\n", 12 | "
Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch\n", 13 | "\n", 14 | "
 \n",
17 | "
\n",
17 | "| \n",
10 | "\n",
11 | "Supplementary code for the Build a Large Language Model From Scratch book by Sebastian Raschka \n", 12 | " Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch\n", 13 | "\n", 14 | " | \n",
15 | "\n",
16 | " \n",
17 | " \n",
17 | " | \n",
18 | "
| \n",
11 | "\n",
12 | "Supplementary code for the Build a Large Language Model From Scratch book by Sebastian Raschka \n", 13 | " Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch\n", 14 | "\n", 15 | " | \n",
16 | "\n",
17 | " \n",
18 | " \n",
18 | " | \n",
19 | "
 16 |
17 |
18 | #### Forward and backward pass
19 |
20 |
16 |
17 |
18 | #### Forward and backward pass
19 |
20 |  21 |
22 |
23 | #### Forward and backward pass after compilation
24 |
25 |
21 |
22 |
23 | #### Forward and backward pass after compilation
24 |
25 |  26 |
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch03/03_understanding-buffers/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Understanding PyTorch Buffers
2 |
3 | - [understanding-buffers.ipynb](understanding-buffers.ipynb) explains the idea behind PyTorch buffers, which are used to implement the causal attention mechanism in chapter 3
4 |
5 |
6 |
26 |
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch03/03_understanding-buffers/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Understanding PyTorch Buffers
2 |
3 | - [understanding-buffers.ipynb](understanding-buffers.ipynb) explains the idea behind PyTorch buffers, which are used to implement the causal attention mechanism in chapter 3
4 |
5 |
6 | | \n",
11 | "\n",
12 | "Supplementary code for the Build a Large Language Model From Scratch book by Sebastian Raschka \n", 13 | " Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch\n", 14 | "\n", 15 | " | \n",
16 | "\n",
17 | " \n",
18 | " \n",
18 | " | \n",
19 | "
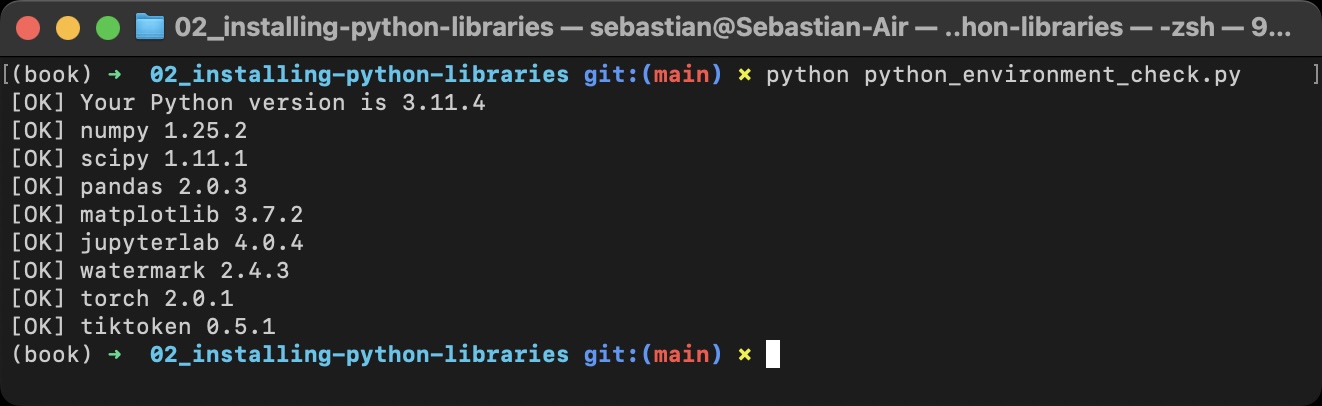 34 |
35 | It's also recommended to check the versions in JupyterLab by running the `python_environment_check.ipynb` in this directory, which should ideally give you the same results as above.
36 |
37 |
34 |
35 | It's also recommended to check the versions in JupyterLab by running the `python_environment_check.ipynb` in this directory, which should ideally give you the same results as above.
