├── .eslintignore
├── .eslintrc
├── .flowconfig
├── .github
└── workflows
│ └── backup.yml
├── .gitignore
├── .npmignore
├── .travis.yml
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── coverageconfig.json
├── docs
├── api-reference.md
├── assets
│ └── exceptions
│ │ ├── flow.sketch
│ │ ├── flow1.png
│ │ ├── flow2.png
│ │ ├── flow3.png
│ │ └── flow4.png
├── exceptions.md
└── promise-vs-task-api.md
├── examples
└── io
│ ├── 1.js
│ └── README.md
├── package.json
├── src
└── index.js
└── test
├── ap.js
├── bimap.js
├── chain.js
├── chainRec.js
├── common.js
├── concat.js
├── do.js
├── empty.js
├── fantasyLand.js
├── fromComputation.js
├── fromPromise.js
├── map.js
├── mapRejected.js
├── of.js
├── orElse.js
├── parallel.js
├── race.js
├── recur.js
├── rejected.js
├── runTimeTypes.js
├── toPromise.js
└── toString.js
/.eslintignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | lib
2 | lib-es
3 | umd
4 | .build-artefacts
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.eslintrc:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "parser": "babel-eslint",
3 | "extends": ["eslint:recommended"],
4 | "plugins": [
5 | "flowtype"
6 | ],
7 | "rules": {
8 | "flowtype/define-flow-type": 1,
9 | "flowtype/type-id-match": [1, "^([A-Z][a-z0-9]+)+$"],
10 | "flowtype/use-flow-type": 1,
11 | "comma-dangle": [2, 'always-multiline']
12 | },
13 | "env": {
14 | "node": true
15 | }
16 | }
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.flowconfig:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [ignore]
2 |
3 | [include]
4 |
5 | [libs]
6 |
7 | [options]
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/backup.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: Backup
2 |
3 | on:
4 | push:
5 | branches: [master]
6 |
7 | jobs:
8 | main:
9 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
10 | steps:
11 | - name: Checkout
12 | uses: actions/checkout@v3
13 | with:
14 | fetch-depth: 0
15 |
16 | - name: Backup to BitBucket
17 | uses: rpominov/git-backup-action@v2
18 | env:
19 | SSH_PRIVATE_KEY: ${{ secrets.BITBUCKET_PRIVATE_KEY }}
20 | REMOTE: "git@bitbucket.org:rpominov/fun-task_backup.git"
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | node_modules
2 | lib
3 | lib-es
4 | umd
5 | npm-debug.log
6 | .nyc_output
7 | .build-artefacts
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.npmignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | npm-debug.log
2 | .nyc_output
3 | .build-artefacts
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.travis.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | language: node_js
2 | sudo: false
3 | node_js:
4 | - '5.10'
5 | cache:
6 | directories:
7 | - node_modules
8 | script:
9 | - npm test
10 | - npm run lobot test coveralls || true
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | The MIT License (MIT)
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2016 Roman Pominov
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # fun-task* [](https://travis-ci.org/rpominov/fun-task) [](https://coveralls.io/github/rpominov/fun-task?branch=master)
2 |
3 | An abstraction for managing asynchronous code in JS.
4 |
5 | \* The name is an abbreviation for "functional task" (this library is based on many ideas
6 | from Functional Programming). The type that library implements is usually referred to in the documentation as just "Task".
7 |
8 |
9 | ## Installation
10 |
11 | ### NPM
12 |
13 | ```
14 | npm install fun-task
15 | ```
16 |
17 | ```js
18 | // modern JavaScript
19 | import Task from 'fun-task'
20 |
21 | // classic JavaScript
22 | var Task = require('fun-task')
23 | ```
24 |
25 | ### CDN
26 |
27 | ```html
28 |
29 |
32 | ```
33 |
34 |
35 | ## What is a Task?
36 |
37 | Task is an abstraction similar to Promises. The key difference is that a
38 | Task represents a computation while a Promise represents only a result of a computation.
39 | If we have a Task we can: start the computation; terminate it before it's finished;
40 | or wait until it finishes, and get the result. While with a Promise we can only get the result.
41 | This difference doesn't make Tasks *better*, they are just different, we can
42 | find legitimate use cases for both abstractions. Let's review it again:
43 |
44 | If we have a Task:
45 |
46 | - We can start the computation that it represents (e.g. a network request)
47 | - We can choose not to start the computation and just throw task away
48 | - We can start it more than once
49 | - While computation is running, we can notify it that we're not interested in the result any more,
50 | and as a response computation may choose to terminate itself
51 | - When computation finishes we get the result
52 |
53 | If we have a Promise:
54 |
55 | - Computation is already running (or finished) and we don't have any control of it
56 | - We can get the result whenever it's ready
57 | - If two or more consumers have a same Promise they all will get the same result
58 |
59 | The last item is important. This might be an advantage of Promises over Tasks.
60 | If two consumers have a same Task, each of them have to spawn
61 | their own instance of the computation in order to get the result,
62 | and they may even get different results.
63 |
64 |
65 | ## What is a computation?
66 |
67 | ```js
68 | function computation(onSuccess, onFailure) {
69 | // ...
70 | return () => {
71 | // ... cancellation logic
72 | }
73 | }
74 | ```
75 |
76 | From Task API perspective, computation is a function that accepts two callbacks.
77 | It should call one of them after completion with the final result.
78 | Also a computation may return a function with cancellation logic, or it can return `undefined`
79 | if particular computation has no cancellation logic.
80 |
81 | Creating a Task from a computation is easy, we just call `task = Task.create(computation)`.
82 | This is very similar to `new Promise(computation)`, but Task won't execute `computation`
83 | immediately, the computation starts only when `task.run()` is called.
84 |
85 |
86 | ## Documentation
87 |
88 | - [API reference](https://github.com/rpominov/fun-task/blob/master/docs/api-reference.md)
89 | - [How exceptions catching work in Task](https://github.com/rpominov/fun-task/blob/master/docs/exceptions.md#how-exceptions-work-in-task)
90 | - [API comparison with Promises](https://github.com/rpominov/fun-task/blob/master/docs/promise-vs-task-api.md)
91 |
92 | ## [Flow](https://flowtype.org/)
93 |
94 | The NPM package ships with Flow definitions. So you can do something like this if you use Flow:
95 |
96 | ```js
97 | // @flow
98 |
99 | import Task from 'fun-task'
100 |
101 | function incrementTask(task: Task): Task {
102 | return task.map(x => x + 1)
103 | }
104 | ```
105 |
106 | ## Specifications compatibility
107 |
108 |
109 |  110 |
111 |
112 |
110 |
111 |
112 | 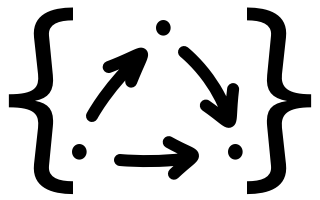 113 |
114 |
115 | Task is compatible with [Fantasy Land](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land) and [Static Land](https://github.com/rpominov/static-land) implementing:
116 |
117 | - [Semigroup](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#semigroup)
118 | - [Monoid](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#monoid)
119 | - [Functor](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#functor)
120 | - [Bifunctor](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#bifunctor)
121 | - [Apply](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#apply)
122 | - [Applicative](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#applicative)
123 | - [Chain](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#chain)
124 | - [ChainRec](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#chainrec)
125 | - [Monad](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#monad)
126 |
127 | ## Development
128 |
129 | ```
130 | npm run lobot -- --help
131 | ```
132 |
133 | Run [lobot](https://github.com/rpominov/lobot) commands as `npm run lobot -- args...`
134 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/coverageconfig.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "coverage": ["./.build-artefacts/lcov.info"]
3 | }
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/api-reference.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Task API Reference
2 |
3 | ## `Task.create(computation)`
4 |
5 | Creates a Task from a computation. Computation is a function that accepts two callbacks.
6 | It should call one of them after completion with the final result (success or failure).
7 | Also a computation may return a function with cancellation logic
8 | or it can return `undefined` if there is no cancellation logic.
9 |
10 | ```js
11 | const task = Task.create((onSuccess, onFailure) => {
12 | // ...
13 | return () => {
14 | // cancellation logic
15 | }
16 | })
17 |
18 | // The computation is executed every time we run the task
19 | const cancel = task.run({
20 | success(result) {
21 | // success result goes here
22 | },
23 | failure(result) {
24 | // failure result goes here
25 | },
26 | })
27 |
28 | // If we cancel the task the cancellation logic from computation
29 | // will be executed (if provided)
30 | cancel()
31 | ```
32 |
33 | Here is some runnable example:
34 |
35 | ```js
36 | const wait5sec = Task.create(onSuccess => {
37 | const timeoutId = setTimeout(() => {
38 | onSuccess('5 seconds')
39 | }, 5000)
40 | return () => { clearTimeout(timeoutId) }
41 | })
42 |
43 | wait5sec.run({
44 | success(timeWaited) {
45 | console.log(`We've waited for ${timeWaited}`)
46 | },
47 | })
48 |
49 | // > We've waited for 5 seconds
50 | ```
51 |
52 | After cancellation or completion the `onSuccess` and `onFailure` callbacks become noop.
53 | Also if `cancel` called second time or after a completion the cancelation logic won't be executed.
54 |
55 | ## `Task.of(value)`
56 |
57 | Creates a task that resolves with a given value.
58 |
59 | ```js
60 | Task.of(2).run({
61 | success(x) {
62 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
63 | },
64 | })
65 |
66 | // > result: 2
67 | ```
68 |
69 | ## `Task.rejected(error)`
70 |
71 | Creates a task that fails with a given error.
72 |
73 | ```js
74 | Task.rejected(2).run({
75 | failure(error) {
76 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
77 | },
78 | })
79 |
80 | // > error: 2
81 | ```
82 |
83 | ## `Task.empty()`
84 |
85 | Creates a task that never completes.
86 |
87 | ```js
88 | Task.empty().run({
89 | success(x) {
90 | // callback never called
91 | },
92 | failure(error) {
93 | // callback never called
94 | },
95 | })
96 | ```
97 |
98 | ## `task.map(fn)`
99 |
100 | > Static alias: `Task.map(fn, task)`
101 |
102 | Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the successful value.
103 |
104 | ```js
105 | Task.of(2).map(x => x * 3).run({
106 | success(x) {
107 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
108 | },
109 | })
110 |
111 | // > result: 6
112 | ```
113 |
114 | ## `task.mapRejected(fn)`
115 |
116 | > Static alias: `Task.mapRejected(fn, task)`
117 |
118 | Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the failure value.
119 |
120 | ```js
121 | Task.rejected(2).mapRejected(x => x * 3).run({
122 | failure(error) {
123 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
124 | },
125 | })
126 |
127 | // > error: 6
128 | ```
129 |
130 | ## `task.bimap(fFn, sFn)`
131 |
132 | > Static alias: `Task.bimap(fFn, sFn, task)`
133 |
134 | Transforms a task by applying `fFn` to the failure value or `sFn` to the successful value.
135 |
136 | ```js
137 | Task.of(2).bimap(x => x, x => x * 3).run({
138 | success(x) {
139 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
140 | },
141 | })
142 |
143 | // > result: 6
144 | ```
145 |
146 | ```js
147 | Task.rejected(2).bimap(x => x * 3, x => x).run({
148 | failure(error) {
149 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
150 | },
151 | })
152 |
153 | // > error: 6
154 | ```
155 |
156 | ## `task.chain(fn)`
157 |
158 | > Static alias: `Task.chain(fn, task)`
159 |
160 | Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the successful value, where `fn` returns a Task.
161 |
162 | ```js
163 | Task.of(2).chain(x => Task.of(x * 3)).run({
164 | success(x) {
165 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
166 | },
167 | })
168 |
169 | // > result: 6
170 | ```
171 |
172 | The function can return a task that fails of course.
173 |
174 | ```js
175 | Task.of(2).chain(x => Task.rejected(x * 3)).run({
176 | failure(error) {
177 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
178 | },
179 | })
180 |
181 | // > error: 6
182 | ```
183 |
184 | ## `task.orElse(fn)`
185 |
186 | > Static alias: `Task.orElse(fn, task)`
187 |
188 | Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the failure value, where `fn` returns a Task.
189 | Similar to `chain` but for failure path.
190 |
191 | ```js
192 | Task.rejected(2).orElse(x => Task.of(x * 3)).run({
193 | success(x) {
194 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
195 | },
196 | })
197 |
198 | // > result: 6
199 | ```
200 |
201 |
202 | ## `task.recur(fn)`
203 |
204 | > Static alias: `Task.recur(fn, task)`
205 |
206 | `task.recur(fn)` is the same as `task.chain(function f(x) { return fn(x).chain(f) })`,
207 | but former is safe from infinite call stack growth and memory leaks.
208 |
209 | ```js
210 | Task.of(5).recur(x => {
211 | x // 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0
212 | return x === 0 ? Task.rejected('done') : Task.of(x - 1)
213 | }).run({
214 | failure(x) {
215 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
216 | },
217 | })
218 |
219 | // > result: done
220 | ```
221 |
222 | ## `Task.chainRec(fn, initial)`
223 |
224 | Implementation of [Fantasy Land's `ChainRec`](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#chainrec).
225 | Covers similar use-case as `task.recur()` but in a spec compatible way.
226 |
227 | ```js
228 | Task.chainRec((next, done, x) => {
229 | x // 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0
230 | return x === 0 ? Task.of(done('done')) : Task.of(next(x - 1))
231 | }, 5).run({
232 | success(x) {
233 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
234 | },
235 | })
236 |
237 | // > result: done
238 | ```
239 |
240 | ## `tX.ap(tFn)`
241 |
242 | > Static alias: `Task.ap(tFn, tX)`
243 |
244 | Applies the successful value of task `tFn` to to the successful value of task `tX`.
245 | Uses `chain` under the hood, if you need parallel execution use `parallel`.
246 |
247 | ```js
248 | Task.of(2).ap(Task.of(x => x * 3)).run({
249 | success(x) {
250 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
251 | },
252 | })
253 |
254 | // > result: 6
255 | ```
256 |
257 |
258 | ## `task.concat(otherTask)`
259 |
260 | > Static alias: `Task.concat(task, otherTask)`
261 |
262 | Selects the earlier of the two tasks. Uses `race` under the hood.
263 |
264 | ```js
265 | const task1 = Task.create(suc => {
266 | const id = setTimeout(() => suc(1), 1000)
267 | return () => { clearTimeout(id) }
268 | })
269 |
270 | const task2 = Task.create(suc => {
271 | const id = setTimeout(() => suc(2), 2000)
272 | return () => { clearTimeout(id) }
273 | })
274 |
275 | task1.concat(task2).run({
276 | success(x) {
277 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
278 | },
279 | })
280 |
281 | // > result: 1
282 | ```
283 |
284 |
285 |
286 | ## `Task.parallel(tasks)`
287 |
288 | Given array of tasks creates a task of array. When result task executed given tasks will be executed in parallel.
289 |
290 | ```js
291 | Task.parallel([Task.of(2), Task.of(3)]).run(
292 | success(xs) {
293 | console.log(`result: ${xs.join(', ')}`)
294 | },
295 | )
296 |
297 | // > result: 2, 3
298 | ```
299 |
300 | If any of given tasks fail, the result taks will also fail with the same error.
301 | In this case tasks that are still running are canceled.
302 |
303 | ```js
304 | Task.parallel([Task.of(2), Task.rejected(3)]).run(
305 | failure(error) {
306 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
307 | },
308 | )
309 |
310 | // > error: 3
311 | ```
312 |
313 | ## `Task.race(tasks)`
314 |
315 | Given array of tasks creates a task that completes with the earliest successful or failure value.
316 | After the fastest task completes other tasks are canceled.
317 |
318 | ```js
319 | const task1 = Task.create(suc => {
320 | const id = setTimeout(() => suc(1), 1000)
321 | return () => {
322 | console.log('canceled: 1')
323 | clearTimeout(id)
324 | }
325 | })
326 |
327 | const task2 = Task.create(suc => {
328 | const id = setTimeout(() => suc(2), 2000)
329 | return () => {
330 | console.log('canceled: 2')
331 | clearTimeout(id)
332 | }
333 | })
334 |
335 | Task.race([task1, task2]).run({
336 | success(x) {
337 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
338 | },
339 | })
340 |
341 | // > canceled: 2
342 | // > result: 1
343 | ```
344 |
345 | ## `Task.do(generator)`
346 |
347 | This is something like [Haskell's do notation](https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Haskell/do_notation)
348 | or JavaScritp's async/await based on [generators](https://developer.mozilla.org/en/docs/Web/JavaScript/Guide/Iterators_and_Generators).
349 |
350 | You pass a generator that `yiels` and `returns` tasks and get a task in return.
351 | The whole proccess is pure, tasks are not being ran until the result task is ran.
352 |
353 | Here is a not runnable but somewhat real-world example:
354 |
355 | ```js
356 | // gets user from our API, returns a Task
357 | const getUserFromAPI = ...
358 |
359 | // gets zip code for given address using 3rd party API, returns a Task
360 | const getZipCode = ...
361 |
362 | function getUsersZip(userId) {
363 | return Task.do(function* () {
364 | const user = yield getUserFromAPI(userId)
365 | if (!user.address) {
366 | return Task.rejected({type: 'user_dont_have_address'})
367 | }
368 | return getZipCode(user.address)
369 | })
370 | }
371 |
372 | // Same function re-written using chain instead of do
373 | function getUsersZip(userId) {
374 | return getUserFromAPI(userId).chain(user => {
375 | if (!user.address) {
376 | return Task.rejected({type: 'user_dont_have_address'})
377 | }
378 | return getZipCode(user.address)
379 | })
380 | }
381 |
382 | getUsersZip(42).run({
383 | success(zip) {
384 | // ...
385 | },
386 | failure(error) {
387 | // The error here is either {type: 'user_dont_have_address'}
388 | // or some of errors that getUserFromAPI or getZipCode can produce
389 | // ...
390 | },
391 | })
392 | ```
393 |
394 | And here's some runnable example:
395 |
396 | ```js
397 | Task.do(function* () {
398 | const a = yield Task.of(2)
399 | const b = yield Task.of(3)
400 | return Task.of(a * b)
401 | }).run({
402 | success(x) {
403 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
404 | },
405 | })
406 |
407 | // > result: 6
408 | ```
409 |
410 |
411 | ## `task.run(handlers)`
412 |
413 | Runs the task. The `handlers` argument can contain 3 kinds of handlers `success`, `failure`, and `catch`.
414 | All handlers are optional, if you want to run task without handlers do it like this `task.run({})`.
415 | If a function passed as `handlers` it's automatically transformend to `{success: fn}`,
416 | so if you need only success handler you can do `task.run(x => ...)`.
417 |
418 | If `failure` handler isn't provided but task fails, an exception is thrown.
419 | You should always provided `failure` handlers for tasks that may fail.
420 | If you want to ignore failure pass a `noop` failure handler explicitly.
421 |
422 | The `catch` handler is for errors thrown from functions passed to `map`, `chain` etc.
423 | [More on how it works](./exceptions.md#how-exceptions-work-in-task).
424 |
425 | ```js
426 | Task.of(2).run({
427 | success(x) {
428 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
429 | },
430 | failure(error) {
431 | // handle failure ...
432 | },
433 | catch(error) {
434 | // handle error thrown from `map(fn)` etc ...
435 | },
436 | })
437 |
438 | // > result: 2
439 | ```
440 |
441 | ## `task.runAndLog()`
442 |
443 | Runs the task and prints results using `console.log()`. Mainly for testing / debugging etc.
444 |
445 | ```js
446 | Task.of(2).runAndLog()
447 |
448 | // > Success: 2
449 | ```
450 |
451 |
452 | ## `task.toPromise([options])`
453 |
454 | Runs the task and returns a Promise that represent the result.
455 | The task's `success` and `failure` branches both correspond to the promise's `success` brach because
456 | [the `error` branch in Promises is reserved for unexpected failures](./exceptions.md#promises-and-expected-failures).
457 | The task's `catch` branch correspond to promise's `error`.
458 |
459 | The promise's success value is either `{success: s}` or `{failure: f}` where `s` and `f` task's
460 | success or failure values.
461 |
462 | If `{catch: false}` is passed as `options` the task is run without `catch` callback.
463 |
464 | ```js
465 | Task.of(2).toPromise().then(result => {
466 | if ('success' in result) {
467 | console.log(`success: ${result.success}`)
468 | } else {
469 | console.log(`failure: ${result.failure}`)
470 | }
471 | })
472 |
473 | // > success: 2
474 | ```
475 |
476 |
477 | ## `Task.fromPromise(promise)`
478 |
479 | Creates a Task from a Promise.
480 |
481 | ```js
482 | Task.fromPromise(Promise.resolve(2)).run({
483 | success(x) {
484 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
485 | },
486 | })
487 |
488 | // result: 2
489 | ```
490 |
491 | The `promise` argument must be either a Promise or a function that wnen called with
492 | no arguments returns a Promise. If a function is used as `promise` argument,
493 | that function is executed on each task's run to retrieve a new promise.
494 |
495 | ```js
496 | Task.fromPromise(() => Promise.resolve(2)).run({
497 | success(x) {
498 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
499 | },
500 | })
501 |
502 | // result: 2
503 | ```
504 |
505 | The promise's `success` corresponds to the task's `success`
506 | and promise's `error` corresponds to the task's `catch`.
507 |
508 | ```js
509 | Task.fromPromise(Promise.reject(2)).run({
510 | catch(x) {
511 | console.log(`error: ${x}`)
512 | },
513 | })
514 |
515 | // error: 2
516 | ```
517 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow.sketch:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow.sketch
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow1.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow1.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow2.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow2.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow3.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow3.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow4.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow4.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/exceptions.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Try..catch in JavaScript async abstractions like Promise or Task
2 |
3 | This article explains the reasoning behind how error catching works in Task.
4 | It starts from the very fundamental concepts, but this is necessary to avoid any misunderstandings
5 | later in the article when some terms from earlier parts are used.
6 | The closer to the end the more practical matters are discussed.
7 |
8 | ## Expected and unexpected code paths
9 |
10 | In any program (especially in JavaScript) there's always expected and unexpected code paths.
11 | When a program goes through an unexpected path we call it "a bug". And when it only goes through the expected paths
12 | it is just normal execution of the program. Consider this example:
13 |
14 | ```js
15 | let x = Math.random() - 0.5
16 | let y
17 | let z
18 |
19 | if (x > 0) {
20 | y = 10
21 | } else {
22 | z = 10
23 | }
24 |
25 | if (x <= 0) {
26 | alert(z + 5)
27 | } else {
28 | alert(y + 5)
29 | }
30 | ```
31 |
32 | Here are two expected paths of this program:
33 |
34 |
113 |
114 |
115 | Task is compatible with [Fantasy Land](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land) and [Static Land](https://github.com/rpominov/static-land) implementing:
116 |
117 | - [Semigroup](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#semigroup)
118 | - [Monoid](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#monoid)
119 | - [Functor](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#functor)
120 | - [Bifunctor](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#bifunctor)
121 | - [Apply](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#apply)
122 | - [Applicative](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#applicative)
123 | - [Chain](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#chain)
124 | - [ChainRec](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#chainrec)
125 | - [Monad](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#monad)
126 |
127 | ## Development
128 |
129 | ```
130 | npm run lobot -- --help
131 | ```
132 |
133 | Run [lobot](https://github.com/rpominov/lobot) commands as `npm run lobot -- args...`
134 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/coverageconfig.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "coverage": ["./.build-artefacts/lcov.info"]
3 | }
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/api-reference.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Task API Reference
2 |
3 | ## `Task.create(computation)`
4 |
5 | Creates a Task from a computation. Computation is a function that accepts two callbacks.
6 | It should call one of them after completion with the final result (success or failure).
7 | Also a computation may return a function with cancellation logic
8 | or it can return `undefined` if there is no cancellation logic.
9 |
10 | ```js
11 | const task = Task.create((onSuccess, onFailure) => {
12 | // ...
13 | return () => {
14 | // cancellation logic
15 | }
16 | })
17 |
18 | // The computation is executed every time we run the task
19 | const cancel = task.run({
20 | success(result) {
21 | // success result goes here
22 | },
23 | failure(result) {
24 | // failure result goes here
25 | },
26 | })
27 |
28 | // If we cancel the task the cancellation logic from computation
29 | // will be executed (if provided)
30 | cancel()
31 | ```
32 |
33 | Here is some runnable example:
34 |
35 | ```js
36 | const wait5sec = Task.create(onSuccess => {
37 | const timeoutId = setTimeout(() => {
38 | onSuccess('5 seconds')
39 | }, 5000)
40 | return () => { clearTimeout(timeoutId) }
41 | })
42 |
43 | wait5sec.run({
44 | success(timeWaited) {
45 | console.log(`We've waited for ${timeWaited}`)
46 | },
47 | })
48 |
49 | // > We've waited for 5 seconds
50 | ```
51 |
52 | After cancellation or completion the `onSuccess` and `onFailure` callbacks become noop.
53 | Also if `cancel` called second time or after a completion the cancelation logic won't be executed.
54 |
55 | ## `Task.of(value)`
56 |
57 | Creates a task that resolves with a given value.
58 |
59 | ```js
60 | Task.of(2).run({
61 | success(x) {
62 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
63 | },
64 | })
65 |
66 | // > result: 2
67 | ```
68 |
69 | ## `Task.rejected(error)`
70 |
71 | Creates a task that fails with a given error.
72 |
73 | ```js
74 | Task.rejected(2).run({
75 | failure(error) {
76 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
77 | },
78 | })
79 |
80 | // > error: 2
81 | ```
82 |
83 | ## `Task.empty()`
84 |
85 | Creates a task that never completes.
86 |
87 | ```js
88 | Task.empty().run({
89 | success(x) {
90 | // callback never called
91 | },
92 | failure(error) {
93 | // callback never called
94 | },
95 | })
96 | ```
97 |
98 | ## `task.map(fn)`
99 |
100 | > Static alias: `Task.map(fn, task)`
101 |
102 | Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the successful value.
103 |
104 | ```js
105 | Task.of(2).map(x => x * 3).run({
106 | success(x) {
107 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
108 | },
109 | })
110 |
111 | // > result: 6
112 | ```
113 |
114 | ## `task.mapRejected(fn)`
115 |
116 | > Static alias: `Task.mapRejected(fn, task)`
117 |
118 | Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the failure value.
119 |
120 | ```js
121 | Task.rejected(2).mapRejected(x => x * 3).run({
122 | failure(error) {
123 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
124 | },
125 | })
126 |
127 | // > error: 6
128 | ```
129 |
130 | ## `task.bimap(fFn, sFn)`
131 |
132 | > Static alias: `Task.bimap(fFn, sFn, task)`
133 |
134 | Transforms a task by applying `fFn` to the failure value or `sFn` to the successful value.
