 3 |
3 | All about orthogonal polynomials.
4 | 5 | 6 | [](https://pypi.org/project/orthopy) 7 | [](https://pypi.org/pypi/orthopy/) 8 | [](https://github.com/nschloe/orthopy) 9 | [](https://pepy.tech/project/orthopy) 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | [](https://discord.gg/hnTJ5MRX2Y) 14 | [](https://github.com/nschloe/orthopy) 15 | 16 | orthopy provides various orthogonal polynomial classes for 17 | [lines](#line-segment--1-1-with-weight-function-1-x%CE%B1-1-x%CE%B2), 18 | [triangles](#triangle-42), 19 | [disks](#disk-s2), 20 | [spheres](#sphere-u2), 21 | [n-cubes](#n-cube-cn), 22 | [the nD space with weight function exp(-r2)](#nd-space-with-weight-function-exp-r2-enr2) 23 | and more. 24 | All computations are done using numerically stable recurrence schemes. Furthermore, all 25 | functions are fully vectorized and can return results in _exact arithmetic_. 26 | 27 | ### Installation 28 | 29 | Install orthopy [from PyPI](https://pypi.org/project/orthopy/) with 30 | 31 | ``` 32 | pip install orthopy 33 | ``` 34 | 35 | ### How to get a license 36 | 37 | Licenses for personal and academic use can be purchased 38 | [here](https://buy.stripe.com/aEUg1H38OgDw5qMfZ3). 39 | You'll receive a confirmation email with a license key. 40 | Install the key with 41 | 42 | ``` 43 | plm add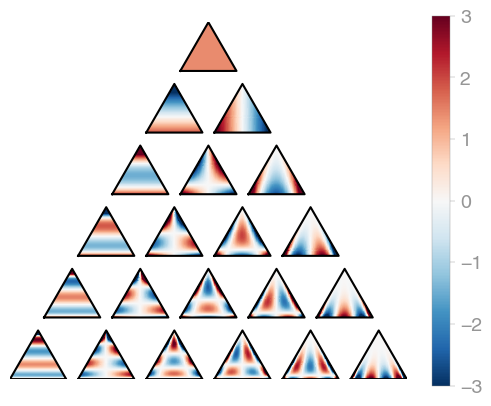 223 |
224 | orthopy's triangle orthogonal polynomials are evaluated in terms of [barycentric
225 | coordinates](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barycentric_coordinate_system), so the
226 | `X.shape[0]` has to be 3.
227 |
228 | ```python
229 | import orthopy
230 |
231 | bary = [0.1, 0.7, 0.2]
232 | evaluator = orthopy.t2.Eval(bary, "normal")
233 | ```
234 |
235 | ### Disk (_S2_)
236 |
237 | |
223 |
224 | orthopy's triangle orthogonal polynomials are evaluated in terms of [barycentric
225 | coordinates](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barycentric_coordinate_system), so the
226 | `X.shape[0]` has to be 3.
227 |
228 | ```python
229 | import orthopy
230 |
231 | bary = [0.1, 0.7, 0.2]
232 | evaluator = orthopy.t2.Eval(bary, "normal")
233 | ```
234 |
235 | ### Disk (_S2_)
236 |
237 | | 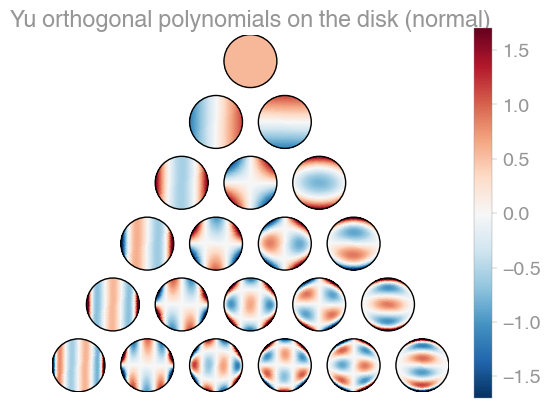 |
|  |
|  |
238 | | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
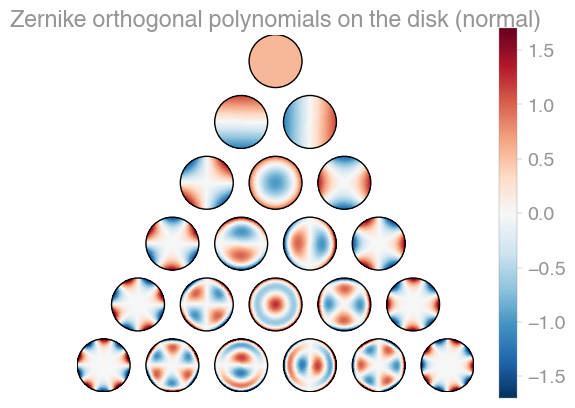
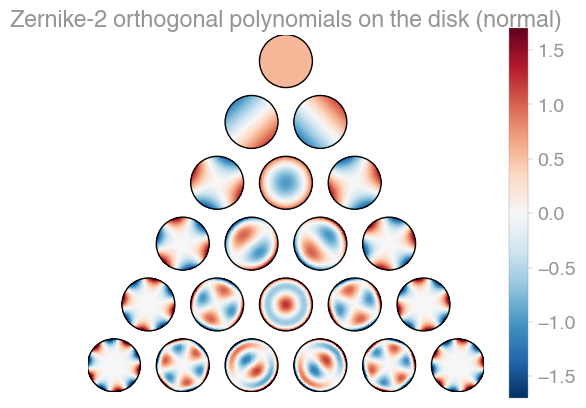
239 | | Xu | [Zernike](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zernike_polynomials) | Zernike 2 |
240 |
241 | orthopy contains several families of orthogonal polynomials on the unit disk: After
242 | [Xu](https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.02709),
243 | [Zernike](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zernike_polynomials), and a simplified version
244 | of Zernike polynomials.