36 |
37 | 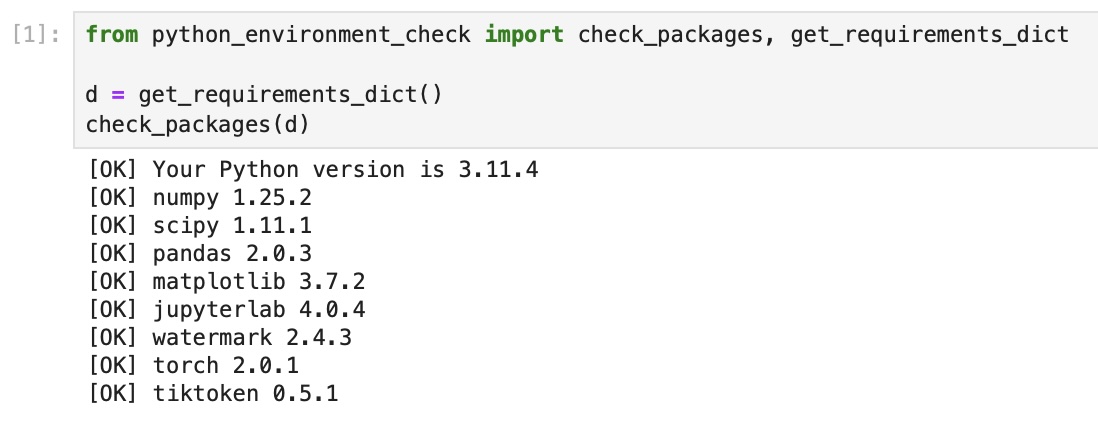 38 |
39 | If you see the following issues, it's likely that your JupyterLab instance is connected to wrong conda environment:
40 |
41 |
38 |
39 | If you see the following issues, it's likely that your JupyterLab instance is connected to wrong conda environment:
40 |
41 | 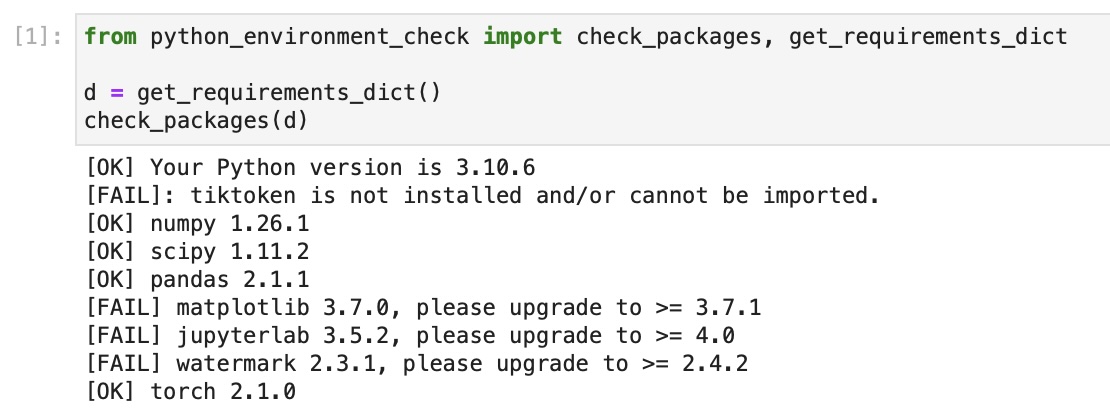 42 |
43 | In this case, you may want to use `watermark` to check if you opened the JupyterLab instance in the right conda environment using the `--conda` flag:
44 |
45 |
42 |
43 | In this case, you may want to use `watermark` to check if you opened the JupyterLab instance in the right conda environment using the `--conda` flag:
44 |
45 | 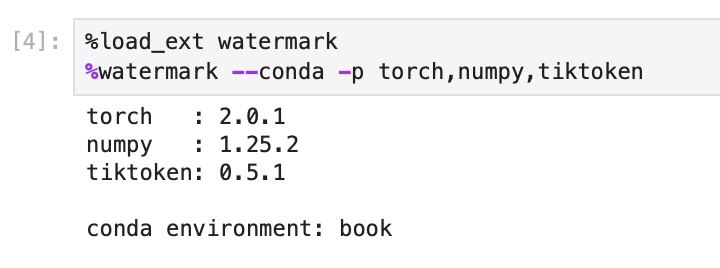 46 |
47 |
48 |
49 | ## Installing PyTorch
50 |
51 | PyTorch can be installed just like any other Python library or package using pip. For example:
52 |
53 | ```bash
54 | pip install torch
55 | ```
56 |
57 | However, since PyTorch is a comprehensive library featuring CPU- and GPU-compatible codes, the installation may require additional settings and explanation (see the *A.1.3 Installing PyTorch in the book for more information*).