135 |
136 | ```js
137 | Task.of(2).bimap(x => x, x => x * 3).run({
138 | success(x) {
139 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
140 | },
141 | })
142 |
143 | // > result: 6
144 | ```
145 |
146 | ```js
147 | Task.rejected(2).bimap(x => x * 3, x => x).run({
148 | failure(error) {
149 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
150 | },
151 | })
152 |
153 | // > error: 6
154 | ```
155 |
156 | ## `task.chain(fn)`
157 |
158 | > Static alias: `Task.chain(fn, task)`
159 |
160 | Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the successful value, where `fn` returns a Task.
161 |
162 | ```js
163 | Task.of(2).chain(x => Task.of(x * 3)).run({
164 | success(x) {
165 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
166 | },
167 | })
168 |
169 | // > result: 6
170 | ```
171 |
172 | The function can return a task that fails of course.
173 |
174 | ```js
175 | Task.of(2).chain(x => Task.rejected(x * 3)).run({
176 | failure(error) {
177 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
178 | },
179 | })
180 |
181 | // > error: 6
182 | ```
183 |
184 | ## `task.orElse(fn)`
185 |
186 | > Static alias: `Task.orElse(fn, task)`
187 |
188 | Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the failure value, where `fn` returns a Task.
189 | Similar to `chain` but for failure path.
190 |
191 | ```js
192 | Task.rejected(2).orElse(x => Task.of(x * 3)).run({
193 | success(x) {
194 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
195 | },
196 | })
197 |
198 | // > result: 6
199 | ```
200 |
201 |
202 | ## `task.recur(fn)`
203 |
204 | > Static alias: `Task.recur(fn, task)`
205 |
206 | `task.recur(fn)` is the same as `task.chain(function f(x) { return fn(x).chain(f) })`,
207 | but former is safe from infinite call stack growth and memory leaks.
208 |
209 | ```js
210 | Task.of(5).recur(x => {
211 | x // 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0
212 | return x === 0 ? Task.rejected('done') : Task.of(x - 1)
213 | }).run({
214 | failure(x) {
215 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
216 | },
217 | })
218 |
219 | // > result: done
220 | ```
221 |
222 | ## `Task.chainRec(fn, initial)`
223 |
224 | Implementation of [Fantasy Land's `ChainRec`](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#chainrec).
225 | Covers similar use-case as `task.recur()` but in a spec compatible way.
226 |
227 | ```js
228 | Task.chainRec((next, done, x) => {
229 | x // 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0
230 | return x === 0 ? Task.of(done('done')) : Task.of(next(x - 1))
231 | }, 5).run({
232 | success(x) {
233 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
234 | },
235 | })
236 |
237 | // > result: done
238 | ```
239 |
240 | ## `tX.ap(tFn)`
241 |
242 | > Static alias: `Task.ap(tFn, tX)`
243 |
244 | Applies the successful value of task `tFn` to to the successful value of task `tX`.
245 | Uses `chain` under the hood, if you need parallel execution use `parallel`.
246 |
247 | ```js
248 | Task.of(2).ap(Task.of(x => x * 3)).run({
249 | success(x) {
250 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
251 | },
252 | })
253 |
254 | // > result: 6
255 | ```
256 |
257 |
258 | ## `task.concat(otherTask)`
259 |
260 | > Static alias: `Task.concat(task, otherTask)`
261 |
262 | Selects the earlier of the two tasks. Uses `race` under the hood.
263 |
264 | ```js
265 | const task1 = Task.create(suc => {
266 | const id = setTimeout(() => suc(1), 1000)
267 | return () => { clearTimeout(id) }
268 | })
269 |
270 | const task2 = Task.create(suc => {
271 | const id = setTimeout(() => suc(2), 2000)
272 | return () => { clearTimeout(id) }
273 | })
274 |
275 | task1.concat(task2).run({
276 | success(x) {
277 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
278 | },
279 | })
280 |
281 | // > result: 1
282 | ```
283 |
284 |
285 |
286 | ## `Task.parallel(tasks)`
287 |
288 | Given array of tasks creates a task of array. When result task executed given tasks will be executed in parallel.
289 |
290 | ```js
291 | Task.parallel([Task.of(2), Task.of(3)]).run(
292 | success(xs) {
293 | console.log(`result: ${xs.join(', ')}`)
294 | },
295 | )
296 |
297 | // > result: 2, 3
298 | ```
299 |
300 | If any of given tasks fail, the result taks will also fail with the same error.
301 | In this case tasks that are still running are canceled.
302 |
303 | ```js
304 | Task.parallel([Task.of(2), Task.rejected(3)]).run(
305 | failure(error) {
306 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
307 | },
308 | )
309 |
310 | // > error: 3
311 | ```
312 |
313 | ## `Task.race(tasks)`
314 |
315 | Given array of tasks creates a task that completes with the earliest successful or failure value.
316 | After the fastest task completes other tasks are canceled.
317 |
318 | ```js
319 | const task1 = Task.create(suc => {
320 | const id = setTimeout(() => suc(1), 1000)
321 | return () => {
322 | console.log('canceled: 1')
323 | clearTimeout(id)
324 | }
325 | })
326 |
327 | const task2 = Task.create(suc => {
328 | const id = setTimeout(() => suc(2), 2000)
329 | return () => {
330 | console.log('canceled: 2')
331 | clearTimeout(id)
332 | }
333 | })
334 |
335 | Task.race([task1, task2]).run({
336 | success(x) {
337 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
338 | },
339 | })
340 |
341 | // > canceled: 2
342 | // > result: 1
343 | ```
344 |
345 | ## `Task.do(generator)`
346 |
347 | This is something like [Haskell's do notation](https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Haskell/do_notation)
348 | or JavaScritp's async/await based on [generators](https://developer.mozilla.org/en/docs/Web/JavaScript/Guide/Iterators_and_Generators).
349 |
350 | You pass a generator that `yiels` and `returns` tasks and get a task in return.
351 | The whole proccess is pure, tasks are not being ran until the result task is ran.
352 |
353 | Here is a not runnable but somewhat real-world example:
354 |
355 | ```js
356 | // gets user from our API, returns a Task
357 | const getUserFromAPI = ...
358 |
359 | // gets zip code for given address using 3rd party API, returns a Task
360 | const getZipCode = ...
361 |
362 | function getUsersZip(userId) {
363 | return Task.do(function* () {
364 | const user = yield getUserFromAPI(userId)
365 | if (!user.address) {
366 | return Task.rejected({type: 'user_dont_have_address'})
367 | }
368 | return getZipCode(user.address)
369 | })
370 | }
371 |
372 | // Same function re-written using chain instead of do
373 | function getUsersZip(userId) {
374 | return getUserFromAPI(userId).chain(user => {
375 | if (!user.address) {
376 | return Task.rejected({type: 'user_dont_have_address'})
377 | }
378 | return getZipCode(user.address)
379 | })
380 | }
381 |
382 | getUsersZip(42).run({
383 | success(zip) {
384 | // ...
385 | },
386 | failure(error) {
387 | // The error here is either {type: 'user_dont_have_address'}
388 | // or some of errors that getUserFromAPI or getZipCode can produce
389 | // ...
390 | },
391 | })
392 | ```
393 |
394 | And here's some runnable example:
395 |
396 | ```js
397 | Task.do(function* () {
398 | const a = yield Task.of(2)
399 | const b = yield Task.of(3)
400 | return Task.of(a * b)
401 | }).run({
402 | success(x) {
403 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
404 | },
405 | })
406 |
407 | // > result: 6
408 | ```
409 |
410 |
411 | ## `task.run(handlers)`
412 |
413 | Runs the task. The `handlers` argument can contain 3 kinds of handlers `success`, `failure`, and `catch`.
414 | All handlers are optional, if you want to run task without handlers do it like this `task.run({})`.
415 | If a function passed as `handlers` it's automatically transformend to `{success: fn}`,
416 | so if you need only success handler you can do `task.run(x => ...)`.
417 |
418 | If `failure` handler isn't provided but task fails, an exception is thrown.
419 | You should always provided `failure` handlers for tasks that may fail.
420 | If you want to ignore failure pass a `noop` failure handler explicitly.
421 |
422 | The `catch` handler is for errors thrown from functions passed to `map`, `chain` etc.
423 | [More on how it works](./exceptions.md#how-exceptions-work-in-task).
424 |
425 | ```js
426 | Task.of(2).run({
427 | success(x) {
428 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
429 | },
430 | failure(error) {
431 | // handle failure ...
432 | },
433 | catch(error) {
434 | // handle error thrown from `map(fn)` etc ...
435 | },
436 | })
437 |
438 | // > result: 2
439 | ```
440 |
441 | ## `task.runAndLog()`
442 |
443 | Runs the task and prints results using `console.log()`. Mainly for testing / debugging etc.
444 |
445 | ```js
446 | Task.of(2).runAndLog()
447 |
448 | // > Success: 2
449 | ```
450 |
451 |
452 | ## `task.toPromise([options])`
453 |
454 | Runs the task and returns a Promise that represent the result.
455 | The task's `success` and `failure` branches both correspond to the promise's `success` brach because
456 | [the `error` branch in Promises is reserved for unexpected failures](./exceptions.md#promises-and-expected-failures).
457 | The task's `catch` branch correspond to promise's `error`.
458 |
459 | The promise's success value is either `{success: s}` or `{failure: f}` where `s` and `f` task's
460 | success or failure values.
461 |
462 | If `{catch: false}` is passed as `options` the task is run without `catch` callback.
463 |
464 | ```js
465 | Task.of(2).toPromise().then(result => {
466 | if ('success' in result) {
467 | console.log(`success: ${result.success}`)
468 | } else {
469 | console.log(`failure: ${result.failure}`)
470 | }
471 | })
472 |
473 | // > success: 2
474 | ```
475 |
476 |
477 | ## `Task.fromPromise(promise)`
478 |
479 | Creates a Task from a Promise.
480 |
481 | ```js
482 | Task.fromPromise(Promise.resolve(2)).run({
483 | success(x) {
484 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
485 | },
486 | })
487 |
488 | // result: 2
489 | ```
490 |
491 | The `promise` argument must be either a Promise or a function that wnen called with
492 | no arguments returns a Promise. If a function is used as `promise` argument,
493 | that function is executed on each task's run to retrieve a new promise.
494 |
495 | ```js
496 | Task.fromPromise(() => Promise.resolve(2)).run({
497 | success(x) {
498 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
499 | },
500 | })
501 |
502 | // result: 2
503 | ```
504 |
505 | The promise's `success` corresponds to the task's `success`
506 | and promise's `error` corresponds to the task's `catch`.
507 |
508 | ```js
509 | Task.fromPromise(Promise.reject(2)).run({
510 | catch(x) {
511 | console.log(`error: ${x}`)
512 | },
513 | })
514 |
515 | // error: 2
516 | ```
517 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow.sketch:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow.sketch
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow1.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow1.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow2.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow2.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow3.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow3.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow4.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow4.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/exceptions.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Try..catch in JavaScript async abstractions like Promise or Task
2 |
3 | This article explains the reasoning behind how error catching works in Task.
4 | It starts from the very fundamental concepts, but this is necessary to avoid any misunderstandings
5 | later in the article when some terms from earlier parts are used.
6 | The closer to the end the more practical matters are discussed.
7 |
8 | ## Expected and unexpected code paths
9 |
10 | In any program (especially in JavaScript) there's always expected and unexpected code paths.
11 | When a program goes through an unexpected path we call it "a bug". And when it only goes through the expected paths
12 | it is just normal execution of the program. Consider this example:
13 |
14 | ```js
15 | let x = Math.random() - 0.5
16 | let y
17 | let z
18 |
19 | if (x > 0) {
20 | y = 10
21 | } else {
22 | z = 10
23 | }
24 |
25 | if (x <= 0) {
26 | alert(z + 5)
27 | } else {
28 | alert(y + 5)
29 | }
30 | ```
31 |
32 | Here are two expected paths of this program:
33 |
34 |  35 |
36 | And here is an unexpected path:
37 |
38 |
35 |
36 | And here is an unexpected path:
37 |
38 |  39 |
40 | We as programmers don't expect this to ever happen with this program.
41 | But if, for example, we change first condition and forget to change second one the program may
42 | run through the unexpected path. That would be a bug.
43 |
44 |
45 | ## Railway oriented programming / split expected path in two
46 |
47 | We can introduce some abstractions and semantics that would split **expected path** into
48 | **expected success** and **expected failure**. If you understand `Either` type you know what I'm talking about.
49 | This is fairly common pattern in FP world, I'll try to explain it briefly, but here are some good
50 | articles that do a much better job:
51 |
52 | - ["Railway oriented programming"](https://fsharpforfunandprofit.com/posts/recipe-part2/)
53 | - ["A Monad in Practicality: First-Class Failures"](http://robotlolita.me/2013/12/08/a-monad-in-practicality-first-class-failures.html)
54 | - ["Practical Intro to Monads in JavaScript: Either"](https://tech.evojam.com/2016/03/21/practical-intro-to-monads-in-javascript-either/)
55 |
56 | Say we build a simple CLI program that takes a number `n` from user and prints `1/n`.
57 |
58 | ```js
59 | function print(str) {
60 | console.log(str)
61 | }
62 |
63 | function main(userInput) {
64 | const number = parseInt(userInput, 10)
65 |
66 | if (Number.isNaN(number)) {
67 | print(`Not a number: ${userInput}`)
68 | } else {
69 | if (number === 0) {
70 | print(`Cannot divide by zero`)
71 | } else {
72 | print(1 / number)
73 | }
74 | }
75 |
76 | }
77 |
78 | // Read a line from stdin somehow and apply main() to it.
79 | // Details of how it's done are not important for this example.
80 | main(inputFromStdin)
81 | ```
82 |
83 | In this example execution flow of the program looks like this:
84 |
85 |
39 |
40 | We as programmers don't expect this to ever happen with this program.
41 | But if, for example, we change first condition and forget to change second one the program may
42 | run through the unexpected path. That would be a bug.
43 |
44 |
45 | ## Railway oriented programming / split expected path in two
46 |
47 | We can introduce some abstractions and semantics that would split **expected path** into
48 | **expected success** and **expected failure**. If you understand `Either` type you know what I'm talking about.
49 | This is fairly common pattern in FP world, I'll try to explain it briefly, but here are some good
50 | articles that do a much better job:
51 |
52 | - ["Railway oriented programming"](https://fsharpforfunandprofit.com/posts/recipe-part2/)
53 | - ["A Monad in Practicality: First-Class Failures"](http://robotlolita.me/2013/12/08/a-monad-in-practicality-first-class-failures.html)
54 | - ["Practical Intro to Monads in JavaScript: Either"](https://tech.evojam.com/2016/03/21/practical-intro-to-monads-in-javascript-either/)
55 |
56 | Say we build a simple CLI program that takes a number `n` from user and prints `1/n`.
57 |
58 | ```js
59 | function print(str) {
60 | console.log(str)
61 | }
62 |
63 | function main(userInput) {
64 | const number = parseInt(userInput, 10)
65 |
66 | if (Number.isNaN(number)) {
67 | print(`Not a number: ${userInput}`)
68 | } else {
69 | if (number === 0) {
70 | print(`Cannot divide by zero`)
71 | } else {
72 | print(1 / number)
73 | }
74 | }
75 |
76 | }
77 |
78 | // Read a line from stdin somehow and apply main() to it.
79 | // Details of how it's done are not important for this example.
80 | main(inputFromStdin)
81 | ```
82 |
83 | In this example execution flow of the program looks like this:
84 |
85 |  86 |
87 | As you can see the program splits in two places. This happens very often in programs.
88 | In some cases all branches look neutral, in other cases (like this) we can consider one path as
89 | a success and another one as a failure. We can make the distinction more formal by
90 | introducing an abstraction:
91 |
92 | ```js
93 | const Either = {
94 | chain(fn, either) {
95 | return ('success' in either) ? fn(either.success) : either
96 | },
97 | fork(onSuccess, onFailure, either) {
98 | return ('success' in either) ? onSuccess(either.success) : onFailure(either.failure)
99 | },
100 | }
101 | ```
102 |
103 | Now we can rewrite our example using `Either`:
104 |
105 | ```js
106 | function print(str) {
107 | console.log(str)
108 | }
109 |
110 | function parse(str) {
111 | const number = parseInt(str, 10)
112 | return Number.isNaN(number) ? {failure: `Not a number: ${str}`} : {success: number}
113 | }
114 |
115 | function calc(number) {
116 | return number === 0 ? {failure: `Cannot divide by zero`} : {success: 1 / number}
117 | }
118 |
119 | function main(userInput) {
120 | const parsed = parse(userInput)
121 | const calculated = Either.chain(calc, parsed)
122 | Either.fork(print, print, calculated)
123 | }
124 | ```
125 |
126 | In this version the flow looks more like the following. It's appears to be simpler, as if we can write code
127 | that cannot fail and the `Either` takes care of managing the failure branch.
128 |
129 |
86 |
87 | As you can see the program splits in two places. This happens very often in programs.
88 | In some cases all branches look neutral, in other cases (like this) we can consider one path as
89 | a success and another one as a failure. We can make the distinction more formal by
90 | introducing an abstraction:
91 |
92 | ```js
93 | const Either = {
94 | chain(fn, either) {
95 | return ('success' in either) ? fn(either.success) : either
96 | },
97 | fork(onSuccess, onFailure, either) {
98 | return ('success' in either) ? onSuccess(either.success) : onFailure(either.failure)
99 | },
100 | }
101 | ```
102 |
103 | Now we can rewrite our example using `Either`:
104 |
105 | ```js
106 | function print(str) {
107 | console.log(str)
108 | }
109 |
110 | function parse(str) {
111 | const number = parseInt(str, 10)
112 | return Number.isNaN(number) ? {failure: `Not a number: ${str}`} : {success: number}
113 | }
114 |
115 | function calc(number) {
116 | return number === 0 ? {failure: `Cannot divide by zero`} : {success: 1 / number}
117 | }
118 |
119 | function main(userInput) {
120 | const parsed = parse(userInput)
121 | const calculated = Either.chain(calc, parsed)
122 | Either.fork(print, print, calculated)
123 | }
124 | ```
125 |
126 | In this version the flow looks more like the following. It's appears to be simpler, as if we can write code
127 | that cannot fail and the `Either` takes care of managing the failure branch.
128 |
129 |  130 |
131 | Maybe this doesn't make much sense to you now (if you're not familiar with Either).
132 | And this is by no means a complete explanation of Either pattern (check out resources
133 | I've mentioned above for better explanations). But for the purpose of this article the only
134 | thing we need to take out of this section is that some paths in program can be
135 | treated formally or informally as **expected failures**.
136 |
137 | Let's recap. We've split all possible paths in programs to three groups:
138 |
139 | - **Expected success** is the main happy path of the program,
140 | it represents how the program behaves when everything goes right.
141 | - **Expected failure** is secondary path that represent
142 | all expected deviations from the happy path e.g., when a user gives an incorrect input.
143 | - **Unexpected failure** is some *unexpected* deviations from main or secondary paths,
144 | something that we call "bugs".
145 |
146 |
147 | ## try..catch
148 |
149 | How does `try..catch` fits into our three code paths groups view? It's great for unexpected failures!
150 | Or we should say: `throw` is great for unexpected failures if we never actually `try..catch`.
151 | It's very good for debugging. The debugger will pause on the exact line that throws.
152 | Also if we don't use a debugger we can still get a nice stack trace in the console, etc. It's sad that in many
153 | cases when a program goes through an unexpected path instead of exception we end up with `NaN`
154 | being propagated through the program or something like that. In these cases it's much harder to track
155 | down where things went wrong, it's much nicer when it just throws.
156 |
157 | On the other hand `try..catch` is bad for expected failures. There're many reasons why, but let's
158 | focus on just one: *it's bad for expected failures because it's already used for unexpected ones.*
159 | We must handle expected failures, so we would need to `try..catch` function that uses
160 | `throw` for expected failure. But if we do that we'll catch not only errors that represent
161 | expected failures, but also random errors that represent bugs. This is bad for two reasons:
162 |
163 | 1. we ruin nice debugging experience (the debugger will no longer pause etc);
164 | 2. in our code that is supposed to handle expected failures we would need to also
165 | handle unexpected failures (which is generally imposible as shown in the next section).
166 |
167 | If a `throw` is used for expected failures in some APIs, we should wrap inside `try..catch` as little code as
168 | possible, so we won't also catch bugs by accident.
169 |
170 |
171 | ## How program should behave in case of unexpected failures
172 |
173 | `Try..catch` provide us with a mechanism for writing code that will be executed in case of *some*
174 | unexpected failures. We can just wrap arbitrary code into `try..catch`, and we catch bugs
175 | that express themselves as exceptions in that code. Should we use this mechanism and what
176 | should the code in `catch(e) {..}` do?
177 |
178 | Let's look at this from theoretical point of view first and then dive into practical
179 | details in next sections.
180 |
181 | First of all let's focus on the fact that this mechanism catches only **some** failures.
182 | In many cases a program may not throw but just behave incorrectly in some way.
183 | In my experience with JavaScript I'd estimate that it throws only in about 30% of cases.
184 | So should we even care to use this mechanism if it works only in 30% cases?
185 |
186 | If we still want to use it, what should the handling code do? I can think of two options:
187 |
188 | 1. Try to completely recover somehow and keep the program running.
189 | 2. Crash / restart the program and log / report about the bug.
190 |
191 | The `#1` option is simply impossible. We can't transition program from arbitrary
192 | unexpected (inconsistent) state to an expected (consistent) state. For the simple reason that
193 | starting state is **unexpected** — we don't know anything about it, because we didn't expect it.
194 | How could we transition from a state of which we don't know anything to any other state?
195 | There is one way to do it though — restart the program, which is our `#2` option.
196 |
197 | Also any code that is executed in response to a bug might have a potential to make things worse.
198 | It transitions a program to even more complicated inconsistent state. Plus if a program continues to run,
199 | the inconsistent state may leak into a database. In this scenario even a restart may not help.
200 | And if many users are connected to a single database they all may start to experience the bug.
201 |
202 | The `#2` is often happens automatically (at least crash part), so maybe we don't
203 | even need to `catch`. But it's ok to catch for `#2` purposes.
204 |
205 |
206 | ## Unexpected failures in Node
207 |
208 | We could restart the server on each unhandled exception, but this is problematic because the server
209 | usually handles several requests concurrently. So if we restart the server
210 | not only requests that have faced a bug will fail, but all other requests that happen to be
211 | handled at the same time will fail as well. Some people think that a better approach is to wrap all of
212 | the code that is responsible for handling each request with some sort of `try..catch` block and when
213 | a error happens only one request will fail. Although we can't use `try..catch` of course because the
214 | code is asynchronous. So we should use some sort of async abstraction that can provide this functionality (e.g. Promises).
215 |
216 | Another option for Node is to let server crash. Yes, this will result in forcefully ending the execution of all other connections, resulting in more than a single user getting an error. But we will benefit from the crash by taking core dumps, (`node --abort_on_uncaught_exception`) etc.
217 |
218 | Also in Node we can use the `uncaughtException` event combined with a tool like [naught](https://github.com/andrewrk/naught). Here is a qoute from naught docs:
219 |
220 | > Using naught a worker can use the 'offline' message to announce that it is dying. At this point, naught prevents it from accepting new connections and spawns a replacement worker, allowing the dying worker to finish up with its current connections and do any cleanup necessary before finally perishing.
221 |
222 | Conclusion: we might want to catch unexpected errors in Node, but there are plenty other options.
223 |
224 |
225 | ## Unexpected failures in browser
226 |
227 | Just as in Node we could restart the program by reloading the webpage. However, that option is usually considered as an awful behavior from
228 | the UX point of view. So instead we may choose not to restart in a hope of
229 | providing a better UX at a risk of leaking inconsistent state to the database, etc. Some bugs are
230 | indeed not fatal for a web page, and it often may continue to work mostly fine. So this is a
231 | trade–off and to not restart is a legitimate option here.
232 |
233 | Sometimes with browser failures we might want the UI to react to the bug in a particular way. But if it's an arbitrary
234 | bug there isn't much we can do.
235 |
236 | In case of an *expected* failure (like the incorrect user input)
237 | we can handle it very well from UI/UX point of view — we could show an error message near the exact
238 | field in the form, or we may disable the submit button, etc.
239 |
240 | If it's bug where we really don't know
241 | what is going on, we can try to show a popup with a very vague message.
242 | But I think this won't be very helpful, it may actually be worse than not showing a popup.
243 |
244 | Maybe the user was not even going to interact with the part of the program that is broken, and a showing popup out
245 | of nowhere may only damage UX. And if user does interact with the broken part they will notice that
246 | it's broken anyway — no need to tell them what they already know.
247 |
248 | Furthermore, if we show a popup to the user, they might
249 | assume that something has failed, but now it's all under control and it's safe to continue to use the
250 | program. But this would be a lie, as nothing is under control in case of a bug.
251 |
252 | Conclusion: we have no reason to catch unexpected errors in browser.
253 |
254 |
255 | ## Promises and expected failures
256 |
257 | Promises support two code paths. There're two callbacks in `then`.
258 | Also Promises automatically catch all exceptions thrown from then's callbacks and put them into
259 | the next failure callback down the chain.
260 |
261 | So the second path is already used for unexpected failures.
262 | That makes it unusable for expected failures (see ["try..catch" section](#trycatch)).
263 | In other words Promises don't support Railways / Either pattern. If you want to use that pattern with Promises
264 | you should wrap Either into Promise. To use Promise's second path for expected failures is a terrible idea.
265 |
266 |
267 | ## Should async abstractions support exceptions catching?
268 |
269 | From previous sections we've learned that we definitely may not want to catch exceptions at all.
270 | In this case we get the best debugging experience. Even if an abstraction will catch exceptions and then
271 | re-throw them, it won't be the same as not catching at all, for instance the debugger won't pause on
272 | the original line of the `throw`.
273 |
274 | But we also may want to catch "async exceptions", for instance in Node web server case.
275 | A perfect solution would be optional catching.
276 |
277 | However, not all abstractions can support optional catching. If we must choose between non-optional
278 | catching and not supporting catching at all we should choose the latter.
279 | Non-optional catching hurts more than helps.
280 |
281 | This part seems to be ok in Promises. If we don't provide a failure callback in `then` and don't use
282 | `catch` method it seems that debugger behaves the same way as if error wasn't caught
283 | (at least in current Chrome). Although it wasn't always this way, previously they would simply
284 | swallow the exceptions if there wasn't a `catch` callback.
285 |
286 |
287 | ## How exceptions work in Task
288 |
289 | In Task we want to support both **optional** errors catching and Railways / Either pattern.
290 | When we `run()` a task we can choose whether errors will be caught or not,
291 | and if they are caught they go into a separate callback.
