├── .github
├── CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
├── CONTRIBUTING.md
├── ISSUE_TEMPLATE
│ ├── bug_report.md
│ └── feature_request.md
└── workflows
│ ├── doc_checks.yml
│ ├── format.yml
│ ├── publish.yml
│ ├── publish_docs.yml
│ └── tests.yaml
├── .gitignore
├── CITATION.cff
├── LICENSE.txt
├── README.md
├── docs
├── Makefile
├── README.md
├── _static
│ ├── css
│ │ └── custom.css
│ ├── favicon.png
│ ├── logo.png
│ ├── qkm
│ │ └── QKM_scheme_pic.jpg
│ ├── qnn
│ │ └── qnn.svg
│ ├── qrc
│ │ ├── QRC_user_guide.png
│ │ ├── qrc_classification_transparent.png
│ │ └── qrc_regression_transparent.png
│ ├── schematic.png
│ └── util
│ │ └── executor.png
├── _templates
│ ├── class.rst
│ ├── class_with_call.rst
│ └── function.rst
├── conf.py
├── examples
│ ├── example_kernel_digit_classification.nblink
│ ├── example_kernel_grid_search.nblink
│ ├── example_qnn_backend_mitigation.nblink
│ ├── example_qnn_ode_solver.nblink
│ ├── example_quantum_bayesian_optimization.nblink
│ └── examples_index.rst
├── index.rst
├── install
│ └── install.rst
├── make.bat
├── modules
│ └── classes.rst
├── qiskit_settings.conf
├── spelling_wordlist.txt
└── user_guide
│ ├── encoding_circuits.rst
│ ├── executor.rst
│ ├── kernel_methods.rst
│ ├── observables.rst
│ ├── quantum_neural_networks.rst
│ ├── quantum_reservoir_computing.rst
│ └── user_guide_index.rst
├── examples
├── encoding_circuits
│ ├── layered_encoding_circuit.ipynb
│ ├── pruning_example.ipynb
│ └── various_encoding_circuit.ipynb
├── executor
│ └── example_executor_qiskit.ipynb
├── integration
│ └── mlflow.ipynb
├── kernel
│ ├── example_fidelity_kernel.ipynb
│ ├── example_projected_kernel.ipynb
│ ├── example_regularization_mitigation.ipynb
│ ├── qgpc_workflow.ipynb
│ ├── qgpr_optimization_workflow.ipynb
│ └── qgpr_workflow.ipynb
├── qnn
│ ├── classification_example.ipynb
│ ├── example_adam.ipynb
│ ├── example_minibatch.ipynb
│ ├── example_qcnn_encoding_circuit.ipynb
│ ├── ode_example.ipynb
│ ├── regression_example.ipynb
│ └── regression_with_variance.ipynb
├── qrc
│ ├── qrc_classification.ipynb
│ └── qrc_regression.ipynb
└── tutorials
│ ├── images
│ ├── QNN_ode_workflow.png
│ ├── encoding_circuit.png
│ ├── pipeline.png
│ ├── projected_quantum_kernel.png
│ └── quantum_bo.png
│ ├── kernel_digit_classification.ipynb
│ ├── kernel_grid_search.ipynb
│ ├── kernel_regression.ipynb
│ ├── qnn_backend_mitigation.ipynb
│ ├── qnn_ode_solver.ipynb
│ └── quantum_bayesian_optimization.ipynb
├── install_lowest_dependencies.py
├── output.png
├── pyproject.toml
├── src
└── squlearn
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── encoding_circuit
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── circuit_library
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── chebyshev_pqc.py
│ │ ├── chebyshev_rx.py
│ │ ├── chebyshev_tower.py
│ │ ├── highdim_encoding_circuit.py
│ │ ├── hubregtsen_encoding_circuit.py
│ │ ├── kyriienko_nonlinear_encoding_circuit.py
│ │ ├── multi_control_encoding_circuit.py
│ │ ├── param_z_feature_map.py
│ │ ├── qcnn_encoding_circuit.py
│ │ ├── qiskit_encoding_circuit.py
│ │ ├── random_encoding_circuit.py
│ │ ├── random_layered_encoding_circuit.py
│ │ └── yz_cx_encoding_circuit.py
│ ├── encoding_circuit_base.py
│ ├── encoding_circuit_derivatives.py
│ ├── layered_encoding_circuit.py
│ ├── pruned_encoding_circuit.py
│ └── transpiled_encoding_circuit.py
│ ├── kernel
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── loss
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── kernel_loss_base.py
│ │ ├── negative_log_likelihood.py
│ │ └── target_alignment.py
│ ├── lowlevel_kernel
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── fidelity_kernel.py
│ │ ├── fidelity_kernel_expectation_value.py
│ │ ├── fidelity_kernel_pennylane.py
│ │ ├── kernel_matrix_base.py
│ │ ├── kernel_optimizer.py
│ │ ├── kernel_util.py
│ │ ├── projected_quantum_kernel.py
│ │ └── regularization.py
│ ├── qgpc.py
│ ├── qgpr.py
│ ├── qkrr.py
│ ├── qsvc.py
│ └── qsvr.py
│ ├── observables
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── observable_base.py
│ ├── observable_derivatives.py
│ └── observable_implemented
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── custom_observable.py
│ │ ├── ising_hamiltonian.py
│ │ ├── single_pauli.py
│ │ ├── single_probability.py
│ │ ├── summed_paulis.py
│ │ └── summed_probabilities.py
│ ├── optimizers
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── adam.py
│ ├── approximated_gradients.py
│ ├── optimizer_base.py
│ ├── optimizers_wrapper.py
│ └── sglbo.py
│ ├── qnn
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── base_qnn.py
│ ├── loss
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── ode_loss.py
│ │ ├── parameter_regularization_loss.py
│ │ ├── qnn_loss_base.py
│ │ ├── squared_loss.py
│ │ └── variance_loss.py
│ ├── lowlevel_qnn
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── lowlevel_qnn.py
│ │ ├── lowlevel_qnn_base.py
│ │ ├── lowlevel_qnn_pennylane.py
│ │ └── lowlevel_qnn_qiskit.py
│ ├── qnnc.py
│ ├── qnnr.py
│ └── util
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── barren_plateau_analysis.py
│ │ └── training.py
│ ├── qrc
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── base_qrc.py
│ ├── qrc_classifier.py
│ └── qrc_regressor.py
│ └── util
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── data_preprocessing.py
│ ├── decompose_to_std.py
│ ├── execution
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── automatic_backend_selection.py
│ ├── hqaa
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── heuristic.py
│ │ └── parser.py
│ ├── parallel_estimator.py
│ └── parallel_sampler.py
│ ├── executor.py
│ ├── optree
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── optree.py
│ ├── optree_derivative.py
│ └── optree_evaluate.py
│ ├── pennylane
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── pennylane_circuit.py
│ └── pennylane_gates.py
│ └── qfi.py
└── tests
├── encoding_circuit
├── test_layered_encoding_circuit.py
└── test_random_encoding_circuits.py
├── kernel
├── matrix
│ ├── test_fidelity_quantum_kernel.py
│ ├── test_kernel_optimizer.py
│ └── test_projected_quantum_kernel.py
└── ml
│ ├── test_qgpc.py
│ ├── test_qgpr.py
│ ├── test_qkrr.py
│ ├── test_qsvc.py
│ └── test_qsvr.py
├── optimizers
└── test_sglbo.py
├── qnn
├── test_base_qnn.py
├── test_qnnc.py
├── test_qnnr.py
└── test_training.py
├── qrc
├── test_base_qrc.py
├── test_qrc_classifier.py
└── test_qrc_regressor.py
└── util
├── execution
├── test_automatic_backend_selection.py
└── test_parallel_primitives.py
├── optree
├── test_optree_derivative.py
└── test_optree_evaluate.py
└── test_executor.py
/.github/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # Contributor Covenant Code of Conduct
3 |
4 | ## Our Pledge
5 |
6 | We as members, contributors, and leaders pledge to make participation in our
7 | community a harassment-free experience for everyone, regardless of age, body
8 | size, visible or invisible disability, ethnicity, sex characteristics, gender
9 | identity and expression, level of experience, education, socio-economic status,
10 | nationality, personal appearance, race, caste, color, religion, or sexual
11 | identity and orientation.
12 |
13 | We pledge to act and interact in ways that contribute to an open, welcoming,
14 | diverse, inclusive, and healthy community.
15 |
16 | ## Our Standards
17 |
18 | Examples of behavior that contributes to a positive environment for our
19 | community include:
20 |
21 | * Demonstrating empathy and kindness toward other people
22 | * Being respectful of differing opinions, viewpoints, and experiences
23 | * Giving and gracefully accepting constructive feedback
24 | * Accepting responsibility and apologizing to those affected by our mistakes,
25 | and learning from the experience
26 | * Focusing on what is best not just for us as individuals, but for the overall
27 | community
28 |
29 | Examples of unacceptable behavior include:
30 |
31 | * The use of sexualized language or imagery, and sexual attention or advances of
32 | any kind
33 | * Trolling, insulting or derogatory comments, and personal or political attacks
34 | * Public or private harassment
35 | * Publishing others' private information, such as a physical or email address,
36 | without their explicit permission
37 | * Other conduct which could reasonably be considered inappropriate in a
38 | professional setting
39 |
40 | ## Enforcement Responsibilities
41 |
42 | Community leaders are responsible for clarifying and enforcing our standards of
43 | acceptable behavior and will take appropriate and fair corrective action in
44 | response to any behavior that they deem inappropriate, threatening, offensive,
45 | or harmful.
46 |
47 | Community leaders have the right and responsibility to remove, edit, or reject
48 | comments, commits, code, wiki edits, issues, and other contributions that are
49 | not aligned to this Code of Conduct, and will communicate reasons for moderation
50 | decisions when appropriate.
51 |
52 | ## Scope
53 |
54 | This Code of Conduct applies within all community spaces, and also applies when
55 | an individual is officially representing the community in public spaces.
56 | Examples of representing our community include using an official e-mail address,
57 | posting via an official social media account, or acting as an appointed
58 | representative at an online or offline event.
59 |
60 | ## Enforcement
61 |
62 | Instances of abusive, harassing, or otherwise unacceptable behavior may be
63 | reported to the community leaders responsible for enforcement at
64 | [squlearn@gmail.com](mailto:squlearn@gmail.com).
65 | All complaints will be reviewed and investigated promptly and fairly.
66 |
67 | All community leaders are obligated to respect the privacy and security of the
68 | reporter of any incident.
69 |
70 | ## Enforcement Guidelines
71 |
72 | Community leaders will follow these Community Impact Guidelines in determining
73 | the consequences for any action they deem in violation of this Code of Conduct:
74 |
75 | ### 1. Correction
76 |
77 | **Community Impact**: Use of inappropriate language or other behavior deemed
78 | unprofessional or unwelcome in the community.
79 |
80 | **Consequence**: A private, written warning from community leaders, providing
81 | clarity around the nature of the violation and an explanation of why the
82 | behavior was inappropriate. A public apology may be requested.
83 |
84 | ### 2. Warning
85 |
86 | **Community Impact**: A violation through a single incident or series of
87 | actions.
88 |
89 | **Consequence**: A warning with consequences for continued behavior. No
90 | interaction with the people involved, including unsolicited interaction with
91 | those enforcing the Code of Conduct, for a specified period of time. This
92 | includes avoiding interactions in community spaces as well as external channels
93 | like social media. Violating these terms may lead to a temporary or permanent
94 | ban.
95 |
96 | ### 3. Temporary Ban
97 |
98 | **Community Impact**: A serious violation of community standards, including
99 | sustained inappropriate behavior.
100 |
101 | **Consequence**: A temporary ban from any sort of interaction or public
102 | communication with the community for a specified period of time. No public or
103 | private interaction with the people involved, including unsolicited interaction
104 | with those enforcing the Code of Conduct, is allowed during this period.
105 | Violating these terms may lead to a permanent ban.
106 |
107 | ### 4. Permanent Ban
108 |
109 | **Community Impact**: Demonstrating a pattern of violation of community
110 | standards, including sustained inappropriate behavior, harassment of an
111 | individual, or aggression toward or disparagement of classes of individuals.
112 |
113 | **Consequence**: A permanent ban from any sort of public interaction within the
114 | community.
115 |
116 | ## Attribution
117 |
118 | This Code of Conduct is adapted from the [Contributor Covenant][homepage],
119 | version 2.1, available at
120 | [https://www.contributor-covenant.org/version/2/1/code_of_conduct.html][v2.1].
121 |
122 | Community Impact Guidelines were inspired by
123 | [Mozilla's code of conduct enforcement ladder][Mozilla CoC].
124 |
125 | For answers to common questions about this code of conduct, see the FAQ at
126 | [https://www.contributor-covenant.org/faq][FAQ]. Translations are available at
127 | [https://www.contributor-covenant.org/translations][translations].
128 |
129 | [homepage]: https://www.contributor-covenant.org
130 | [v2.1]: https://www.contributor-covenant.org/version/2/1/code_of_conduct.html
131 | [Mozilla CoC]: https://github.com/mozilla/diversity
132 | [FAQ]: https://www.contributor-covenant.org/faq
133 | [translations]: https://www.contributor-covenant.org/translations
134 |
135 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/CONTRIBUTING.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Contributing
2 | If you plan to contribute to this project, please read this section carefully and check that your contribution fits the desired process and style.
3 |
4 | ## Install development version
5 | To contribute to sQUlearn install the package from the source code:
6 |
7 | ```bash
8 | git clone https://github.com/sQUlearn/squlearn.git && cd squlearn
9 | git checkout develop
10 | pip install -e .
11 | ```
12 |
13 | > Note that editable installing as above might require an updated version of pip `pip install pip --upgrade`
14 |
15 | ## Devtools
16 | Install the recommended tools with
17 | ```bash
18 | pip install -e .[dev]
19 | ```
20 |
21 | ## Style Guide
22 | ### Code Style
23 | We try to match all of our python code closely to the [PEP8 style guide](https://pep8.org/) with the exception of using a line length of `99`. To ensure this we use the [Black formater](https://black.readthedocs.io/en/stable/index.html) with the configuration specified in [pyproject.toml](https://github.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/blob/main/pyproject.toml). To format your code, run
24 | ```bash
25 | black path/to/folder/or/file.py
26 | ```
27 | from the top level directory to ensure the use of the `pyproject.toml` configuration file.
28 |
29 | We don't enforce but highly encourage the use of the [pylint linter](https://docs.pylint.org/) to check newly written code and adapt accordingly. To run the linter with the desired configuration run
30 | ```bash
31 | pylint path/to/folder/or/file.py
32 | ```
33 | from the top level directory to again ensure the use of the `pyproject.toml` configuration file. Running pylint before and after the contribution shouldn't add violations and/or lower the overall code score.
34 |
35 | ### Docstrings
36 | We furthermore desire to use the [Google Python Style Guide](https://google.github.io/styleguide/pyguide.html#38-comments-and-docstrings) for our Docstrings. Generally we at least expect
37 | - A one-line summary, terminated by a period, and
38 | - a description of the class/method.
39 |
40 | For classes we furthermore expect
41 | - A list of attributes.
42 |
43 | For methods we furthermore expect
44 | - A list of arguments, and
45 | - A list of return values.
46 |
47 | ## Git Flow
48 | We use the Git Flow branch structure specified [here](https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/comparing-workflows/gitflow-workflow) except for release branches.
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug_report.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | name: Bug report
3 | about: Create a report to help us improve
4 | title: ''
5 | labels: ''
6 | assignees: ''
7 |
8 | ---
9 |
10 | **Describe the bug**
11 | A clear and concise description of what the bug is.
12 |
13 | **To Reproduce**
14 | Steps to reproduce the behavior...
15 |
16 | ```
17 | This minimal code example will lead to the bug
18 | ```
19 |
20 | **Expected behavior**
21 | A clear and concise description of what you expected to happen.
22 |
23 | **Additional context**
24 | Add any other context about the problem here. Version of sQUlearn, python, which OS, etc.
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/feature_request.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | name: Feature request
3 | about: Suggest an idea for this project
4 | title: ''
5 | labels: ''
6 | assignees: ''
7 |
8 | ---
9 |
10 | **Is your feature request related to a problem? Please describe.**
11 | A clear and concise description of what the problem is. Ex. I'm always frustrated when [...]
12 |
13 | **Describe the solution you'd like**
14 | A clear and concise description of what you want to happen.
15 |
16 | **Describe alternatives you've considered**
17 | A clear and concise description of any alternative solutions or features you've considered.
18 |
19 | **Additional context**
20 | Add any other context or screenshots about the feature request here.
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/doc_checks.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: Documentation check
2 | on:
3 | - pull_request
4 |
5 | jobs:
6 | doc_checks:
7 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
8 | env:
9 | QISKIT_SETTINGS: ${{github.workspace}}/docs/qiskit_settings.conf
10 |
11 | steps:
12 | - name: Cancel Workflow Action
13 | uses: styfle/cancel-workflow-action@0.11.0
14 |
15 | - uses: actions/checkout@v2
16 | - uses: sQUlearn/sphinx-action@master
17 | with:
18 | docs-folder: "docs/"
19 | pre-build-command: "pip3 install .[docs]"
20 | build-command: "sphinx-build -b html . _build -W --keep-going"
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/format.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: Formatting check
2 | on:
3 | - pull_request
4 |
5 | jobs:
6 | black:
7 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
8 |
9 | steps:
10 | - name: Cancel Workflow Action
11 | uses: styfle/cancel-workflow-action@0.11.0
12 |
13 | - name: Set up Python
14 | uses: actions/setup-python@v2
15 | with:
16 | python-version: 3.9
17 |
18 | - name: Install dependencies
19 | run: pip install black[jupyter]
20 |
21 | - uses: actions/checkout@v2
22 |
23 | - name: Run Black
24 | run: |
25 | black -l 99 src --check
26 | black -l 99 tests --check
27 | black -l 99 --ipynb examples --check
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/publish.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: Publish to PyPI
2 | on:
3 | release:
4 | types: [published]
5 |
6 | jobs:
7 | pypi-publish:
8 | name: Upload release to PyPI
9 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
10 | environment:
11 | name: release
12 | url: https://pypi.org/p/squlearn
13 | permissions:
14 | id-token: write
15 | steps:
16 | - name: Set up Python
17 | uses: actions/setup-python@v2
18 | with:
19 | python-version: 3.9
20 |
21 | - name: Install dependencies
22 | run: pip install flit
23 |
24 | - uses: actions/checkout@v2
25 |
26 | - name: Build
27 | run: flit build
28 |
29 | - name: Publish package distributions to PyPI
30 | uses: pypa/gh-action-pypi-publish@release/v1
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/publish_docs.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: Publish to GH Pages
2 | on:
3 | release:
4 | types: [published]
5 | workflow_dispatch:
6 |
7 | jobs:
8 | publish-pages:
9 | name: Publish to GH Pages
10 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
11 | env:
12 | QISKIT_SETTINGS: ${{github.workspace}}/docs/qiskit_settings.conf
13 | steps:
14 | - name: Checkout Source Code
15 | uses: actions/checkout@v2
16 | - name: Checkout GH Pages
17 | uses: actions/checkout@v2
18 | with:
19 | repository: sQUlearn/squlearn.github.io
20 | fetch-depth: 0
21 | path: "docs/_build"
22 | token: ${{ secrets.PUSH_DOCS_TOKEN }}
23 | - name: Build Docs
24 | uses: sQUlearn/sphinx-action@master
25 | with:
26 | docs-folder: "docs/"
27 | pre-build-command: "pip3 install .[docs]"
28 | build-command: "sphinx-build -E -b html . _build -W"
29 | - name: Commit Files
30 | run: |
31 | cd docs/_build
32 | git config --global user.email "github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com"
33 | git config --global user.name "github-actions[bot]"
34 | git add .
35 | git commit -m "update documentation ${{ github.event.release.tag_name }}"
36 | - name: Tag
37 | run: |
38 | cd docs/_build
39 | git tag -a "${{ github.event.release.tag_name }}" -m "${{ github.event.release.name}}"
40 | if: github.event_name == 'release'
41 | - name: Push Changes
42 | uses: ad-m/github-push-action@master
43 | with:
44 | github_token: ${{ secrets.PUSH_DOCS_TOKEN }}
45 | directory: docs/_build
46 | repository: sQUlearn/squlearn.github.io
47 | force: true
48 | tags: true
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/tests.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: Tests
2 | on:
3 | pull_request:
4 | schedule:
5 | - cron: '23 1 * * *'
6 |
7 | jobs:
8 | pytest_minimal_requirements:
9 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
10 |
11 | steps:
12 | - uses: actions/checkout@v4
13 | - name: Set up Python
14 | uses: actions/setup-python@v5
15 | with:
16 | python-version: '3.9'
17 | - name: Install dependencies
18 | run: |
19 | python -m pip install --upgrade pip
20 | python -m venv venv_minimal
21 | source venv_minimal/bin/activate
22 | pip install toml
23 | python3 install_lowest_dependencies.py
24 | - name: Test with pytest
25 | run: |
26 | source venv_minimal/bin/activate
27 | pip install pytest
28 | pytest tests/
29 | - name: Test examples
30 | run: |
31 | source venv_minimal/bin/activate
32 | pip install nbmake
33 | pytest --nbmake --nbmake-timeout 600 examples/
34 | - name: clean
35 | run: |
36 | rm -rf venv_minimal
37 |
38 | pytest_qiskit_0_46:
39 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
40 |
41 | steps:
42 | - uses: actions/checkout@v4
43 | - name: Set up Python
44 | uses: actions/setup-python@v5
45 | with:
46 | python-version: '3.9'
47 | - name: Install dependencies
48 | run: |
49 | python -m pip install --upgrade pip
50 | python -m venv venv_qiskit_0_46
51 | source venv_qiskit_0_46/bin/activate
52 | pip install .[examples] qiskit==0.46.3 qiskit-ibm-runtime==0.20.0
53 | - name: Test with pytest
54 | run: |
55 | source venv_qiskit_0_46/bin/activate
56 | pip install pytest
57 | pytest tests/
58 | - name: Test examples
59 | run: |
60 | source venv_qiskit_0_46/bin/activate
61 | pip install nbmake
62 | pytest --nbmake --nbmake-timeout 600 examples/
63 | - name: clean
64 | run: |
65 | rm -rf venv_qiskit_0_46
66 |
67 | pytest_qiskit_1:
68 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
69 |
70 | steps:
71 | - uses: actions/checkout@v4
72 | - name: Set up Python
73 | uses: actions/setup-python@v5
74 | with:
75 | python-version: '3.9'
76 | - name: Install dependencies
77 | run: |
78 | python -m pip install --upgrade pip
79 | python -m venv venv_qiskit_1
80 | source venv_qiskit_1/bin/activate
81 | pip install .[examples] qiskit==1.1.2 qiskit-ibm-runtime==0.27.1
82 | - name: Test with pytest
83 | run: |
84 | source venv_qiskit_1/bin/activate
85 | pip install pytest
86 | pytest tests/
87 | - name: Test examples
88 | run: |
89 | source venv_qiskit_1/bin/activate
90 | pip install nbmake
91 | pytest --nbmake --nbmake-timeout 600 examples/
92 | - name: clean
93 | run: |
94 | rm -rf venv_qiskit_1
95 |
96 | pytest_latest:
97 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
98 |
99 | steps:
100 | - uses: actions/checkout@v4
101 | - name: Set up Python
102 | uses: actions/setup-python@v5
103 | with:
104 | python-version: |
105 | 3.12
106 | - name: Install dependencies
107 | run: |
108 | python -m pip install --upgrade pip
109 | python -m venv venv_latest
110 | source venv_latest/bin/activate
111 | pip install .[examples]
112 | - name: Test with pytest
113 | run: |
114 | source venv_latest/bin/activate
115 | pip install pytest
116 | pytest tests/
117 | - name: Test examples
118 | run: |
119 | source venv_latest/bin/activate
120 | pip install nbmake
121 | pytest --nbmake --nbmake-timeout 600 examples/
122 | - name: clean
123 | run: |
124 | rm -rf venv_latest
125 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
2 | __pycache__/
3 | *.py[cod]
4 | *$py.class
5 |
6 | # C extensions
7 | *.so
8 |
9 | # Distribution / packaging
10 | .Python
11 | build/
12 | develop-eggs/
13 | dist/
14 | downloads/
15 | eggs/
16 | .eggs/
17 | lib/
18 | lib64/
19 | parts/
20 | sdist/
21 | var/
22 | wheels/
23 | share/python-wheels/
24 | *.egg-info/
25 | .installed.cfg
26 | *.egg
27 | MANIFEST
28 |
29 | # PyInstaller
30 | # Usually these files are written by a python script from a template
31 | # before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it.
32 | *.manifest
33 | *.spec
34 |
35 | # Installer logs
36 | pip-log.txt
37 | pip-delete-this-directory.txt
38 |
39 | # Unit test / coverage reports
40 | htmlcov/
41 | .tox/
42 | .nox/
43 | .coverage
44 | .coverage.*
45 | .cache
46 | nosetests.xml
47 | coverage.xml
48 | *.cover
49 | *.py,cover
50 | .hypothesis/
51 | .pytest_cache/
52 | cover/
53 |
54 | # Translations
55 | *.mo
56 | *.pot
57 |
58 | # Django stuff:
59 | *.log
60 | local_settings.py
61 | db.sqlite3
62 | db.sqlite3-journal
63 |
64 | # Flask stuff:
65 | instance/
66 | .webassets-cache
67 |
68 | # Scrapy stuff:
69 | .scrapy
70 |
71 | # Sphinx documentation
72 | docs/_build/
73 | docs/modules/generated/*
74 | docs/examples/images
75 |
76 | # PyBuilder
77 | .pybuilder/
78 | target/
79 |
80 | # Jupyter Notebook
81 | .ipynb_checkpoints
82 |
83 | # IPython
84 | profile_default/
85 | ipython_config.py
86 |
87 | # pyenv
88 | # For a library or package, you might want to ignore these files since the code is
89 | # intended to run in multiple environments; otherwise, check them in:
90 | # .python-version
91 |
92 | # pipenv
93 | # According to pypa/pipenv#598, it is recommended to include Pipfile.lock in version control.
94 | # However, in case of collaboration, if having platform-specific dependencies or dependencies
95 | # having no cross-platform support, pipenv may install dependencies that don't work, or not
96 | # install all needed dependencies.
97 | #Pipfile.lock
98 |
99 | # poetry
100 | # Similar to Pipfile.lock, it is generally recommended to include poetry.lock in version control.
101 | # This is especially recommended for binary packages to ensure reproducibility, and is more
102 | # commonly ignored for libraries.
103 | # https://python-poetry.org/docs/basic-usage/#commit-your-poetrylock-file-to-version-control
104 | #poetry.lock
105 |
106 | # pdm
107 | # Similar to Pipfile.lock, it is generally recommended to include pdm.lock in version control.
108 | #pdm.lock
109 | # pdm stores project-wide configurations in .pdm.toml, but it is recommended to not include it
110 | # in version control.
111 | # https://pdm.fming.dev/#use-with-ide
112 | .pdm.toml
113 |
114 | # PEP 582; used by e.g. github.com/David-OConnor/pyflow and github.com/pdm-project/pdm
115 | __pypackages__/
116 |
117 | # Celery stuff
118 | celerybeat-schedule
119 | celerybeat.pid
120 |
121 | # SageMath parsed files
122 | *.sage.py
123 |
124 | # Environments
125 | .env*
126 | .venv*
127 | env*/
128 | venv*/
129 | ENV/
130 | env.bak/
131 | venv.bak/
132 |
133 | # Spyder project settings
134 | .spyderproject
135 | .spyproject
136 |
137 | # Rope project settings
138 | .ropeproject
139 |
140 | # mkdocs documentation
141 | /site
142 |
143 | # mypy
144 | .mypy_cache/
145 | .dmypy.json
146 | dmypy.json
147 |
148 | # Pyre type checker
149 | .pyre/
150 |
151 | # pytype static type analyzer
152 | .pytype/
153 |
154 | # Cython debug symbols
155 | cython_debug/
156 |
157 | # PyCharm
158 | # JetBrains specific template is maintained in a separate JetBrains.gitignore that can
159 | # be found at https://github.com/github/gitignore/blob/main/Global/JetBrains.gitignore
160 | # and can be added to the global gitignore or merged into this file. For a more nuclear
161 | # option (not recommended) you can uncomment the following to ignore the entire idea folder.
