├── __init__.py
├── _shared
├── __init__.py
├── signwriting
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── test_signwriting.py
│ └── signwriting.py
├── tokenizers
│ ├── hamnosys
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── HamNoSysUnicode.ttf
│ │ └── hamnosys_tokenizer.py
│ ├── signwriting
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── signwriting_tokenizer.py
│ │ └── test_signwriting_tokenizer.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── dummy_tokenizer.py
│ ├── sign_language_tokenizer.py
│ └── base_tokenizer.py
├── models
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── README.md
│ └── pose_encoder.py
├── collator
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── collator.py
├── tfds_dataset.py
└── pose_utils.py
├── pose_to_segments
├── __init__.py
└── README.md
├── pose_to_text
├── __init__.py
├── tests
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── model_test.py
├── README.md
├── batch.py
├── train.py
├── dataset.py
├── model.py
├── IDEA.md
├── IDEA-CLIP.md
└── configs
│ └── default.yaml
├── pose_to_video
├── __init__.py
└── README.md
├── text_to_pose
├── __init__.py
├── ham2pose
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── README.md
├── diffusion
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── src
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── metrics
│ │ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ │ ├── dtw.py
│ │ │ └── mse.py
│ │ ├── model
│ │ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ │ ├── image_encoder.py
│ │ │ ├── distribution.py
│ │ │ ├── masked_loss.py
│ │ │ ├── text_encoder.py
│ │ │ ├── schedule.py
│ │ │ └── iterative_decoder.py
│ │ ├── args.py
│ │ ├── data.py
│ │ ├── train.py
│ │ └── pred.py
│ ├── tests
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── distribution_model_test.py
│ │ ├── schedule_test.py
│ │ ├── tokenizer_test.py
│ │ ├── data_test.py
│ │ ├── model_overfit_test.py
│ │ └── model_test.py
│ ├── requirements.txt
│ ├── assets
│ │ ├── loss.png
│ │ └── example
│ │ │ ├── 494_GSL_pred.gif
│ │ │ ├── 494_GSL_text.png
│ │ │ ├── 494_GSL_other.gif
│ │ │ └── 494_GSL_original.gif
│ ├── sweep.yaml
│ ├── IDEA.md
│ └── README.md
└── README.md
├── text_to_text
├── __init__.py
├── README.md
└── video_to_text_idea.md
├── video_to_pose
├── __init__.py
├── tmp_draw.py
├── directory.py
└── bin.py
├── .gitignore
├── Makefile
├── .github
└── workflows
│ ├── text_to_pose.yaml
│ ├── text_to_text.yaml
│ ├── _shared.yaml
│ ├── pose_to_text.yaml
│ ├── video_to_pose.yaml
│ └── pose_to_segments.yaml
├── .pylintrc
├── pyproject.toml
└── README.md
/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pose_to_segments/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pose_to_text/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pose_to_video/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_text/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/video_to_pose/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/signwriting/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pose_to_text/tests/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/ham2pose/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/src/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/tokenizers/hamnosys/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/tokenizers/signwriting/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/tests/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/src/metrics/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/src/model/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/models/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .pose_encoder import *
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/requirements.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # WANDB Video feature
2 | moviepy
3 | imageio
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/collator/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .collator import collate_tensors, zero_pad_collator
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pose_to_video/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Migrated to https://github.com/sign-language-processing/pose-to-video
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pose_to_segments/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Migrated to https://github.com/sign-language-processing/segmentation
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/assets/loss.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sign-language-processing/transcription/main/text_to_pose/diffusion/assets/loss.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/tokenizers/hamnosys/HamNoSysUnicode.ttf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sign-language-processing/transcription/main/_shared/tokenizers/hamnosys/HamNoSysUnicode.ttf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/assets/example/494_GSL_pred.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sign-language-processing/transcription/main/text_to_pose/diffusion/assets/example/494_GSL_pred.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/assets/example/494_GSL_text.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sign-language-processing/transcription/main/text_to_pose/diffusion/assets/example/494_GSL_text.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/assets/example/494_GSL_other.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sign-language-processing/transcription/main/text_to_pose/diffusion/assets/example/494_GSL_other.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/assets/example/494_GSL_original.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sign-language-processing/transcription/main/text_to_pose/diffusion/assets/example/494_GSL_original.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .idea/
2 | __pycache__
3 | .pytest_cache
4 | sign_transcription.egg-info/
5 | build/
6 | models/
7 | lightning_logs/
8 | wandb/
9 | pose_to_segments/PRIVATE.md
10 | slurm-**.out
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/tokenizers/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .hamnosys.hamnosys_tokenizer import HamNoSysTokenizer
2 | from .sign_language_tokenizer import SignLanguageTokenizer
3 | from .signwriting.signwriting_tokenizer import SignWritingTokenizer
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Text-to-Pose
2 |
3 | Text to pose models for sign language pose generation from a text sequence.