292 |
293 | ```js
294 | // exceptions are not caught
295 | task.run({
296 | success(x) {
297 | // handle success
298 | },
299 | failure(x) {
300 | // handle expected failure
301 | },
302 | })
303 |
304 | // if we provide catch callback exceptions are caught
305 | task.run({
306 | success(x) {
307 | // handle success
308 | },
309 | failure(x) {
310 | // handle expected failure
311 | },
312 | catch(e) {
313 | // handle a bug
314 | },
315 | })
316 | ```
317 |
318 | So if a `catch` callback isn't provided, we can enjoy a great debugging experience in the browser (even if we have `failure` callback). And in Node we can still catch exceptions in async code if we wanted to. Also notice that we use a separate callback for exceptions, so we won't have to write code that has to handle both expected and unexpected failures.
319 |
320 | The default behavior is to not catch. This is what we want in browser, and what also may be a legitimate option for Node.
321 |
322 | In Task the `catch` callback is reserved only for bug-exceptions. Expected exceptions must be wrapped in a `try..catch` block manually. All the API and semantics in Task are designed with this assumption in mind.
323 |
324 | Exceptions thrown from `success` and `failure` callbacks are never caught, even if a `catch` callback is provided.
325 |
326 | ```js
327 | task.run({
328 | success() {
329 | // this error won't be caught
330 | throw new Error('')
331 | },
332 | catch(error) {
333 | // the error above will not go here
334 | }
335 | })
336 | ```
337 |
338 | This is done because otherwise we might end up with half of the code for `success` being executed plus the code for `catch`, which in most cases isn't what we want. For example in a web server case, we could start sending response for `success` case, but then continue by sending the response for `catch`. Instead we should catch manually:
339 |
340 | ```js
341 | task.run({
342 | success() {
343 | try {
344 | // ...
345 | res.send(/* some part of success response */)
346 | // ...
347 | // supposedly some code here have thrown
348 | // ...
349 | } catch (e) {
350 | // do something about the exception
351 | // but keep in mind that "some part of success response" was already sent
352 | }
353 | },
354 | catch(error) {
355 | // handle error thrown from .map(fn) , etc.
356 | }
357 | })
358 | ```
359 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/promise-vs-task-api.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # API comparison with Promises
2 |
3 | | Task | Promise & comments |
4 | | ---------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------- |
5 | | `Task.create(computation)` | `new Promise(computation)` |
6 | | `Task.of(x)` | `Promise.resolve(x)`
130 |
131 | Maybe this doesn't make much sense to you now (if you're not familiar with Either).
132 | And this is by no means a complete explanation of Either pattern (check out resources
133 | I've mentioned above for better explanations). But for the purpose of this article the only
134 | thing we need to take out of this section is that some paths in program can be
135 | treated formally or informally as **expected failures**.
136 |
137 | Let's recap. We've split all possible paths in programs to three groups:
138 |
139 | - **Expected success** is the main happy path of the program,
140 | it represents how the program behaves when everything goes right.
141 | - **Expected failure** is secondary path that represent
142 | all expected deviations from the happy path e.g., when a user gives an incorrect input.
143 | - **Unexpected failure** is some *unexpected* deviations from main or secondary paths,
144 | something that we call "bugs".
145 |
146 |
147 | ## try..catch
148 |
149 | How does `try..catch` fits into our three code paths groups view? It's great for unexpected failures!
150 | Or we should say: `throw` is great for unexpected failures if we never actually `try..catch`.
151 | It's very good for debugging. The debugger will pause on the exact line that throws.
152 | Also if we don't use a debugger we can still get a nice stack trace in the console, etc. It's sad that in many
153 | cases when a program goes through an unexpected path instead of exception we end up with `NaN`
154 | being propagated through the program or something like that. In these cases it's much harder to track
155 | down where things went wrong, it's much nicer when it just throws.
156 |
157 | On the other hand `try..catch` is bad for expected failures. There're many reasons why, but let's
158 | focus on just one: *it's bad for expected failures because it's already used for unexpected ones.*
159 | We must handle expected failures, so we would need to `try..catch` function that uses
160 | `throw` for expected failure. But if we do that we'll catch not only errors that represent
161 | expected failures, but also random errors that represent bugs. This is bad for two reasons:
162 |
163 | 1. we ruin nice debugging experience (the debugger will no longer pause etc);
164 | 2. in our code that is supposed to handle expected failures we would need to also
165 | handle unexpected failures (which is generally imposible as shown in the next section).
166 |
167 | If a `throw` is used for expected failures in some APIs, we should wrap inside `try..catch` as little code as
168 | possible, so we won't also catch bugs by accident.
169 |
170 |
171 | ## How program should behave in case of unexpected failures
172 |
173 | `Try..catch` provide us with a mechanism for writing code that will be executed in case of *some*
174 | unexpected failures. We can just wrap arbitrary code into `try..catch`, and we catch bugs
175 | that express themselves as exceptions in that code. Should we use this mechanism and what
176 | should the code in `catch(e) {..}` do?
177 |
178 | Let's look at this from theoretical point of view first and then dive into practical
179 | details in next sections.
180 |
181 | First of all let's focus on the fact that this mechanism catches only **some** failures.
182 | In many cases a program may not throw but just behave incorrectly in some way.
183 | In my experience with JavaScript I'd estimate that it throws only in about 30% of cases.
184 | So should we even care to use this mechanism if it works only in 30% cases?
185 |
186 | If we still want to use it, what should the handling code do? I can think of two options:
187 |
188 | 1. Try to completely recover somehow and keep the program running.
189 | 2. Crash / restart the program and log / report about the bug.
190 |
191 | The `#1` option is simply impossible. We can't transition program from arbitrary
192 | unexpected (inconsistent) state to an expected (consistent) state. For the simple reason that
193 | starting state is **unexpected** — we don't know anything about it, because we didn't expect it.
194 | How could we transition from a state of which we don't know anything to any other state?
195 | There is one way to do it though — restart the program, which is our `#2` option.
196 |
197 | Also any code that is executed in response to a bug might have a potential to make things worse.
198 | It transitions a program to even more complicated inconsistent state. Plus if a program continues to run,
199 | the inconsistent state may leak into a database. In this scenario even a restart may not help.
200 | And if many users are connected to a single database they all may start to experience the bug.
201 |
202 | The `#2` is often happens automatically (at least crash part), so maybe we don't
203 | even need to `catch`. But it's ok to catch for `#2` purposes.
204 |
205 |
206 | ## Unexpected failures in Node
207 |
208 | We could restart the server on each unhandled exception, but this is problematic because the server
209 | usually handles several requests concurrently. So if we restart the server
210 | not only requests that have faced a bug will fail, but all other requests that happen to be
211 | handled at the same time will fail as well. Some people think that a better approach is to wrap all of
212 | the code that is responsible for handling each request with some sort of `try..catch` block and when
213 | a error happens only one request will fail. Although we can't use `try..catch` of course because the
214 | code is asynchronous. So we should use some sort of async abstraction that can provide this functionality (e.g. Promises).
215 |
216 | Another option for Node is to let server crash. Yes, this will result in forcefully ending the execution of all other connections, resulting in more than a single user getting an error. But we will benefit from the crash by taking core dumps, (`node --abort_on_uncaught_exception`) etc.
217 |
218 | Also in Node we can use the `uncaughtException` event combined with a tool like [naught](https://github.com/andrewrk/naught). Here is a qoute from naught docs:
219 |
220 | > Using naught a worker can use the 'offline' message to announce that it is dying. At this point, naught prevents it from accepting new connections and spawns a replacement worker, allowing the dying worker to finish up with its current connections and do any cleanup necessary before finally perishing.
221 |
222 | Conclusion: we might want to catch unexpected errors in Node, but there are plenty other options.
223 |
224 |
225 | ## Unexpected failures in browser
226 |
227 | Just as in Node we could restart the program by reloading the webpage. However, that option is usually considered as an awful behavior from
228 | the UX point of view. So instead we may choose not to restart in a hope of
229 | providing a better UX at a risk of leaking inconsistent state to the database, etc. Some bugs are
230 | indeed not fatal for a web page, and it often may continue to work mostly fine. So this is a
231 | trade–off and to not restart is a legitimate option here.
232 |
233 | Sometimes with browser failures we might want the UI to react to the bug in a particular way. But if it's an arbitrary
234 | bug there isn't much we can do.
235 |
236 | In case of an *expected* failure (like the incorrect user input)
237 | we can handle it very well from UI/UX point of view — we could show an error message near the exact
238 | field in the form, or we may disable the submit button, etc.
239 |
240 | If it's bug where we really don't know
241 | what is going on, we can try to show a popup with a very vague message.
242 | But I think this won't be very helpful, it may actually be worse than not showing a popup.
243 |
244 | Maybe the user was not even going to interact with the part of the program that is broken, and a showing popup out
245 | of nowhere may only damage UX. And if user does interact with the broken part they will notice that
246 | it's broken anyway — no need to tell them what they already know.
247 |
248 | Furthermore, if we show a popup to the user, they might
249 | assume that something has failed, but now it's all under control and it's safe to continue to use the
250 | program. But this would be a lie, as nothing is under control in case of a bug.
251 |
252 | Conclusion: we have no reason to catch unexpected errors in browser.
253 |
254 |
255 | ## Promises and expected failures
256 |
257 | Promises support two code paths. There're two callbacks in `then`.
258 | Also Promises automatically catch all exceptions thrown from then's callbacks and put them into
259 | the next failure callback down the chain.
260 |
261 | So the second path is already used for unexpected failures.
262 | That makes it unusable for expected failures (see ["try..catch" section](#trycatch)).
263 | In other words Promises don't support Railways / Either pattern. If you want to use that pattern with Promises
264 | you should wrap Either into Promise. To use Promise's second path for expected failures is a terrible idea.
265 |
266 |
267 | ## Should async abstractions support exceptions catching?
268 |
269 | From previous sections we've learned that we definitely may not want to catch exceptions at all.
270 | In this case we get the best debugging experience. Even if an abstraction will catch exceptions and then
271 | re-throw them, it won't be the same as not catching at all, for instance the debugger won't pause on
272 | the original line of the `throw`.
273 |
274 | But we also may want to catch "async exceptions", for instance in Node web server case.
275 | A perfect solution would be optional catching.
276 |
277 | However, not all abstractions can support optional catching. If we must choose between non-optional
278 | catching and not supporting catching at all we should choose the latter.
279 | Non-optional catching hurts more than helps.
280 |
281 | This part seems to be ok in Promises. If we don't provide a failure callback in `then` and don't use
282 | `catch` method it seems that debugger behaves the same way as if error wasn't caught
283 | (at least in current Chrome). Although it wasn't always this way, previously they would simply
284 | swallow the exceptions if there wasn't a `catch` callback.
285 |
286 |
287 | ## How exceptions work in Task
288 |
289 | In Task we want to support both **optional** errors catching and Railways / Either pattern.
290 | When we `run()` a task we can choose whether errors will be caught or not,
291 | and if they are caught they go into a separate callback.
292 |
293 | ```js
294 | // exceptions are not caught
295 | task.run({
296 | success(x) {
297 | // handle success
298 | },
299 | failure(x) {
300 | // handle expected failure
301 | },
302 | })
303 |
304 | // if we provide catch callback exceptions are caught
305 | task.run({
306 | success(x) {
307 | // handle success
308 | },
309 | failure(x) {
310 | // handle expected failure
311 | },
312 | catch(e) {
313 | // handle a bug
314 | },
315 | })
316 | ```
317 |
318 | So if a `catch` callback isn't provided, we can enjoy a great debugging experience in the browser (even if we have `failure` callback). And in Node we can still catch exceptions in async code if we wanted to. Also notice that we use a separate callback for exceptions, so we won't have to write code that has to handle both expected and unexpected failures.
319 |
320 | The default behavior is to not catch. This is what we want in browser, and what also may be a legitimate option for Node.
321 |
322 | In Task the `catch` callback is reserved only for bug-exceptions. Expected exceptions must be wrapped in a `try..catch` block manually. All the API and semantics in Task are designed with this assumption in mind.
323 |
324 | Exceptions thrown from `success` and `failure` callbacks are never caught, even if a `catch` callback is provided.
325 |
326 | ```js
327 | task.run({
328 | success() {
329 | // this error won't be caught
330 | throw new Error('')
331 | },
332 | catch(error) {
333 | // the error above will not go here
334 | }
335 | })
336 | ```
337 |
338 | This is done because otherwise we might end up with half of the code for `success` being executed plus the code for `catch`, which in most cases isn't what we want. For example in a web server case, we could start sending response for `success` case, but then continue by sending the response for `catch`. Instead we should catch manually:
339 |
340 | ```js
341 | task.run({
342 | success() {
343 | try {
344 | // ...
345 | res.send(/* some part of success response */)
346 | // ...
347 | // supposedly some code here have thrown
348 | // ...
349 | } catch (e) {
350 | // do something about the exception
351 | // but keep in mind that "some part of success response" was already sent
352 | }
353 | },
354 | catch(error) {
355 | // handle error thrown from .map(fn) , etc.
356 | }
357 | })
358 | ```
359 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/promise-vs-task-api.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # API comparison with Promises
2 |
3 | | Task | Promise & comments |
4 | | ---------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------- |
5 | | `Task.create(computation)` | `new Promise(computation)` |
6 | | `Task.of(x)` | `Promise.resolve(x)`
With Promises behaviour is different if `x` is a Promise (this makes writing generic code more difficult with Promises). |
7 | | `Task.rejected(x)` | `Promise.reject(x)` |
8 | | `task.map(fn)` | `promise.then(fn)`
With Promises behaviour is different if `fn` returns a Promise. |
9 | | `task.chain(fn)` | `promise.then(fn)` |
10 | | `task.mapRejected(fn)` | `promise.then(undefined, fn)`
With Promises behaviour is different if `fn` returns a Promise. |
11 | | `task.orElse(fn)` | `promise.then(undefined, fn)` |
12 | | `task.ap(otherTask)` | `promise.then(fn => otherPromise.then(fn))`
This method exists mainly for compliance with [Fantasy Land Specification](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land).
With Promises behaviour is different if `fn` returns a Promise. |
13 | | `Task.empty()` | `new Promise(() => {})` |
14 | | `task.concat(otherTask)` | `Promise.race([promose, otherPromise])`
Also mainly for Fantasy Land, makes Task a [Monoid](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#monoid). |
15 | | `Task.parallel(tasks)` | `Promise.all(promises)` |
16 | | `Task.race(tasks)` | `Promise.race(promises)` |
17 | | `Task.run({success, failure})` | `Promise.then(successOrFailure)`
In Promises second callback is for exceptions. More about it [here](./exceptions.md). |
18 | | `Task.run({success, failure, catch})` | `Promise.then(successOrFailure, catch)`
By default tasks don't catch exceptions thrown from `map`, `chain` etc. But we can choose to catch them by providing `catch` callback. Also notice that exceptions go into their own callback. |
19 | | `cancel = task.run(...); cancel()` | Promises don't support cancelation or even unsubscribing. |
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/io/1.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 |
3 | import readline from 'readline'
4 | import Task from '../../src'
5 |
6 | type Empty = void & null
7 | const fixEmpty = (x: Empty | T): T => (x: any)
8 |
9 | // wrappers
10 |
11 | // this is actually async, I didn't figured out how to read sync from stdin in Node
12 | const read = (): Task => Task.create(suc => {
13 | const rl = readline.createInterface({input: process.stdin})
14 | rl.on('line', line => { rl.close(); suc(line) })
15 | return () => { rl.close() }
16 | })
17 |
18 | const write = (text: string): Task => Task.create(suc => {
19 | console.log(text) // eslint-disable-line
20 | suc()
21 | })
22 |
23 |
24 | // pure
25 |
26 | const strToNumber = (str: string): Task => /^\d+$/.test(str)
27 | ? Task.of(Number(str))
28 | : Task.rejected('That\'s not a number')
29 |
30 | // This could be in the library
31 | const retryUntilSuccess = (task: Task): Task => {
32 | const recur = () => task.orElse(recur)
33 | return recur()
34 | }
35 |
36 | // This could be in the library (like all() but not parallel)
37 | const sequentially = (task1: Task, task2: Task): Task<[S1, S2], F1 | F2> =>
38 | task1.chain(x1 => task2.map(x2 => [x1, x2]))
39 |
40 | const getNumber = (message: string): Task =>
41 | retryUntilSuccess(
42 | write(message)
43 | .chain(read)
44 | .chain(strToNumber)
45 | .orElse(error => write(fixEmpty(error)).chain(Task.rejected))
46 | )
47 |
48 | const program: Task =
49 | sequentially(getNumber('Give me a number'), getNumber('Give me another number'))
50 | .map(([x, y]) => `${x} * ${y} = ${x * y}`)
51 | .chain(write)
52 |
53 |
54 | // impure
55 |
56 | program.run({})
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/io/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | This shows rather unusual use of Task. Task is used to write synchronous but impure code in pure fashion.
2 |
3 | ```sh
4 | # from project root
5 | npm run lobot run ./examples/io/1.js
6 | ```
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/package.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "name": "fun-task",
3 | "version": "1.5.2",
4 | "description": "An abstraction for managing asynchronous code in JS",
5 | "main": "lib/index.js",
6 | "scripts": {
7 | "lobot": "lobot",
8 | "lint": "eslint .",
9 | "test": "eslint . && flow check && lobot test",
10 | "test:watch-fast": "IGNORE_SLOW_TESTS=1 lobot test watch",
11 | "preversion": "cp src/index.js lib/index.js.flow"
12 | },
13 | "repository": {
14 | "type": "git",
15 | "url": "git+https://github.com/rpominov/fun-task.git"
16 | },
17 | "author": "Roman Pominov ",
18 | "license": "MIT",
19 | "bugs": {
20 | "url": "https://github.com/rpominov/fun-task/issues"
21 | },
22 | "homepage": "https://github.com/rpominov/fun-task#readme",
23 | "devDependencies": {
24 | "babel-core": "6.17.0",
25 | "babel-eslint": "7.0.0",
26 | "babel-polyfill": "6.16.0",
27 | "eslint": "3.8.0",
28 | "eslint-plugin-flowtype": "2.20.0",
29 | "flow-bin": "0.33.0",
30 | "lobot": "0.1.23"
31 | },
32 | "jsnext:main": "lib-es/index.js",
33 | "files": [
34 | "lib",
35 | "lib-es",
36 | "umd"
37 | ],
38 | "dependencies": {
39 | "fantasy-land": "1.0.1"
40 | },
41 | "keywords": [
42 | "task",
43 | "future",
44 | "promise",
45 | "monad",
46 | "applicative",
47 | "functor",
48 | "fantasy-land",
49 | "static-land",
50 | "fantasy land",
51 | "static land",
52 | "fp",
53 | "functional"
54 | ]
55 | }
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/index.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 |
3 | import fl from 'fantasy-land'
4 |
5 | type Cancel = () => void
6 | type Handler<-T> = (x: T) => void
7 | type Handlers<-S, -F> = {|
8 | success: Handler,
9 | failure: Handler,
10 | catch?: Handler,
11 | |}
12 | type LooseHandlers<-S, -F> = Handler | {|
13 | success?: Handler,
14 | failure?: Handler,
15 | catch?: Handler,
16 | |}
17 | type Computation<+S, +F> = (handleSucc: Handler, handleFail: Handler) => ?Cancel
18 |
19 | interface Result<+S, +F> {
20 | success?: S,
21 | failure?: F,
22 | }
23 |
24 | type ExtractSucc = (t: Task) => S
25 |
26 | type ChainRecNext = {type: 'next', value: T}
27 | type ChainRecDone = {type: 'done', value: T}
28 | const chainRecNext = (x: T): ChainRecNext => ({type: 'next', value: x})
29 | const chainRecDone = (x: T): ChainRecDone => ({type: 'done', value: x})
30 |
31 | const defaultFailureHandler: Handler = failure => {
32 | if (failure instanceof Error) {
33 | throw failure
34 | } else {
35 | throw new Error(`Unhandled task failure: ${String(failure)}`)
36 | }
37 | }
38 | const noop = () => {}
39 |
40 | type RunHelperBody = (s: Handler, f: Handler, c?: Handler) => {
41 | onCancel?: Cancel, // called only when user cancels
42 | onClose?: Cancel, // called when user cancels plus when succ/fail/catch are called
43 | }
44 | const runHelper = (body: RunHelperBody, handlers: Handlers): Cancel => {
45 | let {success, failure, catch: catch_} = handlers
46 | let onCancel = noop
47 | let onClose = noop
48 | let close = () => {
49 | onClose()
50 | // The idea here is to kill links to all stuff that we exposed from runHelper closure.
51 | // We expose via the return value (cancelation function) and by passing callbacks to the body.
52 | // We reason from an assumption that outer code may keep links to values that we exposed forever.
53 | // So we look at all things that referenced in the exposed callbacks and kill them.
54 | success = noop
55 | failure = noop
56 | catch_ = noop
57 | onCancel = noop
58 | close = noop
59 | }
60 | const bodyReturn = body(
61 | x => {
62 | const s = success
63 | close()
64 | s(x)
65 | },
66 | x => {
67 | const f = failure
68 | close()
69 | f(x)
70 | },
71 | catch_ && (x => {
72 | const c = (catch_: any)
73 | close()
74 | c(x)
75 | })
76 | )
77 | onCancel = bodyReturn.onCancel || noop
78 | onClose = bodyReturn.onClose || noop
79 | if (close === noop) {
80 | onCancel = noop
81 | onClose()
82 | }
83 | return () => { onCancel(); close() }
84 | }
85 |
86 | function isTask(maybeTask: mixed): boolean {
87 | return maybeTask instanceof Task
88 | }
89 |
90 | function isFun(maybeFunction: mixed): boolean {
91 | return typeof maybeFunction === 'function'
92 | }
93 |
94 | function isArrayOfTasks(maybeArray: mixed): boolean {
95 | if (!Array.isArray(maybeArray)) {
96 | return false
97 | }
98 | for (let i = 0; i < maybeArray.length; i++) {
99 | if (!(maybeArray[i] instanceof Task)) {
100 | return false
101 | }
102 | }
103 | return true
104 | }
105 |
106 | function isThenableOrFn(maybeThenable: mixed): boolean {
107 | return typeof maybeThenable === 'function' ||
108 | (
109 | typeof maybeThenable === 'object' &&
110 | maybeThenable !== null &&
111 | typeof maybeThenable.then === 'function'
112 | )
113 | }
114 |
115 | function inv(shouldBeTrue: boolean, errorMessage: string, actualValue: any): void {
116 | if (!shouldBeTrue) {
117 | throw new TypeError(`${errorMessage}. Actual value: ${actualValue}`)
118 | }
119 | }
120 |
121 |
122 |
123 | export default class Task<+S, +F> {
124 |
125 | constructor() {
126 | if (this.constructor === Task) {
127 | throw new Error('Don\'t call `new Task()`, call `Task.create()` instead')
128 | }
129 | }
130 |
131 | // Creates a task with an arbitrary computation
132 | static create(computation: Computation): Task {
133 | inv(isFun(computation), 'Task.create(f): f is not a function', computation)
134 | return new FromComputation(computation)
135 | }
136 |
137 | // Creates a task that resolves with a given value
138 | static of(value: S): Task {
139 | return new Of(value)
140 | }
141 |
142 | // Creates a task that fails with a given error
143 | static rejected(error: F): Task<*, F> {
144 | return new Rejected(error)
145 | }
146 |
147 | // Creates a task that never completes
148 | static empty(): Task<*, *> {
149 | return new Empty()
150 | }
151 |
152 | // Given array of tasks creates a task of array
153 | static parallel>>(tasks: A): Task<$TupleMap, F> {
154 | inv(isArrayOfTasks(tasks), 'Task.parallel(a): a is not an array of tasks', tasks)
155 | return new Parallel(tasks)
156 | }
157 |
158 | // Given array of tasks creates a task that completes with the earliest value or error
159 | static race(tasks: Array>): Task {
160 | inv(isArrayOfTasks(tasks), 'Task.race(a): a is not an array of tasks', tasks)
161 | return new Race(tasks)
162 | }
163 |
164 | // Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the successful value
165 | static map(fn: (x: S) => S1, task: Task): Task {
166 | inv(isFun(fn), 'Task.map(f, _): f is not a function', fn)
167 | inv(isTask(task), 'Task.map(_, t): t is not a task', task)
168 | return new Map(task, fn)
169 | }
170 | map(fn: (x: S) => S1): Task {
171 | inv(isFun(fn), 'task.map(f): f is not a function', fn)
172 | return new Map(this, fn)
173 | }
174 |
175 | // Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the failure value
176 | static mapRejected(fn: (x: F) => F1, task: Task): Task {
177 | inv(isFun(fn), 'Task.mapRejected(f, _): f is not a function', fn)
178 | inv(isTask(task), 'Task.mapRejected(_, t): t is not a task', task)
179 | return new MapRejected(task, fn)
180 | }
181 | mapRejected(fn: (x: F) => F1): Task {
182 | inv(isFun(fn), 'task.mapRejected(f): f is not a function', fn)
183 | return new MapRejected(this, fn)
184 | }
185 |
186 | // Transforms a task by applying `sf` to the successful value or `ff` to the failure value
187 | static bimap(ff: (x: F) => F1, fs: (x: S) => S1, task: Task): Task {
188 | inv(isFun(ff), 'Task.bimap(f, _, _): f is not a function', ff)
189 | inv(isFun(fs), 'Task.bimap(_, f, _): f is not a function', fs)
190 | inv(isTask(task), 'Task.bimap(_, _, t): t is not a task', task)
191 | return task.map(fs).mapRejected(ff)
192 | }
193 | bimap(ff: (x: F) => F1, fs: (x: S) => S1): Task {
194 | inv(isFun(ff), 'task.bimap(f, _): f is not a function', ff)
195 | inv(isFun(fs), 'task.bimap(_, f): f is not a function', fs)
196 | return this.map(fs).mapRejected(ff)
197 | }
198 |
199 | // Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the successful value, where `fn` returns a Task
200 | static chain(fn: (x: S) => Task, task: Task): Task {
201 | inv(isFun(fn), 'Task.chain(f, _): f is not a function', fn)
202 | inv(isTask(task), 'Task.chain(_, t): t is not a task', task)
203 | return new Chain(task, fn)
204 | }
205 | chain(fn: (x: S) => Task): Task {
206 | inv(isFun(fn), 'task.chain(f): f is not a function', fn)
207 | return new Chain(this, fn)
208 | }
209 |
210 | // Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the failure value, where `fn` returns a Task
211 | static orElse(fn: (x: F) => Task, task: Task): Task {
212 | inv(isFun(fn), 'Task.orElse(f, _): f is not a function', fn)
213 | inv(isTask(task), 'Task.orElse(_, t): t is not a task', task)
214 | return new OrElse(task, fn)
215 | }
216 | orElse(fn: (x: F) => Task): Task {
217 | inv(isFun(fn), 'task.orElse(f): f is not a function', fn)
218 | return new OrElse(this, fn)
219 | }
220 |
221 | static recur(fn: (x: S | S1) => Task, task: Task): Task<*, F | F1> {
222 | inv(isFun(fn), 'Task.recur(f, _): f is not a function', fn)
223 | inv(isTask(task), 'Task.recur(_, t): t is not a task', task)
224 | return new Recur(task, fn)
225 | }
226 | recur(fn: (x: S | S1) => Task): Task<*, F | F1> {
227 | inv(isFun(fn), 'task.recur(f): f is not a function', fn)
228 | return new Recur(this, fn)
229 | }
230 |
231 | static chainRec(
232 | fn: (
233 | next: (x: N) => ChainRecNext,
234 | done: (x: D) => ChainRecDone,
235 | v: N
236 | ) => Task | ChainRecDone, F>,
237 | initial: N
238 | ): Task {
239 | inv(isFun(fn), 'Task.chainRec(f, _): f is not a function', fn)
240 | return new ChainRec(fn, initial)
241 | }
242 |
243 | // Applies the successful value of task `this` to the successful value of task `otherTask`
244 | static ap(tf: Task<(x: A) => B, F1>, tx: Task): Task {
245 | inv(isTask(tf), 'Task.ap(t, _): t is not a task', tf)
246 | inv(isTask(tx), 'Task.ap(_, t): t is not a task', tx)
247 | return tf.chain(f => tx.map(x => f(x)))
248 | }
249 | ap(otherTask: Task<(x: S) => S1, F1>): Task {
250 | inv(isTask(otherTask), 'task.ap(t): t is not a task', otherTask)
251 | return otherTask.chain(f => this.map(x => f(x)))
252 | }
253 |
254 | // Selects the earlier of the two tasks
255 | static concat(a: Task, b: Task): Task {
256 | inv(isTask(a), 'Task.concat(t, _): t is not a task', a)
257 | inv(isTask(b), 'Task.concat(_, t): t is not a task', b)
258 | return Task.race([a, b])
259 | }
260 | concat(otherTask: Task): Task {
261 | inv(isTask(otherTask), 'task.concat(t): t is not a task', otherTask)
262 | return Task.race([this, otherTask])
263 | }
264 |
265 | static do(generator: () => Generator, Task, mixed>): Task {
266 | inv(isFun(generator), 'Task.do(f): f is not a function', generator)
267 | return new Do(generator)
268 | }
269 |
270 | _run(handlers: Handlers): Cancel { // eslint-disable-line
271 | throw new Error('Method run() is not implemented in basic Task class.')