245 |
246 | ```python
247 | import orthopy
248 |
249 | x = [0.1, -0.3]
250 |
251 | evaluator = orthopy.s2.xu.Eval(x, "normal")
252 | # evaluator = orthopy.s2.zernike.Eval(x, "normal")
253 | # evaluator = orthopy.s2.zernike2.Eval(x, "normal")
254 | ```
255 |
256 | ### Sphere (_U3_)
257 |
258 |
|
238 | | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
239 | | Xu | [Zernike](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zernike_polynomials) | Zernike 2 |
240 |
241 | orthopy contains several families of orthogonal polynomials on the unit disk: After
242 | [Xu](https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.02709),
243 | [Zernike](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zernike_polynomials), and a simplified version
244 | of Zernike polynomials.
245 |
246 | ```python
247 | import orthopy
248 |
249 | x = [0.1, -0.3]
250 |
251 | evaluator = orthopy.s2.xu.Eval(x, "normal")
252 | # evaluator = orthopy.s2.zernike.Eval(x, "normal")
253 | # evaluator = orthopy.s2.zernike2.Eval(x, "normal")
254 | ```
255 |
256 | ### Sphere (_U3_)
257 |
258 | 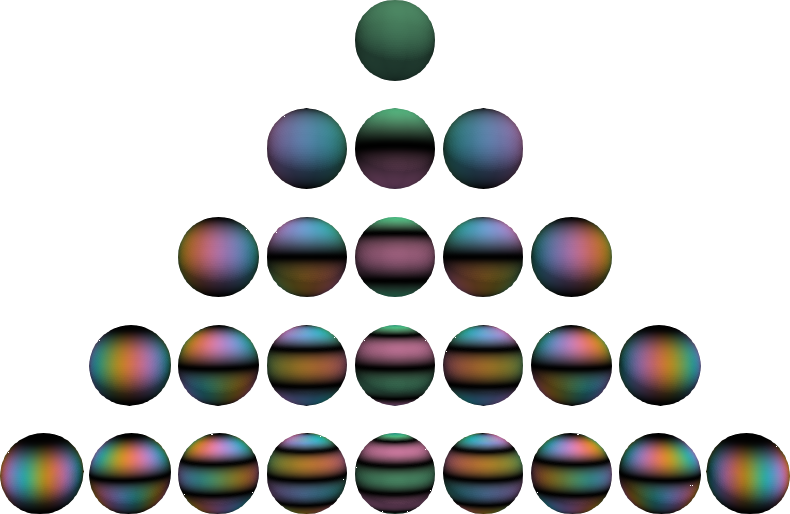 259 |
260 | Complex-valued _spherical harmonics,_ (black=zero, green=real positive,
261 | pink=real negative, blue=imaginary positive, yellow=imaginary negative). The
262 | functions in the middle are real-valued. The complex angle takes _n_ turns on
263 | the nth level.
264 |
265 |
266 |
267 | ```python
268 | evaluator = orthopy.u3.EvalCartesian(
269 | x,
270 | scaling="quantum mechanic" # or "acoustic", "geodetic", "schmidt"
271 | )
272 |
273 | evaluator = orthopy.u3.EvalSpherical(
274 | theta_phi, # polar, azimuthal angles
275 | scaling="quantum mechanic" # or "acoustic", "geodetic", "schmidt"
276 | )
277 | ```
278 |
279 |
280 |
281 |
282 |
283 |
284 |
285 |
286 |
287 |
288 |
289 |
290 | ### _n_-Cube (_Cn_)
291 |
292 | |
259 |
260 | Complex-valued _spherical harmonics,_ (black=zero, green=real positive,
261 | pink=real negative, blue=imaginary positive, yellow=imaginary negative). The
262 | functions in the middle are real-valued. The complex angle takes _n_ turns on
263 | the nth level.