162 | #.idea/
163 |
164 | # VSCode
165 | .vscode/
166 |
167 | #Example logs
168 | examples/qnn/*_log.csv
169 | examples/**/*.log
170 |
171 | #Example caches
172 | **/_cache
173 | examples/integration/mlruns
174 |
175 | # Genereated doc images
176 | docs/examples/images/*
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/CITATION.cff:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | cff-version: 1.2.0
2 | message: "If you use this software, please cite it as follows."
3 | title: sQUlearn
4 | authors:
5 | - family-names: sQUlearn Contributors
6 | url: https://squlearn.github.io
7 | license: Apache-2.0
8 | repository-code: https://github.com/sQUlearn/squlearn
9 | preferred-citation:
10 | type: article
11 | status: preprint
12 | title: "sQUlearn - A Python Library for Quantum Machine Learning"
13 | authors:
14 | - family-names: Kreplin
15 | given-names: David A.
16 | orcid: https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8129-6864
17 | affiliation: Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Engineering and Automation IPA
18 | - family-names: Willmann
19 | given-names: Moritz
20 | orcid: https://orcid.org/0009-0000-8099-425X
21 | affiliation: Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Engineering and Automation IPA
22 | - family-names: Schnabel
23 | given-names: Jan
24 | orcid: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3485-0479
25 | affiliation: Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Engineering and Automation IPA
26 | - family-names: Rapp
27 | given-names: Frederic
28 | orcid: https://orcid.org/0009-0008-6240-8390
29 | affiliation: Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Engineering and Automation IPA
30 | - family-names: Hagelüken
31 | given-names: Manuel
32 | orcid: https://orcid.org/0009-0007-9852-3190
33 | affilliation: Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Engineering and Automation IPA
34 | - family-names: Roth
35 | given-names: Marco
36 | orcid: https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1276-5655
37 | affiliation: Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Engineering and Automation IPA
38 | year: 2023
39 | month: 11
40 | doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2311.08990
41 | url: https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.08990
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |  3 |
3 |
4 |
5 | sQUlearn is a user-friendly, NISQ-ready Python library for quantum machine learning (QML), designed for seamless integration with classical machine learning tools like scikit-learn. The library's dual-layer architecture serves both QML researchers and practitioners, enabling efficient prototyping, experimentation, and pipelining. sQUlearn provides a comprehensive tool set that includes both quantum kernel methods and quantum neural networks, along with features like customizable data encoding strategies, automated execution handling, and specialized kernel regularization techniques. By focusing on NISQ-compatibility and end-to-end automation, sQUlearn aims to bridge the gap between current quantum computing capabilities and practical machine learning applications.
6 |
7 | sQUlearn offers scikit-learn compatible high-level interfaces for various kernel methods, QNNs and quantum reservoir computing. They build on top of the low-level interfaces of the QNN engine and the quantum kernel engine. The executor is used to run experiments on simulated and real backends of the Qiskit or PennyLane frameworks.
8 |
9 |
10 | 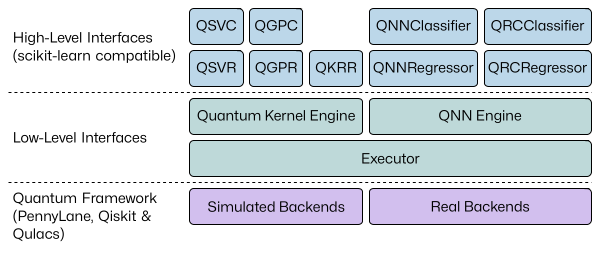 11 |
11 |
12 |
13 | ---
14 |
15 | ## Prerequisites
16 |
17 | The package requires **at least Python 3.9**.
18 | ## Install sQUlearn
19 |
20 | ### Stable Release
21 |
22 | To install the stable release version of sQUlearn, run the following command:
23 | ```bash
24 | pip install squlearn
25 | ```
26 |
27 | Alternatively, you can install sQUlearn directly from GitHub via
28 | ```bash
29 | pip install git+ssh://git@github.com:sQUlearn/squlearn.git
30 | ```
31 |
32 | ## Examples
33 | There are several more elaborate examples available in the folder ``./examples`` which display the features of this package.
34 | Tutorials for beginners can be found at ``./examples/tutorials``.
35 |
36 | To install the required packages, run
37 | ```bash
38 | pip install .[examples]
39 | ```
40 |
41 | ## Contribute to sQUlearn
42 | Thanks for considering contributing to sQUlearn! Please read our [contribution guidelines](https://github.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/blob/main/.github/CONTRIBUTING.md) before you submit a pull request.
43 |
44 | ---
45 | ## License
46 |
47 | sQUlearn is released under the [Apache License 2.0](https://github.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/blob/main/LICENSE.txt)
48 |
49 | ## Cite sQUlearn
50 | If you use sQUlearn in your work, please cite our paper:
51 |
52 | > Kreplin, D. A., Willmann, M., Schnabel, J., Rapp, F., Hagelüken, M., & Roth, M. (2023). sQUlearn - A Python Library for Quantum Machine Learning. [https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2311.08990](https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2311.08990)
53 |
54 | ## Contact
55 | This project is maintained by the quantum computing group at the Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Engineering and Automation IPA.
56 |
57 | [http://www.ipa.fraunhofer.de/quantum](http://www.ipa.fraunhofer.de/quantum)
58 |
59 | For general questions regarding sQUlearn, use the [GitHub Discussions](https://github.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/discussions) or feel free to contact [sQUlearn@gmail.com](mailto:sQUlearn@gmail.com).
60 |
61 | ---
62 | ## Acknowledgements
63 |
64 | This project was supported by the German Federal Ministry of Economic Affairs and Climate Action through the projects AutoQML (grant no. 01MQ22002A) and AQUAS (grant no. 01MQ22003D), as well as the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research through the project H2Giga Degrad-EL3 (grant no. 03HY110D).
65 |
66 | ---
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Makefile:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Minimal makefile for Sphinx documentation
2 | #
3 |
4 | # You can set these variables from the command line, and also
5 | # from the environment for the first two.
6 | SPHINXOPTS =
7 | SPHINXBUILD = sphinx-build
8 | SOURCEDIR = .
9 | BUILDDIR = _build
10 |
11 | # Put it first so that "make" without argument is like "make help".
12 | help:
13 | @$(SPHINXBUILD) -M help "$(SOURCEDIR)" "$(BUILDDIR)" $(SPHINXOPTS) $(O)
14 |
15 | .PHONY: help Makefile
16 |
17 | # Catch-all target: route all unknown targets to Sphinx using the new
18 | # "make mode" option. $(O) is meant as a shortcut for $(SPHINXOPTS).
19 | %: Makefile
20 | @$(SPHINXBUILD) -M $@ "$(SOURCEDIR)" "$(BUILDDIR)" $(SPHINXOPTS) $(O)
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Requirements:
2 |
3 | ```bash
4 | pip install sphinx
5 | pip install sphinx-rtd-theme
6 | ```
7 |
8 | Command for generating the documentation:
9 |
10 | ```bash
11 | sphinx-build.exe -b html . _build/
12 | ```
13 |
14 | Or execute in the windows shell:
15 |
16 | ```bash
17 | make.bat html
18 | ```
19 |
20 | Spell checking with
21 | ```bash
22 | make.bat spelling
23 | ```
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/_static/css/custom.css:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | @import 'theme.css';
2 |
3 | .rst-content .note .admonition-title, .rst-content .note .wy-alert-title, .rst-content .seealso .admonition-title, .rst-content .seealso .wy-alert-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.admonition-todo .admonition-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.admonition-todo .wy-alert-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.admonition .admonition-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.admonition .wy-alert-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.attention .admonition-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.attention .wy-alert-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.caution .admonition-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.caution .wy-alert-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.danger .admonition-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.danger .wy-alert-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.error .admonition-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.error .wy-alert-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.hint .admonition-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.hint .wy-alert-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.important .admonition-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.important .wy-alert-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.tip .admonition-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.tip .wy-alert-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.warning .admonition-title, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.warning .wy-alert-title, .rst-content .wy-alert.wy-alert-info .admonition-title, .wy-alert.wy-alert-info .rst-content .admonition-title, .wy-alert.wy-alert-info .wy-alert-title {
4 | background: #6fd3dd;
5 | }
6 |
7 | .rst-content .note, .rst-content .seealso, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.admonition, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.admonition-todo, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.attention, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.caution, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.danger, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.error, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.hint, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.important, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.tip, .rst-content .wy-alert-info.warning, .wy-alert.wy-alert-info {
8 | background: #e7f7f9;
9 | }
10 |
11 | .rst-content .wy-alert-neutral.admonition-todo a,.rst-content .wy-alert-neutral.admonition a,.rst-content .wy-alert-neutral.attention a,.rst-content .wy-alert-neutral.caution a,.rst-content .wy-alert-neutral.danger a,.rst-content .wy-alert-neutral.error a,.rst-content .wy-alert-neutral.hint a,.rst-content .wy-alert-neutral.important a,.rst-content .wy-alert-neutral.note a,.rst-content .wy-alert-neutral.seealso a,.rst-content .wy-alert-neutral.tip a,.rst-content .wy-alert-neutral.warning a,.wy-alert.wy-alert-neutral a{
12 | color:#0fb6c7
13 | }
14 |
15 | .wy-tray-container li.wy-tray-item-info{
16 | background:#0fb6c7
17 | }
18 |
19 | .btn-info{
20 | background-color:#0fb6c7!important
21 | }
22 |
23 | .btn-info:hover{
24 | background-color:#0C919F!important
25 | }
26 |
27 | .btn-link{
28 | color:#0fb6c7;
29 | }
30 |
31 | .wy-dropdown-menu>dd>a:hover{
32 | background:#0fb6c7;
33 | }
34 |
35 | .wy-dropdown.wy-dropdown-bubble .wy-dropdown-menu a:hover{
36 | background:#0fb6c7;
37 | }
38 |
39 | .wy-inline-validate.wy-inline-validate-info .wy-input-context{
40 | color:#0fb6c7
41 | }
42 |
43 | a{
44 | color:#0fb6c7;
45 | }
46 |
47 | .wy-text-info{
48 | color:#0fb6c7!important
49 | }
50 |
51 | .wy-menu-vertical a:active{
52 | background-color:#0fb6c7;
53 | }
54 |
55 | .wy-side-nav-search{
56 | background-color:#0fb6c7;
57 | }
58 |
59 | .wy-side-nav-search img{
60 | background-color:#0fb6c7;
61 | }
62 |
63 | .wy-side-nav-search > div.version {
64 | color: hsla(0, 0%, 100%, 0.7);
65 | }
66 |
67 | .wy-nav .wy-menu-vertical header{
68 | color:#0fb6c7
69 | }
70 |
71 | .wy-menu-vertical header, .wy-menu-vertical p.caption {
72 | color: #0C919F;
73 | }
74 |
75 | .wy-nav .wy-menu-vertical a:hover{
76 | background-color:#0fb6c7;
77 | }
78 |
79 | .wy-nav-side {
80 | background: #293133;
81 | }
82 |
83 | .wy-nav-top{
84 | background:#0fb6c7;
85 | }
86 |
87 | .wy-nav-top img{
88 | background-color:#0fb6c7;
89 | }
90 |
91 | .rst-versions a{
92 | color:#0fb6c7;
93 | }
94 |
95 | .rst-content a code,.rst-content a tt{
96 | color:#0fb6c7
97 | }
98 |
99 | html.writer-html4 .rst-content dl:not(.docutils)>dt,html.writer-html5 .rst-content dl[class]:not(.option-list):not(.field-list):not(.footnote):not(.citation):not(.glossary):not(.simple)>dt{
100 | color:#0fb6c7;
101 | }
102 |
103 | html.writer-html4 .rst-content dl:not(.docutils) > dt, html.writer-html5 .rst-content dl[class]:not(.option-list):not(.field-list):not(.footnote):not(.citation):not(.glossary):not(.simple) > dt {
104 | background: #e7f7f9;
105 | border-top: 3px solid #6fd3dd;
106 | }
107 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/_static/favicon.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/f21f3ca4a4c90b95d4da763f08c1ff815cb5afdf/docs/_static/favicon.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/_static/logo.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/f21f3ca4a4c90b95d4da763f08c1ff815cb5afdf/docs/_static/logo.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/_static/qkm/QKM_scheme_pic.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/f21f3ca4a4c90b95d4da763f08c1ff815cb5afdf/docs/_static/qkm/QKM_scheme_pic.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/_static/qrc/QRC_user_guide.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/f21f3ca4a4c90b95d4da763f08c1ff815cb5afdf/docs/_static/qrc/QRC_user_guide.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/_static/qrc/qrc_classification_transparent.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/f21f3ca4a4c90b95d4da763f08c1ff815cb5afdf/docs/_static/qrc/qrc_classification_transparent.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/_static/qrc/qrc_regression_transparent.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/f21f3ca4a4c90b95d4da763f08c1ff815cb5afdf/docs/_static/qrc/qrc_regression_transparent.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/_static/schematic.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/f21f3ca4a4c90b95d4da763f08c1ff815cb5afdf/docs/_static/schematic.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/_static/util/executor.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/f21f3ca4a4c90b95d4da763f08c1ff815cb5afdf/docs/_static/util/executor.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/_templates/class.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | :mod:`{{module}}`.\ :spelling:word:`{{objname}}`
2 | {{ underline }}=================================
3 |
4 | .. currentmodule:: {{ module }}
5 |
6 | .. autoclass:: {{ objname }}
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/_templates/class_with_call.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ..
2 | The empty line below should not be removed. It is added such that the `rst_prolog`
3 | is added before the :mod: directive. Otherwise, the rendering will show as a
4 | paragraph instead of a header.
5 |
6 | :mod:`{{module}}`.\ :spelling:word:`{{objname}}`
7 | {{ underline }}=================================
8 |
9 | .. currentmodule:: {{ module }}
10 |
11 | .. autoclass:: {{ objname }}
12 |
13 | {% block methods %}
14 | .. automethod:: __call__
15 | {% endblock %}
16 |
17 | .. raw:: html
18 |
19 |
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/_templates/function.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | :mod:`{{module}}`.\ :spelling:word:`{{objname}}`
2 | {{ underline }}=================================
3 |
4 | .. currentmodule:: {{ module }}
5 |
6 | .. autofunction:: {{ objname }}
7 |
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/conf.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Configuration file for the Sphinx documentation builder.
2 | #
3 | # This file only contains a selection of the most common options. For a full
4 | # list see the documentation:
5 | # https://www.sphinx-doc.org/en/master/usage/configuration.html
6 |
7 | # -- Path setup --------------------------------------------------------------
8 |
9 | # If extensions (or modules to document with autodoc) are in another directory,
10 | # add these directories to sys.path here. If the directory is relative to the
11 | # documentation root, use os.path.abspath to make it absolute, like shown here.
12 | #
13 | import os
14 | import sys
15 |
16 | sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath(".."))
17 |
18 | from squlearn import __version__ as squlearn_version
19 |
20 | # -- Project information -----------------------------------------------------
21 |
22 | project = "sQUlearn"
23 | copyright = "2023, Fraunhofer IPA"
24 | author = "Fraunhofer IPA"
25 |
26 | # The full version, including alpha/beta/rc tags
27 | release = squlearn_version
28 | version = squlearn_version
29 |
30 | # -- General configuration ---------------------------------------------------
31 |
32 | # Add any Sphinx extension module names here, as strings. They can be
33 | # extensions coming with Sphinx (named "sphinx.ext.*") or your custom
34 | # ones.
35 |
36 | extensions = [
37 | "sphinx.ext.autodoc",
38 | "sphinx.ext.autosummary",
39 | "sphinx.ext.intersphinx",
40 | "sphinx.ext.napoleon",
41 | "sphinxcontrib.spelling",
42 | "sphinx_sitemap",
43 | "matplotlib.sphinxext.plot_directive",
44 | "myst_parser",
45 | "nbsphinx",
46 | "nbsphinx_link",
47 | "jupyter_sphinx",
48 | ]
49 |
50 | source_suffix = {
51 | ".rst": "restructuredtext",
52 | ".md": "markdown",
53 | }
54 |
55 | autodoc_default_options = {"members": True, "inherited-members": True}
56 |
57 |
58 | # Skip property members --> They should be defined in Attributes
59 | def skip_property_member(app, what, name, obj, skip, options):
60 | if isinstance(obj, property):
61 | return True
62 |
63 |
64 | def setup(app):
65 | app.connect("autodoc-skip-member", skip_property_member)
66 |
67 |
68 | # Add any paths that contain templates here, relative to this directory.
69 | templates_path = ["_templates"]
70 |
71 | # List of patterns, relative to source directory, that match files and
72 | # directories to ignore when looking for source files.
73 | # This pattern also affects html_static_path and html_extra_path.
74 | exclude_patterns = ["_build", "Thumbs.db", ".DS_Store", "README.md", "**.ipynb_checkpoints"]
75 |
76 | # generate autosummary even if no references
77 | autosummary_generate = True
78 |
79 | # -- Options for HTML output -------------------------------------------------
80 |
81 | # The theme to use for HTML and HTML Help pages. See the documentation for
82 | # a list of builtin themes.
83 | #
84 | html_theme = "sphinx_rtd_theme"
85 |
86 | # Add any paths that contain custom static files (such as style sheets) here,
87 | # relative to this directory. They are copied after the builtin static files,
88 | # so a file named "default.css" will overwrite the builtin "default.css".
89 | html_static_path = ["_static"]
90 | html_logo = "_static/logo.png"
91 | html_favicon = "_static/favicon.png"
92 | html_theme_options = {
93 | "logo_only": True,
94 | "display_version": True,
95 | }
96 | html_css_files = [
97 | "css/custom.css",
98 | ]
99 |
100 | latex_engine = "xelatex"
101 | latex_elements = {
102 | "preamble": r"""
103 | \usepackage{braket}
104 | """,
105 | }
106 |
107 | # intersphinx
108 | intersphinx_mapping = {
109 | "pennylane": ("https://docs.pennylane.ai/en/stable/", None),
110 | "qiskit": ("https://docs.quantum.ibm.com/api/qiskit/", None),
111 | "qiskit-aer": ("https://qiskit.github.io/qiskit-aer/", None),
112 | "qiskit-ibm-runtime": ("https://docs.quantum.ibm.com/api/qiskit-ibm-runtime/", None),
113 | "scipy": ("https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/", None),
114 | "sklearn": ("https://scikit-learn.org/1.4/", None),
115 | }
116 |
117 | suppress_warnings = ["myst.header", "config.cache"]
118 |
119 | # base URL for sphinx_sitemap
120 | html_baseurl = "https://squlearn.github.io/"
121 | sitemap_url_scheme = "{link}"
122 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/examples/example_kernel_digit_classification.nblink:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "path": "../../examples/tutorials/kernel_digit_classification.ipynb",
3 | "extra-media": [
4 | "../../examples/tutorials/images"
5 | ]
6 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/examples/example_kernel_grid_search.nblink:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "path": "../../examples/tutorials/kernel_grid_search.ipynb"
3 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/examples/example_qnn_backend_mitigation.nblink:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "path": "../../examples/tutorials/qnn_backend_mitigation.ipynb",
3 | "extra-media": [
4 | "../../examples/tutorials/images"
5 | ]
6 | }
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/examples/example_qnn_ode_solver.nblink:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "path": "../../examples/tutorials/qnn_ode_solver.ipynb",
3 | "extra-media": [
4 | "../../examples/tutorials/images"
5 | ]
6 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/examples/example_quantum_bayesian_optimization.nblink:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "path": "../../examples/tutorials/quantum_bayesian_optimization.ipynb",
3 | "extra-media": [
4 | "../../examples/tutorials/images"
5 | ]
6 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/examples/examples_index.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _examples:
2 |
3 | Examples
4 | ========
5 |
6 | .. toctree::
7 | :maxdepth: 1
8 | :glob:
9 |
10 | example_kernel_digit_classification
11 | example_kernel_grid_search
12 | example_quantum_bayesian_optimization
13 | example_qnn_backend_mitigation
14 | example_qnn_ode_solver
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/index.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. sQUlearn documentation master file, created by
2 | sphinx-quickstart on Thu Apr 27 16:53:35 2023.
3 | You can adapt this file completely to your liking, but it should at least
4 | contain the root `toctree` directive.
5 |
6 | Welcome to the sQUlearn documentation!
7 | ======================================
8 |
9 | .. include:: ../README.md
10 | :parser: myst_parser.sphinx_
11 | :start-line: 4
12 |
13 | .. toctree::
14 | :maxdepth: 2
15 | :caption: Contents:
16 |
17 | install/install
18 | user_guide/user_guide_index
19 | modules/classes
20 | examples/examples_index
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/install/install.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _install:
2 |
3 | Installation
4 | ============
5 |
6 | Prerequisites
7 | -------------
8 |
9 | sQUlearn requires a recent python3 (>=3.9) installation.
10 | Additionally the following python packages are necessary: ::
11 |
12 | bayesian-optimization>=1.4.3,<2
13 | dill>=0.3.4
14 | mapomatic>=0.10.0
15 | networkx>=3.0
16 | numpy>=1.20
17 | pennylane>=0.34.0
18 | qiskit>=0.45.0
19 | qiskit-aer>=0.12.0
20 | qiskit-algorithms>=0.3.0
21 | qiskit-ibm-runtime>=0.18.0
22 | qiskit-machine-learning>=0.7.0
23 | scipy>=1.8.0
24 | scikit-learn>=1.2.0,<1.4.2
25 | tqdm>=4.1.0
26 |
27 | The packages are automatically installed when installing sQUlearn with pip.
28 |
29 | Stable Release
30 | --------------
31 |
32 | To install the stable release version of sQUlearn, run the following command:
33 |
34 | .. code-block:: bash
35 |
36 | pip install squlearn
37 |
38 |
39 | Bleeding-edge version
40 | ---------------------
41 |
42 | To install the latest master version:
43 |
44 | .. code-block:: bash
45 |
46 | pip install git+https://github.com/sQUlearn/squlearn.git
47 |
48 |
49 | Development version
50 | -------------------
51 |
52 | To install the latest development version:
53 |
54 | .. code-block:: bash
55 |
56 | pip install git+https://github.com/sQUlearn/squlearn.git@develop
57 |
58 |
59 |
60 | Installation with optional dependencies:
61 | ----------------------------------------
62 |
63 | There are several optional dependencies that can be installed with sQUlearn.
64 | To install sQUlearn with the dependencies usefull for development, run the following command:
65 |
66 | .. code-block:: bash
67 |
68 | pip install squlearn[dev]
69 |
70 | To install sQUlearn with the dependencies necessary to run all examples, run the following command:
71 |
72 | .. code-block:: bash
73 |
74 | pip install squlearn[examples]
75 |
76 | And to install sQUlearn with the dependencies necessary to build the documentation,
77 | run the following command:
78 |
79 | .. code-block:: bash
80 |
81 | pip install squlearn[docs]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/make.bat:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | @ECHO OFF
2 |
3 | pushd %~dp0
4 |
5 | REM Command file for Sphinx documentation
6 |
7 | if "%SPHINXBUILD%" == "" (
8 | set SPHINXBUILD=sphinx-build
9 | )
10 | set SOURCEDIR=.
11 | set MODDIR=.\modules\generated
12 | set BUILDDIR=_build
13 | set QISKIT_SETTINGS=%CD%\qiskit_settings.conf
14 |
15 | %SPHINXBUILD% >NUL 2>NUL
16 | if errorlevel 9009 (
17 | echo.
18 | echo.The 'sphinx-build' command was not found. Make sure you have Sphinx
19 | echo.installed, then set the SPHINXBUILD environment variable to point
20 | echo.to the full path of the 'sphinx-build' executable. Alternatively you
21 | echo.may add the Sphinx directory to PATH.
22 | echo.
23 | echo.If you don't have Sphinx installed, grab it from
24 | echo.https://www.sphinx-doc.org/
25 | exit /b 1
26 | )
27 |
28 | if "%1" == "" goto help
29 | if "%1" == "clean" goto clean
30 |
31 | %SPHINXBUILD% -M %1 %SOURCEDIR% %BUILDDIR% %SPHINXOPTS% %O%
32 | goto end
33 |
34 | :help
35 | %SPHINXBUILD% -M help %SOURCEDIR% %BUILDDIR% %SPHINXOPTS% %O%
36 | goto end
37 |
38 | :clean
39 | %SPHINXBUILD% -M clean %SOURCEDIR% %BUILDDIR% %SPHINXOPTS% %O%
40 | if exist %MODDIR% (
41 | echo Removing %MODDIR%
42 | @RD /S /Q %MODDIR%
43 | )
44 |
45 | :end
46 | popd
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/qiskit_settings.conf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [default]
2 | circuit_drawer = mpl
3 | circuit_mpl_style = clifford
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/spelling_wordlist.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Aer
2 | ansatz
3 | backend
4 | backends
5 | Broughton
6 | Chebyshev
7 | Cholesky
8 | CNOT
9 | cov
10 | Hadamard
11 | Hamiltonian
12 | Hamiltonians
13 | Hubregtsen
14 | hyperparameter
15 | hyperparameters
16 | Ising
17 | Laplacian
18 | Matern
19 | Mohseni
20 | multiclass
21 | ndarray
22 | np
23 | opflow
24 | parameterized
25 | Pauli
26 | Paulis
27 | pre
28 | prefactor
29 | preprocessing
30 | pretrained
31 | QFI
32 | Qiskit
33 | qubit
34 | qubits
35 | Rapp
36 | RBF
37 | regressors
38 | runtime
39 | Rx
40 | Rxx
41 | Ry
42 | Ryy
43 | Rz
44 | Rzx
45 | Rzz
46 | scikit
47 | scipy
48 | solvability
49 | squlearn
50 | sQUlearn
51 | transpilation
52 | transpile
53 | transpiled
54 | transpiler
55 | transpiling
56 | untrainability
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/user_guide/observables.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _user_guide_observables:
2 |
3 | ##################################
4 | Observables for expectation values
5 | ##################################
6 |
7 | .. currentmodule:: squlearn.observables
8 |
9 | Observables play a crucial role in computing the expectation value in conjunction with a
10 | wave function. Currently, observables constructed purely from the Pauli group
11 | :math:`\{\hat{X},\hat{Y},\hat{Z},\hat{I}\}` are supported. In the context of sQUlearn,
12 | observables are mandatory inputs for Quantum Neural Networks (QNNs) and can be
13 | employed in the Projected Quantum Kernel program.
14 | All operators follow the Base Class :class:`ObservableBase`. sQulearn features several
15 | predefined observables, but it is also possible to simply construct custom observables.
16 |
17 | Implemented observables.
18 | ----------------------------------
19 |
20 | The following predefined observables are available in the module :class:`squlearn.observables`:
21 |
22 | .. autosummary::
23 | :nosignatures:
24 |
25 | SinglePauli
26 | SummedPaulis
27 | SingleProbability
28 | SummedProbabilities
29 | IsingHamiltonian
30 | CustomObservable
31 |
32 | The observables are simply constructed by initializing the associated class.
33 |
34 | **Example: Summed Pauli observable**
35 |
36 | .. jupyter-execute::
37 |
38 | from squlearn.observables import SummedPaulis
39 |
40 | op = SummedPaulis(num_qubits=2)
41 | print(op)
42 |
43 | Custom observables
44 | --------------------------
45 |
46 |
47 | sQUlearn features several options to construct custom observables.
48 | With the class :class:`CustomObservable`, it is possible to construct observables from a string
49 | containing the letters of the Pauli matrices (``"X"``, ``"Y"``, ``"Z"``, ``"I"``).
50 | The resulting observable can be multiplied by a parameter by setting ``parameterized=True``.
51 | Furthermore, observables can be added by ``+`` or multiplied by ``*`` with each other.
52 | This allows the creation of arbitrary observables.
