\n", 10 | "Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch\n", 11 | "" 12 | ] 13 | }, 14 | { 15 | "cell_type": "code", 16 | "execution_count": 1, 17 | "id": "67f6f7ed-b67d-465b-bf6f-a99b0d996930", 18 | "metadata": {}, 19 | "outputs": [ 20 | { 21 | "name": "stdout", 22 | "output_type": "stream", 23 | "text": [ 24 | "[OK] Your Python version is 3.10.12\n", 25 | "[OK] numpy 1.26.0\n", 26 | "[OK] matplotlib 3.8.2\n", 27 | "[OK] jupyterlab 4.0.6\n", 28 | "[OK] tensorflow 2.15.0\n", 29 | "[OK] torch 2.2.1\n", 30 | "[OK] tqdm 4.66.1\n", 31 | "[OK] tiktoken 0.5.1\n" 32 | ] 33 | } 34 | ], 35 | "source": [ 36 | "from python_environment_check import check_packages, get_requirements_dict\n", 37 | "\n", 38 | "d = get_requirements_dict()\n", 39 | "check_packages(d)" 40 | ] 41 | } 42 | ], 43 | "metadata": { 44 | "kernelspec": { 45 | "display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)", 46 | "language": "python", 47 | "name": "python3" 48 | }, 49 | "language_info": { 50 | "codemirror_mode": { 51 | "name": "ipython", 52 | "version": 3 53 | }, 54 | "file_extension": ".py", 55 | "mimetype": "text/x-python", 56 | "name": "python", 57 | "nbconvert_exporter": "python", 58 | "pygments_lexer": "ipython3", 59 | "version": "3.10.6" 60 | } 61 | }, 62 | "nbformat": 4, 63 | "nbformat_minor": 5 64 | } 65 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch04/README.md: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Chapter 4: Implementing a GPT Model from Scratch to Generate Text 2 | 3 | 4 | ## Main Chapter Code 5 | 6 | - [01_main-chapter-code](01_main-chapter-code) contains the main chapter code. 7 | 8 | 9 | ## Bonus Materials 10 | 11 | - [02_performance-analysis](02_performance-analysis) contains optional code analyzing the performance of the GPT model(s) implemented in the main chapter 12 | - [03_kv-cache](03_kv-cache) implements a KV cache to speed up the text generation during inference 13 | - [07_moe](07_moe) explanation and implementation of Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) 14 | - [ch05/07_gpt_to_llama](../ch05/07_gpt_to_llama) contains a step-by-step guide for converting a GPT architecture implementation to Llama 3.2 and loads pretrained weights from Meta AI (it might be interesting to look at alternative architectures after completing chapter 4, but you can also save that for after reading chapter 5) 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | ## Attention Alternatives 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
 23 |
24 |
25 |
26 | - [04_gqa](04_gqa) contains an introduction to Grouped-Query Attention (GQA), which is used by most modern LLMs (Llama 4, gpt-oss, Qwen3, Gemma 3, and many more) as alternative to regular Multi-Head Attention (MHA)
27 | - [05_mla](05_mla) contains an introduction to Multi-Head Latent Attention (MLA), which is used by DeepSeek V3, as alternative to regular Multi-Head Attention (MHA)
28 | - [06_swa](06_swa) contains an introduction to Sliding Window Attention (SWA), which is used by Gemma 3 and others
29 | - [08_deltanet](08_deltanet) explanation of Gated DeltaNet as a popular linear attention variant (used in Qwen3-Next and Kimi Linear)
30 |
31 |
32 |
33 | ## More
34 |
35 | In the video below, I provide a code-along session that covers some of the chapter contents as supplementary material.
36 |
37 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 | - [04_gqa](04_gqa) contains an introduction to Grouped-Query Attention (GQA), which is used by most modern LLMs (Llama 4, gpt-oss, Qwen3, Gemma 3, and many more) as alternative to regular Multi-Head Attention (MHA)
27 | - [05_mla](05_mla) contains an introduction to Multi-Head Latent Attention (MLA), which is used by DeepSeek V3, as alternative to regular Multi-Head Attention (MHA)
28 | - [06_swa](06_swa) contains an introduction to Sliding Window Attention (SWA), which is used by Gemma 3 and others
29 | - [08_deltanet](08_deltanet) explanation of Gated DeltaNet as a popular linear attention variant (used in Qwen3-Next and Kimi Linear)
30 |
31 |
32 |
33 | ## More
34 |
35 | In the video below, I provide a code-along session that covers some of the chapter contents as supplementary material.
36 |
37 | 38 |
39 | 40 | [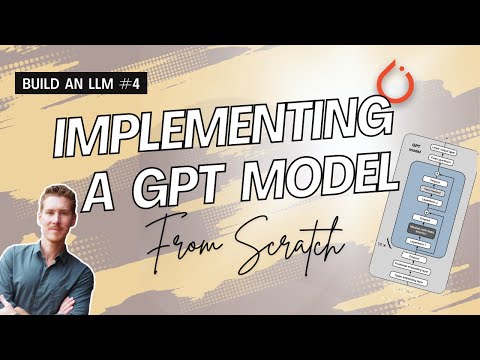](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YSAkgEarBGE) 41 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /pkg/llms_from_scratch/tests/test_appendix_a.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | from llms_from_scratch.appendix_a import NeuralNetwork, ToyDataset 7 | 8 | import torch 9 | import torch.nn.functional as F 10 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader 11 | 12 | 13 | def test_dataset(): 14 | 15 | X_train = torch.tensor([ 16 | [-1.2, 3.1], 17 | [-0.9, 2.9], 18 | [-0.5, 2.6], 19 | [2.3, -1.1], 20 | [2.7, -1.5] 21 | ]) 22 | 23 | y_train = torch.tensor([0, 0, 0, 1, 1]) 24 | train_ds = ToyDataset(X_train, y_train) 25 | 26 | len(train_ds) == 5 27 | torch.manual_seed(123) 28 | 29 | train_loader = DataLoader( 30 | dataset=train_ds, 31 | batch_size=2, 32 | shuffle=True, 33 | num_workers=0 34 | ) 35 | 36 | torch.manual_seed(123) 37 | model = NeuralNetwork(num_inputs=2, num_outputs=2) 38 | optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.5) 39 | 40 | num_epochs = 3 41 | 42 | for epoch in range(num_epochs): 43 | 44 | model.train() 45 | for batch_idx, (features, labels) in enumerate(train_loader): 46 | 47 | logits = model(features) 48 | 49 | loss = F.cross_entropy(logits, labels) 50 | 51 | optimizer.zero_grad() 52 | loss.backward() 53 | optimizer.step() 54 | 55 | print(f"Epoch: {epoch+1:03d}/{num_epochs:03d}" 56 | f" | Batch {batch_idx:03d}/{len(train_loader):03d}" 57 | f" | Train/Val Loss: {loss:.2f}") 58 | 59 | model.eval() 60 | with torch.no_grad(): 61 | outputs = model(X_train) 62 | 63 | expected = torch.tensor([ 64 | [2.8569, -4.1618], 65 | [2.5382, -3.7548], 66 | [2.0944, -3.1820], 67 | [-1.4814, 1.4816], 68 | [-1.7176, 1.7342] 69 | ]) 70 | torch.equal(outputs, expected) 71 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /pkg/llms_from_scratch/kv_cache_batched/generate.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | from ..generate import trim_input_tensor # noqa: F401 7 | from .utils import KVCache 8 | import torch 9 | 10 | 11 | def generate_text_simple(model, idx, max_new_tokens, context_size=None, use_cache=True): 12 | model.eval() 13 | ctx_len = context_size or model.cfg["context_length"] 14 | batch_size = idx.size(0) 15 | 16 | with torch.no_grad(): 17 | if use_cache: 18 | # initialize cache and positions 19 | cache = KVCache(n_layers=model.cfg["n_layers"], batch_size=batch_size) 20 | model.reset_kv_cache(batch_size=batch_size, device=idx.device) 21 | 22 | # initial full-context pass 23 | input_ids = idx[:, -ctx_len:] 24 | seq_len = input_ids.size(1) 25 | start_pos = model.current_pos.clone() 26 | logits = model( 27 | input_ids, 28 | cache=cache, 29 | start_pos=start_pos 30 | ) 31 | model.current_pos += seq_len 32 | 33 | # iterative generation 34 | for _ in range(max_new_tokens): 35 | next_token = logits[:, -1].argmax(dim=-1, keepdim=True) # (B, 1) 36 | logits = model( 37 | next_token, 38 | cache=cache, 39 | start_pos=model.current_pos.clone() 40 | ) 41 | model.current_pos += 1 42 | idx = torch.cat([idx, next_token], dim=1) 43 | else: 44 | # no cache 45 | for _ in range(max_new_tokens): 46 | input_ids = idx[:, -ctx_len:] 47 | logits = model(input_ids, cache=None, start_pos=None) 48 | next_token = logits[:, -1].argmax(dim=-1, keepdim=True) 49 | idx = torch.cat([idx, next_token], dim=1) 50 | 51 | return idx 52 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /.github/workflows/basic-tests-windows-uv.yml.disabled: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | name: Code tests Windows (uv) 2 | 3 | on: 4 | push: 5 | branches: [ main ] 6 | paths: 7 | - '**/*.py' 8 | - '**/*.ipynb' 9 | - '**/*.yaml' 10 | - '**/*.yml' 11 | - '**/*.sh' 12 | pull_request: 13 | branches: [ main ] 14 | paths: 15 | - '**/*.py' 16 | - '**/*.ipynb' 17 | - '**/*.yaml' 18 | - '**/*.yml' 19 | - '**/*.sh' 20 | 21 | jobs: 22 | test: 23 | runs-on: windows-latest 24 | 25 | steps: 26 | - name: Checkout Code 27 | uses: actions/checkout@v4 28 | 29 | - name: Set up Python 30 | uses: actions/setup-python@v5 31 | with: 32 | python-version: "3.13" 33 | 34 | - name: Install dependencies 35 | shell: pwsh 36 | run: | 37 | # Prepend local bin directory to PATH 38 | powershell -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -c "irm https://astral.sh/uv/install.ps1 | iex" 39 | $env:Path = "C:\Users\runneradmin\.local\bin;$env:Path" 40 | uv sync --dev --python=3.10 41 | $env:UV_PIP_OPTS="--no-binary tensorflow-io-gcs-filesystem" 42 | uv pip install -r requirements.txt 43 | uv pip install matplotlib # for some reason Windows requires this 44 | uv pip install -r ch05/07_gpt_to_llama/tests/test-requirements-extra.txt 45 | uv add pytest-ruff nbval 46 | 47 | - name: Run Python Tests 48 | shell: pwsh 49 | run: | 50 | . .\.venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1 51 | pytest --ruff setup/02_installing-python-libraries/tests.py 52 | pytest --ruff ch04/01_main-chapter-code/tests.py 53 | pytest --ruff ch05/01_main-chapter-code/tests.py 54 | pytest --ruff ch06/01_main-chapter-code/tests.py 55 | 56 | - name: Run Jupyter Notebook Tests 57 | shell: pwsh 58 | run: | 59 | . .\.venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1 60 | pytest --ruff --nbval ch02/01_main-chapter-code/dataloader.ipynb 61 | pytest --ruff --nbval ch03/01_main-chapter-code/multihead-attention.ipynb 62 | pytest --ruff --nbval ch02/04_bonus_dataloader-intuition/dataloader-intuition.ipynb 63 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /setup/04_optional-aws-sagemaker-notebook/README.md: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # AWS CloudFormation Template: Jupyter Notebook with LLMs-from-scratch Repo 2 | 3 | This CloudFormation template creates a GPU-enabled Jupyter notebook in Amazon SageMaker with an execution role and the LLMs-from-scratch GitHub repository. 4 | 5 | ## What it does: 6 | 7 | 1. Creates an IAM role with the necessary permissions for the SageMaker notebook instance. 8 | 2. Creates a KMS key and an alias for encrypting the notebook instance. 9 | 3. Configures a notebook instance lifecycle configuration script that: 10 | - Installs a separate Miniconda installation in the user's home directory. 11 | - Creates a custom Python environment with TensorFlow 2.15.0 and PyTorch 2.1.0, both with CUDA support. 12 | - Installs additional packages like Jupyter Lab, Matplotlib, and other useful libraries. 13 | - Registers the custom environment as a Jupyter kernel. 14 | 4. Creates the SageMaker notebook instance with the specified configuration, including the GPU-enabled instance type, the execution role, and the default code repository. 15 | 16 | ## How to use: 17 | 18 | 1. Download the CloudFormation template file (`cloudformation-template.yml`). 19 | 2. In the AWS Management Console, navigate to the CloudFormation service. 20 | 3. Create a new stack and upload the template file. 21 | 4. Provide a name for the notebook instance (e.g., "LLMsFromScratchNotebook") (defaults to the LLMs-from-scratch GitHub repo). 22 | 5. Review and accept the template's parameters, then create the stack. 23 | 6. Once the stack creation is complete, the SageMaker notebook instance will be available in the SageMaker console. 24 | 7. Open the notebook instance and start using the pre-configured environment to work on your LLMs-from-scratch projects. 25 | 26 | ## Key Points: 27 | 28 | - The template creates a GPU-enabled (`ml.g4dn.xlarge`) notebook instance with 50GB of storage. 29 | - It sets up a custom Miniconda environment with TensorFlow 2.15.0 and PyTorch 2.1.0, both with CUDA support. 30 | - The custom environment is registered as a Jupyter kernel, making it available for use in the notebook. 31 | - The template also creates a KMS key for encrypting the notebook instance and an IAM role with the necessary permissions. 32 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /pkg/llms_from_scratch/kv_cache/generate.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | from ..generate import trim_input_tensor # noqa: F401 7 | from .utils import KVCache 8 | import torch 9 | 10 | 11 | def generate_text_simple(model, idx, max_new_tokens, context_size=None, use_cache=True): 12 | model.eval() 13 | ctx_len = context_size or model.cfg["context_length"] 14 | 15 | with torch.no_grad(): 16 | if use_cache: 17 | cache = KVCache(n_layers=model.cfg["n_layers"]) 18 | model.reset_kv_cache() 19 | logits = model(idx[:, -ctx_len:], cache=cache) 20 | 21 | for _ in range(max_new_tokens): 22 | next_idx = logits[:, -1].argmax(dim=-1, keepdim=True) 23 | idx = torch.cat([idx, next_idx], dim=1) 24 | logits = model(next_idx, cache=cache) 25 | else: 26 | for _ in range(max_new_tokens): 27 | logits = model(idx[:, -ctx_len:], cache=None) 28 | next_idx = logits[:, -1].argmax(dim=-1, keepdim=True) 29 | idx = torch.cat([idx, next_idx], dim=1) 30 | 31 | return idx 32 | 33 | 34 | def generate_text_simple_stream(model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=None, context_size=None): 35 | model.eval() 36 | 37 | with torch.no_grad(): 38 | cache = KVCache(n_layers=model.cfg["n_layers"]) 39 | model.reset_kv_cache() 40 | 41 | # Prime the cache with the initial context 42 | logits = model(token_ids, cache=cache) 43 | 44 | for _ in range(max_new_tokens): 45 | next_token = torch.argmax(logits[:, -1], dim=-1, keepdim=True) 46 | 47 | if eos_token_id is not None and torch.all(next_token == eos_token_id): 48 | break 49 | 50 | yield next_token 51 | 52 | token_ids = torch.cat([token_ids, next_token], dim=1) 53 | 54 | # Feed only the new token to the model; cache handles history 55 | logits = model(next_token, cache=cache) 56 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /pyproject.toml: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | [build-system] 2 | requires = ["setuptools>=61.0", "wheel"] 3 | build-backend = "setuptools.build_meta" 4 | 5 | [project] 6 | name = "llms-from-scratch" 7 | version = "1.0.18" 8 | description = "Implement a ChatGPT-like LLM in PyTorch from scratch, step by step" 9 | readme = "README.md" 10 | requires-python = ">=3.10,<3.14" 11 | dependencies = [ 12 | 'torch>=2.6; python_version >= "3.13"', 13 | "torch>=2.2.2,<2.6; sys_platform == 'darwin' and platform_machine == 'x86_64' and python_version < '3.12'", 14 | "torch>=2.2.2; sys_platform == 'darwin' and platform_machine == 'arm64' and python_version < '3.12'", 15 | "torch>=2.2.2; sys_platform == 'linux' and python_version < '3.12'", 16 | "torch>=2.2.2; sys_platform == 'win32' and python_version < '3.12'", 17 | 18 | "tensorflow>=2.16.2; sys_platform == 'darwin' and platform_machine == 'x86_64'", 19 | "tensorflow>=2.18.0; sys_platform == 'darwin' and platform_machine == 'arm64'", 20 | "tensorflow>=2.18.0; sys_platform == 'linux'", 21 | "tensorflow>=2.18.0; sys_platform == 'win32'", 22 | 23 | "jupyterlab>=4.0", 24 | "tiktoken>=0.5.1", 25 | "matplotlib>=3.7.1", 26 | "tqdm>=4.66.1", 27 | "numpy>=1.26", 28 | "pandas>=2.2.1", 29 | "pip>=25.0.1", 30 | "pytest>=8.3.5", 31 | ] 32 | 33 | [tool.uv.sources] 34 | llms-from-scratch = { workspace = true } 35 | 36 | [dependency-groups] 37 | dev = [ 38 | "build>=1.2.2.post1", 39 | "twine>=6.1.0", 40 | "tokenizers>=0.22.0", 41 | "safetensors>=0.6.2", 42 | ] 43 | bonus = [ 44 | "blobfile>=3.0.0", 45 | "chainlit>=1.2.0", 46 | "huggingface_hub>=0.34.4", 47 | "ipywidgets>=8.1.2", 48 | "llms_from_scratch>=1.0.18", 49 | "openai>=1.30.3", 50 | "requests", 51 | "safetensors>=0.6.2", 52 | "scikit-learn>=1.3.1", 53 | "sentencepiece>=0.1.99", 54 | "thop", 55 | "tokenizers>=0.21.1", 56 | "transformers>=4.33.2", 57 | "tqdm>=4.65.0", 58 | ] 59 | 60 | [tool.ruff] 61 | line-length = 140 62 | 63 | [tool.ruff.lint] 64 | exclude = [".venv"] 65 | ignore = [ 66 | "C406", "E226", "E402", "E702", "E703", 67 | "E722", "E731", "E741" 68 | ] 69 | 70 | # `llms_from_scratch` PyPI package 71 | [tool.setuptools] 72 | package-dir = {"" = "pkg"} 73 | 74 | [tool.setuptools.packages.find] 75 | where = ["pkg"] 76 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /.github/workflows/basic-tests-macos-uv.yml: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | name: Code tests macOS 2 | 3 | on: 4 | push: 5 | branches: [ main ] 6 | paths: 7 | - '**/*.py' 8 | - '**/*.ipynb' 9 | - '**/*.yaml' 10 | - '**/*.yml' 11 | - '**/*.sh' 12 | pull_request: 13 | branches: [ main ] 14 | paths: 15 | - '**/*.py' 16 | - '**/*.ipynb' 17 | - '**/*.yaml' 18 | - '**/*.yml' 19 | - '**/*.sh' 20 | workflow_dispatch: 21 | 22 | concurrency: 23 | group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.ref }} 24 | cancel-in-progress: true 25 | 26 | jobs: 27 | uv-tests: 28 | name: Code tests (macOS) 29 | runs-on: macos-latest 30 | steps: 31 | - uses: actions/checkout@v4 32 | 33 | - name: Set up Python (uv) 34 | uses: actions/setup-python@v5 35 | with: 36 | python-version: "3.13" 37 | 38 | - name: Install uv and dependencies 39 | shell: bash 40 | run: | 41 | curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh 42 | uv sync --dev --python=3.10 # tests for backwards compatibility 43 | uv pip install -r ch05/07_gpt_to_llama/tests/test-requirements-extra.txt 44 | uv add pytest-ruff nbval 45 | 46 | - name: Test Selected Python Scripts (uv) 47 | shell: bash 48 | run: | 49 | source .venv/bin/activate 50 | pytest setup/02_installing-python-libraries/tests.py 51 | pytest ch04/01_main-chapter-code/tests.py 52 | pytest ch05/01_main-chapter-code/tests.py 53 | pytest ch05/07_gpt_to_llama/tests/tests_rope_and_parts.py 54 | pytest ch05/07_gpt_to_llama/tests/test_llama32_nb.py 55 | pytest ch05/11_qwen3/tests/test_qwen3_nb.py 56 | pytest ch05/12_gemma3/tests/test_gemma3_nb.py 57 | pytest ch05/12_gemma3/tests/test_gemma3_kv_nb.py 58 | pytest ch06/01_main-chapter-code/tests.py 59 | 60 | - name: Validate Selected Jupyter Notebooks (uv) 61 | shell: bash 62 | run: | 63 | source .venv/bin/activate 64 | pytest --nbval ch02/01_main-chapter-code/dataloader.ipynb 65 | pytest --nbval ch03/01_main-chapter-code/multihead-attention.ipynb 66 | pytest --nbval ch02/04_bonus_dataloader-intuition/dataloader-intuition.ipynb 67 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /.github/workflows/basic-tests-windows-uv-pip.yml: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | name: Code tests Windows (uv/pip) 2 | 3 | on: 4 | push: 5 | branches: [ main ] 6 | paths: 7 | - '**/*.py' 8 | - '**/*.ipynb' 9 | - '**/*.yaml' 10 | - '**/*.yml' 11 | - '**/*.sh' 12 | pull_request: 13 | branches: [ main ] 14 | paths: 15 | - '**/*.py' 16 | - '**/*.ipynb' 17 | - '**/*.yaml' 18 | - '**/*.yml' 19 | - '**/*.sh' 20 | 21 | jobs: 22 | test: 23 | runs-on: windows-latest 24 | 25 | steps: 26 | - name: Checkout Code 27 | uses: actions/checkout@v4 28 | 29 | - name: Set up Python 30 | uses: actions/setup-python@v5 31 | with: 32 | python-version: '3.11' 33 | 34 | - name: Install dependencies 35 | shell: bash 36 | run: | 37 | export PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$PATH" 38 | python -m pip install --upgrade pip 39 | pip install uv 40 | uv venv --python=python3.11 41 | source .venv/Scripts/activate 42 | pip install -r requirements.txt # because of dependency issue on Windows when using `uv pip` 43 | pip install tensorflow-io-gcs-filesystem==0.31.0 # Explicit for Windows 44 | pip install -r ch05/07_gpt_to_llama/tests/test-requirements-extra.txt 45 | pip install pytest-ruff nbval 46 | pip install -e . 