├── chF
├── 02_mmlu
│ ├── requirements-extra.txt
│ ├── random_guessing_baseline.py
│ ├── 1_letter_matching.py
│ ├── 2_logprob.py
│ └── 3_teacher_forcing.py
├── README.md
├── 03_leaderboards
│ ├── 1_elo_leaderboard.py
│ ├── votes.json
│ ├── README.md
│ └── 2_bradley_terry_leaderboard.py
└── 04_llm-judge
│ └── README.md
├── requirements.txt
├── ch01
└── README.md
├── chG
├── 01_main-chapter-code
│ ├── public
│ │ ├── logo_dark.webp
│ │ └── logo_light.webp
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── qwen3_chat_interface.py
│ └── qwen3_chat_interface_multiturn.py
└── README.md
├── chC
└── README.md
├── ch02
├── 01_main-chapter-code
│ └── README.md
├── 02_setup-tips
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── gpu-instructions.md
│ └── python-instructions.md
├── README.md
├── 04_torch-compile-windows
│ └── README.md
├── 05_use_model
│ ├── generate_simple.py
│ ├── chat.py
│ ├── chat_multiturn.py
│ └── README.md
└── 03_optimized-LLM
│ ├── compare_inference.py
│ └── README.md
├── .github
├── ISSUE_TEMPLATE
│ ├── ask-a-question.md
│ └── bug-report.yaml
├── workflows
│ ├── check-spelling-errors.yml
│ ├── tests-linux.yml
│ ├── tests-macos.yml
│ ├── basic-tests-old-pytorch.yml
│ ├── basic-tests-pip.yml
│ ├── basic-test-nightly-pytorch.yml
│ ├── check-links.yml
│ ├── tests-windows.yml
│ └── code-linter.yml
└── scripts
│ ├── check_notebook_line_length.py
│ └── check_double_quotes.py
├── ch03
├── README.md
├── 01_main-chapter-code
│ └── README.md
└── 02_math500-verifier-scripts
│ ├── evaluate_math500.py
│ └── README.md
├── ch04
├── README.md
└── 02_math500-inference-scaling-scripts
│ ├── cot_prompting_math500.py
│ └── README.md
├── ch05
└── README.md
├── tests
├── test_appendix_f.py
├── test_math500_scripts.py
├── test_appendix_c.py
├── conftest.py
├── test_ch02.py
├── test_ch02_ex.py
├── test_ch04.py
├── test_ch05.py
├── test_qwen3_optimized.py
└── test_qwen3_batched_stop.py
├── reasoning_from_scratch
├── __init__.py
├── ch02_ex.py
├── appendix_f.py
├── utils.py
├── ch02.py
├── appendix_c.py
└── ch05.py
├── pyproject.toml
└── .gitignore
/chF/02_mmlu/requirements-extra.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | datasets >= 4.1.1
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/requirements.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | reasoning-from-scratch >= 0.1.2
2 | sympy>=1.14.0 # For verifier in ch03
3 | torch >= 2.7.1
4 | tokenizers >= 0.21.2
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch01/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 1: Understanding Reasoning Models
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 | ## Main chapter code
6 |
7 | There is no code in this chapter.
8 |
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chG/01_main-chapter-code/public/logo_dark.webp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch/HEAD/chG/01_main-chapter-code/public/logo_dark.webp
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chG/01_main-chapter-code/public/logo_light.webp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch/HEAD/chG/01_main-chapter-code/public/logo_light.webp
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chG/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Appendix G: Chat Interface
2 |
3 |
4 | ## Main chapter code
5 |
6 | - [01_main-chapter-code](01_main-chapter-code) contains the main chapter code and exercise solutions
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chC/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Appendix C: Qwen3 LLM Source Code
2 |
3 |
4 | ## Main chapter code
5 |
6 | - [01_main-chapter-code](01_main-chapter-code) contains the main chapter code and exercise solutions
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/01_main-chapter-code/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 2: Generating Text with a Pre-Trained LLM
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 | ## Main chapter code
6 |
7 | - [ch02_main.ipynb](ch02_main.ipynb): main chapter code
8 | - [ch02_exercise-solutions.ipynb](ch02_exercise-solutions.ipynb): exercise solutions
9 |
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/02_setup-tips/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 2: Generating Text with a Pre-Trained LLM
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 | ## Bonus material
7 |
8 | - [python-instructions.md](python-instructions.md): optional Python setup recommendations and instructions
9 | - [gpu-instructions.md](gpu-instructions.md): recommendations for cloud compute resources
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/ask-a-question.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | name: Ask a Question
3 | about: Ask questions related to the book
4 | title: ''
5 | labels: [question]
6 | assignees: rasbt
7 |
8 | ---
9 |
10 | If you have a question that is not a bug, please consider asking it in this GitHub repository's [discussion forum](https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch/discussions).
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch03/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 3: Evaluating Reasoning Models
2 |
3 |
4 | ## Main chapter code
5 |
6 | - [01_main-chapter-code](01_main-chapter-code): main chapter code and exercise solutions
7 |
8 |
9 | ## Bonus material
10 |
11 | - [02_math500-verifier-scripts](02_math500-verifier-scripts): optional Python scripts to run the MATH-500 evaluation from the command line, including a batched version with higher throughput
12 |
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 2: Generating Text with a Pre-Trained LLM
2 |
3 |
4 | ## Main chapter code
5 |
6 | - [01_main-chapter-code](01_main-chapter-code): main chapter code and exercise solutions
7 |
8 |
9 | ## Bonus material
10 |
11 | - [02_setup-tips](02_setup-tips/): optional Python setup recommendations and cloud GPU recommendations
12 | - [03_optimized-LLM](03_optimized-LLM): info on how to use a GPU-optimized version of the LLM
13 |
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch04/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 4: Improving Reasoning with Inference-Time Scaling
2 |
3 |
4 | ## Main chapter code
5 |
6 | - [01_main-chapter-code](01_main-chapter-code): main chapter code and exercise solutions
7 |
8 |
9 | ## Bonus material
10 |
11 | - [02_math500-inference-scaling-scripts](02_math500-inference-scaling-scripts): optional Python scripts to apply the inference scaling techniques covered in this chapter (CoT prompting and self-consistency) to the MATH-500 evaluation from the previous chapter.
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch05/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 5: Inference-Time Scaling via Self-Refinement
2 |
3 |
4 | ## Main chapter code
5 |
6 | - [01_main-chapter-code](01_main-chapter-code): main chapter code and exercise solutions
7 |
8 |
9 | ## Bonus material
10 |
11 | - [02_math500-more-inference-scaling-scripts](02_math500-more-inference-scaling-scripts): optional Python scripts to apply the inference scaling techniques covered in this chapter (Best-of-N and self-refinement) to the MATH-500 evaluation from the previous chapter.
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chF/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Appendix F: Common Approaches to LLM Evaluation
2 |
3 |
4 | ## Main chapter code
5 |
6 | - [01_main-chapter-code](01_main-chapter-code): the main chapter code and exercise solutions
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 | ## Bonus materials
11 |
12 | - [02_mmlu](02_mmlu): MMLU benchmark evaluation with all three different MMLU approaches
13 | - [03_leaderboards](03_leaderboards): Elo and Bradley-Terry implementations of leaderboard rankings
14 | - [04_llm-judge](04_llm-judge): LLM-as-a-judge approach, where a judge LLM evaluates a candidate LLM
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_appendix_f.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | from reasoning_from_scratch.appendix_f import elo_ratings
6 | import math
7 |
8 |
9 | def test_elo_single_match():
10 | r = elo_ratings([("A", "B")], k_factor=32, initial_rating=1000)
11 | assert math.isclose(r["A"], 1016)
12 | assert math.isclose(r["B"], 984)
13 |
14 |
15 | def test_elo_total_points_constant():
16 | votes = [("A", "B"), ("B", "C"), ("A", "C")]
17 | r = elo_ratings(votes)
18 | assert math.isclose(sum(r.values()), 3000)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch03/01_main-chapter-code/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 3: Evaluating Reasoning Models
2 |
3 |
4 | ## Main chapter code
5 |
6 | - [ch03_main.ipynb](ch03_main.ipynb): main chapter code
7 | - [ch03_exercise-solutions.ipynb](ch03_exercise-solutions.ipynb): exercise solutions
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 | ## Bonus materials
12 |
13 | - [../02_math500-verifier-scripts/evaluate_math500.py](../02_math500-verifier-scripts/evaluate_math500.py): standalone script to evaluate models on the MATH-500 dataset
14 | - [../02_math500-verifier-scripts/evaluate_math500_batched.py](../02_math500-verifier-scripts/evaluate_math500_batched.py): same as above, but processes multiple examples in parallel during generation (for higher throughput)
15 |
16 | Both evaluation scripts import functionality from the [`reasoning_from_scratch`](../../reasoning_from_scratch) package to avoid code duplication. (See [chapter 2 setup instructions](../../ch02/02_setup-tips/python-instructions.md) for installation details.)
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/check-spelling-errors.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | name: Spell Check
6 |
7 | on:
8 | push:
9 | branches: [ main ]
10 | pull_request:
11 | branches: [ main ]
12 |
13 | jobs:
14 | spellcheck:
15 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
16 | env:
17 | SKIP_EXPENSIVE: "1"
18 | steps:
19 | - uses: actions/checkout@v4
20 | - name: Set up Python
21 | uses: actions/setup-python@v5
22 | with:
23 | python-version: "3.10"
24 | - name: Install codespell
25 | run: |
26 | curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
27 | uv sync --dev --python=3.10
28 | uv add codespell
29 | - name: Run codespell
30 | run: |
31 | source .venv/bin/activate
32 | codespell -L "ocassion,occassion,ot,te,tje" **/*.{txt,md,py,ipynb}
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/reasoning_from_scratch/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | """
6 | Reasoning package used by the "Reasoning Models From Scratch" book.
7 |
8 | Copyright (c) 2025, Sebastian Raschka
9 |
10 | Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
11 | you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
12 | You may obtain a copy of the License at
13 |
14 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
15 |
16 | or in the top-level LICENSE file of this repository.
17 |
18 | Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
19 | distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
20 | WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
21 | See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
22 | limitations under the License.
23 | """
24 |
25 | __version__ = "0.1.12"
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/tests-linux.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | name: Code tests Linux
6 |
7 | on:
8 | push:
9 | branches: [ main ]
10 | paths:
11 | - '**/*.py'
12 | - '**/*.ipynb'
13 | - '**/*.yaml'
14 | - '**/*.yml'
15 | - '**/*.sh'
16 | pull_request:
17 | branches: [ main ]
18 | paths:
19 | - '**/*.py'
20 | - '**/*.ipynb'
21 | - '**/*.yaml'
22 | - '**/*.yml'
23 | - '**/*.sh'
24 | workflow_dispatch:
25 |
26 | concurrency:
27 | group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.ref }}
28 | cancel-in-progress: true
29 |
30 | jobs:
31 | uv-tests:
32 | name: Code tests Linux
33 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
34 | env:
35 | SKIP_EXPENSIVE: "1"
36 | steps:
37 | - uses: actions/checkout@v4
38 |
39 | - name: Set up Python
40 | uses: actions/setup-python@v5
41 | with:
42 | python-version: "3.13"
43 |
44 | - name: Install uv and dependencies
45 | run: |
46 | curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
47 | uv sync --group dev
48 |
49 | - name: Run tests
50 | run: uv run pytest tests
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/tests-macos.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | name: Code tests macOS
6 |
7 | on:
8 | push:
9 | branches: [ main ]
10 | paths:
11 | - '**/*.py'
12 | - '**/*.ipynb'
13 | - '**/*.yaml'
14 | - '**/*.yml'
15 | - '**/*.sh'
16 | pull_request:
17 | branches: [ main ]
18 | paths:
19 | - '**/*.py'
20 | - '**/*.ipynb'
21 | - '**/*.yaml'
22 | - '**/*.yml'
23 | - '**/*.sh'
24 | workflow_dispatch:
25 |
26 | concurrency:
27 | group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.ref }}
28 | cancel-in-progress: true
29 |
30 | jobs:
31 | uv-tests:
32 | name: Code tests macOS
33 | runs-on: macos-latest
34 | env:
35 | SKIP_EXPENSIVE: "1"
36 | steps:
37 | - uses: actions/checkout@v4
38 |
39 | - name: Set up Python
40 | uses: actions/setup-python@v5
41 | with:
42 | python-version: "3.13"
43 |
44 | - name: Install uv and dependencies
45 | run: |
46 | curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
47 | uv sync --group dev
48 |
49 | - name: Run tests
50 | run: uv run pytest tests
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_math500_scripts.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import subprocess
6 | import sys
7 | from pathlib import Path
8 |
9 | import pytest
10 |
11 |
12 | SCRIPT_PATHS = [
13 | Path("ch03/02_math500-verifier-scripts/evaluate_math500_batched.py"),
14 | Path("ch03/02_math500-verifier-scripts/evaluate_math500.py"),
15 | Path("ch04/02_math500-inference-scaling-scripts/self_consistency_math500.py"),
16 | Path("ch04/02_math500-inference-scaling-scripts/cot_prompting_math500.py"),
17 | ]
18 |
19 |
20 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("script_path", SCRIPT_PATHS)
21 | def test_script_help_runs_without_import_errors(script_path):
22 |
23 | repo_root = Path(__file__).resolve().parent.parent
24 | full_path = repo_root / script_path
25 | assert full_path.exists(), f"Expected script at {full_path}"
26 |
27 | # Run scripts with --help to make sure they work
28 |
29 | result = subprocess.run(
30 | [sys.executable, str(full_path), "--help"],
31 | cwd=repo_root,
32 | capture_output=True,
33 | text=True,
34 | )
35 |
36 | assert result.returncode == 0, result.stderr
37 | assert "usage" in result.stdout.lower()
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_appendix_c.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import os
6 | from pathlib import Path
7 | import sys
8 | import torch
9 | import pytest
10 |
11 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
12 | generate_text_basic,
13 | generate_text_basic_cache,
14 | )
15 | # Local imports
16 | from test_qwen3 import test_model
17 | from conftest import import_definitions_from_notebook
18 |
19 |
20 | ROOT = Path(__file__).resolve().parents[1]
21 | sys.path.insert(0, str(ROOT))
22 |
23 |
24 | nb_path = ROOT / "chC" / "01_main-chapter-code" / "chC_main.ipynb"
25 | mod = import_definitions_from_notebook(nb_path, "chC_chC_main_defs")
26 | Qwen3Model = getattr(mod, "Qwen3Model")
27 |
28 | # Make CI more reproducible & robust
29 | os.environ["MKL_NUM_THREADS"] = "1"
30 | os.environ["OMP_NUM_THREADS"] = "1"
31 | torch.backends.mkldnn.enabled = False
32 | torch.set_num_threads(1)
33 | torch.use_deterministic_algorithms(True)
34 |
35 |
36 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("ModelClass", [Qwen3Model])
37 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("generate_fn", [generate_text_basic, generate_text_basic_cache])
38 | def test_model_here_too(ModelClass, qwen3_weights_path, generate_fn):
39 | test_model(ModelClass, qwen3_weights_path, generate_fn)
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/basic-tests-old-pytorch.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | name: Test Old PyTorch
6 |
7 | on:
8 | push:
9 | branches: [ main ]
10 | paths:
11 | - '**/*.py'
12 | - '**/*.ipynb'
13 | - '**/*.yaml'
14 | - '**/*.yml'
15 | - '**/*.sh'
16 | pull_request:
17 | branches: [ main ]
18 | paths:
19 | - '**/*.py'
20 | - '**/*.ipynb'
21 | - '**/*.yaml'
22 | - '**/*.yml'
23 | - '**/*.sh'
24 | workflow_dispatch:
25 |
26 | concurrency:
27 | group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.ref }}
28 | cancel-in-progress: true
29 |
30 | jobs:
31 | uv-tests:
32 | name: Code tests
33 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
34 | env:
35 | SKIP_EXPENSIVE: "1"
36 | steps:
37 | - uses: actions/checkout@v4
38 |
39 | - name: Set up Python (uv)
40 | uses: actions/setup-python@v5
41 | with:
42 | python-version: "3.13"
43 |
44 | - name: Install uv and dependencies
45 | shell: bash
46 | run: |
47 | curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
48 | uv sync --group dev
49 | uv add pytest-ruff torch==2.7.1
50 |
51 | - name: Test reasoning_from_scratch package
52 | shell: bash
53 | run: |
54 | uv run pytest tests
55 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/basic-tests-pip.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | name: Code Tests (Plain pip)
6 |
7 | on:
8 | push:
9 | branches: [ main ]
10 | paths:
11 | - '**/*.py'
12 | - '**/*.ipynb'
13 | - '**/*.yaml'
14 | - '**/*.yml'
15 | - '**/*.sh'
16 | pull_request:
17 | branches: [ main ]
18 | paths:
19 | - '**/*.py'
20 | - '**/*.ipynb'
21 | - '**/*.yaml'
22 | - '**/*.yml'
23 | - '**/*.sh'
24 | workflow_dispatch:
25 |
26 | concurrency:
27 | group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.ref }}
28 | cancel-in-progress: true
29 |
30 | jobs:
31 | pip-tests:
32 | name: Pip Tests (Ubuntu Only)
33 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
34 | env:
35 | SKIP_EXPENSIVE: "1"
36 | steps:
37 | - uses: actions/checkout@v4
38 |
39 | - name: Set up Python
40 | uses: actions/setup-python@v5
41 | with:
42 | python-version: "3.13"
43 | - name: Create Virtual Environment and Install Dependencies
44 | run: |
45 | python -m venv .venv
46 | source .venv/bin/activate
47 | pip install --upgrade pip
48 | pip install -r requirements.txt
49 | pip install .
50 | pip install pytest
51 | - name: Test Selected Python Scripts
52 | run: |
53 | source .venv/bin/activate
54 | pytest tests
55 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/basic-test-nightly-pytorch.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | name: Test Nightly PyTorch
6 |
7 | on:
8 | push:
9 | branches: [ main ]
10 | paths:
11 | - '**/*.py'
12 | - '**/*.ipynb'
13 | - '**/*.yaml'
14 | - '**/*.yml'
15 | - '**/*.sh'
16 | pull_request:
17 | branches: [ main ]
18 | paths:
19 | - '**/*.py'
20 | - '**/*.ipynb'
21 | - '**/*.yaml'
22 | - '**/*.yml'
23 | - '**/*.sh'
24 | workflow_dispatch:
25 |
26 | concurrency:
27 | group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.ref }}
28 | cancel-in-progress: true
29 |
30 | jobs:
31 | uv-tests:
32 | name: Code tests
33 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
34 | env:
35 | SKIP_EXPENSIVE: "1"
36 | steps:
37 | - uses: actions/checkout@v4
38 |
39 | - name: Set up Python (uv)
40 | uses: actions/setup-python@v5
41 | with:
42 | python-version: "3.13"
43 |
44 | - name: Install uv and dependencies
45 | shell: bash
46 | run: |
47 | curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
48 | uv sync --group dev
49 | uv pip install -U --pre torch --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cpu
50 |
51 | - name: Test reasoning_from_scratch package
52 | shell: bash
53 | run: |
54 | # uv run pytest tests
55 | # temporarily disabled
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/check-links.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | name: Check Hyperlinks
6 |
7 | on:
8 | push:
9 | branches: [ main ]
10 | pull_request:
11 | branches: [ main ]
12 |
13 | jobs:
14 | test:
15 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
16 | env:
17 | SKIP_EXPENSIVE: "1"
18 | steps:
19 | - uses: actions/checkout@v4
20 | - name: Set up Python
21 | uses: actions/setup-python@v5
22 | with:
23 | python-version: "3.10"
24 | - name: Install dependencies
25 | run: |
26 | curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
27 | uv add pytest-check-links
28 | - name: Check links
29 | run: |
30 | source .venv/bin/activate
31 | pytest --check-links ./ \
32 | --check-links-ignore "https://platform.openai.com/*" \
33 | --check-links-ignore "https://openai.com/*" \
34 | --check-links-ignore "https://arena.lmsys.org" \
35 | --check-links-ignore "https://unsloth.ai/blog/gradient" \
36 | --check-links-ignore "https://www.reddit.com/r/*" \
37 | --check-links-ignore "https://code.visualstudio.com/*" \
38 | --check-links-ignore "https://arxiv.org/*" \
39 | --check-links-ignore "https://ai.stanford.edu/~amaas/data/sentiment/" \
40 | --check-links-ignore "https://x.com/*" \
41 | --check-links-ignore "https://scholar.google.com/*" \
42 | --check-links-ignore "https://en.wikipedia.org/*"
43 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/tests-windows.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | name: Code tests Windows
6 |
7 | on:
8 | push:
9 | branches: [ main ]
10 | paths:
11 | - '**/*.py'
12 | - '**/*.ipynb'
13 | - '**/*.yaml'
14 | - '**/*.yml'
15 | - '**/*.sh'
16 | pull_request:
17 | branches: [ main ]
18 | paths:
19 | - '**/*.py'
20 | - '**/*.ipynb'
21 | - '**/*.yaml'
22 | - '**/*.yml'
23 | - '**/*.sh'
24 | workflow_dispatch:
25 |
26 | concurrency:
27 | group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.ref }}
28 | cancel-in-progress: true
29 |
30 | jobs:
31 | uv-tests:
32 | name: Code tests Windows
33 | runs-on: windows-latest
34 | env:
35 | SKIP_EXPENSIVE: "1"
36 | steps:
37 | - uses: actions/checkout@v4
38 |
39 | - name: Set up Python
40 | uses: actions/setup-python@v5
41 | with:
42 | python-version: "3.13"
43 |
44 | - name: Install uv and dependencies
45 | shell: bash
46 | run: |
47 | export PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$PATH"
48 | curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
49 | uv sync --group dev
50 |
51 | - name: Run tests
52 | shell: bash
53 | env:
54 | OMP_NUM_THREADS: "1"
55 | MKL_NUM_THREADS: "1"
56 | CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG: ":16:8"
57 | run: |
58 | export PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$PATH"
59 | uv run pytest tests
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chG/01_main-chapter-code/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Appendix G: Chat Interface
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 | This folder contains code for running a ChatGPT-like user interface to interact with the LLMs used and/or developed in this book, as shown below.
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 | 
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 | To implement this user interface, we use the open-source [Chainlit Python package](https://github.com/Chainlit/chainlit).
14 |
15 |
16 | ## Step 1: Install dependencies
17 |
18 | First, we install the `chainlit` package and dependency:
19 |
20 | ```bash
21 | pip install chainlit
22 | ```
23 |
24 | Or, if you are using `uv`:
25 |
26 | ```bash
27 | uv add chainlit
28 | ```
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 |
33 |
34 | ## Step 2: Run `app` code
35 |
36 | This folder contains 2 files:
37 |
38 | 1. [`qwen3_chat_interface.py`](qwen3_chat_interface.py): This file loads and uses the Qwen3 0.6B model in thinking mode.
39 | 2. [`qwen3_chat_interface_multiturn.py`](qwen3_chat_interface_multiturn.py): The same as above, but configured to remember the message history.
40 |
41 | (Open and inspect these files to learn more.)
42 |
43 | Run one of the following commands from the terminal to start the UI server:
44 |
45 | ```bash
46 | chainlit run qwen3_chat_interface.py
47 | ```
48 |
49 | or, if you are using `uv`:
50 |
51 | ```bash
52 | uv run chainlit run qwen3_chat_interface.py
53 | ```
54 |
55 | Running one of the commands above should open a new browser tab where you can interact with the model. If the browser tab does not open automatically, inspect the terminal command and copy the local address into your browser address bar (usually, the address is `http://localhost:8000`).
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chF/03_leaderboards/1_elo_leaderboard.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 | import json
5 | import argparse
6 |
7 |
8 | def elo_ratings(vote_pairs, k_factor=32, initial_rating=1000):
9 | ratings = {
10 | model: initial_rating
11 | for pair in vote_pairs
12 | for model in pair
13 | }
14 | for winner, loser in vote_pairs:
15 | expected = 1.0 / (
16 | 1.0 + 10 ** (
17 | (ratings[loser] - ratings[winner]) / 400.0
18 | )
19 | )
20 | ratings[winner] += k_factor * (1 - expected)
21 | ratings[loser] += k_factor * (0 - (1 - expected))
22 | return ratings
23 |
24 |
25 | def main():
26 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
27 | description="Compute Elo leaderboard."
28 | )
29 | parser.add_argument("--path", type=str, help="Path to votes JSON")
30 | parser.add_argument("--k", type=int, default=32,
31 | help="Elo k-factor")
32 | parser.add_argument("--init", type=int, default=1000,
33 | help="Initial rating")
34 | args = parser.parse_args()
35 |
36 | with open(args.path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
37 | votes = json.load(f)
38 |
39 | ratings = elo_ratings(votes, args.k, args.init)
40 | leaderboard = sorted(ratings.items(),
41 | key=lambda x: -x[1])
42 |
43 | print("\nLeaderboard (Elo) \n-----------------------")
44 | for i, (model, score) in enumerate(leaderboard, 1):
45 | print(f"{i:>2}. {model:<10} {score:7.1f}")
46 | print()
47 |
48 |
49 | if __name__ == "__main__":
50 | main()
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chF/03_leaderboards/votes.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [
2 | ["GPT-5", "Claude-3"],
3 | ["GPT-5", "Llama-4"],
4 | ["Claude-3", "Llama-3"],
5 | ["Llama-4", "Llama-3"],
6 | ["Claude-3", "Llama-3"],
7 | ["GPT-5", "Llama-3"],
8 | ["Claude-3", "GPT-5"],
9 | ["Llama-4", "Claude-3"],
10 | ["Llama-3", "Llama-4"],
11 | ["GPT-5", "Claude-3"],
12 | ["Claude-3", "Llama-4"],
13 | ["GPT-5", "Llama-4"],
14 | ["Claude-3", "GPT-5"],
15 | ["Llama-4", "Claude-3"],
16 | ["GPT-5", "Llama-3"],
17 | ["Claude-3", "Llama-3"],
18 | ["Llama-3", "Claude-3"],
19 | ["GPT-5", "Llama-4"],
20 | ["Claude-3", "GPT-5"],
21 | ["Llama-4", "GPT-5"],
22 | ["Llama-3", "Claude-3"],
23 | ["GPT-5", "Claude-3"],
24 | ["Claude-3", "Llama-4"],
25 | ["Llama-4", "Llama-3"],
26 | ["GPT-5", "Llama-3"],
27 | ["Claude-3", "Llama-3"],
28 | ["GPT-5", "Claude-3"],
29 | ["Claude-3", "Llama-4"],
30 | ["GPT-5", "Claude-3"],
31 | ["Llama-4", "Llama-3"],
32 | ["Claude-3", "GPT-5"],
33 | ["GPT-5", "Llama-3"],
34 | ["Claude-3", "Llama-3"],
35 | ["Llama-3", "Llama-4"],
36 | ["GPT-5", "Claude-3"],
37 | ["Claude-3", "Llama-4"],
38 | ["GPT-5", "Llama-4"],
39 | ["Claude-3", "GPT-5"],
40 | ["Llama-4", "Claude-3"],
41 | ["GPT-5", "Llama-3"],
42 | ["Claude-3", "Llama-3"],
43 | ["Llama-3", "Claude-3"],
44 | ["GPT-5", "Llama-4"],
45 | ["Claude-3", "GPT-5"],
46 | ["Llama-4", "GPT-5"],
47 | ["Llama-3", "Claude-3"],
48 | ["GPT-5", "Claude-3"],
49 | ["Claude-3", "Llama-4"],
50 | ["Llama-4", "Llama-3"],
51 | ["GPT-5", "Llama-3"],
52 | ["Claude-3", "Llama-3"],
53 | ["GPT-5", "Claude-3"],
54 | ["Claude-3", "Llama-4"],
55 | ["GPT-5", "Claude-3"],
56 | ["Llama-4", "Llama-3"],
57 | ["Claude-3", "GPT-5"],
58 | ["GPT-5", "Llama-3"],
59 | ["Claude-3", "Llama-3"],
60 | ["Llama-3", "Llama-4"],
61 | ["Claude-3", "Llama-3"]
62 | ]
63 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/code-linter.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | name: Code Style Checks
6 |
7 | on:
8 | push:
9 | branches: [ main ]
10 | paths:
11 | - '**/*.py'
12 | - '**/*.ipynb'
13 | - '**/*.yaml'
14 | - '**/*.yml'
15 | - '**/*.sh'
16 | pull_request:
17 | branches: [ main ]
18 | paths:
19 | - '**/*.py'
20 | - '**/*.ipynb'
21 | - '**/*.yaml'
22 | - '**/*.yml'
23 | - '**/*.sh'
24 |
25 | jobs:
26 | flake8:
27 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
28 | env:
29 | SKIP_EXPENSIVE: "1"
30 | steps:
31 | - uses: actions/checkout@v4
32 | - name: Set up Python
33 | uses: actions/setup-python@v5
34 | with:
35 | python-version: "3.13"
36 | - name: Install ruff (a faster flake 8 equivalent)
37 | run: |
38 | curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
39 | uv sync --dev --python=3.13
40 | uv add ruff
41 |
42 | - name: Run ruff with exceptions
43 | run: |
44 | source .venv/bin/activate
45 | ruff check .
46 |
47 | - name: Run quote style check
48 | run: |
49 | source .venv/bin/activate
50 | uv run .github/scripts/check_double_quotes.py
51 |
52 | - name: Run line length check on main chapter notebooks
53 | run: |
54 | source .venv/bin/activate
55 | uv run .github/scripts/check_notebook_line_length.py \
56 | ch02/01_main-chapter-code/ch02_main.ipynb \
57 | ch03/01_main-chapter-code/ch03_main.ipynb \
58 | chC/01_main-chapter-code/chC_main.ipynb \
59 | chF/01_main-chapter-code/chF_main.ipynb
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/reasoning_from_scratch/ch02_ex.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | from .qwen3 import KVCache
6 | import torch
7 |
8 |
9 | @torch.inference_mode()
10 | def generate_text_basic_stream(
11 | model,
12 | token_ids,
13 | max_new_tokens,
14 | eos_token_id=None
15 | ):
16 | # input_length = token_ids.shape[1]
17 | model.eval()
18 |
19 | for _ in range(max_new_tokens):
20 | out = model(token_ids)[:, -1]
21 | next_token = torch.argmax(out, dim=-1, keepdim=True)
22 |
23 | if (eos_token_id is not None
24 | and next_token.item() == eos_token_id):
25 | break
26 |
27 | yield next_token # New: Yield each token as it's generated
28 |
29 | token_ids = torch.cat([token_ids, next_token], dim=1)
30 | # return token_ids[:, input_length:]
31 |
32 |
33 | @torch.inference_mode()
34 | def generate_text_basic_stream_cache(
35 | model,
36 | token_ids,
37 | max_new_tokens,
38 | eos_token_id=None
39 | ):
40 | # input_length = token_ids.shape[1]
41 | model.eval()
42 | cache = KVCache(n_layers=model.cfg["n_layers"])
43 | model.reset_kv_cache()
44 |
45 | out = model(token_ids, cache=cache)[:, -1]
46 | for _ in range(max_new_tokens):
47 | next_token = torch.argmax(out, dim=-1, keepdim=True)
48 |
49 | if (eos_token_id is not None
50 | and next_token.item() == eos_token_id):
51 | break
52 |
53 | yield next_token # New: Yield each token as it's generated
54 | # token_ids = torch.cat([token_ids, next_token], dim=1)
55 | out = model(next_token, cache=cache)[:, -1]
56 |
57 | # return token_ids[:, input_length:]
58 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/reasoning_from_scratch/appendix_f.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
3 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
4 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
5 |
6 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02_ex import generate_text_basic_stream_cache
7 |
8 |
9 | def predict_choice(
10 | model, tokenizer, prompt_fmt, max_new_tokens=8
11 | ):
12 | pred = None
13 | for t in generate_text_basic_stream_cache(
14 | model=model,
15 | token_ids=prompt_fmt,
16 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
17 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
18 | ):
19 | answer = tokenizer.decode(t.squeeze(0).tolist())
20 | for letter in answer:
21 | letter = letter.upper()
22 | if letter in "ABCD":
23 | pred = letter
24 | break
25 | if pred: # stop as soon as a letter appears
26 | break
27 | return pred
28 |
29 |
30 | def elo_ratings(vote_pairs, k_factor=32, initial_rating=1000):
31 | # Initialize all models with the same base rating
32 | ratings = {
33 | model: initial_rating
34 | for pair in vote_pairs
35 | for model in pair
36 | }
37 |
38 | # Update ratings after each match
39 | for winner, loser in vote_pairs:
40 | rating_winner, rating_loser = ratings[winner], ratings[loser]
41 |
42 | # Expected score for the current winner given the ratings
43 | expected_winner = 1.0 / (
44 | 1.0 + 10 ** ((rating_loser - rating_winner) / 400.0)
45 | )
46 |
47 | # k_factor determines sensitivity of rating updates
48 | ratings[winner] = (
49 | rating_winner + k_factor * (1 - expected_winner)
50 | )
51 | ratings[loser] = (
52 | rating_loser + k_factor * (0 - (1 - expected_winner))
53 | )
54 |
55 | return ratings
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pyproject.toml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | [tool.setuptools.dynamic]
6 | version = { attr = "reasoning_from_scratch.__version__" }
7 |
8 | [build-system]
9 | requires = ["setuptools>=61.0", "wheel"]
10 | build-backend = "setuptools.build_meta"
11 |
12 | [project]
13 | name = "reasoning_from_scratch"
14 | dynamic = ["version"]
15 | description = "Reasoning Models From Scratch"
16 | readme = "README.md"
17 |
18 | authors = [
19 | { name = "Sebastian Raschka" }
20 | ]
21 |
22 | license = { file = "LICENSE" }
23 | requires-python = ">=3.10"
24 |
25 | dependencies = [
26 | "jupyterlab>=4.4.7",
27 | "torch>=2.7.1",
28 | "tokenizers>=0.21.2",
29 | "nbformat>=5.10.4",
30 | "sympy>=1.14.0", # For verifier in ch03
31 | "matplotlib>=3.10.7",
32 | ]
33 |
34 | classifiers = [
35 | "License :: OSI Approved :: Apache Software License",
36 | "Programming Language :: Python :: 3.10",
37 | "Programming Language :: Python :: 3.11",
38 | "Programming Language :: Python :: 3.12",
39 | "Programming Language :: Python :: 3.13",
40 | "Intended Audience :: Developers",
41 | "Operating System :: OS Independent"
42 | ]
43 |
44 | [dependency-groups]
45 | dev = [
46 | "pytest>=8.3.5",
47 | "ruff>=0.4.4",
48 | "pytest-ruff>=0.5",
49 | "transformers==4.53.0",
50 | "reasoning-from-scratch",
51 | "twine>=6.1.0",
52 | "build>=1.2.2.post1",
53 | ]
54 |
55 | extra = [
56 | "datasets>=4.1.1", # Appendix F, MMLU
57 | "chainlit>=2.8.3", # Appendix G, Chat UI
58 | ]
59 |
60 | [tool.setuptools.packages.find]
61 | where = ["."]
62 | include = ["reasoning_from_scratch"]
63 |
64 | [tool.uv.sources]
65 | reasoning = { workspace = true }
66 | reasoning-from-scratch = { workspace = true }
67 |
68 | [tool.uv.workspace]
69 | members = [
70 | ".",
71 | ]
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chF/03_leaderboards/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # Leaderboard Rankings
3 |
4 | This bonus material implements two different ways to construct LM Arena (formerly Chatbot Arena) style leaderboards from pairwise comparisons.
5 |
6 | Both implementations take in a list of pairwise preferences (left: winner, right: loser) from a json file via the `--path` argument. Here's an excerpt of the provided [votes.json](votes.json) file:
7 |
8 | ```json
9 | [
10 | ["GPT-5", "Claude-3"],
11 | ["GPT-5", "Llama-4"],
12 | ["Claude-3", "Llama-3"],
13 | ["Llama-4", "Llama-3"],
14 | ...
15 | ]
16 | ```
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 | ---
23 |
24 | **Note**: If you are not a `uv` user, replace `uv run ...py` with `python ...py` in the examples below.
25 |
26 | ---
27 |
28 |
29 | ## Method 1: Elo ratings
30 |
31 | - Implements the popular Elo rating method (inspired by chess rankings) that was originally used by LM Arena
32 | - See the [main notebook](../01_main-chapter-code/chF_main.ipynb) for details
33 |
34 | ```bash
35 | ➜ 03_leaderboards git:(main) ✗ uv run 1_elo_leaderboard.py --path votes.json
36 |
37 | Leaderboard (Elo)
38 | -----------------------
39 | 1. GPT-5 1095.9
40 | 2. Claude-3 1058.7
41 | 3. Llama-4 958.2
42 | 4. Llama-3 887.2
43 | ```
44 |
45 |
46 |
47 |
48 |
49 |
50 |
51 | ## Method 2: Bradley-Terry model
52 |
53 | - Implements a [Bradley-Terry model](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bradley–Terry_model), similar to the new LM Arena leaderboard as described in the official paper ([Chatbot Arena: An Open Platform for Evaluating LLMs by Human Preference](https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.04132))
54 | - Like on the LM Arena leaderboard, the scores are re-scaled to be similar to the original Elo scores
55 | - The code here uses the Adam optimizer from PyTorch to fit the model (for better code familiarity and readability)
56 |
57 |
58 |
59 | ```bash
60 | ➜ 03_leaderboards git:(main) ✗ uv run 2_bradley_terry_leaderboard.py --path votes.json
61 |
62 | Leaderboard (Bradley-Terry)
63 | -----------------------------
64 | 1. GPT-5 1140.6
65 | 2. Claude-3 1058.7
66 | 3. Llama-4 950.3
67 | 4. Llama-3 850.4
68 | ```
69 |
70 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chG/01_main-chapter-code/qwen3_chat_interface.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt).
2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch"
3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch
4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch
5 |
6 |
7 | import torch
8 | import chainlit
9 |
10 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
11 | get_device,
12 | )
13 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02_ex import generate_text_basic_stream_cache
14 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch03 import load_model_and_tokenizer
15 |
16 |
17 | # ============================================================
18 | # EDIT ME: Simple configuration
19 | # ============================================================
20 | WHICH_MODEL = "reasoning" # "base" for base model
21 | MAX_NEW_TOKENS = 38912
22 | LOCAL_DIR = "qwen3"
23 | COMPILE = False
24 | # ============================================================
25 |
26 |
27 | DEVICE = get_device()
28 |
29 | MODEL, TOKENIZER = load_model_and_tokenizer(
30 | which_model=WHICH_MODEL,
31 | device=DEVICE,
32 | use_compile=COMPILE,
33 | local_dir=LOCAL_DIR
34 | )
35 |
36 |
37 | @chainlit.on_chat_start
38 | async def on_start():
39 | chainlit.user_session.set("history", [])
40 | chainlit.user_session.get("history").append(
41 | {"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."}
42 | )
43 |
44 |
45 | @chainlit.on_message
46 | async def main(message: chainlit.Message):
47 | """
48 | The main Chainlit function.
49 | """
50 | # 1) Encode input
51 | input_ids = TOKENIZER.encode(message.content)
52 | input_ids_tensor = torch.tensor(input_ids, device=DEVICE).unsqueeze(0)
53 |
54 | # 2) Start an outgoing message we can stream into
55 | out_msg = chainlit.Message(content="")
56 | await out_msg.send()
57 |
58 | # 3) Stream generation
59 | for tok in generate_text_basic_stream_cache(
60 | model=MODEL,
61 | token_ids=input_ids_tensor,
62 | max_new_tokens=MAX_NEW_TOKENS,
63 | eos_token_id=TOKENIZER.eos_token_id
64 | ):
65 | token_id = tok.squeeze(0)
66 | piece = TOKENIZER.decode(token_id.tolist())
67 | await out_msg.stream_token(piece)
68 |
69 | # 4) Finalize the streamed message
70 | await out_msg.update()
71 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug-report.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: Bug Report
2 | description: Report errors related to the book content or code
3 | title: "Description"
4 | labels: [bug]
5 | assignees: rasbt
6 | body:
7 | - type: markdown
8 | attributes:
9 | value: |
10 | Thank you for taking the time to report an issue. Please fill out the details below to help resolve it.
11 |
12 | - type: textarea
13 | id: bug_description
14 | attributes:
15 | label: Bug description
16 | description: A description of the issue.
17 | placeholder: |
18 | Please provide a description of what the bug or issue is.
19 | validations:
20 | required: true
21 |
22 | - type: dropdown
23 | id: operating_system
24 | attributes:
25 | label: What operating system are you using?
26 | description: If applicable, please select the operating system where you experienced this issue.
27 | options:
28 | - "Unknown"
29 | - "macOS"
30 | - "Linux"
31 | - "Windows"
32 | validations:
33 | required: False
34 |
35 | - type: dropdown
36 | id: compute_environment
37 | attributes:
38 | label: Where do you run your code?
39 | description: Please select the computing environment where you ran this code.
40 | options:
41 | - "Local (laptop, desktop)"
42 | - "Lightning AI Studio"
43 | - "Google Colab"
44 | - "Other cloud environment (AWS, Azure, GCP)"
45 | validations:
46 | required: False
47 |
48 | - type: textarea
49 | id: environment
50 | attributes:
51 | label: Environment
52 | description: |
53 | Please provide details about your Python environment via the environment by pasting the output of the following code:
54 | ```python
55 | import sys
56 | import torch
57 |
58 | print(f"Python version: {sys.version}")
59 | print(f"PyTorch version: {torch.__version__}")
60 | print(f"CUDA available: {torch.cuda.is_available()}")
61 | if torch.cuda.is_available():
62 | print(f"CUDA device: {torch.cuda.get_device_name(0)}")
63 | print(f"CUDA version: {torch.version.cuda}")
64 | print(f"Device count: {torch.cuda.device_count()}")
65 | ```
66 | value: |
67 | ```
68 |
69 |
70 |
71 | ```
72 | validations:
73 | required: false
74 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/reasoning_from_scratch/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | from pathlib import Path
6 | import sys
7 | import requests
8 | from urllib.parse import urlparse
9 |
10 |
11 | def download_file(url, out_dir=".", backup_url=None):
12 | out_dir = Path(out_dir)
13 | out_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
14 | filename = Path(urlparse(url).path).name
15 | dest = out_dir / filename
16 |
17 | def try_download(u):
18 | try:
19 | with requests.get(u, stream=True, timeout=30) as r:
20 | r.raise_for_status()
21 | size_remote = int(r.headers.get("Content-Length", 0))
22 |
23 | # Skip download if already complete
24 | if dest.exists() and size_remote and dest.stat().st_size == size_remote:
25 | print(f"✓ {dest} already up-to-date")
26 | return True
27 |
28 | # Download in 1 MiB chunks with progress display
29 | block = 1024 * 1024
30 | downloaded = 0
31 | with open(dest, "wb") as f:
32 | for chunk in r.iter_content(chunk_size=block):
33 | if not chunk:
34 | continue
35 | f.write(chunk)
36 | downloaded += len(chunk)
37 | if size_remote:
38 | pct = downloaded * 100 // size_remote
39 | sys.stdout.write(
40 | f"\r{filename}: {pct:3d}% "
41 | f"({downloaded // (1024*1024)} MiB / "
42 | f"{size_remote // (1024*1024)} MiB)"
43 | )
44 | sys.stdout.flush()
45 | if size_remote:
46 | sys.stdout.write("\n")
47 | return True
48 | except requests.RequestException:
49 | return False
50 |
51 | # Try main URL first
52 | if try_download(url):
53 | return dest
54 |
55 | # Try backup URL if provided
56 | if backup_url:
57 | print(f"Primary URL ({url}) failed.\nTrying backup URL ({backup_url})...")
58 | if try_download(backup_url):
59 | return dest
60 |
61 | raise RuntimeError(f"Failed to download {filename} from both mirrors.")
62 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chF/03_leaderboards/2_bradley_terry_leaderboard.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import json
6 | import math
7 | import argparse
8 | import torch
9 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import get_device
10 |
11 |
12 | def bradley_terry_torch(vote_pairs, device):
13 |
14 | # Collect all unique model names
15 | models = sorted({m for winner, loser in vote_pairs for m in (winner, loser)})
16 | n = len(models)
17 | idx = {m: i for i, m in enumerate(models)}
18 |
19 | # Convert to index tensors
20 | winners = torch.tensor([idx[winner] for winner, _ in vote_pairs], dtype=torch.long)
21 | losers = torch.tensor([idx[loser] for _, loser in vote_pairs], dtype=torch.long)
22 |
23 | # Learnable parameters
24 | theta = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(n - 1, device=device))
25 | optimizer = torch.optim.Adam([theta], lr=0.01, weight_decay=1e-4)
26 |
27 | def scores():
28 | return torch.cat([theta, torch.zeros(1, device=device)])
29 |
30 | for epoch in range(500):
31 | s = scores()
32 | delta = s[winners] - s[losers] # score difference
33 | loss = -torch.nn.functional.logsigmoid(delta).mean() # negative log-likelihood
34 | optimizer.zero_grad(set_to_none=True)
35 | loss.backward()
36 | optimizer.step()
37 |
38 | # Convert latent scores to Elo-like scale
39 | with torch.no_grad():
40 | s = scores()
41 | scale = 400.0 / math.log(10.0)
42 | R = s * scale
43 | R -= R.mean()
44 | R += 1000.0 # center around 1000
45 |
46 | return {m: float(r) for m, r in zip(models, R.cpu().tolist())}
47 |
48 |
49 | def main():
50 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Bradley-Terry leaderboard.")
51 | parser.add_argument("--path", type=str, help="Path to votes JSON")
52 | args = parser.parse_args()
53 |
54 | with open(args.path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
55 | votes = json.load(f)
56 |
57 | device = get_device()
58 | ratings = bradley_terry_torch(votes, device)
59 |
60 | leaderboard = sorted(ratings.items(),
61 | key=lambda x: -x[1])
62 | print("\nLeaderboard (Bradley-Terry)")
63 | print("-----------------------------")
64 | for i, (model, score) in enumerate(leaderboard, 1):
65 | print(f"{i:>2}. {model:<10} {score:7.1f}")
66 | print()
67 |
68 |
69 | if __name__ == "__main__":
70 | main()
71 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/02_setup-tips/gpu-instructions.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # GPU Cloud Resources
3 |
4 | This section describes cloud alternatives for running the code presented in this book.
5 |
6 | While the code can run on conventional laptops and desktop computers without a dedicated GPU, cloud platforms with NVIDIA GPUs can substantially improve the runtime of the code, especially in chapters 5 to 7.
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 | ## Using Lightning Studio
11 |
12 | For a smooth development experience in the cloud, I recommend the [Lightning AI Studio](https://lightning.ai/) platform, which allows users to set up a persistent environment and use both VSCode and Jupyter Lab on cloud CPUs and GPUs.
13 |
14 | Once you start a new Studio, you can open the terminal and execute the following setup steps to clone the repository and install the dependencies:
15 |
16 | ```bash
17 | git clone https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch.git
18 | cd reasoning-from-scratch
19 | pip install -r requirements.txt
20 | ```
21 |
22 | (In contrast to Google Colab, these only need to be executed once since the Lightning AI Studio environments are persistent, even if you switch between CPU and GPU machines.)
23 |
24 | Then, navigate to the Python script or Jupyter Notebook you want to run. Optionally, you can also easily connect a GPU to accelerate the code's runtime, for example, when you are pretraining the LLM in chapter 5 or finetuning it in chapters 6 and 7.
25 |
26 | 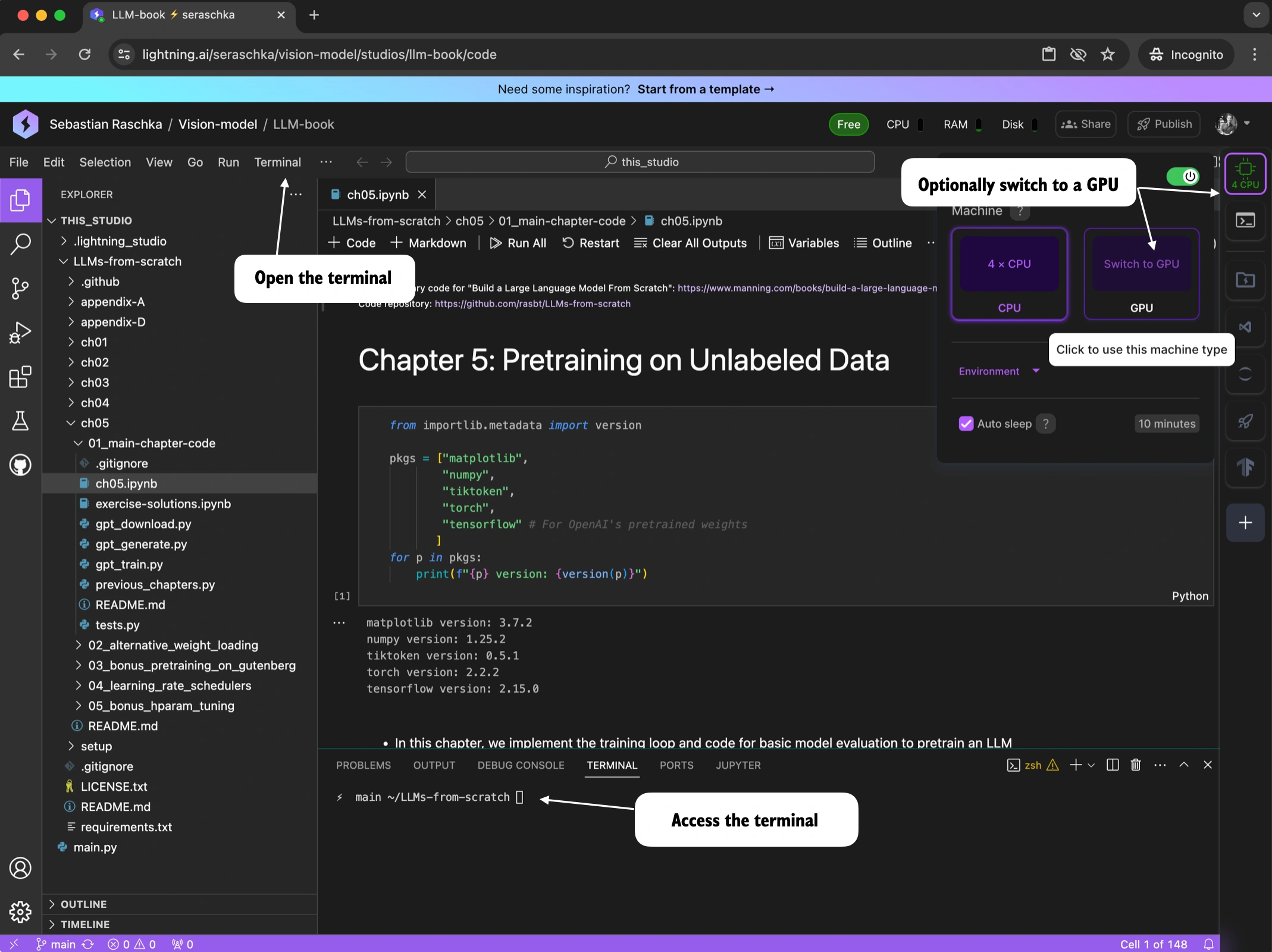 27 |
28 |
29 |
30 | ## Using Google Colab
31 |
32 | To use a Google Colab environment in the cloud, head over to [https://colab.research.google.com/](https://colab.research.google.com/) and open the respective chapter notebook from the GitHub menu or by dragging the notebook into the *Upload* field as shown in the figure below.
33 |
34 |
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 | ## Using Google Colab
31 |
32 | To use a Google Colab environment in the cloud, head over to [https://colab.research.google.com/](https://colab.research.google.com/) and open the respective chapter notebook from the GitHub menu or by dragging the notebook into the *Upload* field as shown in the figure below.