4 |
5 | - [Ham2Pose](ham2pose) - Animating HamNoSys into Pose Sequences
6 | - [Diffusion](diffusion) - A generic framework supporting HamNoSys, SignWriting, and any generic text
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/src/model/image_encoder.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | from torch import nn
3 |
4 |
5 | class ImageEncoderModel(nn.Module):
6 |
7 | def __init__(self):
8 | super().__init__()
9 | raise NotImplementedError()
10 |
11 | def forward(self, images: torch.Tensor):
12 | raise NotImplementedError()
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/video_to_pose/tmp_draw.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from pose_format import Pose
2 | from pose_format.pose_visualizer import PoseVisualizer
3 |
4 | with open("high-res.pose", "rb") as f:
5 | pose = Pose.read(f.read())
6 |
7 | pose.body.fps = 29.970030
8 |
9 | v = PoseVisualizer(pose)
10 |
11 |
12 | v.save_video("high-res-pose.mp4", v.draw_on_video("high-res.mp4"))
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_text/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Text-to-Text
2 |
3 | Translation between spoken and signed language texts.
4 |
5 | Moved to [signbank-plus](https://github.com/sign-language-processing/signbank-plus)
6 |
7 | ## Main Idea
8 |
9 | We use [bergamot](https://browser.mt/) to train machine translation models between spoken and signed language texts (as
10 | SignWriting or HamNoSys).
11 | These models are then available for inference both on server side, and in the browser for offline translation.
12 |
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Makefile:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .PHONY: check format test
2 |
3 | packages=pose_to_segments pose_to_text _shared text_to_pose text_to_text video_to_pose pose_to_video
4 |
5 | # Check formatting issues
6 | check:
7 | pylint --rcfile=.pylintrc ${packages}
8 | yapf -dr ${packages}
9 | #flake8 --max-line-length 120 ${packages}
10 |
11 | # Format source code automatically
12 | format:
13 | isort --profile black ${packages}
14 | yapf -ir ${packages}
15 |
16 | # Run tests for the package
17 | test:
18 | python -m pytest
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pose_to_text/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Pose-to-Text
2 |
3 | Pose to text model, for text generation from a sign language pose sequence.
4 |
5 | ## Main Idea
6 |
7 | An autoregressive seq2seq model, encoding poses, and decoding text. (Using JoeyNMT)
8 |
9 | To get SignWriting to work, need to modify the model:
10 | 1. self.trg_embed should take the tokenized signwriting and draw a sequence of it, at every step
11 | 2. decoder predicts from base/rotation/number distribution, it decides.
12 | 1. In test time, we can constrain it to predict the correct part. (set -inf / 0)
13 |
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pose_to_text/batch.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | from joeynmt.batch import Batch
3 |
4 |
5 | class SignBatch(Batch):
6 |
7 | def __init__(self, device: torch.device, **kwargs):
8 | super().__init__(device=device, **kwargs)
9 | self.src_mask = self._pose_mask(device)
10 |
11 | def _pose_mask(self, device: torch.device) -> torch.Tensor:
12 | max_len = self.src_length.max().item()
13 | mask = torch.arange(max_len, device=device)[None, :] < self.src_length[:, None]
14 | mask = torch.unsqueeze(mask, dim=1)
15 | return mask
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/ham2pose/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Ham2Pose: Animating Sign Language Notation into Pose Sequences
2 |
3 | Ham2Pose allows you to animate the HamNoSys notation into pose sequences. It was forked from
4 | our [diffusion](../diffusion) implementation and have achieved great results.