47 | 48 | - name: Run Python Tests 49 | shell: bash 50 | run: | 51 | source .venv/Scripts/activate 52 | pytest setup/02_installing-python-libraries/tests.py 53 | pytest ch04/01_main-chapter-code/tests.py 54 | pytest ch05/01_main-chapter-code/tests.py 55 | pytest ch05/07_gpt_to_llama/tests/tests_rope_and_parts.py 56 | pytest ch05/07_gpt_to_llama/tests/test_llama32_nb.py 57 | pytest ch05/11_qwen3/tests/test_qwen3_nb.py 58 | pytest ch06/01_main-chapter-code/tests.py 59 | 60 | - name: Run Jupyter Notebook Tests 61 | shell: bash 62 | run: | 63 | source .venv/Scripts/activate 64 | pytest --nbval ch02/01_main-chapter-code/dataloader.ipynb 65 | pytest --nbval ch03/01_main-chapter-code/multihead-attention.ipynb 66 | pytest --nbval ch02/04_bonus_dataloader-intuition/dataloader-intuition.ipynb -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /.github/workflows/basic-tests-windows-uv-pip.yml.disabled: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | name: Code tests Windows (uv/pip) 2 | 3 | on: 4 | push: 5 | branches: [ main ] 6 | paths: 7 | - '**/*.py' 8 | - '**/*.ipynb' 9 | - '**/*.yaml' 10 | - '**/*.yml' 11 | - '**/*.sh' 12 | pull_request: 13 | branches: [ main ] 14 | paths: 15 | - '**/*.py' 16 | - '**/*.ipynb' 17 | - '**/*.yaml' 18 | - '**/*.yml' 19 | - '**/*.sh' 20 | 21 | jobs: 22 | test: 23 | runs-on: windows-latest 24 | 25 | steps: 26 | - name: Checkout Code 27 | uses: actions/checkout@v4 28 | 29 | - name: Set up Python 30 | uses: actions/setup-python@v5 31 | with: 32 | python-version: "3.13" 33 | 34 | - name: Install dependencies 35 | shell: pwsh 36 | run: | 37 | $env:Path = "C:\Users\runneradmin\.local\bin;$env:Path" 38 | python -m pip install --upgrade pip 39 | python -m pip install uv 40 | uv venv --python=python3.11 41 | . .\.venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1 42 | $env:UV_PIP_OPTS="--no-binary tensorflow-io-gcs-filesystem" 43 | uv pip install -r requirements.txt 44 | uv pip install -r ch05/07_gpt_to_llama/tests/test-requirements-extra.txt 45 | uv pip install pytest-ruff nbval 46 | uv pip install --force-reinstall matplotlib "numpy<2.1" 47 | 48 | - name: Run Python Tests 49 | shell: pwsh 50 | run: | 51 | $env:Path = "C:\Users\runneradmin\.local\bin;$env:Path" 52 | . .\.venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1 53 | pytest --ruff setup/02_installing-python-libraries/tests.py 54 | pytest --ruff ch04/01_main-chapter-code/tests.py 55 | pytest --ruff ch05/01_main-chapter-code/tests.py 56 | pytest --ruff ch05/07_gpt_to_llama/tests/tests.py 57 | pytest --ruff ch06/01_main-chapter-code/tests.py 58 | 59 | - name: Run Jupyter Notebook Tests 60 | shell: pwsh 61 | run: | 62 | $env:Path = "C:\Users\runneradmin\.local\bin;$env:Path" 63 | . .\.venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1 64 | pytest --ruff --nbval ch02/01_main-chapter-code/dataloader.ipynb 65 | pytest --ruff --nbval ch03/01_main-chapter-code/multihead-attention.ipynb 66 | pytest --ruff --nbval ch02/04_bonus_dataloader-intuition/dataloader-intuition.ipynb 67 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch05/README.md: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Chapter 5: Pretraining on Unlabeled Data 2 | 3 | 4 | ## Main Chapter Code 5 | 6 | - [01_main-chapter-code](01_main-chapter-code) contains the main chapter code 7 | 8 | 9 | ## Bonus Materials 10 | 11 | - [02_alternative_weight_loading](02_alternative_weight_loading) contains code to load the GPT model weights from alternative places in case the model weights become unavailable from OpenAI 12 | - [03_bonus_pretraining_on_gutenberg](03_bonus_pretraining_on_gutenberg) contains code to pretrain the LLM longer on the whole corpus of books from Project Gutenberg 13 | - [04_learning_rate_schedulers](04_learning_rate_schedulers) contains code implementing a more sophisticated training function including learning rate schedulers and gradient clipping 14 | - [05_bonus_hparam_tuning](05_bonus_hparam_tuning) contains an optional hyperparameter tuning script 15 | - [06_user_interface](06_user_interface) implements an interactive user interface to interact with the pretrained LLM 16 | - [08_memory_efficient_weight_loading](08_memory_efficient_weight_loading) contains a bonus notebook showing how to load model weights via PyTorch's `load_state_dict` method more efficiently 17 | - [09_extending-tokenizers](09_extending-tokenizers) contains a from-scratch implementation of the GPT-2 BPE tokenizer 18 | - [10_llm-training-speed](10_llm-training-speed) shows PyTorch performance tips to improve the LLM training speed 19 | 20 | 21 | ## LLM Architectures From Scratch 22 | 23 |
 24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 | - [07_gpt_to_llama](07_gpt_to_llama) contains a step-by-step guide for converting a GPT architecture implementation to Llama 3.2 and loads pretrained weights from Meta AI
29 | - [11_qwen3](11_qwen3) A from-scratch implementation of Qwen3 0.6B and Qwen3 30B-A3B (Mixture-of-Experts) including code to load the pretrained weights of the base, reasoning, and coding model variants
30 | - [12_gemma3](12_gemma3) A from-scratch implementation of Gemma 3 270M and alternative with KV cache, including code to load the pretrained weights
31 | - [13_olmo3](13_olmo3) A from-scratch implementation of Olmo 3 7B and 32B (Base, Instruct, and Think variants) and alternative with KV cache, including code to load the pretrained weights
32 |
33 |
34 | ## Code-Along Video for This Chapter
35 |
36 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 | - [07_gpt_to_llama](07_gpt_to_llama) contains a step-by-step guide for converting a GPT architecture implementation to Llama 3.2 and loads pretrained weights from Meta AI
29 | - [11_qwen3](11_qwen3) A from-scratch implementation of Qwen3 0.6B and Qwen3 30B-A3B (Mixture-of-Experts) including code to load the pretrained weights of the base, reasoning, and coding model variants
30 | - [12_gemma3](12_gemma3) A from-scratch implementation of Gemma 3 270M and alternative with KV cache, including code to load the pretrained weights
31 | - [13_olmo3](13_olmo3) A from-scratch implementation of Olmo 3 7B and 32B (Base, Instruct, and Think variants) and alternative with KV cache, including code to load the pretrained weights
32 |
33 |
34 | ## Code-Along Video for This Chapter
35 |
36 | 37 |
38 | 39 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Zar2TJv-sE0) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch07/02_dataset-utilities/README.md: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Chapter 7: Finetuning to Follow Instructions 2 | 3 | This folder contains utility code that can be used for preparing an instruction dataset. 4 | 5 | Install the additional package requirements via: 6 | 7 | ```bash 8 | pip install -r requirements-extra.txt 9 | ``` 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | ### Finding Near Duplicates 16 | 17 | The `find-near-duplicates.py` function can be used to identify duplicates and near-duplicates in an instruction dataset. For example, 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | ```bash 22 | python find-near-duplicates.py --json_file instruction-examples.json 23 | ``` 24 | 25 | ``` 26 | scikit-learn version: 1.3.1 27 | 28 | 29 | ================================================== 30 | Searching 'instruction' for duplicates ... 31 | ================================================== 32 | Duplicate pair found with similarity 0.94: 33 | 1. Edit the following sentence to make it more formal. 34 | 2. Edit the sentence to make it more formal. 35 | 36 | Duplicate pair found with similarity 1.00: 37 | 1. Name a dwarf planet in our solar system. 38 | 2. Name a dwarf planet in our solar system. 39 | 40 | Duplicate pair found with similarity 0.91: 41 | 1. Change the sentences from active voice to passive voice. 42 | 2. Change the sentence from passive to active voice. 43 | 44 | 45 | 46 | ================================================== 47 | Searching 'input' for duplicates ... 48 | ================================================== 49 | No duplicates found 50 | 51 | 52 | ================================================== 53 | Searching 'output' for duplicates ... 54 | ================================================== 55 | Duplicate pair found with similarity 1.00: 56 | 1. One dwarf planet in our solar system is Pluto. 57 | 2. One dwarf planet in our solar system is Pluto. 58 | 59 | 60 | ``` 61 | 62 | 63 | You can use the `--threshold` setting with a value between 0 and 1 to decrease or increase the sensitivity. 64 | The default threshold is 0.9. 65 | 66 | 67 | 68 | 69 | ## Creating Passive Voice Entries 70 | 71 | - The [create-passive-voice-entries.ipynb](create-passive-voice-entries.ipynb) notebook uses OpenAI's GPT-4 to create "passive voice" entries for an instruction dataset, as shown in the example below 72 | 73 | ```python 74 | { 75 | 'instruction': 'Identify the verb in the following sentence', 76 | 'input': 'The cat sleeps on the couch.', 77 | 'output': 'The verb in the sentence is "sleeps."', 78 | 'output_2': 'The sentence is "sleeps."' # <---- Newly created entry 79 | } 80 | ``` 81 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /pkg/llms_from_scratch/tests/test_ch04.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | from llms_from_scratch.ch04 import GPTModel, GPTModelFast 7 | from llms_from_scratch.kv_cache.gpt2 import GPTModel as GPTModelKV 8 | from llms_from_scratch.ch04 import generate_text_simple 9 | from llms_from_scratch.kv_cache.generate import generate_text_simple as generate_text_simple_cached 10 | 11 | import pytest 12 | import torch 13 | import tiktoken 14 | 15 | 16 | GPT_CONFIG_124M = { 17 | "vocab_size": 50257, # Vocabulary size 18 | "context_length": 1024, # Context length 19 | "emb_dim": 768, # Embedding dimension 20 | "n_heads": 12, # Number of attention heads 21 | "n_layers": 12, # Number of layers 22 | "drop_rate": 0.1, # Dropout rate 23 | "qkv_bias": False # Query-Key-Value bias 24 | } 25 | 26 | 27 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("ModelClass", [GPTModel, GPTModelFast, GPTModelKV]) 28 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("generate_fn", [generate_text_simple, generate_text_simple_cached]) 29 | def test_gpt_model_variants(ModelClass, generate_fn): 30 | 31 | # Skip incompatible combinations 32 | if generate_fn is generate_text_simple and getattr(ModelClass, "reset_kv_cache", False): 33 | return 34 | if generate_fn is generate_text_simple_cached and not getattr(ModelClass, "reset_kv_cache", False): 35 | return 36 | 37 | torch.manual_seed(123) 38 | model = ModelClass(GPT_CONFIG_124M) 39 | model.eval() # disable dropout 40 | 41 | start_context = "Hello, I am" 42 | 43 | tokenizer = tiktoken.get_encoding("gpt2") 44 | encoded = tokenizer.encode(start_context) 45 | encoded_tensor = torch.tensor(encoded).unsqueeze(0) 46 | 47 | print(f"\n{50*'='}\n{22*' '}IN\n{50*'='}") 48 | print("\nInput text:", start_context) 49 | print("Encoded input text:", encoded) 50 | print("encoded_tensor.shape:", encoded_tensor.shape) 51 | 52 | out = generate_fn( 53 | model=model, 54 | idx=encoded_tensor, 55 | max_new_tokens=10, 56 | context_size=GPT_CONFIG_124M["context_length"] 57 | ) 58 | 59 | expect = torch.tensor([ 60 | [15496, 11, 314, 716, 27018, 24086, 47843, 30961, 42348, 7267, 61 | 49706, 43231, 47062, 34657] 62 | ]) 63 | assert torch.equal(expect, out), "Generated output does not match expected output" 64 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch04/04_gqa/plot_memory_estimates_gqa.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | # Plot KV-cache vs context length for different n_kv_groups 7 | 8 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 9 | 10 | # Import from ./memory_estimator.py 11 | from memory_estimator_gqa import kv_bytes_total, DTYPE_BYTES 12 | 13 | 14 | def bytes_convert(n): 15 | gb = n / (1000 ** 3) 16 | return f"{gb:.2f}" 17 | 18 | 19 | def savings_percent(total_mha, total_gqa): 20 | return (1.0 - (total_gqa / total_mha)) * 100.0 21 | 22 | 23 | def plot_abs_kv_vs_context_multi_groups(): 24 | n_heads = 24 25 | emb_dim = 2048 26 | n_layers = 48 27 | batch_size = 1 28 | dtype = "bf16" 29 | bytes_per_elem = DTYPE_BYTES[dtype] 30 | 31 | # x-axis (log scale) 32 | context_lengths = [ 33 | 256, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192, 34 | 16384, 32768, 65536, 131072 35 | ] 36 | 37 | mha_gb = [] 38 | for L in context_lengths: 39 | total_mha = kv_bytes_total( 40 | batch_size, L, emb_dim, n_heads, 41 | n_heads, # MHA: n_kv_heads = n_heads 42 | n_layers, bytes_per_elem 43 | ) 44 | mha_gb.append(float(bytes_convert(total_mha))) 45 | 46 | plt.figure() 47 | plt.plot(context_lengths, mha_gb, marker="o", label="MHA (KV total)") 48 | 49 | # GQA curves for selected n_kv_groups 50 | groups_list = [4, 8, 12, 24] 51 | for g in groups_list: 52 | n_kv_heads = n_heads // g 53 | gqa_gb = [] 54 | for L in context_lengths: 55 | total_gqa = kv_bytes_total( 56 | batch_size, L, emb_dim, n_heads, 57 | n_kv_heads, n_layers, bytes_per_elem 58 | ) 59 | gqa_gb.append(float(bytes_convert(total_gqa))) 60 | 61 | # Compression rate relative to MHA 62 | comp = (n_heads / n_kv_heads) if n_kv_heads > 0 else float("inf") 63 | plt.plot(context_lengths, gqa_gb, marker="o", 64 | label=f"GQA (n_kv_groups={g}, {comp:,.1f}× compression)") 65 | 66 | plt.xscale("log") 67 | plt.xlabel("context_length (log scale)") 68 | plt.ylabel("Total KV cache (GB)") 69 | plt.title( 70 | "KV-cache vs Context Length — MHA vs GQA (multi-group)\n" 71 | "(n_heads=24, emb_dim=2048, n_layers=48, batch=1, dtype=bf16)", 72 | fontsize=8 73 | ) 74 | plt.grid(True, which="both") 75 | plt.legend() 76 | plt.tight_layout() 77 | plt.savefig("kv_bytes_vs_context_length.pdf") 78 | 79 | 80 | if __name__ == "__main__": 81 | plot_abs_kv_vs_context_multi_groups() 82 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch05/12_gemma3/README.md: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Gemma 3 270M From Scratch 2 | 3 | This [standalone-gemma3.ipynb](standalone-gemma3.ipynb) Jupyter notebook in this folder contains a from-scratch implementation of Gemma 3 270M. It requires about 2 GB of RAM to run. 4 | 5 | The alternative [standalone-gemma3-plus-kvcache.ipynb](standalone-gemma3-plus-kvcache.ipynb) notebook adds a KV cache for better runtime performance (but adds more code complexity). To learn more about KV caching, see my [Understanding and Coding the KV Cache in LLMs from Scratch](https://magazine.sebastianraschka.com/p/coding-the-kv-cache-in-llms) article. 6 | 7 | | Model | Mode | Hardware | Tokens/sec | GPU Memory (VRAM) | 8 | | ----------------- | ----------------- | --------------- | ---------- | ----------------- | 9 | | Gemma3Model 270M | Regular | Mac Mini M4 CPU | 8 | - | 10 | | Gemma3Model 270M | Regular compiled | Mac Mini M4 CPU | 9 | - | 11 | | Gemma3Model 270M | KV cache | Mac Mini M4 CPU | 130 | - | 12 | | Gemma3Model 270M | KV cache compiled | Mac Mini M4 CPU | 224 | - | 13 | | | | | | | 14 | | Gemma3Model 270M | Regular | Mac Mini M4 GPU | 16 | - | 15 | | Gemma3Model 270M | Regular compiled | Mac Mini M4 GPU | Error | - | 16 | | Gemma3Model 270M | KV cache | Mac Mini M4 GPU | 23 | - | 17 | | Gemma3Model 270M | KV cache compiled | Mac Mini M4 GPU | Error | - | 18 | | | | | | | 19 | | Gemma3Model 270M | Regular | Nvidia A100 GPU | 28 | 1.84 GB | 20 | | Gemma3Model 270M | Regular compiled | Nvidia A100 GPU | 128 | 2.12 GB | 21 | | Gemma3Model 270M | KV cache | Nvidia A100 GPU | 26 | 1.77 GB | 22 | | Gemma3Model 270M | KV cache compiled | Nvidia A100 GPU | 99 | 2.12 GB | 23 | 24 | 25 | Below is a side-by-side comparison with Qwen3 0.6B as a reference model; if you are interested in the Qwen3 0.6B standalone notebook, you can find it [here](../11_qwen3). 26 | 27 |