33 |
34 | 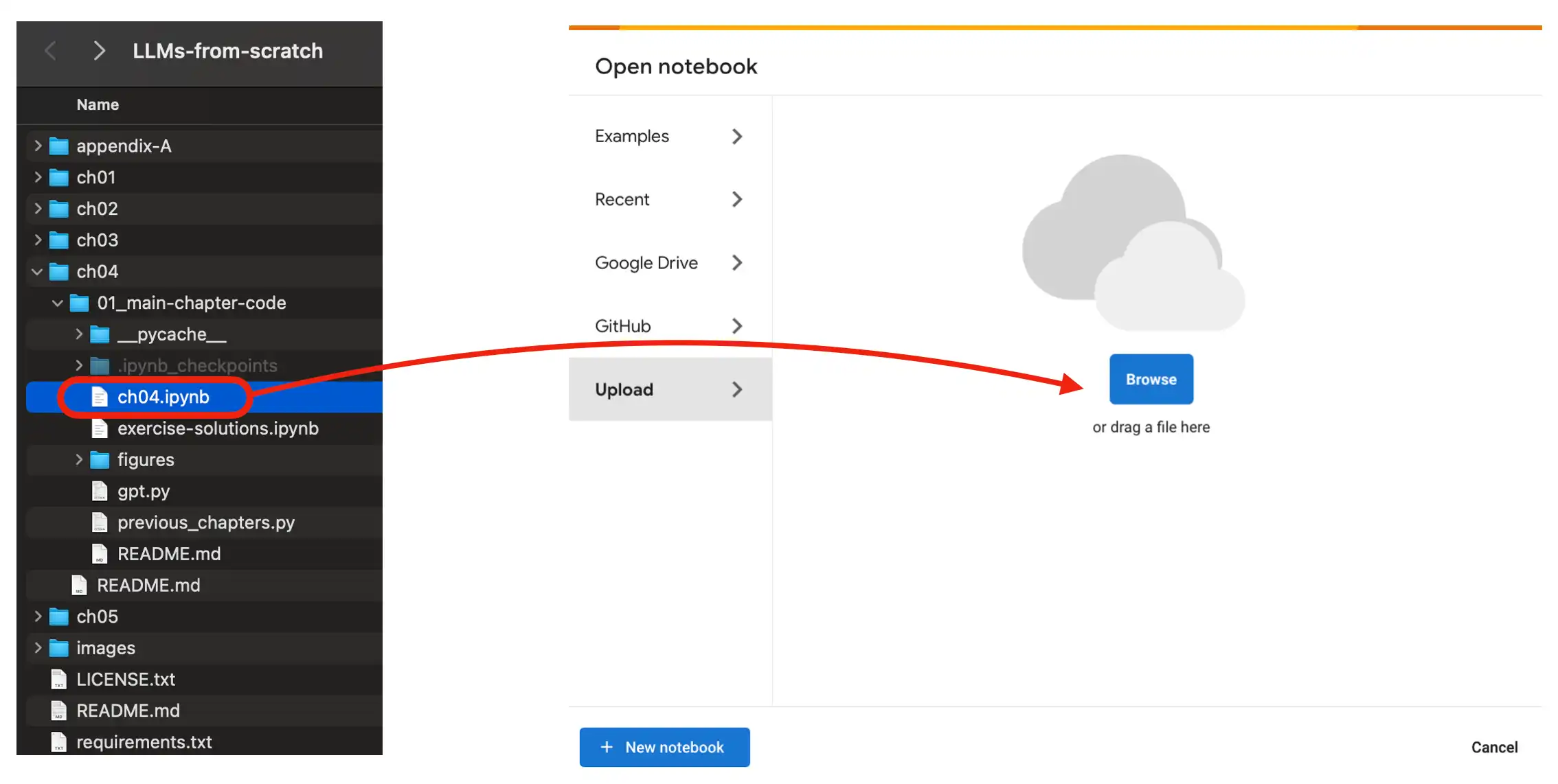 35 |
36 |
37 | Also make sure you upload the relevant files (dataset files and .py files the notebook is importing from) to the Colab environment as well, as shown below.
38 |
39 |
35 |
36 |
37 | Also make sure you upload the relevant files (dataset files and .py files the notebook is importing from) to the Colab environment as well, as shown below.
38 |
39 | 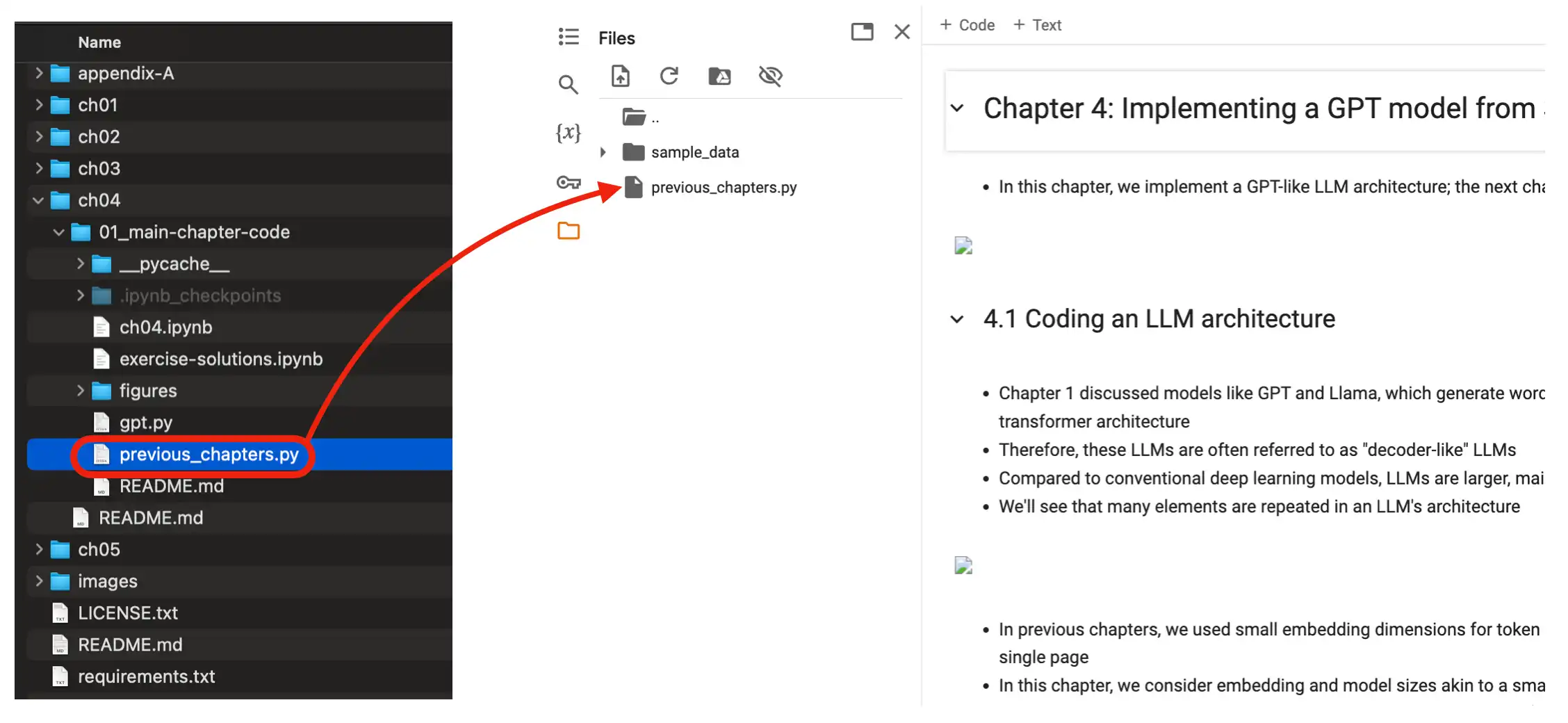 40 |
41 |
42 | You can optionally run the code on a GPU by changing the *Runtime* as illustrated in the figure below.
43 |
44 |
40 |
41 |
42 | You can optionally run the code on a GPU by changing the *Runtime* as illustrated in the figure below.
43 |
44 | 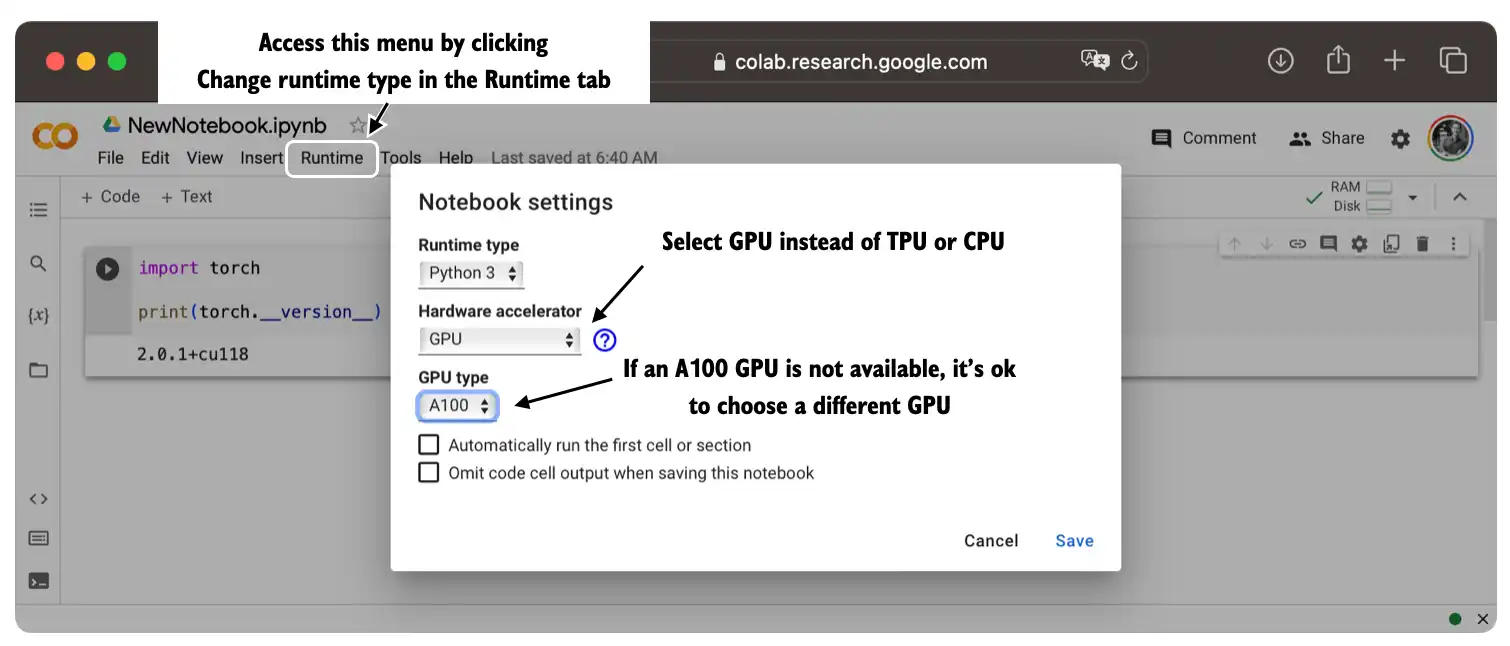 45 |
46 |
47 |
48 | ## Questions?
49 |
50 | If you have any questions, please don't hesitate to reach out via the [Discussions](https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch/discussions) forum in this GitHub repository.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/conftest.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
6 | download_qwen3_small,
7 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B,
8 | Qwen3Model,
9 | )
10 | import sys
11 | import types
12 | import nbformat
13 | import pytest
14 | import torch
15 |
16 |
17 | @pytest.fixture(scope="session")
18 | def qwen3_weights_path(tmp_path_factory):
19 | """Creates and saves a deterministic model for testing."""
20 |
21 | base_path = tmp_path_factory.mktemp("models")
22 | model_path = base_path / "qwen3_test_weights.pt"
23 | download_qwen3_small(kind="base", tokenizer_only=True, out_dir=base_path)
24 |
25 | if not model_path.exists():
26 | torch.manual_seed(123)
27 | model = Qwen3Model(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
28 | torch.save(model.state_dict(), model_path)
29 |
30 | return base_path
31 |
32 |
33 | def import_definitions_from_notebook(nb_path, module_name):
34 | if not nb_path.exists():
35 | raise FileNotFoundError(f"Notebook file not found at: {nb_path}")
36 |
37 | nb = nbformat.read(str(nb_path), as_version=4)
38 |
39 | mod = types.ModuleType(module_name)
40 | sys.modules[module_name] = mod
41 |
42 | # Pass 1: execute only imports (handle multi-line)
43 | for cell in nb.cells:
44 | if cell.cell_type != "code":
45 | continue
46 | lines = cell.source.splitlines()
47 | collecting = False
48 | buf = []
49 | paren_balance = 0
50 | for line in lines:
51 | stripped = line.strip()
52 | if not collecting and (stripped.startswith("import ") or stripped.startswith("from ")):
53 | collecting = True
54 | buf = [line]
55 | paren_balance = line.count("(") - line.count(")")
56 | if paren_balance == 0:
57 | exec("\n".join(buf), mod.__dict__)
58 | collecting = False
59 | buf = []
60 | elif collecting:
61 | buf.append(line)
62 | paren_balance += line.count("(") - line.count(")")
63 | if paren_balance == 0:
64 | exec("\n".join(buf), mod.__dict__)
65 | collecting = False
66 | buf = []
67 |
68 | # Pass 2: execute only def/class definitions
69 | for cell in nb.cells:
70 | if cell.cell_type != "code":
71 | continue
72 | src = cell.source
73 | if "def " in src or "class " in src:
74 | exec(src, mod.__dict__)
75 |
76 | return mod
77 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/04_torch-compile-windows/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Using `torch.compile()` on Windows
2 |
3 | `torch.compile()` relies on *TorchInductor*, which JIT-compiles kernels and requires a working C/C++ compiler toolchain.
4 |
5 | So, on Windows, the setup required to make `torch.compile` work can be a bit more involved than on Linux or macOS, which usually don't require any extra steps besides installing PyTorch.
6 |
7 | If you are a Windows user and using `torch.compile` sounds too tricky or complicated, don't worry, all code examples in this repository will work fine without compilation.
8 |
9 | Below are some tips that I compiled based on recommendations by [Daniel Kleine](https://github.com/d-kleine) and the following [PyTorch guide](https://docs.pytorch.org/tutorials/unstable/inductor_windows.html).
10 |
11 |
12 | ## 1 Basic Setup (CPU or CUDA)
13 |
14 |
15 | ### 1.1 Install Visual Studio 2022
16 |
17 | - Select the **“Desktop development with C++”** workload.
18 | - Make sure to include the **English language pack** (without it, you may run into UTF-8 encoding errors.)
19 |
20 |
21 | ### 1.2 Open the correct command prompt
22 |
23 |
24 | Launch Python from the
25 |
26 | **"x64 Native Tools Command Prompt for VS 2022"**
27 |
28 | or from the
29 |
30 | **"Visual Studio 2022 Developer Command Prompt"**.
31 |
32 | Alternatively, you can initialize the environment manually by running:
33 |
34 | ```bash
35 | "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\Community\VC\Auxiliary\Build\vcvars64.bat"
36 | ```
37 |
38 |
39 | ### 1.3 Verify that the compiler works
40 |
41 | Run
42 |
43 | ```bash
44 | cl.exe
45 | ```
46 |
47 | If you see version information printed, the compiler is ready.
48 |
49 |
50 | ## 2 Troubleshooting Common Errors
51 |
52 |
53 | ### 2.1 Error: `cl not found`
54 |
55 | Install **Visual Studio Build Tools** with the "C++ build tools" workload and run Python from a developer command prompt. (See this Microsoft [guide](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cpp/build/vscpp-step-0-installation?view=msvc-170) for details)
56 |
57 |
58 | ### 2.2 Error: `triton not found` (when using CUDA)
59 |
60 | Install the Windows build of Triton manually:
61 |
62 | ```bash
63 | pip install "triton-windows<3.4"
64 | ```
65 |
66 | or, if you are using `uv`:
67 |
68 | ```bash
69 | uv pip install "triton-windows<3.4"
70 | ```
71 |
72 | (As mentioned earlier, triton is required by TorchInductor for CUDA kernel compilation.)
73 |
74 |
75 |
76 |
77 | ## 3 Additional Notes
78 |
79 | On Windows, the `cl.exe` compiler is only accessible from within the Visual Studio Developer environment. This means that using `torch.compile()` in notebooks such as Jupyter may not work unless the notebook was launched from a Developer Command Prompt.
80 |
81 | As mentioned at the beginning of this article, there is also a [PyTorch guide](https://docs.pytorch.org/tutorials/unstable/inductor_windows.html) that some users found helpful when getting `torch.compile()` running on Windows CPU builds. However, note that it refers to PyTorch's unstable branch, so use it as a reference only.
82 |
83 | **If compilation continues to cause issues, please feel free to skip it. It's a nice bonus, but it's not important to follow the book.**
84 |
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chF/02_mmlu/random_guessing_baseline.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import argparse
6 | import random
7 | import statistics as stats
8 | from collections import Counter
9 |
10 | from datasets import load_dataset
11 |
12 |
13 | # Gold letter is MMLU jargon for correct answer letter
14 | def gold_letter(ans):
15 | if isinstance(ans, int):
16 | return "ABCD"[ans]
17 | s = str(ans).strip().upper()
18 | return s if s in {"A", "B", "C", "D"} else s[:1]
19 |
20 |
21 | def main():
22 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
23 | description="Show gold answer distribution for an MMLU subset and a random-guess baseline."
24 | )
25 | parser.add_argument(
26 | "--subset",
27 | type=str,
28 | default="high_school_mathematics",
29 | help="MMLU subset name (default: 'high_school_mathematics').",
30 | )
31 | parser.add_argument(
32 | "--seed",
33 | type=int,
34 | default=42,
35 | help="Random seed for the random-guess baseline (default: 42).",
36 | )
37 | parser.add_argument(
38 | "--trials",
39 | type=int,
40 | default=10_000,
41 | help="Number of random-guess trials (default: 10,000).",
42 | )
43 | args = parser.parse_args()
44 |
45 | ds = load_dataset("cais/mmlu", args.subset, split="test")
46 |
47 | labels = [gold_letter(ex["answer"]) for ex in ds]
48 | n = len(labels)
49 | counts = Counter(labels)
50 |
51 | print(f"Subset: {args.subset} | split: test | n={n}")
52 | print("Gold distribution provided in the dataset:")
53 | for letter in "ABCD":
54 | c = counts.get(letter, 0)
55 | pct = (c / n) if n else 0.0
56 | print(f" {letter}: {c} ({pct:.2%})")
57 |
58 | if n == 0:
59 | print("\nNo items. Baseline undefined.")
60 | return
61 |
62 | # Repeat random guessing
63 | rng = random.Random(args.seed)
64 | accs = []
65 | for _ in range(args.trials):
66 | guesses = [rng.choice("ABCD") for _ in range(n)]
67 | correct = sum(1 for g, y in zip(guesses, labels) if g == y)
68 | accs.append(correct / n)
69 |
70 | mean_acc = stats.mean(accs)
71 | sd_acc = stats.stdev(accs) if len(accs) > 1 else 0.0
72 |
73 | print(f"\nRandom guessing over {args.trials:,} trials (uniform A/B/C/D, seed={args.seed}):")
74 | print(f" Mean accuracy: {mean_acc:.2%}")
75 | print(f" Std dev across trials: {sd_acc:.2%}")
76 |
77 | # Quantiles
78 | qs = [0.01, 0.05, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 0.95, 0.99]
79 | accs_sorted = sorted(accs)
80 | print("\nSelected quantiles of accuracy:")
81 | for q in qs:
82 | idx = int(q * len(accs_sorted))
83 | print(f" {q:.0%} quantile: {accs_sorted[idx]:.3%}")
84 |
85 | # Frequency table (rounded)
86 | acc_counts = Counter(round(a, 2) for a in accs)
87 | print("\nFull frequency table of accuracies (rounded):")
88 | for acc_val in sorted(acc_counts):
89 | freq = acc_counts[acc_val]
90 | pct = freq / args.trials
91 | print(f" {acc_val:.3f}: {freq} times ({pct:.2%})")
92 |
93 |
94 | if __name__ == "__main__":
95 | main()
96 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/reasoning_from_scratch/ch02.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | from .qwen3 import KVCache
6 | import torch
7 |
8 |
9 | def get_device(enable_tensor_cores=True):
10 | if torch.cuda.is_available():
11 | device = torch.device("cuda")
12 | print("Using NVIDIA CUDA GPU")
13 |
14 | if enable_tensor_cores:
15 | major, minor = map(int, torch.__version__.split(".")[:2])
16 | if (major, minor) >= (2, 9):
17 | torch.backends.cuda.matmul.fp32_precision = "tf32"
18 | torch.backends.cudnn.conv.fp32_precision = "tf32"
19 | else:
20 | torch.backends.cuda.matmul.allow_tf32 = True
21 | torch.backends.cudnn.allow_tf32 = True
22 |
23 | elif torch.backends.mps.is_available():
24 | device = torch.device("mps")
25 | print("Using Apple Silicon GPU (MPS)")
26 |
27 | elif torch.xpu.is_available():
28 | device = torch.device("xpu")
29 | print("Using Intel GPU")
30 |
31 | else:
32 | device = torch.device("cpu")
33 | print("Using CPU")
34 |
35 | return device
36 |
37 |
38 | @torch.inference_mode()
39 | def generate_text_basic(model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=None):
40 | input_length = token_ids.shape[1]
41 | model.eval()
42 |
43 | for _ in range(max_new_tokens):
44 | out = model(token_ids)[:, -1]
45 | next_token = torch.argmax(out, dim=-1, keepdim=True)
46 |
47 | # Stop if all sequences in the batch have generated EOS
48 | if (eos_token_id is not None
49 | and next_token.item() == eos_token_id):
50 | break
51 |
52 | token_ids = torch.cat([token_ids, next_token], dim=1)
53 | return token_ids[:, input_length:]
54 |
55 |
56 | @torch.inference_mode()
57 | def generate_text_basic_cache(
58 | model,
59 | token_ids,
60 | max_new_tokens,
61 | eos_token_id=None
62 | ):
63 |
64 | input_length = token_ids.shape[1]
65 | model.eval()
66 | cache = KVCache(n_layers=model.cfg["n_layers"])
67 | model.reset_kv_cache()
68 | out = model(token_ids, cache=cache)[:, -1]
69 |
70 | for _ in range(max_new_tokens):
71 | next_token = torch.argmax(out, dim=-1, keepdim=True)
72 |
73 | if (eos_token_id is not None
74 | and next_token.item() == eos_token_id):
75 | break
76 |
77 | token_ids = torch.cat([token_ids, next_token], dim=1)
78 | out = model(next_token, cache=cache)[:, -1]
79 |
80 | return token_ids[:, input_length:]
81 |
82 |
83 | def generate_stats(output_token_ids, tokenizer, start_time,
84 | end_time, print_tokens=True):
85 | total_time = end_time - start_time
86 | print(f"Time: {total_time:.2f} sec")
87 | print(f"{int(output_token_ids.numel() / total_time)} tokens/sec")
88 |
89 | for name, backend in (("CUDA", getattr(torch, "cuda", None)),
90 | ("XPU", getattr(torch, "xpu", None))):
91 | if backend is not None and backend.is_available():
92 | max_mem_bytes = backend.max_memory_allocated()
93 | max_mem_gb = max_mem_bytes / (1024 ** 3)
94 | print(f"Max {name} memory allocated: {max_mem_gb:.2f} GB")
95 | backend.reset_peak_memory_stats()
96 |
97 | if print_tokens:
98 | output_text = tokenizer.decode(output_token_ids.squeeze(0).tolist())
99 | print(f"\n{output_text}")
100 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/scripts/check_notebook_line_length.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | # Check if code in notebooks exceeds line length
6 | # Usage: uv run .github/scripts/check_notebook_line_length.py --max-len 76 ch02/01_main-chapter-code/ch02_main.ipynb ch03/01_main-chapter-code/ch03_main.ipynb
7 |
8 | import argparse
9 | import sys
10 | from pathlib import Path
11 | import nbformat as nbf
12 |
13 |
14 | def parse_args():
15 | p = argparse.ArgumentParser(
16 | description="Check code-cell line lengths in specific .ipynb files."
17 | )
18 | p.add_argument(
19 | "--max-len",
20 | type=int,
21 | default=76,
22 | help="Maximum allowed characters per line (default: 76)",
23 | )
24 | p.add_argument(
25 | "notebooks",
26 | nargs="+",
27 | help="Paths to .ipynb files to check.",
28 | )
29 | return p.parse_args()
30 |
31 |
32 | def strip_inline_comment(line):
33 | """Return line with any trailing #... comment removed, but keep # inside quotes."""
34 | in_quote = None
35 | escaped = False
36 | for i, ch in enumerate(line):
37 | if escaped:
38 | escaped = False
39 | continue
40 | if ch == "\\":
41 | escaped = True
42 | continue
43 | if ch in ("'", '"'):
44 | if in_quote is None:
45 | in_quote = ch
46 | elif in_quote == ch:
47 | in_quote = None
48 | continue
49 | if ch == "#" and in_quote is None:
50 | return line[:i].rstrip()
51 | return line.rstrip()
52 |
53 |
54 | def main():
55 | args = parse_args()
56 |
57 | nb_paths = []
58 | for raw in args.notebooks:
59 | p = Path(raw).resolve()
60 | if not p.exists():
61 | print(f"::warning file={raw}::File not found, skipping.")
62 | continue
63 | if p.suffix != ".ipynb":
64 | print(f"::warning file={raw}::Not a .ipynb file, skipping.")
65 | continue
66 | nb_paths.append(p)
67 |
68 | if not nb_paths:
69 | print("No valid notebooks to check.")
70 | return 0
71 |
72 | violations = []
73 |
74 | for nb_path in nb_paths:
75 | try:
76 | nb = nbf.read(nb_path, as_version=4)
77 | except Exception as e:
78 | print(f"::warning file={nb_path}::Failed to read notebook: {e}")
79 | continue
80 |
81 | for ci, cell in enumerate(nb.cells, start=1):
82 | if cell.get("cell_type") != "code":
83 | continue
84 |
85 | src = cell.get("source", "")
86 | lines = src if isinstance(src, list) else src.splitlines()
87 |
88 | for li, line in enumerate(lines, start=1):
89 | code_part = strip_inline_comment(line)
90 | length = len(code_part)
91 | if length > args.max_len:
92 | print(
93 | f"::error file={nb_path}::Line length {length} exceeds "
94 | f"{args.max_len} in code cell {ci}, line {li}"
95 | )
96 | snippet = code_part if len(code_part) <= 120 else code_part[:120] + "…"
97 | violations.append((str(nb_path), ci, li, length, snippet))
98 |
99 | if violations:
100 | print("\nFound lines exceeding the limit:\n")
101 | for path, ci, li, length, snippet in violations:
102 | print(f"- {path} | cell {ci} line {li}: {length} chars\n {snippet}")
103 | return 1
104 |
105 | print(f"All notebooks pass: no code-cell lines exceed {args.max_len} characters.")
106 | return 0
107 |
108 |
109 | if __name__ == "__main__":
110 | sys.exit(main())
111 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch03/02_math500-verifier-scripts/evaluate_math500.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import argparse
6 | import torch
7 |
8 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
9 | Qwen3Model,
10 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B
11 | )
12 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import get_device
13 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch03 import (
14 | load_math500_test,
15 | evaluate_math500_stream,
16 | load_model_and_tokenizer,
17 | load_tokenizer_only
18 | )
19 |
20 |
21 | def parse_args():
22 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
23 | parser.add_argument(
24 | "--device",
25 | type=str,
26 | default="auto",
27 | help="Device to use: 'auto' (default), or any torch device string like 'cpu', 'cuda', 'cuda:0', 'mps'.",
28 | )
29 | parser.add_argument(
30 | "--which_model",
31 | type=str,
32 | default="base",
33 | choices=["base", "reasoning", "instruct"],
34 | help="Model variant to load. Defaults to 'base'.",
35 | )
36 | parser.add_argument(
37 | "--dataset_size",
38 | type=int,
39 | default=10,
40 | help="Number of MATH-500 examples to evaluate. Default: 10",
41 | )
42 | parser.add_argument(
43 | "--max_new_tokens",
44 | type=int,
45 | default=2048,
46 | help="Max new tokens for generation. Default: 2048",
47 | )
48 | parser.add_argument(
49 | "--compile",
50 | action="store_true",
51 | help="Enable torch.compile for the model.",
52 | )
53 | parser.add_argument(
54 | "--checkpoint_path",
55 | type=str,
56 | default=None,
57 | help="Optional path to a .pth checkpoint to load model weights from.",
58 | )
59 | parser.add_argument(
60 | "--verbose",
61 | action="store_true",
62 | help="Print per-sample correctness while evaluating.",
63 | )
64 | return parser.parse_args()
65 |
66 |
67 | if __name__ == "__main__":
68 | args = parse_args()
69 |
70 | if args.device == "auto":
71 | device = get_device()
72 | else:
73 | device = torch.device(args.device)
74 |
75 | which_model = args.which_model
76 | dataset_size = args.dataset_size
77 | max_new_tokens = args.max_new_tokens
78 | use_compile = args.compile
79 |
80 | print("Model:", which_model)
81 | print("Device:", device)
82 | dev_name = str(device).replace(":", "-")
83 |
84 | math_data = load_math500_test()
85 |
86 | if args.which_model == "instruct":
87 | which_model = "reasoning"
88 | else:
89 | which_model = args.which_model
90 |
91 | if args.checkpoint_path:
92 | # To load the saved RL checkpoint files from chapter 6
93 | tokenizer = load_tokenizer_only(which_model=which_model)
94 | model = Qwen3Model(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
95 | model.to(device)
96 | state_dict = torch.load(args.checkpoint_path, map_location=device)
97 | model.load_state_dict(state_dict)
98 | if args.compile:
99 | torch._dynamo.config.allow_unspec_int_on_nn_module = True
100 | model = torch.compile(model)
101 | else:
102 | model, tokenizer = load_model_and_tokenizer(
103 | which_model=which_model,
104 | device=device,
105 | use_compile=args.compile
106 | )
107 |
108 | if args.which_model == "instruct":
109 | tokenizer.add_thinking = False
110 |
111 | model.eval()
112 | torch.set_float32_matmul_precision("high")
113 |
114 | num_correct, num_examples, acc = evaluate_math500_stream(
115 | model=model,
116 | out_path=f"math500_{which_model}-{dev_name}-evaluate-script.jsonl",
117 | tokenizer=tokenizer,
118 | device=device,
119 | math_data=math_data[:dataset_size],
120 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
121 | verbose=args.verbose,
122 | )
123 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chG/01_main-chapter-code/qwen3_chat_interface_multiturn.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt).
2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch"
3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch
4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch
5 |
6 |
7 | import torch
8 | import chainlit
9 |
10 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
11 | get_device,
12 | )
13 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02_ex import generate_text_basic_stream_cache
14 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch03 import load_model_and_tokenizer
15 |
16 | # ============================================================
17 | # EDIT ME: Simple configuration
18 | # ============================================================
19 | WHICH_MODEL = "reasoning" # "base" for base model
20 | MAX_NEW_TOKENS = 38912
21 | LOCAL_DIR = "qwen3"
22 | COMPILE = False
23 | # ============================================================
24 |
25 |
26 | def trim_input_tensor(input_ids_tensor, context_len, max_new_tokens):
27 | assert max_new_tokens < context_len
28 | keep_len = max(1, context_len - max_new_tokens)
29 |
30 | # If the prompt is too long, left-truncate to keep_len
31 | if input_ids_tensor.shape[1] > keep_len:
32 | input_ids_tensor = input_ids_tensor[:, -keep_len:]
33 |
34 | return input_ids_tensor
35 |
36 |
37 | def build_prompt_from_history(history, add_assistant_header=True):
38 | """
39 | history: [{"role": "system"|"user"|"assistant", "content": str}, ...]
40 | """
41 | parts = []
42 | for m in history:
43 | role = m["role"]
44 | content = m["content"]
45 | parts.append(f"<|im_start|>{role}\n{content}<|im_end|>\n")
46 |
47 | if add_assistant_header:
48 | parts.append("<|im_start|>assistant\n")
49 | return "".join(parts)
50 |
51 |
52 | DEVICE = get_device()
53 | MODEL, TOKENIZER = load_model_and_tokenizer(
54 | which_model=WHICH_MODEL,
55 | device=DEVICE,
56 | use_compile=COMPILE,
57 | local_dir=LOCAL_DIR
58 | )
59 |
60 | # Even though the official TOKENIZER.eos_token_id is either <|im_end|> (reasoning)
61 | # or <|endoftext|> (base), the reasoning model sometimes emits both.
62 | EOS_TOKEN_IDS = (
63 | TOKENIZER.encode("<|im_end|>")[0],
64 | TOKENIZER.encode("<|endoftext|>")[0]
65 | )
66 |
67 |
68 | @chainlit.on_chat_start
69 | async def on_start():
70 | chainlit.user_session.set("history", [])
71 | chainlit.user_session.get("history").append(
72 | {"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."}
73 | )
74 |
75 |
76 | @chainlit.on_message
77 | async def main(message: chainlit.Message):
78 | """
79 | The main Chainlit function.
80 | """
81 | # 0) Get and track chat history
82 | history = chainlit.user_session.get("history")
83 | history.append({"role": "user", "content": message.content})
84 |
85 | # 1) Encode input
86 | prompt = build_prompt_from_history(history, add_assistant_header=True)
87 | input_ids = TOKENIZER.encode(prompt)
88 | input_ids_tensor = torch.tensor(input_ids, device=DEVICE).unsqueeze(0)
89 |
90 | # Multi-turn can be very long, so we add this left-trimming
91 | input_ids_tensor = trim_input_tensor(
92 | input_ids_tensor=input_ids_tensor,
93 | context_len=MODEL.cfg["context_length"],
94 | max_new_tokens=MAX_NEW_TOKENS
95 | )
96 |
97 | # 2) Start an outgoing message we can stream into
98 | out_msg = chainlit.Message(content="")
99 | await out_msg.send()
100 |
101 | # 3) Stream generation
102 | for tok in generate_text_basic_stream_cache(
103 | model=MODEL,
104 | token_ids=input_ids_tensor,
105 | max_new_tokens=MAX_NEW_TOKENS,
106 | # eos_token_id=TOKENIZER.eos_token_id
107 | ):
108 | token_id = tok.squeeze(0)
109 | if token_id in EOS_TOKEN_IDS:
110 | break
111 | piece = TOKENIZER.decode(token_id.tolist())
112 | await out_msg.stream_token(piece)
113 |
114 | # 4) Finalize the streamed message
115 | await out_msg.update()
116 |
117 | # 5) Update chat history
118 | history.append({"role": "assistant", "content": out_msg.content})
119 | chainlit.user_session.set("history", history)
120 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_ch02.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import torch
6 |
7 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
8 | get_device,
9 | generate_text_basic,
10 | generate_text_basic_cache,
11 | generate_stats
12 | )
13 |
14 |
15 | # Dummy model for generate_text_basic tests.
16 | class DummyModel:
17 | def __init__(self, fixed_token, vocab_size=5):
18 | self.fixed_token = fixed_token
19 | self.vocab_size = vocab_size
20 | self.eval_called = False
21 |
22 | def eval(self):
23 | self.eval_called = True
24 | return self
25 |
26 | def __call__(self, token_ids, cache=None):
27 | batch_size, seq_len = token_ids.size()
28 | out = torch.zeros(batch_size, seq_len, self.vocab_size)
29 | # Set the fixed_token column to the highest value so argmax returns fixed_token
30 | out[..., self.fixed_token] = 1.0
31 | return out
32 |
33 |
34 | class DummyModelCache(DummyModel):
35 | def __init__(self, fixed_token, vocab_size=5, n_layers=2):
36 | super().__init__(fixed_token, vocab_size)
37 | self.cfg = {"n_layers": n_layers}
38 | self.reset_called = False
39 |
40 | def reset_kv_cache(self):
41 | self.reset_called = True
42 |
43 |
44 | class DummyTokenizer:
45 | def decode(self, token_list):
46 | return " ".join(str(t) for t in token_list)
47 |
48 |
49 | def test_get_device_returns_torch_device(capsys):
50 | device = get_device()
51 | assert isinstance(device, torch.device)
52 | assert device.type in ("cpu", "cuda", "mps")
53 |
54 |
55 | def test_generate_text_basic_stops_on_eos():
56 | # batch_size = 1
57 | # seq_len = 3
58 | max_new_tokens = 10
59 | fixed_token = 2
60 |
61 | dummy_model = DummyModel(fixed_token=fixed_token)
62 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[1, 3, 4]]) # shape (batch, seq_len)
63 |
64 | # Set eos_token_id to be the fixed_token so that generation stops immediately
65 | output = generate_text_basic(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=fixed_token)
66 | assert output.size(1) == 0
67 | assert dummy_model.eval_called is True
68 |
69 |
70 | def test_generate_text_basic_generates_tokens_without_eos():
71 | # batch_size = 1
72 | # seq_len = 2
73 | max_new_tokens = 3
74 | fixed_token = 1
75 |
76 | dummy_model = DummyModel(fixed_token=fixed_token)
77 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[0, 4]])
78 | output = generate_text_basic(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=None)
79 | assert output.size(1) == max_new_tokens
80 | assert torch.all(output == fixed_token)
81 |
82 |
83 | def test_generate_text_basic_cache_stops_on_eos():
84 | # batch_size = 1
85 | # seq_len = 2
86 | max_new_tokens = 10
87 | fixed_token = 3
88 |
89 | dummy_model = DummyModelCache(fixed_token=fixed_token, n_layers=4)
90 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[2, 2]])
91 | output = generate_text_basic_cache(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=fixed_token)
92 | assert output.size(1) == 0
93 | assert dummy_model.reset_called is True
94 |
95 |
96 | def test_generate_text_basic_cache_generates_tokens_without_eos():
97 | # batch_size = 1
98 | # seq_len = 1
99 | max_new_tokens = 4
100 | fixed_token = 0
101 |
102 | dummy_model = DummyModelCache(fixed_token=fixed_token, n_layers=3)
103 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[5]])
104 |
105 | output = generate_text_basic_cache(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=None)
106 | assert output.size(1) == max_new_tokens
107 | assert torch.all(output == fixed_token)
108 | assert dummy_model.reset_called is True
109 |
110 |
111 | def test_generate_stats_prints_output(monkeypatch, capsys):
112 | output_token_ids = torch.tensor([[10, 20, 30]])
113 | tokenizer = DummyTokenizer()
114 | start_time = 100.0
115 | end_time = 102.0
116 |
117 | monkeypatch.setattr(torch.cuda, "is_available", lambda: False)
118 | generate_stats(output_token_ids, tokenizer, start_time, end_time)
119 |
120 | captured = capsys.readouterr().out
121 | assert "Time:" in captured
122 | assert "tokens/sec" in captured
123 | assert "10 20 30" in captured
124 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/05_use_model/generate_simple.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | # Runs the model similar to chapter 2 and 3 in streaming mode with the least
6 | # amount of bells and whistles. Uses KV caching by default.
7 |
8 | import argparse
9 | from pathlib import Path
10 | import time
11 | import torch
12 |
13 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
14 | get_device,
15 | generate_stats
16 | )
17 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02_ex import (
18 | generate_text_basic_stream_cache
19 | )
20 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
21 | download_qwen3_small,
22 | Qwen3Model,
23 | Qwen3Tokenizer,
24 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B
25 | )
26 |
27 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Run Qwen3 text generation")
28 | parser.add_argument(
29 | "--device",
30 | type=str,
31 | default=None,
32 | help="Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). "
33 | "If not provided, will auto-detect with get_device()."
34 | )
35 | parser.add_argument(
36 | "--max_new_tokens",
37 | type=int,
38 | default=2048,
39 | help="Maximum number of new tokens to generate (default: 2048)."
40 | )
41 | parser.add_argument(
42 | "--compile",
43 | action="store_true",
44 | help="Compile PyTorch model (default: False)."
45 | )
46 | parser.add_argument(
47 | "--reasoning",
48 | action="store_true",
49 | help="Use reasoning model variant (default: False)."
50 | )
51 | parser.add_argument(
52 | "--prompt",
53 | type=str,
54 | default=None,
55 | help=("Use a custom prompt. If not explicitly provided, uses the following defaults: "
56 | "'Explain large language models in a single sentence.' for the base model, and "
57 | "'Find all c in Z_3 such that Z_3[x]/(x^2 + c) is a field.' for the reasoning model.")
58 | )
59 |
60 | args = parser.parse_args()
61 | device = torch.device(args.device) if args.device else get_device()
62 |
63 | if args.reasoning:
64 | download_qwen3_small(kind="reasoning", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
65 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-reasoning.json"
66 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth"
67 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
68 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
69 | apply_chat_template=True,
70 | add_generation_prompt=True,
71 | add_thinking=True
72 | )
73 | else:
74 | download_qwen3_small(kind="base", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
75 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-base.json"
76 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-base.pth"
77 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
78 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
79 | apply_chat_template=False,
80 | add_generation_prompt=False,
81 | add_thinking=False
82 | )
83 |
84 | model = Qwen3Model(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
85 | state = torch.load(model_path, map_location=device)
86 | model.load_state_dict(state)
87 | model.to(device)
88 | model.eval()
89 |
90 | if args.compile:
91 | model = torch.compile(model)
92 |
93 |
94 | if args.prompt is None:
95 | if args.reasoning:
96 | prompt = "Find all c in Z_3 such that Z_3[x]/(x^2 + c) is a field."
97 | else:
98 | prompt = "Explain large language models in a single sentence."
99 | else:
100 | prompt = args.prompt
101 |
102 |
103 | input_ids = tokenizer.encode(prompt)
104 | input_token_ids_tensor = torch.tensor(input_ids, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
105 |
106 | print()
107 | print("=" * 60)
108 | print(f"torch : {torch.__version__}")
109 | print(f"device : {device}")
110 | print("cache : True")
111 | print(f"compile : {args.compile}")
112 | print(f"reasoning : {args.reasoning}")
113 | print("=" * 60)
114 | print()
115 |
116 | start_time = time.time()
117 | all_token_ids = []
118 |
119 | for token in generate_text_basic_stream_cache(
120 | model=model,
121 | token_ids=input_token_ids_tensor,
122 | max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens,
123 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id
124 | ):
125 | token_id = token.squeeze(0).item()
126 | print(tokenizer.decode([token_id]), end="", flush=True)
127 | all_token_ids.append(token_id)
128 | end_time = time.time()
129 |
130 | print("\n")
131 | generate_stats(torch.tensor(all_token_ids), tokenizer, start_time, end_time, print_tokens=False)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch03/02_math500-verifier-scripts/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 3: Evaluating Reasoning Models
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 | ## Bonus materials
8 |
9 | - [evaluate_math500.py](evaluate_math500.py): standalone script to evaluate models on the MATH-500 dataset
10 | - [evaluate_math500_batched.py](evaluate_math500_batched.py): same as above, but processes multiple examples in parallel during generation (for higher throughput)
11 |
12 | Both evaluation scripts import functionality from the [`reasoning_from_scratch`](../../reasoning_from_scratch) package to avoid code duplication. (See [chapter 2 setup instructions](../../ch02/02_setup-tips/python-instructions.md) for installation details.)
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
45 |
46 |
47 |
48 | ## Questions?
49 |
50 | If you have any questions, please don't hesitate to reach out via the [Discussions](https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch/discussions) forum in this GitHub repository.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/conftest.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
6 | download_qwen3_small,
7 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B,
8 | Qwen3Model,
9 | )
10 | import sys
11 | import types
12 | import nbformat
13 | import pytest
14 | import torch
15 |
16 |
17 | @pytest.fixture(scope="session")
18 | def qwen3_weights_path(tmp_path_factory):
19 | """Creates and saves a deterministic model for testing."""
20 |
21 | base_path = tmp_path_factory.mktemp("models")
22 | model_path = base_path / "qwen3_test_weights.pt"
23 | download_qwen3_small(kind="base", tokenizer_only=True, out_dir=base_path)
24 |
25 | if not model_path.exists():
26 | torch.manual_seed(123)
27 | model = Qwen3Model(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
28 | torch.save(model.state_dict(), model_path)
29 |
30 | return base_path
31 |
32 |
33 | def import_definitions_from_notebook(nb_path, module_name):
34 | if not nb_path.exists():
35 | raise FileNotFoundError(f"Notebook file not found at: {nb_path}")
36 |
37 | nb = nbformat.read(str(nb_path), as_version=4)
38 |
39 | mod = types.ModuleType(module_name)
40 | sys.modules[module_name] = mod
41 |
42 | # Pass 1: execute only imports (handle multi-line)
43 | for cell in nb.cells:
44 | if cell.cell_type != "code":
45 | continue
46 | lines = cell.source.splitlines()
47 | collecting = False
48 | buf = []
49 | paren_balance = 0
50 | for line in lines:
51 | stripped = line.strip()
52 | if not collecting and (stripped.startswith("import ") or stripped.startswith("from ")):
53 | collecting = True
54 | buf = [line]
55 | paren_balance = line.count("(") - line.count(")")
56 | if paren_balance == 0:
57 | exec("\n".join(buf), mod.__dict__)
58 | collecting = False
59 | buf = []
60 | elif collecting:
61 | buf.append(line)
62 | paren_balance += line.count("(") - line.count(")")
63 | if paren_balance == 0:
64 | exec("\n".join(buf), mod.__dict__)
65 | collecting = False
66 | buf = []
67 |
68 | # Pass 2: execute only def/class definitions
69 | for cell in nb.cells:
70 | if cell.cell_type != "code":
71 | continue
72 | src = cell.source
73 | if "def " in src or "class " in src:
74 | exec(src, mod.__dict__)
75 |
76 | return mod
77 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/04_torch-compile-windows/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Using `torch.compile()` on Windows
2 |
3 | `torch.compile()` relies on *TorchInductor*, which JIT-compiles kernels and requires a working C/C++ compiler toolchain.
4 |
5 | So, on Windows, the setup required to make `torch.compile` work can be a bit more involved than on Linux or macOS, which usually don't require any extra steps besides installing PyTorch.
6 |
7 | If you are a Windows user and using `torch.compile` sounds too tricky or complicated, don't worry, all code examples in this repository will work fine without compilation.
8 |
9 | Below are some tips that I compiled based on recommendations by [Daniel Kleine](https://github.com/d-kleine) and the following [PyTorch guide](https://docs.pytorch.org/tutorials/unstable/inductor_windows.html).
10 |
11 |
12 | ## 1 Basic Setup (CPU or CUDA)
13 |
14 |
15 | ### 1.1 Install Visual Studio 2022
16 |
17 | - Select the **“Desktop development with C++”** workload.
18 | - Make sure to include the **English language pack** (without it, you may run into UTF-8 encoding errors.)
19 |
20 |
21 | ### 1.2 Open the correct command prompt
22 |
23 |
24 | Launch Python from the
25 |
26 | **"x64 Native Tools Command Prompt for VS 2022"**
27 |
28 | or from the
29 |
30 | **"Visual Studio 2022 Developer Command Prompt"**.
31 |
32 | Alternatively, you can initialize the environment manually by running:
33 |
34 | ```bash
35 | "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\Community\VC\Auxiliary\Build\vcvars64.bat"
36 | ```
37 |
38 |
39 | ### 1.3 Verify that the compiler works
40 |
41 | Run
42 |
43 | ```bash
44 | cl.exe
45 | ```
46 |
47 | If you see version information printed, the compiler is ready.
48 |
49 |
50 | ## 2 Troubleshooting Common Errors
51 |
52 |
53 | ### 2.1 Error: `cl not found`
54 |
55 | Install **Visual Studio Build Tools** with the "C++ build tools" workload and run Python from a developer command prompt. (See this Microsoft [guide](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cpp/build/vscpp-step-0-installation?view=msvc-170) for details)
56 |
57 |
58 | ### 2.2 Error: `triton not found` (when using CUDA)
59 |
60 | Install the Windows build of Triton manually:
61 |
62 | ```bash
63 | pip install "triton-windows<3.4"
64 | ```
65 |
66 | or, if you are using `uv`:
67 |
68 | ```bash
69 | uv pip install "triton-windows<3.4"
70 | ```
71 |
72 | (As mentioned earlier, triton is required by TorchInductor for CUDA kernel compilation.)
73 |
74 |
75 |
76 |
77 | ## 3 Additional Notes
78 |
79 | On Windows, the `cl.exe` compiler is only accessible from within the Visual Studio Developer environment. This means that using `torch.compile()` in notebooks such as Jupyter may not work unless the notebook was launched from a Developer Command Prompt.
80 |
81 | As mentioned at the beginning of this article, there is also a [PyTorch guide](https://docs.pytorch.org/tutorials/unstable/inductor_windows.html) that some users found helpful when getting `torch.compile()` running on Windows CPU builds. However, note that it refers to PyTorch's unstable branch, so use it as a reference only.
82 |
83 | **If compilation continues to cause issues, please feel free to skip it. It's a nice bonus, but it's not important to follow the book.**
84 |
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chF/02_mmlu/random_guessing_baseline.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import argparse
6 | import random
7 | import statistics as stats
8 | from collections import Counter
9 |
10 | from datasets import load_dataset
11 |
12 |
13 | # Gold letter is MMLU jargon for correct answer letter
14 | def gold_letter(ans):
15 | if isinstance(ans, int):
16 | return "ABCD"[ans]
17 | s = str(ans).strip().upper()
18 | return s if s in {"A", "B", "C", "D"} else s[:1]
19 |
20 |
21 | def main():
22 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
23 | description="Show gold answer distribution for an MMLU subset and a random-guess baseline."
24 | )
25 | parser.add_argument(
26 | "--subset",
27 | type=str,
28 | default="high_school_mathematics",
29 | help="MMLU subset name (default: 'high_school_mathematics').",
30 | )
31 | parser.add_argument(
32 | "--seed",
33 | type=int,
34 | default=42,
35 | help="Random seed for the random-guess baseline (default: 42).",
36 | )
37 | parser.add_argument(
38 | "--trials",
39 | type=int,
40 | default=10_000,
41 | help="Number of random-guess trials (default: 10,000).",
42 | )
43 | args = parser.parse_args()
44 |
45 | ds = load_dataset("cais/mmlu", args.subset, split="test")
46 |
47 | labels = [gold_letter(ex["answer"]) for ex in ds]
48 | n = len(labels)
49 | counts = Counter(labels)
50 |
51 | print(f"Subset: {args.subset} | split: test | n={n}")
52 | print("Gold distribution provided in the dataset:")
53 | for letter in "ABCD":
54 | c = counts.get(letter, 0)
55 | pct = (c / n) if n else 0.0
56 | print(f" {letter}: {c} ({pct:.2%})")
57 |
58 | if n == 0:
59 | print("\nNo items. Baseline undefined.")