53 |
54 | **Example: Custom observable**
55 |
56 | .. jupyter-execute::
57 |
58 | from squlearn.observables import CustomObservable
59 |
60 | ob1 = CustomObservable(num_qubits=2, operator_string="IX",parameterized=True)
61 | ob2 = CustomObservable(num_qubits=2, operator_string="ZY",parameterized=True)
62 | added_ob = ob1 + ob2
63 | print("Added observable:\n",added_ob,"\n\n")
64 | squared_ob = added_ob*added_ob
65 | print("Squared observable:\n",squared_ob)
66 |
67 | **Example: More complex custom observable**
68 |
69 | It is also possible to construct more complex observables by supplying a list of strings
70 | containing the Pauli matrices. The observable is then constructed by adding the single observables
71 | together.
72 |
73 | .. jupyter-execute::
74 |
75 | from squlearn.observables import CustomObservable
76 |
77 | # It is also possible to add trainable parameters:
78 | ob = CustomObservable(num_qubits=4, operator_string=["ZIZZ", "XIXI"], parameterized=True)
79 | print("Custom observable with multiple operators:\n",ob)
80 |
81 |
82 | Note that in Qiskit, the qubits are counted from the right to the left as in the computational
83 | basis!
84 |
85 | Mapping observables to real qubits
86 | ------------------------------------
87 |
88 |
89 | When running on a backend, the number of physical qubits may change
90 | from the number of qubits the definition of the observable.
91 | If it is necessary, it is possible to adjust the observable to the physical qubits.
92 | This is achieved by providing a map from the qubits of the observable to the
93 | physical qubits utilized for example in the feature map via the function :meth:`set_qubit_map`.
94 | The map can be for example obtained in the transpiled encoding circuit.
95 |
96 | **Example: Use the mapping from the transpiled encoding circuit**
97 |
98 | .. jupyter-execute::
99 |
100 | from squlearn.encoding_circuit import ChebyshevRx,TranspiledEncodingCircuit
101 | from squlearn.observables import SummedPaulis
102 | from qiskit_ibm_runtime.fake_provider import FakeManilaV2
103 | fm = TranspiledEncodingCircuit(ChebyshevRx(3,1),backend=FakeManilaV2(),initial_layout=[0,1,4])
104 | ob = SummedPaulis(num_qubits=3, op_str="Z")
105 | print("Observable before mapping:\n",ob,"\n\n")
106 | ob.set_map(fm.qubit_map, fm.num_physical_qubits)
107 | print("Observable after mapping:\n",ob)
108 |
109 |
110 | Derivatives of the observable
111 | ----------------------------------------------
112 |
113 | .. currentmodule:: squlearn.observables.observable_derivatives
114 |
115 | In sQUlearn it is also possible to calculate derivatives of observables
116 | as for example needed during the training of the QNN.
117 | This is possible with the class :class:`ObservableDerivatives`.
118 | The derivatives are calculated with respect to the parameters of the observable.
119 |
120 |
121 | **Example: first-order derivatives of the Ising Hamiltonian**
122 |
123 | .. jupyter-execute::
124 |
125 | from squlearn.observables import IsingHamiltonian
126 | from squlearn.observables.observable_derivatives import ObservableDerivatives
127 | ob = IsingHamiltonian(num_qubits=3)
128 | print("Observable:\n", ob,"\n\n")
129 | print("Gradient of the observable:\n", ObservableDerivatives(ob).get_derivative("dop"))
130 |
131 |
132 | **Example: higher-order derivative of the cubed SummedPaulis observable**
133 |
134 | Furthermore, arbitrary derivatives can be computed by supplying a tuple, although the
135 | higher-order derivatives are zero for linear parameters.
136 | To achieve this, the function :meth:`ObservableDerivatives.get_derivative` can be used with a tuple
137 | of parameters :meth:`ObservableDerivatives.parameter_vector`.
138 |
139 | .. jupyter-execute::
140 |
141 | from squlearn.observables import SummedPaulis
142 | from squlearn.observables.observable_derivatives import ObservableDerivatives
143 |
144 | # Build cubed SummedPaulis observable
145 | op = SummedPaulis(num_qubits=2)
146 | op3 = op*op*op
147 | print("Cubed operator:\n",op3)
148 |
149 | # Get the Hessian from a tuple
150 | deriv = ObservableDerivatives(op3)
151 | print("Second-order derivative w.r.t. p[0]:\n",
152 | deriv.get_derivative((deriv.parameter_vector[0],deriv.parameter_vector[0])))
153 |
154 |
155 | **Example: Squared summed Pauli Observable**
156 |
157 | It is also possible to calculate the squared observable, which is needed for the
158 | calculation of the variance of the observable.
159 |
160 | .. jupyter-execute::
161 |
162 | from squlearn.observables import SummedPaulis
163 | from squlearn.observables.observable_derivatives import ObservableDerivatives
164 | op = SummedPaulis(num_qubits=3)
165 | print(ObservableDerivatives(op).get_operator_squared())
166 |
167 |
168 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/user_guide/user_guide_index.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. _user_guide:
2 |
3 | User Guide
4 | ============
5 |
6 | .. toctree::
7 | :maxdepth: 1
8 |
9 | executor
10 | observables
11 | encoding_circuits
12 | kernel_methods
13 | quantum_neural_networks
14 | quantum_reservoir_computing
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/tutorials/images/QNN_ode_workflow.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/f21f3ca4a4c90b95d4da763f08c1ff815cb5afdf/examples/tutorials/images/QNN_ode_workflow.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/tutorials/images/encoding_circuit.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/f21f3ca4a4c90b95d4da763f08c1ff815cb5afdf/examples/tutorials/images/encoding_circuit.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/tutorials/images/pipeline.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/f21f3ca4a4c90b95d4da763f08c1ff815cb5afdf/examples/tutorials/images/pipeline.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/tutorials/images/projected_quantum_kernel.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/f21f3ca4a4c90b95d4da763f08c1ff815cb5afdf/examples/tutorials/images/projected_quantum_kernel.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/tutorials/images/quantum_bo.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/f21f3ca4a4c90b95d4da763f08c1ff815cb5afdf/examples/tutorials/images/quantum_bo.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/install_lowest_dependencies.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """This script installs the package with the lowest dependencies."""
2 |
3 | import re
4 | import subprocess
5 | import sys
6 | from typing import List, Optional, Tuple
7 |
8 | import toml
9 |
10 | # Load the pyproject.toml
11 | pyproject = toml.load("pyproject.toml")
12 |
13 | # Extract dependencies
14 | dependencies: List[str] = pyproject.get("project", {}).get("dependencies", []) + pyproject.get(
15 | "project", {}
16 | ).get("optional-dependencies", {}).get("examples", [])
17 |
18 |
19 | # Function to get exactly the minimal specified version
20 | def get_lowest_version(dependency_string: str) -> str:
21 | """Get the lowest version of a dependency."""
22 | pattern = re.compile(r"([\w-]+)(?:>=(\d*(?:\.\d*(?:\.\d*)?)?))?")
23 | match = pattern.match(dependency_string)
24 | if match:
25 | groups: Tuple[Optional[str], Optional[str]] = match.groups()
26 | if groups[1]:
27 | return "==".join(groups)
28 | return groups[0]
29 | return dependency_string
30 |
31 |
32 | # Install the main package without dependencies
33 | subprocess.run([sys.executable, "-m", "pip", "install", ".", "--no-deps"], check=True)
34 |
35 | # Get the lowest version of pennylane
36 | PENNYLANE_VERSION = None
37 | for dependency in dependencies:
38 | if dependency.startswith("pennylane"):
39 | PENNYLANE_VERSION = get_lowest_version(dependency).split("==")[1]
40 | break
41 |
42 | dependencies = [get_lowest_version(dependency) for dependency in dependencies]
43 | if PENNYLANE_VERSION:
44 | dependencies.append(f"pennylane-lightning=={PENNYLANE_VERSION}")
45 | subprocess.run([sys.executable, "-m", "pip", "install"] + dependencies, check=True)
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/output.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/f21f3ca4a4c90b95d4da763f08c1ff815cb5afdf/output.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pyproject.toml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [build-system]
2 | requires = ["flit_core >=3.2,<4"]
3 | build-backend = "flit_core.buildapi"
4 |
5 | [project]
6 | name = "squlearn"
7 | readme = "README.md"
8 | authors = [
9 | {name = "David Kreplin", email = "david.kreplin@ipa.fraunhofer.de"},
10 | {name = "Moritz Willmann", email = "moritz.willmann@ipa.fraunhofer.de"},
11 | {name = "Jan Schnabel", email = "jan.schnabel@ipa.fraunhofer.de"},
12 | {name = "Frederic Rapp", email = "frederic.rapp@ipa.fraunhofer.de"},
13 | {name = "Manuel Hagelüken", email = "manuel.hagelueken@ipa.fraunhofer.de"},
14 | {name = "Marco Roth", email = "marco.roth@ipa.fraunhofer.de"},
15 | ]
16 | maintainers = [
17 | {name = "David Kreplin", email = "david.kreplin@ipa.fraunhofer.de"},
18 | {name = "Moritz Willmann", email = "moritz.willmann@ipa.fraunhofer.de"},
19 | ]
20 | license = {file = "LICENSE.txt"}
21 | classifiers = [
22 | "License :: OSI Approved :: Apache Software License",
23 | "Programming Language :: Python",
24 | "Programming Language :: Python :: 3",
25 | ]
26 | keywords = ["quantum", "machine learning", "qml"]
27 | dependencies = [
28 | "bayesian-optimization>=1.4.3,<2",
29 | "dill>=0.3.4",
30 | "mapomatic>=0.10.0",
31 | "networkx>=3.0",
32 | "numpy>=1.20",
33 | "pennylane>=0.34.0",
34 | "qiskit>=0.45.0,<2",
35 | "qiskit-aer>=0.12.0",
36 | "qiskit-algorithms>=0.3.0",
37 | "qiskit-ibm-runtime>=0.18.0",
38 | "qiskit-machine-learning>=0.7.0",
39 | "scipy>=1.8.0",
40 | "scikit-learn>=1.2.0",
41 | "tqdm>=4.1.0",
42 | ]
43 | requires-python = ">=3.9,<3.13"
44 | dynamic = ["version", "description"]
45 |
46 | [project.optional-dependencies]
47 | dev = [
48 | "black",
49 | "flit",
50 | "nbmake",
51 | "pylint",
52 | "pytest",
53 | ]
54 | examples = [
55 | "jupyter",
56 | "matplotlib>=3.5.1",
57 | "mlflow",
58 | "pandas",
59 | "pylatexenc>=2.10",
60 | "seaborn",
61 | "scikit-optimize",
62 | ]
63 | docs = [
64 | "ipykernel",
65 | "jupyter-sphinx",
66 | "matplotlib>=3.5.1",
67 | "myst-parser",
68 | "nbsphinx",
69 | "nbsphinx_link",
70 | "pylatexenc>=2.10",
71 | "sphinx",
72 | "sphinxcontrib-spelling",
73 | "sphinx-rtd-theme<3.0.0",
74 | "sphinx-sitemap",
75 | ]
76 |
77 | [project.urls]
78 | Homepage = "https://github.com/sQUlearn/squlearn"
79 |
80 | [tool.black]
81 | line-length=99
82 |
83 | [tool.pylint]
84 | max-line-length=99
85 | good-names=["X", "y", "i", "j"]
86 |
87 | [tool.pylint.main]
88 | extension-pkg-allow-list = [
89 | "numpy",
90 | ]
91 |
92 | [tool.pytest.ini_options]
93 | addopts = [
94 | "--import-mode=importlib",
95 | "--ignore=examples/tutorials/qnn_backend_mitigation.ipynb",
96 | "--ignore=examples/tutorials/qnn_ode_solver.ipynb",
97 | ]
98 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """A library for quantum machine learning following the scikit-learn standard."""
2 |
3 | from .util import Executor
4 | from . import observables, encoding_circuit, kernel, optimizers, qnn, util
5 |
6 | __version__ = "0.8.3"
7 |
8 | __all__ = [
9 | "Executor",
10 | "observables",
11 | "encoding_circuit",
12 | "kernel",
13 | "optimizers",
14 | "qnn",
15 | "util",
16 | ]
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/encoding_circuit/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .pruned_encoding_circuit import PrunedEncodingCircuit, automated_pruning, pruning_from_QFI
2 | from .layered_encoding_circuit import LayeredEncodingCircuit
3 | from .transpiled_encoding_circuit import TranspiledEncodingCircuit
4 | from .encoding_circuit_derivatives import EncodingCircuitDerivatives
5 | from .circuit_library.qcnn_encoding_circuit import QCNNEncodingCircuit
6 | from .circuit_library.yz_cx_encoding_circuit import YZ_CX_EncodingCircuit
7 | from .circuit_library.highdim_encoding_circuit import HighDimEncodingCircuit
8 | from .circuit_library.hubregtsen_encoding_circuit import HubregtsenEncodingCircuit
9 | from .circuit_library.chebyshev_tower import ChebyshevTower
10 | from .circuit_library.chebyshev_pqc import ChebyshevPQC
11 | from .circuit_library.multi_control_encoding_circuit import MultiControlEncodingCircuit
12 | from .circuit_library.chebyshev_rx import ChebyshevRx
13 | from .circuit_library.param_z_feature_map import ParamZFeatureMap
14 | from .circuit_library.qiskit_encoding_circuit import QiskitEncodingCircuit
15 | from .circuit_library.random_encoding_circuit import RandomEncodingCircuit
16 | from .circuit_library.random_layered_encoding_circuit import RandomLayeredEncodingCircuit
17 | from .circuit_library.kyriienko_nonlinear_encoding_circuit import KyriienkoEncodingCircuit
18 |
19 | __all__ = [
20 | "PrunedEncodingCircuit",
21 | "TranspiledEncodingCircuit",
22 | "EncodingCircuitDerivatives",
23 | "QCNNEncodingCircuit",
24 | "automated_pruning",
25 | "pruning_from_QFI",
26 | "LayeredEncodingCircuit",
27 | "YZ_CX_EncodingCircuit",
28 | "HighDimEncodingCircuit",
29 | "HubregtsenEncodingCircuit",
30 | "ChebyshevTower",
31 | "ChebyshevPQC",
32 | "MultiControlEncodingCircuit",
33 | "ChebyshevRx",
34 | "ParamZFeatureMap",
35 | "QiskitEncodingCircuit",
36 | "RandomEncodingCircuit",
37 | "RandomLayeredEncodingCircuit",
38 | "KyriienkoEncodingCircuit",
39 | ]
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/encoding_circuit/circuit_library/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/f21f3ca4a4c90b95d4da763f08c1ff815cb5afdf/src/squlearn/encoding_circuit/circuit_library/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/encoding_circuit/circuit_library/multi_control_encoding_circuit.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from typing import Union
3 |
4 | from qiskit.circuit import ParameterVector
5 | from qiskit.circuit import QuantumCircuit
6 |
7 | from ..encoding_circuit_base import EncodingCircuitBase
8 |
9 |
10 | class MultiControlEncodingCircuit(EncodingCircuitBase):
11 | """
12 | Encoding circuit with HZ encoding followed by controlled Rx, Ry Rz rotations.
13 |
14 | **Example for 4 qubits, a 2 dimensional feature vector and 1 layer:**
15 |
16 | .. plot::
17 |
18 | from squlearn.encoding_circuit import MultiControlEncodingCircuit
19 | pqc = MultiControlEncodingCircuit(4, 2, 1)
20 | pqc.draw(output="mpl", style={'fontsize':15,'subfontsize': 10})
21 | plt.tight_layout()
22 |
23 | The circuit is repeated for the number of layers.
24 | The circuit is closed by default, i.e. the last qubit is entangled with the first one.
25 | The encoding can be optionally repeated at the end to make the previous rotations not
26 | redundant in a fidelity kernel setting.
27 |
28 | Args:
29 | num_qubits (int): Number of qubits of the MultiControlEncodingCircuit encoding circuit
30 | num_features (int): Dimension of the feature vector
31 | num_layers (int): Number of layers (default: 1)
32 | closed (bool): If true, the last and the first qubit are entangled;
33 | not necessarily hardware efficient! (default: true)
34 | final_encoding (bool): If True, the encoding is repeated at the end (default: False)
35 | """
36 |
37 | def __init__(
38 | self,
39 | num_qubits: int,
40 | num_features: int,
41 | num_layers: int = 1,
42 | closed: bool = True,
43 | final_encoding=False,
44 | ) -> None:
45 | super().__init__(num_qubits, num_features)
46 |
47 | if self.num_qubits < 2:
48 | raise ValueError("MultiControlEncodingCircuit requires at least two qubits.")
49 |
50 | self.num_layers = num_layers
51 | self.closed = closed
52 | self.final_encoding = final_encoding
53 |
54 | @property
55 | def num_parameters(self) -> int:
56 | """The number of trainable parameters of the MultiControlEncodingCircuit encoding circuit."""
57 | num_param = 3 * (self.num_qubits - 1) * self.num_layers
58 | if self.closed:
59 | num_param += 3 * self.num_layers
60 | return num_param
61 |
62 | @property
63 | def parameter_bounds(self) -> np.ndarray:
64 | """The bounds of the trainable parameters of the MultiControlEncodingCircuit encoding circuit."""
65 | return np.array([[-2.0 * np.pi, 2.0 * np.pi]] * self.num_parameters)
66 |
67 | def get_params(self, deep: bool = True) -> dict:
68 | """
69 | Returns hyper-parameters and their values of the MultiControlEncodingCircuit encoding circuit
70 |
71 | Args:
72 | deep (bool): If True, also the parameters for
73 | contained objects are returned (default=True).
74 |
75 | Return:
76 | Dictionary with hyper-parameters and values.
77 | """
78 | params = super().get_params()
79 | params["num_layers"] = self.num_layers
80 | params["closed"] = self.closed
81 | params["final_encoding"] = self.final_encoding
82 | return params
83 |
84 | def get_circuit(
85 | self,
86 | features: Union[ParameterVector, np.ndarray],
87 | parameters: Union[ParameterVector, np.ndarray],
88 | ) -> QuantumCircuit:
89 | """
90 | Returns the circuit of the MultiControlEncodingCircuit encoding circuit
91 |
92 | Args:
93 | features (Union[ParameterVector,np.ndarray]): Input vector of the features
94 | from which the gate inputs are obtained.
95 | param_vec (Union[ParameterVector,np.ndarray]): Input vector of the parameters
96 | from which the gate inputs are obtained.
97 |
98 | Return:
99 | Returns the circuit in Qiskit's QuantumCircuit format
100 | """
101 |
102 | if self.num_qubits < 2:
103 | raise ValueError("MultiControlEncodingCircuit requires at least two qubits.")
104 |
105 | nfeature = len(features)
106 | nparam = len(parameters)
107 | QC = QuantumCircuit(self.num_qubits)
108 | index_offset = 0
109 | feature_offset = 0
110 |
111 | for layer in range(self.num_layers):
112 | # First ZZ-encoding circuit
113 | QC.h(range(self.num_qubits))
114 | for i in range(self.num_qubits):
115 | QC.rz(features[feature_offset % nfeature], i)
116 | feature_offset += 1
117 |
118 | if self.closed:
119 | istop = self.num_qubits
120 | else:
121 | istop = self.num_qubits - 1
122 |
123 | for i in range(0, istop, 2):
124 | QC.crx(parameters[index_offset % nparam], i, (i + 1) % self.num_qubits)
125 | index_offset += 1
126 | QC.cry(parameters[index_offset % nparam], i, (i + 1) % self.num_qubits)
127 | index_offset += 1
128 | QC.crz(parameters[index_offset % nparam], i, (i + 1) % self.num_qubits)
129 | index_offset += 1
130 |
131 | if self.num_qubits >= 2:
132 | if self.closed:
133 | istop = self.num_qubits
134 | else:
135 | istop = self.num_qubits - 1
136 |
137 | for i in range(1, istop, 2):
138 | QC.crx(parameters[index_offset % nparam], i, (i + 1) % self.num_qubits)
139 | index_offset += 1
140 | QC.cry(parameters[index_offset % nparam], i, (i + 1) % self.num_qubits)
141 | index_offset += 1
142 | QC.crz(parameters[index_offset % nparam], i, (i + 1) % self.num_qubits)
143 | index_offset += 1
144 |
145 | if self.final_encoding:
146 | for i in range(self.num_qubits):
147 | QC.rz(features[feature_offset % nfeature], i)
148 | feature_offset += 1
149 | return QC
150 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/encoding_circuit/circuit_library/param_z_feature_map.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from typing import Union
3 |
4 | from qiskit.circuit import QuantumCircuit
5 | from qiskit.circuit import ParameterVector
6 | from ..encoding_circuit_base import EncodingCircuitBase
7 |
8 |
9 | class ParamZFeatureMap(EncodingCircuitBase):
10 | """
11 | Parameterized Z feature map with optional CNOT gates between the default layers.
12 |
13 | This encoding circuit is based on Qiskit's :class:`qiskit.circuit.library.ZFeatureMap`.
14 |
15 | **Example for 4 qubits, a 2 dimensional feature vector and 2 layers with entangling:**
16 |
17 | .. plot::
18 |
19 | from squlearn.encoding_circuit import ParamZFeatureMap
20 | pqc = ParamZFeatureMap(4, 2, num_layers=2, entangling=True)
21 | plt = pqc.draw(output="mpl", style={'fontsize':15,'subfontsize': 10})
22 | plt.tight_layout()
23 |
24 | Args:
25 | num_qubits (int): Number of qubits
26 | num_features (int): Dimension of the feature vector
27 | num_layers (int): Number of layers of the encoding circuit
28 | entangling (bool): If true, entangling gates are added between the layers
29 |
30 | """
31 |
32 | def __init__(
33 | self, num_qubits: int, num_features: int, num_layers: int = 2, entangling: bool = False
34 | ) -> None:
35 | super().__init__(num_qubits, num_features)
36 | self._num_layers = num_layers
37 | self._entangling = entangling
38 |
39 | @property
40 | def num_parameters(self) -> int:
41 | """The number of trainable parameters of the encoding circuit."""
42 | return max(self._num_qubits, self._num_features) * self._num_layers
43 |
44 | def get_params(self, deep: bool = True) -> dict:
45 | """
46 | Returns hyper-parameters and their values of the parameterized Z feature map.
47 |
48 | Args:
49 | deep (bool): If True, also the parameters for
50 | contained objects are returned (default=True).
51 |
52 | Return:
53 | Dictionary with hyper-parameters and values.
54 | """
55 | params = super().get_params()
56 | params["num_layers"] = self._num_layers
57 | params["entangling"] = self._entangling
58 | return params
59 |
60 | @property
61 | def num_layers(self) -> int:
62 | """The number of layers of the encoding circuit."""
63 | return self._num_layers
64 |
65 | def get_circuit(
66 | self,
67 | features: Union[ParameterVector, np.ndarray],
68 | parameters: Union[ParameterVector, np.ndarray],
69 | ) -> QuantumCircuit:
70 | """
71 | Returns the circuit of the parameterized Z feature map.
72 |
73 | Args:
74 | features (Union[ParameterVector,np.ndarray]): Input vector of the features
75 | from which the gate inputs are obtained.
76 | param_vec (Union[ParameterVector,np.ndarray]): Input vector of the parameters
77 | from which the gate inputs are obtained.
78 |
79 | Return:
80 | The circuit of the parameterized Z feature map in the form of a QuantumCircuit
81 | """
82 |
83 | num_features = len(features)
84 | num_param = len(parameters)
85 |
86 | circuit = QuantumCircuit(self._num_qubits)
87 | index_offset = 0
88 | for _ in range(self._num_layers):
89 | for i in range(max(self._num_qubits, self._num_features)):
90 | if i < self._num_qubits:
91 | circuit.h(i)
92 | circuit.p(
93 | parameters[index_offset % num_param] * features[i % num_features],
94 | i % self._num_qubits,
95 | )
96 | index_offset += 1
97 |
98 | if self._entangling:
99 | if self._num_layers % 2 == 0:
100 | for j in range(self._num_qubits - 1):
101 | circuit.cx(j, j + 1)
102 | else:
103 | for j in range(1, self._num_qubits - 1, 2):
104 | circuit.cx(j, j + 1)
105 |
106 | return circuit
107 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/encoding_circuit/circuit_library/yz_cx_encoding_circuit.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from typing import Union
3 | from qiskit.circuit import QuantumCircuit
4 | from qiskit.circuit import ParameterVector
5 |
6 | from ..encoding_circuit_base import EncodingCircuitBase
7 |
8 |
9 | class YZ_CX_EncodingCircuit(EncodingCircuitBase):
10 | """
11 | Creates the YZ-CX Encoding Circuit from reference [1].
12 |
13 | **Example for 4 qubits, a 4 dimensional feature vector, 2 layers and c = 2.0:**
14 |
15 | .. plot::
16 |
17 | from squlearn.encoding_circuit import YZ_CX_EncodingCircuit
18 | pqc = YZ_CX_EncodingCircuit(4, 4, 2, c=2.0)
19 | plt = pqc.draw(output="mpl", style={'fontsize':15,'subfontsize': 10})
20 | plt.tight_layout()
21 |
22 | One combination of Ry and Rz is considered as a single layer.
23 |
24 | Args:
25 | num_qubits (int): Number of qubits of the YZ-CX Encoding Circuit encoding circuit
26 | num_features (int): Dimension of the feature vector
27 | num_layers (int): Number of layers (default: 1)
28 | c (float): Prefactor :math:`c` for rescaling the data (default: 1.0)
29 |
30 | References
31 | ----------
32 | [1]: T. Haug, C. N. Self and M. S. Kim, "Quantum machine learning of large datasets using
33 | randomized measurements", `arxiv:2108.01039v3 (2021). `_
34 | """
35 |
36 | def __init__(
37 | self,
38 | num_qubits: int,
39 | num_features: int,
40 | num_layers: int = 1,
41 | closed: bool = True,
42 | c: float = 1.0,
43 | ) -> None:
44 | super().__init__(num_qubits, num_features)
45 | self.closed = closed
46 |
47 | self._num_layers = num_layers
48 | self._c = c
49 |
50 | @property
51 | def num_parameters(self) -> int:
52 | """The number of trainable parameters of the YZ-CX Encoding Circuit encoding circuit."""
53 | return 2 * self.num_qubits * self._num_layers
54 |
55 | @property
56 | def parameter_bounds(self) -> np.ndarray:
57 | """The bounds of the trainable parameters of the YZ-CX Encoding Circuit encoding circuit."""
58 | return np.array([[-np.pi, np.pi]] * self.num_parameters)
59 |
60 | @property
61 | def num_layers(self) -> int:
62 | """The number of layers of the YZ-CX Encoding Circuit encoding circuit."""
63 | return self._num_layers
64 |
65 | @property
66 | def c(self) -> int:
67 | """The prefactor :math:`c` of the YZ-CX Encoding Circuit encoding circuit."""
68 | return self._c
69 |
70 | def get_params(self, deep: bool = True) -> dict:
71 | """
72 | Returns hyper-parameters and their values of the YZ-CX Encoding Circuit encoding circuit
73 |
74 | Args:
75 | deep (bool): If True, also the parameters for
76 | contained objects are returned (default=True).
77 |
78 | Return:
79 | Dictionary with hyper-parameters and values.
80 | """
81 | params = super().get_params()
82 | params["num_layers"] = self._num_layers
83 | params["c"] = self._c
84 | return params
85 |
86 | def get_circuit(
87 | self,
88 | features: Union[ParameterVector, np.ndarray],
89 | parameters: Union[ParameterVector, np.ndarray],
90 | ) -> QuantumCircuit:
91 | """
92 | Return the circuit of the YZ-CX encoding circuit.
93 |
94 | Args:
95 | features (Union[ParameterVector,np.ndarray]): Input vector of the features
96 | from which the gate inputs are obtained.
97 | param_vec (Union[ParameterVector,np.ndarray]): Input vector of the parameters
98 | from which the gate inputs are obtained.
99 |
100 | Return:
101 | Returns the circuit in qiskit format.