28 | 29 |
 30 |
31 |
30 |
31 | 32 | 33 | To learn more about the architecture differences and read about comparisons with other architectures, see my [The Big LLM Architecture Comparison: From DeepSeek-V3 to Kimi K2: A Look At Modern LLM Architecture Design](https://magazine.sebastianraschka.com/p/the-big-llm-architecture-comparison) article. 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch05/07_gpt_to_llama/previous_chapters.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | # 6 | # This file collects all the relevant code that we covered thus far 7 | # throughout Chapters 2-4. 8 | # This file can be run as a standalone script. 9 | 10 | import torch 11 | 12 | 13 | ##################################### 14 | # Chapter 5 15 | ##################################### 16 | def text_to_token_ids(text, tokenizer): 17 | encoded = tokenizer.encode(text) 18 | encoded_tensor = torch.tensor(encoded).unsqueeze(0) # add batch dimension 19 | return encoded_tensor 20 | 21 | 22 | def token_ids_to_text(token_ids, tokenizer): 23 | flat = token_ids.squeeze(0) # remove batch dimension 24 | return tokenizer.decode(flat.tolist()) 25 | 26 | 27 | def generate(model, idx, max_new_tokens, context_size, temperature=0.0, top_k=None, eos_id=None): 28 | 29 | # For-loop is the same as before: Get logits, and only focus on last time step 30 | for _ in range(max_new_tokens): 31 | idx_cond = idx[:, -context_size:] 32 | with torch.no_grad(): 33 | logits = model(idx_cond) 34 | logits = logits[:, -1, :] 35 | 36 | # New: Filter logits with top_k sampling 37 | if top_k is not None: 38 | # Keep only top_k values 39 | top_logits, _ = torch.topk(logits, top_k) 40 | min_val = top_logits[:, -1] 41 | logits = torch.where(logits < min_val, torch.tensor(float("-inf")).to(logits.device), logits) 42 | 43 | # New: Apply temperature scaling 44 | if temperature > 0.0: 45 | logits = logits / temperature 46 | 47 | # New (not in book): numerical stability tip to get equivalent results on mps device 48 | # subtract rowwise max before softmax 49 | logits = logits - logits.max(dim=-1, keepdim=True).values 50 | 51 | # Apply softmax to get probabilities 52 | probs = torch.softmax(logits, dim=-1) # (batch_size, context_len) 53 | 54 | # Sample from the distribution 55 | idx_next = torch.multinomial(probs, num_samples=1) # (batch_size, 1) 56 | 57 | # Otherwise same as before: get idx of the vocab entry with the highest logits value 58 | else: 59 | idx_next = torch.argmax(logits, dim=-1, keepdim=True) # (batch_size, 1) 60 | 61 | if idx_next == eos_id: # Stop generating early if end-of-sequence token is encountered and eos_id is specified 62 | break 63 | 64 | # Same as before: append sampled index to the running sequence 65 | idx = torch.cat((idx, idx_next), dim=1) # (batch_size, num_tokens+1) 66 | 67 | return idx 68 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch06/04_user_interface/app.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | from pathlib import Path 7 | import sys 8 | 9 | import tiktoken 10 | import torch 11 | import chainlit 12 | 13 | # For llms_from_scratch installation instructions, see: 14 | # https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/tree/main/pkg 15 | from llms_from_scratch.ch04 import GPTModel 16 | from llms_from_scratch.ch06 import classify_review 17 | 18 | 19 | device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") 20 | 21 | 22 | def get_model_and_tokenizer(): 23 | """ 24 | Code to load finetuned GPT-2 model generated in chapter 6. 25 | This requires that you run the code in chapter 6 first, which generates the necessary model.pth file. 26 | """ 27 | 28 | GPT_CONFIG_124M = { 29 | "vocab_size": 50257, # Vocabulary size 30 | "context_length": 1024, # Context length 31 | "emb_dim": 768, # Embedding dimension 32 | "n_heads": 12, # Number of attention heads 33 | "n_layers": 12, # Number of layers 34 | "drop_rate": 0.1, # Dropout rate 35 | "qkv_bias": True # Query-key-value bias 36 | } 37 | 38 | tokenizer = tiktoken.get_encoding("gpt2") 39 | 40 | model_path = Path("..") / "01_main-chapter-code" / "review_classifier.pth" 41 | if not model_path.exists(): 42 | print( 43 | f"Could not find the {model_path} file. Please run the chapter 6 code" 44 | " (ch06.ipynb) to generate the review_classifier.pth file." 45 | ) 46 | sys.exit() 47 | 48 | # Instantiate model 49 | model = GPTModel(GPT_CONFIG_124M) 50 | 51 | # Convert model to classifier as in section 6.5 in ch06.ipynb 52 | num_classes = 2 53 | model.out_head = torch.nn.Linear(in_features=GPT_CONFIG_124M["emb_dim"], out_features=num_classes) 54 | 55 | # Then load model weights 56 | checkpoint = torch.load(model_path, map_location=device, weights_only=True) 57 | model.load_state_dict(checkpoint) 58 | model.to(device) 59 | model.eval() 60 | 61 | return tokenizer, model 62 | 63 | 64 | # Obtain the necessary tokenizer and model files for the chainlit function below 65 | tokenizer, model = get_model_and_tokenizer() 66 | 67 | 68 | @chainlit.on_message 69 | async def main(message: chainlit.Message): 70 | """ 71 | The main Chainlit function. 72 | """ 73 | user_input = message.content 74 | 75 | label = classify_review(user_input, model, tokenizer, device, max_length=120) 76 | 77 | await chainlit.Message( 78 | content=f"{label}", # This returns the model response to the interface 79 | ).send() 80 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch05/06_user_interface/app_own.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | from pathlib import Path 7 | import sys 8 | 9 | import tiktoken 10 | import torch 11 | import chainlit 12 | 13 | # For llms_from_scratch installation instructions, see: 14 | # https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/tree/main/pkg 15 | from llms_from_scratch.ch04 import GPTModel 16 | from llms_from_scratch.ch05 import ( 17 | generate, 18 | text_to_token_ids, 19 | token_ids_to_text, 20 | ) 21 | 22 | 23 | device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") 24 | 25 | 26 | def get_model_and_tokenizer(): 27 | """ 28 | Code to load a GPT-2 model with pretrained weights generated in chapter 5. 29 | This requires that you run the code in chapter 5 first, which generates the necessary model.pth file. 30 | """ 31 | 32 | GPT_CONFIG_124M = { 33 | "vocab_size": 50257, # Vocabulary size 34 | "context_length": 256, # Shortened context length (orig: 1024) 35 | "emb_dim": 768, # Embedding dimension 36 | "n_heads": 12, # Number of attention heads 37 | "n_layers": 12, # Number of layers 38 | "drop_rate": 0.1, # Dropout rate 39 | "qkv_bias": False # Query-key-value bias 40 | } 41 | 42 | tokenizer = tiktoken.get_encoding("gpt2") 43 | 44 | model_path = Path("..") / "01_main-chapter-code" / "model.pth" 45 | if not model_path.exists(): 46 | print(f"Could not find the {model_path} file. Please run the chapter 5 code (ch05.ipynb) to generate the model.pth file.") 47 | sys.exit() 48 | 49 | checkpoint = torch.load(model_path, weights_only=True) 50 | model = GPTModel(GPT_CONFIG_124M) 51 | model.load_state_dict(checkpoint) 52 | model.to(device) 53 | 54 | return tokenizer, model, GPT_CONFIG_124M 55 | 56 | 57 | # Obtain the necessary tokenizer and model files for the chainlit function below 58 | tokenizer, model, model_config = get_model_and_tokenizer() 59 | 60 | 61 | @chainlit.on_message 62 | async def main(message: chainlit.Message): 63 | """ 64 | The main Chainlit function. 65 | """ 66 | token_ids = generate( # function uses `with torch.no_grad()` internally already 67 | model=model, 68 | idx=text_to_token_ids(message.content, tokenizer).to(device), # The user text is provided via as `message.content` 69 | max_new_tokens=50, 70 | context_size=model_config["context_length"], 71 | top_k=1, 72 | temperature=0.0 73 | ) 74 | 75 | text = token_ids_to_text(token_ids, tokenizer) 76 | 77 | await chainlit.Message( 78 | content=f"{text}", # This returns the model response to the interface 79 | ).send() 80 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /.github/workflows/basic-tests-linux-uv.yml: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | name: Code tests Linux 2 | 3 | on: 4 | push: 5 | branches: [ main ] 6 | paths: 7 | - '**/*.py' 8 | - '**/*.ipynb' 9 | - '**/*.yaml' 10 | - '**/*.yml' 11 | - '**/*.sh' 12 | pull_request: 13 | branches: [ main ] 14 | paths: 15 | - '**/*.py' 16 | - '**/*.ipynb' 17 | - '**/*.yaml' 18 | - '**/*.yml' 19 | - '**/*.sh' 20 | workflow_dispatch: 21 | 22 | concurrency: 23 | group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.ref }} 24 | cancel-in-progress: true 25 | 26 | jobs: 27 | uv-tests: 28 | name: Code tests (Linux) 29 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest 30 | steps: 31 | - uses: actions/checkout@v4 32 | 33 | - name: Set up Python (uv) 34 | uses: actions/setup-python@v5 35 | with: 36 | python-version: "3.13" 37 | 38 | - name: Install uv and dependencies 39 | shell: bash 40 | run: | 41 | curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh 42 | uv sync --dev # tests for backwards compatibility 43 | uv pip install -r ch05/07_gpt_to_llama/tests/test-requirements-extra.txt 44 | uv add pytest-ruff nbval 45 | 46 | - name: Test Selected Python Scripts (uv) 47 | shell: bash 48 | run: | 49 | source .venv/bin/activate 50 | pytest setup/02_installing-python-libraries/tests.py 51 | pytest ch03/02_bonus_efficient-multihead-attention/tests/test_mha_implementations.py 52 | pytest ch04/01_main-chapter-code/tests.py 53 | pytest ch04/03_kv-cache/tests.py 54 | pytest ch05/01_main-chapter-code/tests.py 55 | pytest ch05/07_gpt_to_llama/tests/tests_rope_and_parts.py 56 | pytest ch05/07_gpt_to_llama/tests/test_llama32_nb.py 57 | pytest ch05/11_qwen3/tests/test_qwen3_nb.py 58 | pytest ch05/12_gemma3/tests/test_gemma3_nb.py 59 | pytest ch05/12_gemma3/tests/test_gemma3_kv_nb.py 60 | pytest ch05/13_olmo3/tests/test_olmo3_nb.py 61 | pytest ch05/13_olmo3/tests/test_olmo3_kvcache_nb.py 62 | pytest ch06/01_main-chapter-code/tests.py 63 | 64 | - name: Validate Selected Jupyter Notebooks (uv) 65 | shell: bash 66 | run: | 67 | source .venv/bin/activate 68 | pytest --nbval ch02/01_main-chapter-code/dataloader.ipynb 69 | pytest --nbval ch03/01_main-chapter-code/multihead-attention.ipynb 70 | pytest --nbval ch02/04_bonus_dataloader-intuition/dataloader-intuition.ipynb 71 | 72 | - name: Test Selected Bonus Materials 73 | shell: bash 74 | run: | 75 | source .venv/bin/activate 76 | pytest ch02/05_bpe-from-scratch/tests.py 77 | 78 | - name: Test Selected Bonus Materials 79 | shell: bash 80 | run: | 81 | source .venv/bin/activate 82 | uv pip install transformers 83 | pytest pkg/llms_from_scratch/tests/ 84 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug-report.yaml: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | name: Bug Report 2 | description: Report errors related to the book content or code 3 | title: "Description" 4 | labels: [bug] 5 | assignees: rasbt 6 | body: 7 | - type: markdown 8 | attributes: 9 | value: | 10 | Thank you for taking the time to report an issue. Please fill out the details below to help resolve it. 11 | 12 | - type: textarea 13 | id: bug_description 14 | attributes: 15 | label: Bug description 16 | description: A description of the issue. 17 | placeholder: | 18 | Please provide a description of what the bug or issue is. 19 | validations: 20 | required: true 21 | 22 | - type: dropdown 23 | id: operating_system 24 | attributes: 25 | label: What operating system are you using? 26 | description: If applicable, please select the operating system where you experienced this issue. 27 | options: 28 | - "Unknown" 29 | - "macOS" 30 | - "Linux" 31 | - "Windows" 32 | validations: 33 | required: False 34 | 35 | - type: dropdown 36 | id: compute_environment 37 | attributes: 38 | label: Where do you run your code? 39 | description: Please select the computing environment where you ran this code. 40 | options: 41 | - "Local (laptop, desktop)" 42 | - "Lightning AI Studio" 43 | - "Google Colab" 44 | - "Other cloud environment (AWS, Azure, GCP)" 45 | validations: 46 | required: False 47 | 48 | - type: textarea 49 | id: environment 50 | attributes: 51 | label: Environment 52 | description: | 53 | Please provide details about your Python environment via the environment collection script or notebook located at 54 | https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/tree/main/setup/02_installing-python-libraries. 55 | For your convenience, you can download and run the script from your terminal as follows: 56 | 57 | ```bash 58 | curl --ssl-no-revoke -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/main/setup/02_installing-python-libraries/python_environment_check.py \ 59 | -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/main/requirements.txt 60 | 61 | python python_environment_check.py 62 | ``` 63 | 64 | The script will print your Python environment information in the following format 65 | ```console 66 | [OK] Your Python version is 3.11.4 67 | [OK] torch 2.3.1 68 | [OK] jupyterlab 4.2.2 69 | [OK] tiktoken 0.7.0 70 | [OK] matplotlib 3.9.0 71 | [OK] numpy 1.26.4 72 | [OK] tensorflow 2.16.1 73 | [OK] tqdm 4.66.4 74 | [OK] pandas 2.2.2 75 | [OK] psutil 5.9.8 76 | ``` 77 | You can simply copy and paste the outputs of this script below. 78 | value: | 79 | ``` 80 | 81 | 82 | 83 | ``` 84 | validations: 85 | required: false 86 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch05/13_olmo3/README.md: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Olmo 3 7B and 32B From Scratch 2 | 3 | This [standalone-olmo3.ipynb](standalone-olmo3.ipynb) Jupyter notebook in this folder contains a from-scratch implementation of Olmo 3 7B and 32B and requires about 13 GB of RAM to run. 4 | 5 | The alternative [standalone-olmo3-plus-kvcache.ipynb](standalone-olmo3-plus-kv-cache.ipynb) notebook adds a KV cache for better runtime performance (but adds more code complexity). To learn more about KV caching, see my [Understanding and Coding the KV Cache in LLMs from Scratch](https://magazine.sebastianraschka.com/p/coding-the-kv-cache-in-llms) article. 6 | 7 | Below is a side-by-side comparison with Qwen3 as a reference model; if you are interested in the Qwen3 0.6B standalone notebook, you can find it [here](../11_qwen3). 8 | 9 |
10 | 11 |
 12 |
13 |
12 |
13 |  14 |
15 | Olmo 3 also comes in different flavors, as shown below (the architecture is the same, only the training pipeline differs):
16 |
17 |
14 |
15 | Olmo 3 also comes in different flavors, as shown below (the architecture is the same, only the training pipeline differs):
16 |
17 |  18 |
19 |
20 |
21 | ## How does Olmo 3 compare to Qwen3
22 |
23 | Focusing on the architecture, not the training details, this section provides a brief comparison to Qwen3.
24 |
25 |
26 | The 7B model:
27 |
28 | 1. As we can see in the figures above, the Olmo 3 architecture is relatively similar to Qwen3. However, it's worth noting that this is essentially likely inspired by the Olmo 2 predecessor, not Qwen3.
29 |
30 | 2) Similar to Olmo 2, Olmo 3 still uses a post-norm flavor instead of pre-norm, as they found in the Olmo 2 paper that it stabilizes the training.
31 |
32 | 3) Interestingly, the 7B model still uses multi-head attention similar to Olmo 2.
33 | However, to make things more efficient and reduce the KV cache size, they now use sliding-window attention (e.g., similar to Gemma 3).
34 |
35 | Next, the 32B model:
36 |
37 | 4) Overall, it's the same architecture but just scaled up. Also, the proportions (e.g., going from the input to the intermediate size in the feed-forward layer, and so on) roughly match the ones in Qwen3.
38 |
39 | 5) My guess is the architecture was initially somewhat smaller than Qwen3 due to the smaller vocabulary, and they then scaled up the intermediate size expansion from 5x in Qwen3 to 5.4 in Olmo 3 to have a 32B model for a direct comparison.
40 |
41 | 6) Also, note that the 32B model (finally!) uses grouped query attention.
42 |
43 |
44 |
45 |
46 |
47 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 | ## How does Olmo 3 compare to Qwen3
22 |
23 | Focusing on the architecture, not the training details, this section provides a brief comparison to Qwen3.
24 |
25 |
26 | The 7B model:
27 |
28 | 1. As we can see in the figures above, the Olmo 3 architecture is relatively similar to Qwen3. However, it's worth noting that this is essentially likely inspired by the Olmo 2 predecessor, not Qwen3.
29 |
30 | 2) Similar to Olmo 2, Olmo 3 still uses a post-norm flavor instead of pre-norm, as they found in the Olmo 2 paper that it stabilizes the training.
31 |
32 | 3) Interestingly, the 7B model still uses multi-head attention similar to Olmo 2.
33 | However, to make things more efficient and reduce the KV cache size, they now use sliding-window attention (e.g., similar to Gemma 3).
34 |
35 | Next, the 32B model:
36 |
37 | 4) Overall, it's the same architecture but just scaled up. Also, the proportions (e.g., going from the input to the intermediate size in the feed-forward layer, and so on) roughly match the ones in Qwen3.
38 |
39 | 5) My guess is the architecture was initially somewhat smaller than Qwen3 due to the smaller vocabulary, and they then scaled up the intermediate size expansion from 5x in Qwen3 to 5.4 in Olmo 3 to have a 32B model for a direct comparison.
40 |
41 | 6) Also, note that the 32B model (finally!) uses grouped query attention.
