from linesearch should be similar, in {}'.format(__name__)
56 | )
57 |
58 | return wrapper
59 | return _test_deco
60 |
61 | @_regression_test(True)
62 | def test_whole_eps():
63 | return gen_data('eps_halfdome','whole_eps')
64 |
65 | @_regression_test(False)
66 | def test_whole_rloss():
67 | return gen_data('rloss_halfdome','whole_eps')
68 |
69 | @_regression_test(True)
70 | def test_half_eps():
71 | return gen_data('eps_halfdome','half_eps')
72 |
73 | @_regression_test(False)
74 | def test_half_rloss():
75 | return gen_data('rloss_halfdome','half_eps')
76 |
77 | @_regression_test(True)
78 | def test_weight_eps():
79 | return gen_data('eps_halfdome','weight_eps')
80 |
81 | @_regression_test(False)
82 | def test_weight_rloss():
83 | return gen_data('rloss_halfdome','weight_eps')
84 |
85 | @_regression_test(True)
86 | def test_half_weight_eps():
87 | return gen_data('eps_halfdome','half_weight_eps')
88 |
89 | @_regression_test(False)
90 | def test_half_weight_rloss():
91 | return gen_data('rloss_halfdome','half_weight_eps')
92 |
93 | if __name__ == '__main__':
94 | test_weight_rloss()
95 |
96 | def tearDownModule():
97 | tmp_dir = '/tmp/test_backup'
98 | if os.path.exists(tmp_dir):
99 | shutil.rmtree(tmp_dir)
100 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/tests/test_relaxation_keywords.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from megaman.relaxation.utils import *
2 | from nose.tools import assert_raises
3 | import numpy as np
4 | import numpy.testing
5 | import shutil, warnings
6 |
7 | n, s, d = 1000, 3, 2
8 |
9 | basic_kwds = {
10 | 'verbose': False,
11 | 'niter': 2000,
12 | 'niter_trace': 0,
13 | 'presave': False,
14 | 'sqrd': True,
15 | 'alpha': 0,
16 | 'projected': False,
17 | 'saveiter': 10,
18 | 'printiter': 1,
19 | }
20 |
21 | nonprojected_epsilon_test = {
22 | 'lossf': 'nonprojected_epsilon',
23 | 'projected': False,
24 | 'eps_orth': 0.1,
25 | }
26 |
27 | tmp_dir = '/tmp/test_backup'
28 | def _initialize_kwds(kwds,n,s,d):
29 | kwds['backup_base_dir'] = tmp_dir
30 | return initialize_kwds(kwds,n,s,d)
31 |
32 | def test_default_keywords():
33 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds({},n,s,d)
34 | for k,v in basic_kwds.items():
35 | assert calculated_kwds[k] == v, 'keyword {} do not initialized correctly.'.format(k)
36 |
37 | assert calculated_kwds['weights'].shape[0] == 0, 'initialized weights is not zero.'
38 | np.testing.assert_allclose(
39 | calculated_kwds['subset'], np.arange(n),
40 | err_msg='initialized subset should be arange(n).'
41 | )
42 |
43 | def test_normalize_weights():
44 | weights = np.array([1,4])
45 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds(dict(weights=weights),n,s,d)
46 | np.testing.assert_allclose(
47 | calculated_kwds['weights'], [0.2,0.8],
48 | err_msg='The weights should be normalized'
49 | )
50 |
51 | def test_default_lossf():
52 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds({},n,s,d)
53 | for k,v in nonprojected_epsilon_test.items():
54 | assert calculated_kwds[k] == v, 'keyword {} do not initialized correctly.'.format(k)
55 |
56 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds(dict(projected=True),n,s,d)
57 | assert calculated_kwds['lossf'] == 'projected_epsilon', 'lossf should be projected_epsilon when projected is True'
58 |
59 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds({},n,d,d)
60 | assert calculated_kwds['lossf'] == 'nonprojected_rloss', 'lossf should be nonprojected_rloss for default'
61 |
62 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds(dict(projected=True),n,d,d)
63 | assert calculated_kwds['lossf'] == 'projected_rloss', 'lossf should be projected_epsilon when projected is True'
64 |
65 | def test_update_lossf():
66 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds(dict(eps_orth=0.55),n,s,d)
67 | assert calculated_kwds['eps_orth'] == 0.55, 'eps_orth should be updated to 0.55.'
68 |
69 | def test_raise_lossf_error():
70 | assert_raises(ValueError, _initialize_kwds, dict(lossf='rloss'),n,s,d)
71 | assert_raises(ValueError, _initialize_kwds, dict(lossf='epsilon'),n,d,d)
72 | assert_raises(ValueError, _initialize_kwds, dict(projected=True, subset=np.arange(0,n,5)),n,s,d)
73 |
74 | def test_default_momentum():
75 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds(dict(step_method='momentum',linesearch=False),n,s,d)
76 | test_momentum_kwds = {
77 | 'm': 0.05,
78 | 'eta': 1.0
79 | }
80 | for k,v in test_momentum_kwds.items():
81 | assert calculated_kwds[k] == v, 'keyword {} do not initialized correctly.'.format(k)
82 |
83 | def test_default_fixed():
84 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds(dict(step_method='fixed',linesearch=False),n,s,d)
85 | assert calculated_kwds['eta'] == 1.0, 'Default eta does not match'
86 |
87 | def test_default_linsearch():
88 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds(dict(projected=True),n,s,d)
89 | test_kwds = {
90 | 'linesearch_first': False,
91 | 'eta_max': 2**11,
92 | }
93 | for k,v in test_kwds.items():
94 | assert calculated_kwds[k] == v, 'keyword {} do not initialized correctly.'.format(k)
95 |
96 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds(dict(projected=False),n,s,d)
97 | assert calculated_kwds['eta_max'] == 2**4, 'eta_max should be 2**4 if projected == False'
98 |
99 | def test_backup_dir_function():
100 | tmp_dir = '/tmp/test_backup'
101 | calculated_kwds = initialize_kwds(dict(backup_base_dir=tmp_dir),n,s,d)
102 | assert 'backup_dir' in calculated_kwds
103 | backup_dir = calculated_kwds['backup_dir']
104 | assert tmp_dir in backup_dir
105 | assert os.path.exists(tmp_dir)
106 |
107 | def test_not_int_warnings():
108 | with warnings.catch_warnings(record=True) as w:
109 | calculated_kwds = initialize_kwds(dict(printiter=1.3),n,s,d)
110 | assert issubclass(w[-1].category, RuntimeWarning), \
111 | 'Should raise RuntimeWarning when input is not integer'
112 |
113 | def tearDownModule():
114 | tmp_dir = '/tmp/test_backup'
115 | if os.path.exists(tmp_dir):
116 | shutil.rmtree(tmp_dir)
117 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/tests/test_tracing_var.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import division
2 | from .utils import generate_toy_laplacian
3 | from megaman.relaxation.trace_variable import TracingVariable as tv
4 | from megaman.relaxation import *
5 | import shutil, os
6 |
7 | def test_copy():
8 | n, s, d = 1000, 3, 2
9 | niter = 10
10 | niter_trace = niter//2
11 | ltrace = 2*niter_trace+1
12 | L = generate_toy_laplacian(n)
13 | Y0 = np.zeros((n,s))
14 | rr = run_riemannian_relaxation(L, Y0, d, dict(niter=niter, niter_trace=niter_trace))
15 | copied_tv = rr.trace_var.copy()
16 | copied_tv.H = copied_tv.H[::2,:,:]
17 | assert rr.trace_var.H.shape[0] == ltrace, 'The original size of H should not be affected by downsamping'
18 | assert copied_tv.H.shape[0] == round(ltrace / 2), 'The size of copied H should be downsampled by 2'
19 |
20 | def tearDownModule():
21 | tmp_dir = '/tmp/test_backup'
22 | if os.path.exists(tmp_dir):
23 | shutil.rmtree(tmp_dir)
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/tests/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import scipy as sp
3 | import scipy.sparse
4 | import h5py
5 | import copy, os
6 |
7 | def generate_toy_laplacian(n=1000):
8 | neighbor_counts = 10
9 | adjacency_mat = np.zeros((n,n))
10 | for i in range(n):
11 | x = np.ones(neighbor_counts,dtype=np.int32)*i
12 | y = np.random.choice(n, neighbor_counts, replace=False)
13 | adjacency_mat[(x,y)] = 1
14 |
15 | np.fill_diagonal(adjacency_mat,0)
16 | adjacency_mat = (adjacency_mat.T + adjacency_mat) / 2
17 | degree = np.sum(adjacency_mat,axis=1)
18 | degree_mat = np.diag(degree)
19 |
20 | return sp.sparse.csc_matrix(degree_mat - adjacency_mat)
21 |
22 | def process_test_data():
23 | namelist = ['rloss_halfdome', 'eps_halfdome']
24 | return { name: process_one_loss_test_data(name) for name in namelist }
25 |
26 | def process_one_loss_test_data(name):
27 | file_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
28 | path = os.path.join(file_dir,'{}.mat'.format(name))
29 | f = h5py.File(path)
30 | laplacian_ref = f['/{}/L'.format(name)]
31 | laplacian = sp.sparse.csc_matrix((laplacian_ref['data'], laplacian_ref['ir'], laplacian_ref['jc']))
32 | opts_list = ['whole_eps','half_eps','weight_eps','half_weight_eps']
33 | processed_data = { opts:process_one_test_data(f,name,opts) for opts in opts_list }
34 | processed_data['L'] = laplacian
35 | processed_data['d'] = 2
36 | return processed_data
37 |
38 | def process_one_test_data(f, name, opts):
39 | Y_ref_list = f['/{}/{}/trace/Y'.format(name,opts)]
40 | Y_list = np.array([ f[Y_ref_list[idx,0]] for idx in range(Y_ref_list.shape[0]) ])
41 | Y_list = np.swapaxes(Y_list, 1, 2)
42 |
43 | H_ref_list = f['/{}/{}/trace/H'.format(name,opts)]
44 | H_list = np.array([ f[H_ref_list[idx,0]] for idx in range(H_ref_list.shape[0]) ])
45 |
46 | DL_ref_list = f['/{}/{}/trace/DL'.format(name,opts)]
47 | DL_list = np.array([ f[DL_ref_list[idx,0]] for idx in range(DL_ref_list.shape[0]-1) ])
48 | DL_list = np.swapaxes(DL_list, 1, 2)
49 |
50 | grad_ref_list = f['/{}/{}/trace/grad'.format(name,opts)]
51 | grad_list = np.array([ f[grad_ref_list[idx,0]] for idx in range(grad_ref_list.shape[0]-1) ])
52 | grad_list = np.swapaxes(grad_list, 1, 2)
53 |
54 | loss_list = np.squeeze(np.array(f['/{}/{}/loss'.format(name,opts)]))
55 | etas_list = np.squeeze(np.array(f['/{}/{}/etas'.format(name,opts)]))
56 |
57 | rk_h5py = f['/{}/{}/opts'.format(name,opts)]
58 | relaxation_kwds = {
59 | 'alpha': rk_h5py['alpha'][0,0],
60 | 'lossf': u''.join(chr(c) for c in rk_h5py['lossf']),
61 | 'step_method': 'fixed',
62 | 'linsearch': u''.join(chr(c) for c in rk_h5py['step_method']) == u'linesearch',
63 | 'projected': rk_h5py['projected'][0,0],
64 | 'eta_max': rk_h5py['eta_max'][0,0],
65 | 'backup_base_dir': '/tmp/test_backup',
66 | }
67 | if 'weight' in opts:
68 | weights = np.squeeze(np.array(rk_h5py['w']))
69 | relaxation_kwds['weights'] = weights
70 |
71 | if 'half' in opts:
72 | relaxation_kwds['subset'] = np.arange(0,1000,2)
73 |
74 | if 'epsorth' in rk_h5py:
75 | relaxation_kwds['eps_orth'] = rk_h5py['epsorth'][0,0]
76 | if 'sqrd' in rk_h5py:
77 | relaxation_kwds['sqrd'] = rk_h5py['sqrd'][0,0] == 1
78 | return dict(
79 | Y_list=Y_list, H_list=H_list, DL_list=DL_list, grad_list=grad_list,
80 | loss_list=loss_list, etas_list=etas_list, relaxation_kwds=relaxation_kwds
81 | )
82 |
83 | class Bunch(object):
84 | def __init__(self, adict):
85 | self.__dict__.update(adict)
86 |
87 | data = process_test_data()
88 | def gen_data(name, opts):
89 | test_data = copy.deepcopy(data[name])
90 | test_dict = test_data[opts]
91 | test_dict['laplacian'] = test_data['L']
92 | test_dict['d'] = test_data['d']
93 | return test_dict
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/trace_variable.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Author: Yu-Chia Chen
2 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
3 |
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import os, pickle, pprint, copy
6 |
7 | from .utils import *
8 |
9 | class TracingVariable(object):
10 | """
11 | The TracingVariable is the class to store the variables to trace and
12 | print relaxation reports in each 'printiter' iteration.
13 | """
14 | def __init__(self,n,s,relaxation_kwds,precomputed_kwds,**kwargs):
15 | self.niter_trace = relaxation_kwds['niter_trace']
16 | self.niter = relaxation_kwds['niter']
17 | self.ltrace = 2*self.niter_trace+1
18 |
19 | self.loss = np.zeros(self.niter+1)
20 | self.etas = np.zeros(self.niter+1)
21 | self.H = np.zeros((self.ltrace,n,s,s))
22 | self.Y = np.zeros((self.ltrace,n,s))
23 | self.lmin = np.finfo(np.float64).max
24 |
25 | self.verbose = relaxation_kwds['verbose']
26 | self.printiter = relaxation_kwds['printiter']
27 | self.saveiter = relaxation_kwds['saveiter']
28 | self.backup_dir = relaxation_kwds['backup_dir']
29 |
30 | create_output_dir(self.backup_dir)
31 | self.report_and_save_keywords(relaxation_kwds,precomputed_kwds)
32 |
33 | def copy(self):
34 | return copy.deepcopy(self)
35 |
36 | def report_and_save_keywords(self,relaxation_kwds,precomputed_kwds):
37 | """Save relaxation keywords to .txt and .pyc file"""
38 | report_name = os.path.join(self.backup_dir,'relaxation_keywords.txt')
39 | pretty_relax_kwds = pprint.pformat(relaxation_kwds,indent=4)
40 | with open(report_name,'w') as wf:
41 | wf.write(pretty_relax_kwds)
42 | wf.close()
43 |
44 | origin_name = os.path.join(self.backup_dir,'relaxation_keywords.pyc')
45 | with open(origin_name,'wb') as ro:
46 | pickle.dump(relaxation_kwds,ro,protocol=pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)
47 | ro.close()
48 |
49 | if relaxation_kwds['presave']:
50 | precomp_kwds_name = os.path.join(self.backup_dir,
51 | 'precomputed_keywords.pyc')
52 | with open(precomp_kwds_name, 'wb') as po:
53 | pickle.dump(precomputed_kwds, po,
54 | protocol=pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)
55 | po.close()
56 |
57 | def update(self,iiter,H,Y,eta,loss):
58 | """Update the trace_var in new iteration"""
59 | if iiter <= self.niter_trace+1:
60 | self.H[iiter] = H
61 | self.Y[iiter] = Y
62 | elif iiter >self.niter - self.niter_trace + 1:
63 | self.H[self.ltrace+iiter-self.niter-1] = H
64 | self.Y[self.ltrace+iiter-self.niter-1] = Y
65 |
66 | self.etas[iiter] = eta
67 | self.loss[iiter] = loss
68 | if self.loss[iiter] < self.lmin:
69 | self.Yh = Y
70 | self.lmin = self.loss[iiter]
71 | self.miniter = iiter if not iiter == -1 else self.niter + 1
72 |
73 | def print_report(self,iiter):
74 | if self.verbose and iiter % self.printiter == 0:
75 | print ('Iteration number: {}'.format(iiter))
76 | print ('Last step size eta: {}'.format(self.etas[iiter]))
77 | print ('current loss (before gradient step): {}'
78 | .format(self.loss[iiter]))
79 | print ('minimum loss: {}, at iteration: {}\n'
80 | .format(self.lmin, self.miniter))
81 |
82 | def save_backup(self,iiter):
83 | if iiter % self.saveiter == 0 and iiter != 0:
84 | backup_name = os.path.join(self.backup_dir,'backup_trace.pyc')
85 | TracingVariable.save(self,backup_name)
86 | print ('Save backup at iteration: {}\n'.format(iiter))
87 |
88 | @classmethod
89 | def correct_file_extension(cls,filename):
90 | return os.path.splitext(filename)[0]+'.pyc'
91 |
92 | @classmethod
93 | def save(cls,instance,filename):
94 | """Class method save for saving TracingVariable."""
95 | filename = cls.correct_file_extension(filename)
96 | try:
97 | with open(filename,'wb') as f:
98 | pickle.dump(instance,f,protocol=pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)
99 | except MemoryError as e:
100 | print ('{} occurred, will downsampled the saved file by 20.'
101 | .format(type(e).__name__))
102 | copy_instance = instance.copy()
103 | copy_instance.H = copy_instance.H[::20,:,:]
104 | copy_instance.Y = copy_instance.Y[::20,:]
105 | with open(filename,'wb') as f:
106 | pickle.dump(copy_instance,f,protocol=pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)
107 |
108 | @classmethod
109 | def load(cls,filename):
110 | """Load from stored files"""
111 | filename = cls.correct_file_extension(filename)
112 | with open(filename,'rb') as f:
113 | return pickle.load(f)
114 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import os
4 |
5 | def configuration(parent_package='', top_path=None):
6 | from numpy.distutils.misc_util import Configuration
7 |
8 | config = Configuration('megaman', parent_package, top_path)
9 |
10 | config.add_subpackage('__check_build')
11 | config.add_subpackage('datasets')
12 | config.add_subpackage('embedding')
13 | config.add_subpackage('embedding/tests')
14 | config.add_subpackage('geometry')
15 | config.add_subpackage('geometry/cyflann')
16 | config.add_subpackage('geometry/tests')
17 | config.add_subpackage('plotter')
18 | config.add_subpackage('relaxation')
19 | config.add_subpackage('relaxation/tests')
20 | config.add_subpackage('utils')
21 | config.add_subpackage('utils/tests')
22 | config.add_data_files('geometry/tests/testmegaman_laplacian_rad0_2_lam1_5_n200.mat')
23 | config.add_data_files('relaxation/tests/eps_halfdome.mat')
24 | config.add_data_files('relaxation/tests/rloss_halfdome.mat')
25 | config.add_data_files('datasets/megaman.png')
26 |
27 | return config
28 |
29 | if __name__ == '__main__':
30 | from numpy.distutils.core import setup
31 | setup(**configuration(top_path='').todict())
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/utils/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/covar_plotter.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 |
5 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
6 | from matplotlib.patches import Ellipse
7 |
8 | def plot_point_cov(points, nstd=2, ax=None, **kwargs):
9 | """
10 | Plots an `nstd` sigma ellipse based on the mean and covariance of a point
11 | "cloud" (points, an Nx2 array).
12 |
13 | Parameters
14 | ----------
15 | points : An Nx2 array of the data points.
16 | nstd : The radius of the ellipse in numbers of standard deviations.
17 | Defaults to 2 standard deviations.
18 | ax : The axis that the ellipse will be plotted on. Defaults to the
19 | current axis.
20 | Additional keyword arguments are pass on to the ellipse patch.
21 |
22 | Returns
23 | -------
24 | A matplotlib ellipse artist
25 | """
26 | pos = points.mean(axis=0)
27 | cov = np.cov(points, rowvar=False)
28 | return plot_cov_ellipse(cov, pos, nstd, ax, **kwargs)
29 |
30 | def plot_cov_ellipse(cov, pos, nstd=2, ax=None, **kwargs):
31 | """
32 | Plots an `nstd` sigma error ellipse based on the specified covariance
33 | matrix (`cov`). Additional keyword arguments are passed on to the
34 | ellipse patch artist.
35 |
36 | Parameters
37 | ----------
38 | cov : The 2x2 covariance matrix to base the ellipse on
39 | pos : The location of the center of the ellipse. Expects a 2-element
40 | sequence of [x0, y0].
41 | nstd : The radius of the ellipse in numbers of standard deviations.
42 | Defaults to 2 standard deviations.
43 | ax : The axis that the ellipse will be plotted on. Defaults to the
44 | current axis.
45 | Additional keyword arguments are pass on to the ellipse patch.
46 |
47 | Returns
48 | -------
49 | A matplotlib ellipse artist
50 | """
51 | def eigsorted(cov):
52 | vals, vecs = np.linalg.eigh(cov)
53 | order = vals.argsort()[::-1]
54 | return vals[order], vecs[:,order]
55 |
56 | if ax is None:
57 | ax = plt.gca()
58 |
59 | vals, vecs = eigsorted(cov)
60 | theta = np.degrees(np.arctan2(*vecs[:,0][::-1]))
61 |
62 | # Width and height are "full" widths, not radius
63 | width, height = 2 * nstd * np.sqrt(vals)
64 | ellip = Ellipse(xy=pos, width=width, height=height, angle=theta, **kwargs)
65 |
66 | ax.add_artist(ellip)
67 | return ellip
68 |
69 | if __name__ == '__main__':
70 | #-- Example usage -----------------------
71 | # Generate some random, correlated data
72 | points = np.random.multivariate_normal(
73 | mean=(1,1), cov=[[0.4, 9],[9, 10]], size=1000
74 | )
75 | # Plot the raw points...
76 | x, y = points.T
77 | plt.plot(x, y, 'ro')
78 |
79 | # Plot a transparent 3 standard deviation covariance ellipse
80 | plot_point_cov(points, nstd=3, alpha=0.5, color='green')
81 |
82 | plt.show()
83 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/k_means_clustering.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """K-Means Clustering"""
2 |
3 | # Author: James McQueen
4 | # Xiao Wang
5 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICEN
6 |
7 | import numpy as np
8 | import random
9 |
10 | class Kmeans():
11 | def __init__(self, K):
12 | self.K = K
13 |
14 | def fit(data):
15 | self.labels_ = k_means_clustering(data, self.K)
16 |
17 | def fit_transform(data):
18 | self.fit(data)
19 | return self.labels_
20 |
21 | def k_means_clustering(data,K):
22 | """
23 | K-means clustering is an algorithm that take a data set and
24 | a number of clusters K and returns the labels which represents
25 | the clusters of data which are similar to others
26 |
27 | Parameters
28 | --------------------
29 | data: array-like, shape= (m_samples,n_samples)
30 | K: integer
31 | number of K clusters
32 | Returns
33 | -------
34 | labels: array-like, shape (1,n_samples)
35 | """
36 | N = data.shape[0]
37 | centroids, data_norms = orthogonal_initialization(data,K)
38 | old_centroids= np.zeros((N,K))
39 | labels = []
40 |
41 | # Run the main k-means algorithm
42 | while not _has_converged(centroids, old_centroids):
43 | labels = get_labels(data, centroids,K)
44 | centroids = get_centroids(data,K,labels,centroids,data_norms)
45 | old_centroids = centroids
46 |
47 | return labels
48 |
49 | def orthogonal_initialization(X,K):
50 | """
51 | Initialize the centrodis by orthogonal_initialization.
52 | Parameters
53 | --------------------
54 | X(data): array-like, shape= (m_samples,n_samples)
55 | K: integer
56 | number of K clusters
57 | Returns
58 | -------
59 | centroids: array-like, shape (K,n_samples)
60 | data_norms: array-like, shape=(1,n_samples)
61 | """
62 | N,M = X.shape
63 | centroids= X[np.random.randint(0, N-1,1),:]
64 | data_norms = np.linalg.norm(X, axis = 1)# contains the norm of each data point, only do this once
65 |
66 | center_norms = np.linalg.norm(centroids, axis=1) # contains the norms of the centers, will need to be updated when new center added
67 |
68 | for k in range(1,K):
69 | ## Here's where we compute the cosine of the angle between them:
70 | # Compute the dot (inner) product between each data point and each center
71 | new_center_index,new_center = new_orthogonal_center(X,data_norms,centroids,center_norms =center_norms)
72 | centroids = np.vstack((centroids,new_center))
73 | center_norms = np.hstack((center_norms,data_norms[new_center_index]))
74 | return centroids,data_norms
75 |
76 | def new_orthogonal_center(X,data_norms,centroids,center_norms=None):
77 | """
78 | Initialize the centrodis by orthogonal_initialization.
79 | Parameters
80 | --------------------
81 | X(data): array-like, shape= (m_samples,n_samples)
82 | data_norms: array-like, shape=(1,n_samples)
83 | center_norms:array-like,shape=(centroids.shape[0])
84 | centroids: array-like, shape (K,n_samples)
85 | Returns
86 | -------
87 | new_center: array-like, shape (1,n_samples)
88 | new_center_index: integer
89 | data index of the new center
90 | """
91 | if center_norms is None:
92 | center_norms = np.linalg.norm(centroids, axis=1)
93 | cosine = np.inner(X,centroids) # cosine[i, j] = np.dot(X[i, :],centroids[j,:])
94 | cosine = cosine/center_norms # divide each column by the center norm
95 | cosine = cosine / data_norms[:,np.newaxis] # divide each row by the data norm
96 | max_cosine = np.abs(np.max(cosine, 1)) # the largest (absolute) cosine for each data point
97 |
98 | # then we find the index of the new center:
99 | new_center_index = np.argmin(max_cosine) # the data index of the new center is the smallest max cosine
100 | new_center = X[new_center_index, :]
101 | return new_center_index,new_center
102 |
103 | def get_labels(data, centroids,K):
104 | """
105 | Returns a label for each piece of data in the dataset
106 |
107 | Parameters
108 | ------------
109 | data: array-like, shape= (m_samples,n_samples)
110 | K: integer
111 | number of K clusters
112 | centroids: array-like, shape=(K, n_samples)
113 |
114 | returns
115 | -------------
116 | labels: array-like, shape (1,n_samples)
117 | """
118 | distances = np.sqrt(((data - centroids[:, np.newaxis])**2).sum(axis=2))
119 | return np.argmin(distances, axis=0)
120 |
121 | def get_centroids(data,k,labels,centroids,data_norms):
122 | """
123 | For each element in the dataset, choose the closest centroid
124 |
125 | Parameters
126 | ------------
127 | data: array-like, shape= (m_samples,n_samples)
128 | K: integer, number of K clusters
129 | centroids: array-like, shape=(K, n_samples)
130 | labels: array-like, shape (1,n_samples)
131 | returns
132 | -------------
133 | centroids: array-like, shape (K,n_samples)
134 | """
135 |
136 | D = data.shape[1]
137 | for j in range(k):
138 | cluster_points = np.where(labels == j)
139 | cluster_total = len(cluster_points)
140 | if cluster_total == 0:
141 | _, temp = new_orthogonal_center(data,data_norms,centroids)
142 | else:
143 | temp = np.mean(data[cluster_points,:],axis=1)
144 | centroids[j,:] = temp
145 | return centroids
146 |
147 | def _has_converged(centroids, old_centroids):
148 | """
149 | Stop if centroids stop to update
150 | Parameters
151 | -----------
152 | centroids: array-like, shape=(K, n_samples)
153 | old_centroids: array-like, shape=(K, n_samples)
154 | ------------
155 | returns
156 | True: bool
157 |
158 | """
159 | return (set([tuple(a) for a in centroids]) == set([tuple(a) for a in old_centroids]))
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/large_sparse_functions.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import scipy as sp
3 | import cPickle
4 | from scipy.io import loadmat, savemat
5 | from scipy.sparse import coo_matrix, dia_matrix, identity
6 |
7 | def save_sparse_in_2_parts(A, name):
8 | # mat and coo format easily readable into MATLAB
9 | nz = len(A.data)
10 | A = A.tocoo()
11 | A_1 = {'I1':A.row[xrange(0, int(nz/2))],
12 | 'J1':A.col[xrange(0, int(nz/2))],
13 | 'V1':A.data[xrange(0, int(nz/2))]}
14 | savemat(name + '_part_1.mat', A_1)
15 |
16 | A_2 = {'I2':A.row[xrange(int(nz/2), nz)],
17 | 'J2':A.col[xrange(int(nz/2), nz)],
18 | 'V2':A.data[xrange(int(nz/2), nz)]}
19 | savemat(name + '_part_2.mat', A_2)
20 | return(None)
21 |
22 | def load_sparse_in_2_parts(f1, f2, n):
23 | A_1 = loadmat(f1)
24 | A_2 = loadmat(f2)
25 | row = np.append(A_1['I1'], A_2['I2'])
26 | col = np.append(A_1['J1'], A_2['J2'])
27 | data = np.append(A_1['V1'], A_2['V2'])
28 | A = coo_matrix((data, (row, col)), shape = (n, n))
29 | return(A)
30 |
31 |
32 | def save_sparse_in_k_parts(A, name, k):
33 | nz = len(A.data)
34 | A = A.tocoo()
35 | nk = 0
36 | nper = int(nz / k)
37 | for ii in range(k):
38 | fname = name + '_part_' + str(ii+1) + '.mat'
39 | nkp1 = nk + nper
40 | if ii == k-1:
41 | nkp1 = nz
42 | A_k = {'I':A.row[xrange(nk, nkp1)],
43 | 'J':A.col[xrange(nk, nkp1)],
44 | 'V':A.data[xrange(nk, nkp1)]}
45 | savemat(fname, A_k)
46 | nk = nkp1
47 | return(None)
48 |
49 | def load_sparse_in_k_parts(name, k, n):
50 | row = np.array([])
51 | col = np.array([])
52 | data = np.array([])
53 | for ii in range(k):
54 | fname = name + '_part_' + str(ii+1) + '.mat'
55 | A_k = loadmat(fname)
56 | row = np.append(row, A_k['I'])
57 | col = np.append(col, A_k['J'])
58 | data = np.append(data, A_k['V'])
59 | A = coo_matrix((data, (row, col)), shape = (n, n))
60 | return(A)
61 |
62 | def dump_array_in_k_parts(A, name, k):
63 | n = A.shape[0]
64 | nk = 0
65 | nper = int(n / k)
66 | for ii in range(k):
67 | fname = name + '_part_' + str(ii+1) + '.p'
68 | nkp1 = nk + nper
69 | if ii == k-1:
70 | nkp1 = n
71 | A_k = A[range(nk, nkp1)]
72 | cPickle.dump(A_k, open(fname, 'wb'), -1)
73 | nk = nkp1
74 | return(None)
75 |
76 | def load_array_in_k_parts(name, k):
77 | for ii in range(k):
78 | fname = name + '_part_' + str(ii+1) + '.p'
79 | A_k = cPickle.load(open(fname, 'rb'))
80 | if ii == 0:
81 | A = A_k.copy()
82 | else:
83 | A = np.vstack((A, A_k))
84 | return(A)
85 |
86 | def set_sparse_diag_to_one(mat):
87 | # appears to implicitly convert to csr which might be a problem
88 | (n, n) = mat.shape
89 | # copy the matrix, subtract the diagonal values, add identity matrix
90 | # see http://nbviewer.jupyter.org/gist/Midnighter/9992103 for speed testing
91 | cpy = mat - dia_matrix((mat.diagonal()[sp.newaxis, :], [0]), shape=(n, n)) + identity(n)
92 | return(cpy)
93 |
94 | def set_coo_diag_to_one(mat):
95 | # this function takes a coo matrix and sets diagonal to one
96 | (n, n) = mat.shape
97 | off_diag = np.where(mat.row != mat.col)[0]
98 | row = np.append(mat.row[off_diag], range(n))
99 | col = np.append(mat.col[off_diag], range(n))
100 | data = np.append(mat.data[off_diag], np.ones(n))
101 | cpy = coo_matrix((data, (row, col)), shape = (n, n))
102 | return(cpy)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/nystrom_extension.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
3 | """
4 | Created on Tue Jun 21 11:11:40 2016
5 |
6 | @author: wang1
7 | """
8 | from __future__ import division
9 | import numpy as np
10 | import warnings
11 | from scipy.sparse import isspmatrix
12 | def nystrom_extension(C, e_vec, e_val):
13 | """
14 | Parameters
15 | ----------
16 | C: array-like, shape = (n, l)
17 | Stacking the training and testing data where n
18 | is the total number of data and l is the number of
19 | training data.
20 | e_val: array, shape = (1,s)
21 | If W equals to C[0:l, :], then e_val are the largest s
22 | eig values of W
23 | e_vec: array-like, shape = (l, s)
24 | These are the corresponding eig vectors to e_val
25 |
26 | Returns
27 | -------
28 | eval_nystrom: array-like, shape = (1,s)
29 | These are the estimated largest s eig values of the matrix where C is the
30 | first l columns.