60 | return
61 |
62 | # Repeat random guessing
63 | rng = random.Random(args.seed)
64 | accs = []
65 | for _ in range(args.trials):
66 | guesses = [rng.choice("ABCD") for _ in range(n)]
67 | correct = sum(1 for g, y in zip(guesses, labels) if g == y)
68 | accs.append(correct / n)
69 |
70 | mean_acc = stats.mean(accs)
71 | sd_acc = stats.stdev(accs) if len(accs) > 1 else 0.0
72 |
73 | print(f"\nRandom guessing over {args.trials:,} trials (uniform A/B/C/D, seed={args.seed}):")
74 | print(f" Mean accuracy: {mean_acc:.2%}")
75 | print(f" Std dev across trials: {sd_acc:.2%}")
76 |
77 | # Quantiles
78 | qs = [0.01, 0.05, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 0.95, 0.99]
79 | accs_sorted = sorted(accs)
80 | print("\nSelected quantiles of accuracy:")
81 | for q in qs:
82 | idx = int(q * len(accs_sorted))
83 | print(f" {q:.0%} quantile: {accs_sorted[idx]:.3%}")
84 |
85 | # Frequency table (rounded)
86 | acc_counts = Counter(round(a, 2) for a in accs)
87 | print("\nFull frequency table of accuracies (rounded):")
88 | for acc_val in sorted(acc_counts):
89 | freq = acc_counts[acc_val]
90 | pct = freq / args.trials
91 | print(f" {acc_val:.3f}: {freq} times ({pct:.2%})")
92 |
93 |
94 | if __name__ == "__main__":
95 | main()
96 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/reasoning_from_scratch/ch02.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | from .qwen3 import KVCache
6 | import torch
7 |
8 |
9 | def get_device(enable_tensor_cores=True):
10 | if torch.cuda.is_available():
11 | device = torch.device("cuda")
12 | print("Using NVIDIA CUDA GPU")
13 |
14 | if enable_tensor_cores:
15 | major, minor = map(int, torch.__version__.split(".")[:2])
16 | if (major, minor) >= (2, 9):
17 | torch.backends.cuda.matmul.fp32_precision = "tf32"
18 | torch.backends.cudnn.conv.fp32_precision = "tf32"
19 | else:
20 | torch.backends.cuda.matmul.allow_tf32 = True
21 | torch.backends.cudnn.allow_tf32 = True
22 |
23 | elif torch.backends.mps.is_available():
24 | device = torch.device("mps")
25 | print("Using Apple Silicon GPU (MPS)")
26 |
27 | elif torch.xpu.is_available():
28 | device = torch.device("xpu")
29 | print("Using Intel GPU")
30 |
31 | else:
32 | device = torch.device("cpu")
33 | print("Using CPU")
34 |
35 | return device
36 |
37 |
38 | @torch.inference_mode()
39 | def generate_text_basic(model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=None):
40 | input_length = token_ids.shape[1]
41 | model.eval()
42 |
43 | for _ in range(max_new_tokens):
44 | out = model(token_ids)[:, -1]
45 | next_token = torch.argmax(out, dim=-1, keepdim=True)
46 |
47 | # Stop if all sequences in the batch have generated EOS
48 | if (eos_token_id is not None
49 | and next_token.item() == eos_token_id):
50 | break
51 |
52 | token_ids = torch.cat([token_ids, next_token], dim=1)
53 | return token_ids[:, input_length:]
54 |
55 |
56 | @torch.inference_mode()
57 | def generate_text_basic_cache(
58 | model,
59 | token_ids,
60 | max_new_tokens,
61 | eos_token_id=None
62 | ):
63 |
64 | input_length = token_ids.shape[1]
65 | model.eval()
66 | cache = KVCache(n_layers=model.cfg["n_layers"])
67 | model.reset_kv_cache()
68 | out = model(token_ids, cache=cache)[:, -1]
69 |
70 | for _ in range(max_new_tokens):
71 | next_token = torch.argmax(out, dim=-1, keepdim=True)
72 |
73 | if (eos_token_id is not None
74 | and next_token.item() == eos_token_id):
75 | break
76 |
77 | token_ids = torch.cat([token_ids, next_token], dim=1)
78 | out = model(next_token, cache=cache)[:, -1]
79 |
80 | return token_ids[:, input_length:]
81 |
82 |
83 | def generate_stats(output_token_ids, tokenizer, start_time,
84 | end_time, print_tokens=True):
85 | total_time = end_time - start_time
86 | print(f"Time: {total_time:.2f} sec")
87 | print(f"{int(output_token_ids.numel() / total_time)} tokens/sec")
88 |
89 | for name, backend in (("CUDA", getattr(torch, "cuda", None)),
90 | ("XPU", getattr(torch, "xpu", None))):
91 | if backend is not None and backend.is_available():
92 | max_mem_bytes = backend.max_memory_allocated()
93 | max_mem_gb = max_mem_bytes / (1024 ** 3)
94 | print(f"Max {name} memory allocated: {max_mem_gb:.2f} GB")
95 | backend.reset_peak_memory_stats()
96 |
97 | if print_tokens:
98 | output_text = tokenizer.decode(output_token_ids.squeeze(0).tolist())
99 | print(f"\n{output_text}")
100 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/scripts/check_notebook_line_length.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | # Check if code in notebooks exceeds line length
6 | # Usage: uv run .github/scripts/check_notebook_line_length.py --max-len 76 ch02/01_main-chapter-code/ch02_main.ipynb ch03/01_main-chapter-code/ch03_main.ipynb
7 |
8 | import argparse
9 | import sys
10 | from pathlib import Path
11 | import nbformat as nbf
12 |
13 |
14 | def parse_args():
15 | p = argparse.ArgumentParser(
16 | description="Check code-cell line lengths in specific .ipynb files."
17 | )
18 | p.add_argument(
19 | "--max-len",
20 | type=int,
21 | default=76,
22 | help="Maximum allowed characters per line (default: 76)",
23 | )
24 | p.add_argument(
25 | "notebooks",
26 | nargs="+",
27 | help="Paths to .ipynb files to check.",
28 | )
29 | return p.parse_args()
30 |
31 |
32 | def strip_inline_comment(line):
33 | """Return line with any trailing #... comment removed, but keep # inside quotes."""
34 | in_quote = None
35 | escaped = False
36 | for i, ch in enumerate(line):
37 | if escaped:
38 | escaped = False
39 | continue
40 | if ch == "\\":
41 | escaped = True
42 | continue
43 | if ch in ("'", '"'):
44 | if in_quote is None:
45 | in_quote = ch
46 | elif in_quote == ch:
47 | in_quote = None
48 | continue
49 | if ch == "#" and in_quote is None:
50 | return line[:i].rstrip()
51 | return line.rstrip()
52 |
53 |
54 | def main():
55 | args = parse_args()
56 |
57 | nb_paths = []
58 | for raw in args.notebooks:
59 | p = Path(raw).resolve()
60 | if not p.exists():
61 | print(f"::warning file={raw}::File not found, skipping.")
62 | continue
63 | if p.suffix != ".ipynb":
64 | print(f"::warning file={raw}::Not a .ipynb file, skipping.")
65 | continue
66 | nb_paths.append(p)
67 |
68 | if not nb_paths:
69 | print("No valid notebooks to check.")
70 | return 0
71 |
72 | violations = []
73 |
74 | for nb_path in nb_paths:
75 | try:
76 | nb = nbf.read(nb_path, as_version=4)
77 | except Exception as e:
78 | print(f"::warning file={nb_path}::Failed to read notebook: {e}")
79 | continue
80 |
81 | for ci, cell in enumerate(nb.cells, start=1):
82 | if cell.get("cell_type") != "code":
83 | continue
84 |
85 | src = cell.get("source", "")
86 | lines = src if isinstance(src, list) else src.splitlines()
87 |
88 | for li, line in enumerate(lines, start=1):
89 | code_part = strip_inline_comment(line)
90 | length = len(code_part)
91 | if length > args.max_len:
92 | print(
93 | f"::error file={nb_path}::Line length {length} exceeds "
94 | f"{args.max_len} in code cell {ci}, line {li}"
95 | )
96 | snippet = code_part if len(code_part) <= 120 else code_part[:120] + "…"
97 | violations.append((str(nb_path), ci, li, length, snippet))
98 |
99 | if violations:
100 | print("\nFound lines exceeding the limit:\n")
101 | for path, ci, li, length, snippet in violations:
102 | print(f"- {path} | cell {ci} line {li}: {length} chars\n {snippet}")
103 | return 1
104 |
105 | print(f"All notebooks pass: no code-cell lines exceed {args.max_len} characters.")
106 | return 0
107 |
108 |
109 | if __name__ == "__main__":
110 | sys.exit(main())
111 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch03/02_math500-verifier-scripts/evaluate_math500.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import argparse
6 | import torch
7 |
8 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
9 | Qwen3Model,
10 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B
11 | )
12 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import get_device
13 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch03 import (
14 | load_math500_test,
15 | evaluate_math500_stream,
16 | load_model_and_tokenizer,
17 | load_tokenizer_only
18 | )
19 |
20 |
21 | def parse_args():
22 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
23 | parser.add_argument(
24 | "--device",
25 | type=str,
26 | default="auto",
27 | help="Device to use: 'auto' (default), or any torch device string like 'cpu', 'cuda', 'cuda:0', 'mps'.",
28 | )
29 | parser.add_argument(
30 | "--which_model",
31 | type=str,
32 | default="base",
33 | choices=["base", "reasoning", "instruct"],
34 | help="Model variant to load. Defaults to 'base'.",
35 | )
36 | parser.add_argument(
37 | "--dataset_size",
38 | type=int,
39 | default=10,
40 | help="Number of MATH-500 examples to evaluate. Default: 10",
41 | )
42 | parser.add_argument(
43 | "--max_new_tokens",
44 | type=int,
45 | default=2048,
46 | help="Max new tokens for generation. Default: 2048",
47 | )
48 | parser.add_argument(
49 | "--compile",
50 | action="store_true",
51 | help="Enable torch.compile for the model.",
52 | )
53 | parser.add_argument(
54 | "--checkpoint_path",
55 | type=str,
56 | default=None,
57 | help="Optional path to a .pth checkpoint to load model weights from.",
58 | )
59 | parser.add_argument(
60 | "--verbose",
61 | action="store_true",
62 | help="Print per-sample correctness while evaluating.",
63 | )
64 | return parser.parse_args()
65 |
66 |
67 | if __name__ == "__main__":
68 | args = parse_args()
69 |
70 | if args.device == "auto":
71 | device = get_device()
72 | else:
73 | device = torch.device(args.device)
74 |
75 | which_model = args.which_model
76 | dataset_size = args.dataset_size
77 | max_new_tokens = args.max_new_tokens
78 | use_compile = args.compile
79 |
80 | print("Model:", which_model)
81 | print("Device:", device)
82 | dev_name = str(device).replace(":", "-")
83 |
84 | math_data = load_math500_test()
85 |
86 | if args.which_model == "instruct":
87 | which_model = "reasoning"
88 | else:
89 | which_model = args.which_model
90 |
91 | if args.checkpoint_path:
92 | # To load the saved RL checkpoint files from chapter 6
93 | tokenizer = load_tokenizer_only(which_model=which_model)
94 | model = Qwen3Model(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
95 | model.to(device)
96 | state_dict = torch.load(args.checkpoint_path, map_location=device)
97 | model.load_state_dict(state_dict)
98 | if args.compile:
99 | torch._dynamo.config.allow_unspec_int_on_nn_module = True
100 | model = torch.compile(model)
101 | else:
102 | model, tokenizer = load_model_and_tokenizer(
103 | which_model=which_model,
104 | device=device,
105 | use_compile=args.compile
106 | )
107 |
108 | if args.which_model == "instruct":
109 | tokenizer.add_thinking = False
110 |
111 | model.eval()
112 | torch.set_float32_matmul_precision("high")
113 |
114 | num_correct, num_examples, acc = evaluate_math500_stream(
115 | model=model,
116 | out_path=f"math500_{which_model}-{dev_name}-evaluate-script.jsonl",
117 | tokenizer=tokenizer,
118 | device=device,
119 | math_data=math_data[:dataset_size],
120 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
121 | verbose=args.verbose,
122 | )
123 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chG/01_main-chapter-code/qwen3_chat_interface_multiturn.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt).
2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch"
3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch
4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch
5 |
6 |
7 | import torch
8 | import chainlit
9 |
10 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
11 | get_device,
12 | )
13 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02_ex import generate_text_basic_stream_cache
14 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch03 import load_model_and_tokenizer
15 |
16 | # ============================================================
17 | # EDIT ME: Simple configuration
18 | # ============================================================
19 | WHICH_MODEL = "reasoning" # "base" for base model
20 | MAX_NEW_TOKENS = 38912
21 | LOCAL_DIR = "qwen3"
22 | COMPILE = False
23 | # ============================================================
24 |
25 |
26 | def trim_input_tensor(input_ids_tensor, context_len, max_new_tokens):
27 | assert max_new_tokens < context_len
28 | keep_len = max(1, context_len - max_new_tokens)
29 |
30 | # If the prompt is too long, left-truncate to keep_len
31 | if input_ids_tensor.shape[1] > keep_len:
32 | input_ids_tensor = input_ids_tensor[:, -keep_len:]
33 |
34 | return input_ids_tensor
35 |
36 |
37 | def build_prompt_from_history(history, add_assistant_header=True):
38 | """
39 | history: [{"role": "system"|"user"|"assistant", "content": str}, ...]
40 | """
41 | parts = []
42 | for m in history:
43 | role = m["role"]
44 | content = m["content"]
45 | parts.append(f"<|im_start|>{role}\n{content}<|im_end|>\n")
46 |
47 | if add_assistant_header:
48 | parts.append("<|im_start|>assistant\n")
49 | return "".join(parts)
50 |
51 |
52 | DEVICE = get_device()
53 | MODEL, TOKENIZER = load_model_and_tokenizer(
54 | which_model=WHICH_MODEL,
55 | device=DEVICE,
56 | use_compile=COMPILE,
57 | local_dir=LOCAL_DIR
58 | )
59 |
60 | # Even though the official TOKENIZER.eos_token_id is either <|im_end|> (reasoning)
61 | # or <|endoftext|> (base), the reasoning model sometimes emits both.
62 | EOS_TOKEN_IDS = (
63 | TOKENIZER.encode("<|im_end|>")[0],
64 | TOKENIZER.encode("<|endoftext|>")[0]
65 | )
66 |
67 |
68 | @chainlit.on_chat_start
69 | async def on_start():
70 | chainlit.user_session.set("history", [])
71 | chainlit.user_session.get("history").append(
72 | {"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."}
73 | )
74 |
75 |
76 | @chainlit.on_message
77 | async def main(message: chainlit.Message):
78 | """
79 | The main Chainlit function.
80 | """
81 | # 0) Get and track chat history
82 | history = chainlit.user_session.get("history")
83 | history.append({"role": "user", "content": message.content})
84 |
85 | # 1) Encode input
86 | prompt = build_prompt_from_history(history, add_assistant_header=True)
87 | input_ids = TOKENIZER.encode(prompt)
88 | input_ids_tensor = torch.tensor(input_ids, device=DEVICE).unsqueeze(0)
89 |
90 | # Multi-turn can be very long, so we add this left-trimming
91 | input_ids_tensor = trim_input_tensor(
92 | input_ids_tensor=input_ids_tensor,
93 | context_len=MODEL.cfg["context_length"],
94 | max_new_tokens=MAX_NEW_TOKENS
95 | )
96 |
97 | # 2) Start an outgoing message we can stream into
98 | out_msg = chainlit.Message(content="")
99 | await out_msg.send()
100 |
101 | # 3) Stream generation
102 | for tok in generate_text_basic_stream_cache(
103 | model=MODEL,
104 | token_ids=input_ids_tensor,
105 | max_new_tokens=MAX_NEW_TOKENS,
106 | # eos_token_id=TOKENIZER.eos_token_id
107 | ):
108 | token_id = tok.squeeze(0)
109 | if token_id in EOS_TOKEN_IDS:
110 | break
111 | piece = TOKENIZER.decode(token_id.tolist())
112 | await out_msg.stream_token(piece)
113 |
114 | # 4) Finalize the streamed message
115 | await out_msg.update()
116 |
117 | # 5) Update chat history
118 | history.append({"role": "assistant", "content": out_msg.content})
119 | chainlit.user_session.set("history", history)
120 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_ch02.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import torch
6 |
7 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
8 | get_device,
9 | generate_text_basic,
10 | generate_text_basic_cache,
11 | generate_stats
12 | )
13 |
14 |
15 | # Dummy model for generate_text_basic tests.
16 | class DummyModel:
17 | def __init__(self, fixed_token, vocab_size=5):
18 | self.fixed_token = fixed_token
19 | self.vocab_size = vocab_size
20 | self.eval_called = False
21 |
22 | def eval(self):
23 | self.eval_called = True
24 | return self
25 |
26 | def __call__(self, token_ids, cache=None):
27 | batch_size, seq_len = token_ids.size()
28 | out = torch.zeros(batch_size, seq_len, self.vocab_size)
29 | # Set the fixed_token column to the highest value so argmax returns fixed_token
30 | out[..., self.fixed_token] = 1.0
31 | return out
32 |
33 |
34 | class DummyModelCache(DummyModel):
35 | def __init__(self, fixed_token, vocab_size=5, n_layers=2):
36 | super().__init__(fixed_token, vocab_size)
37 | self.cfg = {"n_layers": n_layers}
38 | self.reset_called = False
39 |
40 | def reset_kv_cache(self):
41 | self.reset_called = True
42 |
43 |
44 | class DummyTokenizer:
45 | def decode(self, token_list):
46 | return " ".join(str(t) for t in token_list)
47 |
48 |
49 | def test_get_device_returns_torch_device(capsys):
50 | device = get_device()
51 | assert isinstance(device, torch.device)
52 | assert device.type in ("cpu", "cuda", "mps")
53 |
54 |
55 | def test_generate_text_basic_stops_on_eos():
56 | # batch_size = 1
57 | # seq_len = 3
58 | max_new_tokens = 10
59 | fixed_token = 2
60 |
61 | dummy_model = DummyModel(fixed_token=fixed_token)
62 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[1, 3, 4]]) # shape (batch, seq_len)
63 |
64 | # Set eos_token_id to be the fixed_token so that generation stops immediately
65 | output = generate_text_basic(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=fixed_token)
66 | assert output.size(1) == 0
67 | assert dummy_model.eval_called is True
68 |
69 |
70 | def test_generate_text_basic_generates_tokens_without_eos():
71 | # batch_size = 1
72 | # seq_len = 2
73 | max_new_tokens = 3
74 | fixed_token = 1
75 |
76 | dummy_model = DummyModel(fixed_token=fixed_token)
77 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[0, 4]])
78 | output = generate_text_basic(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=None)
79 | assert output.size(1) == max_new_tokens
80 | assert torch.all(output == fixed_token)
81 |
82 |
83 | def test_generate_text_basic_cache_stops_on_eos():
84 | # batch_size = 1
85 | # seq_len = 2
86 | max_new_tokens = 10
87 | fixed_token = 3
88 |
89 | dummy_model = DummyModelCache(fixed_token=fixed_token, n_layers=4)
90 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[2, 2]])
91 | output = generate_text_basic_cache(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=fixed_token)
92 | assert output.size(1) == 0
93 | assert dummy_model.reset_called is True
94 |
95 |
96 | def test_generate_text_basic_cache_generates_tokens_without_eos():
97 | # batch_size = 1
98 | # seq_len = 1
99 | max_new_tokens = 4
100 | fixed_token = 0
101 |
102 | dummy_model = DummyModelCache(fixed_token=fixed_token, n_layers=3)
103 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[5]])
104 |
105 | output = generate_text_basic_cache(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=None)
106 | assert output.size(1) == max_new_tokens
107 | assert torch.all(output == fixed_token)
108 | assert dummy_model.reset_called is True
109 |
110 |
111 | def test_generate_stats_prints_output(monkeypatch, capsys):
112 | output_token_ids = torch.tensor([[10, 20, 30]])
113 | tokenizer = DummyTokenizer()
114 | start_time = 100.0
115 | end_time = 102.0
116 |
117 | monkeypatch.setattr(torch.cuda, "is_available", lambda: False)
118 | generate_stats(output_token_ids, tokenizer, start_time, end_time)
119 |
120 | captured = capsys.readouterr().out
121 | assert "Time:" in captured
122 | assert "tokens/sec" in captured
123 | assert "10 20 30" in captured
124 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/05_use_model/generate_simple.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | # Runs the model similar to chapter 2 and 3 in streaming mode with the least
6 | # amount of bells and whistles. Uses KV caching by default.
7 |
8 | import argparse
9 | from pathlib import Path
10 | import time
11 | import torch
12 |
13 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
14 | get_device,
15 | generate_stats
16 | )
17 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02_ex import (
18 | generate_text_basic_stream_cache
19 | )
20 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
21 | download_qwen3_small,
22 | Qwen3Model,
23 | Qwen3Tokenizer,
24 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B
25 | )
26 |
27 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Run Qwen3 text generation")
28 | parser.add_argument(
29 | "--device",
30 | type=str,
31 | default=None,
32 | help="Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). "
33 | "If not provided, will auto-detect with get_device()."
34 | )
35 | parser.add_argument(
36 | "--max_new_tokens",
37 | type=int,
38 | default=2048,
39 | help="Maximum number of new tokens to generate (default: 2048)."
40 | )
41 | parser.add_argument(
42 | "--compile",
43 | action="store_true",
44 | help="Compile PyTorch model (default: False)."
45 | )
46 | parser.add_argument(
47 | "--reasoning",
48 | action="store_true",
49 | help="Use reasoning model variant (default: False)."
50 | )
51 | parser.add_argument(
52 | "--prompt",
53 | type=str,
54 | default=None,
55 | help=("Use a custom prompt. If not explicitly provided, uses the following defaults: "
56 | "'Explain large language models in a single sentence.' for the base model, and "
57 | "'Find all c in Z_3 such that Z_3[x]/(x^2 + c) is a field.' for the reasoning model.")
58 | )
59 |
60 | args = parser.parse_args()
61 | device = torch.device(args.device) if args.device else get_device()
62 |
63 | if args.reasoning:
64 | download_qwen3_small(kind="reasoning", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
65 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-reasoning.json"
66 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth"
67 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
68 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
69 | apply_chat_template=True,
70 | add_generation_prompt=True,
71 | add_thinking=True
72 | )
73 | else:
74 | download_qwen3_small(kind="base", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
75 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-base.json"
76 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-base.pth"
77 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
78 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
79 | apply_chat_template=False,
80 | add_generation_prompt=False,
81 | add_thinking=False
82 | )
83 |
84 | model = Qwen3Model(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
85 | state = torch.load(model_path, map_location=device)
86 | model.load_state_dict(state)
87 | model.to(device)
88 | model.eval()
89 |
90 | if args.compile:
91 | model = torch.compile(model)
92 |
93 |
94 | if args.prompt is None:
95 | if args.reasoning:
96 | prompt = "Find all c in Z_3 such that Z_3[x]/(x^2 + c) is a field."
97 | else:
98 | prompt = "Explain large language models in a single sentence."
99 | else:
100 | prompt = args.prompt
101 |
102 |
103 | input_ids = tokenizer.encode(prompt)
104 | input_token_ids_tensor = torch.tensor(input_ids, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
105 |
106 | print()
107 | print("=" * 60)
108 | print(f"torch : {torch.__version__}")
109 | print(f"device : {device}")
110 | print("cache : True")
111 | print(f"compile : {args.compile}")
112 | print(f"reasoning : {args.reasoning}")
113 | print("=" * 60)
114 | print()
115 |
116 | start_time = time.time()
117 | all_token_ids = []
118 |
119 | for token in generate_text_basic_stream_cache(
120 | model=model,
121 | token_ids=input_token_ids_tensor,
122 | max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens,
123 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id
124 | ):
125 | token_id = token.squeeze(0).item()
126 | print(tokenizer.decode([token_id]), end="", flush=True)
127 | all_token_ids.append(token_id)
128 | end_time = time.time()
129 |
130 | print("\n")
131 | generate_stats(torch.tensor(all_token_ids), tokenizer, start_time, end_time, print_tokens=False)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch03/02_math500-verifier-scripts/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 3: Evaluating Reasoning Models
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 | ## Bonus materials
8 |
9 | - [evaluate_math500.py](evaluate_math500.py): standalone script to evaluate models on the MATH-500 dataset
10 | - [evaluate_math500_batched.py](evaluate_math500_batched.py): same as above, but processes multiple examples in parallel during generation (for higher throughput)
11 |
12 | Both evaluation scripts import functionality from the [`reasoning_from_scratch`](../../reasoning_from_scratch) package to avoid code duplication. (See [chapter 2 setup instructions](../../ch02/02_setup-tips/python-instructions.md) for installation details.)
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 | ---
19 |
20 | **Note**: If you are not a `uv` user, replace `uv run ...py` with `python ...py` in the examples below.
21 |
22 | ---
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 | ## `evaluate_math500.py` usage
29 |
30 | Run with:
31 |
32 | ```bash
33 | python evaluate_math500.py
34 | ```
35 |
36 | Or, with `uv:`
37 |
38 |
39 | ```bash
40 | uv run evaluate_math500.py
41 | ```
42 |
43 | Options:
44 |
45 | ```bash
46 | uv run evaluate_math500.py --help
47 |
48 | options:
49 | -h, --help show this help message and exit
50 | --device DEVICE Device to use: "auto" (default) or any torch device string
51 | (e.g., "cpu", "cuda", "cuda:0", "mps").
52 | --which_model {base,reasoning}
53 | Model variant to load (default: "base").
54 | --dataset_size DATASET_SIZE
55 | Number of MATH-500 examples to evaluate (default: 10).
56 | --max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS
57 | Max new tokens to generate (default: 2048).
58 | --compile Enable torch.compile.
59 | --verbose Print per-sample correctness while evaluating.
60 | ```
61 |
62 |
63 | ## `evaluate_math500_batch.py` usage
64 |
65 | This version extends batching to generation itself, enabling parallel decoding:
66 |
67 | ```bash
68 | uv run evaluate_math500_batched.py --help
69 | ```
70 |
71 | Extra options:
72 |
73 | ```bash
74 | --batch_size BATCH_SIZE
75 | Number of examples to generate in parallel (default: 4).
76 | --disable_efficient_mode
77 | Use a simpler batched inference method. Slower and more
78 | memory-intensive, but easier to debug.
79 | ```
80 |
81 |
82 |
83 |
84 | **Implementation note:**
85 | By default, batched generation halts for sequences that emit a stop token. With `--disable_efficient_mode`, all sequences continue until the longest finishes. This affects compute efficiency only, not qualitative results, since tokens after the stop token are discarded.
86 |
87 |
88 |
89 | **Tip (MPS devices):**
90 | Run with:
91 |
92 | ```bash
93 | PYTORCH_ENABLE_MPS_FALLBACK=1 uv run evaluate_math500_batched.py
94 | ```
95 |
96 | Some PyTorch ops used in efficient batched inference are not yet supported on MPS. As a fallback, you can also use `--disable_efficient_mode`.
97 |
98 |
99 |
100 |
101 |
102 | - `evaluate_math500.py --dataset_size 500`
103 |
104 |
105 | | Device / Dataset size | Base model | Reasoning model |
106 | | ------------------------------------------- | ---------- | --------------- |
107 | | **Mac Mini M4 CPU** (500 examples, sequential | 43.6 min | Didn't run (too hot) |
108 | | **Mac Mini M4 GPU** (500 examples, sequential) | 37.5 min | Didn't run (too hot) |
109 | | **DGX Spark** (500 examples, sequential) | 10.0 min | 182.2 min |
110 | | **H100 GPU** (500 examples, sequential) | 13.3 min | 185.4 min |
111 |
112 |
113 |
114 |
115 | - `evaluate_math500_batched.py --dataset_size 500 --batch_size 128`
116 |
117 | | Device / Dataset size | Base model | Reasoning model |
118 | | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ---------- | --------------- |
119 | | **Mac Mini M4 CPU** (500 examples, batched, `--batch_size 128`) | 167.2 min | Didn't run (too hot) |
120 | | **Mac Mini M4 GPU** (500 examples, batched, `--batch_size 128`) | Error* | Error |
121 | | **DGX Spark** (500 examples, batched, `--batch_size 128`) | 16.3 min | 119.3 min |
122 | | **H100 GPU** (500 examples, batched, `--batch_size 128`) | 3.3 min | 14.6 min |
123 |
124 |
125 |
126 | - The accuracy of the base model is 15.6% (78/500); the accuracy of the reasoning model is 50.8% (254/500).
127 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chF/02_mmlu/1_letter_matching.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import argparse
2 | import time
3 |
4 | import torch
5 | from datasets import load_dataset, get_dataset_config_names
6 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import get_device
7 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02_ex import generate_text_basic_stream_cache
8 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch03 import load_model_and_tokenizer
9 |
10 |
11 | # Same as in main notebook
12 | def format_prompt(example):
13 | return (
14 | f"{example['question']}\n"
15 | f"A. {example['choices'][0]}\n"
16 | f"B. {example['choices'][1]}\n"
17 | f"C. {example['choices'][2]}\n"
18 | f"D. {example['choices'][3]}\n"
19 | "Answer: " # trailing space encourages a single-letter next token
20 | )
21 |
22 |
23 | # Same as in main notebook
24 | def predict_choice(
25 | model, tokenizer, prompt_fmt, max_new_tokens=8
26 | ):
27 | pred = None
28 | for t in generate_text_basic_stream_cache(
29 | model=model,
30 | token_ids=prompt_fmt,
31 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
32 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
33 | ):
34 | answer = tokenizer.decode(t.squeeze(0).tolist())
35 | for letter in answer:
36 | letter = letter.upper()
37 | if letter in "ABCD":
38 | pred = letter
39 | break
40 | if pred: # stop as soon as a letter appears
41 | break
42 | return pred
43 |
44 |
45 | def evaluate_mmlu_letter(
46 | model,
47 | tokenizer,
48 | device,
49 | subsets="high_school_mathematics", # str, list of str, or "all"
50 | split="test",
51 | max_new_tokens=8,
52 | verbose_every=50,
53 | ):
54 | if subsets == "all":
55 | subset_list = get_dataset_config_names("cais/mmlu")
56 | elif isinstance(subsets, str):
57 | subset_list = [s.strip() for s in subsets.split(",")] if "," in subsets else [subsets]
58 | else:
59 | subset_list = list(subsets)
60 |
61 | total = 0
62 | correct = 0
63 | start = time.time()
64 |
65 | for subset in subset_list:
66 | ds = load_dataset("cais/mmlu", subset, split=split)
67 | for ex in ds:
68 | prompt = format_prompt(ex)
69 | tok = torch.tensor(tokenizer.encode(prompt), device=device).unsqueeze(0)
70 | pred = predict_choice(model, tokenizer, tok, max_new_tokens)
71 |
72 | ans = ex["answer"]
73 | # "Gold" is the MMLU jargon for the correct answer (ground truth)
74 | gold = "ABCD"[ans] if isinstance(ans, int) else str(ans).strip().upper()
75 |
76 | total += 1
77 | correct += int(pred == gold)
78 |
79 | if verbose_every and total % verbose_every == 0:
80 | print(f"MMLU {total} acc={correct/total:.3f} [{subset}]")
81 |
82 | acc = correct / max(1, total)
83 | print(
84 | f"\nMMLU letter accuracy: {correct}/{total} = {acc:.2%} "
85 | f"in {time.time()-start:.1f}s"
86 | )
87 | return {"accuracy": acc, "num_examples": total, "subsets": subset_list, "split": split}
88 |
89 |
90 | def main():
91 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
92 | description="Zero-shot MMLU letter evaluator (A/B/C/D matching)."
93 | )
94 | parser.add_argument(
95 | "--device",
96 | type=str,
97 | default="auto",
98 | help="Device to use: 'auto' (default), or any torch device string like "
99 | "'cpu', 'cuda', 'cuda:0', 'mps'.",
100 | )
101 | parser.add_argument(
102 | "--which_model",
103 | type=str,
104 | default="base",
105 | choices=["base", "reasoning"],
106 | help="Model variant to load. Defaults to 'base'.",
107 | )
108 | parser.add_argument(
109 | "--subsets",
110 | type=str,
111 | default="high_school_mathematics",
112 | help="Comma-separated subset names or 'all'. "
113 | "Default: 'high_school_mathematics'.",
114 | )
115 | args = parser.parse_args()
116 |
117 | if args.device == "auto":
118 | device = get_device()
119 | else:
120 | device = torch.device(args.device)
121 | print(f"Using device: {device}")
122 |
123 | model, tokenizer = load_model_and_tokenizer(args.which_model, device, use_compile=False)
124 | model.eval()
125 | torch.set_float32_matmul_precision("high")
126 |
127 | metrics = evaluate_mmlu_letter(
128 | model=model,
129 | tokenizer=tokenizer,
130 | device=device,
131 | subsets=args.subsets,
132 | )
133 | print(metrics)
134 |
135 |
136 | if __name__ == "__main__":
137 | main()
138 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_ch02_ex.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import torch
6 |
7 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
8 | generate_text_basic,
9 | generate_text_basic_cache,
10 | )
11 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02_ex import (
12 | generate_text_basic_stream,
13 | generate_text_basic_stream_cache,
14 | )
15 |
16 |
17 | # Dummy model for generate_text_basic tests.
18 | class DummyModel:
19 | def __init__(self, fixed_token, vocab_size=5):
20 | self.fixed_token = fixed_token
21 | self.vocab_size = vocab_size
22 | self.eval_called = False
23 |
24 | def eval(self):
25 | self.eval_called = True
26 | return self
27 |
28 | def __call__(self, token_ids, cache=None):
29 | batch_size, seq_len = token_ids.size()
30 | out = torch.zeros(batch_size, seq_len, self.vocab_size)
31 | # Set the fixed_token column to the highest value so argmax returns fixed_token
32 | out[..., self.fixed_token] = 1.0
33 | return out
34 |
35 |
36 | class DummyModelCache(DummyModel):
37 | def __init__(self, fixed_token, vocab_size=5, n_layers=2):
38 | super().__init__(fixed_token, vocab_size)
39 | self.cfg = {"n_layers": n_layers}
40 | self.reset_called = False
41 |
42 | def reset_kv_cache(self):
43 | self.reset_called = True
44 |
45 |
46 | class DummyTokenizer:
47 | def decode(self, token_list):
48 | return " ".join(str(t) for t in token_list)
49 |
50 |
51 | def test_generate_text_basic_stream_equivalence():
52 | max_new_tokens = 10
53 | fixed_token = 2
54 |
55 | dummy_model = DummyModel(fixed_token=fixed_token)
56 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[1, 3, 4]]) # shape (batch, seq_len)
57 |
58 | # Set eos_token_id to be the fixed_token so that generation stops immediately
59 | output_1 = generate_text_basic(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=fixed_token)
60 | output_1 = output_1.squeeze(0).tolist()
61 |
62 | output_2 = []
63 | for token in generate_text_basic_stream(
64 | model=dummy_model,
65 | token_ids=token_ids,
66 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
67 | eos_token_id=fixed_token
68 | ):
69 | output_2.append(token.squeeze(0).item())
70 |
71 | assert output_1 == output_2
72 |
73 |
74 | def test_generate_text_basic_stream_generates_tokens_without_eos():
75 | max_new_tokens = 3
76 | fixed_token = 1
77 |
78 | dummy_model = DummyModel(fixed_token=fixed_token)
79 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[0, 4]])
80 | output_1 = generate_text_basic(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=None)
81 | output_1 = output_1.squeeze(0).tolist()
82 |
83 | output_2 = []
84 | for token in generate_text_basic_stream(
85 | model=dummy_model,
86 | token_ids=token_ids,
87 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
88 | eos_token_id=None
89 | ):
90 | output_2.append(token.squeeze(0).item())
91 |
92 | assert output_1 == output_2
93 |
94 |
95 | def test_generate_text_basic_cache_stream_equivalence():
96 | max_new_tokens = 10
97 | fixed_token = 2
98 |
99 | dummy_model = DummyModelCache(fixed_token=fixed_token)
100 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[1, 3, 4]]) # shape (batch, seq_len)
101 |
102 | # Set eos_token_id to be the fixed_token so that generation stops immediately
103 | output_1 = generate_text_basic(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=fixed_token)
104 | output_1 = output_1.squeeze(0).tolist()
105 |
106 | output_2 = []
107 | for token in generate_text_basic_stream_cache(
108 | model=dummy_model,
109 | token_ids=token_ids,
110 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
111 | eos_token_id=fixed_token
112 | ):
113 | output_2.append(token.squeeze(0).item())
114 |
115 | assert output_1 == output_2
116 |
117 |
118 | def test_generate_text_basic_cache_stream_generates_tokens_without_eos():
119 | max_new_tokens = 3
120 | fixed_token = 1
121 |
122 | dummy_model = DummyModelCache(fixed_token=fixed_token)
123 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[0, 4]])
124 | output_1 = generate_text_basic_cache(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=None)
125 | output_1 = output_1.squeeze(0).tolist()
126 |
127 | output_2 = []
128 | for token in generate_text_basic_stream_cache(
129 | model=dummy_model,
130 | token_ids=token_ids,
131 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
132 | eos_token_id=None
133 | ):
134 | output_2.append(token.squeeze(0).item())
135 |
136 | assert output_1 == output_2
137 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Other temporary files
2 | *.jsonl
3 | Untitled.ipynb
4 | qwen3/
5 | tmp
6 | qwen3-0.6B.pth
7 | qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth
8 | qwen3-0.6B-base.pth
9 | tokenizer-reasoning.json
10 | tokenizer.json
11 | tokenizer-base.json
12 | .chainlit
13 | chainlit.md
14 | math500_test.json
15 | math500_base-mps.jsonl
16 | math500_base-cpu.jsonl
17 | math500_base-cuda.jsonl
18 | math500_reasoning-mps.jsonl
19 | math500_reasoning-cpu.jsonl
20 | math500_reasoning-cuda.jsonl
21 |
22 | # Installation artifacts
23 | uv.lock
24 |
25 | # Temporary OS files
26 | .DS_Store
27 |
28 | # Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
29 | __pycache__/
30 | *.py[cod]
31 | *$py.class
32 |
33 | # C extensions
34 | *.so
35 |
36 | # Distribution / packaging
37 | .Python
38 | build/
39 | develop-eggs/
40 | dist/
41 | downloads/
42 | eggs/
43 | .eggs/
44 | lib/
45 | lib64/
46 | parts/
47 | sdist/
48 | var/
49 | wheels/
50 | share/python-wheels/
51 | *.egg-info/
52 | .installed.cfg
53 | *.egg
54 | MANIFEST
55 |
56 | # PyInstaller
57 | # Usually these files are written by a python script from a template
58 | # before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it.
59 | *.manifest
60 | *.spec
61 |
62 | # Installer logs
63 | pip-log.txt
64 | pip-delete-this-directory.txt
65 |
66 | # Unit test / coverage reports
67 | htmlcov/
68 | .tox/
69 | .nox/
70 | .coverage
71 | .coverage.*
72 | .cache
73 | nosetests.xml
74 | coverage.xml
75 | *.cover
76 | *.py,cover
77 | .hypothesis/
78 | .pytest_cache/
79 | cover/
80 |
81 | # Translations
82 | *.mo
83 | *.pot
84 |
85 | # Django stuff:
86 | *.log
87 | local_settings.py
88 | db.sqlite3
89 | db.sqlite3-journal
90 |
91 | # Flask stuff:
92 | instance/
93 | .webassets-cache
94 |
95 | # Scrapy stuff:
96 | .scrapy
97 |
98 | # Sphinx documentation
99 | docs/_build/
100 |
101 | # PyBuilder
102 | .pybuilder/
103 | target/
104 |
105 | # Jupyter Notebook
106 | .ipynb_checkpoints
107 |
108 | # IPython
109 | profile_default/
110 | ipython_config.py
111 |
112 | # pyenv
113 | # For a library or package, you might want to ignore these files since the code is
114 | # intended to run in multiple environments; otherwise, check them in:
115 | # .python-version
116 |
117 | # pipenv
118 | # According to pypa/pipenv#598, it is recommended to include Pipfile.lock in version control.
119 | # However, in case of collaboration, if having platform-specific dependencies or dependencies
120 | # having no cross-platform support, pipenv may install dependencies that don't work, or not
121 | # install all needed dependencies.
122 | #Pipfile.lock
123 |
124 | # UV
125 | # Similar to Pipfile.lock, it is generally recommended to include uv.lock in version control.
126 | # This is especially recommended for binary packages to ensure reproducibility, and is more
127 | # commonly ignored for libraries.
128 | #uv.lock
129 |
130 | # poetry
131 | # Similar to Pipfile.lock, it is generally recommended to include poetry.lock in version control.
132 | # This is especially recommended for binary packages to ensure reproducibility, and is more
133 | # commonly ignored for libraries.
134 | # https://python-poetry.org/docs/basic-usage/#commit-your-poetrylock-file-to-version-control
135 | #poetry.lock
136 |
137 | # pdm
138 | # Similar to Pipfile.lock, it is generally recommended to include pdm.lock in version control.
139 | #pdm.lock
140 | # pdm stores project-wide configurations in .pdm.toml, but it is recommended to not include it
141 | # in version control.
142 | # https://pdm.fming.dev/latest/usage/project/#working-with-version-control
143 | .pdm.toml
144 | .pdm-python
145 | .pdm-build/
146 |
147 | # PEP 582; used by e.g. github.com/David-OConnor/pyflow and github.com/pdm-project/pdm
148 | __pypackages__/
149 |
150 | # Celery stuff
151 | celerybeat-schedule
152 | celerybeat.pid
153 |
154 | # SageMath parsed files
155 | *.sage.py
156 |
157 | # Environments
158 | .env
159 | .venv
160 | env/
161 | venv/
162 | ENV/
163 | env.bak/
164 | venv.bak/
165 |
166 | # Spyder project settings
167 | .spyderproject
168 | .spyproject
169 |
170 | # Rope project settings
171 | .ropeproject
172 |
173 | # mkdocs documentation
174 | /site
175 |
176 | # mypy
177 | .mypy_cache/
178 | .dmypy.json
179 | dmypy.json
180 |
181 | # Pyre type checker
182 | .pyre/
183 |
184 | # pytype static type analyzer
185 | .pytype/
186 |
187 | # Cython debug symbols
188 | cython_debug/
189 |
190 | # PyCharm
191 | # JetBrains specific template is maintained in a separate JetBrains.gitignore that can
192 | # be found at https://github.com/github/gitignore/blob/main/Global/JetBrains.gitignore
193 | # and can be added to the global gitignore or merged into this file. For a more nuclear
194 | # option (not recommended) you can uncomment the following to ignore the entire idea folder.
195 | #.idea/
196 |
197 | # PyPI configuration file
198 | .pypirc
199 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/05_use_model/chat.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | # Runs the model similar to chapter 2 and 3 in streaming mode with the least
6 | # amount of bells and whistles. Uses KV caching by default.
7 | # Similar to generate_simple.py but uses an interactive REPL (without memory).
8 |
9 | import argparse
10 | from pathlib import Path
11 | import time
12 | import torch
13 |
14 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
15 | get_device,
16 | generate_stats
17 | )
18 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02_ex import (
19 | generate_text_basic_stream_cache
20 | )
21 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
22 | download_qwen3_small,
23 | Qwen3Model,
24 | Qwen3Tokenizer,
25 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B
26 | )
27 |
28 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Run Qwen3 text generation (interactive REPL)")
29 | parser.add_argument(
30 | "--device",
31 | type=str,
32 | default=None,
33 | help="Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). "
34 | "If not provided, will auto-detect with get_device()."
35 | )
36 | parser.add_argument(
37 | "--max_new_tokens",
38 | type=int,
39 | default=2048,
40 | help="Maximum number of new tokens to generate (default: 2048)."
41 | )
42 | parser.add_argument(
43 | "--compile",
44 | action="store_true",
45 | help="Compile PyTorch model (default: False)."
46 | )
47 | parser.add_argument(
48 | "--reasoning",
49 | action="store_true",
50 | help="Use reasoning model variant (default: False)."
51 | )
52 |
53 | args = parser.parse_args()
54 | device = torch.device(args.device) if args.device else get_device()
55 |
56 | if args.reasoning:
57 | download_qwen3_small(kind="reasoning", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
58 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-reasoning.json"
59 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth"
60 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
61 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
62 | apply_chat_template=True,
63 | add_generation_prompt=True,
64 | add_thinking=True
65 | )
66 | else:
67 | download_qwen3_small(kind="base", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
68 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-base.json"
69 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-base.pth"
70 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
71 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
72 | apply_chat_template=False,
73 | add_generation_prompt=False,
74 | add_thinking=False
75 | )
76 |
77 | model = Qwen3Model(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
78 | state = torch.load(model_path, map_location=device)
79 | model.load_state_dict(state)
80 | model.to(device)
81 | model.eval()
82 |
83 | if args.compile:
84 | model = torch.compile(model)
85 |
86 | print()
87 | print("=" * 60)
88 | print(f"torch : {torch.__version__}")
89 | print(f"device : {device}")
90 | print("cache : True")
91 | print(f"compile : {args.compile}")
92 | print(f"reasoning : {args.reasoning}")
93 | print("memory : False")
94 | print("=" * 60)
95 | print()
96 | print("Interactive REPL (no memory). Type '\exit' or '\quit' to quit.\n")
97 |
98 |
99 | def run_once(prompt: str):
100 | input_ids = tokenizer.encode(prompt)
101 | input_token_ids_tensor = torch.tensor(input_ids, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
102 |
103 | start_time = time.time()
104 | all_token_ids = []
105 |
106 | print("[Model]\n", end="", flush=True)
107 | for token in generate_text_basic_stream_cache(
108 | model=model,
109 | token_ids=input_token_ids_tensor,
110 | max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens,
111 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id
112 | ):
113 | token_id = token.squeeze(0).item()
114 | print(tokenizer.decode([token_id]), end="", flush=True)
115 |
116 | all_token_ids.append(token_id)
117 |
118 | end_time = time.time()
119 | print("\n")
120 |
121 | print("[Stats]")
122 | generate_stats(
123 | torch.tensor(all_token_ids),
124 | tokenizer,
125 | start_time,
126 | end_time,
127 | print_tokens=False
128 | )
129 | print("-" * 60)
130 |
131 |
132 | # REPL loop
133 | try:
134 | while True:
135 | try:
136 | user_in = input(">> ").strip()
137 | except EOFError:
138 | print("")
139 | break
140 | if user_in.lower() in {"\exit", "\quit"}:
141 | break
142 | if not user_in:
143 | continue
144 |
145 | print("\n" + "-" * 60)
146 | print("[User]")
147 | print(user_in + "\n")
148 | run_once(user_in)
149 | except KeyboardInterrupt:
150 | print("\nInterrupted by user.")
151 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/03_optimized-LLM/compare_inference.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 |
6 | import argparse
7 | from pathlib import Path
8 | import time
9 | import torch
10 |
11 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
12 | get_device,
13 | generate_stats
14 | )
15 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
16 | download_qwen3_small,
17 | Qwen3Tokenizer,
18 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B
19 | )
20 |
21 |
22 | ############################
23 | # Parse command-line args
24 | ############################
25 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Run Qwen3 text generation")
26 | parser.add_argument(
27 | "--device",
28 | type=str,
29 | default=None,
30 | help="Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). "
31 | "If not provided, will auto-detect with get_device()."
32 | )
33 | parser.add_argument(
34 | "--cache",
35 | action="store_true",
36 | help="Use KV cache during generation (default: False)."
37 | )
38 |
39 | parser.add_argument(
40 | "--compile",
41 | action="store_true",
42 | help="Compile PyTorch model (default: False)."
43 | )
44 |
45 | parser.add_argument(
46 | "--reasoning",
47 | action="store_true",
48 | help="Use reasoning model variant."
49 | )
50 |
51 | parser.add_argument(
52 | "--optimized",
53 | action="store_true",
54 | help="Use reasoning model variant."
55 | )
56 |
57 |
58 | args = parser.parse_args()
59 |
60 | if args.optimized:
61 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3_optimized import Qwen3Model
62 | else:
63 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import Qwen3Model
64 |
65 |
66 | if args.cache:
67 | if args.optimized:
68 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3_optimized import generate_text_basic_cache as generate_text_basic
69 | else:
70 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import generate_text_basic_cache as generate_text_basic
71 |
72 | else:
73 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import generate_text_basic
74 |
75 | device = torch.device(args.device) if args.device else get_device()
76 |
77 | #########################
78 | # Model + tokenizer setup
79 | #########################
80 |
81 | if args.reasoning:
82 | download_qwen3_small(kind="reasoning", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
83 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-reasoning.json"
84 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth"
85 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
86 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
87 | apply_chat_template=True,
88 | add_generation_prompt=True,
89 | add_thinking=True
90 | )
91 |
92 | else:
93 | download_qwen3_small(kind="base", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
94 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-base.json"
95 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-base.pth"
96 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path)
97 |
98 | model = Qwen3Model(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
99 | model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path, map_location=device))
100 |
101 | model.to(device)
102 |
103 | if args.compile:
104 | major, minor = map(int, torch.__version__.split(".")[:2])
105 | if (major, minor) >= (2, 8):
106 | # This avoids retriggering model recompilations
107 | # in PyTorch 2.8 and newer
108 | # if the model contains code like self.pos = self.pos + 1
109 | torch._dynamo.config.allow_unspec_int_on_nn_module = True
110 | model = torch.compile(model)
111 |
112 | #########################
113 | # Prompt + generation
114 | #########################
115 |
116 | if args.reasoning:
117 | prompt = "Find all c in Z_3 such that Z_3[x]/(x^2 + c) is a field."
118 | else:
119 | prompt = "Explain large language models in a single sentence."
120 |
121 | input_token_ids_tensor = torch.tensor(
122 | tokenizer.encode(prompt),
123 | device=device
124 | ).unsqueeze(0)
125 |
126 | max_new_tokens = 2048
127 |
128 |
129 | for iteration in range(1, 4):
130 | print("=" * 60)
131 | print(f"Iteration : {iteration}")
132 | print(f"optimized : {args.optimized}")
133 | print(f"torch : {torch.__version__}")
134 | print(f"device : {device}")
135 | print(f"cache : {args.cache}")
136 | print(f"compile : {args.compile}")
137 | print(f"reasoning : {args.reasoning}")
138 | print("=" * 60)
139 |
140 | start_time = time.time()
141 | output_token_ids_tensor = generate_text_basic(
142 | model=model,
143 | token_ids=input_token_ids_tensor,
144 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
145 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
146 | )
147 | end_time = time.time()
148 |
149 | print(f"Output length: {output_token_ids_tensor.numel()}")
150 | generate_stats(output_token_ids_tensor, tokenizer, start_time, end_time)
151 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_ch04.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import pytest
6 | import torch
7 |
8 | import reasoning_from_scratch.ch04 as ch04
9 |
10 |
11 | class DummyTokenizer:
12 | def __init__(self, eos_token_id=None):
13 | self.eos_token_id = eos_token_id
14 | self.decode_map = {7: "X", 8: "Y"}
15 |
16 | def encode(self, prompt):
17 | # Content of the prompt is irrelevant for these tests.