42 |
43 |
44 |
45 |
46 |
47 | 48 | 49 | To learn more about the architecture differences and read about comparisons with other architectures, see my [The Big LLM Architecture Comparison: From DeepSeek-V3 to Kimi K2: A Look At Modern LLM Architecture Design](https://magazine.sebastianraschka.com/p/the-big-llm-architecture-comparison) article. 50 | 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch04/05_mla/plot_memory_estimates_mla.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 7 | 8 | # Bytes per element 9 | DTYPE_BYTES = { 10 | "fp32": 4, 11 | "bf16": 2, 12 | "fp16": 2, 13 | "fp8": 1, 14 | "int8": 1, 15 | } 16 | 17 | 18 | def bytes_to_gb(n_bytes): 19 | return n_bytes / (1000. ** 3) 20 | 21 | 22 | def kv_bytes_total_mha(batch, context_length, emb_dim, n_heads, 23 | n_layers, bytes_per_elem): 24 | head_dim = emb_dim / n_heads 25 | per_layer = batch * context_length * head_dim * n_heads * 2 * bytes_per_elem 26 | return per_layer * n_layers 27 | 28 | 29 | def kv_bytes_total_mla(batch, context_length, n_layers, latent_dim, bytes_per_elem): 30 | return batch * context_length * n_layers * latent_dim * bytes_per_elem 31 | 32 | 33 | def plot_abs_kv_vs_context_multiple(): 34 | n_heads = 24 35 | emb_dim = 2048 36 | n_layers = 48 37 | batch_size = 1 38 | dtype = "bf16" 39 | bytes_per_elem = DTYPE_BYTES[dtype] 40 | 41 | context_lengths = [ 42 | 256, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192, 43 | 16384, 32768, 65536, 131072 44 | ] 45 | 46 | mha_gb = [] 47 | for L in context_lengths: 48 | total_mha = kv_bytes_total_mha( 49 | batch_size, L, emb_dim, n_heads, n_layers, bytes_per_elem 50 | ) 51 | mha_gb.append(bytes_to_gb(total_mha)) 52 | 53 | latent_dims = [1024, 512, 256, 64] 54 | plt.figure() 55 | plt.plot(context_lengths, mha_gb, marker="o", label="MHA (KV total)") 56 | 57 | L_ref = context_lengths[-1] 58 | total_mha_ref = kv_bytes_total_mha(batch_size, L_ref, emb_dim, n_heads, n_layers, bytes_per_elem) 59 | 60 | for latent_dim in latent_dims: 61 | mla_gb = [] 62 | for L in context_lengths: 63 | total_mla = kv_bytes_total_mla( 64 | batch_size, L, n_layers, latent_dim, bytes_per_elem 65 | ) 66 | mla_gb.append(bytes_to_gb(total_mla)) 67 | 68 | total_mla_ref = kv_bytes_total_mla(batch_size, L_ref, n_layers, latent_dim, bytes_per_elem) 69 | comp = total_mha_ref / total_mla_ref if total_mla_ref != 0 else float("inf") 70 | 71 | plt.plot(context_lengths, mla_gb, marker="o", 72 | label=f"MLA (latent_dim={latent_dim}, {comp:,.1f}× compression)") 73 | 74 | plt.xscale("log") 75 | plt.xlabel("context_length (log scale)") 76 | plt.ylabel("Total KV cache (GB)") 77 | plt.title( 78 | "KV-cache vs Context Length — MHA vs MLA\n" 79 | f"(n_heads={n_heads}, emb_dim={emb_dim}, n_layers={n_layers}, " 80 | f"batch={batch_size}, dtype={dtype})", 81 | fontsize=8 82 | ) 83 | plt.grid(True, which="both") 84 | plt.legend() 85 | plt.tight_layout() 86 | plt.savefig("kv_bytes_vs_context_length.pdf") 87 | 88 | 89 | if __name__ == "__main__": 90 | plot_abs_kv_vs_context_multiple() 91 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch05/06_user_interface/app_orig.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | import tiktoken 7 | import torch 8 | import chainlit 9 | 10 | # For llms_from_scratch installation instructions, see: 11 | # https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/tree/main/pkg 12 | from llms_from_scratch.ch04 import GPTModel 13 | from llms_from_scratch.ch05 import ( 14 | download_and_load_gpt2, 15 | generate, 16 | load_weights_into_gpt, 17 | text_to_token_ids, 18 | token_ids_to_text, 19 | ) 20 | 21 | device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") 22 | 23 | 24 | def get_model_and_tokenizer(): 25 | """ 26 | Code to load a GPT-2 model with pretrained weights from OpenAI. 27 | The code is similar to chapter 5. 28 | The model will be downloaded automatically if it doesn't exist in the current folder, yet. 29 | """ 30 | 31 | CHOOSE_MODEL = "gpt2-small (124M)" # Optionally replace with another model from the model_configs dir below 32 | 33 | BASE_CONFIG = { 34 | "vocab_size": 50257, # Vocabulary size 35 | "context_length": 1024, # Context length 36 | "drop_rate": 0.0, # Dropout rate 37 | "qkv_bias": True # Query-key-value bias 38 | } 39 | 40 | model_configs = { 41 | "gpt2-small (124M)": {"emb_dim": 768, "n_layers": 12, "n_heads": 12}, 42 | "gpt2-medium (355M)": {"emb_dim": 1024, "n_layers": 24, "n_heads": 16}, 43 | "gpt2-large (774M)": {"emb_dim": 1280, "n_layers": 36, "n_heads": 20}, 44 | "gpt2-xl (1558M)": {"emb_dim": 1600, "n_layers": 48, "n_heads": 25}, 45 | } 46 | 47 | model_size = CHOOSE_MODEL.split(" ")[-1].lstrip("(").rstrip(")") 48 | 49 | BASE_CONFIG.update(model_configs[CHOOSE_MODEL]) 50 | 51 | settings, params = download_and_load_gpt2(model_size=model_size, models_dir="gpt2") 52 | 53 | gpt = GPTModel(BASE_CONFIG) 54 | load_weights_into_gpt(gpt, params) 55 | gpt.to(device) 56 | gpt.eval() 57 | 58 | tokenizer = tiktoken.get_encoding("gpt2") 59 | 60 | return tokenizer, gpt, BASE_CONFIG 61 | 62 | 63 | # Obtain the necessary tokenizer and model files for the chainlit function below 64 | tokenizer, model, model_config = get_model_and_tokenizer() 65 | 66 | 67 | @chainlit.on_message 68 | async def main(message: chainlit.Message): 69 | """ 70 | The main Chainlit function. 71 | """ 72 | token_ids = generate( # function uses `with torch.no_grad()` internally already 73 | model=model, 74 | idx=text_to_token_ids(message.content, tokenizer).to(device), # The user text is provided via as `message.content` 75 | max_new_tokens=50, 76 | context_size=model_config["context_length"], 77 | top_k=1, 78 | temperature=0.0 79 | ) 80 | 81 | text = token_ids_to_text(token_ids, tokenizer) 82 | 83 | await chainlit.Message( 84 | content=f"{text}", # This returns the model response to the interface 85 | ).send() 86 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch06/03_bonus_imdb-classification/train_sklearn_logreg.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | import pandas as pd 7 | from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer 8 | from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression 9 | from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score 10 | # from sklearn.metrics import balanced_accuracy_score 11 | from sklearn.dummy import DummyClassifier 12 | 13 | 14 | def load_dataframes(): 15 | df_train = pd.read_csv("train.csv") 16 | df_val = pd.read_csv("validation.csv") 17 | df_test = pd.read_csv("test.csv") 18 | 19 | return df_train, df_val, df_test 20 | 21 | 22 | def eval_model(model, X_train, y_train, X_val, y_val, X_test, y_test): 23 | # Making predictions 24 | y_pred_train = model.predict(X_train) 25 | y_pred_val = model.predict(X_val) 26 | y_pred_test = model.predict(X_test) 27 | 28 | # Calculating accuracy and balanced accuracy 29 | accuracy_train = accuracy_score(y_train, y_pred_train) 30 | # balanced_accuracy_train = balanced_accuracy_score(y_train, y_pred_train) 31 | 32 | accuracy_val = accuracy_score(y_val, y_pred_val) 33 | # balanced_accuracy_val = balanced_accuracy_score(y_val, y_pred_val) 34 | 35 | accuracy_test = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_test) 36 | # balanced_accuracy_test = balanced_accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_test) 37 | 38 | # Printing the results 39 | print(f"Training Accuracy: {accuracy_train*100:.2f}%") 40 | print(f"Validation Accuracy: {accuracy_val*100:.2f}%") 41 | print(f"Test Accuracy: {accuracy_test*100:.2f}%") 42 | 43 | # print(f"\nTraining Balanced Accuracy: {balanced_accuracy_train*100:.2f}%") 44 | # print(f"Validation Balanced Accuracy: {balanced_accuracy_val*100:.2f}%") 45 | # print(f"Test Balanced Accuracy: {balanced_accuracy_test*100:.2f}%") 46 | 47 | 48 | if __name__ == "__main__": 49 | df_train, df_val, df_test = load_dataframes() 50 | 51 | ######################################### 52 | # Convert text into bag-of-words model 53 | vectorizer = CountVectorizer() 54 | ######################################### 55 | 56 | X_train = vectorizer.fit_transform(df_train["text"]) 57 | X_val = vectorizer.transform(df_val["text"]) 58 | X_test = vectorizer.transform(df_test["text"]) 59 | y_train, y_val, y_test = df_train["label"], df_val["label"], df_test["label"] 60 | 61 | ##################################### 62 | # Model training and evaluation 63 | ##################################### 64 | 65 | # Create a dummy classifier with the strategy to predict the most frequent class 66 | dummy_clf = DummyClassifier(strategy="most_frequent") 67 | dummy_clf.fit(X_train, y_train) 68 | 69 | print("Dummy classifier:") 70 | eval_model(dummy_clf, X_train, y_train, X_val, y_val, X_test, y_test) 71 | 72 | print("\n\nLogistic regression classifier:") 73 | model = LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000) 74 | model.fit(X_train, y_train) 75 | eval_model(model, X_train, y_train, X_val, y_val, X_test, y_test) 76 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch07/06_user_interface/app.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | from pathlib import Path 7 | import sys 8 | 9 | import tiktoken 10 | import torch 11 | import chainlit 12 | 13 | 14 | # For llms_from_scratch installation instructions, see: 15 | # https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/tree/main/pkg 16 | from llms_from_scratch.ch04 import GPTModel 17 | from llms_from_scratch.ch05 import ( 18 | generate, 19 | text_to_token_ids, 20 | token_ids_to_text, 21 | ) 22 | 23 | device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") 24 | 25 | 26 | def get_model_and_tokenizer(): 27 | """ 28 | Code to load a GPT-2 model with finetuned weights generated in chapter 7. 29 | This requires that you run the code in chapter 7 first, which generates the necessary gpt2-medium355M-sft.pth file. 30 | """ 31 | 32 | GPT_CONFIG_355M = { 33 | "vocab_size": 50257, # Vocabulary size 34 | "context_length": 1024, # Shortened context length (orig: 1024) 35 | "emb_dim": 1024, # Embedding dimension 36 | "n_heads": 16, # Number of attention heads 37 | "n_layers": 24, # Number of layers 38 | "drop_rate": 0.0, # Dropout rate 39 | "qkv_bias": True # Query-key-value bias 40 | } 41 | 42 | tokenizer = tiktoken.get_encoding("gpt2") 43 | 44 | model_path = Path("..") / "01_main-chapter-code" / "gpt2-medium355M-sft.pth" 45 | if not model_path.exists(): 46 | print( 47 | f"Could not find the {model_path} file. Please run the chapter 7 code " 48 | " (ch07.ipynb) to generate the gpt2-medium355M-sft.pt file." 49 | ) 50 | sys.exit() 51 | 52 | checkpoint = torch.load(model_path, weights_only=True) 53 | model = GPTModel(GPT_CONFIG_355M) 54 | model.load_state_dict(checkpoint) 55 | model.to(device) 56 | 57 | return tokenizer, model, GPT_CONFIG_355M 58 | 59 | 60 | def extract_response(response_text, input_text): 61 | return response_text[len(input_text):].replace("### Response:", "").strip() 62 | 63 | 64 | # Obtain the necessary tokenizer and model files for the chainlit function below 65 | tokenizer, model, model_config = get_model_and_tokenizer() 66 | 67 | 68 | @chainlit.on_message 69 | async def main(message: chainlit.Message): 70 | """ 71 | The main Chainlit function. 72 | """ 73 | 74 | torch.manual_seed(123) 75 | 76 | prompt = f"""Below is an instruction that describes a task. Write a response 77 | that appropriately completes the request. 78 | 79 | ### Instruction: 80 | {message.content} 81 | """ 82 | 83 | token_ids = generate( # function uses `with torch.no_grad()` internally already 84 | model=model, 85 | idx=text_to_token_ids(prompt, tokenizer).to(device), # The user text is provided via as `message.content` 86 | max_new_tokens=35, 87 | context_size=model_config["context_length"], 88 | eos_id=50256 89 | ) 90 | 91 | text = token_ids_to_text(token_ids, tokenizer) 92 | response = extract_response(text, prompt) 93 | 94 | await chainlit.Message( 95 | content=f"{response}", # This returns the model response to the interface 96 | ).send() 97 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch07/01_main-chapter-code/README.md: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Chapter 7: Finetuning to Follow Instructions 2 | 3 | ### Main Chapter Code 4 | 5 | - [ch07.ipynb](ch07.ipynb) contains all the code as it appears in the chapter 6 | - [previous_chapters.py](previous_chapters.py) is a Python module that contains the GPT model we coded and trained in previous chapters, alongside many utility functions, which we reuse in this chapter 7 | - [gpt_download.py](gpt_download.py) contains the utility functions for downloading the pretrained GPT model weights 8 | - [exercise-solutions.ipynb](exercise-solutions.ipynb) contains the exercise solutions for this chapter 9 | 10 | 11 | ### Optional Code 12 | 13 | - [load-finetuned-model.ipynb](load-finetuned-model.ipynb) is a standalone Jupyter notebook to load the instruction finetuned model we created in this chapter 14 | 15 | - [gpt_instruction_finetuning.py](gpt_instruction_finetuning.py) is a standalone Python script to instruction finetune the model as described in the main chapter (think of it as a chapter summary focused on the finetuning parts) 16 | 17 | Usage: 18 | 19 | ```bash 20 | python gpt_instruction_finetuning.py 21 | ``` 22 | 23 | ``` 24 | matplotlib version: 3.9.0 25 | tiktoken version: 0.7.0 26 | torch version: 2.3.1 27 | tqdm version: 4.66.4 28 | tensorflow version: 2.16.1 29 | -------------------------------------------------- 30 | Training set length: 935 31 | Validation set length: 55 32 | Test set length: 110 33 | -------------------------------------------------- 34 | Device: cpu 35 | -------------------------------------------------- 36 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/checkpoint 37 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/encoder.json 38 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/hparams.json 39 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/model.ckpt.data-00000-of-00001 40 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/model.ckpt.index 41 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/model.ckpt.meta 42 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/vocab.bpe 43 | Loaded model: gpt2-medium (355M) 44 | -------------------------------------------------- 45 | Initial losses 46 | Training loss: 3.839039182662964 47 | Validation loss: 3.7619192123413088 48 | Ep 1 (Step 000000): Train loss 2.611, Val loss 2.668 49 | Ep 1 (Step 000005): Train loss 1.161, Val loss 1.131 50 | Ep 1 (Step 000010): Train loss 0.939, Val loss 0.973 51 | ... 52 | Training completed in 15.66 minutes. 53 | Plot saved as loss-plot-standalone.pdf 54 | -------------------------------------------------- 55 | Generating responses 56 | 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 110/110 [06:57<00:00, 3.80s/it] 57 | Responses saved as instruction-data-with-response-standalone.json 58 | Model saved as gpt2-medium355M-sft-standalone.pth 59 | ``` 60 | 61 | - [ollama_evaluate.py](ollama_evaluate.py) is a standalone Python script to evaluate the responses of the finetuned model as described in the main chapter (think of it as a chapter summary focused on the evaluation parts) 62 | 63 | Usage: 64 | 65 | ```bash 66 | python ollama_evaluate.py --file_path instruction-data-with-response-standalone.json 67 | ``` 68 | 69 | ``` 70 | Ollama running: True 71 | Scoring entries: 100%|███████████████████████████████████████| 110/110 [01:08<00:00, 1.62it/s] 72 | Number of scores: 110 of 110 73 | Average score: 51.75 74 | ``` 75 | 76 | - [exercise_experiments.py](exercise_experiments.py) is an optional scropt that implements the exercise solutions; for more details see [exercise-solutions.ipynb](exercise-solutions.ipynb) 77 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch04/04_gqa/memory_estimator_gqa.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | # KV-cache memory estimator for MHA vs GQA 7 | 8 | 9 | import argparse 10 | import math 11 | 12 | DTYPE_BYTES = { 13 | "fp32": 4, 14 | "bf16": 2, 15 | "fp16": 2, 16 | "fp8": 1, 17 | "int8": 1, 18 | } 19 | 20 | 21 | def bytes_convert(n): 22 | gb = n / (1000 ** 3) 23 | return f"{gb:,.2f} GB" 24 | 25 | 26 | def kv_bytes_total(batch, context_length, emb_dim, n_heads, 27 | n_kv_heads, n_layers, bytes_per_elem): 28 | head_dim = math.ceil(emb_dim / n_heads) 29 | per_layer = batch * context_length * head_dim * n_kv_heads * 2 * bytes_per_elem 30 | return per_layer * n_layers 31 | 32 | 33 | def main(): 34 | p = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Estimate KV-cache memory for MHA vs GQA") 35 | p.add_argument("--context_length", default=1024, type=int) 36 | p.add_argument("--emb_dim", required=True, type=int) 37 | p.add_argument("--n_heads", required=True, type=int) 38 | p.add_argument("--n_layers", required=True, type=int) 39 | p.add_argument("--n_kv_groups", required=True, type=int) 40 | p.add_argument("--batch_size", default=1, type=int) 41 | p.add_argument("--dtype", choices=DTYPE_BYTES.keys(), default="fp16") 42 | args = p.parse_args() 43 | 44 | cfg = { 45 | "context_length": args.context_length, 46 | "emb_dim": args.emb_dim, 47 | "n_heads": args.n_heads, 48 | "n_layers": args.n_layers, 49 | "n_kv_groups": args.n_kv_groups, 50 | } 51 | 52 | if cfg["n_heads"] % cfg["n_kv_groups"] != 0: 53 | raise ValueError("n_kv_groups must divide n_heads exactly.") 54 | 55 | bytes_per_elem = DTYPE_BYTES[args.dtype] 56 | head_dim = math.ceil(cfg["emb_dim"] / cfg["n_heads"]) 57 | 58 | n_kv_heads_mha = cfg["n_heads"] 59 | n_kv_heads_gqa = cfg["n_heads"] // cfg["n_kv_groups"] 60 | 61 | total_mha = kv_bytes_total( 62 | args.batch_size, 63 | cfg["context_length"], 64 | cfg["emb_dim"], 65 | cfg["n_heads"], 66 | n_kv_heads_mha, 67 | cfg["n_layers"], 68 | bytes_per_elem, 69 | ) 70 | 71 | total_gqa = kv_bytes_total( 72 | args.batch_size, 73 | cfg["context_length"], 74 | cfg["emb_dim"], 75 | cfg["n_heads"], 76 | n_kv_heads_gqa, 77 | cfg["n_layers"], 78 | bytes_per_elem, 79 | ) 80 | 81 | ratio = total_mha / total_gqa 82 | savings = 1 - (total_gqa / total_mha) 83 | 84 | print("==== Config ====") 85 | for k, v in cfg.items(): 86 | print(f"{k:17}: {v}") 87 | print(f"batch_size : {args.batch_size}") 88 | print(f"dtype : {args.dtype} ({bytes_per_elem} Bytes/elem)") 89 | print(f"head_dim : {head_dim}") 90 | print(f"GQA n_kv_heads : {n_kv_heads_gqa}") 91 | print() 92 | 93 | print("==== KV-cache totals across all layers ====") 94 | print(f"MHA total KV cache : {bytes_convert(total_mha)}") 95 | print(f"GQA total KV cache : {bytes_convert(total_gqa)}") 96 | print(f"Ratio (MHA / GQA) : {ratio:,.2f}x") 97 | print(f"Savings (GQA vs MHA): {savings*100:,.2f}%") 98 | 99 | 100 | if __name__ == "__main__": 101 | main() 102 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /setup/02_installing-python-libraries/README.md: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Installing Python Packages and Libraries Used In This Book 2 | 3 | This document provides more information on double-checking your installed Python version and packages. (Please see the [../01_optional-python-setup-preferences](../01_optional-python-setup-preferences) folder for more information on installing Python and Python packages.) 4 | 5 | I used the following libraries listed [here](https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/blob/main/requirements.txt) for this book. Newer versions of these libraries are likely compatible as well. However, if you experience any problems with the code, you can try these library versions as a fallback. 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | > **Note:** 10 | > If you you are using `uv` as described in [Option 1: Using uv](../01_optional-python-setup-preferences/README.md), you can replace `pip` via `uv pip` in the commands below. For example, `pip install -r requirements.txt` becomes `uv pip install -r requirements.txt` 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | To install these requirements most conveniently, you can use the `requirements.txt` file in the root directory for this code repository and execute the following command: 15 | 16 | ```bash 17 | pip install -r requirements.txt 18 | ``` 19 | 20 | Alternatively, you can install it via the GitHub URL as follows: 21 | 22 | ```bash 23 | pip install -r https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/main/requirements.txt 24 | ``` 25 | 26 | 27 | Then, after completing the installation, please check if all the packages are installed and are up to date using 28 | 29 | ```bash 30 | python python_environment_check.py 31 | ``` 32 | 33 |
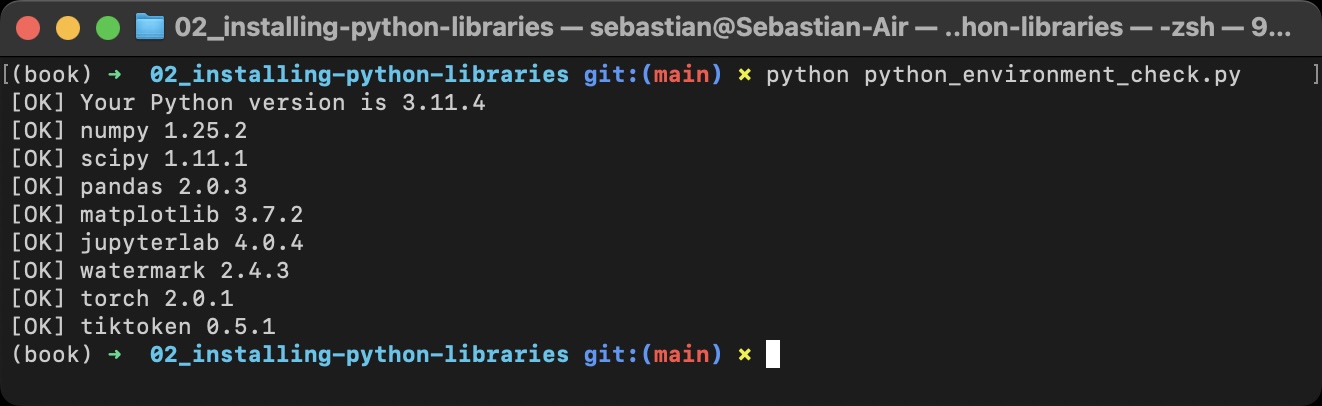 34 |
35 | It's also recommended to check the versions in JupyterLab by running the `python_environment_check.ipynb` in this directory, which should ideally give you the same results as above.