5 |
6 | - GitHub: https://github.com/rotem-shalev/Ham2Pose
7 | - Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.13613
8 | - Website: https://rotem-shalev.github.io/ham-to-pose/
9 |
10 |
11 |  12 |
12 |
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/src/model/distribution.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | from torch import nn
3 |
4 |
5 | class DistributionPredictionModel(nn.Module):
6 |
7 | def __init__(self, input_size: int):
8 | super().__init__()
9 |
10 | self.fc_mu = nn.Linear(input_size, 1)
11 | self.fc_var = nn.Linear(input_size, 1)
12 |
13 | def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor):
14 | mu = self.fc_mu(x)
15 | if not self.training: # In test time, just predict the mean
16 | return mu
17 |
18 | log_var = self.fc_var(x)
19 | # sample z from q
20 | std = torch.exp(log_var / 2)
21 |
22 | q = torch.distributions.Normal(mu, std)
23 | return q.rsample()
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/text_to_pose.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: Text-to-Pose
2 |
3 |
4 | on:
5 | push:
6 | branches: [ master, main ]
7 | pull_request:
8 | branches: [ master, main ]
9 | paths-ignore:
10 | - 'pose_to_segments/**'
11 | - 'text_to_text/**'
12 | - 'pose_to_text/**'
13 | - 'video_to_pose/**'
14 | - 'pose_to_video/**'
15 |
16 |
17 | jobs:
18 | test:
19 | name: text-to-pose
20 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
21 |
22 | steps:
23 | - uses: actions/checkout@v3
24 | - uses: actions/setup-python@v4
25 | with:
26 | python-version: '3.10'
27 |
28 | - name: Install Requirements
29 | run: pip install .[dev]
30 |
31 | - name: Lint Code
32 | run: pylint text_to_pose
33 |
34 | - name: Run tests
35 | run: pytest text_to_pose
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/text_to_text.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: Text-to-Text
2 |
3 |
4 | on:
5 | push:
6 | branches: [ master, main ]
7 | pull_request:
8 | branches: [ master, main ]
9 | paths-ignore:
10 | - 'pose_to_segments/**'
11 | - 'text_to_pose/**'
12 | - 'pose_to_text/**'
13 | - 'video_to_pose/**'
14 | - 'pose_to_video/**'
15 |
16 |
17 | jobs:
18 | test:
19 | name: text-to-text
20 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
21 |
22 | steps:
23 | - uses: actions/checkout@v3
24 | - uses: actions/setup-python@v4
25 | with:
26 | python-version: '3.10'
27 |
28 | - name: Install Requirements
29 | run: pip install .[dev]
30 |
31 | - name: Lint Code
32 | run: pylint text_to_text
33 |
34 | - name: Run tests
35 | run: pytest text_to_text
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/_shared.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: Shared
2 |
3 |
4 | on:
5 | push:
6 | branches: [ master, main ]
7 | pull_request:
8 | branches: [ master, main ]
9 | paths-ignore:
10 | - 'pose_to_segments/**'
11 | - 'text_to_pose/**'
12 | - 'pose_to_video/**'
13 | - 'video_to_pose/**'
14 | - 'text_to_text/**'
15 | - 'pose_to_text/**'
16 |
17 |
18 | jobs:
19 | test:
20 | name: _shared
21 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
22 |
23 | steps:
24 | - uses: actions/checkout@v3
25 | - uses: actions/setup-python@v4
26 | with:
27 | python-version: '3.10'
28 |
29 | - name: Install Requirements
30 | run: pip install .[dev]
31 |
32 | - name: Lint Code
33 | run: pylint _shared
34 |
35 | - name: Run tests
36 | run: pytest _shared
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/pose_to_text.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: Pose-to-Text
2 |
3 |
4 | on:
5 | push:
6 | branches: [ master, main ]
7 | pull_request:
8 | branches: [ master, main ]
9 | paths-ignore:
10 | - 'text_to_pose/**'
11 | - 'text_to_text/**'
12 | - 'pose_to_text/**'
13 | - 'video_to_pose/**'
14 | - 'pose_to_video/**'
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 | jobs:
19 | test:
20 | name: pose-to-text
21 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
22 |
23 | steps:
24 | - uses: actions/checkout@v3
25 | - uses: actions/setup-python@v4
26 | with:
27 | python-version: '3.10'
28 |
29 | - name: Install Requirements
30 | run: pip install .[dev]
31 |
32 | - name: Lint Code
33 | run: pylint pose_to_text
34 |
35 | - name: Run tests
36 | run: pytest pose_to_text
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/video_to_pose.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: Video-to-Pose
2 |
3 |
4 | on:
5 | push:
6 | branches: [ master, main ]
7 | pull_request:
8 | branches: [ master, main ]
9 | paths-ignore:
10 | - 'pose_to_segments/**'
11 | - 'text_to_pose/**'
12 | - 'pose_to_text/**'
13 | - 'text_to_text/**'
14 | - 'pose_to_video/**'
15 |
16 |
17 | jobs:
18 | test:
19 | name: text-to-text
20 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
21 |
22 | steps:
23 | - uses: actions/checkout@v3
24 | - uses: actions/setup-python@v4
25 | with:
26 | python-version: '3.10'
27 |
28 | - name: Install Requirements
29 | run: pip install .[dev]
30 |
31 | - name: Lint Code
32 | run: pylint video_to_pose
33 |
34 | - name: Run tests
35 | run: pytest video_to_pose
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/pose_to_segments.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: Pose-to-Segments
2 |
3 |
4 | on:
5 | push:
6 | branches: [ master, main ]
7 | pull_request:
8 | branches: [ master, main ]
9 | paths-ignore:
10 | - 'text_to_pose/**'
11 | - 'text_to_text/**'
12 | - 'pose_to_text/**'
13 | - 'video_to_pose/**'
14 | - 'pose_to_video/**'
15 |
16 |
17 | jobs:
18 | test:
19 | name: pose-to-segments
20 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
21 |
22 | steps:
23 | - uses: actions/checkout@v3
24 | - uses: actions/setup-python@v4
25 | with:
26 | python-version: '3.10'
27 |
28 | - name: Install Requirements
29 | run: pip install .[dev]
30 |
31 | - name: Lint Code
32 | run: pylint pose_to_segments
33 |
34 | - name: Run tests
35 | run: pytest pose_to_segments
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.pylintrc:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [MASTER]
2 | init-hook='import sys; sys.path.append(".")'
