├── .gitignore
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── demo.ipynb
├── fourier_feature_transform.py
└── test_fourier_feature_transform.py
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
2 | __pycache__/
3 | *.py[cod]
4 | *$py.class
5 |
6 | # C extensions
7 | *.so
8 |
9 | # Distribution / packaging
10 | .Python
11 | build/
12 | develop-eggs/
13 | dist/
14 | downloads/
15 | eggs/
16 | .eggs/
17 | lib/
18 | lib64/
19 | parts/
20 | sdist/
21 | var/
22 | wheels/
23 | pip-wheel-metadata/
24 | share/python-wheels/
25 | *.egg-info/
26 | .installed.cfg
27 | *.egg
28 | MANIFEST
29 |
30 | # PyInstaller
31 | # Usually these files are written by a python script from a template
32 | # before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it.
33 | *.manifest
34 | *.spec
35 |
36 | # Installer logs
37 | pip-log.txt
38 | pip-delete-this-directory.txt
39 |
40 | # Unit test / coverage reports
41 | htmlcov/
42 | .tox/
43 | .nox/
44 | .coverage
45 | .coverage.*
46 | .cache
47 | nosetests.xml
48 | coverage.xml
49 | *.cover
50 | *.py,cover
51 | .hypothesis/
52 | .pytest_cache/
53 |
54 | # Translations
55 | *.mo
56 | *.pot
57 |
58 | # Django stuff:
59 | *.log
60 | local_settings.py
61 | db.sqlite3
62 | db.sqlite3-journal
63 |
64 | # Flask stuff:
65 | instance/
66 | .webassets-cache
67 |
68 | # Scrapy stuff:
69 | .scrapy
70 |
71 | # Sphinx documentation
72 | docs/_build/
73 |
74 | # PyBuilder
75 | target/
76 |
77 | # Jupyter Notebook
78 | .ipynb_checkpoints
79 |
80 | # IPython
81 | profile_default/
82 | ipython_config.py
83 |
84 | # pyenv
85 | .python-version
86 |
87 | # pipenv
88 | # According to pypa/pipenv#598, it is recommended to include Pipfile.lock in version control.
89 | # However, in case of collaboration, if having platform-specific dependencies or dependencies
90 | # having no cross-platform support, pipenv may install dependencies that don't work, or not
91 | # install all needed dependencies.
92 | #Pipfile.lock
93 |
94 | # PEP 582; used by e.g. github.com/David-OConnor/pyflow
95 | __pypackages__/
96 |
97 | # Celery stuff
98 | celerybeat-schedule
99 | celerybeat.pid
100 |
101 | # SageMath parsed files
102 | *.sage.py
103 |
104 | # Environments
105 | .env
106 | .venv
107 | env/
108 | venv/
109 | ENV/
110 | env.bak/
111 | venv.bak/
112 |
113 | # Spyder project settings
114 | .spyderproject
115 | .spyproject
116 |
117 | # Rope project settings
118 | .ropeproject
119 |
120 | # mkdocs documentation
121 | /site
122 |
123 | # mypy
124 | .mypy_cache/
125 | .dmypy.json
126 | dmypy.json
127 |
128 | # Pyre type checker
129 | .pyre/
130 | .idea/
131 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2020 Matthew Tancik
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Pytorch Fourier Feature Networks
2 |
3 | A simple Pytorch adaptation of Gaussian Fourier feature mapping (see info on the original project below the fold).