102 | """
103 |
104 | nfeature = len(features)
105 | nparam = len(parameters)
106 |
107 | # Creates the layers of the encoding circuit
108 | QC = QuantumCircuit(self.num_qubits)
109 | index_offset = 0
110 | feature_offset = 0
111 | for layer in range(self.num_layers):
112 | for i in range(self.num_qubits):
113 | QC.ry(
114 | parameters[index_offset % nparam]
115 | + self.c * features[feature_offset % nfeature],
116 | i,
117 | )
118 | index_offset += 1
119 | QC.rz(
120 | parameters[index_offset % nparam]
121 | + self.c * features[feature_offset % nfeature],
122 | i,
123 | )
124 | index_offset += 1
125 | feature_offset += 1
126 | # Entangling layer depends on odd or even layer
127 | if self.num_qubits >= 2:
128 | for i in range(layer % 2, self.num_qubits + self.closed - 1, 2):
129 | QC.cx(i, (i + 1) % self.num_qubits)
130 | return QC
131 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/kernel/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .lowlevel_kernel import FidelityKernel, ProjectedQuantumKernel, KernelOptimizer
2 |
3 | from .qgpr import QGPR
4 | from .qgpc import QGPC
5 | from .qkrr import QKRR
6 | from .qsvr import QSVR
7 | from .qsvc import QSVC
8 |
9 | __all__ = [
10 | "FidelityKernel",
11 | "ProjectedQuantumKernel",
12 | "KernelOptimizer",
13 | "QGPC",
14 | "QGPR",
15 | "QKRR",
16 | "QSVR",
17 | "QSVC",
18 | ]
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/kernel/loss/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .negative_log_likelihood import NLL
2 | from .target_alignment import TargetAlignment
3 |
4 | __all__ = ["NLL", "TargetAlignment"]
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/kernel/loss/kernel_loss_base.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
3 |
4 | from ..lowlevel_kernel.kernel_matrix_base import KernelMatrixBase
5 |
6 |
7 | class KernelLossBase(ABC):
8 | """Empty parent class for a kernel loss function."""
9 |
10 | def __init__(self) -> None:
11 | self._quantum_kernel = None
12 |
13 | def set_quantum_kernel(self, quantum_kernel: KernelMatrixBase) -> None:
14 | """Set the quantum kernel matrix to be used in the loss.
15 |
16 | Args:
17 | quantum_kernel (KernelMatrixBase): The quantum kernel matrix to be used in the loss.
18 | """
19 | self._quantum_kernel = quantum_kernel
20 |
21 | @abstractmethod
22 | def compute(
23 | self,
24 | quantum_kernel: KernelMatrixBase,
25 | parameter_values: np.array,
26 | data: np.ndarray,
27 | labels: np.ndarray,
28 | ) -> float:
29 | """Compute the target alignment loss.
30 |
31 | Args:
32 | quantum_kernel (KernelMatrixBase): The quantum kernel matrix to be used in the loss.
33 | parameter_values (np.ndarray): The parameter values for the variational quantum
34 | kernel parameters.
35 | data (np.ndarray): The training data to be used for the kernel matrix.
36 | labels (np.ndarray): The training labels.
37 |
38 | Returns:
39 | float: The loss value.
40 | """
41 | raise NotImplementedError
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/kernel/loss/negative_log_likelihood.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Negative log likelihood loss function"""
2 |
3 | import scipy
4 | import numpy as np
5 |
6 | from typing import Sequence
7 | from .kernel_loss_base import KernelLossBase
8 | from ..lowlevel_kernel.kernel_matrix_base import KernelMatrixBase
9 |
10 |
11 | class NLL(KernelLossBase):
12 | r"""
13 | Negative log likelihood loss function.
14 | This class can be used to compute the negative log likelihood loss function
15 | for a given quantum kernel
16 | :math:`K_{\theta}` with variational parameters :math:`\theta`.
17 | The definition of the function is taken from Equation 5.8 Chapter 5.4 of Ref. [1].
18 |
19 | The log-likelihood function is defined as:
20 |
21 | .. math::
22 |
23 | L(\theta) = -\frac{1}{2} log(|K_{\theta} + \sigmaI|)-\frac{1}{2} y^{T}(K_{\theta}
24 | + \sigmaI)^{-1}y-\frac{n}{2} log(2\pi)
25 |
26 | Args:
27 | sigma: (float), default=0.0: Hyperparameter for the regularization strength.
28 |
29 | References
30 | ----------
31 | [1]: `Carl E. Rasmussen and Christopher K.I. Williams,
32 | "Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning",
33 | MIT Press 2006 `_
34 |
35 | Methods:
36 | --------
37 | """
38 |
39 | def __init__(self, sigma=0.0):
40 | super().__init__()
41 | self._sigma = sigma
42 |
43 | def compute(
44 | self,
45 | parameter_values: np.ndarray,
46 | data: np.ndarray,
47 | labels: np.ndarray,
48 | ) -> float:
49 | """Compute the negative log likelihood loss function.
50 |
51 | Args:
52 | parameter_values (np.ndarray): The parameter values for the variational quantum
53 | kernel parameters.
54 | data (np.ndarray): The training data to be used for the kernel matrix.
55 | labels (np.ndarray): The training labels.
56 |
57 | Returns:
58 | float: The negative log likelihood loss value.
59 | """
60 |
61 | if self._quantum_kernel is None:
62 | raise ValueError(
63 | "Quantum kernel is not set, please set the quantum kernel with set_quantum_kernel method"
64 | )
65 |
66 | # Bind training parameters
67 | self._quantum_kernel.assign_parameters(parameter_values)
68 |
69 | # get estimated kernel matrix
70 | kmatrix = self._quantum_kernel.evaluate(data)
71 | kmatrix = kmatrix + self._sigma * np.eye(kmatrix.shape[0])
72 |
73 | # Cholesky decomposition since numerically more stable
74 | L = scipy.linalg.cholesky(kmatrix, lower=True)
75 | S1 = scipy.linalg.solve_triangular(L, labels, lower=True)
76 | S2 = scipy.linalg.solve_triangular(L.T, S1, lower=False)
77 | neg_log_lh = (
78 | np.sum(np.log(np.diagonal(L)))
79 | + 0.5 * labels.T @ S2
80 | + 0.5 * len(data) * np.log(2.0 * np.pi)
81 | )
82 | neg_log_lh = neg_log_lh.reshape(-1)
83 |
84 | return neg_log_lh
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/kernel/loss/target_alignment.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Target alignment loss function for kernel matrices."""
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 |
5 | from .kernel_loss_base import KernelLossBase
6 | from ..lowlevel_kernel.kernel_matrix_base import KernelMatrixBase
7 |
8 |
9 | class TargetAlignment(KernelLossBase):
10 | r"""
11 | Target alignment loss function.
12 | This class can be used to compute the target alignment for a given quantum kernel
13 | :math:`K_{\theta}` with variational parameters :math:`\theta`.
14 | The definition of the function is taken from Equation (27,28) of [1].
15 | The target alignment loss is defined as:
16 |
17 | .. math::
18 |
19 | TA(K_{\theta}) =
20 | \frac{\\um_{i,j} K_{\theta}(x_i, x_j) y_i y_j}
21 | {\sqrt{\sum_{i,j} K_{\theta}(x_i, x_j)^2 \sum_{i,j} y_i^2 y_j^2}}
22 |
23 | Args:
24 | rescale_class_labels (bool): Whether to rescale the class labels to -1 and 1
25 | (default=True).
26 |
27 | References
28 | -----------
29 | [1]: T. Hubregtsen et al.,
30 | "Training Quantum Embedding Kernels on Near-Term Quantum Computers",
31 | `arXiv:2105.02276v1 (2021) `_.
32 |
33 | Methods:
34 | --------
35 | """
36 |
37 | def __init__(self, rescale_class_labels=True) -> None:
38 | """ """
39 | super().__init__()
40 | self._rescale_class_labels = rescale_class_labels
41 |
42 | def compute(
43 | self,
44 | parameter_values: np.ndarray,
45 | data: np.ndarray,
46 | labels: np.ndarray,
47 | ) -> float:
48 | """Compute the target alignment loss.
49 |
50 | Args:
51 | parameter_values (np.ndarray): The parameter values for the variational quantum kernel
52 | parameters.
53 | data (np.ndarray): The training data to be used for the kernel matrix.
54 | labels (np.ndarray): The labels of the training data.
55 |
56 | Returns:
57 | float: The negative target alignment.
58 | """
59 |
60 | if self._quantum_kernel is None:
61 | raise ValueError(
62 | "Quantum kernel is not set, please set the quantum kernel with set_quantum_kernel method"
63 | )
64 |
65 | # Bind training parameters
66 | self._quantum_kernel.assign_parameters(parameter_values)
67 |
68 | # Get estimated kernel matrix
69 | kmatrix = self._quantum_kernel.evaluate(data)
70 | if self._rescale_class_labels:
71 | nplus = np.count_nonzero(np.array(labels) == 1)
72 | nminus = len(labels) - nplus
73 | _Y = np.array([y / nplus if y == 1 else y / nminus for y in labels])
74 | else:
75 | _Y = np.array(labels)
76 |
77 | T = np.outer(_Y, _Y)
78 | inner_product = np.sum(kmatrix * T)
79 | norm = np.sqrt(np.sum(kmatrix * kmatrix) * np.sum(T * T))
80 | alignment = inner_product / norm
81 | return -alignment
82 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/kernel/lowlevel_kernel/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .fidelity_kernel import FidelityKernel
2 | from .projected_quantum_kernel import ProjectedQuantumKernel
3 | from .kernel_optimizer import KernelOptimizer
4 |
5 | __all__ = ["FidelityKernel", "ProjectedQuantumKernel", "KernelOptimizer"]
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/kernel/lowlevel_kernel/kernel_optimizer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Quantum Kernel Optimizer"""
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 | from functools import partial
5 | from typing import Optional, Sequence
6 |
7 | from .kernel_matrix_base import KernelMatrixBase
8 | from ..loss.kernel_loss_base import KernelLossBase
9 | from ...optimizers.optimizer_base import OptimizerBase
10 |
11 |
12 | class KernelOptimizer(KernelMatrixBase):
13 | """
14 | Quantum kernel optimizer.
15 | This class can be used to optimize the variational parameters of a quantum kernel.
16 |
17 | Args:
18 | loss (KernelLossBase): The loss function to be minimized.
19 | optimizer (OptimizerBase): The optimizer to be used.
20 | quantum_kernel (KernelMatrixBase): The quantum kernel to be optimized.
21 | initial_parameters (Optional[Sequence[float]]): Initial parameters for the optimizer.
22 | """
23 |
24 | def __init__(
25 | self,
26 | quantum_kernel: KernelMatrixBase,
27 | loss: KernelLossBase = None,
28 | optimizer: OptimizerBase = None,
29 | initial_parameters: Optional[Sequence[float]] = None,
30 | ) -> None:
31 | super().__init__(
32 | encoding_circuit=quantum_kernel.encoding_circuit,
33 | executor=quantum_kernel._executor,
34 | initial_parameters=initial_parameters,
35 | parameter_seed=quantum_kernel._parameter_seed,
36 | regularization=quantum_kernel._regularization,
37 | )
38 | self._quantum_kernel = quantum_kernel
39 | self._loss = loss
40 | self._optimizer = optimizer
41 | self._initial_parameters = (
42 | initial_parameters
43 | if initial_parameters is not None
44 | else self._quantum_kernel.parameters
45 | )
46 | self._optimal_parameters = None
47 | self._is_trainable = True
48 | self._is_fitted = False
49 |
50 | self._loss.set_quantum_kernel(self._quantum_kernel)
51 |
52 | @property
53 | def is_fitted(self) -> bool:
54 | """Returns whether the quantum kernel has been fitted."""
55 | return self._is_fitted
56 |
57 | def run_optimization(self, X: np.ndarray, y: np.ndarray = None):
58 | """Run the optimization and return the result.
59 |
60 | Args:
61 | X (np.ndarray): The input data.
62 | y (np.ndarray): The labels.
63 |
64 | Returns:
65 | OptimizeResult: The optimization result.
66 | """
67 |
68 | if self._is_fitted:
69 | return None
70 |
71 | if self._quantum_kernel.num_parameters == 0:
72 | return None
73 |
74 | # Perform kernel optimization
75 | loss_function = partial(self._loss.compute, data=X, labels=y)
76 | opt_result = self._optimizer.minimize(fun=loss_function, x0=self._initial_parameters)
77 | self._optimal_parameters = opt_result.x
78 |
79 | # Assign optimal parameters to the quantum kernel
80 | self._quantum_kernel.assign_parameters(self._optimal_parameters)
81 |
82 | self._is_fitted = True
83 |
84 | return opt_result
85 |
86 | def assign_parameters(self, parameters: np.ndarray):
87 | """Set the training parameters of the encoding circuit to numerical values
88 |
89 | Args:
90 | parameters (np.ndarray): Array containing numerical values to be assigned to
91 | the trainable parameters of the encoding circuit
92 | """
93 | self._is_fitted = False
94 | self._quantum_kernel.assign_parameters(parameters)
95 | self._initial_parameters = parameters
96 |
97 | def evaluate(self, x: np.ndarray, y: np.ndarray = None) -> np.ndarray:
98 | """Evaluate the kernel matrix using the current parameters.
99 |
100 | Args:
101 | x (np.ndarray): Vector of training or test data.
102 | y (np.ndarray, optional): Vector of training or test data.
103 |
104 | Returns:
105 | np.ndarray: The evaluated kernel matrix.
106 | """
107 | return self._quantum_kernel.evaluate(x, y)
108 |
109 | def get_optimal_parameters(self) -> np.ndarray:
110 | """Get the optimal parameters.
111 |
112 | Returns:
113 | np.ndarray: The optimal parameters.
114 | """
115 | return self._optimal_parameters
116 |
117 | def set_params(self, **params):
118 | """Sets value of the kernel optimizer hyper-parameters.
119 |
120 | Args:
121 | params: Hyper-parameters and their values, e.g. ``num_qubits=2``
122 | """
123 |
124 | # Create dictionary of valid parameters
125 | valid_params = self.get_params(deep=True).keys()
126 | for key in params.keys():
127 | # Check if parameter is valid
128 | if key not in valid_params:
129 | raise ValueError(
130 | f"Invalid parameter {key!r}. "
131 | f"Valid parameters are {sorted(valid_params)!r}."
132 | )
133 |
134 | if "quantum_kernel" in params:
135 | self._quantum_kernel = params["quantum_kernel"]
136 | self._is_fitted = False
137 | if "loss" in params:
138 | self._loss = params["loss"]
139 | self._is_fitted = False
140 | if "optimizer" in params:
141 | self._optimizer = params["optimizer"]
142 | self._is_fitted = False
143 | if "initial_parameters" in params:
144 | self._initial_parameters = params["initial_parameters"]
145 | self._is_fitted = False
146 |
147 | # Set parameters of the Quantum Kernel and its underlying objects
148 | quantum_kernel_params = self._quantum_kernel.get_params().keys() & params.keys()
149 | if quantum_kernel_params:
150 | self._quantum_kernel.set_params(**{key: params[key] for key in quantum_kernel_params})
151 | self._is_fitted = False
152 |
153 | return self
154 |
155 | def get_params(self, deep=True) -> dict:
156 | """Returns hyper-parameters and their values of the fidelity kernel.
157 |
158 | Args:
159 | deep (bool): If True, also the parameters for
160 | contained objects are returned (default=True).
161 |
162 | Return:
163 | Dictionary with hyper-parameters and values.
164 | """
165 | params = {}
166 | params["quantum_kernel"] = self._quantum_kernel
167 | params["loss"] = self._loss
168 | params["optimizer"] = self._optimizer
169 | params["initial_parameters"] = self._initial_parameters
170 |
171 | if deep:
172 | params.update(self._quantum_kernel.get_params(deep=deep))
173 |
174 | return params
175 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/kernel/lowlevel_kernel/kernel_util.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # kernel util
2 | import numpy as np
3 |
4 | from sklearn.gaussian_process.kernels import Kernel
5 |
6 | from .kernel_matrix_base import KernelMatrixBase
7 |
8 |
9 | def kernel_wrapper(kernel_matrix: KernelMatrixBase):
10 | """
11 | Wrapper for sQUlearn's KernelMatrixBase to scikit-learn kernel objects.
12 |
13 | Args:
14 | kernel_matrix (KernelMatrixBase) :
15 | Quantum kernel matrix which is to be wrapped into scikit-learn kernel
16 | """
17 |
18 | class CustomKernel(Kernel):
19 | def __init__(self, kernel_matrix: KernelMatrixBase):
20 | self.kernel_matrix = kernel_matrix
21 | super().__init__()
22 |
23 | def __call__(self, X, Y=None, eval_gradient=False):
24 | if Y is None:
25 | Y = X
26 | kernel_matrix = self.kernel_matrix.evaluate(X, Y)
27 | if eval_gradient:
28 | raise NotImplementedError("Gradient not yet implemented for this kernel.")
29 | else:
30 | return kernel_matrix
31 |
32 | def diag(self, X):
33 | return np.diag(self.kernel_matrix.evaluate(X))
34 |
35 | @property
36 | def requires_vector_input(self):
37 | return True
38 |
39 | def is_stationary(self):
40 | return self.kernel_matrix.is_stationary()
41 |
42 | return CustomKernel(kernel_matrix)
43 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/kernel/lowlevel_kernel/regularization.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import scipy
3 |
4 |
5 | def thresholding_regularization(gram_matrix):
6 | """
7 | Thresholding regularization method of a Gram matrix (full or training kernel matrix)
8 | according to this `paper `_ to recover positive
9 | semi-definiteness. This method only changes the negative eigenvalues of the matrix by
10 | setting them to zero. This is done via a full eigenvalue decomposition, adjustment of
11 | the negative eigenvalues and composition of the adjusted spectrum and the original
12 | eigenvectors:
13 |
14 | .. math::
15 | D = V^T A V
16 | D'_{ij} = \text{max}\lbrace D_{ij},0 \rbrace
17 | R-THR(A) = V D' V^T
18 |
19 | This approach is equivalent to finding the positive semi-definite matrix closest to A
20 | in any unitarily invariant norm.
21 |
22 | Args:
23 | gram_matrix (np.ndarray) :
24 | Gram matrix.
25 | """
26 | evals, evecs = scipy.linalg.eig(gram_matrix)
27 | reconstruction = evecs @ np.diag(evals.clip(min=0)) @ evecs.T
28 | return np.real(reconstruction)
29 |
30 |
31 | # deprecated regularization technique
32 | def tikhonov_regularization(gram_matrix):
33 | """
34 | Tikhonov regularization method to recover positive semi-definiteness of a Gram matrix.
35 | In this method the spectrum of the matrix is displaced by its smallest eigenvalue
36 | :math:`\sigma_{min}` if it is negative, by subtracting it from all eigenvalues or
37 | equivalently from the diagonal.
38 |
39 | Args:
40 | gram_matrix (np.ndarray) :
41 | Gram matrix.
42 | """
43 | evals = scipy.linalg.eigvals(gram_matrix)
44 | shift = np.min(np.real(evals))
45 | if shift < 0:
46 | gram_matrix -= (shift - 1e-14) * np.identity(gram_matrix.shape[0])
47 | return gram_matrix
48 |
49 |
50 | def regularize_full_kernel(K_train, K_testtrain, K_test):
51 | """
52 | Built full Gram matrix from training-, test-train- and test-test kernel matrices
53 | and the regularize full Gram matrix using the `regularize_kernel()` method.
54 |
55 | Args:
56 | K_train (np.ndarray) :
57 | Training kernel matrix of shape (n_train, n_train)
58 | K_testtrain (np.ndarray) :
59 | Test-Train kernel matrix of shape (n_test, n_train)
60 | K_test (np.ndarray) :
61 | Test kernel matrix of shape (n_test, n_test)
62 | """
63 | gram_matrix_total = np.block([[K_train, K_testtrain.T], [K_testtrain, K_test]])
64 | reconstruction = thresholding_regularization(gram_matrix_total)
65 |
66 | K_train = reconstruction[: K_train.shape[0], : K_train.shape[1]]
67 | K_testtrain = reconstruction[K_train.shape[0] :, : K_testtrain.shape[1]]
68 | K_test = reconstruction[-K_test.shape[0] :, -K_test.shape[1] :]
69 |
70 | return K_train, K_testtrain, K_test
71 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/kernel/qgpc.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Quantum Gaussian Process Classification"""
2 |
3 | from sklearn.gaussian_process import GaussianProcessClassifier
4 |
5 | from .lowlevel_kernel.kernel_matrix_base import KernelMatrixBase
6 | from .lowlevel_kernel.kernel_util import kernel_wrapper
7 |
8 |
9 | class QGPC(GaussianProcessClassifier):
10 | """
11 | Quantum Gaussian process classification (QGPC), that extends the scikit-learn
12 | `sklearn.gaussian_process.GaussianProcessClassifier
13 | `_.
14 | GaussianProcessClassifier class
15 | to use a quantum kernel.
16 |
17 | This class shows how to use a quantum kernel for QGPC. The class inherits its methods
18 | like ``fit`` and ``predict`` from scikit-learn, see the example below.
19 | Read more in the
20 | `scikit-learn user guide
21 | `_.
22 | Additional arguments can be set via ``**kwargs``.
23 |
24 | Args:
25 | quantum_kernel (Union[KernelMatrixBase, str]): The quantum kernel matrix to be used for the GP
26 | (either a fidelity quantum kernel (FQK)
27 | or projected quantum kernel (PQK) must be provided)
28 | **kwargs: Keyword arguments for the quantum kernel matrix, possible arguments can be obtained
29 | by calling ``get_params()``. Can be used to set for example the number of qubits
30 | (``num_qubits=``), or (if supported) the number of layers (``num_layers=``)
31 | of the underlying encoding circuit.
32 |
33 | See Also
34 | --------
35 | squlearn.kernel.QSVC : Quantum Support Vector classification.
36 |
37 | **Example**
38 |
39 | .. code-block::
40 |
41 | from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
42 | from squlearn import Executor
43 | from squlearn.encoding_circuit import HubregtsenEncodingCircuit
44 | from squlearn.kernel.lowlevel_kernel import FidelityKernel
45 | from squlearn.kernel import QGPC
46 | X, y = load_iris(return_X_y=True)
47 |
48 | enc_circ = HubregtsenEncodingCircuit(num_qubits=X.shape[1], num_features=X.shape[1], num_layers=2)
49 | q_kernel = FidelityKernel(encoding_circuit=enc_circ, executor=Executor())
50 | q_kernel.assign_parameters(np.random.rand(enc_circ.num_parameters))
51 | qgpc_ansatz = QGPC(quantum_kernel=q_kernel)
52 | qgpc_ansatz.fit(X, y)
53 | qgpc_ansatz.score(X, y)
54 | 0.98...
55 | qgpc_ansatz.predict_proba(X[:2,:])
56 | array([[0.85643716, 0.07037611, 0.07318673],
57 | [0.80314475, 0.09988938, 0.09696586]])
58 |
59 | Methods:
60 | --------
61 | """
62 |
63 | def __init__(self, quantum_kernel: KernelMatrixBase, **kwargs) -> None:
64 | self._quantum_kernel = quantum_kernel
65 |
66 | # Apply kwargs to set_params of quantum kernel
67 |
68 | print("self.quantum_kernel", self.quantum_kernel)
69 | print("kwargs", kwargs)
70 |
71 | quantum_kernel_update_params = self.quantum_kernel.get_params().keys() & kwargs.keys()
72 | if quantum_kernel_update_params:
73 | self.quantum_kernel.set_params(
74 | **{key: kwargs[key] for key in quantum_kernel_update_params}
75 | )
76 | # remove quantum_kernel_kwargs for SVR initialization
77 | for key in quantum_kernel_update_params:
78 | kwargs.pop(key, None)
79 |
80 | super().__init__(**kwargs)
81 | self.kernel = kernel_wrapper(self._quantum_kernel)
82 |
83 | @classmethod
84 | def _get_param_names(cls):
85 | names = GaussianProcessClassifier._get_param_names()
86 | names.remove("kernel")
87 | names.remove("warm_start")
88 | return names
89 |
90 | def fit(self, X, y):
91 | """Fit Gaussian process classification model.
92 |
93 | Args:
94 | X : array-like of shape (n_samples, n_features) or list of object
95 | Feature vectors or other representations of training data.
96 |
97 | y : array-like of shape (n_samples,)
98 | Target values, must be binary.
99 |
100 | Return:
101 | Returns an instance of self.
102 | """
103 | if self._quantum_kernel.is_trainable:
104 | self._quantum_kernel.run_optimization(X, y)
105 | return super().fit(X, y)
106 |
107 | def get_params(self, deep: bool = True) -> dict:
108 | """
109 | Returns hyper-parameters and their values of the QGPC class.
110 |
111 | Args:
112 | deep (bool): If True, also the parameters for
113 | contained objects are returned (default=True).
114 |
115 | Return:
116 | Dictionary with hyper-parameters and values.
117 | """
118 | params = dict()
119 |
120 | # get parameters from the parent GPC class
121 | for key in self._get_param_names():
122 | params[key] = getattr(self, key)
123 |
124 | # add qgpc specific parameters
125 | params["quantum_kernel"] = self._quantum_kernel
126 | if deep:
127 | params.update(self._quantum_kernel.get_params(deep=deep))
128 |
129 | return params
130 |
131 | def set_params(self, **params) -> None:
132 | """
133 | Sets value of the QGPC hyper-parameters.
134 |
135 | Args:
136 | params: Hyper-parameters and their values, e.g. ``num_qubits=2``.
137 | """
138 | valid_params = self.get_params(deep=True).keys()
139 | for key in params.keys():
140 | if key not in valid_params:
141 | raise ValueError(
142 | f"Invalid parameter {key!r}. "
143 | f"Valid parameters are {sorted(valid_params)!r}."
144 | )
145 |
146 | self_params = self.get_params(deep=False).keys() & params.keys()
147 | for key in self_params:
148 | try:
149 | setattr(self, key, params[key])
150 | except AttributeError:
151 | setattr(self, "_" + key, params[key])
152 |
153 | # Set parameters of the Quantum Kernel and its underlying objects
154 | quantum_kernel_params = self._quantum_kernel.get_params().keys() & params.keys()
155 | if quantum_kernel_params:
156 | self._quantum_kernel.set_params(**{key: params[key] for key in quantum_kernel_params})
157 | return self
158 |
159 | @property
160 | def quantum_kernel(self) -> KernelMatrixBase:
161 | """Returns quantum kernel"""
162 | return self._quantum_kernel
163 |
164 | @quantum_kernel.setter
165 | def quantum_kernel(self, quantum_kernel: KernelMatrixBase):
166 | """Sets quantum kernel"""
167 | self._quantum_kernel = quantum_kernel
168 | self.kernel = kernel_wrapper(quantum_kernel)
169 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/observables/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .observable_implemented.summed_probabilities import SummedProbabilities
2 | from .observable_implemented.summed_paulis import SummedPaulis
3 | from .observable_implemented.single_pauli import SinglePauli
4 | from .observable_implemented.single_probability import SingleProbability
5 | from .observable_implemented.custom_observable import (
6 | CustomObservable,
7 | )
8 | from .observable_implemented.ising_hamiltonian import IsingHamiltonian
9 |
10 | __all__ = [
11 | "SinglePauli",
12 | "SummedPaulis",
13 | "SingleProbability",
14 | "SummedProbabilities",
15 | "CustomObservable",
16 | "IsingHamiltonian",
17 | ]
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/observables/observable_implemented/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sQUlearn/squlearn/f21f3ca4a4c90b95d4da763f08c1ff815cb5afdf/src/squlearn/observables/observable_implemented/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/observables/observable_implemented/custom_observable.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from typing import Union
3 |
4 | from qiskit.circuit import ParameterVector
5 | from qiskit.quantum_info import SparsePauliOp
6 |
7 | from ..observable_base import ObservableBase
8 |
9 |
10 | class CustomObservable(ObservableBase):
11 | r"""
12 | Class for defining a custom observable.
13 |
14 | The operator is supplied as a string of Pauli operators, e.g. ``operator_string='ZI'`` for
15 | a two qubit operator with a Z operator on the second qubit.
16 | Note that the index of the qubits is reversed, i.e. the first qubit is the last character
17 | in the string, similar to the Qiskit computational state numbering.
18 |
19 | Multiple operators that are summed can be specified by a list of strings, e.g.
20 | ``operator_string=['ZZ', 'XX']``.
21 |
22 | Args:
23 | num_qubits (int): Number of qubits.
24 | operator_string (Union[str, list[str], tuple[str]]): String of operator to measure.
25 | Also list or tuples of strings are allowed for multiple operators.
26 | parameterized (bool): If True, the operator is parameterized.
27 |
28 | Attributes:
29 | -----------
30 |
31 | Attributes:
32 | num_qubits (int): Number of qubits.
33 | num_parameters (int): Number of trainable parameters in the custom operator.
34 | operator_string (Union[str, list[str], tuple[str]]): String of operator to measure.
35 | parameterized (bool): If True, the operator is parameterized.
36 |
37 | Methods:
38 | --------
39 | """
40 |
41 | def __init__(
42 | self,
43 | num_qubits: int,
44 | operator_string: Union[str, list[str], tuple[str]],
45 | parameterized: bool = False,
46 | ) -> None:
47 | super().__init__(num_qubits)
48 |
49 | self.operator_string = operator_string
50 | if isinstance(self.operator_string, str):
51 | self.operator_string = [self.operator_string]
52 | self.parameterized = parameterized
53 |
54 | for s in self.operator_string:
55 | if len(s) != self.num_qubits:
56 | raise ValueError(
57 | "Supplied string has not the same size as the number of qubits, "
58 | + "please add missing identities as 'I'"
59 | )
60 | for s_ in s:
61 | if s_ not in ["I", "X", "Y", "Z"]:
62 | raise ValueError("Only Pauli operators I, X, Y, Z are allowed.")
63 |
64 | @property
65 | def num_parameters(self):
66 | """Returns the number of trainable parameters in the custom operator"""
67 | if self.parameterized:
68 | return len(self.operator_string)
69 | else:
70 | return 0
71 |
72 | def get_params(self, deep: bool = True) -> dict:
73 | """
74 | Returns hyper-parameters and their values of the custom operator.
75 |
76 | Args:
77 | deep (bool): If True, also the parameters for
78 | contained objects are returned (default=True).
79 |
80 | Return:
81 | Dictionary with hyper-parameters and values.
82 | """
83 | params = super().get_params()
84 | params["operator_string"] = self.operator_string
85 | params["parameterized"] = self.parameterized
86 | return params
87 |
88 | def get_pauli(self, parameters: Union[ParameterVector, np.ndarray] = None) -> SparsePauliOp:
89 | """
90 | Function for generating the SparsePauliOp expression of the custom operator.
91 |
92 | Args:
93 | parameters (Union[ParameterVector, np.ndarray]): Parameters of the custom operator.
94 |
95 | Returns:
96 | SparsePauliOp expression of the specified custom operator.
97 | """
98 |
99 | op_list = []
100 | param_list = []
101 |
102 | if self.parameterized:
103 | nparam = len(parameters)
104 | op_list.append(self.operator_string[0])
105 | param_list.append(parameters[0 % nparam])
106 |
107 | ioff = 1
108 | for j in range(1, len(self.operator_string)):
109 | op_list.append(self.operator_string[j])
110 | param_list.append(parameters[ioff % nparam])
111 | ioff = ioff + 1
112 | return SparsePauliOp(op_list, param_list)
113 |
114 | else:
115 | op_list.append(self.operator_string[0])
116 | for j in range(1, len(self.operator_string)):
117 | op_list.append(self.operator_string[j])
118 | return SparsePauliOp(op_list)
119 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/observables/observable_implemented/single_pauli.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from typing import Union
3 |
4 | from qiskit.circuit import ParameterVector
5 | from qiskit.quantum_info import SparsePauliOp
6 |
7 | from ..observable_base import ObservableBase
8 |
9 |
10 | class SinglePauli(ObservableBase):
11 | r"""
12 | Observable constructed from a single Pauli operator of a single Qubit.
13 |
14 | **Equation for Z Pauli operator:**
15 |
16 | .. math::
17 |
18 | \hat{H} = \hat{Z_i} \qquad \text{or} \qquad \hat{H} = \theta\hat{Z_i}~~~~
19 | \text{ (parameterized)}
20 |
21 | Can be parameterized or not, the four Pauli operators :math:`\hat{X},\hat{Y},\hat{Z}`
22 | and :math:`\hat{I}` are supported.
23 |
24 | Args:
25 | num_qubits (int): Number of qubits.
26 | qubit (int): Qubit on which the Pauli operator acts.
27 | op_str (str): Pauli operator to measure. Must be one of ``'I'``, ``'X'``, ``'Y'``, ``'Z'``
28 | (default: ``'Z'``).
29 | parameterized (bool): If True, the operator is parameterized (default: False).
30 |
31 | Attributes:
32 | -----------
33 |
34 | Attributes:
35 | num_qubits (int): Number of qubits.
36 | num_parameters (int): Number of trainable parameters in the single Pauli operator.
37 | qubit (int): Qubit on which the Pauli operator acts.
38 | op_str (str): Pauli operator to measure.
39 | parameterized (bool): If True, the operator is parameterized.
40 |
41 | Methods:
42 | --------
43 | """
44 |
45 | def __init__(
46 | self, num_qubits: int, qubit: int = 0, op_str: str = "Z", parameterized: bool = False
47 | ) -> None:
48 | super().__init__(num_qubits)
49 |
50 | self.qubit = qubit
51 | self.op_str = op_str
52 | self.parameterized = parameterized
53 |
54 | if self.op_str not in ["I", "X", "Y", "Z"]:
55 | raise ValueError("Specified operator not supported")
56 |
57 | @property
58 | def num_parameters(self):
59 | """The number of trainable parameters in the single Pauli operator"""
60 |
61 | if self.parameterized:
62 | return 1
63 | else:
64 | return 0
65 |
66 | def get_params(self, deep: bool = True) -> dict:
67 | """
68 | Returns hyper-parameters and their values of the Single Pauli operator.
69 |
70 | Args:
71 | deep (bool): If True, also the parameters for
72 | contained objects are returned (default=True).
73 |
74 | Return:
75 | Dictionary with hyper-parameters and values.
76 | """
77 | params = super().get_params()
78 | params["qubit"] = self.qubit
79 | params["op_str"] = self.op_str
80 | params["parameterized"] = self.parameterized
81 | return params
82 |
83 | def get_pauli(self, parameters: Union[ParameterVector, np.ndarray]) -> SparsePauliOp:
84 | """
85 | Function for generating the SparsePauliOp expression of the single Pauli operator.
86 |
87 | Args:
88 | parameters (Union[ParameterVector, np.ndarray]): Parameters of the single
89 | Pauli operator.
90 |
91 | Return:
92 | SparsePauliOp expression of the specified single Pauli operator.
93 | """
94 |
95 | i = self.qubit
96 | if 0 > i or self.num_qubits <= i:
97 | raise ValueError("Specified qubit out of range")
98 |
99 | H = "I" * self.num_qubits
100 | if self.parameterized:
101 | return SparsePauliOp([H[(i + 1) :] + self.op_str + H[:i]], [parameters[0]])
102 |
103 | return SparsePauliOp([H[(i + 1) :] + self.op_str + H[:i]])
104 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/observables/observable_implemented/single_probability.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from typing import Union
3 |
4 | from qiskit.circuit import ParameterVector
5 | from qiskit.quantum_info import SparsePauliOp
6 |
7 | from ..observable_base import ObservableBase
8 |
9 |
10 | class SingleProbability(ObservableBase):
11 | r"""
12 | Observable for measuring the probability of being in state 0 or 1 of a specified qubit.
13 |
14 | **Equation as the operator is implemented:**
15 |
16 | .. math::
17 |
18 | \hat{H} = 0.5(\hat{I}_i+\hat{Z}_i) (= \ket{0}\bra{0}_i) \qquad \text{or} \qquad
19 | \hat{H} = 0.5(\hat{I}_i-\hat{Z}_i) (= \ket{1}\bra{1}_i)
20 |
21 | Operator can be optionally parameterized.
22 |
23 | Args:
24 | num_qubits (int): Number of qubits.
25 | qubit (int): Qubit to measure the probability of.
26 | one_state (bool): If True, measure the probability of being in state 1, otherwise state 0
27 | (default: False).
28 | parameterized (bool): If True, the operator is parameterized (default: false).
29 |
30 | Attributes:
31 | -----------
32 |
33 | Attributes:
34 | num_qubits (int): Number of qubits.
35 | num_parameters (int): Number of trainable parameters in the single Pauli operator.
36 | qubit (int): Qubit to measure the probability of.
37 | one_state (bool): If True, measure the probability of being in state 1, otherwise state 0.
38 | parameterized (bool): If True, the operator is parameterized.
39 |
40 | Methods:
41 | --------
42 | """
43 |
44 | def __init__(
45 | self,
46 | num_qubits: int,
47 | qubit: int = 0,
48 | one_state: bool = False,
49 | parameterized: bool = False,
50 | ) -> None:
51 | super().__init__(num_qubits)
52 |
53 | self.qubit = qubit
54 | self.one_state = one_state
55 | self.parameterized = parameterized
56 |
57 | @property
58 | def num_parameters(self):
59 | """Number of trainable parameters in the single probability operator."""
60 |
61 | if self.parameterized:
62 | return 1
63 | else:
64 | return 0
65 |
66 | def get_params(self, deep: bool = True) -> dict:
67 | """
68 | Returns hyper-parameters and their values of the single probability operator.
69 |
70 | Args:
71 | deep (bool): If True, also the parameters for
72 | contained objects are returned (default=True).
73 |
74 | Return:
75 | Dictionary with hyper-parameters and values.
76 | """
77 | params = super().get_params()
78 | params["qubit"] = self.qubit
79 | params["one_state"] = self.one_state
80 | params["parameterized"] = self.parameterized
81 | return params
82 |
83 | def get_pauli(self, parameters: Union[ParameterVector, np.ndarray] = None) -> SparsePauliOp:
84 | """
85 | Function for generating the SparsePauliOp expression of the single probability operator.
86 |
87 | Args:
88 | parameters (Union[ParameterVector, np.ndarray]): Parameters of the single
89 | probability operator.
90 |
91 | Return:
92 | SparsePauliOp expression of the specified single probability operator.
93 | """
94 |
95 | i = self.qubit
96 | if 0 > i or self.num_qubits <= i:
97 | raise ValueError("Specified qubit out of range")
98 | I = "I" * self.num_qubits
99 | Z = I[(i + 1) :] + "Z" + I[:i]
100 |
101 | if self.parameterized:
102 | coeff = 0.5 * parameters[0]
103 | else:
104 | coeff = 0.5
105 |
106 | if self.one_state:
107 | return SparsePauliOp([I, Z], [coeff, -coeff])
108 |
109 | else:
110 | return SparsePauliOp([I, Z], [coeff, coeff])
111 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/observables/observable_implemented/summed_paulis.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from typing import Union
3 |
4 | from qiskit.circuit import ParameterVector
5 | from qiskit.quantum_info import SparsePauliOp
6 |
7 | from ..observable_base import ObservableBase
8 |
9 |
10 | class SummedPaulis(ObservableBase):
11 | r"""
12 | Observable for summation of single Pauli operators.
13 |
14 | **Equation for Z Pauli operator:**
15 |
16 | .. math::
17 | \hat{H} = a\hat{I} + \sum_i b_i \hat{Z}_i
18 |
19 | Multiple Pauli operators can be specified by a tuple of strings, e.g. ``op_str=("X","Z")``:
20 |
21 | .. math::
22 | \hat{H} = a\hat{I} + \sum_i b_i \hat{X}_i + \sum_i c_i \hat{Z}_i
23 |
24 | The parameter can optionally be equal for the same kind of Pauli operators.
25 |
26 | Args:
27 | num_qubits (int): Number of qubits.
28 | op_str (Union[str,tuple[str]]): String of the Pauli operator that is measured.
29 | Possible values are ``"I"``, ``"X"``, ``"Y"``, ``"Z"``.
30 | Also a tuples of strings are allowed for multiple Pauli
31 | operators (default: ``"Z"``).
32 | full_sum (bool): If False, only one parameter is used for each Pauli operator,
33 | i.e. the sum is :math:`b\sum_i \hat{Z}_i`
34 | instead of :math:`\sum_i b_i \hat{Z}_i` (default: True).
35 | include_identity (bool): If True, the identity operator is included in the sum.
36 | (default: True)
37 |
38 | Attributes:
39 | -----------
40 |
41 | Attributes:
42 | num_qubits (int): Number of qubits.
43 | num_parameters (int): Number of trainable parameters in the summed Paulis operator.
44 | op_str (Union[str,tuple[str]]): String of the Pauli operator that is measured.
45 | full_sum (bool): If False, only one parameter is used for each Pauli operator.
46 | include_identity (bool): If True, the identity operator is included in the sum.
47 |
48 | Methods:
49 | --------
50 | """
51 |
52 | def __init__(
53 | self,
54 | num_qubits: int,
55 | op_str: Union[str, tuple[str]] = "Z",
56 | full_sum: bool = True,
57 | include_identity: bool = True,
58 | ) -> None:
59 | super().__init__(num_qubits)
60 | self.op_str = op_str
61 | self.full_sum = full_sum
62 | self.include_identity = include_identity
63 |
64 | for s in self.op_str:
65 | if s not in ["I", "X", "Y", "Z"]:
66 | raise ValueError("Only Pauli operators I, X, Y, Z are allowed.")
67 |
68 | @property
69 | def num_parameters(self):
70 | """Number of trainable parameters in the summed Pauli operator"""
71 | num_param = 0
72 | if self.include_identity:
73 | num_param += 1
74 | if self.full_sum:
75 | return num_param + len(self.op_str) * self.num_qubits
76 | else:
77 | return num_param + len(self.op_str)
78 |
79 | def get_params(self, deep: bool = True) -> dict:
80 | """
81 | Returns hyper-parameters and their values of the single summed Pauli operator.
82 |
83 | Args:
84 | deep (bool): If True, also the parameters for
85 | contained objects are returned (default=True).
86 |
87 | Return:
88 | Dictionary with hyper-parameters and values.
89 | """
90 | params = super().get_params()
91 | params["op_str"] = self.op_str
92 | params["full_sum"] = self.full_sum
93 | params["include_identity"] = self.include_identity
94 | return params
95 |
96 | def get_pauli(self, parameters: Union[ParameterVector, np.ndarray]) -> SparsePauliOp:
97 | """
98 | Function for generating the PauliOp expression of the summed Paulis operator.
99 |
100 | Args:
101 | parameters (Union[ParameterVector, np.ndarray]): Parameters of the summed
102 | Paulis operator.
103 |
104 | Return:
105 | PauliOp expression of the specified summed Paulis operator.
106 | """
107 |
108 | def gen_string(i, op_str):
109 | H = "I" * self.num_qubits
110 | H = H[i + 1 :] + op_str + H[:i]
111 | return H
112 |
113 | nparam = len(parameters)
114 | ioff = 0
115 |
116 | op_list = []
117 | param_list = []
118 |
119 | if self.include_identity:
120 | op_list.append("I" * self.num_qubits)
121 | param_list.append(parameters[ioff % nparam])
122 | ioff += 1
123 |
124 | for op_str in self.op_str:
125 | for i in range(self.num_qubits):
126 | op_list.append(gen_string(i, op_str))
127 | param_list.append(parameters[ioff % nparam])
128 | if self.full_sum:
129 | ioff += 1
130 | if not self.full_sum:
131 | ioff += 1
132 |
133 | return SparsePauliOp(op_list, np.array(param_list))
134 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/observables/observable_implemented/summed_probabilities.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from typing import Union
3 |
4 | from qiskit.circuit import ParameterVector
5 | from qiskit.quantum_info import SparsePauliOp
6 |
7 | from ..observable_base import ObservableBase
8 |
9 |
10 | class SummedProbabilities(ObservableBase):
11 | r"""
12 | Observable for summing single Qubit probabilities of binary states.
13 |
14 | **Equation for a sum of 0-states:**
15 |
16 | .. math::
17 | \hat{H} = a\hat{I} + \sum_i b_i (\ket{0}\bra{0})_i
18 |
19 | States are implemented by :math:`\ket{0}\bra{0} = 0.5(\hat{I}+\hat{Z})`
20 | and :math:`\ket{1}\bra{1} = 0.5(\hat{I}-\hat{Z})`.
21 |
22 | The parameter can be optionally equal for all states.
23 |
24 | Args:
25 | num_qubits (int): Number of qubits.
26 | one_state (bool): If false the :math:`\ket{0}\bra{0}` state is measured,
27 | if true the :math:`\ket{1}\bra{1}` state is measured (default: False).
28 | full_sum (bool): If False, the parameter is the same for all states,
29 | i.e. the sum is :math:`b\sum_i (\ket{0}\bra{0})_i`
30 | instead of :math:`\sum_i b_i (\ket{0}\bra{0})_i`
31 | (default: True).
32 | include_identity (bool): If True, the identity operator is included in the sum.
33 | (default: True)
34 |
35 | Attributes:
36 | -----------
37 |
38 | Attributes:
39 | num_qubits (int): Number of qubits.
40 | num_parameters (int): Number of trainable parameters in the summed probabilities operator.
41 | one_state (bool): If false the :math:`\ket{0}\bra{0}` state is measured,
42 | if true the :math:`\ket{1}\bra{1}` state is measured.
43 | full_sum (bool): If False, the parameter is the same for all states.
44 | include_identity (bool): If True, the identity operator is included in the sum.
45 |
46 | Methods:
47 | --------
48 | """
49 |
50 | def __init__(
51 | self,
52 | num_qubits: int,
53 | one_state=False,
54 | full_sum: bool = True,
55 | include_identity: bool = True,
56 | ) -> None:
57 | super().__init__(num_qubits)
58 | self.one_state = one_state
59 | self.full_sum = full_sum
60 | self.include_identity = include_identity
61 |
62 | @property
63 | def num_parameters(self):
64 | """The number of trainable parameters in the summed probabilities operator"""
65 | num_param = 0
66 | if self.include_identity:
67 | num_param += 1
68 | if self.full_sum:
69 | num_param += self.num_qubits
70 | else:
71 | num_param += 1
72 | return num_param
73 |
74 | def get_params(self, deep: bool = True) -> dict:
75 | """
76 | Returns hyper-parameters and their values of the single summed probabilities operator.
77 |
78 | Args:
79 | deep (bool): If True, also the parameters for
80 | contained objects are returned (default=True).
81 |
82 | Return:
83 | Dictionary with hyper-parameters and values.
84 | """
85 | params = super().get_params()
86 | params["one_state"] = self.one_state
87 | params["full_sum"] = self.full_sum
88 | params["include_identity"] = self.include_identity
89 | return params
90 |
91 | def get_pauli(self, parameters: Union[ParameterVector, np.ndarray] = None) -> SparsePauliOp:
92 | """
93 | Function for generating the PauliOp expression of the summed probabilities operator.
94 |
95 | Args:
96 | parameters (Union[ParameterVector, np.ndarray]): Parameters of the summed
97 | probabilities operator.
98 |
99 | Returns:
100 | PauliOp expression of the specified summed probabilities operator.
101 | """
102 |
103 | nparam = len(parameters)
104 |
105 | op_list = []
106 | coeff_list = []
107 |
108 | if self.include_identity:
109 | op_list.append("I" * self.num_qubits)
110 | coeff_list.append(parameters[0 % nparam])
111 |
112 | ioff = 1
113 | for i in range(self.num_qubits):
114 | I = "I" * self.num_qubits
115 | Z = I[(i + 1) :] + "Z" + I[:i]
116 |
117 | if self.one_state:
118 | op_list.append(I)
119 | coeff_list.append(parameters[ioff % nparam] * 0.5)
120 | op_list.append(Z)
121 | coeff_list.append(-parameters[ioff % nparam] * 0.5)
122 | else:
123 | op_list.append(I)
124 | coeff_list.append(parameters[ioff % nparam] * 0.5)
125 | op_list.append(Z)
126 | coeff_list.append(parameters[ioff % nparam] * 0.5)
127 | if self.full_sum:
128 | ioff += 1
129 |
130 | return SparsePauliOp(op_list, coeff_list)
131 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/optimizers/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Module for optimizer implementations and wrappers."""
2 |
3 | from .adam import Adam
4 | from .sglbo import SGLBO
5 | from .optimizers_wrapper import SLSQP, SPSA, LBFGSB
6 | from .approximated_gradients import FiniteDiffGradient, StochasticPerturbationGradient
7 |
8 | __all__ = [
9 | "Adam",
10 | "SGLBO",
11 | "SLSQP",
12 | "SPSA",
13 | "LBFGSB",
14 | "FiniteDiffGradient",
15 | "StochasticPerturbationGradient",
16 | ]
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/optimizers/approximated_gradients.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Classes for approximated gradients"""
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 |
5 |
6 | class ApproxGradientBase:
7 | """Base class for evaluating approximated gradients"""
8 |
9 | def gradient(self, x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
10 | """Function that calculates the approximated gradient for given input x
11 |
12 | Args:
13 | x (np.ndarray): Input location at which the gradient is calculated
14 |
15 | Returns:
16 | Approximated gradient with the same dimension as x (np.ndarray)
17 |
18 | """
19 | raise NotImplementedError()
20 |
21 | def __call__(self, x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
22 | return self.gradient(x)
23 |
24 |
25 | class FiniteDiffGradient(ApproxGradientBase):
26 | """
27 | Class for evaluating the finite differences gradient.
28 |
29 | Possible implementations are:
30 |
31 | Forward: [f(x+eps)-f(x)]/eps
32 | Backwards: [f(x)-f(x-eps)]/eps
33 | Central (default): [f(x+eps)-f(x-eps)]/2*eps
34 | Five-point: [-f(x+2eps)+8f(x+eps)-8f(x-eps)+f(x-2eps)]/12eps
35 |
36 | Args:
37 | fun (callable): Callable function for the gradient evaluation
38 | eps (float): Step for finite differences
39 | formula (str): type of finite differences. Possible values for type are
40 | 'forward', 'backwards', 'central', and 'five-point'
41 | """
42 |
43 | def __init__(self, fun: callable, eps: float = 0.01, formula: str = "central") -> None:
44 | self.fun = fun
45 | self.eps = eps
46 | self.formula = formula
47 |
48 | if formula not in ("central", "forward", "backwards", "five-point"):
49 | raise ValueError("Wrong value of formula: " + formula)
50 |
51 | def gradient(self, x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
52 | """Function that calculates the approximated gradient for given input x
53 |
54 | Args:
55 | x (np.ndarray): Input location at which the gradient is calculated
56 |
57 | Returns:
58 | Approximated gradient with the same dimension as x (np.ndarray)
59 |
60 | """
61 | if len(x.shape) != 1:
62 | raise ValueError("Unsupported shape of x!")
63 |
64 | if self.formula == "forward":
65 | f0 = self.fun(x)
66 | g = np.zeros(len(x))
67 | for i in range(len(x)):
68 | dx = np.eye(1, len(x), k=i)[0] * self.eps
69 | g[i] = ((self.fun(x + dx) - f0)) / self.eps # Extract scalar
70 |
71 | elif self.formula == "backwards":
72 | f0 = self.fun(x)
73 | g = np.zeros(len(x))
74 | for i in range(len(x)):
75 | dx = np.eye(1, len(x), k=i)[0] * self.eps
76 | g[i] = ((f0 - self.fun(x - dx))) / self.eps # Extract scalar
77 |
78 | elif self.formula == "central":
79 | g = np.zeros(len(x))
80 | for i in range(len(x)):
81 | dx = np.eye(1, len(x), k=i)[0] * self.eps
82 | g[i] = ((self.fun(x + dx) - self.fun(x - dx))) / (2.0 * self.eps) # Extract scalar
83 |
84 | elif self.formula == "five-point":
85 | g = np.zeros(len(x))
86 | for i in range(len(x)):
87 | dx = np.eye(1, len(x), k=i)[0] * self.eps
88 | g[i] = (
89 | -1.0 * self.fun(x + 2.0 * dx)
90 | + 8.0 * self.fun(x + 1.0 * dx)
91 | - 8.0 * self.fun(x - 1.0 * dx)
92 | + 1.0 * self.fun(x - 2.0 * dx)
93 | ) / (
94 | 12.0 * self.eps
95 | ) # Extract scalar
96 | else:
97 | raise ValueError("Wrong value of type: " + self.formula)
98 |
99 | return g
100 |
101 |
102 | class StochasticPerturbationGradient(ApproxGradientBase):
103 | """
104 | Class for evaluating the stochastic perturbation gradient estimation.
105 |
106 | g_i = f(x+eps*r)-f(x-eps*r)/2*eps*r_i with random vector r
107 |
108 | This is used in the SPSA optimization.
109 |
110 | Args:
111 | fun (callable): Callable function for the gradient evaluation
112 | eps (float): Step for difference
113 | seed (int): Seed for the random vector generation
114 | """
115 |
116 | def __init__(self, fun: callable, eps: float = 0.1, seed: int = 0) -> None:
117 | self.fun = fun
118 | self.eps = eps
119 | self.rng = np.random.default_rng(seed=seed)
120 |
121 | def set_eps(self, eps) -> None:
122 | """Setter for the eps value (is often dynamically adjusted)"""
123 | self.eps = eps
124 |
125 | def gradient(self, x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
126 | """Function that calculates the approximated gradient for given input x
127 |
128 | Args:
129 | x (np.ndarray): Input location at which the gradient is calculated
130 |
131 | Returns:
132 | Approximated gradient with the same dimension as x (np.ndarray)
133 |
134 | """
135 | if len(x.shape) != 1:
136 | raise ValueError("Unsupported shape of x!")
137 |
138 | pert = self.rng.random(len(x))
139 |
140 | f1 = self.fun(x + self.eps * pert)
141 | f2 = self.fun(x - self.eps * pert)
142 |
143 | return np.divide(f1 - f2, 2.0 * self.eps * pert)
144 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/optimizers/optimizer_base.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Optimization methods in sQUlearn."""
2 |
3 | import abc
4 | import numpy as np
5 |
6 |
7 | def default_callback(*args):
8 | """Default callback function."""
9 | pass
10 |
11 |
12 | class OptimizerResult: # TODO: maybe scipy class?
13 | """Class for holding the final result of the optimization"""
14 |
15 | def __init__(self):
16 | self.x = None
17 | self.nit = 0
18 | self.fun = 0.0
19 |
20 |
21 | class OptimizerBase(abc.ABC):
22 | """Base class for QNN optimizers."""
23 |
24 | def minimize(
25 | self,
26 | fun: callable,
27 | x0: np.ndarray,
28 | grad: callable = None,
29 | bounds=None, # pylint: disable=invalid-name
30 | ) -> OptimizerResult:
31 | """Function to minimize a given function.
32 |
33 | Args:
34 | fun (callable): Function to minimize.
35 | x0 (numpy.ndarray): Initial guess.
36 | grad (callable): Gradient of the function to minimize.
37 | bounds (sequence): Bounds for the parameters.
38 |
39 | Returns:
40 | Result of the optimization in class:`OptimizerResult` format.
41 | """
42 | raise NotImplementedError()
43 |
44 | def set_callback(self, callback):
45 | """Set the callback function."""
46 | self.callback = callback
47 |
48 |
49 | class IterativeMixin:
50 | """Mixin for iteration based optimizers."""
51 |
52 | def __init__(self):
53 | self.iteration = 0
54 |
55 |
56 | class StepwiseMixin(IterativeMixin):
57 | """Mixin for optimizer for which we can execute single steps."""
58 |
59 | def step(self, **kwargs):
60 | """Perform one update step."""
61 | raise NotImplementedError()
62 |
63 |
64 | class SGDMixin(StepwiseMixin, abc.ABC):
65 | """Mixin for stochastic gradient descent based optimizers."""
66 |
67 | def step(self, **kwargs):
68 | """Perform one update step.
69 |
70 | Args:
71 | x: Current value
72 | grad: Precomputed gradient
73 |
74 | Returns:
75 | Updated x
76 | """
77 | if "x" in kwargs:
78 | x = kwargs["x"]
79 | else:
80 | raise TypeError("x argument is missing in step function.")
81 | if "grad" in kwargs:
82 | grad = kwargs["grad"]
83 | else:
84 | raise TypeError("grad argument is missing in step function.")
85 |
86 | update = self._get_update(grad)
87 | x_return = x + update
88 | self.iteration += 1
89 | self._update_lr()
90 | return x_return
91 |
92 | def reset(self):
93 | """
94 | Resets the object to its initial state.
95 |
96 | This function does not take any parameters.
97 |
98 | Returns:
99 | None: This function does not return anything.
100 | """
101 | pass
102 |
103 | @abc.abstractmethod
104 | def _get_update(self, grad: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
105 | """Function that returns the update for a given gradient."""
106 | raise NotImplementedError()
107 |
108 | @abc.abstractmethod
109 | def _update_lr(self) -> None:
110 | """Function for updating the learning rate."""
111 | raise NotImplementedError()
112 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/qnn/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """QNN module for classification and regression."""
2 |
3 | from .loss import ConstantLoss, ODELoss, ParameterRegularizationLoss, SquaredLoss, VarianceLoss
4 | from .qnnc import QNNClassifier
5 | from .qnnr import QNNRegressor
6 |
7 | __all__ = [
8 | "ConstantLoss",
9 | "ODELoss",
10 | "ParameterRegularizationLoss",
11 | "SquaredLoss",
12 | "VarianceLoss",
13 | "QNNClassifier",
14 | "QNNRegressor",
15 | ]
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/qnn/loss/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Loss functions for QNNs."""
2 |
3 | from .ode_loss import ODELoss
4 | from .parameter_regularization_loss import ParameterRegularizationLoss
5 | from .qnn_loss_base import ConstantLoss
6 | from .squared_loss import SquaredLoss
7 | from .variance_loss import VarianceLoss
8 |
9 | __all__ = [
10 | "ConstantLoss",
11 | "ODELoss",
12 | "ParameterRegularizationLoss",
13 | "SquaredLoss",
14 | "VarianceLoss",
15 | ]
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/qnn/loss/squared_loss.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Squared Loss for QNNs."""
2 |
3 | from typing import Union
4 |
5 | import numpy as np
6 |
7 | from .qnn_loss_base import QNNLossBase
8 |
9 |
10 | class SquaredLoss(QNNLossBase):
11 | """Squared loss for regression."""
12 |
13 | @property
14 | def loss_variance_available(self) -> bool:
15 | """Returns True since the squared loss function has a variance function."""
16 | return True
17 |
18 | @property
19 | def loss_args_tuple(self) -> tuple:
20 | """Returns evaluation tuple for the squared loss calculation."""
21 | return ("f",)
22 |
23 | @property
24 | def variance_args_tuple(self) -> tuple:
25 | """Returns evaluation tuple for the squared loss variance calculation."""
26 | return ("f", "var")
27 |
28 | @property
29 | def gradient_args_tuple(self) -> tuple:
30 | """Returns evaluation tuple for the squared loss gradient calculation."""
31 | if self._opt_param_op:
32 | return ("f", "dfdp", "dfdop")
33 | return ("f", "dfdp")
34 |
35 | def value(self, value_dict: dict, **kwargs) -> float:
36 | r"""Calculates the squared loss.
37 |
38 | This function calculates the squared loss between the values in value_dict and ground_truth
39 | as
40 |
41 | .. math::
42 | \sum_i w_i \left|f\left(x_i\right)-f_ref\left(x_i\right)\right|^2
43 |
44 | Args:
45 | value_dict (dict): Contains calculated values of the model
46 | ground_truth (np.ndarray): The true values :math:`f_ref\left(x_i\right)`
47 | weights (np.ndarray): Weight for each data point, if None all data points count the
48 | same
49 |
50 | Returns:
51 | Loss value
52 | """
53 | if "ground_truth" not in kwargs:
54 | raise AttributeError("SquaredLoss requires ground_truth.")
55 | ground_truth = kwargs["ground_truth"]
56 | if "weights" in kwargs and kwargs["weights"] is not None:
57 | weights = kwargs["weights"]
58 | else:
59 | weights = np.ones_like(ground_truth)
60 | return np.sum(np.multiply(np.square(value_dict["f"] - ground_truth), weights))
61 |
62 | def variance(self, value_dict: dict, **kwargs) -> float:
63 | r"""Calculates the approximated variance of the squared loss.
64 |
65 | This function calculates the approximated variance of the squared loss
66 |
67 | .. math::
68 | 4\sum_i w_i \left|f\left(x_i\right)-f_ref\left(x_i\right)\right|^2 \sigma_f^2(x_i)
69 |
70 | Args:
71 | value_dict (dict): Contains calculated values of the model
72 | ground_truth (np.ndarray): The true values :math:`f_ref\left(x_i\right)`
73 | weights (np.ndarray): Weight for each data point, if None all data points count the
74 | same
75 |
76 | Returns:
77 | Loss value
78 | """
79 | if "ground_truth" not in kwargs:
80 | raise AttributeError("SquaredLoss requires ground_truth.")
81 | ground_truth = kwargs["ground_truth"]
82 | if "weights" in kwargs and kwargs["weights"] is not None:
83 | weights = kwargs["weights"]
84 | else:
85 | weights = np.ones_like(ground_truth)
86 |
87 | diff_square = np.multiply(weights, np.square(value_dict["f"] - ground_truth))
88 | return np.sum(4 * np.multiply(diff_square, value_dict["var"]))
89 |
90 | def gradient(
91 | self, value_dict: dict, **kwargs
92 | ) -> Union[np.ndarray, tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]]:
93 | r"""Returns the gradient of the squared loss.
94 |
95 | This function calculates the gradient of the squared loss between the values in value_dict
96 | and ground_truth as
97 |
98 | .. math::
99 | 2\sum_j \sum_i w_i \left(f\left(x_i\right)-f_ref\left(x_i\right)\right)
100 | \frac{\partial f(x_i)}{\partial p_j}
101 |
102 | Args:
103 | value_dict (dict): Contains calculated values of the model
104 | ground_truth (np.ndarray): The true values :math:`f_ref\left(x_i\right)`
105 | weights (np.ndarray): Weight for each data point, if None all data points count the
106 | same
107 | multiple_output (bool): True if the QNN has multiple outputs
108 |
109 | Returns:
110 | Gradient values
111 | """
112 |
113 | if "ground_truth" not in kwargs:
114 | raise AttributeError("SquaredLoss requires ground_truth.")
115 |
116 | ground_truth = kwargs["ground_truth"]
117 | if "weights" in kwargs and kwargs["weights"] is not None:
118 | weights = kwargs["weights"]
119 | else:
120 | weights = np.ones_like(ground_truth)
121 | multiple_output = "multiple_output" in kwargs and kwargs["multiple_output"]
122 |
123 | weighted_diff = np.multiply((value_dict["f"] - ground_truth), weights)
124 |
125 | if value_dict["dfdp"].shape[0] == 0:
126 | d_p = np.array([])
127 | else:
128 | if multiple_output:
129 | d_p = 2.0 * np.einsum("ij,ijk->k", weighted_diff, value_dict["dfdp"])
130 | else:
131 | d_p = 2.0 * np.einsum("j,jk->k", weighted_diff, value_dict["dfdp"])
132 |
133 | # Extra code for the cost operator derivatives
134 | if not self._opt_param_op:
135 | return d_p
136 |
137 | if value_dict["dfdop"].shape[0] == 0:
138 | d_op = np.array([])
139 | else:
140 | if multiple_output:
141 | d_op = 2.0 * np.einsum("ij,ijk->k", weighted_diff, value_dict["dfdop"])
142 | else:
143 | d_op = 2.0 * np.einsum("j,jk->k", weighted_diff, value_dict["dfdop"])
144 | return d_p, d_op
145 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/qnn/loss/variance_loss.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Variance Loss for QNNs."""
2 |
3 | from collections.abc import Callable
4 | from typing import Union
5 |
6 | import numpy as np
7 |
8 | from .qnn_loss_base import QNNLossBase
9 |
10 |
11 | class VarianceLoss(QNNLossBase):
12 | r"""Variance loss for regression.
13 |
14 | Args:
15 | alpha (float, Callable[[int], float]): Weight value :math:`\alpha`
16 | """
17 |
18 | def __init__(self, alpha: Union[float, Callable[[int], float]] = 0.005):
19 | super().__init__()
20 | self._alpha = alpha
21 |
22 | @property
23 | def loss_variance_available(self) -> bool:
24 | """Returns True since we neglect the variance of the variance."""
25 | return True
26 |
27 | @property
28 | def loss_args_tuple(self) -> tuple:
29 | """Returns evaluation tuple for loss calculation."""
30 | return ("var",)
31 |
32 | @property
33 | def variance_args_tuple(self) -> tuple:
34 | """Returns evaluation tuple for variance calculation."""
35 | return tuple()
36 |
37 | @property
38 | def gradient_args_tuple(self) -> tuple:
39 | """Returns evaluation tuple for loss gradient calculation."""
40 | if self._opt_param_op:
41 | return ("var", "dvardp", "dvardop")
42 | return ("var", "dvardp")
43 |
44 | def value(self, value_dict: dict, **kwargs) -> float:
45 | r"""Returns the variance.
46 |
47 | This function returns the weighted variance as
48 |
49 | .. math::
50 | L_\operatorname{Var} = \alpha \sum_i \operatorname{Var}_i
51 |
52 | Args:
53 | value_dict (dict): Contains calculated values of the model
54 | iteration (int): iteration number, if alpha is a callable function
55 |
56 | Returns:
57 | Loss value
58 | """
59 |
60 | if callable(self._alpha):
61 | if "iteration" not in kwargs:
62 | raise AttributeError("If alpha is callable, iteration is required.")
63 | alpha = self._alpha(kwargs["iteration"])
64 | else:
65 | alpha = self._alpha
66 |
67 | return alpha * np.sum(value_dict["var"])
68 |
69 | def variance(self, value_dict: dict, **kwargs) -> float:
70 | """Returns 0 since we neglect the variance of the variance."""
71 | return 0.0
72 |
73 | def gradient(
74 | self, value_dict: dict, **kwargs
75 | ) -> Union[np.ndarray, tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]]:
76 | """Returns the gradient of the variance.
77 |
78 | This function calculates the gradient of the variance values in value_dict.
79 |
80 | Args:
81 | value_dict (dict): Contains calculated values of the model
82 | iteration (int): iteration number, if variance_factor is a function
83 | multiple_output (bool): True if the QNN has multiple outputs
84 |
85 | Returns:
86 | Gradient values
87 | """
88 | if callable(self._alpha):
89 | if "iteration" not in kwargs:
90 | raise AttributeError("If alpha is callable, iteration is required.")
91 | alpha = self._alpha(kwargs["iteration"])
92 | else:
93 | alpha = self._alpha
94 |
95 | multiple_output = "multiple_output" in kwargs and kwargs["multiple_output"]
96 | if value_dict["dfdp"].shape[0] == 0:
97 | d_p = np.array([])
98 | else:
99 | if multiple_output:
100 | d_p = alpha * np.sum(value_dict["dvardp"], axis=(0, 1))
101 | else:
102 | d_p = alpha * np.sum(value_dict["dvardp"], axis=0)
103 |
104 | # Extra code for the cost operator derivatives
105 | if not self._opt_param_op:
106 | return d_p
107 |
108 | if value_dict["dfdop"].shape[0] == 0:
109 | d_op = np.array([])
110 | else:
111 | if multiple_output:
112 | d_op = alpha * np.sum(value_dict["dvardop"], axis=(0, 1))
113 | else:
114 | d_op = alpha * np.sum(value_dict["dvardop"], axis=0)
115 |
116 | return d_p, d_op
117 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/qnn/lowlevel_qnn/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .lowlevel_qnn import LowLevelQNN
2 |
3 | __all__ = ["LowLevelQNN"]
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/qnn/lowlevel_qnn/lowlevel_qnn.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | "Low-level QNN Factory."
2 |
3 | from typing import Union
4 | from warnings import warn
5 |
6 | from ...observables.observable_base import ObservableBase
7 | from ...encoding_circuit.encoding_circuit_base import EncodingCircuitBase
8 | from ...util import Executor
9 |
10 | from .lowlevel_qnn_pennylane import LowLevelQNNPennyLane
11 | from .lowlevel_qnn_qiskit import LowLevelQNNQiskit
12 |
13 |
14 | class LowLevelQNN:
15 | """
16 | Low-level QNN factory, which creates the specific low-level QNN based on the quantum framework.
17 |
18 | Args:
19 | pqc (EncodingCircuitBase): The parameterized quantum circuit.
20 | observable (Union[ObservableBase, list]): The observable(s) to measure.
21 | executor (Executor): The executor for the quantum circuit.
22 | *args: Additional arguments that are passed to the specific QNN.
23 | **kwargs: Additional keyword arguments that are passed to the specific QNN.
24 |
25 | Returns
26 | LowLevelQNNBase: The specific low-level QNN based on the quantum framework.
27 | """
28 |
29 | def __new__(
30 | cls,
31 | parameterized_quantum_circuit: EncodingCircuitBase,
32 | observable: Union[ObservableBase, list],
33 | executor: Executor,
34 | *args,
35 | **kwargs,
36 | ) -> [LowLevelQNNPennyLane, LowLevelQNNQiskit]:
37 |
38 | if executor.quantum_framework == "pennylane":
39 | if "primitive" in kwargs:
40 | warn("Primitive argument is not supported for PennyLane. Ignoring...")
41 | kwargs.pop("primitive")
42 | return LowLevelQNNPennyLane(
43 | parameterized_quantum_circuit, observable, executor, *args, **kwargs
44 | )
45 | elif executor.quantum_framework == "qiskit":
46 | return LowLevelQNNQiskit(
47 | parameterized_quantum_circuit, observable, executor, *args, **kwargs
48 | )
49 | else:
50 | raise RuntimeError("Quantum framework not supported")
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/qnn/lowlevel_qnn/lowlevel_qnn_base.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import abc
2 | from typing import Union
3 | import numpy as np
4 | import copy
5 |
6 | from qiskit.circuit import ParameterVector
7 | from qiskit.circuit.parametervector import ParameterVectorElement
8 |
9 | from ...observables.observable_base import ObservableBase
10 | from ...encoding_circuit.encoding_circuit_base import EncodingCircuitBase
11 | from ...util import Executor
12 |
13 |
14 | class LowLevelQNNBase(abc.ABC):
15 | """Base class for low-level QNNs.
16 |
17 | Args:
18 | pqc (EncodingCircuitBase): The parameterized quantum circuit.
19 | observable (Union[ObservableBase, list]): The observable(s) to measure.
20 | executor (Executor): The executor for the quantum circuit.
21 | """
22 |
23 | def __init__(
24 | self,
25 | parameterized_quantum_circuit: EncodingCircuitBase,
26 | observable: Union[ObservableBase, list],
27 | executor: Executor,
28 | ) -> None:
29 | self._pqc = copy.copy(parameterized_quantum_circuit)
30 | self._observable = copy.copy(observable)
31 | self._executor = executor
32 |
33 | @abc.abstractmethod
34 | def set_params(self, **params) -> None:
35 | """Set the parameters of the QNN."""
36 | raise NotImplementedError
37 |
38 | @abc.abstractmethod
39 | def get_params(self, deep: bool = True) -> dict:
40 | """Get the parameters of the QNN."""
41 | raise NotImplementedError
42 |
43 | @property
44 | @abc.abstractmethod
45 | def num_qubits(self) -> int:
46 | """Return the number of qubits of the QNN"""
47 | raise NotImplementedError
48 |
49 | @property
50 | @abc.abstractmethod
51 | def num_features(self) -> int:
52 | """Return the dimension of the features of the PQC"""
53 | raise NotImplementedError
54 |
55 | @property
56 | @abc.abstractmethod
57 | def num_parameters(self) -> int:
58 | """Return the number of trainable parameters of the PQC"""
59 | raise NotImplementedError
60 |
61 | @property
62 | def num_operator(self) -> int:
63 | """Return the number outputs"""
64 | raise NotImplementedError
65 |
66 | @property
67 | def num_parameters_observable(self) -> int:
68 | """Return the number of trainable parameters of the expectation value operator"""
69 | raise NotImplementedError
70 |
71 | @property
72 | def multiple_output(self) -> bool:
73 | """Return true if multiple outputs are used"""
74 | raise NotImplementedError
75 |
76 | @abc.abstractmethod
77 | def evaluate(
78 | self,
79 | x: Union[float, np.ndarray],
80 | param: Union[float, np.ndarray],
81 | param_obs: Union[float, np.ndarray],
82 | *values: Union[
83 | str,
84 | ParameterVector,
85 | ParameterVectorElement,
86 | tuple,
87 | ],
88 | ) -> dict:
89 | """General function for evaluating the output of derivatives of the QNN.
90 |
91 | Evaluation works for given combination of
92 | input features `x` and parameters `param` and `param_op`.
93 | The function includes caching of results
94 |
95 | If `x`, `param`, and/or `param_op` are given as a nested list
96 | (for example multiple sets of parameters),
97 | the values are returned in a nested list.
98 |
99 | Args:
100 | x (np.ndarray): Values of the input feature data.
101 | param (np.ndarray): Parameter values of the PQC parameters
102 | param_op (np.ndarray): Parameter values of the operator parameters
103 | values : Derivatives (or values) of the QNN that are evaluated. Higher order
104 | derivatives are given as tuples of parameters or vectors.
105 |
106 | Results:
107 | Returns a dictionary with the computed values.
108 | The keys of the dictionary are given by the entries in the values tuple
109 |
110 | """
111 | raise NotImplementedError
112 |
113 | def gradient(
114 | self,
115 | x: Union[float, np.ndarray],
116 | param: Union[float, np.ndarray],
117 | param_obs: Union[float, np.ndarray],
118 | ):
119 | """Return the gradient wrt. trainable parameters of the QNN.
120 |
121 | Args:
122 | x (Union[float, np.ndarray]): Input data.
123 | param (Union[float, np.ndarray]): Parameters of the PQC.
124 | param_obs (Union[float, np.ndarray]): Parameters of the observable.
125 |
126 | Returns:
127 | np.ndarray: Gradient of the QNN.
128 |
129 | """
130 | return np.concatenate(
131 | (
132 | self.evaluate(x, param, param_obs, "dfdp")["dfdp"],
133 | self.evaluate(x, param, param_obs, "dfdop")["dfdop"],
134 | ),
135 | axis=None,
136 | )
137 |
138 | def __call__(
139 | self,
140 | x: Union[float, np.ndarray],
141 | param: Union[float, np.ndarray],
142 | param_obs: Union[float, np.ndarray],
143 | ):
144 | """
145 | Function for evaluating the QNN.
146 |
147 | Args:
148 | x (Union[float, np.ndarray]): Input data.
149 | param (Union[float, np.ndarray]): Parameters of the PQC.
150 | param_obs (Union[float, np.ndarray]): Parameters of the observable.
151 |
152 | Returns:
153 | np.ndarray: The output of the QNN.
154 |
155 | """
156 | return self.evaluate(x, param, param_obs, "f")["f"]
157 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/qnn/util/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """QNN Utilities."""
2 |
3 | from .training import get_variance_fac, get_lr_decay, ShotsFromRSTD
4 |
5 | __all__ = ["get_variance_fac", "get_lr_decay", "ShotsFromRSTD"]
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/qrc/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Quantum Reservoir Computing module for classification and regression."""
2 |
3 | from .qrc_classifier import QRCClassifier
4 | from .qrc_regressor import QRCRegressor
5 |
6 | __all__ = ["QRCClassifier", "QRCRegressor"]
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/qrc/qrc_classifier.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from typing import Union
3 |
4 | from sklearn.base import ClassifierMixin
5 | from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
6 | from sklearn.linear_model import Perceptron
7 | from sklearn.svm import SVC
8 |
9 | from ..observables.observable_base import ObservableBase
10 | from ..encoding_circuit.encoding_circuit_base import EncodingCircuitBase
11 |
12 | from .base_qrc import BaseQRC
13 | from ..util import Executor
14 |
15 |
16 | class QRCClassifier(BaseQRC, ClassifierMixin):
17 | """Quantum Reservoir Computing for classification.
18 |
19 | This class implements a Quantum Reservoir Computing (QRC) framework designed for
20 | regression tasks. In QRC, data is encoded into a quantum system—referred to as the
21 | quantum reservoir—using an encoding circuit. The state of the quantum reservoir is then
22 | measured using a set of quantum operators, often randomly chosen. The measured values,
23 | also known as expectation values, are used as features for a classical machine learning model
24 | to perform the classification. As a default a simple classification based on a single
25 | perceptron is used.
26 |
27 | Args:
28 | encoding_circuit (EncodingCircuitBase): The encoding circuit to use for encoding the data
29 | into the reservoir.
30 | executor (Executor): Executor instance
31 | ml_model (str): The classical machine learning model to use (default: linear), possible
32 | values are:
33 |
34 | * ``"mlp"`` for a multi-layer perceptron classification model.
35 | * ``"linear"`` for a single layer perceptron.
36 | * ``"kernel"`` for a Support Vector Classifier with a RBF kernel.
37 |
38 | ml_model_options (dict): The options for the machine learning model. Default options of the
39 | sklearn model are used if None.
40 | operators (Union[ObservableBase, list[ObservableBase], str]): Strategy for generating the
41 | operators used to measure the quantum reservoir. Possible values are:
42 |
43 | * ``"random_paulis"`` generates random Pauli operators (default).
44 | * ``"single_paulis"`` generates single qubit Pauli operators.
45 |
46 | Alternatively, a list of ObservableBase objects can be provided.
47 | num_operators (int): The number of random Pauli operators to generate for
48 | ``"operators = random_paulis"`` (default: 100).
49 | operator_seed (int): The seed for the random operator generation for
50 | ``"operators = random_paulis"`` (default: 0).
51 | param_ini (Union[np.ndarray, None]): The parameters for the encoding circuit.
52 | param_op_ini (Union[np.ndarray, None]): The initial parameters for the operators.
53 | parameter_seed (Union[int, None]): The seed for the initial parameter generation if no
54 | parameters are given.
55 | caching (bool): Whether to cache the results of the evaluated expectation values.
56 |
57 | See Also
58 | --------
59 | squlearn.qrc.QRCRegressor: Quantum Reservoir Computing for Regression.
60 | squlearn.qrc.base_qrc.BaseQRC: Base class for Quantum Reservoir Computing.
61 |
62 | **Example: Classification of Moon example with Quantum Reservoir Computing**
63 |
64 | .. code-block:: python
65 |
66 | from squlearn import Executor
67 | from squlearn.encoding_circuit import HubregtsenEncodingCircuit
68 | from squlearn.qrc import QRCClassifier
69 | from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
70 | from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
71 |
72 | X, y = make_moons(n_samples=1000, noise=0.2, random_state=42)
73 |
74 | X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
75 | X, y, test_size=0.33, random_state=42)
76 |
77 | clf = QRCClassifier(HubregtsenEncodingCircuit(num_qubits=4, num_features=2),
78 | Executor(),
79 | ml_model="linear",
80 | operators="random_paulis",
81 | num_operators=300,
82 | )
83 |
84 | clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
85 | y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
86 |
87 | Methods:
88 | --------
89 | """
90 |
91 | def __init__(
92 | self,
93 | encoding_circuit: EncodingCircuitBase,
94 | executor: Executor,
95 | ml_model: str = "linear",
96 | ml_model_options: Union[dict, None] = None,
97 | operators: Union[ObservableBase, list[ObservableBase], str] = "random_paulis",
98 | num_operators: int = 100,
99 | operator_seed: int = 0,
100 | param_ini: Union[np.ndarray, None] = None,
101 | param_op_ini: Union[np.ndarray, None] = None,
102 | parameter_seed: Union[int, None] = 0,
103 | caching: bool = True,
104 | ) -> None:
105 |
106 | super().__init__(
107 | encoding_circuit=encoding_circuit,
108 | executor=executor,
109 | ml_model=ml_model,
110 | ml_model_options=ml_model_options,
111 | operators=operators,
112 | num_operators=num_operators,
113 | operator_seed=operator_seed,
114 | param_ini=param_ini,
115 | param_op_ini=param_op_ini,
116 | parameter_seed=parameter_seed,
117 | caching=caching,
118 | )
119 |
120 | def _initialize_ml_model(self):
121 |
122 | if self.ml_model_options is None:
123 | self.ml_model_options = {}
124 |
125 | if self.ml_model == "mlp":
126 | self._ml_model = MLPClassifier(**self.ml_model_options)
127 | elif self.ml_model == "linear":
128 | self._ml_model = Perceptron(**self.ml_model_options)
129 | elif self.ml_model == "kernel":
130 | self._ml_model = SVC(**self.ml_model_options)
131 | else:
132 | raise ValueError("Invalid ml_model. Please choose 'mlp', 'linear' or 'kernel'.")
133 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/qrc/qrc_regressor.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from typing import Union
3 |
4 | from sklearn.base import RegressorMixin
5 | from sklearn.neural_network import MLPRegressor
6 | from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
7 | from sklearn.kernel_ridge import KernelRidge
8 |
9 | from ..observables.observable_base import ObservableBase
10 | from ..encoding_circuit.encoding_circuit_base import EncodingCircuitBase
11 |
12 | from .base_qrc import BaseQRC
13 | from ..util import Executor
14 |
15 |
16 | class QRCRegressor(BaseQRC, RegressorMixin):
17 | """Quantum Reservoir Computing for regression.
18 |
19 | This class implements a Quantum Reservoir Computing (QRC) framework designed for
20 | regression tasks. In QRC, data is encoded into a quantum system—referred to as the
21 | quantum reservoir—using an encoding circuit. The state of the quantum reservoir is then
22 | measured using a set of quantum operators, often randomly chosen. The measured values,
23 | also known as expectation values, are used as features for a classical machine learning model,
24 | usually a simple linear regression, to perform the regression.
25 |
26 | Args:
27 | encoding_circuit (EncodingCircuitBase): The encoding circuit to use for encoding the data
28 | into the reservoir.
29 | executor (Executor): Executor instance
30 | ml_model (str): The classical machine learning model to use (default: linear). Possible
31 | values are:
32 |
33 | * ``"mlp"`` for a multi-layer perceptron regression model.
34 | * ``"linear"`` for a linear regression model.
35 | * ``"kernel"`` for a kernel ridge regression with a linear kernel.
36 |
37 | ml_model_options (dict): The options for the machine learning model. Default options of the
38 | sklearn model are used if None.
39 | operators (Union[ObservableBase, list[ObservableBase], str]): Strategy for generating the
40 | operators used to measure the quantum reservoir. Possible values are:
41 |
42 | * ``"random_paulis"`` generates random Pauli operators (default).
43 | * ``"single_paulis"`` generates single qubit Pauli operators.
44 |
45 | Alternatively, a list of ObservableBase objects can be provided.
46 | num_operators (int): The number of random Pauli operators to generate for
47 | ``"operators = random_paulis"`` (default: 100).
48 | operator_seed (int): The seed for the random operator generation for
49 | ``"operators = random_paulis"`` (default: 0).
50 | param_ini (Union[np.ndarray, None]): The parameters for the encoding circuit.
51 | param_op_ini (Union[np.ndarray, None]): The initial parameters for the operators.
52 | parameter_seed (Union[int, None]): The seed for the initial parameter generation if no
53 | parameters are given.
54 | caching (bool): Whether to cache the results of the evaluated expectation values.
55 |
56 | See Also
57 | --------
58 | squlearn.qrc.QRCClassifier: Quantum Reservoir Computing for Classification.
59 | squlearn.qrc.base_qrc.BaseQRC: Base class for Quantum Reservoir Computing.
60 |
61 | **Example: Fitting the logarithm function with Quantum Reservoir Computing**
62 |
63 | .. code-block:: python
64 |
65 | import numpy as np
66 | from squlearn import Executor
67 | from squlearn.encoding_circuit import HubregtsenEncodingCircuit
68 | from squlearn.qrc import QRCRegressor
69 | from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
70 |
71 | X, y = np.arange(0.1, 0.9, 0.01), np.log(np.arange(0.1, 0.9, 0.01))
72 | X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
73 | X, y, test_size=0.33, random_state=42)
74 |
75 | reg = QRCRegressor(HubregtsenEncodingCircuit(num_qubits=4, num_features=1),
76 | Executor(),
77 | ml_model="linear",
78 | operators="random_paulis",
79 | num_operators=300,
80 | )
81 |
82 | reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
83 | y_pred = reg.predict(X_test)
84 |
85 | Methods:
86 | --------
87 | """
88 |
89 | def __init__(
90 | self,
91 | encoding_circuit: EncodingCircuitBase,
92 | executor: Executor,
93 | ml_model: str = "linear",
94 | ml_model_options: Union[dict, None] = None,
95 | operators: Union[ObservableBase, list[ObservableBase], str] = "random_paulis",
96 | num_operators: int = 100,
97 | operator_seed: int = 0,
98 | param_ini: Union[np.ndarray, None] = None,
99 | param_op_ini: Union[np.ndarray, None] = None,
100 | parameter_seed: Union[int, None] = 0,
101 | caching: bool = True,
102 | ) -> None:
103 |
104 | super().__init__(
105 | encoding_circuit=encoding_circuit,
106 | executor=executor,
107 | ml_model=ml_model,
108 | ml_model_options=ml_model_options,
109 | operators=operators,
110 | num_operators=num_operators,
111 | operator_seed=operator_seed,
112 | param_ini=param_ini,
113 | param_op_ini=param_op_ini,
114 | parameter_seed=parameter_seed,
115 | caching=caching,
116 | )
117 |
118 | def _initialize_ml_model(self):
119 |
120 | if self.ml_model_options is None:
121 | self.ml_model_options = {}
122 |
123 | if self.ml_model == "mlp":
124 | self._ml_model = MLPRegressor(**self.ml_model_options)
125 | elif self.ml_model == "linear":
126 | self._ml_model = LinearRegression(**self.ml_model_options)
127 | elif self.ml_model == "kernel":
128 | self._ml_model = KernelRidge(**self.ml_model_options)
129 | else:
130 | raise ValueError("Invalid ml_model. Please choose 'mlp', 'linear' or 'kernel'.")
131 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/util/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .executor import Executor
2 | from .optree import OpTree
3 |
4 | __all__ = ["Executor", "OpTree"]
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/util/data_preprocessing.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from typing import Tuple, Union
3 |
4 |
5 | def adjust_features(x: Union[np.ndarray, float], x_length: int) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, bool]:
6 | """Adjust the feature vector to the form [[]] if necessary.
7 |
8 | Args:
9 | x (np.ndarray): Input array.
10 | x_length (int): Dimension of the input array, e.g. feature dimension.
11 |
12 | Return:
13 | Adjusted feature array and a boolean flag for multiple inputs.
14 | """
15 |
16 | return _adjust_input(x, x_length, allow_single_array=False)
17 |
18 |
19 | def adjust_parameters(x: np.ndarray, x_length: int) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, bool]:
20 | """Adjust the parameter vector to the form [[]] if necessary.
21 |
22 | In contrast to feature vectors, one dimensional parameters are not considered
23 | as multiple inputs.
24 |
25 | Args:
26 | x (np.ndarray): Input array.
27 | x_length (int): Dimension of the input array, e.g. feature dimension.
28 |
29 | Return:
30 | Adjusted parameter array and a boolean flag for multiple inputs.
31 | """
32 |
33 | return _adjust_input(x, x_length, allow_single_array=True)
34 |
35 |
36 | def _adjust_input(
37 | x: Union[float, np.ndarray], x_length: int, allow_single_array: bool
38 | ) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, bool]:
39 | """Adjust the input to the form [[]] if necessary.
40 |
41 | If allow_single_array is True, a one dimensional array is not considered as multiple outputs.
42 |
43 | Args:
44 | x (np.ndarray): Input array.
45 | x_length (int): Dimension of the input array, e.g. feature dimension.
46 | allow_single_array (bool): If True, a one dimensional array is not considered as
47 | multiple outputs.
48 |
49 | Return:
50 | Adjusted input array and a boolean flag for multiple inputs.
51 | """
52 | multiple_inputs = False
53 | error = False
54 | shape = np.shape(x)
55 |
56 | if shape == () and x_length == 1:
57 | # Single floating point number
58 | xx = np.array([[x]])
59 | elif sum(shape) == 0 and x_length > 0:
60 | # Empty array although x_length not zero
61 | error = True
62 | elif len(shape) == 1:
63 | if x_length == 1:
64 | xx = np.array([np.array([xx]) for xx in x])
65 | if allow_single_array:
66 | multiple_inputs = shape[0] != 1
67 | else:
68 | multiple_inputs = True
69 | else:
70 | # We have a single multi dimensional x (e.g. parameter vector)
71 | if len(x) == x_length:
72 | xx = np.array([x])
73 | else:
74 | error = True
75 | elif len(shape) == 2:
76 | if shape[1] == x_length:
77 | xx = x
78 | multiple_inputs = True
79 | else:
80 | error = True
81 | else:
82 | error = True
83 |
84 | if error:
85 | raise ValueError("Wrong format of an input variable.")
86 |
87 | return convert_to_float64(xx), multiple_inputs
88 |
89 |
90 | def convert_to_float64(x: Union[float, np.ndarray, list]) -> np.ndarray:
91 | """Convert to float64 format, raise Error for complex values
92 |
93 | Args:
94 | x (Union[float, np.ndarray]): Data that is converted
95 |
96 | Returns:
97 | Converted numpy float64 array
98 | """
99 | if not isinstance(x, np.ndarray):
100 | x = np.array(x)
101 | if x.dtype != np.float64:
102 | x = np.real_if_close(x)
103 | if np.iscomplexobj(x):
104 | raise ValueError(
105 | "Only real values for parameters and features are supported in sQUlearn!"
106 | )
107 | x = np.array(x, dtype=np.float64)
108 |
109 | return x
110 |
111 |
112 | def to_tuple(x: Union[float, np.ndarray, list, tuple], flatten: bool = True) -> Tuple:
113 | """Function for converting data into hashable tuples
114 |
115 | Args:
116 | x (Union[float,np.ndarray,list,tuple]): Input data.
117 |
118 | Return:
119 | Flattened tuple of the input data
120 | """
121 |
122 | if flatten:
123 |
124 | def recursive_flatten(container):
125 | for i in container:
126 | if isinstance(i, (list, tuple, np.ndarray)):
127 | for j in recursive_flatten(i):
128 | yield j
129 | else:
130 | yield i
131 |
132 | if isinstance(x, float):
133 | return tuple([x])
134 | elif len(np.shape(x)) == 1:
135 | return tuple(list(x))
136 | else:
137 | return tuple(recursive_flatten(x))
138 |
139 | else:
140 |
141 | def array_to_nested_tuple(arr):
142 | if isinstance(arr, (list, tuple, np.ndarray)):
143 | return tuple(array_to_nested_tuple(subarr) for subarr in arr)
144 | else:
145 | return arr
146 |
147 | if isinstance(x, (list, tuple, np.ndarray)):
148 | return array_to_nested_tuple(x)
149 | else:
150 | return tuple([x])
151 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/util/decompose_to_std.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from qiskit.circuit.library import standard_gates
2 | from qiskit.circuit import QuantumCircuit
3 | from typing import Union
4 |
5 |
6 | def decompose_to_std(
7 | circuit: QuantumCircuit, gate_list: Union[None, list] = None
8 | ) -> QuantumCircuit:
9 | """
10 | Function to decompose the circuit to standard gates.
11 |
12 | Args:
13 | circuit (QuantumCircuit): The Circuit, which is supposed to be decomposed.
14 | gate_list (Union[None,list]): List of gates, which are considered as standard gates.
15 | If the gate is not in the list, it will be decomposed. If the list is empty,
16 | all gates from `qiskit.circuit.library.standard_gates` and
17 | `["cx","cy","cz","measure"]` are considered as standard gates.
18 |
19 | Returns:
20 | QuantumCircuit: The decomposed circuit.
21 | """
22 | if not gate_list:
23 | gate_list = [*dir(standard_gates), "cx", "cy", "cz", "measure"]
24 | decompose_names = [
25 | instruction.operation.name
26 | for instruction in circuit.data
27 | if instruction.operation.name not in gate_list
28 | ]
29 | circuit_new = circuit.decompose(decompose_names)
30 |
31 | while decompose_names and circuit != circuit_new:
32 | circuit = circuit_new
33 | decompose_names = [
34 | instruction.operation.name
35 | for instruction in circuit.data
36 | if instruction.operation.name not in gate_list
37 | ]
38 | circuit_new = circuit.decompose(decompose_names)
39 |
40 | return circuit_new
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/util/execution/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .automatic_backend_selection import AutomaticBackendSelection
2 | from .parallel_estimator import ParallelEstimator
3 | from .parallel_sampler import ParallelSampler
4 |
5 | __all__ = [
6 | "AutomaticBackendSelection",
7 | "ParallelEstimator",
8 | "ParallelSampler",
9 | ]
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/util/execution/hqaa/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .heuristic import heuristic
2 | from .parser import parse_openqasm
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/util/execution/hqaa/parser.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import networkx as nx
2 | import re
3 |
4 |
5 | def parse_openqasm(lines: str, number_qubits: int) -> nx.Graph:
6 | """
7 | Parses OPENQASM code to generate a traffic graph representing single and double qubit gate frequencies.
8 |
9 | Args:
10 | lines (str): The OPENQASM code as a string.
11 | number_qubits (int): The number of qubits in the quantum circuit.
12 |
13 | Returns:
14 | nx.Graph: A NetworkX graph representing the traffic of the quantum circuit, with nodes for qubits and edges indicating gate operations.
15 | """
16 | traffic = nx.Graph()
17 |
18 | for i in range(0, number_qubits):
19 | traffic.add_node(i, single=0)
20 | for j in range(0, number_qubits):
21 | for k in range(number_qubits - 1, 0, -1):
22 | if j != k:
23 | traffic.add_edge(j, k, double=0)
24 |
25 | # Update the lists for OPENQASM 3
26 | list_s_gates = ["x", "h", "rx", "ry", "rz", "sx"]
27 | list_m_gates = ["cx", "cz", "swap", "ccx", "ecr"]
28 |
29 | for j in range(0, len(list_s_gates)):
30 | for line in lines.split("\n"):
31 | if line.startswith(list_s_gates[j]):
32 | match = re.search(r"q\[(\d+)\]", line)
33 | if match:
34 | number_single_gate = int(match.group(1))
35 | traffic.nodes[number_single_gate]["single"] += 1
36 |
37 | for k in range(0, len(list_m_gates)):
38 | for line in lines.split("\n"):
39 | if line.startswith(list_m_gates[k]):
40 | match = re.findall(r"q\[(\d+)\]", line)
41 | if match:
42 | qubits = list(map(int, match))
43 | for i in range(len(qubits) - 1):
44 | traffic[qubits[i]][qubits[i + 1]]["double"] += 1
45 |
46 | # Remove edges with "double" = 0
47 | double_0_new = [(i, j) for i, j, data in traffic.edges(data=True) if data["double"] == 0]
48 | for i, j in double_0_new:
49 | traffic.remove_edge(i, j)
50 |
51 | return traffic
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/util/optree/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .optree import (
2 | OpTree,
3 | OpTreeList,
4 | OpTreeSum,
5 | OpTreeCircuit,
6 | OpTreeOperator,
7 | OpTreeContainer,
8 | OpTreeExpectationValue,
9 | OpTreeMeasuredOperator,
10 | OpTreeValue,
11 | )
12 |
13 | from .optree_evaluate import OpTreeEvaluate
14 | from .optree_derivative import OpTreeDerivative
15 |
16 | __all__ = [
17 | "OpTree",
18 | "OpTreeEvaluate",
19 | "OpTreeDerivative",
20 | "OpTreeList",
21 | "OpTreeSum",
22 | "OpTreeCircuit",
23 | "OpTreeOperator",
24 | "OpTreeExpectationValue",
25 | "OpTreeMeasuredOperator",
26 | "OpTreeContainer",
27 | "OpTreeValue",
28 | ]
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/util/pennylane/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .pennylane_circuit import PennyLaneCircuit
2 | from .pennylane_gates import qiskit_pennylane_gate_dict
3 |
4 | __all__ = ["PennyLaneCircuit", "qiskit_pennylane_gate_dict"]
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/squlearn/util/pennylane/pennylane_gates.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import pennylane as qml
2 |
3 |
4 | def RXX(theta, wires):
5 | """RXX gate."""
6 | return qml.PauliRot(theta, "XX", wires=wires)
7 |
8 |
9 | def RYY(theta, wires):
10 | """RYY gate."""
11 | return qml.PauliRot(theta, "YY", wires=wires)
12 |
13 |
14 | def RZZ(theta, wires):
15 | """RZZ gate."""
16 | return qml.PauliRot(theta, "ZZ", wires=wires)
17 |
18 |
19 | def RXZ(theta, wires):
20 | """RXZ gate."""
21 | return qml.PauliRot(theta, "XZ", wires=wires)
22 |
23 |
24 | def reset(wires):
25 | """Reset gate, implemented by measure and reset."""
26 | return qml.measure(wires=wires, reset=True)
27 |
28 |
29 | def tdg(wires):
30 | """T-dagger gate."""
31 | return qml.adjoint(qml.T(wires=wires))
32 |
33 |
34 | def sdg(wires):
35 | """S-dagger gate."""
36 | return qml.adjoint(qml.S(wires=wires))
37 |
38 |
39 | def cs(wires):
40 | """CS gate."""
41 | if len(wires) != 2:
42 | raise ValueError("CS gate requires two wires.")
43 | return qml.ctrl(qml.S(wires[1]), wires[0])
44 |
45 |
46 | def csx(wires):
47 | """CSX gate."""
48 | if len(wires) != 2:
49 | raise ValueError("CSX gate requires two wires.")
50 | return qml.ctrl(qml.SX(wires[1]), wires[0])
51 |
52 |
53 | # Dictionary of conversion Qiskit gates (from string) to PennyLane gates
54 | qiskit_pennylane_gate_dict = {
55 | "i": qml.Identity,
56 | "h": qml.Hadamard,
57 | "x": qml.PauliX,
58 | "y": qml.PauliY,
59 | "z": qml.PauliZ,
60 | "s": qml.S,
61 | "t": qml.T,
62 | "toffoli": qml.Toffoli,
63 | "sx": qml.SX,
64 | "swap": qml.SWAP,
65 | "iswap": qml.ISWAP,
66 | "cswap": qml.CSWAP,
67 | "ecr": qml.ECR,
68 | "ch": qml.CH,
69 | "rx": qml.RX,
70 | "ry": qml.RY,
71 | "rz": qml.RZ,
72 | "p": qml.PhaseShift,
73 | "cp": qml.ControlledPhaseShift,
74 | "cx": qml.CNOT,
75 | "cnot": qml.CNOT,
76 | "cy": qml.CY,
77 | "cz": qml.CZ,
78 | "crx": qml.CRX,
79 | "cry": qml.CRY,
80 | "crz": qml.CRZ,
81 | "rxx": RXX,
82 | "ryy": RYY,
83 | "rzz": RZZ,
84 | "rxz": RXZ,
85 | "barrier": qml.Barrier,
86 | "u": qml.U3,
87 | "measure": qml.measure,
88 | "reset": reset,
89 | "tdg": tdg,
90 | "sdg": sdg,
91 | "cs": cs,
92 | "csx": csx,
93 | }
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/encoding_circuit/test_random_encoding_circuits.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import pytest
2 |
3 | from squlearn.encoding_circuit import RandomLayeredEncodingCircuit, RandomEncodingCircuit
4 |
5 | from qiskit.circuit import ParameterVector
6 |
7 |
8 | class TestRandomEncodingCircuits:
9 |
10 | def test_random_layered_encoding_circuit(self):
11 | """
12 | Test for the RandomLayeredEncodingCircuit class.
13 |
14 | The test checks if the circuit is generated correctly and uniquly for a given seed
15 | and set of parameters.
16 | """
17 |
18 | reference1 = [
19 | "Instruction(name='rz', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[0.7853981633974483])",
20 | "Instruction(name='rz', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[0.7853981633974483])",
21 | "Instruction(name='ry', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterExpression(3.14159265358979*x[0])])",
22 | "Instruction(name='ry', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterExpression(3.14159265358979*x[1])])",
23 | "Instruction(name='rz', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterExpression(atan(x[2]))])",
24 | "Instruction(name='rz', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterExpression(atan(x[3]))])",
25 | ]
26 | reference2 = [
27 | "Instruction(name='rz', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[0.7853981633974483])",
28 | "Instruction(name='rz', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[0.7853981633974483])",
29 | "Instruction(name='rz', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[0.7853981633974483])",
30 | "Instruction(name='rx', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[1.5707963267948966])",
31 | "Instruction(name='rx', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[1.5707963267948966])",
32 | "Instruction(name='rx', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[1.5707963267948966])",
33 | "Instruction(name='rz', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterExpression(atan(x[0]))])",
34 | "Instruction(name='rz', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterExpression(atan(x[1]))])",
35 | "Instruction(name='rz', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterExpression(atan(x[2]))])",
36 | ]
37 | reference3 = [
38 | "Instruction(name='z', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[])",
39 | "Instruction(name='z', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[])",
40 | "Instruction(name='z', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[])",
41 | "Instruction(name='cx', num_qubits=2, num_clbits=0, params=[])",
42 | "Instruction(name='cx', num_qubits=2, num_clbits=0, params=[])",
43 | "Instruction(name='rx', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterVectorElement(x[0])])",
44 | "Instruction(name='rx', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterVectorElement(x[1])])",
45 | "Instruction(name='rx', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterVectorElement(x[2])])",
46 | ]
47 |
48 | pqc = RandomLayeredEncodingCircuit(num_qubits=2, num_features=4, max_num_layers=3)
49 | x = ParameterVector("x", 4)
50 | check_list1 = [str(op[0]) for op in pqc.get_circuit(x, [])]
51 | assert check_list1 == reference1
52 |
53 | pqc.set_params(num_qubits=3, num_features=3, max_num_layers=3)
54 | x = ParameterVector("x", 3)
55 | check_list2 = [str(op[0]) for op in pqc.get_circuit(x, [])]
56 | assert check_list2 == reference2
57 |
58 | pqc.set_params(seed=1234)
59 | check_list3 = [str(op[0]) for op in pqc.get_circuit(x, [])]
60 | assert check_list3 == reference3
61 |
62 | def test_random_encoding_circuit(self):
63 | """
64 | Test for the RandomEncodingCircuit class.
65 |
66 | The test checks if the circuit is generated correctly and uniquly for a given seed
67 | and set of parameters.
68 | """
69 | reference1 = [
70 | "Instruction(name='z', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[])",
71 | "Instruction(name='rx', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterExpression(3.14159265358979*x[3])])",
72 | "Instruction(name='cx', num_qubits=2, num_clbits=0, params=[])",
73 | "Instruction(name='rxx', num_qubits=2, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterExpression(p[0]*x[1])])",
74 | "Instruction(name='ryy', num_qubits=2, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterExpression(p[1]*atan(x[0]))])",
75 | "Instruction(name='cz', num_qubits=2, num_clbits=0, params=[])",
76 | "Instruction(name='cy', num_qubits=2, num_clbits=0, params=[])",
77 | "Instruction(name='x', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[])",
78 | "Instruction(name='cry', num_qubits=2, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterExpression(3.14159265358979*x[2])])",
79 | "Instruction(name='rzx', num_qubits=2, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterExpression(p[2]*atan(x[1]))])",
80 | "Instruction(name='cry', num_qubits=2, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterExpression(p[3]*atan(x[0]))])",
81 | "Instruction(name='rxx', num_qubits=2, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterExpression(p[4]*x[2])])",
82 | "Instruction(name='ryy', num_qubits=2, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterExpression(p[5]*atan(x[3]))])",
83 | ]
84 | reference2 = [
85 | "Instruction(name='z', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[])",
86 | "Instruction(name='rz', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterExpression(atan(x[2]))])",
87 | "Instruction(name='cx', num_qubits=2, num_clbits=0, params=[])",
88 | "Instruction(name='rzz', num_qubits=2, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterExpression(p[0]*x[1])])",
89 | "Instruction(name='rx', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterVectorElement(x[0])])",
90 | ]
91 | reference3 = [
92 | "Instruction(name='rzx', num_qubits=2, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterExpression(p[0]*atan(x[0]))])",
93 | "Instruction(name='rx', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterVectorElement(x[2])])",
94 | "Instruction(name='rxx', num_qubits=2, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterVectorElement(p[1])])",
95 | "Instruction(name='z', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[])",
96 | "Instruction(name='rz', num_qubits=1, num_clbits=0, params=[ParameterExpression(atan(x[1]))])",
97 | ]
98 |
99 | pqc = RandomEncodingCircuit(num_qubits=2, num_features=4, seed=2)
100 | x = ParameterVector("x", 4)
101 | p = ParameterVector("p", pqc.num_parameters)
102 | check_list1 = [str(op[0]) for op in pqc.get_circuit(x, p)]
103 | assert check_list1 == reference1
104 |
105 | pqc.set_params(num_qubits=3, num_features=3, min_gates=3, max_gates=5)
106 | x = ParameterVector("x", 3)
107 | p = ParameterVector("p", pqc.num_parameters)
108 | check_list2 = [str(op[0]) for op in pqc.get_circuit(x, p)]
109 | assert check_list2 == reference2
110 |
111 | pqc.set_params(seed=1234)
112 | p = ParameterVector("p", pqc.num_parameters)
113 | check_list3 = [str(op[0]) for op in pqc.get_circuit(x, p)]
114 | assert check_list3 == reference3
115 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/kernel/matrix/test_fidelity_quantum_kernel.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Tests for FidelityKernel"""
2 |
3 | import pytest
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import sympy as sp
6 |
7 | from unittest.mock import MagicMock
8 |
9 | from squlearn import Executor
10 | from squlearn.encoding_circuit import LayeredEncodingCircuit
11 | from squlearn.kernel.lowlevel_kernel import FidelityKernel
12 |
13 |
14 | class TestFidelityKernel:
15 | """Test class for FidelityKernels"""
16 |
17 | @pytest.fixture
18 | def setup_single_variable(self):
19 | x, y, p = sp.symbols("x y p")
20 | sympy_K = (
21 | 0.375 * (1 - sp.cos(p)) ** 2 * sp.cos(x - y)
22 | + 0.125 * (1 - sp.cos(p)) ** 2 * sp.cos(x + y)
23 | - 0.5 * (1 - sp.cos(p)) ** 2
24 | - 1.0 * sp.cos(p)
25 | - 0.3125 * sp.cos(x - y)
26 | - 0.1875 * sp.cos(x + y)
27 | - 0.03125 * sp.cos(-2 * p + x + y)
28 | + 0.125 * sp.cos(-p + x + y)
29 | + 0.375 * sp.cos(p - x + y)
30 | + 0.375 * sp.cos(p + x - y)
31 | + 0.125 * sp.cos(p + x + y)
32 | + 0.03125 * sp.cos(2 * p - x + y)
33 | + 0.03125 * sp.cos(2 * p + x - y)
34 | - 0.03125 * sp.cos(2 * p + x + y)
35 | + 1.5
36 | )
37 |
38 | sympy_values = {
39 | "K": sympy_K,
40 | "dKdx": sp.diff(sympy_K, x),
41 | "dKdy": sp.diff(sympy_K, y),
42 | "dKdxdx": sp.diff(sp.diff(sympy_K, x), x),
43 | "dKdp": sp.diff(sympy_K, p),
44 | }
45 |
46 | return x, y, p, sympy_values
47 |
48 | @pytest.fixture
49 | def setup_multi_variable(self):
50 | x0, y0, p0 = sp.symbols("x0 y0 p0")
51 | x1, y1, p1 = sp.symbols("x1 y1 p1")
52 |
53 | sympy_K = (
54 | 0.25 * sp.cos(x0 - y0)
55 | + 0.25 * sp.cos(x1 - y1)
56 | + 0.125 * sp.cos(x0 - x1 - y0 + y1)
57 | + 0.125 * sp.cos(x0 + x1 - y0 - y1)
58 | + 0.25
59 | )
60 |
61 | sympy_values = {
62 | "K": sympy_K,
63 | "dKdx0": sp.diff(sympy_K, x0),
64 | "dKdx1": sp.diff(sympy_K, x1),
65 | "dKdy0": sp.diff(sympy_K, y0),
66 | "dKdy1": sp.diff(sympy_K, y1),
67 | "dKdp0": sp.diff(sympy_K, p0),
68 | "dKdp1": sp.diff(sympy_K, p1),
69 | }
70 |
71 | return x0, y0, x1, y1, p0, p1, sympy_values
72 |
73 | def create_fidelity_kernel(
74 | self, num_features, initial_parameters, executor, use_expectation, evaluate_duplicates
75 | ):
76 | executor = executor
77 | encoding_circuit = LayeredEncodingCircuit(
78 | num_qubits=num_features, num_features=num_features
79 | )
80 |
81 | if num_features == 1:
82 | encoding_circuit.Ry("p") # For 1 feature, the FQK analytical kernel is: Rx(x)@Ry(p)
83 | elif num_features == 2:
84 | encoding_circuit.Rx(
85 | "p"
86 | ) # For 2 features, the FQK analytical kernel is: Rx(x0)@Ry(p0) x Rx(x1)@Ry(p1)
87 | encoding_circuit.Rx("x")
88 |
89 | kernel = FidelityKernel(
90 | encoding_circuit,
91 | executor=executor,
92 | caching=False,
93 | use_expectation=use_expectation,
94 | initial_parameters=initial_parameters,
95 | evaluate_duplicates=evaluate_duplicates,
96 | )
97 |
98 | return kernel
99 |
100 | def test_single_variable_derivatives(self, setup_single_variable):
101 | x, y, p, sympy_values = setup_single_variable
102 |
103 | x_num, y_num = 0.79, -0.31
104 | p_num = -0.63
105 |
106 | subs = {x: x_num, y: y_num, p: p_num}
107 | sympy_num_values = {key: sympy_values[key].evalf(subs=subs) for key in sympy_values}
108 |
109 | kernel = self.create_fidelity_kernel(1, [p_num], Executor("pennylane"), True, "all")
110 |
111 | values = kernel.evaluate_derivatives(
112 | np.array([[x_num]]), np.array([[y_num]]), ["K", "dKdx", "dKdy", "dKdxdx", "dKdp"]
113 | )
114 | for key in ["K", "dKdx", "dKdy", "dKdxdx", "dKdp"]:
115 | assert np.allclose(
116 | np.array(values[key]).flatten().astype(float),
117 | np.array(sympy_num_values[key]).astype(float),
118 | atol=1e-7,
119 | )
120 |
121 | def test_multi_variable_derivatives(self, setup_multi_variable):
122 | x0, y0, x1, y1, p0, p1, sympy_values = setup_multi_variable
123 |
124 | x0_num, y0_num = 0.79, -0.31
125 | x1_num, y1_num = 0.9, -1.31
126 | p_num = -0.63
127 |
128 | subs = {
129 | x0: x0_num,
130 | y0: y0_num,
131 | x1: x1_num,
132 | y1: y1_num,
133 | p0: p_num,
134 | p1: p_num,
135 | }
136 | sympy_num_values = {
137 | "K": sympy_values["K"].evalf(subs=subs),
138 | "dKdx": [
139 | sympy_values["dKdx0"].evalf(subs=subs),
140 | sympy_values["dKdx1"].evalf(subs=subs),
141 | ],
142 | "dKdy": [
143 | sympy_values["dKdy0"].evalf(subs=subs),
144 | sympy_values["dKdy1"].evalf(subs=subs),
145 | ],
146 | "dKdp": [
147 | sympy_values["dKdp0"].evalf(subs=subs),
148 | sympy_values["dKdp1"].evalf(subs=subs),
149 | ],
150 | }
151 |
152 | kernel = self.create_fidelity_kernel(2, [p_num, p_num], Executor("pennylane"), True, "all")
153 |
154 | values = kernel.evaluate_derivatives(
155 | np.array([[x0_num, x1_num]]),
156 | np.array([[y0_num, y1_num]]),
157 | ["K", "dKdx", "dKdy", "dKdp"],
158 | )
159 |
160 | for key in ["K", "dKdx", "dKdy", "dKdp"]:
161 | assert np.allclose(
162 | np.array(values[key]).flatten().astype(float),
163 | np.array(sympy_num_values[key]).astype(float),
164 | atol=1e-7,
165 | )
166 |
167 | def test_with_and_without_duplicates(self):
168 | np.random.seed(0)
169 | x_train = np.random.rand(10, 2)
170 | p_num = -0.63
171 |
172 | # Check if FidelityKernelExpectationValue and FidelityKernelPennylane give the same results for no duplicates
173 | kernel_without_duplicates_and_expectation_value = self.create_fidelity_kernel(
174 | 2, [p_num, p_num], Executor("pennylane"), True, "none"
175 | )
176 |
177 | kernel_without_duplicates_and_pure_pennylane = self.create_fidelity_kernel(
178 | 2, [p_num, p_num], Executor("pennylane"), False, "none"
179 | )
180 |
181 | values_expecation_value = (
182 | kernel_without_duplicates_and_expectation_value.evaluate_derivatives(
183 | x_train, x_train, "K"
184 | )
185 | )
186 | values_pennylane = kernel_without_duplicates_and_pure_pennylane.evaluate(x_train, x_train)
187 | assert np.allclose(values_expecation_value, values_pennylane, atol=1e-7)
188 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/kernel/matrix/test_kernel_optimizer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import pytest
3 |
4 | from sklearn.datasets import make_regression, make_classification
5 |
6 | from squlearn import Executor
7 | from squlearn.encoding_circuit.circuit_library.yz_cx_encoding_circuit import YZ_CX_EncodingCircuit
8 | from squlearn.kernel import FidelityKernel, ProjectedQuantumKernel, KernelOptimizer
9 | from squlearn.kernel import KernelOptimizer
10 | from squlearn.kernel import QGPR, QGPC, QKRR, QSVC, QSVR
11 | from squlearn.kernel.loss import NLL, TargetAlignment
12 |
13 | from squlearn.optimizers.adam import Adam
14 |
15 |
16 | @pytest.fixture(scope="module")
17 | def setup_kernel_optimizer_for_regressor():
18 | """Setup kernel optimizer for regression tasks."""
19 | enc_circ = YZ_CX_EncodingCircuit(num_qubits=4, num_features=4, num_layers=2)
20 | q_kernel = FidelityKernel(
21 | encoding_circuit=enc_circ,
22 | executor=Executor("pennylane"),
23 | parameter_seed=0,
24 | regularization="tikhonov",
25 | )
26 | nll_loss = NLL()
27 | optimzer = Adam(options={"maxiter": 3, "lr": 0.1})
28 | kernel_optimizer = KernelOptimizer(quantum_kernel=q_kernel, loss=nll_loss, optimizer=optimzer)
29 | regression_data = make_regression(n_samples=10, n_features=4, random_state=0)
30 | return kernel_optimizer, regression_data
31 |
32 |
33 | @pytest.fixture(scope="module")
34 | def setup_kernel_optimizer_for_classifier():
35 | """Setup kernel optimizer for classification tasks."""
36 | enc_circ = YZ_CX_EncodingCircuit(4, num_features=4, num_layers=2, c=1.0)
37 | q_kernel = ProjectedQuantumKernel(
38 | encoding_circuit=enc_circ,
39 | executor=Executor("pennylane"),
40 | parameter_seed=0,
41 | regularization="tikhonov",
42 | )
43 | nll_loss = TargetAlignment()
44 | optimzer = Adam(options={"maxiter": 3, "lr": 0.1})
45 | kernel_optimizer = KernelOptimizer(quantum_kernel=q_kernel, loss=nll_loss, optimizer=optimzer)
46 | classification_data = make_classification(n_samples=10, n_features=4, random_state=0)
47 | return kernel_optimizer, classification_data
48 |
49 |
50 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("high_level_class", [QGPR, QKRR, QSVR])
51 | def test_kernel_optimizer_for_regressor_classes(
52 | setup_kernel_optimizer_for_regressor,
53 | high_level_class,
54 | ):
55 | """Test kernel optimizer for high-level regression methods.
56 |
57 | Args:
58 | setup_kernel_optimizer_for_regressor: A fixture that returns a kernel optimizer and
59 | regression data.
60 | high_level_class: A high-level regression class
61 | """
62 | kernel_optimizer, regression_data = setup_kernel_optimizer_for_regressor
63 | model = high_level_class(quantum_kernel=kernel_optimizer)
64 | model.fit(regression_data[0], regression_data[1])
65 | assert kernel_optimizer.get_optimal_parameters() is not None
66 | assert kernel_optimizer._optimizer is not None
67 | assert kernel_optimizer.is_fitted
68 |
69 |
70 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("high_level_class", [QGPC, QSVC])
71 | def test_kernel_opimizer_for_classification_classes(
72 | setup_kernel_optimizer_for_classifier,
73 | high_level_class,
74 | ):
75 | """Test kernel optimizer for high-level classification methods.
76 |
77 | Args:
78 | setup_kernel_optimizer_for_classifier: A fixture that returns a kernel optimizer and
79 | classification data.
80 | high_level_class: A high-level classification class
81 | """
82 | kernel_optimizer, classification_data = setup_kernel_optimizer_for_classifier
83 | model = high_level_class(quantum_kernel=kernel_optimizer)
84 | model.fit(classification_data[0], classification_data[1])
85 | assert kernel_optimizer.get_optimal_parameters() is not None
86 | assert kernel_optimizer._optimizer is not None
87 | assert kernel_optimizer.is_fitted
88 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/kernel/matrix/test_projected_quantum_kernel.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Tests for ProjectedQuantumKernel"""
2 |
3 | import pytest
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import sympy as sp
6 |
7 | from unittest.mock import MagicMock
8 |
9 | from squlearn import Executor
10 | from squlearn.encoding_circuit import LayeredEncodingCircuit
11 | from squlearn.kernel.lowlevel_kernel import ProjectedQuantumKernel
12 |
13 |
14 | class TestProjectedQuantumKernel:
15 | """Test class for ProjectedQuantumKernel"""
16 |
17 | @pytest.fixture
18 | def setup_single_variable(self):
19 | x, y, gamma_sp, p = sp.symbols("x y gamma p")
20 | sympy_K = sp.exp(-2 * gamma_sp * (1 - sp.cos(x - y)) * sp.cos(p) ** 2)
21 |
22 | sympy_values = {
23 | "K": sympy_K,
24 | "dKdx": sp.diff(sympy_K, x),
25 | "dKdy": sp.diff(sympy_K, y),
26 | "dKdxdx": sp.diff(sp.diff(sympy_K, x), x),
27 | "dKdp": sp.diff(sympy_K, p),
28 | }
29 |
30 | return x, y, gamma_sp, p, sympy_values
31 |
32 | @pytest.fixture
33 | def setup_multi_variable(self):
34 | x0, y0, gamma_sp, p0 = sp.symbols("x0 y0 gamma p0")
35 | x1, y1, p1 = sp.symbols("x1 y1 p1")
36 |
37 | sympy_K = sp.exp(
38 | -2.0
39 | * gamma_sp
40 | * (
41 | -sp.cos(p0) ** 2 * sp.cos(x0 - y0)
42 | + sp.cos(p0) ** 2
43 | - sp.cos(p1) ** 2 * sp.cos(x1 - y1)
44 | + sp.cos(p1) ** 2
45 | )
46 | )
47 |
48 | sympy_values = {
49 | "K": sympy_K,
50 | "dKdx0": sp.diff(sympy_K, x0),
51 | "dKdx1": sp.diff(sympy_K, x1),
52 | "dKdy0": sp.diff(sympy_K, y0),
53 | "dKdy1": sp.diff(sympy_K, y1),
54 | "dKdp0": sp.diff(sympy_K, p0),
55 | "dKdp1": sp.diff(sympy_K, p1),
56 | }
57 |
58 | return x0, y0, x1, y1, gamma_sp, p0, p1, sympy_values
59 |
60 | def create_projected_quantum_kernel(self, num_features, gamma_num, initial_parameters):
61 | executor = Executor()
62 | encoding_circuit = LayeredEncodingCircuit(
63 | num_qubits=num_features, num_features=num_features
64 | )
65 | encoding_circuit.Ry("p")
66 | encoding_circuit.Rx("x")
67 |
68 | kernel = ProjectedQuantumKernel(
69 | encoding_circuit=encoding_circuit,
70 | executor=executor,
71 | outer_kernel="gaussian",
72 | gamma=gamma_num,
73 | initial_parameters=np.array(initial_parameters),
74 | )
75 | return kernel
76 |
77 | def test_single_variable_derivatives(self, setup_single_variable):
78 | x, y, gamma_sp, p, sympy_values = setup_single_variable
79 |
80 | x_num, y_num = 0.79, -0.31
81 | p_num = -0.63
82 | gamma_num = 0.08
83 |
84 | subs = {x: x_num, y: y_num, gamma_sp: gamma_num, p: p_num}
85 | sympy_num_values = {key: sympy_values[key].evalf(subs=subs) for key in sympy_values}
86 |
87 | kernel = self.create_projected_quantum_kernel(1, gamma_num, [p_num])
88 |
89 | values = kernel.evaluate_derivatives(
90 | [x_num], [y_num], ["K", "dKdx", "dKdy", "dKdxdx", "dKdp"]
91 | )
92 | for key in ["K", "dKdx", "dKdy", "dKdxdx", "dKdp"]:
93 | assert np.allclose(
94 | np.array(values[key]).flatten().astype(float),
95 | np.array(sympy_num_values[key]).astype(float),
96 | atol=1e-7,
97 | )
98 |
99 | def test_multi_variable_derivatives(self, setup_multi_variable):
100 | x0, y0, x1, y1, gamma_sp, p0, p1, sympy_values = setup_multi_variable
101 |
102 | x0_num, y0_num = 0.79, -0.31
103 | x1_num, y1_num = 0.9, -1.31
104 | p_num = -0.63
105 | gamma_num = 0.08
106 |
107 | subs = {
108 | x0: x0_num,
109 | y0: y0_num,
110 | x1: x1_num,
111 | y1: y1_num,
112 | gamma_sp: gamma_num,
113 | p0: p_num,
114 | p1: p_num,
115 | }
116 | sympy_num_values = {
117 | "K": sympy_values["K"].evalf(subs=subs),
118 | "dKdx": [
119 | sympy_values["dKdx0"].evalf(subs=subs),
120 | sympy_values["dKdx1"].evalf(subs=subs),
121 | ],
122 | "dKdy": [
123 | sympy_values["dKdy0"].evalf(subs=subs),
124 | sympy_values["dKdy1"].evalf(subs=subs),
125 | ],
126 | "dKdp": [
127 | sympy_values["dKdp0"].evalf(subs=subs),
128 | sympy_values["dKdp1"].evalf(subs=subs),
129 | ],
130 | }
131 |
132 | kernel = self.create_projected_quantum_kernel(2, gamma_num, [p_num, p_num])
133 |
134 | values = kernel.evaluate_derivatives(
135 | [[x0_num, x1_num]], [[y0_num, y1_num]], ["K", "dKdx", "dKdy", "dKdp"]
136 | )
137 |
138 | for key in ["K", "dKdx", "dKdy", "dKdp"]:
139 | assert np.allclose(
140 | np.array(values[key]).flatten().astype(float),
141 | np.array(sympy_num_values[key]).astype(float),
142 | atol=1e-7,
143 | )
144 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/optimizers/test_sglbo.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Tests for the SGLBO optimizer."""
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 |
5 | from squlearn.optimizers.sglbo import SGLBO
6 |
7 |
8 | # define the function to be optimized
9 | def quadratic(x):
10 | return np.sum(x**2)
11 |
12 |
13 | class TestSGLBO:
14 | """Test class for SGLBO optimizer."""
15 |
16 | def test_minimize(self):
17 | """Test the minimize method of SGLBO."""
18 | x0 = np.array([1.0, 2.0])
19 |
20 | optimizer = SGLBO()
21 |
22 | result = optimizer.minimize(quadratic, x0)
23 |
24 | assert np.isclose(result.fun, 0.0, atol=1e-6)
25 |
26 | def test_step(self):
27 | """Test the step method of SGLBO."""
28 |
29 | def gradient_function(x):
30 | return 2 * x
31 |
32 | x0 = np.array([2.0])
33 |
34 | optimizer = SGLBO()
35 | optimizer.x = x0
36 | optimizer.func = quadratic
37 |
38 | result = optimizer.step(x=optimizer.x, grad=gradient_function(optimizer.x))
39 |
40 | assert result < x0
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/qnn/test_base_qnn.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Tests for BaseQNN"""
2 |
3 | import pytest
4 |
5 | import numpy as np
6 |
7 | from squlearn import Executor
8 | from squlearn.observables import IsingHamiltonian
9 | from squlearn.encoding_circuit import ChebyshevPQC
10 | from squlearn.optimizers import SLSQP
11 | from squlearn.qnn import SquaredLoss
12 | from squlearn.qnn.base_qnn import BaseQNN
13 |
14 |
15 | class MockBaseQNN(BaseQNN):
16 | """Mock class for BaseQNN."""
17 |
18 | def _fit(self, X: np.ndarray, y: np.ndarray, weights: np.ndarray = None) -> None:
19 | pass
20 |
21 |
22 | class TestBaseQNN:
23 | """Test class for BaseQNN."""
24 |
25 | @pytest.fixture(scope="module")
26 | def qnn_single_op(self) -> MockBaseQNN:
27 | """BaseQNN module with single operator."""
28 | np.random.seed(42)
29 | executor = Executor()
30 | pqc = ChebyshevPQC(num_qubits=4, num_features=1, num_layers=2)
31 | operator = IsingHamiltonian(num_qubits=4, I="S", Z="S", ZZ="S")
32 | loss = SquaredLoss()
33 | optimizer = SLSQP(options={"maxiter": 2})
34 | return MockBaseQNN(pqc, operator, executor, loss, optimizer)
35 |
36 | @pytest.fixture(scope="module")
37 | def qnn_multi_op(self) -> MockBaseQNN:
38 | """BaseQNN module with multiple operators."""
39 | np.random.seed(42)
40 | executor = Executor()
41 | pqc = ChebyshevPQC(num_qubits=4, num_features=1, num_layers=2)
42 | operator = [IsingHamiltonian(num_qubits=4, I="S", Z="S", ZZ="S") for _ in range(5)]
43 | loss = SquaredLoss()
44 | optimizer = SLSQP(options={"maxiter": 2})
45 | return MockBaseQNN(pqc, operator, executor, loss, optimizer)
46 |
47 | def test_set_params_invalid_param(self, qnn_single_op: MockBaseQNN):
48 | """
49 | Test if setting an invalid parameter raises a ValueError.
50 |
51 | Args:
52 | qnn_single_op (MockBaseQNN): The MockBaseQNN object to test.
53 |
54 | Returns:
55 | None
56 | """
57 | with pytest.raises(ValueError):
58 | qnn_single_op.set_params(invalid_param=3)
59 |
60 | def test_set_params_seed(self, qnn_single_op: MockBaseQNN):
61 | """
62 | Test `set_params` with `parameter_seed`.
63 |
64 | Args:
65 | qnn_single_op (MockBaseQNN): An instance of the `MockBaseQNN` class.
66 |
67 | Returns:
68 | None
69 | """
70 | qnn_single_op.set_params(parameter_seed=42)
71 | assert qnn_single_op.parameter_seed == 42
72 |
73 | def test_set_params_num_qubits_single_op(self, qnn_single_op: MockBaseQNN):
74 | """
75 | Test `set_params` with `num_qubits` for single operator.
76 |
77 | Args:
78 | qnn_single_op (MockBaseQNN): An instance of the `MockBaseQNN` class.
79 |
80 | Returns:
81 | None
82 | """
83 | qnn_single_op.set_params(num_qubits=5)
84 | assert qnn_single_op.encoding_circuit.num_qubits == 5
85 | assert qnn_single_op.operator.num_qubits == 5
86 | assert qnn_single_op._qnn.num_qubits == 5
87 |
88 | def test_set_params_num_qubits_multi_op(self, qnn_multi_op):
89 | """
90 | Test `set_params` with `num_qubits` for multiple operators.
91 |
92 | Args:
93 | qnn_multi_op (MockBaseQNN): An instance of the `MockBaseQNN` class.
94 |
95 | Returns:
96 | None
97 | """
98 | qnn_multi_op.set_params(num_qubits=5)
99 | assert qnn_multi_op.encoding_circuit.num_qubits == 5
100 | for operator in qnn_multi_op.operator:
101 | assert operator.num_qubits == 5
102 | assert qnn_multi_op._qnn.num_qubits == 5
103 |
104 | def test_set_params_encoding_circuit(self, qnn_single_op):
105 | """
106 | Test `set_params` for pqc parameters.
107 |
108 | Args:
109 | qnn_single_op (MockBaseQNN): An instance of the `MockBaseQNN` class.
110 |
111 | Returns:
112 | None
113 | """
114 | qnn_single_op.set_params(num_layers=3, closed=True)
115 | assert qnn_single_op.encoding_circuit.num_layers == 3
116 | assert qnn_single_op.encoding_circuit.closed
117 | assert qnn_single_op._qnn._pqc.get_params()["num_layers"] == 3
118 | assert qnn_single_op._qnn._pqc.get_params()["closed"]
119 |
120 | def test_set_params_single_operator(self, qnn_single_op):
121 | """
122 | Test `set_params` for single operator parameters.
123 |
124 | Args:
125 | qnn_single_op (MockBaseQNN): An instance of the `MockBaseQNN` class.
126 |
127 | Returns:
128 | None
129 | """
130 | qnn_single_op.set_params(X="S", Z="N")
131 | assert qnn_single_op.operator.X == "S"
132 | assert qnn_single_op.operator.Z == "N"
133 | assert qnn_single_op._qnn._observable.X == "S"
134 | assert qnn_single_op._qnn._observable.Z == "N"
135 |
136 | def test_set_params_multi_operator(self, qnn_multi_op):
137 | """
138 | Test `set_params` for multiple operator parameters.
139 |
140 | Args:
141 | qnn_multi_op (MockBaseQNN): An instance of the `MockBaseQNN` class.
142 |
143 | Returns:
144 | None
145 | """
146 | qnn_multi_op.set_params(op0__X="S", op3__Z="N")
147 | assert qnn_multi_op.operator[0].X == "S"
148 | assert qnn_multi_op.operator[3].Z == "N"
149 | assert qnn_multi_op._qnn._observable[0].X == "S"
150 | assert qnn_multi_op._qnn._observable[3].Z == "N"
151 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/qrc/test_base_qrc.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Tests for BaseQRC"""
2 |
3 | import pytest
4 |
5 | import numpy as np
6 |
7 | from squlearn import Executor
8 | from squlearn.encoding_circuit import HubregtsenEncodingCircuit
9 | from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
10 | from squlearn.qrc.base_qrc import BaseQRC
11 |
12 |
13 | class MockBaseQRC(BaseQRC):
14 | """Mock class for BaseQRC."""
15 |
16 | def _initialize_ml_model(self) -> None:
17 | """Initialize the machine learning model, has to be implemented in the child class"""
18 | self._ml_model = LinearRegression()
19 |
20 |
21 | class TestBaseQRC:
22 | """Test class for BaseQRC."""
23 |
24 | @pytest.fixture(scope="module")
25 | def qrc_class(self) -> MockBaseQRC:
26 | """BaseQRC module."""
27 | executor = Executor()
28 | encoding_circuit = HubregtsenEncodingCircuit(num_qubits=4, num_features=2)
29 | return MockBaseQRC(encoding_circuit, executor)
30 |
31 | def test_set_params_invalid_param(self, qrc_class: MockBaseQRC):
32 | """
33 | Test if setting an invalid parameter raises a ValueError.
34 |
35 | Args:
36 | qrc_class (MockBaseQRC): The MockBaseQRC object to test.
37 |
38 | Returns:
39 | None
40 | """
41 | with pytest.raises(ValueError):
42 | qrc_class.set_params(invalid_param=3)
43 |
44 | def test_set_params_seed(self, qrc_class: MockBaseQRC):
45 | """
46 | Test `set_params` with `parameter_seed`.
47 |
48 | Args:
49 | qrc_class (MockBaseQRC): An instance of the `MockBaseQRC` class.
50 |
51 | Returns:
52 | None
53 | """
54 | qrc_class.set_params(parameter_seed=42)
55 | assert qrc_class.parameter_seed == 42
56 |
57 | def test_set_params_num_qubits(self, qrc_class: MockBaseQRC):
58 | """
59 | Test `set_params` with `num_qubits` for QRC base class.
60 |
61 | Args:
62 | qrc_class (MockBaseQRC): An instance of the `MockBaseQRC` class.
63 |
64 | Returns:
65 | None
66 | """
67 | qrc_class.set_params(num_qubits=5)
68 | assert qrc_class.encoding_circuit.num_qubits == 5
69 | assert qrc_class._operators[0].num_qubits == 5
70 | assert qrc_class._qnn.num_qubits == 5
71 |
72 | def test_set_params_num_operators(self, qrc_class: MockBaseQRC):
73 | """
74 | Test `set_params` with `num_operators` for QRC base class
75 |
76 | Args:
77 | qrc_class (MockBaseQRC): An instance of the `MockBaseQRC` class.
78 |
79 | Returns:
80 | None
81 | """
82 | qrc_class.set_params(num_operators=12)
83 | assert len(qrc_class._operators) == 12
84 | assert qrc_class.num_operators == 12
85 | qrc_class.fit(np.array([[0.1, 0.2], [0.1, 0.2]]), np.array([0.3, 0.4]))
86 | assert qrc_class._ml_model.n_features_in_ == 12
87 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/qrc/test_qrc_classifier.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Tests for QRCClassifier"""
2 |
3 | import pytest
4 |
5 | import numpy as np
6 | from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
7 | from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
8 |
9 | from squlearn import Executor
10 | from squlearn.encoding_circuit import HubregtsenEncodingCircuit
11 | from squlearn.qrc.qrc_classifier import QRCClassifier
12 |
13 |
14 | class TestQRCClassifier:
15 | """Test class for QRCClassifier."""
16 |
17 | @pytest.fixture(scope="module")
18 | def data(self) -> tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
19 | """Test data module."""
20 | # pylint: disable=unbalanced-tuple-unpacking
21 | X, y = make_classification(n_samples=6, n_features=4, random_state=42)
22 | scl = MinMaxScaler((0.1, 0.9))
23 | X = scl.fit_transform(X, y)
24 | return X, y
25 |
26 | def qrc_classifier(self, ml_model: str) -> QRCClassifier:
27 | """QNNClassifier module."""
28 | pqc = HubregtsenEncodingCircuit(num_qubits=4, num_features=4, num_layers=1)
29 | return QRCClassifier(pqc, Executor(), ml_model=ml_model)
30 |
31 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
32 | "ml_model",
33 | [
34 | "linear",
35 | "mlp",
36 | "kernel",
37 | ],
38 | )
39 | def test_fit_predict(self, data, ml_model):
40 | """Tests fit and predict methods of QRCClassifier."""
41 | X, y = data
42 | qrc_classifier = self.qrc_classifier(ml_model)
43 |
44 | if ml_model == "mlp":
45 | qrc_classifier.set_params(ml_model_options={"random_state": 0, "max_iter": 1000})
46 |
47 | qrc_classifier.fit(X, y)
48 | values = qrc_classifier.predict(X)
49 |
50 | referece_values = {
51 | "linear": np.array([0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1]),
52 | "mlp": np.array([0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1]),
53 | "kernel": np.array([0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1]),
54 | }
55 | assert np.allclose(values, referece_values[ml_model], atol=1e-7)
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/qrc/test_qrc_regressor.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Tests for QRCRegressor"""
2 |
3 | import pytest
4 |
5 | import numpy as np
6 | from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
7 | from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
8 |
9 | from squlearn import Executor
10 | from squlearn.encoding_circuit import HubregtsenEncodingCircuit
11 | from squlearn.qrc.qrc_regressor import QRCRegressor
12 |
13 |
14 | class TestQRCRegressor:
15 | """Test class for QRCRegressor."""
16 |
17 | @pytest.fixture(scope="module")
18 | def data(self) -> tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
19 | """Test data module."""
20 | # pylint: disable=unbalanced-tuple-unpacking
21 | X, y = make_regression(n_samples=6, n_features=1, random_state=42)
22 | scl = MinMaxScaler((0.1, 0.9))
23 | X = scl.fit_transform(X, y)
24 | return X, y
25 |
26 | def qrc_regressor(self, ml_model: str) -> QRCRegressor:
27 | """QNNRegressor module."""
28 | pqc = HubregtsenEncodingCircuit(num_qubits=2, num_features=1, num_layers=1)
29 | return QRCRegressor(pqc, Executor(), ml_model=ml_model)
30 |
31 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
32 | "ml_model",
33 | [
34 | "linear",
35 | "mlp",
36 | "kernel",
37 | ],
38 | )
39 | def test_fit_predict(self, data, ml_model):
40 | """Tests fit and predict methods of QRCRegressor."""
41 | X, y = data
42 | qrc_regressor = self.qrc_regressor(ml_model)
43 |
44 | if ml_model == "mlp":
45 | qrc_regressor.set_params(ml_model_options={"random_state": 0, "max_iter": 1000})
46 |
47 | qrc_regressor.fit(X, y)
48 | values = qrc_regressor.predict(X)
49 |
50 | referece_values = {
51 | "linear": np.array(
52 | [2.88509523, -0.80308901, 3.76200899, -1.35995202, 8.84630756, -1.36004739]
53 | ),
54 | "mlp": np.array(
55 | [3.06585455, -0.96776248, 4.0395428, -1.52636054, 8.80042369, -1.52645433]
56 | ),
57 | "kernel": np.array(
58 | [2.87653068, -0.65406699, 3.74209315, -1.13894099, 8.15484098, -1.13902237]
59 | ),
60 | }
61 |
62 | assert np.allclose(values, referece_values[ml_model], atol=1e-7)
63 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/util/execution/test_parallel_primitives.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import pytest
2 | import numpy as np
3 |
4 | from qiskit.circuit import QuantumCircuit
5 | from qiskit.quantum_info import SparsePauliOp
6 | from qiskit_ibm_runtime.fake_provider import FakeManilaV2
7 | from squlearn.util import Executor
8 | from squlearn.util.executor import BaseEstimatorV1, BaseEstimatorV2, BaseSamplerV1, BaseSamplerV2
9 |
10 |
11 | class TestParallelExecutor:
12 |
13 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("parallel_mode", ["auto", 2])
14 | def test_parallel_sampler(self, parallel_mode):
15 | """
16 | Script for testing parallel execution of the sampler primitive.
17 | """
18 | qc = QuantumCircuit(2)
19 | qc.x([0, 1])
20 | qc.measure_all()
21 | executor = Executor(FakeManilaV2(), seed=0, shots=10000, qpu_parallelization=parallel_mode)
22 | sampler = executor.get_sampler()
23 | if isinstance(sampler, BaseSamplerV1):
24 | result = sampler.run(qc).result()
25 | assert result.metadata[0]["shots"] == 10000
26 | else:
27 | result = sampler.run([(qc,)]).result()
28 | assert result[0].metadata["shots"] == 10000
29 |
30 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("parallel_mode", ["auto", 2])
31 | def test_parallel_estimator(self, parallel_mode):
32 | """
33 | Script for testing parallel execution of the estimator primitive.
34 | """
35 | qc = QuantumCircuit(2)
36 | qc.x([0, 1])
37 | obs = SparsePauliOp("ZZ")
38 | executor = Executor(FakeManilaV2(), seed=0, shots=10000, qpu_parallelization=parallel_mode)
39 | estimator = executor.get_estimator()
40 | if isinstance(estimator, BaseEstimatorV1):
41 | result = estimator.run(qc, obs).result()
42 | assert result.metadata[0]["shots"] == 10000
43 | else:
44 | result = estimator.run([(qc, obs)]).result()
45 | assert result[0].metadata["shots"] == 10000
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 3 |
3 |  3 |
3 |  11 |
11 |