3 | disable=
4 | W0221, # (arguments-differ)
5 | W0223, # (abstract-method)
6 | R0801, # (duplicate-code)
7 | R0901, # (too-many-ancestors)
8 | R0902, # (too-many-instance-attributes)
9 | R0903, # (too-few-public-methods)
10 | R0913, # (too-many-arguments)
11 | R0914, # (too-many-locals)
12 | R1732, # (consider-using-with)
13 | R1735, # (use-dict-literal)
14 | C0103, # (invalid-name)
15 | C0114, # (missing-module-docstring)
16 | C0115, # (missing-class-docstring)
17 | C0116 # (missing-function-docstring)
18 |
19 | [FORMAT]
20 | max-line-length=120
21 | good-names-rgxs=^[_a-z][_a-z0-9]?$
22 |
23 | [TYPECHECK]
24 | # List of members which are set dynamically and missed by Pylint inference
25 | # system, and so shouldn't trigger E1101 when accessed.
26 | generated-members=numpy.*, torch.*, cv2.*
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/src/model/masked_loss.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import torch
3 |
4 |
5 | def masked_loss(loss_type: str,
6 | tensor1: torch.Tensor,
7 | tensor2: torch.Tensor,
8 | confidence: torch.Tensor,
9 | model_num_steps: int = 10):
10 | # Loss by confidence. If missing data, no loss. If less likely data, fewer gradients.
11 | difference = tensor1 - tensor2
12 |
13 | if loss_type == 'l1':
14 | error = torch.abs(difference).sum(-1)
15 | elif loss_type == 'l2':
16 | error = torch.pow(difference, 2).sum(-1)
17 | else:
18 | raise NotImplementedError()
19 |
20 | # normalization of the loss (Section 5.4)
21 | num_steps_norm = np.log(model_num_steps)**2 if model_num_steps != 1 else 1
22 |
23 | return (error * confidence).mean() * num_steps_norm
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/tokenizers/dummy_tokenizer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from typing import List
2 |
3 | import torch
4 |
5 | from .base_tokenizer import BaseTokenizer
6 |
7 |
8 | class DummyTokenizer(BaseTokenizer):
9 |
10 | def __init__(self, **kwargs):
11 | super().__init__(['a'], **kwargs)
12 |
13 | def tokens_to_text(self, tokens: List[str]) -> str:
14 | return " ".join(tokens)
15 |
16 | def __call__(self, texts: List[str], is_tokenized=None, device=None):
17 | desired_shape = (len(texts), 3)
18 | return {
19 | "tokens_ids": torch.tensor([[4, 1, 3]], dtype=torch.long, device=device).expand(desired_shape),
20 | "positions": torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3]], dtype=torch.int, device=device).expand(desired_shape),
21 | "attention_mask": torch.tensor([[0, 0, 0]], dtype=torch.bool, device=device).expand(desired_shape),
22 | }
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/tests/distribution_model_test.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import unittest
2 |
3 | import torch
4 |
5 | from text_to_pose.diffusion.src.model.distribution import DistributionPredictionModel
6 |
7 |
8 | class DistributionModelTestCase(unittest.TestCase):
9 |
10 | def test_prediction_in_eval_should_be_consistent(self):
11 | model = DistributionPredictionModel(input_size=10)
12 | model.eval()
13 | tensor = torch.randn(size=[10])
14 | pred_1 = float(model(tensor))
15 | pred_2 = float(model(tensor))
16 |
17 | self.assertEqual(pred_1, pred_2)
18 |
19 | def test_prediction_in_eval_should_be_inconsistent(self):
20 | model = DistributionPredictionModel(input_size=10)
21 | model.train()
22 | tensor = torch.randn(size=[10])
23 | pred_1 = float(model(tensor))
24 | pred_2 = float(model(tensor))
25 |
26 | self.assertNotEqual(pred_1, pred_2)
27 |
28 |