36 |
37 |
34 |
35 | It's also recommended to check the versions in JupyterLab by running the `python_environment_check.ipynb` in this directory, which should ideally give you the same results as above.
36 |
37 | 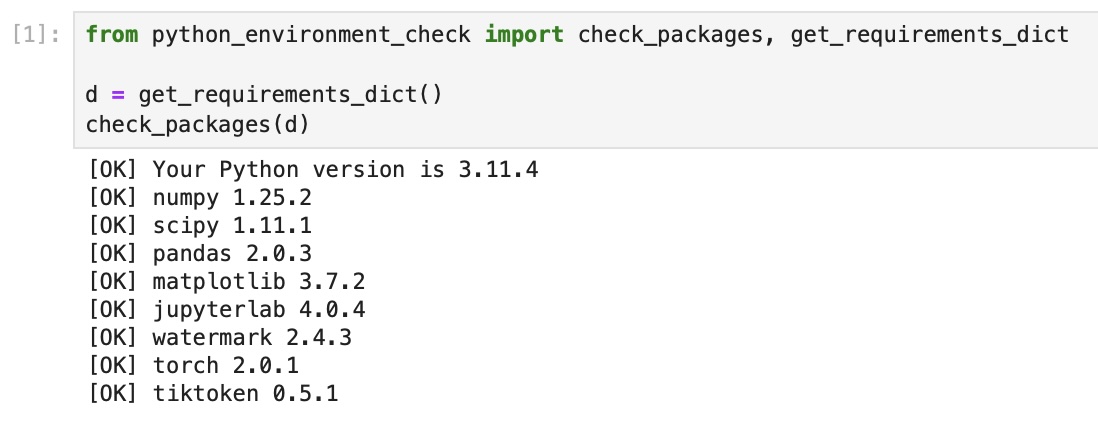 38 |
39 | If you see the following issues, it's likely that your JupyterLab instance is connected to wrong conda environment:
40 |
41 |
38 |
39 | If you see the following issues, it's likely that your JupyterLab instance is connected to wrong conda environment:
40 |
41 | 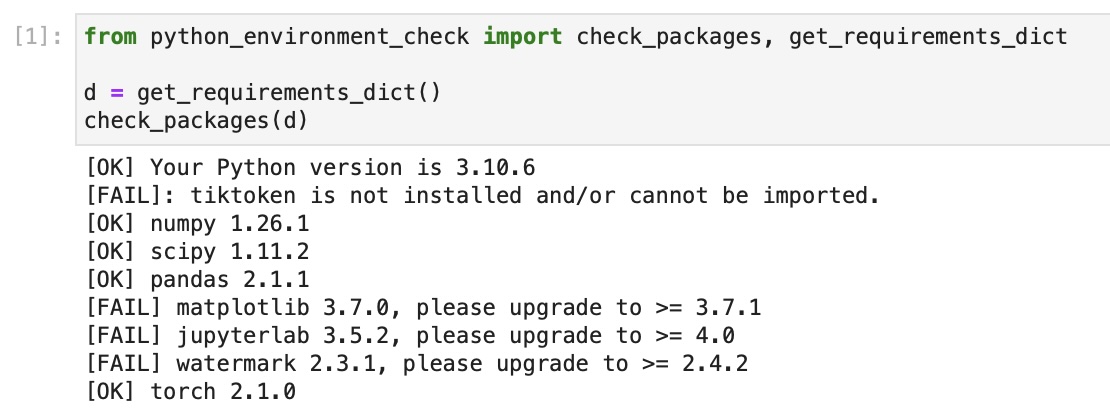 42 |
43 | In this case, you may want to use `watermark` to check if you opened the JupyterLab instance in the right conda environment using the `--conda` flag:
44 |
45 |
42 |
43 | In this case, you may want to use `watermark` to check if you opened the JupyterLab instance in the right conda environment using the `--conda` flag:
44 |
45 | 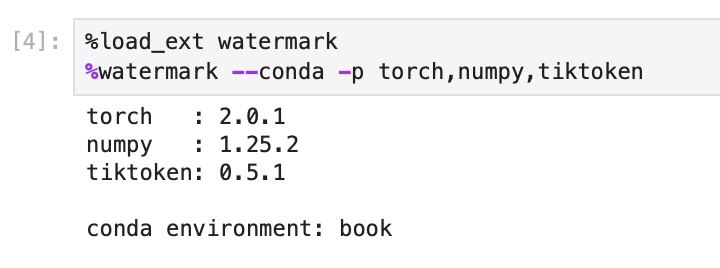 46 |
47 |
48 |
49 | ## Installing PyTorch
50 |
51 | PyTorch can be installed just like any other Python library or package using pip. For example:
52 |
53 | ```bash
54 | pip install torch
55 | ```
56 |
57 | However, since PyTorch is a comprehensive library featuring CPU- and GPU-compatible codes, the installation may require additional settings and explanation (see the *A.1.3 Installing PyTorch in the book for more information*).
58 |
59 | It's also highly recommended to consult the installation guide menu on the official PyTorch website at [https://pytorch.org](https://pytorch.org).
60 |
61 |
46 |
47 |
48 |
49 | ## Installing PyTorch
50 |
51 | PyTorch can be installed just like any other Python library or package using pip. For example:
52 |
53 | ```bash
54 | pip install torch
55 | ```
56 |
57 | However, since PyTorch is a comprehensive library featuring CPU- and GPU-compatible codes, the installation may require additional settings and explanation (see the *A.1.3 Installing PyTorch in the book for more information*).
58 |
59 | It's also highly recommended to consult the installation guide menu on the official PyTorch website at [https://pytorch.org](https://pytorch.org).
60 |
61 | 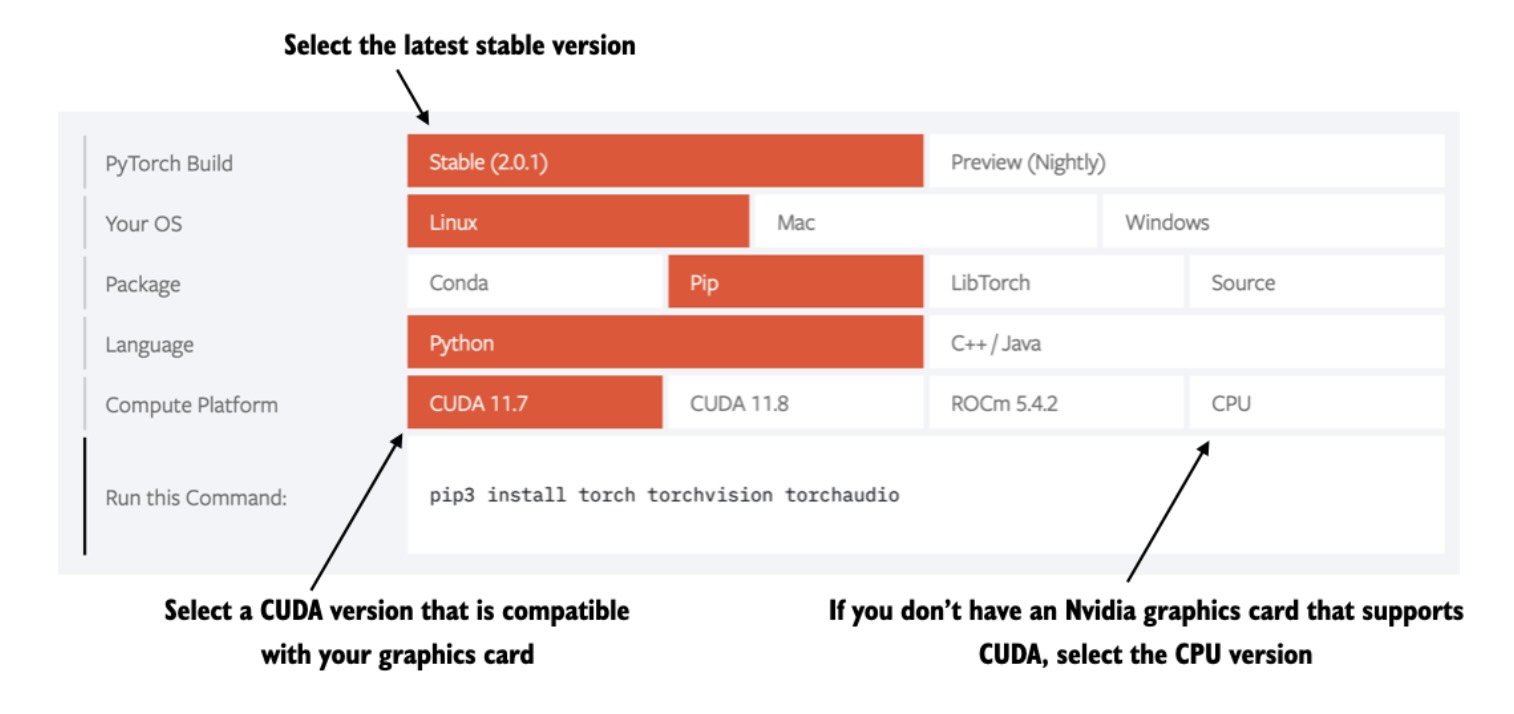 62 |
63 |
62 |
63 | 64 | 65 | --- 66 | 67 | 68 | 69 | 70 | Any questions? Please feel free to reach out in the [Discussion Forum](https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/discussions). 71 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch06/03_bonus_imdb-classification/download_prepare_dataset.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | import os 7 | import sys 8 | import tarfile 9 | import time 10 | import requests 11 | import pandas as pd 12 | 13 | 14 | def reporthook(count, block_size, total_size): 15 | global start_time 16 | if count == 0: 17 | start_time = time.time() 18 | else: 19 | duration = time.time() - start_time 20 | progress_size = int(count * block_size) 21 | percent = count * block_size * 100 / total_size 22 | 23 | speed = int(progress_size / (1024 * duration)) if duration else 0 24 | sys.stdout.write( 25 | f"\r{int(percent)}% | {progress_size / (1024**2):.2f} MB " 26 | f"| {speed:.2f} MB/s | {duration:.2f} sec elapsed" 27 | ) 28 | sys.stdout.flush() 29 | 30 | 31 | def download_and_extract_dataset(dataset_url, target_file, directory): 32 | if not os.path.exists(directory): 33 | if os.path.exists(target_file): 34 | os.remove(target_file) 35 | 36 | response = requests.get(dataset_url, stream=True, timeout=60) 37 | response.raise_for_status() 38 | 39 | with open(target_file, "wb") as f: 40 | for chunk in response.iter_content(chunk_size=8192): 41 | if chunk: 42 | f.write(chunk) 43 | 44 | print("\nExtracting dataset ...") 45 | with tarfile.open(target_file, "r:gz") as tar: 46 | tar.extractall() 47 | else: 48 | print(f"Directory `{directory}` already exists. Skipping download.") 49 | 50 | 51 | def load_dataset_to_dataframe(basepath="aclImdb", labels={"pos": 1, "neg": 0}): 52 | data_frames = [] # List to store each chunk of DataFrame 53 | for subset in ("test", "train"): 54 | for label in ("pos", "neg"): 55 | path = os.path.join(basepath, subset, label) 56 | for file in sorted(os.listdir(path)): 57 | with open(os.path.join(path, file), "r", encoding="utf-8") as infile: 58 | # Create a DataFrame for each file and add it to the list 59 | data_frames.append(pd.DataFrame({"text": [infile.read()], "label": [labels[label]]})) 60 | # Concatenate all DataFrame chunks together 61 | df = pd.concat(data_frames, ignore_index=True) 62 | df = df.sample(frac=1, random_state=123).reset_index(drop=True) # Shuffle the DataFrame 63 | return df 64 | 65 | 66 | def partition_and_save(df, sizes=(35000, 5000, 10000)): 67 | # Shuffle the DataFrame 68 | df_shuffled = df.sample(frac=1, random_state=123).reset_index(drop=True) 69 | 70 | # Get indices for where to split the data 71 | train_end = sizes[0] 72 | val_end = sizes[0] + sizes[1] 73 | 74 | # Split the DataFrame 75 | train = df_shuffled.iloc[:train_end] 76 | val = df_shuffled.iloc[train_end:val_end] 77 | test = df_shuffled.iloc[val_end:] 78 | 79 | # Save to CSV files 80 | train.to_csv("train.csv", index=False) 81 | val.to_csv("validation.csv", index=False) 82 | test.to_csv("test.csv", index=False) 83 | 84 | 85 | if __name__ == "__main__": 86 | dataset_url = "http://ai.stanford.edu/~amaas/data/sentiment/aclImdb_v1.tar.gz" 87 | print("Downloading dataset ...") 88 | download_and_extract_dataset(dataset_url, "aclImdb_v1.tar.gz", "aclImdb") 89 | print("Creating data frames ...") 90 | df = load_dataset_to_dataframe() 91 | print("Partitioning and saving data frames ...") 92 | partition_and_save(df) 93 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch05/01_main-chapter-code/tests.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | # File for internal use (unit tests) 7 | 8 | import pytest 9 | from gpt_train import main 10 | import requests 11 | 12 | @pytest.fixture 13 | def gpt_config(): 14 | return { 15 | "vocab_size": 50257, 16 | "context_length": 12, # small for testing efficiency 17 | "emb_dim": 32, # small for testing efficiency 18 | "n_heads": 4, # small for testing efficiency 19 | "n_layers": 2, # small for testing efficiency 20 | "drop_rate": 0.1, 21 | "qkv_bias": False 22 | } 23 | 24 | 25 | @pytest.fixture 26 | def other_settings(): 27 | return { 28 | "learning_rate": 5e-4, 29 | "num_epochs": 1, # small for testing efficiency 30 | "batch_size": 2, 31 | "weight_decay": 0.1 32 | } 33 | 34 | 35 | def test_main(gpt_config, other_settings): 36 | train_losses, val_losses, tokens_seen, model = main(gpt_config, other_settings) 37 | 38 | assert len(train_losses) == 39, "Unexpected number of training losses" 39 | assert len(val_losses) == 39, "Unexpected number of validation losses" 40 | assert len(tokens_seen) == 39, "Unexpected number of tokens seen" 41 | 42 | 43 | def check_file_size(url, expected_size): 44 | try: 45 | response = requests.head(url, allow_redirects=True, timeout=30) 46 | if response.status_code != 200: 47 | return False, f"{url} not accessible" 48 | 49 | size = response.headers.get("Content-Length") 50 | if size is None: 51 | return False, "Content-Length header is missing" 52 | 53 | size = int(size) 54 | if size != expected_size: 55 | return False, f"{url} file has expected size {expected_size}, but got {size}" 56 | 57 | return True, f"{url} file size is correct" 58 | 59 | except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e: 60 | return False, f"Failed to access {url}: {e}" 61 | 62 | 63 | def test_model_files(): 64 | def check_model_files(base_url): 65 | 66 | model_size = "124M" 67 | files = { 68 | "checkpoint": 77, 69 | "encoder.json": 1042301, 70 | "hparams.json": 90, 71 | "model.ckpt.data-00000-of-00001": 497759232, 72 | "model.ckpt.index": 5215, 73 | "model.ckpt.meta": 471155, 74 | "vocab.bpe": 456318 75 | } 76 | 77 | for file_name, expected_size in files.items(): 78 | url = f"{base_url}/{model_size}/{file_name}" 79 | valid, message = check_file_size(url, expected_size) 80 | assert valid, message 81 | 82 | model_size = "355M" 83 | files = { 84 | "checkpoint": 77, 85 | "encoder.json": 1042301, 86 | "hparams.json": 91, 87 | "model.ckpt.data-00000-of-00001": 1419292672, 88 | "model.ckpt.index": 10399, 89 | "model.ckpt.meta": 926519, 90 | "vocab.bpe": 456318 91 | } 92 | 93 | for file_name, expected_size in files.items(): 94 | url = f"{base_url}/{model_size}/{file_name}" 95 | valid, message = check_file_size(url, expected_size) 96 | assert valid, message 97 | 98 | check_model_files(base_url="https://openaipublic.blob.core.windows.net/gpt-2/models") 99 | check_model_files(base_url="https://f001.backblazeb2.com/file/LLMs-from-scratch/gpt2") 100 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch04/03_kv-cache/tests.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Code to test the GPT model implementation against the KV cache variants 2 | 3 | import pytest 4 | import torch 5 | import tiktoken 6 | 7 | from gpt_ch04 import GPTModel as GPTModelBase 8 | from gpt_ch04 import generate_text_simple 9 | 10 | from gpt_with_kv_cache import GPTModel as GPTModelKV1 11 | from gpt_with_kv_cache_optimized import GPTModel as GPTModelKV2 12 | from gpt_with_kv_cache import generate_text_simple_cached 13 | 14 | 15 | GPT_CONFIG_124M = { 16 | "vocab_size": 50257, 17 | "context_length": 1024, 18 | "emb_dim": 768, 19 | "n_heads": 12, 20 | "n_layers": 12, 21 | "drop_rate": 0.1, 22 | "qkv_bias": False, 23 | } 24 | 25 | 26 | device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") 27 | 28 | 29 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("ModelClass", [GPTModelBase, GPTModelKV1, GPTModelKV2]) 30 | def test_gpt_model_equivalence_not_cached(ModelClass): 31 | torch.manual_seed(123) 32 | 33 | model = ModelClass(GPT_CONFIG_124M).to(device) 34 | model.eval() 35 | 36 | tokenizer = tiktoken.get_encoding("gpt2") 37 | prompt = "Hello, I am" 38 | encoded = tokenizer.encode(prompt) 39 | encoded_tensor = torch.tensor(encoded, device=device).unsqueeze(0) 40 | 41 | model_name = ModelClass.__module__ + "." + ModelClass.__name__ 42 | 43 | token_ids = generate_text_simple( 44 | model=model, 45 | idx=encoded_tensor, 46 | max_new_tokens=30, 47 | context_size=GPT_CONFIG_124M["context_length"] 48 | ) 49 | 50 | if not hasattr(test_gpt_model_equivalence_not_cached, "results"): 51 | test_gpt_model_equivalence_not_cached.results = [] 52 | 53 | test_gpt_model_equivalence_not_cached.results.append((model_name, token_ids)) 54 | 55 | if len(test_gpt_model_equivalence_not_cached.results) == 3: 56 | base_name, base_output = test_gpt_model_equivalence_not_cached.results[0] 57 | for other_name, other_output in test_gpt_model_equivalence_not_cached.results[1:]: 58 | assert torch.equal(base_output, other_output), ( 59 | f"Mismatch between {base_name} and {other_name}" 60 | ) 61 | 62 | 63 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("ModelClass", [GPTModelBase, GPTModelKV1, GPTModelKV2]) 64 | def test_gpt_model_equivalence_cached(ModelClass): 65 | torch.manual_seed(123) 66 | 67 | model = ModelClass(GPT_CONFIG_124M).to(device) 68 | model.eval() 69 | 70 | tokenizer = tiktoken.get_encoding("gpt2") 71 | prompt = "Hello, I am" 72 | encoded_tensor = torch.tensor(tokenizer.encode(prompt), device=device).unsqueeze(0) 73 | 74 | model_name = ModelClass.__module__ + "." + ModelClass.__name__ 75 | 76 | if ModelClass is GPTModelBase: 77 | token_ids = generate_text_simple( 78 | model=model, 79 | idx=encoded_tensor, 80 | max_new_tokens=30, 81 | context_size=GPT_CONFIG_124M["context_length"] 82 | ) 83 | else: 84 | token_ids = generate_text_simple_cached( 85 | model=model, 86 | idx=encoded_tensor, 87 | max_new_tokens=30, 88 | context_size=GPT_CONFIG_124M["context_length"] 89 | ) 90 | 91 | if not hasattr(test_gpt_model_equivalence_cached, "results"): 92 | test_gpt_model_equivalence_cached.results = [] 93 | 94 | test_gpt_model_equivalence_cached.results.append((model_name, token_ids)) 95 | 96 | if len(test_gpt_model_equivalence_cached.results) == 3: 97 | base_name, base_output = test_gpt_model_equivalence_cached.results[0] 98 | for other_name, other_output in test_gpt_model_equivalence_cached.results[1:]: 99 | assert torch.equal(base_output, other_output), ( 100 | f"Mismatch between {base_name} and {other_name}" 101 | ) 102 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch04/08_deltanet/plot_memory_estimates_gated_deltanet.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | import argparse 7 | import numpy as np 8 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 9 | 10 | # Bytes per element 11 | DTYPE_BYTES = { 12 | "fp32": 4, 13 | "bf16": 2, 14 | "fp16": 2, 15 | "fp8": 1, 16 | "int8": 1, 17 | } 18 | 19 | 20 | def kv_bytes_total_mha(batch, context_length, emb_dim, n_layers, bytes_per_elem, n_heads): 21 | # Full attention (MHA) 22 | d_head = emb_dim // n_heads 23 | per_layer = batch * context_length * n_heads * d_head * 2 * bytes_per_elem 24 | return per_layer * n_layers 25 | 26 | 27 | def kv_bytes_total_deltanet_no_conv(batch, emb_dim, n_layers, bytes_per_elem, n_heads): 28 | # Simple Gated DeltaNet (no convolutional mixing) 29 | d_head = emb_dim // n_heads 30 | per_layer = batch * n_heads * d_head * d_head * bytes_per_elem 31 | return per_layer * n_layers 32 | 33 | 34 | def gb(x): 35 | return x / 1e9 36 | 37 | 38 | def main(): 39 | p = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Memory vs. Context Length: MHA vs. DeltaNet (3:1 mix)") 40 | p.add_argument("--batch", type=int, default=1) 41 | p.add_argument("--emb_dim", type=int, default=2048) 42 | p.add_argument("--n_heads", type=int, default=16) 43 | p.add_argument("--n_layers", type=int, default=48) 44 | p.add_argument("--dtype", choices=DTYPE_BYTES.keys(), default="bf16") 45 | p.add_argument("--min_ctx", type=int, default=128) 46 | p.add_argument("--max_ctx", type=int, default=131_072) 47 | args = p.parse_args() 48 | 49 | step = 100 50 | ctx = np.arange(args.min_ctx, args.max_ctx + 1, step, dtype=int) 51 | bytes_per_elem = DTYPE_BYTES[args.dtype] 52 | 53 | # 1) Full attention only 54 | mha_bytes = np.array([ 55 | kv_bytes_total_mha(args.batch, int(t), args.emb_dim, args.n_layers, 56 | bytes_per_elem, args.n_heads) 57 | for t in ctx 58 | ], dtype=float) 59 | 60 | # 2) DeltaNet only 61 | dnet_bytes_const = kv_bytes_total_deltanet_no_conv( 62 | args.batch, args.emb_dim, args.n_layers, 63 | bytes_per_elem, args.n_heads 64 | ) 65 | dnet_bytes = np.full_like(mha_bytes, fill_value=dnet_bytes_const, dtype=float) 66 | 67 | # 3) 3:1 layer ratio (3 DeltaNet : 1 Full Attention) 68 | n_mha_layers = args.n_layers / 4 69 | n_dnet_layers = args.n_layers - n_mha_layers 70 | mix_bytes = np.array([ 71 | kv_bytes_total_mha(args.batch, int(t), args.emb_dim, n_mha_layers, 72 | bytes_per_elem, args.n_heads) 73 | + kv_bytes_total_deltanet_no_conv(args.batch, args.emb_dim, n_dnet_layers, 74 | bytes_per_elem, args.n_heads) 75 | for t in ctx 76 | ], dtype=float) 77 | 78 | # Convert to GB 79 | mha_gb = gb(mha_bytes) 80 | dnet_gb = gb(dnet_bytes) 81 | mix_gb = gb(mix_bytes) 82 | 83 | # Plot 84 | fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 4.5)) 85 | ax.plot(ctx, mha_gb, label="Full Attention (MHA) KV cache") 86 | ax.plot(ctx, dnet_gb, label="All Gated DeltaNet (no conv)") 87 | ax.plot(ctx, mix_gb, label="3:1 layer ratio (3 DeltaNet : 1 Full Attention)") 88 | 89 | ax.set_xlabel("Context length (number of tokens)") 90 | ax.set_ylabel("KV cache size (GB)") 91 | ax.grid(True, which="both", linestyle="--", linewidth=0.5, alpha=0.6) 92 | ax.legend() 93 | 94 | fig.tight_layout() 95 | plt.savefig("deltanet_memory_plot.pdf", dpi=160) 96 | plt.close(fig) 97 | 98 | 99 | if __name__ == "__main__": 100 | main() 101 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch05/03_bonus_pretraining_on_gutenberg/prepare_dataset.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | """ 7 | Script that processes the Project Gutenberg files into fewer larger files. 