272 | }
273 |
274 | _toString(): string {
275 | return ''
276 | }
277 |
278 | toString() {
279 | return `Task.${this._toString()}`
280 | }
281 |
282 | run(h: LooseHandlers): Cancel {
283 | const handlers = typeof h === 'function'
284 | ? {success: h, failure: defaultFailureHandler}
285 | : {success: h.success || noop, failure: h.failure || defaultFailureHandler, catch: h.catch}
286 | return this._run(handlers)
287 | }
288 |
289 | toPromise(options?: {catch: boolean} = {catch: true}): Promise> {
290 | return new Promise((suc, err) => {
291 | this.run({
292 | success(x) { suc({success: x}) },
293 | failure(x) { suc({failure: x}) },
294 | catch: options.catch ? err : undefined,
295 | })
296 | })
297 | }
298 |
299 | static fromPromise(promise: Promise | () => Promise): Task {
300 | inv(isThenableOrFn(promise), 'Task.fromPromise(p): p is not a promise', promise)
301 | return new FromPromise(promise)
302 | }
303 |
304 | runAndLog(): void {
305 | this.run({
306 | success(x) { console.log('Success:', x) }, // eslint-disable-line
307 | failure(x) { console.log('Failure:', x) }, // eslint-disable-line
308 | })
309 | }
310 |
311 | }
312 |
313 | /* We should put Fantasy Land methods to class like this:
314 | *
315 | * class Task {
316 | * 'fantasy-land/of'(value: S): Task { return Task.of(value) }
317 | * }
318 | *
319 | * but unfortunately Flow yields "literal properties not yet supported".
320 | */
321 | function makeFLCompatible(constructor: any) {
322 | constructor.prototype[fl.of] = constructor[fl.of] = constructor.of
323 | constructor.prototype[fl.empty] = constructor[fl.empty] = constructor.empty
324 | constructor.prototype[fl.chainRec] = constructor[fl.chainRec] = constructor.chainRec
325 | constructor.prototype[fl.concat] = constructor.prototype.concat
326 | constructor.prototype[fl.map] = constructor.prototype.map
327 | constructor.prototype[fl.bimap] = constructor.prototype.bimap
328 | constructor.prototype[fl.ap] = constructor.prototype.ap
329 | constructor.prototype[fl.chain] = constructor.prototype.chain
330 | }
331 |
332 | makeFLCompatible(Task)
333 |
334 |
335 |
336 | class FromComputation extends Task {
337 |
338 | _computation: Computation;
339 |
340 | constructor(computation: Computation) {
341 | super()
342 | this._computation = computation
343 | }
344 |
345 | _run(handlers: Handlers) {
346 | const {_computation} = this
347 | return runHelper((s, f, c) => {
348 | let cancel
349 | if (c) {
350 | try {
351 | cancel = _computation(s, f)
352 | } catch (e) { c(e) }
353 | } else {
354 | cancel = _computation(s, f)
355 | }
356 | return {onCancel: cancel || noop}
357 | }, handlers)
358 | }
359 |
360 | _toString() {
361 | return 'create(..)'
362 | }
363 |
364 | }
365 |
366 | class Of extends Task {
367 |
368 | _value: S;
369 |
370 | constructor(value: S) {
371 | super()
372 | this._value = value
373 | }
374 |
375 | _run(handlers: Handlers): Cancel {
376 | const {success} = handlers
377 | success(this._value)
378 | return noop
379 | }
380 |
381 | _toString() {
382 | return 'of(..)'
383 | }
384 |
385 | }
386 |
387 | class Rejected extends Task<*, F> {
388 |
389 | _error: F;
390 |
391 | constructor(error: F) {
392 | super()
393 | this._error = error
394 | }
395 |
396 | _run(handlers: Handlers<*, F>): Cancel {
397 | const {failure} = handlers
398 | failure(this._error)
399 | return noop
400 | }
401 |
402 | _toString() {
403 | return 'rejected(..)'
404 | }
405 |
406 | }
407 |
408 | class Empty extends Task<*, *> {
409 |
410 | run(): Cancel {
411 | return noop
412 | }
413 |
414 | _toString() {
415 | return `empty()`
416 | }
417 |
418 | }
419 |
420 | class Parallel extends Task {
421 |
422 | _tasks: Array>;
423 |
424 | constructor(tasks: Array>) {
425 | super()
426 | this._tasks = tasks
427 | }
428 |
429 | _run(handlers: Handlers): Cancel {
430 | return runHelper((s, f, c) => {
431 | const length = this._tasks.length
432 | const values: Array = Array(length)
433 | let completedCount = 0
434 | const runTask = (task, index) => task.run({
435 | success(x) {
436 | values[index] = x
437 | completedCount++
438 | if (completedCount === length) {
439 | s((values: any))
440 | }
441 | },
442 | failure: f,
443 | catch: c,
444 | })
445 | const cancels = this._tasks.map(runTask)
446 | return {onClose() { cancels.forEach(cancel => cancel()) }}
447 | }, handlers)
448 | }
449 |
450 | _toString() {
451 | return `parallel([${this._tasks.map(x => x._toString()).join(', ')}])`
452 | }
453 |
454 | }
455 |
456 | class Race extends Task {
457 |
458 | _tasks: Array>;
459 |
460 | constructor(tasks: Array>) {
461 | super()
462 | this._tasks = tasks
463 | }
464 |
465 | _run(handlers: Handlers): Cancel {
466 | return runHelper((success, failure, _catch) => {
467 | const handlers = {success, failure, catch: _catch}
468 | const cancels = this._tasks.map(task => task.run(handlers))
469 | return {onClose() { cancels.forEach(cancel => cancel()) }}
470 | }, handlers)
471 | }
472 |
473 | _toString() {
474 | return `race([${this._tasks.map(x => x._toString()).join(', ')}])`
475 | }
476 |
477 | }
478 |
479 | class Map extends Task {
480 |
481 | _task: Task;
482 | _fn: (x: SIn) => SOut;
483 |
484 | constructor(task: Task, fn: (x: SIn) => SOut) {
485 | super()
486 | this._task = task
487 | this._fn = fn
488 | }
489 |
490 | _run(handlers: Handlers): Cancel {
491 | const {_fn} = this
492 | const {success, failure, catch: catch_} = handlers
493 | return this._task.run({
494 | success(x) {
495 | let value
496 | if (catch_) {
497 | try {
498 | value = _fn(x)
499 | } catch (e) {
500 | catch_(e)
501 | return
502 | }
503 | } else {
504 | value = _fn(x)
505 | }
506 | success(value)
507 | },
508 | failure,
509 | catch: catch_,
510 | })
511 | }
512 |
513 | _toString() {
514 | return `${this._task._toString()}.map(..)`
515 | }
516 | }
517 |
518 | class MapRejected extends Task {
519 |
520 | _task: Task;
521 | _fn: (x: FIn) => FOut;
522 |
523 | constructor(task: Task, fn: (x: FIn) => FOut) {
524 | super()
525 | this._task = task
526 | this._fn = fn
527 | }
528 |
529 | _run(handlers: Handlers): Cancel {
530 | const {_fn} = this
531 | const {success, failure, catch: catch_} = handlers
532 | return this._task.run({
533 | success,
534 | failure(x) {
535 | let value
536 | if (catch_) {
537 | try {
538 | value = _fn(x)
539 | } catch (e) {
540 | catch_(e)
541 | return
542 | }
543 | } else {
544 | value = _fn(x)
545 | }
546 | failure(value)
547 | },
548 | catch: catch_,
549 | })
550 | }
551 |
552 | _toString() {
553 | return `${this._task._toString()}.mapRejected(..)`
554 | }
555 | }
556 |
557 | class Chain extends Task {
558 |
559 | _task: Task;
560 | _fn: (x: SIn) => Task;
561 |
562 | constructor(task: Task, fn: (x: SIn) => Task) {
563 | super()
564 | this._task = task
565 | this._fn = fn
566 | }
567 |
568 | _run(handlers: Handlers): Cancel {
569 | const {_fn, _task} = this
570 | return runHelper((success, failure, catch_) => {
571 | let cancel = noop
572 | let spawnedHasBeenRun = false
573 | const cancel1 = _task.run({ // #1
574 | success(x) {
575 | let spawned
576 | if (catch_) {
577 | try {
578 | spawned = _fn(x)
579 | } catch (e) { catch_(e) }
580 | } else {
581 | spawned = _fn(x)
582 | }
583 | if (spawned) {
584 | cancel = spawned.run({success, failure, catch: catch_}) // #2
585 | spawnedHasBeenRun = true
586 | }
587 | },
588 | failure,
589 | catch: catch_,
590 | })
591 | if (!spawnedHasBeenRun) { // #2 run() may return before #1 run() returns
592 | cancel = cancel1
593 | }
594 | return {onCancel() { cancel() }}
595 | }, handlers)
596 | }
597 |
598 | _toString() {
599 | return `${this._task._toString()}.chain(..)`
600 | }
601 | }
602 |
603 | class OrElse extends Task {
604 |
605 | _task: Task;
606 | _fn: (x: FIn) => Task;
607 |
608 | constructor(task: Task, fn: (x: FIn) => Task) {
609 | super()
610 | this._task = task
611 | this._fn = fn
612 | }
613 |
614 | _run(handlers: Handlers): Cancel {
615 | const {_fn, _task} = this
616 | return runHelper((success, failure, catch_) => {
617 | let cancel = noop
618 | let spawnedHasBeenRun = false
619 | const cancel1 = _task.run({ // #1
620 | success,
621 | failure(x) {
622 | let spawned
623 | if (catch_) {
624 | try {
625 | spawned = _fn(x)
626 | } catch (e) { catch_(e) }
627 | } else {
628 | spawned = _fn(x)
629 | }
630 | if (spawned) {
631 | cancel = spawned.run({success, failure, catch: catch_}) // #2
632 | spawnedHasBeenRun = true
633 | }
634 | },
635 | catch: catch_,
636 | })
637 | if (!spawnedHasBeenRun) { // #2 run() may return before #1 run() returns
638 | cancel = cancel1
639 | }
640 | return {onCancel() { cancel() }}
641 | }, handlers)
642 |
643 | }
644 |
645 | _toString() {
646 | return `${this._task._toString()}.orElse(..)`
647 | }
648 | }
649 |
650 | class Recur extends Task<*, F | F1> {
651 |
652 | _task: Task;
653 | _fn: (x: S | S1) => Task;
654 |
655 | constructor(task: Task, fn: (x: S | S1) => Task) {
656 | super()
657 | this._task = task
658 | this._fn = fn
659 | }
660 |
661 | _run(handlers: Handlers): Cancel {
662 | const {_fn, _task} = this
663 | return runHelper((_, failure, catch_) => {
664 | let x
665 | let haveNewX = false
666 | let inLoop = false
667 | let spawnedHasBeenRun = false
668 | let sharedCancel = noop
669 | const success = _x => {
670 | haveNewX = true
671 | x = _x
672 | if (inLoop) {
673 | return
674 | }
675 | inLoop = true
676 | while(haveNewX) {
677 | haveNewX = false
678 | let spawned
679 | if (catch_) {
680 | try {
681 | spawned = _fn(x)
682 | } catch (e) { catch_(e) }
683 | } else {
684 | spawned = _fn(x)
685 | }
686 | if (spawned) {
687 | sharedCancel = spawned.run({success, failure, catch: catch_}) // #2
688 | spawnedHasBeenRun = true
689 | }
690 | }
691 | inLoop = false
692 | }
693 | const cancel = _task.run({success, failure, catch: catch_}) // #1
694 | if (!spawnedHasBeenRun) { // #2 run() may return before #1 run() returns
695 | sharedCancel = cancel
696 | }
697 | return {onCancel() { sharedCancel() }}
698 | }, handlers)
699 | }
700 |
701 | _toString() {
702 | return `${this._task._toString()}.recur(..)`
703 | }
704 | }
705 |
706 |
707 | class ChainRec extends Task {
708 |
709 | _fn: (
710 | next: (x: N) => ChainRecNext,
711 | done: (x: D) => ChainRecDone,
712 | v: N
713 | ) => Task | ChainRecDone, F>;
714 | _initial: N;
715 |
716 | constructor(
717 | fn: (
718 | next: (x: N) => ChainRecNext,
719 | done: (x: D) => ChainRecDone,
720 | v: N
721 | ) => Task | ChainRecDone, F>,
722 | initial: N
723 | ) {
724 | super()
725 | this._fn = fn
726 | this._initial = initial
727 | }
728 |
729 | _run(handlers: Handlers): Cancel {
730 | const {_fn, _initial} = this
731 | return runHelper((success, failure, catch_) => {
732 | let newNext = null
733 | let haveNewNext = false
734 | let inLoop = false
735 | let sharedCancel = noop
736 | const step = (result) => {
737 | if (result.type === 'done') {
738 | success(result.value)
739 | return
740 | }
741 | newNext = result.value
742 | haveNewNext = true
743 | if (inLoop) {
744 | return
745 | }
746 | inLoop = true
747 | while(haveNewNext) {
748 | haveNewNext = false
749 | let spawned
750 | if (catch_) {
751 | try {
752 | spawned = _fn(chainRecNext, chainRecDone, newNext)
753 | } catch (e) { catch_(e) }
754 | } else {
755 | spawned = _fn(chainRecNext, chainRecDone, newNext)
756 | }
757 | if (spawned) {
758 | sharedCancel = spawned.run({success: step, failure, catch: catch_})
759 | }
760 | }
761 | inLoop = false
762 | }
763 | step(chainRecNext(_initial))
764 | return {onCancel() { sharedCancel() }}
765 | }, handlers)
766 | }
767 |
768 | _toString() {
769 | return `chainRec(..)`
770 | }
771 |
772 | }
773 |
774 |
775 | class Do extends Task {
776 |
777 | _generator: () => Generator, Task, mixed>;
778 |
779 | constructor(generator: () => Generator, Task, mixed>) {
780 | super()
781 | this._generator = generator
782 | }
783 |
784 | _run(handlers: Handlers): Cancel {
785 | const {_generator} = this
786 | return runHelper((success, failure, catch_) => {
787 | const iterator = _generator()
788 | let x
789 | let haveNewX = false
790 | let inLoop = false
791 | let sharedCancel = noop
792 | const step = _x => {
793 | haveNewX = true
794 | x = _x
795 | if (inLoop) {
796 | return
797 | }
798 | inLoop = true
799 | while(haveNewX) {
800 | haveNewX = false
801 | let iteratorNext
802 | if (catch_) {
803 | try {
804 | iteratorNext = iterator.next(x)
805 | } catch (e) { catch_(e) }
806 | } else {
807 | iteratorNext = iterator.next(x)
808 | }
809 | if (iteratorNext) {
810 | const {value: spawned, done} = iteratorNext
811 | sharedCancel = (spawned: any).run({success: done ? success : step, failure, catch: catch_})
812 | }
813 | }
814 | inLoop = false
815 | }
816 | step(undefined)
817 | return {onCancel() { sharedCancel() }}
818 | }, handlers)
819 | }
820 |
821 | _toString() {
822 | return `do(..)`
823 | }
824 |
825 | }
826 |
827 |
828 | class FromPromise extends Task {
829 |
830 | _promise: Promise | () => Promise;
831 |
832 | constructor(promise: Promise | () => Promise) {
833 | super()
834 | this._promise = promise
835 | }
836 |
837 | _run(handlers: Handlers) {
838 | const {_promise} = this
839 | const promise = typeof _promise === 'function' ? _promise() : _promise
840 | return runHelper((success, _, catch_) => {
841 | promise.then(success, catch_)
842 | return {}
843 | }, handlers)
844 | }
845 |
846 | _toString() {
847 | return 'fromPromise(..)'
848 | }
849 |
850 | }
851 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/ap.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 |
3 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
4 | import Task from '../src'
5 |
6 | const test = _test.wrap('ap')
7 |
8 | test('works', 1, t => {
9 | Task.of(2).ap(Task.of(x => x + 1)).run(t.calledWith(3))
10 | })
11 |
12 | test('static alias works', 1, t => {
13 | Task.ap(Task.of(x => x + 1), Task.of(2)).run(t.calledWith(3))
14 | })
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/bimap.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 |
3 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
4 | import Task from '../src'
5 |
6 | const test = _test.wrap('bimap')
7 |
8 | test('works with of', 1, t => {
9 | Task.of(2).bimap(x => x, x => x + 10).run(t.calledWith(12))
10 | })
11 |
12 | test('works with .rejected', 1, t => {
13 | Task.rejected(2).bimap(x => x + 10, x => x).run({failure: t.calledWith(12)})
14 | })
15 |
16 | test('static alias works', 2, t => {
17 | Task.bimap(x => x, x => x + 10, Task.of(2)).run(t.calledWith(12))
18 | Task.bimap(x => x + 10, x => x, Task.rejected(2)).run({failure: t.calledWith(12)})
19 | })
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/chain.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 |
3 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
4 | import Task from '../src'
5 |
6 | const test = _test.wrap('chain')
7 |
8 | test('works with of + of', 1, t => {
9 | Task.of(2).chain(x => Task.of(x + 10)).run(t.calledWith(12))
10 | })
11 |
12 | test('static alias works', 1, t => {
13 | Task.chain(x => Task.of(x + 10), Task.of(2)).run(t.calledWith(12))
14 | })
15 |
16 | test('works with of + rejected', 1, t => {
17 | Task.of(2).chain(x => Task.rejected(x + 10)).run({failure: t.calledWith(12)})
18 | })
19 |
20 | test('works with rejected + of', 1, t => {
21 | Task.rejected(2).chain(x => Task.of(x + 10)).run({failure: t.calledWith(2)})
22 | })
23 |
24 | test('cancelation - orig. task', 1, t => {
25 | Task.create(() => t.calledOnce()).chain(() => Task.of()).run({})()
26 | })
27 |
28 | test('cancelation - spawned task - orig. sync', 1, t => {
29 | Task.of().chain(() => Task.create(() => t.calledOnce())).run({})()
30 | })
31 |
32 | test('cancelation - spawned task - orig. async', 1, t => {
33 | let s: any = null
34 | const orig = Task.create(_s => {s = _s})
35 | const spawned = Task.create(() => t.calledOnce())
36 | const cancel = orig.chain(() => spawned).run({})
37 | s()
38 | cancel()
39 | })
40 |
41 | test('exception thrown from fn (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
42 | t.throws(() => {
43 | Task.of().chain(() => { throw new Error('err1') }).run({})
44 | }, /err1/)
45 | })
46 |
47 | test('exception thrown from fn (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
48 | Task.of().chain(() => { throw 2 }).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
49 | })
50 |
51 | const thrower1 = Task.create(() => { throw new Error('err1') })
52 | const thrower2 = Task.create(() => { throw 2 })
53 |
54 | test('exception thrown from parent task (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
55 | t.throws(() => {
56 | thrower1.chain(() => Task.of()).run({})
57 | }, /err1/)
58 | })
59 |
60 | test('exception thrown from parent task (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
61 | thrower2.chain(() => Task.of()).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
62 | })
63 |
64 | test('exception thrown from child task (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
65 | t.throws(() => {
66 | Task.of().chain(() => thrower1).run({})
67 | }, /err1/)
68 | })
69 |
70 | test('exception thrown from child task (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
71 | Task.of().chain(() => thrower2).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
72 | })
73 |
74 | test('exception thrown from child task (with catch cb, async)', 1, t => {
75 | let s = (null: any)
76 | let thrower = Task.create(_s => { s = _s }).chain(() => { throw 2 })
77 | Task.of().chain(() => thrower).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
78 | s()
79 | })
80 |
81 | test('exception thrown from child task (no catch cb, async)', 1, t => {
82 | let s = (null: any)
83 | let thrower = Task.create(_s => { s = _s }).chain(() => { throw new Error('err1') })
84 | Task.of().chain(() => thrower).run({})
85 | t.throws(s, /err1/)
86 | })
87 |
88 | test('this==undefined in success cd', 1, t => {
89 | Task.of(2).chain(x => Task.of(x)).run({success() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
90 | })
91 |
92 | test('this==undefined in failure cd', 1, t => {
93 | Task.rejected(2).chain(x => Task.of(x)).run({failure() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
94 | })
95 |
96 | test('this==undefined in fn', 1, t => {
97 | Task.of(2).chain(function(x) { t.equal(this, undefined); return Task.of(x) }).run({})
98 | })
99 |
100 |
101 | // Flow
102 |
103 | Task.of(2).chain(x => x > 10 ? Task.of('') : Task.rejected(true)).run({
104 | success(x) {
105 | (x: string)
106 | },
107 | failure(x) {
108 | (x: boolean)
109 | },
110 | })
111 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/chainRec.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 |
3 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
4 | import Task from '../src'
5 |
6 | function computeMaxCallStackSize() {
7 | try {
8 | return 1 + computeMaxCallStackSize()
9 | } catch (e) {
10 | return 1
11 | }
12 | }
13 | const MAX_STACK_SIZE = computeMaxCallStackSize()
14 |
15 | const test = _test.wrap('chainRec')
16 |
17 | const later = x => Task.create(s => { setTimeout(() => { s(x) }) })
18 |
19 | test('0 iterations', 1, t => {
20 | const fn = (_, d, x) => Task.of(d(x))
21 | Task.chainRec(fn, 2).run({success: t.calledWith(2)})
22 | })
23 |
24 | test('1 iteration (sync)', 1, t => {
25 | const fn = (n, d, x) => x === 0 ? Task.of(d(x)) : Task.of(n(x - 1))
26 | Task.chainRec(fn, 1).run({success: t.calledWith(0)})
27 | })
28 |
29 | test.async('1 iteration (async)', 1, t => {
30 | const fn = (n, d, x) => x === 0 ? Task.of(d(x)) : later(n(x - 1))
31 | Task.chainRec(fn, 1).run({success: t.calledWith(0)})
32 | })
33 |
34 | test('cancelation - first spawned', 1, t => {
35 | const spawned = Task.create(() => t.calledOnce())
36 | Task.chainRec(() => spawned, 0).run({})()
37 | })
38 |
39 | test('cancelation - second spawned - first sync', 1, t => {
40 | const spawned = Task.create(() => t.calledOnce())
41 | Task.chainRec((n, d, x) => x === 1 ? Task.of(n(2)) : spawned, 1).run({})()
42 | })
43 |
44 | test('cancelation - second spawned - first async', 1, t => {
45 | let s: any = null
46 | const first = n => Task.create(_s => {s = x => _s(n(x))})
47 | const second = Task.create(() => t.calledOnce())
48 | const cancel = Task.chainRec((n, d, x) => x === 1 ? first(n) : second, 1).run({})
49 | s(2)
50 | cancel()
51 | })
52 |
53 | test('count down sync', 7, t => {
54 | const stub = t.calledWith(5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0)
55 | const fn = (n, d, x) => {
56 | stub(x)
57 | return x === 0 ? Task.of(d(x)) : Task.of(n(x - 1))
58 | }
59 | Task.chainRec(fn, 5).run({success: t.calledWith(0)})
60 | })
61 |
62 | test.async('count down async', 7, t => {
63 | const stub = t.calledWith(5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0)
64 | const fn = (n, d, x) => {
65 | stub(x)
66 | return x === 0 ? Task.of(d(x)) : later(n(x - 1))
67 | }
68 | Task.chainRec(fn, 5).run({success: t.calledWith(0)})
69 | })
70 |
71 | if (!process.env.IGNORE_SLOW_TESTS) {
72 | test('works with a lot of sync iterations', 1, t => {
73 | const fn = (n, d, x) => x === 0 ? Task.of(d(x)) : Task.of(n(x - 1))
74 | Task.chainRec(fn, MAX_STACK_SIZE + 1).run({success: t.calledWith(0)})
75 | })
76 | }
77 |
78 | test('exception thrown from fn (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
79 | t.throws(() => {
80 | Task.chainRec(() => { throw new Error('err1') }, 1).run({})
81 | }, /err1/)
82 | })
83 |
84 | test('exception thrown from fn (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
85 | Task.chainRec(() => { throw 2 }, 1).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
86 | })
87 |
88 | const thrower1 = Task.create(() => { throw new Error('err1') })
89 | const thrower2 = Task.create(() => { throw 2 })
90 |
91 | test('exception thrown from first spawned (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
92 | t.throws(() => {
93 | Task.chainRec(() => thrower1, 1).run({})
94 | }, /err1/)
95 | })
96 |
97 | test('exception thrown from second spawned (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
98 | t.throws(() => {
99 | Task.chainRec((n, d, x) => x === 1 ? Task.of(n(2)) : thrower1, 1).run({})
100 | }, /err1/)
101 | })
102 |
103 | test('exception thrown from first spawned (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
104 | Task.chainRec(() => thrower2, 1).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
105 | })
106 |
107 | test('exception thrown from second spawned (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
108 | Task.chainRec((n, d, x) => x === 1 ? Task.of(n(2)) : thrower2, 1).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
109 | })
110 |
111 | test('exception thrown from second spawned (with catch cb, async)', 1, t => {
112 | let s = (null: any)
113 | let thrower = Task.create(_s => { s = _s }).chain(() => { throw 2 })
114 | Task.chainRec((n, d, x) => x === 1 ? Task.of(n(2)) : thrower, 1).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
115 | s()
116 | })
117 |
118 | test('exception thrown from second spawned (no catch cb, async)', 1, t => {
119 | let s = (null: any)
120 | let thrower = Task.create(_s => { s = _s }).chain(() => { throw new Error('err1') })
121 | Task.chainRec((n, d, x) => x === 1 ? Task.of(n(2)) : thrower, 1).run({})
122 | t.throws(s, /err1/)
123 | })
124 |
125 | test('this==undefined in success cd', 1, t => {
126 | Task.chainRec((n, d, x) => Task.of(d(x)), 0).run({success() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
127 | })
128 |
129 | test('this==undefined in failure cd', 1, t => {
130 | Task.chainRec(() => Task.rejected(), 0).run({failure() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
131 | })
132 |
133 | test('this==undefined in fn', 1, t => {
134 | Task.chainRec(function() {
135 | t.equal(this, undefined)
136 | return Task.rejected()
137 | }, 0).run({failure(){}})
138 | })
139 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/common.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 |
3 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
4 | import Task from '../src'
5 |
6 | const test = _test.wrap('common')
7 |
8 | test('new Task() throws', 1, t => {
9 | t.throws(() => new Task(), /Task\.create/)
10 | })
11 |
12 | test('default onFail cb in run works', 1, t => {
13 | t.throws(() => Task.rejected('err1').run({}), /err1/)
14 | })
15 |
16 | test('default onFail cb throws the same Error if argument is an Error', 1, t => {
17 | const e = new Error('')
18 | try {
19 | Task.rejected(e).run({})
20 | } catch (_e) {
21 | t.ok(e === _e)
22 | }
23 | })
24 |
25 | test('runAndLog works (success)', 0, () => {
26 | // something goes sideways if we try to mock console,
27 | // so we just check that method exists and runs fine
28 | Task.of(2).runAndLog()
29 | })
30 |
31 | test('runAndLog works (failure)', 0, () => {
32 | // same deal...