29 | if __name__ == "__main__":
30 | unittest.main()
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/tokenizers/hamnosys/hamnosys_tokenizer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from pathlib import Path
2 | from typing import List
3 |
4 | from fontTools.ttLib import TTFont
5 |
6 | from ..base_tokenizer import BaseTokenizer
7 |
8 |
9 | class HamNoSysTokenizer(BaseTokenizer):
10 |
11 | def __init__(self, starting_index=None, **kwargs):
12 | self.font_path = Path(__file__).parent.joinpath("HamNoSysUnicode.ttf")
13 |
14 | with TTFont(self.font_path) as font:
15 | tokens = [chr(key) for key in font["cmap"].getBestCmap().keys()]
16 |
17 | super().__init__(tokens=tokens, starting_index=starting_index, **kwargs)
18 |
19 | def text_to_tokens(self, text: str) -> List[str]:
20 | return [self.bos_token] + list(text)
21 |
22 | def tokens_to_text(self, tokens: List[str]) -> str:
23 | if tokens[0] == self.bos_token:
24 | tokens = tokens[1:]
25 |
26 | return "".join(tokens)
27 |
28 |
29 | if __name__ == "__main__":
30 | tokenizer = HamNoSysTokenizer()
31 | print(tokenizer(["\ue000\ue071", "\ue000\ue071\ue012\ue029\ue03f\ue089\ue0c6\ue0d8"]))
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/tests/schedule_test.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import unittest
2 |
3 | import torch
4 |
5 | from text_to_pose.diffusion.src.model.schedule import get_alphas
6 |
7 |
8 | class ScheduleTestCase(unittest.TestCase):
9 |
10 | def test_alphas(self):
11 | betas = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1])
12 | alphas = get_alphas(betas).tolist()
13 |
14 | self.assertAlmostEqual(1 / 10, alphas[0], delta=1e-6)
15 | self.assertAlmostEqual(1 / 9, alphas[1], delta=1e-6)
16 | self.assertAlmostEqual(1 / 8, alphas[2], delta=1e-6)
17 | self.assertAlmostEqual(1 / 7, alphas[3], delta=1e-6)
18 | self.assertAlmostEqual(1 / 6, alphas[4], delta=1e-6)
19 | self.assertAlmostEqual(1 / 5, alphas[5], delta=1e-6)
20 | self.assertAlmostEqual(1 / 4, alphas[6], delta=1e-6)
21 | self.assertAlmostEqual(1 / 3, alphas[7], delta=1e-6)
22 | self.assertAlmostEqual(1 / 2, alphas[8], delta=1e-6)
23 | self.assertAlmostEqual(1 / 1, alphas[9], delta=1e-6)
24 |
25 |
26 | if __name__ == "__main__":
27 | unittest.main()
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/video_to_pose/directory.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import argparse
2 | import os
3 |
4 | from tqdm import tqdm
5 |
6 | from video_to_pose.bin import pose_video
7 |
8 |
9 | def find_missing_pose_files(directory: str):
10 | all_files = os.listdir(directory)
11 | mp4_files = [f for f in all_files if f.endswith(".mp4")]
12 | pose_files = {f.removesuffix(".pose") for f in all_files if f.endswith(".pose")}
13 | missing_pose_files = []
14 |
15 | for mp4_file in mp4_files:
16 | base_name = mp4_file.removesuffix(".mp4")
17 | if base_name not in pose_files:
18 | missing_pose_files.append(os.path.join(directory, mp4_file))
19 |
20 | return sorted(missing_pose_files)
21 |
22 |
23 | def main(directory: str):
24 | missing_pose_files = find_missing_pose_files(directory)
25 |
26 | for mp4_path in tqdm(missing_pose_files):
27 | pose_file_name = mp4_path.removesuffix(".mp4") + ".pose"
28 | pose_video(mp4_path, pose_file_name, 'mediapipe')
29 |
30 |
31 | if __name__ == "__main__":
32 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
33 | parser.add_argument("--directory", type=str, required=True)
34 | args = parser.parse_args()
35 |
36 | main(args.directory)