264 |
265 |
266 |
267 | ```python
268 | evaluator = orthopy.u3.EvalCartesian(
269 | x,
270 | scaling="quantum mechanic" # or "acoustic", "geodetic", "schmidt"
271 | )
272 |
273 | evaluator = orthopy.u3.EvalSpherical(
274 | theta_phi, # polar, azimuthal angles
275 | scaling="quantum mechanic" # or "acoustic", "geodetic", "schmidt"
276 | )
277 | ```
278 |
279 |
280 |
281 |
282 |
283 |
284 |
285 |
286 |
287 |
288 |
289 |
290 | ### _n_-Cube (_Cn_)
291 |
292 | | 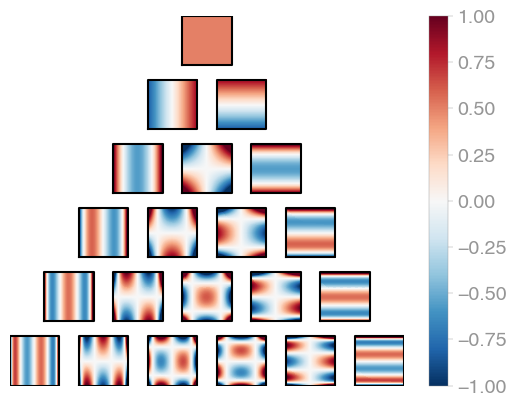 |
| 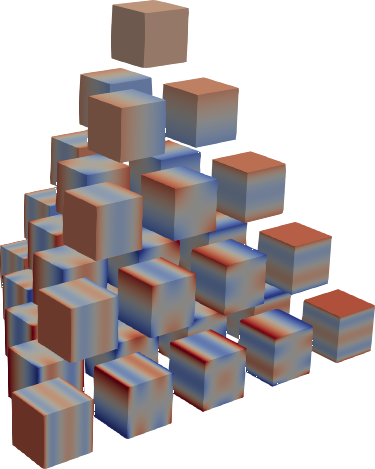 |
293 | | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
294 | | C1 (Legendre) | C2 | C3 |
295 |
296 | Jacobi product polynomials.
297 | All polynomials are normalized on the n-dimensional cube. The dimensionality is
298 | determined by `X.shape[0]`.
299 |
300 |
301 |
302 | ```python
303 | evaluator = orthopy.cn.Eval(X, alpha=0, beta=0)
304 | values, degrees = next(evaluator)
305 | ```
306 |
307 | ### nD space with weight function exp(-r2) (_Enr2_)
308 |
309 | |
|
293 | | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
294 | | C1 (Legendre) | C2 | C3 |
295 |
296 | Jacobi product polynomials.
297 | All polynomials are normalized on the n-dimensional cube. The dimensionality is
298 | determined by `X.shape[0]`.
299 |
300 |
301 |
302 | ```python
303 | evaluator = orthopy.cn.Eval(X, alpha=0, beta=0)
304 | values, degrees = next(evaluator)
305 | ```
306 |
307 | ### nD space with weight function exp(-r2) (_Enr2_)
308 |
309 | | 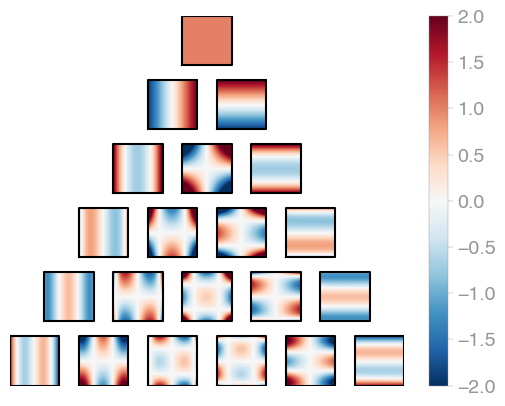 |
| 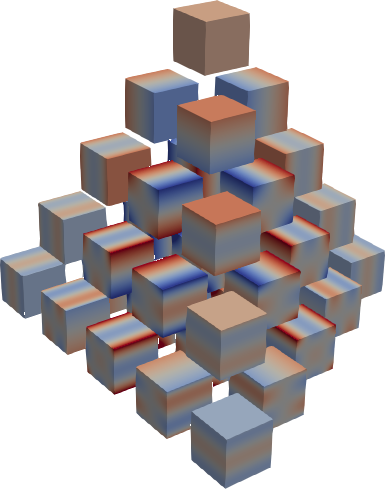 |
310 | | :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
311 | | _E1r2_ | _E2r2_ | _E3r2_ |
312 |
313 | Hermite product polynomials.