31 | evec_nystrom: arrau-like, shape = (n, s)
32 | These are the corresponding eig vectors to eval_nystrom
33 |
34 | """
35 | n,l = C.shape
36 | W = C[0:l, :]
37 | eval_nystrom = (n/l)*e_val
38 | eval_inv = e_val.copy()
39 | e_nonzero = np.where(e_val != 0)
40 | # e_nonzero = [i for i, e in enumerate(e_val) if e != 0] #np.nonzero(a)[0]
41 | eval_inv[e_nonzero] = 1.0/e_val[e_nonzero]
42 |
43 | if isspmatrix(C):
44 | evec_nystrom = np.sqrt(l/n)*C.dot(e_vec)*eval_inv
45 | else:
46 | evec_nystrom = np.sqrt(l/n)*np.dot(C,e_vec)*eval_inv
47 | return eval_nystrom,evec_nystrom
48 |
49 |
50 |
51 |
52 |
53 |
54 |
55 |
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/tests/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/utils/tests/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/tests/test_analyze_dimension_and_radius.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from numpy.random import RandomState
3 | from scipy.spatial.distance import squareform, pdist
4 | import megaman.utils.analyze_dimension_and_radius as adar
5 | from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
6 | from numpy.testing import assert_array_almost_equal
7 |
8 | def test_dim_distance_passed_vs_computed(seed=1234):
9 | rng = RandomState(seed)
10 | X = rng.randn(100, 10)
11 | dists = csr_matrix(squareform(pdist(X)))
12 | rmin = 2
13 | rmax = 10.0
14 | nradii = 10
15 | radii = 10**(np.linspace(np.log10(rmin), np.log10(rmax), nradii))
16 |
17 | results_passed = adar.neighborhood_analysis(dists, radii)
18 | avg_neighbors = results_passed['avg_neighbors'].flatten()
19 | radii = results_passed['radii'].flatten()
20 | fit_range = range(len(radii))
21 | dim_passed = adar.find_dimension_plot(avg_neighbors, radii, fit_range)
22 | results_computed, dim_computed = adar.run_analyze_dimension_and_radius(X, rmin, rmax, nradii)
23 | assert(dim_passed == dim_computed)
24 | assert_array_almost_equal(results_passed['avg_neighbors'], results_computed['avg_neighbors'])
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/tests/test_eigendecomp.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | from megaman.utils.eigendecomp import (eigen_decomposition, null_space,
4 | EIGEN_SOLVERS)
5 | from numpy.testing import assert_array_almost_equal
6 | import numpy as np
7 |
8 |
9 | SPD_SOLVERS = EIGEN_SOLVERS
10 | NON_SPD_SOLVERS = ['auto', 'dense', 'arpack']
11 | SOLVER_KWDS_DICT = {'auto':None,
12 | 'dense':{'turbo':True, 'type':1},
13 | 'arpack':{'mode':'normal', 'tol':0, 'maxiter':None},
14 | 'lobpcg':{'maxiter':20, 'tol':None},
15 | 'amg':{'maxiter':20, 'tol':None,'aggregate':'standard'}}
16 |
17 | def _check_with_col_sign_flipping(A, B, tol=0.0):
18 | """ Check array A and B are equal with possible sign flipping on
19 | each columns"""
20 | sign = True
21 | for column_idx in range(A.shape[1]):
22 | sign = sign and ((((A[:, column_idx] -
23 | B[:, column_idx]) ** 2).mean() <= tol ** 2) or
24 | (((A[:, column_idx] +
25 | B[:, column_idx]) ** 2).mean() <= tol ** 2))
26 | if not sign:
27 | return False
28 | return True
29 |
30 | def _test_all_solvers(solvers_to_test, S, solver_kwds_dict={}):
31 | for largest in [True, False]:
32 | Lambdas = {};
33 | for eigen_solver in solvers_to_test:
34 | if eigen_solver in solver_kwds_dict.keys():
35 | solver_kwds = solver_kwds_dict[eigen_solver]
36 | else:
37 | solver_kwds = None
38 | lambdas, diffusion_map = eigen_decomposition(S, n_components = 3,
39 | eigen_solver = eigen_solver,
40 | largest = largest, drop_first = False,
41 | solver_kwds=solver_kwds)
42 | Lambdas[eigen_solver] = np.sort(lambdas)
43 | # pairwise comparison:
44 | for i in range(len(solvers_to_test)):
45 | for j in range(i+1, len(solvers_to_test)):
46 | print(largest)
47 | print(str(solvers_to_test[i]) + " + " + str(solvers_to_test[j]))
48 | assert_array_almost_equal(Lambdas[solvers_to_test[i]],
49 | Lambdas[solvers_to_test[j]])
50 |
51 | def _test_all_null_solvers(solvers_to_test, S, solver_kwds_dict={}):
52 | for largest in [True, False]:
53 | Null_Space = {};
54 | for eigen_solver in solvers_to_test:
55 | if eigen_solver in solver_kwds_dict.keys():
56 | solver_kwds = solver_kwds_dict[eigen_solver]
57 | else:
58 | solver_kwds = None
59 | nullspace, errors = null_space(S, k = 3, eigen_solver = eigen_solver, solver_kwds=solver_kwds)
60 | Null_Space[eigen_solver] = nullspace
61 | # pairwise comparison:
62 | for i in range(len(solvers_to_test)):
63 | for j in range(i+1, len(solvers_to_test)):
64 | print(largest)
65 | print(str(solvers_to_test[i]) + " + " + str(solvers_to_test[j]))
66 | _check_with_col_sign_flipping(Null_Space[solvers_to_test[i]],
67 | Null_Space[solvers_to_test[j]], 0.05)
68 | def test_sym_pos_def_agreement():
69 | solvers_to_test = SPD_SOLVERS
70 | rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
71 | X = rng.uniform(size=(100, 40))
72 | S = np.dot(X.T, X)
73 | _test_all_solvers(solvers_to_test, S)
74 |
75 | def test_null_space_sym_pos_def_agreement():
76 | solvers_to_test = SPD_SOLVERS
77 | solvers_to_test = SPD_SOLVERS
78 | rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
79 | X = rng.uniform(size=(100, 100))
80 | S = np.dot(X.T, X)
81 | _test_all_null_solvers(solvers_to_test, S)
82 |
83 | def test_null_space_sym_agreement():
84 | solvers_to_test = NON_SPD_SOLVERS
85 | solvers_to_test = NON_SPD_SOLVERS
86 | rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
87 | X = rng.uniform(size=(16, 16))
88 | S = X + X.T
89 | _test_all_null_solvers(solvers_to_test, S)
90 |
91 | def test_null_space_non_sym_agreement():
92 | solvers_to_test = NON_SPD_SOLVERS
93 | rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
94 | S = rng.uniform(size=(16, 16))
95 | _test_all_null_solvers(solvers_to_test, S)
96 |
97 | def test_base_eigen_solver_kwds():
98 | solvers_to_test = SPD_SOLVERS
99 | rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
100 | X = rng.uniform(size=(100, 40))
101 | S = np.dot(X.T, X)
102 | _test_all_solvers(solvers_to_test, S, solver_kwds_dict=SOLVER_KWDS_DICT)
103 |
104 | def test_null_eigen_solver_kwds():
105 | solvers_to_test = SPD_SOLVERS
106 | rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
107 | X = rng.uniform(size=(100, 40))
108 | S = np.dot(X.T, X)
109 | _test_all_null_solvers(solvers_to_test, S, solver_kwds_dict=SOLVER_KWDS_DICT)
110 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/tests/test_estimate_radius.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from numpy.random import RandomState
3 | from scipy.spatial.distance import squareform, pdist
4 | from megaman.utils.estimate_radius import run_estimate_radius
5 | from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
6 | from numpy.testing import assert_array_almost_equal
7 |
8 | def test_radius_serial_vs_parallel(seed=1234):
9 | rng = RandomState(seed)
10 | X = rng.randn(100, 10)
11 | dists = csr_matrix(squareform(pdist(X)))
12 | sample = range(100)
13 | d = 3
14 | rmin = 2
15 | rmax = 10.0
16 | ntry = 10
17 | run_parallel = True
18 | results_parallel = run_estimate_radius(X, dists, sample, d, rmin, rmax, ntry, run_parallel)
19 | print(results_parallel)
20 | results_serial = run_estimate_radius(X, dists, sample, d, rmin, rmax, ntry, False)
21 | print(results_serial)
22 | assert_array_almost_equal(results_parallel, results_serial)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/tests/test_nystrom.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from numpy import absolute
3 | from numpy.linalg import qr
4 | from megaman.utils.nystrom_extension import nystrom_extension
5 | from numpy.testing import assert_array_almost_equal
6 |
7 |
8 | def test_nystrom_extension(seed=123):
9 | """ Test Nystrom Extension: low rank approximation is exact when
10 | G is itself low rank
11 | """
12 | n = 10
13 | s = 2
14 | rng = np.random.RandomState(seed)
15 | X = rng.randn(n, s)
16 | G = np.dot(X, X.T) # has rank s
17 |
18 | # find the linearly independent columns of
19 | q = qr(G)[1]
20 | q = absolute(q)
21 | sums = np.sum(q,axis=1)
22 | i = 0
23 | dims = list()
24 | while( i < n ): #dim is the matrix dimension
25 | if(sums[i] > 1.e-10):
26 | dims.append(i)
27 | i += 1
28 |
29 | # Find the eigendecomposition of the full rank portion:
30 | W = G[dims,:]
31 | W = W[:,dims]
32 | eval, evec = np.linalg.eigh(W)
33 |
34 | # pass the dims columns of G
35 | C = G[:,dims]
36 | # Find the estimated eigendecomposition using Nystrom
37 | eval_nystrom, evec_nystrom = nystrom_extension(C, evec, eval)
38 |
39 | # reconstruct G using Nystrom Approximatiuon
40 | G_nystrom = np.dot(np.dot(evec_nystrom, np.diag(eval_nystrom)),evec_nystrom.T)
41 | # since rank(W) = rank(G) = s the nystrom approximation of G is exact:
42 | assert_array_almost_equal(G_nystrom, G)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/tests/test_spectral_clustering.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from sklearn import neighbors
2 | import numpy as np
3 |
4 | from megaman.utils.eigendecomp import EIGEN_SOLVERS
5 | from megaman.utils.spectral_clustering import SpectralClustering
6 |
7 | def test_spectral_clustering():
8 | K = 3
9 | num_per_cluster = 100
10 | c = np.array([[1,0,0], [0,1,0], [0,0,1]])
11 | X = np.repeat(c, np.repeat(num_per_cluster, K), axis = 0)
12 | radius = 5
13 | rng = np.random.RandomState(36)
14 | def check_labels(stabalize, renormalize, eigen_solver):
15 | if eigen_solver in ['dense', 'auto']:
16 | solver_kwds = {}
17 | else:
18 | solver_kwds = {'maxiter':100000, 'tol':1e-5}
19 | SC = SpectralClustering(K=K, radius=radius, stabalize=stabalize, renormalize=renormalize,
20 | eigen_solver = eigen_solver, solver_kwds=solver_kwds, random_state = rng,
21 | additional_vectors = 0)
22 | labels = SC.fit_transform(X, input_type= 'data')
23 | for k in range(K):
24 | cluster_labs = labels[range((k*num_per_cluster),((k+1)*num_per_cluster))]
25 | first_lab = cluster_labs[0]
26 | assert(np.all(cluster_labs == first_lab))
27 |
28 | for stabalize in [True, False]:
29 | for renormalize in [True, False]:
30 | for solver in EIGEN_SOLVERS:
31 | yield check_labels, stabalize, renormalize, solver
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/tests/test_testing.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import warnings
4 | import sys
5 | import unittest
6 | from nose.tools import assert_raises, assert_equal
7 |
8 | from megaman.utils.testing import assert_raise_message, assert_no_warnings, assert_warns
9 |
10 | def test_assert_raise_message():
11 | def _raise_ValueError(message):
12 | raise ValueError(message)
13 |
14 | def _no_raise():
15 | pass
16 |
17 | assert_raise_message(ValueError, "test",
18 | _raise_ValueError, "test")
19 |
20 | assert_raises(AssertionError,
21 | assert_raise_message, ValueError, "something else",
22 | _raise_ValueError, "test")
23 |
24 | assert_raises(ValueError,
25 | assert_raise_message, TypeError, "something else",
26 | _raise_ValueError, "test")
27 |
28 | assert_raises(AssertionError,
29 | assert_raise_message, ValueError, "test",
30 | _no_raise)
31 |
32 | # multiple exceptions in a tuple
33 | assert_raises(AssertionError,
34 | assert_raise_message, (ValueError, AttributeError),
35 | "test", _no_raise)
36 |
37 |
38 | # This class is inspired from numpy 1.7 with an alteration to check
39 | # the reset warning filters after calls to assert_warns.
40 | # This assert_warns behavior is specific to scikit-learn because
41 | #`clean_warning_registry()` is called internally by assert_warns
42 | # and clears all previous filters.
43 | class TestWarns(unittest.TestCase):
44 | def test_warn(self):
45 | def f():
46 | warnings.warn("yo")
47 | return 3
48 |
49 | # Test that assert_warns is not impacted by externally set
50 | # filters and is reset internally.
51 | # This is because `clean_warning_registry()` is called internally by
52 | # assert_warns and clears all previous filters.
53 | warnings.simplefilter("ignore", UserWarning)
54 | assert_equal(assert_warns(UserWarning, f), 3)
55 |
56 | # Test that the warning registry is empty after assert_warns
57 | assert_equal(sys.modules['warnings'].filters, [])
58 |
59 | assert_raises(AssertionError, assert_no_warnings, f)
60 | assert_equal(assert_no_warnings(lambda x: x, 1), 1)
61 |
62 | def test_warn_wrong_warning(self):
63 | def f():
64 | warnings.warn("yo", DeprecationWarning)
65 |
66 | failed = False
67 | filters = sys.modules['warnings'].filters[:]
68 | try:
69 | try:
70 | # Should raise an AssertionError
71 | assert_warns(UserWarning, f)
72 | failed = True
73 | except AssertionError:
74 | pass
75 | finally:
76 | sys.modules['warnings'].filters = filters
77 |
78 | if failed:
79 | raise AssertionError("wrong warning caught by assert_warn")
80 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Setup script for megaman: scalable manifold learning
2 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
3 |
4 | import io
5 | import os
6 | import re
7 | import sys
8 | import subprocess
9 |
10 | PY2 = sys.version_info[0] == 2
11 | PY3 = not PY2
12 | if PY3:
13 | import importlib.machinery
14 |
15 |
16 | def read(path, encoding='utf-8'):
17 | path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), path)
18 | with io.open(path, encoding=encoding) as fp:
19 | return fp.read()
20 |
21 |
22 | def version(path):
23 | """Obtain the packge version from a python file e.g. pkg/__init__.py
24 |
25 | See .
26 | """
27 | version_file = read(path)
28 | version_match = re.search(r"""^__version__ = ['"]([^'"]*)['"]""",
29 | version_file, re.M)
30 | if version_match:
31 | return version_match.group(1)
32 | raise RuntimeError("Unable to find version string.")
33 |
34 |
35 | def generate_cython():
36 | cwd = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__))
37 | print("Cythonizing sources")
38 | p = subprocess.call([sys.executable,
39 | os.path.join(cwd, 'tools', 'cythonize.py'),
40 | 'megaman'],
41 | cwd=cwd)
42 | if p != 0:
43 | raise RuntimeError("Running cythonize failed!")
44 |
45 |
46 | def configuration(parent_package='',top_path=None):
47 | from numpy.distutils.misc_util import Configuration
48 | config = Configuration(None, parent_package, top_path)
49 | config.set_options(ignore_setup_xxx_py=True,
50 | assume_default_configuration=True,
51 | delegate_options_to_subpackages=True,
52 | quiet=True)
53 |
54 | config.add_subpackage('megaman')
55 |
56 | return config
57 |
58 | DESCRIPTION = "megaman: Manifold Learning for Millions of Points"
59 | LONG_DESCRIPTION = """
60 | megaman: Manifold Learning for Millions of Points
61 | =================================================
62 |
63 | This repository contains a scalable implementation of several manifold learning
64 | algorithms, making use of FLANN for fast approximate nearest neighbors and
65 | PyAMG, LOBPCG, ARPACK, and other routines for fast matrix decompositions.
66 |
67 | For more information, visit https://github.com/mmp2/megaman
68 | """
69 | NAME = "megaman"
70 | AUTHOR = "Marina Meila"
71 | AUTHOR_EMAIL = "mmp@stat.washington.delete_this.edu"
72 | URL = 'https://github.com/mmp2/megaman'
73 | DOWNLOAD_URL = 'https://github.com/mmp2/megaman'
74 | LICENSE = 'BSD 3'
75 |
76 | VERSION = version('megaman/__init__.py')
77 |
78 |
79 | def setup_package():
80 | from numpy.distutils.core import setup
81 |
82 | old_path = os.getcwd()
83 | local_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(sys.argv[0]))
84 | src_path = local_path
85 |
86 | os.chdir(local_path)
87 | sys.path.insert(0, local_path)
88 |
89 | # Run build
90 | old_path = os.getcwd()
91 | os.chdir(src_path)
92 | sys.path.insert(0, src_path)
93 |
94 | cwd = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__))
95 | if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(cwd, 'PKG-INFO')):
96 | # Generate Cython sources, unless building from source release
97 | generate_cython()
98 |
99 | try:
100 | setup(name='megaman',
101 | author=AUTHOR,
102 | author_email=AUTHOR_EMAIL,
103 | url=URL,
104 | download_url=DOWNLOAD_URL,
105 | description=DESCRIPTION,
106 | long_description = LONG_DESCRIPTION,
107 | version=VERSION,
108 | license=LICENSE,
109 | configuration=configuration,
110 | classifiers=[
111 | 'Development Status :: 4 - Beta',
112 | 'Environment :: Console',
113 | 'Intended Audience :: Science/Research',
114 | 'License :: OSI Approved :: BSD License',
115 | 'Natural Language :: English',
116 | 'Programming Language :: Python :: 2.7',
117 | 'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.4',
118 | 'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.5'])
119 | finally:
120 | del sys.path[0]
121 | os.chdir(old_path)
122 |
123 | return
124 |
125 |
126 | if __name__ == '__main__':
127 | setup_package()
128 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4 |
5 | [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/megaman)
6 | [](https://travis-ci.org/mmp2/megaman)
7 | [](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/megaman)
8 | [](https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE)
9 |
10 | ``megaman`` is a scalable manifold learning package implemented in
11 | python. It has a front-end API designed to be familiar
12 | to [scikit-learn](http://scikit-learn.org/) but harnesses
13 | the C++ Fast Library for Approximate Nearest Neighbors (FLANN)
14 | and the Sparse Symmetric Positive Definite (SSPD) solver
15 | Locally Optimal Block Precodition Gradient (LOBPCG) method
16 | to scale manifold learning algorithms to large data sets.
17 | On a personal computer megaman can embed 1 million data points
18 | with hundreds of dimensions in 10 minutes.
19 | megaman is designed for researchers and as such caches intermediary
20 | steps and indices to allow for fast re-computation with new parameters.
21 |
22 | Package documentation can be found at http://mmp2.github.io/megaman/
23 |
24 | If you use our software please cite the following JMLR paper:
25 |
26 | McQueen, Meila, VanderPlas, & Zhang, "Megaman: Scalable Manifold Learning in Python",
27 | Journal of Machine Learning Research, Vol 17 no. 14, 2016.
28 | http://jmlr.org/papers/v17/16-109.html
29 |
30 | You can also find our arXiv paper at http://arxiv.org/abs/1603.02763
31 |
32 | ## Examples
33 |
34 | - [Tutorial Notebook]( https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/examples/megaman_tutorial.ipynb)
35 |
36 | ## Installation and Examples in Google Colab
37 |
38 | Below it's a tutorial to install megaman on Google Colab, through Conda environment.
39 |
40 | It also provides tutorial of using megaman to build spectral embedding on uniform swiss roll dataset.
41 |
42 | - [Install & Example script]( https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1ms22YK3TvrIx0gji6UZqG0zoSNRCWtXj?usp=sharing)
43 | - [You can download the Jupyter Notebook version here]( https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/examples/megaman_install_usage_colab.ipynb)
44 |
45 | ## ~~Installation with Conda~~
46 |
47 |
59 |
60 | Due to the change of API,
61 | `$ conda install -c conda-forge megaman`
62 | is no longer supported.
63 | We are currently working on fixing the bug.
64 |
65 | Please see the full install instructions below to build `megaman` from source.
66 |
67 | ## Installation from source
68 |
69 | To install megaman from source requires the following:
70 |
71 | - [python](http://python.org) tested with versions 2.7, 3.5 and 3.6
72 | - [numpy](http://numpy.org) version 1.8 or higher
73 | - [scipy](http://scipy.org) version 0.16.0 or higher
74 | - [scikit-learn](http://scikit-learn.org)
75 | - [FLANN](http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/)
76 | - [pyflann](http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/) which offers another method of computing distance matrices (this is bundled with the FLANN source code)
77 | - [cython](http://cython.org/)
78 | - a C++ compiler such as ``gcc``/``g++``
79 |
80 | Optional requirements include
81 |
82 | - [pyamg](http://pyamg.org/), which allows for faster decompositions of large matrices
83 | - [nose](https://nose.readthedocs.org/) for running the unit tests
84 | - [h5py](http://www.h5py.org) for reading testing .mat files
85 | - [plotly](https://plot.ly) an graphing library for interactive plot
86 |
87 |
88 | These requirements can be installed on Linux and MacOSX using the following conda command:
89 |
90 | ```shell
91 | $ conda create -n manifold_env python=3.5 -y
92 | # can also use python=2.7 or python=3.6
93 |
94 | $ source activate manifold_env
95 | $ conda install --channel=conda-forge -y pip nose coverage cython numpy scipy \
96 | scikit-learn pyflann pyamg h5py plotly
97 | ```
98 |
99 | Clone this repository and `cd` into source repository
100 |
101 | ```shell
102 | $ cd /tmp/
103 | $ git clone https://github.com/mmp2/megaman.git
104 | $ cd megaman
105 | ```
106 |
107 | Finally, within the source repository, run this command to install the ``megaman`` package itself:
108 | ```shell
109 | $ python setup.py install
110 | ```
111 |
112 | ## Unit Tests
113 | megaman uses ``nose`` for unit tests. With ``nose`` installed, type
114 | ```
115 | $ make test
116 | ```
117 | to run the unit tests. ``megaman`` is tested on Python versions 2.7, 3.4, and 3.5.
118 |
119 | ## Authors
120 | - [James McQueen](http://www.stat.washington.edu/people/jmcq/)
121 | - [Marina Meila](http://www.stat.washington.edu/mmp/)
122 | - [Zhongyue Zhang](https://github.com/Jerryzcn)
123 | - [Jake VanderPlas](http://www.vanderplas.com)
124 | - [Yu-Chia Chen](https://github.com/yuchaz)
125 |
126 | ## Other Contributors
127 |
128 | - Xiao Wang: lazy rmetric, Nystrom Extension
129 | - [Hangliang Ren (Harry)](https://github.com/Harryahh): Installation tutorials, Spectral Embedding
130 |
131 | ## Future Work
132 |
133 | See this issues list for what we have planned for upcoming releases:
134 |
135 | [Future Work](https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/issues/47)
136 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Conda recipes
2 |
3 | This directory contains conda build recipes for megaman and its dependencies.
4 | For more information see the
5 | [Conda Build documentation](http://conda.pydata.org/docs/build_tutorials/pkgs2.html)
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/build_all.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | conda config --set anaconda_upload yes
2 | conda build flann
3 | conda build --py all pyflann
4 | conda build --python 2.7 --python 3.4 --python 3.5 --numpy 1.9 --numpy 1.10 pyamg
5 | conda build --python 2.7 --python 3.4 --python 3.5 --numpy 1.10 megaman
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/flann/.binstar.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package: flann
2 | platform:
3 | - osx-64
4 | - osx-32
5 | - linux-64
6 | - linux-32
7 | script:
8 | - conda build .
9 | build_targets:
10 | - conda
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/flann/build.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | # cannot build flann from within the source directory
4 | mkdir build
5 | cd build
6 |
7 | # On OSX, we need to ensure we're using conda's gcc/g++
8 | if [[ `uname` == Darwin ]]; then
9 | export CC=gcc
10 | export CXX=g++
11 | fi
12 |
13 | cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=$PREFIX -DBUILD_MATLAB_BINDINGS:BOOL=OFF -DBUILD_PYTHON_BINDINGS:BOOL=OFF -DBUILD_EXAMPLES:BOOL=OFF
14 |
15 | make -j$CPU_COUNT install
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/flann/meta.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package:
2 | name: flann
3 | version: "1.8.5dev"
4 |
5 | source:
6 | git_url: https://github.com/mariusmuja/flann.git
7 | git_tag: b8a442fd98f8ce32ae3465bfd3427b5cbc36f6a5
8 |
9 | build:
10 | number: 2
11 | string: {{PKG_BUILDNUM}}_g{{GIT_FULL_HASH[:7]}}
12 |
13 | requirements:
14 | build:
15 | - gcc 4.8* # [osx]
16 | - hdf5
17 | - cmake
18 | run:
19 | - libgcc 4.8* #[osx]
20 | - hdf5
21 |
22 | about:
23 | home: http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/
24 | license: BSD
25 | license_file: COPYING
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/megaman/.binstar.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package: megaman
2 | platform:
3 | - osx-64
4 | - osx-32
5 | - linux-64
6 | - linux-32
7 | script:
8 | - conda build .
9 | build_targets:
10 | - conda
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/megaman/build.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | # On OSX, we need to ensure we're using conda's gcc/g++
4 | if [[ `uname` == Darwin ]]; then
5 | export CC=gcc
6 | export CXX=g++
7 | fi
8 |
9 | $PYTHON setup.py install
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/megaman/meta.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package:
2 | name: megaman
3 | version: 0.1.1
4 |
5 | source:
6 | git_url: https://github.com/mmp2/megaman.git
7 | git_tag: v0.1.1
8 |
9 | build:
10 | number: 2
11 | string: np{{CONDA_NPY}}py{{CONDA_PY}}_{{PKG_BUILDNUM}}
12 |
13 | requirements:
14 | build:
15 | - python >=2.7,<3|>=3.4,{{PY_VER}}*
16 | - numpy {{NPY_VER}}*
17 | - cython
18 | - flann
19 | - gcc 4.8* # [osx]
20 | run:
21 | - python {{PY_VER}}*
22 | - numpy {{NPY_VER}}*
23 | - scipy >=0.16
24 | - scikit-learn >=0.17
25 | - pyamg
26 | - pyflann
27 | - libgcc 4.8* # [osx]
28 |
29 | test:
30 | requires:
31 | - nose
32 | imports:
33 | - megaman
34 | - megaman.geometry
35 | - megaman.embedding
36 | - megaman.utils
37 |
38 | about:
39 | home: http://mmp2.github.io/megaman
40 | license: BSD
41 | license_file: LICENSE
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/megaman/run_test.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | nosetests -v megaman
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyamg/.binstar.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package: pyamg
2 | platform:
3 | - osx-64
4 | - osx-32
5 | - linux-64
6 | - linux-32
7 | script:
8 | - conda build .
9 | build_targets:
10 | - conda
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyamg/build.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | # On OSX, we need to ensure we're using conda's gcc/g++
4 | if [[ `uname` == Darwin ]]; then
5 | export CC=gcc
6 | export CXX=g++
7 | fi
8 |
9 | $PYTHON setup.py install
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyamg/meta.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package:
2 | name: pyamg
3 | version: "3.0.2"
4 |
5 | source:
6 | git_url: https://github.com/pyamg/pyamg.git
7 | git_tag: v3.0.2
8 |
9 | build:
10 | number: 2
11 | string: np{{CONDA_NPY}}py{{CONDA_PY}}_{{PKG_BUILDNUM}}
12 |
13 | requirements:
14 | build:
15 | - python >=2.7,<3|>=3.4,{{PY_VER}}*
16 | - numpy {{NPY_VER}}*
17 | - scipy
18 | - nose
19 | - zlib # [linux]
20 | - gcc 4.8* # [osx]
21 | run:
22 | - python {{PY_VER}}*
23 | - numpy {{NPY_VER}}*
24 | - scipy
25 | - zlib # [linux]
26 |
27 | test:
28 | requires:
29 | - nose
30 | imports:
31 | - pyamg
32 |
33 | about:
34 | home: http://www.pyamg.org/
35 | license: MIT
36 | license_file: LICENSE.txt
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyamg/run_test.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | if [[ `uname` == Darwin ]] && [ $PY_VER == "2.7" ]; then
4 | echo "skipping tests; see https://github.com/pyamg/pyamg/issues/165"
5 | else
6 | nosetests -v pyamg
7 | fi
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyflann/.binstar.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package: pyflann
2 | platform:
3 | - osx-64
4 | - osx-32
5 | - linux-64
6 | - linux-32
7 | script:
8 | - conda build .
9 | build_targets:
10 | - conda
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyflann/build.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | cd src/python
4 | cmake . -DLIBRARY_OUTPUT_PATH=$PREFIX/lib -DFLANN_VERSION="$PKG_VERSION"
5 | $PYTHON setup.py install
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyflann/meta.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package:
2 | name: pyflann
3 | version: "1.8.5dev"
4 |
5 | source:
6 | git_url: https://github.com/mariusmuja/flann.git
7 | git_tag: b8a442fd98f8ce32ae3465bfd3427b5cbc36f6a5
8 |
9 | build:
10 | number: 2
11 | string: py{{CONDA_PY}}_{{PKG_BUILDNUM}}_g{{GIT_FULL_HASH[:7]}}
12 |
13 | requirements:
14 | build:
15 | - python {{PY_VER}}*
16 | - setuptools
17 | - flann 1.8.5dev
18 | - cmake
19 | run:
20 | - python {{PY_VER}}*
21 | - flann 1.8.5dev
22 | - numpy
23 |
24 | test:
25 | imports:
26 | - pyflann
27 |
28 | about:
29 | home: http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/
30 | license: BSD
31 | license_file: COPYING
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | _build
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/embedding/API.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _embedding_API:
2 |
3 | .. testsetup:: *
4 |
5 | from megaman.embedding import *
6 |
7 | API Documentation
8 | =================
9 |
10 | .. automodule:: megaman.embedding.spectral_embedding
11 | :members:
12 |
13 | .. automodule:: megaman.embedding.isomap
14 | :members:
15 |
16 | .. automodule:: megaman.embedding.locally_linear
17 | :members:
18 |
19 | .. automodule:: megaman.embedding.ltsa
20 | :members:
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/embedding/index.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _embedding:
2 |
3 | ***************************************************
4 | Tools for Embedding (``megaman.embedding``)
5 | ***************************************************
6 |
7 | This module contains tools for nonlinear embedding data sets.
8 | These tools include Isomap, Spectral Embedding & Diffusion
9 | Maps, Local Tangent Space Alignment, and Locally Linear
10 | Embedding
11 |
12 | .. toctree::
13 | :maxdepth: 2
14 |
15 | isomap.rst
16 | locally_linear.rst
17 | ltsa.rst
18 | spectral_embedding.rst
19 | API
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/embedding/isomap.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _isomap:
2 |
3 | Isomap
4 | ======
5 |
6 | Isomap is one of the embeddings implemented in the megaman package.
7 | Isomap uses Multidimensional Scaling (MDS) to preserve pairwsise
8 | graph shortest distance computed using a sparse neighborhood graph.
9 |
10 | For more information see:
11 |
12 | * Tenenbaum, J.B.; De Silva, V.; & Langford, J.C.
13 | A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction.
14 | Science 290 (5500)
15 |
16 | :class:'~megaman.embedding.Isomap'
17 | This class is used to interface with isomap embedding function.
18 | Like all embedding functions in megaman it operates using a
19 | Geometry object. The Isomap class allows you to optionally
20 | pass an exiting Geometry object, otherwise it creates one.
21 |
22 | API of Isomap
23 | -------------
24 |
25 | The Isomap model, along with all the other models in megaman, have an API
26 | designed to follow in the same vein of
27 | `scikit-learn `_ API.
28 |
29 | Consequentially, the Isomap class functions as follows
30 |
31 | 1. At class instantiation `.Isomap()` parameters are passed. See API
32 | documementation for more information. An existing Geometry object
33 | can be passed to `.Isomap()`.
34 | 2. The `.fit()` method creates a Geometry object if one was not
35 | already passed and then calculates th embedding.
36 | The number of components and eigen solver can also be passed to the
37 | `.fit()` function. Since Isomap caches important quantities
38 | (like the graph distance matrix) which do not change by selecting
39 | different eigen solvers and embeding dimension these can be passed
40 | and a new embedding computed without re-computing existing quantities.
41 | the `.fit()` function does not return anything but it does create
42 | the attribute `self.embedding_` only one `self.embedding_` exists
43 | at a given time. If a new embedding is computed the old one is overwritten.
44 | 3. The `.fit_transform()` function calls the `fit()` function and returns
45 | the embedding. It does not allow for changing parameters.
46 |
47 | See the API documentation for further information.
48 |
49 | Example Usage
50 | -------------
51 |
52 | Here is an example using the function on a random data set::
53 |
54 | import numpy as np
55 | from megaman.geometry import Geometry
56 | from megaman.embedding import Isomap
57 |
58 | X = np.random.randn(100, 10)
59 | radius = 5
60 | adjacency_method = 'cyflann'
61 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':radius} # ignore distances above this radius
62 |
63 | geom = Geometry(adjacency_method=adjacency_method, adjacency_kwds=adjacency_kwds)
64 |
65 | isomap = Isomap(n_components=n_components, eigen_solver='arpack', geom=geom)
66 | embed_isomap = isomap.fit_transform(X)
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/embedding/locally_linear.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _locally_linear:
2 |
3 | Locally Linear Embedding
4 | ========================
5 |
6 | Locally linear embedding is one of the methods implemented in the megaman package.
7 | Locally Linear Embedding uses reconstruction weights estiamted on the original
8 | data set to produce an embedding that preserved the original reconstruction
9 | weights.
10 |
11 | For more information see:
12 |
13 | * Roweis, S. & Saul, L. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction
14 | by locally linear embedding. Science 290:2323 (2000).
15 |
16 | :class:'~megaman.embedding.LocallyLinearEmbedding'
17 | This class is used to interface with locally linear embedding function.
18 | Like all embedding functions in megaman it operates using a
19 | Geometry object. The Locally Linear class allows you to optionally
20 | pass an exiting Geometry object, otherwise it creates one.
21 |
22 |
23 | API of Locally Linear Embedding
24 | -------------------------------
25 |
26 | The Locally Linear model, along with all the other models in megaman, have an API
27 | designed to follow in the same vein of
28 | `scikit-learn `_ API.
29 |
30 | Consequentially, the Locally Linear class functions as follows
31 |
32 | 1. At class instantiation `.LocallyLinear()` parameters are passed. See API
33 | documementation for more information. An existing Geometry object
34 | can be passed to `.LocallyLinear()`.
35 | 2. The `.fit()` method creates a Geometry object if one was not
36 | already passed and then calculates th embedding.
37 | The number of components and eigen solver can also be passed to the
38 | `.fit()` function. WARNING: NOT COMPLETED
39 | Since LocallyLinear caches important quantities
40 | (like the barycenter weight matrix) which do not change by selecting
41 | different eigen solvers and embeding dimension these can be passed
42 | and a new embedding computed without re-computing existing quantities.
43 | the `.fit()` function does not return anything but it does create
44 | the attribute `self.embedding_` only one `self.embedding_` exists
45 | at a given time. If a new embedding is computed the old one is overwritten.
46 | 3. The `.fit_transform()` function calls the `fit()` function and returns
47 | the embedding. It does not allow for changing parameters.
48 |
49 | See the API documentation for further information.
50 |
51 | Example Usage
52 | -------------
53 |
54 | Here is an example using the function on a random data set::
55 |
56 | import numpy as np
57 | from megaman.geometry import Geometry
58 | from megaman.embedding import (Isomap, LocallyLinearEmbedding, LTSA, SpectralEmbedding)
59 |
60 | X = np.random.randn(100, 10)
61 | radius = 5
62 | adjacency_method = 'cyflann'
63 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':radius} # ignore distances above this radius
64 |
65 | geom = Geometry(adjacency_method=adjacency_method, adjacency_kwds=adjacency_kwds)
66 | lle = LocallyLinearEmbedding(n_components=n_components, eigen_solver='arpack', geom=geom)
67 | embed_lle = lle.fit_transform(X)
68 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/embedding/ltsa.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _ltsa:
2 |
3 | Local Tangent Space Alignment
4 | =============================
5 |
6 | Local Tangent Space Alignment is one of the methods implemented in the megaman package.
7 | Local Tangent Space Alighment uses independent estimates of the local tangent
8 | space at each point and then uses a global alignment procedure with a
9 | unit-scale condition to create a single embedding from each local tangent
10 | space.
11 |
12 | For more information see:
13 |
14 | * Zhang, Z. & Zha, H. Principal manifolds and nonlinear
15 | dimensionality reduction via tangent space alignment.
16 | Journal of Shanghai Univ. 8:406 (2004)
17 |
18 | :class:'~megaman.embedding.LTSA'
19 | This class is used to interface with local tangent space
20 | alignment embedding function.
21 | Like all embedding functions in megaman it operates using a
22 | Geometry object. The Locally Linear class allows you to optionally
23 | pass an exiting Geometry object, otherwise it creates one.
24 |
25 |
26 | API of Local Tangent Space Alignment
27 | ------------------------------------
28 |
29 | The Locally Tangent Space Alignment model, along with all the other models in megaman,
30 | have an API designed to follow in the same vein of
31 | `scikit-learn `_ API.
32 |
33 | Consequentially, the LTSA class functions as follows
34 |
35 | 1. At class instantiation `.LTSA()` parameters are passed. See API
36 | documementation for more information. An existing Geometry object
37 | can be passed to `.LTSA()`.
38 | 2. The `.fit()` method creates a Geometry object if one was not
39 | already passed and then calculates th embedding.
40 | The eigen solver can also be passed to the
41 | `.fit()` function. WARNING: NOT COMPLETED
42 | Since LTSA caches important quantities
43 | (like the local tangent spaces) which do not change by selecting
44 | different eigen solvers and this can be passed
45 | and a new embedding computed without re-computing existing quantities.
46 | the `.fit()` function does not return anything but it does create
47 | the attribute `self.embedding_` only one `self.embedding_` exists
48 | at a given time. If a new embedding is computed the old one is overwritten.
49 | 3. The `.fit_transform()` function calls the `fit()` function and returns
50 | the embedding. It does not allow for changing parameters.
51 |
52 | See the API documentation for further information.
53 |
54 | Example Usage
55 | -------------
56 |
57 | Here is an example using the function on a random data set::
58 |
59 | import numpy as np
60 | from megaman.geometry import Geometry
61 | from megaman.embedding import (Isomap, LocallyLinearEmbedding, LTSA, SpectralEmbedding)
62 |
63 | X = np.random.randn(100, 10)
64 | radius = 5
65 | adjacency_method = 'cyflann'
66 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':radius} # ignore distances above this radius
67 |
68 | geom = Geometry(adjacency_method=adjacency_method, adjacency_kwds=adjacency_kwds)
69 |
70 | ltsa =LTSA(n_components=n_components, eigen_solver='arpack', geom=geom)
71 | embed_ltsa = ltsa.fit_transform(X)
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/embedding/spectral_embedding.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _spectral_embedding:
2 |
3 | Spectral Embedding
4 | ==================
5 |
6 | Spectral Embedding is on of the methods implemented in the megaman package.