8 | """ 9 | 10 | import argparse 11 | import os 12 | import re 13 | from tqdm import tqdm 14 | from gutenberg.src.cleanup import strip_headers 15 | 16 | 17 | def is_english(text, threshold=0.9): 18 | ascii_chars = sum(1 for c in text if ord(c) < 128) 19 | return ascii_chars / len(text) > threshold 20 | 21 | 22 | def combine_files(file_paths, target_dir, max_size_mb=500, separator="<|endoftext|>", fallback_encoding="latin1"): 23 | if not os.path.exists(target_dir): 24 | os.makedirs(target_dir) 25 | 26 | current_content = [] 27 | current_size = 0 28 | file_counter = 1 29 | 30 | for file_path in tqdm(file_paths): 31 | try: 32 | with open(file_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as file: 33 | content = file.read() 34 | except UnicodeDecodeError: 35 | # Attempt to read the file with a fallback encoding 36 | tqdm.write(f"Warning: UnicodeDecodeError encountered. Trying fallback encoding for {file_path}") 37 | with open(file_path, "r", encoding=fallback_encoding) as file: 38 | content = file.read() 39 | 40 | if not is_english(content): 41 | tqdm.write(f"Skipping {file_path} as it does not contain primarily English text.") 42 | continue 43 | content = strip_headers(content) 44 | 45 | # Regular expression to replace multiple blank lines with a single blank line 46 | content = re.sub(r"\n\s*\n", "\n\n", content) 47 | estimated_size = len(content.encode("utf-8")) 48 | 49 | if current_size + estimated_size > max_size_mb * 1024 * 1024: 50 | target_file_path = os.path.join(target_dir, f"combined_{file_counter}.txt") 51 | with open(target_file_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as target_file: 52 | target_file.write(separator.join(current_content)) 53 | file_counter += 1 54 | current_content = [content] 55 | current_size = estimated_size 56 | else: 57 | current_content.append(content) 58 | current_size += estimated_size 59 | 60 | if current_content: 61 | target_file_path = os.path.join(target_dir, f"combined_{file_counter}.txt") 62 | with open(target_file_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as target_file: 63 | target_file.write(separator.join(current_content)) 64 | return file_counter 65 | 66 | 67 | if __name__ == "__main__": 68 | 69 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Preprocess and combine text files for pretraining") 70 | 71 | parser.add_argument("--data_dir", type=str, default="gutenberg/data/raw", 72 | help="Directory containing the downloaded raw training data") 73 | parser.add_argument("--max_size_mb", type=int, default=500, 74 | help="The maximum file size for each concatenated file in megabytes") 75 | parser.add_argument("--output_dir", type=str, default="gutenberg_preprocessed", 76 | help="Directory where the preprocessed data will be saved") 77 | 78 | args = parser.parse_args() 79 | 80 | all_files = [os.path.join(path, name) for path, subdirs, files in os.walk(args.data_dir) 81 | for name in files if name.endswith((".txt", ".txt.utf8"))] 82 | 83 | print(f"{len(all_files)} file(s) to process.") 84 | file_counter = combine_files(all_files, args.output_dir, max_size_mb=args.max_size_mb) 85 | print(f"{file_counter} file(s) saved in {os.path.abspath(args.output_dir)}") 86 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /pkg/llms_from_scratch/tests/test_ch07.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | from llms_from_scratch.ch04 import GPTModel 7 | from llms_from_scratch.ch05 import train_model_simple 8 | from llms_from_scratch.ch07 import ( 9 | download_and_load_file, InstructionDataset, format_input, custom_collate_fn 10 | ) 11 | 12 | from functools import partial 13 | 14 | import torch 15 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader 16 | import tiktoken 17 | 18 | 19 | def test_instruction_finetune(tmp_path): 20 | 21 | ####################################### 22 | # Download and prepare dataset 23 | ####################################### 24 | file_path = tmp_path / "instruction-data.json" 25 | url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/main/ch07/01_main-chapter-code/instruction-data.json" 26 | data = download_and_load_file(file_path, url) 27 | 28 | train_portion = int(len(data) * 0.85) # 85% for training 29 | test_portion = int(len(data) * 0.1) # 10% for testing 30 | 31 | train_data = data[:train_portion] 32 | test_data = data[train_portion:train_portion + test_portion] 33 | val_data = data[train_portion + test_portion:] 34 | 35 | # Use very small subset for testing purposes 36 | train_data = train_data[:15] 37 | val_data = val_data[:15] 38 | test_data = test_data[:15] 39 | 40 | tokenizer = tiktoken.get_encoding("gpt2") 41 | device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") 42 | 43 | customized_collate_fn = partial(custom_collate_fn, device=device, allowed_max_length=100) 44 | 45 | num_workers = 0 46 | batch_size = 8 47 | 48 | torch.manual_seed(123) 49 | 50 | train_dataset = InstructionDataset(train_data, tokenizer) 51 | train_loader = DataLoader( 52 | train_dataset, 53 | batch_size=batch_size, 54 | collate_fn=customized_collate_fn, 55 | shuffle=True, 56 | drop_last=True, 57 | num_workers=num_workers 58 | ) 59 | 60 | val_dataset = InstructionDataset(val_data, tokenizer) 61 | val_loader = DataLoader( 62 | val_dataset, 63 | batch_size=batch_size, 64 | collate_fn=customized_collate_fn, 65 | shuffle=False, 66 | drop_last=False, 67 | num_workers=num_workers 68 | ) 69 | 70 | ####################################### 71 | # Load pretrained model 72 | ####################################### 73 | 74 | # Small GPT model for testing purposes 75 | BASE_CONFIG = { 76 | "vocab_size": 50257, 77 | "context_length": 120, 78 | "drop_rate": 0.0, 79 | "qkv_bias": False, 80 | "emb_dim": 12, 81 | "n_layers": 1, 82 | "n_heads": 2 83 | } 84 | model = GPTModel(BASE_CONFIG) 85 | model.eval() 86 | device = "cpu" 87 | CHOOSE_MODEL = "Small test model" 88 | 89 | print("Loaded model:", CHOOSE_MODEL) 90 | print(50*"-") 91 | 92 | ####################################### 93 | # Finetuning the model 94 | ####################################### 95 | 96 | num_epochs = 10 97 | optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=5e-5, weight_decay=0.1) 98 | 99 | torch.manual_seed(123) 100 | train_losses, val_losses, tokens_seen = train_model_simple( 101 | model, train_loader, val_loader, optimizer, device, 102 | num_epochs=num_epochs, eval_freq=5, eval_iter=5, 103 | start_context=format_input(val_data[0]), tokenizer=tokenizer 104 | ) 105 | 106 | assert round(train_losses[0], 1) == 10.9 107 | assert round(val_losses[0], 1) == 10.9 108 | assert train_losses[-1] < train_losses[0] 109 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /setup/01_optional-python-setup-preferences/native-pixi.md: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Native pixi Python and package management 2 | 3 | This tutorial is an alternative to the [`./native-uv.md`](native-uv.md) document for those who prefer `pixi`'s native commands over traditional environment and package managers like `conda` and `pip`. 4 | 5 | Note that pixi uses `uv add` under the hood, as described in [`./native-uv.md`](native-uv.md). 6 | 7 | Pixi and uv are both modern package and environment management tools for Python, but pixi is a polyglot package manager designed for managing not just Python but also other languages (similar to conda), while uv is a Python-specific tool optimized for ultra-fast dependency resolution and package installation. 8 | 9 | Someone might choose pixi over uv if they need a polyglot package manager that supports multiple languages (not just Python) or prefer a declarative environment management approach similar to conda. For more information, please visit the official [pixi documentation](https://pixi.sh/latest/). 10 | 11 | In this tutorial, I am using a computer running macOS, but this workflow is similar for Linux machines and may work for other operating systems as well. 12 | 13 | 14 | ## 1. Install pixi 15 | 16 | Pixi can be installed as follows, depending on your operating system. 17 | 18 |
19 | 20 | **macOS and Linux** 21 | 22 | ```bash 23 | curl -fsSL https://pixi.sh/install.sh | sh 24 | ``` 25 | 26 | or 27 | 28 | ```bash 29 | wget -qO- https://pixi.sh/install.sh | sh 30 | ``` 31 | 32 |
33 | 34 | **Windows** 35 | 36 | Download the installer from the official [documentation](https://pixi.sh/latest/installation/#__tabbed_1_2) or run the listed PowerShell command. 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 | > **Note:** 41 | > For more installation options, please refer to the official [pixi documentation](https://pixi.sh/latest/). 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 | ## 1. Install Python 46 | 47 | You can install Python using pixi: 48 | 49 | ```bash 50 | pixi add python=3.10 51 | ``` 52 | 53 | > **Note:** 54 | > I recommend installing a Python version that is at least 2 versions older than the most recent release to ensure PyTorch compatibility. For example, if the most recent version is Python 3.13, I recommend installing version 3.10 or 3.11. You can find out the most recent Python version by visiting [python.org](https://www.python.org). 55 | 56 | 57 | ## 3. Install Python packages and dependencies 58 | 59 | To install all required packages from a `pixi.toml` file (such as the one located at the top level of this GitHub repository), run the following command, assuming the file is in the same directory as your terminal session: 60 | 61 | ```bash 62 | pixi install 63 | ``` 64 | 65 | > **Note:** 66 | > If you encounter issues with dependencies (for example, if you are using Windows), you can always fall back to pip: `pixi run pip install -U -r requirements.txt` 67 | 68 | By default, `pixi install` will create a separate virtual environment specific to the project. 69 | 70 | You can install new packages that are not specified in `pixi.toml` via `pixi add`, for example: 71 | 72 | ```bash 73 | pixi add packaging 74 | ``` 75 | 76 | And you can remove packages via `pixi remove`, for example, 77 | 78 | ```bash 79 | pixi remove packaging 80 | ``` 81 | 82 | 83 | ## 4. Run Python code 84 | 85 | Your environment should now be ready to run the code in the repository. 86 | 87 | Optionally, you can run an environment check by executing the `python_environment_check.py` script in this repository: 88 | 89 | ```bash 90 | pixi run python setup/02_installing-python-libraries/python_environment_check.py 91 | ``` 92 | 93 |
94 | 95 | **Launching JupyterLab** 96 | 97 | You can launch a JupyterLab instance via: 98 | 99 | ```bash 100 | pixi run jupyter lab 101 | ``` 102 | 103 | 104 | --- 105 | 106 | Any questions? Please feel free to reach out in the [Discussion Forum](https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/discussions). 107 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /pkg/llms_from_scratch/tests/test_ch05.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | from llms_from_scratch.ch02 import create_dataloader_v1 7 | from llms_from_scratch.ch04 import GPTModel, GPTModelFast 8 | from llms_from_scratch.ch05 import train_model_simple 9 | 10 | import os 11 | 12 | import requests 13 | import pytest 14 | import tiktoken 15 | import torch 16 | from torch.utils.data import Subset, DataLoader 17 | 18 | 19 | GPT_CONFIG_124M = { 20 | "vocab_size": 50257, 21 | "context_length": 256, # Shortened for test speed 22 | "emb_dim": 768, 23 | "n_heads": 12, 24 | "n_layers": 12, 25 | "drop_rate": 0.1, 26 | "qkv_bias": False 27 | } 28 | 29 | OTHER_SETTINGS = { 30 | "learning_rate": 5e-4, 31 | "num_epochs": 2, 32 | "batch_size": 1, 33 | "weight_decay": 0.1 34 | } 35 | 36 | 37 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("ModelClass", [GPTModel, GPTModelFast]) 38 | def test_train_simple(tmp_path, ModelClass): 39 | torch.manual_seed(123) 40 | device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") 41 | 42 | ############################## 43 | # Download data if necessary 44 | ############################## 45 | file_path = tmp_path / "the-verdict.txt" 46 | url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/main/ch02/01_main-chapter-code/the-verdict.txt" 47 | 48 | if not os.path.exists(file_path): 49 | response = requests.get(url, timeout=30) 50 | response.raise_for_status() 51 | text_data = response.text 52 | with open(file_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f: 53 | f.write(text_data) 54 | else: 55 | with open(file_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f: 56 | text_data = f.read() 57 | 58 | ############################## 59 | # Set up dataloaders 60 | ############################## 61 | train_ratio = 0.90 62 | split_idx = int(train_ratio * len(text_data)) 63 | 64 | train_loader = create_dataloader_v1( 65 | text_data[:split_idx], 66 | batch_size=OTHER_SETTINGS["batch_size"], 67 | max_length=GPT_CONFIG_124M["context_length"], 68 | stride=GPT_CONFIG_124M["context_length"], 69 | drop_last=True, 70 | shuffle=True, 71 | num_workers=0 72 | ) 73 | 74 | val_loader = create_dataloader_v1( 75 | text_data[split_idx:], 76 | batch_size=OTHER_SETTINGS["batch_size"], 77 | max_length=GPT_CONFIG_124M["context_length"], 78 | stride=GPT_CONFIG_124M["context_length"], 79 | drop_last=False, 80 | shuffle=False, 81 | num_workers=0 82 | ) 83 | 84 | # Limit to 1 batch for speed 85 | train_subset = Subset(train_loader.dataset, range(1)) 86 | one_batch_train_loader = DataLoader(train_subset, batch_size=1) 87 | val_subset = Subset(val_loader.dataset, range(1)) 88 | one_batch_val_loader = DataLoader(val_subset, batch_size=1) 89 | 90 | ############################## 91 | # Train model 92 | ############################## 93 | model = ModelClass(GPT_CONFIG_124M) 94 | model.to(device) 95 | 96 | optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW( 97 | model.parameters(), 98 | lr=OTHER_SETTINGS["learning_rate"], 99 | weight_decay=OTHER_SETTINGS["weight_decay"] 100 | ) 101 | 102 | tokenizer = tiktoken.get_encoding("gpt2") 103 | 104 | train_losses, val_losses, tokens_seen = train_model_simple( 105 | model, one_batch_train_loader, one_batch_val_loader, optimizer, device, 106 | num_epochs=OTHER_SETTINGS["num_epochs"], eval_freq=1, eval_iter=1, 107 | start_context="Every effort moves you", tokenizer=tokenizer 108 | ) 109 | 110 | assert round(train_losses[0], 1) == 7.6 111 | assert round(val_losses[0], 1) == 10.1 112 | assert train_losses[-1] < train_losses[0] 113 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch07/01_main-chapter-code/ollama_evaluate.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | # 6 | # A minimal instruction finetuning file based on the code in chapter 7 7 | 8 | import json 9 | import psutil 10 | from tqdm import tqdm 11 | import requests 12 | 13 | 14 | def query_model(prompt, model="llama3", url="http://localhost:11434/api/chat"): 15 | # Create the data payload as a dictionary 16 | data = { 17 | "model": model, 18 | "messages": [ 19 | {"role": "user", "content": prompt} 20 | ], 21 | "options": { # Settings below are required for deterministic responses 22 | "seed": 123, 23 | "temperature": 0, 24 | "num_ctx": 2048 25 | } 26 | } 27 | 28 | # Send the POST request 29 | with requests.post(url, json=data, stream=True, timeout=30) as r: 30 | r.raise_for_status() 31 | response_data = "" 32 | for line in r.iter_lines(decode_unicode=True): 33 | if not line: 34 | continue 35 | response_json = json.loads(line) 36 | if "message" in response_json: 37 | response_data += response_json["message"]["content"] 38 | 39 | return response_data 40 | 41 | 42 | def check_if_running(process_name): 43 | running = False 44 | for proc in psutil.process_iter(["name"]): 45 | if process_name in proc.info["name"]: 46 | running = True 47 | break 48 | return running 49 | 50 | 51 | def format_input(entry): 52 | instruction_text = ( 53 | f"Below is an instruction that describes a task. " 54 | f"Write a response that appropriately completes the request." 55 | f"\n\n### Instruction:\n{entry['instruction']}" 56 | ) 57 | 58 | input_text = f"\n\n### Input:\n{entry['input']}" if entry["input"] else "" 59 | 60 | return instruction_text + input_text 61 | 62 | 63 | def main(file_path): 64 | ollama_running = check_if_running("ollama") 65 | 66 | if not ollama_running: 67 | raise RuntimeError("Ollama not running. Launch ollama before proceeding.") 