314 | All polynomials are normalized over the measure. The dimensionality is determined by
315 | `X.shape[0]`.
316 |
317 |
318 |
319 | ```python
320 | evaluator = orthopy.enr2.Eval(
321 | x,
322 | standardization="probabilists" # or "physicists"
323 | )
324 | values, degrees = next(evaluator)
325 | ```
326 |
327 | ### Other tools
328 |
329 | - Generating recurrence coefficients for 1D domains with
330 | [Stieltjes](https://github.com/nschloe/orthopy/wiki/Generating-1D-recurrence-coefficients-for-a-given-weight#stieltjes),
331 | [Golub-Welsch](https://github.com/nschloe/orthopy/wiki/Generating-1D-recurrence-coefficients-for-a-given-weight#golub-welsch),
332 | [Chebyshev](https://github.com/nschloe/orthopy/wiki/Generating-1D-recurrence-coefficients-for-a-given-weight#chebyshev), and
333 | [modified
334 | Chebyshev](https://github.com/nschloe/orthopy/wiki/Generating-1D-recurrence-coefficients-for-a-given-weight#modified-chebyshev).
335 |
336 | - The the sanity of recurrence coefficients with test 3 from [Gautschi's article](https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02218441):
337 | computing the weighted sum of orthogonal polynomials:
338 |
339 |
340 | ```python
341 | orthopy.tools.gautschi_test_3(moments, alpha, beta)
342 | ```
343 |
344 | - [Clenshaw algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Clenshaw_algorithm) for
345 | computing the weighted sum of orthogonal polynomials:
346 |
347 | ```python
348 | vals = orthopy.c1.clenshaw(a, alpha, beta, t)
349 | ```
350 |
351 | ### Relevant publications
352 |
353 | - [Robert C. Kirby, Singularity-free evaluation of collapsed-coordinate orthogonal polynomials, ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software (TOMS), Volume 37, Issue 1, January 2010](https://doi.org/10.1145/1644001.1644006)
354 | - [Abedallah Rababah, Recurrence Relations for Orthogonal Polynomials on Triangular Domains, MDPI Mathematics 2016, 4(2)](https://doi.org/10.3390/math4020025)
355 | - [Yuan Xu, Orthogonal polynomials of several variables, arxiv.org, January 2017](https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.02709)
356 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
310 | | :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
311 | | _E1r2_ | _E2r2_ | _E3r2_ |
312 |
313 | Hermite product polynomials.
314 | All polynomials are normalized over the measure. The dimensionality is determined by
315 | `X.shape[0]`.
316 |
317 |
318 |
319 | ```python
320 | evaluator = orthopy.enr2.Eval(
321 | x,
322 | standardization="probabilists" # or "physicists"
323 | )
324 | values, degrees = next(evaluator)
325 | ```
326 |
327 | ### Other tools
328 |
329 | - Generating recurrence coefficients for 1D domains with
330 | [Stieltjes](https://github.com/nschloe/orthopy/wiki/Generating-1D-recurrence-coefficients-for-a-given-weight#stieltjes),
331 | [Golub-Welsch](https://github.com/nschloe/orthopy/wiki/Generating-1D-recurrence-coefficients-for-a-given-weight#golub-welsch),
332 | [Chebyshev](https://github.com/nschloe/orthopy/wiki/Generating-1D-recurrence-coefficients-for-a-given-weight#chebyshev), and
333 | [modified
334 | Chebyshev](https://github.com/nschloe/orthopy/wiki/Generating-1D-recurrence-coefficients-for-a-given-weight#modified-chebyshev).
335 |
336 | - The the sanity of recurrence coefficients with test 3 from [Gautschi's article](https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02218441):
337 | computing the weighted sum of orthogonal polynomials:
338 |
339 |
340 | ```python
341 | orthopy.tools.gautschi_test_3(moments, alpha, beta)
342 | ```
343 |
344 | - [Clenshaw algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Clenshaw_algorithm) for
345 | computing the weighted sum of orthogonal polynomials:
346 |
347 | ```python
348 | vals = orthopy.c1.clenshaw(a, alpha, beta, t)
349 | ```
350 |
351 | ### Relevant publications
352 |
353 | - [Robert C. Kirby, Singularity-free evaluation of collapsed-coordinate orthogonal polynomials, ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software (TOMS), Volume 37, Issue 1, January 2010](https://doi.org/10.1145/1644001.1644006)
354 | - [Abedallah Rababah, Recurrence Relations for Orthogonal Polynomials on Triangular Domains, MDPI Mathematics 2016, 4(2)](https://doi.org/10.3390/math4020025)
355 | - [Yuan Xu, Orthogonal polynomials of several variables, arxiv.org, January 2017](https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.02709)
356 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------