7 | Spectral embedding (and diffusion maps) uses the spectrum (eigen vectors
8 | and eigen values) of a graph Laplacian estimated from the data set. There
9 | are a number of different graph Laplacians that can be used.
10 |
11 | For more information see:
12 |
13 | * A Tutorial on Spectral Clustering, 2007
14 | Ulrike von Luxburg
15 | http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.165.9323
16 |
17 | :class:'~megaman.embedding.SpectralEmbedding'
18 | This class is used to interface with spectral embedding function.
19 | Like all embedding functions in megaman it operates using a
20 | Geometry object. The Isomap class allows you to optionally
21 | pass an exiting Geometry object, otherwise it creates one.
22 |
23 | API of Spectral Embedding
24 | -------------------------
25 |
26 | The Spectral Embedding model, along with all the other models in megaman,
27 | have an API designed to follow in the same vein of
28 | `scikit-learn `_ API.
29 |
30 | Consequentially, the LTSA class functions as follows
31 |
32 | 1. At class instantiation `.SpectralEmbedding()` parameters are passed. See API
33 | documementation for more information. An existing Geometry object
34 | can be passed to `.SpectralEmbedding()`. Here is also where
35 | you have the option to use diffusion maps.
36 | 2. The `.fit()` method creates a Geometry object if one was not
37 | already passed and then calculates th embedding.
38 | The eigen solver can also be passed to the
39 | `.fit()` function. WARNING: NOT COMPLETED
40 | Since Geometry caches important quantities
41 | (like the graph Laplacian) which do not change by selecting
42 | different eigen solvers and this can be passed
43 | and a new embedding computed without re-computing existing quantities.
44 | the `.fit()` function does not return anything but it does create
45 | the attribute `self.embedding_` only one `self.embedding_` exists
46 | at a given time. If a new embedding is computed the old one is overwritten.
47 | 3. The `.fit_transform()` function calls the `fit()` function and returns
48 | the embedding. It does not allow for changing parameters.
49 |
50 | See the API documentation for further information.
51 |
52 | Example Usage
53 | -------------
54 |
55 | Here is an example using the function on a random data set::
56 |
57 | import numpy as np
58 | from megaman.geometry import Geometry
59 | from megaman.embedding import SpectralEmbedding
60 |
61 | X = np.random.randn(100, 10)
62 | radius = 5
63 | adjacency_method = 'cyflann'
64 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':radius} # ignore distances above this radius
65 | affinity_method = 'gaussian'
66 | affinity_kwds = {'radius':radius} # A = exp(-||x - y||/radius^2)
67 | laplacian_method = 'geometric'
68 | laplacian_kwds = {'scaling_epps':radius} # scaling ensures convergence to Laplace-Beltrami operator
69 |
70 | geom = Geometry(adjacency_method=adjacency_method, adjacency_kwds=adjacency_kwds,
71 | affinity_method=affinity_method, affinity_kwds=affinity_kwds,
72 | laplacian_method=laplacian_method, laplacian_kwds=laplacian_kwds)
73 |
74 | spectral = SpectralEmbedding(n_components=n_components, eigen_solver='arpack',
75 | geom=geom)
76 | embed_spectral = spectral.fit_transform(X)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/geometry/API.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _geometry_API:
2 |
3 | .. testsetup:: *
4 |
5 | from megaman.geometry import *
6 |
7 | API Documentation
8 | =================
9 |
10 | .. automodule:: megaman.geometry.geometry
11 | :members:
12 |
13 | .. automodule:: megaman.geometry.rmetric
14 | :members:
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/geometry/geometry.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _geom:
2 |
3 | Geometry
4 | ========
5 |
6 | One of the fundamental objectives of manifold learning is to understand
7 | the geometry of the data. As such the primary class of this package
8 | is the geometry class:
9 |
10 | :class:'~megaman.geometry.Geometry'
11 | This class is used as the interface to compute various quantities
12 | on the original data set including: pairwise distance graphs,
13 | affinity matrices, and laplacian matrices. It also caches these
14 | quantities and allows for fast re-computation with new parameters.
15 |
16 | API of Geometry
17 | ---------------
18 |
19 | The Geometry class is used to interface with functions that compute various
20 | geometric quantities with respect to the original data set. This is the object
21 | that is passed (or computed) within each embedding function. It is how
22 | megaman caches important quantities allowing for fast re-computation with
23 | various new parameters. Beyond instantiation, the Geometry class offers
24 | three types of functions: compute, set & delete that work with the four
25 | primary data matrices: (raw) data, adjacency matrix, affinity matrix,
26 | and Laplacian Matrix.
27 |
28 | 1. Class instantiation : during class instantiation you input the parameters
29 | concerning the original data matrix such as the distance calculation method,
30 | neighborhood and affinity radius, laplacian type. Each of the three
31 | computed matrices (adjacency, affinity, laplacian) have their
32 | own keyword dictionaries which permit these methods to easily be extended.
33 | 2. `set_[some]_matrix` : these functions allow you to assign a matrix of data
34 | to the geometry object. In particular these are used to fit the geometry
35 | to your input data (which may be of the form data_matrix, adjacency_matrix,
36 | or affinity_matrix). You can also set a Laplacian matrix.
37 | 3. `compute_[some]_matrix` : these functions are designed to compute the
38 | selected matrix (e.g. adjacency). Additional keyword arguments can be
39 | passed which override the ones passed at instantiation. NB: this method
40 | will always re-compute a matrix.
41 | 4. Geometry Attributes. Other than the parameters passed at instantiation each
42 | matrix that is computed is stored as an attribute e.g. geom.adjacency_matrix,
43 | geom.adjacency_matrix, geom.laplacian_matrix. Raw data is stored as geom.X.
44 | If you want to query for these matrices without recomputing you should use
45 | these attributes e.g. my_affinity = geom.affinity_matrix.
46 | 5. `delete_[some]_matrix` : if you are working with large data sets and choose
47 | an algorithm (e.g. Isomap or Spectral Embedding) that do not require the
48 | original data_matrix, these methods can be used to clear memory.
49 |
50 | See the API documentation for further information.
51 |
52 | Example Usage
53 | -------------
54 |
55 | Here is an example using the function on a random data set::
56 |
57 | import numpy as np
58 | from megaman.geometry import Geometry
59 |
60 | X = np.random.randn(100, 10)
61 | radius = 5
62 | adjacency_method = 'cyflann'
63 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':radius} # ignore distances above this radius
64 | affinity_method = 'gaussian'
65 | affinity_kwds = {'radius':radius} # A = exp(-||x - y||/radius^2)
66 | laplacian_method = 'geometric'
67 | laplacian_kwds = {'scaling_epps':radius} # scaling ensures convergence to Laplace-Beltrami operator
68 |
69 | geom = Geometry(adjacency_method=adjacency_method, adjacency_kwds=adjacency_kwds,
70 | affinity_method=affinity_method, affinity_kwds=affinity_kwds,
71 | laplacian_method=laplacian_method, laplacian_kwds=laplacian_kwds)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/geometry/index.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _geometry:
2 |
3 | ***************************************************
4 | Tools for Geometric Analysis (``megaman.geometry``)
5 | ***************************************************
6 |
7 | This module contains tools for analyzing inherent geometry of a data set.
8 | These tools include pairwise distance calculation, as well as affinity and
9 | Laplacian construction (e.g. :class:`~megaman.geometry.Geometry`).
10 |
11 | .. toctree::
12 | :maxdepth: 2
13 |
14 | geometry.rst
15 | API
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/images/circle_to_ellipse_embedding.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/doc/images/circle_to_ellipse_embedding.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/images/index.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _images:
2 |
3 | *********************
4 | Figures from Megaman
5 | *********************
6 |
7 | This section contains some experimental results from using the
8 | megaman package.
9 |
10 | .. toctree::
11 | :maxdepth: 2
12 |
13 | spectra_Halpha.rst
14 | word2vec.rst
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/images/spectra_D4000.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/doc/images/spectra_D4000.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/images/spectra_Halpha.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/doc/images/spectra_Halpha.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/images/spectra_Halpha.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _spectrum_Halpha:
2 |
3 | Spectrum Halpha Plot
4 | ====================
5 |
6 | .. figure:: spectra_Halpha.png
7 | :scale: 50 %
8 | :alt: spectrm Halpha
9 |
10 | A three-dimensional embedding of the main sample of galaxy spectra
11 | from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (approximately 675,000 spectra
12 | observed in 3750 dimensions). Colors in the above figure indicate
13 | the strength of Hydrogen alpha emission, a very nonlinear feature
14 | which requires dozens of dimensions to be captured in a linear embedding.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/images/word2vec.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _word2vec:
2 |
3 | Word2Vec Plot
4 | ====================
5 |
6 | .. figure:: word2vec_rmetric_plot_no_digits.png
7 | :scale: 50 %
8 | :alt: word2vec embedding with R. metric
9 |
10 | 3,000,000 words and phrases mapped by word2vec using Google News into 300
11 | dimensions. The data was then embedded into 2 dimensions using Spectral
12 | Embedding. The plot shows a sample of 10,000 points displaying the overall
13 | shape of the embedding as well as the estimated "stretch"
14 | (i.e. dual push-forward Riemannian metric) at various locations in the embedding.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/images/word2vec_rmetric_plot_no_digits.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/doc/images/word2vec_rmetric_plot_no_digits.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/index.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. image:: images/spectra_Halpha.png
2 | :height: 238 px
3 | :width: 318 px
4 | :align: left
5 | :target: /megaman/images/spectra_Halpha
6 | .. image:: images/word2vec_rmetric_plot_no_digits.png
7 | :height: 250 px
8 | :width: 220 px
9 | :align: right
10 | :target: /megaman/images/word2vec
11 |
12 |
13 | megaman: Manifold Learning for Millions of Points
14 | =================================================
15 |
16 | megaman is a scalable manifold learning package implemented in
17 | python. It has a front-end API designed to be familiar
18 | to `scikit-learn `_ but harnesses
19 | the C++ Fast Library for Approximate Nearest Neighbors (FLANN)
20 | and the Sparse Symmetric Positive Definite (SSPD) solver
21 | Locally Optimal Block Precodition Gradient (LOBPCG) method
22 | to scale manifold learning algorithms to large data sets.
23 | It is designed for researchers and as such caches intermediary
24 | steps and indices to allow for fast re-computation with new parameters.
25 |
26 | For issues & contributions, see the source
27 | `repository on github `_.
28 |
29 | For example notebooks see the
30 | `index on github `_.
31 |
32 | You can also read our
33 | `arXiv paper `_.
34 |
35 | Documentation
36 | =============
37 |
38 | .. toctree::
39 | :maxdepth: 2
40 |
41 | installation
42 | geometry/index
43 | embedding/index
44 | utils/index
45 | images/index
46 |
47 |
48 | Indices and tables
49 | ==================
50 |
51 | * :ref:`genindex`
52 | * :ref:`modindex`
53 | * :ref:`search`
54 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/installation.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Installation
2 | ============
3 |
4 | Though ``megaman`` has a fair number of compiled dependencies, it is
5 | straightforward to install using the cross-platform conda_ package manager.
6 |
7 | Installation with Conda
8 | -----------------------
9 |
10 | To install ``megaman`` and all its dependencies using conda_, run::
11 |
12 | $ conda install megaman --channel=conda-forge
13 |
14 | Currently builds are available for OSX and Linux, on Python 2.7, 3.4, and 3.5.
15 | For other operating systems, see the full install instructions below.
16 |
17 | Installation from Source
18 | ------------------------
19 |
20 | To install ``megaman`` from source requires the following:
21 |
22 | - python_: tested with versions 2.7, 3.4, and 3.5
23 | - numpy_: version 1.8 or higher
24 | - scipy_: version 0.16.0 or higher
25 | - scikit-learn_: version 0.16.0 or higher
26 | - FLANN_: version 1.8 or higher
27 | - cython_: version 0.23 or higher
28 | - a C++ compiler such as ``gcc``/``g++`` (we recommend version 4.8.*)
29 |
30 | Optional requirements include:
31 |
32 | - pyamg_, which provides fast decompositions of large sparse matrices
33 | - pyflann_, which offers an alternative FLANN interface for computing distance matrices (this is bundled with the FLANN source code)
34 | - nose_ for running the unit tests
35 |
36 | These requirements can be installed on Linux and MacOSX using the following conda command::
37 |
38 | $ conda install --channel=jakevdp pip nose coverage gcc cython numpy scipy scikit-learn pyflann pyamg
39 |
40 | Finally, within the source repository, run this command to install the ``megaman`` package itself::
41 |
42 | $ python setup.py install
43 |
44 | Unit Tests
45 | ----------
46 | ``megaman`` uses nose_ for unit tests. To run the unit tests once ``nose`` is installed, type in the source directory::
47 |
48 | $ make test
49 |
50 | or, outside the source directory once ``megaman`` is installed::
51 |
52 | $ nosetests megaman
53 |
54 | ``megaman`` is tested on Python versions 2.7, 3.4, and 3.5.
55 |
56 | .. _conda: http://conda.pydata.org/miniconda.html
57 | .. _python: http://python.org
58 | .. _numpy: http://numpy.org
59 | .. _scipy: http://scipy.org
60 | .. _scikit-learn: http://scikit-learn.org
61 | .. _FLANN: http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/
62 | .. _pyamg: http://pyamg.org/
63 | .. _pyflann: http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/
64 | .. _nose: https://nose.readthedocs.org/
65 | .. _cython: http://cython.org/
66 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import division, absolute_import, print_function
2 |
3 | from .numpydoc import setup
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/astropyautosummary.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Licensed under a 3-clause BSD style license - see LICENSE.rst
2 | """
3 | This sphinx extension builds off of `sphinx.ext.autosummary` to
4 | clean up some issues it presents in the Astropy docs.
5 |
6 | The main issue this fixes is the summary tables getting cut off before the
7 | end of the sentence in some cases.
8 |
9 | Note: Sphinx 1.2 appears to have fixed the the main issues in the stock
10 | autosummary extension that are addressed by this extension. So use of this
11 | extension with newer versions of Sphinx is deprecated.
12 | """
13 |
14 | import re
15 |
16 | from distutils.version import LooseVersion
17 |
18 | import sphinx
19 |
20 | from sphinx.ext.autosummary import Autosummary
21 |
22 | from ...utils import deprecated
23 |
24 | # used in AstropyAutosummary.get_items
25 | _itemsummrex = re.compile(r'^([A-Z].*?\.(?:\s|$))')
26 |
27 |
28 | @deprecated('1.0', message='AstropyAutosummary is only needed when used '
29 | 'with Sphinx versions less than 1.2')
30 | class AstropyAutosummary(Autosummary):
31 | def get_items(self, names):
32 | """Try to import the given names, and return a list of
33 | ``[(name, signature, summary_string, real_name), ...]``.
34 | """
35 | from sphinx.ext.autosummary import (get_import_prefixes_from_env,
36 | import_by_name, get_documenter, mangle_signature)
37 |
38 | env = self.state.document.settings.env
39 |
40 | prefixes = get_import_prefixes_from_env(env)
41 |
42 | items = []
43 |
44 | max_item_chars = 50
45 |
46 | for name in names:
47 | display_name = name
48 | if name.startswith('~'):
49 | name = name[1:]
50 | display_name = name.split('.')[-1]
51 |
52 | try:
53 | import_by_name_values = import_by_name(name, prefixes=prefixes)
54 | except ImportError:
55 | self.warn('[astropyautosummary] failed to import %s' % name)
56 | items.append((name, '', '', name))
57 | continue
58 |
59 | # to accommodate Sphinx v1.2.2 and v1.2.3
60 | if len(import_by_name_values) == 3:
61 | real_name, obj, parent = import_by_name_values
62 | elif len(import_by_name_values) == 4:
63 | real_name, obj, parent, module_name = import_by_name_values
64 |
65 | # NB. using real_name here is important, since Documenters
66 | # handle module prefixes slightly differently
67 | documenter = get_documenter(obj, parent)(self, real_name)
68 | if not documenter.parse_name():
69 | self.warn('[astropyautosummary] failed to parse name %s' % real_name)
70 | items.append((display_name, '', '', real_name))
71 | continue
72 | if not documenter.import_object():
73 | self.warn('[astropyautosummary] failed to import object %s' % real_name)
74 | items.append((display_name, '', '', real_name))
75 | continue
76 |
77 | # -- Grab the signature
78 |
79 | sig = documenter.format_signature()
80 | if not sig:
81 | sig = ''
82 | else:
83 | max_chars = max(10, max_item_chars - len(display_name))
84 | sig = mangle_signature(sig, max_chars=max_chars)
85 | sig = sig.replace('*', r'\*')
86 |
87 | # -- Grab the summary
88 |
89 | doc = list(documenter.process_doc(documenter.get_doc()))
90 |
91 | while doc and not doc[0].strip():
92 | doc.pop(0)
93 | m = _itemsummrex.search(" ".join(doc).strip())
94 | if m:
95 | summary = m.group(1).strip()
96 | elif doc:
97 | summary = doc[0].strip()
98 | else:
99 | summary = ''
100 |
101 | items.append((display_name, sig, summary, real_name))
102 |
103 | return items
104 |
105 |
106 | def setup(app):
107 | # need autosummary, of course
108 | app.setup_extension('sphinx.ext.autosummary')
109 |
110 | # Don't make the replacement if Sphinx is at least 1.2
111 | if LooseVersion(sphinx.__version__) < LooseVersion('1.2.0'):
112 | # this replaces the default autosummary with the astropy one
113 | app.add_directive('autosummary', AstropyAutosummary)
114 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/autodoc_enhancements.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Miscellaneous enhancements to help autodoc along.
3 | """
4 |
5 |
6 | # See
7 | # https://github.com/astropy/astropy-helpers/issues/116#issuecomment-71254836
8 | # for further background on this.
9 | def type_object_attrgetter(obj, attr, *defargs):
10 | """
11 | This implements an improved attrgetter for type objects (i.e. classes)
12 | that can handle class attributes that are implemented as properties on
13 | a metaclass.
14 |
15 | Normally `getattr` on a class with a `property` (say, "foo"), would return
16 | the `property` object itself. However, if the class has a metaclass which
17 | *also* defines a `property` named "foo", ``getattr(cls, 'foo')`` will find
18 | the "foo" property on the metaclass and resolve it. For the purposes of
19 | autodoc we just want to document the "foo" property defined on the class,
20 | not on the metaclass.
21 |
22 | For example::
23 |
24 | >>> class Meta(type):
25 | ... @property
26 | ... def foo(cls):
27 | ... return 'foo'
28 | ...
29 | >>> class MyClass(metaclass=Meta):
30 | ... @property
31 | ... def foo(self):
32 | ... \"\"\"Docstring for MyClass.foo property.\"\"\"
33 | ... return 'myfoo'
34 | ...
35 | >>> getattr(MyClass, 'foo')
36 | 'foo'
37 | >>> type_object_attrgetter(MyClass, 'foo')
38 |
39 | >>> type_object_attrgetter(MyClass, 'foo').__doc__
40 | 'Docstring for MyClass.foo property.'
41 |
42 | The last line of the example shows the desired behavior for the purposes
43 | of autodoc.
44 | """
45 |
46 | for base in obj.__mro__:
47 | if attr in base.__dict__:
48 | if isinstance(base.__dict__[attr], property):
49 | # Note, this should only be used for properties--for any other
50 | # type of descriptor (classmethod, for example) this can mess
51 | # up existing expectations of what getattr(cls, ...) returns
52 | return base.__dict__[attr]
53 | break
54 |
55 | return getattr(obj, attr, *defargs)
56 |
57 |
58 | def setup(app):
59 | app.add_autodoc_attrgetter(type, type_object_attrgetter)
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/changelog_links.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Licensed under a 3-clause BSD style license - see LICENSE.rst
2 | """
3 | This sphinx extension makes the issue numbers in the changelog into links to
4 | GitHub issues.
5 | """
6 |
7 | from __future__ import print_function
8 |
9 | import re
10 |
11 | from docutils.nodes import Text, reference
12 |
13 | BLOCK_PATTERN = re.compile('\[#.+\]', flags=re.DOTALL)
14 | ISSUE_PATTERN = re.compile('#[0-9]+')
15 |
16 |
17 | def process_changelog_links(app, doctree, docname):
18 | for rex in app.changelog_links_rexes:
19 | if rex.match(docname):
20 | break
21 | else:
22 | # if the doc doesn't match any of the changelog regexes, don't process
23 | return
24 |
25 | app.info('[changelog_links] Adding changelog links to "{0}"'.format(docname))
26 |
27 | for item in doctree.traverse():
28 |
29 | if not isinstance(item, Text):
30 | continue
31 |
32 | # We build a new list of items to replace the current item. If
33 | # a link is found, we need to use a 'reference' item.
34 | children = []
35 |
36 | # First cycle through blocks of issues (delimited by []) then
37 | # iterate inside each one to find the individual issues.
38 | prev_block_end = 0
39 | for block in BLOCK_PATTERN.finditer(item):
40 | block_start, block_end = block.start(), block.end()
41 | children.append(Text(item[prev_block_end:block_start]))
42 | block = item[block_start:block_end]
43 | prev_end = 0
44 | for m in ISSUE_PATTERN.finditer(block):
45 | start, end = m.start(), m.end()
46 | children.append(Text(block[prev_end:start]))
47 | issue_number = block[start:end]
48 | refuri = app.config.github_issues_url + issue_number[1:]
49 | children.append(reference(text=issue_number,
50 | name=issue_number,
51 | refuri=refuri))
52 | prev_end = end
53 |
54 | prev_block_end = block_end
55 |
56 | # If no issues were found, this adds the whole item,
57 | # otherwise it adds the remaining text.
58 | children.append(Text(block[prev_end:block_end]))
59 |
60 | # If no blocks were found, this adds the whole item, otherwise
61 | # it adds the remaining text.
62 | children.append(Text(item[prev_block_end:]))
63 |
64 | # Replace item by the new list of items we have generated,
65 | # which may contain links.
66 | item.parent.replace(item, children)
67 |
68 |
69 | def setup_patterns_rexes(app):
70 | app.changelog_links_rexes = [re.compile(pat) for pat in
71 | app.config.changelog_links_docpattern]
72 |
73 |
74 | def setup(app):
75 | app.connect('doctree-resolved', process_changelog_links)
76 | app.connect('builder-inited', setup_patterns_rexes)
77 | app.add_config_value('github_issues_url', None, True)
78 | app.add_config_value('changelog_links_docpattern', ['.*changelog.*', 'whatsnew/.*'], True)
79 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/comment_eater.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import division, absolute_import, print_function
2 |
3 | import sys
4 | if sys.version_info[0] >= 3:
5 | from io import StringIO
6 | else:
7 | from io import StringIO
8 |
9 | import compiler
10 | import inspect
11 | import textwrap
12 | import tokenize
13 |
14 | from .compiler_unparse import unparse
15 |
16 |
17 | class Comment(object):
18 | """ A comment block.
19 | """
20 | is_comment = True
21 | def __init__(self, start_lineno, end_lineno, text):
22 | # int : The first line number in the block. 1-indexed.
23 | self.start_lineno = start_lineno
24 | # int : The last line number. Inclusive!
25 | self.end_lineno = end_lineno
26 | # str : The text block including '#' character but not any leading spaces.
27 | self.text = text
28 |
29 | def add(self, string, start, end, line):
30 | """ Add a new comment line.
31 | """
32 | self.start_lineno = min(self.start_lineno, start[0])
33 | self.end_lineno = max(self.end_lineno, end[0])
34 | self.text += string
35 |
36 | def __repr__(self):
37 | return '%s(%r, %r, %r)' % (self.__class__.__name__, self.start_lineno,
38 | self.end_lineno, self.text)
39 |
40 |
41 | class NonComment(object):
42 | """ A non-comment block of code.
43 | """
44 | is_comment = False
45 | def __init__(self, start_lineno, end_lineno):
46 | self.start_lineno = start_lineno
47 | self.end_lineno = end_lineno
48 |
49 | def add(self, string, start, end, line):
50 | """ Add lines to the block.
51 | """
52 | if string.strip():
53 | # Only add if not entirely whitespace.
54 | self.start_lineno = min(self.start_lineno, start[0])
55 | self.end_lineno = max(self.end_lineno, end[0])
56 |
57 | def __repr__(self):
58 | return '%s(%r, %r)' % (self.__class__.__name__, self.start_lineno,
59 | self.end_lineno)
60 |
61 |
62 | class CommentBlocker(object):
63 | """ Pull out contiguous comment blocks.
64 | """
65 | def __init__(self):
66 | # Start with a dummy.
67 | self.current_block = NonComment(0, 0)
68 |
69 | # All of the blocks seen so far.
70 | self.blocks = []
71 |
72 | # The index mapping lines of code to their associated comment blocks.
73 | self.index = {}
74 |
75 | def process_file(self, file):
76 | """ Process a file object.
77 | """
78 | if sys.version_info[0] >= 3:
79 | nxt = file.__next__
80 | else:
81 | nxt = file.next
82 | for token in tokenize.generate_tokens(nxt):
83 | self.process_token(*token)
84 | self.make_index()
85 |
86 | def process_token(self, kind, string, start, end, line):
87 | """ Process a single token.
88 | """
89 | if self.current_block.is_comment:
90 | if kind == tokenize.COMMENT:
91 | self.current_block.add(string, start, end, line)
92 | else:
93 | self.new_noncomment(start[0], end[0])
94 | else:
95 | if kind == tokenize.COMMENT:
96 | self.new_comment(string, start, end, line)
97 | else:
98 | self.current_block.add(string, start, end, line)
99 |
100 | def new_noncomment(self, start_lineno, end_lineno):
101 | """ We are transitioning from a noncomment to a comment.
102 | """
103 | block = NonComment(start_lineno, end_lineno)
104 | self.blocks.append(block)
105 | self.current_block = block
106 |
107 | def new_comment(self, string, start, end, line):
108 | """ Possibly add a new comment.
109 |
110 | Only adds a new comment if this comment is the only thing on the line.
111 | Otherwise, it extends the noncomment block.
112 | """
113 | prefix = line[:start[1]]
114 | if prefix.strip():
115 | # Oops! Trailing comment, not a comment block.
116 | self.current_block.add(string, start, end, line)
117 | else:
118 | # A comment block.
119 | block = Comment(start[0], end[0], string)
120 | self.blocks.append(block)
121 | self.current_block = block
122 |
123 | def make_index(self):
124 | """ Make the index mapping lines of actual code to their associated
125 | prefix comments.
126 | """
127 | for prev, block in zip(self.blocks[:-1], self.blocks[1:]):
128 | if not block.is_comment:
129 | self.index[block.start_lineno] = prev
130 |
131 | def search_for_comment(self, lineno, default=None):
132 | """ Find the comment block just before the given line number.
133 |
134 | Returns None (or the specified default) if there is no such block.
135 | """
136 | if not self.index:
137 | self.make_index()
138 | block = self.index.get(lineno, None)
139 | text = getattr(block, 'text', default)
140 | return text
141 |
142 |
143 | def strip_comment_marker(text):
144 | """ Strip # markers at the front of a block of comment text.
145 | """
146 | lines = []
147 | for line in text.splitlines():
148 | lines.append(line.lstrip('#'))
149 | text = textwrap.dedent('\n'.join(lines))
150 | return text
151 |
152 |
153 | def get_class_traits(klass):
154 | """ Yield all of the documentation for trait definitions on a class object.
155 | """
156 | # FIXME: gracefully handle errors here or in the caller?
157 | source = inspect.getsource(klass)
158 | cb = CommentBlocker()
159 | cb.process_file(StringIO(source))
160 | mod_ast = compiler.parse(source)
161 | class_ast = mod_ast.node.nodes[0]
162 | for node in class_ast.code.nodes:
163 | # FIXME: handle other kinds of assignments?
164 | if isinstance(node, compiler.ast.Assign):
165 | name = node.nodes[0].name
166 | rhs = unparse(node.expr).strip()
167 | doc = strip_comment_marker(cb.search_for_comment(node.lineno, default=''))
168 | yield name, rhs, doc
169 |
170 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/doctest.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Licensed under a 3-clause BSD style license - see LICENSE.rst
2 | """
3 | This is a set of three directives that allow us to insert metadata
4 | about doctests into the .rst files so the testing framework knows
5 | which tests to skip.
6 |
7 | This is quite different from the doctest extension in Sphinx itself,
8 | which actually does something. For astropy, all of the testing is
9 | centrally managed from py.test and Sphinx is not used for running
10 | tests.
11 | """
12 | import re
13 | from docutils.nodes import literal_block
14 | from sphinx.util.compat import Directive
15 |
16 |
17 | class DoctestSkipDirective(Directive):
18 | has_content = True
19 |
20 | def run(self):
21 | # Check if there is any valid argument, and skip it. Currently only
22 | # 'win32' is supported in astropy.tests.pytest_plugins.
23 | if re.match('win32', self.content[0]):
24 | self.content = self.content[2:]
25 | code = '\n'.join(self.content)
26 | return [literal_block(code, code)]
27 |
28 |
29 | class DoctestRequiresDirective(DoctestSkipDirective):
30 | # This is silly, but we really support an unbounded number of
31 | # optional arguments
32 | optional_arguments = 64
33 |
34 |
35 | def setup(app):
36 | app.add_directive('doctest-requires', DoctestRequiresDirective)
37 | app.add_directive('doctest-skip', DoctestSkipDirective)
38 | app.add_directive('doctest-skip-all', DoctestSkipDirective)
39 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/smart_resolver.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Licensed under a 3-clause BSD style license - see LICENSE.rst
2 | """
3 | The classes in the astropy docs are documented by their API location,
4 | which is not necessarily where they are defined in the source. This
5 | causes a problem when certain automated features of the doc build,
6 | such as the inheritance diagrams or the `Bases` list of a class
7 | reference a class by its canonical location rather than its "user"
8 | location.
9 |
10 | In the `autodoc-process-docstring` event, a mapping from the actual
11 | name to the API name is maintained. Later, in the `missing-reference`
12 | event, unresolved references are looked up in this dictionary and
13 | corrected if possible.
14 | """
15 |
16 | from docutils.nodes import literal, reference
17 |
18 |
19 | def process_docstring(app, what, name, obj, options, lines):
20 | if isinstance(obj, type):
21 | env = app.env
22 | if not hasattr(env, 'class_name_mapping'):
23 | env.class_name_mapping = {}
24 | mapping = env.class_name_mapping
25 | mapping[obj.__module__ + '.' + obj.__name__] = name
26 |
27 |
28 | def missing_reference_handler(app, env, node, contnode):
29 | if not hasattr(env, 'class_name_mapping'):
30 | env.class_name_mapping = {}
31 | mapping = env.class_name_mapping
32 | reftype = node['reftype']
33 | reftarget = node['reftarget']
34 | if reftype in ('obj', 'class', 'exc', 'meth'):
35 | reftarget = node['reftarget']
36 | suffix = ''
37 | if reftarget not in mapping:
38 | if '.' in reftarget:
39 | front, suffix = reftarget.rsplit('.', 1)
40 | else:
41 | suffix = reftarget
42 |
43 | if suffix.startswith('_') and not suffix.startswith('__'):
44 | # If this is a reference to a hidden class or method,
45 | # we can't link to it, but we don't want to have a
46 | # nitpick warning.
47 | return node[0].deepcopy()
48 |
49 | if reftype in ('obj', 'meth') and '.' in reftarget:
50 | if front in mapping:
51 | reftarget = front
52 | suffix = '.' + suffix
53 |
54 | if (reftype in ('class', ) and '.' in reftarget
55 | and reftarget not in mapping):
56 |
57 | if '.' in front:
58 | reftarget, _ = front.rsplit('.', 1)
59 | suffix = '.' + suffix
60 | reftarget = reftarget + suffix
61 | prefix = reftarget.rsplit('.')[0]
62 | if (reftarget not in mapping and
63 | prefix in env.intersphinx_named_inventory):
64 |
65 | if reftarget in env.intersphinx_named_inventory[prefix]['py:class']:
66 | newtarget = env.intersphinx_named_inventory[prefix]['py:class'][reftarget][2]
67 | if not node['refexplicit'] and \
68 | '~' not in node.rawsource:
69 | contnode = literal(text=reftarget)
70 | newnode = reference('', '', internal=True)
71 | newnode['reftitle'] = reftarget
72 | newnode['refuri'] = newtarget
73 | newnode.append(contnode)
74 |
75 | return newnode
76 |
77 | if reftarget in mapping:
78 | newtarget = mapping[reftarget] + suffix
79 | if not node['refexplicit'] and not '~' in node.rawsource:
80 | contnode = literal(text=newtarget)
81 | newnode = env.domains['py'].resolve_xref(
82 | env, node['refdoc'], app.builder, 'class', newtarget,
83 | node, contnode)
84 | if newnode is not None:
85 | newnode['reftitle'] = reftarget
86 | return newnode
87 |
88 |
89 | def setup(app):
90 | app.connect('autodoc-process-docstring', process_docstring)
91 |
92 | app.connect('missing-reference', missing_reference_handler)
93 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/tocdepthfix.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from sphinx import addnodes
2 |
3 |
4 | def fix_toc_entries(app, doctree):
5 | # Get the docname; I don't know why this isn't just passed in to the
6 | # callback
7 | # This seems a bit unreliable as it's undocumented, but it's not "private"
8 | # either:
9 | docname = app.builder.env.temp_data['docname']
10 | if app.builder.env.metadata[docname].get('tocdepth', 0) != 0:
11 | # We need to reprocess any TOC nodes in the doctree and make sure all
12 | # the files listed in any TOCs are noted
13 | for treenode in doctree.traverse(addnodes.toctree):
14 | app.builder.env.note_toctree(docname, treenode)
15 |
16 |
17 | def setup(app):
18 | app.connect('doctree-read', fix_toc_entries)
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/traitsdoc.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | =========
3 | traitsdoc
4 | =========
5 |
6 | Sphinx extension that handles docstrings in the Numpy standard format, [1]
7 | and support Traits [2].
8 |
9 | This extension can be used as a replacement for ``numpydoc`` when support
10 | for Traits is required.
11 |
12 | .. [1] http://projects.scipy.org/numpy/wiki/CodingStyleGuidelines#docstring-standard
13 | .. [2] http://code.enthought.com/projects/traits/
14 |
15 | """
16 | from __future__ import division, absolute_import, print_function
17 |
18 | import inspect
19 | import os
20 | import pydoc
21 | import collections
22 |
23 | from . import docscrape
24 | from . import docscrape_sphinx
25 | from .docscrape_sphinx import SphinxClassDoc, SphinxFunctionDoc, SphinxDocString
26 |
27 | from . import numpydoc
28 |
29 | from . import comment_eater
30 |
31 | class SphinxTraitsDoc(SphinxClassDoc):
32 | def __init__(self, cls, modulename='', func_doc=SphinxFunctionDoc):
33 | if not inspect.isclass(cls):
34 | raise ValueError("Initialise using a class. Got %r" % cls)
35 | self._cls = cls
36 |
37 | if modulename and not modulename.endswith('.'):
38 | modulename += '.'
39 | self._mod = modulename
40 | self._name = cls.__name__
41 | self._func_doc = func_doc
42 |
43 | docstring = pydoc.getdoc(cls)
44 | docstring = docstring.split('\n')
45 |
46 | # De-indent paragraph
47 | try:
48 | indent = min(len(s) - len(s.lstrip()) for s in docstring
49 | if s.strip())
50 | except ValueError:
51 | indent = 0
52 |
53 | for n,line in enumerate(docstring):
54 | docstring[n] = docstring[n][indent:]
55 |
56 | self._doc = docscrape.Reader(docstring)
57 | self._parsed_data = {
58 | 'Signature': '',
59 | 'Summary': '',
60 | 'Description': [],
61 | 'Extended Summary': [],
62 | 'Parameters': [],
63 | 'Returns': [],
64 | 'Raises': [],
65 | 'Warns': [],
66 | 'Other Parameters': [],
67 | 'Traits': [],
68 | 'Methods': [],
69 | 'See Also': [],
70 | 'Notes': [],
71 | 'References': '',
72 | 'Example': '',
73 | 'Examples': '',
74 | 'index': {}
75 | }
76 |
77 | self._parse()
78 |
79 | def _str_summary(self):
80 | return self['Summary'] + ['']
81 |
82 | def _str_extended_summary(self):
83 | return self['Description'] + self['Extended Summary'] + ['']
84 |
85 | def __str__(self, indent=0, func_role="func"):
86 | out = []
87 | out += self._str_signature()
88 | out += self._str_index() + ['']
89 | out += self._str_summary()
90 | out += self._str_extended_summary()
91 | for param_list in ('Parameters', 'Traits', 'Methods',
92 | 'Returns','Raises'):
93 | out += self._str_param_list(param_list)
94 | out += self._str_see_also("obj")
95 | out += self._str_section('Notes')
96 | out += self._str_references()
97 | out += self._str_section('Example')
98 | out += self._str_section('Examples')
99 | out = self._str_indent(out,indent)
100 | return '\n'.join(out)
101 |
102 | def looks_like_issubclass(obj, classname):
103 | """ Return True if the object has a class or superclass with the given class
104 | name.