68 | print("Ollama running:", check_if_running("ollama")) 69 | 70 | with open(file_path, "r") as file: 71 | test_data = json.load(file) 72 | 73 | model = "llama3" 74 | scores = generate_model_scores(test_data, "model_response", model) 75 | print(f"Number of scores: {len(scores)} of {len(test_data)}") 76 | print(f"Average score: {sum(scores)/len(scores):.2f}\n") 77 | 78 | 79 | def generate_model_scores(json_data, json_key, model="llama3"): 80 | scores = [] 81 | for entry in tqdm(json_data, desc="Scoring entries"): 82 | if entry[json_key] == "": 83 | scores.append(0) 84 | else: 85 | prompt = ( 86 | f"Given the input `{format_input(entry)}` " 87 | f"and correct output `{entry['output']}`, " 88 | f"score the model response `{entry[json_key]}`" 89 | f" on a scale from 0 to 100, where 100 is the best score. " 90 | f"Respond with the integer number only." 91 | ) 92 | score = query_model(prompt, model) 93 | try: 94 | scores.append(int(score)) 95 | except ValueError: 96 | print(f"Could not convert score: {score}") 97 | continue 98 | 99 | return scores 100 | 101 | 102 | if __name__ == "__main__": 103 | 104 | import argparse 105 | 106 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser( 107 | description="Evaluate model responses with ollama" 108 | ) 109 | parser.add_argument( 110 | "--file_path", 111 | required=True, 112 | help=( 113 | "The path to the test dataset `.json` file with the" 114 | " `'output'` and `'model_response'` keys" 115 | ) 116 | ) 117 | args = parser.parse_args() 118 | 119 | main(file_path=args.file_path) 120 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch05/07_gpt_to_llama/tests/test_llama32_nb.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | import importlib 7 | from pathlib import Path 8 | 9 | import pytest 10 | import torch 11 | 12 | from llms_from_scratch.utils import import_definitions_from_notebook 13 | 14 | 15 | transformers_installed = importlib.util.find_spec("transformers") is not None 16 | 17 | 18 | @pytest.fixture 19 | def nb_imports(): 20 | nb_dir = Path(__file__).resolve().parents[1] 21 | mod = import_definitions_from_notebook(nb_dir, "standalone-llama32.ipynb") 22 | return mod 23 | 24 | 25 | @pytest.fixture 26 | def dummy_input(): 27 | torch.manual_seed(123) 28 | return torch.randint(0, 100, (1, 8)) # batch size 1, seq length 8 29 | 30 | 31 | @pytest.fixture 32 | def dummy_cfg_base(): 33 | return { 34 | "vocab_size": 100, 35 | "emb_dim": 32, # hidden_size 36 | "hidden_dim": 64, # intermediate_size (FFN) 37 | "n_layers": 2, 38 | "n_heads": 4, 39 | "head_dim": 8, 40 | "n_kv_groups": 1, 41 | "dtype": torch.float32, 42 | "rope_base": 500_000.0, 43 | "rope_freq": { 44 | "factor": 8.0, 45 | "low_freq_factor": 1.0, 46 | "high_freq_factor": 4.0, 47 | "original_context_length": 8192, 48 | }, 49 | "context_length": 64, 50 | } 51 | 52 | 53 | @torch.inference_mode() 54 | def test_dummy_llama3_forward(dummy_cfg_base, dummy_input, nb_imports): 55 | torch.manual_seed(123) 56 | model = nb_imports.Llama3Model(dummy_cfg_base) 57 | out = model(dummy_input) 58 | assert out.shape == (1, dummy_input.size(1), dummy_cfg_base["vocab_size"]) 59 | 60 | 61 | @torch.inference_mode() 62 | @pytest.mark.skipif(not transformers_installed, reason="transformers not installed") 63 | def test_llama3_base_equivalence_with_transformers(nb_imports): 64 | from transformers.models.llama import LlamaConfig, LlamaForCausalLM 65 | cfg = { 66 | "vocab_size": 257, 67 | "context_length": 8192, 68 | "emb_dim": 32, 69 | "n_heads": 4, 70 | "n_layers": 2, 71 | "hidden_dim": 64, 72 | "n_kv_groups": 2, 73 | "rope_base": 500_000.0, 74 | "rope_freq": { 75 | "factor": 32.0, 76 | "low_freq_factor": 1.0, 77 | "high_freq_factor": 4.0, 78 | "original_context_length": 8192, 79 | }, 80 | "dtype": torch.float32, 81 | } 82 | 83 | ours = nb_imports.Llama3Model(cfg) 84 | 85 | hf_cfg = LlamaConfig( 86 | vocab_size=cfg["vocab_size"], 87 | hidden_size=cfg["emb_dim"], 88 | num_attention_heads=cfg["n_heads"], 89 | num_key_value_heads=cfg["n_kv_groups"], 90 | num_hidden_layers=cfg["n_layers"], 91 | intermediate_size=cfg["hidden_dim"], 92 | max_position_embeddings=cfg["context_length"], 93 | rms_norm_eps=1e-5, 94 | attention_bias=False, 95 | rope_theta=cfg["rope_base"], 96 | tie_word_embeddings=False, 97 | attn_implementation="eager", 98 | torch_dtype=torch.float32, 99 | rope_scaling={ 100 | "type": "llama3", 101 | "factor": cfg["rope_freq"]["factor"], 102 | "low_freq_factor": cfg["rope_freq"]["low_freq_factor"], 103 | "high_freq_factor": cfg["rope_freq"]["high_freq_factor"], 104 | "original_max_position_embeddings": cfg["rope_freq"]["original_context_length"], 105 | }, 106 | ) 107 | theirs = LlamaForCausalLM(hf_cfg) 108 | 109 | hf_state = theirs.state_dict() 110 | nb_imports.load_weights_into_llama(ours, {"n_layers": cfg["n_layers"], "hidden_dim": cfg["hidden_dim"]}, hf_state) 111 | 112 | x = torch.randint(0, cfg["vocab_size"], (2, 8), dtype=torch.long) 113 | ours_logits = ours(x) 114 | theirs_logits = theirs(x).logits.to(ours_logits.dtype) 115 | 116 | torch.testing.assert_close(ours_logits, theirs_logits, rtol=1e-5, atol=1e-5) 117 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch05/12_gemma3/tests/test_gemma3_nb.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | import importlib 7 | from pathlib import Path 8 | 9 | import pytest 10 | import torch 11 | 12 | from llms_from_scratch.utils import import_definitions_from_notebook 13 | 14 | 15 | transformers_installed = importlib.util.find_spec("transformers") is not None 16 | 17 | 18 | @pytest.fixture 19 | def nb_imports(): 20 | nb_dir = Path(__file__).resolve().parents[1] 21 | mod = import_definitions_from_notebook(nb_dir, "standalone-gemma3.ipynb") 22 | return mod 23 | 24 | 25 | @pytest.fixture 26 | def dummy_input(): 27 | torch.manual_seed(123) 28 | return torch.randint(0, 100, (1, 8)) # batch size 1, seq length 8 29 | 30 | 31 | @pytest.fixture 32 | def dummy_cfg_base(): 33 | return { 34 | "vocab_size": 100, 35 | "emb_dim": 32, 36 | "hidden_dim": 64, 37 | "n_layers": 2, 38 | "n_heads": 4, 39 | "head_dim": 8, 40 | "n_kv_groups": 1, 41 | "qk_norm": True, # Gemma3 uses q/k RMSNorm 42 | "dtype": torch.float32, 43 | "rope_base": 1_000_000.0, # global RoPE base 44 | "rope_local_base": 10_000.0, # local RoPE base (unused in these tests) 45 | "context_length": 64, 46 | "sliding_window": 16, 47 | "layer_types": ["full_attention", "full_attention"], 48 | "query_pre_attn_scalar": 256, 49 | } 50 | 51 | 52 | @torch.inference_mode() 53 | def test_dummy_gemma3_forward(dummy_cfg_base, dummy_input, nb_imports): 54 | torch.manual_seed(123) 55 | model = nb_imports.Gemma3Model(dummy_cfg_base) 56 | out = model(dummy_input) 57 | assert out.shape == (1, dummy_input.size(1), dummy_cfg_base["vocab_size"]) 58 | 59 | 60 | @torch.inference_mode() 61 | @pytest.mark.skipif(not transformers_installed, reason="transformers not installed") 62 | def test_gemma3_base_equivalence_with_transformers(nb_imports): 63 | from transformers import Gemma3TextConfig, Gemma3ForCausalLM 64 | 65 | # Tiny config so the test is fast 66 | cfg = { 67 | "vocab_size": 257, 68 | "context_length": 8, 69 | "emb_dim": 32, 70 | "n_heads": 4, 71 | "n_layers": 2, 72 | "hidden_dim": 64, 73 | "head_dim": 8, 74 | "qk_norm": True, 75 | "n_kv_groups": 2, 76 | "rope_base": 1_000_000.0, 77 | "rope_local_base": 10_000.0, 78 | "sliding_window": 4, 79 | "layer_types": ["full_attention", "full_attention"], 80 | "dtype": torch.float32, 81 | "query_pre_attn_scalar": 256, 82 | } 83 | model = nb_imports.Gemma3Model(cfg) 84 | 85 | hf_cfg = Gemma3TextConfig( 86 | vocab_size=cfg["vocab_size"], 87 | max_position_embeddings=cfg["context_length"], 88 | hidden_size=cfg["emb_dim"], 89 | num_attention_heads=cfg["n_heads"], 90 | num_hidden_layers=cfg["n_layers"], 91 | intermediate_size=cfg["hidden_dim"], 92 | head_dim=cfg["head_dim"], 93 | num_key_value_heads=cfg["n_kv_groups"], 94 | rope_theta=cfg["rope_base"], 95 | rope_local_base_freq=cfg["rope_local_base"], 96 | layer_types=cfg["layer_types"], 97 | sliding_window=cfg["sliding_window"], 98 | tie_word_embeddings=False, 99 | attn_implementation="eager", 100 | torch_dtype=torch.float32, 101 | query_pre_attn_scalar=cfg["query_pre_attn_scalar"], 102 | rope_scaling={"rope_type": "default"}, 103 | ) 104 | hf_model = Gemma3ForCausalLM(hf_cfg) 105 | 106 | hf_state = hf_model.state_dict() 107 | param_config = {"n_layers": cfg["n_layers"], "hidden_dim": cfg["hidden_dim"]} 108 | nb_imports.load_weights_into_gemma(model, param_config, hf_state) 109 | 110 | x = torch.randint(0, cfg["vocab_size"], (2, cfg["context_length"]), dtype=torch.long) 111 | ours_logits = model(x) 112 | theirs_logits = hf_model(x).logits 113 | torch.testing.assert_close(ours_logits, theirs_logits, rtol=1e-5, atol=1e-5) 114 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch05/12_gemma3/tests/test_gemma3_kv_nb.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | import importlib 7 | from pathlib import Path 8 | 9 | import pytest 10 | import torch 11 | 12 | from llms_from_scratch.utils import import_definitions_from_notebook 13 | 14 | 15 | transformers_installed = importlib.util.find_spec("transformers") is not None 16 | 17 | 18 | @pytest.fixture 19 | def nb_imports(): 20 | nb_dir = Path(__file__).resolve().parents[1] 21 | mod = import_definitions_from_notebook(nb_dir, "standalone-gemma3-plus-kvcache.ipynb") 22 | return mod 23 | 24 | 25 | @pytest.fixture 26 | def dummy_input(): 27 | torch.manual_seed(123) 28 | return torch.randint(0, 100, (1, 8)) # batch size 1, seq length 8 29 | 30 | 31 | @pytest.fixture 32 | def dummy_cfg_base(): 33 | return { 34 | "vocab_size": 100, 35 | "emb_dim": 32, 36 | "hidden_dim": 64, 37 | "n_layers": 2, 38 | "n_heads": 4, 39 | "head_dim": 8, 40 | "n_kv_groups": 1, 41 | "qk_norm": True, # Gemma3 uses q/k RMSNorm 42 | "dtype": torch.float32, 43 | "rope_base": 1_000_000.0, # global RoPE base 44 | "rope_local_base": 10_000.0, # local RoPE base (unused in these tests) 45 | "context_length": 64, 46 | "sliding_window": 16, 47 | "layer_types": ["full_attention", "full_attention"], 48 | "query_pre_attn_scalar": 256, 49 | } 50 | 51 | 52 | @torch.inference_mode() 53 | def test_dummy_gemma3_forward(dummy_cfg_base, dummy_input, nb_imports): 54 | torch.manual_seed(123) 55 | model = nb_imports.Gemma3Model(dummy_cfg_base) 56 | out = model(dummy_input) 57 | assert out.shape == (1, dummy_input.size(1), dummy_cfg_base["vocab_size"]) 58 | 59 | 60 | @torch.inference_mode() 61 | @pytest.mark.skipif(not transformers_installed, reason="transformers not installed") 62 | def test_gemma3_base_equivalence_with_transformers(nb_imports): 63 | from transformers import Gemma3TextConfig, Gemma3ForCausalLM 64 | 65 | # Tiny config so the test is fast 66 | cfg = { 67 | "vocab_size": 257, 68 | "context_length": 8, 69 | "emb_dim": 32, 70 | "n_heads": 4, 71 | "n_layers": 2, 72 | "hidden_dim": 64, 73 | "head_dim": 8, 74 | "qk_norm": True, 75 | "n_kv_groups": 2, 76 | "rope_base": 1_000_000.0, 77 | "rope_local_base": 10_000.0, 78 | "sliding_window": 4, 79 | "layer_types": ["full_attention", "full_attention"], 80 | "dtype": torch.float32, 81 | "query_pre_attn_scalar": 256, 82 | } 83 | model = nb_imports.Gemma3Model(cfg) 84 | 85 | hf_cfg = Gemma3TextConfig( 86 | vocab_size=cfg["vocab_size"], 87 | max_position_embeddings=cfg["context_length"], 88 | hidden_size=cfg["emb_dim"], 89 | num_attention_heads=cfg["n_heads"], 90 | num_hidden_layers=cfg["n_layers"], 91 | intermediate_size=cfg["hidden_dim"], 92 | head_dim=cfg["head_dim"], 93 | num_key_value_heads=cfg["n_kv_groups"], 94 | rope_theta=cfg["rope_base"], 95 | rope_local_base_freq=cfg["rope_local_base"], 96 | layer_types=cfg["layer_types"], 97 | sliding_window=cfg["sliding_window"], 98 | tie_word_embeddings=False, 99 | attn_implementation="eager", 100 | torch_dtype=torch.float32, 101 | query_pre_attn_scalar=cfg["query_pre_attn_scalar"], 102 | rope_scaling={"rope_type": "default"}, 103 | ) 104 | hf_model = Gemma3ForCausalLM(hf_cfg) 105 | 106 | hf_state = hf_model.state_dict() 107 | param_config = {"n_layers": cfg["n_layers"], "hidden_dim": cfg["hidden_dim"]} 108 | nb_imports.load_weights_into_gemma(model, param_config, hf_state) 109 | 110 | x = torch.randint(0, cfg["vocab_size"], (2, cfg["context_length"]), dtype=torch.long) 111 | ours_logits = model(x) 112 | theirs_logits = hf_model(x).logits 113 | torch.testing.assert_close(ours_logits, theirs_logits, rtol=1e-5, atol=1e-5) 114 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /pkg/llms_from_scratch/appendix_d.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | from .ch05 import calc_loss_batch, evaluate_model, generate_and_print_sample 7 | 8 | import math 9 | import torch 10 | 11 | 12 | def find_highest_gradient(model): 13 | max_grad = None 14 | for param in model.parameters(): 15 | if param.grad is not None: 16 | grad_values = param.grad.data.flatten() 17 | max_grad_param = grad_values.max() 18 | if max_grad is None or max_grad_param > max_grad: 19 | max_grad = max_grad_param 20 | return max_grad 21 | 22 | 23 | def train_model(model, train_loader, val_loader, optimizer, device, 24 | n_epochs, eval_freq, eval_iter, start_context, tokenizer, 25 | warmup_steps, initial_lr=3e-05, min_lr=1e-6, orig_book_version=False): 26 | 27 | train_losses, val_losses, track_tokens_seen, track_lrs = [], [], [], [] 28 | tokens_seen, global_step = 0, -1 29 | 30 | # Retrieve the maximum learning rate from the optimizer 31 | peak_lr = optimizer.param_groups[0]["lr"] 32 | 33 | # Calculate the total number of iterations in the training process 34 | total_training_steps = len(train_loader) * n_epochs 35 | 36 | # Calculate the learning rate increment during the warmup phase 37 | lr_increment = (peak_lr - initial_lr) / warmup_steps 38 | 39 | for epoch in range(n_epochs): 40 | model.train() 41 | for input_batch, target_batch in train_loader: 42 | optimizer.zero_grad() 43 | global_step += 1 44 | 45 | # Adjust the learning rate based on the current phase (warmup or cosine annealing) 46 | if global_step < warmup_steps: 47 | # Linear warmup 48 | lr = initial_lr + global_step * lr_increment 49 | else: 50 | # Cosine annealing after warmup 51 | progress = ((global_step - warmup_steps) / 52 | (total_training_steps - warmup_steps)) 53 | lr = min_lr + (peak_lr - min_lr) * 0.5 * (1 + math.cos(math.pi * progress)) 54 | 55 | # Apply the calculated learning rate to the optimizer 56 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups: 57 | param_group["lr"] = lr 58 | track_lrs.append(lr) # Store the current learning rate 59 | 60 | # Calculate and backpropagate the loss 61 | loss = calc_loss_batch(input_batch, target_batch, model, device) 62 | loss.backward() 63 | 64 | # Apply gradient clipping after the warmup phase to avoid exploding gradients 65 | if orig_book_version: 66 | if global_step > warmup_steps: 67 | torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=1.0) 68 | else: 69 | if global_step >= warmup_steps: # the book originally used global_step > warmup_steps, which led to a skipped clipping step after warmup 70 | torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=1.0) 71 | 72 | optimizer.step() 73 | tokens_seen += input_batch.numel() 74 | 75 | # Periodically evaluate the model on the training and validation sets 76 | if global_step % eval_freq == 0: 77 | train_loss, val_loss = evaluate_model( 78 | model, train_loader, val_loader, 79 | device, eval_iter 80 | ) 81 | train_losses.append(train_loss) 82 | val_losses.append(val_loss) 83 | track_tokens_seen.append(tokens_seen) 84 | # Print the current losses 85 | print(f"Ep {epoch+1} (Iter {global_step:06d}): " 86 | f"Train loss {train_loss:.3f}, " 87 | f"Val loss {val_loss:.3f}") 88 | 89 | # Generate and print a sample from the model to monitor progress 90 | generate_and_print_sample( 91 | model, tokenizer, device, start_context 92 | ) 93 | 94 | return train_losses, val_losses, track_tokens_seen, track_lrs 95 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch05/11_qwen3/tests/test_qwen3_nb.