18 | return [1, 2]
19 |
20 | def decode(self, ids):
21 | if isinstance(ids, int):
22 | ids = [ids]
23 | return "".join(self.decode_map.get(i, str(i)) for i in ids)
24 |
25 |
26 | class DummyModelCache:
27 | def __init__(self, fixed_token, vocab_size=5, n_layers=2):
28 | self.fixed_token = fixed_token
29 | self.vocab_size = vocab_size
30 | self.cfg = {"n_layers": n_layers}
31 | self.reset_called = False
32 | self.eval_called = False
33 |
34 | def eval(self):
35 | self.eval_called = True
36 | return self
37 |
38 | def reset_kv_cache(self):
39 | self.reset_called = True
40 |
41 | def __call__(self, token_ids, cache=None):
42 | batch_size, seq_len = token_ids.size()
43 | logits = torch.zeros(batch_size, seq_len, self.vocab_size)
44 | logits[..., self.fixed_token] = 1.0
45 | return logits
46 |
47 |
48 | def test_generate_text_stream_concat_flex_uses_custom_generator():
49 | calls = []
50 |
51 | def fake_generate_func(**kwargs):
52 | calls.append(kwargs)
53 | for tok in (torch.tensor([7]), torch.tensor([8])):
54 | yield tok
55 |
56 | tok = DummyTokenizer(eos_token_id=0)
57 | out = ch04.generate_text_stream_concat_flex(
58 | model=None,
59 | tokenizer=tok,
60 | prompt="ignored",
61 | device="cpu",
62 | max_new_tokens=2,
63 | generate_func=fake_generate_func,
64 | temperature=0.5,
65 | )
66 |
67 | assert out == "XY"
68 | assert calls, "Generator should have been invoked"
69 | assert calls[0]["temperature"] == 0.5
70 | assert calls[0]["eos_token_id"] == tok.eos_token_id
71 |
72 |
73 | def test_scale_logits_by_temperature_validates_and_scales():
74 | logits = torch.tensor([[2.0, 4.0]])
75 | scaled = ch04.scale_logits_by_temperature(logits, 2.0)
76 | assert torch.allclose(scaled, logits / 2.0)
77 |
78 | with pytest.raises(ValueError):
79 | ch04.scale_logits_by_temperature(logits, 0.0)
80 |
81 |
82 | def test_top_p_filter_truncates_and_renormalizes():
83 | probas = torch.tensor([[0.5, 0.4, 0.1]])
84 | filtered = ch04.top_p_filter(probas, top_p=0.6)
85 | assert torch.allclose(filtered, torch.tensor([[1.0, 0.0, 0.0]]))
86 |
87 | # When no filtering is needed, output should match input
88 | unfiltered = ch04.top_p_filter(probas, top_p=1.0)
89 | assert torch.allclose(unfiltered, probas)
90 |
91 |
92 | def test_generate_text_temp_stream_cache_stops_on_eos():
93 | model = DummyModelCache(fixed_token=3)
94 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[0, 1]])
95 |
96 | out = list(
97 | ch04.generate_text_temp_stream_cache(
98 | model,
99 | token_ids=token_ids,
100 | max_new_tokens=5,
101 | eos_token_id=3,
102 | temperature=0.0,
103 | )
104 | )
105 |
106 | assert out == []
107 | assert model.reset_called is True
108 | assert model.eval_called is True
109 |
110 |
111 | def test_self_consistency_vote_majority(monkeypatch):
112 | answers = ["2", "2", "3"]
113 |
114 | def fake_generate_text_stream_concat_flex(**kwargs):
115 | idx = kwargs.pop("_call_idx", None)
116 | idx = idx if idx is not None else 0
117 | return answers[idx % len(answers)]
118 |
119 | # Wrap to inject call index so we can cycle through answers deterministically
120 | call_counter = {"i": 0}
121 |
122 | def wrapped_generate(**kwargs):
123 | kwargs["_call_idx"] = call_counter["i"]
124 | call_counter["i"] += 1
125 | return fake_generate_text_stream_concat_flex(**kwargs)
126 |
127 | monkeypatch.setattr(ch04, "generate_text_stream_concat_flex", wrapped_generate)
128 |
129 | result = ch04.self_consistency_vote(
130 | model=None,
131 | tokenizer=DummyTokenizer(),
132 | prompt="unused",
133 | device="cpu",
134 | num_samples=3,
135 | temperature=0.7,
136 | top_p=0.9,
137 | max_new_tokens=5,
138 | show_progress=False,
139 | show_long_answer=False,
140 | seed=123,
141 | )
142 |
143 | assert result["final_answer"] == "2"
144 | assert result["counts"]["2"] == 2
145 | assert result["majority_winners"] == ["2"]
146 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chF/04_llm-judge/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # LLM-as-a-judge
3 |
4 | This bonus material implements an LLM-as-a-judge approach, where gpt-oss:20b (via the open-source Ollama library) evaluates Qwen3 0.6B base and reasoning variants on MATH-500.
5 |
6 |  7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 | - Ollama is an open-source application to run LLMs efficiently
13 | - It is a wrapper around llama.cpp ([https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp)), which implements LLMs in pure C/C++ to maximize efficiency
14 | - Note that it is a to ol for using LLMs to generate text (inference), not training or finetuning LLMs
15 | - Before running the code below, install ollama by visiting [https://ollama.com](https://ollama.com) and following the instructions (for instance, clicking on the "Download" button and downloading the ollama application for your operating system)
16 | - For macOS and Windows users, click on the ollama application you downloaded; if it prompts you to install the command line usage, say "yes"
17 | - Linux users can use the installation command provided on the ollama website
18 | - There are 3 ways we can run ollama on our computer:
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 | **1. `ollama serve`**
23 |
24 | - This runs the ollama backend as a server, usually on `http://localhost:11434`. It doesn't load a model until we call it through the API. This is what we want if we want to use ollama through Python.
25 |
26 | **2. `ollama run gpt-oss:20b`**
27 |
28 | - This is a convenience wrapper. If the server is not already running, it will start it, then download the model (the first time), and drop us into an interactive terminal where we can chat with the model. Behind the scenes, it uses the same server API.
29 |
30 | **3. Ollama desktop app**
31 |
32 | - This runs the same backend automatically and provides a GUI on top of it (as shown in the figure above).
33 | It also applies defaults (system prompt, temperature, stop sequences), which can explain why answers look different from raw API usage.
34 |
35 |
36 |
37 | ## Usage
38 |
39 |
40 |
41 | The options and defaults are shown below.
42 |
43 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 | - Ollama is an open-source application to run LLMs efficiently
13 | - It is a wrapper around llama.cpp ([https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp)), which implements LLMs in pure C/C++ to maximize efficiency
14 | - Note that it is a to ol for using LLMs to generate text (inference), not training or finetuning LLMs
15 | - Before running the code below, install ollama by visiting [https://ollama.com](https://ollama.com) and following the instructions (for instance, clicking on the "Download" button and downloading the ollama application for your operating system)
16 | - For macOS and Windows users, click on the ollama application you downloaded; if it prompts you to install the command line usage, say "yes"
17 | - Linux users can use the installation command provided on the ollama website
18 | - There are 3 ways we can run ollama on our computer:
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 | **1. `ollama serve`**
23 |
24 | - This runs the ollama backend as a server, usually on `http://localhost:11434`. It doesn't load a model until we call it through the API. This is what we want if we want to use ollama through Python.
25 |
26 | **2. `ollama run gpt-oss:20b`**
27 |
28 | - This is a convenience wrapper. If the server is not already running, it will start it, then download the model (the first time), and drop us into an interactive terminal where we can chat with the model. Behind the scenes, it uses the same server API.
29 |
30 | **3. Ollama desktop app**
31 |
32 | - This runs the same backend automatically and provides a GUI on top of it (as shown in the figure above).
33 | It also applies defaults (system prompt, temperature, stop sequences), which can explain why answers look different from raw API usage.
34 |
35 |
36 |
37 | ## Usage
38 |
39 |
40 |
41 | The options and defaults are shown below.
42 |
43 |
44 |
45 | ---
46 |
47 | **Note**: If you are not a `uv` user, replace `uv run ...py` with `python ...py` in the examples below.
48 |
49 | ---
50 |
51 |
52 |
53 | ```bash
54 | uv run ollama-judge.py --help
55 | usage: ollama-judge.py [-h] [--device DEVICE]
56 | [--which_model {base,reasoning}]
57 | [--dataset_size DATASET_SIZE]
58 | [--max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS]
59 | [--url URL]
60 | [--judge_model JUDGE_MODEL]
61 |
62 | options:
63 | -h, --help show this help message and
64 | exit
65 | --device DEVICE Device e.g., "cpu",
66 | "cuda", "cuda:0", "mps".
67 | --which_model {base,reasoning}
68 | Candidate variant to use.
69 | Defaults to "base".
70 | --dataset_size DATASET_SIZE
71 | Number of MATH-500
72 | examples to evaluate.
73 | Default: 10
74 | --max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS
75 | Max new tokens for
76 | candidate generation.
77 | Default: 2048
78 | --url URL Ollama chat endpoint for
79 | the judge. Default: "http:
80 | //localhost:11434/api/chat
81 | "
82 | --judge_model JUDGE_MODEL
83 | Judge model name (Ollama).
84 | Used only for scoring.
85 | Default: "gpt-oss:20b"
86 | ```
87 |
88 |
89 |
90 | **Base model**
91 |
92 | ```bash
93 | ➜ uv run ollama-judge.py
94 | Using Apple Silicon GPU (MPS)
95 | Model: base
96 | Device: mps
97 | ✓ qwen3/qwen3-0.6B-base.pth already up-to-date
98 | ✓ qwen3/tokenizer-base.json already up-to-date
99 | Ollama running: True
100 | [1/10] score=5
101 | [2/10] score=1
102 | [3/10] score=5
103 | [4/10] score=5
104 | [5/10] score=3
105 | [6/10] score=5
106 | [7/10] score=5
107 | [8/10] score=3
108 | [9/10] score=5
109 | [10/10] score=1
110 |
111 | Summary
112 | -------
113 | Average score: 3.800 over 10 example(s)
114 | Counts: 1:2 2:0 3:2 4:0 5:6
115 | ```
116 |
117 | **Reasoning model**
118 |
119 | ```bash
120 | ➜ uv run ollama-judge.py --which_model reasoning
121 | Using Apple Silicon GPU (MPS)
122 | Model: reasoning
123 | Device: mps
124 | ✓ qwen3/qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth already up-to-date
125 | ✓ qwen3/tokenizer-reasoning.json already up-to-date
126 | Ollama running: True
127 | [1/10] score=5
128 | [2/10] score=5
129 | [3/10] score=5
130 | [4/10] score=5
131 | [5/10] score=4
132 | [6/10] score=5
133 | [7/10] score=5
134 | [8/10] score=1
135 | [9/10] score=5
136 | [10/10] score=3
137 |
138 | Summary
139 | -------
140 | Average score: 4.300 over 10 example(s)
141 | Counts: 1:1 2:0 3:1 4:1 5:7
142 | ```
143 |
144 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/scripts/check_double_quotes.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | # Verify that Python source files and notebooks use double quotes for strings.
6 |
7 | import ast
8 | import io
9 | import json
10 | import sys
11 | import tokenize
12 | from pathlib import Path
13 |
14 | EXCLUDED_DIRS = {
15 | ".git",
16 | ".hg",
17 | ".mypy_cache",
18 | ".pytest_cache",
19 | ".ruff_cache",
20 | ".svn",
21 | ".tox",
22 | ".venv",
23 | "__pycache__",
24 | "build",
25 | "dist",
26 | "node_modules",
27 | }
28 |
29 | PREFIX_CHARS = {"r", "u", "f", "b"}
30 | SINGLE_QUOTE = "'"
31 | DOUBLE_QUOTE = "\""
32 | TRIPLE_SINGLE = SINGLE_QUOTE * 3
33 | TRIPLE_DOUBLE = DOUBLE_QUOTE * 3
34 |
35 |
36 | def should_skip(path):
37 | parts = set(path.parts)
38 | return bool(EXCLUDED_DIRS & parts)
39 |
40 |
41 | def collect_fstring_expr_string_positions(source):
42 | """
43 | Return set of (lineno, col_offset) for string literals that appear inside
44 | formatted expressions of f-strings. These should be exempt from the double
45 | quote check, since enforcing double quotes there is unnecessarily strict.
46 | """
47 | try:
48 | tree = ast.parse(source)
49 | except SyntaxError:
50 | return set()
51 |
52 | positions = set()
53 |
54 | class Collector(ast.NodeVisitor):
55 | def visit_JoinedStr(self, node):
56 | for value in node.values:
57 | if isinstance(value, ast.FormattedValue):
58 | self._collect_from_expr(value.value)
59 | # Continue walking to catch nested f-strings within expressions
60 | self.generic_visit(node)
61 |
62 | def _collect_from_expr(self, node):
63 | if isinstance(node, ast.Constant) and isinstance(node.value, str):
64 | positions.add((node.lineno, node.col_offset))
65 | else:
66 | for child in ast.iter_child_nodes(node):
67 | self._collect_from_expr(child)
68 |
69 | Collector().visit(tree)
70 | return positions
71 |
72 |
73 | def check_quotes_in_source(source, path):
74 | violations = []
75 | ignored_positions = collect_fstring_expr_string_positions(source)
76 | tokens = tokenize.generate_tokens(io.StringIO(source).readline)
77 | lines = source.splitlines()
78 |
79 | for tok_type, tok_str, start, _, _ in tokens:
80 | if tok_type == tokenize.STRING:
81 | line_no, col = start
82 |
83 | # Skip if the line contains both quote types (e.g. if ch in ("'", '"'))
84 | if line_no - 1 < len(lines):
85 | line_text = lines[line_no - 1]
86 | if "'" in line_text and '"' in line_text:
87 | continue
88 |
89 | if start in ignored_positions:
90 | continue
91 |
92 | lowered = tok_str.lower()
93 | # ignore triple-quoted strings
94 | if lowered.startswith((TRIPLE_DOUBLE, TRIPLE_SINGLE)):
95 | continue
96 |
97 | # find the prefix and quote type
98 | for c in PREFIX_CHARS:
99 | if lowered.startswith(c):
100 | lowered = lowered[1:]
101 | break
102 |
103 | # report if not using double quotes
104 | if lowered.startswith(SINGLE_QUOTE):
105 | violations.append(f"{path}:{line_no}:{col}: uses single quotes")
106 | return violations
107 |
108 |
109 | def check_file(path):
110 | try:
111 | if path.suffix == ".ipynb":
112 | return check_notebook(path)
113 | else:
114 | text = path.read_text(encoding="utf-8")
115 | return check_quotes_in_source(text, path)
116 | except Exception as e:
117 | return [f"{path}: failed to check ({e})"]
118 |
119 |
120 | def check_notebook(path):
121 | violations = []
122 | with open(path, encoding="utf-8") as f:
123 | nb = json.load(f)
124 | for cell in nb.get("cells", []):
125 | if cell.get("cell_type") == "code":
126 | src = "".join(cell.get("source", []))
127 | violations.extend(check_quotes_in_source(src, path))
128 | return violations
129 |
130 |
131 | def main():
132 | project_root = Path(".").resolve()
133 | py_files = sorted(project_root.rglob("*.py"))
134 | notebook_files = sorted(project_root.rglob("*.ipynb"))
135 |
136 | violations = []
137 | for path in py_files + notebook_files:
138 | if should_skip(path):
139 | continue
140 | violations.extend(check_file(path))
141 |
142 | if violations:
143 | print("\n".join(violations))
144 | print(f"\n{len(violations)} violations found.")
145 | return 1
146 |
147 | print("All files use double quotes correctly.")
148 | return 0
149 |
150 |
151 | if __name__ == "__main__":
152 | sys.exit(main())
153 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chF/02_mmlu/2_logprob.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import argparse
6 | import time
7 |
8 | import torch
9 | from datasets import load_dataset, get_dataset_config_names
10 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import get_device
11 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch03 import load_model_and_tokenizer
12 |
13 |
14 | # Same as in main notebook
15 | def format_prompt(example):
16 | return (
17 | f"{example['question']}\n"
18 | f"A. {example['choices'][0]}\n"
19 | f"B. {example['choices'][1]}\n"
20 | f"C. {example['choices'][2]}\n"
21 | f"D. {example['choices'][3]}\n"
22 | "Answer: " # trailing space encourages a single-letter next token
23 | )
24 |
25 |
26 | def common_prefix_len(a, b):
27 | i = 0
28 | n = min(len(a), len(b))
29 | while i < n and a[i] == b[i]:
30 | i += 1
31 | return i
32 |
33 |
34 | def first_new_token_id(tokenizer, prompt, prompt_ids, continuation):
35 | ids_full = tokenizer.encode(prompt + continuation)
36 | j = common_prefix_len(ids_full, prompt_ids)
37 | if j >= len(ids_full):
38 | raise ValueError("Continuation produced no new tokens.")
39 | return ids_full[j]
40 |
41 |
42 | def predict_choice_logprobs(model, tokenizer, prompt_fmt, prompt, prompt_ids, example):
43 | with torch.no_grad():
44 | logits = model(prompt_fmt) # [1, T, V]
45 | next_logp = torch.log_softmax(logits[0, -1], dim=-1)
46 |
47 | scores = {}
48 | for letter in "ABCD":
49 | tok_id = first_new_token_id(tokenizer, prompt, prompt_ids, letter)
50 | scores[letter] = next_logp[tok_id].item()
51 |
52 | pred = max(scores, key=scores.get)
53 | return pred, scores
54 |
55 |
56 | def evaluate_mmlu_logprobs(
57 | model,
58 | tokenizer,
59 | device,
60 | subsets="high_school_mathematics", # str, list of str, or "all"
61 | split="test",
62 | verbose_every=50,
63 | ):
64 | if subsets == "all":
65 | subset_list = get_dataset_config_names("cais/mmlu")
66 | elif isinstance(subsets, str):
67 | subset_list = [s.strip() for s in subsets.split(",")] if "," in subsets else [subsets]
68 | else:
69 | subset_list = list(subsets)
70 |
71 | total = 0
72 | correct = 0
73 | start = time.time()
74 |
75 | for subset in subset_list:
76 | ds = load_dataset("cais/mmlu", subset, split=split)
77 | for ex in ds:
78 | prompt = format_prompt(ex)
79 | prompt_ids = tokenizer.encode(prompt)
80 | prompt_fmt = torch.tensor(prompt_ids, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
81 |
82 | pred, _scores = predict_choice_logprobs(
83 | model, tokenizer, prompt_fmt, prompt, prompt_ids, ex
84 | )
85 |
86 | ans = ex["answer"]
87 | # "Gold" is the MMLU jargon for the correct answer (ground truth)
88 | gold = "ABCD"[ans] if isinstance(ans, int) else str(ans).strip().upper()
89 |
90 | total += 1
91 | correct += int(pred == gold)
92 |
93 | if verbose_every and total % verbose_every == 0:
94 | print(f"MMLU {total} acc={correct/total:.3f} [{subset}]")
95 |
96 | acc = correct / max(1, total)
97 | print(
98 | f"\nMMLU letter accuracy (log-prob): {correct}/{total} = {acc:.2%} "
99 | f"in {time.time()-start:.1f}s"
100 | )
101 | return {"accuracy": acc, "num_examples": total, "subsets": subset_list, "split": split}
102 |
103 |
104 | def main():
105 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
106 | description="Zero-shot MMLU evaluator via next-token log-prob scoring (A/B/C/D)."
107 | )
108 | parser.add_argument(
109 | "--device",
110 | type=str,
111 | default="auto",
112 | help="Device to use: 'auto' (default), or any torch device string like "
113 | "'cpu', 'cuda', 'cuda:0', 'mps'.",
114 | )
115 | parser.add_argument(
116 | "--which_model",
117 | type=str,
118 | default="base",
119 | choices=["base", "reasoning"],
120 | help="Model variant to load. Defaults to 'base'.",
121 | )
122 | parser.add_argument(
123 | "--subsets",
124 | type=str,
125 | default="high_school_mathematics",
126 | help="Comma-separated subset names or 'all'. "
127 | "Default: 'high_school_mathematics'.",
128 | )
129 | args = parser.parse_args()
130 |
131 | device = get_device() if args.device == "auto" else torch.device(args.device)
132 | print(f"Using device: {device}")
133 | model, tokenizer = load_model_and_tokenizer(args.which_model, device, use_compile=False)
134 | model.eval()
135 | torch.set_float32_matmul_precision("high")
136 |
137 | metrics = evaluate_mmlu_logprobs(
138 | model=model,
139 | tokenizer=tokenizer,
140 | device=device,
141 | subsets=args.subsets,
142 | )
143 | print(metrics)
144 |
145 |
146 | if __name__ == "__main__":
147 | main()
148 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_ch05.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 |
6 | import math
7 | import torch
8 |
9 | import reasoning_from_scratch.ch05 as ch05
10 |
11 |
12 | class DummyTokenizer:
13 | def __init__(self, mapping=None):
14 | self.mapping = mapping or {}
15 | self.eos_token_id = 0
16 |
17 | def encode(self, text):
18 | if text in self.mapping:
19 | return self.mapping[text]
20 | return [len(text) % 10]
21 |
22 |
23 | class DummyLogitModel:
24 | def __init__(self, base_logits):
25 | self.base_logits = torch.tensor(base_logits, dtype=torch.float32)
26 |
27 | def __call__(self, token_ids):
28 | seq_len = token_ids.size(1)
29 | logits = self.base_logits.repeat(seq_len, 1)
30 | return logits.unsqueeze(0)
31 |
32 |
33 | def test_heuristic_score_rewards_boxed_answers_more_than_numbers():
34 | boxed = "Result \\boxed{7}"
35 | number_only = "The answer is 7"
36 |
37 | boxed_score = ch05.heuristic_score(boxed)
38 | number_score = ch05.heuristic_score(number_only)
39 |
40 | expected_boxed = 2.0 + 1.5 * math.exp(-len(boxed) / 500.0)
41 | expected_number = 1.0 + 1.5 * math.exp(-len(number_only) / 500.0)
42 |
43 | assert math.isclose(boxed_score, expected_boxed, rel_tol=1e-6)
44 | assert math.isclose(number_score, expected_number, rel_tol=1e-6)
45 | assert boxed_score > number_score
46 |
47 |
48 | def test_heuristic_score_adds_fulltext_bonus_when_no_number():
49 | response = "No numeric result here"
50 | score = ch05.heuristic_score(
51 | response, brevity_bonus=100.0, fulltext_bonus=0.3
52 | )
53 |
54 | expected = 0.3 + 1.5 * math.exp(-len(response) / 100.0)
55 | assert math.isclose(score, expected, rel_tol=1e-6)
56 |
57 |
58 | def test_avg_logprob_answer_uses_answer_token_logprobs():
59 | tokenizer = DummyTokenizer(
60 | mapping={
61 | "prompt": [1, 2],
62 | "answer": [3, 4],
63 | }
64 | )
65 | base_logits = [0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4]
66 | model = DummyLogitModel(base_logits)
67 |
68 | expected_logprobs = torch.log_softmax(
69 | model.base_logits, dim=-1
70 | )
71 | expected = torch.mean(expected_logprobs[[3, 4]]).item()
72 |
73 | out = ch05.avg_logprob_answer(
74 | model=model,
75 | tokenizer=tokenizer,
76 | prompt="prompt",
77 | answer="answer",
78 | device="cpu",
79 | )
80 |
81 | assert math.isclose(out, expected, rel_tol=1e-6)
82 |
83 |
84 | def test_prompt_builders_embed_question_and_context():
85 | raw_prompt = "What is 1+1?"
86 | draft = "It is \\boxed{2}."
87 | critique_text = "Looks fine."
88 |
89 | critique_prompt = ch05.make_critique_prompt(raw_prompt, draft)
90 | assert "meticulous reviewer" in critique_prompt
91 | assert f"Question:\n{raw_prompt}" in critique_prompt
92 | assert f"Draft answer:\n{draft}" in critique_prompt
93 | assert critique_prompt.strip().endswith("Critique:")
94 |
95 | refine_prompt = ch05.make_refine_prompt(
96 | raw_prompt, draft, critique_text
97 | )
98 | assert "Revised answer:" in refine_prompt
99 | assert f"Previous answer:\n{draft}" in refine_prompt
100 | assert f"Critique:\n{critique_text}" in refine_prompt
101 | assert refine_prompt.strip().endswith("Revised answer:")
102 |
103 |
104 | def test_self_refinement_loop_accepts_improving_revisions(monkeypatch):
105 | responses = iter(
106 | [
107 | "initial draft", # initial generation
108 | "first critique", # critique 1
109 | "draft with more detail", # refine 1 (accepted)
110 | "second critique", # critique 2
111 | "bad", # refine 2 (rejected)
112 | ]
113 | )
114 | prompts_seen = []
115 |
116 | def fake_generate_text_stream_concat_flex(**kwargs):
117 | prompts_seen.append(kwargs.get("prompt"))
118 | return next(responses)
119 |
120 | monkeypatch.setattr(
121 | ch05, "generate_text_stream_concat_flex",
122 | fake_generate_text_stream_concat_flex
123 | )
124 |
125 | def score_fn(answer, prompt):
126 | return len(answer)
127 |
128 | result = ch05.self_refinement_loop(
129 | model=None,
130 | tokenizer=DummyTokenizer(),
131 | raw_prompt="Compute something",
132 | device="cpu",
133 | iterations=2,
134 | score_fn=score_fn,
135 | prompt_renderer=lambda x: f"Q: {x}",
136 | temperature=0.3,
137 | top_p=0.8,
138 | )
139 |
140 | assert result["final_extracted"] == "draft with more detail"
141 | assert len(result["steps"]) == 2
142 | assert result["steps"][0]["draft_full"] == "initial draft"
143 | assert result["steps"][0]["revised_full"] == "draft with more detail"
144 | assert result["steps"][1]["draft_full"] == "draft with more detail"
145 | assert result["steps"][1]["revised_full"] == "bad"
146 | assert result["steps"][0]["score_after"] >= result["steps"][0]["score_before"]
147 | assert result["steps"][1]["score_after"] < result["steps"][1]["score_before"]
148 | assert len(prompts_seen) == 5
149 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/02_setup-tips/python-instructions.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Python Setup Recommendations
2 |
3 | The code in this book is largely self-contained, and I have made an effort to minimize external dependencies. However, to keep the book accessible, readable, and well under 2000 pages, a few Python packages are necessary.
4 |
5 | This section introduces two beginner-friendly methods for installing the required packages so you can run the code examples.
6 |
7 | There are, of course, many other ways to install and manage Python packages. If you are an experienced Python user and already have your own setup or preferences, feel free to skip this section.
8 |
9 | If neither of the two options below works for you, please do not hesitate to reach out, for example, by opening a [Discussion](https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch/discussions).
10 |
11 |
12 | ## Option 1: Using `pip` (built-in, works everywhere)
13 |
14 | If you are using a recent version of Python already, you can install packages using the built-in `pip` installer.
15 |
16 | I used Python 3.12 for this book. However, older versions like 3.11 and 3.10 will also work fine. You can check your Python version by running:
17 |
18 | ```bash
19 | python --version
20 | ```
21 |
22 | If you are using Python 3.9 or older, consider installing the latest from [python.org](https://www.python.org/downloads/) or using a tool like [`pyenv`](https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv) to manage versions. However, if you are installing a new Python version, please make sure that it is supported by PyTorch by checking the recommendation on the [official PyTorch website](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/). PyTorch typically lags a few months behind the latest Python release, so newly released Python versions are not supported or recommended immediately.
23 |
24 | To install new packages, as needed, (for example, PyTorch and Jupyter Lab), run:
25 |
26 | ```bash
27 | pip install torch jupyterlab
28 | ```
29 |
30 | Alternatively, you can install all required Python package used in this book all once via the [`requirements.txt`](https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch/blob/main/requirements.txt) file:
31 |
32 | ```bash
33 | pip install -r https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch/refs/heads/main/requirements.txt
34 | ```
35 |
36 |
37 |
38 | ## Option 2: Use `uv` (faster and widely recommended)
39 |
40 | While `pip` remains the classic and official way to install Python packages, [`uv`](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv) is a modern and widely recommended Python package manager that automatically:
41 |
42 | - Creates and manages a virtual environment
43 | - Installs packages quickly
44 | - Keeps a lockfile for reproducible installs
45 | - Supports `pip`-like commands
46 |
47 |
48 | ### Installing `uv` and Python packages
49 |
50 | To install `uv`, you can use the commands below (also see the official [Installation](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/getting-started/installation/) page for the latest recommendations).
51 |
52 |
53 | **macOS / Linux:**
54 |
55 | ```bash
56 | curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
57 | ```
58 |
59 |
60 | **Windows (PowerShell):**
61 |
62 | ```powershell
63 | powershell -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -c "irm https://astral.sh/uv/install.ps1 | iex"
64 | ```
65 |
66 | Once installed, you can install new Python packages similar to how you would do it via `pip` as described in the previous section, except that you replace `pip` with `uv pip`. For example
67 |
68 | ```bash
69 | uv pip install torch jupyterlab
70 | ```
71 |
72 | However, if you are using `uv`, which I recommend and use myself, it's even better to use the native `uv` syntax instead of `uv pip`, as described below.
73 |
74 |
75 | ### Recommended `uv` workflow
76 |
77 | Instead of using `uv pip`, I recommend and use the native `uv` worklow.
78 |
79 | First, clone the GitHub repository to your local machine:
80 |
81 |
82 |
83 | ```bash
84 | git clone https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch.git
85 | ```
86 |
87 | Next, navigate into this folder, e.g., on Linux and MacOS:
88 |
89 | ```bash
90 | cd reasoning-from-scratch
91 | ```
92 |
93 | Then, since this folder contains a `pyproject.toml` file, you are already good to go: `uv` will automatically create a (by default invisible) virtual environment folder (`.venv`) for this `reasoning-from-scratch` project into which it installs all the dependencies the first time you run a script or open Jupyter Lab.
94 |
95 | You will probably not need it but in general, you can install additional packages, which are not already part of the requirements listed in `pyproject.toml`, via `uv add`:
96 |
97 |
98 | ```bash
99 | uv add llms_from_scratch
100 | ```
101 |
102 | The above command will then add the package to the virtual environment and `pyproject.toml` file.
103 |
104 |
105 | ### Running code via `uv`
106 |
107 | This section describes the `uv` commands to run Jupyter Lab and Python scripts.
108 |
109 | To open Jupyter Lab, execute:
110 |
111 | ```python
112 | uv run jupyter lab
113 | ```
114 |
115 | Python scripts can be run via:
116 |
117 | ```bash
118 | uv run python script.py
119 | ```
120 |
121 |
122 |
123 |
124 | > **Advanced usage:** This section describes a simple way to use `uv` that looks familiar to `pip` users. If you are interested in more advanced usage, please see [this document](https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/tree/main/setup/01_optional-python-setup-preferences) for more explicit instructions on managing virtual environments in `uv`.
125 | > If you are a macOS or Linux user and prefer the native uv commands, please refer to [this tutorial](https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/blob/main/setup/01_optional-python-setup-preferences/native-uv.md). I also recommend checking the [official uv documentation](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/) for additional information.
126 |
127 |
128 |
129 |
130 | ## Questions?
131 |
132 | If you have any questions, please don't hesitate to reach out via the [Discussions](https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch/discussions) forum in this GitHub repository.
133 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_qwen3_optimized.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import importlib
6 | import os
7 | import pytest
8 | import torch
9 | from pathlib import Path
10 |
11 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
12 | generate_text_basic_cache,
13 | )
14 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
15 | download_qwen3_small,
16 | load_hf_weights_into_qwen,
17 | Qwen3Tokenizer,
18 | Qwen3Model,
19 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B,
20 | )
21 |
22 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3_optimized import (
23 | Qwen3Model as Qwen3ModelOptimized,
24 | generate_text_basic_cache as generate_text_basic_cache_optimized,
25 | )
26 |
27 |
28 | skip_expensive = os.environ.get("SKIP_EXPENSIVE", "0") == "1"
29 | transformers_installed = importlib.util.find_spec("transformers") is not None
30 |
31 | # Make CI more reproducible & robust
32 | os.environ["MKL_NUM_THREADS"] = "1"
33 | os.environ["OMP_NUM_THREADS"] = "1"
34 | torch.backends.mkldnn.enabled = False
35 | torch.set_num_threads(1)
36 | torch.use_deterministic_algorithms(True)
37 |
38 |
39 | @torch.inference_mode()
40 | @pytest.mark.skipif(not transformers_installed, reason="transformers not installed")
41 | def test_qwen3_base_equivalence_with_transformers():
42 |
43 | from transformers.models.qwen3 import Qwen3Config, Qwen3ForCausalLM
44 |
45 | # Tiny config so the test is fast
46 | cfg = {
47 | "vocab_size": 257,
48 | "context_length": 8,
49 | "emb_dim": 32,
50 | "n_heads": 4,
51 | "n_layers": 2,
52 | "hidden_dim": 64,
53 | "head_dim": 8,
54 | "qk_norm": True,
55 | "n_kv_groups": 2,
56 | "rope_base": 1_000_000.0,
57 | "dtype": torch.float32,
58 | }
59 | model = Qwen3Model(cfg)
60 |
61 | hf_cfg = Qwen3Config(
62 | vocab_size=cfg["vocab_size"],
63 | max_position_embeddings=cfg["context_length"],
64 | hidden_size=cfg["emb_dim"],
65 | num_attention_heads=cfg["n_heads"],
66 | num_hidden_layers=cfg["n_layers"],
67 | intermediate_size=cfg["hidden_dim"],
68 | head_dim=cfg["head_dim"],
69 | num_key_value_heads=cfg["n_kv_groups"],
70 | rope_theta=cfg["rope_base"],
71 | tie_word_embeddings=False,
72 | attn_implementation="eager",
73 | torch_dtype=torch.float32,
74 | )
75 | hf_model = Qwen3ForCausalLM(hf_cfg)
76 |
77 | hf_state = hf_model.state_dict()
78 | param_config = {"n_layers": cfg["n_layers"], "hidden_dim": cfg["hidden_dim"]}
79 | load_hf_weights_into_qwen(model, param_config, hf_state)
80 |
81 | x = torch.randint(0, cfg["vocab_size"], (2, cfg["context_length"]), dtype=torch.long)
82 | ours_logits = model(x)
83 | theirs_logits = hf_model(x).logits
84 | torch.testing.assert_close(ours_logits, theirs_logits, rtol=1e-5, atol=1e-5)
85 |
86 |
87 | @pytest.mark.skipif(skip_expensive, reason="Skipping expensive test on CI")
88 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("reasoning", [False, True])
89 | def test_qwen3_vs_optimized_qwen3(reasoning):
90 |
91 | device = "cpu" # get_device()
92 |
93 | # Download and init tokenizer
94 | kind = "reasoning" if reasoning else "base"
95 | download_qwen3_small(kind=kind, tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
96 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / (
97 | "tokenizer-reasoning.json" if reasoning else "tokenizer-base.json"
98 | )
99 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / (
100 | "qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth" if reasoning else "qwen3-0.6B-base.pth"
101 | )
102 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
103 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
104 | apply_chat_template=True if reasoning else False,
105 | add_generation_prompt=True if reasoning else False,
106 | add_thinking=True if reasoning else False,
107 | )
108 |
109 | # Models
110 | model = Qwen3Model(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
111 | model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path, map_location=device))
112 | model.to(device)
113 | model.eval()
114 |
115 | model_optimized = Qwen3ModelOptimized(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B, exact=True)
116 | model_optimized.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path, map_location=device))
117 | model_optimized.to(device)
118 | model_optimized.eval()
119 |
120 | # Prompts
121 | prompts = [
122 | "Explain large language models in two sentences.",
123 | "Explain large language models in one sentence.",
124 | "1+1?"
125 | ]
126 |
127 | single_inputs = [
128 | torch.tensor(tokenizer.encode(p), device=device).unsqueeze(0)
129 | for p in prompts
130 | ]
131 |
132 | # Generation
133 | max_new_tokens = 12 # cheap but enough to check consistency
134 | outputs_simple = []
135 | for input_ids in single_inputs:
136 | out = generate_text_basic_cache(
137 | model=model,
138 | token_ids=input_ids,
139 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
140 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
141 | )
142 | outputs_simple.append(out[0].tolist())
143 |
144 | outputs_optimized = []
145 | for input_ids in single_inputs:
146 | out = generate_text_basic_cache_optimized(
147 | model=model_optimized,
148 | token_ids=input_ids,
149 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
150 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
151 | )
152 | outputs_optimized.append(out[0])
153 |
154 | # Check equivalency
155 | for idx, out_single in enumerate(outputs_simple):
156 | out_batch = outputs_optimized[idx].tolist()
157 |
158 | text_single = tokenizer.decode(out_single)
159 | text_batch = tokenizer.decode(out_batch)
160 |
161 | # Assert the text beyond the first token is identical
162 | assert text_single == text_batch, (
163 | f"Mismatch after first token at prompt {idx}:\n"
164 | f"single={text_single}\n"
165 | f"batched={text_batch}"
166 | )
167 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch04/02_math500-inference-scaling-scripts/cot_prompting_math500.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import argparse
6 | import json
7 | from pathlib import Path
8 | import time
9 |
10 | import torch
11 |
12 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import get_device
13 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch03 import (
14 | load_math500_test,
15 | eta_progress_message,
16 | extract_final_candidate,
17 | render_prompt,
18 | grade_answer,
19 | generate_text_stream_concat,
20 | load_model_and_tokenizer
21 | )
22 |
23 |
24 | def evaluate_math500_stream(
25 | model,
26 | tokenizer,
27 | device,
28 | math_data,
29 | out_path=None,
30 | max_new_tokens=512,
31 | verbose=False,
32 | prompt_suffix="" # NEW
33 | ):
34 |
35 | if out_path is None:
36 | dev_name = str(device).replace(":", "-")
37 | out_path = Path(f"math500-{dev_name}.jsonl")
38 |
39 | num_examples = len(math_data)
40 | num_correct = 0
41 | start_time = time.time()
42 |
43 | with open(out_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
44 | for i, row in enumerate(math_data, start=1):
45 | prompt = render_prompt(row["problem"])
46 | prompt += prompt_suffix # NEW
47 | gen_text = generate_text_stream_concat(
48 | model, tokenizer, prompt, device,
49 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
50 | verbose=verbose,
51 | )
52 |
53 | extracted = extract_final_candidate(
54 | gen_text
55 | )
56 | is_correct = grade_answer(
57 | extracted, row["answer"]
58 | )
59 | num_correct += int(is_correct)
60 |
61 | record = {
62 | "index": i,
63 | "problem": row["problem"],
64 | "gtruth_answer": row["answer"],
65 | "generated_text": gen_text,
66 | "extracted": extracted,
67 | "correct": bool(is_correct),
68 | }
69 | f.write(json.dumps(record, ensure_ascii=False) + "\n")
70 |
71 | progress_msg = eta_progress_message(
72 | processed=i,
73 | total=num_examples,
74 | start_time=start_time,
75 | show_eta=True,
76 | label="MATH-500",
77 | )
78 | print(progress_msg, end="\r", flush=True)
79 | if verbose:
80 | print(
81 | f"\n\n{'='*50}\n{progress_msg}\n"
82 | f"{'='*50}\nExtracted: {extracted}\n"
83 | f"Expected: {row['answer']}\n"
84 | f"Correct so far: {num_correct}\n{'-'*50}"
85 | )
86 |
87 | seconds_elapsed = time.time() - start_time
88 | acc = num_correct / num_examples if num_examples else 0.0
89 | print(f"\nAccuracy: {acc*100:.1f}% ({num_correct}/{num_examples})")
90 | print(f"Total time: {seconds_elapsed/60:.1f} min")
91 | print(f"Logs written to: {out_path}")
92 | return num_correct, num_examples, acc
93 |
94 |
95 | def parse_args():
96 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
97 | parser.add_argument(
98 | "--device",
99 | type=str,
100 | default="auto",
101 | help="Device to use: 'auto' (default), or any torch device string like 'cpu', 'cuda', 'cuda:0', 'mps'.",
102 | )
103 | parser.add_argument(
104 | "--which_model",
105 | type=str,
106 | default="base",
107 | choices=["base", "reasoning", "instruct"],
108 | help="Model variant to load. Defaults to 'base'.",
109 | )
110 | parser.add_argument(
111 | "--dataset_size",
112 | type=int,
113 | default=10,
114 | help="Number of MATH-500 examples to evaluate. Default: 10",
115 | )
116 | parser.add_argument(
117 | "--max_new_tokens",
118 | type=int,
119 | default=2048,
120 | help="Max new tokens for generation. Default: 2048",
121 | )
122 | parser.add_argument(
123 | "--compile",
124 | action="store_true",
125 | help="Enable torch.compile for the model.",
126 | )
127 | parser.add_argument(
128 | "--prompt_suffix",
129 | type=str,
130 | default="",
131 | help="Can be used to adds a chain-of-thought prompt (default: '')",
132 | )
133 | parser.add_argument(
134 | "--verbose",
135 | action="store_true",
136 | help="Print per-sample correctness while evaluating.",
137 | )
138 | return parser.parse_args()
139 |
140 |
141 | if __name__ == "__main__":
142 | args = parse_args()
143 |
144 | if args.device == "auto":
145 | device = get_device()
146 | else:
147 | device = torch.device(args.device)
148 |
149 | which_model = args.which_model
150 | dataset_size = args.dataset_size
151 | max_new_tokens = args.max_new_tokens
152 | use_compile = args.compile
153 |
154 | print("Model:", which_model)
155 | print("Device:", device)
156 | dev_name = str(device).replace(":", "-")
157 |
158 | math_data = load_math500_test()
159 |
160 | if args.which_model == "instruct":
161 | which_model = "reasoning"
162 | else:
163 | which_model = args.which_model
164 |
165 | model, tokenizer = load_model_and_tokenizer(
166 | which_model=which_model,
167 | device=device,
168 | use_compile=args.compile
169 | )
170 | if args.which_model == "instruct":
171 | tokenizer.add_thinking = False
172 |
173 | model.eval()
174 | torch.set_float32_matmul_precision("high")
175 |
176 | num_correct, num_examples, acc = evaluate_math500_stream(
177 | model=model,
178 | out_path=f"math500_{which_model}-{dev_name}-evaluate-script.jsonl",
179 | tokenizer=tokenizer,
180 | device=device,
181 | math_data=math_data[:dataset_size],
182 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
183 | verbose=args.verbose,
184 | prompt_suffix=args.prompt_suffix # NEW
185 | )
186 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chF/02_mmlu/3_teacher_forcing.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import argparse
6 | import time
7 |
8 | import torch
9 | from datasets import load_dataset, get_dataset_config_names
10 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import get_device
11 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch03 import load_model_and_tokenizer
12 |
13 |
14 | # Same as before
15 | def format_prompt(example):
16 | return (
17 | f"{example['question']}\n"
18 | f"A. {example['choices'][0]}\n"
19 | f"B. {example['choices'][1]}\n"
20 | f"C. {example['choices'][2]}\n"
21 | f"D. {example['choices'][3]}\n"
22 | "Answer: " # trailing space encourages a single-letter next token
23 | )
24 |
25 |
26 | def common_prefix_len(a, b):
27 | i = 0
28 | n = min(len(a), len(b))
29 | while i < n and a[i] == b[i]:
30 | i += 1
31 | return i
32 |
33 |
34 | def avg_logprob_teacher_forced(model, tokenizer, prompt_fmt, prompt, prompt_ids, letter, choice_text):
35 | # Build full answer text and then just extract the continuation token IDs
36 | answer_text = f"{letter}. {choice_text}"
37 | ids_full = tokenizer.encode(prompt + answer_text)
38 | j = common_prefix_len(ids_full, prompt_ids)
39 | if j >= len(ids_full):
40 | raise ValueError("Continuation produced no new tokens.")
41 | answer_ids = ids_full[j:] # tokens for the answer continuation
42 |
43 | # Input to model is "prompt + all" except for last answer token (to predict each next)
44 | device = prompt_fmt.device
45 | if len(answer_ids) == 0:
46 | return float("-inf")
47 |
48 | answer_prefix = torch.tensor(answer_ids[:-1], dtype=torch.long, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
49 | combined = torch.cat([prompt_fmt, answer_prefix], dim=1)
50 |
51 | with torch.no_grad():
52 | # Logits for every position in `combined``
53 | scores = model(combined).squeeze(0) # shape [num_tokens, vocab_size]
54 | logp = torch.log_softmax(scores, dim=-1)
55 |
56 | prompt_len = prompt_fmt.shape[1]
57 | answer_len = len(answer_ids)
58 |
59 | # Slice the exact rows where the model predicts the answer tokens
60 | steps = logp[prompt_len-1:prompt_len-1+answer_len, :] # [answer_len, vocab_size]
61 |
62 | # Gather log-probs of the ground-truth answer tokens
63 | targets = torch.tensor(answer_ids, dtype=torch.long, device=device).unsqueeze(1) # [answer_len, 1]
64 | avg_logp = steps.gather(dim=1, index=targets).mean().item()
65 | return avg_logp
66 |
67 |
68 | def predict_choice_teacher_forced(model, tokenizer, prompt_fmt, prompt, prompt_ids, example):
69 | scores = {}
70 | for letter in "ABCD":
71 | idx = ord(letter) - ord("A")
72 | choice_text = example["choices"][idx]
73 | scores[letter] = avg_logprob_teacher_forced(
74 | model, tokenizer, prompt_fmt, prompt, prompt_ids, letter, choice_text
75 | )
76 | pred = max(scores, key=scores.get)
77 | return pred, scores
78 |
79 |
80 | def evaluate_mmlu_teacher_forced(
81 | model,
82 | tokenizer,
83 | device,
84 | subsets="high_school_mathematics", # str, list of str, or "all"
85 | split="test",
86 | verbose_every=50,
87 | ):
88 | if subsets == "all":
89 | subset_list = get_dataset_config_names("cais/mmlu")
90 | elif isinstance(subsets, str):
91 | subset_list = [s.strip() for s in subsets.split(",")] if "," in subsets else [subsets]
92 | else:
93 | subset_list = list(subsets)
94 |
95 | total = 0
96 | correct = 0
97 | start = time.time()
98 |
99 | for subset in subset_list:
100 | ds = load_dataset("cais/mmlu", subset, split=split)
101 | for ex in ds:
102 | prompt = format_prompt(ex)
103 | prompt_ids = tokenizer.encode(prompt)
104 | prompt_fmt = torch.tensor(prompt_ids, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
105 |
106 | pred, _scores = predict_choice_teacher_forced(
107 | model, tokenizer, prompt_fmt, prompt, prompt_ids, ex
108 | )
109 |
110 | ans = ex["answer"]
111 | gold = "ABCD"[ans] if isinstance(ans, int) else str(ans).strip().upper()
112 |
113 | total += 1
114 | correct += int(pred == gold)
115 |
116 | if verbose_every and total % verbose_every == 0:
117 | print(f"MMLU {total} acc={correct/total:.3f} [{subset}]")
118 |
119 | acc = correct / max(1, total)
120 | print(
121 | f"\nMMLU letter accuracy (teacher-forced): {correct}/{total} = {acc:.2%} "
122 | f"in {time.time()-start:.1f}s"
123 | )
124 | return {"accuracy": acc, "num_examples": total, "subsets": subset_list, "split": split}
125 |
126 |
127 | def main():
128 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
129 | description="Zero-shot MMLU via teacher-forced log-prob over 'A. '."
130 | )
131 | parser.add_argument(
132 | "--device",
133 | type=str,
134 | default="auto",
135 | help="Device to use: 'auto' (default), or any torch device string like "
136 | "'cpu', 'cuda', 'cuda:0', 'mps'.",
137 | )
138 | parser.add_argument(
139 | "--which_model",
140 | type=str,
141 | default="base",
142 | choices=["base", "reasoning"],
143 | help="Model variant to load. Defaults to 'base'.",
144 | )
145 | parser.add_argument(
146 | "--subsets",
147 | type=str,
148 | default="high_school_mathematics",
149 | help="Comma-separated subset names or 'all'. "
150 | "Default: 'high_school_mathematics'.",
151 | )
152 | args = parser.parse_args()
153 |
154 | device = get_device() if args.device == "auto" else torch.device(args.device)
155 | print(f"Using device: {device}")
156 |
157 | model, tokenizer = load_model_and_tokenizer(args.which_model, device, use_compile=False)
158 | model.eval()
159 | torch.set_float32_matmul_precision("high")
160 |
161 | metrics = evaluate_mmlu_teacher_forced(
162 | model=model,
163 | tokenizer=tokenizer,
164 | device=device,
165 | subsets=args.subsets,
166 | )
167 | print(metrics)
168 |
169 |
170 | if __name__ == "__main__":
171 | main()
172 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch04/02_math500-inference-scaling-scripts/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 4: Improving Reasoning with Inference-Time Scaling
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 | ## Bonus materials
6 |
7 | - [cot_prompting_math500.py](cot_prompting_math500.py): standalone script to evaluate models with chain-of-thought prompting on the MATH-500 dataset
8 | - [self_consistency_math500.py](self_consistency_math500.py): standalone script to evaluate models with self-consistency sampling on the MATH-500 dataset
9 |
10 | Both evaluation scripts import functionality from the [`reasoning_from_scratch`](../../reasoning_from_scratch) package to avoid code duplication. (See [chapter 2 setup instructions](../../ch02/02_setup-tips/python-instructions.md) for installation details.)
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 | ---
17 |
18 | **Note**: If you are not a `uv` user, replace `uv run ...py` with `python ...py` in the examples below.
19 |
20 | ---
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 | ## Chain-of-thought prompting
27 |
28 | The [`cot_prompting_math500.py`](self_consistency_math500.py) script implements the chain-of-thought prompting method from chapter 4.
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 |  33 |
34 |
35 |
36 | The table below compares this approach (row 3) with the baselines from chapter 3:
37 |
38 | | | Method | Model | Accuracy | Time |
39 | |----|----------------------------------------------|-----------|----------|------------|
40 | | 1 | Baseline (chapter 3), greedy decoding | Base | 15.2% | 10.1 min |
41 | | 2 | Baseline (chapter 3), greedy decoding | Reasoning | 48.2% | 182.1 min |
42 | | 3 | Chain-of-thought prompting ("CoT") | Base | 40.6% | 84.5 min |
43 |
44 | The accuracy values and runtimes shown in the table were computed on all 500 samples in the MATH-500 test set using a "cuda" GPU (DGX Spark).
45 |
46 | To run the experiment in row one, use:
47 |
48 | ```bash
49 | python cot_prompting_math500.py \
50 | --which_model "base" \
51 | --dataset_size 500
52 | ```
53 |
54 | Or, with `uv:`
55 |
56 |
57 | ```bash
58 | uv run cot_prompting_math500.py \
59 | --which_model "base" \
60 | --dataset_size 500
61 | ```
62 |
63 | For additional options, use the `--help` flag.
64 |
65 |
66 |
67 |
68 | ## Self-consistency sampling
69 |
70 | The [`self_consistency_math500.py`](self_consistency_math500.py) script implements the sampling method from chapter 4.
71 |
72 | (Optionally, there is a [`self_consistency_math500_batched.py`](self_consistency_math500_batched.py) variant, which executes all `--num_samples` as a batch for faster processing. Note that this requires more compute memory though.)
73 |
74 |
75 |
76 |
33 |
34 |
35 |
36 | The table below compares this approach (row 3) with the baselines from chapter 3:
37 |
38 | | | Method | Model | Accuracy | Time |
39 | |----|----------------------------------------------|-----------|----------|------------|
40 | | 1 | Baseline (chapter 3), greedy decoding | Base | 15.2% | 10.1 min |
41 | | 2 | Baseline (chapter 3), greedy decoding | Reasoning | 48.2% | 182.1 min |
42 | | 3 | Chain-of-thought prompting ("CoT") | Base | 40.6% | 84.5 min |
43 |
44 | The accuracy values and runtimes shown in the table were computed on all 500 samples in the MATH-500 test set using a "cuda" GPU (DGX Spark).
45 |
46 | To run the experiment in row one, use:
47 |
48 | ```bash
49 | python cot_prompting_math500.py \
50 | --which_model "base" \
51 | --dataset_size 500
52 | ```
53 |
54 | Or, with `uv:`
55 |
56 |
57 | ```bash
58 | uv run cot_prompting_math500.py \
59 | --which_model "base" \
60 | --dataset_size 500
61 | ```
62 |
63 | For additional options, use the `--help` flag.
64 |
65 |
66 |
67 |
68 | ## Self-consistency sampling
69 |
70 | The [`self_consistency_math500.py`](self_consistency_math500.py) script implements the sampling method from chapter 4.
71 |
72 | (Optionally, there is a [`self_consistency_math500_batched.py`](self_consistency_math500_batched.py) variant, which executes all `--num_samples` as a batch for faster processing. Note that this requires more compute memory though.)
73 |
74 |
75 |
76 |  77 |
78 |
79 |
80 | The table below compares this approach (row 4-12) with the baselines from chapter 3 (rows 1-2):
81 |
82 | | | Method | Model | Accuracy | Time |
83 | | ---- | ----------------------------------------- | --------- | -------- | --------- |
84 | | 1 | Baseline (chapter 3), greedy decoding | Base | 15.2% | 10.1 min |
85 | | 2 | Baseline (chapter 3), greedy decoding | Reasoning | 48.2% | 182.1 min |
86 | | 3 | Chain-of-thought prompting ("CoT") | Base | 40.6% | 84.5 min |
87 | | 4 | Temperature and top-p ("Top-p") | Base | 17.8% | 30.7 min |
88 | | 5 | "Top-p" + Self-consistency (n=3) | Base | 29.6% | 97.6 min |
89 | | 6 | "Top-p" + Self-consistency (n=5) | Base | 27.8% | 116.8 min |
90 | | 7 | "Top-p" + Self-consistency (n=10) | Base | 31.6% | 300.4 min |
91 | | 8 | "Top-p" + "CoT" | Base | 33.4% | 129.2 min |
92 | | 9 | Self-consistency (n=3) + "Top-p" + "CoT" | Base | 42.2% | 211.6 min |
93 | | 10 | Self-consistency (n=5) + "Top-p" + "CoT" | Base | 48.0% | 452.9 min |
94 | | 11 | Self-consistency (n=10) + "Top-p" + "CoT" | Base | 52.0% | 862.6 min |
95 | | 12 | Self-consistency (n=3) + "Top-p" + "CoT" | Reasoning | 55.2% | 544.4 min |
96 |
97 | The accuracy values and runtimes shown in the table were computed on all 500 samples in the MATH-500 test set using a "cuda" GPU (DGX Spark).