105 |
106 | Ignores old-style classes.
107 | """
108 | t = obj
109 | if t.__name__ == classname:
110 | return True
111 | for klass in t.__mro__:
112 | if klass.__name__ == classname:
113 | return True
114 | return False
115 |
116 | def get_doc_object(obj, what=None, config=None):
117 | if what is None:
118 | if inspect.isclass(obj):
119 | what = 'class'
120 | elif inspect.ismodule(obj):
121 | what = 'module'
122 | elif isinstance(obj, collections.Callable):
123 | what = 'function'
124 | else:
125 | what = 'object'
126 | if what == 'class':
127 | doc = SphinxTraitsDoc(obj, '', func_doc=SphinxFunctionDoc, config=config)
128 | if looks_like_issubclass(obj, 'HasTraits'):
129 | for name, trait, comment in comment_eater.get_class_traits(obj):
130 | # Exclude private traits.
131 | if not name.startswith('_'):
132 | doc['Traits'].append((name, trait, comment.splitlines()))
133 | return doc
134 | elif what in ('function', 'method'):
135 | return SphinxFunctionDoc(obj, '', config=config)
136 | else:
137 | return SphinxDocString(pydoc.getdoc(obj), config=config)
138 |
139 | def setup(app):
140 | # init numpydoc
141 | numpydoc.setup(app, get_doc_object)
142 |
143 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/sphinxext/numpy_ext/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import inspect
2 | import sys
3 |
4 |
5 | def find_mod_objs(modname, onlylocals=False):
6 | """ Returns all the public attributes of a module referenced by name.
7 |
8 | .. note::
9 | The returned list *not* include subpackages or modules of
10 | `modname`,nor does it include private attributes (those that
11 | beginwith '_' or are not in `__all__`).
12 |
13 | Parameters
14 | ----------
15 | modname : str
16 | The name of the module to search.
17 | onlylocals : bool
18 | If True, only attributes that are either members of `modname` OR one of
19 | its modules or subpackages will be included.
20 |
21 | Returns
22 | -------
23 | localnames : list of str
24 | A list of the names of the attributes as they are named in the
25 | module `modname` .
26 | fqnames : list of str
27 | A list of the full qualified names of the attributes (e.g.,
28 | ``astropy.utils.misc.find_mod_objs``). For attributes that are
29 | simple variables, this is based on the local name, but for
30 | functions or classes it can be different if they are actually
31 | defined elsewhere and just referenced in `modname`.
32 | objs : list of objects
33 | A list of the actual attributes themselves (in the same order as
34 | the other arguments)
35 |
36 | """
37 |
38 | __import__(modname)
39 | mod = sys.modules[modname]
40 |
41 | if hasattr(mod, '__all__'):
42 | pkgitems = [(k, mod.__dict__[k]) for k in mod.__all__]
43 | else:
44 | pkgitems = [(k, mod.__dict__[k]) for k in dir(mod) if k[0] != '_']
45 |
46 | # filter out modules and pull the names and objs out
47 | ismodule = inspect.ismodule
48 | localnames = [k for k, v in pkgitems if not ismodule(v)]
49 | objs = [v for k, v in pkgitems if not ismodule(v)]
50 |
51 | # fully qualified names can be determined from the object's module
52 | fqnames = []
53 | for obj, lnm in zip(objs, localnames):
54 | if hasattr(obj, '__module__') and hasattr(obj, '__name__'):
55 | fqnames.append(obj.__module__ + '.' + obj.__name__)
56 | else:
57 | fqnames.append(modname + '.' + lnm)
58 |
59 | if onlylocals:
60 | valids = [fqn.startswith(modname) for fqn in fqnames]
61 | localnames = [e for i, e in enumerate(localnames) if valids[i]]
62 | fqnames = [e for i, e in enumerate(fqnames) if valids[i]]
63 | objs = [e for i, e in enumerate(objs) if valids[i]]
64 |
65 | return localnames, fqnames, objs
66 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/utils/API.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _utils_API:
2 |
3 | .. testsetup:: *
4 |
5 | from megaman.utils import *
6 |
7 | API Documentation
8 | =================
9 |
10 | .. automodule:: megaman.utils.eigendecomp
11 | :members:
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/utils/index.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _utils:
2 |
3 | ***************************************************
4 | Utility tools for megaman (``megaman.utils``)
5 | ***************************************************
6 |
7 | This module contains utility functions used inside
8 | megaman. In particular the eigendecomposition.
9 |
10 | .. toctree::
11 | :maxdepth: 2
12 |
13 | API
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/example.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import sys
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import scipy as sp
4 | import scipy.sparse as sparse
5 | from megaman.geometry import Geometry
6 | from sklearn import datasets
7 | from megaman.embedding import (Isomap, LocallyLinearEmbedding,
8 | LTSA, SpectralEmbedding)
9 |
10 | # Generate an example data set
11 | N = 10
12 | X, color = datasets.samples_generator.make_s_curve(N, random_state=0)
13 |
14 | # Geometry is the main class that will Cache things like distance, affinity, and laplacian.
15 | # you instantiate the Geometry class with the parameters & methods for the three main components:
16 | # Adjacency: an NxN (sparse) pairwise matrix indicating neighborhood regions
17 | # Affinity an NxN (sparse) pairwise matrix insicated similarity between points
18 | # Laplacian an NxN (sparse) pairwsie matrix containing geometric manifold information
19 |
20 | radius = 5
21 | adjacency_method = 'cyflann'
22 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':radius} # ignore distances above this radius
23 | affinity_method = 'gaussian'
24 | affinity_kwds = {'radius':radius} # A = exp(-||x - y||/radius^2)
25 | laplacian_method = 'geometric'
26 | laplacian_kwds = {'scaling_epps':radius} # scaling ensures convergence to Laplace-Beltrami operator
27 |
28 | geom = Geometry(adjacency_method=adjacency_method, adjacency_kwds=adjacency_kwds,
29 | affinity_method=affinity_method, affinity_kwds=affinity_kwds,
30 | laplacian_method=laplacian_method, laplacian_kwds=laplacian_kwds)
31 |
32 | # You can/should also use the set_data_matrix, set_adjacency_matrix, set_affinity_matrix
33 | # to send your data set (in whichever form it takes) this way.
34 | geom.set_data_matrix(X)
35 |
36 | # You can get the distance, affinity etc with e.g: Geometry.get_distance_matrix()
37 | # you can update the keyword arguments passed inially using these functions
38 | adjacency_matrix = geom.compute_adjacency_matrix()
39 | # by defualt this is pass-by-reference. Use copy=True to get a copied version.
40 |
41 | # If you don't want to pre-compute a Geometry you can pass a dictionary or geometry
42 | # arguments to one of the embedding classes.
43 | geom = {'adjacency_method':adjacency_method, 'adjacency_kwds':adjacency_kwds,
44 | 'affinity_method':affinity_method, 'affinity_kwds':affinity_kwds,
45 | 'laplacian_method':laplacian_method, 'laplacian_kwds':laplacian_kwds}
46 |
47 |
48 | # an example follows for creating each embedding into 2 dimensions.
49 | n_components = 2
50 |
51 | # LTSA
52 | ltsa =LTSA(n_components=n_components, eigen_solver='arpack',
53 | geom=geom)
54 | embed_ltsa = ltsa.fit_transform(X)
55 |
56 | # LLE
57 | lle = LocallyLinearEmbedding(n_components=n_components, eigen_solver='arpack',
58 | geom=geom)
59 | embed_lle = lle.fit_transform(X)
60 |
61 | # Isomap
62 | isomap = Isomap(n_components=n_components, eigen_solver='arpack',
63 | geom=geom)
64 | embed_isomap = isomap.fit_transform(X)
65 |
66 | # Spectral Embedding
67 | spectral = SpectralEmbedding(n_components=n_components, eigen_solver='arpack',
68 | geom=geom)
69 | embed_spectral = spectral.fit_transform(X)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/examples_index.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "markdown",
5 | "metadata": {},
6 | "source": [
7 | "# `megaman`: Manifold Learning for Millions of Points "
8 | ]
9 | },
10 | {
11 | "cell_type": "markdown",
12 | "metadata": {},
13 | "source": [
14 | "This noteook contains links to examples of using `megaman` to perform manifold learning on data. \n",
15 | "\n",
16 | "See also the [megaman documentation](http://mmp2.github.io/megaman/)."
17 | ]
18 | },
19 | {
20 | "cell_type": "markdown",
21 | "metadata": {},
22 | "source": [
23 | "* [megaman_tutorial.ipynb](https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/examples/megaman_tutorial.ipynb)\n",
24 | "* [manifold_intro.ipynb](https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/examples/manifold_intro.ipynb)"
25 | ]
26 | },
27 | {
28 | "cell_type": "code",
29 | "execution_count": null,
30 | "metadata": {
31 | "collapsed": true
32 | },
33 | "outputs": [],
34 | "source": []
35 | }
36 | ],
37 | "metadata": {
38 | "kernelspec": {
39 | "display_name": "Python 2",
40 | "language": "python",
41 | "name": "python2"
42 | },
43 | "language_info": {
44 | "codemirror_mode": {
45 | "name": "ipython",
46 | "version": 2
47 | },
48 | "file_extension": ".py",
49 | "mimetype": "text/x-python",
50 | "name": "python",
51 | "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
52 | "pygments_lexer": "ipython2",
53 | "version": "2.7.11"
54 | }
55 | },
56 | "nbformat": 4,
57 | "nbformat_minor": 0
58 | }
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/rad_est_utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import scipy
3 | import scipy.linalg
4 | import os
5 | import plotly.graph_objs as go
6 |
7 | try:
8 | from tqdm import *
9 | tqdm_installed = True
10 | except ImportError as e:
11 | tqdm_installed = False
12 | print('tqdm not installed, will not show the progress bar')
13 |
14 | def find_neighbors(idx, dist):
15 | nbr = dist[idx, :].nonzero()[1]
16 | if idx not in nbr:
17 | return np.append(nbr, idx)
18 | else:
19 | return nbr
20 |
21 |
22 | def find_local_singular_values(data, idx, dist, dim=15):
23 | nbr = find_neighbors(idx, dist)
24 | if nbr.shape[0] == 1:
25 | return np.zeros(dim)
26 | else:
27 | local_pca_data = data[nbr, :]
28 | local_center = np.mean(local_pca_data, axis=0)
29 | local_pca_data -= local_center[None, :]
30 |
31 | sing = scipy.linalg.svd(local_pca_data, compute_uv=False)
32 | sing_return = sing[:dim]
33 | return np.pad(sing_return, (0, dim - sing_return.shape[0]), 'constant')
34 |
35 |
36 | def find_all_singular_values(data, rad, dist):
37 | dist_copy = dist.copy()
38 | dist_copy[dist_copy > rad] = 0.0
39 | dist_copy.eliminate_zeros()
40 | dim = data.shape[1]
41 | singular_list = np.array([find_local_singular_values(data, idx, dist_copy, dim)
42 | for idx in range(data.shape[0])])
43 | return singular_list
44 |
45 |
46 | def find_mean_singular_values(data, rad, dist):
47 | singular_list = find_all_singular_values(data, rad, dist)
48 | return np.mean(singular_list, axis=0)
49 |
50 |
51 | def find_argmax_dimension(data, dist, optimal_rad):
52 | singular_list = find_all_singular_values(data, optimal_rad, dist)
53 | singular_gap = np.hstack(
54 | (-1 * np.diff(singular_list, axis=1), singular_list[:, -1, None]))
55 | return np.argmax(singular_gap, axis=1) + 1
56 |
57 |
58 | def ordinal (n):
59 | return "%d%s" % (n,"tsnrhtdd"[(n//10%10!=1)*(n%10<4)*n%10::4])
60 |
61 |
62 | def estimate_dimension(data, dist, rad_search_space=None):
63 | if rad_search_space is None:
64 | rad_search_space = np.logspace(np.log10(1e-1), np.log10(5), 50)
65 |
66 | rad_iterator = rad_search_space if not tqdm_installed else tqdm(
67 | rad_search_space)
68 | sgv = np.array([find_mean_singular_values(data, rad, dist)
69 | for rad in rad_iterator])
70 |
71 | return rad_search_space, sgv
72 |
73 |
74 | def plot_singular_values_versus_radius(singular_values, rad_search_space, start_idx, end_idx):
75 | all_trace = []
76 | singular_gap = -np.diff(singular_values,axis=1)
77 | for idx, sing in enumerate(singular_values.T):
78 | singular_line = go.Scatter(
79 | x=rad_search_space, y=sing, name='{} singular value'.format(ordinal(idx+1))
80 | )
81 | if idx <= 2:
82 | singular_line['text'] = [ 'Singular gap: {:.2f}'.format(singular_gap[rid, idx]) for rid in range(50) ]
83 | if idx > 3:
84 | singular_line['hoverinfo'] = 'none'
85 | all_trace.append(singular_line)
86 | if idx == 2:
87 | # HACK: just specify the color manually, need to generate each later.
88 | all_trace.append(go.Scatter(
89 | x=rad_search_space[start_idx:end_idx], y=singular_values[start_idx:end_idx,2],
90 | mode='lines',marker=dict(color='green'),
91 | showlegend=False, hoverinfo='none'
92 | ))
93 | all_trace.append(go.Scatter(
94 | x=rad_search_space[start_idx:end_idx], y=singular_values[start_idx:end_idx,1],
95 | fill='tonexty', mode='none', showlegend=False, hoverinfo='none'
96 | ))
97 | return all_trace
98 |
99 | def generate_layouts(start_idx, end_idx, est_rad_dim1, est_rad_dim2, rad_search_space):
100 | return go.Layout(
101 | title='Singular values - radii plot',
102 | xaxis=dict(
103 | title='$\\text{Radius } r $',
104 | # type='log',
105 | autorange=True
106 | ),
107 | yaxis=dict(title='$\\text{Singular value } \\sigma$'),
108 | shapes=[{
109 | 'type': 'rect',
110 | 'xref': 'x',
111 | 'yref': 'paper',
112 | 'x0': rad_search_space[start_idx],
113 | 'y0': 0,
114 | 'x1': rad_search_space[end_idx-1],
115 | 'y1': 1,
116 | 'fillcolor': '#d3d3d3',
117 | 'opacity': 0.4,
118 | 'line': {
119 | 'width': 0,
120 | }
121 | }],
122 | annotations=[
123 | dict(
124 | x=est_rad_dim1,
125 | y=0,
126 | xref='x',
127 | yref='y',
128 | text='$\\hat{r}_{d=1}$',
129 | font = dict(size = 30),
130 | showarrow=True,
131 | arrowhead=7,
132 | ax=20,
133 | ay=30
134 | ),
135 | dict(
136 | x=est_rad_dim2,
137 | y=0,
138 | xref='x',
139 | yref='y',
140 | text='$\\hat{r}_{d=2}$',
141 | font = dict(size = 30),
142 | showarrow=True,
143 | arrowhead=7,
144 | ax=-20,
145 | ay=30
146 | )
147 | ])
148 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/tutorial_data_plot.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/examples/tutorial_data_plot.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/tutorial_embeddings.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/examples/tutorial_embeddings.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/tutorial_isomap_plot.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/examples/tutorial_isomap_plot.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/tutorial_spectral_plot.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/examples/tutorial_spectral_plot.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/__check_build/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Author: Jake VanderPlas
2 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
3 | #
4 | # Adapted from scikit-learn's similar utility
5 |
6 | """ Module to give helpful messages to the user that did not
7 | compile megaman properly (adapted from scikit-learn's check_build utility)
8 | """
9 | import os
10 |
11 | INPLACE_MSG = """
12 | It appears that you are importing a local megaman source tree.
13 | Please either use an inplace install or try from another location."""
14 |
15 | STANDARD_MSG = """
16 | If you have used an installer, please check that it is suited for your
17 | Python version, your operating system and your platform."""
18 |
19 | ERROR_TEMPLATE = """{error}
20 | ___________________________________________________________________________
21 | Contents of {local_dir}:
22 | {contents}
23 | ___________________________________________________________________________
24 | It seems that megaman has not been built correctly.
25 |
26 | If you have installed megaman from source, please do not forget
27 | to build the package before using it: run `python setup.py install`
28 | in the source directory.
29 | {msg}"""
30 |
31 |
32 | def raise_build_error(e):
33 | # Raise a comprehensible error and list the contents of the
34 | # directory to help debugging on the mailing list.
35 | local_dir = os.path.split(__file__)[0]
36 | msg = STANDARD_MSG
37 | if local_dir == "megaman/__check_build":
38 | # Picking up the local install: this will work only if the
39 | # install is an 'inplace build'
40 | msg = INPLACE_MSG
41 | dir_content = list()
42 | for i, filename in enumerate(os.listdir(local_dir)):
43 | if ((i + 1) % 3):
44 | dir_content.append(filename.ljust(26))
45 | else:
46 | dir_content.append(filename + '\n')
47 | contents = ''.join(dir_content).strip()
48 | raise ImportError(ERROR_TEMPLATE.format(error=e,
49 | local_dir=local_dir,
50 | contents=contents,
51 | msg=msg))
52 |
53 | try:
54 | from ._check_build import check_build
55 | except ImportError as e:
56 | raise_build_error(e)
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/__check_build/_check_build.pyx:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | def check_build():
4 | return
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/__check_build/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import numpy
4 |
5 |
6 | def configuration(parent_package='', top_path=None):
7 | from numpy.distutils.misc_util import Configuration
8 | config = Configuration('__check_build', parent_package, top_path)
9 | config.add_extension('_check_build',
10 | sources=['_check_build.c'])
11 |
12 | return config
13 |
14 | if __name__ == '__main__':
15 | from numpy.distutils.core import setup
16 | setup(**configuration(top_path='').todict())
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """megaman: Scalable Manifold Learning"""
2 |
3 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
4 |
5 | __version__ = "0.3.dev0"
6 |
7 | from . import __check_build
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/datasets/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .datasets import (get_megaman_image, generate_megaman_data,
2 | generate_megaman_manifold, generate_noisefree_hourglass,
3 | generate_noisy_hourglass)
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/datasets/datasets.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Some sample datasets"""
2 | from __future__ import division
3 |
4 | import os
5 |
6 | import numpy as np
7 | from scipy import ndimage
8 | from sklearn.utils import check_random_state
9 |
10 | import collections
11 |
12 | def get_megaman_image(factor=1):
13 | """Return an RGBA representation of the megaman icon"""
14 | imfile = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'megaman.png')
15 | data = ndimage.imread(imfile) / 255
16 | if factor > 1:
17 | data = data.repeat(factor, axis=0).repeat(factor, axis=1)
18 | return data
19 |
20 |
21 | def generate_megaman_data(sampling=2):
22 | """Generate 2D point data of the megaman image"""
23 | data = get_megaman_image()
24 | x = np.arange(sampling * data.shape[1]) / float(sampling)
25 | y = np.arange(sampling * data.shape[0]) / float(sampling)
26 | X, Y = map(np.ravel, np.meshgrid(x, y))
27 | C = data[np.floor(Y.max() - Y).astype(int),
28 | np.floor(X).astype(int)]
29 | return np.vstack([X, Y]).T, C
30 |
31 |
32 | def _make_S_curve(x, range=(-0.75, 0.75)):
33 | """Make a 2D S-curve from a 1D vector"""
34 | assert x.ndim == 1
35 | x = x - x.min()
36 | theta = 2 * np.pi * (range[0] + (range[1] - range[0]) * x / x.max())
37 | X = np.empty((x.shape[0], 2), dtype=float)
38 | X[:, 0] = np.sign(theta) * (1 - np.cos(theta))
39 | X[:, 1] = np.sin(theta)
40 | X *= x.max() / (2 * np.pi * (range[1] - range[0]))
41 | return X
42 |
43 |
44 | def generate_megaman_manifold(sampling=2, nfolds=2,
45 | rotate=True, random_state=None):
46 | """Generate a manifold of the megaman data"""
47 | X, c = generate_megaman_data(sampling)
48 | for i in range(nfolds):
49 | X = np.hstack([_make_S_curve(x) for x in X.T])
50 |
51 | if rotate:
52 | rand = check_random_state(random_state)
53 | R = rand.randn(X.shape[1], X.shape[1])
54 | U, s, VT = np.linalg.svd(R)
55 | X = np.dot(X, U)
56 |
57 | return X, c
58 |
59 | def generate_noisefree_hourglass(n_size, scaling_factor=1.75, seed=None):
60 | if seed is not None:
61 | np.random.seed(seed)
62 | fz = lambda z: -4*z**4 + 4*z**2 + 1
63 | X = np.random.normal(0,1,[n_size,3])
64 | sphere = X / np.linalg.norm(X,axis=1)[:,None]
65 | r = np.linalg.norm(sphere,axis=1)
66 |
67 | x,y,z = sphere.T
68 | theta = np.arctan2(y,x)
69 | phi = np.arccos(z/r)
70 |
71 | r_hour = fz(z)
72 | theta_hour = theta
73 | z_hour = z
74 | phi_hour = np.arccos(z_hour/r_hour)
75 |
76 | x_hour = r_hour*np.cos(theta_hour)*np.sin(phi_hour)
77 | y_hour = r_hour*np.sin(theta_hour)*np.sin(phi_hour)
78 | z_hour = r_hour*np.cos(phi_hour)
79 |
80 | x_hour *= 0.5
81 | y_hour *= 0.5
82 |
83 | hourglass = np.vstack((x_hour,y_hour,z_hour)).T
84 | hourglass *= scaling_factor
85 |
86 | return hourglass
87 |
88 | def _genereate_noises(sigmas, size, dimensions, seed=None):
89 | if seed is not None:
90 | np.random.seed(seed)
91 | if isinstance(sigmas, (collections.Sequence, np.ndarray)):
92 | assert len(sigmas) == dimensions, \
93 | 'The size of sigmas should be the same as noises dimensions'
94 | return np.random.multivariate_normal(np.zeros(dimensions),
95 | np.diag(sigmas), size)
96 | else:
97 | return np.random.normal(0,sigmas,[size,dimensions])
98 |
99 | def _add_noises_on_primary_dimensions(data,sigmas=0.1,seed=None):
100 | size,dim = data.shape
101 | noises = _genereate_noises(sigmas,size,dim)
102 | return data + noises
103 |
104 | def _add_noises_on_additional_dimensions(data,addition_dims,sigmas=1,seed=None):
105 | if addition_dims == 0:
106 | return data
107 | else:
108 | noises = _genereate_noises(sigmas,data.shape[0],addition_dims,seed)
109 | return np.hstack((data,noises))
110 |
111 | def generate_noisy_hourglass(size, sigma_primary=0.05, addition_dims=0,
112 | sigma_additional=0.1, scaling_factor=1.75, seed=None):
113 | hourglass = generate_noisefree_hourglass(size, scaling_factor, seed)
114 | hourglass = _add_noises_on_primary_dimensions(hourglass, sigma_primary)
115 | hourglass = _add_noises_on_additional_dimensions(hourglass, addition_dims,
116 | sigma_additional)
117 | return hourglass
118 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/datasets/megaman.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/datasets/megaman.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/embedding/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | The :mod:`sklearn.megaman` module implements data embedding techniques.
3 | """
4 |
5 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
6 |
7 | from .locally_linear import LocallyLinearEmbedding
8 | from .isomap import Isomap
9 | from .ltsa import LTSA
10 | from .spectral_embedding import SpectralEmbedding
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/embedding/base.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """ base estimator class for megaman """
2 |
3 | # Author: James McQueen --
4 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
5 |
6 | import numpy as np
7 | from scipy.sparse import isspmatrix
8 |
9 | from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin
10 | from sklearn.utils.validation import check_array
11 |
12 | from ..geometry.geometry import Geometry
13 |
14 | # from sklearn.utils.validation import FLOAT_DTYPES
15 | FLOAT_DTYPES = (np.float64, np.float32, np.float16)
16 |
17 |
18 | class BaseEmbedding(BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin):
19 | """ Base Class for all megaman embeddings.
20 |
21 | Inherits BaseEstimator and TransformerMixin from sklearn.
22 |
23 | BaseEmbedding creates the common interface to the geometry
24 | class for all embeddings as well as providing a common
25 | .fit_transform().
26 |
27 | Parameters
28 | ----------
29 | n_components : integer
30 | number of coordinates for the manifold.
31 | radius : float (optional)
32 | radius for adjacency and affinity calculations. Will be overridden if
33 | either is set in `geom`
34 | geom : dict or megaman.geometry.Geometry object
35 | specification of geometry parameters: keys are
36 | ["adjacency_method", "adjacency_kwds", "affinity_method",
37 | "affinity_kwds", "laplacian_method", "laplacian_kwds"]
38 |
39 | Attributes
40 | ----------
41 | geom_ : a fitted megaman.geometry.Geometry object.
42 | """
43 | def __init__(self, n_components=2, radius=None, geom=None):
44 | self.n_components = n_components
45 | self.radius = radius
46 | self.geom = geom
47 |
48 | def _validate_input(self, X, input_type):
49 | if input_type == 'data':
50 | sparse_formats = None
51 | elif input_type in ['adjacency', 'affinity']:
52 | sparse_formats = ['csr', 'coo', 'lil', 'bsr', 'dok', 'dia']
53 | else:
54 | raise ValueError("unrecognized input_type: {0}".format(input_type))
55 | return check_array(X, dtype=FLOAT_DTYPES, accept_sparse=sparse_formats)
56 |
57 | # # The world is not ready for this...
58 | # def estimate_radius(self, X, input_type='data', intrinsic_dim=None):
59 | # """Estimate a radius based on the data and intrinsic dimensionality
60 | #
61 | # Parameters
62 | # ----------
63 | # X : array_like, [n_samples, n_features]
64 | # dataset for which radius is estimated
65 | # intrinsic_dim : int (optional)
66 | # estimated intrinsic dimensionality of the manifold. If not
67 | # specified, then intrinsic_dim = self.n_components
68 | #
69 | # Returns
70 | # -------
71 | # radius : float
72 | # The estimated radius for the fit
73 | # """
74 | # if input_type == 'affinity':
75 | # return None
76 | # elif input_type == 'adjacency':
77 | # return X.max()
78 | # elif input_type == 'data':
79 | # if intrinsic_dim is None:
80 | # intrinsic_dim = self.n_components
81 | # mean_std = np.std(X, axis=0).mean()
82 | # n_features = X.shape[1]
83 | # return 0.5 * mean_std / n_features ** (1. / (intrinsic_dim + 6))
84 | # else:
85 | # raise ValueError("Unrecognized input_type: {0}".format(input_type))
86 |
87 | def fit_geometry(self, X=None, input_type='data'):
88 | """Inputs self.geom, and produces the fitted geometry self.geom_"""
89 | if self.geom is None:
90 | self.geom_ = Geometry()
91 | elif isinstance(self.geom, Geometry):
92 | self.geom_ = self.geom
93 | else:
94 | try:
95 | kwds = dict(**self.geom)
96 | except TypeError:
97 | raise ValueError("geom must be a Geometry instance or "
98 | "a mappable/dictionary")
99 | self.geom_ = Geometry(**kwds)
100 |
101 | if self.radius is not None:
102 | self.geom_.set_radius(self.radius, override=False)
103 |
104 | # if self.radius == 'auto':
105 | # if X is not None and input_type != 'affinity':
106 | # self.geom_.set_radius(self.estimate_radius(X, input_type),
107 | # override=False)
108 | # else:
109 | # self.geom_.set_radius(self.radius,
110 | # override=False)
111 |
112 | if X is not None:
113 | self.geom_.set_matrix(X, input_type)
114 |
115 | return self
116 |
117 | def fit_transform(self, X, y=None, input_type='data'):
118 | """Fit the model from data in X and transform X.
119 |
120 | Parameters
121 | ----------
122 | input_type : string, one of: 'data', 'distance' or 'affinity'.
123 | The values of input data X. (default = 'data')
124 | X: array-like, shape (n_samples, n_features)
125 | Training vector, where n_samples in the number of samples
126 | and n_features is the number of features.
127 |
128 | If self.input_type is 'distance':
129 |
130 | X : array-like, shape (n_samples, n_samples),
131 | Interpret X as precomputed distance or adjacency graph
132 | computed from samples.
133 |
134 | Returns
135 | -------
136 | X_new: array-like, shape (n_samples, n_components)
137 | """
138 | self.fit(X, y=y, input_type=input_type)
139 | return self.embedding_
140 |
141 | def transform(self, X, y=None, input_type='data'):
142 | raise NotImplementedError("transform() not implemented. "
143 | "Try fit_transform()")
144 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/embedding/tests/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/embedding/tests/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/embedding/tests/test_base.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 | from numpy.testing import assert_allclose
5 |
6 | from megaman.utils.testing import assert_raise_message
7 | from megaman.geometry.geometry import Geometry
8 | from megaman.embedding.base import BaseEmbedding
9 |
10 |
11 | def test_geometry_dict():
12 | """ Test passing a dictionary and confirm the output """
13 | geom_dict = dict(adjacency_method = 'auto',
14 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':4},
15 | affinity_method = 'auto',
16 | affinity_kwds = {'radius':4},
17 | laplacian_method = 'geometric',
18 | laplacian_kwds = {'scaling_eps':4})
19 | g1 = Geometry(**geom_dict)
20 | base_embedding = BaseEmbedding(geom=geom_dict).fit_geometry()
21 | assert(g1.__dict__ == base_embedding.geom_.__dict__)
22 |
23 |
24 | def test_geometry_object():
25 | """ Test passing a geometry object and confirm the output """
26 | g1 = Geometry(adjacency_method = 'auto',
27 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':4},
28 | affinity_method = 'auto',
29 | affinity_kwds = {'radius':4},
30 | laplacian_method = 'geometric',
31 | laplacian_kwds = {'scaling_eps':4})
32 | base_embedding = BaseEmbedding(geom=g1).fit_geometry()
33 | assert(g1.__dict__ == base_embedding.geom_.__dict__)
34 |
35 |
36 | def test_geometry_update():
37 | """ Test passing geometry object then independently update a parameter and confirm that the embedding
38 | geometry is also updated """
39 | g1 = Geometry(adjacency_method = 'auto',
40 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':4},
41 | affinity_method = 'auto',
42 | affinity_kwds = {'radius':4},
43 | laplacian_method = 'geometric',
44 | laplacian_kwds = {'scaling_eps':4})
45 | base_embedding = BaseEmbedding(geom=g1)
46 | X = np.random.rand(10, 2)
47 | # Now update g1 -- object that was passed
48 | g1.set_data_matrix(X)
49 | # confirm internal object is updated
50 | assert_allclose(g1.X, base_embedding.geom.X)
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/embedding/tests/test_embeddings.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """General tests for embeddings"""
2 |
3 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
4 |
5 | from itertools import product
6 |
7 | import numpy as np
8 | from numpy.testing import assert_raises, assert_allclose
9 |
10 | from megaman.embedding import (Isomap, LocallyLinearEmbedding,
11 | LTSA, SpectralEmbedding)
12 | from megaman.geometry.geometry import Geometry
13 |
14 | EMBEDDINGS = [Isomap, LocallyLinearEmbedding, LTSA, SpectralEmbedding]
15 |
16 | # # TODO: make estimator_checks pass!
17 | # def test_estimator_checks():
18 | # from sklearn.utils.estimator_checks import check_estimator
19 | # for Embedding in EMBEDDINGS:
20 | # yield check_estimator, Embedding
21 |
22 |
23 | def test_embeddings_fit_vs_transform():
24 | rand = np.random.RandomState(42)
25 | X = rand.rand(100, 5)
26 | geom = Geometry(adjacency_kwds = {'radius':1.0},
27 | affinity_kwds = {'radius':1.0})
28 |
29 | def check_embedding(Embedding, n_components):
30 | model = Embedding(n_components=n_components,
31 | geom=geom, random_state=rand)
32 | embedding = model.fit_transform(X)
33 | assert model.embedding_.shape == (X.shape[0], n_components)
34 | assert_allclose(embedding, model.embedding_)
35 |
36 | for Embedding in EMBEDDINGS:
37 | for n_components in [1, 2, 3]:
38 | yield check_embedding, Embedding, n_components
39 |
40 |
41 | def test_embeddings_bad_arguments():
42 | rand = np.random.RandomState(32)
43 | X = rand.rand(100, 3)
44 |
45 | def check_bad_args(Embedding):
46 | # no radius set
47 | embedding = Embedding()
48 | assert_raises(ValueError, embedding.fit, X)
49 |
50 | # unrecognized geometry
51 | embedding = Embedding(radius=2, geom='blah')
52 | assert_raises(ValueError, embedding.fit, X)
53 |
54 | for Embedding in EMBEDDINGS:
55 | yield check_bad_args, Embedding
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/embedding/tests/test_isomap.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import sys
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import scipy as sp
6 | import scipy.sparse as sparse
7 | from scipy.spatial.distance import squareform, pdist
8 | from itertools import product
9 | from sklearn import manifold, datasets
10 | from sklearn.neighbors import NearestNeighbors
11 |
12 | from numpy.testing import assert_array_almost_equal
13 |
14 | import megaman.embedding.isomap as iso
15 | import megaman.geometry.geometry as geom
16 | from megaman.utils.eigendecomp import EIGEN_SOLVERS
17 |
18 |
19 | def _check_with_col_sign_flipping(A, B, tol=0.0):
20 | """ Check array A and B are equal with possible sign flipping on
21 | each columns"""
22 | sign = True
23 | for column_idx in range(A.shape[1]):
24 | sign = sign and ((((A[:, column_idx] -
25 | B[:, column_idx]) ** 2).mean() <= tol ** 2) or
26 | (((A[:, column_idx] +
27 | B[:, column_idx]) ** 2).mean() <= tol ** 2))
28 | if not sign:
29 | return False
30 | return True
31 |
32 | def test_isomap_with_sklearn():
33 | N = 10
34 | X, color = datasets.samples_generator.make_s_curve(N, random_state=0)
35 | n_components = 2
36 | n_neighbors = 3
37 | knn = NearestNeighbors(n_neighbors + 1).fit(X)
38 | # Assign the geometry matrix to get the same answer since sklearn using k-neighbors instead of radius-neighbors
39 | g = geom.Geometry(X)
40 | g.set_adjacency_matrix(knn.kneighbors_graph(X, mode = 'distance'))
41 | # test Isomap with sklearn
42 | sk_Y_iso = manifold.Isomap(n_neighbors, n_components, eigen_solver = 'arpack').fit_transform(X)
43 | mm_Y_iso = iso.isomap(g, n_components)
44 | assert(_check_with_col_sign_flipping(sk_Y_iso, mm_Y_iso, 0.05))
45 |
46 | def test_isomap_simple_grid():
47 | # Isomap should preserve distances when all neighbors are used
48 | N_per_side = 5
49 | Npts = N_per_side ** 2
50 | radius = 10
51 | # grid of equidistant points in 2D, n_components = n_dim
52 | X = np.array(list(product(range(N_per_side), repeat=2)))
53 | # distances from each point to all others
54 | G = squareform(pdist(X))
55 | g = geom.Geometry(adjacency_kwds = {'radius':radius})
56 | for eigen_solver in EIGEN_SOLVERS:
57 | clf = iso.Isomap(n_components = 2, eigen_solver = eigen_solver, geom=g)
58 | clf.fit(X)
59 | G_iso = squareform(pdist(clf.embedding_))
60 | assert_array_almost_equal(G, G_iso)
61 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/embedding/tests/test_lle.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import sys
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import scipy as sp
6 | import scipy.sparse as sparse
7 | from scipy.spatial.distance import squareform, pdist
8 | from itertools import product
9 | from numpy.testing import assert_array_almost_equal
10 |
11 | from sklearn import manifold, datasets
12 | from sklearn.neighbors import NearestNeighbors
13 |
14 | import megaman.embedding.locally_linear as lle
15 | import megaman.geometry.geometry as geom
16 | from megaman.utils.eigendecomp import EIGEN_SOLVERS
17 |
18 |
19 | def _check_with_col_sign_flipping(A, B, tol=0.0):
20 | """ Check array A and B are equal with possible sign flipping on
21 | each columns"""
22 | sign = True
23 | for column_idx in range(A.shape[1]):
24 | sign = sign and ((((A[:, column_idx] -
25 | B[:, column_idx]) ** 2).mean() <= tol ** 2) or
26 | (((A[:, column_idx] +
27 | B[:, column_idx]) ** 2).mean() <= tol ** 2))
28 | if not sign:
29 | return False
30 | return True
31 |
32 | def test_lle_with_sklearn():
33 | N = 10
34 | X, color = datasets.samples_generator.make_s_curve(N, random_state=0)
35 | n_components = 2
36 | n_neighbors = 3
37 | knn = NearestNeighbors(n_neighbors + 1).fit(X)
38 | G = geom.Geometry()
39 | G.set_data_matrix(X)
40 | G.set_adjacency_matrix(knn.kneighbors_graph(X, mode = 'distance'))
41 | sk_Y_lle = manifold.LocallyLinearEmbedding(n_neighbors, n_components, method = 'standard').fit_transform(X)
42 | (mm_Y_lle, err) = lle.locally_linear_embedding(G, n_components)
43 | assert(_check_with_col_sign_flipping(sk_Y_lle, mm_Y_lle, 0.05))
44 |
45 | def test_barycenter_kneighbors_graph():
46 | X = np.array([[0, 1], [1.01, 1.], [2, 0]])
47 | distance_matrix = squareform(pdist(X))
48 | A = lle.barycenter_graph(distance_matrix, X)
49 | # check that columns sum to one
50 | assert_array_almost_equal(np.sum(A.toarray(), 1), np.ones(3))
51 | pred = np.dot(A.toarray(), X)
52 | assert(np.linalg.norm(pred - X) / X.shape[0] < 1)
53 |
54 | def test_lle_simple_grid():
55 | # note: ARPACK is numerically unstable, so this test will fail for
56 | # some random seeds. We choose 20 because the tests pass.