33 | Task.rejected(2).runAndLog()
34 | })
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/concat.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 |
3 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
4 | import Task from '../src'
5 |
6 | const test = _test.wrap('concat')
7 |
8 | test('works', 1, t => {
9 | Task.of(1).concat(Task.of(2)).run(t.calledWith(1))
10 | })
11 |
12 | test('static alias works', 1, t => {
13 | Task.concat(Task.of(1), Task.of(2)).run(t.calledWith(1))
14 | })
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/do.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /* eslint-disable require-yield */
2 |
3 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
4 | import Task from '../src'
5 |
6 | import 'babel-polyfill'
7 |
8 | function computeMaxCallStackSize() {
9 | try {
10 | return 1 + computeMaxCallStackSize()
11 | } catch (e) {
12 | return 1
13 | }
14 | }
15 | const MAX_STACK_SIZE = computeMaxCallStackSize()
16 |
17 | const test = _test.wrap('do')
18 |
19 | const later = x => Task.create(s => { setTimeout(() => { s(x) }) })
20 |
21 | test('0 iterations', 1, t => {
22 | Task.do(function* () {return Task.of(2)}).run(t.calledWith(2))
23 | })
24 |
25 | test('0 iterations (2 runs)', 2, t => {
26 | const task = Task.do(function* () {return Task.of(2)})
27 | task.run(t.calledWith(2))
28 | task.run(t.calledWith(2))
29 | })
30 |
31 | test('1 sync iteration', 1, t => {
32 | Task.do(function* () {
33 | const x = yield Task.of(1)
34 | return Task.of(x + 1)
35 | }).run(t.calledWith(2))
36 | })
37 |
38 | test.async('1 async iteration', 1, t => {
39 | Task.do(function* () {
40 | const x = yield later(1)
41 | return Task.of(x + 1)
42 | }).run(t.calledWith(2))
43 | })
44 |
45 | test('1 sync iteration (2 runs)', 2, t => {
46 | const task = Task.do(function* () {
47 | const x = yield Task.of(1)
48 | return Task.of(x + 1)
49 | })
50 | task.run(t.calledWith(2))
51 | task.run(t.calledWith(2))
52 | })
53 |
54 | test('2 sync iterations', 1, t => {
55 | Task.do(function* () {
56 | const x = yield Task.of(2)
57 | const y = yield Task.of(3)
58 | return Task.of(x * y)
59 | }).run(t.calledWith(6))
60 | })
61 |
62 | test.async('2 async iterations', 1, t => {
63 | Task.do(function* () {
64 | const x = yield later(2)
65 | const y = yield later(3)
66 | return Task.of(x * y)
67 | }).run(t.calledWith(6))
68 | })
69 |
70 | test('2 sync iterations (2 runs)', 2, t => {
71 | const task = Task.do(function* () {
72 | const x = yield Task.of(2)
73 | const y = yield Task.of(3)
74 | return Task.of(x * y)
75 | })
76 | task.run(t.calledWith(6))
77 | task.run(t.calledWith(6))
78 | })
79 |
80 | test('cancelation (0 returned)', 1, t => {
81 | const spawned = Task.create(() => t.calledOnce())
82 | Task.do(function* () {return spawned}).run({})()
83 | })
84 |
85 | test('cancelation (0 yielded)', 1, t => {
86 | const spawned = Task.create(() => t.calledOnce())
87 | Task.do(function* () {
88 | yield spawned
89 | t.fail()
90 | return Task.of(1)
91 | }).run({})()
92 | })
93 |
94 | test('cancelation (1 returned)', 1, t => {
95 | const spawned = Task.create(() => t.calledOnce())
96 | Task.do(function* () {
97 | yield Task.of(1)
98 | return spawned
99 | }).run({})()
100 | })
101 |
102 | test('cancelation (1 returned, async yield)', 1, t => {
103 | let s = null
104 | const zero = Task.create(_s => {s = _s})
105 | const first = Task.create(() => t.calledOnce())
106 | const cancel = Task.do(function* () {
107 | yield zero
108 | return first
109 | }).run({})
110 | s(2)
111 | cancel()
112 | })
113 |
114 | test('count down sync', 7, t => {
115 | const stub = t.calledWith(5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0)
116 | Task.do(function* () {
117 | let n = 5
118 | while (n > 0) {
119 | stub(n)
120 | n = yield Task.of(n - 1)
121 | }
122 | stub(n)
123 | return Task.of(n)
124 | }).run({success: t.calledWith(0)})
125 | })
126 |
127 | test.async('count down async', 7, t => {
128 | const stub = t.calledWith(5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0)
129 | Task.do(function* () {
130 | let n = 5
131 | while (n > 0) {
132 | stub(n)
133 | n = yield later(n - 1)
134 | }
135 | stub(n)
136 | return later(n)
137 | }).run({success: t.calledWith(0)})
138 | })
139 |
140 | test('0 iterations (rejected)', 1, t => {
141 | Task.do(function* () {return Task.rejected(2)}).run({failure: t.calledWith(2)})
142 | })
143 |
144 | test('part of generator after `yield rejected` is not executed', 1, t => {
145 | Task.do(function* () {
146 | yield Task.rejected(2)
147 | t.fail()
148 | return Task.of(1)
149 | }).run({failure: t.calledWith(2)})
150 | })
151 |
152 | if (!process.env.IGNORE_SLOW_TESTS) {
153 | test('works with big loops', 1, t => {
154 | Task.do(function* () {
155 | let i = MAX_STACK_SIZE + 2
156 | while (i !== 0) {
157 | i = yield Task.of(i - 1)
158 | }
159 | return Task.of(i)
160 | }).run(t.calledWith(0))
161 | })
162 | }
163 |
164 | test('this==undefined in success cd', 1, t => {
165 | Task.do(function*() {return Task.of()}).run({success() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
166 | })
167 |
168 | test('this==undefined in failure cd', 1, t => {
169 | Task.do(function*() {return Task.rejected()}).run({failure() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
170 | })
171 |
172 | test('this==undefined in fn', 1, t => {
173 | Task.do(function*() {
174 | t.equal(this, undefined)
175 | return Task.rejected()
176 | }).run({failure(){}})
177 | })
178 |
179 | test('exception thrown from fn (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
180 | t.throws(() => {
181 | Task.do(function*() { throw new Error('err1') }, 1).run({})
182 | }, /err1/)
183 | })
184 |
185 | test('exception thrown from fn (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
186 | Task.do(function*() { throw 2 }, 1).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
187 | })
188 |
189 | const thrower1 = Task.create(() => { throw new Error('err1') })
190 | const thrower2 = Task.create(() => { throw 2 })
191 |
192 | test('exception thrown from spawned (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
193 | t.throws(() => {
194 | Task.do(function*() { return thrower1 }).run({})
195 | }, /err1/)
196 | })
197 |
198 | test('exception thrown from spawned (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
199 | Task.do(function*() { return thrower2 }).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
200 | })
201 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/empty.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 |
3 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
4 | import Task from '../src'
5 |
6 | const test = _test.wrap('empty')
7 |
8 | test('doens\'t call cbs', 0, t => {
9 | Task.empty().run({success: t.fail, failure: t.fail})
10 | })
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fantasyLand.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
2 | import Task from '../src'
3 | import fl from 'fantasy-land'
4 |
5 | const test = _test.wrap('fantasy-land')
6 |
7 | test('of', 3, t => {
8 | t.equal(typeof Task.of, 'function')
9 | t.equal(Task.of, Task[fl.of])
10 | t.equal(Task.of, Task.prototype[fl.of])
11 | })
12 |
13 | test('empty', 3, t => {
14 | t.equal(typeof Task.empty, 'function')
15 | t.equal(Task.empty, Task[fl.empty])
16 | t.equal(Task.empty, Task.prototype[fl.empty])
17 | })
18 |
19 | test('chainRec', 3, t => {
20 | t.equal(typeof Task.chainRec, 'function')
21 | t.equal(Task.chainRec, Task[fl.chainRec])
22 | t.equal(Task.chainRec, Task.prototype[fl.chainRec])
23 | })
24 |
25 | test('concat', 2, t => {
26 | t.equal(typeof Task.prototype.concat, 'function')
27 | t.equal(Task.prototype.concat, Task.prototype[fl.concat])
28 | })
29 |
30 | test('map', 2, t => {
31 | t.equal(typeof Task.prototype.map, 'function')
32 | t.equal(Task.prototype.map, Task.prototype[fl.map])
33 | })
34 |
35 | test('bimap', 2, t => {
36 | t.equal(typeof Task.prototype.bimap, 'function')
37 | t.equal(Task.prototype.bimap, Task.prototype[fl.bimap])
38 | })
39 |
40 | test('ap', 2, t => {
41 | t.equal(typeof Task.prototype.ap, 'function')
42 | t.equal(Task.prototype.ap, Task.prototype[fl.ap])
43 | })
44 |
45 | test('cahin', 2, t => {
46 | t.equal(typeof Task.prototype.chain, 'function')
47 | t.equal(Task.prototype.cahin, Task.prototype[fl.cahin])
48 | })
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fromComputation.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 |
3 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
4 | import Task from '../src'
5 |
6 | const test = _test.wrap('fromComputation')
7 |
8 | test('succ value from computation is passed to run() cb', 1, t => {
9 | Task.create(s => s(2)).run(t.calledWith(2))
10 | })
11 |
12 | test('cancelation cb returned by computation is called', 1, t => {
13 | Task.create(() => t.calledOnce()).run({})()
14 | })
15 |
16 | test('cancelation cb returned by computation is called only once', 1, t => {
17 | const cancel = Task.create(() => t.calledOnce()).run({})
18 | cancel()
19 | cancel()
20 | })
21 |
22 | test('after a cuss, cancelation cb returned by computation isn\'t called', 0, t => {
23 | Task.create((s) => { s(1); return t.fail }).run({})()
24 | })
25 |
26 | test('after a cuss, cancelation cb returned by computation isn\'t called (async)', 0, t => {
27 | let s: any = null
28 | const cancel = Task.create((_s) => { s = _s; return t.fail }).run({})
29 | s()
30 | cancel()
31 | })
32 |
33 | test('after a cuss, cancelation cb returned by computation isn\'t called (cancelation in success cb)', 0, t => {
34 | let s: any = null
35 | const cancel = Task.create((_s) => { s = _s; return t.fail }).run({
36 | success() {
37 | cancel()
38 | },
39 | })
40 | s()
41 | })
42 |
43 | test('after a cuss, all calls of computation cbs are ignored', 1, t => {
44 | let s = (null: any)
45 | let f = (null: any)
46 | const task = Task.create((_s, _f) => {s = _s; f = _f})
47 | task.run({success: t.calledOnce(), failure: t.fail})
48 | s()
49 | s()
50 | f()
51 | })
52 |
53 | test('after a fail, all calls of computation cbs are ignored', 1, t => {
54 | let s = (null: any)
55 | let f = (null: any)
56 | const task = Task.create((_s, _f) => {s = _s; f = _f})
57 | task.run({success: t.fail, failure: t.calledOnce()})
58 | f()
59 | f()
60 | s()
61 | })
62 |
63 | test('after cancelation, all calls of computation cbs are ignored', 0, t => {
64 | let s = (null: any)
65 | let f = (null: any)
66 | const task = Task.create((_s, _f) => {s = _s; f = _f})
67 | task.run({success: t.fail, failure: t.fail})()
68 | s()
69 | f()
70 | })
71 |
72 | test('exception thrown from computation (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
73 | t.throws(() => Task.create(() => { throw new Error('err1') }).run({}), /err1/)
74 | })
75 |
76 | test('exception thrown from computation (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
77 | Task.create(() => { throw 2 }).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
78 | })
79 |
80 | test('this==undefined in success cb', 1, t => {
81 | Task.create(s => s(2)).run({success() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
82 | })
83 |
84 | test('this==undefined in failure cb', 1, t => {
85 | Task.create((_, f) => f(2)).run({failure() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
86 | })
87 |
88 | test('this==undefined in fn', 1, t => {
89 | Task.create(function() { t.equal(this, undefined) }).run({})
90 | })
91 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fromPromise.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 | /* global Promise */
3 |
4 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
5 | import Task from '../src'
6 |
7 | const test = _test.wrap('fromPromise')
8 |
9 | test.async('fromPromise(resolve(..))', 1, t => {
10 | Task.fromPromise(Promise.resolve(2)).run({success: t.calledWith(2)})
11 | })
12 |
13 | test.async('fromPromise(() => resolve(..))', 1, t => {
14 | Task.fromPromise(() => Promise.resolve(2)).run({success: t.calledWith(2)})
15 | })
16 |
17 | test('fromPromise(reject(..)).run({})', 1, t => {
18 | const fakePromise: any = {then(s, e) {t.equal(e, undefined)}}
19 | Task.fromPromise(fakePromise).run({})
20 | })
21 |
22 | test.async('fromPromise(reject(..)).run({catch})', 1, t => {
23 | Task.fromPromise(Promise.reject(2)).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
24 | })
25 |
26 | test.async('cancelation works (success)', 0, t => {
27 | let s: any = null
28 | const promise = new Promise(_s => {s = _s})
29 | const cancel = Task.fromPromise(promise).run({success: t.fail})
30 | setTimeout(() => {
31 | cancel()
32 | s()
33 | t.end()
34 | }, 1)
35 | })
36 |
37 | test.async('cancelation works (catch)', 0, t => {
38 | let s: any = null
39 | const promise = new Promise((_, _s) => {s = _s})
40 | const cancel = Task.fromPromise(promise).run({catch: t.fail})
41 | setTimeout(() => {
42 | cancel()
43 | s()
44 | t.end()
45 | }, 1)
46 | })
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/map.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 |
3 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
4 | import Task from '../src'
5 |
6 | const test = _test.wrap('map')
7 |
8 | test('works with of', 1, t => {
9 | Task.of(2).map(x => x + 10).run(t.calledWith(12))
10 | })
11 |
12 | test('static alias works', 1, t => {
13 | Task.map(x => x + 10, Task.of(2)).run(t.calledWith(12))
14 | })
15 |
16 | test('this==undefined in success cd', 1, t => {
17 | Task.of(2).map(x => x).run({success() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
18 | })
19 |
20 | test('this==undefined in failure cd', 1, t => {
21 | Task.rejected(2).map(x => x).run({failure() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
22 | })
23 |
24 | test('this==undefined in fn', 1, t => {
25 | Task.of(2).map(function(x) { t.equal(this, undefined); return x }).run({})
26 | })
27 |
28 | const thrower1 = Task.create(() => { throw new Error('err1') })
29 | const thrower2 = Task.create(() => { throw 2 })
30 |
31 | test('exception thrown from parent task (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
32 | t.throws(() => {
33 | thrower1.map(x => x).run({})
34 | }, /err1/)
35 | })
36 |
37 | test('exception thrown from parent task (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
38 | thrower2.map(x => x).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
39 | })
40 |
41 | test('exception thrown from fn (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
42 | t.throws(() => {
43 | Task.of(1).map(() => { throw new Error('err1') }).run({})
44 | }, /err1/)
45 | })
46 |
47 | test('exception thrown from fn (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
48 | Task.of(1).map(() => { throw 2 }).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
49 | })
50 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/mapRejected.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 |
3 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
4 | import Task from '../src'
5 |
6 | const test = _test.wrap('mapRejected')
7 |
8 | test('works with .rejected', 1, t => {
9 | Task.rejected(2).mapRejected(x => x + 10).run({failure: t.calledWith(12)})
10 | })
11 |
12 | test('static alias works', 1, t => {
13 | Task.mapRejected(x => x + 10, Task.rejected(2)).run({failure: t.calledWith(12)})
14 | })
15 |
16 | test('this==undefined in success cd', 1, t => {
17 | Task.of(2).mapRejected(x => x).run({success() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
18 | })
19 |
20 | test('this==undefined in failure cd', 1, t => {
21 | Task.rejected(2).mapRejected(x => x).run({failure() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
22 | })
23 |
24 | test('this==undefined in fn', 1, t => {
25 | Task.rejected(2).mapRejected(function(x) { t.equal(this, undefined); return x }).run({failure(){}})
26 | })
27 |
28 | const thrower1 = Task.create(() => { throw new Error('err1') })
29 | const thrower2 = Task.create(() => { throw 2 })
30 |
31 | test('exception thrown from parent task (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
32 | t.throws(() => {
33 | thrower1.mapRejected(x => x).run({})
34 | }, /err1/)
35 | })
36 |
37 | test('exception thrown from parent task (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
38 | thrower2.mapRejected(x => x).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
39 | })
40 |
41 | test('exception thrown from fn (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
42 | t.throws(() => {
43 | Task.rejected(1).mapRejected(() => { throw new Error('err1') }).run({})
44 | }, /err1/)
45 | })
46 |
47 | test('exception thrown from fn (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
48 | Task.rejected(1).mapRejected(() => { throw 2 }).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
49 | })
50 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/of.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 |
3 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
4 | import Task from '../src'
5 |
6 | const test = _test.wrap('of')
7 |
8 | test('passes value to cb', 1, t => {
9 | Task.of(2).run(t.calledWith(2))
10 | })
11 |
12 | test('this==undefined in cd', 1, t => {
13 | Task.of(2).run(function() { t.equal(this, undefined) })
14 | })
15 |
16 |
17 | // Flow tests
18 |
19 | Task.of(1).run({
20 | success(x) {
21 | // $FlowFixMe
22 | (x: string)
23 | },
24 | })
25 |
26 | Task.of(1).run(x => {
27 | // $FlowFixMe
28 | (x: string)
29 | })
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/orElse.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 |
3 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
4 | import Task from '../src'
5 |
6 | const test = _test.wrap('orElse')
7 |
8 | test('works with of + of', 1, t => {
9 | Task.of(2).orElse(x => Task.of(x + 10)).run(t.calledWith(2))
10 | })
11 |
12 | test('static alias works', 1, t => {
13 | Task.orElse(x => Task.of(x + 10), Task.of(2)).run(t.calledWith(2))
14 | })
15 |
16 | test('works with of + rejected', 1, t => {
17 | Task.of(2).orElse(x => Task.rejected(x + 10)).run(t.calledWith(2))
18 | })
19 |
20 | test('works with rejected + of', 1, t => {
21 | Task.rejected(2).orElse(x => Task.of(x + 10)).run(t.calledWith(12))
22 | })
23 |
24 | test('works with rejected + rejected', 1, t => {
25 | Task.rejected(2).orElse(x => Task.rejected(x + 10)).run({failure: t.calledWith(12)})
26 | })
27 |
28 | test('cancelation - orig. task', 1, t => {
29 | Task.create(() => t.calledOnce()).orElse(() => Task.of()).run({})()
30 | })
31 |
32 | test('cancelation - spawned task - orig. sync', 1, t => {
33 | Task.rejected().orElse(() => Task.create(() => t.calledOnce())).run({})()
34 | })
35 |
36 | test('cancelation - spawned task - orig. async', 1, t => {
37 | let s: any = null
38 | const orig = Task.create((_, _s) => {s = _s})
39 | const spawned = Task.create(() => t.calledOnce())
40 | const cancel = orig.orElse(() => spawned).run({})
41 | s()
42 | cancel()
43 | })
44 |
45 | test('exception thrown from fn (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
46 | t.throws(() => {
47 | Task.rejected().orElse(() => { throw new Error('err1') }).run({})
48 | }, /err1/)
49 | })
50 |
51 | test('exception thrown from fn (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
52 | Task.rejected().orElse(() => { throw 2 }).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
53 | })
54 |
55 | const thrower1 = Task.create(() => { throw new Error('err1') })
56 | const thrower2 = Task.create(() => { throw 2 })
57 |
58 | test('exception thrown from parent task (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
59 | t.throws(() => {
60 | thrower1.orElse(() => Task.of()).run({})
61 | }, /err1/)
62 | })
63 |
64 | test('exception thrown from parent task (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
65 | thrower2.orElse(() => Task.of()).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
66 | })
67 |
68 | test('exception thrown from child task (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
69 | t.throws(() => {
70 | Task.rejected().orElse(() => thrower1).run({})
71 | }, /err1/)
72 | })
73 |
74 | test('exception thrown from child task (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
75 | Task.rejected().orElse(() => thrower2).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
76 | })
77 |
78 | test('exception thrown from child task (with catch cb, async)', 1, t => {
79 | let f = (null: any)
80 | let thrower = Task.create((_, _f) => { f = _f }).orElse(() => { throw 2 })
81 | Task.of().chain(() => thrower).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
82 | f()
83 | })
84 |
85 | test('exception thrown from child task (no catch cb, async)', 1, t => {
86 | let f = (null: any)
87 | let thrower = Task.create((_, _f) => { f = _f }).orElse(() => { throw new Error('err1') })
88 | Task.of().chain(() => thrower).run({})
89 | t.throws(f, /err1/)
90 | })
91 |
92 | test('this==undefined in success cd', 1, t => {
93 | Task.of(2).chain(x => Task.of(x)).run({success() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
94 | })
95 |
96 | test('this==undefined in success cd', 1, t => {
97 | Task.of(2).orElse(x => Task.rejected(x)).run({success() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
98 | })
99 |
100 | test('this==undefined in failure cd', 1, t => {
101 | Task.rejected(2).orElse(x => Task.rejected(x)).run({failure() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
102 | })
103 |
104 | test('this==undefined in fn', 1, t => {
105 | Task.rejected(2).orElse(function(x) { t.equal(this, undefined); return Task.of(x) }).run({})
106 | })
107 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/parallel.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 |
3 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
4 | import Task from '../src'
5 |
6 | const test = _test.wrap('parallel')
7 |
8 | test('works with of', 1, t => {
9 | Task.parallel([Task.of(2), Task.of('42')]).run(t.calledWith([2, '42']))
10 | })
11 |
12 | test('works with rejected', 1, t => {
13 | Task.parallel([Task.of(2), Task.rejected('42')]).run({failure: t.calledWith('42')})
14 | })
15 |
16 | test('cancelation works', 2, t => {
17 | Task.parallel([
18 | Task.create(() => t.calledOnce()),
19 | Task.create(() => t.calledOnce()),
20 | ]).run({})()
21 | })
22 |
23 | test('after one task fails others are canceled (sync fail)', 1, t => {
24 | Task.parallel([
25 | Task.rejected(2),
26 | Task.create(() => t.calledOnce()),
27 | ]).run({failure(){}})
28 | })
29 |
30 | test('after one task fails others are canceled (async fail)', 1, t => {
31 | let f = (null: any)
32 | Task.parallel([
33 | Task.create((_, _f) => { f = _f }),
34 | Task.create(() => t.calledOnce()),
35 | ]).run({failure(){}})
36 | f()
37 | })
38 |
39 | const of1 = Task.of(1)
40 | const thrower1 = Task.create(() => { throw new Error('err1') })
41 | const thrower2 = Task.create(() => { throw 2 })
42 |
43 | test('exception thrown in a child task (no catch cb)', 2, t => {
44 | t.throws(() => {
45 | Task.parallel([of1, thrower1]).run({})
46 | }, /err1/)
47 | t.throws(() => {
48 | Task.parallel([thrower1, of1]).run({})
49 | }, /err1/)
50 | })
51 |
52 | test('exception thrown in a child task (with catch cb, exception is the first completion)', 1, t => {
53 | Task.parallel([thrower2, of1]).run({catch: t.calledWith(2), success: t.fail})
54 | })
55 |
56 | test('exception thrown in a child task (with catch cb, exception is the second completion)', 1, t => {
57 | Task.parallel([of1, thrower2]).run({catch: t.calledWith(2), success: t.fail})
58 | })
59 |
60 | test('this==undefined in success cd', 1, t => {
61 | Task.parallel([Task.of(2)]).run({success() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
62 | })
63 |
64 | test('this==undefined in failure cd', 1, t => {
65 | Task.parallel([Task.rejected(2)]).run({failure() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
66 | })
67 |
68 |
69 | // Flow tests
70 |
71 | /* eslint-disable no-unused-vars */
72 |
73 | const t1: Task<[number, string], *> = Task.parallel([Task.of(2), Task.of('')])
74 | // $FlowFixMe
75 | const t2: Task<[number, number], *> = Task.parallel([Task.of(2), Task.of('')])
76 |
77 | const t3: Task<[*, *], number | string> = Task.parallel([Task.rejected(2), Task.rejected('')])
78 | // $FlowFixMe
79 | const t4: Task<[*, *], number> = Task.parallel([Task.rejected(2), Task.rejected('')])