98 |
99 | The following codes give instructions on how to run the self-consistency experiments in rows 4-12 (replace `uv run` with `python` if you are not a `uv` user).
100 |
101 | **Row 4:**
102 |
103 | ```bash
104 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
105 | --which_model "base" \
106 | --temperature 0.9 \
107 | --top_p 0.9 \
108 | --num_samples 1 \
109 | --dataset_size 500
110 | ```
111 |
112 | **Row 5:**
113 |
114 | ```bash
115 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
116 | --which_model "base" \
117 | --temperature 0.9 \
118 | --top_p 0.9 \
119 | --num_samples 3 \
120 | --dataset_size 500
121 | ```
122 |
123 | **Row 6:**
124 |
125 | ```bash
126 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
127 | --which_model "base" \
128 | --temperature 0.9 \
129 | --top_p 0.9 \
130 | --num_samples 5 \
131 | --dataset_size 500
132 | ```
133 |
134 | **Row 7:**
135 |
136 | ```bash
137 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
138 | --which_model "base" \
139 | --temperature 0.9 \
140 | --top_p 0.9 \
141 | --num_samples 10 \
142 | --dataset_size 500
143 | ```
144 |
145 | **Row 8:**
146 |
147 | ```bash
148 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
149 | --which_model "base" \
150 | --temperature 0.9 \
151 | --top_p 0.9 \
152 | --num_samples 1 \
153 | --dataset_size 500 \
154 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
155 | ```
156 |
157 | **Row 9:**
158 |
159 | ```bash
160 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
161 | --which_model "base" \
162 | --temperature 0.9 \
163 | --top_p 0.9 \
164 | --num_samples 3 \
165 | --dataset_size 500 \
166 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
167 | ```
168 |
169 | **Row 10:**
170 |
171 | ```bash
172 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
173 | --which_model "base" \
174 | --temperature 0.9 \
175 | --top_p 0.9 \
176 | --num_samples 5 \
177 | --dataset_size 500 \
178 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
179 | ```
180 |
181 | **Row 11:**
182 |
183 | ```bash
184 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
185 | --which_model "base" \
186 | --temperature 0.9 \
187 | --top_p 0.9 \
188 | --num_samples 10 \
189 | --dataset_size 500 \
190 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
191 | ```
192 |
193 | **Row 12:**
194 |
195 | ```bash
196 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
197 | --which_model "reasoning" \
198 | --temperature 0.9 \
199 | --top_p 0.9 \
200 | --num_samples 3 \
201 | --dataset_size 500 \
202 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
203 | ```
204 |
205 |
206 | For additional options, use the `--help` flag.
207 |
208 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_qwen3_batched_stop.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import os
6 | import torch
7 | import pytest
8 | from pathlib import Path
9 |
10 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import get_device
11 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
12 | download_qwen3_small,
13 | Qwen3Tokenizer,
14 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B,
15 | )
16 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3_batched import (
17 | generate_text_basic_batched_cache,
18 | generate_text_basic_batched_cache_stop,
19 | generate_text_basic_batched_stream_cache,
20 | generate_text_basic_batched_stream_cache_stop,
21 | Qwen3Model as Qwen3ModelBatched,
22 | )
23 |
24 | skip_expensive = os.environ.get("SKIP_EXPENSIVE", "0") == "1"
25 |
26 | # Make CI more reproducible & robust
27 | os.environ["MKL_NUM_THREADS"] = "1"
28 | os.environ["OMP_NUM_THREADS"] = "1"
29 | torch.backends.mkldnn.enabled = False
30 | torch.set_num_threads(1)
31 | torch.use_deterministic_algorithms(True)
32 |
33 |
34 | @pytest.mark.skipif(skip_expensive, reason="Skipping expensive test on CI")
35 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("reasoning", [False, True])
36 | def test_batched_vs_batched_stop_equivalence(reasoning):
37 |
38 | device = get_device()
39 |
40 | # Download and init tokenizer
41 | kind = "reasoning" if reasoning else "base"
42 | download_qwen3_small(kind=kind, tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
43 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / (
44 | "tokenizer-reasoning.json" if reasoning else "tokenizer-base.json"
45 | )
46 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / (
47 | "qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth" if reasoning else "qwen3-0.6B-base.pth"
48 | )
49 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
50 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
51 | apply_chat_template=reasoning,
52 | add_generation_prompt=reasoning,
53 | add_thinking=reasoning,
54 | )
55 |
56 | # Model
57 | model_batched = Qwen3ModelBatched(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
58 | model_batched.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path, map_location=device))
59 | model_batched.to(device).eval()
60 |
61 | # Prompts
62 | prompts = [
63 | "Explain large language models in two sentences.",
64 | "Explain large language models in one sentence.",
65 | "1+1?",
66 | ]
67 |
68 | # Batched inputs (left-padded)
69 | tokenized = [tokenizer.encode(p) for p in prompts]
70 | max_len = max(len(t) for t in tokenized)
71 | pad_id = tokenizer.pad_token_id
72 | left_padded = [[pad_id] * (max_len - len(t)) + t for t in tokenized]
73 | attn_mask = [
74 | [0] * (max_len - len(t)) + [1] * len(t) for t in tokenized
75 | ]
76 | input_ids_batched = torch.tensor(left_padded, device=device)
77 | attn_mask_batched = torch.tensor(attn_mask, device=device, dtype=torch.bool)
78 |
79 | # Generation
80 | max_new_tokens = 12
81 | outputs_reg = generate_text_basic_batched_cache(
82 | model=model_batched,
83 | token_ids=input_ids_batched,
84 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
85 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
86 | attn_mask=attn_mask_batched,
87 | pad_id=pad_id,
88 | )
89 | outputs_stop = generate_text_basic_batched_cache_stop(
90 | model=model_batched,
91 | token_ids=input_ids_batched,
92 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
93 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
94 | attn_mask=attn_mask_batched,
95 | pad_id=pad_id,
96 | )
97 |
98 | # Check equivalency
99 | for idx in range(len(prompts)):
100 | reg_toks = outputs_reg[idx].tolist()
101 | stop_toks = outputs_stop[idx].tolist()
102 | assert reg_toks == stop_toks, (
103 | f"Token mismatch at prompt {idx}:\n"
104 | f"regular_tokens={reg_toks}\n"
105 | f"stop_tokens ={stop_toks}\n"
106 | f"regular_text={tokenizer.decode(reg_toks)}\n"
107 | f"stop_text ={tokenizer.decode(stop_toks)}"
108 | )
109 |
110 |
111 | @pytest.mark.skipif(skip_expensive, reason="Skipping expensive test on CI")
112 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("reasoning", [False, True])
113 | def test_stream_vs_stream_stop_equivalence(reasoning):
114 |
115 | device = get_device()
116 |
117 | # Download and init tokenizer
118 | kind = "reasoning" if reasoning else "base"
119 | download_qwen3_small(kind=kind, tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
120 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / (
121 | "tokenizer-reasoning.json" if reasoning else "tokenizer-base.json"
122 | )
123 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / (
124 | "qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth" if reasoning else "qwen3-0.6B-base.pth"
125 | )
126 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
127 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
128 | apply_chat_template=reasoning,
129 | add_generation_prompt=reasoning,
130 | add_thinking=reasoning,
131 | )
132 |
133 | # Model
134 | model_batched = Qwen3ModelBatched(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
135 | model_batched.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path, map_location=device))
136 | model_batched.to(device).eval()
137 |
138 | # Prompts
139 | prompts = [
140 | "Explain large language models in two sentences.",
141 | "Explain large language models in one sentence.",
142 | "1+1?",
143 | ]
144 |
145 | # Batched inputs (left-padded)
146 | tokenized = [tokenizer.encode(p) for p in prompts]
147 | max_len = max(len(t) for t in tokenized)
148 | pad_id = tokenizer.pad_token_id
149 | left_padded = [[pad_id] * (max_len - len(t)) + t for t in tokenized]
150 | attn_mask = [
151 | [0] * (max_len - len(t)) + [1] * len(t) for t in tokenized
152 | ]
153 | input_ids_batched = torch.tensor(left_padded, device=device)
154 | attn_mask_batched = torch.tensor(attn_mask, device=device, dtype=torch.bool)
155 |
156 | # Generation
157 | max_new_tokens = 12
158 | B = input_ids_batched.size(0)
159 |
160 | # Regular streaming
161 | reg_stream_tokens = [[] for _ in range(B)]
162 | for step_tokens in generate_text_basic_batched_stream_cache(
163 | model=model_batched,
164 | token_ids=input_ids_batched,
165 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
166 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
167 | attn_mask=attn_mask_batched,
168 | pad_id=pad_id,
169 | ):
170 | step_tokens = step_tokens.squeeze(1)
171 | for b in range(B):
172 | reg_stream_tokens[b].append(int(step_tokens[b].item()))
173 |
174 | # Stop streaming
175 | stop_stream_tokens = [[] for _ in range(B)]
176 | for step_tokens in generate_text_basic_batched_stream_cache_stop(
177 | model=model_batched,
178 | token_ids=input_ids_batched,
179 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
180 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
181 | attn_mask=attn_mask_batched,
182 | pad_id=pad_id,
183 | ):
184 | step_tokens = step_tokens.squeeze(1)
185 | for b in range(B):
186 | stop_stream_tokens[b].append(int(step_tokens[b].item()))
187 |
188 | # Check equivalency
189 | for idx in range(B):
190 | assert reg_stream_tokens[idx] == stop_stream_tokens[idx], (
191 | f"Token mismatch at prompt {idx}:\n"
192 | f"regular_tokens={reg_stream_tokens[idx]}\n"
193 | f"stop_tokens ={stop_stream_tokens[idx]}\n"
194 | f"regular_text={tokenizer.decode(reg_stream_tokens[idx])}\n"
195 | f"stop_text ={tokenizer.decode(stop_stream_tokens[idx])}"
196 | )
197 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/05_use_model/chat_multiturn.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | # Runs the model similar to chapter 2 and 3 in streaming mode with the least
6 | # amount of bells and whistles. Uses KV caching by default.
7 | # Interactive REPL (Read, Evaluate, Print, Loop) with multiturn memory.
8 |
9 | import argparse
10 | from pathlib import Path
11 | import time
12 | import torch
13 |
14 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
15 | get_device,
16 | generate_stats
17 | )
18 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02_ex import (
19 | generate_text_basic_stream_cache
20 | )
21 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
22 | download_qwen3_small,
23 | Qwen3Model,
24 | Qwen3Tokenizer,
25 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B
26 | )
27 |
28 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Run Qwen3 text generation (interactive REPL)")
29 | parser.add_argument(
30 | "--device",
31 | type=str,
32 | default=None,
33 | help="Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). "
34 | "If not provided, will auto-detect with get_device()."
35 | )
36 | parser.add_argument(
37 | "--max_new_tokens",
38 | type=int,
39 | default=2048,
40 | help="Maximum number of new tokens to generate in each turn (default: 2048)."
41 | )
42 | parser.add_argument(
43 | "--compile",
44 | action="store_true",
45 | help="Compile PyTorch model (default: False)."
46 | )
47 | parser.add_argument(
48 | "--reasoning",
49 | action="store_true",
50 | help="Use reasoning model variant (default: False)."
51 | )
52 |
53 | args = parser.parse_args()
54 | device = torch.device(args.device) if args.device else get_device()
55 |
56 | if args.reasoning:
57 | download_qwen3_small(kind="reasoning", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
58 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-reasoning.json"
59 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth"
60 | else:
61 | download_qwen3_small(kind="base", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
62 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-base.json"
63 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-base.pth"
64 |
65 | # We will apply the chat template manually later
66 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
67 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
68 | apply_chat_template=False
69 | )
70 |
71 | model = Qwen3Model(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
72 | state = torch.load(model_path, map_location=device)
73 | model.load_state_dict(state)
74 | model.to(device)
75 | model.eval()
76 |
77 | if args.compile:
78 | model = torch.compile(model)
79 |
80 | # The reasoning model may emit <|im_end|>; base may emit <|endoftext|>.
81 | EOS_TOKEN_IDS = (
82 | tokenizer.encode("<|im_end|>")[0],
83 | tokenizer.encode("<|endoftext|>")[0]
84 | )
85 |
86 | print()
87 | print("=" * 60)
88 | print(f"torch : {torch.__version__}")
89 | print(f"device : {device}")
90 | print("cache : True")
91 | print(f"compile : {args.compile}")
92 | print(f"reasoning : {args.reasoning}")
93 | print("memory : True")
94 | print(f"max_new_tokens (per turn): {args.max_new_tokens}")
95 | print(f"context_length: {model.cfg['context_length']}")
96 | print("=" * 60)
97 | print()
98 | print("Interactive REPL with memory. Type '\\exit' or '\\quit' to quit.")
99 | print("Commands: \\clear (forget memory), \\history (show turn count)\n")
100 |
101 | # Multi-turn memory as a list of role-content dicts
102 | # Example: {"role": "system"|"user"|"assistant", "content": str}
103 | history = [
104 | {"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."}
105 | ]
106 |
107 |
108 | def build_prompt_from_history(history, add_assistant_header=True):
109 | """
110 | history: [{"role": "system"|"user"|"assistant", "content": str}, ...]
111 | """
112 | parts = []
113 | for m in history:
114 | role = m["role"]
115 | content = m["content"]
116 | parts.append(f"<|im_start|>{role}\n{content}<|im_end|>\n")
117 |
118 | if add_assistant_header:
119 | parts.append("<|im_start|>assistant\n")
120 | return "".join(parts)
121 |
122 |
123 | def trim_input_tensor(input_ids_tensor, context_len, max_new_tokens):
124 | assert max_new_tokens < context_len
125 | keep_len = max(1, context_len - max_new_tokens)
126 |
127 | # If the prompt is too long, left-truncate to keep_len
128 | if input_ids_tensor.shape[1] > keep_len:
129 | input_ids_tensor = input_ids_tensor[:, -keep_len:]
130 |
131 | return input_ids_tensor
132 |
133 |
134 | def run_generate(user_text):
135 | # Add user prompt to history
136 | history.append({"role": "user", "content": user_text})
137 |
138 | # Encode full history
139 | prompt = build_prompt_from_history(history, add_assistant_header=True)
140 | input_ids = tokenizer.encode(prompt)
141 | input_token_ids_tensor = torch.tensor(input_ids, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
142 |
143 | # Left-tuncate (to make space for generation)
144 | input_token_ids_tensor = trim_input_tensor(
145 | input_ids_tensor=input_token_ids_tensor,
146 | context_len=model.cfg["context_length"],
147 | max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens
148 | )
149 |
150 | start_time = time.time()
151 | all_token_ids = []
152 |
153 | print("[Model]\n", end="", flush=True)
154 | for tok in generate_text_basic_stream_cache(
155 | model=model,
156 | token_ids=input_token_ids_tensor,
157 | max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens,
158 | # eos_token_id=TOKENIZER.eos_token_id
159 | ):
160 | token_id = tok.squeeze(0)
161 | if token_id in EOS_TOKEN_IDS: # Manually break at stop tokens
162 | break
163 | piece = tokenizer.decode(token_id.tolist())
164 | print(piece, end="", flush=True)
165 | all_token_ids.append(token_id.item())
166 |
167 | end_time = time.time()
168 | print("\n")
169 |
170 | print("[Stats]")
171 | generate_stats(
172 | torch.tensor(all_token_ids),
173 | tokenizer,
174 | start_time,
175 | end_time,
176 | print_tokens=False
177 | )
178 | print("-" * 60)
179 |
180 | # Add model reply to history
181 | assistant_text = tokenizer.decode(all_token_ids)
182 | history.append({"role": "assistant", "content": assistant_text})
183 | return assistant_text
184 |
185 |
186 | # Interactive REPL (Read, Evaluate, Print, Loop)
187 | try:
188 | while True:
189 | try:
190 | user_in = input(">> ").strip()
191 | except EOFError:
192 | print("")
193 | break
194 |
195 | low = user_in.lower()
196 | if low in {r"\exit", r"\quit"}:
197 | break
198 | if low == r"\clear":
199 | # Reset history but keep the system prompt
200 | system_entries = [m for m in history if m["role"] == "system"]
201 | history.clear()
202 | if system_entries:
203 | history.extend(system_entries)
204 | else:
205 | history.append({"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."})
206 | print("(memory cleared)\n")
207 | continue
208 | if low == r"\history":
209 | # Count assistant turns as the number of model replies so far
210 | assistant_turns = sum(1 for m in history if m["role"] == "assistant")
211 | print(f"(stored turns: {assistant_turns})\n")
212 | continue
213 | if not user_in:
214 | continue
215 |
216 | print("\n" + "-" * 60)
217 | print("[User]")
218 | print(user_in + "\n")
219 | run_generate(user_in)
220 |
221 | except KeyboardInterrupt:
222 | print("\nInterrupted by user.")
223 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/03_optimized-LLM/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Optimized Qwen3
2 |
3 | The Qwen3 from-scratch implementation used in this book strikes a balance between being efficient (both on CPU and GPU) and lean while remaining easy to read by a human.
4 |
5 | As an alternative, you can use the optional `Qwen3Model` drop-in replacement, which is slightly more GPU-efficient. The optimized version in [`qwen3_optimized.py`](../../reasoning_from_scratch/qwen3_optimized.py) (discussed further in Appendix C) differs from the baseline implementation in [`qwen3.py`](../../reasoning_from_scratch/qwen3.py) in two key ways:
6 |
7 | - It implements attention using PyTorch’s built-in `torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product` instead of a custom implementation.
8 | - It introduces a modified `KVCache` that pre-allocates key/value tensors. This increases memory usage but avoids repeatedly allocating new storage during execution.
9 |
10 |
11 | To explore the differences, I recommend opening [`qwen3.py`](../../reasoning_from_scratch/qwen3.py) and [`qwen3_optimized.py`](../../reasoning_from_scratch/qwen3_optimized.py) side by side and/or looking at a file-diff:
12 |
13 |
77 |
78 |
79 |
80 | The table below compares this approach (row 4-12) with the baselines from chapter 3 (rows 1-2):
81 |
82 | | | Method | Model | Accuracy | Time |
83 | | ---- | ----------------------------------------- | --------- | -------- | --------- |
84 | | 1 | Baseline (chapter 3), greedy decoding | Base | 15.2% | 10.1 min |
85 | | 2 | Baseline (chapter 3), greedy decoding | Reasoning | 48.2% | 182.1 min |
86 | | 3 | Chain-of-thought prompting ("CoT") | Base | 40.6% | 84.5 min |
87 | | 4 | Temperature and top-p ("Top-p") | Base | 17.8% | 30.7 min |
88 | | 5 | "Top-p" + Self-consistency (n=3) | Base | 29.6% | 97.6 min |
89 | | 6 | "Top-p" + Self-consistency (n=5) | Base | 27.8% | 116.8 min |
90 | | 7 | "Top-p" + Self-consistency (n=10) | Base | 31.6% | 300.4 min |
91 | | 8 | "Top-p" + "CoT" | Base | 33.4% | 129.2 min |
92 | | 9 | Self-consistency (n=3) + "Top-p" + "CoT" | Base | 42.2% | 211.6 min |
93 | | 10 | Self-consistency (n=5) + "Top-p" + "CoT" | Base | 48.0% | 452.9 min |
94 | | 11 | Self-consistency (n=10) + "Top-p" + "CoT" | Base | 52.0% | 862.6 min |
95 | | 12 | Self-consistency (n=3) + "Top-p" + "CoT" | Reasoning | 55.2% | 544.4 min |
96 |
97 | The accuracy values and runtimes shown in the table were computed on all 500 samples in the MATH-500 test set using a "cuda" GPU (DGX Spark).
98 |
99 | The following codes give instructions on how to run the self-consistency experiments in rows 4-12 (replace `uv run` with `python` if you are not a `uv` user).
100 |
101 | **Row 4:**
102 |
103 | ```bash
104 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
105 | --which_model "base" \
106 | --temperature 0.9 \
107 | --top_p 0.9 \
108 | --num_samples 1 \
109 | --dataset_size 500
110 | ```
111 |
112 | **Row 5:**
113 |
114 | ```bash
115 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
116 | --which_model "base" \
117 | --temperature 0.9 \
118 | --top_p 0.9 \
119 | --num_samples 3 \
120 | --dataset_size 500
121 | ```
122 |
123 | **Row 6:**
124 |
125 | ```bash
126 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
127 | --which_model "base" \
128 | --temperature 0.9 \
129 | --top_p 0.9 \
130 | --num_samples 5 \
131 | --dataset_size 500
132 | ```
133 |
134 | **Row 7:**
135 |
136 | ```bash
137 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
138 | --which_model "base" \
139 | --temperature 0.9 \
140 | --top_p 0.9 \
141 | --num_samples 10 \
142 | --dataset_size 500
143 | ```
144 |
145 | **Row 8:**
146 |
147 | ```bash
148 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
149 | --which_model "base" \
150 | --temperature 0.9 \
151 | --top_p 0.9 \
152 | --num_samples 1 \
153 | --dataset_size 500 \
154 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
155 | ```
156 |
157 | **Row 9:**
158 |
159 | ```bash
160 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
161 | --which_model "base" \
162 | --temperature 0.9 \
163 | --top_p 0.9 \
164 | --num_samples 3 \
165 | --dataset_size 500 \
166 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
167 | ```
168 |
169 | **Row 10:**
170 |
171 | ```bash
172 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
173 | --which_model "base" \
174 | --temperature 0.9 \
175 | --top_p 0.9 \
176 | --num_samples 5 \
177 | --dataset_size 500 \
178 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
179 | ```
180 |
181 | **Row 11:**
182 |
183 | ```bash
184 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
185 | --which_model "base" \
186 | --temperature 0.9 \
187 | --top_p 0.9 \
188 | --num_samples 10 \
189 | --dataset_size 500 \
190 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
191 | ```
192 |
193 | **Row 12:**
194 |
195 | ```bash
196 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
197 | --which_model "reasoning" \
198 | --temperature 0.9 \
199 | --top_p 0.9 \
200 | --num_samples 3 \
201 | --dataset_size 500 \
202 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
203 | ```
204 |
205 |
206 | For additional options, use the `--help` flag.
207 |
208 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_qwen3_batched_stop.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import os
6 | import torch
7 | import pytest
8 | from pathlib import Path
9 |
10 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import get_device
11 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
12 | download_qwen3_small,
13 | Qwen3Tokenizer,
14 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B,
15 | )
16 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3_batched import (
17 | generate_text_basic_batched_cache,
18 | generate_text_basic_batched_cache_stop,
19 | generate_text_basic_batched_stream_cache,
20 | generate_text_basic_batched_stream_cache_stop,
21 | Qwen3Model as Qwen3ModelBatched,
22 | )
23 |
24 | skip_expensive = os.environ.get("SKIP_EXPENSIVE", "0") == "1"
25 |
26 | # Make CI more reproducible & robust
27 | os.environ["MKL_NUM_THREADS"] = "1"
28 | os.environ["OMP_NUM_THREADS"] = "1"
29 | torch.backends.mkldnn.enabled = False
30 | torch.set_num_threads(1)
31 | torch.use_deterministic_algorithms(True)
32 |
33 |
34 | @pytest.mark.skipif(skip_expensive, reason="Skipping expensive test on CI")
35 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("reasoning", [False, True])
36 | def test_batched_vs_batched_stop_equivalence(reasoning):
37 |
38 | device = get_device()
39 |
40 | # Download and init tokenizer
41 | kind = "reasoning" if reasoning else "base"
42 | download_qwen3_small(kind=kind, tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
43 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / (
44 | "tokenizer-reasoning.json" if reasoning else "tokenizer-base.json"
45 | )
46 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / (
47 | "qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth" if reasoning else "qwen3-0.6B-base.pth"
48 | )
49 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
50 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
51 | apply_chat_template=reasoning,
52 | add_generation_prompt=reasoning,
53 | add_thinking=reasoning,
54 | )
55 |
56 | # Model
57 | model_batched = Qwen3ModelBatched(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
58 | model_batched.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path, map_location=device))
59 | model_batched.to(device).eval()
60 |
61 | # Prompts
62 | prompts = [
63 | "Explain large language models in two sentences.",
64 | "Explain large language models in one sentence.",
65 | "1+1?",
66 | ]
67 |
68 | # Batched inputs (left-padded)
69 | tokenized = [tokenizer.encode(p) for p in prompts]
70 | max_len = max(len(t) for t in tokenized)
71 | pad_id = tokenizer.pad_token_id
72 | left_padded = [[pad_id] * (max_len - len(t)) + t for t in tokenized]
73 | attn_mask = [
74 | [0] * (max_len - len(t)) + [1] * len(t) for t in tokenized
75 | ]
76 | input_ids_batched = torch.tensor(left_padded, device=device)
77 | attn_mask_batched = torch.tensor(attn_mask, device=device, dtype=torch.bool)
78 |
79 | # Generation
80 | max_new_tokens = 12
81 | outputs_reg = generate_text_basic_batched_cache(
82 | model=model_batched,
83 | token_ids=input_ids_batched,
84 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
85 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
86 | attn_mask=attn_mask_batched,
87 | pad_id=pad_id,
88 | )
89 | outputs_stop = generate_text_basic_batched_cache_stop(
90 | model=model_batched,
91 | token_ids=input_ids_batched,
92 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
93 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
94 | attn_mask=attn_mask_batched,
95 | pad_id=pad_id,
96 | )
97 |
98 | # Check equivalency
99 | for idx in range(len(prompts)):
100 | reg_toks = outputs_reg[idx].tolist()
101 | stop_toks = outputs_stop[idx].tolist()
102 | assert reg_toks == stop_toks, (
103 | f"Token mismatch at prompt {idx}:\n"
104 | f"regular_tokens={reg_toks}\n"
105 | f"stop_tokens ={stop_toks}\n"
106 | f"regular_text={tokenizer.decode(reg_toks)}\n"
107 | f"stop_text ={tokenizer.decode(stop_toks)}"
108 | )
109 |
110 |
111 | @pytest.mark.skipif(skip_expensive, reason="Skipping expensive test on CI")
112 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("reasoning", [False, True])
113 | def test_stream_vs_stream_stop_equivalence(reasoning):
114 |
115 | device = get_device()
116 |
117 | # Download and init tokenizer
118 | kind = "reasoning" if reasoning else "base"
119 | download_qwen3_small(kind=kind, tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
120 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / (
121 | "tokenizer-reasoning.json" if reasoning else "tokenizer-base.json"
122 | )
123 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / (
124 | "qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth" if reasoning else "qwen3-0.6B-base.pth"
125 | )
126 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
127 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
128 | apply_chat_template=reasoning,
129 | add_generation_prompt=reasoning,
130 | add_thinking=reasoning,
131 | )
132 |
133 | # Model
134 | model_batched = Qwen3ModelBatched(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
135 | model_batched.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path, map_location=device))
136 | model_batched.to(device).eval()
137 |
138 | # Prompts
139 | prompts = [
140 | "Explain large language models in two sentences.",
141 | "Explain large language models in one sentence.",
142 | "1+1?",
143 | ]
144 |
145 | # Batched inputs (left-padded)
146 | tokenized = [tokenizer.encode(p) for p in prompts]
147 | max_len = max(len(t) for t in tokenized)
148 | pad_id = tokenizer.pad_token_id
149 | left_padded = [[pad_id] * (max_len - len(t)) + t for t in tokenized]
150 | attn_mask = [
151 | [0] * (max_len - len(t)) + [1] * len(t) for t in tokenized
152 | ]
153 | input_ids_batched = torch.tensor(left_padded, device=device)
154 | attn_mask_batched = torch.tensor(attn_mask, device=device, dtype=torch.bool)
155 |
156 | # Generation
157 | max_new_tokens = 12
158 | B = input_ids_batched.size(0)
159 |
160 | # Regular streaming
161 | reg_stream_tokens = [[] for _ in range(B)]
162 | for step_tokens in generate_text_basic_batched_stream_cache(
163 | model=model_batched,
164 | token_ids=input_ids_batched,
165 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
166 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
167 | attn_mask=attn_mask_batched,
168 | pad_id=pad_id,
169 | ):
170 | step_tokens = step_tokens.squeeze(1)
171 | for b in range(B):
172 | reg_stream_tokens[b].append(int(step_tokens[b].item()))
173 |
174 | # Stop streaming
175 | stop_stream_tokens = [[] for _ in range(B)]
176 | for step_tokens in generate_text_basic_batched_stream_cache_stop(
177 | model=model_batched,
178 | token_ids=input_ids_batched,
179 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
180 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
181 | attn_mask=attn_mask_batched,
182 | pad_id=pad_id,
183 | ):
184 | step_tokens = step_tokens.squeeze(1)
185 | for b in range(B):
186 | stop_stream_tokens[b].append(int(step_tokens[b].item()))
187 |
188 | # Check equivalency
189 | for idx in range(B):
190 | assert reg_stream_tokens[idx] == stop_stream_tokens[idx], (
191 | f"Token mismatch at prompt {idx}:\n"
192 | f"regular_tokens={reg_stream_tokens[idx]}\n"
193 | f"stop_tokens ={stop_stream_tokens[idx]}\n"
194 | f"regular_text={tokenizer.decode(reg_stream_tokens[idx])}\n"
195 | f"stop_text ={tokenizer.decode(stop_stream_tokens[idx])}"
196 | )
197 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/05_use_model/chat_multiturn.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | # Runs the model similar to chapter 2 and 3 in streaming mode with the least
6 | # amount of bells and whistles. Uses KV caching by default.
7 | # Interactive REPL (Read, Evaluate, Print, Loop) with multiturn memory.
8 |
9 | import argparse
10 | from pathlib import Path
11 | import time
12 | import torch
13 |
14 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
15 | get_device,
16 | generate_stats
17 | )
18 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02_ex import (
19 | generate_text_basic_stream_cache
20 | )
21 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
22 | download_qwen3_small,
23 | Qwen3Model,
24 | Qwen3Tokenizer,
25 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B
26 | )
27 |
28 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Run Qwen3 text generation (interactive REPL)")
29 | parser.add_argument(
30 | "--device",
31 | type=str,
32 | default=None,
33 | help="Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). "
34 | "If not provided, will auto-detect with get_device()."
35 | )
36 | parser.add_argument(
37 | "--max_new_tokens",
38 | type=int,
39 | default=2048,
40 | help="Maximum number of new tokens to generate in each turn (default: 2048)."
41 | )
42 | parser.add_argument(
43 | "--compile",
44 | action="store_true",
45 | help="Compile PyTorch model (default: False)."
46 | )
47 | parser.add_argument(
48 | "--reasoning",
49 | action="store_true",
50 | help="Use reasoning model variant (default: False)."
51 | )
52 |
53 | args = parser.parse_args()
54 | device = torch.device(args.device) if args.device else get_device()
55 |
56 | if args.reasoning:
57 | download_qwen3_small(kind="reasoning", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
58 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-reasoning.json"
59 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth"
60 | else:
61 | download_qwen3_small(kind="base", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
62 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-base.json"
63 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-base.pth"
64 |
65 | # We will apply the chat template manually later
66 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
67 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
68 | apply_chat_template=False
69 | )
70 |
71 | model = Qwen3Model(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
72 | state = torch.load(model_path, map_location=device)
73 | model.load_state_dict(state)
74 | model.to(device)
75 | model.eval()
76 |
77 | if args.compile:
78 | model = torch.compile(model)
79 |
80 | # The reasoning model may emit <|im_end|>; base may emit <|endoftext|>.
81 | EOS_TOKEN_IDS = (
82 | tokenizer.encode("<|im_end|>")[0],
83 | tokenizer.encode("<|endoftext|>")[0]
84 | )
85 |
86 | print()
87 | print("=" * 60)
88 | print(f"torch : {torch.__version__}")
89 | print(f"device : {device}")
90 | print("cache : True")
91 | print(f"compile : {args.compile}")
92 | print(f"reasoning : {args.reasoning}")
93 | print("memory : True")
94 | print(f"max_new_tokens (per turn): {args.max_new_tokens}")
95 | print(f"context_length: {model.cfg['context_length']}")
96 | print("=" * 60)
97 | print()
98 | print("Interactive REPL with memory. Type '\\exit' or '\\quit' to quit.")
99 | print("Commands: \\clear (forget memory), \\history (show turn count)\n")
100 |
101 | # Multi-turn memory as a list of role-content dicts
102 | # Example: {"role": "system"|"user"|"assistant", "content": str}
103 | history = [
104 | {"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."}
105 | ]
106 |
107 |
108 | def build_prompt_from_history(history, add_assistant_header=True):
109 | """
110 | history: [{"role": "system"|"user"|"assistant", "content": str}, ...]
111 | """
112 | parts = []
113 | for m in history:
114 | role = m["role"]
115 | content = m["content"]
116 | parts.append(f"<|im_start|>{role}\n{content}<|im_end|>\n")
117 |
118 | if add_assistant_header:
119 | parts.append("<|im_start|>assistant\n")
120 | return "".join(parts)
121 |
122 |
123 | def trim_input_tensor(input_ids_tensor, context_len, max_new_tokens):
124 | assert max_new_tokens < context_len
125 | keep_len = max(1, context_len - max_new_tokens)
126 |
127 | # If the prompt is too long, left-truncate to keep_len
128 | if input_ids_tensor.shape[1] > keep_len:
129 | input_ids_tensor = input_ids_tensor[:, -keep_len:]
130 |
131 | return input_ids_tensor
132 |
133 |
134 | def run_generate(user_text):
135 | # Add user prompt to history
136 | history.append({"role": "user", "content": user_text})
137 |
138 | # Encode full history
139 | prompt = build_prompt_from_history(history, add_assistant_header=True)
140 | input_ids = tokenizer.encode(prompt)
141 | input_token_ids_tensor = torch.tensor(input_ids, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
142 |
143 | # Left-tuncate (to make space for generation)
144 | input_token_ids_tensor = trim_input_tensor(
145 | input_ids_tensor=input_token_ids_tensor,
146 | context_len=model.cfg["context_length"],
147 | max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens
148 | )
149 |
150 | start_time = time.time()
151 | all_token_ids = []
152 |
153 | print("[Model]\n", end="", flush=True)
154 | for tok in generate_text_basic_stream_cache(
155 | model=model,
156 | token_ids=input_token_ids_tensor,
157 | max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens,
158 | # eos_token_id=TOKENIZER.eos_token_id
159 | ):
160 | token_id = tok.squeeze(0)
161 | if token_id in EOS_TOKEN_IDS: # Manually break at stop tokens
162 | break
163 | piece = tokenizer.decode(token_id.tolist())
164 | print(piece, end="", flush=True)
165 | all_token_ids.append(token_id.item())
166 |
167 | end_time = time.time()
168 | print("\n")
169 |
170 | print("[Stats]")
171 | generate_stats(
172 | torch.tensor(all_token_ids),
173 | tokenizer,
174 | start_time,
175 | end_time,
176 | print_tokens=False
177 | )
178 | print("-" * 60)
179 |
180 | # Add model reply to history
181 | assistant_text = tokenizer.decode(all_token_ids)
182 | history.append({"role": "assistant", "content": assistant_text})
183 | return assistant_text
184 |
185 |
186 | # Interactive REPL (Read, Evaluate, Print, Loop)
187 | try:
188 | while True:
189 | try:
190 | user_in = input(">> ").strip()
191 | except EOFError:
192 | print("")
193 | break
194 |
195 | low = user_in.lower()
196 | if low in {r"\exit", r"\quit"}:
197 | break
198 | if low == r"\clear":
199 | # Reset history but keep the system prompt
200 | system_entries = [m for m in history if m["role"] == "system"]
201 | history.clear()
202 | if system_entries:
203 | history.extend(system_entries)
204 | else:
205 | history.append({"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."})
206 | print("(memory cleared)\n")
207 | continue
208 | if low == r"\history":
209 | # Count assistant turns as the number of model replies so far
210 | assistant_turns = sum(1 for m in history if m["role"] == "assistant")
211 | print(f"(stored turns: {assistant_turns})\n")
212 | continue
213 | if not user_in:
214 | continue
215 |
216 | print("\n" + "-" * 60)
217 | print("[User]")
218 | print(user_in + "\n")
219 | run_generate(user_in)
220 |
221 | except KeyboardInterrupt:
222 | print("\nInterrupted by user.")
223 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/03_optimized-LLM/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Optimized Qwen3
2 |
3 | The Qwen3 from-scratch implementation used in this book strikes a balance between being efficient (both on CPU and GPU) and lean while remaining easy to read by a human.
4 |
5 | As an alternative, you can use the optional `Qwen3Model` drop-in replacement, which is slightly more GPU-efficient. The optimized version in [`qwen3_optimized.py`](../../reasoning_from_scratch/qwen3_optimized.py) (discussed further in Appendix C) differs from the baseline implementation in [`qwen3.py`](../../reasoning_from_scratch/qwen3.py) in two key ways:
6 |
7 | - It implements attention using PyTorch’s built-in `torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product` instead of a custom implementation.
8 | - It introduces a modified `KVCache` that pre-allocates key/value tensors. This increases memory usage but avoids repeatedly allocating new storage during execution.
9 |
10 |
11 | To explore the differences, I recommend opening [`qwen3.py`](../../reasoning_from_scratch/qwen3.py) and [`qwen3_optimized.py`](../../reasoning_from_scratch/qwen3_optimized.py) side by side and/or looking at a file-diff:
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 | 
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 | ## How to use
21 |
22 | The optimized code can be used as drop-in replacement for the code used in the main chapters as shown below.
23 |
24 | **Before:**
25 |
26 | ```python
27 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import Qwen3Model
28 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import generate_text_basic_cache
29 | ```
30 |
31 |
32 | **After:**
33 |
34 | ```python
35 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3_optimized import Qwen3Model
36 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3_optimized import generate_text_basic_cache
37 | ```
38 |
39 |
40 | ## How to run comparisons
41 |
42 | To evaluate the performance on your system, you can use the [`compare_inference.py`](compare_inference.py) function contained in this folder:
43 |
44 | ```python
45 | python compare_inference.py
46 | ```
47 |
48 | or
49 |
50 | ```python
51 | uv run compare_inference.py
52 | ```
53 |
54 | Then, add the following flags:
55 |
56 | - `--device`: Select the device, e.g., `cpu`, `mps`, or `cuda`
57 | - `--cache`: Enables the KV cache
58 | - `--compile`: Uses `torch.compile`
59 | - `--reasoning`: Uses the Qwen3 reasoning variant instead of the base model. The base model generates approximately 50 tokens in response to the given prompt. The reasoning variant generates about 2000 tokens.
60 | - `--optimize`: Uses the optimized model from `qwen3_optimized.py` instead of the standard model from `qwen3.py`.
61 |
62 |
63 |
64 |
65 | ### Standard model
66 |
67 |
68 |
69 | | Model | Mode | Command | Hardware | Tokens/sec | GPU Memory (VRAM) |
70 | | -------- | ----------------- | ------------------------------- | --------------- | ------------- | ----------------- |
71 | | qwen3.py | Regular | --device cpu | Mac Mini M4 CPU | 6 | - |
72 | | qwen3.py | Regular compiled | --device cpu --compile | Mac Mini M4 CPU | 6 | - |
73 | | qwen3.py | KV cache | --device cpu --cache | Mac Mini M4 CPU | 28 | - |
74 | | qwen3.py | KV cache compiled | --device cpu --compile --cache | Mac Mini M4 CPU | 68 | - |
75 | | | | | | | |
76 | | qwen3.py | Regular | --device mps | Mac Mini M4 GPU | 17 | - |
77 | | qwen3.py | Regular compiled | --device mps --compile | Mac Mini M4 GPU | InductorError | - |
78 | | qwen3.py | KV cache | --device mps --cache | Mac Mini M4 GPU | 18 | - |
79 | | qwen3.py | KV cache compiled | --device mps --compile --cache | Mac Mini M4 GPU | InductorError | - |
80 | | | | | | | |
81 | | qwen3.py | Regular | --device cuda | NVIDIA H100 GPU | 51 | 1.55 GB |
82 | | qwen3.py | Regular compiled | --device cuda --compile | NVIDIA H100 GPU | 164 | 1.81 GB |
83 | | qwen3.py | KV cache | --device cuda --cache | NVIDIA H100 GPU | 48 | 1.52 GB |
84 | | qwen3.py | KV cache compiled | --device cuda --compile --cache | NVIDIA H100 GPU | 141 | 1.81 GB |
85 |
86 |
87 |
88 |
89 | ### Optimized model
90 |
91 |
92 | | Model | Mode | Command | Hardware | Tokens/sec | GPU Memory (VRAM) |
93 | | ------------------ | ----------------- | ------------------------------------------- | --------------- | ---------- | ----------------- |
94 | | qwen3_optimized.py | Regular | --optimized --device cpu | Mac Mini M4 CPU | 5 | - |
95 | | qwen3_optimized.py | Regular compiled | --optimized --device cpu --compile | Mac Mini M4 CPU | 7 | - |
96 | | qwen3_optimized.py | KV cache | --optimized --device cpu --cache | Mac Mini M4 CPU | 49 | - |
97 | | qwen3_optimized.py | KV cache compiled | --optimized --device cpu --compile --cache | Mac Mini M4 CPU | 51 | - |
98 | | | | | | | |
99 | | qwen3_optimized.py | Regular | --optimized --device mps | Mac Mini M4 GPU | 21 | - |
100 | | qwen3_optimized.py | Regular compiled | --optimized --device mps --compile | Mac Mini M4 GPU | NameError | - |
101 | | qwen3_optimized.py | KV cache | --optimized --device mps --cache | Mac Mini M4 GPU | 29 | - |
102 | | qwen3_optimized.py | KV cache compiled | --optimized --device mps --compile --cache | Mac Mini M4 GPU | 38 | - |
103 | | | | | | | |
104 | | qwen3_optimized.py | Regular | --optimized --device cuda | NVIDIA H100 GPU | 55 | 1.50 GB |
105 | | qwen3_optimized.py | Regular compiled | --optimized --device cuda --compile | NVIDIA H100 GPU | 173 | 1.81 GB |
106 | | qwen3_optimized.py | KV cache | --optimized --device cuda --cache | NVIDIA H100 GPU | 56 | 5.85 GB |
107 | | qwen3_optimized.py | KV cache compiled | --optimized --device cuda --compile --cache | NVIDIA H100 GPU | 177 | 5.85 GB |
108 |
109 |
110 |
111 | Comparing the 2 tables above, we can see that the optimized variant is clearly faster in terms of tokens/second in most cases.
112 |
113 | However, note that the unoptimized version is faster (68 tok/sec) than the optimized version (51 tok/sec) when using the compiled version with KV cache.
114 |
115 | The optimized version also uses more base RAM (5.85 GB with KV Cache) than the unoptimized version (1.5 GB). This is because it pre-allocates the tensors holding the KV values for the maximum supported context length. (So, when running the unoptimized version on a prompt with 41k context length, the RAM usage would be approximately similar.)
116 |
117 | **Perhaps the best recommendation is to use the unoptimized version (with `--cache` and `--compile`) when using a CPU. When using a GPU, use the optimized version (with `--cache` and `--compile`).**
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/reasoning_from_scratch/appendix_c.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
3 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
4 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
5 |
6 | import os
7 | import json
8 | import torch
9 |
10 |
11 | QWEN3_CONFIG_1_7B = {
12 | "vocab_size": 151_936,
13 | "context_length": 40_960,
14 | "emb_dim": 2048, # 2x larger than 0.6B model
15 | "n_heads": 16,
16 | "n_layers": 28,
17 | "hidden_dim": 6144, # 2x larger than 0.6B model
18 | "head_dim": 128,
19 | "qk_norm": True,
20 | "n_kv_groups": 8,
21 | "rope_base": 1_000_000.0,
22 | "dtype": torch.bfloat16,
23 | }
24 |
25 | # 4 billion parameters
26 | QWEN3_CONFIG_4B = {
27 | "vocab_size": 151_936,
28 | "context_length": 40_960,
29 | "emb_dim": 2560, # 25% larger than above
30 | "n_heads": 32, # 2x larger than above
31 | "n_layers": 36, # 29% larger than above
32 | "hidden_dim": 9728, # ~3x larger than above
33 | "head_dim": 128,
34 | "qk_norm": True,
35 | "n_kv_groups": 8,
36 | "rope_base": 1_000_000.0,
37 | "dtype": torch.bfloat16,
38 | }
39 |
40 | # 8 billion parameters
41 | QWEN3_CONFIG_8B = {
42 | "vocab_size": 151_936,
43 | "context_length": 40_960,
44 | "emb_dim": 4096, # 60% larger than above
45 | "n_heads": 32,
46 | "n_layers": 36, # 26% larger than above
47 | "hidden_dim": 12288,
48 | "head_dim": 128,
49 | "qk_norm": True,
50 | "n_kv_groups": 8,
51 | "rope_base": 1_000_000.0,
52 | "dtype": torch.bfloat16,
53 | }
54 |
55 | # 14 billion parameters
56 | QWEN3_CONFIG_14B = {
57 | "vocab_size": 151_936,
58 | "context_length": 40_960,
59 | "emb_dim": 5120, # 25% larger than above
60 | "n_heads": 40, # 25% larger than above
61 | "n_layers": 40, # 11% larger than above
62 | "hidden_dim": 17408, # 42% larger than above
63 | "head_dim": 128,
64 | "qk_norm": True,
65 | "n_kv_groups": 8,
66 | "rope_base": 1_000_000.0,
67 | "dtype": torch.bfloat16,
68 | }
69 |
70 | QWEN3_CONFIG_32B = {
71 | "vocab_size": 151_936,
72 | "context_length": 40_960,
73 | "emb_dim": 5120,
74 | "n_heads": 64, # 60% larger than above
75 | "n_layers": 64, # 60% larger than above
76 | "hidden_dim": 25600, # 47% larger than above
77 | "head_dim": 128,
78 | "qk_norm": True,
79 | "n_kv_groups": 8,
80 | "rope_base": 1_000_000.0,
81 | "dtype": torch.bfloat16,
82 | }
83 |
84 |
85 | def load_weights_into_qwen(model, param_config, params):
86 | def assign(left, right, tensor_name="unknown"):
87 | if left.shape != right.shape:
88 | raise ValueError(f"Shape mismatch in tensor '{tensor_name}'. Left: {left.shape}, Right: {right.shape}")
89 | return torch.nn.Parameter(right.clone().detach() if isinstance(right, torch.Tensor) else torch.tensor(right))
90 |
91 | model.tok_emb.weight = assign(model.tok_emb.weight, params["model.embed_tokens.weight"], "model.embed_tokens.weight")
92 |
93 | for ln in range(param_config["n_layers"]):
94 | block = model.trf_blocks[ln]
95 | att = block.att
96 |
97 | # Q, K, V projections
98 | att.W_query.weight = assign(
99 | att.W_query.weight,
100 | params[f"model.layers.{ln}.self_attn.q_proj.weight"],
101 | f"model.layers.{ln}.self_attn.q_proj.weight"
102 | )
103 | att.W_key.weight = assign(
104 | att.W_key.weight,
105 | params[f"model.layers.{ln}.self_attn.k_proj.weight"],
106 | f"model.layers.{ln}.self_attn.k_proj.weight"
107 | )
108 | att.W_value.weight = assign(
109 | att.W_value.weight,
110 | params[f"model.layers.{ln}.self_attn.v_proj.weight"],
111 | f"model.layers.{ln}.self_attn.v_proj.weight"
112 | )
113 |
114 | # Output projection
115 | att.out_proj.weight = assign(
116 | att.out_proj.weight,
117 | params[f"model.layers.{ln}.self_attn.o_proj.weight"],
118 | f"model.layers.{ln}.self_attn.o_proj.weight"
119 | )
120 |
121 | # QK norms
122 | if hasattr(att, "q_norm") and att.q_norm is not None:
123 | att.q_norm.scale = assign(
124 | att.q_norm.scale,
125 | params[f"model.layers.{ln}.self_attn.q_norm.weight"],
126 | f"model.layers.{ln}.self_attn.q_norm.weight"
127 | )
128 | if hasattr(att, "k_norm") and att.k_norm is not None:
129 | att.k_norm.scale = assign(
130 | att.k_norm.scale,
131 | params[f"model.layers.{ln}.self_attn.k_norm.weight"],
132 | f"model.layers.{ln}.self_attn.k_norm.weight"
133 | )
134 |
135 | # Attention layernorm
136 | block.norm1.scale = assign(
137 | block.norm1.scale,
138 | params[f"model.layers.{ln}.input_layernorm.weight"],
139 | f"model.layers.{ln}.input_layernorm.weight"
140 | )
141 |
142 | # Feedforward weights
143 | block.ff.fc1.weight = assign(
144 | block.ff.fc1.weight,
145 | params[f"model.layers.{ln}.mlp.gate_proj.weight"],
146 | f"model.layers.{ln}.mlp.gate_proj.weight"
147 | )
148 | block.ff.fc2.weight = assign(
149 | block.ff.fc2.weight,
150 | params[f"model.layers.{ln}.mlp.up_proj.weight"],
151 | f"model.layers.{ln}.mlp.up_proj.weight"
152 | )
153 | block.ff.fc3.weight = assign(
154 | block.ff.fc3.weight,
155 | params[f"model.layers.{ln}.mlp.down_proj.weight"],
156 | f"model.layers.{ln}.mlp.down_proj.weight"
157 | )
158 | block.norm2.scale = assign(
159 | block.norm2.scale,
160 | params[f"model.layers.{ln}.post_attention_layernorm.weight"],
161 | f"model.layers.{ln}.post_attention_layernorm.weight"
162 | )
163 |
164 | # Final normalization and output head
165 | model.final_norm.scale = assign(model.final_norm.scale, params["model.norm.weight"], "model.norm.weight")
166 |
167 | # Model uses weight tying, hence we reuse the embedding layer weights here
168 | model.out_head.weight = assign(model.out_head.weight, params["model.embed_tokens.weight"], "model.embed_tokens.weight")
169 |
170 |
171 | def download_from_huggingface_from_snapshots(repo_id, local_dir):
172 | from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download, snapshot_download
173 | from safetensors.torch import load_file # or your preferred loader
174 |
175 | repo_dir = snapshot_download(repo_id=repo_id, local_dir=local_dir)
176 |
177 | index_path = os.path.join(repo_dir, "model.safetensors.index.json")
178 | single_file_path = os.path.join(repo_dir, "model.safetensors")
179 |
180 | if os.path.exists(index_path):
181 | # Multi-shard model
182 | with open(index_path, "r") as f:
183 | index = json.load(f)
184 |
185 | weights_dict = {}
186 | for filename in set(index["weight_map"].values()):
187 | shard_path = os.path.join(repo_dir, filename)
188 | shard = load_file(shard_path)
189 | weights_dict.update(shard)
190 | elif os.path.exists(single_file_path):
191 | # Single-shard model
192 | weights_file = hf_hub_download(
193 | repo_id=repo_id,
194 | filename="model.safetensors",
195 | local_dir=local_dir,
196 | )
197 | weights_dict = load_file(weights_file)
198 | else:
199 | raise FileNotFoundError("No model.safetensors or model.safetensors.index.json found.")
200 |
201 | return weights_dict
202 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/05_use_model/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Run Inference and Chat With the Model
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |  6 |
7 |
8 |
9 | This folder contains standalone example scripts to generate text with the model we loaded in chapter 2 (and exercises):
10 |
11 | - `generate_simple.py`: Generates text similar to the main chapter.
12 | - `chat.py`: Similar to the code above, as an interactive wrapper so that we can prompt the model multiple times without having to reload the model into memory each time.
13 | - `chat_multiturn.py`: Same as above, but with a memory feature to remember the message history.