57 | rng = np.random.RandomState(20)
58 | tol = 0.1
59 | # grid of equidistant points in 2D, n_components = n_dim
60 | X = np.array(list(product(range(5), repeat=2)))
61 | X = X + 1e-10 * rng.uniform(size=X.shape)
62 | n_components = 2
63 | G = geom.Geometry(adjacency_kwds = {'radius':3})
64 | G.set_data_matrix(X)
65 | tol = 0.1
66 | distance_matrix = G.compute_adjacency_matrix()
67 | N = lle.barycenter_graph(distance_matrix, X).todense()
68 | reconstruction_error = np.linalg.norm(np.dot(N, X) - X, 'fro')
69 | assert(reconstruction_error < tol)
70 | for eigen_solver in EIGEN_SOLVERS:
71 | clf = lle.LocallyLinearEmbedding(n_components = n_components, geom = G,
72 | eigen_solver = eigen_solver, random_state = rng)
73 | clf.fit(X)
74 | assert(clf.embedding_.shape[1] == n_components)
75 | reconstruction_error = np.linalg.norm(
76 | np.dot(N, clf.embedding_) - clf.embedding_, 'fro') ** 2
77 | assert(reconstruction_error < tol)
78 |
79 | def test_lle_manifold():
80 | rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
81 | # similar test on a slightly more complex manifold
82 | X = np.array(list(product(np.arange(18), repeat=2)))
83 | X = np.c_[X, X[:, 0] ** 2 / 18]
84 | X = X + 1e-10 * rng.uniform(size=X.shape)
85 | n_components = 2
86 | G = geom.Geometry(adjacency_kwds = {'radius':3})
87 | G.set_data_matrix(X)
88 | distance_matrix = G.compute_adjacency_matrix()
89 | tol = 1.5
90 | N = lle.barycenter_graph(distance_matrix, X).todense()
91 | reconstruction_error = np.linalg.norm(np.dot(N, X) - X)
92 | assert(reconstruction_error < tol)
93 | for eigen_solver in EIGEN_SOLVERS:
94 | clf = lle.LocallyLinearEmbedding(n_components = n_components, geom = G,
95 | eigen_solver = eigen_solver, random_state = rng)
96 | clf.fit(X)
97 | assert(clf.embedding_.shape[1] == n_components)
98 | reconstruction_error = np.linalg.norm(
99 | np.dot(N, clf.embedding_) - clf.embedding_, 'fro') ** 2
100 | assert(reconstruction_error < tol)
101 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/embedding/tests/test_ltsa.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import sys
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import scipy as sp
6 | import scipy.sparse as sparse
7 | from itertools import product
8 |
9 | from sklearn import manifold, datasets
10 | from sklearn.neighbors import NearestNeighbors
11 |
12 | from numpy.testing import assert_array_almost_equal
13 | import megaman.embedding.ltsa as ltsa
14 | from megaman.embedding.locally_linear import barycenter_graph
15 | import megaman.geometry.geometry as geom
16 | from megaman.utils.eigendecomp import EIGEN_SOLVERS
17 |
18 |
19 | def _check_with_col_sign_flipping(A, B, tol=0.0):
20 | """ Check array A and B are equal with possible sign flipping on
21 | each columns"""
22 | sign = True
23 | for column_idx in range(A.shape[1]):
24 | sign = sign and ((((A[:, column_idx] -
25 | B[:, column_idx]) ** 2).mean() <= tol ** 2) or
26 | (((A[:, column_idx] +
27 | B[:, column_idx]) ** 2).mean() <= tol ** 2))
28 | if not sign:
29 | return False
30 | return True
31 |
32 |
33 | def test_ltsa_with_sklearn():
34 | N = 10
35 | X, color = datasets.samples_generator.make_s_curve(N, random_state=0)
36 | n_components = 2
37 | n_neighbors = 3
38 | knn = NearestNeighbors(n_neighbors + 1).fit(X)
39 | G = geom.Geometry()
40 | G.set_data_matrix(X)
41 | G.set_adjacency_matrix(knn.kneighbors_graph(X, mode = 'distance'))
42 | sk_Y_ltsa = manifold.LocallyLinearEmbedding(n_neighbors, n_components,
43 | method = 'ltsa',
44 | eigen_solver = 'arpack').fit_transform(X)
45 | (mm_Y_ltsa, err) = ltsa.ltsa(G, n_components, eigen_solver = 'arpack')
46 | assert(_check_with_col_sign_flipping(sk_Y_ltsa, mm_Y_ltsa, 0.05))
47 |
48 |
49 | def test_ltsa_eigendecomps():
50 | N = 10
51 | X, color = datasets.samples_generator.make_s_curve(N, random_state=0)
52 | n_components = 2
53 | G = geom.Geometry(adjacency_method = 'brute', adjacency_kwds = {'radius':2})
54 | G.set_data_matrix(X)
55 | mm_ltsa_ref, err_ref = ltsa.ltsa(G, n_components,
56 | eigen_solver=EIGEN_SOLVERS[0])
57 | for eigen_solver in EIGEN_SOLVERS[1:]:
58 | mm_ltsa, err = ltsa.ltsa(G, n_components, eigen_solver=eigen_solver)
59 | assert(_check_with_col_sign_flipping(mm_ltsa, mm_ltsa_ref, 0.05))
60 |
61 |
62 | def test_ltsa_manifold():
63 | rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
64 | # similar test on a slightly more complex manifold
65 | X = np.array(list(product(np.arange(18), repeat=2)))
66 | X = np.c_[X, X[:, 0] ** 2 / 18]
67 | X = X + 1e-10 * rng.uniform(size=X.shape)
68 | n_components = 2
69 | G = geom.Geometry(adjacency_kwds = {'radius':3})
70 | G.set_data_matrix(X)
71 | distance_matrix = G.compute_adjacency_matrix()
72 | tol = 1.5
73 | N = barycenter_graph(distance_matrix, X).todense()
74 | reconstruction_error = np.linalg.norm(np.dot(N, X) - X)
75 | assert(reconstruction_error < tol)
76 | for eigen_solver in EIGEN_SOLVERS:
77 | clf = ltsa.LTSA(n_components = n_components, geom = G,
78 | eigen_solver = eigen_solver, random_state = rng)
79 | clf.fit(X)
80 | assert(clf.embedding_.shape[1] == n_components)
81 | reconstruction_error = np.linalg.norm(
82 | np.dot(N, clf.embedding_) - clf.embedding_, 'fro') ** 2
83 | assert(reconstruction_error < tol)
84 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | from .rmetric import RiemannMetric
4 | from .geometry import Geometry
5 | from .adjacency import Adjacency, compute_adjacency_matrix, adjacency_methods
6 | from .affinity import Affinity, compute_affinity_matrix, affinity_methods
7 | from .laplacian import Laplacian, compute_laplacian_matrix, laplacian_methods
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/affinity.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | from __future__ import division
4 | import numpy as np
5 | from scipy.sparse import isspmatrix
6 | from sklearn.utils.validation import check_array
7 |
8 | from .utils import RegisterSubclasses
9 |
10 |
11 | def compute_affinity_matrix(adjacency_matrix, method='auto', **kwargs):
12 | """Compute the affinity matrix with the given method"""
13 | if method == 'auto':
14 | method = 'gaussian'
15 | return Affinity.init(method, **kwargs).affinity_matrix(adjacency_matrix)
16 |
17 |
18 | def affinity_methods():
19 | """Return the list of valid affinity methods"""
20 | return ['auto'] + list(Affinity.methods())
21 |
22 |
23 | class Affinity(RegisterSubclasses):
24 | """Base class for computing affinity matrices"""
25 | def __init__(self, radius=None, symmetrize=True):
26 | if radius is None:
27 | raise ValueError("must specify radius for affinity matrix")
28 | self.radius = radius
29 | self.symmetrize = symmetrize
30 |
31 | def affinity_matrix(self, adjacency_matrix):
32 | raise NotImplementedError()
33 |
34 |
35 | class GaussianAffinity(Affinity):
36 | name = "gaussian"
37 |
38 | @staticmethod
39 | def _symmetrize(A):
40 | # TODO: make this more efficient?
41 | # Also, need to maintain explicit zeros!
42 | return 0.5 * (A + A.T)
43 |
44 | def affinity_matrix(self, adjacency_matrix):
45 | A = check_array(adjacency_matrix, dtype=float, copy=True,
46 | accept_sparse=['csr', 'csc', 'coo'])
47 |
48 | if isspmatrix(A):
49 | data = A.data
50 | else:
51 | data = A
52 |
53 | # in-place computation of
54 | # data = np.exp(-(data / radius) ** 2)
55 | data **= 2
56 | data /= -self.radius ** 2
57 | np.exp(data, out=data)
58 |
59 | if self.symmetrize:
60 | A = self._symmetrize(A)
61 |
62 | # for sparse, need a true zero on the diagonal
63 | # TODO: make this more efficient?
64 | if isspmatrix(A):
65 | A.setdiag(1)
66 |
67 | return A
68 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/complete_adjacency_matrix.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 | from .adjacency import CyFLANNAdjacency, compute_adjacency_matrix
3 | from scipy.sparse import vstack, hstack
4 |
5 | def complete_adjacency_matrix(Dtrain, Xtrain, Xtest, adjacency_kwds):
6 | if 'cyflann_kwds' in adjacency_kwds.keys():
7 | cyflann_kwds = adjacency_kwds['cyflann_kwds']
8 | else:
9 | cyflann_kwds = {}
10 | radius = adjacency_kwds['radius']
11 | Cyflann = CyFLANNAdjacency(radius=radius, **cyflann_kwds)
12 | train_index = Cyflann.build_index(Xtrain)
13 | test_train_adjacency = train_index.radius_neighbors_graph(Xtest, radius)
14 | test_test_adjacency = compute_adjacency_matrix(Xtest, method='cyflann', **adjacency_kwds)
15 | train_adjacency = hstack([Dtrain, test_train_adjacency.transpose()])
16 | test_adjacency = hstack([test_train_adjacency, test_test_adjacency])
17 | return vstack([train_adjacency, test_adjacency])
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/cyflann/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/geometry/cyflann/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/cyflann/cyflann_index.cc:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /* Authors: Zhongyue Zhang
2 |
3 | LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
4 | ================================================= */
5 |
6 | #include "cyflann_index.h"
7 |
8 | CyflannIndex::CyflannIndex(const std::vector& dataset, int num_dims) {
9 | int num_pts = dataset.size() / num_dims;
10 | dataset_ = new float[dataset.size()];
11 | std::copy(dataset.begin(), dataset.end(), dataset_);
12 | Matrix data(dataset_, num_pts, num_dims);
13 | // TODO: add support for different distance metric.
14 | index_ = new Index< L2 >(data, KMeansIndexParams());
15 | }
16 |
17 | CyflannIndex::CyflannIndex(const std::vector& dataset, int num_dims,
18 | std::string index_type, int num_trees, int branching, int iterations,
19 | float cb_index) {
20 | int num_pts = dataset.size() / num_dims;
21 | dataset_ = new float[dataset.size()];
22 | std::copy(dataset.begin(), dataset.end(), dataset_);
23 | Matrix data(dataset_, num_pts, num_dims);
24 | // TODO: wrap all info into a class in the future.
25 | if (index_type == "kdtrees") {
26 | index_ = new Index< L2 >(data, KDTreeIndexParams(num_trees));
27 | } else if (index_type == "kmeans") {
28 | index_ = new Index< L2 >(data, KMeansIndexParams(branching,
29 | iterations, FLANN_CENTERS_RANDOM, cb_index));
30 | } else {
31 | index_ = new Index< L2 >(data, CompositeIndexParams(num_trees,
32 | branching, iterations, FLANN_CENTERS_RANDOM, cb_index));
33 | }
34 | }
35 |
36 | CyflannIndex::CyflannIndex(const std::vector& dataset, int num_dims,
37 | float target_precision, float build_weight, float memory_weight,
38 | float sample_fraction) {
39 | int num_pts = dataset.size() / num_dims;
40 | dataset_ = new float[dataset.size()];
41 | std::copy(dataset.begin(), dataset.end(), dataset_);
42 | Matrix data(dataset_, num_pts, num_dims);
43 | // TODO: add support for different distance metric.
44 | index_ = new Index< L2 >(data, AutotunedIndexParams(
45 | target_precision, build_weight, memory_weight, sample_fraction));
46 | }
47 |
48 | CyflannIndex::CyflannIndex(const std::vector& dataset, int num_dims,
49 | std::string filename) {
50 | int num_pts = dataset.size() / num_dims;
51 | dataset_ = new float[dataset.size()];
52 | std::copy(dataset.begin(), dataset.end(), dataset_);
53 | Matrix data(dataset_, num_pts, num_dims);
54 | // TODO: add support for different distance metric.
55 | index_ = new Index< L2 >(data, SavedIndexParams(filename));
56 | }
57 |
58 | CyflannIndex::~CyflannIndex() {
59 | delete index_;
60 | delete[] dataset_;
61 | }
62 |
63 | void CyflannIndex::buildIndex(){
64 | index_->buildIndex();
65 | }
66 |
67 | int CyflannIndex::knnSearch(const std::vector& queries,
68 | std::vector< std::vector >& indices,
69 | std::vector< std::vector >& dists,
70 | int knn, int num_dims, int num_checks) {
71 | int num_pts = queries.size() / num_dims;
72 | float* array = new float[queries.size()];
73 | std::copy(queries.begin(), queries.end(), array);
74 | Matrix qpts(array, num_pts, num_dims);
75 | int res = index_->knnSearch(qpts, indices, dists, knn,
76 | SearchParams(num_checks));
77 | delete[] array;
78 | return res;
79 | }
80 |
81 | int CyflannIndex::radiusSearch(const std::vector& queries,
82 | std::vector< std::vector >& indices,
83 | std::vector< std::vector >& dists,
84 | float radius, int num_dims, int num_checks) {
85 | int num_pts = queries.size() / num_dims;
86 | float* array = new float[queries.size()];
87 | std::copy(queries.begin(), queries.end(), array);
88 | Matrix dataset(array, num_pts, num_dims);
89 | int res = index_->radiusSearch(dataset, indices, dists, radius,
90 | SearchParams(num_checks));
91 | delete[] array;
92 | return res;
93 | }
94 |
95 | void CyflannIndex::save(std::string filename) {
96 | index_->save(filename);
97 | }
98 |
99 | int CyflannIndex::veclen() { return index_->veclen(); }
100 |
101 | int CyflannIndex::size() { return index_->size(); }
102 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/cyflann/cyflann_index.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /* Authors: Zhongyue Zhang
2 |
3 | LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
4 | ================================================= */
5 | #ifndef CYFLANN_INDEX_H_
6 | #define CYFLANN_INDEX_H_
7 |
8 | #include
9 | #include
10 | using namespace flann;
11 |
12 | class CyflannIndex {
13 | public:
14 |
15 | CyflannIndex(const std::vector& dataset, int num_dims);
16 |
17 | CyflannIndex(const std::vector& dataset, int num_dims,
18 | std::string index_type, int num_trees, int branching, int iterations,
19 | float cb_index);
20 |
21 | CyflannIndex(const std::vector& dataset, int num_dims,
22 | float target_precision, float build_weight, float memory_weight,
23 | float sample_fraction);
24 |
25 | CyflannIndex(const std::vector& dataset, int num_dims,
26 | std::string filename);
27 |
28 | ~CyflannIndex();
29 |
30 | void buildIndex();
31 |
32 | int knnSearch(const std::vector& queries,
33 | std::vector< std::vector >& indices,
34 | std::vector< std::vector >& dists,
35 | int knn, int num_dims, int num_checks);
36 |
37 | int radiusSearch(const std::vector& queries,
38 | std::vector< std::vector >& indices,
39 | std::vector< std::vector >& dists,
40 | float radius, int num_dims, int num_checks);
41 |
42 | void save(std::string filename);
43 |
44 | int veclen();
45 |
46 | int size();
47 |
48 | private:
49 | float* dataset_;
50 | Index< L2 >* index_;
51 | };
52 |
53 | // Takes a flattened matrix queries, with dimension num_dims.
54 | // For each data point in queries, search for neighbors within the radius.
55 | int radiusSearch(const std::vector& queries,
56 | std::vector< std::vector >& indices,
57 | std::vector< std::vector >& dists,
58 | float radius, int num_dims);
59 |
60 | #endif // CYFLANN_INDEX_H_
61 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/cyflann/index.pxd:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Authors: Zhongyue Zhang
2 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
3 |
4 | from __future__ import division
5 | import cython
6 | import numpy as np
7 | cimport numpy as np
8 | from libcpp.vector cimport vector
9 | from libcpp.string cimport string
10 |
11 | ctypedef np.float32_t dtype_t
12 | ctypedef np.int32_t dtypei_t
13 |
14 | cdef extern from "cyflann_index.h":
15 | cdef cppclass CyflannIndex:
16 | CyflannIndex(const vector[dtype_t]& dataset, dtypei_t ndim) except +
17 | CyflannIndex(const vector[dtype_t]& dataset, dtypei_t num_dims,
18 | string index_type, dtypei_t num_trees, dtypei_t branching,
19 | dtypei_t iterations, dtype_t cb_index)
20 | CyflannIndex(const vector[dtype_t]& dataset, dtypei_t ndim,
21 | dtype_t target_precision, dtype_t build_weight,
22 | dtype_t memory_weight, dtype_t sample_fraction)
23 | CyflannIndex(const vector[dtype_t]& dataset, dtypei_t ndim,
24 | string filename)
25 | void buildIndex()
26 | int knnSearch(const vector[dtype_t]& queries,
27 | vector[vector[dtypei_t]]& indices,
28 | vector[vector[dtype_t]]& dists,
29 | dtypei_t knn, dtypei_t num_dims, dtypei_t num_checks)
30 | int radiusSearch(const vector[dtype_t]& queries,
31 | vector[vector[dtypei_t]]& indices,
32 | vector[vector[dtype_t]]& dists,
33 | dtype_t radius, dtypei_t num_dims, dtypei_t num_checks)
34 | void save(string filename)
35 | int veclen()
36 | int size()
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/cyflann/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import os
4 | import sys
5 | import platform
6 |
7 | FLANN_ROOT = os.environ.get('FLANN_ROOT', sys.exec_prefix)
8 | CONDA_BUILD = os.environ.get('CONDA_BUILD', 0)
9 |
10 | def configuration(parent_package='', top_path=None):
11 | import numpy
12 | from numpy.distutils.misc_util import Configuration
13 |
14 | config = Configuration('geometry/cyflann', parent_package, top_path)
15 | libraries = ['flann', 'flann_cpp']
16 | if os.name == 'posix':
17 | libraries.append('m')
18 |
19 | kwds = {}
20 | flann_include = os.path.join(FLANN_ROOT, 'include')
21 | flann_lib = os.path.join(FLANN_ROOT, 'lib')
22 |
23 | if CONDA_BUILD:
24 | # conda uses relative dynamic library paths
25 | pass
26 | else:
27 | # direct installations use absolute library paths
28 | print("Compiling FLANN with FLANN_ROOT={0}".format(FLANN_ROOT))
29 |
30 | # from http://stackoverflow.com/questions/19123623/python-runtime-library-dirs-doesnt-work-on-mac
31 | if platform.system() == 'Darwin':
32 | kwds['extra_link_args'] = ['-Wl,-rpath,'+flann_lib]
33 | kwds['runtime_library_dirs'] = [flann_lib]
34 |
35 | config.add_extension("index",
36 | sources=["index.cxx", "cyflann_index.cc"],
37 | include_dirs=[numpy.get_include(), flann_include],
38 | libraries=libraries,
39 | library_dirs=[flann_lib],
40 | extra_compile_args=["-O3"],
41 | **kwds)
42 |
43 | return config
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/tests/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/geometry/tests/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/tests/test_adjacency.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | from nose import SkipTest
4 |
5 | import numpy as np
6 | from numpy.testing import assert_allclose, assert_raises, assert_equal
7 | from scipy.sparse import isspmatrix
8 | from scipy.spatial.distance import cdist, pdist, squareform
9 |
10 | from megaman.geometry import (Geometry, compute_adjacency_matrix, Adjacency,
11 | adjacency_methods)
12 |
13 |
14 | try:
15 | import pyflann as pyf
16 | NO_PYFLANN = False
17 | except ImportError:
18 | NO_PYFLANN = True
19 |
20 |
21 | def test_adjacency_methods():
22 | assert_equal(set(adjacency_methods()),
23 | {'auto', 'pyflann', 'ball_tree',
24 | 'cyflann', 'brute', 'kd_tree'})
25 |
26 |
27 | def test_adjacency_input_validation():
28 | X = np.random.rand(20, 3)
29 | # need to specify radius or n_neighbors
30 | assert_raises(ValueError, compute_adjacency_matrix, X)
31 | # cannot specify both radius and n_neighbors
32 | assert_raises(ValueError, compute_adjacency_matrix, X,
33 | radius=1, n_neighbors=10)
34 |
35 |
36 | def test_adjacency():
37 | rng = np.random.RandomState(36)
38 | X = rng.rand(100, 3)
39 | Gtrue = {}
40 |
41 | exact_methods = [m for m in Adjacency.methods()
42 | if not m.endswith('flann')]
43 |
44 | def check_kneighbors(n_neighbors, method):
45 | if method == 'pyflann' and NO_PYFLANN:
46 | raise SkipTest("pyflann not installed")
47 |
48 | G = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, method=method,
49 | n_neighbors=n_neighbors)
50 | assert isspmatrix(G)
51 | assert G.shape == (X.shape[0], X.shape[0])
52 | if method in exact_methods:
53 | assert_allclose(G.toarray(), Gtrue[n_neighbors].toarray())
54 |
55 | def check_radius(radius, method):
56 | if method == 'pyflann' and NO_PYFLANN:
57 | raise SkipTest("pyflann not installed")
58 |
59 | G = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, method=method,
60 | radius=radius)
61 | assert isspmatrix(G)
62 | assert G.shape == (X.shape[0], X.shape[0])
63 | if method in exact_methods:
64 | assert_allclose(G.toarray(), Gtrue[radius].toarray())
65 |
66 | for n_neighbors in [5, 10, 15]:
67 | Gtrue[n_neighbors] = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, method='brute',
68 | n_neighbors=n_neighbors)
69 | for method in Adjacency.methods():
70 | yield check_kneighbors, n_neighbors, method
71 |
72 | for radius in [0.1, 0.5, 1.0]:
73 | Gtrue[radius] = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, method='brute',
74 | radius=radius)
75 | for method in Adjacency.methods():
76 | yield check_radius, radius, method
77 |
78 |
79 | def test_unknown_method():
80 | X = np.arange(20).reshape((10, 2))
81 | assert_raises(ValueError, compute_adjacency_matrix, X, 'foo')
82 |
83 |
84 | def test_all_methods_close():
85 | rand = np.random.RandomState(36)
86 | X = rand.randn(10, 2)
87 | D_true = squareform(pdist(X))
88 | D_true[D_true > 0.5] = 0
89 |
90 | def check_method(method):
91 | kwargs = {}
92 | if method == 'pyflann':
93 | try:
94 | import pyflann as pyf
95 | except ImportError:
96 | raise SkipTest("pyflann not installed.")
97 | flindex = pyf.FLANN()
98 | flindex.build_index(X, algorithm='kmeans',
99 | target_precision=0.9)
100 | kwargs['flann_index'] = flindex
101 | this_D = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, method=method, radius=0.5,
102 | **kwargs)
103 | assert_allclose(this_D.toarray(), D_true, rtol=1E-5)
104 |
105 | for method in ['auto', 'cyflann', 'pyflann', 'brute']:
106 | yield check_method, method
107 |
108 |
109 | def test_custom_adjacency():
110 | class CustomAdjacency(Adjacency):
111 | name = "custom"
112 | def adjacency_graph(self, X):
113 | return squareform(pdist(X))
114 |
115 | rand = np.random.RandomState(42)
116 | X = rand.rand(10, 2)
117 | D = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, method='custom', radius=1)
118 | assert_allclose(D, cdist(X, X))
119 |
120 | Adjacency._remove_from_registry("custom")
121 |
122 | def test_cyflann_index_type():
123 | rand = np.random.RandomState(36)
124 | X = rand.randn(10, 2)
125 | D_true = squareform(pdist(X))
126 | D_true[D_true > 1.5] = 0
127 |
128 | def check_index_type(index_type):
129 | method = 'cyflann'
130 | radius = 1.5
131 | cyflann_kwds = {'index_type':index_type}
132 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':radius, 'cyflann_kwds':cyflann_kwds}
133 | this_D = compute_adjacency_matrix(X=X, method = 'cyflann', **adjacency_kwds)
134 | assert_allclose(this_D.toarray(), D_true, rtol=1E-5, atol=1E-5)
135 |
136 | for index_type in ['kmeans', 'kdtrees']:
137 | yield check_index_type, index_type
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/tests/test_affinity.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | from __future__ import division ## removes integer division
4 |
5 | import os
6 |
7 | import numpy as np
8 | from numpy.testing import assert_allclose, assert_equal, assert_raises
9 |
10 | from scipy.spatial.distance import cdist, pdist, squareform
11 | from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
12 | from scipy import io
13 |
14 | from megaman.geometry import (compute_adjacency_matrix,
15 | compute_affinity_matrix, Affinity,
16 | affinity_methods)
17 |
18 | random_state = np.random.RandomState(36)
19 | n_sample = 10
20 | d = 2
21 | X = random_state.randn(n_sample, d)
22 | D = squareform(pdist(X))
23 | D[D > 1/d] = 0
24 |
25 |
26 | TEST_DATA = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__),
27 | 'testmegaman_laplacian_rad0_2_lam1_5_n200.mat')
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 | def test_affinity_methods():
32 | assert_equal(set(affinity_methods()), {'auto', 'gaussian'})
33 |
34 |
35 | def test_affinity_input_validation():
36 | X = np.random.rand(20, 3)
37 | D = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, radius=1)
38 | assert_raises(ValueError, compute_affinity_matrix, X)
39 |
40 |
41 | def test_affinity_sparse_vs_dense():
42 | """
43 | Test that A_sparse is the same as A_dense for a small A matrix
44 | """
45 | rad = 2.
46 | n_samples = 6
47 | X = np.arange(n_samples)
48 | X = X[ :,np.newaxis]
49 | X = np.concatenate((X,np.zeros((n_samples,1),dtype=float)),axis=1)
50 | X = np.asarray( X, order="C" )
51 | test_dist_matrix = compute_adjacency_matrix( X, method = 'auto', radius = rad )
52 | A_dense = compute_affinity_matrix(test_dist_matrix.toarray(), method = 'auto',
53 | radius = rad, symmetrize = False )
54 | A_sparse = compute_affinity_matrix(csr_matrix(test_dist_matrix),
55 | method = 'auto', radius = rad, symmetrize = False)
56 | A_spdense = A_sparse.toarray()
57 | A_spdense[ A_spdense == 0 ] = 1.
58 | assert_allclose(A_dense, A_spdense)
59 |
60 |
61 | def test_affinity_vs_matlab():
62 | """Test that the affinity calculation matches the matlab result"""
63 | matlab = io.loadmat(TEST_DATA)
64 |
65 | D = np.sqrt(matlab['S']) # matlab outputs squared distances
66 | A_matlab = matlab['A']
67 | radius = matlab['rad'][0]
68 |
69 | # check dense affinity computation
70 | A_dense = compute_affinity_matrix(D, radius=radius)
71 | assert_allclose(A_dense, A_matlab)
72 |
73 | # check sparse affinity computation
74 | A_sparse = compute_affinity_matrix(csr_matrix(D), radius=radius)
75 | assert_allclose(A_sparse.toarray(), A_matlab)
76 |
77 |
78 | def test_affinity():
79 | rand = np.random.RandomState(42)
80 | X = np.random.rand(20, 3)
81 | D = cdist(X, X)
82 |
83 | def check_affinity(adjacency_radius, affinity_radius, symmetrize):
84 | adj = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, radius=adjacency_radius)
85 | aff = compute_affinity_matrix(adj, radius=affinity_radius,
86 | symmetrize=True)
87 |
88 | A = np.exp(-(D / affinity_radius) ** 2)
89 | A[D > adjacency_radius] = 0
90 | assert_allclose(aff.toarray(), A)
91 |
92 | for adjacency_radius in [0.5, 1.0, 5.0]:
93 | for affinity_radius in [0.1, 0.5, 1.0]:
94 | for symmetrize in [True, False]:
95 | yield (check_affinity, adjacency_radius,
96 | affinity_radius, symmetrize)
97 |
98 |
99 | def test_custom_affinity():
100 | class CustomAffinity(Affinity):
101 | name = "custom"
102 | def affinity_matrix(self, adjacency_matrix):
103 | return np.exp(-abs(adjacency_matrix.toarray()))
104 |
105 | rand = np.random.RandomState(42)
106 | X = rand.rand(10, 2)
107 | D = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, radius=10)
108 | A = compute_affinity_matrix(D, method='custom', radius=1)
109 | assert_allclose(A, np.exp(-abs(D.toarray())))
110 |
111 | Affinity._remove_from_registry("custom")
112 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/tests/test_complete_adjacency_matrix.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from scipy.spatial.distance import cdist, pdist, squareform
2 | from megaman.geometry.adjacency import compute_adjacency_matrix
3 | from megaman.geometry.complete_adjacency_matrix import complete_adjacency_matrix
4 | import numpy as np
5 | from numpy.testing import assert_allclose
6 |
7 | def test_complete_adjacency():
8 | rand = np.random.RandomState(36)
9 | radius = 1.5
10 | X = rand.randn(10, 2)
11 | Xtest = rand.randn(4, 2)
12 |
13 | Xtotal = np.vstack([X, Xtest])
14 | D_true = squareform(pdist(Xtotal))
15 | D_true[D_true > radius] = 0
16 |
17 | adjacency_kwds = {'radius':radius}
18 | Dtrain = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, method='cyflann', radius = radius)
19 | this_D = complete_adjacency_matrix(Dtrain, X, Xtest, adjacency_kwds)
20 |
21 | assert_allclose(this_D.toarray(), D_true, rtol=1E-4)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/tests/test_laplacian.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | % generates the test data used by test_laplacian.py
2 | % LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
3 | %
4 |
5 | %addpath /mnt/costila/speclust/code-dominique-rmetric/
6 | addpath /mnt/costila/mmp/research/spectral/dominique-epsilon/EpsilonDemo/
7 |
8 | outfroot = 'testmegaman_laplacian'
9 | rad = 0.2;
10 | renormlam = 1.5; % renormalization exponent
11 | opts.lam = renormlam;
12 | n = 200;
13 | seed = 36;
14 | rand( 'seed', seed );
15 | xx1 = rand( 1, n );
16 | xx2 = rand( 1, n );
17 | xx3 = sin( 2*pi*xx1).*sqrt(xx2);
18 |
19 | xx = [ xx1; xx2; xx3 ];
20 |
21 | epps = rad*rad;
22 | [ A, S ] = similarity( xx', epps );
23 | norms = {'geometric', 'unormalized', 'randomwalk', 'symmetricnormalized', 'renormalized' };
24 | names = {'geom', 'unnorm', 'rw', 'symnorm', 'reno1_5' };
25 |
26 | for ii = 1:length( norms );
27 | disp( norms{ ii } )
28 | opts.lapType = norms{ ii };
29 | [ L, phi, lam, flag ] = laplacian( A, 2, epps, opts );
30 | eval( [ 'L' names{ ii } '=L;']);
31 | eval( [ 'phi' names{ ii } '=phi;']);
32 | eval( [ 'lam' names{ ii } '=lam;']);
33 | end;
34 |
35 | [G, VV, LL, Ginv ] = rmetric( Lgeom, phigeom, 2, 0 );
36 |
37 | rad
38 | num2str_(rad)
39 | renormlam
40 | num2str_(renormlam)
41 | outfname = [ outfroot '_rad' num2str_(rad) '_lam' num2str_(renormlam) '_n' num2str( n ) '.mat' ]
42 |
43 | save( outfname )
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/tests/test_laplacian.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import os
4 |
5 | import numpy as np
6 | from numpy.testing import assert_allclose, assert_equal, assert_raises
7 |
8 | from scipy.sparse import isspmatrix, csr_matrix
9 | from scipy import io
10 |
11 | from megaman.geometry import (compute_adjacency_matrix,
12 | compute_affinity_matrix,
13 | Laplacian, compute_laplacian_matrix,
14 | laplacian_methods)
15 |
16 |
17 | TEST_DATA = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__),
18 | 'testmegaman_laplacian_rad0_2_lam1_5_n200.mat')
19 |
20 |
21 | def test_laplacian_methods():
22 | assert_equal(set(laplacian_methods()),
23 | {'auto', 'renormalized', 'symmetricnormalized',
24 | 'geometric', 'randomwalk', 'unnormalized'})
25 |
26 |
27 | def test_laplacian_vs_matlab():
28 | # Test that the laplacian calculation matches the matlab result
29 | matlab = io.loadmat(TEST_DATA)
30 |
31 | laplacians = {'unnormalized': matlab['Lunnorm'],
32 | 'symmetricnormalized': matlab['Lsymnorm'],
33 | 'geometric': matlab['Lgeom'],
34 | 'randomwalk': matlab['Lrw'],
35 | 'renormalized': matlab['Lreno1_5']}
36 |
37 | radius = matlab['rad'][0]
38 |
39 | def check_laplacian(input_type, laplacian_method):
40 | kwargs = {'scaling_epps': radius}
41 | if laplacian_method == 'renormalized':
42 | kwargs['renormalization_exponent'] = 1.5
43 | adjacency = input_type(np.sqrt(matlab['S']))
44 | affinity = compute_affinity_matrix(adjacency, radius=radius)
45 | laplacian = compute_laplacian_matrix(affinity,
46 | method=laplacian_method,
47 | **kwargs)
48 | if input_type is csr_matrix:
49 | laplacian = laplacian.toarray()
50 | assert_allclose(laplacian, laplacians[laplacian_method])
51 |
52 | for input_type in [np.array, csr_matrix]:
53 | for laplacian_method in laplacians:
54 | yield check_laplacian, input_type, laplacian_method
55 |
56 |
57 | def test_laplacian_smoketest():
58 | rand = np.random.RandomState(42)
59 | X = rand.rand(20, 2)
60 | adj = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, radius=0.5)
61 | aff = compute_affinity_matrix(adj, radius=0.1)
62 |
63 | def check_laplacian(method):
64 | lap = compute_laplacian_matrix(aff, method=method)
65 |
66 | assert isspmatrix(lap)
67 | assert_equal(lap.shape, (X.shape[0], X.shape[0]))
68 |
69 | for method in Laplacian.asymmetric_methods():
70 | yield check_laplacian, method
71 |
72 |
73 | def test_laplacian_unknown_method():
74 | """Test that laplacian fails with an unknown method type"""
75 | A = np.array([[ 5, 2, 1 ], [ 2, 3, 2 ],[1,2,5]])
76 | assert_raises(ValueError, compute_laplacian_matrix, A, method='')
77 |
78 |
79 | def test_laplacian_full_output():
80 | # Test that full_output symmetrized laplacians have the right form
81 | rand = np.random.RandomState(42)
82 | X = rand.rand(20, 2)
83 |
84 | def check_symmetric(method, adjacency_radius, affinity_radius):
85 | adj = compute_adjacency_matrix(X, radius=adjacency_radius)
86 | aff = compute_affinity_matrix(adj, radius=affinity_radius)
87 | lap, lapsym, w = compute_laplacian_matrix(aff, method=method,
88 | full_output=True)
89 |
90 | sym = w[:, np.newaxis] * (lap.toarray() + np.eye(*lap.shape))
91 |
92 | assert_allclose(lapsym.toarray(), sym)
93 |
94 | for method in Laplacian.asymmetric_methods():
95 | for adjacency_radius in [0.5, 1.0]:
96 | for affinity_radius in [0.1, 0.3]:
97 | yield check_symmetric, method, adjacency_radius, affinity_radius
98 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/tests/test_rmetric.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import os
4 |
5 | from nose.tools import assert_true
6 | from nose.tools import assert_equal
7 | import scipy.io
8 | from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
9 | from scipy.sparse import csc_matrix
10 | from scipy.sparse import isspmatrix
11 | import numpy as np
12 | from numpy.testing import assert_array_almost_equal, assert_array_equal, assert_allclose
13 |
14 | from nose.tools import assert_raises
15 | from nose.plugins.skip import SkipTest
16 |
17 | from megaman.geometry.rmetric import *
18 | from megaman.embedding.spectral_embedding import _graph_is_connected
19 |
20 | TEST_DATA = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__),
21 | 'testmegaman_laplacian_rad0_2_lam1_5_n200.mat')
22 |
23 | def _load_test_data():
24 | """ Loads a .mat file from . and extract the following dense matrices
25 | test_dist_matrix = matrix of distances
26 | L = the geometric Laplacian
27 | Ginv = the dual Riemann metric [n,2,2] array
28 | G = the Riemann metric [n,2,2] array
29 | phi = embedding in 2 dimensions [n, 2] array
30 | rad = scalar, radius used in affinity calculations, Laplacians
31 | Note: rad is returned as an array of dimension 1. Outside one must
32 | make it a scalar by rad = rad[0]
33 |
34 | """
35 | xdict = scipy.io.loadmat(TEST_DATA)
36 | rad = xdict[ 'rad' ]
37 | test_dist_matrix = xdict[ 'S' ] # S contains squared distances
38 | test_dist_matrix = np.sqrt( test_dist_matrix ) #unused
39 | A = xdict[ 'A' ] #unused
40 | L = xdict[ 'Lgeom' ]
41 | G = xdict[ 'G' ]
42 | H = xdict[ 'Ginv' ]
43 | H = np.transpose( H, ( 2, 0, 1 ))
44 | G = np.transpose( G, ( 2, 0, 1 ))
45 | phi = xdict[ 'phigeom' ]
46 |
47 | print( 'phi.shape = ', phi.shape )
48 | print( 'G.shape = ', G.shape )
49 | print( 'H.shape = ', H.shape )
50 | print( 'L.shape = ', L.shape )
51 | return rad, L, G, H, phi
52 |
53 | def test_equal_original(almost_equal_decimals = 5):
54 | """ Loads the results from a matlab run and checks that our results
55 | are the same. The results loaded are the Laplacian, embedding phi,
56 | Riemannian metric G[2,2,200], and dual Riemannian metric H[2,2,200]
57 |
58 | Currently, this tests the riemann_metric() function only.