80 |
81 | Task.parallel([Task.of(2), Task.of('')]).run((xs) => {
82 | (xs[0]: number);
83 | (xs[1]: string);
84 | // $FlowFixMe
85 | (xs[0]: string);
86 | // $FlowFixMe
87 | (xs[1]: number);
88 | })
89 |
90 | function f() {
91 | const strArr: Array> = (null: any)
92 | Task.parallel(strArr).run((xs: Array) => {})
93 | // $FlowFixMe
94 | Task.parallel(strArr).run((xs: Array) => {})
95 | }
96 |
97 | /* eslint-enable no-unused-vars */
98 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/race.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 |
3 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
4 | import Task from '../src'
5 |
6 | const test = _test.wrap('race')
7 |
8 | test('works with of', 1, t => {
9 | Task.race([Task.of(2), Task.of(3), Task.rejected(4)]).run({success: t.calledWith(2), failure: t.fail})
10 | })
11 |
12 | test('works with rejected', 1, t => {
13 | Task.race([Task.rejected(2), Task.of(3), Task.rejected(4)]).run({success: t.fail, failure: t.calledWith(2)})
14 | })
15 |
16 | test('cancelation works', 2, t => {
17 | Task.race([
18 | Task.create(() => t.calledOnce()),
19 | Task.create(() => t.calledOnce()),
20 | ]).run({})()
21 | })
22 |
23 | test('after one task comletes others a canceled', 1, t => {
24 | Task.race([
25 | Task.of(2),
26 | Task.create(() => t.calledOnce()),
27 | ]).run({})
28 | })
29 |
30 | test('after one task comletes others a canceled (async)', 1, t => {
31 | let s: any = null
32 | Task.race([
33 | Task.create((_s) => {s = _s; return t.fail}),
34 | Task.create(() => t.calledOnce()),
35 | ]).run({})
36 | s()
37 | })
38 |
39 | const of1 = Task.of(1)
40 | const thrower1 = Task.create(() => { throw new Error('err1') })
41 | const thrower2 = Task.create(() => { throw 2 })
42 |
43 | test('exception thrown in a child task (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
44 | t.throws(() => {
45 | Task.race([thrower1, of1]).run({})
46 | }, /err1/)
47 | })
48 |
49 | test('exception thrown in a child task (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
50 | Task.race([thrower2, of1]).run({catch: t.calledWith(2), success: t.fail})
51 | })
52 |
53 | test('this==undefined in success cd', 1, t => {
54 | Task.race([Task.of(2)]).run({success() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
55 | })
56 |
57 | test('this==undefined in failure cd', 1, t => {
58 | Task.race([Task.rejected(2)]).run({failure() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
59 | })
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/recur.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 |
3 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
4 | import Task from '../src'
5 |
6 | function computeMaxCallStackSize() {
7 | try {
8 | return 1 + computeMaxCallStackSize()
9 | } catch (e) {
10 | return 1
11 | }
12 | }
13 | const MAX_STACK_SIZE = computeMaxCallStackSize()
14 |
15 | const test = _test.wrap('recur')
16 |
17 | const later = x => Task.create(s => { setTimeout(() => { s(x) }) })
18 |
19 | test('0 iterations', 1, t => {
20 | Task.of(2).recur(x => Task.rejected(x)).run({failure: t.calledWith(2)})
21 | })
22 |
23 | test('0 iterations (static alias)', 1, t => {
24 | Task.recur(x => Task.rejected(x), Task.of(2)).run({failure: t.calledWith(2)})
25 | })
26 |
27 | test('1 iteration (sync)', 1, t => {
28 | Task.of(1).recur(x => x === 0 ? Task.rejected(x) : Task.of(x - 1)).run({failure: t.calledWith(0)})
29 | })
30 |
31 | test.async('1 iteration (async)', 1, t => {
32 | Task.of(1).recur(x => x === 0 ? Task.rejected(x) : later(x - 1)).run({failure: t.calledWith(0)})
33 | })
34 |
35 | test('cancelation - initial', 1, t => {
36 | Task.create(() => t.calledOnce()).recur(() => Task.of(1)).run({})()
37 | })
38 |
39 | test('cancelation - first spawned - initial sync', 1, t => {
40 | Task.of(1).recur( () => Task.create(() => t.calledOnce()) ).run({})()
41 | })
42 |
43 | test('cancelation - first spawned - initial async', 1, t => {
44 | let s: any = null
45 | const orig = Task.create(_s => {s = _s})
46 | const spawned = Task.create(() => t.calledOnce())
47 | const cancel = orig.recur(() => spawned).run({})
48 | s()
49 | cancel()
50 | })
51 |
52 | test('count down sync', 7, t => {
53 | const stub = t.calledWith(5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0)
54 | Task.of(5).recur(x => {
55 | stub(x)
56 | return x === 0 ? Task.rejected(0) : Task.of(x - 1)
57 | }).run({failure: t.calledWith(0)})
58 | })
59 |
60 | test.async('count down async', 7, t => {
61 | const stub = t.calledWith(5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0)
62 | Task.of(5).recur(x => {
63 | stub(x)
64 | return x === 0 ? Task.rejected(0) : later(x - 1)
65 | }).run({failure: t.calledWith(0)})
66 | })
67 |
68 | if (!process.env.IGNORE_SLOW_TESTS) {
69 | test('works with a lot of sync iterations', 1, t => {
70 | Task.of(MAX_STACK_SIZE + 1).recur(x => {
71 | return x === 0 ? Task.rejected(0) : Task.of(x - 1)
72 | }).run({failure: t.calledWith(0)})
73 | })
74 | }
75 |
76 | test('exception thrown from fn (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
77 | t.throws(() => {
78 | Task.of().recur(() => { throw new Error('err1') }).run({})
79 | }, /err1/)
80 | })
81 |
82 | test('exception thrown from fn (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
83 | Task.of().recur(() => { throw 2 }).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
84 | })
85 |
86 | const thrower1 = Task.create(() => { throw new Error('err1') })
87 | const thrower2 = Task.create(() => { throw 2 })
88 |
89 | test('exception thrown from parent task (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
90 | t.throws(() => {
91 | thrower1.recur(() => Task.of()).run({})
92 | }, /err1/)
93 | })
94 |
95 | test('exception thrown from parent task (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
96 | thrower2.chain(() => Task.of()).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
97 | })
98 |
99 | test('exception thrown from child task (no catch cb)', 1, t => {
100 | t.throws(() => {
101 | Task.of().recur(() => thrower1).run({})
102 | }, /err1/)
103 | })
104 |
105 | test('exception thrown from child task (with catch cb)', 1, t => {
106 | Task.of().recur(() => thrower2).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
107 | })
108 |
109 | test('exception thrown from child task (with catch cb, async)', 1, t => {
110 | let s = (null: any)
111 | let thrower = Task.create(_s => { s = _s }).chain(() => { throw 2 })
112 | Task.of().recur(() => thrower).run({catch: t.calledWith(2)})
113 | s()
114 | })
115 |
116 | test('exception thrown from child task (no catch cb, async)', 1, t => {
117 | let s = (null: any)
118 | let thrower = Task.create(_s => { s = _s }).chain(() => { throw new Error('err1') })
119 | Task.of().recur(() => thrower).run({})
120 | t.throws(s, /err1/)
121 | })
122 |
123 | test('this==undefined in failure cd (initial)', 1, t => {
124 | Task.rejected(2).recur(x => Task.of(x)).run({failure() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
125 | })
126 |
127 | test('this==undefined in failure cd (spawned)', 1, t => {
128 | Task.of(2).recur(x => Task.rejected(x)).run({failure() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
129 | })
130 |
131 | test('this==undefined in fn', 1, t => {
132 | Task.of(2).recur(function(x) { t.equal(this, undefined); return Task.rejected(x) }).run({failure(){}})
133 | })
134 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/rejected.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 |
3 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
4 | import Task from '../src'
5 |
6 | const test = _test.wrap('rejected')
7 |
8 | test('passes value to cb', 1, t => {
9 | Task.rejected(2).run({success: t.fail, failure: t.calledWith(2)})
10 | })
11 |
12 | test('this==undefined in cd', 1, t => {
13 | Task.rejected(2).run({failure() { t.equal(this, undefined) }})
14 | })
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/runTimeTypes.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
2 | import Task from '../src'
3 |
4 | const test = _test.wrap('run-time types')
5 |
6 | test('create', 1, t => {
7 | t.throws(() => {
8 | Task.create(1)
9 | }, /Task.create\(f\): f is not a function\. Actual value: 1/)
10 | })
11 |
12 | test('parallel', 2, t => {
13 | t.throws(() => {
14 | Task.parallel(1)
15 | }, /Task.parallel\(a\): a is not an array of tasks\. Actual value: 1/)
16 | t.throws(() => {
17 | Task.parallel([1, 2])
18 | }, /Task.parallel\(a\): a is not an array of tasks\. Actual value: 1,2$/)
19 | })
20 |
21 | test('race', 2, t => {
22 | t.throws(() => {
23 | Task.race(1)
24 | }, /Task.race\(a\): a is not an array of tasks\. Actual value: 1/)
25 | t.throws(() => {
26 | Task.race([1, 2])
27 | }, /Task.race\(a\): a is not an array of tasks\. Actual value: 1,2$/)
28 | })
29 |
30 | test('map', 3, t => {
31 | t.throws(() => {
32 | Task.map(1, 2)
33 | }, /Task.map\(f, _\): f is not a function\. Actual value: 1/)
34 | t.throws(() => {
35 | Task.map(() => {}, 2)
36 | }, /Task.map\(_, t\): t is not a task\. Actual value: 2/)
37 | t.throws(() => {
38 | Task.of(1).map(1)
39 | }, /task.map\(f\): f is not a function\. Actual value: 1/)
40 | })
41 |
42 | test('mapRejected', 3, t => {
43 | t.throws(() => {
44 | Task.mapRejected(1, 2)
45 | }, /Task.mapRejected\(f, _\): f is not a function\. Actual value: 1/)
46 | t.throws(() => {
47 | Task.mapRejected(() => {}, 2)
48 | }, /Task.mapRejected\(_, t\): t is not a task\. Actual value: 2/)
49 | t.throws(() => {
50 | Task.of(1).mapRejected(1)
51 | }, /task.mapRejected\(f\): f is not a function\. Actual value: 1/)
52 | })
53 |
54 | test('bimap', 5, t => {
55 | t.throws(() => {
56 | Task.bimap(1, 2, 3)
57 | }, /Task.bimap\(f, _, _\): f is not a function\. Actual value: 1/)
58 | t.throws(() => {
59 | Task.bimap(() => {}, 2, 3)
60 | }, /Task.bimap\(_, f, _\): f is not a function\. Actual value: 2/)
61 | t.throws(() => {
62 | Task.bimap(() => {}, () => {}, 3)
63 | }, /Task.bimap\(_, _, t\): t is not a task\. Actual value: 3/)
64 | t.throws(() => {
65 | Task.of(1).bimap(1, 2)
66 | }, /task.bimap\(f, _\): f is not a function\. Actual value: 1/)
67 | t.throws(() => {
68 | Task.of(1).bimap(() => {}, 2)
69 | }, /task.bimap\(_, f\): f is not a function\. Actual value: 2/)
70 | })
71 |
72 | test('chain', 3, t => {
73 | t.throws(() => {
74 | Task.chain(1, 2)
75 | }, /Task.chain\(f, _\): f is not a function\. Actual value: 1/)
76 | t.throws(() => {
77 | Task.chain(() => {}, 2)
78 | }, /Task.chain\(_, t\): t is not a task\. Actual value: 2/)
79 | t.throws(() => {
80 | Task.of(1).chain(1)
81 | }, /task.chain\(f\): f is not a function\. Actual value: 1/)
82 | })
83 |
84 | test('orElse', 3, t => {
85 | t.throws(() => {
86 | Task.orElse(1, 2)
87 | }, /Task.orElse\(f, _\): f is not a function\. Actual value: 1/)
88 | t.throws(() => {
89 | Task.orElse(() => {}, 2)
90 | }, /Task.orElse\(_, t\): t is not a task\. Actual value: 2/)
91 | t.throws(() => {
92 | Task.of(1).orElse(1)
93 | }, /task.orElse\(f\): f is not a function\. Actual value: 1/)
94 | })
95 |
96 | test('recur', 3, t => {
97 | t.throws(() => {
98 | Task.recur(1, 2)
99 | }, /Task.recur\(f, _\): f is not a function\. Actual value: 1/)
100 | t.throws(() => {
101 | Task.recur(() => {}, 2)
102 | }, /Task.recur\(_, t\): t is not a task\. Actual value: 2/)
103 | t.throws(() => {
104 | Task.of(1).recur(1)
105 | }, /task.recur\(f\): f is not a function\. Actual value: 1/)
106 | })
107 |
108 | test('chainRec', 1, t => {
109 | t.throws(() => {
110 | Task.chainRec(1, 2)
111 | }, /Task.chainRec\(f, _\): f is not a function\. Actual value: 1/)
112 | })
113 |
114 | test('ap', 3, t => {
115 | t.throws(() => {
116 | Task.ap(1, 2)
117 | }, /Task.ap\(t, _\): t is not a task\. Actual value: 1/)
118 | t.throws(() => {
119 | Task.ap(Task.of(1), 2)
120 | }, /Task.ap\(_, t\): t is not a task\. Actual value: 2/)
121 | t.throws(() => {
122 | Task.of(1).ap(1)
123 | }, /task.ap\(t\): t is not a task\. Actual value: 1/)
124 | })
125 |
126 | test('concat', 3, t => {
127 | t.throws(() => {
128 | Task.concat(1, 2)
129 | }, /Task.concat\(t, _\): t is not a task\. Actual value: 1/)
130 | t.throws(() => {
131 | Task.concat(Task.of(1), 2)
132 | }, /Task.concat\(_, t\): t is not a task\. Actual value: 2/)
133 | t.throws(() => {
134 | Task.of(1).concat(1)
135 | }, /task.concat\(t\): t is not a task\. Actual value: 1/)
136 | })
137 |
138 | test('do', 1, t => {
139 | t.throws(() => {
140 | Task.do(1)
141 | }, /Task.do\(f\): f is not a function\. Actual value: 1/)
142 | })
143 |
144 | test('fromPromise', 1, t => {
145 | t.throws(() => {
146 | Task.fromPromise(1)
147 | }, /Task.fromPromise\(p\): p is not a promise\. Actual value: 1/)
148 | })
149 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/toPromise.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 | /* global Promise */
3 |
4 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
5 | import Task from '../src'
6 |
7 | const test = _test.wrap('toPromise')
8 |
9 | test('returns a Promise', 1, t => {
10 | t.ok(Task.of(2).toPromise() instanceof Promise)
11 | })
12 |
13 | test.async('success works', 1, t => {
14 | Task.of(2).toPromise().then(x => {
15 | t.deepEqual(x, {success: 2})
16 | t.end()
17 | })
18 | })
19 |
20 | test.async('failure works', 1, t => {
21 | Task.rejected(2).toPromise().then(x => {
22 | t.deepEqual(x, {failure: 2})
23 | t.end()
24 | })
25 | })
26 |
27 | const thrower = Task.create(() => { throw 2 })
28 |
29 | test.async('sync throw, {catch: true}', 1, t => {
30 | thrower.toPromise().then(
31 | t.fail,
32 | x => {
33 | t.equal(x, 2)
34 | t.end()
35 | }
36 | )
37 | })
38 |
39 | test.async('sync throw, {catch: false}', 1, t => {
40 | thrower.toPromise({catch: false}).then(
41 | t.fail,
42 | x => {
43 | t.equal(x, 2)
44 | t.end()
45 | }
46 | )
47 | })
48 |
49 | test.async('async throw, {catch: true}', 1, t => {
50 | let s: any = null
51 | const task = Task.create(_s => {s = _s})
52 | const thrower = task.map(() => { throw 2 })
53 | thrower.toPromise().then(
54 | t.fail,
55 | x => {
56 | t.equal(x, 2)
57 | t.end()
58 | }
59 | )
60 | setTimeout(s, 1)
61 | })
62 |
63 | test.async('async throw, {catch: false}', 1, t => {
64 | let s: any = null
65 | const task = Task.create(_s => {s = _s})
66 | const thrower = task.map(() => { throw 2 })
67 | thrower.toPromise({catch: false}).then(t.fail, t.fail)
68 | setTimeout(() => {
69 | t.throws(s)
70 | t.end()
71 | }, 1)
72 | })
73 |
74 |
75 |
76 | // Flow tests
77 | // See https://github.com/facebook/flow/issues/2354
78 |
79 | class Animal {}
80 | class Dog extends Animal {}
81 |
82 | const t1: Task = Task.of(new Dog)
83 | const t2: Task = t1
84 |
85 | t1.toPromise().then(x => {
86 | if (x.success) {
87 | (x.success: Dog)
88 | }
89 | })
90 |
91 | t2.toPromise().then(x => {
92 | if (x.success) {
93 | (x.success: Animal)
94 | }
95 | })
96 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/toString.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // @flow
2 | /* global Promise */
3 |
4 | import _test from 'lobot/test'
5 | import Task from '../src'
6 |
7 | const test = _test.wrap('toString')
8 |
9 | test('of', 1, t => {
10 | t.equals(Task.of(1).toString(), 'Task.of(..)')
11 | })
12 |
13 | test('rejected', 1, t => {
14 | t.equals(Task.rejected(1).toString(), 'Task.rejected(..)')
15 | })
16 |
17 | test('create', 1, t => {
18 | t.equals(Task.create(() => {}).toString(), 'Task.create(..)')
19 | })
20 |
21 | test('empty', 1, t => {
22 | t.equals(Task.empty().toString(), 'Task.empty()')
23 | })
24 |
25 | test('parallel', 1, t => {
26 | t.equals(Task.parallel([Task.empty(), Task.of(1)]).toString(), 'Task.parallel([empty(), of(..)])')
27 | })
28 |
29 | test('race', 1, t => {
30 | t.equals(Task.race([Task.empty(), Task.of(1)]).toString(), 'Task.race([empty(), of(..)])')
31 | })
32 |
33 | test('concat', 1, t => {
34 | t.equals(Task.empty().concat(Task.of(1)).toString(), 'Task.race([empty(), of(..)])')
35 | })
36 |
37 | test('map', 1, t => {
38 | t.equals(Task.of(1).map(x => x).toString(), 'Task.of(..).map(..)')
39 | })
40 |
41 | test('map', 1, t => {
42 | t.equals(Task.of(1).bimap(x => x, x => x).toString(), 'Task.of(..).map(..).mapRejected(..)')
43 | })
44 |
45 | test('mapRejected', 1, t => {
46 | t.equals(Task.of(1).mapRejected(x => x).toString(), 'Task.of(..).mapRejected(..)')
47 | })
48 |
49 | test('chain', 1, t => {
50 | t.equals(Task.of(1).chain(x => Task.of(x)).toString(), 'Task.of(..).chain(..)')
51 | })
52 |
53 | test('orElse', 1, t => {
54 | t.equals(Task.rejected(1).orElse(x => Task.of(x)).toString(), 'Task.rejected(..).orElse(..)')
55 | })
56 |
57 | test('recur', 1, t => {
58 | t.equals(Task.of(1).recur(x => Task.of(x)).toString(), 'Task.of(..).recur(..)')
59 | })
60 |
61 | test('chainRec', 1, t => {
62 | t.equals(Task.chainRec(() => Task.rejected(), 1).toString(), 'Task.chainRec(..)')
63 | })
64 |
65 | test('ap', 1, t => {
66 | t.equals(Task.of(1).ap(Task.of(x => x)).toString(), 'Task.of(..).chain(..)')
67 | })
68 |
69 | test('fromPromise', 1, t => {
70 | t.equals(Task.fromPromise(Promise.resolve(2)).toString(), 'Task.fromPromise(..)')
71 | })
72 |
73 | test('do', 1, t => {
74 | t.equals(Task.do(function*(){yield Task.of(1); return Task.of(1)}).toString(), 'Task.do(..)')
75 | })
76 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 110 |
111 |
112 |
110 |
111 |
112 |  113 |
114 |
115 | Task is compatible with [Fantasy Land](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land) and [Static Land](https://github.com/rpominov/static-land) implementing:
116 |
117 | - [Semigroup](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#semigroup)
118 | - [Monoid](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#monoid)
119 | - [Functor](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#functor)
120 | - [Bifunctor](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#bifunctor)
121 | - [Apply](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#apply)
122 | - [Applicative](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#applicative)
123 | - [Chain](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#chain)
124 | - [ChainRec](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#chainrec)
125 | - [Monad](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#monad)
126 |
127 | ## Development
128 |
129 | ```
130 | npm run lobot -- --help
131 | ```
132 |
133 | Run [lobot](https://github.com/rpominov/lobot) commands as `npm run lobot -- args...`
134 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/coverageconfig.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "coverage": ["./.build-artefacts/lcov.info"]
3 | }
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/api-reference.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Task API Reference
2 |
3 | ## `Task.create(computation)`
4 |
5 | Creates a Task from a computation. Computation is a function that accepts two callbacks.
6 | It should call one of them after completion with the final result (success or failure).
7 | Also a computation may return a function with cancellation logic
8 | or it can return `undefined` if there is no cancellation logic.
9 |
10 | ```js
11 | const task = Task.create((onSuccess, onFailure) => {
12 | // ...
13 | return () => {
14 | // cancellation logic
15 | }
16 | })
17 |
18 | // The computation is executed every time we run the task
19 | const cancel = task.run({
20 | success(result) {
21 | // success result goes here
22 | },
23 | failure(result) {
24 | // failure result goes here
25 | },
26 | })
27 |
28 | // If we cancel the task the cancellation logic from computation
29 | // will be executed (if provided)
30 | cancel()
31 | ```
32 |
33 | Here is some runnable example:
34 |
35 | ```js
36 | const wait5sec = Task.create(onSuccess => {
37 | const timeoutId = setTimeout(() => {
38 | onSuccess('5 seconds')
39 | }, 5000)
40 | return () => { clearTimeout(timeoutId) }
41 | })
42 |
43 | wait5sec.run({
44 | success(timeWaited) {
45 | console.log(`We've waited for ${timeWaited}`)
46 | },
47 | })
48 |
49 | // > We've waited for 5 seconds
50 | ```
51 |
52 | After cancellation or completion the `onSuccess` and `onFailure` callbacks become noop.
53 | Also if `cancel` called second time or after a completion the cancelation logic won't be executed.
54 |
55 | ## `Task.of(value)`
56 |
57 | Creates a task that resolves with a given value.
58 |
59 | ```js
60 | Task.of(2).run({
61 | success(x) {
62 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
63 | },
64 | })
65 |
66 | // > result: 2
67 | ```
68 |
69 | ## `Task.rejected(error)`
70 |
71 | Creates a task that fails with a given error.
72 |
73 | ```js
74 | Task.rejected(2).run({
75 | failure(error) {
76 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
77 | },
78 | })
79 |
80 | // > error: 2
81 | ```
82 |
83 | ## `Task.empty()`
84 |
85 | Creates a task that never completes.
86 |
87 | ```js
88 | Task.empty().run({
89 | success(x) {
90 | // callback never called
91 | },
92 | failure(error) {
93 | // callback never called
94 | },
95 | })
96 | ```
97 |
98 | ## `task.map(fn)`
99 |
100 | > Static alias: `Task.map(fn, task)`
101 |
102 | Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the successful value.
103 |
104 | ```js
105 | Task.of(2).map(x => x * 3).run({
106 | success(x) {
107 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
108 | },
109 | })
110 |
111 | // > result: 6
112 | ```
113 |
114 | ## `task.mapRejected(fn)`
115 |
116 | > Static alias: `Task.mapRejected(fn, task)`
117 |
118 | Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the failure value.
119 |
120 | ```js
121 | Task.rejected(2).mapRejected(x => x * 3).run({
122 | failure(error) {
123 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
124 | },
125 | })
126 |
127 | // > error: 6
128 | ```
129 |
130 | ## `task.bimap(fFn, sFn)`
131 |
132 | > Static alias: `Task.bimap(fFn, sFn, task)`
133 |
134 | Transforms a task by applying `fFn` to the failure value or `sFn` to the successful value.
135 |
136 | ```js
137 | Task.of(2).bimap(x => x, x => x * 3).run({
138 | success(x) {
139 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
140 | },
141 | })
142 |
143 | // > result: 6
144 | ```
145 |
146 | ```js
147 | Task.rejected(2).bimap(x => x * 3, x => x).run({
148 | failure(error) {
149 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
150 | },
151 | })
152 |
153 | // > error: 6
154 | ```
155 |
156 | ## `task.chain(fn)`
157 |
158 | > Static alias: `Task.chain(fn, task)`
159 |
160 | Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the successful value, where `fn` returns a Task.
161 |
162 | ```js
163 | Task.of(2).chain(x => Task.of(x * 3)).run({
164 | success(x) {
165 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
166 | },
167 | })
168 |
169 | // > result: 6
170 | ```
171 |
172 | The function can return a task that fails of course.
173 |
174 | ```js
175 | Task.of(2).chain(x => Task.rejected(x * 3)).run({
176 | failure(error) {
177 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
178 | },
179 | })
180 |
181 | // > error: 6
182 | ```
183 |
184 | ## `task.orElse(fn)`
185 |
186 | > Static alias: `Task.orElse(fn, task)`
187 |
188 | Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the failure value, where `fn` returns a Task.
189 | Similar to `chain` but for failure path.
190 |
191 | ```js
192 | Task.rejected(2).orElse(x => Task.of(x * 3)).run({
193 | success(x) {
194 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
195 | },
196 | })
197 |
198 | // > result: 6
199 | ```
200 |
201 |
202 | ## `task.recur(fn)`
203 |
204 | > Static alias: `Task.recur(fn, task)`
205 |
206 | `task.recur(fn)` is the same as `task.chain(function f(x) { return fn(x).chain(f) })`,
207 | but former is safe from infinite call stack growth and memory leaks.
208 |
209 | ```js
210 | Task.of(5).recur(x => {
211 | x // 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0
212 | return x === 0 ? Task.rejected('done') : Task.of(x - 1)
213 | }).run({
214 | failure(x) {
215 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
216 | },
217 | })
218 |
219 | // > result: done
220 | ```
221 |
222 | ## `Task.chainRec(fn, initial)`
223 |
224 | Implementation of [Fantasy Land's `ChainRec`](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#chainrec).
225 | Covers similar use-case as `task.recur()` but in a spec compatible way.