4 |
5 | Open this demo in Google Colab: [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ndahlquist/pytorch-fourier-feature-networks/blob/master/demo.ipynb)
6 |
7 |
8 | ----
9 |
10 | # Fourier Features Let Networks Learn High Frequency Functions in Low Dimensional Domains
11 | ### [Project Page](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~bmild/fourfeat/) | [Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.10739)
12 | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/tancik/fourier-feature-networks/blob/master/Demo.ipynb)
13 |
14 | [Matthew Tancik](http://tancik.com/)\*1,
15 | [Pratul P. Srinivasan](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~pratul/)\*1,2,
16 | [Ben Mildenhall](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~bmild/)\*1,
17 | [Sara Fridovich-Keil](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~sfk/)1,
18 | [Nithin Raghavan](https://www.linkedin.com/in/nithinraghavan//)1,
19 | [Utkarsh Singhal](https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=lvA86MYAAAAJ&hl=en)1,
20 | [Ravi Ramamoorthi](http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/~ravir/)3,
21 | [Jonathan T. Barron](http://jonbarron.info/)2,
22 | [Ren Ng](https://www2.eecs.berkeley.edu/Faculty/Homepages/yirenng.html)1
23 |
24 | 1UC Berkeley, 2Google Research, 3UC San Diego
25 | *denotes equal contribution
26 |
27 |
28 | ## Abstract
29 | 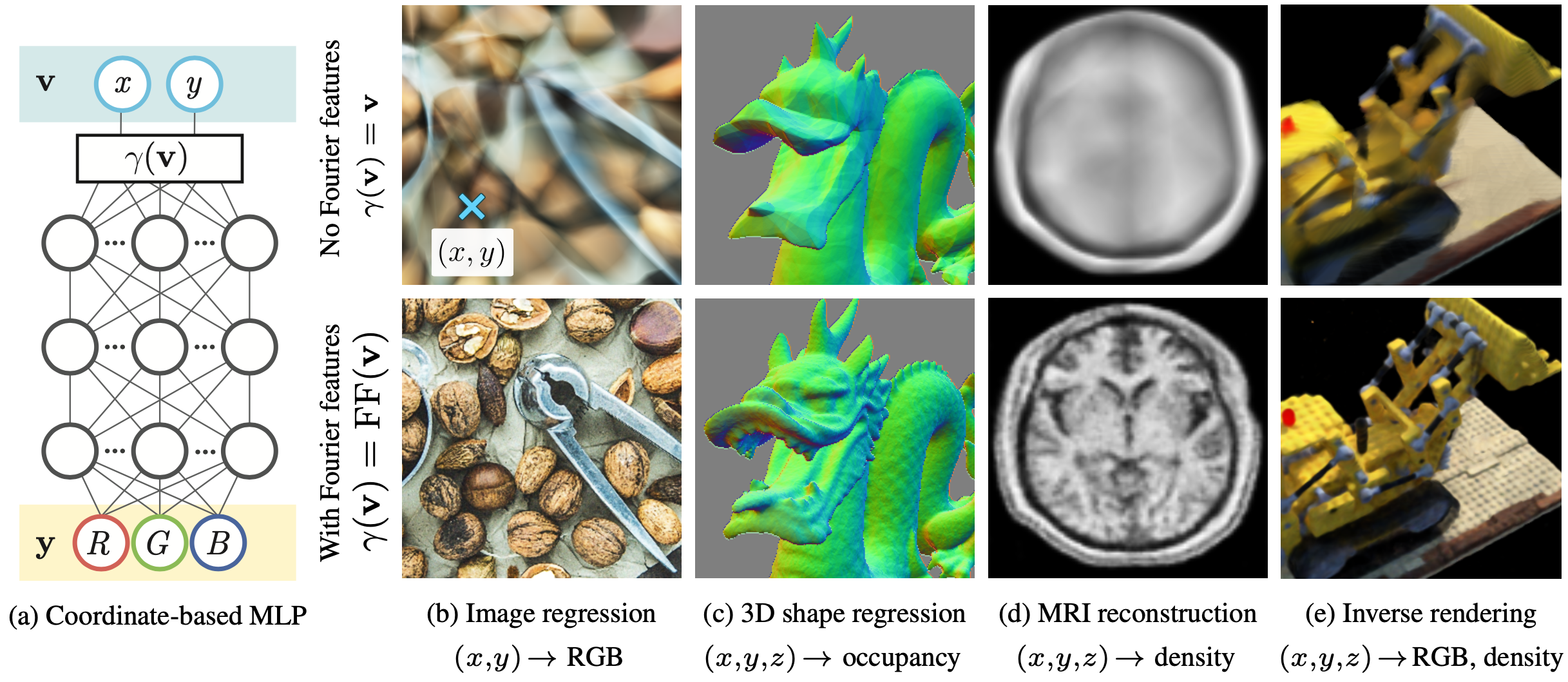
30 |
31 | We show that passing input points through a simple Fourier feature mapping enables a multilayer perceptron (MLP) to learn high-frequency functions in low-dimensional problem domains. These results shed light on recent advances in computer vision and graphics that achieve state-of-the-art results by using MLPs to represent complex 3D objects and scenes. Using tools from the neural tangent kernel (NTK) literature, we show that a standard MLP fails to learn high frequencies both in theory and in practice. To overcome this spectral bias, we use a Fourier feature mapping to transform the effective NTK into a stationary kernel with a tunable bandwidth. We suggest an approach for selecting problem-specific Fourier features that greatly improves the performance of MLPs for low-dimensional regression tasks relevant to the computer vision and graphics communities.