59 | TODO: to test the class RiemannMetric
60 |
61 | Only riemann_metric with given L is tested. For other inputs, to test
62 | later after the structure of the code is stabilized. (I.e I may remove
63 | the computation of the L to another function.
64 | """
65 | rad, L, Gtest, Htest, phi = _load_test_data()
66 |
67 | H = riemann_metric( phi, laplacian = L, n_dim = 2, invert_h = False )[0]
68 | n = phi.shape[ 0 ]
69 | assert_array_almost_equal( Htest, H, almost_equal_decimals )
70 |
71 | # To prevent the accumulation of small numerical errors, change the
72 | # generation process of G from invert H to invertion of Htest
73 | G = compute_G_from_H(Htest)[0]
74 | tol = np.mean( Gtest[:,0,0])*10**(-almost_equal_decimals )
75 | assert_allclose( Gtest, G, tol)
76 | # assert_array_max_ulp( Gtest, G, almost_equal_decimals )
77 | # this assertion fails because Gtest is generally asymmetric. G is
78 | # mostly symmetric but not always. I suspect this is due to the
79 | # numerical errors, as many of these 2x2 matrices are very poorly
80 | # conditioned. What to do? Perhaps generate another matlab test set
81 | # with better condition numbers...
82 |
83 | def test_lazy_rmetric(almost_equal_decimals=5):
84 | """ Load results from matlab and check lazy rmetric gets the
85 | same value as the full rmetric on a subset
86 | """
87 | rad, L, Gtest, Htest, phi = _load_test_data()
88 | n = phi.shape[0]
89 | sample = np.random.choice(range(n), min(50, n), replace=False)
90 | H = riemann_metric(phi, laplacian = L, n_dim = 2)[0]
91 | Hlazy = riemann_metric_lazy(phi, sample=sample, laplacian=L, n_dim=2)[0]
92 | assert_array_almost_equal( Hlazy, H[sample, :,:], almost_equal_decimals)
93 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/tests/testmegaman_laplacian_rad0_2_lam1_5_n200.mat:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/geometry/tests/testmegaman_laplacian_rad0_2_lam1_5_n200.mat
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/geometry/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | __all__ = ["RegisterSubclasses"]
4 |
5 |
6 | # From six.py
7 | def with_metaclass(meta, *bases):
8 | """Create a base class with a metaclass."""
9 | # Use a dummy metaclass that replaces itself with the actual metaclass.
10 | class metaclass(type):
11 | def __new__(cls, name, this_bases, d):
12 | return meta(name, bases, d)
13 | return type.__new__(metaclass, '_TemporaryClass', (), {})
14 |
15 |
16 | class RegistryMeta(type):
17 | """Metaclass for object type which registers subclasses"""
18 | def __init__(cls, name, bases, dct):
19 | if name in ['_TemporaryClass', 'RegisterSubclasses']:
20 | # these are hidden baseclasses. Do nothing
21 | pass
22 | elif not hasattr(cls, '_method_registry'):
23 | # this is a registry class. Create an empty registry
24 | cls._method_registry = {}
25 | elif hasattr(cls, 'name'):
26 | # this is a labeled derived class. Add cls to the registry
27 | cls._method_registry[cls.name] = cls
28 |
29 | super(RegistryMeta, cls).__init__(name, bases, dct)
30 |
31 |
32 | class RegisterSubclasses(with_metaclass(RegistryMeta)):
33 | @classmethod
34 | def get_method(cls, method):
35 | if method not in cls._method_registry:
36 | raise ValueError("method={0} not valid. Must be one of "
37 | "{1}".format(method, list(cls.methods())))
38 | return cls._method_registry[method]
39 |
40 | @classmethod
41 | def init(cls, method, *args, **kwargs):
42 | Method = cls.get_method(method)
43 | return Method(*args, **kwargs)
44 |
45 | @classmethod
46 | def _remove_from_registry(cls, method):
47 | cls._method_registry.pop(method, None)
48 |
49 | @classmethod
50 | def methods(cls):
51 | return cls._method_registry.keys()
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/plotter/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | from .plotter import (plot_with_plotly, plot_embedding_with_plotly,
4 | plot_with_matplotlib, plot_embedding_with_matplotlib)
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/plotter/plotter.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Author: Yu-Chia Chen
2 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
3 |
4 | import numpy as np
5 | from .utils import *
6 | from .utils import _check_backend
7 | from .scatter_3d import scatter_plot3d_plotly, scatter_plot3d_matplotlib
8 | from .covar_plotter3 import covar_plotter3d_plotly, covar_plotter3d_matplotlib
9 |
10 | @_check_backend('plotly')
11 | def plot_with_plotly( embedding, rieman_metric, nstd=2,
12 | color_by_ratio=True, if_ellipse=False ):
13 | from plotly.offline import iplot
14 | import plotly.graph_objs as go
15 | sigma_norms = get_top_two_sigma_norm(rieman_metric, color_by_ratio)
16 | colors, colorscale = generate_colors_and_colorscale('gist_rainbow',
17 | sigma_norms)
18 | scatter_pt = scatter_plot3d_plotly(embedding, coloring=sigma_norms,
19 | colorscale=colorscale)
20 | index = generate_grid(embedding.shape[0])
21 |
22 | if if_ellipse:
23 | ellipses_pt = covar_plotter3d_plotly(embedding,
24 | rieman_metric, index, colors)
25 | scatter_pt = ellipses_pt + scatter_pt
26 |
27 | layout = plotly_layout(embedding)
28 | fig = go.Figure(data=scatter_pt,layout=layout)
29 | iplot(fig,filename='scatter-3d-plotly')
30 |
31 | def plot_embedding_with_plotly(trace_var,idx,if_ellipse=False):
32 | plot_with_plotly(trace_var.Y[idx],trace_var.H[idx]/30,if_ellipse=if_ellipse)
33 |
34 | @_check_backend('matplotlib')
35 | def plot_with_matplotlib(embedding, rieman_metric, nstd=2,
36 | color_by_ratio=True, if_ellipse=False):
37 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
38 | sigma_norms = get_top_two_sigma_norm(rieman_metric, color_by_ratio)
39 | colors, _ncor = get_colors_array('gist_rainbow', sigma_norms, base255=False)
40 | fig,ax = scatter_plot3d_matplotlib(embedding, sigma_norms)
41 |
42 | index = generate_grid(embedding.shape[0])
43 | if if_ellipse:
44 | ax = covar_plotter3d_matplotlib(embedding, rieman_metric,
45 | index, ax, colors)
46 | plt.show()
47 |
48 | def plot_embedding_with_matplotlib(trace_var,idx,if_ellipse=False):
49 | plot_with_matplotlib(trace_var.Y[idx],trace_var.H[idx]/30,if_ellipse=if_ellipse)
50 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/plotter/scatter_3d.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Author: Yu-Chia Chen
2 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
3 |
4 | import numpy as np
5 | from .utils import _check_backend
6 |
7 | @_check_backend('matplotlib')
8 | def scatter_plot3d_matplotlib(embedding, coloring=None, fig=None,
9 | subplot=False, subplot_grid=None, **kwargs):
10 | from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import art3d, Axes3D
11 | if fig is None:
12 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
13 | fig = plt.figure()
14 | if subplot and subplot_grid is not None:
15 | sx,sy,sz = subplot_grid
16 | ax = fig.add_subplot(sx,sy,sz,projection='3d')
17 | else:
18 | if subplot is None and subplot:
19 | import warnings
20 | warnings.warn(
21 | 'Subplot grid is not provided, switching to non-subplot mode')
22 | ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
23 |
24 | ax.set_aspect('equal')
25 | s = [2 for i in range(embedding.shape[0])]
26 | x,y,z = embedding[:,:3].T
27 |
28 | if isinstance(coloring, str) and coloring.lower() in 'xyz':
29 | color_idx = 'xyz'.find(coloring)
30 | coloring = embedding[:,color_idx].flatten()
31 |
32 | if coloring is None:
33 | ax.scatter(x,y,z,s=s,**kwargs)
34 | else:
35 | sc = ax.scatter(x,y,z,c=coloring,cmap='gist_rainbow',s=s,**kwargs)
36 | fig.colorbar(sc)
37 |
38 | max_range = np.array(
39 | [x.max()-x.min(), y.max()-y.min(), z.max()-z.min()]).max() / 2.0
40 |
41 | mid_x = (x.max()+x.min()) * 0.5
42 | mid_y = (y.max()+y.min()) * 0.5
43 | mid_z = (z.max()+z.min()) * 0.5
44 | ax.set_xlim(mid_x - max_range, mid_x + max_range)
45 | ax.set_ylim(mid_y - max_range, mid_y + max_range)
46 | ax.set_zlim(mid_z - max_range, mid_z + max_range)
47 |
48 | return fig, ax
49 |
50 | @_check_backend('plotly')
51 | def scatter_plot3d_plotly(embedding, coloring=None,
52 | colorscale='Rainbow', **kwargs):
53 | import plotly.graph_objs as go
54 | x,y,z = embedding[:,:3].T
55 | if isinstance(coloring, str) and coloring.lower() in 'xyz':
56 | color_idx = 'xyz'.find(coloring)
57 | coloring = embedding[:,color_idx].flatten()
58 |
59 | marker = kwargs.pop('marker',None)
60 | name = kwargs.pop('name','Embedding')
61 | scatter_plot = go.Scatter3d(
62 | x=x,
63 | y=y,
64 | z=z,
65 | mode='markers',
66 | marker=dict(
67 | size=2,
68 | opacity=0.8,
69 | ),
70 | name=name,
71 | **kwargs
72 | )
73 | if coloring is not None:
74 | scatter_plot['marker'].update(dict(
75 | color=coloring,
76 | colorscale=colorscale,
77 | showscale=True,
78 | ))
79 | elif marker is not None:
80 | scatter_plot['marker'].update(marker)
81 |
82 | return [scatter_plot]
83 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/plotter/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Author: Yu-Chia Chen
2 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
3 |
4 | import numpy as np
5 |
6 | def _check_backend(backend):
7 | def decorator(func):
8 | def wrapper(*args,**kwargs):
9 | import warnings
10 | warnings.warn(
11 | 'Be careful in using megaman.plotter modules'
12 | ' API will change in the next release.',
13 | FutureWarning
14 | )
15 | import pkgutil
16 | package = pkgutil.find_loader(backend)
17 | if package is not None:
18 | return func(*args,**kwargs)
19 | else:
20 | raise ImportError('plotting backend {} not installed'.format(backend))
21 | return wrapper
22 | return decorator
23 |
24 | @_check_backend('matplotlib')
25 | def get_colors_array(name,coloring,base255=True):
26 | from matplotlib import colors, cm
27 | cmap = cm.get_cmap(name=name)
28 | norm = colors.Normalize()
29 | normalized_coloring = norm(coloring)
30 | colors_array = (cmap(normalized_coloring)[:,:3]*255).astype(np.uint8) \
31 | if base255 else cmap(normalized_coloring)
32 | return colors_array, normalized_coloring
33 |
34 | def generate_plotly_colorscale(name,num=256):
35 | colormap, normalized_coloring = get_colors_array(name,np.arange(num))
36 | return [ [n_coloring, 'rgb({},{},{})'.format(*colormap[idx])] \
37 | for idx, n_coloring in enumerate(normalized_coloring) ]
38 |
39 | def generate_colors_and_colorscale(name,coloring,**kwargs):
40 | colors_array, _ncor = get_colors_array(name,coloring)
41 | colorscale = generate_plotly_colorscale(name,**kwargs)
42 | return colors_array, colorscale
43 |
44 | def generate_grid(size,num_groups=100):
45 | return np.arange(0,size,num_groups)
46 |
47 | @_check_backend('plotly')
48 | def plotly_layout(embedding):
49 | import plotly.graph_objs as go
50 | max_value = 1.2*np.max(np.absolute(embedding[:,:3]))
51 | axis_range = [-max_value,max_value]
52 | layout = go.Layout(
53 | title='Plot with ellipse',
54 | height=600,
55 | width=600,
56 | scene=dict(
57 | xaxis=dict(
58 | gridcolor='rgb(255, 255, 255)',
59 | zerolinecolor='rgb(255, 255, 255)',
60 | showbackground=True,
61 | backgroundcolor='rgb(230, 230,230)',
62 | range=axis_range,
63 | ),
64 | yaxis=dict(
65 | gridcolor='rgb(255, 255, 255)',
66 | zerolinecolor='rgb(255, 255, 255)',
67 | showbackground=True,
68 | backgroundcolor='rgb(230, 230,230)',
69 | range=axis_range,
70 | ),
71 | zaxis=dict(
72 | gridcolor='rgb(255, 255, 255)',
73 | zerolinecolor='rgb(255, 255, 255)',
74 | showbackground=True,
75 | backgroundcolor='rgb(230, 230,230)',
76 | range=axis_range,
77 | ),
78 | )
79 | )
80 | return layout
81 |
82 | def get_top_two_sigma_norm(H,color_by_ratio=True):
83 | eigen_vals = np.array([ sorted_eigh(Hk)[0][:2] for Hk in H ])
84 | if color_by_ratio == True:
85 | toptwo_eigen_vals_norm = eigen_vals[:,1] / eigen_vals[:,0]
86 | else:
87 | toptwo_eigen_vals_norm = eigen_vals[:,0]
88 | return toptwo_eigen_vals_norm
89 |
90 | def sorted_eigh(M):
91 | vals, vecs = np.linalg.eigh(M)
92 | return vals[::-1], vecs[:,::-1]
93 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | from .riemannian_relaxation import *
4 | from .trace_variable import TracingVariable
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/optimizer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Author: Yu-Chia Chen
2 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
3 |
4 | from __future__ import division
5 | from megaman.geometry.utils import RegisterSubclasses
6 |
7 | def init_optimizer(**kwargs):
8 | optimizer = kwargs.get('step_method', 'fixed')
9 | return BaseOptimizer.init(optimizer, **kwargs)
10 |
11 | class BaseOptimizer(RegisterSubclasses):
12 | """
13 | Base class for the optimizer.
14 |
15 | BaseOptimizer creates the common interface to the optimzer class
16 | as well as providing a common apply_optimization() which can be used
17 | in RiemannianRelaxation class to update the embeddings.
18 |
19 | Parameters
20 | ----------
21 | linesearch : bool
22 | If use linesearch to search for optima eta.
23 | eta_max : float
24 | (Linesearch mode) The maximum learning rate (eta) to start search with.
25 | eta : float
26 | (Non linesearch mode) The fixed learning rate (eta) to use.
27 | linesearch_first : bool
28 | (Linesearch mode) If do linesearch at first iteration.
29 | """
30 | def __init__(self, linesearch=False, eta_max=None, eta=None,
31 | linesearch_first=False, **kwargs):
32 | self.linesearch = linesearch
33 | if self.linesearch:
34 | self.linesearch_first = linesearch_first
35 | if eta_max is not None:
36 | self.eta_max = eta_max
37 | self.eta_min = 2**-10
38 | else:
39 | raise ValueError('Should provide eta_max keyword '
40 | 'when linesearch method is used.')
41 | else:
42 | if eta is not None:
43 | self.eta = eta
44 | else:
45 | raise ValueError('Should provide eta keyword '
46 | 'when fixed method is used.')
47 |
48 | def apply_optimization(self, update_embedding_with, grad, **kwargs):
49 | """
50 | Calculating (Obtaining) the learning rate (eta) and apply optimizations
51 | on the embedding states by the specified method.
52 |
53 | Parameters
54 | ----------
55 | update_embedding_with : function
56 | Function used to update the state of RiemannianRelaxation
57 | class (Y or S).
58 |
59 | grad : (n x s) array
60 | Gradients used in updating the embedding.
61 |
62 | calc_loss : function (used by its child function)
63 | Function used to calculated the loss from the temperary state of
64 | RiemannianRelaxation instance. (YT or ST)
65 |
66 | loss : float (used by its child function)
67 | Loss of the current state of RiemannianRelaxation instance.
68 | """
69 | if self.linesearch:
70 | return self._apply_linesearch_optimzation(update_embedding_with,
71 | grad, **kwargs)
72 | else:
73 | return self._apply_fixed_optimization(update_embedding_with,
74 | grad, **kwargs)
75 |
76 | def _apply_linesearch_optimzation(self, update_embedding_with, grad,
77 | calc_loss, loss, **kwargs):
78 | self.eta = self.eta_max
79 | if kwargs.get('first_iter',False) and not self.linesearch_first:
80 | self.eta = kwargs.get('eta_first',1)
81 | loss_diff = 1
82 | while loss_diff > 0:
83 | loss_diff, temp_embedding, delta = self._linesearch_once(
84 | update_embedding_with,grad,calc_loss,loss,**kwargs)
85 | if self.eta <= self.eta_min and loss_diff > 0:
86 | loss_diff, temp_embedding, delta = self._linesearch_once(
87 | update_embedding_with,grad,calc_loss,loss,**kwargs)
88 | loss_diff = -1
89 | self.eta *= 2
90 | update_embedding_with(new_embedding=temp_embedding)
91 | return delta
92 |
93 | def _linesearch_once(self, update_embedding_with, grad,
94 | calc_loss, loss, **kwargs):
95 | delta = self._calc_delta(grad)
96 | temp_embedding = update_embedding_with(delta=delta,copy=True)
97 | loss_diff = calc_loss(temp_embedding) - loss
98 | self.eta /= 2
99 | return loss_diff, temp_embedding, delta
100 |
101 | def _apply_fixed_optimization(self,update_embedding_with,grad,**kwargs):
102 | delta = self._calc_delta(grad)
103 | update_embedding_with(delta=delta)
104 | return delta
105 |
106 | def _calc_delta(self,grad,**kwargs):
107 | raise NotImplementedError()
108 |
109 | class FixedOptimizer(BaseOptimizer):
110 | """Optimizer for fixed (non-momentum) method."""
111 | name='fixed'
112 | def _calc_delta(self,grad,**kwargs):
113 | return -self.eta*grad
114 |
115 | class MomentumOptimizer(BaseOptimizer):
116 | """Optimizer for momentum method."""
117 | name='momentum'
118 | def __init__(self,momentum,**kwargs):
119 | BaseOptimizer.__init__(**kwargs)
120 | self.momentum = momentum
121 | self.last_delta = 0
122 |
123 | def _calc_delta(self,grad,**kwargs):
124 | return -self.eta * grad + self.momentum * self.last_delta
125 |
126 | def apply_optimization(self,update_embedding_with,grad,**kwargs):
127 | self.last_delta = BaseOptimizer.apply_optimization(
128 | self,update_embedding_with,grad,**kwargs)
129 | return self.last_delta
130 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/tests/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/relaxation/tests/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/tests/eps_halfdome.mat:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/relaxation/tests/eps_halfdome.mat
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/tests/rloss_halfdome.mat:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/relaxation/tests/rloss_halfdome.mat
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/tests/test_precomputed_S.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from megaman.relaxation.precomputed import *
2 | from .utils import generate_toy_laplacian
3 |
4 | class BaseTestARkNeighbors(object):
5 | def generate_laplacian(self):
6 | raise NotImplementedError()
7 | def setup_message(self):
8 | raise NotImplementedError()
9 |
10 | def setUp(self):
11 | self.generate_laplacian_and_range()
12 | self.setup_message()
13 | self.A, self.pairs = makeA(self.laplacian)
14 |
15 | # HACK: A is somehow sorted by column, so here I'll change it manually.
16 | sortbyrow = np.lexsort((self.pairs[:,1],self.pairs[:,0]))
17 | self.A = self.A[sortbyrow]
18 | self.pairs = self.pairs[sortbyrow]
19 |
20 | # self.Rk_tensor, self.nbk = compute_Rk(self.laplacian,self.A,self.n)
21 | self.correct_S, self.correct_pairs = self.project_S_from_laplacian()
22 |
23 | def generate_laplacian_and_range(self):
24 | self.laplacian = self.generate_laplacian()
25 | self.n = self.laplacian.shape[0]
26 | self.range = np.arange(self.n)
27 | self.Y = self.generate_toy_Y()
28 |
29 | def generate_toy_Y(self):
30 | return np.random.uniform(size=self.n)
31 |
32 | def ij_is_neighbors(self,i,j):
33 | return self.laplacian[i,j] != 0
34 |
35 | def project_S_from_laplacian(self):
36 | # TODO: make the test process faster!
37 | S = [ self.Y[i]-self.Y[j] for i in np.arange(self.n) \
38 | for j in np.arange(i+1,self.n) \
39 | if self.ij_is_neighbors(i,j) ]
40 | pairs = [ [i,j] for i in np.arange(self.n) \
41 | for j in np.arange(i+1,self.n) \
42 | if self.ij_is_neighbors(i,j) ]
43 | return np.array(S), np.array(pairs)
44 |
45 | def test_A_length_equality(self):
46 | A_length = self.A.shape[0]
47 | correct_A_length = self.correct_S.shape[0]
48 | assert A_length == correct_A_length, 'The first dimension of A is calculated wrong.'
49 |
50 | def test_pairs(self):
51 | np.testing.assert_array_equal(
52 | self.pairs, self.correct_pairs,
53 | err_msg='Sorted pairs should be the same.'
54 | )
55 |
56 | def test_A(self):
57 | testing_S = self.A.dot(self.Y)
58 | np.testing.assert_allclose(
59 | testing_S, self.correct_S,
60 | err_msg='A*y should be the same as yj-yi for all j>i'
61 | )
62 |
63 | def _test_ATAinv(self):
64 | # TODO: why this test will running out of the memory?
65 | ATAinv = np.linalg.pinv(self.A.T.dot(self.A).todense())
66 | S = self.A.dot(self.Y)
67 | testing_Y = ATAinv.dot(self.A.T).dot(S)
68 | np.testing.assert_allclose(
69 | testing_Y, self.Y,
70 | err_msg='ATAinv * AT * S should be the same as original Y'
71 | )
72 |
73 | def _test_Rk(self):
74 | # TODO: Need to understand what Rk means.
75 | pass
76 |
77 | class TestAkRkNbkFromToyLaplacian(BaseTestARkNeighbors):
78 | def generate_laplacian(self):
79 | return generate_toy_laplacian(n=200)
80 | def setup_message(self):
81 | print ('Tesking Rk properties for toy laplacian.')
82 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/tests/test_regression_test.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from megaman.relaxation import *
2 | from functools import wraps
3 |
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import numpy.testing
6 |
7 | from .utils import gen_data, Bunch
8 | import shutil
9 |
10 | def _regression_test(if_epsilon):
11 | def _test_deco(func):
12 | @wraps(func)
13 | def wrapper():
14 | test_dict = func()
15 | var = Bunch(test_dict)
16 |
17 | rr = run_riemannian_relaxation(var.laplacian, var.Y_list[0], var.d, var.relaxation_kwds)
18 |
19 | calculated_loss_list = []
20 | calculated_DL_list = []
21 | calculated_Y_list = []
22 |
23 | for idx,Y in enumerate(var.Y_list):
24 | rr.Y = Y
25 | rr.H = np.copy(var.H_list[idx])
26 | if if_epsilon and idx >= 1:
27 | rr.UU, rr.IUUEPS = compute_principal_plane(var.H_list[idx-1],rr.epsI,var.d)
28 | calculated_loss_list.append(rr.rieman_loss())
29 |
30 | for idx,H in enumerate(var.H_list):
31 | rr.H = H
32 | rr.Y = np.copy(var.Y_list[idx])
33 | calculated_DL_list.append(rr.compute_gradient())
34 |
35 | for idx,grad in enumerate(var.grad_list):
36 | rr.grad = grad
37 | rr.Y = np.copy(var.Y_list[idx])
38 | rr.loss = var.loss_list[idx]
39 | if if_epsilon:
40 | rr.H = rr.compute_dual_rmetric()
41 | rr.UU, rr.IUUEPS = compute_principal_plane(rr.H,rr.epsI,var.d)
42 | rr.make_optimization_step(first_iter=(idx == 0))
43 | calculated_Y_list.append(rr.Y)
44 |
45 | np.testing.assert_allclose(
46 | calculated_loss_list, var.loss_list,
47 | err_msg='Loss calculated from matlab should be similar to that calculated from python, in {}'.format(__name__)
48 | )
49 | np.testing.assert_allclose(
50 | calculated_DL_list[:-1], var.DL_list,
51 | err_msg='gradient difference calculated from matlab should be similar to that calculated from python, in {}'.format(__name__)
52 | )
53 | np.testing.assert_allclose(
54 | calculated_Y_list, var.Y_list[1:],
55 | err_msg='Y calculated from linesearch should be similar, in {}'.format(__name__)
56 | )
57 |
58 | return wrapper
59 | return _test_deco
60 |
61 | @_regression_test(True)
62 | def test_whole_eps():
63 | return gen_data('eps_halfdome','whole_eps')
64 |
65 | @_regression_test(False)
66 | def test_whole_rloss():
67 | return gen_data('rloss_halfdome','whole_eps')
68 |
69 | @_regression_test(True)
70 | def test_half_eps():
71 | return gen_data('eps_halfdome','half_eps')
72 |
73 | @_regression_test(False)
74 | def test_half_rloss():
75 | return gen_data('rloss_halfdome','half_eps')
76 |
77 | @_regression_test(True)
78 | def test_weight_eps():
79 | return gen_data('eps_halfdome','weight_eps')
80 |
81 | @_regression_test(False)
82 | def test_weight_rloss():
83 | return gen_data('rloss_halfdome','weight_eps')
84 |
85 | @_regression_test(True)
86 | def test_half_weight_eps():
87 | return gen_data('eps_halfdome','half_weight_eps')
88 |
89 | @_regression_test(False)
90 | def test_half_weight_rloss():
91 | return gen_data('rloss_halfdome','half_weight_eps')
92 |
93 | if __name__ == '__main__':
94 | test_weight_rloss()
95 |
96 | def tearDownModule():
97 | tmp_dir = '/tmp/test_backup'
98 | if os.path.exists(tmp_dir):
99 | shutil.rmtree(tmp_dir)
100 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/tests/test_relaxation_keywords.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from megaman.relaxation.utils import *
2 | from nose.tools import assert_raises
3 | import numpy as np
4 | import numpy.testing
5 | import shutil, warnings
6 |
7 | n, s, d = 1000, 3, 2
8 |
9 | basic_kwds = {
10 | 'verbose': False,
11 | 'niter': 2000,
12 | 'niter_trace': 0,
13 | 'presave': False,
14 | 'sqrd': True,
15 | 'alpha': 0,
16 | 'projected': False,
17 | 'saveiter': 10,
18 | 'printiter': 1,
19 | }
20 |
21 | nonprojected_epsilon_test = {
22 | 'lossf': 'nonprojected_epsilon',
23 | 'projected': False,
24 | 'eps_orth': 0.1,
25 | }
26 |
27 | tmp_dir = '/tmp/test_backup'
28 | def _initialize_kwds(kwds,n,s,d):
29 | kwds['backup_base_dir'] = tmp_dir
30 | return initialize_kwds(kwds,n,s,d)
31 |
32 | def test_default_keywords():
33 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds({},n,s,d)
34 | for k,v in basic_kwds.items():
35 | assert calculated_kwds[k] == v, 'keyword {} do not initialized correctly.'.format(k)
36 |
37 | assert calculated_kwds['weights'].shape[0] == 0, 'initialized weights is not zero.'
38 | np.testing.assert_allclose(
39 | calculated_kwds['subset'], np.arange(n),
40 | err_msg='initialized subset should be arange(n).'
41 | )
42 |
43 | def test_normalize_weights():
44 | weights = np.array([1,4])
45 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds(dict(weights=weights),n,s,d)
46 | np.testing.assert_allclose(
47 | calculated_kwds['weights'], [0.2,0.8],
48 | err_msg='The weights should be normalized'
49 | )
50 |
51 | def test_default_lossf():
52 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds({},n,s,d)
53 | for k,v in nonprojected_epsilon_test.items():
54 | assert calculated_kwds[k] == v, 'keyword {} do not initialized correctly.'.format(k)
55 |
56 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds(dict(projected=True),n,s,d)
57 | assert calculated_kwds['lossf'] == 'projected_epsilon', 'lossf should be projected_epsilon when projected is True'
58 |
59 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds({},n,d,d)
60 | assert calculated_kwds['lossf'] == 'nonprojected_rloss', 'lossf should be nonprojected_rloss for default'
61 |
62 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds(dict(projected=True),n,d,d)
63 | assert calculated_kwds['lossf'] == 'projected_rloss', 'lossf should be projected_epsilon when projected is True'
64 |
65 | def test_update_lossf():
66 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds(dict(eps_orth=0.55),n,s,d)
67 | assert calculated_kwds['eps_orth'] == 0.55, 'eps_orth should be updated to 0.55.'