226 |
227 | ```js
228 | Task.chainRec((next, done, x) => {
229 | x // 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0
230 | return x === 0 ? Task.of(done('done')) : Task.of(next(x - 1))
231 | }, 5).run({
232 | success(x) {
233 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
234 | },
235 | })
236 |
237 | // > result: done
238 | ```
239 |
240 | ## `tX.ap(tFn)`
241 |
242 | > Static alias: `Task.ap(tFn, tX)`
243 |
244 | Applies the successful value of task `tFn` to to the successful value of task `tX`.
245 | Uses `chain` under the hood, if you need parallel execution use `parallel`.
246 |
247 | ```js
248 | Task.of(2).ap(Task.of(x => x * 3)).run({
249 | success(x) {
250 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
251 | },
252 | })
253 |
254 | // > result: 6
255 | ```
256 |
257 |
258 | ## `task.concat(otherTask)`
259 |
260 | > Static alias: `Task.concat(task, otherTask)`
261 |
262 | Selects the earlier of the two tasks. Uses `race` under the hood.
263 |
264 | ```js
265 | const task1 = Task.create(suc => {
266 | const id = setTimeout(() => suc(1), 1000)
267 | return () => { clearTimeout(id) }
268 | })
269 |
270 | const task2 = Task.create(suc => {
271 | const id = setTimeout(() => suc(2), 2000)
272 | return () => { clearTimeout(id) }
273 | })
274 |
275 | task1.concat(task2).run({
276 | success(x) {
277 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
278 | },
279 | })
280 |
281 | // > result: 1
282 | ```
283 |
284 |
285 |
286 | ## `Task.parallel(tasks)`
287 |
288 | Given array of tasks creates a task of array. When result task executed given tasks will be executed in parallel.
289 |
290 | ```js
291 | Task.parallel([Task.of(2), Task.of(3)]).run(
292 | success(xs) {
293 | console.log(`result: ${xs.join(', ')}`)
294 | },
295 | )
296 |
297 | // > result: 2, 3
298 | ```
299 |
300 | If any of given tasks fail, the result taks will also fail with the same error.
301 | In this case tasks that are still running are canceled.
302 |
303 | ```js
304 | Task.parallel([Task.of(2), Task.rejected(3)]).run(
305 | failure(error) {
306 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
307 | },
308 | )
309 |
310 | // > error: 3
311 | ```
312 |
313 | ## `Task.race(tasks)`
314 |
315 | Given array of tasks creates a task that completes with the earliest successful or failure value.
316 | After the fastest task completes other tasks are canceled.
317 |
318 | ```js
319 | const task1 = Task.create(suc => {
320 | const id = setTimeout(() => suc(1), 1000)
321 | return () => {
322 | console.log('canceled: 1')
323 | clearTimeout(id)
324 | }
325 | })
326 |
327 | const task2 = Task.create(suc => {
328 | const id = setTimeout(() => suc(2), 2000)
329 | return () => {
330 | console.log('canceled: 2')
331 | clearTimeout(id)
332 | }
333 | })
334 |
335 | Task.race([task1, task2]).run({
336 | success(x) {
337 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
338 | },
339 | })
340 |
341 | // > canceled: 2
342 | // > result: 1
343 | ```
344 |
345 | ## `Task.do(generator)`
346 |
347 | This is something like [Haskell's do notation](https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Haskell/do_notation)
348 | or JavaScritp's async/await based on [generators](https://developer.mozilla.org/en/docs/Web/JavaScript/Guide/Iterators_and_Generators).
349 |
350 | You pass a generator that `yiels` and `returns` tasks and get a task in return.
351 | The whole proccess is pure, tasks are not being ran until the result task is ran.
352 |
353 | Here is a not runnable but somewhat real-world example:
354 |
355 | ```js
356 | // gets user from our API, returns a Task
357 | const getUserFromAPI = ...
358 |
359 | // gets zip code for given address using 3rd party API, returns a Task
360 | const getZipCode = ...
361 |
362 | function getUsersZip(userId) {
363 | return Task.do(function* () {
364 | const user = yield getUserFromAPI(userId)
365 | if (!user.address) {
366 | return Task.rejected({type: 'user_dont_have_address'})
367 | }
368 | return getZipCode(user.address)
369 | })
370 | }
371 |
372 | // Same function re-written using chain instead of do
373 | function getUsersZip(userId) {
374 | return getUserFromAPI(userId).chain(user => {
375 | if (!user.address) {
376 | return Task.rejected({type: 'user_dont_have_address'})
377 | }
378 | return getZipCode(user.address)
379 | })
380 | }
381 |
382 | getUsersZip(42).run({
383 | success(zip) {
384 | // ...
385 | },
386 | failure(error) {
387 | // The error here is either {type: 'user_dont_have_address'}
388 | // or some of errors that getUserFromAPI or getZipCode can produce
389 | // ...
390 | },
391 | })
392 | ```
393 |
394 | And here's some runnable example:
395 |
396 | ```js
397 | Task.do(function* () {
398 | const a = yield Task.of(2)
399 | const b = yield Task.of(3)
400 | return Task.of(a * b)
401 | }).run({
402 | success(x) {
403 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
404 | },
405 | })
406 |
407 | // > result: 6
408 | ```
409 |
410 |
411 | ## `task.run(handlers)`
412 |
413 | Runs the task. The `handlers` argument can contain 3 kinds of handlers `success`, `failure`, and `catch`.
414 | All handlers are optional, if you want to run task without handlers do it like this `task.run({})`.
415 | If a function passed as `handlers` it's automatically transformend to `{success: fn}`,
416 | so if you need only success handler you can do `task.run(x => ...)`.
417 |
418 | If `failure` handler isn't provided but task fails, an exception is thrown.
419 | You should always provided `failure` handlers for tasks that may fail.
420 | If you want to ignore failure pass a `noop` failure handler explicitly.
421 |
422 | The `catch` handler is for errors thrown from functions passed to `map`, `chain` etc.
423 | [More on how it works](./exceptions.md#how-exceptions-work-in-task).
424 |
425 | ```js
426 | Task.of(2).run({
427 | success(x) {
428 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
429 | },
430 | failure(error) {
431 | // handle failure ...
432 | },
433 | catch(error) {
434 | // handle error thrown from `map(fn)` etc ...
435 | },
436 | })
437 |
438 | // > result: 2
439 | ```
440 |
441 | ## `task.runAndLog()`
442 |
443 | Runs the task and prints results using `console.log()`. Mainly for testing / debugging etc.
444 |
445 | ```js
446 | Task.of(2).runAndLog()
447 |
448 | // > Success: 2
449 | ```
450 |
451 |
452 | ## `task.toPromise([options])`
453 |
454 | Runs the task and returns a Promise that represent the result.
455 | The task's `success` and `failure` branches both correspond to the promise's `success` brach because
456 | [the `error` branch in Promises is reserved for unexpected failures](./exceptions.md#promises-and-expected-failures).
457 | The task's `catch` branch correspond to promise's `error`.
458 |
459 | The promise's success value is either `{success: s}` or `{failure: f}` where `s` and `f` task's
460 | success or failure values.
461 |
462 | If `{catch: false}` is passed as `options` the task is run without `catch` callback.
463 |
464 | ```js
465 | Task.of(2).toPromise().then(result => {
466 | if ('success' in result) {
467 | console.log(`success: ${result.success}`)
468 | } else {
469 | console.log(`failure: ${result.failure}`)
470 | }
471 | })
472 |
473 | // > success: 2
474 | ```
475 |
476 |
477 | ## `Task.fromPromise(promise)`
478 |
479 | Creates a Task from a Promise.
480 |
481 | ```js
482 | Task.fromPromise(Promise.resolve(2)).run({
483 | success(x) {
484 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
485 | },
486 | })
487 |
488 | // result: 2
489 | ```
490 |
491 | The `promise` argument must be either a Promise or a function that wnen called with
492 | no arguments returns a Promise. If a function is used as `promise` argument,
493 | that function is executed on each task's run to retrieve a new promise.
494 |
495 | ```js
496 | Task.fromPromise(() => Promise.resolve(2)).run({
497 | success(x) {
498 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
499 | },
500 | })
501 |
502 | // result: 2
503 | ```
504 |
505 | The promise's `success` corresponds to the task's `success`
506 | and promise's `error` corresponds to the task's `catch`.
507 |
508 | ```js
509 | Task.fromPromise(Promise.reject(2)).run({
510 | catch(x) {
511 | console.log(`error: ${x}`)
512 | },
513 | })
514 |
515 | // error: 2
516 | ```
517 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow.sketch:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow.sketch
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow1.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow1.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow2.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow2.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow3.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow3.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow4.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow4.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/exceptions.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Try..catch in JavaScript async abstractions like Promise or Task
2 |
3 | This article explains the reasoning behind how error catching works in Task.
4 | It starts from the very fundamental concepts, but this is necessary to avoid any misunderstandings
5 | later in the article when some terms from earlier parts are used.
6 | The closer to the end the more practical matters are discussed.
7 |
8 | ## Expected and unexpected code paths
9 |
10 | In any program (especially in JavaScript) there's always expected and unexpected code paths.
11 | When a program goes through an unexpected path we call it "a bug". And when it only goes through the expected paths
12 | it is just normal execution of the program. Consider this example:
13 |
14 | ```js
15 | let x = Math.random() - 0.5
16 | let y
17 | let z
18 |
19 | if (x > 0) {
20 | y = 10
21 | } else {
22 | z = 10
23 | }
24 |
25 | if (x <= 0) {
26 | alert(z + 5)
27 | } else {
28 | alert(y + 5)
29 | }
30 | ```
31 |
32 | Here are two expected paths of this program:
33 |
34 |
113 |
114 |
115 | Task is compatible with [Fantasy Land](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land) and [Static Land](https://github.com/rpominov/static-land) implementing:
116 |
117 | - [Semigroup](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#semigroup)
118 | - [Monoid](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#monoid)
119 | - [Functor](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#functor)
120 | - [Bifunctor](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#bifunctor)
121 | - [Apply](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#apply)
122 | - [Applicative](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#applicative)
123 | - [Chain](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#chain)
124 | - [ChainRec](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#chainrec)
125 | - [Monad](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#monad)
126 |
127 | ## Development
128 |
129 | ```
130 | npm run lobot -- --help
131 | ```
132 |
133 | Run [lobot](https://github.com/rpominov/lobot) commands as `npm run lobot -- args...`
134 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/coverageconfig.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "coverage": ["./.build-artefacts/lcov.info"]
3 | }
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/api-reference.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Task API Reference
2 |
3 | ## `Task.create(computation)`
4 |
5 | Creates a Task from a computation. Computation is a function that accepts two callbacks.
6 | It should call one of them after completion with the final result (success or failure).
7 | Also a computation may return a function with cancellation logic
8 | or it can return `undefined` if there is no cancellation logic.
9 |
10 | ```js
11 | const task = Task.create((onSuccess, onFailure) => {
12 | // ...
13 | return () => {
14 | // cancellation logic
15 | }
16 | })
17 |
18 | // The computation is executed every time we run the task
19 | const cancel = task.run({
20 | success(result) {
21 | // success result goes here
22 | },
23 | failure(result) {
24 | // failure result goes here
25 | },
26 | })
27 |
28 | // If we cancel the task the cancellation logic from computation
29 | // will be executed (if provided)
30 | cancel()
31 | ```
32 |
33 | Here is some runnable example:
34 |
35 | ```js
36 | const wait5sec = Task.create(onSuccess => {
37 | const timeoutId = setTimeout(() => {
38 | onSuccess('5 seconds')
39 | }, 5000)
40 | return () => { clearTimeout(timeoutId) }
41 | })
42 |
43 | wait5sec.run({
44 | success(timeWaited) {
45 | console.log(`We've waited for ${timeWaited}`)
46 | },
47 | })
48 |
49 | // > We've waited for 5 seconds
50 | ```
51 |
52 | After cancellation or completion the `onSuccess` and `onFailure` callbacks become noop.
53 | Also if `cancel` called second time or after a completion the cancelation logic won't be executed.
54 |
55 | ## `Task.of(value)`
56 |
57 | Creates a task that resolves with a given value.
58 |
59 | ```js
60 | Task.of(2).run({
61 | success(x) {
62 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
63 | },
64 | })
65 |
66 | // > result: 2
67 | ```
68 |
69 | ## `Task.rejected(error)`
70 |
71 | Creates a task that fails with a given error.
72 |
73 | ```js
74 | Task.rejected(2).run({
75 | failure(error) {
76 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
77 | },
78 | })
79 |
80 | // > error: 2
81 | ```
82 |
83 | ## `Task.empty()`
84 |
85 | Creates a task that never completes.
86 |
87 | ```js
88 | Task.empty().run({
89 | success(x) {
90 | // callback never called
91 | },
92 | failure(error) {
93 | // callback never called
94 | },
95 | })
96 | ```
97 |
98 | ## `task.map(fn)`
99 |
100 | > Static alias: `Task.map(fn, task)`
101 |
102 | Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the successful value.
103 |
104 | ```js
105 | Task.of(2).map(x => x * 3).run({
106 | success(x) {
107 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
108 | },
109 | })
110 |
111 | // > result: 6
112 | ```
113 |
114 | ## `task.mapRejected(fn)`
115 |
116 | > Static alias: `Task.mapRejected(fn, task)`
117 |
118 | Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the failure value.
119 |
120 | ```js
121 | Task.rejected(2).mapRejected(x => x * 3).run({
122 | failure(error) {
123 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
124 | },
125 | })
126 |
127 | // > error: 6
128 | ```
129 |
130 | ## `task.bimap(fFn, sFn)`
131 |
132 | > Static alias: `Task.bimap(fFn, sFn, task)`
133 |
134 | Transforms a task by applying `fFn` to the failure value or `sFn` to the successful value.
135 |
136 | ```js
137 | Task.of(2).bimap(x => x, x => x * 3).run({
138 | success(x) {
139 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
140 | },
141 | })
142 |
143 | // > result: 6
144 | ```
145 |
146 | ```js
147 | Task.rejected(2).bimap(x => x * 3, x => x).run({
148 | failure(error) {
149 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
150 | },
151 | })
152 |
153 | // > error: 6
154 | ```
155 |
156 | ## `task.chain(fn)`
157 |
158 | > Static alias: `Task.chain(fn, task)`
159 |
160 | Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the successful value, where `fn` returns a Task.
161 |
162 | ```js
163 | Task.of(2).chain(x => Task.of(x * 3)).run({
164 | success(x) {
165 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
166 | },
167 | })
168 |
169 | // > result: 6
170 | ```
171 |
172 | The function can return a task that fails of course.
173 |
174 | ```js
175 | Task.of(2).chain(x => Task.rejected(x * 3)).run({
176 | failure(error) {
177 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
178 | },
179 | })
180 |
181 | // > error: 6
182 | ```
183 |
184 | ## `task.orElse(fn)`
185 |
186 | > Static alias: `Task.orElse(fn, task)`
187 |
188 | Transforms a task by applying `fn` to the failure value, where `fn` returns a Task.
189 | Similar to `chain` but for failure path.
190 |
191 | ```js
192 | Task.rejected(2).orElse(x => Task.of(x * 3)).run({
193 | success(x) {
194 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
195 | },
196 | })
197 |
198 | // > result: 6
199 | ```
200 |
201 |
202 | ## `task.recur(fn)`
203 |
204 | > Static alias: `Task.recur(fn, task)`
205 |
206 | `task.recur(fn)` is the same as `task.chain(function f(x) { return fn(x).chain(f) })`,
207 | but former is safe from infinite call stack growth and memory leaks.
208 |
209 | ```js
210 | Task.of(5).recur(x => {
211 | x // 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0
212 | return x === 0 ? Task.rejected('done') : Task.of(x - 1)
213 | }).run({
214 | failure(x) {
215 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
216 | },
217 | })
218 |
219 | // > result: done
220 | ```
221 |
222 | ## `Task.chainRec(fn, initial)`
223 |
224 | Implementation of [Fantasy Land's `ChainRec`](https://github.com/fantasyland/fantasy-land#chainrec).
225 | Covers similar use-case as `task.recur()` but in a spec compatible way.
226 |
227 | ```js
228 | Task.chainRec((next, done, x) => {
229 | x // 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0
230 | return x === 0 ? Task.of(done('done')) : Task.of(next(x - 1))
231 | }, 5).run({
232 | success(x) {
233 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
234 | },
235 | })
236 |
237 | // > result: done
238 | ```
239 |
240 | ## `tX.ap(tFn)`
241 |
242 | > Static alias: `Task.ap(tFn, tX)`
243 |
244 | Applies the successful value of task `tFn` to to the successful value of task `tX`.
245 | Uses `chain` under the hood, if you need parallel execution use `parallel`.
246 |
247 | ```js
248 | Task.of(2).ap(Task.of(x => x * 3)).run({
249 | success(x) {
250 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
251 | },
252 | })
253 |
254 | // > result: 6
255 | ```
256 |
257 |
258 | ## `task.concat(otherTask)`
259 |
260 | > Static alias: `Task.concat(task, otherTask)`
261 |
262 | Selects the earlier of the two tasks. Uses `race` under the hood.
263 |
264 | ```js
265 | const task1 = Task.create(suc => {
266 | const id = setTimeout(() => suc(1), 1000)
267 | return () => { clearTimeout(id) }
268 | })
269 |
270 | const task2 = Task.create(suc => {
271 | const id = setTimeout(() => suc(2), 2000)
272 | return () => { clearTimeout(id) }
273 | })
274 |
275 | task1.concat(task2).run({
276 | success(x) {
277 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
278 | },
279 | })
280 |
281 | // > result: 1
282 | ```
283 |
284 |
285 |
286 | ## `Task.parallel(tasks)`
287 |
288 | Given array of tasks creates a task of array. When result task executed given tasks will be executed in parallel.
289 |
290 | ```js
291 | Task.parallel([Task.of(2), Task.of(3)]).run(
292 | success(xs) {
293 | console.log(`result: ${xs.join(', ')}`)
294 | },
295 | )
296 |
297 | // > result: 2, 3
298 | ```
299 |
300 | If any of given tasks fail, the result taks will also fail with the same error.
301 | In this case tasks that are still running are canceled.
302 |
303 | ```js
304 | Task.parallel([Task.of(2), Task.rejected(3)]).run(
305 | failure(error) {
306 | console.log(`error: ${error}`)
307 | },
308 | )
309 |
310 | // > error: 3
311 | ```
312 |
313 | ## `Task.race(tasks)`
314 |
315 | Given array of tasks creates a task that completes with the earliest successful or failure value.
316 | After the fastest task completes other tasks are canceled.
317 |
318 | ```js
319 | const task1 = Task.create(suc => {
320 | const id = setTimeout(() => suc(1), 1000)
321 | return () => {
322 | console.log('canceled: 1')
323 | clearTimeout(id)
324 | }
325 | })
326 |
327 | const task2 = Task.create(suc => {
328 | const id = setTimeout(() => suc(2), 2000)
329 | return () => {
330 | console.log('canceled: 2')
331 | clearTimeout(id)
332 | }
333 | })
334 |
335 | Task.race([task1, task2]).run({
336 | success(x) {
337 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
338 | },
339 | })
340 |
341 | // > canceled: 2
342 | // > result: 1
343 | ```
344 |
345 | ## `Task.do(generator)`
346 |
347 | This is something like [Haskell's do notation](https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Haskell/do_notation)
348 | or JavaScritp's async/await based on [generators](https://developer.mozilla.org/en/docs/Web/JavaScript/Guide/Iterators_and_Generators).
349 |
350 | You pass a generator that `yiels` and `returns` tasks and get a task in return.
351 | The whole proccess is pure, tasks are not being ran until the result task is ran.
352 |
353 | Here is a not runnable but somewhat real-world example:
354 |
355 | ```js
356 | // gets user from our API, returns a Task
357 | const getUserFromAPI = ...
358 |
359 | // gets zip code for given address using 3rd party API, returns a Task
360 | const getZipCode = ...
361 |
362 | function getUsersZip(userId) {
363 | return Task.do(function* () {
364 | const user = yield getUserFromAPI(userId)
365 | if (!user.address) {
366 | return Task.rejected({type: 'user_dont_have_address'})
367 | }
368 | return getZipCode(user.address)
369 | })
370 | }
371 |
372 | // Same function re-written using chain instead of do
373 | function getUsersZip(userId) {
374 | return getUserFromAPI(userId).chain(user => {
375 | if (!user.address) {
376 | return Task.rejected({type: 'user_dont_have_address'})
377 | }
378 | return getZipCode(user.address)
379 | })
380 | }
381 |
382 | getUsersZip(42).run({
383 | success(zip) {
384 | // ...
385 | },
386 | failure(error) {
387 | // The error here is either {type: 'user_dont_have_address'}
388 | // or some of errors that getUserFromAPI or getZipCode can produce
389 | // ...
390 | },
391 | })
392 | ```
393 |
394 | And here's some runnable example:
395 |
396 | ```js
397 | Task.do(function* () {
398 | const a = yield Task.of(2)
399 | const b = yield Task.of(3)
400 | return Task.of(a * b)
401 | }).run({
402 | success(x) {
403 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
404 | },
405 | })
406 |
407 | // > result: 6
408 | ```
409 |
410 |
411 | ## `task.run(handlers)`
412 |
413 | Runs the task. The `handlers` argument can contain 3 kinds of handlers `success`, `failure`, and `catch`.
414 | All handlers are optional, if you want to run task without handlers do it like this `task.run({})`.
415 | If a function passed as `handlers` it's automatically transformend to `{success: fn}`,
416 | so if you need only success handler you can do `task.run(x => ...)`.
417 |
418 | If `failure` handler isn't provided but task fails, an exception is thrown.
419 | You should always provided `failure` handlers for tasks that may fail.
420 | If you want to ignore failure pass a `noop` failure handler explicitly.
421 |
422 | The `catch` handler is for errors thrown from functions passed to `map`, `chain` etc.
423 | [More on how it works](./exceptions.md#how-exceptions-work-in-task).
424 |
425 | ```js
426 | Task.of(2).run({
427 | success(x) {
428 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
429 | },
430 | failure(error) {
431 | // handle failure ...
432 | },
433 | catch(error) {
434 | // handle error thrown from `map(fn)` etc ...
435 | },
436 | })
437 |
438 | // > result: 2
439 | ```
440 |
441 | ## `task.runAndLog()`
442 |
443 | Runs the task and prints results using `console.log()`. Mainly for testing / debugging etc.
444 |
445 | ```js
446 | Task.of(2).runAndLog()
447 |
448 | // > Success: 2
449 | ```
450 |
451 |
452 | ## `task.toPromise([options])`
453 |
454 | Runs the task and returns a Promise that represent the result.
455 | The task's `success` and `failure` branches both correspond to the promise's `success` brach because
456 | [the `error` branch in Promises is reserved for unexpected failures](./exceptions.md#promises-and-expected-failures).
457 | The task's `catch` branch correspond to promise's `error`.
458 |
459 | The promise's success value is either `{success: s}` or `{failure: f}` where `s` and `f` task's
460 | success or failure values.
461 |
462 | If `{catch: false}` is passed as `options` the task is run without `catch` callback.
463 |
464 | ```js
465 | Task.of(2).toPromise().then(result => {
466 | if ('success' in result) {
467 | console.log(`success: ${result.success}`)
468 | } else {
469 | console.log(`failure: ${result.failure}`)
470 | }
471 | })
472 |
473 | // > success: 2
474 | ```
475 |
476 |
477 | ## `Task.fromPromise(promise)`
478 |
479 | Creates a Task from a Promise.
480 |
481 | ```js
482 | Task.fromPromise(Promise.resolve(2)).run({
483 | success(x) {
484 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
485 | },
486 | })
487 |
488 | // result: 2
489 | ```
490 |
491 | The `promise` argument must be either a Promise or a function that wnen called with
492 | no arguments returns a Promise. If a function is used as `promise` argument,
493 | that function is executed on each task's run to retrieve a new promise.
494 |
495 | ```js
496 | Task.fromPromise(() => Promise.resolve(2)).run({
497 | success(x) {
498 | console.log(`result: ${x}`)
499 | },
500 | })
501 |
502 | // result: 2
503 | ```
504 |
505 | The promise's `success` corresponds to the task's `success`
506 | and promise's `error` corresponds to the task's `catch`.
507 |
508 | ```js
509 | Task.fromPromise(Promise.reject(2)).run({
510 | catch(x) {
511 | console.log(`error: ${x}`)
512 | },
513 | })
514 |
515 | // error: 2
516 | ```
517 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow.sketch:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow.sketch
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow1.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow1.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow2.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow2.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow3.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow3.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/exceptions/flow4.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rpominov/fun-task/640419d1877ef1084cfe7666c99fa4a729ade297/docs/assets/exceptions/flow4.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/exceptions.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Try..catch in JavaScript async abstractions like Promise or Task
2 |
3 | This article explains the reasoning behind how error catching works in Task.
4 | It starts from the very fundamental concepts, but this is necessary to avoid any misunderstandings
5 | later in the article when some terms from earlier parts are used.
6 | The closer to the end the more practical matters are discussed.
7 |
8 | ## Expected and unexpected code paths
9 |
10 | In any program (especially in JavaScript) there's always expected and unexpected code paths.
11 | When a program goes through an unexpected path we call it "a bug". And when it only goes through the expected paths
12 | it is just normal execution of the program. Consider this example:
13 |
14 | ```js
15 | let x = Math.random() - 0.5
16 | let y
17 | let z
18 |
19 | if (x > 0) {
20 | y = 10
21 | } else {
22 | z = 10
23 | }
24 |
25 | if (x <= 0) {
26 | alert(z + 5)
27 | } else {
28 | alert(y + 5)
29 | }
30 | ```
31 |
32 | Here are two expected paths of this program:
33 |
34 |  35 |
36 | And here is an unexpected path:
37 |
38 |
35 |
36 | And here is an unexpected path:
37 |
38 |  39 |
40 | We as programmers don't expect this to ever happen with this program.
41 | But if, for example, we change first condition and forget to change second one the program may
42 | run through the unexpected path. That would be a bug.
43 |
44 |
45 | ## Railway oriented programming / split expected path in two
46 |
47 | We can introduce some abstractions and semantics that would split **expected path** into
48 | **expected success** and **expected failure**. If you understand `Either` type you know what I'm talking about.
49 | This is fairly common pattern in FP world, I'll try to explain it briefly, but here are some good
50 | articles that do a much better job:
51 |
52 | - ["Railway oriented programming"](https://fsharpforfunandprofit.com/posts/recipe-part2/)
53 | - ["A Monad in Practicality: First-Class Failures"](http://robotlolita.me/2013/12/08/a-monad-in-practicality-first-class-failures.html)
54 | - ["Practical Intro to Monads in JavaScript: Either"](https://tech.evojam.com/2016/03/21/practical-intro-to-monads-in-javascript-either/)
55 |
56 | Say we build a simple CLI program that takes a number `n` from user and prints `1/n`.