32 |
33 | ## Code
34 | We provide a [demo IPython notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/tancik/fourier-feature-networks/blob/master/Demo.ipynb) as a simple reference for the core idea. The scripts used to generate the paper plots and tables are located in the [Experiments](https://github.com/tancik/fourier-feature-networks/tree/master/Experiments) directory.
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fourier_feature_transform.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from math import pi
2 |
3 | import torch
4 |
5 |
6 | class GaussianFourierFeatureTransform(torch.nn.Module):
7 | """
8 | An implementation of Gaussian Fourier feature mapping.
9 |
10 | "Fourier Features Let Networks Learn High Frequency Functions in Low Dimensional Domains":
11 | https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.10739
12 | https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~bmild/fourfeat/index.html
13 |
14 | Given an input of size [batches, num_input_channels, width, height],
15 | returns a tensor of size [batches, mapping_size*2, width, height].
16 | """
17 |
18 | def __init__(self, num_input_channels, mapping_size=256, scale=10):
19 | super().__init__()
20 |
21 | self._num_input_channels = num_input_channels
22 | self._mapping_size = mapping_size
23 | self._B = torch.randn((num_input_channels, mapping_size)) * scale
24 |
25 | def forward(self, x):
26 | assert x.dim() == 4, 'Expected 4D input (got {}D input)'.format(x.dim())
27 |
28 | batches, channels, width, height = x.shape
29 |
30 | assert channels == self._num_input_channels,\
31 | "Expected input to have {} channels (got {} channels)".format(self._num_input_channels, channels)
32 |
33 | # Make shape compatible for matmul with _B.
34 | # From [B, C, W, H] to [(B*W*H), C].
35 | x = x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).reshape(batches * width * height, channels)
36 |
37 | x = x @ self._B.to(x.device)
38 |
39 | # From [(B*W*H), C] to [B, W, H, C]
40 | x = x.view(batches, width, height, self._mapping_size)
41 | # From [B, W, H, C] to [B, C, W, H]
42 | x = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
43 |
44 | x = 2 * pi * x
45 | return torch.cat([torch.sin(x), torch.cos(x)], dim=1)
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test_fourier_feature_transform.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import pytest
2 | import torch
3 |
4 | from fourier_feature_transform import GaussianFourierFeatureTransform
5 |
6 |
7 | def test_basic_tensor():
8 | x = torch.randn((1, 2, 256, 256))
9 |
10 | x = GaussianFourierFeatureTransform(2, 50, 10)(x)
11 |
12 | assert x.shape == (1, 100, 256, 256)
13 |
14 |
15 | def test_nonsquare_tensor():
16 | x = torch.randn((1, 2, 256, 257))
17 |
18 | x = GaussianFourierFeatureTransform(2, 50, 10)(x)
19 |
20 | assert x.shape == (1, 100, 256, 257)
21 |
22 |
23 | def test_one_width_height():
24 | x = torch.randn((1, 2, 1, 1))
25 |
26 | x = GaussianFourierFeatureTransform(2, 50, 10)(x)
27 |
28 | assert x.shape == (1, 100, 1, 1)
29 |
30 |
31 | def test_wrong_num_dims():
32 | x = torch.randn((1, 2, 1))
33 |
34 | with pytest.raises(AssertionError) as excinfo:
35 | _ = GaussianFourierFeatureTransform(3, 50, 10)(x)
36 |
37 | assert "Expected 4D input (got 3D input)" in str(excinfo.value)
38 |
39 |
40 | def test_mismatched_input_channels():
41 | x = torch.randn((1, 2, 1, 1))
42 |
43 | with pytest.raises(AssertionError) as excinfo:
44 | _ = GaussianFourierFeatureTransform(3, 50, 10)(x)
45 |
46 | assert "Expected input to have 3 channels (got 2 channels)" in str(excinfo.value)
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------