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 | More usage details are provided in the sections below.
18 |
19 |
20 | ## generate_simple.py
21 |
22 | This simple function loads the model as described in chapter 2 and uses the `generate_text_simple_cache_stream` function from the chapter 2 exercises. You can use the function as follows (replace `uv run` with `python` if you are not using `uv`):
23 |
24 | ```bash
25 | uv run ch02/05_use_model/generate_simple.py
26 | Using Apple Silicon GPU (MPS)
27 | ✓ qwen3/qwen3-0.6B-base.pth already up-to-date
28 |
29 | ============================================================
30 | torch : 2.7.1
31 | device : mps
32 | cache : True
33 | compile : False
34 | reasoning : False
35 | ============================================================
36 |
37 | Large language models are artificial intelligence systems that can understand, generate, and process human language, enabling them to perform a wide range of tasks, from answering questions to writing essays.
38 |
39 | Time: 1.52 sec
40 | 22 tokens/sec
41 | ```
42 |
43 | The function is useful if you want to quickly try out different prompts with the base or reasoning variant. The additional options are listed below:
44 |
45 | ```bash
46 | usage: generate_simple.py [-h] [--device DEVICE]
47 | [--max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS] [--compile]
48 | [--reasoning] [--prompt PROMPT]
49 |
50 | Run Qwen3 text generation
51 |
52 | options:
53 | -h, --help show this help message and exit
54 | --device DEVICE Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). If not
55 | provided, will auto-detect with get_device().
56 | --max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS
57 | Maximum number of new tokens to generate (default:
58 | 2048).
59 | --compile Compile PyTorch model (default: False).
60 | --reasoning Use reasoning model variant (default: False).
61 | --prompt PROMPT Use a custom prompt. If not explicitly provided, uses
62 | the following defaults: 'Explain large language models
63 | in a single sentence.' for the base model, and 'Find
64 | all c in Z_3 such that Z_3[x]/(x^2 + c) is a field.'
65 | for the reasoning model.
66 | ```
67 |
68 |
69 | ## chat.py
70 |
71 | Similar to the function above, this function is useful to try different prompts on the base and reasoning models.
72 |
73 | However, in contrast to the previous function, this function keeps the user in an interactive mode so that the model doesn't have to be reloaded each time:
74 |
75 | ```bash
76 | uv run ch02/05_use_model/chat.py
77 | Using Apple Silicon GPU (MPS)
78 | ✓ qwen3/qwen3-0.6B-base.pth already up-to-date
79 |
80 | ============================================================
81 | torch : 2.7.1
82 | device : mps
83 | cache : True
84 | compile : False
85 | reasoning : False
86 | memory : False
87 | ============================================================
88 |
89 | Interactive REPL (no memory). Type '\exit' or '\quit' to quit.
90 |
91 | >> Explain language models in 1 sentence
92 |
93 | ------------------------------------------------------------
94 | [User]
95 | Explain language models in 1 sentence
96 |
97 | [Model]
98 |
99 | Language models are algorithms that analyze and predict the likelihood of future words in a text based on the words already seen, enabling them to generate coherent and contextually relevant text.
100 |
101 | [Stats]
102 | Time: 1.53 sec
103 | 22 tokens/sec
104 | ------------------------------------------------------------
105 | >> Explain machine learning in 1 sentence.
106 |
107 | ------------------------------------------------------------
108 | [User]
109 | Explain machine learning in 1 sentence.
110 |
111 | [Model]
112 | Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that enables computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed.
113 |
114 | [Stats]
115 | Time: 1.04 sec
116 | 24 tokens/sec
117 | ------------------------------------------------------------
118 | ```
119 |
120 | Additional options are listed below:
121 |
122 | ```bash
123 | usage: chat.py [-h] [--device DEVICE] [--max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS] [--compile]
124 | [--reasoning]
125 |
126 | Run Qwen3 text generation (interactive REPL)
127 |
128 | options:
129 | -h, --help show this help message and exit
130 | --device DEVICE Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). If not provided,
131 | will auto-detect with get_device().
132 | --max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS
133 | Maximum number of new tokens to generate (default: 2048).
134 | --compile Compile PyTorch model (default: False).
135 | --reasoning Use reasoning model variant (default: False).
136 | ```
137 |
138 |
139 |
140 |
141 |
142 | ## chat_multiturn.py
143 |
144 | This function is similar to the one above, except it adds a multi-turn memory so that the LLM remembers the conversation from the past turns. It is highly recommended to use the reasoning variant here as the base model struggles with conversations:
145 |
146 |
147 |
148 | ```bash
149 | uv run ch02/05_use_model/chat_multiturn.py --reasoning
150 | Using Apple Silicon GPU (MPS)
151 | ✓ qwen3/qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth already up-to-date
152 | ✓ qwen3/tokenizer-reasoning.json already up-to-date
153 |
154 | ============================================================
155 | torch : 2.7.1
156 | device : mps
157 | cache : True
158 | compile : False
159 | reasoning : True
160 | memory : True
161 | max_new_tokens (per turn): 2048
162 | context_length: 40960
163 | ============================================================
164 |
165 | Interactive REPL with memory. Type '\exit' or '\quit' to quit.
166 | Commands: \clear (forget memory), \history (show turn count)
167 |
168 | >> What is 1+1 in short?
169 |
170 | ------------------------------------------------------------
171 | [User]
172 | What is 1+1 in short?
173 |
174 | [Model]
175 |
176 | Okay, the user is asking, "What is 1+1 in short?" Let me break this down. First, they want to know the result of adding 1 and 1. In math, 1 plus 1 equals 2. But the question says "in short," which probably means they want a concise answer without the full calculation.
177 |
178 | So, the answer is straightforward. 1+1=2. But maybe they want a more concise way to write it? Like, "2" or "2+2"? But "2" is more direct. Let me check if there's any trick here. Sometimes people might think of 1+1 as something else, but no, it's just two ones.
179 |
180 | I should make sure to present the answer clearly. Since the user is asking in a short form, maybe they just want the number 2. So the final answer is 2.
181 |
182 |
183 | 1+1 equals 2.
184 |
185 | [Stats]
186 | Time: 8.27 sec
187 | 23 tokens/sec
188 | ------------------------------------------------------------
189 | >> What were you just asked?
190 |
191 | ------------------------------------------------------------
192 | [User]
193 | What were you just asked?
194 |
195 | [Model]
196 |
197 | Okay, the user just asked, "What were you just asked?" and I responded with "1+1 equals 2." Now, they're asking again. Let me check if there's any hidden context or if they want more information. Since the previous answer was clear, maybe they want confirmation or a different interpretation. But since the user is asking again, perhaps they want to know if I provided the answer correctly. I should confirm that 1+1 is indeed 2 and that the answer is correct. No further information is needed here. Just a simple confirmation.
198 |
199 | [Stats]
200 | Time: 5.21 sec
201 | 22 tokens/sec
202 | ------------------------------------------------------------
203 | ```
204 |
205 |
206 |
207 | Additional options are listed below:
208 |
209 | ```bash
210 | usage: chat_multiturn.py [-h] [--device DEVICE] [--max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS]
211 | [--compile] [--reasoning]
212 |
213 | Run Qwen3 text generation (interactive REPL)
214 |
215 | options:
216 | -h, --help show this help message and exit
217 | --device DEVICE Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). If not provided,
218 | will auto-detect with get_device().
219 | --max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS
220 | Maximum number of new tokens to generate in each turn (default:
221 | 2048).
222 | --compile Compile PyTorch model (default: False).
223 | --reasoning Use reasoning model variant (default: False).
224 | ```
225 |
226 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/reasoning_from_scratch/ch05.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | from .ch03 import extract_final_candidate, render_prompt
6 | from .ch04 import (
7 | generate_text_stream_concat_flex,
8 | generate_text_top_p_stream_cache
9 | )
10 | import math
11 | import torch
12 |
13 |
14 | def heuristic_score(
15 | answer,
16 | prompt=None, # Placeholder that is ignored
17 | brevity_bonus=500.0,
18 | boxed_bonus=2.0,
19 | extract_bonus=1.0,
20 | fulltext_bonus=0.0,
21 | ):
22 | score = 0.0
23 |
24 | # Reward answers that have a final boxed value
25 | cand = extract_final_candidate(answer, fallback="none")
26 | if cand:
27 | score += boxed_bonus
28 |
29 | # Give weaker rewards if answer doesn't have a boxed value
30 | else:
31 | cand = extract_final_candidate(answer, fallback="number_only")
32 | if cand:
33 | score += extract_bonus
34 | else:
35 | cand = extract_final_candidate(
36 | answer, fallback="number_then_full"
37 | )
38 | if cand:
39 | score += fulltext_bonus
40 |
41 | # Add a brevity reward that decays with text length
42 | score += 1.5 * math.exp(-len(answer) / brevity_bonus)
43 | return score
44 |
45 |
46 | @torch.inference_mode()
47 | def calc_next_token_probas(model, tokenizer, prompt, device):
48 |
49 | token_ids = torch.tensor(tokenizer.encode(prompt), device=device)
50 |
51 | # Get logits and probabilities similar to text generation functions
52 | logits = model(token_ids.unsqueeze(0)).squeeze(0)
53 | all_probas = torch.softmax(logits, dim=-1)
54 |
55 | # Positions we score (here: all)
56 | t_idx = torch.arange(0, token_ids.shape[0] - 1, device=device)
57 |
58 | # Since we have the text, we know the true next tokens
59 | next_ids = token_ids[1:]
60 |
61 | # Get probabilities for each next token
62 | next_token_probas = all_probas[t_idx, next_ids]
63 |
64 | print(
65 | "Next-token probabilities:",
66 | [p.item() for p in next_token_probas]
67 | )
68 |
69 | # Likelihood of the sequence is the product of the probability scores
70 | print(
71 | "Joint probability:",
72 | torch.prod(next_token_probas)
73 | )
74 |
75 |
76 | @torch.inference_mode()
77 | def calc_next_token_logprobas(model, tokenizer, prompt, device):
78 |
79 | token_ids = torch.tensor(tokenizer.encode(prompt), device=device)
80 |
81 | logits = model(token_ids.unsqueeze(0)).squeeze(0)
82 | # We now use log_softmax
83 | all_logprobas = torch.log_softmax(logits, dim=-1)
84 |
85 | t_idx = torch.arange(0, token_ids.shape[0] - 1, device=device)
86 | next_ids = token_ids[1:]
87 | next_token_logprobas = all_logprobas[t_idx, next_ids]
88 |
89 | print(
90 | "Next-token log-probabilities:",
91 | [p.item() for p in next_token_logprobas]
92 | )
93 | # We replace the product with a sum
94 | print(
95 | "Joint log-probability:",
96 | torch.sum(next_token_logprobas)
97 | )
98 |
99 |
100 | @torch.inference_mode()
101 | def avg_logprob_answer(model, tokenizer, prompt, answer, device="cpu"):
102 |
103 | # Encode prompt and answer tokens separately to get the prompt length later
104 | prompt_ids = tokenizer.encode(prompt)
105 | answer_ids = tokenizer.encode(answer)
106 | full_ids = torch.tensor(prompt_ids + answer_ids, device=device)
107 |
108 | # Same as in calc_next_token_logprobas before
109 | logits = model(full_ids.unsqueeze(0)).squeeze(0)
110 | logprobs = torch.log_softmax(logits, dim=-1)
111 |
112 | # Index range for positions corresponding to answer tokens
113 | start = len(prompt_ids) - 1
114 | end = full_ids.shape[0] - 1
115 |
116 | # Same as before, except for using start and end
117 | t_idx = torch.arange(start, end, device=device)
118 | next_tokens = full_ids[start + 1 : end + 1]
119 | next_token_logps = logprobs[t_idx, next_tokens]
120 |
121 | # Average over the answer token scores
122 | return torch.mean(next_token_logps).item()
123 |
124 |
125 | def make_critique_prompt(raw_prompt, draft):
126 | return (
127 | "You are a meticulous reviewer. Identify logical errors, missing "
128 | "steps, or arithmetic mistakes. If the answer seems correct, "
129 | "say so briefly. Then propose a concise plan to fix issues.\n\n"
130 | f"Question:\n{raw_prompt}\n\n"
131 | f"Draft answer:\n{draft}\n\n"
132 | "Write a short critique and bullet-point fix plan "
133 | "(under ~120 words).\n"
134 | "Critique:"
135 | )
136 |
137 |
138 | def make_refine_prompt(raw_prompt, draft, critique):
139 | return (
140 | "Revise the answer using the critique. Keep it concise and "
141 | "end with a final boxed result: \\boxed{ANSWER}\n\n"
142 | f"Question:\n{raw_prompt}\n\n"
143 | f"Previous answer:\n{draft}\n\n"
144 | f"Critique:\n{critique}\n\n"
145 | "Revised answer:"
146 | )
147 |
148 |
149 | def self_refinement_loop(
150 | model,
151 | tokenizer,
152 | raw_prompt,
153 | device,
154 | iterations=2,
155 | max_response_tokens=2048,
156 | max_critique_tokens=256,
157 | score_fn=None,
158 | prompt_renderer=render_prompt,
159 | prompt_suffix="",
160 | verbose=False,
161 | temperature=0.7,
162 | top_p=0.9,
163 | ):
164 | steps = []
165 |
166 | # Initial response (draft)
167 | prompt = prompt_renderer(raw_prompt) + prompt_suffix
168 | current_full = generate_text_stream_concat_flex(
169 | model=model,
170 | tokenizer=tokenizer,
171 | prompt=prompt,
172 | device=device,
173 | max_new_tokens=max_response_tokens,
174 | verbose=False,
175 | generate_func=generate_text_top_p_stream_cache,
176 | temperature=temperature,
177 | top_p=top_p,
178 | )
179 |
180 | current_extracted = extract_final_candidate(
181 | current_full, fallback="number_then_full"
182 | )
183 | if score_fn:
184 | current_score = score_fn(answer=current_full, prompt=prompt)
185 | else:
186 | current_score = 0.0
187 |
188 | # Run for one or more iterations
189 | for it in range(iterations):
190 | draft_before_full = current_full
191 | draft_before_extracted = current_extracted
192 | score_before = current_score
193 |
194 | # Critique the response
195 | critique_prompt = make_critique_prompt(
196 | raw_prompt, draft_before_full
197 | )
198 | critique_full = generate_text_stream_concat_flex(
199 | model=model,
200 | tokenizer=tokenizer,
201 | prompt=critique_prompt,
202 | device=device,
203 | max_new_tokens=max_critique_tokens,
204 | verbose=False,
205 | generate_func=generate_text_top_p_stream_cache,
206 | temperature=temperature,
207 | top_p=top_p,
208 | )
209 |
210 | # Refine the response
211 | refine_prompt = make_refine_prompt(
212 | raw_prompt, draft_before_full, critique_full
213 | )
214 | revised_full = generate_text_stream_concat_flex(
215 | model=model,
216 | tokenizer=tokenizer,
217 | prompt=refine_prompt,
218 | device=device,
219 | max_new_tokens=max_response_tokens,
220 | verbose=False,
221 | generate_func=generate_text_top_p_stream_cache,
222 | temperature=temperature,
223 | top_p=top_p,
224 | )
225 |
226 | revised_extracted = extract_final_candidate(
227 | revised_full, fallback="number_then_full"
228 | )
229 | if score_fn:
230 | revised_score = score_fn(
231 | answer=revised_full, prompt=prompt # Still use original prompt here
232 | )
233 | else:
234 | revised_score = 0.0
235 |
236 | # Log the results
237 | step = {
238 | "iteration": it + 1,
239 | "draft_full": draft_before_full,
240 | "draft_extracted": draft_before_extracted,
241 | "critique": critique_full,
242 | "revised_full": revised_full,
243 | "revised_extracted": revised_extracted,
244 | "score_before": score_before,
245 | "score_after": revised_score,
246 | }
247 | steps.append(step)
248 |
249 | if verbose:
250 | print(
251 | f"[Refinement {it+1}/{iterations}]"
252 | f"\nCurrent: {draft_before_extracted}"
253 | f"\nRevised: {revised_extracted}"
254 | f"\nScore before: {score_before:.3f}"
255 | f"\nScore after: {revised_score:.3f}"
256 | f"\n{'=' * 25}"
257 | )
258 |
259 | # Accept revised response if it's not worse
260 | if revised_score >= current_score:
261 | current_full = revised_full
262 | current_extracted = revised_extracted
263 | current_score = revised_score
264 |
265 | return {
266 | "final_full": current_full,
267 | "final_extracted": current_extracted,
268 | "steps": steps,
269 | }
270 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 | This folder contains standalone example scripts to generate text with the model we loaded in chapter 2 (and exercises):
10 |
11 | - `generate_simple.py`: Generates text similar to the main chapter.
12 | - `chat.py`: Similar to the code above, as an interactive wrapper so that we can prompt the model multiple times without having to reload the model into memory each time.
13 | - `chat_multiturn.py`: Same as above, but with a memory feature to remember the message history.
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 | More usage details are provided in the sections below.
18 |
19 |
20 | ## generate_simple.py
21 |
22 | This simple function loads the model as described in chapter 2 and uses the `generate_text_simple_cache_stream` function from the chapter 2 exercises. You can use the function as follows (replace `uv run` with `python` if you are not using `uv`):
23 |
24 | ```bash
25 | uv run ch02/05_use_model/generate_simple.py
26 | Using Apple Silicon GPU (MPS)
27 | ✓ qwen3/qwen3-0.6B-base.pth already up-to-date
28 |
29 | ============================================================
30 | torch : 2.7.1
31 | device : mps
32 | cache : True
33 | compile : False
34 | reasoning : False
35 | ============================================================
36 |
37 | Large language models are artificial intelligence systems that can understand, generate, and process human language, enabling them to perform a wide range of tasks, from answering questions to writing essays.
38 |
39 | Time: 1.52 sec
40 | 22 tokens/sec
41 | ```
42 |
43 | The function is useful if you want to quickly try out different prompts with the base or reasoning variant. The additional options are listed below:
44 |
45 | ```bash
46 | usage: generate_simple.py [-h] [--device DEVICE]
47 | [--max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS] [--compile]
48 | [--reasoning] [--prompt PROMPT]
49 |
50 | Run Qwen3 text generation
51 |
52 | options:
53 | -h, --help show this help message and exit
54 | --device DEVICE Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). If not
55 | provided, will auto-detect with get_device().
56 | --max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS
57 | Maximum number of new tokens to generate (default:
58 | 2048).
59 | --compile Compile PyTorch model (default: False).
60 | --reasoning Use reasoning model variant (default: False).
61 | --prompt PROMPT Use a custom prompt. If not explicitly provided, uses
62 | the following defaults: 'Explain large language models
63 | in a single sentence.' for the base model, and 'Find
64 | all c in Z_3 such that Z_3[x]/(x^2 + c) is a field.'
65 | for the reasoning model.
66 | ```
67 |
68 |
69 | ## chat.py
70 |
71 | Similar to the function above, this function is useful to try different prompts on the base and reasoning models.
72 |
73 | However, in contrast to the previous function, this function keeps the user in an interactive mode so that the model doesn't have to be reloaded each time:
74 |
75 | ```bash
76 | uv run ch02/05_use_model/chat.py
77 | Using Apple Silicon GPU (MPS)
78 | ✓ qwen3/qwen3-0.6B-base.pth already up-to-date
79 |
80 | ============================================================
81 | torch : 2.7.1
82 | device : mps
83 | cache : True
84 | compile : False
85 | reasoning : False
86 | memory : False
87 | ============================================================
88 |
89 | Interactive REPL (no memory). Type '\exit' or '\quit' to quit.
90 |
91 | >> Explain language models in 1 sentence
92 |
93 | ------------------------------------------------------------
94 | [User]
95 | Explain language models in 1 sentence
96 |
97 | [Model]
98 |
99 | Language models are algorithms that analyze and predict the likelihood of future words in a text based on the words already seen, enabling them to generate coherent and contextually relevant text.
100 |
101 | [Stats]
102 | Time: 1.53 sec
103 | 22 tokens/sec
104 | ------------------------------------------------------------
105 | >> Explain machine learning in 1 sentence.
106 |
107 | ------------------------------------------------------------
108 | [User]
109 | Explain machine learning in 1 sentence.
110 |
111 | [Model]
112 | Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that enables computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed.
113 |
114 | [Stats]
115 | Time: 1.04 sec
116 | 24 tokens/sec
117 | ------------------------------------------------------------
118 | ```
119 |
120 | Additional options are listed below:
121 |
122 | ```bash
123 | usage: chat.py [-h] [--device DEVICE] [--max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS] [--compile]
124 | [--reasoning]
125 |
126 | Run Qwen3 text generation (interactive REPL)
127 |
128 | options:
129 | -h, --help show this help message and exit
130 | --device DEVICE Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). If not provided,
131 | will auto-detect with get_device().
132 | --max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS
133 | Maximum number of new tokens to generate (default: 2048).
134 | --compile Compile PyTorch model (default: False).
135 | --reasoning Use reasoning model variant (default: False).
136 | ```
137 |
138 |
139 |
140 |
141 |
142 | ## chat_multiturn.py
143 |
144 | This function is similar to the one above, except it adds a multi-turn memory so that the LLM remembers the conversation from the past turns. It is highly recommended to use the reasoning variant here as the base model struggles with conversations:
145 |
146 |
147 |
148 | ```bash
149 | uv run ch02/05_use_model/chat_multiturn.py --reasoning
150 | Using Apple Silicon GPU (MPS)
151 | ✓ qwen3/qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth already up-to-date
152 | ✓ qwen3/tokenizer-reasoning.json already up-to-date
153 |
154 | ============================================================
155 | torch : 2.7.1
156 | device : mps
157 | cache : True
158 | compile : False
159 | reasoning : True
160 | memory : True
161 | max_new_tokens (per turn): 2048
162 | context_length: 40960
163 | ============================================================
164 |
165 | Interactive REPL with memory. Type '\exit' or '\quit' to quit.
166 | Commands: \clear (forget memory), \history (show turn count)
167 |
168 | >> What is 1+1 in short?
169 |
170 | ------------------------------------------------------------
171 | [User]
172 | What is 1+1 in short?
173 |
174 | [Model]
175 |
176 | Okay, the user is asking, "What is 1+1 in short?" Let me break this down. First, they want to know the result of adding 1 and 1. In math, 1 plus 1 equals 2. But the question says "in short," which probably means they want a concise answer without the full calculation.
177 |
178 | So, the answer is straightforward. 1+1=2. But maybe they want a more concise way to write it? Like, "2" or "2+2"? But "2" is more direct. Let me check if there's any trick here. Sometimes people might think of 1+1 as something else, but no, it's just two ones.
179 |
180 | I should make sure to present the answer clearly. Since the user is asking in a short form, maybe they just want the number 2. So the final answer is 2.
181 |
182 |
183 | 1+1 equals 2.
184 |
185 | [Stats]
186 | Time: 8.27 sec
187 | 23 tokens/sec
188 | ------------------------------------------------------------
189 | >> What were you just asked?
190 |
191 | ------------------------------------------------------------
192 | [User]
193 | What were you just asked?
194 |
195 | [Model]
196 |
197 | Okay, the user just asked, "What were you just asked?" and I responded with "1+1 equals 2." Now, they're asking again. Let me check if there's any hidden context or if they want more information. Since the previous answer was clear, maybe they want confirmation or a different interpretation. But since the user is asking again, perhaps they want to know if I provided the answer correctly. I should confirm that 1+1 is indeed 2 and that the answer is correct. No further information is needed here. Just a simple confirmation.
198 |
199 | [Stats]
200 | Time: 5.21 sec
201 | 22 tokens/sec
202 | ------------------------------------------------------------
203 | ```
204 |
205 |
206 |
207 | Additional options are listed below:
208 |
209 | ```bash
210 | usage: chat_multiturn.py [-h] [--device DEVICE] [--max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS]
211 | [--compile] [--reasoning]
212 |
213 | Run Qwen3 text generation (interactive REPL)
214 |
215 | options:
216 | -h, --help show this help message and exit
217 | --device DEVICE Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). If not provided,
218 | will auto-detect with get_device().
219 | --max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS
220 | Maximum number of new tokens to generate in each turn (default:
221 | 2048).
222 | --compile Compile PyTorch model (default: False).
223 | --reasoning Use reasoning model variant (default: False).
224 | ```
225 |
226 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/reasoning_from_scratch/ch05.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | from .ch03 import extract_final_candidate, render_prompt
6 | from .ch04 import (
7 | generate_text_stream_concat_flex,
8 | generate_text_top_p_stream_cache
9 | )
10 | import math
11 | import torch
12 |
13 |
14 | def heuristic_score(
15 | answer,
16 | prompt=None, # Placeholder that is ignored
17 | brevity_bonus=500.0,
18 | boxed_bonus=2.0,
19 | extract_bonus=1.0,
20 | fulltext_bonus=0.0,
21 | ):
22 | score = 0.0
23 |
24 | # Reward answers that have a final boxed value
25 | cand = extract_final_candidate(answer, fallback="none")
26 | if cand:
27 | score += boxed_bonus
28 |
29 | # Give weaker rewards if answer doesn't have a boxed value
30 | else:
31 | cand = extract_final_candidate(answer, fallback="number_only")
32 | if cand:
33 | score += extract_bonus
34 | else:
35 | cand = extract_final_candidate(
36 | answer, fallback="number_then_full"
37 | )
38 | if cand:
39 | score += fulltext_bonus
40 |
41 | # Add a brevity reward that decays with text length
42 | score += 1.5 * math.exp(-len(answer) / brevity_bonus)
43 | return score
44 |
45 |
46 | @torch.inference_mode()
47 | def calc_next_token_probas(model, tokenizer, prompt, device):
48 |
49 | token_ids = torch.tensor(tokenizer.encode(prompt), device=device)
50 |
51 | # Get logits and probabilities similar to text generation functions
52 | logits = model(token_ids.unsqueeze(0)).squeeze(0)
53 | all_probas = torch.softmax(logits, dim=-1)
54 |
55 | # Positions we score (here: all)
56 | t_idx = torch.arange(0, token_ids.shape[0] - 1, device=device)
57 |
58 | # Since we have the text, we know the true next tokens
59 | next_ids = token_ids[1:]
60 |
61 | # Get probabilities for each next token
62 | next_token_probas = all_probas[t_idx, next_ids]
63 |
64 | print(
65 | "Next-token probabilities:",
66 | [p.item() for p in next_token_probas]
67 | )
68 |
69 | # Likelihood of the sequence is the product of the probability scores
70 | print(
71 | "Joint probability:",
72 | torch.prod(next_token_probas)
73 | )
74 |
75 |
76 | @torch.inference_mode()
77 | def calc_next_token_logprobas(model, tokenizer, prompt, device):
78 |
79 | token_ids = torch.tensor(tokenizer.encode(prompt), device=device)
80 |
81 | logits = model(token_ids.unsqueeze(0)).squeeze(0)
82 | # We now use log_softmax
83 | all_logprobas = torch.log_softmax(logits, dim=-1)
84 |
85 | t_idx = torch.arange(0, token_ids.shape[0] - 1, device=device)
86 | next_ids = token_ids[1:]
87 | next_token_logprobas = all_logprobas[t_idx, next_ids]
88 |
89 | print(
90 | "Next-token log-probabilities:",
91 | [p.item() for p in next_token_logprobas]
92 | )
93 | # We replace the product with a sum
94 | print(
95 | "Joint log-probability:",
96 | torch.sum(next_token_logprobas)
97 | )
98 |
99 |
100 | @torch.inference_mode()
101 | def avg_logprob_answer(model, tokenizer, prompt, answer, device="cpu"):
102 |
103 | # Encode prompt and answer tokens separately to get the prompt length later
104 | prompt_ids = tokenizer.encode(prompt)
105 | answer_ids = tokenizer.encode(answer)
106 | full_ids = torch.tensor(prompt_ids + answer_ids, device=device)
107 |
108 | # Same as in calc_next_token_logprobas before
109 | logits = model(full_ids.unsqueeze(0)).squeeze(0)
110 | logprobs = torch.log_softmax(logits, dim=-1)
111 |
112 | # Index range for positions corresponding to answer tokens
113 | start = len(prompt_ids) - 1
114 | end = full_ids.shape[0] - 1
115 |
116 | # Same as before, except for using start and end
117 | t_idx = torch.arange(start, end, device=device)
118 | next_tokens = full_ids[start + 1 : end + 1]
119 | next_token_logps = logprobs[t_idx, next_tokens]
120 |
121 | # Average over the answer token scores
122 | return torch.mean(next_token_logps).item()
123 |
124 |
125 | def make_critique_prompt(raw_prompt, draft):
126 | return (
127 | "You are a meticulous reviewer. Identify logical errors, missing "
128 | "steps, or arithmetic mistakes. If the answer seems correct, "
129 | "say so briefly. Then propose a concise plan to fix issues.\n\n"
130 | f"Question:\n{raw_prompt}\n\n"
131 | f"Draft answer:\n{draft}\n\n"
132 | "Write a short critique and bullet-point fix plan "
133 | "(under ~120 words).\n"
134 | "Critique:"
135 | )
136 |
137 |
138 | def make_refine_prompt(raw_prompt, draft, critique):
139 | return (
140 | "Revise the answer using the critique. Keep it concise and "
141 | "end with a final boxed result: \\boxed{ANSWER}\n\n"
142 | f"Question:\n{raw_prompt}\n\n"
143 | f"Previous answer:\n{draft}\n\n"
144 | f"Critique:\n{critique}\n\n"
145 | "Revised answer:"
146 | )
147 |
148 |
149 | def self_refinement_loop(
150 | model,
151 | tokenizer,
152 | raw_prompt,
153 | device,
154 | iterations=2,
155 | max_response_tokens=2048,
156 | max_critique_tokens=256,
157 | score_fn=None,
158 | prompt_renderer=render_prompt,
159 | prompt_suffix="",
160 | verbose=False,
161 | temperature=0.7,
162 | top_p=0.9,
163 | ):
164 | steps = []
165 |
166 | # Initial response (draft)
167 | prompt = prompt_renderer(raw_prompt) + prompt_suffix
168 | current_full = generate_text_stream_concat_flex(
169 | model=model,
170 | tokenizer=tokenizer,
171 | prompt=prompt,
172 | device=device,
173 | max_new_tokens=max_response_tokens,
174 | verbose=False,
175 | generate_func=generate_text_top_p_stream_cache,
176 | temperature=temperature,
177 | top_p=top_p,
178 | )
179 |
180 | current_extracted = extract_final_candidate(
181 | current_full, fallback="number_then_full"
182 | )
183 | if score_fn:
184 | current_score = score_fn(answer=current_full, prompt=prompt)
185 | else:
186 | current_score = 0.0
187 |
188 | # Run for one or more iterations
189 | for it in range(iterations):
190 | draft_before_full = current_full
191 | draft_before_extracted = current_extracted
192 | score_before = current_score
193 |
194 | # Critique the response
195 | critique_prompt = make_critique_prompt(
196 | raw_prompt, draft_before_full
197 | )
198 | critique_full = generate_text_stream_concat_flex(
199 | model=model,
200 | tokenizer=tokenizer,
201 | prompt=critique_prompt,
202 | device=device,
203 | max_new_tokens=max_critique_tokens,
204 | verbose=False,
205 | generate_func=generate_text_top_p_stream_cache,
206 | temperature=temperature,
207 | top_p=top_p,
208 | )
209 |
210 | # Refine the response
211 | refine_prompt = make_refine_prompt(
212 | raw_prompt, draft_before_full, critique_full
213 | )
214 | revised_full = generate_text_stream_concat_flex(
215 | model=model,
216 | tokenizer=tokenizer,
217 | prompt=refine_prompt,
218 | device=device,
219 | max_new_tokens=max_response_tokens,
220 | verbose=False,
221 | generate_func=generate_text_top_p_stream_cache,
222 | temperature=temperature,
223 | top_p=top_p,
224 | )
225 |
226 | revised_extracted = extract_final_candidate(
227 | revised_full, fallback="number_then_full"
228 | )
229 | if score_fn:
230 | revised_score = score_fn(
231 | answer=revised_full, prompt=prompt # Still use original prompt here
232 | )
233 | else:
234 | revised_score = 0.0
235 |
236 | # Log the results
237 | step = {
238 | "iteration": it + 1,
239 | "draft_full": draft_before_full,
240 | "draft_extracted": draft_before_extracted,
241 | "critique": critique_full,
242 | "revised_full": revised_full,
243 | "revised_extracted": revised_extracted,
244 | "score_before": score_before,
245 | "score_after": revised_score,
246 | }
247 | steps.append(step)
248 |
249 | if verbose:
250 | print(
251 | f"[Refinement {it+1}/{iterations}]"
252 | f"\nCurrent: {draft_before_extracted}"
253 | f"\nRevised: {revised_extracted}"
254 | f"\nScore before: {score_before:.3f}"
255 | f"\nScore after: {revised_score:.3f}"
256 | f"\n{'=' * 25}"
257 | )
258 |
259 | # Accept revised response if it's not worse
260 | if revised_score >= current_score:
261 | current_full = revised_full
262 | current_extracted = revised_extracted
263 | current_score = revised_score
264 |
265 | return {
266 | "final_full": current_full,
267 | "final_extracted": current_extracted,
268 | "steps": steps,
269 | }
270 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 33 |
34 |
35 |
36 | The table below compares this approach (row 3) with the baselines from chapter 3:
37 |
38 | | | Method | Model | Accuracy | Time |
39 | |----|----------------------------------------------|-----------|----------|------------|
40 | | 1 | Baseline (chapter 3), greedy decoding | Base | 15.2% | 10.1 min |
41 | | 2 | Baseline (chapter 3), greedy decoding | Reasoning | 48.2% | 182.1 min |
42 | | 3 | Chain-of-thought prompting ("CoT") | Base | 40.6% | 84.5 min |
43 |
44 | The accuracy values and runtimes shown in the table were computed on all 500 samples in the MATH-500 test set using a "cuda" GPU (DGX Spark).
45 |
46 | To run the experiment in row one, use:
47 |
48 | ```bash
49 | python cot_prompting_math500.py \
50 | --which_model "base" \
51 | --dataset_size 500
52 | ```
53 |
54 | Or, with `uv:`
55 |
56 |
57 | ```bash
58 | uv run cot_prompting_math500.py \
59 | --which_model "base" \
60 | --dataset_size 500
61 | ```
62 |
63 | For additional options, use the `--help` flag.
64 |
65 |
66 |
67 |
68 | ## Self-consistency sampling
69 |
70 | The [`self_consistency_math500.py`](self_consistency_math500.py) script implements the sampling method from chapter 4.
71 |
72 | (Optionally, there is a [`self_consistency_math500_batched.py`](self_consistency_math500_batched.py) variant, which executes all `--num_samples` as a batch for faster processing. Note that this requires more compute memory though.)
73 |
74 |
75 |
76 |
33 |
34 |
35 |
36 | The table below compares this approach (row 3) with the baselines from chapter 3:
37 |
38 | | | Method | Model | Accuracy | Time |
39 | |----|----------------------------------------------|-----------|----------|------------|
40 | | 1 | Baseline (chapter 3), greedy decoding | Base | 15.2% | 10.1 min |
41 | | 2 | Baseline (chapter 3), greedy decoding | Reasoning | 48.2% | 182.1 min |
42 | | 3 | Chain-of-thought prompting ("CoT") | Base | 40.6% | 84.5 min |
43 |
44 | The accuracy values and runtimes shown in the table were computed on all 500 samples in the MATH-500 test set using a "cuda" GPU (DGX Spark).
45 |
46 | To run the experiment in row one, use:
47 |
48 | ```bash
49 | python cot_prompting_math500.py \
50 | --which_model "base" \
51 | --dataset_size 500
52 | ```
53 |
54 | Or, with `uv:`
55 |
56 |
57 | ```bash
58 | uv run cot_prompting_math500.py \
59 | --which_model "base" \
60 | --dataset_size 500
61 | ```
62 |
63 | For additional options, use the `--help` flag.
64 |
65 |
66 |
67 |
68 | ## Self-consistency sampling
69 |
70 | The [`self_consistency_math500.py`](self_consistency_math500.py) script implements the sampling method from chapter 4.
71 |
72 | (Optionally, there is a [`self_consistency_math500_batched.py`](self_consistency_math500_batched.py) variant, which executes all `--num_samples` as a batch for faster processing. Note that this requires more compute memory though.)
73 |
74 |
75 |
76 |  77 |
78 |
79 |
80 | The table below compares this approach (row 4-12) with the baselines from chapter 3 (rows 1-2):
81 |
82 | | | Method | Model | Accuracy | Time |
83 | | ---- | ----------------------------------------- | --------- | -------- | --------- |
84 | | 1 | Baseline (chapter 3), greedy decoding | Base | 15.2% | 10.1 min |
85 | | 2 | Baseline (chapter 3), greedy decoding | Reasoning | 48.2% | 182.1 min |
86 | | 3 | Chain-of-thought prompting ("CoT") | Base | 40.6% | 84.5 min |
87 | | 4 | Temperature and top-p ("Top-p") | Base | 17.8% | 30.7 min |
88 | | 5 | "Top-p" + Self-consistency (n=3) | Base | 29.6% | 97.6 min |
89 | | 6 | "Top-p" + Self-consistency (n=5) | Base | 27.8% | 116.8 min |
90 | | 7 | "Top-p" + Self-consistency (n=10) | Base | 31.6% | 300.4 min |
91 | | 8 | "Top-p" + "CoT" | Base | 33.4% | 129.2 min |
92 | | 9 | Self-consistency (n=3) + "Top-p" + "CoT" | Base | 42.2% | 211.6 min |
93 | | 10 | Self-consistency (n=5) + "Top-p" + "CoT" | Base | 48.0% | 452.9 min |
94 | | 11 | Self-consistency (n=10) + "Top-p" + "CoT" | Base | 52.0% | 862.6 min |
95 | | 12 | Self-consistency (n=3) + "Top-p" + "CoT" | Reasoning | 55.2% | 544.4 min |
96 |
97 | The accuracy values and runtimes shown in the table were computed on all 500 samples in the MATH-500 test set using a "cuda" GPU (DGX Spark).
98 |
99 | The following codes give instructions on how to run the self-consistency experiments in rows 4-12 (replace `uv run` with `python` if you are not a `uv` user).
100 |
101 | **Row 4:**
102 |
103 | ```bash
104 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
105 | --which_model "base" \
106 | --temperature 0.9 \
107 | --top_p 0.9 \
108 | --num_samples 1 \
109 | --dataset_size 500
110 | ```
111 |
112 | **Row 5:**
113 |
114 | ```bash
115 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
116 | --which_model "base" \
117 | --temperature 0.9 \
118 | --top_p 0.9 \
119 | --num_samples 3 \
120 | --dataset_size 500
121 | ```
122 |
123 | **Row 6:**
124 |
125 | ```bash
126 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
127 | --which_model "base" \
128 | --temperature 0.9 \
129 | --top_p 0.9 \
130 | --num_samples 5 \
131 | --dataset_size 500
132 | ```
133 |
134 | **Row 7:**
135 |
136 | ```bash
137 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
138 | --which_model "base" \
139 | --temperature 0.9 \
140 | --top_p 0.9 \
141 | --num_samples 10 \
142 | --dataset_size 500
143 | ```
144 |
145 | **Row 8:**
146 |
147 | ```bash
148 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
149 | --which_model "base" \
150 | --temperature 0.9 \
151 | --top_p 0.9 \
152 | --num_samples 1 \
153 | --dataset_size 500 \
154 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
155 | ```
156 |
157 | **Row 9:**
158 |
159 | ```bash
160 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
161 | --which_model "base" \
162 | --temperature 0.9 \
163 | --top_p 0.9 \
164 | --num_samples 3 \
165 | --dataset_size 500 \
166 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
167 | ```
168 |
169 | **Row 10:**
170 |
171 | ```bash
172 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
173 | --which_model "base" \
174 | --temperature 0.9 \
175 | --top_p 0.9 \
176 | --num_samples 5 \
177 | --dataset_size 500 \
178 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
179 | ```
180 |
181 | **Row 11:**
182 |
183 | ```bash
184 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
185 | --which_model "base" \
186 | --temperature 0.9 \
187 | --top_p 0.9 \
188 | --num_samples 10 \
189 | --dataset_size 500 \
190 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
191 | ```
192 |
193 | **Row 12:**
194 |
195 | ```bash
196 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
197 | --which_model "reasoning" \
198 | --temperature 0.9 \
199 | --top_p 0.9 \
200 | --num_samples 3 \
201 | --dataset_size 500 \
202 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
203 | ```
204 |
205 |
206 | For additional options, use the `--help` flag.
207 |
208 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_qwen3_batched_stop.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import os
6 | import torch
7 | import pytest
8 | from pathlib import Path
9 |
10 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import get_device
11 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
12 | download_qwen3_small,
13 | Qwen3Tokenizer,
14 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B,
15 | )
16 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3_batched import (
17 | generate_text_basic_batched_cache,
18 | generate_text_basic_batched_cache_stop,
19 | generate_text_basic_batched_stream_cache,
20 | generate_text_basic_batched_stream_cache_stop,
21 | Qwen3Model as Qwen3ModelBatched,
22 | )
23 |
24 | skip_expensive = os.environ.get("SKIP_EXPENSIVE", "0") == "1"
25 |
26 | # Make CI more reproducible & robust
27 | os.environ["MKL_NUM_THREADS"] = "1"
28 | os.environ["OMP_NUM_THREADS"] = "1"
29 | torch.backends.mkldnn.enabled = False
30 | torch.set_num_threads(1)
31 | torch.use_deterministic_algorithms(True)
32 |
33 |
34 | @pytest.mark.skipif(skip_expensive, reason="Skipping expensive test on CI")
35 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("reasoning", [False, True])
36 | def test_batched_vs_batched_stop_equivalence(reasoning):
37 |
38 | device = get_device()
39 |
40 | # Download and init tokenizer
41 | kind = "reasoning" if reasoning else "base"
42 | download_qwen3_small(kind=kind, tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
43 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / (
44 | "tokenizer-reasoning.json" if reasoning else "tokenizer-base.json"
45 | )
46 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / (
47 | "qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth" if reasoning else "qwen3-0.6B-base.pth"
48 | )
49 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
50 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
51 | apply_chat_template=reasoning,
52 | add_generation_prompt=reasoning,
53 | add_thinking=reasoning,
54 | )
55 |
56 | # Model
57 | model_batched = Qwen3ModelBatched(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
58 | model_batched.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path, map_location=device))
59 | model_batched.to(device).eval()
60 |
61 | # Prompts
62 | prompts = [
63 | "Explain large language models in two sentences.",
64 | "Explain large language models in one sentence.",
65 | "1+1?",
66 | ]
67 |
68 | # Batched inputs (left-padded)
69 | tokenized = [tokenizer.encode(p) for p in prompts]
70 | max_len = max(len(t) for t in tokenized)
71 | pad_id = tokenizer.pad_token_id
72 | left_padded = [[pad_id] * (max_len - len(t)) + t for t in tokenized]
73 | attn_mask = [
74 | [0] * (max_len - len(t)) + [1] * len(t) for t in tokenized
75 | ]
76 | input_ids_batched = torch.tensor(left_padded, device=device)
77 | attn_mask_batched = torch.tensor(attn_mask, device=device, dtype=torch.bool)
78 |
79 | # Generation
80 | max_new_tokens = 12
81 | outputs_reg = generate_text_basic_batched_cache(
82 | model=model_batched,
83 | token_ids=input_ids_batched,
84 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
85 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
86 | attn_mask=attn_mask_batched,
87 | pad_id=pad_id,
88 | )
89 | outputs_stop = generate_text_basic_batched_cache_stop(
90 | model=model_batched,
91 | token_ids=input_ids_batched,
92 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
93 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
94 | attn_mask=attn_mask_batched,
95 | pad_id=pad_id,
96 | )
97 |
98 | # Check equivalency
99 | for idx in range(len(prompts)):
100 | reg_toks = outputs_reg[idx].tolist()
101 | stop_toks = outputs_stop[idx].tolist()
102 | assert reg_toks == stop_toks, (
103 | f"Token mismatch at prompt {idx}:\n"
104 | f"regular_tokens={reg_toks}\n"
105 | f"stop_tokens ={stop_toks}\n"
106 | f"regular_text={tokenizer.decode(reg_toks)}\n"
107 | f"stop_text ={tokenizer.decode(stop_toks)}"
108 | )
109 |
110 |
111 | @pytest.mark.skipif(skip_expensive, reason="Skipping expensive test on CI")
112 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("reasoning", [False, True])
113 | def test_stream_vs_stream_stop_equivalence(reasoning):
114 |
115 | device = get_device()
116 |
117 | # Download and init tokenizer
118 | kind = "reasoning" if reasoning else "base"
119 | download_qwen3_small(kind=kind, tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
120 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / (
121 | "tokenizer-reasoning.json" if reasoning else "tokenizer-base.json"
122 | )
123 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / (
124 | "qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth" if reasoning else "qwen3-0.6B-base.pth"
125 | )
126 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
127 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
128 | apply_chat_template=reasoning,
129 | add_generation_prompt=reasoning,
130 | add_thinking=reasoning,
131 | )
132 |
133 | # Model
134 | model_batched = Qwen3ModelBatched(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
135 | model_batched.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path, map_location=device))
136 | model_batched.to(device).eval()
137 |
138 | # Prompts
139 | prompts = [
140 | "Explain large language models in two sentences.",
141 | "Explain large language models in one sentence.",
142 | "1+1?",
143 | ]
144 |
145 | # Batched inputs (left-padded)
146 | tokenized = [tokenizer.encode(p) for p in prompts]
147 | max_len = max(len(t) for t in tokenized)
148 | pad_id = tokenizer.pad_token_id
149 | left_padded = [[pad_id] * (max_len - len(t)) + t for t in tokenized]
150 | attn_mask = [
151 | [0] * (max_len - len(t)) + [1] * len(t) for t in tokenized
152 | ]
153 | input_ids_batched = torch.tensor(left_padded, device=device)
154 | attn_mask_batched = torch.tensor(attn_mask, device=device, dtype=torch.bool)
155 |
156 | # Generation
157 | max_new_tokens = 12
158 | B = input_ids_batched.size(0)
159 |
160 | # Regular streaming
161 | reg_stream_tokens = [[] for _ in range(B)]
162 | for step_tokens in generate_text_basic_batched_stream_cache(
163 | model=model_batched,
164 | token_ids=input_ids_batched,
165 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
166 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
167 | attn_mask=attn_mask_batched,
168 | pad_id=pad_id,
169 | ):
170 | step_tokens = step_tokens.squeeze(1)
171 | for b in range(B):
172 | reg_stream_tokens[b].append(int(step_tokens[b].item()))
173 |
174 | # Stop streaming
175 | stop_stream_tokens = [[] for _ in range(B)]
176 | for step_tokens in generate_text_basic_batched_stream_cache_stop(
177 | model=model_batched,
178 | token_ids=input_ids_batched,
179 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
180 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
181 | attn_mask=attn_mask_batched,
182 | pad_id=pad_id,
183 | ):
184 | step_tokens = step_tokens.squeeze(1)
185 | for b in range(B):
186 | stop_stream_tokens[b].append(int(step_tokens[b].item()))
187 |
188 | # Check equivalency
189 | for idx in range(B):
190 | assert reg_stream_tokens[idx] == stop_stream_tokens[idx], (
191 | f"Token mismatch at prompt {idx}:\n"
192 | f"regular_tokens={reg_stream_tokens[idx]}\n"
193 | f"stop_tokens ={stop_stream_tokens[idx]}\n"
194 | f"regular_text={tokenizer.decode(reg_stream_tokens[idx])}\n"
195 | f"stop_text ={tokenizer.decode(stop_stream_tokens[idx])}"
196 | )
197 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/05_use_model/chat_multiturn.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | # Runs the model similar to chapter 2 and 3 in streaming mode with the least
6 | # amount of bells and whistles. Uses KV caching by default.
7 | # Interactive REPL (Read, Evaluate, Print, Loop) with multiturn memory.
8 |
9 | import argparse
10 | from pathlib import Path
11 | import time
12 | import torch
13 |
14 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
15 | get_device,
16 | generate_stats
17 | )
18 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02_ex import (
19 | generate_text_basic_stream_cache
20 | )
21 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
22 | download_qwen3_small,
23 | Qwen3Model,
24 | Qwen3Tokenizer,
25 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B
26 | )
27 |
28 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Run Qwen3 text generation (interactive REPL)")
29 | parser.add_argument(
30 | "--device",
31 | type=str,
32 | default=None,
33 | help="Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). "
34 | "If not provided, will auto-detect with get_device()."
35 | )
36 | parser.add_argument(
37 | "--max_new_tokens",
38 | type=int,
39 | default=2048,
40 | help="Maximum number of new tokens to generate in each turn (default: 2048)."
41 | )
42 | parser.add_argument(
43 | "--compile",
44 | action="store_true",
45 | help="Compile PyTorch model (default: False)."
46 | )
47 | parser.add_argument(
48 | "--reasoning",
49 | action="store_true",
50 | help="Use reasoning model variant (default: False)."
51 | )
52 |
53 | args = parser.parse_args()
54 | device = torch.device(args.device) if args.device else get_device()
55 |
56 | if args.reasoning:
57 | download_qwen3_small(kind="reasoning", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
58 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-reasoning.json"
59 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth"
60 | else:
61 | download_qwen3_small(kind="base", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
62 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-base.json"
63 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-base.pth"
64 |
65 | # We will apply the chat template manually later
66 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
67 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
68 | apply_chat_template=False
69 | )
70 |
71 | model = Qwen3Model(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
72 | state = torch.load(model_path, map_location=device)
73 | model.load_state_dict(state)
74 | model.to(device)
75 | model.eval()
76 |
77 | if args.compile:
78 | model = torch.compile(model)
79 |
80 | # The reasoning model may emit <|im_end|>; base may emit <|endoftext|>.
81 | EOS_TOKEN_IDS = (
82 | tokenizer.encode("<|im_end|>")[0],
83 | tokenizer.encode("<|endoftext|>")[0]
84 | )
85 |
86 | print()
87 | print("=" * 60)
88 | print(f"torch : {torch.__version__}")
89 | print(f"device : {device}")
90 | print("cache : True")
91 | print(f"compile : {args.compile}")
92 | print(f"reasoning : {args.reasoning}")
93 | print("memory : True")
94 | print(f"max_new_tokens (per turn): {args.max_new_tokens}")
95 | print(f"context_length: {model.cfg['context_length']}")
96 | print("=" * 60)
97 | print()
98 | print("Interactive REPL with memory. Type '\\exit' or '\\quit' to quit.")
99 | print("Commands: \\clear (forget memory), \\history (show turn count)\n")
100 |
101 | # Multi-turn memory as a list of role-content dicts
102 | # Example: {"role": "system"|"user"|"assistant", "content": str}
103 | history = [
104 | {"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."}
105 | ]
106 |
107 |
108 | def build_prompt_from_history(history, add_assistant_header=True):
109 | """
110 | history: [{"role": "system"|"user"|"assistant", "content": str}, ...]