68 |
69 | def test_raise_lossf_error():
70 | assert_raises(ValueError, _initialize_kwds, dict(lossf='rloss'),n,s,d)
71 | assert_raises(ValueError, _initialize_kwds, dict(lossf='epsilon'),n,d,d)
72 | assert_raises(ValueError, _initialize_kwds, dict(projected=True, subset=np.arange(0,n,5)),n,s,d)
73 |
74 | def test_default_momentum():
75 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds(dict(step_method='momentum',linesearch=False),n,s,d)
76 | test_momentum_kwds = {
77 | 'm': 0.05,
78 | 'eta': 1.0
79 | }
80 | for k,v in test_momentum_kwds.items():
81 | assert calculated_kwds[k] == v, 'keyword {} do not initialized correctly.'.format(k)
82 |
83 | def test_default_fixed():
84 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds(dict(step_method='fixed',linesearch=False),n,s,d)
85 | assert calculated_kwds['eta'] == 1.0, 'Default eta does not match'
86 |
87 | def test_default_linsearch():
88 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds(dict(projected=True),n,s,d)
89 | test_kwds = {
90 | 'linesearch_first': False,
91 | 'eta_max': 2**11,
92 | }
93 | for k,v in test_kwds.items():
94 | assert calculated_kwds[k] == v, 'keyword {} do not initialized correctly.'.format(k)
95 |
96 | calculated_kwds = _initialize_kwds(dict(projected=False),n,s,d)
97 | assert calculated_kwds['eta_max'] == 2**4, 'eta_max should be 2**4 if projected == False'
98 |
99 | def test_backup_dir_function():
100 | tmp_dir = '/tmp/test_backup'
101 | calculated_kwds = initialize_kwds(dict(backup_base_dir=tmp_dir),n,s,d)
102 | assert 'backup_dir' in calculated_kwds
103 | backup_dir = calculated_kwds['backup_dir']
104 | assert tmp_dir in backup_dir
105 | assert os.path.exists(tmp_dir)
106 |
107 | def test_not_int_warnings():
108 | with warnings.catch_warnings(record=True) as w:
109 | calculated_kwds = initialize_kwds(dict(printiter=1.3),n,s,d)
110 | assert issubclass(w[-1].category, RuntimeWarning), \
111 | 'Should raise RuntimeWarning when input is not integer'
112 |
113 | def tearDownModule():
114 | tmp_dir = '/tmp/test_backup'
115 | if os.path.exists(tmp_dir):
116 | shutil.rmtree(tmp_dir)
117 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/tests/test_tracing_var.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import division
2 | from .utils import generate_toy_laplacian
3 | from megaman.relaxation.trace_variable import TracingVariable as tv
4 | from megaman.relaxation import *
5 | import shutil, os
6 |
7 | def test_copy():
8 | n, s, d = 1000, 3, 2
9 | niter = 10
10 | niter_trace = niter//2
11 | ltrace = 2*niter_trace+1
12 | L = generate_toy_laplacian(n)
13 | Y0 = np.zeros((n,s))
14 | rr = run_riemannian_relaxation(L, Y0, d, dict(niter=niter, niter_trace=niter_trace))
15 | copied_tv = rr.trace_var.copy()
16 | copied_tv.H = copied_tv.H[::2,:,:]
17 | assert rr.trace_var.H.shape[0] == ltrace, 'The original size of H should not be affected by downsamping'
18 | assert copied_tv.H.shape[0] == round(ltrace / 2), 'The size of copied H should be downsampled by 2'
19 |
20 | def tearDownModule():
21 | tmp_dir = '/tmp/test_backup'
22 | if os.path.exists(tmp_dir):
23 | shutil.rmtree(tmp_dir)
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/tests/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import scipy as sp
3 | import scipy.sparse
4 | import h5py
5 | import copy, os
6 |
7 | def generate_toy_laplacian(n=1000):
8 | neighbor_counts = 10
9 | adjacency_mat = np.zeros((n,n))
10 | for i in range(n):
11 | x = np.ones(neighbor_counts,dtype=np.int32)*i
12 | y = np.random.choice(n, neighbor_counts, replace=False)
13 | adjacency_mat[(x,y)] = 1
14 |
15 | np.fill_diagonal(adjacency_mat,0)
16 | adjacency_mat = (adjacency_mat.T + adjacency_mat) / 2
17 | degree = np.sum(adjacency_mat,axis=1)
18 | degree_mat = np.diag(degree)
19 |
20 | return sp.sparse.csc_matrix(degree_mat - adjacency_mat)
21 |
22 | def process_test_data():
23 | namelist = ['rloss_halfdome', 'eps_halfdome']
24 | return { name: process_one_loss_test_data(name) for name in namelist }
25 |
26 | def process_one_loss_test_data(name):
27 | file_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
28 | path = os.path.join(file_dir,'{}.mat'.format(name))
29 | f = h5py.File(path)
30 | laplacian_ref = f['/{}/L'.format(name)]
31 | laplacian = sp.sparse.csc_matrix((laplacian_ref['data'], laplacian_ref['ir'], laplacian_ref['jc']))
32 | opts_list = ['whole_eps','half_eps','weight_eps','half_weight_eps']
33 | processed_data = { opts:process_one_test_data(f,name,opts) for opts in opts_list }
34 | processed_data['L'] = laplacian
35 | processed_data['d'] = 2
36 | return processed_data
37 |
38 | def process_one_test_data(f, name, opts):
39 | Y_ref_list = f['/{}/{}/trace/Y'.format(name,opts)]
40 | Y_list = np.array([ f[Y_ref_list[idx,0]] for idx in range(Y_ref_list.shape[0]) ])
41 | Y_list = np.swapaxes(Y_list, 1, 2)
42 |
43 | H_ref_list = f['/{}/{}/trace/H'.format(name,opts)]
44 | H_list = np.array([ f[H_ref_list[idx,0]] for idx in range(H_ref_list.shape[0]) ])
45 |
46 | DL_ref_list = f['/{}/{}/trace/DL'.format(name,opts)]
47 | DL_list = np.array([ f[DL_ref_list[idx,0]] for idx in range(DL_ref_list.shape[0]-1) ])
48 | DL_list = np.swapaxes(DL_list, 1, 2)
49 |
50 | grad_ref_list = f['/{}/{}/trace/grad'.format(name,opts)]
51 | grad_list = np.array([ f[grad_ref_list[idx,0]] for idx in range(grad_ref_list.shape[0]-1) ])
52 | grad_list = np.swapaxes(grad_list, 1, 2)
53 |
54 | loss_list = np.squeeze(np.array(f['/{}/{}/loss'.format(name,opts)]))
55 | etas_list = np.squeeze(np.array(f['/{}/{}/etas'.format(name,opts)]))
56 |
57 | rk_h5py = f['/{}/{}/opts'.format(name,opts)]
58 | relaxation_kwds = {
59 | 'alpha': rk_h5py['alpha'][0,0],
60 | 'lossf': u''.join(chr(c) for c in rk_h5py['lossf']),
61 | 'step_method': 'fixed',
62 | 'linsearch': u''.join(chr(c) for c in rk_h5py['step_method']) == u'linesearch',
63 | 'projected': rk_h5py['projected'][0,0],
64 | 'eta_max': rk_h5py['eta_max'][0,0],
65 | 'backup_base_dir': '/tmp/test_backup',
66 | }
67 | if 'weight' in opts:
68 | weights = np.squeeze(np.array(rk_h5py['w']))
69 | relaxation_kwds['weights'] = weights
70 |
71 | if 'half' in opts:
72 | relaxation_kwds['subset'] = np.arange(0,1000,2)
73 |
74 | if 'epsorth' in rk_h5py:
75 | relaxation_kwds['eps_orth'] = rk_h5py['epsorth'][0,0]
76 | if 'sqrd' in rk_h5py:
77 | relaxation_kwds['sqrd'] = rk_h5py['sqrd'][0,0] == 1
78 | return dict(
79 | Y_list=Y_list, H_list=H_list, DL_list=DL_list, grad_list=grad_list,
80 | loss_list=loss_list, etas_list=etas_list, relaxation_kwds=relaxation_kwds
81 | )
82 |
83 | class Bunch(object):
84 | def __init__(self, adict):
85 | self.__dict__.update(adict)
86 |
87 | data = process_test_data()
88 | def gen_data(name, opts):
89 | test_data = copy.deepcopy(data[name])
90 | test_dict = test_data[opts]
91 | test_dict['laplacian'] = test_data['L']
92 | test_dict['d'] = test_data['d']
93 | return test_dict
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/relaxation/trace_variable.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Author: Yu-Chia Chen
2 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
3 |
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import os, pickle, pprint, copy
6 |
7 | from .utils import *
8 |
9 | class TracingVariable(object):
10 | """
11 | The TracingVariable is the class to store the variables to trace and
12 | print relaxation reports in each 'printiter' iteration.
13 | """
14 | def __init__(self,n,s,relaxation_kwds,precomputed_kwds,**kwargs):
15 | self.niter_trace = relaxation_kwds['niter_trace']
16 | self.niter = relaxation_kwds['niter']
17 | self.ltrace = 2*self.niter_trace+1
18 |
19 | self.loss = np.zeros(self.niter+1)
20 | self.etas = np.zeros(self.niter+1)
21 | self.H = np.zeros((self.ltrace,n,s,s))
22 | self.Y = np.zeros((self.ltrace,n,s))
23 | self.lmin = np.finfo(np.float64).max
24 |
25 | self.verbose = relaxation_kwds['verbose']
26 | self.printiter = relaxation_kwds['printiter']
27 | self.saveiter = relaxation_kwds['saveiter']
28 | self.backup_dir = relaxation_kwds['backup_dir']
29 |
30 | create_output_dir(self.backup_dir)
31 | self.report_and_save_keywords(relaxation_kwds,precomputed_kwds)
32 |
33 | def copy(self):
34 | return copy.deepcopy(self)
35 |
36 | def report_and_save_keywords(self,relaxation_kwds,precomputed_kwds):
37 | """Save relaxation keywords to .txt and .pyc file"""
38 | report_name = os.path.join(self.backup_dir,'relaxation_keywords.txt')
39 | pretty_relax_kwds = pprint.pformat(relaxation_kwds,indent=4)
40 | with open(report_name,'w') as wf:
41 | wf.write(pretty_relax_kwds)
42 | wf.close()
43 |
44 | origin_name = os.path.join(self.backup_dir,'relaxation_keywords.pyc')
45 | with open(origin_name,'wb') as ro:
46 | pickle.dump(relaxation_kwds,ro,protocol=pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)
47 | ro.close()
48 |
49 | if relaxation_kwds['presave']:
50 | precomp_kwds_name = os.path.join(self.backup_dir,
51 | 'precomputed_keywords.pyc')
52 | with open(precomp_kwds_name, 'wb') as po:
53 | pickle.dump(precomputed_kwds, po,
54 | protocol=pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)
55 | po.close()
56 |
57 | def update(self,iiter,H,Y,eta,loss):
58 | """Update the trace_var in new iteration"""
59 | if iiter <= self.niter_trace+1:
60 | self.H[iiter] = H
61 | self.Y[iiter] = Y
62 | elif iiter >self.niter - self.niter_trace + 1:
63 | self.H[self.ltrace+iiter-self.niter-1] = H
64 | self.Y[self.ltrace+iiter-self.niter-1] = Y
65 |
66 | self.etas[iiter] = eta
67 | self.loss[iiter] = loss
68 | if self.loss[iiter] < self.lmin:
69 | self.Yh = Y
70 | self.lmin = self.loss[iiter]
71 | self.miniter = iiter if not iiter == -1 else self.niter + 1
72 |
73 | def print_report(self,iiter):
74 | if self.verbose and iiter % self.printiter == 0:
75 | print ('Iteration number: {}'.format(iiter))
76 | print ('Last step size eta: {}'.format(self.etas[iiter]))
77 | print ('current loss (before gradient step): {}'
78 | .format(self.loss[iiter]))
79 | print ('minimum loss: {}, at iteration: {}\n'
80 | .format(self.lmin, self.miniter))
81 |
82 | def save_backup(self,iiter):
83 | if iiter % self.saveiter == 0 and iiter != 0:
84 | backup_name = os.path.join(self.backup_dir,'backup_trace.pyc')
85 | TracingVariable.save(self,backup_name)
86 | print ('Save backup at iteration: {}\n'.format(iiter))
87 |
88 | @classmethod
89 | def correct_file_extension(cls,filename):
90 | return os.path.splitext(filename)[0]+'.pyc'
91 |
92 | @classmethod
93 | def save(cls,instance,filename):
94 | """Class method save for saving TracingVariable."""
95 | filename = cls.correct_file_extension(filename)
96 | try:
97 | with open(filename,'wb') as f:
98 | pickle.dump(instance,f,protocol=pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)
99 | except MemoryError as e:
100 | print ('{} occurred, will downsampled the saved file by 20.'
101 | .format(type(e).__name__))
102 | copy_instance = instance.copy()
103 | copy_instance.H = copy_instance.H[::20,:,:]
104 | copy_instance.Y = copy_instance.Y[::20,:]
105 | with open(filename,'wb') as f:
106 | pickle.dump(copy_instance,f,protocol=pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)
107 |
108 | @classmethod
109 | def load(cls,filename):
110 | """Load from stored files"""
111 | filename = cls.correct_file_extension(filename)
112 | with open(filename,'rb') as f:
113 | return pickle.load(f)
114 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import os
4 |
5 | def configuration(parent_package='', top_path=None):
6 | from numpy.distutils.misc_util import Configuration
7 |
8 | config = Configuration('megaman', parent_package, top_path)
9 |
10 | config.add_subpackage('__check_build')
11 | config.add_subpackage('datasets')
12 | config.add_subpackage('embedding')
13 | config.add_subpackage('embedding/tests')
14 | config.add_subpackage('geometry')
15 | config.add_subpackage('geometry/cyflann')
16 | config.add_subpackage('geometry/tests')
17 | config.add_subpackage('plotter')
18 | config.add_subpackage('relaxation')
19 | config.add_subpackage('relaxation/tests')
20 | config.add_subpackage('utils')
21 | config.add_subpackage('utils/tests')
22 | config.add_data_files('geometry/tests/testmegaman_laplacian_rad0_2_lam1_5_n200.mat')
23 | config.add_data_files('relaxation/tests/eps_halfdome.mat')
24 | config.add_data_files('relaxation/tests/rloss_halfdome.mat')
25 | config.add_data_files('datasets/megaman.png')
26 |
27 | return config
28 |
29 | if __name__ == '__main__':
30 | from numpy.distutils.core import setup
31 | setup(**configuration(top_path='').todict())
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/utils/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/covar_plotter.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 |
5 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
6 | from matplotlib.patches import Ellipse
7 |
8 | def plot_point_cov(points, nstd=2, ax=None, **kwargs):
9 | """
10 | Plots an `nstd` sigma ellipse based on the mean and covariance of a point
11 | "cloud" (points, an Nx2 array).
12 |
13 | Parameters
14 | ----------
15 | points : An Nx2 array of the data points.
16 | nstd : The radius of the ellipse in numbers of standard deviations.
17 | Defaults to 2 standard deviations.
18 | ax : The axis that the ellipse will be plotted on. Defaults to the
19 | current axis.
20 | Additional keyword arguments are pass on to the ellipse patch.
21 |
22 | Returns
23 | -------
24 | A matplotlib ellipse artist
25 | """
26 | pos = points.mean(axis=0)
27 | cov = np.cov(points, rowvar=False)
28 | return plot_cov_ellipse(cov, pos, nstd, ax, **kwargs)
29 |
30 | def plot_cov_ellipse(cov, pos, nstd=2, ax=None, **kwargs):
31 | """
32 | Plots an `nstd` sigma error ellipse based on the specified covariance
33 | matrix (`cov`). Additional keyword arguments are passed on to the
34 | ellipse patch artist.
35 |
36 | Parameters
37 | ----------
38 | cov : The 2x2 covariance matrix to base the ellipse on
39 | pos : The location of the center of the ellipse. Expects a 2-element
40 | sequence of [x0, y0].
41 | nstd : The radius of the ellipse in numbers of standard deviations.
42 | Defaults to 2 standard deviations.
43 | ax : The axis that the ellipse will be plotted on. Defaults to the
44 | current axis.
45 | Additional keyword arguments are pass on to the ellipse patch.
46 |
47 | Returns
48 | -------
49 | A matplotlib ellipse artist
50 | """
51 | def eigsorted(cov):
52 | vals, vecs = np.linalg.eigh(cov)
53 | order = vals.argsort()[::-1]
54 | return vals[order], vecs[:,order]
55 |
56 | if ax is None:
57 | ax = plt.gca()
58 |
59 | vals, vecs = eigsorted(cov)
60 | theta = np.degrees(np.arctan2(*vecs[:,0][::-1]))
61 |
62 | # Width and height are "full" widths, not radius
63 | width, height = 2 * nstd * np.sqrt(vals)
64 | ellip = Ellipse(xy=pos, width=width, height=height, angle=theta, **kwargs)
65 |
66 | ax.add_artist(ellip)
67 | return ellip
68 |
69 | if __name__ == '__main__':
70 | #-- Example usage -----------------------
71 | # Generate some random, correlated data
72 | points = np.random.multivariate_normal(
73 | mean=(1,1), cov=[[0.4, 9],[9, 10]], size=1000
74 | )
75 | # Plot the raw points...
76 | x, y = points.T
77 | plt.plot(x, y, 'ro')
78 |
79 | # Plot a transparent 3 standard deviation covariance ellipse
80 | plot_point_cov(points, nstd=3, alpha=0.5, color='green')
81 |
82 | plt.show()
83 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/k_means_clustering.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """K-Means Clustering"""
2 |
3 | # Author: James McQueen
4 | # Xiao Wang
5 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICEN
6 |
7 | import numpy as np
8 | import random
9 |
10 | class Kmeans():
11 | def __init__(self, K):
12 | self.K = K
13 |
14 | def fit(data):
15 | self.labels_ = k_means_clustering(data, self.K)
16 |
17 | def fit_transform(data):
18 | self.fit(data)
19 | return self.labels_
20 |
21 | def k_means_clustering(data,K):
22 | """
23 | K-means clustering is an algorithm that take a data set and
24 | a number of clusters K and returns the labels which represents
25 | the clusters of data which are similar to others
26 |
27 | Parameters
28 | --------------------
29 | data: array-like, shape= (m_samples,n_samples)
30 | K: integer
31 | number of K clusters
32 | Returns
33 | -------
34 | labels: array-like, shape (1,n_samples)
35 | """
36 | N = data.shape[0]
37 | centroids, data_norms = orthogonal_initialization(data,K)
38 | old_centroids= np.zeros((N,K))
39 | labels = []
40 |
41 | # Run the main k-means algorithm
42 | while not _has_converged(centroids, old_centroids):
43 | labels = get_labels(data, centroids,K)
44 | centroids = get_centroids(data,K,labels,centroids,data_norms)
45 | old_centroids = centroids
46 |
47 | return labels
48 |
49 | def orthogonal_initialization(X,K):
50 | """
51 | Initialize the centrodis by orthogonal_initialization.
52 | Parameters
53 | --------------------
54 | X(data): array-like, shape= (m_samples,n_samples)
55 | K: integer
56 | number of K clusters
57 | Returns
58 | -------
59 | centroids: array-like, shape (K,n_samples)
60 | data_norms: array-like, shape=(1,n_samples)
61 | """
62 | N,M = X.shape
63 | centroids= X[np.random.randint(0, N-1,1),:]
64 | data_norms = np.linalg.norm(X, axis = 1)# contains the norm of each data point, only do this once
65 |
66 | center_norms = np.linalg.norm(centroids, axis=1) # contains the norms of the centers, will need to be updated when new center added
67 |
68 | for k in range(1,K):
69 | ## Here's where we compute the cosine of the angle between them:
70 | # Compute the dot (inner) product between each data point and each center
71 | new_center_index,new_center = new_orthogonal_center(X,data_norms,centroids,center_norms =center_norms)
72 | centroids = np.vstack((centroids,new_center))
73 | center_norms = np.hstack((center_norms,data_norms[new_center_index]))
74 | return centroids,data_norms
75 |
76 | def new_orthogonal_center(X,data_norms,centroids,center_norms=None):
77 | """
78 | Initialize the centrodis by orthogonal_initialization.
79 | Parameters
80 | --------------------
81 | X(data): array-like, shape= (m_samples,n_samples)
82 | data_norms: array-like, shape=(1,n_samples)
83 | center_norms:array-like,shape=(centroids.shape[0])
84 | centroids: array-like, shape (K,n_samples)
85 | Returns
86 | -------
87 | new_center: array-like, shape (1,n_samples)
88 | new_center_index: integer
89 | data index of the new center
90 | """
91 | if center_norms is None:
92 | center_norms = np.linalg.norm(centroids, axis=1)
93 | cosine = np.inner(X,centroids) # cosine[i, j] = np.dot(X[i, :],centroids[j,:])
94 | cosine = cosine/center_norms # divide each column by the center norm
95 | cosine = cosine / data_norms[:,np.newaxis] # divide each row by the data norm
96 | max_cosine = np.abs(np.max(cosine, 1)) # the largest (absolute) cosine for each data point
97 |
98 | # then we find the index of the new center:
99 | new_center_index = np.argmin(max_cosine) # the data index of the new center is the smallest max cosine
100 | new_center = X[new_center_index, :]
101 | return new_center_index,new_center
102 |
103 | def get_labels(data, centroids,K):
104 | """
105 | Returns a label for each piece of data in the dataset
106 |
107 | Parameters
108 | ------------
109 | data: array-like, shape= (m_samples,n_samples)
110 | K: integer
111 | number of K clusters
112 | centroids: array-like, shape=(K, n_samples)
113 |
114 | returns
115 | -------------
116 | labels: array-like, shape (1,n_samples)
117 | """
118 | distances = np.sqrt(((data - centroids[:, np.newaxis])**2).sum(axis=2))
119 | return np.argmin(distances, axis=0)
120 |
121 | def get_centroids(data,k,labels,centroids,data_norms):
122 | """
123 | For each element in the dataset, choose the closest centroid
124 |
125 | Parameters
126 | ------------
127 | data: array-like, shape= (m_samples,n_samples)
128 | K: integer, number of K clusters
129 | centroids: array-like, shape=(K, n_samples)
130 | labels: array-like, shape (1,n_samples)
131 | returns
132 | -------------
133 | centroids: array-like, shape (K,n_samples)
134 | """
135 |
136 | D = data.shape[1]
137 | for j in range(k):
138 | cluster_points = np.where(labels == j)
139 | cluster_total = len(cluster_points)
140 | if cluster_total == 0:
141 | _, temp = new_orthogonal_center(data,data_norms,centroids)
142 | else:
143 | temp = np.mean(data[cluster_points,:],axis=1)
144 | centroids[j,:] = temp
145 | return centroids
146 |
147 | def _has_converged(centroids, old_centroids):
148 | """
149 | Stop if centroids stop to update
150 | Parameters
151 | -----------
152 | centroids: array-like, shape=(K, n_samples)
153 | old_centroids: array-like, shape=(K, n_samples)
154 | ------------
155 | returns
156 | True: bool
157 |
158 | """
159 | return (set([tuple(a) for a in centroids]) == set([tuple(a) for a in old_centroids]))
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/large_sparse_functions.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import scipy as sp
3 | import cPickle
4 | from scipy.io import loadmat, savemat
5 | from scipy.sparse import coo_matrix, dia_matrix, identity
6 |
7 | def save_sparse_in_2_parts(A, name):
8 | # mat and coo format easily readable into MATLAB
9 | nz = len(A.data)
10 | A = A.tocoo()
11 | A_1 = {'I1':A.row[xrange(0, int(nz/2))],
12 | 'J1':A.col[xrange(0, int(nz/2))],
13 | 'V1':A.data[xrange(0, int(nz/2))]}
14 | savemat(name + '_part_1.mat', A_1)
15 |
16 | A_2 = {'I2':A.row[xrange(int(nz/2), nz)],
17 | 'J2':A.col[xrange(int(nz/2), nz)],
18 | 'V2':A.data[xrange(int(nz/2), nz)]}
19 | savemat(name + '_part_2.mat', A_2)
20 | return(None)
21 |
22 | def load_sparse_in_2_parts(f1, f2, n):
23 | A_1 = loadmat(f1)
24 | A_2 = loadmat(f2)
25 | row = np.append(A_1['I1'], A_2['I2'])
26 | col = np.append(A_1['J1'], A_2['J2'])
27 | data = np.append(A_1['V1'], A_2['V2'])
28 | A = coo_matrix((data, (row, col)), shape = (n, n))
29 | return(A)
30 |
31 |
32 | def save_sparse_in_k_parts(A, name, k):
33 | nz = len(A.data)
34 | A = A.tocoo()
35 | nk = 0
36 | nper = int(nz / k)
37 | for ii in range(k):
38 | fname = name + '_part_' + str(ii+1) + '.mat'
39 | nkp1 = nk + nper
40 | if ii == k-1:
41 | nkp1 = nz
42 | A_k = {'I':A.row[xrange(nk, nkp1)],
43 | 'J':A.col[xrange(nk, nkp1)],
44 | 'V':A.data[xrange(nk, nkp1)]}
45 | savemat(fname, A_k)
46 | nk = nkp1
47 | return(None)
48 |
49 | def load_sparse_in_k_parts(name, k, n):
50 | row = np.array([])
51 | col = np.array([])
52 | data = np.array([])
53 | for ii in range(k):
54 | fname = name + '_part_' + str(ii+1) + '.mat'
55 | A_k = loadmat(fname)
56 | row = np.append(row, A_k['I'])
57 | col = np.append(col, A_k['J'])
58 | data = np.append(data, A_k['V'])
59 | A = coo_matrix((data, (row, col)), shape = (n, n))
60 | return(A)
61 |
62 | def dump_array_in_k_parts(A, name, k):
63 | n = A.shape[0]
64 | nk = 0
65 | nper = int(n / k)
66 | for ii in range(k):
67 | fname = name + '_part_' + str(ii+1) + '.p'
68 | nkp1 = nk + nper
69 | if ii == k-1:
70 | nkp1 = n
71 | A_k = A[range(nk, nkp1)]
72 | cPickle.dump(A_k, open(fname, 'wb'), -1)
73 | nk = nkp1
74 | return(None)
75 |
76 | def load_array_in_k_parts(name, k):
77 | for ii in range(k):
78 | fname = name + '_part_' + str(ii+1) + '.p'
79 | A_k = cPickle.load(open(fname, 'rb'))
80 | if ii == 0:
81 | A = A_k.copy()
82 | else:
83 | A = np.vstack((A, A_k))
84 | return(A)
85 |
86 | def set_sparse_diag_to_one(mat):
87 | # appears to implicitly convert to csr which might be a problem
88 | (n, n) = mat.shape
89 | # copy the matrix, subtract the diagonal values, add identity matrix
90 | # see http://nbviewer.jupyter.org/gist/Midnighter/9992103 for speed testing
91 | cpy = mat - dia_matrix((mat.diagonal()[sp.newaxis, :], [0]), shape=(n, n)) + identity(n)
92 | return(cpy)
93 |
94 | def set_coo_diag_to_one(mat):
95 | # this function takes a coo matrix and sets diagonal to one
96 | (n, n) = mat.shape
97 | off_diag = np.where(mat.row != mat.col)[0]
98 | row = np.append(mat.row[off_diag], range(n))
99 | col = np.append(mat.col[off_diag], range(n))
100 | data = np.append(mat.data[off_diag], np.ones(n))
101 | cpy = coo_matrix((data, (row, col)), shape = (n, n))
102 | return(cpy)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/nystrom_extension.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
3 | """
4 | Created on Tue Jun 21 11:11:40 2016
5 |
6 | @author: wang1
7 | """
8 | from __future__ import division
9 | import numpy as np
10 | import warnings
11 | from scipy.sparse import isspmatrix
12 | def nystrom_extension(C, e_vec, e_val):
13 | """
14 | Parameters
15 | ----------
16 | C: array-like, shape = (n, l)
17 | Stacking the training and testing data where n
18 | is the total number of data and l is the number of
19 | training data.
20 | e_val: array, shape = (1,s)
21 | If W equals to C[0:l, :], then e_val are the largest s
22 | eig values of W
23 | e_vec: array-like, shape = (l, s)
24 | These are the corresponding eig vectors to e_val
25 |
26 | Returns
27 | -------
28 | eval_nystrom: array-like, shape = (1,s)
29 | These are the estimated largest s eig values of the matrix where C is the
30 | first l columns.
31 | evec_nystrom: arrau-like, shape = (n, s)
32 | These are the corresponding eig vectors to eval_nystrom
33 |
34 | """
35 | n,l = C.shape
36 | W = C[0:l, :]
37 | eval_nystrom = (n/l)*e_val
38 | eval_inv = e_val.copy()
39 | e_nonzero = np.where(e_val != 0)
40 | # e_nonzero = [i for i, e in enumerate(e_val) if e != 0] #np.nonzero(a)[0]
41 | eval_inv[e_nonzero] = 1.0/e_val[e_nonzero]
42 |
43 | if isspmatrix(C):
44 | evec_nystrom = np.sqrt(l/n)*C.dot(e_vec)*eval_inv
45 | else:
46 | evec_nystrom = np.sqrt(l/n)*np.dot(C,e_vec)*eval_inv
47 | return eval_nystrom,evec_nystrom
48 |
49 |
50 |
51 |
52 |
53 |
54 |
55 |
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/tests/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mmp2/megaman/249a7d725de1f99ea7f6ba169a5a89468fc423ec/megaman/utils/tests/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/tests/test_analyze_dimension_and_radius.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from numpy.random import RandomState
3 | from scipy.spatial.distance import squareform, pdist
4 | import megaman.utils.analyze_dimension_and_radius as adar
5 | from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
6 | from numpy.testing import assert_array_almost_equal
7 |
8 | def test_dim_distance_passed_vs_computed(seed=1234):
9 | rng = RandomState(seed)
10 | X = rng.randn(100, 10)
11 | dists = csr_matrix(squareform(pdist(X)))
12 | rmin = 2
13 | rmax = 10.0
14 | nradii = 10
15 | radii = 10**(np.linspace(np.log10(rmin), np.log10(rmax), nradii))
16 |
17 | results_passed = adar.neighborhood_analysis(dists, radii)
18 | avg_neighbors = results_passed['avg_neighbors'].flatten()
19 | radii = results_passed['radii'].flatten()
20 | fit_range = range(len(radii))
21 | dim_passed = adar.find_dimension_plot(avg_neighbors, radii, fit_range)
22 | results_computed, dim_computed = adar.run_analyze_dimension_and_radius(X, rmin, rmax, nradii)
23 | assert(dim_passed == dim_computed)
24 | assert_array_almost_equal(results_passed['avg_neighbors'], results_computed['avg_neighbors'])
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/tests/test_eigendecomp.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | from megaman.utils.eigendecomp import (eigen_decomposition, null_space,
4 | EIGEN_SOLVERS)
5 | from numpy.testing import assert_array_almost_equal
6 | import numpy as np
7 |
8 |
9 | SPD_SOLVERS = EIGEN_SOLVERS
10 | NON_SPD_SOLVERS = ['auto', 'dense', 'arpack']
11 | SOLVER_KWDS_DICT = {'auto':None,
12 | 'dense':{'turbo':True, 'type':1},
13 | 'arpack':{'mode':'normal', 'tol':0, 'maxiter':None},
14 | 'lobpcg':{'maxiter':20, 'tol':None},
15 | 'amg':{'maxiter':20, 'tol':None,'aggregate':'standard'}}
16 |
17 | def _check_with_col_sign_flipping(A, B, tol=0.0):
18 | """ Check array A and B are equal with possible sign flipping on
19 | each columns"""
20 | sign = True
21 | for column_idx in range(A.shape[1]):
22 | sign = sign and ((((A[:, column_idx] -
23 | B[:, column_idx]) ** 2).mean() <= tol ** 2) or
24 | (((A[:, column_idx] +
25 | B[:, column_idx]) ** 2).mean() <= tol ** 2))
26 | if not sign:
27 | return False
28 | return True
29 |
30 | def _test_all_solvers(solvers_to_test, S, solver_kwds_dict={}):
31 | for largest in [True, False]:
32 | Lambdas = {};
33 | for eigen_solver in solvers_to_test:
34 | if eigen_solver in solver_kwds_dict.keys():
35 | solver_kwds = solver_kwds_dict[eigen_solver]
36 | else:
37 | solver_kwds = None
38 | lambdas, diffusion_map = eigen_decomposition(S, n_components = 3,
39 | eigen_solver = eigen_solver,
40 | largest = largest, drop_first = False,
41 | solver_kwds=solver_kwds)
42 | Lambdas[eigen_solver] = np.sort(lambdas)
43 | # pairwise comparison:
44 | for i in range(len(solvers_to_test)):
45 | for j in range(i+1, len(solvers_to_test)):
46 | print(largest)
47 | print(str(solvers_to_test[i]) + " + " + str(solvers_to_test[j]))
48 | assert_array_almost_equal(Lambdas[solvers_to_test[i]],
49 | Lambdas[solvers_to_test[j]])
50 |
51 | def _test_all_null_solvers(solvers_to_test, S, solver_kwds_dict={}):
52 | for largest in [True, False]:
53 | Null_Space = {};
54 | for eigen_solver in solvers_to_test:
55 | if eigen_solver in solver_kwds_dict.keys():
56 | solver_kwds = solver_kwds_dict[eigen_solver]
57 | else:
58 | solver_kwds = None
59 | nullspace, errors = null_space(S, k = 3, eigen_solver = eigen_solver, solver_kwds=solver_kwds)
60 | Null_Space[eigen_solver] = nullspace
61 | # pairwise comparison:
62 | for i in range(len(solvers_to_test)):
63 | for j in range(i+1, len(solvers_to_test)):
64 | print(largest)
65 | print(str(solvers_to_test[i]) + " + " + str(solvers_to_test[j]))
66 | _check_with_col_sign_flipping(Null_Space[solvers_to_test[i]],
67 | Null_Space[solvers_to_test[j]], 0.05)
68 | def test_sym_pos_def_agreement():
69 | solvers_to_test = SPD_SOLVERS
70 | rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
71 | X = rng.uniform(size=(100, 40))
72 | S = np.dot(X.T, X)
73 | _test_all_solvers(solvers_to_test, S)
74 |
75 | def test_null_space_sym_pos_def_agreement():
76 | solvers_to_test = SPD_SOLVERS
77 | solvers_to_test = SPD_SOLVERS
78 | rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
79 | X = rng.uniform(size=(100, 100))
80 | S = np.dot(X.T, X)
81 | _test_all_null_solvers(solvers_to_test, S)
82 |
83 | def test_null_space_sym_agreement():
84 | solvers_to_test = NON_SPD_SOLVERS
85 | solvers_to_test = NON_SPD_SOLVERS
86 | rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
87 | X = rng.uniform(size=(16, 16))
88 | S = X + X.T
89 | _test_all_null_solvers(solvers_to_test, S)
90 |
91 | def test_null_space_non_sym_agreement():
92 | solvers_to_test = NON_SPD_SOLVERS
93 | rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
94 | S = rng.uniform(size=(16, 16))
95 | _test_all_null_solvers(solvers_to_test, S)
96 |
97 | def test_base_eigen_solver_kwds():
98 | solvers_to_test = SPD_SOLVERS
99 | rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
100 | X = rng.uniform(size=(100, 40))
101 | S = np.dot(X.T, X)
102 | _test_all_solvers(solvers_to_test, S, solver_kwds_dict=SOLVER_KWDS_DICT)
103 |
104 | def test_null_eigen_solver_kwds():
105 | solvers_to_test = SPD_SOLVERS
106 | rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
107 | X = rng.uniform(size=(100, 40))
108 | S = np.dot(X.T, X)
109 | _test_all_null_solvers(solvers_to_test, S, solver_kwds_dict=SOLVER_KWDS_DICT)
110 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/tests/test_estimate_radius.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from numpy.random import RandomState
3 | from scipy.spatial.distance import squareform, pdist
4 | from megaman.utils.estimate_radius import run_estimate_radius
5 | from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
6 | from numpy.testing import assert_array_almost_equal
7 |
8 | def test_radius_serial_vs_parallel(seed=1234):
9 | rng = RandomState(seed)
10 | X = rng.randn(100, 10)
11 | dists = csr_matrix(squareform(pdist(X)))
12 | sample = range(100)
13 | d = 3
14 | rmin = 2
15 | rmax = 10.0
16 | ntry = 10
17 | run_parallel = True
18 | results_parallel = run_estimate_radius(X, dists, sample, d, rmin, rmax, ntry, run_parallel)
19 | print(results_parallel)
20 | results_serial = run_estimate_radius(X, dists, sample, d, rmin, rmax, ntry, False)
21 | print(results_serial)
22 | assert_array_almost_equal(results_parallel, results_serial)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/tests/test_nystrom.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from numpy import absolute
3 | from numpy.linalg import qr
4 | from megaman.utils.nystrom_extension import nystrom_extension
5 | from numpy.testing import assert_array_almost_equal
6 |
7 |
8 | def test_nystrom_extension(seed=123):
9 | """ Test Nystrom Extension: low rank approximation is exact when
10 | G is itself low rank
11 | """
12 | n = 10
13 | s = 2
14 | rng = np.random.RandomState(seed)
15 | X = rng.randn(n, s)
16 | G = np.dot(X, X.T) # has rank s
17 |
18 | # find the linearly independent columns of
19 | q = qr(G)[1]
20 | q = absolute(q)
21 | sums = np.sum(q,axis=1)
22 | i = 0
23 | dims = list()
24 | while( i < n ): #dim is the matrix dimension
25 | if(sums[i] > 1.e-10):
26 | dims.append(i)
27 | i += 1
28 |
29 | # Find the eigendecomposition of the full rank portion:
30 | W = G[dims,:]
31 | W = W[:,dims]
32 | eval, evec = np.linalg.eigh(W)
33 |
34 | # pass the dims columns of G
35 | C = G[:,dims]
36 | # Find the estimated eigendecomposition using Nystrom
37 | eval_nystrom, evec_nystrom = nystrom_extension(C, evec, eval)
38 |
39 | # reconstruct G using Nystrom Approximatiuon
40 | G_nystrom = np.dot(np.dot(evec_nystrom, np.diag(eval_nystrom)),evec_nystrom.T)
41 | # since rank(W) = rank(G) = s the nystrom approximation of G is exact:
42 | assert_array_almost_equal(G_nystrom, G)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/tests/test_spectral_clustering.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from sklearn import neighbors
2 | import numpy as np
3 |
4 | from megaman.utils.eigendecomp import EIGEN_SOLVERS
5 | from megaman.utils.spectral_clustering import SpectralClustering
6 |
7 | def test_spectral_clustering():
8 | K = 3
9 | num_per_cluster = 100
10 | c = np.array([[1,0,0], [0,1,0], [0,0,1]])
11 | X = np.repeat(c, np.repeat(num_per_cluster, K), axis = 0)
12 | radius = 5
13 | rng = np.random.RandomState(36)
14 | def check_labels(stabalize, renormalize, eigen_solver):
15 | if eigen_solver in ['dense', 'auto']:
16 | solver_kwds = {}
17 | else:
18 | solver_kwds = {'maxiter':100000, 'tol':1e-5}
19 | SC = SpectralClustering(K=K, radius=radius, stabalize=stabalize, renormalize=renormalize,
20 | eigen_solver = eigen_solver, solver_kwds=solver_kwds, random_state = rng,
21 | additional_vectors = 0)
22 | labels = SC.fit_transform(X, input_type= 'data')
23 | for k in range(K):
24 | cluster_labs = labels[range((k*num_per_cluster),((k+1)*num_per_cluster))]
25 | first_lab = cluster_labs[0]
26 | assert(np.all(cluster_labs == first_lab))
27 |
28 | for stabalize in [True, False]:
29 | for renormalize in [True, False]:
30 | for solver in EIGEN_SOLVERS:
31 | yield check_labels, stabalize, renormalize, solver
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/megaman/utils/tests/test_testing.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
2 |
3 | import warnings
4 | import sys
5 | import unittest
6 | from nose.tools import assert_raises, assert_equal
7 |
8 | from megaman.utils.testing import assert_raise_message, assert_no_warnings, assert_warns
9 |
10 | def test_assert_raise_message():
11 | def _raise_ValueError(message):
12 | raise ValueError(message)
13 |
14 | def _no_raise():
15 | pass
16 |
17 | assert_raise_message(ValueError, "test",
18 | _raise_ValueError, "test")
19 |
20 | assert_raises(AssertionError,
21 | assert_raise_message, ValueError, "something else",
22 | _raise_ValueError, "test")
23 |
24 | assert_raises(ValueError,
25 | assert_raise_message, TypeError, "something else",
26 | _raise_ValueError, "test")
27 |
28 | assert_raises(AssertionError,
29 | assert_raise_message, ValueError, "test",
30 | _no_raise)
31 |
32 | # multiple exceptions in a tuple
33 | assert_raises(AssertionError,
34 | assert_raise_message, (ValueError, AttributeError),
35 | "test", _no_raise)
36 |
37 |
38 | # This class is inspired from numpy 1.7 with an alteration to check
39 | # the reset warning filters after calls to assert_warns.