58 |
59 | It's also highly recommended to consult the installation guide menu on the official PyTorch website at [https://pytorch.org](https://pytorch.org).
60 |
61 |
46 |
47 |
48 |
49 | ## Installing PyTorch
50 |
51 | PyTorch can be installed just like any other Python library or package using pip. For example:
52 |
53 | ```bash
54 | pip install torch
55 | ```
56 |
57 | However, since PyTorch is a comprehensive library featuring CPU- and GPU-compatible codes, the installation may require additional settings and explanation (see the *A.1.3 Installing PyTorch in the book for more information*).
58 |
59 | It's also highly recommended to consult the installation guide menu on the official PyTorch website at [https://pytorch.org](https://pytorch.org).
60 |
61 | 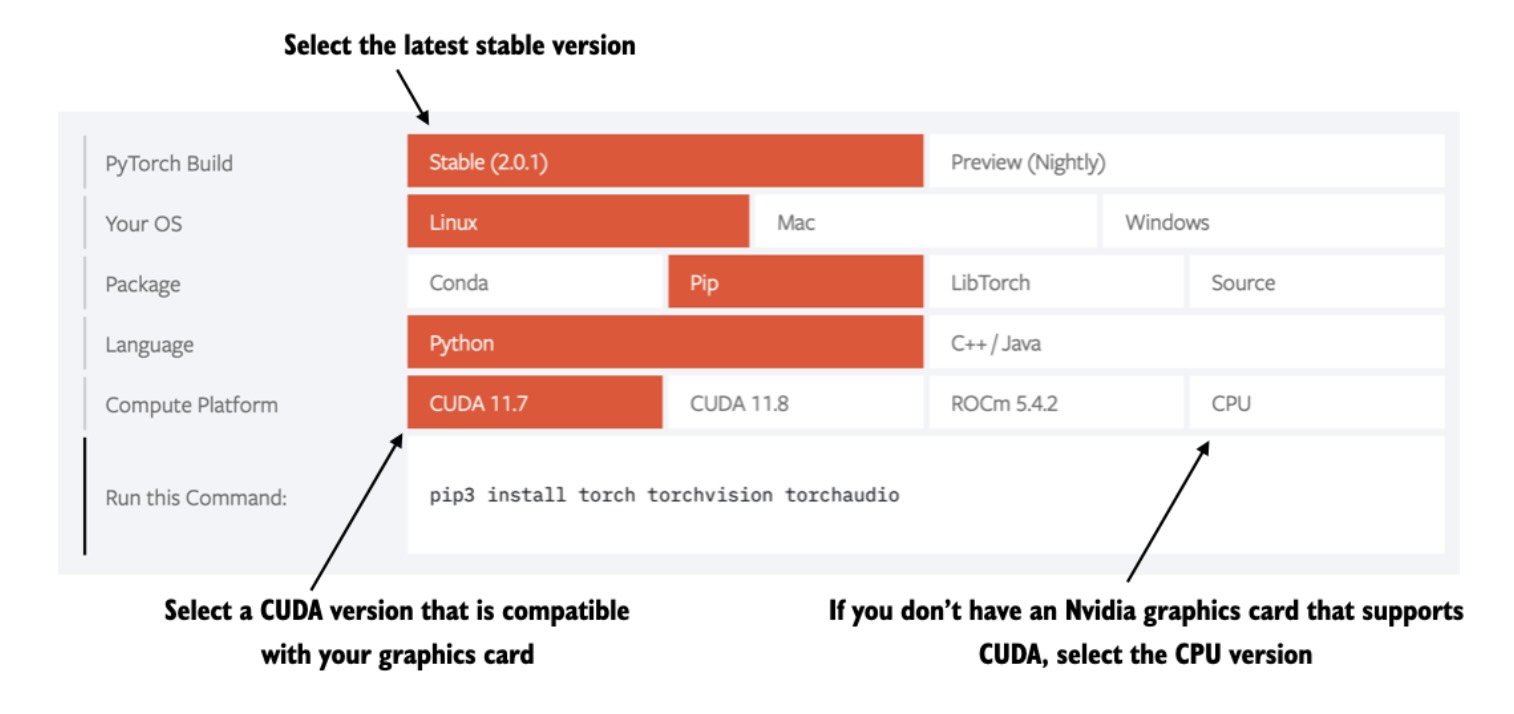 62 |
63 |
62 |
63 |