111 | """
112 | parts = []
113 | for m in history:
114 | role = m["role"]
115 | content = m["content"]
116 | parts.append(f"<|im_start|>{role}\n{content}<|im_end|>\n")
117 |
118 | if add_assistant_header:
119 | parts.append("<|im_start|>assistant\n")
120 | return "".join(parts)
121 |
122 |
123 | def trim_input_tensor(input_ids_tensor, context_len, max_new_tokens):
124 | assert max_new_tokens < context_len
125 | keep_len = max(1, context_len - max_new_tokens)
126 |
127 | # If the prompt is too long, left-truncate to keep_len
128 | if input_ids_tensor.shape[1] > keep_len:
129 | input_ids_tensor = input_ids_tensor[:, -keep_len:]
130 |
131 | return input_ids_tensor
132 |
133 |
134 | def run_generate(user_text):
135 | # Add user prompt to history
136 | history.append({"role": "user", "content": user_text})
137 |
138 | # Encode full history
139 | prompt = build_prompt_from_history(history, add_assistant_header=True)
140 | input_ids = tokenizer.encode(prompt)
141 | input_token_ids_tensor = torch.tensor(input_ids, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
142 |
143 | # Left-tuncate (to make space for generation)
144 | input_token_ids_tensor = trim_input_tensor(
145 | input_ids_tensor=input_token_ids_tensor,
146 | context_len=model.cfg["context_length"],
147 | max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens
148 | )
149 |
150 | start_time = time.time()
151 | all_token_ids = []
152 |
153 | print("[Model]\n", end="", flush=True)
154 | for tok in generate_text_basic_stream_cache(
155 | model=model,
156 | token_ids=input_token_ids_tensor,
157 | max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens,
158 | # eos_token_id=TOKENIZER.eos_token_id
159 | ):
160 | token_id = tok.squeeze(0)
161 | if token_id in EOS_TOKEN_IDS: # Manually break at stop tokens
162 | break
163 | piece = tokenizer.decode(token_id.tolist())
164 | print(piece, end="", flush=True)
165 | all_token_ids.append(token_id.item())
166 |
167 | end_time = time.time()
168 | print("\n")
169 |
170 | print("[Stats]")
171 | generate_stats(
172 | torch.tensor(all_token_ids),
173 | tokenizer,
174 | start_time,
175 | end_time,
176 | print_tokens=False
177 | )
178 | print("-" * 60)
179 |
180 | # Add model reply to history
181 | assistant_text = tokenizer.decode(all_token_ids)
182 | history.append({"role": "assistant", "content": assistant_text})
183 | return assistant_text
184 |
185 |
186 | # Interactive REPL (Read, Evaluate, Print, Loop)
187 | try:
188 | while True:
189 | try:
190 | user_in = input(">> ").strip()
191 | except EOFError:
192 | print("")
193 | break
194 |
195 | low = user_in.lower()
196 | if low in {r"\exit", r"\quit"}:
197 | break
198 | if low == r"\clear":
199 | # Reset history but keep the system prompt
200 | system_entries = [m for m in history if m["role"] == "system"]
201 | history.clear()
202 | if system_entries:
203 | history.extend(system_entries)
204 | else:
205 | history.append({"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."})
206 | print("(memory cleared)\n")
207 | continue
208 | if low == r"\history":
209 | # Count assistant turns as the number of model replies so far
210 | assistant_turns = sum(1 for m in history if m["role"] == "assistant")
211 | print(f"(stored turns: {assistant_turns})\n")
212 | continue
213 | if not user_in:
214 | continue
215 |
216 | print("\n" + "-" * 60)
217 | print("[User]")
218 | print(user_in + "\n")
219 | run_generate(user_in)
220 |
221 | except KeyboardInterrupt:
222 | print("\nInterrupted by user.")
223 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/03_optimized-LLM/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Optimized Qwen3
2 |
3 | The Qwen3 from-scratch implementation used in this book strikes a balance between being efficient (both on CPU and GPU) and lean while remaining easy to read by a human.
4 |
5 | As an alternative, you can use the optional `Qwen3Model` drop-in replacement, which is slightly more GPU-efficient. The optimized version in [`qwen3_optimized.py`](../../reasoning_from_scratch/qwen3_optimized.py) (discussed further in Appendix C) differs from the baseline implementation in [`qwen3.py`](../../reasoning_from_scratch/qwen3.py) in two key ways:
6 |
7 | - It implements attention using PyTorch’s built-in `torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product` instead of a custom implementation.
8 | - It introduces a modified `KVCache` that pre-allocates key/value tensors. This increases memory usage but avoids repeatedly allocating new storage during execution.
9 |
10 |
11 | To explore the differences, I recommend opening [`qwen3.py`](../../reasoning_from_scratch/qwen3.py) and [`qwen3_optimized.py`](../../reasoning_from_scratch/qwen3_optimized.py) side by side and/or looking at a file-diff:
12 |
13 |
77 |
78 |
79 |
80 | The table below compares this approach (row 4-12) with the baselines from chapter 3 (rows 1-2):
81 |
82 | | | Method | Model | Accuracy | Time |
83 | | ---- | ----------------------------------------- | --------- | -------- | --------- |
84 | | 1 | Baseline (chapter 3), greedy decoding | Base | 15.2% | 10.1 min |
85 | | 2 | Baseline (chapter 3), greedy decoding | Reasoning | 48.2% | 182.1 min |
86 | | 3 | Chain-of-thought prompting ("CoT") | Base | 40.6% | 84.5 min |
87 | | 4 | Temperature and top-p ("Top-p") | Base | 17.8% | 30.7 min |
88 | | 5 | "Top-p" + Self-consistency (n=3) | Base | 29.6% | 97.6 min |
89 | | 6 | "Top-p" + Self-consistency (n=5) | Base | 27.8% | 116.8 min |
90 | | 7 | "Top-p" + Self-consistency (n=10) | Base | 31.6% | 300.4 min |
91 | | 8 | "Top-p" + "CoT" | Base | 33.4% | 129.2 min |
92 | | 9 | Self-consistency (n=3) + "Top-p" + "CoT" | Base | 42.2% | 211.6 min |
93 | | 10 | Self-consistency (n=5) + "Top-p" + "CoT" | Base | 48.0% | 452.9 min |
94 | | 11 | Self-consistency (n=10) + "Top-p" + "CoT" | Base | 52.0% | 862.6 min |
95 | | 12 | Self-consistency (n=3) + "Top-p" + "CoT" | Reasoning | 55.2% | 544.4 min |
96 |
97 | The accuracy values and runtimes shown in the table were computed on all 500 samples in the MATH-500 test set using a "cuda" GPU (DGX Spark).
98 |
99 | The following codes give instructions on how to run the self-consistency experiments in rows 4-12 (replace `uv run` with `python` if you are not a `uv` user).
100 |
101 | **Row 4:**
102 |
103 | ```bash
104 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
105 | --which_model "base" \
106 | --temperature 0.9 \
107 | --top_p 0.9 \
108 | --num_samples 1 \
109 | --dataset_size 500
110 | ```
111 |
112 | **Row 5:**
113 |
114 | ```bash
115 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
116 | --which_model "base" \
117 | --temperature 0.9 \
118 | --top_p 0.9 \
119 | --num_samples 3 \
120 | --dataset_size 500
121 | ```
122 |
123 | **Row 6:**
124 |
125 | ```bash
126 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
127 | --which_model "base" \
128 | --temperature 0.9 \
129 | --top_p 0.9 \
130 | --num_samples 5 \
131 | --dataset_size 500
132 | ```
133 |
134 | **Row 7:**
135 |
136 | ```bash
137 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
138 | --which_model "base" \
139 | --temperature 0.9 \
140 | --top_p 0.9 \
141 | --num_samples 10 \
142 | --dataset_size 500
143 | ```
144 |
145 | **Row 8:**
146 |
147 | ```bash
148 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
149 | --which_model "base" \
150 | --temperature 0.9 \
151 | --top_p 0.9 \
152 | --num_samples 1 \
153 | --dataset_size 500 \
154 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
155 | ```
156 |
157 | **Row 9:**
158 |
159 | ```bash
160 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
161 | --which_model "base" \
162 | --temperature 0.9 \
163 | --top_p 0.9 \
164 | --num_samples 3 \
165 | --dataset_size 500 \
166 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
167 | ```
168 |
169 | **Row 10:**
170 |
171 | ```bash
172 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
173 | --which_model "base" \
174 | --temperature 0.9 \
175 | --top_p 0.9 \
176 | --num_samples 5 \
177 | --dataset_size 500 \
178 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
179 | ```
180 |
181 | **Row 11:**
182 |
183 | ```bash
184 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
185 | --which_model "base" \
186 | --temperature 0.9 \
187 | --top_p 0.9 \
188 | --num_samples 10 \
189 | --dataset_size 500 \
190 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
191 | ```
192 |
193 | **Row 12:**
194 |
195 | ```bash
196 | uv run self_consistency_math500.py \
197 | --which_model "reasoning" \
198 | --temperature 0.9 \
199 | --top_p 0.9 \
200 | --num_samples 3 \
201 | --dataset_size 500 \
202 | --prompt_suffix "\n\nExplain step by step."
203 | ```
204 |
205 |
206 | For additional options, use the `--help` flag.
207 |
208 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_qwen3_batched_stop.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import os
6 | import torch
7 | import pytest
8 | from pathlib import Path
9 |
10 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import get_device
11 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
12 | download_qwen3_small,
13 | Qwen3Tokenizer,
14 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B,
15 | )
16 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3_batched import (
17 | generate_text_basic_batched_cache,
18 | generate_text_basic_batched_cache_stop,
19 | generate_text_basic_batched_stream_cache,
20 | generate_text_basic_batched_stream_cache_stop,
21 | Qwen3Model as Qwen3ModelBatched,
22 | )
23 |
24 | skip_expensive = os.environ.get("SKIP_EXPENSIVE", "0") == "1"
25 |
26 | # Make CI more reproducible & robust
27 | os.environ["MKL_NUM_THREADS"] = "1"
28 | os.environ["OMP_NUM_THREADS"] = "1"
29 | torch.backends.mkldnn.enabled = False
30 | torch.set_num_threads(1)
31 | torch.use_deterministic_algorithms(True)
32 |
33 |
34 | @pytest.mark.skipif(skip_expensive, reason="Skipping expensive test on CI")
35 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("reasoning", [False, True])
36 | def test_batched_vs_batched_stop_equivalence(reasoning):
37 |
38 | device = get_device()
39 |
40 | # Download and init tokenizer
41 | kind = "reasoning" if reasoning else "base"
42 | download_qwen3_small(kind=kind, tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
43 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / (
44 | "tokenizer-reasoning.json" if reasoning else "tokenizer-base.json"
45 | )
46 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / (
47 | "qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth" if reasoning else "qwen3-0.6B-base.pth"
48 | )
49 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
50 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
51 | apply_chat_template=reasoning,
52 | add_generation_prompt=reasoning,
53 | add_thinking=reasoning,
54 | )
55 |
56 | # Model
57 | model_batched = Qwen3ModelBatched(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
58 | model_batched.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path, map_location=device))
59 | model_batched.to(device).eval()
60 |
61 | # Prompts
62 | prompts = [
63 | "Explain large language models in two sentences.",
64 | "Explain large language models in one sentence.",
65 | "1+1?",
66 | ]
67 |
68 | # Batched inputs (left-padded)
69 | tokenized = [tokenizer.encode(p) for p in prompts]
70 | max_len = max(len(t) for t in tokenized)
71 | pad_id = tokenizer.pad_token_id
72 | left_padded = [[pad_id] * (max_len - len(t)) + t for t in tokenized]
73 | attn_mask = [
74 | [0] * (max_len - len(t)) + [1] * len(t) for t in tokenized
75 | ]
76 | input_ids_batched = torch.tensor(left_padded, device=device)
77 | attn_mask_batched = torch.tensor(attn_mask, device=device, dtype=torch.bool)
78 |
79 | # Generation
80 | max_new_tokens = 12
81 | outputs_reg = generate_text_basic_batched_cache(
82 | model=model_batched,
83 | token_ids=input_ids_batched,
84 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
85 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
86 | attn_mask=attn_mask_batched,
87 | pad_id=pad_id,
88 | )
89 | outputs_stop = generate_text_basic_batched_cache_stop(
90 | model=model_batched,
91 | token_ids=input_ids_batched,
92 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
93 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
94 | attn_mask=attn_mask_batched,
95 | pad_id=pad_id,
96 | )
97 |
98 | # Check equivalency
99 | for idx in range(len(prompts)):
100 | reg_toks = outputs_reg[idx].tolist()
101 | stop_toks = outputs_stop[idx].tolist()
102 | assert reg_toks == stop_toks, (
103 | f"Token mismatch at prompt {idx}:\n"
104 | f"regular_tokens={reg_toks}\n"
105 | f"stop_tokens ={stop_toks}\n"
106 | f"regular_text={tokenizer.decode(reg_toks)}\n"
107 | f"stop_text ={tokenizer.decode(stop_toks)}"
108 | )
109 |
110 |
111 | @pytest.mark.skipif(skip_expensive, reason="Skipping expensive test on CI")
112 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("reasoning", [False, True])
113 | def test_stream_vs_stream_stop_equivalence(reasoning):
114 |
115 | device = get_device()
116 |
117 | # Download and init tokenizer
118 | kind = "reasoning" if reasoning else "base"
119 | download_qwen3_small(kind=kind, tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
120 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / (
121 | "tokenizer-reasoning.json" if reasoning else "tokenizer-base.json"
122 | )
123 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / (
124 | "qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth" if reasoning else "qwen3-0.6B-base.pth"
125 | )
126 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
127 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
128 | apply_chat_template=reasoning,
129 | add_generation_prompt=reasoning,
130 | add_thinking=reasoning,
131 | )
132 |
133 | # Model
134 | model_batched = Qwen3ModelBatched(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
135 | model_batched.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path, map_location=device))
136 | model_batched.to(device).eval()
137 |
138 | # Prompts
139 | prompts = [
140 | "Explain large language models in two sentences.",
141 | "Explain large language models in one sentence.",
142 | "1+1?",
143 | ]
144 |
145 | # Batched inputs (left-padded)
146 | tokenized = [tokenizer.encode(p) for p in prompts]
147 | max_len = max(len(t) for t in tokenized)
148 | pad_id = tokenizer.pad_token_id
149 | left_padded = [[pad_id] * (max_len - len(t)) + t for t in tokenized]
150 | attn_mask = [
151 | [0] * (max_len - len(t)) + [1] * len(t) for t in tokenized
152 | ]
153 | input_ids_batched = torch.tensor(left_padded, device=device)
154 | attn_mask_batched = torch.tensor(attn_mask, device=device, dtype=torch.bool)
155 |
156 | # Generation
157 | max_new_tokens = 12
158 | B = input_ids_batched.size(0)
159 |
160 | # Regular streaming
161 | reg_stream_tokens = [[] for _ in range(B)]
162 | for step_tokens in generate_text_basic_batched_stream_cache(
163 | model=model_batched,
164 | token_ids=input_ids_batched,
165 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
166 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
167 | attn_mask=attn_mask_batched,
168 | pad_id=pad_id,
169 | ):
170 | step_tokens = step_tokens.squeeze(1)
171 | for b in range(B):
172 | reg_stream_tokens[b].append(int(step_tokens[b].item()))
173 |
174 | # Stop streaming
175 | stop_stream_tokens = [[] for _ in range(B)]
176 | for step_tokens in generate_text_basic_batched_stream_cache_stop(
177 | model=model_batched,
178 | token_ids=input_ids_batched,
179 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
180 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
181 | attn_mask=attn_mask_batched,
182 | pad_id=pad_id,
183 | ):
184 | step_tokens = step_tokens.squeeze(1)
185 | for b in range(B):
186 | stop_stream_tokens[b].append(int(step_tokens[b].item()))
187 |
188 | # Check equivalency
189 | for idx in range(B):
190 | assert reg_stream_tokens[idx] == stop_stream_tokens[idx], (
191 | f"Token mismatch at prompt {idx}:\n"
192 | f"regular_tokens={reg_stream_tokens[idx]}\n"
193 | f"stop_tokens ={stop_stream_tokens[idx]}\n"
194 | f"regular_text={tokenizer.decode(reg_stream_tokens[idx])}\n"
195 | f"stop_text ={tokenizer.decode(stop_stream_tokens[idx])}"
196 | )
197 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/05_use_model/chat_multiturn.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | # Runs the model similar to chapter 2 and 3 in streaming mode with the least
6 | # amount of bells and whistles. Uses KV caching by default.
7 | # Interactive REPL (Read, Evaluate, Print, Loop) with multiturn memory.
8 |
9 | import argparse
10 | from pathlib import Path
11 | import time
12 | import torch
13 |
14 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
15 | get_device,
16 | generate_stats
17 | )
18 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02_ex import (
19 | generate_text_basic_stream_cache
20 | )
21 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
22 | download_qwen3_small,
23 | Qwen3Model,
24 | Qwen3Tokenizer,
25 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B
26 | )
27 |
28 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Run Qwen3 text generation (interactive REPL)")
29 | parser.add_argument(
30 | "--device",
31 | type=str,
32 | default=None,
33 | help="Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). "
34 | "If not provided, will auto-detect with get_device()."
35 | )
36 | parser.add_argument(
37 | "--max_new_tokens",
38 | type=int,
39 | default=2048,
40 | help="Maximum number of new tokens to generate in each turn (default: 2048)."
41 | )
42 | parser.add_argument(
43 | "--compile",
44 | action="store_true",
45 | help="Compile PyTorch model (default: False)."
46 | )
47 | parser.add_argument(
48 | "--reasoning",
49 | action="store_true",
50 | help="Use reasoning model variant (default: False)."
51 | )
52 |
53 | args = parser.parse_args()
54 | device = torch.device(args.device) if args.device else get_device()
55 |
56 | if args.reasoning:
57 | download_qwen3_small(kind="reasoning", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
58 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-reasoning.json"
59 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth"
60 | else:
61 | download_qwen3_small(kind="base", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
62 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-base.json"
63 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-base.pth"
64 |
65 | # We will apply the chat template manually later
66 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
67 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
68 | apply_chat_template=False
69 | )
70 |
71 | model = Qwen3Model(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
72 | state = torch.load(model_path, map_location=device)
73 | model.load_state_dict(state)
74 | model.to(device)
75 | model.eval()
76 |
77 | if args.compile:
78 | model = torch.compile(model)
79 |
80 | # The reasoning model may emit <|im_end|>; base may emit <|endoftext|>.
81 | EOS_TOKEN_IDS = (
82 | tokenizer.encode("<|im_end|>")[0],
83 | tokenizer.encode("<|endoftext|>")[0]
84 | )
85 |
86 | print()
87 | print("=" * 60)
88 | print(f"torch : {torch.__version__}")
89 | print(f"device : {device}")
90 | print("cache : True")
91 | print(f"compile : {args.compile}")
92 | print(f"reasoning : {args.reasoning}")
93 | print("memory : True")
94 | print(f"max_new_tokens (per turn): {args.max_new_tokens}")
95 | print(f"context_length: {model.cfg['context_length']}")
96 | print("=" * 60)
97 | print()
98 | print("Interactive REPL with memory. Type '\\exit' or '\\quit' to quit.")
99 | print("Commands: \\clear (forget memory), \\history (show turn count)\n")
100 |
101 | # Multi-turn memory as a list of role-content dicts
102 | # Example: {"role": "system"|"user"|"assistant", "content": str}
103 | history = [
104 | {"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."}
105 | ]
106 |
107 |
108 | def build_prompt_from_history(history, add_assistant_header=True):
109 | """
110 | history: [{"role": "system"|"user"|"assistant", "content": str}, ...]
111 | """
112 | parts = []
113 | for m in history:
114 | role = m["role"]
115 | content = m["content"]
116 | parts.append(f"<|im_start|>{role}\n{content}<|im_end|>\n")
117 |
118 | if add_assistant_header:
119 | parts.append("<|im_start|>assistant\n")
120 | return "".join(parts)
121 |
122 |
123 | def trim_input_tensor(input_ids_tensor, context_len, max_new_tokens):
124 | assert max_new_tokens < context_len
125 | keep_len = max(1, context_len - max_new_tokens)
126 |
127 | # If the prompt is too long, left-truncate to keep_len
128 | if input_ids_tensor.shape[1] > keep_len:
129 | input_ids_tensor = input_ids_tensor[:, -keep_len:]
130 |
131 | return input_ids_tensor
132 |
133 |
134 | def run_generate(user_text):
135 | # Add user prompt to history
136 | history.append({"role": "user", "content": user_text})
137 |
138 | # Encode full history
139 | prompt = build_prompt_from_history(history, add_assistant_header=True)
140 | input_ids = tokenizer.encode(prompt)
141 | input_token_ids_tensor = torch.tensor(input_ids, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
142 |
143 | # Left-tuncate (to make space for generation)
144 | input_token_ids_tensor = trim_input_tensor(
145 | input_ids_tensor=input_token_ids_tensor,
146 | context_len=model.cfg["context_length"],
147 | max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens
148 | )
149 |
150 | start_time = time.time()
151 | all_token_ids = []
152 |
153 | print("[Model]\n", end="", flush=True)
154 | for tok in generate_text_basic_stream_cache(
155 | model=model,
156 | token_ids=input_token_ids_tensor,
157 | max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens,
158 | # eos_token_id=TOKENIZER.eos_token_id
159 | ):
160 | token_id = tok.squeeze(0)
161 | if token_id in EOS_TOKEN_IDS: # Manually break at stop tokens
162 | break
163 | piece = tokenizer.decode(token_id.tolist())
164 | print(piece, end="", flush=True)
165 | all_token_ids.append(token_id.item())
166 |
167 | end_time = time.time()
168 | print("\n")
169 |
170 | print("[Stats]")
171 | generate_stats(
172 | torch.tensor(all_token_ids),
173 | tokenizer,
174 | start_time,
175 | end_time,
176 | print_tokens=False
177 | )
178 | print("-" * 60)
179 |
180 | # Add model reply to history
181 | assistant_text = tokenizer.decode(all_token_ids)
182 | history.append({"role": "assistant", "content": assistant_text})
183 | return assistant_text
184 |
185 |
186 | # Interactive REPL (Read, Evaluate, Print, Loop)
187 | try:
188 | while True:
189 | try:
190 | user_in = input(">> ").strip()
191 | except EOFError:
192 | print("")
193 | break
194 |
195 | low = user_in.lower()
196 | if low in {r"\exit", r"\quit"}:
197 | break
198 | if low == r"\clear":
199 | # Reset history but keep the system prompt
200 | system_entries = [m for m in history if m["role"] == "system"]
201 | history.clear()
202 | if system_entries:
203 | history.extend(system_entries)
204 | else:
205 | history.append({"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."})
206 | print("(memory cleared)\n")
207 | continue
208 | if low == r"\history":
209 | # Count assistant turns as the number of model replies so far
210 | assistant_turns = sum(1 for m in history if m["role"] == "assistant")
211 | print(f"(stored turns: {assistant_turns})\n")
212 | continue
213 | if not user_in:
214 | continue
215 |
216 | print("\n" + "-" * 60)
217 | print("[User]")
218 | print(user_in + "\n")
219 | run_generate(user_in)
220 |
221 | except KeyboardInterrupt:
222 | print("\nInterrupted by user.")
223 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/03_optimized-LLM/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Optimized Qwen3
2 |
3 | The Qwen3 from-scratch implementation used in this book strikes a balance between being efficient (both on CPU and GPU) and lean while remaining easy to read by a human.
4 |
5 | As an alternative, you can use the optional `Qwen3Model` drop-in replacement, which is slightly more GPU-efficient. The optimized version in [`qwen3_optimized.py`](../../reasoning_from_scratch/qwen3_optimized.py) (discussed further in Appendix C) differs from the baseline implementation in [`qwen3.py`](../../reasoning_from_scratch/qwen3.py) in two key ways:
6 |
7 | - It implements attention using PyTorch’s built-in `torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product` instead of a custom implementation.
8 | - It introduces a modified `KVCache` that pre-allocates key/value tensors. This increases memory usage but avoids repeatedly allocating new storage during execution.
9 |
10 |
11 | To explore the differences, I recommend opening [`qwen3.py`](../../reasoning_from_scratch/qwen3.py) and [`qwen3_optimized.py`](../../reasoning_from_scratch/qwen3_optimized.py) side by side and/or looking at a file-diff:
12 |
13 |  6 |
7 |
8 |
9 | This folder contains standalone example scripts to generate text with the model we loaded in chapter 2 (and exercises):
10 |
11 | - `generate_simple.py`: Generates text similar to the main chapter.
12 | - `chat.py`: Similar to the code above, as an interactive wrapper so that we can prompt the model multiple times without having to reload the model into memory each time.
13 | - `chat_multiturn.py`: Same as above, but with a memory feature to remember the message history.
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 | More usage details are provided in the sections below.
18 |
19 |
20 | ## generate_simple.py
21 |
22 | This simple function loads the model as described in chapter 2 and uses the `generate_text_simple_cache_stream` function from the chapter 2 exercises. You can use the function as follows (replace `uv run` with `python` if you are not using `uv`):
23 |
24 | ```bash
25 | uv run ch02/05_use_model/generate_simple.py
26 | Using Apple Silicon GPU (MPS)
27 | ✓ qwen3/qwen3-0.6B-base.pth already up-to-date
28 |
29 | ============================================================
30 | torch : 2.7.1
31 | device : mps
32 | cache : True
33 | compile : False
34 | reasoning : False
35 | ============================================================
36 |
37 | Large language models are artificial intelligence systems that can understand, generate, and process human language, enabling them to perform a wide range of tasks, from answering questions to writing essays.
38 |
39 | Time: 1.52 sec
40 | 22 tokens/sec
41 | ```
42 |
43 | The function is useful if you want to quickly try out different prompts with the base or reasoning variant. The additional options are listed below:
44 |
45 | ```bash
46 | usage: generate_simple.py [-h] [--device DEVICE]
47 | [--max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS] [--compile]
48 | [--reasoning] [--prompt PROMPT]
49 |
50 | Run Qwen3 text generation
51 |
52 | options:
53 | -h, --help show this help message and exit
54 | --device DEVICE Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). If not
55 | provided, will auto-detect with get_device().
56 | --max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS
57 | Maximum number of new tokens to generate (default:
58 | 2048).
59 | --compile Compile PyTorch model (default: False).
60 | --reasoning Use reasoning model variant (default: False).
61 | --prompt PROMPT Use a custom prompt. If not explicitly provided, uses
62 | the following defaults: 'Explain large language models
63 | in a single sentence.' for the base model, and 'Find
64 | all c in Z_3 such that Z_3[x]/(x^2 + c) is a field.'
65 | for the reasoning model.
66 | ```
67 |
68 |
69 | ## chat.py
70 |
71 | Similar to the function above, this function is useful to try different prompts on the base and reasoning models.
72 |
73 | However, in contrast to the previous function, this function keeps the user in an interactive mode so that the model doesn't have to be reloaded each time:
74 |
75 | ```bash
76 | uv run ch02/05_use_model/chat.py
77 | Using Apple Silicon GPU (MPS)
78 | ✓ qwen3/qwen3-0.6B-base.pth already up-to-date
79 |
80 | ============================================================
81 | torch : 2.7.1
82 | device : mps
83 | cache : True
84 | compile : False
85 | reasoning : False
86 | memory : False
87 | ============================================================
88 |
89 | Interactive REPL (no memory). Type '\exit' or '\quit' to quit.
90 |
91 | >> Explain language models in 1 sentence
92 |
93 | ------------------------------------------------------------
94 | [User]
95 | Explain language models in 1 sentence
96 |
97 | [Model]
98 |
99 | Language models are algorithms that analyze and predict the likelihood of future words in a text based on the words already seen, enabling them to generate coherent and contextually relevant text.
100 |
101 | [Stats]
102 | Time: 1.53 sec
103 | 22 tokens/sec
104 | ------------------------------------------------------------
105 | >> Explain machine learning in 1 sentence.
106 |
107 | ------------------------------------------------------------
108 | [User]
109 | Explain machine learning in 1 sentence.
110 |
111 | [Model]
112 | Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that enables computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed.
113 |
114 | [Stats]
115 | Time: 1.04 sec
116 | 24 tokens/sec
117 | ------------------------------------------------------------
118 | ```
119 |
120 | Additional options are listed below:
121 |
122 | ```bash
123 | usage: chat.py [-h] [--device DEVICE] [--max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS] [--compile]
124 | [--reasoning]
125 |
126 | Run Qwen3 text generation (interactive REPL)
127 |
128 | options:
129 | -h, --help show this help message and exit
130 | --device DEVICE Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). If not provided,
131 | will auto-detect with get_device().
132 | --max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS
133 | Maximum number of new tokens to generate (default: 2048).
134 | --compile Compile PyTorch model (default: False).
135 | --reasoning Use reasoning model variant (default: False).
136 | ```
137 |
138 |
139 |
140 |
141 |
142 | ## chat_multiturn.py
143 |
144 | This function is similar to the one above, except it adds a multi-turn memory so that the LLM remembers the conversation from the past turns. It is highly recommended to use the reasoning variant here as the base model struggles with conversations:
145 |
146 |
147 |
148 | ```bash
149 | uv run ch02/05_use_model/chat_multiturn.py --reasoning
150 | Using Apple Silicon GPU (MPS)
151 | ✓ qwen3/qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth already up-to-date
152 | ✓ qwen3/tokenizer-reasoning.json already up-to-date
153 |
154 | ============================================================
155 | torch : 2.7.1
156 | device : mps
157 | cache : True
158 | compile : False
159 | reasoning : True
160 | memory : True
161 | max_new_tokens (per turn): 2048
162 | context_length: 40960
163 | ============================================================
164 |
165 | Interactive REPL with memory. Type '\exit' or '\quit' to quit.
166 | Commands: \clear (forget memory), \history (show turn count)
167 |
168 | >> What is 1+1 in short?
169 |
170 | ------------------------------------------------------------
171 | [User]
172 | What is 1+1 in short?
173 |
174 | [Model]
175 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 | This folder contains standalone example scripts to generate text with the model we loaded in chapter 2 (and exercises):
10 |
11 | - `generate_simple.py`: Generates text similar to the main chapter.
12 | - `chat.py`: Similar to the code above, as an interactive wrapper so that we can prompt the model multiple times without having to reload the model into memory each time.
13 | - `chat_multiturn.py`: Same as above, but with a memory feature to remember the message history.
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 | More usage details are provided in the sections below.
18 |
19 |
20 | ## generate_simple.py
21 |
22 | This simple function loads the model as described in chapter 2 and uses the `generate_text_simple_cache_stream` function from the chapter 2 exercises. You can use the function as follows (replace `uv run` with `python` if you are not using `uv`):
23 |
24 | ```bash
25 | uv run ch02/05_use_model/generate_simple.py
26 | Using Apple Silicon GPU (MPS)
27 | ✓ qwen3/qwen3-0.6B-base.pth already up-to-date
28 |
29 | ============================================================
30 | torch : 2.7.1
31 | device : mps
32 | cache : True
33 | compile : False
34 | reasoning : False
35 | ============================================================
36 |
37 | Large language models are artificial intelligence systems that can understand, generate, and process human language, enabling them to perform a wide range of tasks, from answering questions to writing essays.
38 |
39 | Time: 1.52 sec
40 | 22 tokens/sec
41 | ```
42 |
43 | The function is useful if you want to quickly try out different prompts with the base or reasoning variant. The additional options are listed below:
44 |
45 | ```bash
46 | usage: generate_simple.py [-h] [--device DEVICE]
47 | [--max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS] [--compile]
48 | [--reasoning] [--prompt PROMPT]
49 |
50 | Run Qwen3 text generation
51 |
52 | options:
53 | -h, --help show this help message and exit
54 | --device DEVICE Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). If not
55 | provided, will auto-detect with get_device().
56 | --max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS
57 | Maximum number of new tokens to generate (default:
58 | 2048).
59 | --compile Compile PyTorch model (default: False).
60 | --reasoning Use reasoning model variant (default: False).
61 | --prompt PROMPT Use a custom prompt. If not explicitly provided, uses
62 | the following defaults: 'Explain large language models
63 | in a single sentence.' for the base model, and 'Find
64 | all c in Z_3 such that Z_3[x]/(x^2 + c) is a field.'
65 | for the reasoning model.
66 | ```
67 |
68 |
69 | ## chat.py
70 |
71 | Similar to the function above, this function is useful to try different prompts on the base and reasoning models.
72 |
73 | However, in contrast to the previous function, this function keeps the user in an interactive mode so that the model doesn't have to be reloaded each time:
74 |
75 | ```bash
76 | uv run ch02/05_use_model/chat.py
77 | Using Apple Silicon GPU (MPS)
78 | ✓ qwen3/qwen3-0.6B-base.pth already up-to-date
79 |
80 | ============================================================
81 | torch : 2.7.1
82 | device : mps
83 | cache : True
84 | compile : False
85 | reasoning : False
86 | memory : False
87 | ============================================================
88 |
89 | Interactive REPL (no memory). Type '\exit' or '\quit' to quit.
90 |
91 | >> Explain language models in 1 sentence
92 |
93 | ------------------------------------------------------------
94 | [User]
95 | Explain language models in 1 sentence
96 |
97 | [Model]
98 |
99 | Language models are algorithms that analyze and predict the likelihood of future words in a text based on the words already seen, enabling them to generate coherent and contextually relevant text.
100 |
101 | [Stats]
102 | Time: 1.53 sec
103 | 22 tokens/sec
104 | ------------------------------------------------------------
105 | >> Explain machine learning in 1 sentence.
106 |
107 | ------------------------------------------------------------
108 | [User]
109 | Explain machine learning in 1 sentence.
110 |
111 | [Model]
112 | Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that enables computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed.
113 |
114 | [Stats]
115 | Time: 1.04 sec
116 | 24 tokens/sec
117 | ------------------------------------------------------------
118 | ```
119 |
120 | Additional options are listed below:
121 |
122 | ```bash
123 | usage: chat.py [-h] [--device DEVICE] [--max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS] [--compile]
124 | [--reasoning]
125 |
126 | Run Qwen3 text generation (interactive REPL)
127 |
128 | options:
129 | -h, --help show this help message and exit
130 | --device DEVICE Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). If not provided,
131 | will auto-detect with get_device().
132 | --max_new_tokens MAX_NEW_TOKENS
133 | Maximum number of new tokens to generate (default: 2048).
134 | --compile Compile PyTorch model (default: False).
135 | --reasoning Use reasoning model variant (default: False).
136 | ```
137 |
138 |
139 |
140 |
141 |
142 | ## chat_multiturn.py
143 |
144 | This function is similar to the one above, except it adds a multi-turn memory so that the LLM remembers the conversation from the past turns. It is highly recommended to use the reasoning variant here as the base model struggles with conversations:
145 |
146 |
147 |
148 | ```bash
149 | uv run ch02/05_use_model/chat_multiturn.py --reasoning
150 | Using Apple Silicon GPU (MPS)
151 | ✓ qwen3/qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth already up-to-date
152 | ✓ qwen3/tokenizer-reasoning.json already up-to-date
153 |
154 | ============================================================
155 | torch : 2.7.1
156 | device : mps
157 | cache : True
158 | compile : False
159 | reasoning : True
160 | memory : True
161 | max_new_tokens (per turn): 2048
162 | context_length: 40960
163 | ============================================================
164 |
165 | Interactive REPL with memory. Type '\exit' or '\quit' to quit.
166 | Commands: \clear (forget memory), \history (show turn count)
167 |
168 | >> What is 1+1 in short?
169 |
170 | ------------------------------------------------------------
171 | [User]
172 | What is 1+1 in short?
173 |
174 | [Model]
175 |  27 |
28 |
29 |
30 | ## Using Google Colab
31 |
32 | To use a Google Colab environment in the cloud, head over to [https://colab.research.google.com/](https://colab.research.google.com/) and open the respective chapter notebook from the GitHub menu or by dragging the notebook into the *Upload* field as shown in the figure below.
33 |
34 |
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 | ## Using Google Colab
31 |
32 | To use a Google Colab environment in the cloud, head over to [https://colab.research.google.com/](https://colab.research.google.com/) and open the respective chapter notebook from the GitHub menu or by dragging the notebook into the *Upload* field as shown in the figure below.
33 |
34 |  35 |
36 |
37 | Also make sure you upload the relevant files (dataset files and .py files the notebook is importing from) to the Colab environment as well, as shown below.
38 |
39 |
35 |
36 |
37 | Also make sure you upload the relevant files (dataset files and .py files the notebook is importing from) to the Colab environment as well, as shown below.
38 |
39 |  40 |
41 |
42 | You can optionally run the code on a GPU by changing the *Runtime* as illustrated in the figure below.
43 |
44 |
40 |
41 |
42 | You can optionally run the code on a GPU by changing the *Runtime* as illustrated in the figure below.
43 |
44 |  45 |
46 |
47 |
48 | ## Questions?
49 |
50 | If you have any questions, please don't hesitate to reach out via the [Discussions](https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch/discussions) forum in this GitHub repository.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/conftest.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
6 | download_qwen3_small,
7 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B,
8 | Qwen3Model,
9 | )
10 | import sys
11 | import types
12 | import nbformat
13 | import pytest
14 | import torch
15 |
16 |
17 | @pytest.fixture(scope="session")
18 | def qwen3_weights_path(tmp_path_factory):
19 | """Creates and saves a deterministic model for testing."""
20 |
21 | base_path = tmp_path_factory.mktemp("models")
22 | model_path = base_path / "qwen3_test_weights.pt"
23 | download_qwen3_small(kind="base", tokenizer_only=True, out_dir=base_path)
24 |
25 | if not model_path.exists():
26 | torch.manual_seed(123)
27 | model = Qwen3Model(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
28 | torch.save(model.state_dict(), model_path)
29 |
30 | return base_path
31 |
32 |
33 | def import_definitions_from_notebook(nb_path, module_name):
34 | if not nb_path.exists():
35 | raise FileNotFoundError(f"Notebook file not found at: {nb_path}")
36 |
37 | nb = nbformat.read(str(nb_path), as_version=4)
38 |
39 | mod = types.ModuleType(module_name)
40 | sys.modules[module_name] = mod
41 |
42 | # Pass 1: execute only imports (handle multi-line)
43 | for cell in nb.cells:
44 | if cell.cell_type != "code":
45 | continue
46 | lines = cell.source.splitlines()
47 | collecting = False
48 | buf = []
49 | paren_balance = 0
50 | for line in lines:
51 | stripped = line.strip()
52 | if not collecting and (stripped.startswith("import ") or stripped.startswith("from ")):
53 | collecting = True
54 | buf = [line]
55 | paren_balance = line.count("(") - line.count(")")
56 | if paren_balance == 0:
57 | exec("\n".join(buf), mod.__dict__)
58 | collecting = False
59 | buf = []
60 | elif collecting:
61 | buf.append(line)
62 | paren_balance += line.count("(") - line.count(")")
63 | if paren_balance == 0:
64 | exec("\n".join(buf), mod.__dict__)
65 | collecting = False
66 | buf = []
67 |
68 | # Pass 2: execute only def/class definitions
69 | for cell in nb.cells:
70 | if cell.cell_type != "code":
71 | continue
72 | src = cell.source
73 | if "def " in src or "class " in src:
74 | exec(src, mod.__dict__)
75 |
76 | return mod
77 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/04_torch-compile-windows/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Using `torch.compile()` on Windows
2 |
3 | `torch.compile()` relies on *TorchInductor*, which JIT-compiles kernels and requires a working C/C++ compiler toolchain.
4 |
5 | So, on Windows, the setup required to make `torch.compile` work can be a bit more involved than on Linux or macOS, which usually don't require any extra steps besides installing PyTorch.
6 |
7 | If you are a Windows user and using `torch.compile` sounds too tricky or complicated, don't worry, all code examples in this repository will work fine without compilation.
8 |
9 | Below are some tips that I compiled based on recommendations by [Daniel Kleine](https://github.com/d-kleine) and the following [PyTorch guide](https://docs.pytorch.org/tutorials/unstable/inductor_windows.html).
10 |
11 |
12 | ## 1 Basic Setup (CPU or CUDA)
13 |
14 |
15 | ### 1.1 Install Visual Studio 2022
16 |
17 | - Select the **“Desktop development with C++”** workload.
18 | - Make sure to include the **English language pack** (without it, you may run into UTF-8 encoding errors.)
19 |
20 |
21 | ### 1.2 Open the correct command prompt
22 |
23 |
24 | Launch Python from the
25 |
26 | **"x64 Native Tools Command Prompt for VS 2022"**
27 |
28 | or from the
29 |
30 | **"Visual Studio 2022 Developer Command Prompt"**.
31 |
32 | Alternatively, you can initialize the environment manually by running:
33 |
34 | ```bash
35 | "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\Community\VC\Auxiliary\Build\vcvars64.bat"
36 | ```
37 |
38 |
39 | ### 1.3 Verify that the compiler works
40 |
41 | Run
42 |
43 | ```bash
44 | cl.exe
45 | ```
46 |
47 | If you see version information printed, the compiler is ready.
48 |
49 |
50 | ## 2 Troubleshooting Common Errors
51 |
52 |
53 | ### 2.1 Error: `cl not found`
54 |
55 | Install **Visual Studio Build Tools** with the "C++ build tools" workload and run Python from a developer command prompt. (See this Microsoft [guide](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cpp/build/vscpp-step-0-installation?view=msvc-170) for details)
56 |
57 |
58 | ### 2.2 Error: `triton not found` (when using CUDA)
59 |
60 | Install the Windows build of Triton manually:
61 |
62 | ```bash
63 | pip install "triton-windows<3.4"
64 | ```
65 |
66 | or, if you are using `uv`:
67 |
68 | ```bash
69 | uv pip install "triton-windows<3.4"
70 | ```
71 |
72 | (As mentioned earlier, triton is required by TorchInductor for CUDA kernel compilation.)
73 |
74 |
75 |
76 |
77 | ## 3 Additional Notes
78 |
79 | On Windows, the `cl.exe` compiler is only accessible from within the Visual Studio Developer environment. This means that using `torch.compile()` in notebooks such as Jupyter may not work unless the notebook was launched from a Developer Command Prompt.
80 |
81 | As mentioned at the beginning of this article, there is also a [PyTorch guide](https://docs.pytorch.org/tutorials/unstable/inductor_windows.html) that some users found helpful when getting `torch.compile()` running on Windows CPU builds. However, note that it refers to PyTorch's unstable branch, so use it as a reference only.
82 |
83 | **If compilation continues to cause issues, please feel free to skip it. It's a nice bonus, but it's not important to follow the book.**
84 |
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chF/02_mmlu/random_guessing_baseline.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import argparse
6 | import random
7 | import statistics as stats
8 | from collections import Counter
9 |
10 | from datasets import load_dataset
11 |
12 |
13 | # Gold letter is MMLU jargon for correct answer letter
14 | def gold_letter(ans):
15 | if isinstance(ans, int):
16 | return "ABCD"[ans]
17 | s = str(ans).strip().upper()
18 | return s if s in {"A", "B", "C", "D"} else s[:1]
19 |
20 |
21 | def main():
22 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
23 | description="Show gold answer distribution for an MMLU subset and a random-guess baseline."
24 | )
25 | parser.add_argument(
26 | "--subset",
27 | type=str,
28 | default="high_school_mathematics",
29 | help="MMLU subset name (default: 'high_school_mathematics').",
30 | )
31 | parser.add_argument(
32 | "--seed",
33 | type=int,
34 | default=42,
35 | help="Random seed for the random-guess baseline (default: 42).",
36 | )
37 | parser.add_argument(
38 | "--trials",
39 | type=int,
40 | default=10_000,
41 | help="Number of random-guess trials (default: 10,000).",
42 | )
43 | args = parser.parse_args()
44 |
45 | ds = load_dataset("cais/mmlu", args.subset, split="test")
46 |
47 | labels = [gold_letter(ex["answer"]) for ex in ds]
48 | n = len(labels)
49 | counts = Counter(labels)
50 |
51 | print(f"Subset: {args.subset} | split: test | n={n}")
52 | print("Gold distribution provided in the dataset:")
53 | for letter in "ABCD":
54 | c = counts.get(letter, 0)
55 | pct = (c / n) if n else 0.0
56 | print(f" {letter}: {c} ({pct:.2%})")
57 |
58 | if n == 0:
59 | print("\nNo items. Baseline undefined.")
60 | return
61 |
62 | # Repeat random guessing
63 | rng = random.Random(args.seed)
64 | accs = []
65 | for _ in range(args.trials):
66 | guesses = [rng.choice("ABCD") for _ in range(n)]
67 | correct = sum(1 for g, y in zip(guesses, labels) if g == y)
68 | accs.append(correct / n)
69 |
70 | mean_acc = stats.mean(accs)
71 | sd_acc = stats.stdev(accs) if len(accs) > 1 else 0.0
72 |
73 | print(f"\nRandom guessing over {args.trials:,} trials (uniform A/B/C/D, seed={args.seed}):")
74 | print(f" Mean accuracy: {mean_acc:.2%}")
75 | print(f" Std dev across trials: {sd_acc:.2%}")
76 |
77 | # Quantiles
78 | qs = [0.01, 0.05, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 0.95, 0.99]
79 | accs_sorted = sorted(accs)
80 | print("\nSelected quantiles of accuracy:")
81 | for q in qs:
82 | idx = int(q * len(accs_sorted))
83 | print(f" {q:.0%} quantile: {accs_sorted[idx]:.3%}")
84 |
85 | # Frequency table (rounded)
86 | acc_counts = Counter(round(a, 2) for a in accs)
87 | print("\nFull frequency table of accuracies (rounded):")
88 | for acc_val in sorted(acc_counts):
89 | freq = acc_counts[acc_val]
90 | pct = freq / args.trials
91 | print(f" {acc_val:.3f}: {freq} times ({pct:.2%})")
92 |
93 |
94 | if __name__ == "__main__":
95 | main()
96 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/reasoning_from_scratch/ch02.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | from .qwen3 import KVCache
6 | import torch
7 |
8 |
9 | def get_device(enable_tensor_cores=True):
10 | if torch.cuda.is_available():
11 | device = torch.device("cuda")
12 | print("Using NVIDIA CUDA GPU")
13 |
14 | if enable_tensor_cores:
15 | major, minor = map(int, torch.__version__.split(".")[:2])
16 | if (major, minor) >= (2, 9):
17 | torch.backends.cuda.matmul.fp32_precision = "tf32"
18 | torch.backends.cudnn.conv.fp32_precision = "tf32"
19 | else:
20 | torch.backends.cuda.matmul.allow_tf32 = True
21 | torch.backends.cudnn.allow_tf32 = True
22 |
23 | elif torch.backends.mps.is_available():
24 | device = torch.device("mps")
25 | print("Using Apple Silicon GPU (MPS)")
26 |
27 | elif torch.xpu.is_available():
28 | device = torch.device("xpu")
29 | print("Using Intel GPU")
30 |
31 | else:
32 | device = torch.device("cpu")
33 | print("Using CPU")
34 |
35 | return device
36 |
37 |
38 | @torch.inference_mode()
39 | def generate_text_basic(model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=None):
40 | input_length = token_ids.shape[1]
41 | model.eval()
42 |
43 | for _ in range(max_new_tokens):
44 | out = model(token_ids)[:, -1]
45 | next_token = torch.argmax(out, dim=-1, keepdim=True)
46 |
47 | # Stop if all sequences in the batch have generated EOS
48 | if (eos_token_id is not None
49 | and next_token.item() == eos_token_id):
50 | break
51 |
52 | token_ids = torch.cat([token_ids, next_token], dim=1)
53 | return token_ids[:, input_length:]
54 |
55 |
56 | @torch.inference_mode()
57 | def generate_text_basic_cache(
58 | model,
59 | token_ids,
60 | max_new_tokens,
61 | eos_token_id=None
62 | ):
63 |
64 | input_length = token_ids.shape[1]
65 | model.eval()
66 | cache = KVCache(n_layers=model.cfg["n_layers"])
67 | model.reset_kv_cache()
68 | out = model(token_ids, cache=cache)[:, -1]
69 |
70 | for _ in range(max_new_tokens):
71 | next_token = torch.argmax(out, dim=-1, keepdim=True)
72 |
73 | if (eos_token_id is not None
74 | and next_token.item() == eos_token_id):
75 | break
76 |
77 | token_ids = torch.cat([token_ids, next_token], dim=1)
78 | out = model(next_token, cache=cache)[:, -1]
79 |
80 | return token_ids[:, input_length:]
81 |
82 |
83 | def generate_stats(output_token_ids, tokenizer, start_time,
84 | end_time, print_tokens=True):
85 | total_time = end_time - start_time
86 | print(f"Time: {total_time:.2f} sec")
87 | print(f"{int(output_token_ids.numel() / total_time)} tokens/sec")
88 |
89 | for name, backend in (("CUDA", getattr(torch, "cuda", None)),
90 | ("XPU", getattr(torch, "xpu", None))):
91 | if backend is not None and backend.is_available():
92 | max_mem_bytes = backend.max_memory_allocated()
93 | max_mem_gb = max_mem_bytes / (1024 ** 3)
94 | print(f"Max {name} memory allocated: {max_mem_gb:.2f} GB")
95 | backend.reset_peak_memory_stats()
96 |
97 | if print_tokens:
98 | output_text = tokenizer.decode(output_token_ids.squeeze(0).tolist())
99 | print(f"\n{output_text}")
100 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/scripts/check_notebook_line_length.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | # Check if code in notebooks exceeds line length
6 | # Usage: uv run .github/scripts/check_notebook_line_length.py --max-len 76 ch02/01_main-chapter-code/ch02_main.ipynb ch03/01_main-chapter-code/ch03_main.ipynb
7 |
8 | import argparse
9 | import sys
10 | from pathlib import Path
11 | import nbformat as nbf
12 |
13 |
14 | def parse_args():
15 | p = argparse.ArgumentParser(
16 | description="Check code-cell line lengths in specific .ipynb files."
17 | )
18 | p.add_argument(
19 | "--max-len",
20 | type=int,
21 | default=76,
22 | help="Maximum allowed characters per line (default: 76)",
23 | )
24 | p.add_argument(
25 | "notebooks",
26 | nargs="+",
27 | help="Paths to .ipynb files to check.",
28 | )
29 | return p.parse_args()
30 |
31 |
32 | def strip_inline_comment(line):
33 | """Return line with any trailing #... comment removed, but keep # inside quotes."""
34 | in_quote = None
35 | escaped = False
36 | for i, ch in enumerate(line):
37 | if escaped:
38 | escaped = False
39 | continue
40 | if ch == "\\":
41 | escaped = True
42 | continue
43 | if ch in ("'", '"'):
44 | if in_quote is None:
45 | in_quote = ch
46 | elif in_quote == ch:
47 | in_quote = None
48 | continue
49 | if ch == "#" and in_quote is None:
50 | return line[:i].rstrip()
51 | return line.rstrip()
52 |
53 |
54 | def main():
55 | args = parse_args()
56 |
57 | nb_paths = []
58 | for raw in args.notebooks:
59 | p = Path(raw).resolve()
60 | if not p.exists():
61 | print(f"::warning file={raw}::File not found, skipping.")
62 | continue
63 | if p.suffix != ".ipynb":
64 | print(f"::warning file={raw}::Not a .ipynb file, skipping.")
65 | continue
66 | nb_paths.append(p)
67 |
68 | if not nb_paths:
69 | print("No valid notebooks to check.")
70 | return 0
71 |
72 | violations = []
73 |
74 | for nb_path in nb_paths:
75 | try:
76 | nb = nbf.read(nb_path, as_version=4)
77 | except Exception as e:
78 | print(f"::warning file={nb_path}::Failed to read notebook: {e}")
79 | continue
80 |
81 | for ci, cell in enumerate(nb.cells, start=1):
82 | if cell.get("cell_type") != "code":
83 | continue
84 |
85 | src = cell.get("source", "")
86 | lines = src if isinstance(src, list) else src.splitlines()
87 |
88 | for li, line in enumerate(lines, start=1):
89 | code_part = strip_inline_comment(line)
90 | length = len(code_part)
91 | if length > args.max_len:
92 | print(
93 | f"::error file={nb_path}::Line length {length} exceeds "
94 | f"{args.max_len} in code cell {ci}, line {li}"
95 | )
96 | snippet = code_part if len(code_part) <= 120 else code_part[:120] + "…"
97 | violations.append((str(nb_path), ci, li, length, snippet))
98 |
99 | if violations:
100 | print("\nFound lines exceeding the limit:\n")
101 | for path, ci, li, length, snippet in violations:
102 | print(f"- {path} | cell {ci} line {li}: {length} chars\n {snippet}")
103 | return 1
104 |
105 | print(f"All notebooks pass: no code-cell lines exceed {args.max_len} characters.")
106 | return 0
107 |
108 |
109 | if __name__ == "__main__":
110 | sys.exit(main())
111 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch03/02_math500-verifier-scripts/evaluate_math500.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import argparse
6 | import torch
7 |
8 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
9 | Qwen3Model,
10 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B
11 | )
12 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import get_device
13 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch03 import (
14 | load_math500_test,
15 | evaluate_math500_stream,
16 | load_model_and_tokenizer,
17 | load_tokenizer_only
18 | )
19 |
20 |
21 | def parse_args():
22 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
23 | parser.add_argument(
24 | "--device",
25 | type=str,
26 | default="auto",
27 | help="Device to use: 'auto' (default), or any torch device string like 'cpu', 'cuda', 'cuda:0', 'mps'.",
28 | )
29 | parser.add_argument(
30 | "--which_model",
31 | type=str,
32 | default="base",
33 | choices=["base", "reasoning", "instruct"],
34 | help="Model variant to load. Defaults to 'base'.",
35 | )
36 | parser.add_argument(
37 | "--dataset_size",
38 | type=int,
39 | default=10,
40 | help="Number of MATH-500 examples to evaluate. Default: 10",
41 | )
42 | parser.add_argument(
43 | "--max_new_tokens",
44 | type=int,
45 | default=2048,
46 | help="Max new tokens for generation. Default: 2048",
47 | )
48 | parser.add_argument(
49 | "--compile",
50 | action="store_true",
51 | help="Enable torch.compile for the model.",
52 | )
53 | parser.add_argument(
54 | "--checkpoint_path",
55 | type=str,
56 | default=None,
57 | help="Optional path to a .pth checkpoint to load model weights from.",
58 | )
59 | parser.add_argument(
60 | "--verbose",
61 | action="store_true",
62 | help="Print per-sample correctness while evaluating.",
63 | )
64 | return parser.parse_args()
65 |
66 |
67 | if __name__ == "__main__":
68 | args = parse_args()
69 |
70 | if args.device == "auto":
71 | device = get_device()
72 | else:
73 | device = torch.device(args.device)
74 |
75 | which_model = args.which_model
76 | dataset_size = args.dataset_size
77 | max_new_tokens = args.max_new_tokens
78 | use_compile = args.compile
79 |
80 | print("Model:", which_model)
81 | print("Device:", device)
82 | dev_name = str(device).replace(":", "-")
83 |
84 | math_data = load_math500_test()
85 |
86 | if args.which_model == "instruct":
87 | which_model = "reasoning"
88 | else:
89 | which_model = args.which_model
90 |
91 | if args.checkpoint_path:
92 | # To load the saved RL checkpoint files from chapter 6
93 | tokenizer = load_tokenizer_only(which_model=which_model)
94 | model = Qwen3Model(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
95 | model.to(device)
96 | state_dict = torch.load(args.checkpoint_path, map_location=device)
97 | model.load_state_dict(state_dict)
98 | if args.compile:
99 | torch._dynamo.config.allow_unspec_int_on_nn_module = True
100 | model = torch.compile(model)
101 | else:
102 | model, tokenizer = load_model_and_tokenizer(
103 | which_model=which_model,
104 | device=device,
105 | use_compile=args.compile
106 | )
107 |
108 | if args.which_model == "instruct":
109 | tokenizer.add_thinking = False
110 |
111 | model.eval()
112 | torch.set_float32_matmul_precision("high")
113 |
114 | num_correct, num_examples, acc = evaluate_math500_stream(
115 | model=model,
116 | out_path=f"math500_{which_model}-{dev_name}-evaluate-script.jsonl",
117 | tokenizer=tokenizer,
118 | device=device,
119 | math_data=math_data[:dataset_size],
120 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
121 | verbose=args.verbose,
122 | )
123 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chG/01_main-chapter-code/qwen3_chat_interface_multiturn.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt).
2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch"
3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch
4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch
5 |
6 |
7 | import torch
8 | import chainlit
9 |
10 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
11 | get_device,
12 | )
13 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02_ex import generate_text_basic_stream_cache
14 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch03 import load_model_and_tokenizer
15 |
16 | # ============================================================
17 | # EDIT ME: Simple configuration
18 | # ============================================================
19 | WHICH_MODEL = "reasoning" # "base" for base model
20 | MAX_NEW_TOKENS = 38912
21 | LOCAL_DIR = "qwen3"
22 | COMPILE = False
23 | # ============================================================
24 |
25 |
26 | def trim_input_tensor(input_ids_tensor, context_len, max_new_tokens):
27 | assert max_new_tokens < context_len
28 | keep_len = max(1, context_len - max_new_tokens)
29 |
30 | # If the prompt is too long, left-truncate to keep_len
31 | if input_ids_tensor.shape[1] > keep_len:
32 | input_ids_tensor = input_ids_tensor[:, -keep_len:]
33 |
34 | return input_ids_tensor
35 |
36 |
37 | def build_prompt_from_history(history, add_assistant_header=True):
38 | """
39 | history: [{"role": "system"|"user"|"assistant", "content": str}, ...]
40 | """
41 | parts = []
42 | for m in history:
43 | role = m["role"]
44 | content = m["content"]
45 | parts.append(f"<|im_start|>{role}\n{content}<|im_end|>\n")
46 |
47 | if add_assistant_header:
48 | parts.append("<|im_start|>assistant\n")
49 | return "".join(parts)
50 |
51 |
52 | DEVICE = get_device()
53 | MODEL, TOKENIZER = load_model_and_tokenizer(
54 | which_model=WHICH_MODEL,
55 | device=DEVICE,
56 | use_compile=COMPILE,
57 | local_dir=LOCAL_DIR
58 | )
59 |
60 | # Even though the official TOKENIZER.eos_token_id is either <|im_end|> (reasoning)
61 | # or <|endoftext|> (base), the reasoning model sometimes emits both.
62 | EOS_TOKEN_IDS = (
63 | TOKENIZER.encode("<|im_end|>")[0],
64 | TOKENIZER.encode("<|endoftext|>")[0]
65 | )
66 |
67 |
68 | @chainlit.on_chat_start
69 | async def on_start():
70 | chainlit.user_session.set("history", [])
71 | chainlit.user_session.get("history").append(
72 | {"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."}
73 | )
74 |
75 |
76 | @chainlit.on_message
77 | async def main(message: chainlit.Message):
78 | """
79 | The main Chainlit function.
80 | """
81 | # 0) Get and track chat history
82 | history = chainlit.user_session.get("history")
83 | history.append({"role": "user", "content": message.content})
84 |
85 | # 1) Encode input
86 | prompt = build_prompt_from_history(history, add_assistant_header=True)
87 | input_ids = TOKENIZER.encode(prompt)
88 | input_ids_tensor = torch.tensor(input_ids, device=DEVICE).unsqueeze(0)
89 |
90 | # Multi-turn can be very long, so we add this left-trimming
91 | input_ids_tensor = trim_input_tensor(
92 | input_ids_tensor=input_ids_tensor,
93 | context_len=MODEL.cfg["context_length"],
94 | max_new_tokens=MAX_NEW_TOKENS
95 | )
96 |
97 | # 2) Start an outgoing message we can stream into
98 | out_msg = chainlit.Message(content="")
99 | await out_msg.send()
100 |
101 | # 3) Stream generation
102 | for tok in generate_text_basic_stream_cache(
103 | model=MODEL,
104 | token_ids=input_ids_tensor,
105 | max_new_tokens=MAX_NEW_TOKENS,
106 | # eos_token_id=TOKENIZER.eos_token_id
107 | ):
108 | token_id = tok.squeeze(0)
109 | if token_id in EOS_TOKEN_IDS:
110 | break
111 | piece = TOKENIZER.decode(token_id.tolist())
112 | await out_msg.stream_token(piece)
113 |
114 | # 4) Finalize the streamed message
115 | await out_msg.update()
116 |
117 | # 5) Update chat history
118 | history.append({"role": "assistant", "content": out_msg.content})
119 | chainlit.user_session.set("history", history)
120 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_ch02.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import torch
6 |
7 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
8 | get_device,
9 | generate_text_basic,
10 | generate_text_basic_cache,
11 | generate_stats
12 | )
13 |
14 |
15 | # Dummy model for generate_text_basic tests.
16 | class DummyModel:
17 | def __init__(self, fixed_token, vocab_size=5):
18 | self.fixed_token = fixed_token
19 | self.vocab_size = vocab_size
20 | self.eval_called = False
21 |
22 | def eval(self):
23 | self.eval_called = True
24 | return self
25 |
26 | def __call__(self, token_ids, cache=None):
27 | batch_size, seq_len = token_ids.size()
28 | out = torch.zeros(batch_size, seq_len, self.vocab_size)
29 | # Set the fixed_token column to the highest value so argmax returns fixed_token
30 | out[..., self.fixed_token] = 1.0
31 | return out
32 |
33 |
34 | class DummyModelCache(DummyModel):
35 | def __init__(self, fixed_token, vocab_size=5, n_layers=2):
36 | super().__init__(fixed_token, vocab_size)
37 | self.cfg = {"n_layers": n_layers}
38 | self.reset_called = False
39 |
40 | def reset_kv_cache(self):
41 | self.reset_called = True
42 |
43 |
44 | class DummyTokenizer:
45 | def decode(self, token_list):
46 | return " ".join(str(t) for t in token_list)
47 |
48 |
49 | def test_get_device_returns_torch_device(capsys):
50 | device = get_device()
51 | assert isinstance(device, torch.device)
52 | assert device.type in ("cpu", "cuda", "mps")
53 |
54 |
55 | def test_generate_text_basic_stops_on_eos():
56 | # batch_size = 1
57 | # seq_len = 3
58 | max_new_tokens = 10
59 | fixed_token = 2
60 |
61 | dummy_model = DummyModel(fixed_token=fixed_token)
62 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[1, 3, 4]]) # shape (batch, seq_len)
63 |
64 | # Set eos_token_id to be the fixed_token so that generation stops immediately
65 | output = generate_text_basic(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=fixed_token)
66 | assert output.size(1) == 0
67 | assert dummy_model.eval_called is True
68 |
69 |
70 | def test_generate_text_basic_generates_tokens_without_eos():
71 | # batch_size = 1
72 | # seq_len = 2
73 | max_new_tokens = 3
74 | fixed_token = 1
75 |
76 | dummy_model = DummyModel(fixed_token=fixed_token)
77 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[0, 4]])
78 | output = generate_text_basic(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=None)
79 | assert output.size(1) == max_new_tokens
80 | assert torch.all(output == fixed_token)
81 |
82 |
83 | def test_generate_text_basic_cache_stops_on_eos():
84 | # batch_size = 1
85 | # seq_len = 2
86 | max_new_tokens = 10
87 | fixed_token = 3
88 |
89 | dummy_model = DummyModelCache(fixed_token=fixed_token, n_layers=4)
90 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[2, 2]])
91 | output = generate_text_basic_cache(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=fixed_token)
92 | assert output.size(1) == 0
93 | assert dummy_model.reset_called is True
94 |
95 |
96 | def test_generate_text_basic_cache_generates_tokens_without_eos():
97 | # batch_size = 1
98 | # seq_len = 1
99 | max_new_tokens = 4
100 | fixed_token = 0
101 |
102 | dummy_model = DummyModelCache(fixed_token=fixed_token, n_layers=3)
103 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[5]])
104 |
105 | output = generate_text_basic_cache(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=None)
106 | assert output.size(1) == max_new_tokens
107 | assert torch.all(output == fixed_token)
108 | assert dummy_model.reset_called is True
109 |
110 |
111 | def test_generate_stats_prints_output(monkeypatch, capsys):
112 | output_token_ids = torch.tensor([[10, 20, 30]])
113 | tokenizer = DummyTokenizer()
114 | start_time = 100.0
115 | end_time = 102.0
116 |
117 | monkeypatch.setattr(torch.cuda, "is_available", lambda: False)
118 | generate_stats(output_token_ids, tokenizer, start_time, end_time)
119 |
120 | captured = capsys.readouterr().out
121 | assert "Time:" in captured
122 | assert "tokens/sec" in captured
123 | assert "10 20 30" in captured
124 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/05_use_model/generate_simple.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | # Runs the model similar to chapter 2 and 3 in streaming mode with the least
6 | # amount of bells and whistles. Uses KV caching by default.
7 |
8 | import argparse
9 | from pathlib import Path
10 | import time
11 | import torch
12 |
13 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
14 | get_device,
15 | generate_stats
16 | )
17 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02_ex import (
18 | generate_text_basic_stream_cache
19 | )
20 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
21 | download_qwen3_small,
22 | Qwen3Model,
23 | Qwen3Tokenizer,
24 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B
25 | )
26 |
27 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Run Qwen3 text generation")
28 | parser.add_argument(
29 | "--device",
30 | type=str,
31 | default=None,
32 | help="Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). "
33 | "If not provided, will auto-detect with get_device()."
34 | )
35 | parser.add_argument(
36 | "--max_new_tokens",
37 | type=int,
38 | default=2048,
39 | help="Maximum number of new tokens to generate (default: 2048)."
40 | )
41 | parser.add_argument(
42 | "--compile",
43 | action="store_true",
44 | help="Compile PyTorch model (default: False)."
45 | )
46 | parser.add_argument(
47 | "--reasoning",
48 | action="store_true",
49 | help="Use reasoning model variant (default: False)."
50 | )
51 | parser.add_argument(
52 | "--prompt",
53 | type=str,
54 | default=None,
55 | help=("Use a custom prompt. If not explicitly provided, uses the following defaults: "
56 | "'Explain large language models in a single sentence.' for the base model, and "
57 | "'Find all c in Z_3 such that Z_3[x]/(x^2 + c) is a field.' for the reasoning model.")
58 | )
59 |
60 | args = parser.parse_args()
61 | device = torch.device(args.device) if args.device else get_device()
62 |
63 | if args.reasoning:
64 | download_qwen3_small(kind="reasoning", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
65 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-reasoning.json"
66 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth"
67 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
68 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
69 | apply_chat_template=True,
70 | add_generation_prompt=True,
71 | add_thinking=True
72 | )
73 | else:
74 | download_qwen3_small(kind="base", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
75 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-base.json"
76 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-base.pth"
77 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
78 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
79 | apply_chat_template=False,
80 | add_generation_prompt=False,
81 | add_thinking=False
82 | )
83 |
84 | model = Qwen3Model(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
85 | state = torch.load(model_path, map_location=device)
86 | model.load_state_dict(state)
87 | model.to(device)
88 | model.eval()
89 |
90 | if args.compile:
91 | model = torch.compile(model)
92 |
93 |
94 | if args.prompt is None:
95 | if args.reasoning:
96 | prompt = "Find all c in Z_3 such that Z_3[x]/(x^2 + c) is a field."
97 | else:
98 | prompt = "Explain large language models in a single sentence."
99 | else:
100 | prompt = args.prompt
101 |
102 |
103 | input_ids = tokenizer.encode(prompt)
104 | input_token_ids_tensor = torch.tensor(input_ids, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
105 |
106 | print()
107 | print("=" * 60)
108 | print(f"torch : {torch.__version__}")
109 | print(f"device : {device}")
110 | print("cache : True")
111 | print(f"compile : {args.compile}")
112 | print(f"reasoning : {args.reasoning}")
113 | print("=" * 60)
114 | print()
115 |
116 | start_time = time.time()
117 | all_token_ids = []
118 |
119 | for token in generate_text_basic_stream_cache(
120 | model=model,
121 | token_ids=input_token_ids_tensor,
122 | max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens,
123 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id
124 | ):
125 | token_id = token.squeeze(0).item()
126 | print(tokenizer.decode([token_id]), end="", flush=True)
127 | all_token_ids.append(token_id)
128 | end_time = time.time()
129 |
130 | print("\n")
131 | generate_stats(torch.tensor(all_token_ids), tokenizer, start_time, end_time, print_tokens=False)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch03/02_math500-verifier-scripts/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 3: Evaluating Reasoning Models
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 | ## Bonus materials
8 |
9 | - [evaluate_math500.py](evaluate_math500.py): standalone script to evaluate models on the MATH-500 dataset
10 | - [evaluate_math500_batched.py](evaluate_math500_batched.py): same as above, but processes multiple examples in parallel during generation (for higher throughput)
11 |
12 | Both evaluation scripts import functionality from the [`reasoning_from_scratch`](../../reasoning_from_scratch) package to avoid code duplication. (See [chapter 2 setup instructions](../../ch02/02_setup-tips/python-instructions.md) for installation details.)
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
45 |
46 |
47 |
48 | ## Questions?
49 |
50 | If you have any questions, please don't hesitate to reach out via the [Discussions](https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch/discussions) forum in this GitHub repository.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/conftest.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
6 | download_qwen3_small,
7 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B,
8 | Qwen3Model,
9 | )
10 | import sys
11 | import types
12 | import nbformat
13 | import pytest
14 | import torch
15 |
16 |
17 | @pytest.fixture(scope="session")
18 | def qwen3_weights_path(tmp_path_factory):
19 | """Creates and saves a deterministic model for testing."""
20 |
21 | base_path = tmp_path_factory.mktemp("models")
22 | model_path = base_path / "qwen3_test_weights.pt"
23 | download_qwen3_small(kind="base", tokenizer_only=True, out_dir=base_path)
24 |
25 | if not model_path.exists():
26 | torch.manual_seed(123)
27 | model = Qwen3Model(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
28 | torch.save(model.state_dict(), model_path)
29 |
30 | return base_path
31 |
32 |
33 | def import_definitions_from_notebook(nb_path, module_name):
34 | if not nb_path.exists():
35 | raise FileNotFoundError(f"Notebook file not found at: {nb_path}")
36 |
37 | nb = nbformat.read(str(nb_path), as_version=4)
38 |
39 | mod = types.ModuleType(module_name)
40 | sys.modules[module_name] = mod
41 |
42 | # Pass 1: execute only imports (handle multi-line)
43 | for cell in nb.cells:
44 | if cell.cell_type != "code":
45 | continue
46 | lines = cell.source.splitlines()
47 | collecting = False
48 | buf = []
49 | paren_balance = 0
50 | for line in lines:
51 | stripped = line.strip()
52 | if not collecting and (stripped.startswith("import ") or stripped.startswith("from ")):
53 | collecting = True
54 | buf = [line]
55 | paren_balance = line.count("(") - line.count(")")
56 | if paren_balance == 0:
57 | exec("\n".join(buf), mod.__dict__)
58 | collecting = False
59 | buf = []
60 | elif collecting:
61 | buf.append(line)
62 | paren_balance += line.count("(") - line.count(")")
63 | if paren_balance == 0:
64 | exec("\n".join(buf), mod.__dict__)
65 | collecting = False
66 | buf = []
67 |
68 | # Pass 2: execute only def/class definitions
69 | for cell in nb.cells:
70 | if cell.cell_type != "code":
71 | continue
72 | src = cell.source
73 | if "def " in src or "class " in src:
74 | exec(src, mod.__dict__)
75 |
76 | return mod
77 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/04_torch-compile-windows/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Using `torch.compile()` on Windows
2 |
3 | `torch.compile()` relies on *TorchInductor*, which JIT-compiles kernels and requires a working C/C++ compiler toolchain.
4 |
5 | So, on Windows, the setup required to make `torch.compile` work can be a bit more involved than on Linux or macOS, which usually don't require any extra steps besides installing PyTorch.
6 |
7 | If you are a Windows user and using `torch.compile` sounds too tricky or complicated, don't worry, all code examples in this repository will work fine without compilation.
8 |
9 | Below are some tips that I compiled based on recommendations by [Daniel Kleine](https://github.com/d-kleine) and the following [PyTorch guide](https://docs.pytorch.org/tutorials/unstable/inductor_windows.html).
10 |
11 |
12 | ## 1 Basic Setup (CPU or CUDA)
13 |
14 |
15 | ### 1.1 Install Visual Studio 2022
16 |
17 | - Select the **“Desktop development with C++”** workload.
18 | - Make sure to include the **English language pack** (without it, you may run into UTF-8 encoding errors.)
19 |
20 |
21 | ### 1.2 Open the correct command prompt
22 |
23 |
24 | Launch Python from the
25 |
26 | **"x64 Native Tools Command Prompt for VS 2022"**
27 |
28 | or from the
29 |
30 | **"Visual Studio 2022 Developer Command Prompt"**.
31 |
32 | Alternatively, you can initialize the environment manually by running:
33 |
34 | ```bash
35 | "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\Community\VC\Auxiliary\Build\vcvars64.bat"
36 | ```
37 |
38 |
39 | ### 1.3 Verify that the compiler works
40 |
41 | Run
42 |
43 | ```bash
44 | cl.exe
45 | ```
46 |
47 | If you see version information printed, the compiler is ready.
48 |
49 |
50 | ## 2 Troubleshooting Common Errors
51 |
52 |
53 | ### 2.1 Error: `cl not found`
54 |
55 | Install **Visual Studio Build Tools** with the "C++ build tools" workload and run Python from a developer command prompt. (See this Microsoft [guide](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cpp/build/vscpp-step-0-installation?view=msvc-170) for details)
56 |
57 |
58 | ### 2.2 Error: `triton not found` (when using CUDA)
59 |
60 | Install the Windows build of Triton manually:
61 |
62 | ```bash
63 | pip install "triton-windows<3.4"
64 | ```
65 |
66 | or, if you are using `uv`:
67 |
68 | ```bash
69 | uv pip install "triton-windows<3.4"
70 | ```
71 |
72 | (As mentioned earlier, triton is required by TorchInductor for CUDA kernel compilation.)
73 |
74 |
75 |
76 |
77 | ## 3 Additional Notes
78 |
79 | On Windows, the `cl.exe` compiler is only accessible from within the Visual Studio Developer environment. This means that using `torch.compile()` in notebooks such as Jupyter may not work unless the notebook was launched from a Developer Command Prompt.
80 |
81 | As mentioned at the beginning of this article, there is also a [PyTorch guide](https://docs.pytorch.org/tutorials/unstable/inductor_windows.html) that some users found helpful when getting `torch.compile()` running on Windows CPU builds. However, note that it refers to PyTorch's unstable branch, so use it as a reference only.
82 |
83 | **If compilation continues to cause issues, please feel free to skip it. It's a nice bonus, but it's not important to follow the book.**
84 |
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chF/02_mmlu/random_guessing_baseline.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import argparse
6 | import random
7 | import statistics as stats
8 | from collections import Counter
9 |
10 | from datasets import load_dataset
11 |
12 |
13 | # Gold letter is MMLU jargon for correct answer letter
14 | def gold_letter(ans):
15 | if isinstance(ans, int):
16 | return "ABCD"[ans]
17 | s = str(ans).strip().upper()
18 | return s if s in {"A", "B", "C", "D"} else s[:1]
19 |
20 |
21 | def main():
22 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
23 | description="Show gold answer distribution for an MMLU subset and a random-guess baseline."
24 | )
25 | parser.add_argument(
26 | "--subset",
27 | type=str,
28 | default="high_school_mathematics",
29 | help="MMLU subset name (default: 'high_school_mathematics').",
30 | )
31 | parser.add_argument(
32 | "--seed",
33 | type=int,
34 | default=42,
35 | help="Random seed for the random-guess baseline (default: 42).",
36 | )
37 | parser.add_argument(
38 | "--trials",
39 | type=int,
40 | default=10_000,
41 | help="Number of random-guess trials (default: 10,000).",
42 | )
43 | args = parser.parse_args()
44 |
45 | ds = load_dataset("cais/mmlu", args.subset, split="test")
46 |
47 | labels = [gold_letter(ex["answer"]) for ex in ds]
48 | n = len(labels)
49 | counts = Counter(labels)
50 |
51 | print(f"Subset: {args.subset} | split: test | n={n}")
52 | print("Gold distribution provided in the dataset:")
53 | for letter in "ABCD":
54 | c = counts.get(letter, 0)
55 | pct = (c / n) if n else 0.0
56 | print(f" {letter}: {c} ({pct:.2%})")
57 |
58 | if n == 0:
59 | print("\nNo items. Baseline undefined.")
60 | return
61 |
62 | # Repeat random guessing
63 | rng = random.Random(args.seed)
64 | accs = []
65 | for _ in range(args.trials):
66 | guesses = [rng.choice("ABCD") for _ in range(n)]
67 | correct = sum(1 for g, y in zip(guesses, labels) if g == y)
68 | accs.append(correct / n)
69 |
70 | mean_acc = stats.mean(accs)
71 | sd_acc = stats.stdev(accs) if len(accs) > 1 else 0.0
72 |
73 | print(f"\nRandom guessing over {args.trials:,} trials (uniform A/B/C/D, seed={args.seed}):")
74 | print(f" Mean accuracy: {mean_acc:.2%}")
75 | print(f" Std dev across trials: {sd_acc:.2%}")
76 |
77 | # Quantiles
78 | qs = [0.01, 0.05, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 0.95, 0.99]
79 | accs_sorted = sorted(accs)
80 | print("\nSelected quantiles of accuracy:")
81 | for q in qs:
82 | idx = int(q * len(accs_sorted))
83 | print(f" {q:.0%} quantile: {accs_sorted[idx]:.3%}")
84 |
85 | # Frequency table (rounded)
86 | acc_counts = Counter(round(a, 2) for a in accs)
87 | print("\nFull frequency table of accuracies (rounded):")
88 | for acc_val in sorted(acc_counts):
89 | freq = acc_counts[acc_val]
90 | pct = freq / args.trials
91 | print(f" {acc_val:.3f}: {freq} times ({pct:.2%})")
92 |
93 |
94 | if __name__ == "__main__":
95 | main()
96 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/reasoning_from_scratch/ch02.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | from .qwen3 import KVCache
6 | import torch
7 |
8 |
9 | def get_device(enable_tensor_cores=True):
10 | if torch.cuda.is_available():
11 | device = torch.device("cuda")
12 | print("Using NVIDIA CUDA GPU")
13 |
14 | if enable_tensor_cores:
15 | major, minor = map(int, torch.__version__.split(".")[:2])
16 | if (major, minor) >= (2, 9):
17 | torch.backends.cuda.matmul.fp32_precision = "tf32"
18 | torch.backends.cudnn.conv.fp32_precision = "tf32"
19 | else:
20 | torch.backends.cuda.matmul.allow_tf32 = True
21 | torch.backends.cudnn.allow_tf32 = True
22 |
23 | elif torch.backends.mps.is_available():
24 | device = torch.device("mps")
25 | print("Using Apple Silicon GPU (MPS)")
26 |
27 | elif torch.xpu.is_available():
28 | device = torch.device("xpu")
29 | print("Using Intel GPU")
30 |
31 | else:
32 | device = torch.device("cpu")
33 | print("Using CPU")
34 |
35 | return device
36 |
37 |
38 | @torch.inference_mode()
39 | def generate_text_basic(model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=None):
40 | input_length = token_ids.shape[1]
41 | model.eval()
42 |
43 | for _ in range(max_new_tokens):
44 | out = model(token_ids)[:, -1]
45 | next_token = torch.argmax(out, dim=-1, keepdim=True)
46 |
47 | # Stop if all sequences in the batch have generated EOS
48 | if (eos_token_id is not None
49 | and next_token.item() == eos_token_id):
50 | break
51 |
52 | token_ids = torch.cat([token_ids, next_token], dim=1)
53 | return token_ids[:, input_length:]
54 |
55 |
56 | @torch.inference_mode()
57 | def generate_text_basic_cache(
58 | model,
59 | token_ids,
60 | max_new_tokens,
61 | eos_token_id=None
62 | ):
63 |
64 | input_length = token_ids.shape[1]
65 | model.eval()
66 | cache = KVCache(n_layers=model.cfg["n_layers"])
67 | model.reset_kv_cache()
68 | out = model(token_ids, cache=cache)[:, -1]
69 |
70 | for _ in range(max_new_tokens):
71 | next_token = torch.argmax(out, dim=-1, keepdim=True)
72 |
73 | if (eos_token_id is not None
74 | and next_token.item() == eos_token_id):
75 | break
76 |
77 | token_ids = torch.cat([token_ids, next_token], dim=1)
78 | out = model(next_token, cache=cache)[:, -1]
79 |
80 | return token_ids[:, input_length:]
81 |
82 |
83 | def generate_stats(output_token_ids, tokenizer, start_time,
84 | end_time, print_tokens=True):
85 | total_time = end_time - start_time
86 | print(f"Time: {total_time:.2f} sec")
87 | print(f"{int(output_token_ids.numel() / total_time)} tokens/sec")
88 |
89 | for name, backend in (("CUDA", getattr(torch, "cuda", None)),
90 | ("XPU", getattr(torch, "xpu", None))):
91 | if backend is not None and backend.is_available():
92 | max_mem_bytes = backend.max_memory_allocated()
93 | max_mem_gb = max_mem_bytes / (1024 ** 3)
94 | print(f"Max {name} memory allocated: {max_mem_gb:.2f} GB")
95 | backend.reset_peak_memory_stats()
96 |
97 | if print_tokens:
98 | output_text = tokenizer.decode(output_token_ids.squeeze(0).tolist())
99 | print(f"\n{output_text}")
100 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/scripts/check_notebook_line_length.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | # Check if code in notebooks exceeds line length
6 | # Usage: uv run .github/scripts/check_notebook_line_length.py --max-len 76 ch02/01_main-chapter-code/ch02_main.ipynb ch03/01_main-chapter-code/ch03_main.ipynb
7 |
8 | import argparse
9 | import sys
10 | from pathlib import Path
11 | import nbformat as nbf
12 |
13 |
14 | def parse_args():
15 | p = argparse.ArgumentParser(
16 | description="Check code-cell line lengths in specific .ipynb files."
17 | )
18 | p.add_argument(
19 | "--max-len",
20 | type=int,
21 | default=76,
22 | help="Maximum allowed characters per line (default: 76)",
23 | )
24 | p.add_argument(
25 | "notebooks",
26 | nargs="+",
27 | help="Paths to .ipynb files to check.",
28 | )
29 | return p.parse_args()
30 |
31 |
32 | def strip_inline_comment(line):
33 | """Return line with any trailing #... comment removed, but keep # inside quotes."""
34 | in_quote = None
35 | escaped = False
36 | for i, ch in enumerate(line):
37 | if escaped:
38 | escaped = False
39 | continue
40 | if ch == "\\":
41 | escaped = True
42 | continue
43 | if ch in ("'", '"'):
44 | if in_quote is None:
45 | in_quote = ch
46 | elif in_quote == ch:
47 | in_quote = None
48 | continue
49 | if ch == "#" and in_quote is None:
50 | return line[:i].rstrip()
51 | return line.rstrip()
52 |
53 |
54 | def main():
55 | args = parse_args()
56 |
57 | nb_paths = []
58 | for raw in args.notebooks:
59 | p = Path(raw).resolve()
60 | if not p.exists():
61 | print(f"::warning file={raw}::File not found, skipping.")
62 | continue
63 | if p.suffix != ".ipynb":
64 | print(f"::warning file={raw}::Not a .ipynb file, skipping.")
65 | continue
66 | nb_paths.append(p)
67 |
68 | if not nb_paths:
69 | print("No valid notebooks to check.")
70 | return 0
71 |
72 | violations = []
73 |
74 | for nb_path in nb_paths:
75 | try:
76 | nb = nbf.read(nb_path, as_version=4)
77 | except Exception as e:
78 | print(f"::warning file={nb_path}::Failed to read notebook: {e}")
79 | continue
80 |
81 | for ci, cell in enumerate(nb.cells, start=1):
82 | if cell.get("cell_type") != "code":
83 | continue
84 |
85 | src = cell.get("source", "")
86 | lines = src if isinstance(src, list) else src.splitlines()
87 |
88 | for li, line in enumerate(lines, start=1):
89 | code_part = strip_inline_comment(line)
90 | length = len(code_part)
91 | if length > args.max_len:
92 | print(
93 | f"::error file={nb_path}::Line length {length} exceeds "
94 | f"{args.max_len} in code cell {ci}, line {li}"
95 | )
96 | snippet = code_part if len(code_part) <= 120 else code_part[:120] + "…"
97 | violations.append((str(nb_path), ci, li, length, snippet))
98 |
99 | if violations:
100 | print("\nFound lines exceeding the limit:\n")
101 | for path, ci, li, length, snippet in violations:
102 | print(f"- {path} | cell {ci} line {li}: {length} chars\n {snippet}")
103 | return 1
104 |
105 | print(f"All notebooks pass: no code-cell lines exceed {args.max_len} characters.")
106 | return 0
107 |
108 |
109 | if __name__ == "__main__":
110 | sys.exit(main())
111 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch03/02_math500-verifier-scripts/evaluate_math500.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import argparse
6 | import torch
7 |
8 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
9 | Qwen3Model,
10 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B
11 | )
12 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import get_device
13 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch03 import (
14 | load_math500_test,
15 | evaluate_math500_stream,
16 | load_model_and_tokenizer,
17 | load_tokenizer_only
18 | )
19 |
20 |
21 | def parse_args():
22 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
23 | parser.add_argument(
24 | "--device",
25 | type=str,
26 | default="auto",
27 | help="Device to use: 'auto' (default), or any torch device string like 'cpu', 'cuda', 'cuda:0', 'mps'.",
28 | )
29 | parser.add_argument(
30 | "--which_model",
31 | type=str,
32 | default="base",
33 | choices=["base", "reasoning", "instruct"],
34 | help="Model variant to load. Defaults to 'base'.",
35 | )
36 | parser.add_argument(
37 | "--dataset_size",
38 | type=int,
39 | default=10,
40 | help="Number of MATH-500 examples to evaluate. Default: 10",
41 | )
42 | parser.add_argument(
43 | "--max_new_tokens",
44 | type=int,
45 | default=2048,
46 | help="Max new tokens for generation. Default: 2048",
47 | )
48 | parser.add_argument(
49 | "--compile",
50 | action="store_true",
51 | help="Enable torch.compile for the model.",
52 | )
53 | parser.add_argument(
54 | "--checkpoint_path",
55 | type=str,
56 | default=None,
57 | help="Optional path to a .pth checkpoint to load model weights from.",
58 | )
59 | parser.add_argument(
60 | "--verbose",
61 | action="store_true",
62 | help="Print per-sample correctness while evaluating.",
63 | )
64 | return parser.parse_args()
65 |
66 |
67 | if __name__ == "__main__":
68 | args = parse_args()
69 |
70 | if args.device == "auto":
71 | device = get_device()
72 | else:
73 | device = torch.device(args.device)
74 |
75 | which_model = args.which_model
76 | dataset_size = args.dataset_size
77 | max_new_tokens = args.max_new_tokens
78 | use_compile = args.compile
79 |
80 | print("Model:", which_model)
81 | print("Device:", device)
82 | dev_name = str(device).replace(":", "-")
83 |
84 | math_data = load_math500_test()
85 |
86 | if args.which_model == "instruct":
87 | which_model = "reasoning"
88 | else:
89 | which_model = args.which_model
90 |
91 | if args.checkpoint_path:
92 | # To load the saved RL checkpoint files from chapter 6
93 | tokenizer = load_tokenizer_only(which_model=which_model)
94 | model = Qwen3Model(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
95 | model.to(device)
96 | state_dict = torch.load(args.checkpoint_path, map_location=device)
97 | model.load_state_dict(state_dict)
98 | if args.compile:
99 | torch._dynamo.config.allow_unspec_int_on_nn_module = True
100 | model = torch.compile(model)
101 | else:
102 | model, tokenizer = load_model_and_tokenizer(
103 | which_model=which_model,
104 | device=device,
105 | use_compile=args.compile
106 | )
107 |
108 | if args.which_model == "instruct":
109 | tokenizer.add_thinking = False
110 |
111 | model.eval()
112 | torch.set_float32_matmul_precision("high")
113 |
114 | num_correct, num_examples, acc = evaluate_math500_stream(
115 | model=model,
116 | out_path=f"math500_{which_model}-{dev_name}-evaluate-script.jsonl",
117 | tokenizer=tokenizer,
118 | device=device,
119 | math_data=math_data[:dataset_size],
120 | max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
121 | verbose=args.verbose,
122 | )
123 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/chG/01_main-chapter-code/qwen3_chat_interface_multiturn.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt).
2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch"
3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch
4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch
5 |
6 |
7 | import torch
8 | import chainlit
9 |
10 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
11 | get_device,
12 | )
13 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02_ex import generate_text_basic_stream_cache
14 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch03 import load_model_and_tokenizer
15 |
16 | # ============================================================
17 | # EDIT ME: Simple configuration
18 | # ============================================================
19 | WHICH_MODEL = "reasoning" # "base" for base model
20 | MAX_NEW_TOKENS = 38912
21 | LOCAL_DIR = "qwen3"
22 | COMPILE = False
23 | # ============================================================
24 |
25 |
26 | def trim_input_tensor(input_ids_tensor, context_len, max_new_tokens):
27 | assert max_new_tokens < context_len
28 | keep_len = max(1, context_len - max_new_tokens)
29 |
30 | # If the prompt is too long, left-truncate to keep_len
31 | if input_ids_tensor.shape[1] > keep_len:
32 | input_ids_tensor = input_ids_tensor[:, -keep_len:]
33 |
34 | return input_ids_tensor
35 |
36 |
37 | def build_prompt_from_history(history, add_assistant_header=True):
38 | """
39 | history: [{"role": "system"|"user"|"assistant", "content": str}, ...]
40 | """
41 | parts = []
42 | for m in history:
43 | role = m["role"]
44 | content = m["content"]
45 | parts.append(f"<|im_start|>{role}\n{content}<|im_end|>\n")
46 |
47 | if add_assistant_header:
48 | parts.append("<|im_start|>assistant\n")
49 | return "".join(parts)
50 |
51 |
52 | DEVICE = get_device()
53 | MODEL, TOKENIZER = load_model_and_tokenizer(
54 | which_model=WHICH_MODEL,
55 | device=DEVICE,
56 | use_compile=COMPILE,
57 | local_dir=LOCAL_DIR
58 | )
59 |
60 | # Even though the official TOKENIZER.eos_token_id is either <|im_end|> (reasoning)
61 | # or <|endoftext|> (base), the reasoning model sometimes emits both.
62 | EOS_TOKEN_IDS = (
63 | TOKENIZER.encode("<|im_end|>")[0],
64 | TOKENIZER.encode("<|endoftext|>")[0]
65 | )
66 |
67 |
68 | @chainlit.on_chat_start
69 | async def on_start():
70 | chainlit.user_session.set("history", [])
71 | chainlit.user_session.get("history").append(
72 | {"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."}
73 | )
74 |
75 |
76 | @chainlit.on_message
77 | async def main(message: chainlit.Message):
78 | """
79 | The main Chainlit function.
80 | """
81 | # 0) Get and track chat history
82 | history = chainlit.user_session.get("history")
83 | history.append({"role": "user", "content": message.content})
84 |
85 | # 1) Encode input
86 | prompt = build_prompt_from_history(history, add_assistant_header=True)
87 | input_ids = TOKENIZER.encode(prompt)
88 | input_ids_tensor = torch.tensor(input_ids, device=DEVICE).unsqueeze(0)
89 |
90 | # Multi-turn can be very long, so we add this left-trimming
91 | input_ids_tensor = trim_input_tensor(
92 | input_ids_tensor=input_ids_tensor,
93 | context_len=MODEL.cfg["context_length"],
94 | max_new_tokens=MAX_NEW_TOKENS
95 | )
96 |
97 | # 2) Start an outgoing message we can stream into
98 | out_msg = chainlit.Message(content="")
99 | await out_msg.send()
100 |
101 | # 3) Stream generation
102 | for tok in generate_text_basic_stream_cache(
103 | model=MODEL,
104 | token_ids=input_ids_tensor,
105 | max_new_tokens=MAX_NEW_TOKENS,
106 | # eos_token_id=TOKENIZER.eos_token_id
107 | ):
108 | token_id = tok.squeeze(0)
109 | if token_id in EOS_TOKEN_IDS:
110 | break
111 | piece = TOKENIZER.decode(token_id.tolist())
112 | await out_msg.stream_token(piece)
113 |
114 | # 4) Finalize the streamed message
115 | await out_msg.update()
116 |
117 | # 5) Update chat history
118 | history.append({"role": "assistant", "content": out_msg.content})
119 | chainlit.user_session.set("history", history)
120 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_ch02.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | import torch
6 |
7 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
8 | get_device,
9 | generate_text_basic,
10 | generate_text_basic_cache,
11 | generate_stats
12 | )
13 |
14 |
15 | # Dummy model for generate_text_basic tests.
16 | class DummyModel:
17 | def __init__(self, fixed_token, vocab_size=5):
18 | self.fixed_token = fixed_token
19 | self.vocab_size = vocab_size
20 | self.eval_called = False
21 |
22 | def eval(self):
23 | self.eval_called = True
24 | return self
25 |
26 | def __call__(self, token_ids, cache=None):
27 | batch_size, seq_len = token_ids.size()
28 | out = torch.zeros(batch_size, seq_len, self.vocab_size)
29 | # Set the fixed_token column to the highest value so argmax returns fixed_token
30 | out[..., self.fixed_token] = 1.0
31 | return out
32 |
33 |
34 | class DummyModelCache(DummyModel):
35 | def __init__(self, fixed_token, vocab_size=5, n_layers=2):
36 | super().__init__(fixed_token, vocab_size)
37 | self.cfg = {"n_layers": n_layers}
38 | self.reset_called = False
39 |
40 | def reset_kv_cache(self):
41 | self.reset_called = True
42 |
43 |
44 | class DummyTokenizer:
45 | def decode(self, token_list):
46 | return " ".join(str(t) for t in token_list)
47 |
48 |
49 | def test_get_device_returns_torch_device(capsys):
50 | device = get_device()
51 | assert isinstance(device, torch.device)
52 | assert device.type in ("cpu", "cuda", "mps")
53 |
54 |
55 | def test_generate_text_basic_stops_on_eos():
56 | # batch_size = 1
57 | # seq_len = 3
58 | max_new_tokens = 10
59 | fixed_token = 2
60 |
61 | dummy_model = DummyModel(fixed_token=fixed_token)
62 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[1, 3, 4]]) # shape (batch, seq_len)
63 |
64 | # Set eos_token_id to be the fixed_token so that generation stops immediately
65 | output = generate_text_basic(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=fixed_token)
66 | assert output.size(1) == 0
67 | assert dummy_model.eval_called is True
68 |
69 |
70 | def test_generate_text_basic_generates_tokens_without_eos():
71 | # batch_size = 1
72 | # seq_len = 2
73 | max_new_tokens = 3
74 | fixed_token = 1
75 |
76 | dummy_model = DummyModel(fixed_token=fixed_token)
77 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[0, 4]])
78 | output = generate_text_basic(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=None)
79 | assert output.size(1) == max_new_tokens
80 | assert torch.all(output == fixed_token)
81 |
82 |
83 | def test_generate_text_basic_cache_stops_on_eos():
84 | # batch_size = 1
85 | # seq_len = 2
86 | max_new_tokens = 10
87 | fixed_token = 3
88 |
89 | dummy_model = DummyModelCache(fixed_token=fixed_token, n_layers=4)
90 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[2, 2]])
91 | output = generate_text_basic_cache(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=fixed_token)
92 | assert output.size(1) == 0
93 | assert dummy_model.reset_called is True
94 |
95 |
96 | def test_generate_text_basic_cache_generates_tokens_without_eos():
97 | # batch_size = 1
98 | # seq_len = 1
99 | max_new_tokens = 4
100 | fixed_token = 0
101 |
102 | dummy_model = DummyModelCache(fixed_token=fixed_token, n_layers=3)
103 | token_ids = torch.tensor([[5]])
104 |
105 | output = generate_text_basic_cache(dummy_model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=None)
106 | assert output.size(1) == max_new_tokens
107 | assert torch.all(output == fixed_token)
108 | assert dummy_model.reset_called is True
109 |
110 |
111 | def test_generate_stats_prints_output(monkeypatch, capsys):
112 | output_token_ids = torch.tensor([[10, 20, 30]])
113 | tokenizer = DummyTokenizer()
114 | start_time = 100.0
115 | end_time = 102.0
116 |
117 | monkeypatch.setattr(torch.cuda, "is_available", lambda: False)
118 | generate_stats(output_token_ids, tokenizer, start_time, end_time)
119 |
120 | captured = capsys.readouterr().out
121 | assert "Time:" in captured
122 | assert "tokens/sec" in captured
123 | assert "10 20 30" in captured
124 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch02/05_use_model/generate_simple.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt)
2 | # Source for "Build a Reasoning Model (From Scratch)": https://mng.bz/lZ5B
3 | # Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/reasoning-from-scratch
4 |
5 | # Runs the model similar to chapter 2 and 3 in streaming mode with the least
6 | # amount of bells and whistles. Uses KV caching by default.
7 |
8 | import argparse
9 | from pathlib import Path
10 | import time
11 | import torch
12 |
13 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02 import (
14 | get_device,
15 | generate_stats
16 | )
17 | from reasoning_from_scratch.ch02_ex import (
18 | generate_text_basic_stream_cache
19 | )
20 | from reasoning_from_scratch.qwen3 import (
21 | download_qwen3_small,
22 | Qwen3Model,
23 | Qwen3Tokenizer,
24 | QWEN_CONFIG_06_B
25 | )
26 |
27 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Run Qwen3 text generation")
28 | parser.add_argument(
29 | "--device",
30 | type=str,
31 | default=None,
32 | help="Device to run on (e.g. 'cpu', 'cuda', 'mps'). "
33 | "If not provided, will auto-detect with get_device()."
34 | )
35 | parser.add_argument(
36 | "--max_new_tokens",
37 | type=int,
38 | default=2048,
39 | help="Maximum number of new tokens to generate (default: 2048)."
40 | )
41 | parser.add_argument(
42 | "--compile",
43 | action="store_true",
44 | help="Compile PyTorch model (default: False)."
45 | )
46 | parser.add_argument(
47 | "--reasoning",
48 | action="store_true",
49 | help="Use reasoning model variant (default: False)."
50 | )
51 | parser.add_argument(
52 | "--prompt",
53 | type=str,
54 | default=None,
55 | help=("Use a custom prompt. If not explicitly provided, uses the following defaults: "
56 | "'Explain large language models in a single sentence.' for the base model, and "
57 | "'Find all c in Z_3 such that Z_3[x]/(x^2 + c) is a field.' for the reasoning model.")
58 | )
59 |
60 | args = parser.parse_args()
61 | device = torch.device(args.device) if args.device else get_device()
62 |
63 | if args.reasoning:
64 | download_qwen3_small(kind="reasoning", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
65 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-reasoning.json"
66 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-reasoning.pth"
67 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
68 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
69 | apply_chat_template=True,
70 | add_generation_prompt=True,
71 | add_thinking=True
72 | )
73 | else:
74 | download_qwen3_small(kind="base", tokenizer_only=False, out_dir="qwen3")
75 | tokenizer_path = Path("qwen3") / "tokenizer-base.json"
76 | model_path = Path("qwen3") / "qwen3-0.6B-base.pth"
77 | tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(
78 | tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_path,
79 | apply_chat_template=False,
80 | add_generation_prompt=False,
81 | add_thinking=False
82 | )
83 |
84 | model = Qwen3Model(QWEN_CONFIG_06_B)
85 | state = torch.load(model_path, map_location=device)
86 | model.load_state_dict(state)
87 | model.to(device)
88 | model.eval()
89 |
90 | if args.compile:
91 | model = torch.compile(model)
92 |
93 |
94 | if args.prompt is None:
95 | if args.reasoning:
96 | prompt = "Find all c in Z_3 such that Z_3[x]/(x^2 + c) is a field."
97 | else:
98 | prompt = "Explain large language models in a single sentence."
99 | else:
100 | prompt = args.prompt
101 |
102 |
103 | input_ids = tokenizer.encode(prompt)
104 | input_token_ids_tensor = torch.tensor(input_ids, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
105 |
106 | print()
107 | print("=" * 60)
108 | print(f"torch : {torch.__version__}")
109 | print(f"device : {device}")
110 | print("cache : True")
111 | print(f"compile : {args.compile}")
112 | print(f"reasoning : {args.reasoning}")
113 | print("=" * 60)
114 | print()
115 |
116 | start_time = time.time()
117 | all_token_ids = []
118 |
119 | for token in generate_text_basic_stream_cache(
120 | model=model,
121 | token_ids=input_token_ids_tensor,
122 | max_new_tokens=args.max_new_tokens,
123 | eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id
124 | ):
125 | token_id = token.squeeze(0).item()
126 | print(tokenizer.decode([token_id]), end="", flush=True)
127 | all_token_ids.append(token_id)
128 | end_time = time.time()
129 |
130 | print("\n")
131 | generate_stats(torch.tensor(all_token_ids), tokenizer, start_time, end_time, print_tokens=False)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch03/02_math500-verifier-scripts/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 3: Evaluating Reasoning Models
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 | ## Bonus materials
8 |
9 | - [evaluate_math500.py](evaluate_math500.py): standalone script to evaluate models on the MATH-500 dataset
10 | - [evaluate_math500_batched.py](evaluate_math500_batched.py): same as above, but processes multiple examples in parallel during generation (for higher throughput)
11 |
12 | Both evaluation scripts import functionality from the [`reasoning_from_scratch`](../../reasoning_from_scratch) package to avoid code duplication. (See [chapter 2 setup instructions](../../ch02/02_setup-tips/python-instructions.md) for installation details.)
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |  7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 | - Ollama is an open-source application to run LLMs efficiently
13 | - It is a wrapper around llama.cpp ([https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp)), which implements LLMs in pure C/C++ to maximize efficiency
14 | - Note that it is a to ol for using LLMs to generate text (inference), not training or finetuning LLMs
15 | - Before running the code below, install ollama by visiting [https://ollama.com](https://ollama.com) and following the instructions (for instance, clicking on the "Download" button and downloading the ollama application for your operating system)
16 | - For macOS and Windows users, click on the ollama application you downloaded; if it prompts you to install the command line usage, say "yes"
17 | - Linux users can use the installation command provided on the ollama website
18 | - There are 3 ways we can run ollama on our computer:
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 | **1. `ollama serve`**
23 |
24 | - This runs the ollama backend as a server, usually on `http://localhost:11434`. It doesn't load a model until we call it through the API. This is what we want if we want to use ollama through Python.
25 |
26 | **2. `ollama run gpt-oss:20b`**
27 |
28 | - This is a convenience wrapper. If the server is not already running, it will start it, then download the model (the first time), and drop us into an interactive terminal where we can chat with the model. Behind the scenes, it uses the same server API.
29 |
30 | **3. Ollama desktop app**
31 |
32 | - This runs the same backend automatically and provides a GUI on top of it (as shown in the figure above).
33 | It also applies defaults (system prompt, temperature, stop sequences), which can explain why answers look different from raw API usage.
34 |
35 |
36 |
37 | ## Usage
38 |
39 |
40 |
41 | The options and defaults are shown below.
42 |
43 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 | - Ollama is an open-source application to run LLMs efficiently
13 | - It is a wrapper around llama.cpp ([https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp)), which implements LLMs in pure C/C++ to maximize efficiency
14 | - Note that it is a to ol for using LLMs to generate text (inference), not training or finetuning LLMs
15 | - Before running the code below, install ollama by visiting [https://ollama.com](https://ollama.com) and following the instructions (for instance, clicking on the "Download" button and downloading the ollama application for your operating system)
16 | - For macOS and Windows users, click on the ollama application you downloaded; if it prompts you to install the command line usage, say "yes"
17 | - Linux users can use the installation command provided on the ollama website
18 | - There are 3 ways we can run ollama on our computer:
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 | **1. `ollama serve`**
23 |
24 | - This runs the ollama backend as a server, usually on `http://localhost:11434`. It doesn't load a model until we call it through the API. This is what we want if we want to use ollama through Python.
25 |
26 | **2. `ollama run gpt-oss:20b`**
27 |
28 | - This is a convenience wrapper. If the server is not already running, it will start it, then download the model (the first time), and drop us into an interactive terminal where we can chat with the model. Behind the scenes, it uses the same server API.
29 |
30 | **3. Ollama desktop app**
31 |
32 | - This runs the same backend automatically and provides a GUI on top of it (as shown in the figure above).
33 | It also applies defaults (system prompt, temperature, stop sequences), which can explain why answers look different from raw API usage.
34 |
35 |
36 |
37 | ## Usage
38 |
39 |
40 |
41 | The options and defaults are shown below.
42 |
43 |