57 |
58 | ```js
59 | function print(str) {
60 | console.log(str)
61 | }
62 |
63 | function main(userInput) {
64 | const number = parseInt(userInput, 10)
65 |
66 | if (Number.isNaN(number)) {
67 | print(`Not a number: ${userInput}`)
68 | } else {
69 | if (number === 0) {
70 | print(`Cannot divide by zero`)
71 | } else {
72 | print(1 / number)
73 | }
74 | }
75 |
76 | }
77 |
78 | // Read a line from stdin somehow and apply main() to it.
79 | // Details of how it's done are not important for this example.
80 | main(inputFromStdin)
81 | ```
82 |
83 | In this example execution flow of the program looks like this:
84 |
85 |
39 |
40 | We as programmers don't expect this to ever happen with this program.
41 | But if, for example, we change first condition and forget to change second one the program may
42 | run through the unexpected path. That would be a bug.
43 |
44 |
45 | ## Railway oriented programming / split expected path in two
46 |
47 | We can introduce some abstractions and semantics that would split **expected path** into
48 | **expected success** and **expected failure**. If you understand `Either` type you know what I'm talking about.
49 | This is fairly common pattern in FP world, I'll try to explain it briefly, but here are some good
50 | articles that do a much better job:
51 |
52 | - ["Railway oriented programming"](https://fsharpforfunandprofit.com/posts/recipe-part2/)
53 | - ["A Monad in Practicality: First-Class Failures"](http://robotlolita.me/2013/12/08/a-monad-in-practicality-first-class-failures.html)
54 | - ["Practical Intro to Monads in JavaScript: Either"](https://tech.evojam.com/2016/03/21/practical-intro-to-monads-in-javascript-either/)
55 |
56 | Say we build a simple CLI program that takes a number `n` from user and prints `1/n`.
57 |
58 | ```js
59 | function print(str) {
60 | console.log(str)
61 | }
62 |
63 | function main(userInput) {
64 | const number = parseInt(userInput, 10)
65 |
66 | if (Number.isNaN(number)) {
67 | print(`Not a number: ${userInput}`)
68 | } else {
69 | if (number === 0) {
70 | print(`Cannot divide by zero`)
71 | } else {
72 | print(1 / number)
73 | }
74 | }
75 |
76 | }
77 |
78 | // Read a line from stdin somehow and apply main() to it.
79 | // Details of how it's done are not important for this example.
80 | main(inputFromStdin)
81 | ```
82 |
83 | In this example execution flow of the program looks like this:
84 |
85 |  86 |
87 | As you can see the program splits in two places. This happens very often in programs.
88 | In some cases all branches look neutral, in other cases (like this) we can consider one path as
89 | a success and another one as a failure. We can make the distinction more formal by
90 | introducing an abstraction:
91 |
92 | ```js
93 | const Either = {
94 | chain(fn, either) {
95 | return ('success' in either) ? fn(either.success) : either
96 | },
97 | fork(onSuccess, onFailure, either) {
98 | return ('success' in either) ? onSuccess(either.success) : onFailure(either.failure)
99 | },
100 | }
101 | ```
102 |
103 | Now we can rewrite our example using `Either`:
104 |
105 | ```js
106 | function print(str) {
107 | console.log(str)
108 | }
109 |
110 | function parse(str) {
111 | const number = parseInt(str, 10)
112 | return Number.isNaN(number) ? {failure: `Not a number: ${str}`} : {success: number}
113 | }
114 |
115 | function calc(number) {
116 | return number === 0 ? {failure: `Cannot divide by zero`} : {success: 1 / number}
117 | }
118 |
119 | function main(userInput) {
120 | const parsed = parse(userInput)
121 | const calculated = Either.chain(calc, parsed)
122 | Either.fork(print, print, calculated)
123 | }
124 | ```
125 |
126 | In this version the flow looks more like the following. It's appears to be simpler, as if we can write code
127 | that cannot fail and the `Either` takes care of managing the failure branch.
128 |
129 |
86 |
87 | As you can see the program splits in two places. This happens very often in programs.
88 | In some cases all branches look neutral, in other cases (like this) we can consider one path as
89 | a success and another one as a failure. We can make the distinction more formal by
90 | introducing an abstraction:
91 |
92 | ```js
93 | const Either = {
94 | chain(fn, either) {
95 | return ('success' in either) ? fn(either.success) : either
96 | },
97 | fork(onSuccess, onFailure, either) {
98 | return ('success' in either) ? onSuccess(either.success) : onFailure(either.failure)
99 | },
100 | }
101 | ```
102 |
103 | Now we can rewrite our example using `Either`:
104 |
105 | ```js
106 | function print(str) {
107 | console.log(str)
108 | }
109 |
110 | function parse(str) {
111 | const number = parseInt(str, 10)
112 | return Number.isNaN(number) ? {failure: `Not a number: ${str}`} : {success: number}
113 | }
114 |
115 | function calc(number) {
116 | return number === 0 ? {failure: `Cannot divide by zero`} : {success: 1 / number}
117 | }
118 |
119 | function main(userInput) {
120 | const parsed = parse(userInput)
121 | const calculated = Either.chain(calc, parsed)
122 | Either.fork(print, print, calculated)
123 | }
124 | ```
125 |
126 | In this version the flow looks more like the following. It's appears to be simpler, as if we can write code
127 | that cannot fail and the `Either` takes care of managing the failure branch.
128 |
129 |  130 |
131 | Maybe this doesn't make much sense to you now (if you're not familiar with Either).
132 | And this is by no means a complete explanation of Either pattern (check out resources
133 | I've mentioned above for better explanations). But for the purpose of this article the only
134 | thing we need to take out of this section is that some paths in program can be
135 | treated formally or informally as **expected failures**.
136 |
137 | Let's recap. We've split all possible paths in programs to three groups:
138 |
139 | - **Expected success** is the main happy path of the program,
140 | it represents how the program behaves when everything goes right.
141 | - **Expected failure** is secondary path that represent
142 | all expected deviations from the happy path e.g., when a user gives an incorrect input.
143 | - **Unexpected failure** is some *unexpected* deviations from main or secondary paths,
144 | something that we call "bugs".
145 |
146 |
147 | ## try..catch
148 |
149 | How does `try..catch` fits into our three code paths groups view? It's great for unexpected failures!
150 | Or we should say: `throw` is great for unexpected failures if we never actually `try..catch`.
151 | It's very good for debugging. The debugger will pause on the exact line that throws.
152 | Also if we don't use a debugger we can still get a nice stack trace in the console, etc. It's sad that in many
153 | cases when a program goes through an unexpected path instead of exception we end up with `NaN`
154 | being propagated through the program or something like that. In these cases it's much harder to track
155 | down where things went wrong, it's much nicer when it just throws.
156 |
157 | On the other hand `try..catch` is bad for expected failures. There're many reasons why, but let's
158 | focus on just one: *it's bad for expected failures because it's already used for unexpected ones.*
159 | We must handle expected failures, so we would need to `try..catch` function that uses
160 | `throw` for expected failure. But if we do that we'll catch not only errors that represent
161 | expected failures, but also random errors that represent bugs. This is bad for two reasons:
162 |
163 | 1. we ruin nice debugging experience (the debugger will no longer pause etc);
164 | 2. in our code that is supposed to handle expected failures we would need to also
165 | handle unexpected failures (which is generally imposible as shown in the next section).
166 |
167 | If a `throw` is used for expected failures in some APIs, we should wrap inside `try..catch` as little code as
168 | possible, so we won't also catch bugs by accident.
169 |
170 |
171 | ## How program should behave in case of unexpected failures
172 |
173 | `Try..catch` provide us with a mechanism for writing code that will be executed in case of *some*
174 | unexpected failures. We can just wrap arbitrary code into `try..catch`, and we catch bugs
175 | that express themselves as exceptions in that code. Should we use this mechanism and what
176 | should the code in `catch(e) {..}` do?
177 |
178 | Let's look at this from theoretical point of view first and then dive into practical
179 | details in next sections.
180 |
181 | First of all let's focus on the fact that this mechanism catches only **some** failures.
182 | In many cases a program may not throw but just behave incorrectly in some way.
183 | In my experience with JavaScript I'd estimate that it throws only in about 30% of cases.
184 | So should we even care to use this mechanism if it works only in 30% cases?
185 |
186 | If we still want to use it, what should the handling code do? I can think of two options:
187 |
188 | 1. Try to completely recover somehow and keep the program running.
189 | 2. Crash / restart the program and log / report about the bug.
190 |
191 | The `#1` option is simply impossible. We can't transition program from arbitrary
192 | unexpected (inconsistent) state to an expected (consistent) state. For the simple reason that
193 | starting state is **unexpected** — we don't know anything about it, because we didn't expect it.
194 | How could we transition from a state of which we don't know anything to any other state?
195 | There is one way to do it though — restart the program, which is our `#2` option.
196 |
197 | Also any code that is executed in response to a bug might have a potential to make things worse.
198 | It transitions a program to even more complicated inconsistent state. Plus if a program continues to run,
199 | the inconsistent state may leak into a database. In this scenario even a restart may not help.
200 | And if many users are connected to a single database they all may start to experience the bug.
201 |
202 | The `#2` is often happens automatically (at least crash part), so maybe we don't
203 | even need to `catch`. But it's ok to catch for `#2` purposes.
204 |
205 |
206 | ## Unexpected failures in Node
207 |
208 | We could restart the server on each unhandled exception, but this is problematic because the server
209 | usually handles several requests concurrently. So if we restart the server
210 | not only requests that have faced a bug will fail, but all other requests that happen to be
211 | handled at the same time will fail as well. Some people think that a better approach is to wrap all of
212 | the code that is responsible for handling each request with some sort of `try..catch` block and when
213 | a error happens only one request will fail. Although we can't use `try..catch` of course because the
214 | code is asynchronous. So we should use some sort of async abstraction that can provide this functionality (e.g. Promises).
215 |
216 | Another option for Node is to let server crash. Yes, this will result in forcefully ending the execution of all other connections, resulting in more than a single user getting an error. But we will benefit from the crash by taking core dumps, (`node --abort_on_uncaught_exception`) etc.
217 |
218 | Also in Node we can use the `uncaughtException` event combined with a tool like [naught](https://github.com/andrewrk/naught). Here is a qoute from naught docs:
219 |
220 | > Using naught a worker can use the 'offline' message to announce that it is dying. At this point, naught prevents it from accepting new connections and spawns a replacement worker, allowing the dying worker to finish up with its current connections and do any cleanup necessary before finally perishing.
221 |
222 | Conclusion: we might want to catch unexpected errors in Node, but there are plenty other options.
223 |
224 |
225 | ## Unexpected failures in browser
226 |
227 | Just as in Node we could restart the program by reloading the webpage. However, that option is usually considered as an awful behavior from
228 | the UX point of view. So instead we may choose not to restart in a hope of
229 | providing a better UX at a risk of leaking inconsistent state to the database, etc. Some bugs are
230 | indeed not fatal for a web page, and it often may continue to work mostly fine. So this is a
231 | trade–off and to not restart is a legitimate option here.
232 |
233 | Sometimes with browser failures we might want the UI to react to the bug in a particular way. But if it's an arbitrary
234 | bug there isn't much we can do.
235 |
236 | In case of an *expected* failure (like the incorrect user input)
237 | we can handle it very well from UI/UX point of view — we could show an error message near the exact
238 | field in the form, or we may disable the submit button, etc.
239 |
240 | If it's bug where we really don't know
241 | what is going on, we can try to show a popup with a very vague message.
242 | But I think this won't be very helpful, it may actually be worse than not showing a popup.
243 |
244 | Maybe the user was not even going to interact with the part of the program that is broken, and a showing popup out
245 | of nowhere may only damage UX. And if user does interact with the broken part they will notice that
246 | it's broken anyway — no need to tell them what they already know.
247 |
248 | Furthermore, if we show a popup to the user, they might
249 | assume that something has failed, but now it's all under control and it's safe to continue to use the
250 | program. But this would be a lie, as nothing is under control in case of a bug.
251 |
252 | Conclusion: we have no reason to catch unexpected errors in browser.
253 |
254 |
255 | ## Promises and expected failures
256 |
257 | Promises support two code paths. There're two callbacks in `then`.
258 | Also Promises automatically catch all exceptions thrown from then's callbacks and put them into
259 | the next failure callback down the chain.
260 |
261 | So the second path is already used for unexpected failures.
262 | That makes it unusable for expected failures (see ["try..catch" section](#trycatch)).
263 | In other words Promises don't support Railways / Either pattern. If you want to use that pattern with Promises
264 | you should wrap Either into Promise. To use Promise's second path for expected failures is a terrible idea.
265 |
266 |
267 | ## Should async abstractions support exceptions catching?
268 |
269 | From previous sections we've learned that we definitely may not want to catch exceptions at all.
270 | In this case we get the best debugging experience. Even if an abstraction will catch exceptions and then
271 | re-throw them, it won't be the same as not catching at all, for instance the debugger won't pause on
272 | the original line of the `throw`.
273 |
274 | But we also may want to catch "async exceptions", for instance in Node web server case.
275 | A perfect solution would be optional catching.
276 |
277 | However, not all abstractions can support optional catching. If we must choose between non-optional
278 | catching and not supporting catching at all we should choose the latter.
279 | Non-optional catching hurts more than helps.
280 |
281 | This part seems to be ok in Promises. If we don't provide a failure callback in `then` and don't use
282 | `catch` method it seems that debugger behaves the same way as if error wasn't caught
283 | (at least in current Chrome). Although it wasn't always this way, previously they would simply
284 | swallow the exceptions if there wasn't a `catch` callback.
285 |
286 |
287 | ## How exceptions work in Task
288 |
289 | In Task we want to support both **optional** errors catching and Railways / Either pattern.
290 | When we `run()` a task we can choose whether errors will be caught or not,
291 | and if they are caught they go into a separate callback.
292 |
293 | ```js
294 | // exceptions are not caught
295 | task.run({
296 | success(x) {
297 | // handle success
298 | },
299 | failure(x) {
300 | // handle expected failure
301 | },
302 | })
303 |
304 | // if we provide catch callback exceptions are caught
305 | task.run({
306 | success(x) {
307 | // handle success
308 | },
309 | failure(x) {
310 | // handle expected failure
311 | },
312 | catch(e) {
313 | // handle a bug
314 | },
315 | })
316 | ```
317 |
318 | So if a `catch` callback isn't provided, we can enjoy a great debugging experience in the browser (even if we have `failure` callback). And in Node we can still catch exceptions in async code if we wanted to. Also notice that we use a separate callback for exceptions, so we won't have to write code that has to handle both expected and unexpected failures.
319 |
320 | The default behavior is to not catch. This is what we want in browser, and what also may be a legitimate option for Node.
321 |
322 | In Task the `catch` callback is reserved only for bug-exceptions. Expected exceptions must be wrapped in a `try..catch` block manually. All the API and semantics in Task are designed with this assumption in mind.
323 |
324 | Exceptions thrown from `success` and `failure` callbacks are never caught, even if a `catch` callback is provided.
325 |
326 | ```js
327 | task.run({
328 | success() {
329 | // this error won't be caught
330 | throw new Error('')
331 | },
332 | catch(error) {
333 | // the error above will not go here
334 | }
335 | })
336 | ```
337 |
338 | This is done because otherwise we might end up with half of the code for `success` being executed plus the code for `catch`, which in most cases isn't what we want. For example in a web server case, we could start sending response for `success` case, but then continue by sending the response for `catch`. Instead we should catch manually:
339 |
340 | ```js
341 | task.run({
342 | success() {
343 | try {
344 | // ...
345 | res.send(/* some part of success response */)
346 | // ...
347 | // supposedly some code here have thrown
348 | // ...
349 | } catch (e) {
350 | // do something about the exception
351 | // but keep in mind that "some part of success response" was already sent
352 | }
353 | },
354 | catch(error) {
355 | // handle error thrown from .map(fn) , etc.
356 | }
357 | })
358 | ```
359 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/promise-vs-task-api.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # API comparison with Promises
2 |
3 | | Task | Promise & comments |
4 | | ---------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------- |
5 | | `Task.create(computation)` | `new Promise(computation)` |
6 | | `Task.of(x)` | `Promise.resolve(x)`
130 |
131 | Maybe this doesn't make much sense to you now (if you're not familiar with Either).
132 | And this is by no means a complete explanation of Either pattern (check out resources
133 | I've mentioned above for better explanations). But for the purpose of this article the only
134 | thing we need to take out of this section is that some paths in program can be
135 | treated formally or informally as **expected failures**.
136 |
137 | Let's recap. We've split all possible paths in programs to three groups:
138 |
139 | - **Expected success** is the main happy path of the program,
140 | it represents how the program behaves when everything goes right.
141 | - **Expected failure** is secondary path that represent
142 | all expected deviations from the happy path e.g., when a user gives an incorrect input.
143 | - **Unexpected failure** is some *unexpected* deviations from main or secondary paths,
144 | something that we call "bugs".
145 |
146 |
147 | ## try..catch
148 |
149 | How does `try..catch` fits into our three code paths groups view? It's great for unexpected failures!
150 | Or we should say: `throw` is great for unexpected failures if we never actually `try..catch`.
151 | It's very good for debugging. The debugger will pause on the exact line that throws.
152 | Also if we don't use a debugger we can still get a nice stack trace in the console, etc. It's sad that in many
153 | cases when a program goes through an unexpected path instead of exception we end up with `NaN`
154 | being propagated through the program or something like that. In these cases it's much harder to track
155 | down where things went wrong, it's much nicer when it just throws.
156 |
157 | On the other hand `try..catch` is bad for expected failures. There're many reasons why, but let's
158 | focus on just one: *it's bad for expected failures because it's already used for unexpected ones.*
159 | We must handle expected failures, so we would need to `try..catch` function that uses
160 | `throw` for expected failure. But if we do that we'll catch not only errors that represent
161 | expected failures, but also random errors that represent bugs. This is bad for two reasons:
162 |
163 | 1. we ruin nice debugging experience (the debugger will no longer pause etc);
164 | 2. in our code that is supposed to handle expected failures we would need to also
165 | handle unexpected failures (which is generally imposible as shown in the next section).
166 |
167 | If a `throw` is used for expected failures in some APIs, we should wrap inside `try..catch` as little code as
168 | possible, so we won't also catch bugs by accident.
169 |
170 |
171 | ## How program should behave in case of unexpected failures
172 |
173 | `Try..catch` provide us with a mechanism for writing code that will be executed in case of *some*
174 | unexpected failures. We can just wrap arbitrary code into `try..catch`, and we catch bugs
175 | that express themselves as exceptions in that code. Should we use this mechanism and what
176 | should the code in `catch(e) {..}` do?
177 |
178 | Let's look at this from theoretical point of view first and then dive into practical
179 | details in next sections.
180 |
181 | First of all let's focus on the fact that this mechanism catches only **some** failures.
182 | In many cases a program may not throw but just behave incorrectly in some way.
183 | In my experience with JavaScript I'd estimate that it throws only in about 30% of cases.
184 | So should we even care to use this mechanism if it works only in 30% cases?
185 |
186 | If we still want to use it, what should the handling code do? I can think of two options:
187 |
188 | 1. Try to completely recover somehow and keep the program running.
189 | 2. Crash / restart the program and log / report about the bug.
190 |
191 | The `#1` option is simply impossible. We can't transition program from arbitrary
192 | unexpected (inconsistent) state to an expected (consistent) state. For the simple reason that
193 | starting state is **unexpected** — we don't know anything about it, because we didn't expect it.
194 | How could we transition from a state of which we don't know anything to any other state?
195 | There is one way to do it though — restart the program, which is our `#2` option.
196 |
197 | Also any code that is executed in response to a bug might have a potential to make things worse.
198 | It transitions a program to even more complicated inconsistent state. Plus if a program continues to run,
199 | the inconsistent state may leak into a database. In this scenario even a restart may not help.
200 | And if many users are connected to a single database they all may start to experience the bug.
201 |
202 | The `#2` is often happens automatically (at least crash part), so maybe we don't
203 | even need to `catch`. But it's ok to catch for `#2` purposes.
204 |
205 |
206 | ## Unexpected failures in Node
207 |
208 | We could restart the server on each unhandled exception, but this is problematic because the server
209 | usually handles several requests concurrently. So if we restart the server
210 | not only requests that have faced a bug will fail, but all other requests that happen to be
211 | handled at the same time will fail as well. Some people think that a better approach is to wrap all of
212 | the code that is responsible for handling each request with some sort of `try..catch` block and when
213 | a error happens only one request will fail. Although we can't use `try..catch` of course because the
214 | code is asynchronous. So we should use some sort of async abstraction that can provide this functionality (e.g. Promises).
215 |
216 | Another option for Node is to let server crash. Yes, this will result in forcefully ending the execution of all other connections, resulting in more than a single user getting an error. But we will benefit from the crash by taking core dumps, (`node --abort_on_uncaught_exception`) etc.
217 |
218 | Also in Node we can use the `uncaughtException` event combined with a tool like [naught](https://github.com/andrewrk/naught). Here is a qoute from naught docs:
219 |
220 | > Using naught a worker can use the 'offline' message to announce that it is dying. At this point, naught prevents it from accepting new connections and spawns a replacement worker, allowing the dying worker to finish up with its current connections and do any cleanup necessary before finally perishing.
221 |
222 | Conclusion: we might want to catch unexpected errors in Node, but there are plenty other options.
223 |
224 |
225 | ## Unexpected failures in browser
226 |
227 | Just as in Node we could restart the program by reloading the webpage. However, that option is usually considered as an awful behavior from
228 | the UX point of view. So instead we may choose not to restart in a hope of
229 | providing a better UX at a risk of leaking inconsistent state to the database, etc. Some bugs are
230 | indeed not fatal for a web page, and it often may continue to work mostly fine. So this is a
231 | trade–off and to not restart is a legitimate option here.
232 |
233 | Sometimes with browser failures we might want the UI to react to the bug in a particular way. But if it's an arbitrary
234 | bug there isn't much we can do.
235 |
236 | In case of an *expected* failure (like the incorrect user input)
237 | we can handle it very well from UI/UX point of view — we could show an error message near the exact
238 | field in the form, or we may disable the submit button, etc.
239 |
240 | If it's bug where we really don't know
241 | what is going on, we can try to show a popup with a very vague message.
242 | But I think this won't be very helpful, it may actually be worse than not showing a popup.
243 |
244 | Maybe the user was not even going to interact with the part of the program that is broken, and a showing popup out
245 | of nowhere may only damage UX. And if user does interact with the broken part they will notice that
246 | it's broken anyway — no need to tell them what they already know.
247 |
248 | Furthermore, if we show a popup to the user, they might
249 | assume that something has failed, but now it's all under control and it's safe to continue to use the
250 | program. But this would be a lie, as nothing is under control in case of a bug.
251 |
252 | Conclusion: we have no reason to catch unexpected errors in browser.
253 |
254 |
255 | ## Promises and expected failures
256 |
257 | Promises support two code paths. There're two callbacks in `then`.
258 | Also Promises automatically catch all exceptions thrown from then's callbacks and put them into
259 | the next failure callback down the chain.
260 |
261 | So the second path is already used for unexpected failures.
262 | That makes it unusable for expected failures (see ["try..catch" section](#trycatch)).
263 | In other words Promises don't support Railways / Either pattern. If you want to use that pattern with Promises
264 | you should wrap Either into Promise. To use Promise's second path for expected failures is a terrible idea.
265 |
266 |
267 | ## Should async abstractions support exceptions catching?
268 |
269 | From previous sections we've learned that we definitely may not want to catch exceptions at all.
270 | In this case we get the best debugging experience. Even if an abstraction will catch exceptions and then
271 | re-throw them, it won't be the same as not catching at all, for instance the debugger won't pause on
272 | the original line of the `throw`.
273 |
274 | But we also may want to catch "async exceptions", for instance in Node web server case.
275 | A perfect solution would be optional catching.
276 |
277 | However, not all abstractions can support optional catching. If we must choose between non-optional
278 | catching and not supporting catching at all we should choose the latter.
279 | Non-optional catching hurts more than helps.
280 |
281 | This part seems to be ok in Promises. If we don't provide a failure callback in `then` and don't use
282 | `catch` method it seems that debugger behaves the same way as if error wasn't caught
283 | (at least in current Chrome). Although it wasn't always this way, previously they would simply
284 | swallow the exceptions if there wasn't a `catch` callback.
285 |
286 |
287 | ## How exceptions work in Task
288 |
289 | In Task we want to support both **optional** errors catching and Railways / Either pattern.
290 | When we `run()` a task we can choose whether errors will be caught or not,
291 | and if they are caught they go into a separate callback.
292 |
293 | ```js
294 | // exceptions are not caught
295 | task.run({
296 | success(x) {
297 | // handle success
298 | },
299 | failure(x) {
300 | // handle expected failure
301 | },
302 | })
303 |
304 | // if we provide catch callback exceptions are caught
305 | task.run({
306 | success(x) {
307 | // handle success
308 | },
309 | failure(x) {
310 | // handle expected failure
311 | },
312 | catch(e) {
313 | // handle a bug
314 | },
315 | })
316 | ```
317 |
318 | So if a `catch` callback isn't provided, we can enjoy a great debugging experience in the browser (even if we have `failure` callback). And in Node we can still catch exceptions in async code if we wanted to. Also notice that we use a separate callback for exceptions, so we won't have to write code that has to handle both expected and unexpected failures.
319 |
320 | The default behavior is to not catch. This is what we want in browser, and what also may be a legitimate option for Node.
321 |
322 | In Task the `catch` callback is reserved only for bug-exceptions. Expected exceptions must be wrapped in a `try..catch` block manually. All the API and semantics in Task are designed with this assumption in mind.
323 |
324 | Exceptions thrown from `success` and `failure` callbacks are never caught, even if a `catch` callback is provided.
325 |
326 | ```js
327 | task.run({
328 | success() {
329 | // this error won't be caught
330 | throw new Error('')
331 | },
332 | catch(error) {
333 | // the error above will not go here
334 | }
335 | })
336 | ```
337 |
338 | This is done because otherwise we might end up with half of the code for `success` being executed plus the code for `catch`, which in most cases isn't what we want. For example in a web server case, we could start sending response for `success` case, but then continue by sending the response for `catch`. Instead we should catch manually:
339 |
340 | ```js
341 | task.run({
342 | success() {
343 | try {
344 | // ...
345 | res.send(/* some part of success response */)
346 | // ...
347 | // supposedly some code here have thrown
348 | // ...
349 | } catch (e) {
350 | // do something about the exception
351 | // but keep in mind that "some part of success response" was already sent
352 | }
353 | },
354 | catch(error) {
355 | // handle error thrown from .map(fn) , etc.
356 | }
357 | })
358 | ```
359 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/promise-vs-task-api.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # API comparison with Promises
2 |
3 | | Task | Promise & comments |
4 | | ---------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------- |
5 | | `Task.create(computation)` | `new Promise(computation)` |
6 | | `Task.of(x)` | `Promise.resolve(x)`