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | import importlib 7 | from pathlib import Path 8 | 9 | import pytest 10 | import torch 11 | 12 | from llms_from_scratch.utils import import_definitions_from_notebook 13 | 14 | 15 | transformers_installed = importlib.util.find_spec("transformers") is not None 16 | 17 | 18 | @pytest.fixture 19 | def nb_imports(): 20 | nb_dir = Path(__file__).resolve().parents[1] 21 | mod = import_definitions_from_notebook(nb_dir, "standalone-qwen3.ipynb") 22 | return mod 23 | 24 | 25 | @pytest.fixture 26 | def dummy_input(): 27 | torch.manual_seed(123) 28 | return torch.randint(0, 100, (1, 8)) # batch size 1, seq length 8 29 | 30 | 31 | @pytest.fixture 32 | def dummy_cfg_base(): 33 | return { 34 | "vocab_size": 100, 35 | "emb_dim": 32, 36 | "hidden_dim": 64, 37 | "n_layers": 2, 38 | "n_heads": 4, 39 | "head_dim": 8, 40 | "n_kv_groups": 1, 41 | "qk_norm": False, 42 | "dtype": torch.float32, 43 | "rope_base": 10000, 44 | "context_length": 64, 45 | "num_experts": 0, 46 | } 47 | 48 | 49 | @pytest.fixture 50 | def dummy_cfg_moe(dummy_cfg_base): 51 | cfg = dummy_cfg_base.copy() 52 | cfg.update({ 53 | "num_experts": 4, 54 | "num_experts_per_tok": 2, 55 | "moe_intermediate_size": 64, 56 | }) 57 | return cfg 58 | 59 | 60 | @torch.inference_mode() 61 | def test_dummy_qwen3_forward(dummy_cfg_base, dummy_input, nb_imports): 62 | torch.manual_seed(123) 63 | model = nb_imports.Qwen3Model(dummy_cfg_base) 64 | out = model(dummy_input) 65 | assert out.shape == (1, dummy_input.size(1), dummy_cfg_base["vocab_size"]), \ 66 | f"Expected shape (1, seq_len, vocab_size), got {out.shape}" 67 | 68 | 69 | @torch.inference_mode() 70 | @pytest.mark.skipif(not transformers_installed, reason="transformers not installed") 71 | def test_qwen3_base_equivalence_with_transformers(nb_imports): 72 | from transformers import Qwen3Config, Qwen3ForCausalLM 73 | 74 | # Tiny config so the test is fast 75 | cfg = { 76 | "vocab_size": 257, 77 | "context_length": 8, 78 | "emb_dim": 32, 79 | "n_heads": 4, 80 | "n_layers": 2, 81 | "hidden_dim": 64, 82 | "head_dim": 8, 83 | "qk_norm": True, 84 | "n_kv_groups": 2, 85 | "rope_base": 1_000_000.0, 86 | "rope_local_base": 10_000.0, 87 | "sliding_window": 4, 88 | "layer_types": ["full_attention", "full_attention"], 89 | "dtype": torch.float32, 90 | "query_pre_attn_scalar": 256, 91 | } 92 | model = nb_imports.Qwen3Model(cfg) 93 | 94 | hf_cfg = Qwen3Config( 95 | vocab_size=cfg["vocab_size"], 96 | max_position_embeddings=cfg["context_length"], 97 | hidden_size=cfg["emb_dim"], 98 | num_attention_heads=cfg["n_heads"], 99 | num_hidden_layers=cfg["n_layers"], 100 | intermediate_size=cfg["hidden_dim"], 101 | head_dim=cfg["head_dim"], 102 | num_key_value_heads=cfg["n_kv_groups"], 103 | rope_theta=cfg["rope_base"], 104 | rope_local_base_freq=cfg["rope_local_base"], 105 | layer_types=cfg["layer_types"], 106 | sliding_window=cfg["sliding_window"], 107 | tie_word_embeddings=False, 108 | attn_implementation="eager", 109 | torch_dtype=torch.float32, 110 | query_pre_attn_scalar=cfg["query_pre_attn_scalar"], 111 | rope_scaling={"rope_type": "default"}, 112 | ) 113 | hf_model = Qwen3ForCausalLM(hf_cfg) 114 | 115 | hf_state = hf_model.state_dict() 116 | param_config = {"n_layers": cfg["n_layers"], "hidden_dim": cfg["hidden_dim"]} 117 | nb_imports.load_weights_into_qwen(model, param_config, hf_state) 118 | 119 | x = torch.randint(0, cfg["vocab_size"], (2, cfg["context_length"]), dtype=torch.long) 120 | ours_logits = model(x) 121 | theirs_logits = hf_model(x).logits 122 | torch.testing.assert_close(ours_logits, theirs_logits, rtol=1e-5, atol=1e-5) 123 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch05/11_qwen3/tests/test_qwen3_kvcache_nb.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | import importlib 7 | from pathlib import Path 8 | 9 | import pytest 10 | import torch 11 | 12 | from llms_from_scratch.utils import import_definitions_from_notebook 13 | 14 | 15 | transformers_installed = importlib.util.find_spec("transformers") is not None 16 | 17 | 18 | @pytest.fixture 19 | def nb_imports(): 20 | nb_dir = Path(__file__).resolve().parents[1] 21 | mod = import_definitions_from_notebook(nb_dir, "standalone-qwen3-plus-kvcache.ipynb") 22 | return mod 23 | 24 | 25 | @pytest.fixture 26 | def dummy_input(): 27 | torch.manual_seed(123) 28 | return torch.randint(0, 100, (1, 8)) # batch size 1, seq length 8 29 | 30 | 31 | @pytest.fixture 32 | def dummy_cfg_base(): 33 | return { 34 | "vocab_size": 100, 35 | "emb_dim": 32, 36 | "hidden_dim": 64, 37 | "n_layers": 2, 38 | "n_heads": 4, 39 | "head_dim": 8, 40 | "n_kv_groups": 1, 41 | "qk_norm": False, 42 | "dtype": torch.float32, 43 | "rope_base": 10000, 44 | "context_length": 64, 45 | "num_experts": 0, 46 | } 47 | 48 | 49 | @pytest.fixture 50 | def dummy_cfg_moe(dummy_cfg_base): 51 | cfg = dummy_cfg_base.copy() 52 | cfg.update({ 53 | "num_experts": 4, 54 | "num_experts_per_tok": 2, 55 | "moe_intermediate_size": 64, 56 | }) 57 | return cfg 58 | 59 | 60 | @torch.inference_mode() 61 | def test_dummy_qwen3_forward(dummy_cfg_base, dummy_input, nb_imports): 62 | torch.manual_seed(123) 63 | model = nb_imports.Qwen3Model(dummy_cfg_base) 64 | out = model(dummy_input) 65 | assert out.shape == (1, dummy_input.size(1), dummy_cfg_base["vocab_size"]), \ 66 | f"Expected shape (1, seq_len, vocab_size), got {out.shape}" 67 | 68 | 69 | @torch.inference_mode() 70 | @pytest.mark.skipif(not transformers_installed, reason="transformers not installed") 71 | def test_qwen3_base_equivalence_with_transformers(nb_imports): 72 | from transformers import Qwen3Config, Qwen3ForCausalLM 73 | 74 | # Tiny config so the test is fast 75 | cfg = { 76 | "vocab_size": 257, 77 | "context_length": 8, 78 | "emb_dim": 32, 79 | "n_heads": 4, 80 | "n_layers": 2, 81 | "hidden_dim": 64, 82 | "head_dim": 8, 83 | "qk_norm": True, 84 | "n_kv_groups": 2, 85 | "rope_base": 1_000_000.0, 86 | "rope_local_base": 10_000.0, 87 | "sliding_window": 4, 88 | "layer_types": ["full_attention", "full_attention"], 89 | "dtype": torch.float32, 90 | "query_pre_attn_scalar": 256, 91 | } 92 | model = nb_imports.Qwen3Model(cfg) 93 | 94 | hf_cfg = Qwen3Config( 95 | vocab_size=cfg["vocab_size"], 96 | max_position_embeddings=cfg["context_length"], 97 | hidden_size=cfg["emb_dim"], 98 | num_attention_heads=cfg["n_heads"], 99 | num_hidden_layers=cfg["n_layers"], 100 | intermediate_size=cfg["hidden_dim"], 101 | head_dim=cfg["head_dim"], 102 | num_key_value_heads=cfg["n_kv_groups"], 103 | rope_theta=cfg["rope_base"], 104 | rope_local_base_freq=cfg["rope_local_base"], 105 | layer_types=cfg["layer_types"], 106 | sliding_window=cfg["sliding_window"], 107 | tie_word_embeddings=False, 108 | attn_implementation="eager", 109 | torch_dtype=torch.float32, 110 | query_pre_attn_scalar=cfg["query_pre_attn_scalar"], 111 | rope_scaling={"rope_type": "default"}, 112 | ) 113 | hf_model = Qwen3ForCausalLM(hf_cfg) 114 | 115 | hf_state = hf_model.state_dict() 116 | param_config = {"n_layers": cfg["n_layers"], "hidden_dim": cfg["hidden_dim"]} 117 | nb_imports.load_weights_into_qwen(model, param_config, hf_state) 118 | 119 | x = torch.randint(0, cfg["vocab_size"], (2, cfg["context_length"]), dtype=torch.long) 120 | ours_logits = model(x) 121 | theirs_logits = hf_model(x).logits 122 | torch.testing.assert_close(ours_logits, theirs_logits, rtol=1e-5, atol=1e-5) 123 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /ch04/07_moe/plot_memory_estimates_moe.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt). 2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch" 3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch 4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch 5 | 6 | 7 | import argparse 8 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 9 | from ffn_moe_memory_estimator import ( 10 | estimate_params_and_hidden, 11 | ffn_params, 12 | router_params, 13 | ) 14 | 15 | 16 | def moe_active_and_total( 17 | emb_dim, 18 | hidden_dim, 19 | ffn_type, 20 | num_experts, 21 | top_k, 22 | match_dense=True, 23 | ): 24 | if match_dense: 25 | dense_params = ffn_params(emb_dim, hidden_dim, ffn_type) 26 | router = router_params(emb_dim, num_experts) 27 | if dense_params <= router: 28 | match_dense = False 29 | 30 | stats = estimate_params_and_hidden( 31 | emb_dim=emb_dim, 32 | hidden_dim=hidden_dim, 33 | ffn_type=ffn_type, 34 | num_experts=num_experts, 35 | match_dense=match_dense, 36 | ) 37 | 38 | active = stats["router"] + top_k * stats["per_expert_params"] 39 | return active, stats["moe_total"] 40 | 41 | 42 | def plot_active_params_vs_experts( 43 | emb_dim, 44 | hidden_dim, 45 | ffn_type="swiglu", 46 | top_k=2, 47 | max_experts=512, 48 | y_log=True, 49 | save_path=None, 50 | match_dense=True, 51 | ): 52 | experts = [1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 192, 256, 384, 512] 53 | experts = [e for e in experts if e <= max_experts] 54 | 55 | dense_active = ffn_params(emb_dim, hidden_dim, ffn_type) 56 | moe_active = [] 57 | moe_total = [] 58 | for e in experts: 59 | active, total = moe_active_and_total( 60 | emb_dim=emb_dim, 61 | hidden_dim=hidden_dim, 62 | ffn_type=ffn_type, 63 | num_experts=e, 64 | top_k=top_k, 65 | match_dense=match_dense, 66 | ) 67 | moe_active.append(active) 68 | moe_total.append(total) 69 | 70 | plt.figure(figsize=(7, 5)) 71 | plt.plot(experts, moe_active, marker="o", label="MoE active per token") 72 | plt.plot(experts, moe_total, marker="s", linestyle="--", label="MoE total parameters") 73 | plt.axhline(dense_active, linestyle=":", color="gray", 74 | label="FFN dense (active = total)") 75 | 76 | plt.xlabel(f"Number of experts (top_k = {top_k})") 77 | plt.ylabel("Parameters") 78 | if y_log: 79 | plt.yscale("log") 80 | plt.title( 81 | f"Active vs Total Parameters per Token\n" 82 | f"(emb_dim={emb_dim}, hidden_dim={hidden_dim}, ffn={ffn_type}, top_k={top_k})" 83 | ) 84 | plt.legend() 85 | plt.tight_layout() 86 | if save_path: 87 | plt.savefig(save_path, dpi=200) 88 | print(f"Saved plot to {save_path}") 89 | else: 90 | plt.show() 91 | 92 | 93 | def main(): 94 | p = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Plot Dense vs MoE active parameters.") 95 | p.add_argument("--emb_dim", type=int, required=True, help="Embedding dimension") 96 | p.add_argument("--hidden_dim", type=int, required=True, help="Dense FFN hidden size") 97 | p.add_argument("--ffn_type", choices=["gelu", "swiglu"], default="swiglu") 98 | p.add_argument("--top_k", type=int, default=2, help="Active experts per token") 99 | p.add_argument("--max_experts", type=int, default=512, help="Max experts on x-axis") 100 | p.add_argument("--no_log", action="store_true", help="Disable log-scale y-axis") 101 | p.add_argument("--save", type=str, default=None, help="Optional path to save PNG") 102 | p.add_argument( 103 | "--no_match_dense", 104 | action="store_true", 105 | help=("Disable matching MoE parameters to dense FFN total; " 106 | "uses provided hidden_dim instead."), 107 | ) 108 | args = p.parse_args() 109 | 110 | plot_active_params_vs_experts( 111 | emb_dim=args.emb_dim, 112 | hidden_dim=args.hidden_dim, 113 | ffn_type=args.ffn_type, 114 | top_k=args.top_k, 115 | max_experts=args.max_experts, 116 | y_log=not args.no_log, 117 | save_path=args.save, 118 | match_dense=not args.no_match_dense, 119 | ) 120 | 121 | 122 | if __name__ == "__main__": 123 | main() 124 | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 16 |
17 |
18 | #### Forward and backward pass
19 |
20 |
16 |
17 |
18 | #### Forward and backward pass
19 |
20 |  21 |
22 |
23 | #### Forward and backward pass after compilation
24 |
25 |
21 |
22 |
23 | #### Forward and backward pass after compilation
24 |
25 |  26 |
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch05/01_main-chapter-code/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 5: Pretraining on Unlabeled Data
2 |
3 | ### Main Chapter Code
4 |
5 | - [ch05.ipynb](ch05.ipynb) contains all the code as it appears in the chapter
6 | - [previous_chapters.py](previous_chapters.py) is a Python module that contains the `MultiHeadAttention` module and `GPTModel` class from the previous chapters, which we import in [ch05.ipynb](ch05.ipynb) to pretrain the GPT model
7 | - [gpt_download.py](gpt_download.py) contains the utility functions for downloading the pretrained GPT model weights
8 | - [exercise-solutions.ipynb](exercise-solutions.ipynb) contains the exercise solutions for this chapter
9 |
10 | ### Optional Code
11 |
12 | - [gpt_train.py](gpt_train.py) is a standalone Python script file with the code that we implemented in [ch05.ipynb](ch05.ipynb) to train the GPT model (you can think of it as a code file summarizing this chapter)
13 | - [gpt_generate.py](gpt_generate.py) is a standalone Python script file with the code that we implemented in [ch05.ipynb](ch05.ipynb) to load and use the pretrained model weights from OpenAI
14 |
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch07/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 7: Finetuning to Follow Instructions
2 |
3 |
4 | ## Main Chapter Code
5 |
6 | - [01_main-chapter-code](01_main-chapter-code) contains the main chapter code and exercise solutions
7 |
8 |
9 | ## Bonus Materials
10 |
11 | - [02_dataset-utilities](02_dataset-utilities) contains utility code that can be used for preparing an instruction dataset
12 | - [03_model-evaluation](03_model-evaluation) contains utility code for evaluating instruction responses using a local Llama 3 model and the GPT-4 API
13 | - [04_preference-tuning-with-dpo](04_preference-tuning-with-dpo) implements code for preference finetuning with Direct Preference Optimization (DPO)
14 | - [05_dataset-generation](05_dataset-generation) contains code to generate and improve synthetic datasets for instruction finetuning
15 | - [06_user_interface](06_user_interface) implements an interactive user interface to interact with the pretrained LLM
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
26 |
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch05/01_main-chapter-code/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 5: Pretraining on Unlabeled Data
2 |
3 | ### Main Chapter Code
4 |
5 | - [ch05.ipynb](ch05.ipynb) contains all the code as it appears in the chapter
6 | - [previous_chapters.py](previous_chapters.py) is a Python module that contains the `MultiHeadAttention` module and `GPTModel` class from the previous chapters, which we import in [ch05.ipynb](ch05.ipynb) to pretrain the GPT model
7 | - [gpt_download.py](gpt_download.py) contains the utility functions for downloading the pretrained GPT model weights
8 | - [exercise-solutions.ipynb](exercise-solutions.ipynb) contains the exercise solutions for this chapter
9 |
10 | ### Optional Code
11 |
12 | - [gpt_train.py](gpt_train.py) is a standalone Python script file with the code that we implemented in [ch05.ipynb](ch05.ipynb) to train the GPT model (you can think of it as a code file summarizing this chapter)
13 | - [gpt_generate.py](gpt_generate.py) is a standalone Python script file with the code that we implemented in [ch05.ipynb](ch05.ipynb) to load and use the pretrained model weights from OpenAI
14 |
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch07/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 7: Finetuning to Follow Instructions
2 |
3 |
4 | ## Main Chapter Code
5 |
6 | - [01_main-chapter-code](01_main-chapter-code) contains the main chapter code and exercise solutions
7 |
8 |
9 | ## Bonus Materials
10 |
11 | - [02_dataset-utilities](02_dataset-utilities) contains utility code that can be used for preparing an instruction dataset
12 | - [03_model-evaluation](03_model-evaluation) contains utility code for evaluating instruction responses using a local Llama 3 model and the GPT-4 API
13 | - [04_preference-tuning-with-dpo](04_preference-tuning-with-dpo) implements code for preference finetuning with Direct Preference Optimization (DPO)
14 | - [05_dataset-generation](05_dataset-generation) contains code to generate and improve synthetic datasets for instruction finetuning
15 | - [06_user_interface](06_user_interface) implements an interactive user interface to interact with the pretrained LLM
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |