├── .gitignore
├── .pre-commit-config.yaml
├── LICENSE
├── Makefile
├── README.md
├── docs
├── ROADMAP.md
└── assets
│ ├── voltron-banner-alpha.png
│ ├── voltron-banner.png
│ └── voltron-framework.png
├── examples
├── pretrain
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── preprocess.py
│ └── pretrain.py
├── usage.py
├── verification
│ ├── img
│ │ ├── peel-carrot-final.png
│ │ ├── peel-carrot-initial.png
│ │ ├── place-bottle-final.png
│ │ ├── place-bottle-grasp.png
│ │ └── place-bottle-initial.png
│ └── verify.py
└── xla-reference
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── xpreprocess.py
│ └── xpretrain.py
├── pyproject.toml
├── setup.py
└── voltron
├── __init__.py
├── conf
├── __init__.py
├── accelerators.py
├── datasets.py
├── models.py
└── tracking.py
├── datasets
├── __init__.py
├── datasets.py
└── v1
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── stream_datasets.py
├── models
├── __init__.py
├── core
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── vcond.py
│ ├── vdual.py
│ └── vgen.py
├── instantiate.py
├── materialize.py
├── reproductions
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── vmvp.py
│ ├── vr3m.py
│ └── vrn3m.py
└── util
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── extraction.py
│ ├── optimization.py
│ └── transformer.py
├── overwatch
├── __init__.py
└── overwatch.py
├── preprocessing
├── __init__.py
├── core.py
├── process.py
├── transforms.py
└── v1
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── process.py
│ ├── transforms.py
│ └── utils.py
└── util
├── __init__.py
├── checkpointing.py
├── metrics.py
├── utilities.py
└── v1
├── __init__.py
├── checkpointing.py
├── distributed.py
├── random.py
└── xla_logger.py
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
2 | __pycache__/
3 | *.py[cod]
4 | *$py.class
5 |
6 | # C extensions
7 | *.so
8 |
9 | # Distribution / packaging
10 | .Python
11 | build/
12 | develop-eggs/
13 | dist/
14 | downloads/
15 | eggs/
16 | .eggs/
17 | lib/
18 | lib64/
19 | parts/
20 | sdist/
21 | var/
22 | wheels/
23 | pip-wheel-metadata/
24 | share/python-wheels/
25 | *.egg-info/
26 | .installed.cfg
27 | *.egg
28 | MANIFEST
29 |
30 | # PyInstaller
31 | # Usually these files are written by a python script from a template
32 | # before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it.
33 | *.manifest
34 | *.spec
35 |
36 | # Installer logs
37 | pip-log.txt
38 | pip-delete-this-directory.txt
39 |
40 | # Unit test / coverage reports
41 | htmlcov/
42 | .tox/
43 | .nox/
44 | .coverage
45 | .coverage.*
46 | .cache
47 | nosetests.xml
48 | coverage.xml
49 | *.cover
50 | *.py,cover
51 | .hypothesis/
52 | .pytest_cache/
53 |
54 | # Translations
55 | *.mo
56 | *.pot
57 |
58 | # Django stuff:
59 | *.log
60 | local_settings.py
61 | db.sqlite3
62 | db.sqlite3-journal
63 |
64 | # Flask stuff:
65 | instance/
66 | .webassets-cache
67 |
68 | # Scrapy stuff:
69 | .scrapy
70 |
71 | # Sphinx documentation
72 | docs/_build/
73 |
74 | # PyBuilder
75 | target/
76 |
77 | # Jupyter Notebook
78 | .ipynb_checkpoints
79 |
80 | # IPython
81 | profile_default/
82 | ipython_config.py
83 |
84 | # pyenv
85 | .python-version
86 |
87 | # pipenv
88 | # According to pypa/pipenv#598, it is recommended to include Pipfile.lock in version control.
89 | # However, in case of collaboration, if having platform-specific dependencies or dependencies
90 | # having no cross-platform support, pipenv may install dependencies that don't work, or not
91 | # install all needed dependencies.
92 | #Pipfile.lock
93 |
94 | # PEP 582; used by e.g. github.com/David-OConnor/pyflow
95 | __pypackages__/
96 |
97 | # Celery stuff
98 | celerybeat-schedule
99 | celerybeat.pid
100 |
101 | # SageMath parsed files
102 | *.sage.py
103 |
104 | # Environments
105 | .env
106 | .venv
107 | env/
108 | venv/
109 | ENV/
110 | env.bak/
111 | venv.bak/
112 |
113 | # Spyder project settings
114 | .spyderproject
115 | .spyproject
116 |
117 | # Rope project settings
118 | .ropeproject
119 |
120 | # mkdocs documentation
121 | /site
122 |
123 | # mypy
124 | .mypy_cache/
125 | .dmypy.json
126 | dmypy.json
127 |
128 | # Pyre type checker
129 | .pyre/
130 |
131 | # Ruff
132 | .ruff_cache/
133 |
134 | # IDE caches
135 | .idea/
136 | .vscode/
137 |
138 | # Mac OS
139 | .DS_Store
140 |
141 | # Cache
142 | data/
143 | cache/
144 |
145 | # Scratch
146 | scratch/
147 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.pre-commit-config.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # See https://pre-commit.com for more information
2 | # See https://pre-commit.com/hooks.html for more hooks
3 | exclude: ".git"
4 |
5 | repos:
6 | - repo: https://github.com/charliermarsh/ruff-pre-commit
7 | rev: v0.0.252
8 | hooks:
9 | - id: ruff
10 | args: [ --fix, --exit-non-zero-on-fix ]
11 |
12 | - repo: https://github.com/psf/black
13 | rev: 23.1.0
14 | hooks:
15 | - id: black
16 |
17 | - repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
18 | rev: v4.4.0
19 | hooks:
20 | - id: check-added-large-files
21 | args: ["--maxkb=40000"]
22 | - id: check-ast
23 | - id: check-case-conflict
24 | - id: check-merge-conflict
25 | - id: check-toml
26 | - id: check-yaml
27 | - id: end-of-file-fixer
28 | - id: trailing-whitespace
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2021-present, Siddharth Karamcheti and other contributors.
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Makefile:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .PHONY: help check autoformat
2 | .DEFAULT: help
3 |
4 | # Generates a useful overview/help message for various make features - add to this as necessary!
5 | help:
6 | @echo "make check"
7 | @echo " Run code style and linting (black, ruff) *without* changing files!"
8 | @echo "make autoformat"
9 | @echo " Run code styling (black, ruff) and update in place - committing with pre-commit also does this."
10 |
11 | check:
12 | black --check .
13 | ruff check --show-source .
14 |
15 | autoformat:
16 | black .
17 | ruff check --fix --show-fixes .
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |

3 |
6 |
7 | [](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.12766)
8 | [](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/)
9 | [](https://github.com/psf/black)
10 | [](https://github.com/charliermarsh/ruff)
11 | 
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 | ---
16 |
17 | # Language-Driven Representation Learning for Robotics
18 |
19 | Package repository for Voltron: Language-Driven Representation Learning for Robotics. Provides code for loading
20 | pretrained Voltron, R3M, and MVP representations for adaptation to downstream tasks, as well as code for pretraining
21 | such representations on arbitrary datasets.
22 |
23 | ---
24 |
25 | ## Quickstart
26 |
27 | This repository is built with PyTorch; while specified as a dependency for the package, we highly recommend that
28 | you install the desired version (e.g., with accelerator support) for your given hardware and environment
29 | manager (e.g., `conda`).
30 |
31 | PyTorch installation instructions [can be found here](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/). This repository
32 | should work with PyTorch >= 1.12. Releases before 1.1.0 have been thoroughly tested with PyTorch 1.12.0,
33 | Torchvision 0.13.0, and Torchaudio 0.12.0. **Note**: Releases 1.1.0 and after *assume PyTorch 2.0*!
34 |
35 | Once PyTorch has been properly installed, you can install this package via PyPI, and you're off!
36 |
37 | ```bash
38 | pip install voltron-robotics
39 | ```
40 |
41 | You can also install this package locally via an editable installation in case you want to run examples/extend the
42 | current functionality:
43 |
44 | ```bash
45 | git clone https://github.com/siddk/voltron-robotics
46 | cd voltron-robotics
47 | pip install -e .
48 | ```
49 |
50 | ## Usage
51 |
52 | Voltron Robotics (package: `voltron`) is structured to provide easy access to pretrained Voltron models (and
53 | reproductions), to facilitate use for various downstream tasks. Using a pretrained Voltron model is easy:
54 |
55 | ```python
56 | from torchvision.io import read_image
57 | from voltron import instantiate_extractor, load
58 |
59 | # Load a frozen Voltron (V-Cond) model & configure a vector extractor
60 | vcond, preprocess = load("v-cond", device="cuda", freeze=True)
61 | vector_extractor = instantiate_extractor(vcond)()
62 |
63 | # Obtain & Preprocess an image =>> can be from a dataset, or camera on a robot, etc.
64 | # => Feel free to add any language if you have it (Voltron models work either way!)
65 | img = preprocess(read_image("examples/img/peel-carrot-initial.png"))[None, ...].to("cuda")
66 | lang = ["peeling a carrot"]
67 |
68 | # Extract both multimodal AND vision-only embeddings!
69 | multimodal_embeddings = vcond(img, lang, mode="multimodal")
70 | visual_embeddings = vcond(img, mode="visual")
71 |
72 | # Use the `vector_extractor` to output dense vector representations for downstream applications!
73 | # => Pass this representation to model of your choice (object detector, control policy, etc.)
74 | representation = vector_extractor(multimodal_embeddings)
75 | ```
76 |
77 | Voltron representations can be used for a variety of different applications; in the
78 | [`voltron-evaluation`](https://github.com/siddk/voltron-evaluation) repository, you can find code for adapting Voltron
79 | representations to various downstream tasks (segmentation, object detection, control, etc.); all the applications from
80 | our paper.
81 |
82 | ---
83 |
84 | ## API
85 |
86 | 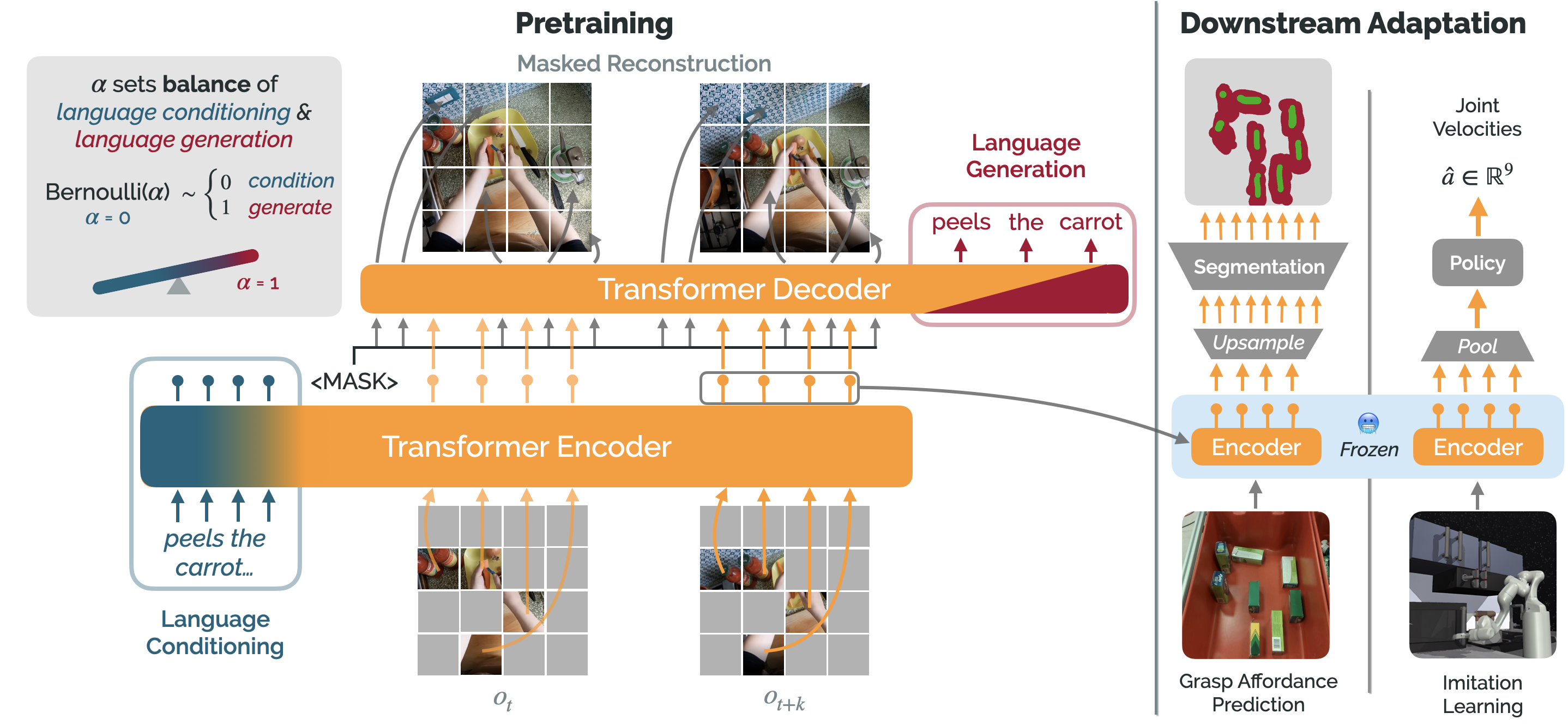
87 |
88 | The package `voltron` provides the following functionality for using and adapting existing representations:
89 |
90 | #### `voltron.available_models()`
91 |
92 | Returns the name of available Voltron models; right now, the following models (all models trained in the paper) are
93 | available:
94 |
95 | - `v-cond` – V-Cond (ViT-Small) trained on Sth-Sth; single-frame w/ language-conditioning.
96 | - `v-dual` – V-Dual (ViT-Small) trained on Sth-Sth; dual-frame w/ language-conditioning.
97 | - `v-gen` – V-Gen (ViT-Small) trained on Sth-Sth; dual-frame w/ language conditioning AND generation.
98 | - `r-mvp` – R-MVP (ViT-Small); reproduction of [MVP](https://github.com/ir413/mvp) trained on Sth-Sth.
99 | - `r-r3m-vit` – R-R3M (ViT-Small); reproduction of [R3M](https://github.com/facebookresearch/r3m) trained on Sth-Sth.
100 | - `r-r3m-rn50` – R-R3M (ResNet-50); reproduction of [R3M](https://github.com/facebookresearch/r3m) trained on Sth-Sth.
101 | - `v-cond-base` – V-Cond (ViT-Base) trained on Sth-Sth; larger (86M parameter) variant of V-Cond.
102 |
103 | #### `voltron.load(name: str, device: str, freeze: bool, cache: str = cache/)`
104 |
105 | Returns the model and the Torchvision Transform needed by the model, where `name` is one of the strings returned
106 | by `voltron.available_models()`; this in general follows the same API as
107 | [OpenAI's CLIP](https://github.com/openai/CLIP).
108 |
109 | ---
110 |
111 | Voltron models (`v-{cond, dual, gen, ...}`) returned by `voltron.load()` support the following:
112 |
113 | #### `model(img: Tensor, lang: Optional[List[str]], mode: str = "multimodal")`
114 |
115 | Returns a sequence of embeddings corresponding to the output of the multimodal encoder; note that `lang` can be None,
116 | which is totally fine for Voltron models! However, if you have any language (even a coarse task description), it'll
117 | probably be helpful!
118 |
119 | The parameter `mode` in `["multimodal", "visual"]` controls whether the output will contain the fused image patch and
120 | language embeddings, or only the image patch embeddings.
121 |
122 | **Note:** For the API for the non-Voltron models (e.g., R-MVP, R-R3M), take a look at
123 | [`examples/verify.py`](examples/verify.py); this file shows how representations from *every* model can be extracted.
124 |
125 | ### Adaptation
126 |
127 | See [`examples/usage.py`](examples/usage.py) and the [`voltron-evaluation`](https://github.com/siddk/voltron-evaluation)
128 | repository for more examples on the various ways to adapt/use Voltron representations.
129 |
130 | ---
131 |
132 | ## Contributing
133 |
134 | Before committing to the repository, make sure to set up your dev environment!
135 | Here are the basic development environment setup guidelines:
136 |
137 | + Fork/clone the repository, performing an editable installation. Make sure to install with the development dependencies
138 | (e.g., `pip install -e ".[dev]"`); this will install `black`, `ruff`, and `pre-commit`.
139 |
140 | + Install `pre-commit` hooks (`pre-commit install`).
141 |
142 | + Branch for the specific feature/issue, issuing PR against the upstream repository for review.
143 |
144 | Additional Contribution Notes:
145 | - This project has migrated to the recommended
146 | [`pyproject.toml` based configuration for setuptools](https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/userguide/quickstart.html).
147 | However, as some tools haven't yet adopted [PEP 660](https://peps.python.org/pep-0660/), we provide a
148 | [`setup.py` file](https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/userguide/pyproject_config.html).
149 |
150 | - This package follows the [`flat-layout` structure](https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/userguide/package_discovery.html#flat-layout)
151 | described in `setuptools`.
152 |
153 | - Make sure to add any new dependencies to the `project.toml` file!
154 |
155 | ---
156 |
157 | ## Repository Structure
158 |
159 | High-level overview of repository/project file-tree:
160 |
161 | + `docs/` - Package documentation & assets - including project roadmap.
162 | + `voltron` - Package source code; has all core utilities for model specification, loading, feature extraction,
163 | preprocessing, etc.
164 | + `examples/` - Standalone examples scripts for demonstrating various functionality (e.g., extracting different types
165 | of representations, adapting representations in various contexts, pretraining, amongst others).
166 | + `.pre-commit-config.yaml` - Pre-commit configuration file (sane defaults + `black` + `ruff`).
167 | + `LICENSE` - Code is made available under the MIT License.
168 | + `Makefile` - Top-level Makefile (by default, supports linting - checking & auto-fix); extend as needed.
169 | + `pyproject.toml` - Following PEP 621, this file has all project configuration details (including dependencies), as
170 | well as tool configurations (for `black` and `ruff`).
171 | + `README.md` - You are here!
172 |
173 | ---
174 |
175 | ## Citation
176 |
177 | Please cite [our paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.12766) if using any of the Voltron models, evaluation suite, or other parts of our framework in your work.
178 |
179 | ```bibtex
180 | @inproceedings{karamcheti2023voltron,
181 | title={Language-Driven Representation Learning for Robotics},
182 | author={Siddharth Karamcheti and Suraj Nair and Annie S. Chen and Thomas Kollar and Chelsea Finn and Dorsa Sadigh and Percy Liang},
183 | booktitle={Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS)},
184 | year={2023}
185 | }
186 | ```
187 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/ROADMAP.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Project Roadmap
2 |
3 | We document the future of this project (new features to be added, issues to address) here. For the most part, any
4 | new features/bugfixes are documented as [Github Issues](https://github.com/siddk/voltron-robotics/issues).
5 |
6 | ## Timeline
7 |
8 | [X] - **February 26th, 2023**: Initial Voltron-Robotics release with support for loading/adapting all pretrained models,
9 | with comprehensive verification scripts & a small adaptation example.
10 |
11 | [X] - **April 4, 2023**: [#1](https://github.com/siddk/voltron-robotics/issues/1) - Add `xpretrain.py` reference script,
12 | mostly for completeness. Refactor/rewrite the preprocessing and pretraining pipeline to reflect
13 | the Qualcomm Sth-Sth data format, as well as PyTorch DDP vs. the patched PyTorch XLA!
14 |
15 | [X] - **April 11, 2023**: [#2](https://github.com/siddk/voltron-robotics/issues/2) - Add support and a more general API
16 | for pretraining on other datasets.
17 |
18 | [ ] - **Future**: [#5](https://github.com/siddk/voltron-robotics/issues/5) - Add better documentation and examples
19 | around using the MAP extractor (especially for adaptation tasks).
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/voltron-banner-alpha.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddk/voltron-robotics/1b299bf5cfa06673a3738aa6e15423b92a9922cd/docs/assets/voltron-banner-alpha.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/voltron-banner.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddk/voltron-robotics/1b299bf5cfa06673a3738aa6e15423b92a9922cd/docs/assets/voltron-banner.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/assets/voltron-framework.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddk/voltron-robotics/1b299bf5cfa06673a3738aa6e15423b92a9922cd/docs/assets/voltron-framework.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/pretrain/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Pretraining Voltron Models
2 |
3 | We provide scripts for pretraining Voltron models on various datasets. Below, we provide the full pipeline from
4 | downloading the raw Something-Something-v2 Dataset from Qualcomm, running preprocessing, then running Distributed
5 | Data Parallel (DDP) pretraining on 1+ GPUs via `torchrun`. Adding support for new datasets should follow this same
6 | general flow.
7 |
8 | ---
9 |
10 | ## Dataset Preprocessing
11 |
12 | We provide end-to-end instructions for downloading, preprocessing, and serializing various pretraining datasets (and
13 | combinations thereof). Where possible, we provide links to batch/dataset index files.
14 |
15 | **Note:** We make a key assumption that you have enough local disk space (e.g., on your server, attached NFS volume) to
16 | store all *raw* and *preprocessed* data; this can range from 100s of GBs to 10s of TBs! We did not have access to such
17 | storage in the original work, necessitating the *streaming* dataloaders defined in
18 | `voltron/datasets/v1/stream_datasets.py`. Given your resources, you might consider adopting a similar approach; feel
19 | free to post an issue with any questions!
20 |
21 | We currently support pretraining on the following datasets:
22 |
23 | - [Something-Something-v2](https://developer.qualcomm.com/software/ai-datasets/something-something)
24 |
25 | Instructions for downloading/preprocessing each dataset can be found below!
26 |
27 | ---
28 |
29 | ### Something-Something-v2
30 |
31 | Dataset Download: [Qualcomm AI Datasets](https://developer.qualcomm.com/software/ai-datasets/something-something)
32 |
33 | #### Obtaining the Raw Dataset
34 |
35 | Follow the instructions [at the above link](https://developer.qualcomm.com/software/ai-datasets/something-something) to
36 | download the dataset. Qualcomm requires that you register for a
37 | [Qualcomm OneID Account](https://myaccount.qualcomm.com/signup?target=https%3A%2F%2Fdeveloper.qualcomm.com)
38 | to get access to the data. Approval might take some time.
39 |
40 | After registering for an account, make sure to download all of the following files to a directory of your choosing
41 | (we create a directory `data/raw/something-something-v2/downloaded/`). *You will need to manually download all 22 of
42 | the following files from the Qualcomm site*:
43 |
44 | 1. Datasheet / Instructions (PDF – optional, but useful): `20bn-something-something_download_instructions_-_091622.pdf`
45 | 2. Labels (includes language annotations): `20bn-something-something_download-package-labels.zip`
46 | 3. Chunked Videos (should be 20 `.zip` archives):
47 | + `20bn-something-something-v2-00.zip`
48 | + ...
49 | + `20bn-something-something-v2-19.zip`
50 |
51 | To extract all the given files (we extract to `data/raw/something-something-v2/`) - *execute the following from inside
52 | the `downloaded/` subdirectory)*:
53 |
54 | ```bash
55 | # Labels (annotations/language) --> creates `data/raw/something-something-v2/labels`
56 | unzip 20bn-something-something-download-package-labels.zip -d ../
57 |
58 | # Videos (following instructions in `20-bn-something-something_download_instructions_-_091622.pdf`)
59 | unzip "20bn-something-something-v2-*.zip" -d ../videos
60 | cd ../videos
61 | cat 20bn-something-something-?? | tar -xvzf -
62 | find . -maxdepth 1 -type f -delete
63 | cd 20bn-something-something-v2/
64 | find . -mindepth 1 -maxdepth 1 -exec mv -t .. -- {} +
65 | cd ..
66 | rm -r 20bn-something-something-v2
67 | ls | wc # Should have 220847 `.webm` files!
68 | ```
69 |
70 | #### Dataset Information & Statistics
71 |
72 | Something-Something-v2 consists of 220,847 `.webm` clips (168,913 in the `train` split) each with a height of exactly
73 | 240px, and variable width. The frames are encoded at a fixed 12 FPS.
74 |
75 | There are an average of 45 frames per clip (approx ~7 KB per jpeg); ~7.6M frames total (~56 GB).
76 |
77 | #### Video/Image Transformations --> from Video Clip to "frame" --> "tensor"
78 |
79 | ```python
80 | import av
81 | from PIL import Image, ImageOps
82 |
83 | # Resolutions for "preprocessing" (serialize to disk) and "training"
84 | PREPROCESS_RESOLUTION, TRAIN_RESOLUTION = 240, 224
85 |
86 | # Define Preprocessing Transformation
87 | def preprocess_transform(frames: List[Image.Image]) -> List[Image.Image]:
88 | # Assert width >= height and height >= PREPROCESS_RESOLUTION
89 | orig_w, orig_h = frames[0].size
90 | assert orig_w >= orig_h >= PREPROCESS_RESOLUTION
91 |
92 | # Compute scale factor --> just a function of height and PREPROCESS_RESOLUTION
93 | scale_factor = PREPROCESS_RESOLUTION / orig_h
94 |
95 | # Full Transformation --> scale (preserve aspect ratio, then get square)
96 | for idx in range(len(frames)):
97 | frames[idx] = ImageOps.scale(frames[idx], factor=scale_factor)
98 | left = (frames[idx].size[0] - PREPROCESS_RESOLUTION) // 2
99 | frames[idx] = frames[idx].crop((left, 0, left + PREPROCESS_RESOLUTION, PREPROCESS_RESOLUTION))
100 |
101 | return frames
102 |
103 | def train_transform(img) -> torch.Tensor:
104 | # Assumes square, just resizes to TRAIN_RESOLUTION via `torchvision.transforms`
105 | ...
106 |
107 | def extract_frames(webm_file: str) -> None:
108 | container = av.open(webm_file)
109 | assert int(container.streams.video[0].average_rate) == 12, "FPS for `sth-sth-v2` should be 12!"
110 |
111 | # Extract --> then serialize via `Image.save("frame_{idx}.jpg")`
112 | frames = preprocess_transform([f.to_image() for f in container.decode(video=0)])
113 | ...
114 | ```
115 |
116 |
117 | #### Citation
118 |
119 | If you are pretraining on this dataset, make sure to cite the original research; Something-Something-v2 is the product
120 | of two papers:
121 |
122 | ```bibtex
123 | @inproceedings{goyal2017sthsthv1,
124 | author = {Raghav Goyal and Samira Ebrahimi Kahou and Vincent Michalski and Joanna Materzynska and Susanne Westphal and Heuna Kim and Valentin Haenel and Ingo Fründ and Peter N. Yianilos and Moritz Mueller-Freitag and Florian Hoppe and Christian Thurau and Ingo Bax and Roland Memisevic},
125 | booktitle = {International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)},
126 | title = {The ``Something Something'' Video Database for Learning and Evaluating Visual Common Sense},
127 | year = {2017},
128 | }
129 | @article{mahidisoltani2018sthsthv2,
130 | author={Farzaneh Mahdisoltani and Guillaume Berger and Waseem Gharbieh and David J. Fleet and Roland Memisevic},
131 | journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.09235},
132 | title={On the Effectiveness of Task Granularity for Transfer Learning},
133 | year={2018}
134 | }
135 | ```
136 |
137 | ---
138 |
139 | ## PyTorch Native Pretraining Pipeline
140 |
141 | To pretrain a Voltron model (e.g., `v-cond`) on the processed data, make sure to read `examples/pretrain/preprocess.py`.
142 | A sample launch command to run with the Something-Something-v2 dataset on a single node with 8 GPUs is as follows:
143 |
144 | ```bash
145 | torchrun --standalone --nnodes 1 --nproc-per-node 8 examples/pretrain/pretrain.py
146 | ```
147 |
148 | Make sure to check the following configuration files and either update them manually (adding your own dataclass,
149 | overriding [DEFAULTS](https://github.com/siddk/voltron-robotics/blob/main/examples/pretrain/pretrain.py#L38)), or by
150 | using Hydra semantics to override them at the command line (e.g., `... pretrain.py dataset.path="" ...`):
151 |
152 | - [Accelerator Config](../../voltron/conf/accelerators.py): Depending on hardware, might need to tune `num_workers`
153 | - [Dataset Config](../../voltron/conf/datasets.py): Make sure to override `path` and `artifact_path`
154 | - [Tracking Config](../../voltron/conf/tracking.py): Disable Weights & Biases / change default entity/name
155 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/pretrain/preprocess.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | preprocess.py
3 |
4 | Centralized script for preprocessing various video/vision-language datasets for GPU pretraining, using a multi-stage,
5 | multiprocessing approach.
6 |
7 | Run as a standalone script, *prior* to calling `pretrain.py` =>> mostly because we want to preprocess the data once, as
8 | a fixed cost.
9 | """
10 | import logging
11 | from dataclasses import dataclass, field
12 | from typing import Any, Dict, List
13 |
14 | import hydra
15 | from hydra.core.config_store import ConfigStore
16 | from omegaconf import MISSING
17 |
18 | from voltron.conf import DatasetConfig
19 | from voltron.overwatch import OverwatchRich
20 | from voltron.preprocessing import extract_frames, preprocess_language, unify_batches
21 | from voltron.util import set_global_seed
22 |
23 | # Grab Logger
24 | overwatch = logging.getLogger(__file__)
25 |
26 |
27 | # Set Defaults (Hydra w/ Structured Configs)
28 | DEFAULTS = ["_self_", {"dataset": "sth-sth-v2"}, {"override hydra/job_logging": "overwatch_rich"}]
29 |
30 |
31 | @dataclass
32 | class PreprocessingConfig:
33 | # fmt: off
34 | defaults: List[Any] = field(default_factory=lambda: DEFAULTS)
35 | hydra: Dict[str, Any] = field(
36 | default_factory=lambda: {"run": {"dir": "./runs/preprocessing/${now:%m-%d}/dataset-${dataset.name}"}}
37 | )
38 |
39 | # Command Line Arguments
40 | seed: int = 21 # Random Seed (for reproducibility)
41 | dry_run: bool = False # Dry Run --> Get a sense of preprocessing/serialization footprint
42 |
43 | # Composable / Structured Arguments
44 | dataset: DatasetConfig = MISSING # Dataset(s) for pretraining/preprocessing
45 | # fmt: on
46 |
47 |
48 | # Hydra Setup :: Retrieve ConfigStore (Singleton) & Register Components
49 | cs = ConfigStore.instance()
50 | cs.store(group="hydra/job_logging", name="overwatch_rich", node=OverwatchRich)
51 | cs.store(name="config", node=PreprocessingConfig)
52 |
53 |
54 | @hydra.main(config_path=None, config_name="config")
55 | def preprocess(cfg: PreprocessingConfig) -> None:
56 | overwatch.info("Preprocessing :: Running Phases for Frame Extraction, Language Compilation, and Batching...")
57 |
58 | # Set Randomness
59 | set_global_seed(cfg.seed)
60 |
61 | # Phase 1 :: Serialize Frames from Video Clips --> get `registry` (index files) for train and validation
62 | train_registry, val_registry, train_dir, val_dir = extract_frames(
63 | cfg.dataset.name,
64 | path=cfg.dataset.path,
65 | artifact_path=cfg.dataset.artifact_path,
66 | preprocess_resolution=cfg.dataset.preprocess_resolution,
67 | n_val_videos=cfg.dataset.n_val_videos,
68 | dry_run=cfg.dry_run,
69 | )
70 |
71 | # Phase 2 :: Normalize & Tokenize Language --> create `index.pt` and `index.json` files
72 | index_dir = preprocess_language(
73 | cfg.dataset.name,
74 | train_registry,
75 | val_registry,
76 | artifact_path=cfg.dataset.artifact_path,
77 | max_lang_len=cfg.dataset.max_lang_len,
78 | language_model=cfg.dataset.language_model,
79 | hf_cache=cfg.dataset.hf_cache,
80 | )
81 |
82 | # Phase 3 :: Assemble "Data-Locked" Batch Sets for Various Models (e.g., for single-frame/dual-frame/quintet)
83 | unify_batches(
84 | cfg.dataset.name,
85 | train_registry,
86 | val_registry,
87 | train_dir,
88 | val_dir,
89 | index_dir,
90 | batch_formats=cfg.dataset.batch_formats,
91 | max_epochs=cfg.dataset.max_epochs,
92 | initial_final_alpha=cfg.dataset.initial_final_alpha,
93 | )
94 |
95 | overwatch.info("Preprocessing Complete!")
96 |
97 |
98 | if __name__ == "__main__":
99 | preprocess()
100 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/usage.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | usage.py
3 |
4 | Example script demonstrating how to load a Voltron model (`V-Cond`) and instantiate a Multiheaded Attention Pooling
5 | extractor head for downstream tasks.
6 |
7 | This is the basic formula/protocol for using Voltron for arbitrary downstream applications.
8 |
9 | Run with (from root of repository): `python examples/usage.py`
10 | """
11 | import torch
12 | from torchvision.io import read_image
13 |
14 | from voltron import instantiate_extractor, load
15 |
16 |
17 | def usage() -> None:
18 | print("[*] Demonstrating Voltron Usage for Various Adaptation Applications")
19 |
20 | # Get `torch.device` for loading model (note -- we'll load weights directly onto device!)
21 | device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
22 |
23 | # Load Voltron model --> specify `freeze`, `device` and get model (nn.Module) and preprocessor
24 | vcond, preprocess = load("v-cond", device=device, freeze=True)
25 |
26 | # Obtain and preprocess an image =>> can be from a dataset, from a camera on a robot, etc.
27 | img = preprocess(read_image("examples/img/peel-carrot-initial.png"))[None, ...].to(device)
28 | lang = ["peeling a carrot"]
29 |
30 | # Get various representations...
31 | with torch.no_grad():
32 | multimodal_features = vcond(img, lang, mode="multimodal") # Fused vision & language features
33 | visual_features = vcond(img, mode="visual") # Vision-only features (no language)
34 |
35 | # Can instantiate various extractors for downstream applications
36 | vector_extractor = instantiate_extractor(vcond, n_latents=1, device=device)()
37 | seq_extractor = instantiate_extractor(vcond, n_latents=64, device=device)()
38 |
39 | # Assertions...
40 | assert list(vector_extractor(multimodal_features).shape) == [1, vcond.embed_dim], "Should return a dense vector!"
41 | assert list(seq_extractor(visual_features).shape) == [1, 64, vcond.embed_dim], "Should return a sequence!"
42 |
43 |
44 | if __name__ == "__main__":
45 | usage()
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/verification/img/peel-carrot-final.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddk/voltron-robotics/1b299bf5cfa06673a3738aa6e15423b92a9922cd/examples/verification/img/peel-carrot-final.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/verification/img/peel-carrot-initial.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddk/voltron-robotics/1b299bf5cfa06673a3738aa6e15423b92a9922cd/examples/verification/img/peel-carrot-initial.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/verification/img/place-bottle-final.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddk/voltron-robotics/1b299bf5cfa06673a3738aa6e15423b92a9922cd/examples/verification/img/place-bottle-final.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/verification/img/place-bottle-grasp.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddk/voltron-robotics/1b299bf5cfa06673a3738aa6e15423b92a9922cd/examples/verification/img/place-bottle-grasp.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/verification/img/place-bottle-initial.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddk/voltron-robotics/1b299bf5cfa06673a3738aa6e15423b92a9922cd/examples/verification/img/place-bottle-initial.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/verification/verify.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | verify.py
3 |
4 | Example script demonstrating how to load all Voltron models (and reproduced models), take input image(s), and get the
5 | various (e.g., multimodal, image-only) representations.
6 |
7 | Also serves to verify that representation loading is working as advertised.
8 |
9 | Run with (from root of repository): `python examples/verification/verify.py`
10 | """
11 | import torch
12 | from torchvision.io import read_image
13 |
14 | from voltron import load
15 |
16 | # Available Models
17 | MODELS = ["v-cond", "v-dual", "v-gen", "r-mvp", "r-r3m-vit", "r-r3m-rn50"]
18 |
19 | # Sample Inputs
20 | IMG_A, IMG_B = "examples/verification/img/peel-carrot-initial.png", "examples/verification/img/peel-carrot-final.png"
21 | LANGUAGE = "peeling a carrot"
22 |
23 |
24 | def verify() -> None:
25 | print("[*] Running `verify` =>> Verifying Model Representations!")
26 |
27 | # Read both images (we'll use the second image for the dual-frame models)
28 | image_a, image_b = read_image(IMG_A), read_image(IMG_B)
29 |
30 | # Get `torch.device` for loading model (note -- we'll load weights directly onto device!)
31 | device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
32 |
33 | for model_id in MODELS:
34 | print(f"\t=> Loading Model ID `{model_id}` and Verifying Representation Shapes!")
35 | model, preprocess = load(model_id, device=device, freeze=True)
36 |
37 | # Preprocess image, run feature extraction --> assert on shapes!
38 | if model_id in {"v-cond", "v-cond-base"}:
39 | for modality, expected in [("multimodal", 196 + 20), ("visual", 196)]:
40 | representation = model(preprocess(image_a)[None, ...].to(device), [LANGUAGE], mode=modality)
41 | assert representation.squeeze(dim=0).shape[0] == expected, "Shape not expected!"
42 |
43 | elif model_id in {"v-dual", "v-gen"}:
44 | for modality, expected in [("multimodal", 196 + 20), ("visual", 196)]:
45 | dual_img = torch.stack([preprocess(image_a), preprocess(image_b)])[None, ...].to(device)
46 | representation = model(dual_img, [LANGUAGE], mode=modality)
47 | assert representation.squeeze(dim=0).shape[0] == expected, "Shape not expected!"
48 |
49 | elif model_id == "r-mvp":
50 | for mode, expected in [("patch", 196), ("cls", 1)]:
51 | representation = model(preprocess(image_a)[None, ...].to(device), mode=mode)
52 | assert representation.squeeze(dim=0).shape[0] == expected, "Shape not expected!"
53 |
54 | elif model_id in {"r-r3m-vit", "r-r3m-rn50"}:
55 | representation = model(preprocess(image_a)[None, ...].to(device))
56 | assert representation.squeeze(dim=0).shape[0] == 1, "Shape not expected!"
57 |
58 | else:
59 | raise ValueError(f"Model {model_id} not supported!")
60 |
61 | # We're good!
62 | print("[*] All representations & shapes verified! Yay!")
63 |
64 |
65 | if __name__ == "__main__":
66 | verify()
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/xla-reference/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # XLA Reference
2 |
3 | *Note :: This code was written for the experimental PyTorch XLA build in PyTorch 1.12; no guarantees it works with later
4 | versions!*
5 |
6 | We trained the original Voltron models (and data-locked reproductions of R3M and MVP) on TPU v3-8 nodes generously
7 | provided by the [TPU Research Cloud (TRC)](https://sites.research.google/trc/about/) program. At the time we started
8 | the project, PyTorch XLA still had some bumps, which was further complicated by the switch from
9 | [TPU Nodes to TPU VMs](https://cloud.google.com/tpu/docs/system-architecture-tpu-vm#tpu-arch).
10 |
11 | To get things to work, we had to add some non-intuitive code to facilitate PyTorch + TPUs (vs. a standard distributed
12 | data parallel training pipeline). As a result, `xpretrain.py` is here mostly for documentation purposes, with a fully
13 | refactored version `pretrain.py` forthcoming.
14 |
15 | We also include the original cloud preprocessing script `xpreprocess.py` for completeness (this is more general).
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/xla-reference/xpreprocess.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | xpreprocess.py
3 |
4 | Centralized script for preprocessing Sth-Sth-v2 for TPU/GCP pretraining, using a multi-stage, multiprocessing strategy.
5 |
6 | Run as a standalone script, *prior* to calling `xpretrain.py` =>> mostly because we want to preprocess the data
7 | once, as a fixed cost.
8 | """
9 | import logging
10 | from dataclasses import dataclass, field
11 | from typing import Any, Dict, List
12 |
13 | import hydra
14 | from hydra.core.config_store import ConfigStore
15 | from omegaconf import MISSING
16 |
17 | from voltron.conf import DatasetConfig
18 | from voltron.overwatch import OverwatchRich
19 | from voltron.preprocessing.v1 import index, jsonify_language, preprocess_language, preprocess_videos, unify_batches
20 | from voltron.util.v1.random import set_global_seed
21 |
22 | # Grab Logger
23 | overwatch = logging.getLogger(__file__)
24 |
25 |
26 | # Set Defaults (Hydra w/ Structured Configs)
27 | DEFAULTS = ["_self_", {"dataset": "sth-sth-v2"}, {"override hydra/job_logging": "overwatch_rich"}]
28 |
29 |
30 | @dataclass
31 | class PreprocessingConfig:
32 | # fmt: off
33 | defaults: List[Any] = field(default_factory=lambda: DEFAULTS)
34 | hydra: Dict[str, Any] = field(
35 | default_factory=lambda: {"run": {"dir": "./runs/preprocessing/${now:%m-%d}/dataset-${dataset.name}"}}
36 | )
37 |
38 | # Command Line Arguments
39 | seed: int = 21 # Random Seed (for reproducibility)
40 | dry_run: bool = False # Dry Run --> Get a sense of preprocessing/serialization footprint
41 |
42 | # Composable / Structured Arguments
43 | dataset: DatasetConfig = MISSING # Dataset(s) for pretraining/preprocessing
44 | # fmt: on
45 |
46 |
47 | # Hydra Setup :: Retrieve ConfigStore (Singleton) & Register Components
48 | cs = ConfigStore.instance()
49 | cs.store(group="hydra/job_logging", name="overwatch_rich", node=OverwatchRich)
50 | cs.store(name="config", node=PreprocessingConfig)
51 |
52 |
53 | @hydra.main(config_path=None, config_name="config")
54 | def xpreprocess(cfg: PreprocessingConfig) -> None:
55 | overwatch.info("Preprocessing :: Running Phases for Frame Extraction, Language Compilation, and Batching...")
56 |
57 | # Set Randomness
58 | set_global_seed(cfg.seed)
59 |
60 | # Phase 1 :: Serialize Frames from Video Clips --> Get `registry` for train and val (index structure)
61 | train_registry, val_registry, train_dir, val_dir = preprocess_videos(
62 | cfg.dataset.name,
63 | path=cfg.dataset.path,
64 | artifact_path=cfg.dataset.artifact_path,
65 | resolution=cfg.dataset.resolution,
66 | n_val_videos=cfg.dataset.n_val_videos,
67 | dry_run=cfg.dry_run,
68 | )
69 |
70 | # Phase 2 :: Normalize & Tokenize Language --> Create `index.pt` & `index.json` files
71 | preprocess_language(
72 | cfg.dataset.name,
73 | train_registry,
74 | val_registry,
75 | max_lang_len=cfg.dataset.max_lang_len,
76 | language_model=cfg.dataset.language_model,
77 | hf_cache=cfg.dataset.hf_cache,
78 | )
79 | jsonify_language(train_registry, val_registry)
80 | index_dir = index(train_registry, val_registry, cfg.dataset.name, artifact_path=cfg.dataset.artifact_path)
81 |
82 | # Phase 3 :: Assemble & Unify Batch "Sets" across the Varied Dataset Formats (for each Model =>> "data-locked")
83 | unify_batches(
84 | cfg.dataset.artifact_path,
85 | cfg.dataset.name,
86 | train_registry,
87 | val_registry,
88 | train_dir,
89 | val_dir,
90 | index_dir,
91 | cfg.dataset.batch_formats,
92 | max_epochs=cfg.dataset.max_epochs,
93 | initial_final_alpha=cfg.dataset.initial_final_alpha,
94 | )
95 |
96 |
97 | if __name__ == "__main__":
98 | xpreprocess()
99 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pyproject.toml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [build-system]
2 | requires = ["setuptools"]
3 | build-backend = "setuptools.build_meta"
4 |
5 | [project]
6 | name = "voltron-robotics"
7 | authors = [
8 | {name = "Siddharth Karamcheti", email="skaramcheti@cs.stanford.edu"}
9 | ]
10 | description = "Voltron: Language-Driven Representation Learning for Robotics."
11 | version = "1.1.0"
12 | readme = "README.md"
13 | requires-python = ">=3.8"
14 | keywords = ["robotics", "representation learning", "natural language processing", "machine learning"]
15 | license = {file = "LICENSE"}
16 | classifiers = [
17 | "Development Status :: 3 - Alpha",
18 | "Intended Audience :: Developers",
19 | "Intended Audience :: Education",
20 | "Intended Audience :: Science/Research",
21 | "License :: OSI Approved :: MIT License",
22 | "Operating System :: OS Independent",
23 | "Programming Language :: Python :: 3",
24 | "Programming Language :: Python :: 3.8",
25 | "Programming Language :: Python :: 3.9",
26 | "Programming Language :: Python :: 3.10",
27 | "Programming Language :: Python :: 3 :: Only",
28 | "Topic :: Scientific/Engineering :: Artificial Intelligence",
29 | ]
30 | dependencies = [
31 | "av",
32 | "einops",
33 | "gdown",
34 | "google-cloud-storage",
35 | "h5py",
36 | "hurry.filesize",
37 | "hydra-core==1.1.1", # Lock Hydra =>> future versions break!
38 | "jsonlines",
39 | "omegaconf==2.1.2", # Lock OmegaConf =>> future versions break!
40 | "opencv-python",
41 | "pandas",
42 | "rich",
43 | "torch>=2.0.0", # Native PyTorch Code (Release 2.0.0) uses PyTorch 2.0!
44 | "torchvision>=0.15.0",
45 | "transformers",
46 | "wandb",
47 | ]
48 |
49 | [project.optional-dependencies]
50 | dev = [
51 | "black",
52 | "ipython",
53 | "pre-commit",
54 | "ruff",
55 | ]
56 |
57 | [project.urls]
58 | homepage = "https://github.com/siddk/voltron-robotics"
59 | repository = "https://github.com/siddk/voltron-robotics"
60 | documentation = "https://github.com/siddk/voltron-robotics"
61 |
62 | [tool.black]
63 | line-length = 121
64 | target-version = ["py38", "py39", "py310"]
65 | preview = true
66 |
67 | [tool.ruff]
68 | line-length = 121
69 | target-version = "py38"
70 | select = ["A", "B", "C90", "E", "F", "I", "RUF", "W"]
71 |
72 | [tool.ruff.per-file-ignores]
73 | "__init__.py" = ["E402", "F401"]
74 |
75 | [tool.setuptools.packages.find]
76 | where = ["."]
77 | exclude = ["cache"]
78 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | setup.py
3 |
4 | PEP 621 switches most of Packaging to `pyproject.toml` -- yet keep a "dummy" setup.py for external code that has not
5 | yet upgraded.
6 | """
7 | from setuptools import setup
8 |
9 | setup()
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .models.materialize import available_models, load
2 | from .models.util import instantiate_extractor
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/conf/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .accelerators import AcceleratorConfig
2 | from .datasets import DatasetConfig
3 | from .models import ModelConfig
4 | from .tracking import TrackingConfig
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/conf/accelerators.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | accelerator.py
3 |
4 | Base Hydra Structured Configs for defining various accelerator schemes. Uses a simple single inheritance structure.
5 | """
6 | import os
7 | from dataclasses import dataclass
8 |
9 | from hydra.core.config_store import ConfigStore
10 | from omegaconf import MISSING
11 |
12 | # === Vanilla Accelerators (Deprecated; mostly for XLA code) ===
13 |
14 |
15 | @dataclass
16 | class AcceleratorConfig:
17 | accelerator: str = MISSING
18 | num_accelerators: int = MISSING
19 | num_workers: int = MISSING
20 |
21 |
22 | @dataclass
23 | class TPUv2OneConfig(AcceleratorConfig):
24 | accelerator = "tpu"
25 | num_accelerators = 1
26 | num_workers = 4
27 |
28 |
29 | @dataclass
30 | class TPUv2EightConfig(AcceleratorConfig):
31 | accelerator = "tpu"
32 | num_accelerators = 8
33 | num_workers = 4
34 |
35 |
36 | @dataclass
37 | class TPUv3OneConfig(AcceleratorConfig):
38 | accelerator = "tpu"
39 | num_accelerators = 1
40 | num_workers = 8
41 |
42 |
43 | @dataclass
44 | class TPUv3EightConfig(AcceleratorConfig):
45 | accelerator = "tpu"
46 | num_accelerators = 8
47 | num_workers = 8
48 |
49 |
50 | # === GPU Default Config --> just set `num_workers`; `torchrun` takes care of the rest! ===
51 | # > Note :: Defaults to 1 GPU if WORLD_SIZE not set (e.g., not running with `torchrun`)
52 |
53 |
54 | @dataclass
55 | class TorchRunDefaultConfig(AcceleratorConfig):
56 | accelerator = "gpu"
57 | num_accelerators = int(os.environ["WORLD_SIZE"] if "WORLD_SIZE" in os.environ else 1)
58 | num_workers = 8
59 |
60 |
61 | # Create a configuration group `accelerator` and populate with the above...
62 | cs = ConfigStore.instance()
63 | cs.store(group="accelerator", name="tpu-v2-1", node=TPUv2OneConfig)
64 | cs.store(group="accelerator", name="tpu-v2-8", node=TPUv2EightConfig)
65 | cs.store(group="accelerator", name="tpu-v3-1", node=TPUv3OneConfig)
66 | cs.store(group="accelerator", name="tpu-v3-8", node=TPUv3EightConfig)
67 |
68 | cs.store(group="accelerator", name="torchrun", node=TorchRunDefaultConfig)
69 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/conf/datasets.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | datasets.py
3 |
4 | Base Hydra Structured Config for defining various pretraining datasets and appropriate configurations. Uses a simple,
5 | single inheritance structure.
6 | """
7 | from dataclasses import dataclass
8 | from typing import Any, Tuple
9 |
10 | from hydra.core.config_store import ConfigStore
11 | from hydra.utils import to_absolute_path
12 | from omegaconf import MISSING
13 |
14 |
15 | @dataclass
16 | class DatasetConfig:
17 | name: str = MISSING
18 | path: str = MISSING
19 | artifact_path: str = MISSING
20 |
21 | # Streaming Parameters (assumes fully preprocessed dataset lives at `stream_prefix/...`)
22 | # =>> Deprecated as of `v2`
23 | stream: bool = True
24 | stream_prefix: str = "data/processed"
25 |
26 | # Dataset-Specific Parameters
27 | resolution: int = 224
28 | normalization: Tuple[Any, Any] = MISSING
29 |
30 | # For preprocessing --> maximum size of saved frames (assumed square)
31 | preprocess_resolution: int = MISSING
32 |
33 | # Validation Parameters
34 | n_val_videos: int = MISSING
35 |
36 | # Language Modeling Parameters
37 | language_model: str = "distilbert-base-uncased"
38 | hf_cache: str = to_absolute_path("data/hf-cache")
39 |
40 | # Maximum Length for truncating language inputs... should be computed after the fact (set to -1 to compute!)
41 | max_lang_len: int = MISSING
42 |
43 | # Dataset sets the number of pretraining epochs (general rule :: warmup should be ~5% of full)
44 | warmup_epochs: int = MISSING
45 | max_epochs: int = MISSING
46 |
47 | # Plausible Formats --> These are instantiations each "batch" could take, with a small DSL
48 | # > Note: Assumes final element of the list is the "most expressive" --> used to back-off
49 | batch_formats: Any = (
50 | ("state", ("state_i",)),
51 | ("state+language", ("state_i", "language")),
52 | ("state+ok", ("state_initial", "state_i", "language")),
53 | ("quintet+language", ("state_initial", "state_i", "state_j", "state_k", "state_final", "language")),
54 | )
55 |
56 | # Preprocessing :: Frame-Sampling Parameters
57 | initial_final_alpha: float = 0.2
58 |
59 |
60 | @dataclass
61 | class SthSthv2Config(DatasetConfig):
62 | # fmt: off
63 | name: str = "sth-sth-v2"
64 | path: str = to_absolute_path("data/raw/sth-sth-v2")
65 | artifact_path: str = to_absolute_path("data/processed/sth-sth-v2")
66 |
67 | # Dataset Specific arguments
68 | normalization: Tuple[Any, Any] = ( # Mean & Standard Deviation (default :: ImageNet)
69 | (0.485, 0.456, 0.406),
70 | (0.229, 0.224, 0.225),
71 | )
72 |
73 | # Sth-Sth-v2 Videos have a fixed height of 240; we'll crop to square at this resolution!
74 | preprocess_resolution: int = 240
75 |
76 | # Validation Parameters
77 | n_val_videos: int = 1000 # Number of Validation Clips (fast evaluation!)
78 |
79 | # Epochs for Dataset
80 | warmup_epochs: int = 20
81 | max_epochs: int = 400
82 |
83 | # Language Modeling Parameters
84 | max_lang_len: int = 20
85 | # fmt: on
86 |
87 |
88 | # Create a configuration group `dataset` and populate with the above...
89 | # =>> Note :: this is meant to be extendable --> add arbitrary datasets & mixtures!
90 | cs = ConfigStore.instance()
91 | cs.store(group="dataset", name="sth-sth-v2", node=SthSthv2Config)
92 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/conf/tracking.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | tracking.py
3 |
4 | Base Hydra Structured Config for defining various run & experiment tracking configurations, e.g., via Weights & Biases.
5 | Uses a simple single inheritance structure.
6 | """
7 | from dataclasses import dataclass, field
8 | from typing import List, Optional, Tuple
9 |
10 | from hydra.core.config_store import ConfigStore
11 | from omegaconf import MISSING
12 |
13 |
14 | @dataclass
15 | class TrackingConfig:
16 | # Active Loggers --> List of Loggers
17 | active_loggers: List[str] = field(default_factory=lambda: ["jsonl", "wandb"])
18 |
19 | # Generic Logging Frequency --> Matters more for XLA/TPUs... set this to be as large as you can stomach!
20 | log_frequency: int = 100
21 |
22 | # Checkpointing Strategy --> Save each epoch, keep most recent `idx[0]` checkpoints & *every* `idx[1]` checkpoints
23 | # Additionally, save (locally) a checkpoint every `idx[2]` steps for the current epoch (-1).
24 | checkpoint_strategy: Tuple[int, int, int] = (1, 1, 1500)
25 |
26 | # Weights & Biases Setup
27 | project: str = "voltron-pretraining"
28 | entity: str = "voltron-robotics"
29 |
30 | # Notes & Tags are at the discretion of the user... see below
31 | notes: str = MISSING
32 | tags: Optional[List[str]] = None
33 |
34 | # Directory to save W&B Metadata & Logs in General -- if None, defaults to `logs/` in the Hydra CWD
35 | directory: Optional[str] = None
36 |
37 |
38 | @dataclass
39 | class VoltronTrackingConfig(TrackingConfig):
40 | # Note: I really like using notes to keep track of things, so will crash unless specified with run.
41 | # > For `tags` I like to populate based on other args in the script, so letting it remain None
42 | notes: str = MISSING
43 |
44 |
45 | # Create a configuration group `trackers` and populate with the above...
46 | cs = ConfigStore.instance()
47 | cs.store(group="tracking", name="voltron-tracking", node=VoltronTrackingConfig)
48 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/datasets/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .datasets import get_datasets
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/datasets/v1/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddk/voltron-robotics/1b299bf5cfa06673a3738aa6e15423b92a9922cd/voltron/datasets/v1/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/models/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .instantiate import VMVP, VR3M, VRN3M, VCond, VDual, VGen, get_model_optimizer
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/models/core/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddk/voltron-robotics/1b299bf5cfa06673a3738aa6e15423b92a9922cd/voltron/models/core/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/models/instantiate.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | instantiate.py
3 |
4 | Simple wrapping script for instantiating a core Voltron/reproduction model and configuring the torch.Optimizer for DDP
5 | pretraining. Meant to be modular and extensible!
6 | """
7 | from typing import Callable, Tuple
8 |
9 | import torch.nn as nn
10 | from torch.optim import Optimizer
11 |
12 | from voltron.conf import DatasetConfig, ModelConfig
13 |
14 | from .core.vcond import VCond
15 | from .core.vdual import VDual
16 | from .core.vgen import VGen
17 | from .reproductions.vmvp import VMVP
18 | from .reproductions.vr3m import VR3M
19 | from .reproductions.vrn3m import VRN3M
20 |
21 |
22 | def get_model_optimizer(
23 | model_cfg: ModelConfig, dataset_cfg: DatasetConfig
24 | ) -> Tuple[nn.Module, Optimizer, Callable[[int, float], float]]:
25 | """Switch on `model_cfg.arch` --> instantiate the correct nn.Module and Optimizer (on CPU/default device)."""
26 |
27 | # Data-Locked Reproductions
28 | if model_cfg.arch == "v-mvp":
29 | model = VMVP(
30 | resolution=dataset_cfg.resolution,
31 | patch_size=model_cfg.patch_size,
32 | encoder_depth=model_cfg.encoder_depth,
33 | encoder_embed_dim=model_cfg.encoder_embed_dim,
34 | encoder_n_heads=model_cfg.encoder_n_heads,
35 | decoder_depth=model_cfg.decoder_depth,
36 | decoder_embed_dim=model_cfg.decoder_embed_dim,
37 | decoder_n_heads=model_cfg.decoder_n_heads,
38 | optimizer=model_cfg.optimizer,
39 | schedule=model_cfg.schedule,
40 | base_lr=model_cfg.base_lr,
41 | min_lr=model_cfg.min_lr,
42 | effective_bsz=model_cfg.effective_bsz,
43 | betas=model_cfg.betas,
44 | weight_decay=model_cfg.weight_decay,
45 | warmup_epochs=dataset_cfg.warmup_epochs,
46 | max_epochs=dataset_cfg.max_epochs,
47 | mlp_ratio=model_cfg.mlp_ratio,
48 | norm_pixel_loss=model_cfg.norm_pixel_loss,
49 | )
50 |
51 | elif model_cfg.arch == "v-r3m":
52 | model = VR3M(
53 | resolution=dataset_cfg.resolution,
54 | patch_size=model_cfg.patch_size,
55 | depth=model_cfg.depth,
56 | embed_dim=model_cfg.embed_dim,
57 | n_heads=model_cfg.n_heads,
58 | language_model=model_cfg.language_model,
59 | hf_cache=model_cfg.hf_cache,
60 | language_dim=model_cfg.language_dim,
61 | reward_dim=model_cfg.reward_dim,
62 | n_negatives=model_cfg.n_negatives,
63 | lang_reward_weight=model_cfg.lang_reward_weight,
64 | tcn_weight=model_cfg.tcn_weight,
65 | l1_weight=model_cfg.l1_weight,
66 | l2_weight=model_cfg.l2_weight,
67 | optimizer=model_cfg.optimizer,
68 | schedule=model_cfg.schedule,
69 | lr=model_cfg.lr,
70 | min_lr=model_cfg.min_lr,
71 | warmup_epochs=dataset_cfg.warmup_epochs,
72 | max_epochs=dataset_cfg.max_epochs,
73 | mlp_ratio=model_cfg.mlp_ratio,
74 | )
75 |
76 | elif model_cfg.arch == "v-rn3m":
77 | model = VRN3M(
78 | resolution=dataset_cfg.resolution,
79 | fc_dim=model_cfg.fc_dim,
80 | language_model=model_cfg.language_model,
81 | hf_cache=model_cfg.hf_cache,
82 | language_dim=model_cfg.language_dim,
83 | reward_dim=model_cfg.reward_dim,
84 | n_negatives=model_cfg.n_negatives,
85 | lang_reward_weight=model_cfg.lang_reward_weight,
86 | tcn_weight=model_cfg.tcn_weight,
87 | l1_weight=model_cfg.l1_weight,
88 | l2_weight=model_cfg.l2_weight,
89 | optimizer=model_cfg.optimizer,
90 | lr=model_cfg.lr,
91 | )
92 |
93 | # Voltron Models
94 | elif model_cfg.arch == "v-cond":
95 | model = VCond(
96 | resolution=dataset_cfg.resolution,
97 | patch_size=model_cfg.patch_size,
98 | encoder_depth=model_cfg.encoder_depth,
99 | encoder_embed_dim=model_cfg.encoder_embed_dim,
100 | encoder_n_heads=model_cfg.encoder_n_heads,
101 | decoder_depth=model_cfg.decoder_depth,
102 | decoder_embed_dim=model_cfg.decoder_embed_dim,
103 | decoder_n_heads=model_cfg.decoder_n_heads,
104 | language_model=model_cfg.language_model,
105 | hf_cache=model_cfg.hf_cache,
106 | language_dim=model_cfg.language_dim,
107 | optimizer=model_cfg.optimizer,
108 | schedule=model_cfg.schedule,
109 | base_lr=model_cfg.base_lr,
110 | min_lr=model_cfg.min_lr,
111 | effective_bsz=model_cfg.effective_bsz,
112 | betas=model_cfg.betas,
113 | weight_decay=model_cfg.weight_decay,
114 | warmup_epochs=dataset_cfg.warmup_epochs,
115 | max_epochs=dataset_cfg.max_epochs,
116 | mlp_ratio=model_cfg.mlp_ratio,
117 | norm_pixel_loss=model_cfg.norm_pixel_loss,
118 | )
119 |
120 | elif model_cfg.arch == "v-dual":
121 | model = VDual(
122 | resolution=dataset_cfg.resolution,
123 | patch_size=model_cfg.patch_size,
124 | encoder_depth=model_cfg.encoder_depth,
125 | encoder_embed_dim=model_cfg.encoder_embed_dim,
126 | encoder_n_heads=model_cfg.encoder_n_heads,
127 | decoder_depth=model_cfg.decoder_depth,
128 | decoder_embed_dim=model_cfg.decoder_embed_dim,
129 | decoder_n_heads=model_cfg.decoder_n_heads,
130 | language_model=model_cfg.language_model,
131 | hf_cache=model_cfg.hf_cache,
132 | language_dim=model_cfg.language_dim,
133 | optimizer=model_cfg.optimizer,
134 | schedule=model_cfg.schedule,
135 | base_lr=model_cfg.base_lr,
136 | min_lr=model_cfg.min_lr,
137 | effective_bsz=model_cfg.effective_bsz,
138 | betas=model_cfg.betas,
139 | weight_decay=model_cfg.weight_decay,
140 | warmup_epochs=dataset_cfg.warmup_epochs,
141 | max_epochs=dataset_cfg.max_epochs,
142 | mlp_ratio=model_cfg.mlp_ratio,
143 | norm_pixel_loss=model_cfg.norm_pixel_loss,
144 | )
145 |
146 | elif model_cfg.arch == "v-gen":
147 | model = VGen(
148 | resolution=dataset_cfg.resolution,
149 | patch_size=model_cfg.patch_size,
150 | encoder_depth=model_cfg.encoder_depth,
151 | encoder_embed_dim=model_cfg.encoder_embed_dim,
152 | encoder_n_heads=model_cfg.encoder_n_heads,
153 | decoder_depth=model_cfg.decoder_depth,
154 | decoder_embed_dim=model_cfg.decoder_embed_dim,
155 | decoder_n_heads=model_cfg.decoder_n_heads,
156 | language_model=model_cfg.language_model,
157 | hf_cache=model_cfg.hf_cache,
158 | language_dim=model_cfg.language_dim,
159 | max_lang_len=dataset_cfg.max_lang_len,
160 | vocab_size=model_cfg.vocab_size,
161 | mae_weight=model_cfg.mae_weight,
162 | lm_weight=model_cfg.lm_weight,
163 | optimizer=model_cfg.optimizer,
164 | schedule=model_cfg.schedule,
165 | base_lr=model_cfg.base_lr,
166 | min_lr=model_cfg.min_lr,
167 | effective_bsz=model_cfg.effective_bsz,
168 | betas=model_cfg.betas,
169 | weight_decay=model_cfg.weight_decay,
170 | warmup_epochs=dataset_cfg.warmup_epochs,
171 | max_epochs=dataset_cfg.max_epochs,
172 | mlp_ratio=model_cfg.mlp_ratio,
173 | norm_pixel_loss=model_cfg.norm_pixel_loss,
174 | )
175 |
176 | else:
177 | raise ValueError(f"Model Architecture `{model_cfg.arch}` is not implemented!")
178 |
179 | # Configure Optimizer --> on same device (CPU)
180 | optimizer, update_lr = model.configure_optimizer()
181 |
182 | return model, optimizer, update_lr
183 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/models/materialize.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | materialize.py
3 |
4 | Core functionality for using pretrained models; defines the package-level `load` functionality for downloading and
5 | instantiating pretrained Voltron (and baseline) models.
6 | """
7 | import json
8 | import os
9 | from pathlib import Path
10 | from typing import Callable, List, Tuple
11 |
12 | import gdown
13 | import torch
14 | import torch.nn as nn
15 | import torchvision.transforms as T
16 |
17 | from voltron.models import VMVP, VR3M, VRN3M, VCond, VDual, VGen
18 |
19 | # === Define Useful Variables for Loading Models ===
20 | DEFAULT_CACHE = "cache/"
21 | NORMALIZATION = ((0.485, 0.456, 0.406), (0.229, 0.224, 0.225))
22 |
23 | # Pretrained Model Registry :: "model id" -> {"config" -> gdown ID, "checkpoint" -> gdown ID, "cls" -> Model Class}
24 | MODEL_REGISTRY = {
25 | # === Voltron ViT-Small (Sth-Sth) Models ===
26 | "v-cond": {
27 | "config": "1O4oqRIblfS6PdFlZzUcYIX-Rqe6LbvnD",
28 | "checkpoint": "12g5QckQSMKqrfr4lFY3UPdy7oLw4APpG",
29 | "cls": VCond,
30 | },
31 | "v-dual": {
32 | "config": "1zgKiK81SF9-0lg0XbMZwNhUh1Q7YdZZU",
33 | "checkpoint": "1CCRqrwcvF8xhIbJJmwnCbcWfWTJCK40T",
34 | "cls": VDual,
35 | },
36 | "v-gen": {
37 | "config": "18-mUBDsr-2_-KrGoL2E2YzjcUO8JOwUF",
38 | "checkpoint": "1TzSQpKVKBWKCSvYJf22c45hrKczTQz24",
39 | "cls": VGen,
40 | },
41 | # === Voltron ViT-Base Model ===
42 | "v-cond-base": {
43 | "config": "1CLe7CaIzTEcGCijIgw_S-uqMXHfBFSLI",
44 | "checkpoint": "1PwczOijL0hfYD8DI4xLOPLf1xL_7Kg9S",
45 | "cls": VCond,
46 | },
47 | # === Data-Locked Reproductions ===
48 | "r-mvp": {
49 | "config": "1KKNWag6aS1xkUiUjaJ1Khm9D6F3ROhCR",
50 | "checkpoint": "1-ExshZ6EC8guElOv_s-e8gOJ0R1QEAfj",
51 | "cls": VMVP,
52 | },
53 | "r-r3m-vit": {
54 | "config": "1JGk32BLXwI79uDLAGcpbw0PiupBknf-7",
55 | "checkpoint": "1Yby5oB4oPc33IDQqYxwYjQV3-56hjCTW",
56 | "cls": VR3M,
57 | },
58 | "r-r3m-rn50": {
59 | "config": "1OS3mB4QRm-MFzHoD9chtzSmVhOA-eL_n",
60 | "checkpoint": "1t1gkQYr6JbRSkG3fGqy_9laFg_54IIJL",
61 | "cls": VRN3M,
62 | },
63 | }
64 |
65 |
66 | def available_models() -> List[str]:
67 | return list(MODEL_REGISTRY.keys())
68 |
69 |
70 | def load(
71 | model_id: str, device: torch.device = "cpu", freeze: bool = True, cache: str = DEFAULT_CACHE
72 | ) -> Tuple[nn.Module, Callable[[torch.Tensor], torch.Tensor]]:
73 | """
74 | Download & cache specified model configuration & checkpoint, then load & return module & image processor.
75 |
76 | Note :: We *override* the default `forward()` method of each of the respective model classes with the
77 | `extract_features` method --> by default passing "NULL" language for any language-conditioned models.
78 | This can be overridden either by passing in language (as a `str) or by invoking the corresponding methods.
79 | """
80 | assert model_id in MODEL_REGISTRY, f"Model ID `{model_id}` not valid, try one of {list(MODEL_REGISTRY.keys())}"
81 |
82 | # Download Config & Checkpoint (if not in cache)
83 | model_cache = Path(cache) / model_id
84 | config_path, checkpoint_path = model_cache / f"{model_id}-config.json", model_cache / f"{model_id}.pt"
85 | os.makedirs(model_cache, exist_ok=True)
86 | if not checkpoint_path.exists() or not config_path.exists():
87 | gdown.download(id=MODEL_REGISTRY[model_id]["config"], output=str(config_path), quiet=False)
88 | gdown.download(id=MODEL_REGISTRY[model_id]["checkpoint"], output=str(checkpoint_path), quiet=False)
89 |
90 | # Load Configuration --> patch `hf_cache` key if present (don't download to random locations on filesystem)
91 | with open(config_path, "r") as f:
92 | model_kwargs = json.load(f)
93 | if "hf_cache" in model_kwargs:
94 | model_kwargs["hf_cache"] = str(Path(cache) / "hf-cache")
95 |
96 | # By default, the model's `__call__` method defaults to `forward` --> for downstream applications, override!
97 | # > Switch `__call__` to `get_representations`
98 | MODEL_REGISTRY[model_id]["cls"].__call__ = MODEL_REGISTRY[model_id]["cls"].get_representations
99 |
100 | # Materialize Model (load weights from checkpoint; note that unused element `_` are the optimizer states...)
101 | model = MODEL_REGISTRY[model_id]["cls"](**model_kwargs)
102 | state_dict, _ = torch.load(checkpoint_path, map_location=device)
103 | model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=True)
104 | model.to(device)
105 | model.eval()
106 |
107 | # Freeze model parameters if specified (default: True)
108 | if freeze:
109 | for _, param in model.named_parameters():
110 | param.requires_grad = False
111 |
112 | # Build Visual Preprocessing Transform (assumes image is read into a torch.Tensor, but can be adapted)
113 | if model_id in {"v-cond", "v-dual", "v-gen", "v-cond-base", "r-mvp"}:
114 | # All models except R3M are by default normalized subject to default IN1K normalization...
115 | preprocess = T.Compose(
116 | [
117 | T.Resize(model_kwargs["resolution"]),
118 | T.CenterCrop(model_kwargs["resolution"]),
119 | T.ConvertImageDtype(torch.float),
120 | T.Normalize(mean=NORMALIZATION[0], std=NORMALIZATION[1]),
121 | ]
122 | )
123 | else:
124 | # R3M models (following original work) expect unnormalized images with values in range [0 - 255)
125 | preprocess = T.Compose(
126 | [
127 | T.Resize(model_kwargs["resolution"]),
128 | T.CenterCrop(model_kwargs["resolution"]),
129 | T.ConvertImageDtype(torch.float),
130 | T.Lambda(lambda x: x * 255.0),
131 | ]
132 | )
133 |
134 | return model, preprocess
135 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/models/reproductions/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddk/voltron-robotics/1b299bf5cfa06673a3738aa6e15423b92a9922cd/voltron/models/reproductions/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/models/reproductions/vmvp.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | vmvp.py
3 |
4 | PyTorch Module defining a basic MAE a la Masked Visual Pretraining for Motor Control (MVP), with the requisite
5 | hyperparameters - as defined in the original ImageMAE paper, and as used by both MVP papers.
6 |
7 | References:
8 | - https://github.com/facebookresearch/mae
9 | - https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/timm/models/vision_transformer.py
10 | """
11 | from typing import Callable, Optional, Tuple
12 |
13 | import torch
14 | import torch.nn as nn
15 | from einops import rearrange
16 |
17 | from voltron.models.util.optimization import get_lr_update
18 | from voltron.models.util.transformer import Block, PatchEmbed, get_2D_position_embeddings
19 |
20 |
21 | class VMVP(nn.Module):
22 | def __init__(
23 | self,
24 | resolution: int,
25 | patch_size: int,
26 | encoder_depth: int,
27 | encoder_embed_dim: int,
28 | encoder_n_heads: int,
29 | decoder_depth: int,
30 | decoder_embed_dim: int,
31 | decoder_n_heads: int,
32 | optimizer: str,
33 | schedule: str,
34 | base_lr: float,
35 | min_lr: float,
36 | effective_bsz: float,
37 | betas: Tuple[float, float],
38 | weight_decay: float,
39 | warmup_epochs: int,
40 | max_epochs: int,
41 | mask_ratio: float = 0.75,
42 | mlp_ratio: float = 4.0,
43 | in_channels: int = 3,
44 | norm_pixel_loss: bool = True,
45 | ):
46 | """
47 | Initialize an VMVP (MAE) model with the requisite architecture parameters.
48 |
49 | :param resolution: Base image resolution -- usually 224 (ImageNet size).
50 | :param patch_size: Height/Width of each patch in pixels -- usually 16.
51 | :param encoder_depth: Number of Transformer blocks in the encoder -- should be greater than decoder.
52 | :param encoder_embed_dim: Core embedding/hidden dimension for encoder vision transformer backbone.
53 | :param encoder_n_heads: Number of heads for encoder multi-headed self-attention.
54 | :param decoder_depth: Number of Transformer blocks in the decoder -- should be relatively shallow.
55 | :param decoder_embed_dim: Core embedding/hidden dimension for encoder vision transformer backbone.
56 | :param decoder_n_heads: Number of heads for encoder multi-headed self-attention.
57 | :param optimizer: String denoting which optimizer to use (for MAEs, usually `adamw`)
58 | :param schedule: Learning rate schedule to use; for Transformers a linear warmup + decay is recommended!
59 | :param base_lr: Base learning rate, to be scaled via a linear scaling rule (from scaling laws).
60 | :param min_lr: Minimum learning rate to decay to over the course of learning (usually 0.0)
61 | :param effective_bsz: Global batch size for update, dictates the scaling of the base_lr.
62 | :param betas: Adam optimizer betas (only applicable for `adam` and `adamw`. Prevents early loss spiking.
63 | :param weight_decay: Weight decay for global weight regularization (only applied to non-bias, non-LN layers).
64 | :param warmup_epochs: Number of epochs to warmup learning rate for linear warmup schedule.
65 | :param max_epochs: Total number of training epochs to be run.
66 | :param mask_ratio: Ratio for number of patches to mask out for MAE -- should be fairly high!
67 | :param mlp_ratio: Ratio for embedding size to Position-wise FeedForward MLP (gets shrunk back down).
68 | :param in_channels: Default number of channels in the base image -- almost always 3.
69 | :param norm_pixel_loss: Normalize decoder pixel targets for reconstruction (better perf, not interpretable).
70 | """
71 | super().__init__()
72 | self.resolution, self.patch_size, self.mask_ratio = resolution, patch_size, mask_ratio
73 | self.in_channels, self.norm_pixel_loss, self.mlp_ratio = in_channels, norm_pixel_loss, mlp_ratio
74 | self.optimizer, self.schedule, self.betas, self.weight_decay = optimizer, schedule, betas, weight_decay
75 | self.lr, self.base_lr, self.min_lr, self.effective_bsz = None, base_lr, min_lr, effective_bsz
76 | self.warmup_epochs, self.max_epochs = warmup_epochs, max_epochs
77 |
78 | # Encoder/Decoder Parameters
79 | self.encoder_depth, self.decoder_depth = encoder_depth, decoder_depth
80 | self.encoder_embed_dim, self.encoder_n_heads = encoder_embed_dim, encoder_n_heads
81 | self.decoder_embed_dim, self.decoder_n_heads = decoder_embed_dim, decoder_n_heads
82 |
83 | # MAE Encoder Parameters --> MVP uses a CLS Token for feature extraction!
84 | self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, 1, self.encoder_embed_dim))
85 | self.patch2embed = PatchEmbed(
86 | self.resolution, self.patch_size, self.encoder_embed_dim, in_channels=self.in_channels
87 | )
88 | self.encoder_pe = nn.Parameter(
89 | torch.zeros(1, self.patch2embed.num_patches + 1, self.encoder_embed_dim), requires_grad=False
90 | )
91 | self.encoder_blocks = nn.ModuleList(
92 | [Block(self.encoder_embed_dim, self.encoder_n_heads, self.mlp_ratio) for _ in range(self.encoder_depth)]
93 | )
94 | self.encoder_norm = nn.LayerNorm(self.encoder_embed_dim, eps=1e-6)
95 |
96 | # Projection from Encoder to Decoder
97 | self.encoder2decoder = nn.Linear(self.encoder_embed_dim, self.decoder_embed_dim)
98 |
99 | # MAE Decoder Parameters -- Remember the CLS Token!
100 | self.mask_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, 1, self.decoder_embed_dim))
101 | self.decoder_pe = nn.Parameter(
102 | torch.zeros(1, self.patch2embed.num_patches + 1, self.decoder_embed_dim), requires_grad=False
103 | )
104 | self.decoder_blocks = nn.ModuleList(
105 | [Block(self.decoder_embed_dim, self.decoder_n_heads, self.mlp_ratio) for _ in range(self.decoder_depth)]
106 | )
107 | self.decoder_norm = nn.LayerNorm(self.decoder_embed_dim, eps=1e-6)
108 | self.decoder_prediction = nn.Linear(self.decoder_embed_dim, (patch_size**2) * in_channels, bias=True)
109 |
110 | # Initialize all Weights
111 | self.initialize_weights()
112 |
113 | def initialize_weights(self) -> None:
114 | # Position Encoding -- Fixed 2D Sine-Cosine Embeddings
115 | enc_pe = get_2D_position_embeddings(self.encoder_embed_dim, int(self.patch2embed.num_patches**0.5), True)
116 | self.encoder_pe.data.copy_(torch.from_numpy(enc_pe).float().unsqueeze(0))
117 | dec_pe = get_2D_position_embeddings(self.decoder_embed_dim, int(self.patch2embed.num_patches**0.5), True)
118 | self.decoder_pe.data.copy_(torch.from_numpy(dec_pe).float().unsqueeze(0))
119 |
120 | # Initialize PatchEmbedding as a Linear...
121 | nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.patch2embed.proj.weight.data.view([self.patch2embed.proj.weight.data.shape[0], -1]))
122 |
123 | # Initialize CLS Token & Mask Token w/ Truncated Normal
124 | nn.init.normal_(self.cls_token, std=0.02)
125 | nn.init.normal_(self.mask_token, std=0.02)
126 |
127 | # Everything else...
128 | self.apply(self.transformer_initializer)
129 |
130 | @staticmethod
131 | def transformer_initializer(m: nn.Module) -> None:
132 | if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
133 | # Use xavier_uniform following Jax ViT
134 | torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
135 | if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None:
136 | nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0.0)
137 | elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):
138 | nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
139 | nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0.0)
140 |
141 | def mask(
142 | self, patches: torch.Tensor, mask_ratio: Optional[float] = None
143 | ) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
144 | """Perform per-sample random masking by shuffling :: uses argsort random noise to identify masked patches"""
145 | bsz, n_patches, embed_dim = patches.shape
146 | if mask_ratio is not None:
147 | n_keep = int(n_patches * (1 - mask_ratio))
148 | else:
149 | n_keep = int(n_patches * (1 - self.mask_ratio))
150 |
151 | # Sample some noise of n_patches size, argsort to get shuffled IDs (keep small), argsort again to "unshuffle"
152 | # > For clarity -- argsort is an invertible transformation (if argsort `restore`, recovers `shuffle`)
153 | shuffle_idxs = torch.argsort(torch.rand(bsz, n_patches, device=patches.device), dim=1)
154 | restore_idxs = torch.argsort(shuffle_idxs, dim=1)
155 |
156 | # Get "keep" (visible) patches
157 | visible_patches = torch.gather(patches, dim=1, index=shuffle_idxs[:, :n_keep, None].repeat(1, 1, embed_dim))
158 |
159 | # Generate the binary mask --> IMPORTANT :: `0` is keep, `1` is remove (following FAIR MAE convention)
160 | mask = torch.ones(bsz, n_patches, device=patches.device)
161 | mask[:, :n_keep] = 0
162 | mask = torch.gather(mask, dim=1, index=restore_idxs)
163 |
164 | return visible_patches, mask, restore_idxs
165 |
166 | def get_representations(self, img: torch.Tensor, mode: str = "patch") -> torch.Tensor:
167 | """
168 | Given a single image, extract representations subject to the specified mode in < patch | cls >, where "cls"
169 | denotes extracting the token embedding; for our experiments, we find that running multiheaded attention
170 | pooling on top of the "patch" embeddings is *always* better!
171 |
172 | :param img: Processed batch of images :: [bsz, 3, 224, 224]
173 | :param mode: Type of representation to extract -- `patch` (sequence of patch embeddings) or `cls` ()
174 |
175 | :return: Extracted representations given img input.
176 | """
177 | assert img.ndim == 4, "Invalid input to `get_representations()`"
178 | assert mode in {"patch", "cls"}, f"Extraction mode `{mode}` not supported!"
179 |
180 | # Extract desired representations
181 | representations = self.encode(img)
182 | return representations[:, 1:] if mode == "patch" else representations[:, :1]
183 |
184 | def encode(self, img: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
185 | """Run a single image through the MAE and extract patch embeddings."""
186 |
187 | # Note: All of this code is taken near-verbatim from the MVP repository...
188 | # > Ref: https://github.com/ir413/mvp/blob/master/mvp/backbones/vit.py#L30
189 | patches = self.patch2embed(img)
190 | cls_tokens = self.cls_token.expand(img.shape[0], -1, -1)
191 | cls_patches = torch.cat([cls_tokens, patches]) + self.encoder_pe
192 |
193 | # Apply Transformer Blocks...
194 | for block in self.encoder_blocks:
195 | cls_patches = block(cls_patches)
196 | cls_patches = self.encoder_norm(cls_patches)
197 | return cls_patches
198 |
199 | def forward_encoder(
200 | self, imgs: torch.Tensor, mask_ratio: Optional[float] = None
201 | ) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
202 | # Patchify + Position Embedding (without the CLS Token)
203 | patches = self.patch2embed(imgs)
204 | patches_pe = patches + self.encoder_pe[:, 1:, :]
205 |
206 | # Create mask (and go ahead and mask out patches at the same time)
207 | visible_patches, mask, restore_idxs = self.mask(patches_pe, mask_ratio)
208 |
209 | # Add the CLS Token
210 | cls_token = self.cls_token + self.encoder_pe[:, :1, :]
211 | cls_tokens = cls_token.expand(imgs.shape[0], -1, -1)
212 | cls_visible_patches = torch.cat([cls_tokens, visible_patches], dim=1)
213 |
214 | # Apply Transformer Blocks...
215 | for block in self.encoder_blocks:
216 | cls_visible_patches = block(cls_visible_patches)
217 | cls_visible_patches = self.encoder_norm(cls_visible_patches)
218 |
219 | return cls_visible_patches, mask, restore_idxs
220 |
221 | def forward_decoder(self, visible_patches: torch.Tensor, restore_idxs: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
222 | # Project patches into decoder embedding dimension
223 | projected_patches = self.encoder2decoder(visible_patches)
224 |
225 | # Add Mask Tokens to Sequence
226 | mask_tokens = self.mask_token.repeat(
227 | projected_patches.shape[0], restore_idxs.shape[1] - visible_patches.shape[1] + 1, 1
228 | )
229 |
230 | # Remove & add back CLS Token as part of the "unshuffling"
231 | concatenated_patches = torch.cat([projected_patches[:, 1:, :], mask_tokens], dim=1) # Skip CLS Token
232 | unshuffled_patches = torch.gather(
233 | concatenated_patches, dim=1, index=restore_idxs[..., None].repeat(1, 1, self.decoder_embed_dim)
234 | )
235 | cls_unshuffled_patches = torch.cat([projected_patches[:, :1, :], unshuffled_patches], dim=1) # Add CLS Token
236 |
237 | # Add Position Embeddings
238 | cls_decoder_patches = cls_unshuffled_patches + self.decoder_pe
239 |
240 | # Apply Transformer Blocks...
241 | for block in self.decoder_blocks:
242 | cls_decoder_patches = block(cls_decoder_patches)
243 | cls_decoder_patches = self.decoder_norm(cls_decoder_patches)
244 |
245 | # Run final projection, remove the CLS token, and return
246 | cls_decoder_prediction = self.decoder_prediction(cls_decoder_patches)
247 | decoder_prediction = cls_decoder_prediction[:, 1:, :]
248 | return decoder_prediction
249 |
250 | def patchify(self, imgs: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
251 | """Convert a batch of images to their patched equivalents, by naive reshaping"""
252 | return rearrange(
253 | imgs,
254 | "bsz c (height patch_h) (width patch_w) -> bsz (height width) (patch_h patch_w c)",
255 | patch_h=self.patch_size,
256 | patch_w=self.patch_size,
257 | )
258 |
259 | def compute_loss(self, imgs: torch.Tensor, reconstructions: torch.Tensor, mask: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
260 | assert self.norm_pixel_loss, "`norm_pixel_loss` should always be true... false only for visualizations!"
261 | targets = self.patchify(imgs)
262 |
263 | # Normalize targets...
264 | mu, var = targets.mean(dim=-1, keepdim=True), targets.var(dim=-1, unbiased=True, keepdim=True)
265 | targets = (targets - mu) / ((var + 1e-6) ** 0.5)
266 |
267 | # Compute mean loss per patch first...
268 | mse = (reconstructions - targets) ** 2
269 | avg_loss_per_patch = mse.mean(dim=-1)
270 |
271 | # Compute mean loss only on *removed* patches and return
272 | return (avg_loss_per_patch * mask).sum() / mask.sum()
273 |
274 | def forward(
275 | self, imgs: torch.Tensor, mask_ratio: Optional[float] = None
276 | ) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
277 | visible_patches, mask, restore_idxs = self.forward_encoder(imgs, mask_ratio)
278 | reconstructions = self.forward_decoder(visible_patches, restore_idxs)
279 | loss = self.compute_loss(imgs, reconstructions, mask)
280 |
281 | return loss, reconstructions, mask
282 |
283 | def configure_optimizer(self) -> Tuple[torch.optim.Optimizer, Callable[[int, float], float]]:
284 | # Short-Circuit on Valid Optimizers
285 | if self.optimizer not in ["adamw"]:
286 | raise NotImplementedError(f"Optimizer `{self.optimizer}` not supported - try [`adamw`] instead!")
287 |
288 | # Create Parameter Groups --> Bias terms, Normalization layer parameters shouldn't be decayed...
289 | # > This is a compact rewrite of `param_groups_weight_decay()` from TIMM because I don't want the dependency
290 | decay, no_decay = [], []
291 | for name, param in self.named_parameters():
292 | if not param.requires_grad:
293 | continue
294 |
295 | # Check on any parameters with fewer than 2 dimensions or with "bias" in the name...
296 | if param.ndim <= 1 or name.endswith(".bias"):
297 | no_decay.append(param)
298 | else:
299 | decay.append(param)
300 |
301 | # Build Parameter Groups
302 | groups = [{"params": decay, "weight_decay": self.weight_decay}, {"params": no_decay, "weight_decay": 0.0}]
303 |
304 | # Compute LR -- MAE uses the `linear scaling rule` :: lr = base_lr * (effective_bsz / 256)
305 | # > https://github.com/facebookresearch/mae/blob/main/PRETRAIN.md
306 | self.lr = self.base_lr * (self.effective_bsz / 256)
307 |
308 | # Create Optimizer & LR Scheduler
309 | optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(groups, lr=self.lr, betas=self.betas)
310 | update_lr = get_lr_update(optimizer, self.schedule, self.lr, self.min_lr, self.warmup_epochs, self.max_epochs)
311 | return optimizer, update_lr
312 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/models/reproductions/vrn3m.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | vrn3m.py
3 |
4 | PyTorch Module defining an R3M model (with a ResNet 50 encoder), exactly as described in Nair et. al. 2021, with all the
5 | requisite hyperparameters.
6 |
7 | Reference:
8 | - https://github.com/facebookresearch/r3m
9 | """
10 | from typing import Callable, Tuple
11 |
12 | import torch
13 | import torch.nn as nn
14 | import transformers
15 | from einops import rearrange
16 | from torchvision.models import resnet50
17 |
18 | from voltron.models.util.optimization import get_lr_update
19 |
20 | # Suppress Transformers Logging
21 | transformers.logging.set_verbosity_error()
22 |
23 |
24 | class VRN3M(nn.Module):
25 | def __init__(
26 | self,
27 | resolution: int,
28 | fc_dim: int,
29 | language_model: str,
30 | hf_cache: str,
31 | language_dim: int,
32 | reward_dim: int,
33 | n_negatives: int,
34 | lang_reward_weight: float,
35 | tcn_weight: float,
36 | l1_weight: float,
37 | l2_weight: float,
38 | optimizer: str,
39 | lr: float,
40 | eps: float = 1e-8,
41 | ):
42 | """
43 | Initialize an ResNet-50 R3M model with the required architecture parameters.
44 |
45 | :param resolution: Base image resolution -- usually 224 (ImageNet size).
46 | :param fc_dim: Dimensionality of the pooled embedding coming out of the ResNet (for RN50, fc_dim = 2048)
47 | :param language_model: Language model to freeze for encoding narrations/utterances.
48 | :param hf_cache: Cache directory to store pretrained models, for safe distributed training.
49 | :param language_dim: Dimensionality of the language embedding coming out of the pretrained LM.
50 | :param reward_dim: Hidden layer dimensionality for the language-reward MLP.
51 | :param n_negatives: Number of cross-batch negatives to sample for contrastive learning.
52 | :param lang_reward_weight: Weight applied to the contrastive "language alignment" loss term.
53 | :param tcn_weight: Weight applied to the time contrastive loss term.
54 | :param l1_weight: Weight applied to the L1 regularization loss term.
55 | :param l2_weight: Weight applied to the L2 regularization loss term.
56 | :param optimizer: String denoting which optimizer to use (for R3M, usually `adam`).
57 | :param lr: Learning rate (fixed for ResNet R3M models) for training.
58 | :param eps: Epsilon for preventing divide by zero in the InfoNCE loss terms.
59 | """
60 | super().__init__()
61 | self.resolution, self.fc_dim, self.n_negatives, self.eps = resolution, fc_dim, n_negatives, eps
62 | self.language_dim, self.reward_dim, self.optimizer, self.lr = language_dim, reward_dim, optimizer, lr
63 | self.embed_dim = self.fc_dim
64 |
65 | # Weights for each loss term
66 | self.lang_reward_weight, self.tcn_weight = lang_reward_weight, tcn_weight
67 | self.l1_weight, self.l2_weight = l1_weight, l2_weight
68 |
69 | # Create ResNet50 --> set `rn.fc` to the Identity() to extract final features of dim = `fc_dim`
70 | self.resnet = resnet50(weights=None)
71 | self.resnet.fc = nn.Identity()
72 | self.resnet.train()
73 |
74 | # Create Language Reward Model
75 | self.language_reward = nn.Sequential(
76 | nn.Linear(self.fc_dim + self.fc_dim + self.language_dim, self.reward_dim),
77 | nn.ReLU(),
78 | nn.Linear(self.reward_dim, self.reward_dim),
79 | nn.ReLU(),
80 | nn.Linear(self.reward_dim, self.reward_dim),
81 | nn.ReLU(),
82 | nn.Linear(self.reward_dim, self.reward_dim),
83 | nn.ReLU(),
84 | nn.Linear(self.reward_dim, 1),
85 | nn.Sigmoid(),
86 | )
87 |
88 | # Create Language Model & Language Reward MLP --> LM has requires_grad = False
89 | # > For BERT models, our "embedding" is just going to be the last hidden state
90 | # > Assumes inputs to forward pass are pre-tokenized!
91 | self.tokenizer = transformers.AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(language_model, cache_dir=hf_cache)
92 | self.lm = transformers.AutoModel.from_pretrained(language_model, cache_dir=hf_cache)
93 | self.lm.eval()
94 |
95 | # Shape Assertion -- make sure self.language_dim actually is the same as the LM dimension!
96 | assert self.lm.config.dim == self.language_dim, "Language model embedding dimension != self.language_dim!"
97 |
98 | # Freeze the LM
99 | for _name, param in self.lm.named_parameters():
100 | param.requires_grad = False
101 |
102 | def get_representations(self, img: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
103 | """
104 | Given a single image, extract R3M "default" (ResNet pooled) dense representation.
105 |
106 | :param img: Processed batch of images :: [bsz, 3, 224, 224]
107 | :return: Extracted R3M dense representation given img input.
108 | """
109 | assert img.ndim == 4, "Invalid input to `get_representations()`"
110 | representation = self.resnet(img)
111 | return representation.unsqueeze(1)
112 |
113 | def encode_images(self, imgs: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
114 | """Feed images through ResNet-50 to get single embedding after global average pooling."""
115 | return self.resnet(imgs)
116 |
117 | def encode_language(self, lang: torch.Tensor, lang_mask: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
118 | """Encode language by feeding the *pre-tokenized text* through the frozen language model."""
119 | self.lm.eval()
120 | with torch.no_grad():
121 | transformer_embeddings = self.lm(lang, attention_mask=lang_mask).last_hidden_state
122 | return transformer_embeddings.mean(dim=1)
123 |
124 | def get_reward(self, initial: torch.Tensor, later: torch.Tensor, lang: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
125 | return self.language_reward(torch.cat([initial, later, lang], dim=-1)).squeeze()
126 |
127 | def extract_features(self, img: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
128 | """Run a single image of shape [1, 3, 224, 224] through the ResNet and extract the feature."""
129 | return self.encode_images(img).detach()
130 |
131 | def forward(self, imgs: torch.Tensor, lang: torch.Tensor, lang_mask: torch.Tensor) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, ...]:
132 | """
133 | Run a forward pass through the model, computing the *full* R3M loss -- the TCN contrastive loss, the Language
134 | Alignment loss, and both sparsity losses, as well as the full loss (which will get optimized)!
135 |
136 | :param imgs: A [bsz, 5, in_channels, resolution, resolution] tensor of (start, i, j, k, end) sequences.
137 | :param lang: Tokenized language of dimensionality [bsz, seq_len] to be fed to the language model.
138 | :param lang_mask: Attention mask computed by the tokenizer, as a result of padding to the max_seq_len.
139 |
140 | :return: Tuple of losses, as follows:
141 | > (combined_loss, tcn_loss, reward_loss, l1_loss, l2_loss, tcn_acc, reward_acc)
142 | """
143 | # Encode each image separately... feed to transformer... then reshape
144 | all_images = rearrange(imgs, "bsz n_states c res1 res2 -> (bsz n_states) c res1 res2", n_states=5)
145 | all_embeddings = self.encode_images(all_images)
146 | initial, state_i, state_j, state_k, final = rearrange(
147 | all_embeddings, "(bsz n_states) embed -> n_states bsz embed", n_states=5
148 | )
149 |
150 | # Compute Regularization Losses
151 | l1_loss = torch.linalg.norm(all_embeddings, ord=1, dim=-1).mean()
152 | l2_loss = torch.linalg.norm(all_embeddings, ord=2, dim=-1).mean()
153 |
154 | # Compute TCN Loss
155 | tcn_loss, tcn_acc = self.get_time_contrastive_loss(state_i, state_j, state_k)
156 |
157 | # Compute Language Alignment/Predictive Loss
158 | lang_reward_loss, rew_acc = self.get_reward_loss(lang, lang_mask, initial, state_i, state_j, state_k, final)
159 |
160 | # Compute full weighted loss & return...
161 | loss = (
162 | (self.l1_weight * l1_loss)
163 | + (self.l2_weight * l2_loss)
164 | + (self.tcn_weight * tcn_loss)
165 | + (self.lang_reward_weight * lang_reward_loss)
166 | )
167 | return loss, tcn_loss, lang_reward_loss, l1_loss, l2_loss, tcn_acc, rew_acc
168 |
169 | @staticmethod
170 | def time_similarity(state_x: torch.Tensor, state_y: torch.Tensor, use_l2: bool = True) -> torch.Tensor:
171 | """Computes similarity between embeddings via -L2 distance."""
172 | assert use_l2, "Non-L2 time-similarity functions not yet implemented!"
173 | return -torch.linalg.norm(state_x - state_y, dim=-1)
174 |
175 | def get_time_contrastive_loss(
176 | self, state_i: torch.Tensor, state_j: torch.Tensor, state_k: torch.Tensor
177 | ) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, ...]:
178 | """Evaluates the Time-Contrastive Loss, computed via InfoNCE."""
179 |
180 | # *Punchline* - we want `sim(i, j)` to be higher than `sim(i, k)` for some k > j (goes both ways)
181 | # `Reward(s*_0, s*_ As our positive examples --> we sample (s_i, s_j) and (s_j, s_k).
183 | # > Our negatives --> other pairs from the triplet, cross-batch negatives!
184 | sim_i_j_exp = torch.exp(self.time_similarity(state_i, state_j))
185 | sim_j_k_exp = torch.exp(self.time_similarity(state_j, state_k))
186 |
187 | # Add a "hard" negative!
188 | neg_i_k_exp = torch.exp(self.time_similarity(state_i, state_k))
189 |
190 | # Obtain *cross-batch* negatives
191 | bsz, neg_i, neg_j = state_i.shape[0], [], []
192 | for _ in range(self.n_negatives):
193 | neg_idx = torch.randperm(bsz)
194 | state_i_shuf = state_i[neg_idx]
195 | neg_idx = torch.randperm(bsz)
196 | state_j_shuf = state_j[neg_idx]
197 | neg_i.append(self.time_similarity(state_i, state_i_shuf))
198 | neg_j.append(self.time_similarity(state_j, state_j_shuf))
199 | neg_i_exp, neg_j_exp = torch.exp(torch.stack(neg_i, -1)), torch.exp(torch.stack(neg_j, -1))
200 |
201 | # Compute InfoNCE
202 | denominator_i = sim_i_j_exp + neg_i_k_exp + neg_i_exp.sum(-1)
203 | denominator_j = sim_j_k_exp + neg_i_k_exp + neg_j_exp.sum(-1)
204 | nce_i = -torch.log(self.eps + (sim_i_j_exp / (self.eps + denominator_i)))
205 | nce_j = -torch.log(self.eps + (sim_j_k_exp / (self.eps + denominator_j)))
206 | nce = (nce_i + nce_j) / 2
207 |
208 | # Compute "accuracy"
209 | i_j_acc = (1.0 * (sim_i_j_exp > neg_i_k_exp)).mean()
210 | j_k_acc = (1.0 * (sim_j_k_exp > neg_i_k_exp)).mean()
211 | acc = (i_j_acc + j_k_acc) / 2
212 |
213 | return nce.mean(), acc
214 |
215 | def get_reward_loss(
216 | self,
217 | lang: torch.Tensor,
218 | lang_mask: torch.Tensor,
219 | initial: torch.Tensor,
220 | state_i: torch.Tensor,
221 | state_j: torch.Tensor,
222 | state_k: torch.Tensor,
223 | final: torch.Tensor,
224 | ) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, ...]:
225 | """Evaluates the Language-Alignment Reward Loss, computed via InfoNCE."""
226 | lang_embed = self.encode_language(lang, lang_mask)
227 |
228 | # *Punchline* - we want `Reward(s_0, s_t, l)` to be higher than `Reward(s_0, s_ As our positive examples --> we sample s_j, s_k, and s_final (excluding s_i)
231 | pos_final_exp = torch.exp(self.get_reward(initial, final, lang_embed))
232 | pos_j_exp = torch.exp(self.get_reward(initial, state_j, lang_embed))
233 | pos_k_exp = torch.exp(self.get_reward(initial, state_k, lang_embed))
234 |
235 | # Add the within-context negatives <--> these are the most informative examples!
236 | # > We use initial, initial as a negative for the first one, just to get reward model to "capture progress"
237 | negs_final = [self.get_reward(initial, initial, lang_embed)]
238 | negs_j = [self.get_reward(initial, state_i, lang_embed)]
239 | negs_k = [self.get_reward(initial, state_j, lang_embed)]
240 |
241 | # Cross Batch Negatives -- same as positives (indexing), but from a different batch!
242 | # > @SK :: Unclear how well this will unroll on TPUs...
243 | bsz = initial.shape[0]
244 | for _ in range(self.n_negatives):
245 | # We get three random indices to further minimize correlation... from the R3M codebase!
246 | neg_idx = torch.randperm(bsz)
247 | negs_final.append(self.get_reward(initial[neg_idx], final[neg_idx], lang_embed))
248 | neg_idx = torch.randperm(bsz)
249 | negs_j.append(self.get_reward(initial[neg_idx], state_j[neg_idx], lang_embed))
250 | neg_idx = torch.randperm(bsz)
251 | negs_k.append(self.get_reward(initial[neg_idx], state_k[neg_idx], lang_embed))
252 |
253 | # Flatten & exponentiate; get ready for the InfoNCE
254 | negs_final, negs_j, negs_k = torch.stack(negs_final, -1), torch.stack(negs_j, -1), torch.stack(negs_k, -1)
255 | negs_final_exp, negs_j_exp, negs_k_exp = torch.exp(negs_final), torch.exp(negs_j), torch.exp(negs_k)
256 |
257 | # Compute InfoNCE
258 | denominator_final = pos_final_exp + negs_final_exp.sum(-1)
259 | denominator_j = pos_j_exp + negs_j_exp.sum(-1)
260 | denominator_k = pos_k_exp + negs_k_exp.sum(-1)
261 |
262 | nce_final = -torch.log(self.eps + (pos_final_exp / (self.eps + denominator_final)))
263 | nce_j = -torch.log(self.eps + (pos_j_exp / (self.eps + denominator_j)))
264 | nce_k = -torch.log(self.eps + (pos_k_exp / (self.eps + denominator_k)))
265 |
266 | # Compute "accuracy"
267 | acc_final = (1.0 * (negs_final_exp.max(dim=-1)[0] < pos_final_exp)).mean()
268 | acc_j = (1.0 * (negs_j_exp.max(dim=-1)[0] < pos_j_exp)).mean()
269 | acc_k = (1.0 * (negs_k_exp.max(dim=-1)[0] < pos_k_exp)).mean()
270 | acc = (acc_final + acc_j + acc_k) / 3
271 | nce = (nce_final + nce_j + nce_k) / 3
272 |
273 | return nce.mean(), acc
274 |
275 | def configure_optimizer(self) -> Tuple[torch.optim.Optimizer, Callable[[int, float], float]]:
276 | # Short-Circuit on Valid Optimizers
277 | if self.optimizer not in ["adam"]:
278 | raise NotImplementedError(f"Optimizer `{self.optimizer}` not supported - try [`adam`] instead!")
279 |
280 | # Create Optimizer and (No-Op) LR Scheduler
281 | optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=self.lr)
282 | update_lr = get_lr_update(
283 | optimizer, schedule="none", lr=self.lr, min_lr=self.lr, warmup_epochs=-1, max_epochs=-1
284 | )
285 | return optimizer, update_lr
286 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/models/util/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .extraction import instantiate_extractor
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/models/util/extraction.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | extraction.py
3 |
4 | General Extraction module definitions & associated utilities.
5 |
6 | References:
7 | - Set Transformers (MAP): https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.00825.pdf
8 | """
9 | from typing import Callable
10 |
11 | import torch
12 | import torch.nn as nn
13 | from einops import repeat
14 |
15 | from voltron.models.util.transformer import RMSNorm, SwishGLU
16 |
17 | # === Multiheaded Attention Pooling ===
18 |
19 |
20 | # As defined in Set Transformers () -- basically the above, additionally taking in
21 | # a set of $k$ learned "seed vectors" that are used to "pool" information.
22 | class MAPAttention(nn.Module):
23 | def __init__(self, embed_dim: int, n_heads: int) -> None:
24 | """Multi-Input Multi-Headed Attention Operation"""
25 | super().__init__()
26 | assert embed_dim % n_heads == 0, "`embed_dim` must be divisible by `n_heads`!"
27 | self.n_heads, self.scale = n_heads, (embed_dim // n_heads) ** -0.5
28 |
29 | # Projections (no bias) --> separate for Q (seed vector), and KV ("pool" inputs)
30 | self.q, self.kv = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim, bias=False), nn.Linear(embed_dim, 2 * embed_dim, bias=False)
31 | self.proj = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim)
32 |
33 | def forward(self, seed: torch.Tensor, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
34 | (B_s, K, C_s), (B_x, N, C_x) = seed.shape, x.shape
35 | assert C_s == C_x, "Seed vectors and pool inputs must have the same embedding dimensionality!"
36 |
37 | # Project Seed Vectors to `queries`
38 | q = self.q(seed).reshape(B_s, K, self.n_heads, C_s // self.n_heads).permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
39 | kv = self.kv(x).reshape(B_x, N, 2, self.n_heads, C_x // self.n_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
40 | k, v = kv.unbind(0)
41 |
42 | # Attention --> compute weighted sum over values!
43 | scores = q @ (k.transpose(-2, -1) * self.scale)
44 | attn = scores.softmax(dim=-1)
45 | vals = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B_s, K, C_s)
46 |
47 | # Project back to `embed_dim`
48 | return self.proj(vals)
49 |
50 |
51 | class MAPBlock(nn.Module):
52 | def __init__(
53 | self,
54 | n_latents: int,
55 | embed_dim: int,
56 | n_heads: int,
57 | mlp_ratio: float = 4.0,
58 | do_rms_norm: bool = True,
59 | do_swish_glu: bool = True,
60 | ) -> None:
61 | """Multiheaded Attention Pooling Block -- note that for MAP, we adopt earlier post-norm conventions."""
62 | super().__init__()
63 | self.n_latents, self.embed_dim, self.n_heads = n_latents, embed_dim, 2 * n_heads
64 |
65 | # Projection Operator
66 | self.projection = nn.Linear(embed_dim, self.embed_dim)
67 |
68 | # Initialize Latents
69 | self.latents = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(self.n_latents, self.embed_dim))
70 | nn.init.normal_(self.latents, std=0.02)
71 |
72 | # Custom MAP Attention (seed, encoder outputs) -> seed
73 | self.attn_norm = RMSNorm(self.embed_dim) if do_rms_norm else nn.LayerNorm(self.embed_dim, eps=1e-6)
74 | self.attn = MAPAttention(self.embed_dim, n_heads=self.n_heads)
75 |
76 | # Position-wise Feed-Forward Components
77 | self.mlp_norm = RMSNorm(self.embed_dim) if do_rms_norm else nn.LayerNorm(self.embed_dim, eps=1e-6)
78 | self.mlp = nn.Sequential(
79 | # Handle SwishGLU vs. GELU MLP...
80 | (
81 | SwishGLU(self.embed_dim, int(mlp_ratio * self.embed_dim))
82 | if do_swish_glu
83 | else nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(self.embed_dim, int(mlp_ratio * self.embed_dim)), nn.GELU())
84 | ),
85 | nn.Linear(int(mlp_ratio * self.embed_dim), self.embed_dim),
86 | )
87 |
88 | def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
89 | latents = repeat(self.latents, "n_latents d -> bsz n_latents d", bsz=x.shape[0])
90 | latents = self.attn_norm(latents + self.attn(latents, self.projection(x)))
91 | latents = self.mlp_norm(latents + self.mlp(latents))
92 | return latents.squeeze(dim=1)
93 |
94 |
95 | # MAP Extractor Instantiation --> factory for creating extractors with the given parameters.
96 | def instantiate_extractor(backbone: nn.Module, n_latents: int = 1) -> Callable[[], nn.Module]:
97 | def initialize() -> nn.Module:
98 | return MAPBlock(n_latents, backbone.embed_dim, backbone.n_heads)
99 |
100 | return initialize
101 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/models/util/optimization.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | optimization.py
3 |
4 | General utilities for optimization, e.g., schedulers such as Linear Warmup w/ Cosine Decay for Transformer training.
5 | Notably *does not* use the base PyTorch LR Scheduler, since we call it continuously, across epochs, across steps;
6 | PyTorch has no built-in way of separating the two without coupling to the DataLoader, so may as well make this explicit
7 | in the parent loop.
8 |
9 | References
10 | - MAE: https://github.com/facebookresearch/mae/blob/efb2a8062c206524e35e47d04501ed4f544c0ae8/util/lr_sched.py
11 | - ⚡️-Bolts: https://github.com/PyTorchLightning/lightning-bolts/blob/master/pl_bolts/optimizers/lr_scheduler.py
12 | """
13 | import math
14 | from typing import Callable
15 |
16 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
17 |
18 |
19 | def get_lr_update(
20 | opt: Optimizer, schedule: str, lr: float, min_lr: float, warmup_epochs: int, max_epochs: int
21 | ) -> Callable[[int, float], float]:
22 | if schedule == "linear-warmup+cosine-decay":
23 |
24 | def lr_update(epoch: int, fractional_progress: float) -> float:
25 | """Run the warmup check for linear increase, else cosine decay."""
26 | if (epoch + fractional_progress) < warmup_epochs:
27 | new_lr = lr * (epoch + fractional_progress) / max(1.0, warmup_epochs)
28 | else:
29 | # Cosine Decay --> as defined in the SGDR Paper...
30 | progress = ((epoch + fractional_progress) - warmup_epochs) / max(1.0, max_epochs - warmup_epochs)
31 | new_lr = min_lr + (lr - min_lr) * (0.5 * (1 + math.cos(math.pi * progress)))
32 |
33 | # Apply...
34 | for group in opt.param_groups:
35 | if "lr_scale" in group:
36 | group["lr"] = new_lr * group["lr_scale"]
37 | else:
38 | group["lr"] = new_lr
39 |
40 | return new_lr
41 |
42 | elif schedule == "none":
43 |
44 | def lr_update(_: int, __: float) -> float:
45 | return lr
46 |
47 | else:
48 | raise NotImplementedError(f"Schedule `{schedule}` not implemented!")
49 |
50 | return lr_update
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/models/util/transformer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | transformer.py
3 |
4 | General Transformer modules & utilities.
5 |
6 | References:
7 | - https://github.com/facebookresearch/mae
8 | - https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/timm/models/vision_transformer.py
9 | """
10 | from typing import Optional
11 |
12 | import numpy as np
13 | import torch
14 | import torch.nn as nn
15 | from einops import rearrange
16 |
17 | # === Position Encoding Utilities ===
18 |
19 |
20 | # Helper/Utility Function -- computes simple 1D sinusoidal position embeddings for both 1D/2D use cases.
21 | # > We'll be combining two 1D sin-cos (traditional) position encodings for height/width of an image (grid features).
22 | def get_1D_sine_cosine(dim: int, pos: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
23 | omega = np.arange(dim // 2, dtype=np.float32) / (dim / 2.0)
24 | omega = 1.0 / (10000**omega)
25 | out = np.einsum("m,d->md", pos.reshape(-1), omega) # [flatten(pos) x omega] -- outer product!
26 | emb_sin, emb_cos = np.sin(out), np.cos(out)
27 | return np.concatenate([emb_sin, emb_cos], axis=1) # [flatten(pos) x D]
28 |
29 |
30 | # 1D Sine-Cosine Position Embedding -- standard from "Attention is all you need!"
31 | def get_1D_position_embeddings(embed_dim: int, length: int) -> np.ndarray:
32 | return get_1D_sine_cosine(embed_dim, np.arange(length))
33 |
34 |
35 | # 2D Sine-Cosine Position Embedding (from MAE repository)
36 | # > https://github.com/facebookresearch/mae/blob/efb2a8062c206524e35e47d04501ed4f544c0ae8/util/pos_embed.py#L20
37 | def get_2D_position_embeddings(embed_dim: int, grid_size: int, cls_token: bool = False) -> np.ndarray:
38 | # Create 2D Position embeddings by taking cross product of height and width and splicing 1D embeddings...
39 | grid_h, grid_w = np.arange(grid_size, dtype=np.float32), np.arange(grid_size, dtype=np.float32)
40 | grid = np.stack(np.meshgrid(grid_w, grid_h), axis=0).reshape(2, 1, grid_size, grid_size) # w goes first?
41 |
42 | # Use half of dimensions to encode grid_h, other half to encode grid_w
43 | emb_h, emb_w = get_1D_sine_cosine(embed_dim // 2, grid[0]), get_1D_sine_cosine(embed_dim // 2, grid[1])
44 | pos_embed = np.concatenate([emb_h, emb_w], axis=1)
45 |
46 | # CLS token handling (only for R-MVP)
47 | if cls_token:
48 | pos_embed = np.concatenate([np.zeros([1, embed_dim]), pos_embed], axis=0)
49 |
50 | return pos_embed
51 |
52 |
53 | # === Vision Transformer Building Blocks ===
54 |
55 |
56 | # Patch Embedding Module
57 | class PatchEmbed(nn.Module):
58 | def __init__(
59 | self,
60 | resolution: int,
61 | patch_size: int,
62 | embed_dim: int,
63 | in_channels: int = 3,
64 | flatten: bool = True,
65 | ):
66 | super().__init__()
67 | self.resolution, self.patch_size = (resolution, resolution), (patch_size, patch_size)
68 | self.grid_size = (self.resolution[0] // self.patch_size[0], self.resolution[1] // self.patch_size[1])
69 | self.num_patches = self.grid_size[0] * self.grid_size[1]
70 | self.flatten = flatten
71 | self.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, embed_dim, kernel_size=self.patch_size, stride=self.patch_size)
72 |
73 | def forward(self, patches: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
74 | patch_embeddings = self.proj(patches)
75 | if self.flatten:
76 | return rearrange(patch_embeddings, "bsz embed patch_h patch_w -> bsz (patch_h patch_w) embed")
77 | return patch_embeddings
78 |
79 |
80 | # === Stability Utilities ===
81 |
82 |
83 | # LayerScale -- Trainable scaling for residual blocks -- Mistral/CaIT
84 | class LayerScale(nn.Module):
85 | def __init__(self, dim: int, init_values: float = 0.1) -> None: # CaIT :: 0.1 -> lay 12, 1e-5 -> lay 24, 1e-6...
86 | super().__init__()
87 | self.gamma = nn.Parameter(init_values * torch.ones(dim))
88 |
89 | def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
90 | return x * self.gamma
91 |
92 |
93 | # RMSNorm -- Better, simpler alternative to LayerNorm
94 | class RMSNorm(nn.Module):
95 | def __init__(self, dim: int, eps: float = 1e-8) -> None:
96 | super().__init__()
97 | self.scale, self.eps = dim**-0.5, eps
98 | self.g = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(dim))
99 |
100 | def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
101 | norm = torch.norm(x, dim=-1, keepdim=True) * self.scale
102 | return x / norm.clamp(min=self.eps) * self.g
103 |
104 |
105 | # SwishGLU -- A Gated Linear Unit (GLU) with the Swish activation; always better than GELU MLP!
106 | class SwishGLU(nn.Module):
107 | def __init__(self, in_dim: int, out_dim: int) -> None:
108 | super().__init__()
109 | self.act, self.project = nn.SiLU(), nn.Linear(in_dim, 2 * out_dim)
110 |
111 | def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
112 | projected, gate = self.project(x).tensor_split(2, dim=-1)
113 | return projected * self.act(gate)
114 |
115 |
116 | # === Fundamental Transformer Building Blocks ===
117 |
118 |
119 | class Attention(nn.Module):
120 | def __init__(self, embed_dim: int, n_heads: int, dropout: float = 0.0) -> None:
121 | """Multi-Headed Self-Attention Operation"""
122 | super().__init__()
123 | assert embed_dim % n_heads == 0, "`embed_dim` must be divisible by `n_heads`!"
124 | self.n_heads, self.scale = n_heads, (embed_dim // n_heads) ** -0.5
125 | self.attn_softmax = None
126 |
127 | # Projections
128 | self.qkv, self.proj = nn.Linear(embed_dim, 3 * embed_dim, bias=True), nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim)
129 | self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
130 |
131 | def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor, mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None) -> torch.Tensor:
132 | B, N, C = x.shape
133 |
134 | # Project to Q-K-V
135 | qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B, N, 3, self.n_heads, C // self.n_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
136 | q, k, v = qkv.unbind(0)
137 |
138 | # Self-attention -- with masking!
139 | scores = q @ (k.transpose(-2, -1) * self.scale)
140 | if mask is not None:
141 | if mask.ndim == 2:
142 | mask = rearrange(mask, "bsz seq -> bsz 1 seq 1")
143 | elif mask.ndim != 4:
144 | raise NotImplementedError("Attention got `mask` of shape not in {2, 4}!")
145 |
146 | # Mask out by filling indices with negative infinity...
147 | scores = scores.masked_fill(mask == 0, torch.finfo(scores.dtype).min)
148 |
149 | # Compute weighted sum over values
150 | self.attn_softmax = scores.softmax(dim=-1)
151 | vals = (self.attn_softmax @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, N, C)
152 |
153 | # Project back to `embed_dim` -- with optional dropout
154 | vals = self.dropout(self.proj(vals))
155 | return vals
156 |
157 |
158 | class Block(nn.Module):
159 | def __init__(
160 | self,
161 | embed_dim: int,
162 | n_heads: int,
163 | mlp_ratio: float = 4.0,
164 | dropout: float = 0.0,
165 | do_rms_norm: bool = False,
166 | do_swish_glu: bool = False,
167 | do_layer_scale: bool = False,
168 | ) -> None:
169 | """
170 | Transformer Block Implementation (modality-agnostic).
171 |
172 | :param embed_dim: Core embedding/hidden dimension for vision transformer backbone.
173 | :param n_heads: Number of heads for multi-headed self-attention.
174 | :param mlp_ratio: Ratio for embedding size to position-wise feed-forward MLP (gets shrunk back down).
175 | :param dropout: [Optional] dropout for projection layer and MLPs -- for MAEs, always 0.0!
176 | :param do_rms_norm: Boolean whether or not to use RMSNorm in lieu of LayerNorm within block.
177 | :param do_swish_glu: Use the Swish-variant of the Gated Linear Unit for the feed-forward layers.
178 | :param do_layer_scale: Boolean whether or not to use LayerScale from Mistral/CaIT w/ initialization of 0.1.
179 | """
180 | super().__init__()
181 | self.embed_dim, self.n_heads, self.do_layer_scale = embed_dim, n_heads, do_layer_scale
182 |
183 | # Attention Components
184 | self.pre_norm_attn = RMSNorm(self.embed_dim) if do_rms_norm else nn.LayerNorm(self.embed_dim, eps=1e-6)
185 | self.attn = Attention(self.embed_dim, n_heads=n_heads, dropout=dropout)
186 | if do_layer_scale:
187 | self.layer_scale_attn = LayerScale(self.embed_dim)
188 |
189 | # Position-wise Feed-Forward Components
190 | self.pre_norm_mlp = RMSNorm(self.embed_dim) if do_rms_norm else nn.LayerNorm(self.embed_dim, eps=1e-6)
191 | self.mlp = nn.Sequential(
192 | # Handle SwishGLU vs. GELU MLP...
193 | (
194 | SwishGLU(embed_dim, int(mlp_ratio * embed_dim))
195 | if do_swish_glu
196 | else nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(embed_dim, int(mlp_ratio * embed_dim)), nn.GELU())
197 | ),
198 | nn.Dropout(dropout),
199 | nn.Linear(int(mlp_ratio * embed_dim), embed_dim),
200 | )
201 | if self.do_layer_scale:
202 | self.layer_scale_mlp = LayerScale(self.embed_dim)
203 |
204 | def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor, mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None) -> torch.Tensor:
205 | if self.do_layer_scale:
206 | x = x + self.layer_scale_attn(self.attn(self.pre_norm_attn(x), mask))
207 | x = x + self.layer_scale_mlp(self.mlp(self.pre_norm_mlp(x)))
208 | else:
209 | x = x + self.attn(self.pre_norm_attn(x), mask)
210 | x = x + self.mlp(self.pre_norm_mlp(x))
211 | return x
212 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/overwatch/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .overwatch import OverwatchRich
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/overwatch/overwatch.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | overwatch.py
3 |
4 | Utility class for creating a centralized/standardized logger (to pass to Hydra), with a sane default format.
5 | """
6 | from dataclasses import dataclass, field
7 | from typing import Any, Dict
8 |
9 | # Overwatch Default Format String
10 | FORMATTER, DATEFMT = "[*] %(asctime)s - %(name)s >> %(levelname)s :: %(message)s", "%m/%d [%H:%M:%S]"
11 | RICH_FORMATTER = "| >> %(message)s"
12 |
13 |
14 | # Rich Overwatch Variant --> Good for debugging, and tracing!
15 | @dataclass
16 | class OverwatchRich:
17 | version: int = 1
18 | formatters: Dict[str, Any] = field(
19 | default_factory=lambda: {
20 | "simple-console": {"format": RICH_FORMATTER, "datefmt": DATEFMT},
21 | "simple-file": {"format": FORMATTER, "datefmt": DATEFMT},
22 | }
23 | )
24 | handlers: Dict[str, Any] = field(
25 | default_factory=lambda: {
26 | "console": {
27 | "class": "rich.logging.RichHandler",
28 | "formatter": "simple-console",
29 | "rich_tracebacks": True,
30 | "show_level": True,
31 | "show_path": True,
32 | "show_time": True,
33 | },
34 | "file": {
35 | "class": "logging.FileHandler",
36 | "formatter": "simple-file",
37 | "filename": "${hydra.job.name}.log",
38 | },
39 | }
40 | )
41 | root: Dict[str, Any] = field(default_factory=lambda: {"level": "INFO", "handlers": ["console", "file"]})
42 | disable_existing_loggers: bool = True
43 |
44 |
45 | # Standard Overwatch Variant --> Performant, no bells & whistles
46 | @dataclass
47 | class OverwatchStandard:
48 | version: int = 1
49 | formatters: Dict[str, Any] = field(default_factory=lambda: {"simple": {"format": FORMATTER, "datefmt": DATEFMT}})
50 | handlers: Dict[str, Any] = field(
51 | default_factory=lambda: {
52 | "console": {"class": "logging.StreamHandler", "formatter": "simple", "stream": "ext://sys.stdout"},
53 | "file": {
54 | "class": "logging.FileHandler",
55 | "formatter": "simple",
56 | "filename": "${hydra.job.name}.log",
57 | },
58 | }
59 | )
60 | root: Dict[str, Any] = field(default_factory=lambda: {"level": "INFO", "handlers": ["console", "file"]})
61 | disable_existing_loggers: bool = True
62 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/preprocessing/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .process import extract_frames, preprocess_language, unify_batches
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/preprocessing/core.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | utils.py
3 |
4 | Preprocessing utilities, including dry-run and single-video (single-example) processing. This file effectively defines
5 | the "atomic" logic (take one video --> extract all frames, etc.), while the `process.py` functions invoke each unit
6 | in a multiprocessing pool.
7 | """
8 | import glob
9 | import json
10 | import logging
11 | import os
12 | import time
13 | from pathlib import Path
14 | from typing import Any, Callable, Dict, List, Optional, Set, Tuple
15 |
16 | import av
17 | import h5py
18 | import numpy as np
19 | import pandas as pd
20 | from hurry.filesize import alternative, size
21 | from PIL import Image
22 | from rich.progress import track
23 | from tqdm import tqdm
24 |
25 | # Grab Logger
26 | overwatch = logging.getLogger(__file__)
27 | logging.getLogger("libav").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
28 |
29 |
30 | # === General Utilities ===
31 |
32 |
33 | # Videos are saved as `train_dir/{vid}/{vid}_idx={i}.jpg || if `relpath` then *relative path* `{split}/{vid}/...
34 | def get_path(save_dir: Path, v: str, i: int, relpath: bool = False) -> str:
35 | return str((save_dir if not relpath else Path(save_dir.name)) / v / f"{v}_idx={i}.jpg")
36 |
37 |
38 | # === Dry-Run Functionality ===
39 |
40 |
41 | def do_dry_run(
42 | name: str,
43 | path: str,
44 | train_ids: List[str],
45 | val_ids: List[str],
46 | preprocess_transform: Callable[[List[Image.Image]], List[Image.Image]],
47 | n_train_videos: int = 1000,
48 | n_val_videos: int = 100,
49 | n_samples: int = 1000,
50 | ) -> None:
51 | """Iterates through a small subset of the total dataset, logs n_frames & average image size for estimation."""
52 | overwatch.info(f"Performing Dry-Run with {n_train_videos} Train Videos and {n_val_videos} Validation Videos")
53 | dry_run_metrics = {
54 | "n_frames": [],
55 | "jpg_sizes": [],
56 | "n_samples": n_samples,
57 | "time_per_example": [],
58 | "blank": str(Path(path) / "blank.jpg"),
59 | }
60 |
61 | # Switch on dataset (`name`)
62 | if name == "sth-sth-v2":
63 | for k, n_iter, vids in [("train", n_train_videos, train_ids), ("val", n_val_videos, val_ids)]:
64 | for idx in track(range(n_iter), description=f"Reading {k.capitalize()} Videos =>> ", transient=True):
65 | container = av.open(str(Path(path) / "videos" / f"{vids[idx]}.webm"))
66 | assert int(container.streams.video[0].average_rate) == 12, "FPS for `sth-sth-v2` should be 12!"
67 | try:
68 | imgs = [f.to_image() for f in container.decode(video=0)]
69 | except (RuntimeError, ZeroDivisionError) as e:
70 | overwatch.error(f"{type(e).__name__}: WebM reader cannot open `{vids[idx]}.webm` - continuing...")
71 | continue
72 | container.close()
73 |
74 | # Apply `preprocess_transform`
75 | imgs = preprocess_transform(imgs)
76 |
77 | # Dry-Run Handling --> write a dummy JPEG to collect size statistics, dump, and move on...
78 | dry_run_metrics["n_frames"].append(len(imgs))
79 | while dry_run_metrics["n_samples"] > 0 and len(imgs) > 0:
80 | img = imgs.pop(0)
81 | img.save(str(dry_run_metrics["blank"]))
82 | dry_run_metrics["jpg_sizes"].append(os.path.getsize(dry_run_metrics["blank"]))
83 | dry_run_metrics["n_samples"] -= 1
84 |
85 | # Compute nice totals for "dry-run" estimate...
86 | total_clips = len(train_ids) + len(val_ids)
87 |
88 | else:
89 | raise ValueError(f"Dry Run for Dataset `{name}` not implemented!")
90 |
91 | # Compute aggregate statistics and gently exit...
92 | avg_size, avg_frames = np.mean(dry_run_metrics["jpg_sizes"]), int(np.mean(dry_run_metrics["n_frames"]))
93 | overwatch.info("Dry-Run Statistics =>>")
94 | overwatch.info(f"\t> A video has on average `{avg_frames}` frames at {size(avg_size, system=alternative)}")
95 | overwatch.info(f"\t> So - 1 video ~ {size(avg_frames * avg_size, system=alternative)}")
96 | overwatch.info(
97 | f"\t> With the full dataset of {total_clips} Train + Val videos ~"
98 | f" {size(total_clips * avg_frames * avg_size, system=alternative)}"
99 | )
100 | overwatch.info("Dry-Run complete, do what you will... exiting ✌️")
101 |
102 | # Remove dummy file...
103 | os.remove(dry_run_metrics["blank"])
104 | exit(0)
105 |
106 |
107 | # === Atomic "Processing" Steps ===
108 |
109 |
110 | def process_clip(
111 | name: str,
112 | path: Path,
113 | save: Path,
114 | preprocess_transform: Callable[[List[Image.Image]], List[Image.Image]],
115 | item: Tuple[str, str],
116 | ) -> Tuple[Optional[str], Optional[Dict[str, Any]]]:
117 | """Processes a single video clip and extracts/serializes all frames (as jpeg), returning the registry contents."""
118 | if name == "sth-sth-v2":
119 | vid, lang = item
120 | container, registration = av.open(str(Path(path) / "videos" / f"{vid}.webm")), {"language": lang, "n_frames": 0}
121 | assert int(container.streams.video[0].average_rate) == 12, "FPS for `sth-sth-v2` should be 12!"
122 | try:
123 | imgs = [f.to_image() for f in container.decode(video=0)]
124 | except (RuntimeError, ZeroDivisionError) as e:
125 | overwatch.error(f"{type(e).__name__}: WebM reader cannot open `{vid}.webm` - continuing...")
126 | return None, None
127 | container.close()
128 |
129 | # Book-Keeping
130 | os.makedirs(save / vid, exist_ok=True)
131 | registration["n_frames"] = len(imgs)
132 |
133 | # Short Circuit --> Writes are Expensive!
134 | if len(glob.glob1(save / vid, "*.jpg")) == len(imgs):
135 | return vid, registration
136 |
137 | # Apply `preprocess_transform` --> write individual frames, register, and move on!
138 | imgs = preprocess_transform(imgs)
139 | for idx in range(len(imgs)):
140 | imgs[idx].save(get_path(save, vid, idx))
141 |
142 | # Return title & registration
143 | return vid, registration
144 |
145 | else:
146 | raise ValueError(f"Clip Processing for Dataset `{name}` is not implemented!")
147 |
148 |
149 | # ruff: noqa: C901
150 | def serialize_epoch(
151 | index_dir: Path,
152 | registry: Dict[str, Any],
153 | vid_dir: Path,
154 | batch_formats: Tuple[Tuple[str, Tuple[str, ...]], ...],
155 | do_initial: bool,
156 | do_final: bool,
157 | initial_final_alpha: float,
158 | n_int: int,
159 | epoch: int,
160 | is_validation: bool = False,
161 | ) -> Tuple[int, int, Optional[Set[str]]]:
162 | index_file = "validation-batches.json" if is_validation else f"train-epoch={epoch}-batches.json"
163 | index_hdf5 = "validation-batches.hdf5" if is_validation else f"train-epoch={epoch}-batches.hdf5"
164 |
165 | # Short-Circuit
166 | if all([(index_dir / key / index_file).exists() for key, _ in batch_formats]):
167 | return -1, -1, None
168 |
169 | # Random seed is inherited from parent process... we want new randomness w/ each process
170 | np.random.seed((os.getpid() * int(time.time())) % 123456789)
171 |
172 | # Create Tracking Variables
173 | unique_states, batches = set(), {b: [] for b, _ in batch_formats}
174 |
175 | # Iterate through Registry --> Note we're using `tqdm` instead of `track` here because of `position` feature!
176 | for vid in tqdm(registry.keys(), desc=f"Epoch {epoch}", total=len(registry), position=epoch):
177 | # The initial/final states are sampled from the first [0, \alpha) and final 1-\alpha, 1] percent of the video
178 | n_frames = registry[vid]["n_frames"]
179 | initial_idx, final_idx = 0, n_frames - 1
180 | if do_initial:
181 | initial_idx = np.random.randint(0, np.around(n_frames * initial_final_alpha))
182 |
183 | if do_final:
184 | final_idx = np.random.randint(np.around(n_frames * (1 - initial_final_alpha)), n_frames)
185 |
186 | # Assertion --> initial_idx < final_idx - len(state_elements)
187 | assert initial_idx < final_idx - n_int, "Initial & Final are too close... no way to sample!"
188 |
189 | # Assume remaining elements are just random "interior" states --> sort to get ordering!
190 | sampled_idxs = np.random.choice(np.arange(initial_idx + 1, final_idx), size=n_int, replace=False)
191 | sampled_idxs = sorted(list(sampled_idxs))
192 |
193 | # Compile full-set "batch"
194 | retrieved_states = [get_path(vid_dir, vid, x, relpath=True) for x in [initial_idx, *sampled_idxs] + [final_idx]]
195 |
196 | # Add batch to index for specific batch_format key...
197 | batches[batch_formats[-1][0]].append({"vid": vid, "states": retrieved_states, "n_frames": n_frames})
198 | unique_states.update(retrieved_states)
199 |
200 | # Add all other batch formats to indices...
201 | for key, elements in batch_formats[:-1]:
202 | n_states = len([x for x in elements if "state_" in x])
203 | assert (n_states <= 2) or (
204 | n_states == len(retrieved_states)
205 | ), f"Strange value of n_states={n_states} > 2 and not equal to total possible of {len(retrieved_states)}"
206 |
207 | # States are all independent -- each of the retrieved states is its own example...
208 | if n_states == 1:
209 | for idx in range(len(retrieved_states)):
210 | batches[key].append({"vid": vid, "state": retrieved_states[idx], "n_frames": n_frames})
211 |
212 | # OK-Context is the only "valid" context for n_states == 2
213 | elif n_states == 2:
214 | assert elements == ["state_initial", "state_i", "language"], "n_states = 2 but not 0K context?"
215 |
216 | # Append 0th state to each of the remaining sampled contexts (usually 2 or 4)... each pair is an example
217 | for idx in range(1, len(retrieved_states)):
218 | batches[key].append(
219 | {"vid": vid, "states": [retrieved_states[0], retrieved_states[idx]], "n_frames": n_frames}
220 | )
221 |
222 | # We're treating the entire sequence of retrieved states as a single example (for TCN/R3M/Temporal Models)
223 | else:
224 | batches[key].append({"vid": vid, "states": retrieved_states, "n_frames": n_frames})
225 |
226 | # Write JSON Index directly to disk...
227 | for key in batches:
228 | with open(index_dir / key / index_file, "w") as f:
229 | json.dump(batches[key], f)
230 |
231 | # Write HDF5 Index directly to disk...
232 | for key, elements in batch_formats[:-1]:
233 | n_states = len([x for x in elements if "state_" in x])
234 |
235 | # Create HDF5 File
236 | df = pd.DataFrame(batches[key])
237 | h5 = h5py.File(index_dir / key / index_hdf5, "w")
238 | for k in ["vid", "n_frames"]:
239 | h5.create_dataset(k, data=df[k].values)
240 |
241 | # Handle "state(s)" --> (image path strings) --> add leading dimension (`n_states`)
242 | if n_states == 1:
243 | dfs = df["state"].apply(pd.Series)
244 | h5.create_dataset("states", data=dfs.values)
245 |
246 | else:
247 | dfs = df["states"].apply(pd.Series)
248 | h5.create_dataset("states", data=dfs.values)
249 |
250 | # Close HDF5 File
251 | h5.close()
252 |
253 | return epoch, len(batches["state"]), unique_states
254 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/preprocessing/process.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | process.py
3 |
4 | Utility functions for preprocessing large-scale video/vision-language datasets in multiple passes, using multiprocessing
5 | for parallelization. Exposes a three-phase sequence for preprocessing --> batching data:
6 | - Phase I (`extract_frames`): Read in raw (video clip, language) pairs, extract and serialize *all frames* to disk.
7 |
8 | This script tries to be smart where it can, using multiprocessing.Pool in Phase I to speed up extraction; however, for
9 | larger datasets YMMV. You might consider extracting the relevant logic, and using tools like SLURM Job Arrays, AWS
10 | Lambda Functions, or GCP Cloud Run to "burst preprocess" data.
11 | """
12 | import json
13 | import logging
14 | import multiprocessing as mp
15 | import os
16 | import shutil
17 | from functools import partial
18 | from pathlib import Path
19 | from typing import Tuple
20 |
21 | import torch
22 | from rich.progress import track
23 | from transformers import AutoTokenizer
24 |
25 | from voltron.preprocessing.core import do_dry_run, process_clip, serialize_epoch
26 | from voltron.preprocessing.transforms import get_preprocess_transform
27 |
28 | # Grab Logger
29 | overwatch = logging.getLogger(__file__)
30 |
31 |
32 | def extract_frames(
33 | name: str,
34 | path: str,
35 | artifact_path: str,
36 | preprocess_resolution: int,
37 | n_val_videos: int,
38 | dry_run: bool = False,
39 | ) -> Tuple[Path, Path, Path, Path]:
40 | """Phase I: Extract and serialize *all frames* from video clips; uses multiprocessing to parallelize."""
41 | overwatch.info(f"Phase 1 Preprocessing :: Extracting Frames for Dataset `{name}`")
42 |
43 | # Overview of Return Values:
44 | # `t_registry` and `v_registry` =>> store mappings of "video id" -> {metadata}
45 | # `t_dir` and `v_dir` =>> store "processed data" (extracted frames)
46 | t_dir, v_dir = Path(artifact_path) / name / "train", Path(artifact_path) / name / "val"
47 | t_registry, v_registry = t_dir / "registry.json", v_dir / "registry.json"
48 |
49 | # Short-Circuit
50 | if t_registry.exists() and v_registry.exists():
51 | return t_registry, v_registry, t_dir, v_dir
52 |
53 | # Setup / Book-Keeping
54 | os.makedirs(t_dir, exist_ok=True)
55 | os.makedirs(v_dir, exist_ok=True)
56 |
57 | # Retrieve "pre-serialization" frame transform --> we scale down video frames (*while preserving aspect ratios*)
58 | # and center crop each frame to `(preprocess_resolution, preprocess_resolution)`; saves on disk space (by a lot!)
59 | preprocess_transform = get_preprocess_transform(name, preprocess_resolution=preprocess_resolution)
60 |
61 | # Switch on dataset (`name`)
62 | if name == "sth-sth-v2":
63 | with open(Path(path) / "labels/train.json", "r") as f:
64 | annotations = json.load(f)
65 | train_ids, train_lang = [x["id"] for x in annotations], [x["label"] for x in annotations]
66 |
67 | with open(Path(path) / "labels/validation.json", "r") as f:
68 | annotations = json.load(f)[:n_val_videos]
69 | val_ids, val_lang = [x["id"] for x in annotations], [x["label"] for x in annotations]
70 |
71 | else:
72 | raise ValueError(f"Language/Metadata Extraction Pipeline for Dataset `{name}` not implemented!")
73 |
74 | # Run Dry-Run (if specified) --> single-threaded for debugging
75 | if dry_run:
76 | do_dry_run(name, path, train_ids, val_ids, preprocess_transform)
77 |
78 | # Otherwise =>> Iterate through all videos, dump all frames subject to the following structure:
79 | # |-> .../processed/something-something-v2/
80 | # |-> /
81 | # |-> /frames<0..k>.jpg
82 | #
83 | # We'll build a single metadata file with a mapping : ("language", n_frames)
84 | # > To speed up serialization, we'll use a multiprocessing.Pool and max out CPU workers
85 | with mp.Pool(mp.cpu_count()) as pool:
86 | for k, save, vids, langs in [("train", t_dir, train_ids, train_lang), ("val", v_dir, val_ids, val_lang)]:
87 | overwatch.info(f"\tWriting `{k}` videos to disk...")
88 |
89 | # Spawn!
90 | process_fn, registration = partial(process_clip, name, Path(path), save, preprocess_transform), {}
91 | for key, value in track(
92 | pool.imap_unordered(process_fn, zip(vids, langs)),
93 | total=len(vids),
94 | transient=True,
95 | ):
96 | if key is not None:
97 | registration[key] = value
98 |
99 | # Write Registration to Disk
100 | with open(t_registry if k == "train" else v_registry, "w") as f:
101 | json.dump(registration, f)
102 |
103 | # Return Paths to Registry & Extract Directories...
104 | return t_registry, v_registry, t_dir, v_dir
105 |
106 |
107 | def preprocess_language(
108 | name: str,
109 | train_registry: Path,
110 | val_registry: Path,
111 | artifact_path: str,
112 | max_lang_len: int,
113 | language_model: str,
114 | hf_cache: str,
115 | ) -> Path:
116 | """Phase II: Iterate through Language Captions/Narrations and Normalize/Tokenize (truncate/pad to max length)."""
117 | overwatch.info(f"Phase 2 Preprocessing :: Normalizing & Tokenizing Language for Dataset `{name}`")
118 | t_index, v_index = train_registry.parent / "index.pt", val_registry.parent / "index.pt"
119 | t_json, v_json = train_registry.parent / "index.json", val_registry.parent / "index.json"
120 | index_dir = Path(artifact_path) / name / "index"
121 | os.makedirs(index_dir, exist_ok=True)
122 |
123 | # Short-Circuit
124 | if (index_dir / "train-language-index.json").exists() and (index_dir / "val-language-index.json").exists():
125 | return index_dir
126 |
127 | # Grab Language --> retain metadata for building index structures!
128 | with open(train_registry, "r") as f:
129 | train_metadata = json.load(f)
130 | train = [(vid, train_metadata[vid]["language"], train_metadata[vid]) for vid in train_metadata]
131 |
132 | with open(val_registry, "r") as f:
133 | val_metadata = json.load(f)
134 | val = [(vid, val_metadata[vid]["language"], val_metadata[vid]) for vid in val_metadata]
135 |
136 | # Assemble *all* language
137 | language = [x[1] for x in train + val]
138 |
139 | # Build AutoTokenizer (from `language_model` identifier)
140 | tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(language_model, cache_dir=hf_cache)
141 |
142 | # If `max_lang_len` not specified, dump some statistics to compute...
143 | if max_lang_len == -1:
144 | # Naively tokenizes and pads to the "maximum length" of _all_ language... long tail is a problem!
145 | encoded_language = tokenizer(language, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
146 | lengths = encoded_language["attention_mask"].sum(dim=1)
147 |
148 | # Compute a histogram of lengths
149 | hist = lengths.float().histc(bins=lengths.max()).int()
150 | overwatch.info(f"Histogram: {hist.numpy().tolist()}")
151 | raise AssertionError("Compute max length and update dataset configuration!")
152 |
153 | # Otherwise, we've already set the maximum length, so let's use it!
154 | overwatch.info(f"\tTokenizing all language in dataset to maximum length `{max_lang_len}`")
155 | encoded_language = tokenizer(
156 | language, return_tensors="pt", max_length=max_lang_len, truncation=True, padding="max_length"
157 | )
158 | input_ids, attention_mask = encoded_language["input_ids"], encoded_language["attention_mask"]
159 | train_input_ids, train_attention_mask = input_ids[: len(train)], attention_mask[: len(train)]
160 | val_input_ids, val_attention_mask = input_ids[len(train) :], attention_mask[len(train) :]
161 |
162 | # Assertion, just to sanity check
163 | assert len(val_input_ids) == len(val_attention_mask) == len(val), "Something went wrong tokenizing language..."
164 |
165 | # Compute `index.pt` contents
166 | overwatch.info("\tAssembling `train` and `val` index structures...")
167 | train_pt = {
168 | train[i][0]: {**train[i][2], **{"input_ids": train_input_ids[i], "attention_mask": train_attention_mask[i]}}
169 | for i in range(len(train))
170 | }
171 | val_pt = {
172 | val[i][0]: {**val[i][2], **{"input_ids": val_input_ids[i], "attention_mask": val_attention_mask[i]}}
173 | for i in range(len(val))
174 | }
175 |
176 | # Additionally dump JSON versions of the same --> downstream interpretability, XLA
177 | overwatch.info("JSONifying both Train and Validation Language")
178 | train_json, val_json = {}, {}
179 | for vid in track(train_pt, description="Train Language :: ", transient=True):
180 | train_json[vid] = {
181 | "language": train_pt[vid]["language"],
182 | "n_frames": train_pt[vid]["n_frames"],
183 | "input_ids": train_pt[vid]["input_ids"].numpy().tolist(),
184 | "attention_mask": train_pt[vid]["attention_mask"].numpy().tolist(),
185 | }
186 |
187 | for vid in track(val_pt, description="Validation Language :: ", transient=True):
188 | val_json[vid] = {
189 | "language": val_pt[vid]["language"],
190 | "n_frames": val_pt[vid]["n_frames"],
191 | "input_ids": val_pt[vid]["input_ids"].numpy().tolist(),
192 | "attention_mask": val_pt[vid]["attention_mask"].numpy().tolist(),
193 | }
194 |
195 | # Dump Structures...
196 | overwatch.info(f"Saving Torch indices to `{t_index}` and `{v_index}` respectively...")
197 | torch.save(train_pt, t_index)
198 | torch.save(val_pt, v_index)
199 |
200 | overwatch.info(f"Saving JSON indices to `{t_json}` and `{v_json}` respectively...")
201 | with open(t_json, "w") as f:
202 | json.dump(train_json, f)
203 |
204 | with open(v_json, "w") as f:
205 | json.dump(val_json, f)
206 |
207 | # Pull relevant files out into their own `index` directory...
208 | shutil.copy(t_json, index_dir / "train-language-index.json")
209 | shutil.copy(v_json, index_dir / "val-language-index.json")
210 |
211 | return index_dir
212 |
213 |
214 | def unify_batches(
215 | name: str,
216 | train_registry: Path,
217 | val_registry: Path,
218 | train_dir: Path,
219 | val_dir: Path,
220 | index_dir: Path,
221 | batch_formats: Tuple[Tuple[str, Tuple[str, ...]], ...],
222 | max_epochs: int = 400,
223 | initial_final_alpha: float = 0.2,
224 | ) -> None:
225 | """Phase III: Assemble "Data-Locked" Batches for *all models* for *all epochs* for consistency!"""
226 | overwatch.info(f"Phase 3 Preprocessing :: Assembling *Data-Locked* Batches for Dataset `{name}`")
227 |
228 | # Load Registries
229 | with open(train_registry, "r") as f:
230 | train_registrations = json.load(f)
231 |
232 | with open(val_registry, "r") as f:
233 | val_registrations = json.load(f)
234 |
235 | # Assert last element of `batch_formats` assumes all prior subsets...
236 | full_set_inputs = set(batch_formats[-1][1])
237 | for _, subset_inputs in batch_formats[:-1]:
238 | assert full_set_inputs.issuperset(set(subset_inputs)), "We have a problem with batch formats..."
239 |
240 | # Assemble Tracking Data
241 | b_keys, unique_states = {b[0] for b in batch_formats}, set()
242 |
243 | # Parse out all "state"-specific Elements...
244 | state_elements = [s for s in full_set_inputs if "state_" in s]
245 | do_initial, do_final = "state_initial" in state_elements, "state_final" in state_elements
246 | n_int = len(state_elements) - 2 if ("state_initial" in state_elements and "state_final" in state_elements) else 0
247 |
248 | # Serialize Epochs
249 | overwatch.info("\tSerializing Epochs to JSON --> Storing mapping of Epoch -> Image Paths")
250 | for b in b_keys:
251 | os.makedirs(index_dir / b, exist_ok=True)
252 |
253 | # We only write the Validation Epoch once --> held constant across *all* of training!
254 | overwatch.info("\tWriting Validation Epoch to Disk")
255 | val_epoch_idx, _, uniq_s = serialize_epoch(
256 | index_dir,
257 | val_registrations,
258 | val_dir,
259 | batch_formats,
260 | do_initial,
261 | do_final,
262 | initial_final_alpha,
263 | n_int,
264 | epoch=0,
265 | is_validation=True,
266 | )
267 |
268 | # Update Trackers...
269 | if val_epoch_idx != -1:
270 | unique_states |= uniq_s
271 |
272 | # Compute length of epochs --> CPU Count should be no higher...
273 | epochs, n_frames_per_epoch = list(range(max_epochs)), -1
274 |
275 | # Parallelize Train Epoch Serialization
276 | overwatch.info("\tPlacing the Train Registry into Shared Memory")
277 | manager = mp.Manager()
278 | mg_registry = manager.dict(train_registrations)
279 |
280 | # Multiprocess --> the memory demands here are a bit higher, so limit workers by factor of 4
281 | with mp.Pool(mp.cpu_count() // 4) as pool:
282 | overwatch.info("\tWriting Train Batches per Epoch to Disk")
283 | precompute_fn = partial(
284 | serialize_epoch,
285 | index_dir,
286 | mg_registry,
287 | train_dir,
288 | batch_formats,
289 | do_initial,
290 | do_final,
291 | initial_final_alpha,
292 | n_int,
293 | )
294 | for epoch_idx, n_frames, uniq_s in pool.imap_unordered(precompute_fn, epochs):
295 | if epoch_idx == -1:
296 | continue
297 |
298 | # Update Trackers
299 | unique_states |= uniq_s
300 | n_frames_per_epoch = n_frames
301 |
302 | # Dump Statistics (Note :: Only makes sense on "initial" computation --> uninterrupted!)
303 | overwatch.info(f"Train Uniqueness: {len(unique_states)} States & {len(mg_registry)} Utterances")
304 | overwatch.info(f"Final Statistics :: 1 Epoch has ~ {n_frames_per_epoch} Frames...")
305 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/preprocessing/transforms.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | transforms.py
3 |
4 | Default video/image transforms for Voltron preprocessing and training. Provides utilities for defining different scale
5 | and crop transformations on a dataset-specific basis.
6 |
7 | There are two key desiderata we ensure with the transforms:
8 | - Aspect Ratio --> We *never* naively reshape images in a way that distorts the aspect ratio; we crop instead!
9 | - Minimum Size --> We *never* upsample images; processing strictly reduces dimensionality!
10 | """
11 | from functools import partial
12 | from typing import Any, Callable, List, Tuple
13 |
14 | import torch
15 | from PIL import Image, ImageOps
16 | from torchvision.transforms import Compose, ConvertImageDtype, Lambda, Normalize, Resize
17 |
18 |
19 | # Simple Identity Function --> needs to be top-level/pickleable for mp/distributed.spawn()
20 | def identity(x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
21 | return x.float()
22 |
23 |
24 | def scaled_center_crop(target_resolution: int, frames: List[Image.Image]) -> Image.Image:
25 | # Assert width >= height and height >= target_resolution
26 | orig_w, orig_h = frames[0].size
27 | assert orig_w >= orig_h >= target_resolution
28 |
29 | # Compute scale factor --> just a function of height and target_resolution
30 | scale_factor = target_resolution / orig_h
31 | for idx in range(len(frames)):
32 | frames[idx] = ImageOps.scale(frames[idx], factor=scale_factor)
33 | left = (frames[idx].size[0] - target_resolution) // 2
34 | frames[idx] = frames[idx].crop((left, 0, left + target_resolution, target_resolution))
35 |
36 | # Return "scaled and squared" images
37 | return frames
38 |
39 |
40 | def get_preprocess_transform(
41 | dataset_name: str, preprocess_resolution: int
42 | ) -> Callable[[List[Image.Image]], List[Image.Image]]:
43 | """Returns a transform that extracts square crops of `preprocess_resolution` from videos (as [T x H x W x C])."""
44 | if dataset_name == "sth-sth-v2":
45 | return partial(scaled_center_crop, preprocess_resolution)
46 | else:
47 | raise ValueError(f"Preprocessing transform for dataset `{dataset_name}` is not defined!")
48 |
49 |
50 | def get_online_transform(
51 | dataset_name: str, model_arch: str, online_resolution: int, normalization: Tuple[Any, Any]
52 | ) -> Compose:
53 | """Returns an "online" torchvision Transform to be applied during training (batching/inference)."""
54 | if dataset_name == "sth-sth-v2":
55 | # Note: R3M does *not* expect normalized 0-1 (then ImageNet normalized) images --> drop the identity.
56 | if model_arch in {"v-r3m", "v-rn3m"}:
57 | return Compose([Resize((online_resolution, online_resolution), antialias=True), Lambda(identity)])
58 | else:
59 | return Compose(
60 | [
61 | Resize((online_resolution, online_resolution), antialias=True),
62 | ConvertImageDtype(torch.float),
63 | Normalize(mean=normalization[0], std=normalization[1]),
64 | ]
65 | )
66 | else:
67 | raise ValueError(f"Online Transforms for Dataset `{dataset_name}` not implemented!")
68 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/preprocessing/v1/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .process import index, jsonify_language, preprocess_language, preprocess_videos, unify_batches
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/preprocessing/v1/process.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | process.py
3 |
4 | Utility functions for serializing datasets in multiple passes, using multiprocessing for efficient parallelization.
5 | Exposes a three-phase sequence for preprocessing:
6 | - Phase I: Read in raw videos (and language), serialize *all extracted* frames to a subdirectory for easy retrieval.
7 | - Phase II: Given image paths and language, assemble language statistics & pre-tokenize for easy batching.
8 | - Phase III: Given a total number of "conceivable epochs", create data-controlled "epoch" sets for each model.
9 |
10 | This script tries to be smart where it can, using multiprocessing.Pool in Phase I to speed up the serialization
11 | process. It also tries to be somewhat safe & efficient, producing idempotent resumes.
12 |
13 | Note :: This code represents the `v1` (initial release) preprocessing flow; this will eventually be deprecated!
14 | """
15 | import json
16 | import logging
17 | import multiprocessing as mp
18 | import os
19 | import shutil
20 | from functools import partial
21 | from pathlib import Path
22 | from typing import Tuple
23 |
24 | import torch
25 | from rich.progress import track
26 | from transformers import AutoTokenizer
27 |
28 | from voltron.preprocessing.v1.transforms import get_pre_transform
29 | from voltron.preprocessing.v1.utils import do_dry_run, precompute_epoch, process_video
30 |
31 | # Grab Logger
32 | overwatch = logging.getLogger(__file__)
33 |
34 |
35 | def preprocess_videos(
36 | name: str,
37 | path: str,
38 | artifact_path: str = "data/processed",
39 | resolution: int = 224,
40 | n_val_videos: int = 1000,
41 | dry_run: bool = False,
42 | ) -> Tuple[Path, Path, Path, Path]:
43 | """Phase I of Preprocessing :: Uses Multiprocessing to Read Videos & Serialize Frames."""
44 | overwatch.info(f"Phase 1 Preprocessing :: Frame serializing videos for dataset `{name}`")
45 |
46 | if name == "sth-sth-v2":
47 | # Overview of Return Values:
48 | # `t_registry` and `v_registry` =>> store mappings of "vid_id" -> {metadata}
49 | # `t_dir` and `v_dir` =>> store "processed data" (extracted frames)
50 | t_dir, v_dir = Path(artifact_path) / name / "train", Path(artifact_path) / name / "val"
51 | t_registry, v_registry = t_dir / "registry.json", v_dir / "registry.json"
52 |
53 | # Short-Circuit / Caching Logic
54 | if t_registry.exists() and v_registry.exists():
55 | return t_registry, v_registry, t_dir, v_dir
56 |
57 | # Setup / Book-Keeping
58 | os.makedirs(t_dir, exist_ok=True)
59 | os.makedirs(v_dir, exist_ok=True)
60 |
61 | # Retrieve Image Transforms (pre-serialization, while running "offline" pass); we crop and scale once, so we're
62 | # not overdoing it on disk storage...
63 | pre_transform = get_pre_transform(name, resolution=resolution)
64 |
65 | # Open & Extract Video ID & Language Metadata
66 | with open(Path(path) / "something-something-v2-train.json", "r") as f:
67 | annotations = json.load(f)
68 | train_ids, train_lang = [x["id"] for x in annotations], [x["label"] for x in annotations]
69 |
70 | with open(Path(path) / "something-something-v2-validation.json", "r") as f:
71 | annotations = json.load(f)[:n_val_videos]
72 | val_ids, val_lang = [x["id"] for x in annotations], [x["label"] for x in annotations]
73 |
74 | # Do Dry-Run --> Single-Threaded!
75 | if dry_run:
76 | do_dry_run(
77 | name,
78 | path,
79 | n_train_videos=1000,
80 | n_val_videos=100,
81 | train_ids=train_ids,
82 | val_ids=val_ids,
83 | pre_transform=pre_transform,
84 | )
85 |
86 | # Go Go Go =>> Iterate through all videos, dump all frames subject to the following structure:
87 | # |-> data/processed/sth-sth-v2/
88 | # |-> /
89 | # |-> /frames<0...k>.jpg
90 | # We'll track a single metadata file with the map of : ("language", n_frames).
91 | # > To speed up the serialization, we'll use a multiprocessing.Pool and max out CPU workers
92 | with mp.Pool(mp.cpu_count()) as pool:
93 | for k, save, vids, langs in [("train", t_dir, train_ids, train_lang), ("val", v_dir, val_ids, val_lang)]:
94 | overwatch.info(f"\tWriting `{k}` videos to disk...")
95 |
96 | # Multiprocess!
97 | process_fn, registration = partial(process_video, name, Path(path), save, pre_transform), {}
98 | for key, value in track(
99 | pool.imap_unordered(process_fn, zip(vids, langs)),
100 | description=f"\t[*] Processing {k}...",
101 | total=len(vids),
102 | transient=True,
103 | ):
104 | if key is not None:
105 | registration[key] = value
106 |
107 | # Write Registration to Disk
108 | with open(t_registry if k == "train" else v_registry, "w") as f:
109 | json.dump(registration, f)
110 |
111 | # Return Paths...
112 | return t_registry, v_registry, t_dir, v_dir
113 |
114 | else:
115 | raise NotImplementedError(f"Preprocessing Pipeline for Dataset `{name}` not implemented!")
116 |
117 |
118 | def preprocess_language(
119 | name: str, train_registry: Path, val_registry: Path, max_lang_len: int, language_model: str, hf_cache: str
120 | ) -> None:
121 | """Phase II of Preprocessing :: Iterate through Language & Normalize/Tokenize to Max Length."""
122 | overwatch.info(f"Phase 2 Preprocessing :: Normalizing & tokenizing language for dataset `{name}`")
123 | t_index, v_index = train_registry.parent / "index.pt", val_registry.parent / "index.pt"
124 | t_json, v_json = train_registry.parent / "index.json", val_registry.parent / "index.json"
125 |
126 | # Short-Circuit Logic
127 | if (t_index.exists() and v_index.exists()) or (t_json.exists() and v_json.exists()):
128 | return t_index, v_index
129 |
130 | # Grab Language, Retaining Metadata for Building Index Structures...
131 | with open(train_registry, "r") as f:
132 | train_metadata = json.load(f)
133 | train = [(vid, train_metadata[vid]["language"], train_metadata[vid]) for vid in train_metadata]
134 |
135 | with open(val_registry, "r") as f:
136 | val_metadata = json.load(f)
137 | val = [(vid, val_metadata[vid]["language"], val_metadata[vid]) for vid in val_metadata]
138 |
139 | # Assemble *all* language
140 | language = [x[1] for x in train + val]
141 |
142 | # Build AutoTokenizer (from `language_model` identifier)
143 | tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(language_model, cache_dir=hf_cache)
144 |
145 | # If `max_lang_len` not specified, dump some statistics to compute...
146 | if max_lang_len == -1:
147 | # Naively tokenizes and pads to the "maximum length" of _all_ language... long tail is a problem!
148 | encoded_language = tokenizer(language, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
149 | lengths = encoded_language["attention_mask"].sum(dim=1)
150 |
151 | # Compute a histogram of lengths
152 | hist = lengths.float().histc(bins=lengths.max()).int()
153 | overwatch.info(f"Histogram: {hist.numpy().tolist()}")
154 | raise NotImplementedError("Compute max length and update dataset configuration!")
155 |
156 | # Otherwise, we've already set the maximum length, so let's use it!
157 | else:
158 | overwatch.info(f"\tTokenizing all language in dataset to maximum length `{max_lang_len}`")
159 | encoded_language = tokenizer(
160 | language, return_tensors="pt", max_length=max_lang_len, truncation=True, padding="max_length"
161 | )
162 | input_ids, attention_mask = encoded_language["input_ids"], encoded_language["attention_mask"]
163 | train_input_ids, train_attention_mask = input_ids[: len(train)], attention_mask[: len(train)]
164 | val_input_ids, val_attention_mask = input_ids[len(train) :], attention_mask[len(train) :]
165 |
166 | # Assertion, just to sanity check
167 | assert len(val_input_ids) == len(val_attention_mask) == len(val), "Something went wrong tokenizing language..."
168 |
169 | # Compute `index.pt` contents
170 | overwatch.info("\tAssembling `train` and `val` index structures...")
171 | train_pt = {
172 | train[i][0]: {**train[i][2], **{"input_ids": train_input_ids[i], "attention_mask": train_attention_mask[i]}}
173 | for i in range(len(train))
174 | }
175 | val_pt = {
176 | val[i][0]: {**val[i][2], **{"input_ids": val_input_ids[i], "attention_mask": val_attention_mask[i]}}
177 | for i in range(len(val))
178 | }
179 |
180 | # Dump structures...
181 | overwatch.info(f"Saving index structures to `{t_index}` and `{v_index}` respectively...")
182 | torch.save(train_pt, t_index)
183 | torch.save(val_pt, v_index)
184 |
185 |
186 | def jsonify_language(train_registry: Path, val_registry: Path) -> None:
187 | """Phase 2.5 (Aggregation) :: XLA is weird, won't load torch.Tensors in Dataset; JSONify instead."""
188 | overwatch.info("\tPhase 2 Aggregation :: JSONifying Language Index")
189 | t_index, v_index = train_registry.parent / "index.pt", val_registry.parent / "index.pt"
190 | t_json, v_json = train_registry.parent / "index.json", val_registry.parent / "index.json"
191 | train_json, val_json = {}, {}
192 |
193 | # Short-Circuit Logic
194 | if t_json.exists() and v_json.exists():
195 | return
196 |
197 | # Load Data, iterate through and "de-tensorize", while building up JSON symmetric structure...
198 | train_data, val_data = torch.load(t_index), torch.load(v_index)
199 | overwatch.info("JSONifying both Train and Validation")
200 | for vid in track(train_data, description="Train Language...", transient=True):
201 | train_json[vid] = {
202 | "language": train_data[vid]["language"],
203 | "n_frames": train_data[vid]["n_frames"],
204 | "input_ids": train_data[vid]["input_ids"].numpy().tolist(),
205 | "attention_mask": train_data[vid]["attention_mask"].numpy().tolist(),
206 | }
207 | for vid in track(val_data, description="Val Language...", transient=True):
208 | val_json[vid] = {
209 | "language": val_data[vid]["language"],
210 | "n_frames": val_data[vid]["n_frames"],
211 | "input_ids": val_data[vid]["input_ids"].numpy().tolist(),
212 | "attention_mask": val_data[vid]["attention_mask"].numpy().tolist(),
213 | }
214 |
215 | # Write Data to Disk
216 | overwatch.info("Writing JSON Indices")
217 | with open(t_json, "w") as f:
218 | json.dump(train_json, f)
219 |
220 | with open(v_json, "w") as f:
221 | json.dump(val_json, f)
222 |
223 |
224 | def index(train_registry: Path, val_registry: Path, name: str, artifact_path: str = "data/processed") -> Path:
225 | """Phase 2.75 (Indexing) :: Pull out language.json & other `absolutely necessary` indices to separate directory."""
226 | overwatch.info("\tPhase 2 Indexing :: Indexing Language & Registry Files =>> Extracting to Separate Directory")
227 |
228 | # Create "index" directory...
229 | index_dir = Path(artifact_path) / name / "index"
230 | os.makedirs(index_dir, exist_ok=True)
231 |
232 | # Short-Circuit Logic
233 | if (index_dir / "train-language-index.json").exists() and (index_dir / "val-language-index.json").exists():
234 | return index_dir
235 |
236 | # Retrieve Language JSON indices (train & validation) & copy to new directory...
237 | t_json, v_json = train_registry.parent / "index.json", val_registry.parent / "index.json"
238 | shutil.copy(t_json, index_dir / "train-language-index.json")
239 | shutil.copy(v_json, index_dir / "val-language-index.json")
240 |
241 | return index_dir
242 |
243 |
244 | def unify_batches(
245 | artifact_path: Path,
246 | name: str,
247 | train_registry: Path,
248 | val_registry: Path,
249 | train_dir: Path,
250 | val_dir: Path,
251 | index_dir: Path,
252 | batch_formats: Tuple[Tuple[str, Tuple[str, ...]], ...],
253 | max_epochs: int = 400,
254 | initial_final_alpha: float = 0.2,
255 | ) -> None:
256 | """Phase III of Preprocessing :: Assemble Batches for *all models* for *all epochs* in a consistent manner."""
257 | overwatch.info("Phase 3 Preprocessing :: Assembling Data-Equivalent Epochs for each Model Format")
258 |
259 | # Load Registry Files
260 | with open(train_registry, "r") as f:
261 | train_registrations = json.load(f)
262 |
263 | with open(val_registry, "r") as f:
264 | val_registrations = json.load(f)
265 |
266 | # Assert last element of `batch_formats` assumes all prior subsets...
267 | full_set_inputs = set(batch_formats[-1][1])
268 | for _, subset_inputs in batch_formats[:-1]:
269 | assert full_set_inputs.issuperset(set(subset_inputs)), "We have a problem with batch formats..."
270 |
271 | # Assemble Tracking Data
272 | b_keys, unique_states = {b[0] for b in batch_formats}, set()
273 |
274 | # Parse out all "state"-specific elements...
275 | state_elements = [s for s in full_set_inputs if "state_" in s]
276 | do_initial, do_final = "state_initial" in state_elements, "state_final" in state_elements
277 | n_int = len(state_elements) - 2 if ("state_initial" in state_elements and "state_final" in state_elements) else 0
278 |
279 | # Serialize Epochs to Disk
280 | overwatch.info("\tSerializing epochs to json file, pointing to image paths on disk via a dictionary...")
281 | for b in b_keys:
282 | os.makedirs(index_dir / b, exist_ok=True)
283 |
284 | # We only write the validation epoch once --> held constant across _all_ of training!
285 | overwatch.info("\tWriting Validation Epoch to Disk...")
286 | val_epoch_idx, _, uniq_s = precompute_epoch(
287 | index_dir,
288 | val_registrations,
289 | val_dir,
290 | batch_formats,
291 | do_initial,
292 | do_final,
293 | initial_final_alpha,
294 | n_int,
295 | 0,
296 | is_validation=True,
297 | )
298 |
299 | # Update Trackers...
300 | if val_epoch_idx != -1:
301 | unique_states |= uniq_s
302 |
303 | # Compute length of epochs --> CPU Count should be no higher...
304 | epochs, n_frames_per_epoch = list(range(max_epochs)), -1
305 |
306 | # Load "existing" verification file (if possible)
307 | overwatch.info("\tLoading batch verification file (if possible)...")
308 | verified_batches = Path(artifact_path) / name / "verified-batches.json"
309 | if verified_batches.exists():
310 | with open(verified_batches, "r") as f:
311 | missing_epochs_per_format = json.load(f)
312 |
313 | # Set epochs list by taking union of missing epochs over formats...
314 | epochs = sorted(list(set().union(*missing_epochs_per_format.values())))
315 |
316 | # Dump the big objects into an mp.Manager() so that we can read efficiently from other workers...
317 | overwatch.info("\tPlacing the Train Registry into Shared Memory...")
318 | manager = mp.Manager()
319 | mg_registry = manager.dict(train_registrations)
320 |
321 | with mp.Pool(4) as pool:
322 | overwatch.info("\tWriting Train Batches per Epoch to Disk...")
323 |
324 | # Create partial function for multiprocessing pool...
325 | precompute_fn = partial(
326 | precompute_epoch,
327 | index_dir,
328 | mg_registry,
329 | train_dir,
330 | batch_formats,
331 | do_initial,
332 | do_final,
333 | initial_final_alpha,
334 | n_int,
335 | )
336 | for epoch_idx, n_frames, uniq_s in pool.imap_unordered(precompute_fn, epochs):
337 | if epoch_idx == -1:
338 | continue
339 |
340 | # Update Trackers
341 | unique_states |= uniq_s
342 | n_frames_per_epoch = n_frames
343 |
344 | # Statistics only make sense on initial computation... should unify with code above!
345 | overwatch.info(f"Train Uniqueness: {len(unique_states)} States & {len(mg_registry)} Utterances")
346 | overwatch.info(f"Final Statistics :: 1 Epoch has ~ {n_frames_per_epoch} Frames...")
347 | overwatch.info("Preprocessing Complete!")
348 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/preprocessing/v1/transforms.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | transforms.py
3 |
4 | Default image/video transformations for various datasets.
5 | """
6 | from typing import Any, Tuple
7 |
8 | import cv2
9 | import numpy as np
10 | import torch
11 | from torchvision.transforms import Compose, ConvertImageDtype, Lambda, Normalize
12 |
13 |
14 | # Definitions of Video Transformations (Reference: `something-something-v2-baseline`)
15 | class ComposeMix:
16 | def __init__(self, transforms):
17 | self.transforms = transforms
18 |
19 | def __call__(self, imgs):
20 | for transformation, scope in self.transforms:
21 | if scope == "img":
22 | for idx, img in enumerate(imgs):
23 | imgs[idx] = transformation(img)
24 | elif scope == "vid":
25 | imgs = transformation(imgs)
26 | else:
27 | raise ValueError("Please specify a valid transformation...")
28 | return imgs
29 |
30 |
31 | class RandomCropVideo:
32 | def __init__(self, size):
33 | self.size = size
34 |
35 | def __call__(self, imgs):
36 | th, tw = self.size
37 | h, w = imgs[0].shape[:2]
38 | x1, y1 = np.random.randint(0, w - tw), np.random.randint(0, h - th)
39 | for idx, img in enumerate(imgs):
40 | imgs[idx] = img[y1 : y1 + th, x1 : x1 + tw]
41 | return imgs
42 |
43 |
44 | class Scale:
45 | def __init__(self, size):
46 | self.size = size
47 |
48 | def __call__(self, img):
49 | return cv2.resize(img, tuple(self.size))
50 |
51 |
52 | def identity(x):
53 | """Transform needs to be pickleable for multiprocessing.spawn()."""
54 | return x.float()
55 |
56 |
57 | def get_pre_transform(dataset: str, resolution: int, scale_factor: float = 1.1) -> ComposeMix:
58 | """Defines a `pre` transform to be applied *when serializing the images* (first pass)."""
59 | if dataset == "sth-sth-v2":
60 | if scale_factor > 1:
61 | transform = ComposeMix(
62 | [
63 | [Scale((int(resolution * scale_factor), int(resolution * scale_factor))), "img"],
64 | [RandomCropVideo((resolution, resolution)), "vid"],
65 | ]
66 | )
67 | else:
68 | transform = ComposeMix(
69 | [
70 | [Scale((int(resolution * scale_factor), int(resolution * scale_factor))), "img"],
71 | ]
72 | )
73 |
74 | return transform
75 | else:
76 | raise NotImplementedError(f"(Pre) transforms for dataset `{dataset}` not yet implemented!")
77 |
78 |
79 | def get_online_transform(dataset: str, model_arch: str, normalization: Tuple[Any, Any]) -> Compose:
80 | """Defines an `online` transform to be applied *when batching the images* (during training/validation)."""
81 | if dataset == "sth-sth-v2":
82 | # Note: R3M does *not* expect normalized 0-1 (then ImageNet normalized) images --> drop the identity.
83 | if model_arch in {"v-r3m", "v-rn3m"}:
84 | return Compose([Lambda(identity)])
85 | else:
86 | return Compose([ConvertImageDtype(torch.float), Normalize(mean=normalization[0], std=normalization[1])])
87 | else:
88 | raise NotImplementedError(f"(Online) transforms for dataset `{dataset} not yet implemented!")
89 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/preprocessing/v1/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | utils.py
3 |
4 | Preprocessing utilities, including functions for dry-runs and processing a single video (helpers for multiprocessing
5 | calls down the lines).
6 | """
7 | import glob
8 | import json
9 | import logging
10 | import os
11 | import sys
12 | import time
13 | from pathlib import Path
14 | from typing import Any, Dict, List, Optional, Set, Tuple
15 |
16 | import av
17 | import cv2
18 | import numpy as np
19 | from hurry.filesize import alternative, size
20 | from rich.progress import track
21 | from tqdm import tqdm
22 |
23 | from voltron.preprocessing.v1.transforms import ComposeMix
24 |
25 | # Grab Logger
26 | overwatch = logging.getLogger(__file__)
27 | logging.getLogger("libav").setLevel(logging.ERROR)
28 |
29 |
30 | # Videos are saved as `train_dir/{vid}/{vid}_idx={i}.jpg
31 | def get_path(save_dir: Path, v: str, i: int) -> str:
32 | return str(save_dir / v / f"{v}_idx={i}.jpg")
33 |
34 |
35 | def do_dry_run(
36 | name: str,
37 | path: str,
38 | n_train_videos: int,
39 | n_val_videos: int,
40 | train_ids: List[str],
41 | val_ids: List[str],
42 | pre_transform: ComposeMix,
43 | n_samples: int = 1000,
44 | ) -> None:
45 | """Iterates through a small subset of the total dataset, logs n_frames & average image size for estimation."""
46 | dry_run_metrics = {
47 | "n_frames": [],
48 | "jpg_sizes": [],
49 | "n_samples": n_samples,
50 | "time_per_example": [],
51 | "blank": str(Path(path) / "blank.jpg"),
52 | }
53 | if name == "sth-sth-v2":
54 | for k, n_iter, vids in [("train", n_train_videos, train_ids), ("val", n_val_videos, val_ids)]:
55 | for idx in track(range(n_iter), description=f"Reading {k.capitalize()} Videos =>> ", transient=True):
56 | vid = vids[idx]
57 | container = av.open(str(Path(path) / "videos" / f"{vid}.webm"))
58 | try:
59 | imgs = [f.to_rgb().to_ndarray() for f in container.decode(video=0)]
60 | except (RuntimeError, ZeroDivisionError) as e:
61 | overwatch.error(f"{type(e).__name__}: WebM reader cannot open `{vid}.webm` - continuing...")
62 | continue
63 |
64 | # Close container
65 | container.close()
66 |
67 | # Apply `pre_transform`
68 | imgs = pre_transform(imgs)
69 |
70 | # Dry-Run Handling --> write a dummy JPEG to collect size statistics, dump, and move on...
71 | dry_run_metrics["n_frames"].append(len(imgs))
72 | while dry_run_metrics["n_samples"] > 0 and len(imgs) > 0:
73 | img = imgs.pop(0)
74 | cv2.imwrite(str(dry_run_metrics["blank"]), cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR))
75 | dry_run_metrics["jpg_sizes"].append(os.path.getsize(dry_run_metrics["blank"]))
76 | dry_run_metrics["n_samples"] -= 1
77 |
78 | # Compute nice totals for "dry-run" estimation
79 | total_clips = len(train_ids) + len(val_ids)
80 |
81 | else:
82 | raise NotImplementedError(f"Dry Run for Dataset `{name}` not yet implemented!")
83 |
84 | # Compute Aggregate Statistics and gently exit...
85 | avg_size, avg_frames = np.mean(dry_run_metrics["jpg_sizes"]), int(np.mean(dry_run_metrics["n_frames"]))
86 | overwatch.info("Dry-Run Statistics =>>")
87 | overwatch.info(f"\t> A video has on average `{avg_frames}` frames at {size(avg_size, system=alternative)}")
88 | overwatch.info(f"\t> So - 1 video ~ {size(avg_frames * avg_size, system=alternative)}")
89 | overwatch.info(
90 | f"\t> With the full dataset of {total_clips} Train + Val videos ~"
91 | f" {size(total_clips * avg_frames * avg_size, system=alternative)}"
92 | )
93 | overwatch.info("Dry-Run complete, do what you will... exiting ✌️")
94 |
95 | # Remove dummy file...
96 | os.remove(dry_run_metrics["blank"])
97 | sys.exit(0)
98 |
99 |
100 | def process_video(
101 | name: str, path: Path, save: Path, pre_transform: ComposeMix, item: Tuple[str, str]
102 | ) -> Tuple[Optional[str], Optional[Dict[str, Any]]]:
103 | """Processes a single video file, dumps to series of image files, and returns the registry contents."""
104 | if name == "sth-sth-v2":
105 | # For sth-sth-v2, `item` corresponds to a single video clip, so just a tuple!
106 | vid, lang = item
107 | container, registration = av.open(str(Path(path) / "videos" / f"{vid}.webm")), {"language": lang, "n_frames": 0}
108 | try:
109 | imgs = [f.to_rgb().to_ndarray() for f in container.decode(video=0)]
110 | except (RuntimeError, ZeroDivisionError) as e:
111 | overwatch.error(f"{type(e).__name__}: WebM reader cannot open `{vid}.webm` - skipping...")
112 | return None, None
113 |
114 | # Close container
115 | container.close()
116 |
117 | # Book-keeping
118 | os.makedirs(save / vid, exist_ok=True)
119 | registration["n_frames"] = len(imgs)
120 |
121 | # Early exit (writes are expensive)
122 | if len(glob.glob1(save / vid, "*.jpg")) == len(imgs):
123 | return vid, registration
124 |
125 | # Apply `pre_transform` --> write individual frames, register, and return
126 | imgs = pre_transform(imgs)
127 | for i in range(len(imgs)):
128 | cv2.imwrite(get_path(save, vid, i), cv2.cvtColor(imgs[i], cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR))
129 |
130 | # Return title & registration
131 | return vid, registration
132 |
133 | else:
134 | raise NotImplementedError(f"Process Video for Dataset `{name}` not yet implemented!")
135 |
136 |
137 | # ruff: noqa: C901
138 | def precompute_epoch(
139 | index_dir: Path,
140 | registry: Dict[str, Any],
141 | vid_dir: Path,
142 | batch_formats: Tuple[Tuple[str, Tuple[str, ...]], ...],
143 | do_initial: bool,
144 | do_final: bool,
145 | initial_final_alpha: float,
146 | n_int: int,
147 | epoch: int,
148 | is_validation: bool = False,
149 | ) -> Tuple[int, int, Optional[Set[str]]]:
150 | index_file = "validation-batches.json" if is_validation else f"train-epoch={epoch}-batches.json"
151 |
152 | # Short-Circuit
153 | if all([(index_dir / key / index_file).exists() for key, _ in batch_formats]):
154 | return -1, -1, None
155 |
156 | # Random seed is inherited from parent process... we want new randomness w/ each process
157 | np.random.seed((os.getpid() * int(time.time())) % 123456789)
158 |
159 | # Create Tracking Variables
160 | unique_states, batches = set(), {b: [] for b, _ in batch_formats}
161 |
162 | # Iterate through Registry...
163 | for vid in tqdm(registry.keys(), desc=f"Epoch {epoch}", total=len(registry), position=epoch):
164 | # The initial/final states are sampled from the first [0, \alpha) and final 1-\alpha, 1] percent of the video
165 | n_frames = registry[vid]["n_frames"]
166 | initial_idx, final_idx = 0, n_frames - 1
167 | if do_initial:
168 | initial_idx = np.random.randint(0, np.around(n_frames * initial_final_alpha))
169 |
170 | if do_final:
171 | final_idx = np.random.randint(np.around(n_frames * (1 - initial_final_alpha)), n_frames)
172 |
173 | # Assertion --> initial_idx < final_idx - len(state_elements)
174 | assert initial_idx < final_idx - n_int, "Initial & Final are too close... no way to sample!"
175 |
176 | # Assume remaining elements are just random "interior" states --> sort to get ordering!
177 | sampled_idxs = np.random.choice(np.arange(initial_idx + 1, final_idx), size=n_int, replace=False)
178 | sampled_idxs = sorted(list(sampled_idxs))
179 |
180 | # Compile full-set "batch"
181 | retrieved_states = [get_path(vid_dir, vid, x) for x in [initial_idx, *sampled_idxs] + [final_idx]]
182 |
183 | # Add batch to index for specific batch_format key...
184 | batches[batch_formats[-1][0]].append({"vid": vid, "states": retrieved_states, "n_frames": n_frames})
185 | unique_states.update(retrieved_states)
186 |
187 | # Add all other batch formats to indices...
188 | for key, elements in batch_formats[:-1]:
189 | n_states = len([x for x in elements if "state_" in x])
190 | assert (n_states <= 2) or (
191 | n_states == len(retrieved_states)
192 | ), f"Strange value of n_states={n_states} > 2 and not equal to total possible of {len(retrieved_states)}"
193 |
194 | # States are all independent -- each of the retrieved states is its own example...
195 | if n_states == 1:
196 | for idx in range(len(retrieved_states)):
197 | batches[key].append({"vid": vid, "state": retrieved_states[idx], "n_frames": n_frames})
198 |
199 | # OK-Context is the only "valid" context for n_states == 2
200 | elif n_states == 2:
201 | assert elements == ["state_initial", "state_i", "language"], "n_states = 2 but not 0K context?"
202 |
203 | # Append 0th state to each of the remaining sampled contexts (usually 2 or 4)... each pair is an example
204 | for idx in range(1, len(retrieved_states)):
205 | batches[key].append(
206 | {"vid": vid, "states": [retrieved_states[0], retrieved_states[idx]], "n_frames": n_frames}
207 | )
208 |
209 | # We're treating the entire sequence of retrieved states as a single example (for TCN/R3M/Temporal Models)
210 | else:
211 | batches[key].append({"vid": vid, "states": retrieved_states, "n_frames": n_frames})
212 |
213 | # Write JSON Index directly to disk...
214 | for key in batches:
215 | with open(index_dir / key / index_file, "w") as f:
216 | json.dump(batches[key], f)
217 |
218 | return epoch, len(batches["state"]), unique_states
219 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/util/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .checkpointing import CheckpointSaver, do_resume
2 | from .metrics import Metrics
3 | from .utilities import ResumeableDistributedSampler, set_global_seed
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/util/checkpointing.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | checkpointing.py
3 |
4 | Core utility class for handling model/optimizer serialization & checkpointing -- including resume from checkpoint logic.
5 |
6 | Support the following strategies:
7 | - (k, -1, -1) --> Keep only the most recent "k" epoch checkpoints
8 | - (k, m, -1) --> Keep the most recent "k" epoch checkpoints and *every* m epoch checkpoint
9 | - (k, m, s = 2500) --> Keep "k" and "m" subject to above, but also keep *s* step checkpoints for current epoch
10 | """
11 | import logging
12 | import os
13 | import re
14 | from collections import deque
15 | from pathlib import Path
16 | from typing import Any, Optional, Tuple
17 |
18 | import torch
19 | import torch.nn as nn
20 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
21 |
22 | # Grab Logger
23 | overwatch = logging.getLogger(__file__)
24 |
25 |
26 | class FixedDeck(deque):
27 | def __init__(self, maxlen: int) -> None:
28 | super().__init__(maxlen=maxlen)
29 |
30 | def append(self, x: Any) -> Any:
31 | pop_value = None
32 | if self.__len__() == self.maxlen:
33 | pop_value = self.__getitem__(0)
34 |
35 | # Perform parent append and return popped value, if any!
36 | super().append(x)
37 | return pop_value
38 |
39 |
40 | class CheckpointSaver:
41 | def __init__(self, strategy: Tuple[int, int, int], run_dir: str, is_rank_zero: bool = False) -> None:
42 | """
43 | Create a checkpoint saver with the provided strategy that saves to the given path.
44 |
45 | :param strategy: Strategy, following the (k, -1, -1) -- (k, m, -1) -- (k, m, s) description above.
46 | :param run_dir: Path to root of `run_dir`.
47 | :param is_rank_zero: Boolean whether this process is global zero (no-op if not)!
48 | """
49 | (self.k, self.m, self.s), self.run_dir, self.is_rank_zero = strategy, run_dir, is_rank_zero
50 | self.recents, self.intervals, self.step_checkpoints = FixedDeck(maxlen=self.k), set(), set()
51 |
52 | # If `self.s == -1` --> *Disable* step checkpoints (only at save end of epoch!)
53 | self.enable_step = self.s != -1
54 |
55 | # Create "checkpoints" subdirectory
56 | self.path = Path(run_dir) / "checkpoints"
57 | if self.is_rank_zero:
58 | os.makedirs(self.path, exist_ok=True)
59 |
60 | # Populate `step_checkpoints` on __init__ (if resuming *within* an epoch!)
61 | self.step_checkpoints.update([c for c in self.path.iterdir() if "local-epoch=" in str(c)])
62 |
63 | # Created Saver...
64 | overwatch.info(f"Created CheckpointSaver with `k = {self.k}` -- `m = {self.m}` -- s = {self.s}!")
65 |
66 | def save(
67 | self,
68 | epoch: int,
69 | is_local_step: bool,
70 | model: nn.Module,
71 | optimizer: Optimizer,
72 | duration: int,
73 | local_step: Optional[int] = None,
74 | train_loss: Optional[float] = None,
75 | val_loss: Optional[float] = None,
76 | ) -> None:
77 | """Performs a global zero save operation, unlinking stale checkpoints if necessary."""
78 | if not self.is_rank_zero:
79 | return
80 |
81 | # Check if saving a `local_step` (within an epoch) or if end of epoch...
82 | if self.enable_step and is_local_step and (local_step % self.s) == 0:
83 | step_checkpoint = self.path / f"local-epoch={epoch}-step={local_step}-t={duration}.pt"
84 | torch.save(
85 | {"model_state_dict": model.state_dict(), "optimizer_state_dict": optimizer.state_dict()}, step_checkpoint
86 | )
87 |
88 | # Update Relevant Trackers...
89 | self.step_checkpoints.add(step_checkpoint)
90 |
91 | elif not is_local_step:
92 | if train_loss is None and val_loss is None:
93 | checkpoint = self.path / f"epoch={epoch}-train=inf-val=inf-t={duration}.pt"
94 | else:
95 | checkpoint = self.path / f"epoch={epoch}-train={train_loss:.4f}-val={val_loss:.4f}-t={duration}.pt"
96 | torch.save(
97 | {"model_state_dict": model.state_dict(), "optimizer_state_dict": optimizer.state_dict()}, checkpoint
98 | )
99 |
100 | # Update Relevant Trackers
101 | if epoch % self.m == 0:
102 | self.intervals.add(checkpoint)
103 |
104 | # Remove all "step_checkpoints" now that we've made it to the end of an epoch!
105 | while len(self.step_checkpoints) > 0:
106 | os.remove(self.step_checkpoints.pop())
107 |
108 | # Add to recents & flush stale checkpoints...
109 | to_remove = self.recents.append(checkpoint)
110 | if to_remove is not None and to_remove not in self.intervals:
111 | os.remove(to_remove)
112 |
113 |
114 | def do_resume(resume: bool, run_dir: str) -> Tuple[Optional[Path], int, int]:
115 | """Handle `resume` logic --> consists of retrieving checkpoint_path and epoch/step computation (if resuming)."""
116 | if not resume:
117 | # We're starting a fresh run --> return None for checkpoint_path, resume_epoch = 0, resume_step = 0
118 | return None, 0, 0
119 |
120 | # === Auto-Resume Logic ===
121 | # **IMPORTANT**: We're making a few assumptions on resuming that should eventually become explicit checks:
122 | # - `accumulate_grad_batches` is exactly the same when resuming; this means:
123 | # + `model_cfg.effective_bsz`, `model_cfg.fabric_bsz`, & `accelerator_cfg.num_accelerators` are the same!
124 | # - The Weights & Biases directory `run_dir/wandb` only contains a *single run*
125 | # - The `param_groups` in `optimizer.state_dict()` are exactly the same across resumes!
126 | # + This means that (and generally should be true for resuming altogether) the architecture is the same!
127 | # - The `cfg.seed` should be the same (again, should generally be true...)
128 | all_checkpoints_path, resume_checkpoint, resume_epoch, resume_step = Path(run_dir) / "checkpoints", None, 0, 0
129 | if all_checkpoints_path.exists() and any(all_checkpoints_path.iterdir()):
130 | # Parse out the latest "complete" epoch checkpoint, as well as any "local step" checkpoints...
131 | checkpoints = list(all_checkpoints_path.iterdir())
132 | complete_checkpoint, complete_epoch = max(
133 | [
134 | (c, int(re.search("epoch=(.+?)-train", c.name).group(1)))
135 | for c in checkpoints
136 | if "local-epoch=" not in str(c)
137 | ],
138 | key=lambda x: x[1],
139 | )
140 |
141 | # Case 1 :: We have "local step" checkpoints --> will always override any "full epoch" checkpoints...
142 | local = [
143 | (
144 | c,
145 | int(re.search("local-epoch=(.+?)-step", c.name).group(1)),
146 | int(re.search("step=(.+?)[.-]", c.name).group(1)),
147 | )
148 | for c in checkpoints
149 | if "local-epoch=" in str(c)
150 | ]
151 | if len(local) > 0:
152 | # Parse out (epoch, "highest" step) + assert no great "full epoch" checkpoint exists!
153 | resume_checkpoint, resume_epoch, resume_step = max(local, key=lambda x: x[1:])
154 | assert resume_epoch == complete_epoch, "Epoch mismatch in `resume` from local_step!"
155 |
156 | # Case 2 :: Otherwise, we're just going to start with the last "complete" epoch
157 | else:
158 | resume_checkpoint, resume_epoch = complete_checkpoint, complete_epoch
159 |
160 | return resume_checkpoint, resume_epoch, resume_step
161 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/util/metrics.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | metrics.py
3 |
4 | Utility classes defining Metrics containers with model-specific logging to various endpoints (JSONL local logs, W&B).
5 | """
6 | import os
7 | import re
8 | import time
9 | from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
10 | from collections import deque
11 | from datetime import datetime
12 | from pathlib import Path
13 | from typing import Any, Dict, List, Optional, Tuple, Union
14 |
15 | import jsonlines
16 | import numpy as np
17 | import torch
18 | import wandb
19 |
20 | from voltron.conf import TrackingConfig
21 |
22 | # === Define Loggers (`Logger` is an abstract base class) ===
23 |
24 |
25 | class Logger(ABC):
26 | def __init__(self, run_id: str, hparams: Dict[str, Any], is_rank_zero: bool = False) -> None:
27 | self.run_id, self.hparams, self.is_rank_zero = run_id, hparams, is_rank_zero
28 |
29 | @abstractmethod
30 | def write_hyperparameters(self) -> None:
31 | raise NotImplementedError("Logger is an abstract class!")
32 |
33 | @abstractmethod
34 | def write(self, global_step: int, metrics: Dict[str, Union[int, float]]) -> None:
35 | raise NotImplementedError("Logger is an abstract class!")
36 |
37 | def finalize(self) -> None:
38 | time.sleep(1)
39 |
40 |
41 | class JSONLinesLogger(Logger):
42 | def write_hyperparameters(self) -> None:
43 | if not self.is_rank_zero:
44 | return
45 |
46 | # Only log if `is_rank_zero`
47 | with jsonlines.open(f"{self.run_id}.jsonl", mode="w", sort_keys=True) as js_logger:
48 | js_logger.write(
49 | {
50 | "run_id": self.run_id,
51 | "start_time": datetime.now().strftime("%m-%d-%H:%M"),
52 | "hparams": self.hparams,
53 | }
54 | )
55 |
56 | def write(self, global_step: int, metrics: Dict[str, Union[int, float]]) -> None:
57 | if not self.is_rank_zero:
58 | return
59 |
60 | # Only log if `is_rank_zero`
61 | with jsonlines.open(f"{self.run_id}.jsonl", mode="a", sort_keys=True) as js_logger:
62 | js_logger.write(metrics)
63 |
64 |
65 | class WeightsBiasesLogger(Logger):
66 | def __init__(
67 | self,
68 | run_id: str,
69 | hparams: Dict[str, Any],
70 | tracking_cfg: TrackingConfig,
71 | tags: List[str],
72 | resume: bool = False,
73 | resume_id: Optional[str] = None,
74 | is_rank_zero: bool = False,
75 | ) -> None:
76 | super().__init__(run_id, hparams, is_rank_zero)
77 | self.tracking_cfg, self.tags, self.resume, self.resume_id = tracking_cfg, tags, resume, resume_id
78 | self.path = Path(os.getcwd() if self.tracking_cfg.directory is None else self.tracking_cfg.directory)
79 |
80 | # Handle (Automatic) Resume if `resume = True`
81 | if self.resume and self.resume_id is None:
82 | wandb_path = self.path / "wandb"
83 | if wandb_path.exists() and any((wandb_path / "latest-run").iterdir()):
84 | # Parse unique `run_id` from the `.wandb.` file...
85 | wandb_fns = [f.name for f in (wandb_path / "latest-run").iterdir() if f.name.endswith(".wandb")]
86 | assert len(wandb_fns) == 1, f"There should only be 1 `.wandb.` file... found {len(wandb_fns)}!"
87 |
88 | # Regex Match on `run-{id}.wandb`
89 | self.resume_id = re.search("run-(.+?).wandb", wandb_fns[0]).group(1)
90 |
91 | elif wandb_path.exists():
92 | raise ValueError("Starting Training from Scratch with Preexisting W&B Directory; Remove to Continue!")
93 |
94 | # Call W&B.init()
95 | self.initialize()
96 |
97 | def initialize(self) -> None:
98 | """Run W&B.init on the guarded / rank-zero process."""
99 | if not self.is_rank_zero:
100 | return
101 |
102 | # Only initialize / log if `is_rank_zero`
103 | wandb.init(
104 | project=self.tracking_cfg.project,
105 | entity=self.tracking_cfg.entity,
106 | config=self.hparams,
107 | name=self.run_id,
108 | dir=self.path,
109 | tags=self.tags,
110 | notes=self.tracking_cfg.notes,
111 | resume="allow" if self.resume else False,
112 | id=self.resume_id,
113 | )
114 |
115 | def write_hyperparameters(self) -> None:
116 | if not self.is_rank_zero:
117 | return
118 |
119 | # Only log if `is_rank_zero`
120 | wandb.config = self.hparams
121 |
122 | def write(self, global_step: int, metrics: Dict[str, Union[int, float]]) -> None:
123 | if not self.is_rank_zero:
124 | return
125 |
126 | # Only log if `is_rank_zero`
127 | wandb.log(metrics, step=global_step)
128 |
129 | def finalize(self) -> None:
130 | wandb.finish()
131 | time.sleep(150)
132 |
133 |
134 | # === Core Metrics Container :: Responsible for Initializing Loggers and Compiling/Pushing Metrics ===
135 |
136 |
137 | class Metrics:
138 | def __init__(
139 | self,
140 | active_loggers: List[str],
141 | run_id: str,
142 | hparams: Dict[str, Any],
143 | model_arch: str,
144 | is_rank_zero: bool,
145 | tracking_cfg: Optional[TrackingConfig] = None,
146 | tags: Optional[List[str]] = None,
147 | resume: bool = False,
148 | resume_id: Optional[str] = None,
149 | window: int = 128,
150 | ) -> None:
151 | """High-Level Container Logic for Metrics Logging; logic defined for each model architecture!"""
152 | self.model_arch, self.is_rank_zero, self.window = model_arch, is_rank_zero, window
153 |
154 | # Initialize Loggers
155 | self.loggers = []
156 | for log_type in active_loggers:
157 | if log_type == "jsonl":
158 | logger = JSONLinesLogger(run_id, hparams, is_rank_zero=is_rank_zero)
159 | elif log_type == "wandb":
160 | logger = WeightsBiasesLogger(
161 | run_id, hparams, tracking_cfg, tags, resume, resume_id, is_rank_zero=is_rank_zero
162 | )
163 | else:
164 | raise ValueError(f"Logger `{log_type}` is not defined!")
165 |
166 | # Add Hyperparameters --> Add to `self.loggers`
167 | logger.write_hyperparameters()
168 | self.loggers.append(logger)
169 |
170 | # Create Universal Trackers
171 | self.global_step, self.start_time, self.resume_time, self.step_start_time = 0, time.time(), 0, time.time()
172 | self.tracker = {
173 | "loss": deque(maxlen=self.window),
174 | "lr": [],
175 | "step_time": deque(maxlen=self.window),
176 | }
177 |
178 | # Create Model-Specific Trackers
179 | if self.model_arch == "v-mvp":
180 | self.tracker.update({"reconstruction_loss": deque(maxlen=self.window)})
181 |
182 | elif self.model_arch in {"v-r3m", "v-rn3m"}:
183 | self.tracker.update(
184 | {
185 | "tcn_loss": deque(maxlen=self.window),
186 | "reward_loss": deque(maxlen=self.window),
187 | "l1_loss": deque(maxlen=self.window),
188 | "l2_loss": deque(maxlen=self.window),
189 | "tcn_accuracy": deque(maxlen=self.window),
190 | "reward_accuracy": deque(maxlen=self.window),
191 | }
192 | )
193 |
194 | elif self.model_arch == "v-cond":
195 | self.tracker.update({"reconstruction_loss": deque(maxlen=self.window)})
196 |
197 | elif self.model_arch == "v-dual":
198 | self.tracker.update(
199 | {
200 | "reconstruction_loss": deque(maxlen=self.window),
201 | "zero_reconstruction_loss": deque(maxlen=self.window),
202 | "k_reconstruction_loss": deque(maxlen=self.window),
203 | }
204 | )
205 |
206 | elif self.model_arch == "v-gen":
207 | self.tracker.update(
208 | {
209 | "reconstruction_loss": deque(maxlen=self.window),
210 | "zero_reconstruction_loss": deque(maxlen=self.window),
211 | "k_reconstruction_loss": deque(maxlen=self.window),
212 | "lm_loss": deque(maxlen=self.window),
213 | "lm_ppl": deque(maxlen=self.window),
214 | }
215 | )
216 |
217 | else:
218 | raise ValueError(f"Metrics for Model `{self.model_arch}` are not implemented!")
219 |
220 | def itemize(self) -> Dict[str, torch.Tensor]:
221 | """Utility method for converting `deque[torch.Tensor] --> mean over Tensors."""
222 | return {
223 | k: torch.stack(list(v)).mean().item()
224 | for k, v in self.tracker.items()
225 | if k not in {"loss", "lr", "step_time"}
226 | }
227 |
228 | def log(self, global_step: int, metrics: Dict[str, Union[int, float]]) -> None:
229 | for logger in self.loggers:
230 | logger.write(global_step, metrics)
231 |
232 | def finalize(self) -> None:
233 | for logger in self.loggers:
234 | logger.finalize()
235 |
236 | def get_status(self, epoch: int, loss: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None) -> str:
237 | lr = self.tracker["lr"][-1] if len(self.tracker["lr"]) > 0 else 0
238 | if loss is None:
239 | return f"=>> [Epoch {epoch:03d}] Global Step {self.global_step:06d} =>> LR :: {lr:.6f}"
240 |
241 | # Otherwise, embed `loss` in status!
242 | return f"=>> [Epoch {epoch:03d}] Global Step {self.global_step:06d} =>> LR :: {lr:.6f} -- Loss :: {loss:.4f}"
243 |
244 | def commit(
245 | self,
246 | *,
247 | global_step: Optional[int] = None,
248 | resume_time: Optional[int] = None,
249 | lr: Optional[float] = None,
250 | update_step_time: bool = False,
251 | **kwargs,
252 | ) -> None:
253 | """Update all metrics in `self.tracker` by iterating through special positional arguments & kwargs."""
254 | if not self.is_rank_zero:
255 | return
256 |
257 | # Special Positional Arguments
258 | if global_step is not None:
259 | self.global_step = global_step
260 |
261 | if resume_time is not None:
262 | self.resume_time = resume_time
263 |
264 | if lr is not None:
265 | self.tracker["lr"].append(lr)
266 |
267 | if update_step_time:
268 | self.tracker["step_time"].append(time.time() - self.step_start_time)
269 | self.step_start_time = time.time()
270 |
271 | # Generic Keyword Arguments
272 | for key, value in kwargs.items():
273 | self.tracker[key].append(value.detach())
274 |
275 | def push(self, epoch: int) -> str:
276 | """Push current metrics to loggers with model-specific handling."""
277 | if not self.is_rank_zero:
278 | return
279 |
280 | loss = torch.stack(list(self.tracker["loss"])).mean().item()
281 | step_time, lr = np.mean(list(self.tracker["step_time"])), self.tracker["lr"][-1]
282 | status = self.get_status(epoch, loss)
283 |
284 | # Model-Specific Handling
285 | itemized = self.itemize()
286 | if self.model_arch == "v-mvp":
287 | self.log(
288 | self.global_step,
289 | metrics={
290 | "Pretrain/Step": self.global_step,
291 | "Pretrain/Epoch": epoch,
292 | "Pretrain/V-MVP Train Loss": loss,
293 | "Pretrain/Reconstruction Loss": itemized["reconstruction_loss"],
294 | "Pretrain/Learning Rate": lr,
295 | "Pretrain/Step Time": step_time,
296 | },
297 | )
298 |
299 | elif self.model_arch in {"v-r3m", "v-rn3m"}:
300 | self.log(
301 | self.global_step,
302 | metrics={
303 | "Pretrain/Step": self.global_step,
304 | "Pretrain/Epoch": epoch,
305 | f"Pretrain/V-{'R3M' if self.model_arch == 'v-r3m' else 'RN3M'} Train Loss": loss,
306 | "Pretrain/TCN Loss": itemized["tcn_loss"],
307 | "Pretrain/Reward Loss": itemized["reward_loss"],
308 | "Pretrain/L1 Loss": itemized["l1_loss"],
309 | "Pretrain/L2 Loss": itemized["l2_loss"],
310 | "Pretrain/TCN Accuracy": itemized["tcn_accuracy"],
311 | "Pretrain/Reward Accuracy": itemized["reward_accuracy"],
312 | "Pretrain/Learning Rate": lr,
313 | "Pretrain/Step Time": step_time,
314 | },
315 | )
316 |
317 | elif self.model_arch == "v-cond":
318 | self.log(
319 | self.global_step,
320 | metrics={
321 | "Pretrain/Step": self.global_step,
322 | "Pretrain/Epoch": epoch,
323 | "Pretrain/V-Cond Train Loss": loss,
324 | "Pretrain/Reconstruction Loss": itemized["reconstruction_loss"],
325 | "Pretrain/Learning Rate": lr,
326 | "Pretrain/Step Time": step_time,
327 | },
328 | )
329 |
330 | elif self.model_arch == "v-dual":
331 | self.log(
332 | self.global_step,
333 | metrics={
334 | "Pretrain/Step": self.global_step,
335 | "Pretrain/Epoch": epoch,
336 | "Pretrain/V-Dual Train Loss": loss,
337 | "Pretrain/Reconstruction Loss": itemized["reconstruction_loss"],
338 | "Pretrain/Zero Reconstruction Loss": itemized["zero_reconstruction_loss"],
339 | "Pretrain/K Reconstruction Loss": itemized["k_reconstruction_loss"],
340 | "Pretrain/Learning Rate": lr,
341 | "Pretrain/Step Time": step_time,
342 | },
343 | )
344 |
345 | elif self.model_arch == "v-gen":
346 | self.log(
347 | self.global_step,
348 | metrics={
349 | "Pretrain/Step": self.global_step,
350 | "Pretrain/Epoch": epoch,
351 | "Pretrain/V-Gen Train Loss": loss,
352 | "Pretrain/Reconstruction Loss": itemized["reconstruction_loss"],
353 | "Pretrain/Zero Reconstruction Loss": itemized["zero_reconstruction_loss"],
354 | "Pretrain/K Reconstruction Loss": itemized["k_reconstruction_loss"],
355 | "Pretrain/CLM Loss": itemized["lm_loss"],
356 | "Pretrain/CLM Perplexity": itemized["lm_ppl"],
357 | "Pretrain/LM Loss": itemized["lm_loss"],
358 | "Pretrain/LM Perplexity": itemized["lm_ppl"],
359 | "Pretrain/Learning Rate": lr,
360 | "Pretrain/Step Time": step_time,
361 | },
362 | )
363 |
364 | else:
365 | raise ValueError(f"Metrics.push() for Model `{self.model_arch}` is not implemented!")
366 |
367 | return status
368 |
369 | def push_epoch(self, epoch: int, val_loss: torch.Tensor) -> Tuple[str, torch.Tensor, int]:
370 | """End-of-Epoch => Push accumulated metrics to loggers with model-specific handling."""
371 | if not self.is_rank_zero:
372 | return
373 |
374 | # Compute End-of-Epoch Specialized Metrics
375 | loss, step_time = torch.stack(list(self.tracker["loss"])).mean(), np.mean(list(self.tracker["step_time"]))
376 | lr, duration = self.tracker["lr"][-1], int(time.time() - self.start_time) + self.resume_time
377 | epoch_status = (
378 | f"[Epoch {epoch:03d}] Global Step {self.global_step:06d} =>> LR :: {lr:.6f} -- Loss :: {loss:.4f} "
379 | f"-- Val Loss :: {val_loss:.4f} -- Total Time (sec) :: {duration}"
380 | )
381 |
382 | # Log for Model
383 | p_arch = {
384 | "v-mvp": "MVP",
385 | "v-r3m": "R3M (ViT)",
386 | "v-rn3m": "R3M (RN)",
387 | "v-cond": "V-Cond",
388 | "v-dual": "V-Dual",
389 | "v-gen": "V-Gen",
390 | }[self.model_arch]
391 | self.log(
392 | self.global_step,
393 | metrics={
394 | "Pretrain/Step": self.global_step,
395 | "Pretrain/Epoch": epoch,
396 | "Pretrain/Training Duration": duration,
397 | f"Pretrain/{p_arch} Train Epoch Loss": loss.item(),
398 | f"Pretrain/{p_arch} Train Loss": loss.item(),
399 | f"Pretrain/{p_arch} Validation Loss": val_loss.item(),
400 | "Pretrain/Learning Rate": lr,
401 | "Pretrain/Step Time": step_time,
402 | },
403 | )
404 |
405 | return epoch_status, loss, duration
406 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/util/utilities.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | utilities.py
3 |
4 | General utilities for randomness, distributed training, and miscellaneous checks in PyTorch.
5 |
6 | === Randomness ===
7 |
8 | Random `seed_everything` functionality is taken directly from PyTorch-Lighting:
9 | > Ref: https://github.com/PyTorchLightning/pytorch-lightning/blob/master/pytorch_lightning/utilities/seed.py
10 |
11 | This is pretty important to get right if we're every randomly generating our masks (or prefix dropout) inside our
12 | Dataset __getitem__() with multiple workers... if not handled properly, we will get repeated augmentations anytime
13 | we inject randomness from non-PyTorch sources (e.g., numpy, random)!
14 | > Ref: https://tanelp.github.io/posts/a-bug-that-plagues-thousands-of-open-source-ml-projects/
15 |
16 | === Distributed / DDP Training ====
17 |
18 | Utilities provide a standard API across single-GPU/multi-GPU/multi-node training. Assumes that code is running with
19 | one of the following strategies:
20 | - Single Process (on CPU?, GPU)
21 | - DDP (GPU, Multi-Node GPU) --> uses the `torchrun`/`torch.distributed` API & semantics
22 |
23 | Key Terminology
24 | -> World Size :: Total number of processes distributed over (# nodes x # devices) -- assumed homogenous!
25 | -> Rank :: Integer index of current process in the total world size
26 | -> Local Rank :: Local index on given node in [0, Devices per Node]
27 | """
28 | import os
29 | import random
30 | from typing import Callable, Iterator, Optional, TypeVar
31 |
32 | import numpy as np
33 | import torch
34 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
35 | from torch.utils.data.distributed import DistributedSampler
36 |
37 | T_co = TypeVar("T_co", covariant=True)
38 |
39 |
40 | # === Randomness ===
41 |
42 |
43 | def worker_init_function(worker_id: int) -> None:
44 | """
45 | Borrowed directly from PyTorch-Lightning; inspired by this issue comment in the PyTorch repo:
46 | > Ref: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/5059#issuecomment-817392562
47 |
48 | Intuition: You can think of the seed sequence spawn function as a "janky" torch.Generator() or jax.PRNGKey that
49 | you can run iterative splitting on to get new (predictable) randomness.
50 |
51 | :param worker_id: Identifier for the given worker [0, num_workers) for the Dataloader in question.
52 | """
53 | # Get current `rank` (if running distributed) and `process_seed`
54 | global_rank, process_seed = int(os.environ["LOCAL_RANK"]), torch.initial_seed()
55 |
56 | # Back out the "base" (original) seed - the per-worker seed is set in PyTorch:
57 | # > https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/data.html#data-loading-randomness
58 | base_seed = process_seed - worker_id
59 |
60 | # "Magic" code --> basically creates a seed sequence that mixes different "sources" and seeds every library...
61 | seed_seq = np.random.SeedSequence([base_seed, worker_id, global_rank])
62 |
63 | # Use 128 bits (4 x 32-bit words) to represent seed --> generate_state(k) produces a `k` element array!
64 | np.random.seed(seed_seq.generate_state(4))
65 |
66 | # Spawn distinct child sequences for PyTorch (reseed) and stdlib random
67 | torch_seed_seq, random_seed_seq = seed_seq.spawn(2)
68 |
69 | # Torch Manual seed takes 64 bits (so just specify a dtype of uint64
70 | torch.manual_seed(torch_seed_seq.generate_state(1, dtype=np.uint64)[0])
71 |
72 | # Use 128 Bits for `random`, but express as integer instead of as an array
73 | random_seed = (random_seed_seq.generate_state(2, dtype=np.uint64).astype(list) * [1 << 64, 1]).sum()
74 | random.seed(random_seed)
75 |
76 |
77 | def set_global_seed(seed: int, get_worker_init_fn: bool = False) -> Optional[Callable[[int], None]]:
78 | """Sets seed for all randomness libraries (mostly random, numpy, torch) and produces a `worker_init_fn`"""
79 | assert np.iinfo(np.uint32).min < seed < np.iinfo(np.uint32).max, "Seed outside the np.uint32 bounds!"
80 |
81 | # Set Seed as an Environment Variable
82 | os.environ["EXPERIMENT_GLOBAL_SEED"] = str(seed)
83 | random.seed(seed)
84 | np.random.seed(seed)
85 | torch.manual_seed(seed)
86 |
87 | return worker_init_function if get_worker_init_fn else None
88 |
89 |
90 | # === Distributed Training ===
91 |
92 |
93 | class ResumeableDistributedSampler(DistributedSampler):
94 | def __init__(
95 | self,
96 | seen_examples: int,
97 | resume_epoch: int,
98 | dataset: Dataset,
99 | num_replicas: int,
100 | rank: int,
101 | shuffle: bool = True,
102 | seed: int = 0,
103 | ) -> None:
104 | super().__init__(dataset, num_replicas=num_replicas, rank=rank, shuffle=shuffle, seed=seed)
105 | self.seen_examples, self.resume_epoch, self.do_resume = seen_examples, resume_epoch, True
106 |
107 | # Set `seen_examples_per_replica` --> this is necessary for when we re-wrap the iterator in self.__iter__()
108 | # > Note: `seen_examples` is across _all_ replicas --> so divide!
109 | self.seen_examples_per_replica = self.seen_examples // self.num_replicas
110 |
111 | def __iter__(self) -> Iterator[T_co]:
112 | epoch_iterator = super().__iter__()
113 | if self.do_resume:
114 | # Unpack iterator --> list, slice off the first `seen_examples_per_replica` examples, and re-wrap!
115 | leftover_idxs = list(epoch_iterator)[self.seen_examples_per_replica :]
116 | return iter(leftover_idxs)
117 | else:
118 | return epoch_iterator
119 |
120 | def __len__(self) -> int:
121 | if self.do_resume:
122 | # Remove the "seen" sample from self.num_samples; num_samples is *per replica*!
123 | return self.num_samples - self.seen_examples_per_replica
124 | else:
125 | return self.num_samples
126 |
127 | def set_epoch(self, epoch: int) -> None:
128 | # If epoch != self.resume_epoch --> we're in "regular DistributedSampler" mode (just a wrapper class)
129 | # > Intuition: We should *only* truncate examples on the first epoch upon resuming!
130 | self.epoch = epoch
131 | if self.epoch != self.resume_epoch:
132 | self.do_resume = False
133 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/util/v1/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/siddk/voltron-robotics/1b299bf5cfa06673a3738aa6e15423b92a9922cd/voltron/util/v1/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/util/v1/checkpointing.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | checkpointing.py
3 |
4 | XLA-specific utility class for handling model/optimizer serialization & checkpointing.
5 |
6 | Support the following strategies:
7 | - (k, -1, -1) --> Keep only the most recent "k" epoch checkpoints
8 | - (k, m, -1) --> Keep the most recent "k" epoch checkpoints and *every* m epoch checkpoint
9 | - (k, m, s = 2500) --> Keep "k" and "m" subject to above, but also keep *s* step checkpoints for current epoch
10 | """
11 | import os
12 | from collections import deque
13 | from pathlib import Path
14 | from typing import Any, Optional, Tuple
15 |
16 | import torch.nn as nn
17 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
18 |
19 |
20 | class FixedDeck(deque):
21 | def __init__(self, maxlen: int) -> None:
22 | super().__init__(maxlen=maxlen)
23 |
24 | def append(self, x: Any) -> Any:
25 | pop_value = None
26 | if self.__len__() == self.maxlen:
27 | pop_value = self.__getitem__(0)
28 |
29 | # Perform parent append and return popped value, if any!
30 | super().append(x)
31 | return pop_value
32 |
33 |
34 | class XLACheckpointSaver:
35 | def __init__(self, strategy: Tuple[int, int, int], run_dir: str) -> None:
36 | """
37 | Create a checkpoint saver with the provided strategy that saves to the given path, with XLA-specific handling.
38 |
39 | :param strategy: Strategy, following the (k, -1, -1) -- (k, m, -1) -- (k, m, s) description above.
40 | :param run_dir: Path to root of `run_dir`
41 | """
42 | import torch_xla.core.xla_model as xm
43 |
44 | (self.k, self.m, self.s), self.run_dir = strategy, run_dir
45 | self.recents, self.intervals, self.step_checkpoints = FixedDeck(maxlen=self.k), set(), set()
46 |
47 | # If `self.s` is -1 --> disable step_checkpoints
48 | self.enable_step = self.s != -1
49 |
50 | # Create "checkpoints" subdirectory
51 | self.path = Path(run_dir) / "checkpoints"
52 | if xm.is_master_ordinal(local=False):
53 | os.makedirs(self.path, exist_ok=True)
54 |
55 | # Populate `step_checkpoints` on __init__ (if resuming *within* an epoch...)
56 | self.step_checkpoints.update([c for c in self.path.iterdir() if "local-epoch=" in str(c)])
57 |
58 | # Create Saver
59 | xm.master_print(f"Created Saver w/ `k` = {self.k}, `m` = {self.m}`, `s` = {self.s}!")
60 |
61 | def save(
62 | self,
63 | epoch: int,
64 | is_local_step: bool,
65 | model: nn.Module,
66 | optimizer: Optimizer,
67 | duration: int,
68 | local_step: Optional[int] = None,
69 | train_loss: Optional[float] = None,
70 | val_loss: Optional[float] = None,
71 | ) -> None:
72 | """Performs the save operation, unlinking existing stale checkpoints, if necessary."""
73 | import torch_xla.core.xla_model as xm
74 |
75 | # Check if saving a `local_step` (within an epoch) or if saving an `epoch`
76 | if self.enable_step and is_local_step and (local_step % self.s) == 0:
77 | # Create filename
78 | step_checkpoint = self.path / f"local-epoch={epoch}-step={local_step}-t={duration}.pt"
79 |
80 | # Perform actual save action...
81 | # > IMPORTANT --> XLA/XM will throw an error if optimizer has "param_groups" so only save "state"...
82 | xm.save([model.state_dict(), optimizer.state_dict()["state"]], step_checkpoint)
83 | if xm.is_master_ordinal(local=False):
84 | self.step_checkpoints.add(step_checkpoint)
85 |
86 | elif not is_local_step:
87 | # Create filename
88 | if train_loss is None and val_loss is None:
89 | checkpoint = self.path / f"epoch={epoch}-train=inf-val=inf-t={duration}.pt"
90 | else:
91 | checkpoint = self.path / f"epoch={epoch}-train={train_loss:.4f}-val={val_loss:.4f}-t={duration}.pt"
92 |
93 | # Perform actual save action...
94 | # > IMPORTANT --> XLA/XM will throw an error if optimizer has "param_groups" so only save "state"...
95 | xm.save([model.state_dict(), optimizer.state_dict()["state"]], checkpoint)
96 |
97 | if xm.is_master_ordinal(local=False):
98 | # Conditional Check for M -- Keep if modulated by interval
99 | if epoch % self.m == 0:
100 | self.intervals.add(checkpoint)
101 |
102 | # Remove all "step_checkpoints" now that we successfully made it to the end of the epoch!
103 | while len(self.step_checkpoints) > 0:
104 | os.remove(self.step_checkpoints.pop())
105 |
106 | # Finally, recency add & unlink/delete if necessary
107 | to_remove = self.recents.append(checkpoint)
108 | if to_remove is not None and to_remove not in self.intervals:
109 | os.remove(to_remove)
110 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/util/v1/distributed.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | distributed.py
3 |
4 | Key distributed utilities; notably provides a standard API for getting relevant data from either CPU/GPU or XLA (TPU)
5 | devices, since the underlying implementation does differ substantially.
6 |
7 | Assumes that code is running with one of the following strategies:
8 | - Single Process (on CPU, GPU)
9 | - DDP (CPU, GPU)... uses the torch.distributed.launch API & semantics
10 | - XMP Spawn (TPU)... TPU based XLA + Multiprocessing Spawn semantics
11 |
12 | Key Terminology
13 | -> World Size :: Total number of processes distributed over (# nodes x # devices) -- assumed homogenous!
14 | -> Rank :: Integer index of current process in the total world size
15 | -> Local Rank :: Local index on given node in [0, Devices per Node]
16 | """
17 | from importlib.util import find_spec
18 | from typing import Iterator, TypeVar
19 |
20 | import torch
21 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
22 | from torch.utils.data.distributed import DistributedSampler
23 |
24 | T_co = TypeVar("T_co", covariant=True)
25 |
26 |
27 | class ResumeableDistributedSampler(DistributedSampler):
28 | def __init__(
29 | self,
30 | seen_examples: int,
31 | resume_epoch: int,
32 | dataset: Dataset,
33 | num_replicas: int,
34 | rank: int,
35 | shuffle: bool = True,
36 | seed: int = 0,
37 | ) -> None:
38 | super().__init__(dataset, num_replicas=num_replicas, rank=rank, shuffle=shuffle, seed=seed)
39 | self.seen_examples, self.resume_epoch, self.do_resume = seen_examples, resume_epoch, True
40 |
41 | # Set `seen_examples_per_replica` --> this is necessary for when we re-wrap the iterator in self.__iter__()
42 | # > Note: `seen_examples` is across _all_ replicas --> so divide!
43 | self.seen_examples_per_replica = self.seen_examples // self.num_replicas
44 |
45 | def __iter__(self) -> Iterator[T_co]:
46 | epoch_iterator = super().__iter__()
47 | if self.do_resume:
48 | # Unpack iterator --> list, slice off the first `seen_examples_per_replica` examples, and re-wrap!
49 | leftover_idxs = list(epoch_iterator)[self.seen_examples_per_replica :]
50 | return iter(leftover_idxs)
51 | else:
52 | return epoch_iterator
53 |
54 | def __len__(self) -> int:
55 | if self.do_resume:
56 | # Remove the "seen" sample from self.num_samples; num_samples is *per replica*!
57 | return self.num_samples - self.seen_examples_per_replica
58 | else:
59 | return self.num_samples
60 |
61 | def set_epoch(self, epoch: int) -> None:
62 | # If epoch != self.resume_epoch --> we're in "regular DistributedSampler" mode (just a wrapper class)
63 | # > Intuition: We should *only* truncate examples on the first epoch upon resuming!
64 | self.epoch = epoch
65 | if self.epoch != self.resume_epoch:
66 | self.do_resume = False
67 |
68 |
69 | def xla_available() -> bool:
70 | try:
71 | return find_spec("torch_xla") is not None
72 | except ModuleNotFoundError:
73 | return False
74 |
75 |
76 | def get_rank() -> int:
77 | """Returns the global rank [0, World Size) of the current process."""
78 | if xla_available():
79 | import torch_xla.core.xla_model as xm
80 |
81 | # By default, if XLA is available, assume we're running under XMP Spawn
82 | return xm.get_ordinal()
83 |
84 | # Try to get rank via torch.distributed, but catch error if only single process
85 | try:
86 | return torch.distributed.get_rank()
87 |
88 | # RuntimeError => not running distributed (single process)
89 | except RuntimeError:
90 | return 0
91 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/util/v1/random.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | random.py
3 |
4 | Utilities for dealing with randomness for PyTorch, across devices (CPU, GPU, TPU).
5 |
6 | Loosely inspired by functionality in PyTorch-Lightning:
7 | > Ref: https://github.com/PyTorchLightning/pytorch-lightning/blob/master/pytorch_lightning/utilities/seed.py
8 |
9 | This is pretty important to get right if we're every randomly generating our masks (or prefix dropout) inside our
10 | Dataset __getitem__() with multiple workers... if not handled properly, we will get repeated augmentations anytime
11 | we inject randomness from non-PyTorch sources (e.g., numpy, random)!
12 | > Ref: https://tanelp.github.io/posts/a-bug-that-plagues-thousands-of-open-source-ml-projects/
13 | """
14 | import os
15 | import random
16 | from typing import Callable
17 |
18 | import numpy as np
19 | import torch
20 |
21 | from voltron.util.v1.distributed import get_rank
22 |
23 |
24 | def set_global_seed(seed: int) -> Callable[[int], None]:
25 | """Sets seed for all randomness libraries (mostly random, numpy, torch) and produces a `worker_init_fn`"""
26 | assert np.iinfo(np.uint32).min < seed < np.iinfo(np.uint32).max, "Seed outside the np.uint32 bounds!"
27 |
28 | # Set Seed as an Environment Variable
29 | os.environ["EXPERIMENT_GLOBAL_SEED"] = str(seed)
30 | random.seed(seed)
31 | np.random.seed(seed)
32 | torch.manual_seed(seed)
33 |
34 | return worker_init_function
35 |
36 |
37 | def worker_init_function(worker_id: int) -> None:
38 | """
39 | Borrowed directly from PyTorch-Lightning; inspired by this issue comment in the PyTorch repo:
40 | > Ref: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/5059#issuecomment-817392562
41 |
42 | Intuition: You can think of the seed sequence spawn function as a "janky" torch.Generator() or jax.PRNGKey that
43 | you can run iterative splitting on to get new (predictable) randomness.
44 |
45 | :param worker_id: Identifier for the given worker [0, num_workers) for the Dataloader in question.
46 | """
47 | # Get current `rank` (if running distributed) and `process_seed`
48 | global_rank, process_seed = get_rank(), torch.initial_seed()
49 |
50 | # Back out the "base" (original) seed - the per-worker seed is set in PyTorch:
51 | # > https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/data.html#data-loading-randomness
52 | base_seed = process_seed - worker_id
53 |
54 | # "Magic" code --> basically creates a seed sequence that mixes different "sources" and seeds every library...
55 | seed_seq = np.random.SeedSequence([base_seed, worker_id, global_rank])
56 |
57 | # Use 128 bits (4 x 32-bit words) to represent seed --> generate_state(k) produces a `k` element array!
58 | np.random.seed(seed_seq.generate_state(4))
59 |
60 | # Spawn distinct child sequences for PyTorch (reseed) and stdlib random
61 | torch_seed_seq, random_seed_seq = seed_seq.spawn(2)
62 |
63 | # Torch Manual seed takes 64 bits (so just specify a dtype of uint64
64 | torch.manual_seed(torch_seed_seq.generate_state(1, dtype=np.uint64)[0])
65 |
66 | # Use 128 Bits for `random`, but express as integer instead of as an array
67 | random_seed = (random_seed_seq.generate_state(2, dtype=np.uint64).astype(list) * [1 << 64, 1]).sum()
68 | random.seed(random_seed)
69 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/voltron/util/v1/xla_logger.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | xla_logger.py
3 |
4 | Utility class defining various XLA logging methods (called within marked closures), for logging metrics periodically
5 | through training & validation.
6 | """
7 | from typing import List
8 |
9 | import jsonlines
10 | import numpy as np
11 | import torch
12 | import torch_xla.core.xla_model as xm
13 | import wandb
14 |
15 |
16 | # === Generic (Cross-Model) Epoch End Update ===
17 | def log_epoch_end_update(
18 | arch: str,
19 | epoch: int,
20 | global_step: int,
21 | run_id: str,
22 | duration: int,
23 | train_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
24 | val_loss: float,
25 | lr: float,
26 | step_times: List[float],
27 | ) -> None:
28 | train_loss = torch.stack(list(train_losses)).mean()
29 | average_step_time = np.mean(list(step_times))
30 |
31 | # Console Logging --> Unclear if it'll work?
32 | xm.master_print(
33 | f"Epoch {epoch:03d}, Global Step {global_step:06d} || LR :: {lr:.6f} -- Train Loss :: {train_loss:.4f} "
34 | f"-- Val Loss :: {val_loss:.4f} -- Total Time (sec) :: {duration}"
35 | )
36 |
37 | # Get Log-Friendly Arch
38 | p_arch = {
39 | "v-mvp": "MVP",
40 | "v-r3m": "R3M (ViT)",
41 | "v-rn3m": "R3M (RN)",
42 | "v-cond": "V-Cond",
43 | "v-dual": "V-Dual",
44 | "v-gen": "V-Gen",
45 | }[arch]
46 |
47 | # Log to Weights & Biases & JSONL
48 | blob = {
49 | "Pretrain/Step": global_step,
50 | "Pretrain/Epoch": epoch,
51 | "Pretrain/Training Duration": duration,
52 | "Pretrain/Step Time": average_step_time,
53 | f"Pretrain/{p_arch} Train Epoch Loss": train_loss.item(),
54 | f"Pretrain/{p_arch} Train Loss": train_loss.item(),
55 | f"Pretrain/{p_arch} Validation Loss": val_loss,
56 | "Pretrain/Learning Rate": lr,
57 | }
58 |
59 | wandb.log(blob, step=global_step)
60 | with jsonlines.open(f"{run_id}.jsonl", mode="a", sort_keys=True) as js_logger:
61 | js_logger.write(blob)
62 |
63 |
64 | # === Data-Locked Reproductions ===
65 |
66 |
67 | def log_vmvp_train_update(
68 | epoch: int,
69 | global_step: int,
70 | run_id: str,
71 | train_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
72 | lr: float,
73 | reconstruction_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
74 | step_times: List[float],
75 | ) -> None:
76 | train_loss = torch.stack(list(train_losses)).mean()
77 | reconstruction_loss = torch.stack(list(reconstruction_losses)).mean()
78 | average_step_time = np.mean(list(step_times))
79 |
80 | # Console Logging --> Just log the aggregated train loss...
81 | xm.master_print(
82 | f"Epoch {epoch:03d}, Global Step {global_step:06d} || LR :: {lr:.6f} -- Train Loss :: {train_loss:.4f}"
83 | )
84 |
85 | # Log to Weights & Biases + JSONL
86 | blob = {
87 | "Pretrain/Step": global_step,
88 | "Pretrain/Epoch": epoch,
89 | "Pretrain/V-MVP Train Loss": train_loss.item(),
90 | "Pretrain/Reconstruction Loss": reconstruction_loss.item(),
91 | "Pretrain/Learning Rate": lr,
92 | "Pretrain/Step Time": average_step_time,
93 | }
94 | wandb.log(blob, step=global_step)
95 | with jsonlines.open(f"{run_id}.jsonl", mode="a", sort_keys=True) as js_logger:
96 | js_logger.write(blob)
97 |
98 |
99 | def log_vr3m_train_update(
100 | epoch: int,
101 | global_step: int,
102 | run_id: str,
103 | train_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
104 | lr: float,
105 | tcn_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
106 | reward_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
107 | l1_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
108 | l2_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
109 | tcn_accuracies: List[torch.Tensor],
110 | reward_accuracies: List[torch.Tensor],
111 | step_times: List[float],
112 | ) -> None:
113 | train_loss = torch.stack(list(train_losses)).mean()
114 | tcn_loss = torch.stack(list(tcn_losses)).mean()
115 | reward_loss = torch.stack(list(reward_losses)).mean()
116 | l1_loss, l2_loss = torch.stack(list(l1_losses)).mean(), torch.stack(list(l2_losses)).mean()
117 | tcn_accuracy = torch.stack(list(tcn_accuracies)).mean()
118 | reward_accuracy = torch.stack(list(reward_accuracies)).mean()
119 | average_step_time = np.mean(list(step_times))
120 |
121 | # Console Logging --> Just log the aggregated train loss...
122 | xm.master_print(
123 | f"Epoch {epoch:03d}, Global Step {global_step:06d} || LR :: {lr:.6f} -- Train Loss :: {train_loss:.4f}"
124 | )
125 |
126 | # Log to Weights & Biases + JSONL
127 | blob = {
128 | "Pretrain/Step": global_step,
129 | "Pretrain/Epoch": epoch,
130 | "Pretrain/V-R3M Train Loss": train_loss.item(),
131 | "Pretrain/TCN Loss": tcn_loss.item(),
132 | "Pretrain/Reward Loss": reward_loss.item(),
133 | "Pretrain/L1 Loss": l1_loss.item(),
134 | "Pretrain/L2 Loss": l2_loss.item(),
135 | "Pretrain/TCN Accuracy": tcn_accuracy.item(),
136 | "Pretrain/Reward Accuracy": reward_accuracy.item(),
137 | "Pretrain/Learning Rate": lr,
138 | "Pretrain/Step Time": average_step_time,
139 | }
140 | wandb.log(blob, step=global_step)
141 | with jsonlines.open(f"{run_id}.jsonl", mode="a", sort_keys=True) as js_logger:
142 | js_logger.write(blob)
143 |
144 |
145 | def log_vrn3m_train_update(
146 | epoch: int,
147 | global_step: int,
148 | run_id: str,
149 | train_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
150 | lr: float,
151 | tcn_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
152 | reward_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
153 | l1_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
154 | l2_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
155 | tcn_accuracies: List[torch.Tensor],
156 | reward_accuracies: List[torch.Tensor],
157 | step_times: List[float],
158 | ) -> None:
159 | train_loss = torch.stack(list(train_losses)).mean()
160 | tcn_loss = torch.stack(list(tcn_losses)).mean()
161 | reward_loss = torch.stack(list(reward_losses)).mean()
162 | l1_loss, l2_loss = torch.stack(list(l1_losses)).mean(), torch.stack(list(l2_losses)).mean()
163 | tcn_accuracy = torch.stack(list(tcn_accuracies)).mean()
164 | reward_accuracy = torch.stack(list(reward_accuracies)).mean()
165 | average_step_time = np.mean(list(step_times))
166 |
167 | # Console Logging --> Just log the aggregated train loss...
168 | xm.master_print(
169 | f"Epoch {epoch:03d}, Global Step {global_step:06d} || LR :: {lr:.6f} -- Train Loss :: {train_loss:.4f}"
170 | )
171 |
172 | # Log to Weights & Biases + JSONL
173 | blob = {
174 | "Pretrain/Step": global_step,
175 | "Pretrain/Epoch": epoch,
176 | "Pretrain/V-RN3M Train Loss": train_loss.item(),
177 | "Pretrain/TCN Loss": tcn_loss.item(),
178 | "Pretrain/Reward Loss": reward_loss.item(),
179 | "Pretrain/L1 Loss": l1_loss.item(),
180 | "Pretrain/L2 Loss": l2_loss.item(),
181 | "Pretrain/TCN Accuracy": tcn_accuracy.item(),
182 | "Pretrain/Reward Accuracy": reward_accuracy.item(),
183 | "Pretrain/Learning Rate": lr,
184 | "Pretrain/Step Time": average_step_time,
185 | }
186 | wandb.log(blob, step=global_step)
187 | with jsonlines.open(f"{run_id}.jsonl", mode="a", sort_keys=True) as js_logger:
188 | js_logger.write(blob)
189 |
190 |
191 | # === Voltron Models ===
192 | def log_vcond_train_update(
193 | epoch: int,
194 | global_step: int,
195 | run_id: str,
196 | train_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
197 | lr: float,
198 | reconstruction_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
199 | step_times: List[float],
200 | ) -> None:
201 | train_loss = torch.stack(list(train_losses)).mean()
202 | reconstruction_loss = torch.stack(list(reconstruction_losses)).mean()
203 | average_step_time = np.mean(list(step_times))
204 |
205 | # Console Logging --> Just log the aggregated train loss...
206 | xm.master_print(
207 | f"Epoch {epoch:03d}, Global Step {global_step:06d} || LR :: {lr:.6f} -- Train Loss :: {train_loss:.4f}"
208 | )
209 |
210 | # Log to Weights & Biases + JSONL
211 | blob = {
212 | "Pretrain/Step": global_step,
213 | "Pretrain/Epoch": epoch,
214 | "Pretrain/V-Cond Train Loss": train_loss.item(),
215 | "Pretrain/Reconstruction Loss": reconstruction_loss.item(),
216 | "Pretrain/Learning Rate": lr,
217 | "Pretrain/Step Time": average_step_time,
218 | }
219 | wandb.log(blob, step=global_step)
220 | with jsonlines.open(f"{run_id}.jsonl", mode="a", sort_keys=True) as js_logger:
221 | js_logger.write(blob)
222 |
223 |
224 | def log_vdual_train_update(
225 | epoch: int,
226 | global_step: int,
227 | run_id: str,
228 | train_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
229 | lr: float,
230 | reconstruction_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
231 | zero_reconstruction_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
232 | k_reconstruction_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
233 | step_times: List[float],
234 | ) -> None:
235 | train_loss = torch.stack(list(train_losses)).mean()
236 | reconstruction_loss = torch.stack(list(reconstruction_losses)).mean()
237 | zero_reconstruction_loss = torch.stack(list(zero_reconstruction_losses)).mean()
238 | k_reconstruction_loss = torch.stack(list(k_reconstruction_losses)).mean()
239 | average_step_time = np.mean(list(step_times))
240 |
241 | # Console Logging --> Just log the aggregated train loss...
242 | xm.master_print(
243 | f"Epoch {epoch:03d}, Global Step {global_step:06d} || LR :: {lr:.6f} -- Train Loss :: {train_loss:.4f}"
244 | )
245 |
246 | # Log to Weights & Biases + JSONL
247 | blob = {
248 | "Pretrain/Step": global_step,
249 | "Pretrain/Epoch": epoch,
250 | "Pretrain/V-Dual Train Loss": train_loss.item(),
251 | "Pretrain/Reconstruction Loss": reconstruction_loss.item(),
252 | "Pretrain/Zero Reconstruction Loss": zero_reconstruction_loss.item(),
253 | "Pretrain/K Reconstruction Loss": k_reconstruction_loss.item(),
254 | "Pretrain/Learning Rate": lr,
255 | "Pretrain/Step Time": average_step_time,
256 | }
257 | wandb.log(blob, step=global_step)
258 | with jsonlines.open(f"{run_id}.jsonl", mode="a", sort_keys=True) as js_logger:
259 | js_logger.write(blob)
260 |
261 |
262 | def log_vgen_train_update(
263 | epoch: int,
264 | global_step: int,
265 | run_id: str,
266 | train_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
267 | lr: float,
268 | reconstruction_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
269 | lm_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
270 | lm_ppl: List[torch.Tensor],
271 | zero_reconstruction_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
272 | k_reconstruction_losses: List[torch.Tensor],
273 | step_times: List[float],
274 | ) -> None:
275 | train_loss = torch.stack(list(train_losses)).mean()
276 | reconstruction_loss = torch.stack(list(reconstruction_losses)).mean()
277 | lm_loss = torch.stack(list(lm_losses)).mean()
278 | lm_perplexity = torch.stack(list(lm_ppl)).mean()
279 | zero_reconstruction_loss = torch.stack(list(zero_reconstruction_losses)).mean()
280 | k_reconstruction_loss = torch.stack(list(k_reconstruction_losses)).mean()
281 | average_step_time = np.mean(list(step_times))
282 |
283 | # Console Logging --> Just log the aggregated train loss...
284 | xm.master_print(
285 | f"Epoch {epoch:03d}, Global Step {global_step:06d} || LR :: {lr:.6f} -- Train Loss :: {train_loss:.4f} --"
286 | f" Reconstruction Loss {reconstruction_loss:.4f} -- LM Loss {lm_loss:.4f}"
287 | )
288 |
289 | # Log to Weights & Biases + JSONL
290 | blob = {
291 | "Pretrain/Step": global_step,
292 | "Pretrain/Epoch": epoch,
293 | "Pretrain/V-Gen Train Loss": train_loss.item(),
294 | "Pretrain/Reconstruction Loss": reconstruction_loss.item(),
295 | "Pretrain/CLM Loss": lm_loss.item(),
296 | "Pretrain/CLM Perplexity": lm_perplexity.item(),
297 | "Pretrain/LM Loss": lm_loss.item(),
298 | "Pretrain/LM Perplexity": lm_perplexity.item(),
299 | "Pretrain/Zero Reconstruction Loss": zero_reconstruction_loss.item(),
300 | "Pretrain/K Reconstruction Loss": k_reconstruction_loss.item(),
301 | "Pretrain/Learning Rate": lr,
302 | "Pretrain/Step Time": average_step_time,
303 | }
304 | wandb.log(blob, step=global_step)
305 | with jsonlines.open(f"{run_id}.jsonl", mode="a", sort_keys=True) as js_logger:
306 | js_logger.write(blob)
307 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 3 |
3 |  3 |
3 |