40 | # This assert_warns behavior is specific to scikit-learn because
41 | #`clean_warning_registry()` is called internally by assert_warns
42 | # and clears all previous filters.
43 | class TestWarns(unittest.TestCase):
44 | def test_warn(self):
45 | def f():
46 | warnings.warn("yo")
47 | return 3
48 |
49 | # Test that assert_warns is not impacted by externally set
50 | # filters and is reset internally.
51 | # This is because `clean_warning_registry()` is called internally by
52 | # assert_warns and clears all previous filters.
53 | warnings.simplefilter("ignore", UserWarning)
54 | assert_equal(assert_warns(UserWarning, f), 3)
55 |
56 | # Test that the warning registry is empty after assert_warns
57 | assert_equal(sys.modules['warnings'].filters, [])
58 |
59 | assert_raises(AssertionError, assert_no_warnings, f)
60 | assert_equal(assert_no_warnings(lambda x: x, 1), 1)
61 |
62 | def test_warn_wrong_warning(self):
63 | def f():
64 | warnings.warn("yo", DeprecationWarning)
65 |
66 | failed = False
67 | filters = sys.modules['warnings'].filters[:]
68 | try:
69 | try:
70 | # Should raise an AssertionError
71 | assert_warns(UserWarning, f)
72 | failed = True
73 | except AssertionError:
74 | pass
75 | finally:
76 | sys.modules['warnings'].filters = filters
77 |
78 | if failed:
79 | raise AssertionError("wrong warning caught by assert_warn")
80 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Setup script for megaman: scalable manifold learning
2 | # LICENSE: Simplified BSD https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE
3 |
4 | import io
5 | import os
6 | import re
7 | import sys
8 | import subprocess
9 |
10 | PY2 = sys.version_info[0] == 2
11 | PY3 = not PY2
12 | if PY3:
13 | import importlib.machinery
14 |
15 |
16 | def read(path, encoding='utf-8'):
17 | path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), path)
18 | with io.open(path, encoding=encoding) as fp:
19 | return fp.read()
20 |
21 |
22 | def version(path):
23 | """Obtain the packge version from a python file e.g. pkg/__init__.py
24 |
25 | See .
26 | """
27 | version_file = read(path)
28 | version_match = re.search(r"""^__version__ = ['"]([^'"]*)['"]""",
29 | version_file, re.M)
30 | if version_match:
31 | return version_match.group(1)
32 | raise RuntimeError("Unable to find version string.")
33 |
34 |
35 | def generate_cython():
36 | cwd = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__))
37 | print("Cythonizing sources")
38 | p = subprocess.call([sys.executable,
39 | os.path.join(cwd, 'tools', 'cythonize.py'),
40 | 'megaman'],
41 | cwd=cwd)
42 | if p != 0:
43 | raise RuntimeError("Running cythonize failed!")
44 |
45 |
46 | def configuration(parent_package='',top_path=None):
47 | from numpy.distutils.misc_util import Configuration
48 | config = Configuration(None, parent_package, top_path)
49 | config.set_options(ignore_setup_xxx_py=True,
50 | assume_default_configuration=True,
51 | delegate_options_to_subpackages=True,
52 | quiet=True)
53 |
54 | config.add_subpackage('megaman')
55 |
56 | return config
57 |
58 | DESCRIPTION = "megaman: Manifold Learning for Millions of Points"
59 | LONG_DESCRIPTION = """
60 | megaman: Manifold Learning for Millions of Points
61 | =================================================
62 |
63 | This repository contains a scalable implementation of several manifold learning
64 | algorithms, making use of FLANN for fast approximate nearest neighbors and
65 | PyAMG, LOBPCG, ARPACK, and other routines for fast matrix decompositions.
66 |
67 | For more information, visit https://github.com/mmp2/megaman
68 | """
69 | NAME = "megaman"
70 | AUTHOR = "Marina Meila"
71 | AUTHOR_EMAIL = "mmp@stat.washington.delete_this.edu"
72 | URL = 'https://github.com/mmp2/megaman'
73 | DOWNLOAD_URL = 'https://github.com/mmp2/megaman'
74 | LICENSE = 'BSD 3'
75 |
76 | VERSION = version('megaman/__init__.py')
77 |
78 |
79 | def setup_package():
80 | from numpy.distutils.core import setup
81 |
82 | old_path = os.getcwd()
83 | local_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(sys.argv[0]))
84 | src_path = local_path
85 |
86 | os.chdir(local_path)
87 | sys.path.insert(0, local_path)
88 |
89 | # Run build
90 | old_path = os.getcwd()
91 | os.chdir(src_path)
92 | sys.path.insert(0, src_path)
93 |
94 | cwd = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__))
95 | if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(cwd, 'PKG-INFO')):
96 | # Generate Cython sources, unless building from source release
97 | generate_cython()
98 |
99 | try:
100 | setup(name='megaman',
101 | author=AUTHOR,
102 | author_email=AUTHOR_EMAIL,
103 | url=URL,
104 | download_url=DOWNLOAD_URL,
105 | description=DESCRIPTION,
106 | long_description = LONG_DESCRIPTION,
107 | version=VERSION,
108 | license=LICENSE,
109 | configuration=configuration,
110 | classifiers=[
111 | 'Development Status :: 4 - Beta',
112 | 'Environment :: Console',
113 | 'Intended Audience :: Science/Research',
114 | 'License :: OSI Approved :: BSD License',
115 | 'Natural Language :: English',
116 | 'Programming Language :: Python :: 2.7',
117 | 'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.4',
118 | 'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.5'])
119 | finally:
120 | del sys.path[0]
121 | os.chdir(old_path)
122 |
123 | return
124 |
125 |
126 | if __name__ == '__main__':
127 | setup_package()
128 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------


 4 |
5 | [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/megaman)
6 | [](https://travis-ci.org/mmp2/megaman)
7 | [](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/megaman)
8 | [](https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE)
9 |
10 | ``megaman`` is a scalable manifold learning package implemented in
11 | python. It has a front-end API designed to be familiar
12 | to [scikit-learn](http://scikit-learn.org/) but harnesses
13 | the C++ Fast Library for Approximate Nearest Neighbors (FLANN)
14 | and the Sparse Symmetric Positive Definite (SSPD) solver
15 | Locally Optimal Block Precodition Gradient (LOBPCG) method
16 | to scale manifold learning algorithms to large data sets.
17 | On a personal computer megaman can embed 1 million data points
18 | with hundreds of dimensions in 10 minutes.
19 | megaman is designed for researchers and as such caches intermediary
20 | steps and indices to allow for fast re-computation with new parameters.
21 |
22 | Package documentation can be found at http://mmp2.github.io/megaman/
23 |
24 | If you use our software please cite the following JMLR paper:
25 |
26 | McQueen, Meila, VanderPlas, & Zhang, "Megaman: Scalable Manifold Learning in Python",
27 | Journal of Machine Learning Research, Vol 17 no. 14, 2016.
28 | http://jmlr.org/papers/v17/16-109.html
29 |
30 | You can also find our arXiv paper at http://arxiv.org/abs/1603.02763
31 |
32 | ## Examples
33 |
34 | - [Tutorial Notebook]( https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/examples/megaman_tutorial.ipynb)
35 |
36 | ## Installation and Examples in Google Colab
37 |
38 | Below it's a tutorial to install megaman on Google Colab, through Conda environment.
39 |
40 | It also provides tutorial of using megaman to build spectral embedding on uniform swiss roll dataset.
41 |
42 | - [Install & Example script]( https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1ms22YK3TvrIx0gji6UZqG0zoSNRCWtXj?usp=sharing)
43 | - [You can download the Jupyter Notebook version here]( https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/examples/megaman_install_usage_colab.ipynb)
44 |
45 | ## ~~Installation with Conda~~
46 |
47 |
59 |
60 | Due to the change of API,
61 | `$ conda install -c conda-forge megaman`
62 | is no longer supported.
63 | We are currently working on fixing the bug.
64 |
65 | Please see the full install instructions below to build `megaman` from source.
66 |
67 | ## Installation from source
68 |
69 | To install megaman from source requires the following:
70 |
71 | - [python](http://python.org) tested with versions 2.7, 3.5 and 3.6
72 | - [numpy](http://numpy.org) version 1.8 or higher
73 | - [scipy](http://scipy.org) version 0.16.0 or higher
74 | - [scikit-learn](http://scikit-learn.org)
75 | - [FLANN](http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/)
76 | - [pyflann](http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/) which offers another method of computing distance matrices (this is bundled with the FLANN source code)
77 | - [cython](http://cython.org/)
78 | - a C++ compiler such as ``gcc``/``g++``
79 |
80 | Optional requirements include
81 |
82 | - [pyamg](http://pyamg.org/), which allows for faster decompositions of large matrices
83 | - [nose](https://nose.readthedocs.org/) for running the unit tests
84 | - [h5py](http://www.h5py.org) for reading testing .mat files
85 | - [plotly](https://plot.ly) an graphing library for interactive plot
86 |
87 |
88 | These requirements can be installed on Linux and MacOSX using the following conda command:
89 |
90 | ```shell
91 | $ conda create -n manifold_env python=3.5 -y
92 | # can also use python=2.7 or python=3.6
93 |
94 | $ source activate manifold_env
95 | $ conda install --channel=conda-forge -y pip nose coverage cython numpy scipy \
96 | scikit-learn pyflann pyamg h5py plotly
97 | ```
98 |
99 | Clone this repository and `cd` into source repository
100 |
101 | ```shell
102 | $ cd /tmp/
103 | $ git clone https://github.com/mmp2/megaman.git
104 | $ cd megaman
105 | ```
106 |
107 | Finally, within the source repository, run this command to install the ``megaman`` package itself:
108 | ```shell
109 | $ python setup.py install
110 | ```
111 |
112 | ## Unit Tests
113 | megaman uses ``nose`` for unit tests. With ``nose`` installed, type
114 | ```
115 | $ make test
116 | ```
117 | to run the unit tests. ``megaman`` is tested on Python versions 2.7, 3.4, and 3.5.
118 |
119 | ## Authors
120 | - [James McQueen](http://www.stat.washington.edu/people/jmcq/)
121 | - [Marina Meila](http://www.stat.washington.edu/mmp/)
122 | - [Zhongyue Zhang](https://github.com/Jerryzcn)
123 | - [Jake VanderPlas](http://www.vanderplas.com)
124 | - [Yu-Chia Chen](https://github.com/yuchaz)
125 |
126 | ## Other Contributors
127 |
128 | - Xiao Wang: lazy rmetric, Nystrom Extension
129 | - [Hangliang Ren (Harry)](https://github.com/Harryahh): Installation tutorials, Spectral Embedding
130 |
131 | ## Future Work
132 |
133 | See this issues list for what we have planned for upcoming releases:
134 |
135 | [Future Work](https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/issues/47)
136 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Conda recipes
2 |
3 | This directory contains conda build recipes for megaman and its dependencies.
4 | For more information see the
5 | [Conda Build documentation](http://conda.pydata.org/docs/build_tutorials/pkgs2.html)
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/build_all.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | conda config --set anaconda_upload yes
2 | conda build flann
3 | conda build --py all pyflann
4 | conda build --python 2.7 --python 3.4 --python 3.5 --numpy 1.9 --numpy 1.10 pyamg
5 | conda build --python 2.7 --python 3.4 --python 3.5 --numpy 1.10 megaman
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/flann/.binstar.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package: flann
2 | platform:
3 | - osx-64
4 | - osx-32
5 | - linux-64
6 | - linux-32
7 | script:
8 | - conda build .
9 | build_targets:
10 | - conda
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/flann/build.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | # cannot build flann from within the source directory
4 | mkdir build
5 | cd build
6 |
7 | # On OSX, we need to ensure we're using conda's gcc/g++
8 | if [[ `uname` == Darwin ]]; then
9 | export CC=gcc
10 | export CXX=g++
11 | fi
12 |
13 | cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=$PREFIX -DBUILD_MATLAB_BINDINGS:BOOL=OFF -DBUILD_PYTHON_BINDINGS:BOOL=OFF -DBUILD_EXAMPLES:BOOL=OFF
14 |
15 | make -j$CPU_COUNT install
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/flann/meta.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package:
2 | name: flann
3 | version: "1.8.5dev"
4 |
5 | source:
6 | git_url: https://github.com/mariusmuja/flann.git
7 | git_tag: b8a442fd98f8ce32ae3465bfd3427b5cbc36f6a5
8 |
9 | build:
10 | number: 2
11 | string: {{PKG_BUILDNUM}}_g{{GIT_FULL_HASH[:7]}}
12 |
13 | requirements:
14 | build:
15 | - gcc 4.8* # [osx]
16 | - hdf5
17 | - cmake
18 | run:
19 | - libgcc 4.8* #[osx]
20 | - hdf5
21 |
22 | about:
23 | home: http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/
24 | license: BSD
25 | license_file: COPYING
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/megaman/.binstar.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package: megaman
2 | platform:
3 | - osx-64
4 | - osx-32
5 | - linux-64
6 | - linux-32
7 | script:
8 | - conda build .
9 | build_targets:
10 | - conda
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/megaman/build.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | # On OSX, we need to ensure we're using conda's gcc/g++
4 | if [[ `uname` == Darwin ]]; then
5 | export CC=gcc
6 | export CXX=g++
7 | fi
8 |
9 | $PYTHON setup.py install
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/megaman/meta.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package:
2 | name: megaman
3 | version: 0.1.1
4 |
5 | source:
6 | git_url: https://github.com/mmp2/megaman.git
7 | git_tag: v0.1.1
8 |
9 | build:
10 | number: 2
11 | string: np{{CONDA_NPY}}py{{CONDA_PY}}_{{PKG_BUILDNUM}}
12 |
13 | requirements:
14 | build:
15 | - python >=2.7,<3|>=3.4,{{PY_VER}}*
16 | - numpy {{NPY_VER}}*
17 | - cython
18 | - flann
19 | - gcc 4.8* # [osx]
20 | run:
21 | - python {{PY_VER}}*
22 | - numpy {{NPY_VER}}*
23 | - scipy >=0.16
24 | - scikit-learn >=0.17
25 | - pyamg
26 | - pyflann
27 | - libgcc 4.8* # [osx]
28 |
29 | test:
30 | requires:
31 | - nose
32 | imports:
33 | - megaman
34 | - megaman.geometry
35 | - megaman.embedding
36 | - megaman.utils
37 |
38 | about:
39 | home: http://mmp2.github.io/megaman
40 | license: BSD
41 | license_file: LICENSE
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/megaman/run_test.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | nosetests -v megaman
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyamg/.binstar.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package: pyamg
2 | platform:
3 | - osx-64
4 | - osx-32
5 | - linux-64
6 | - linux-32
7 | script:
8 | - conda build .
9 | build_targets:
10 | - conda
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyamg/build.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | # On OSX, we need to ensure we're using conda's gcc/g++
4 | if [[ `uname` == Darwin ]]; then
5 | export CC=gcc
6 | export CXX=g++
7 | fi
8 |
9 | $PYTHON setup.py install
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyamg/meta.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package:
2 | name: pyamg
3 | version: "3.0.2"
4 |
5 | source:
6 | git_url: https://github.com/pyamg/pyamg.git
7 | git_tag: v3.0.2
8 |
9 | build:
10 | number: 2
11 | string: np{{CONDA_NPY}}py{{CONDA_PY}}_{{PKG_BUILDNUM}}
12 |
13 | requirements:
14 | build:
15 | - python >=2.7,<3|>=3.4,{{PY_VER}}*
16 | - numpy {{NPY_VER}}*
17 | - scipy
18 | - nose
19 | - zlib # [linux]
20 | - gcc 4.8* # [osx]
21 | run:
22 | - python {{PY_VER}}*
23 | - numpy {{NPY_VER}}*
24 | - scipy
25 | - zlib # [linux]
26 |
27 | test:
28 | requires:
29 | - nose
30 | imports:
31 | - pyamg
32 |
33 | about:
34 | home: http://www.pyamg.org/
35 | license: MIT
36 | license_file: LICENSE.txt
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyamg/run_test.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | if [[ `uname` == Darwin ]] && [ $PY_VER == "2.7" ]; then
4 | echo "skipping tests; see https://github.com/pyamg/pyamg/issues/165"
5 | else
6 | nosetests -v pyamg
7 | fi
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyflann/.binstar.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package: pyflann
2 | platform:
3 | - osx-64
4 | - osx-32
5 | - linux-64
6 | - linux-32
7 | script:
8 | - conda build .
9 | build_targets:
10 | - conda
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyflann/build.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | cd src/python
4 | cmake . -DLIBRARY_OUTPUT_PATH=$PREFIX/lib -DFLANN_VERSION="$PKG_VERSION"
5 | $PYTHON setup.py install
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyflann/meta.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package:
2 | name: pyflann
3 | version: "1.8.5dev"
4 |
5 | source:
6 | git_url: https://github.com/mariusmuja/flann.git
7 | git_tag: b8a442fd98f8ce32ae3465bfd3427b5cbc36f6a5
8 |
9 | build:
10 | number: 2
11 | string: py{{CONDA_PY}}_{{PKG_BUILDNUM}}_g{{GIT_FULL_HASH[:7]}}
12 |
13 | requirements:
14 | build:
15 | - python {{PY_VER}}*
16 | - setuptools
17 | - flann 1.8.5dev
18 | - cmake
19 | run:
20 | - python {{PY_VER}}*
21 | - flann 1.8.5dev
22 | - numpy
23 |
24 | test:
25 | imports:
26 | - pyflann
27 |
28 | about:
29 | home: http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/
30 | license: BSD
31 | license_file: COPYING
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | _build
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/embedding/API.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _embedding_API:
2 |
3 | .. testsetup:: *
4 |
5 | from megaman.embedding import *
6 |
7 | API Documentation
8 | =================
9 |
10 | .. automodule:: megaman.embedding.spectral_embedding
11 | :members:
12 |
13 | .. automodule:: megaman.embedding.isomap
14 | :members:
15 |
16 | .. automodule:: megaman.embedding.locally_linear
17 | :members:
18 |
19 | .. automodule:: megaman.embedding.ltsa
20 | :members:
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/embedding/index.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _embedding:
2 |
3 | ***************************************************
4 | Tools for Embedding (``megaman.embedding``)
5 | ***************************************************
6 |
7 | This module contains tools for nonlinear embedding data sets.
8 | These tools include Isomap, Spectral Embedding & Diffusion
9 | Maps, Local Tangent Space Alignment, and Locally Linear
10 | Embedding
11 |
12 | .. toctree::
13 | :maxdepth: 2
14 |
15 | isomap.rst
16 | locally_linear.rst
17 | ltsa.rst
18 | spectral_embedding.rst
19 | API
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/embedding/isomap.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _isomap:
2 |
3 | Isomap
4 | ======
5 |
6 | Isomap is one of the embeddings implemented in the megaman package.
7 | Isomap uses Multidimensional Scaling (MDS) to preserve pairwsise
8 | graph shortest distance computed using a sparse neighborhood graph.
9 |
10 | For more information see:
11 |
12 | * Tenenbaum, J.B.; De Silva, V.; & Langford, J.C.
13 | A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction.
14 | Science 290 (5500)
15 |
16 | :class:'~megaman.embedding.Isomap'
17 | This class is used to interface with isomap embedding function.
18 | Like all embedding functions in megaman it operates using a
19 | Geometry object. The Isomap class allows you to optionally
20 | pass an exiting Geometry object, otherwise it creates one.
21 |
22 | API of Isomap
23 | -------------
24 |
25 | The Isomap model, along with all the other models in megaman, have an API
26 | designed to follow in the same vein of
27 | `scikit-learn
4 |
5 | [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/megaman)
6 | [](https://travis-ci.org/mmp2/megaman)
7 | [](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/megaman)
8 | [](https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/LICENSE)
9 |
10 | ``megaman`` is a scalable manifold learning package implemented in
11 | python. It has a front-end API designed to be familiar
12 | to [scikit-learn](http://scikit-learn.org/) but harnesses
13 | the C++ Fast Library for Approximate Nearest Neighbors (FLANN)
14 | and the Sparse Symmetric Positive Definite (SSPD) solver
15 | Locally Optimal Block Precodition Gradient (LOBPCG) method
16 | to scale manifold learning algorithms to large data sets.
17 | On a personal computer megaman can embed 1 million data points
18 | with hundreds of dimensions in 10 minutes.
19 | megaman is designed for researchers and as such caches intermediary
20 | steps and indices to allow for fast re-computation with new parameters.
21 |
22 | Package documentation can be found at http://mmp2.github.io/megaman/
23 |
24 | If you use our software please cite the following JMLR paper:
25 |
26 | McQueen, Meila, VanderPlas, & Zhang, "Megaman: Scalable Manifold Learning in Python",
27 | Journal of Machine Learning Research, Vol 17 no. 14, 2016.
28 | http://jmlr.org/papers/v17/16-109.html
29 |
30 | You can also find our arXiv paper at http://arxiv.org/abs/1603.02763
31 |
32 | ## Examples
33 |
34 | - [Tutorial Notebook]( https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/examples/megaman_tutorial.ipynb)
35 |
36 | ## Installation and Examples in Google Colab
37 |
38 | Below it's a tutorial to install megaman on Google Colab, through Conda environment.
39 |
40 | It also provides tutorial of using megaman to build spectral embedding on uniform swiss roll dataset.
41 |
42 | - [Install & Example script]( https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1ms22YK3TvrIx0gji6UZqG0zoSNRCWtXj?usp=sharing)
43 | - [You can download the Jupyter Notebook version here]( https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/blob/master/examples/megaman_install_usage_colab.ipynb)
44 |
45 | ## ~~Installation with Conda~~
46 |
47 |
59 |
60 | Due to the change of API,
61 | `$ conda install -c conda-forge megaman`
62 | is no longer supported.
63 | We are currently working on fixing the bug.
64 |
65 | Please see the full install instructions below to build `megaman` from source.
66 |
67 | ## Installation from source
68 |
69 | To install megaman from source requires the following:
70 |
71 | - [python](http://python.org) tested with versions 2.7, 3.5 and 3.6
72 | - [numpy](http://numpy.org) version 1.8 or higher
73 | - [scipy](http://scipy.org) version 0.16.0 or higher
74 | - [scikit-learn](http://scikit-learn.org)
75 | - [FLANN](http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/)
76 | - [pyflann](http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/) which offers another method of computing distance matrices (this is bundled with the FLANN source code)
77 | - [cython](http://cython.org/)
78 | - a C++ compiler such as ``gcc``/``g++``
79 |
80 | Optional requirements include
81 |
82 | - [pyamg](http://pyamg.org/), which allows for faster decompositions of large matrices
83 | - [nose](https://nose.readthedocs.org/) for running the unit tests
84 | - [h5py](http://www.h5py.org) for reading testing .mat files
85 | - [plotly](https://plot.ly) an graphing library for interactive plot
86 |
87 |
88 | These requirements can be installed on Linux and MacOSX using the following conda command:
89 |
90 | ```shell
91 | $ conda create -n manifold_env python=3.5 -y
92 | # can also use python=2.7 or python=3.6
93 |
94 | $ source activate manifold_env
95 | $ conda install --channel=conda-forge -y pip nose coverage cython numpy scipy \
96 | scikit-learn pyflann pyamg h5py plotly
97 | ```
98 |
99 | Clone this repository and `cd` into source repository
100 |
101 | ```shell
102 | $ cd /tmp/
103 | $ git clone https://github.com/mmp2/megaman.git
104 | $ cd megaman
105 | ```
106 |
107 | Finally, within the source repository, run this command to install the ``megaman`` package itself:
108 | ```shell
109 | $ python setup.py install
110 | ```
111 |
112 | ## Unit Tests
113 | megaman uses ``nose`` for unit tests. With ``nose`` installed, type
114 | ```
115 | $ make test
116 | ```
117 | to run the unit tests. ``megaman`` is tested on Python versions 2.7, 3.4, and 3.5.
118 |
119 | ## Authors
120 | - [James McQueen](http://www.stat.washington.edu/people/jmcq/)
121 | - [Marina Meila](http://www.stat.washington.edu/mmp/)
122 | - [Zhongyue Zhang](https://github.com/Jerryzcn)
123 | - [Jake VanderPlas](http://www.vanderplas.com)
124 | - [Yu-Chia Chen](https://github.com/yuchaz)
125 |
126 | ## Other Contributors
127 |
128 | - Xiao Wang: lazy rmetric, Nystrom Extension
129 | - [Hangliang Ren (Harry)](https://github.com/Harryahh): Installation tutorials, Spectral Embedding
130 |
131 | ## Future Work
132 |
133 | See this issues list for what we have planned for upcoming releases:
134 |
135 | [Future Work](https://github.com/mmp2/megaman/issues/47)
136 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Conda recipes
2 |
3 | This directory contains conda build recipes for megaman and its dependencies.
4 | For more information see the
5 | [Conda Build documentation](http://conda.pydata.org/docs/build_tutorials/pkgs2.html)
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/build_all.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | conda config --set anaconda_upload yes
2 | conda build flann
3 | conda build --py all pyflann
4 | conda build --python 2.7 --python 3.4 --python 3.5 --numpy 1.9 --numpy 1.10 pyamg
5 | conda build --python 2.7 --python 3.4 --python 3.5 --numpy 1.10 megaman
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/flann/.binstar.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package: flann
2 | platform:
3 | - osx-64
4 | - osx-32
5 | - linux-64
6 | - linux-32
7 | script:
8 | - conda build .
9 | build_targets:
10 | - conda
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/flann/build.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | # cannot build flann from within the source directory
4 | mkdir build
5 | cd build
6 |
7 | # On OSX, we need to ensure we're using conda's gcc/g++
8 | if [[ `uname` == Darwin ]]; then
9 | export CC=gcc
10 | export CXX=g++
11 | fi
12 |
13 | cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=$PREFIX -DBUILD_MATLAB_BINDINGS:BOOL=OFF -DBUILD_PYTHON_BINDINGS:BOOL=OFF -DBUILD_EXAMPLES:BOOL=OFF
14 |
15 | make -j$CPU_COUNT install
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/flann/meta.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package:
2 | name: flann
3 | version: "1.8.5dev"
4 |
5 | source:
6 | git_url: https://github.com/mariusmuja/flann.git
7 | git_tag: b8a442fd98f8ce32ae3465bfd3427b5cbc36f6a5
8 |
9 | build:
10 | number: 2
11 | string: {{PKG_BUILDNUM}}_g{{GIT_FULL_HASH[:7]}}
12 |
13 | requirements:
14 | build:
15 | - gcc 4.8* # [osx]
16 | - hdf5
17 | - cmake
18 | run:
19 | - libgcc 4.8* #[osx]
20 | - hdf5
21 |
22 | about:
23 | home: http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/
24 | license: BSD
25 | license_file: COPYING
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/megaman/.binstar.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package: megaman
2 | platform:
3 | - osx-64
4 | - osx-32
5 | - linux-64
6 | - linux-32
7 | script:
8 | - conda build .
9 | build_targets:
10 | - conda
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/megaman/build.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | # On OSX, we need to ensure we're using conda's gcc/g++
4 | if [[ `uname` == Darwin ]]; then
5 | export CC=gcc
6 | export CXX=g++
7 | fi
8 |
9 | $PYTHON setup.py install
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/megaman/meta.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package:
2 | name: megaman
3 | version: 0.1.1
4 |
5 | source:
6 | git_url: https://github.com/mmp2/megaman.git
7 | git_tag: v0.1.1
8 |
9 | build:
10 | number: 2
11 | string: np{{CONDA_NPY}}py{{CONDA_PY}}_{{PKG_BUILDNUM}}
12 |
13 | requirements:
14 | build:
15 | - python >=2.7,<3|>=3.4,{{PY_VER}}*
16 | - numpy {{NPY_VER}}*
17 | - cython
18 | - flann
19 | - gcc 4.8* # [osx]
20 | run:
21 | - python {{PY_VER}}*
22 | - numpy {{NPY_VER}}*
23 | - scipy >=0.16
24 | - scikit-learn >=0.17
25 | - pyamg
26 | - pyflann
27 | - libgcc 4.8* # [osx]
28 |
29 | test:
30 | requires:
31 | - nose
32 | imports:
33 | - megaman
34 | - megaman.geometry
35 | - megaman.embedding
36 | - megaman.utils
37 |
38 | about:
39 | home: http://mmp2.github.io/megaman
40 | license: BSD
41 | license_file: LICENSE
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/megaman/run_test.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | nosetests -v megaman
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyamg/.binstar.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package: pyamg
2 | platform:
3 | - osx-64
4 | - osx-32
5 | - linux-64
6 | - linux-32
7 | script:
8 | - conda build .
9 | build_targets:
10 | - conda
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyamg/build.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | # On OSX, we need to ensure we're using conda's gcc/g++
4 | if [[ `uname` == Darwin ]]; then
5 | export CC=gcc
6 | export CXX=g++
7 | fi
8 |
9 | $PYTHON setup.py install
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyamg/meta.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package:
2 | name: pyamg
3 | version: "3.0.2"
4 |
5 | source:
6 | git_url: https://github.com/pyamg/pyamg.git
7 | git_tag: v3.0.2
8 |
9 | build:
10 | number: 2
11 | string: np{{CONDA_NPY}}py{{CONDA_PY}}_{{PKG_BUILDNUM}}
12 |
13 | requirements:
14 | build:
15 | - python >=2.7,<3|>=3.4,{{PY_VER}}*
16 | - numpy {{NPY_VER}}*
17 | - scipy
18 | - nose
19 | - zlib # [linux]
20 | - gcc 4.8* # [osx]
21 | run:
22 | - python {{PY_VER}}*
23 | - numpy {{NPY_VER}}*
24 | - scipy
25 | - zlib # [linux]
26 |
27 | test:
28 | requires:
29 | - nose
30 | imports:
31 | - pyamg
32 |
33 | about:
34 | home: http://www.pyamg.org/
35 | license: MIT
36 | license_file: LICENSE.txt
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyamg/run_test.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | if [[ `uname` == Darwin ]] && [ $PY_VER == "2.7" ]; then
4 | echo "skipping tests; see https://github.com/pyamg/pyamg/issues/165"
5 | else
6 | nosetests -v pyamg
7 | fi
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyflann/.binstar.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package: pyflann
2 | platform:
3 | - osx-64
4 | - osx-32
5 | - linux-64
6 | - linux-32
7 | script:
8 | - conda build .
9 | build_targets:
10 | - conda
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyflann/build.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 |
3 | cd src/python
4 | cmake . -DLIBRARY_OUTPUT_PATH=$PREFIX/lib -DFLANN_VERSION="$PKG_VERSION"
5 | $PYTHON setup.py install
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/conda_recipes/pyflann/meta.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package:
2 | name: pyflann
3 | version: "1.8.5dev"
4 |
5 | source:
6 | git_url: https://github.com/mariusmuja/flann.git
7 | git_tag: b8a442fd98f8ce32ae3465bfd3427b5cbc36f6a5
8 |
9 | build:
10 | number: 2
11 | string: py{{CONDA_PY}}_{{PKG_BUILDNUM}}_g{{GIT_FULL_HASH[:7]}}
12 |
13 | requirements:
14 | build:
15 | - python {{PY_VER}}*
16 | - setuptools
17 | - flann 1.8.5dev
18 | - cmake
19 | run:
20 | - python {{PY_VER}}*
21 | - flann 1.8.5dev
22 | - numpy
23 |
24 | test:
25 | imports:
26 | - pyflann
27 |
28 | about:
29 | home: http://www.cs.ubc.ca/research/flann/
30 | license: BSD
31 | license_file: COPYING
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | _build
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/embedding/API.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _embedding_API:
2 |
3 | .. testsetup:: *
4 |
5 | from megaman.embedding import *
6 |
7 | API Documentation
8 | =================
9 |
10 | .. automodule:: megaman.embedding.spectral_embedding
11 | :members:
12 |
13 | .. automodule:: megaman.embedding.isomap
14 | :members:
15 |
16 | .. automodule:: megaman.embedding.locally_linear
17 | :members:
18 |
19 | .. automodule:: megaman.embedding.ltsa
20 | :members:
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/embedding/index.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _embedding:
2 |
3 | ***************************************************
4 | Tools for Embedding (``megaman.embedding``)
5 | ***************************************************
6 |
7 | This module contains tools for nonlinear embedding data sets.
8 | These tools include Isomap, Spectral Embedding & Diffusion
9 | Maps, Local Tangent Space Alignment, and Locally Linear
10 | Embedding
11 |
12 | .. toctree::
13 | :maxdepth: 2
14 |
15 | isomap.rst
16 | locally_linear.rst
17 | ltsa.rst
18 | spectral_embedding.rst
19 | API
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/doc/embedding/isomap.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _isomap:
2 |
3 | Isomap
4 | ======
5 |
6 | Isomap is one of the embeddings implemented in the megaman package.
7 | Isomap uses Multidimensional Scaling (MDS) to preserve pairwsise
8 | graph shortest distance computed using a sparse neighborhood graph.
9 |
10 | For more information see:
11 |
12 | * Tenenbaum, J.B.; De Silva, V.; & Langford, J.C.
13 | A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction.
14 | Science 290 (5500)
15 |
16 | :class:'~megaman.embedding.Isomap'
17 | This class is used to interface with isomap embedding function.
18 | Like all embedding functions in megaman it operates using a
19 | Geometry object. The Isomap class allows you to optionally
20 | pass an exiting Geometry object, otherwise it creates one.
21 |
22 | API of Isomap
23 | -------------
24 |
25 | The Isomap model, along with all the other models in megaman, have an API
26 | designed to follow in the same vein of
27 | `scikit-learn