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pyproject.toml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [project]
2 | name = "sign-transcription"
3 | description = "Models involved in transcribing sign language"
4 | version = "0.0.1"
5 | authors = [
6 | { name = "Amit Moryossef", email = "amitmoryossef@gmail.com" }
7 | ]
8 | readme = "README.md"
9 | dependencies = [
10 | "joeynmt",
11 | "sentencepiece",
12 | "numpy",
13 | "opencv-python",
14 | "pose-format",
15 | "torch",
16 | "tqdm"
17 | ]
18 |
19 | [project.optional-dependencies]
20 | dev = [
21 | "tensorflow",
22 | "fonttools",
23 | "tensorflow-datasets",
24 | "sign-language-datasets",
25 | "wandb",
26 | "pytorch_lightning",
27 | "mediapipe",
28 | "scikit-learn",
29 | "pytest",
30 | "pylint"
31 | ]
32 |
33 | [tool.yapf]
34 | based_on_style = "google"
35 | column_limit = 120
36 |
37 | [tool.setuptools]
38 | packages = [
39 | "_shared",
40 |
41 | "video_to_pose",
42 |
43 | "pose_to_text",
44 |
45 | "text_to_pose",
46 |
47 | "text_to_text",
48 | ]
49 |
50 |
51 | [tool.pytest.ini_options]
52 | addopts = "-v"
53 | testpaths = [
54 | "_shared",
55 | "video_to_pose",
56 | "pose_to_text",
57 | "text_to_pose"
58 | ]
59 |
60 | [project.scripts]
61 | video_to_pose = "video_to_pose.bin:main"
62 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/sweep.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | command:
2 | - ${env}
3 | - /home/nlp/amit/libs/anaconda3/envs/transcription/bin/python
4 | - -m
5 | - ${program}
6 | - ${args}
7 |
8 | program: text_to_pose.diffusion.src.train
9 |
10 | method: bayes
11 |
12 | metric:
13 | goal: minimize
14 | name: validation_dtw_mje
15 |
16 | parameters:
17 | batch_size:
18 | distribution: int_uniform
19 | max: 64
20 | min: 16
21 | encoder_dim_feedforward:
22 | distribution: categorical
23 | values:
24 | - 512
25 | - 1024
26 | - 2048
27 | encoder_heads:
28 | distribution: categorical
29 | values:
30 | - 2
31 | - 4
32 | - 8
33 | hidden_dim:
34 | distribution: categorical
35 | values:
36 | - 64
37 | - 128
38 | - 256
39 | - 512
40 | learning_rate:
41 | distribution: log_uniform_values
42 | max: 1e-3
43 | min: 1e-5
44 | noise_epsilon:
45 | distribution: uniform
46 | max: 0.1
47 | min: 0.001
48 | num_steps:
49 | distribution: categorical
50 | values:
51 | - 4
52 | - 8
53 | - 16
54 | - 32
55 | - 64
56 | - 128
57 | pose_encoder_depth:
58 | distribution: int_uniform
59 | max: 8
60 | min: 2
61 | text_encoder_depth:
62 | distribution: int_uniform
63 | max: 4
64 | min: 1
65 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/src/metrics/dtw.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from numpy import ma
2 | from numpy.ma import MaskedArray
3 | from pose_format import PoseBody
4 | from scipy.spatial.distance import euclidean
5 | from fastdtw import fastdtw
6 |
7 |
8 | def masked_euclidean(point1: MaskedArray, point2: MaskedArray):
9 | if ma.is_masked(point1):
10 | # reference label keypoint is missing
11 | return 0
12 | elif ma.is_masked(point2):
13 | # reference label keypoint is not missing, other label keypoint is missing
14 | print("SHOULD NEVER GET HERE")
15 | return euclidean((0, 0), point2) / 2
16 | d = euclidean(point1, point2)
17 | return d
18 |
19 |
20 | def dynamic_time_warping_mean_joint_error(pose1: PoseBody, pose2: PoseBody):
21 | # Huang, W., Pan, W., Zhao, Z., & Tian, Q. (2021, October). Towards fast and high-quality sign language production.
22 | # In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia (pp. 3172-3181).
23 | frames, people, joints, _ = pose1.data.shape
24 | total_distance = 0
25 | for i in range(joints):
26 | trajectory1 = pose1.data[:, 0, i] # (frames, dim)
27 | trajectory2 = pose2.data[:, 0, i] # (frames, dim)
28 |
29 | distance, best_path = fastdtw(trajectory1, trajectory2, dist=masked_euclidean)
30 | total_distance += distance
31 |
32 | return total_distance
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/src/metrics/mse.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 |
3 |
4 | def pad_shorter_trajectory(trajectory1: np.ndarray, trajectory2: np.ndarray) -> (np.ndarray, np.ndarray):
5 | # Pad the shorter trajectory with zeros to make both trajectories the same length
6 | if len(trajectory1) < len(trajectory2):
7 | diff = len(trajectory2) - len(trajectory1)
8 | trajectory1 = np.concatenate((trajectory1, np.zeros((diff, 2))))
9 | elif len(trajectory2) < len(trajectory1):
10 | trajectory2 = np.concatenate((trajectory2, np.zeros((len(trajectory1) - len(trajectory2), 2))))
11 | return trajectory1, trajectory2
12 |
13 |
14 | def _squared_error(trajectory1: np.ndarray, trajectory2: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
15 | # Pad the shorter trajectory with zeros to make both trajectories the same length
16 | trajectory1, trajectory2 = pad_shorter_trajectory(trajectory1, trajectory2)
17 |
18 | # Calculate squared error and apply confidence mask
19 | return np.power(trajectory1 - trajectory2, 2).sum(-1)
20 |
21 |
22 | def masked_mse(trajectory1: np.ndarray, trajectory2: np.ndarray, confidence: np.ndarray) -> float:
23 | sq_error = _squared_error(trajectory1, trajectory2)
24 | return (sq_error * confidence).mean()
25 |
26 |
27 | def mse(trajectory1: np.ndarray, trajectory2: np.ndarray) -> float:
28 | sq_error = _squared_error(trajectory1, trajectory2)
29 | return sq_error.mean()
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/signwriting/test_signwriting.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import unittest
2 |
3 | from .signwriting import fsw_to_sign, join_signs
4 |
5 |
6 | class ParseSignCase(unittest.TestCase):
7 |
8 | def test_get_box(self):
9 | fsw = 'M123x456S1f720487x492'
10 | sign = fsw_to_sign(fsw)
11 | self.assertEqual(sign["box"]["symbol"], "M")
12 | self.assertEqual(sign["box"]["position"], (123, 456))
13 |
14 |
15 | class JoinSignsCase(unittest.TestCase):
16 |
17 | def test_join_two_characters(self):
18 | char_a = 'M507x507S1f720487x492'
19 | char_b = 'M507x507S14720493x485'
20 | result_sign = join_signs(char_a, char_b)
21 | self.assertEqual(result_sign, 'M500x500S1f720487x493S14720493x508')
22 |
23 | def test_join_alphabet_characters(self):
24 | chars = [
25 | "M510x508S1f720490x493", "M507x511S14720493x489", "M509x510S16d20492x490", "M508x515S10120492x485",
26 | "M508x508S14a20493x493", "M511x515S1ce20489x485", "M515x508S1f000486x493", "M515x508S11502485x493",
27 | "M511x510S19220490x491", "M519x518S19220498x499S2a20c482x483"
28 | ]
29 | result_sign = join_signs(*chars, spacing=10)
30 | # pylint: disable=line-too-long
31 | self.assertEqual(
32 | result_sign,
33 | 'M500x500S1f720490x362S14720493x387S16d20492x419S10120492x449S14a20493x489S1ce20489x514S1f000486x554S11502485x579S19220490x604S19220498x649S2a20c482x633' # noqa: E501
34 | )
35 |
36 |
37 | if __name__ == '__main__':
38 | unittest.main()
39 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/tests/tokenizer_test.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import unittest
2 |
3 | import torch
4 |
5 | from _shared.tokenizers import HamNoSysTokenizer
6 |
7 |
8 | class TokenizerTestCase(unittest.TestCase):
9 |
10 | def test_expected_token_id(self):
11 | tokenizer = HamNoSysTokenizer()
12 | tokenized = tokenizer(["\ue000\ue071"])
13 | self.assertEqual(tokenized['tokens_ids'][0][0], 2)
14 | self.assertEqual(tokenized['tokens_ids'][0][1], 13)
15 | self.assertEqual(tokenized['tokens_ids'][0][2], 97)
16 |
17 | def test_multiple_sentence(self):
18 | expected = {
19 | 'tokens_ids':
20 | torch.tensor([[2, 13, 97, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
21 | [2, 13, 97, 30, 42, 58, 120, 178, 192]],
22 | dtype=torch.int32),
23 | 'positions':
24 | torch.tensor([[0, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
25 | [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]],
26 | dtype=torch.int32),
27 | 'attention_mask':
28 | torch.tensor([[False, False, False, True, True, True, True, True, True],
29 | [False, False, False, False, False, False, False, False, False]],
30 | dtype=torch.bool)
31 | }
32 |
33 | tokenizer = HamNoSysTokenizer()
34 | tokenized = tokenizer(["\ue000\ue071", "\ue000\ue071\ue012\ue029\ue03f\ue089\ue0c6\ue0d8"])
35 |
36 | for key, value in expected.items():
37 | self.assertTrue(torch.all(torch.eq(value, tokenized[key])))
38 |
39 |
40 | if __name__ == '__main__':
41 | unittest.main()
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/tokenizers/sign_language_tokenizer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from typing import List
2 |
3 | from .base_tokenizer import BaseTokenizer
4 | from .hamnosys.hamnosys_tokenizer import HamNoSysTokenizer
5 | from .signwriting.signwriting_tokenizer import SignWritingTokenizer
6 |
7 |
8 | class SignLanguageTokenizer(BaseTokenizer):
9 |
10 | def __init__(self, **kwargs) -> None:
11 | self.hamnosys_tokenizer = HamNoSysTokenizer(**kwargs)
12 | self.signwriting_tokenizer = SignWritingTokenizer(**kwargs, starting_index=len(self.hamnosys_tokenizer))
13 |
14 | super().__init__([])
15 |
16 | self.i2s = {**self.hamnosys_tokenizer.i2s, **self.signwriting_tokenizer.i2s}
17 | self.s2i = {**self.hamnosys_tokenizer.s2i, **self.signwriting_tokenizer.s2i}
18 |
19 | def tokenize(self, text: str, bos=False, eos=False) -> List[str]:
20 | if text.isascii():
21 | return self.signwriting_tokenizer.tokenize(text, bos=bos, eos=eos)
22 |
23 | return self.hamnosys_tokenizer.tokenize(text, bos=bos, eos=eos)
24 |
25 | def text_to_tokens(self, text: str) -> List[str]:
26 | if text.isascii():
27 | return self.signwriting_tokenizer.text_to_tokens(text)
28 |
29 | return self.hamnosys_tokenizer.text_to_tokens(text)
30 |
31 | def tokens_to_text(self, tokens: List[str]) -> str:
32 | if all(t.isascii() for t in tokens):
33 | return self.signwriting_tokenizer.tokens_to_text(tokens)
34 |
35 | return self.hamnosys_tokenizer.tokens_to_text(tokens)
36 |
37 | # pylint: disable=unused-argument
38 | def post_process(self, tokens: List[str], generate_unk: bool = True):
39 | """
40 | JoeyNMT expects this method to exist for BLEU calculation.
41 | """
42 | return " ".join(tokens)
43 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/collator/collator.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from typing import Dict, List, Tuple, Union
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 | import torch
5 | from pose_format.torch.masked import MaskedTensor, MaskedTorch
6 |
7 |
8 | def collate_tensors(batch: List, pad_value=0) -> Union[torch.Tensor, List]:
9 | datum = batch[0]
10 |
11 | if isinstance(datum, dict): # Recurse over dictionaries
12 | return zero_pad_collator(batch)
13 |
14 | if isinstance(datum, (int, np.int32)):
15 | return torch.tensor(batch, dtype=torch.long)
16 |
17 | if isinstance(datum, (MaskedTensor, torch.Tensor)):
18 | max_len = max(len(t) for t in batch)
19 | if max_len == 1:
20 | return torch.stack(batch)
21 |
22 | torch_cls = MaskedTorch if isinstance(datum, MaskedTensor) else torch
23 |
24 | new_batch = []
25 | for tensor in batch:
26 | missing = list(tensor.shape)
27 | missing[0] = max_len - tensor.shape[0]
28 |
29 | if missing[0] > 0:
30 | padding_tensor = torch.full(missing, fill_value=pad_value, dtype=tensor.dtype, device=tensor.device)
31 | tensor = torch_cls.cat([tensor, padding_tensor], dim=0)
32 |
33 | new_batch.append(tensor)
34 |
35 | return torch_cls.stack(new_batch, dim=0)
36 |
37 | return batch
38 |
39 |
40 | def zero_pad_collator(batch) -> Union[Dict[str, torch.Tensor], Tuple[torch.Tensor]]:
41 | datum = batch[0]
42 |
43 | # For strings
44 | if isinstance(datum, str):
45 | return batch
46 |
47 | # For tuples
48 | if isinstance(datum, tuple):
49 | return tuple(collate_tensors([b[i] for b in batch]) for i in range(len(datum)))
50 |
51 | # For dictionaries
52 | keys = datum.keys()
53 | return {k: collate_tensors([b[k] for b in batch]) for k in keys}
54 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/models/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Pose Encoder
2 |
3 | ## Current Implementation
4 |
5 | Given the pose data, sequence mask, and optionally additional sequence,
6 | this model uses a transformer to encode the sequences.
7 | It has a limited length (marked with `max_seq_size`) given that it relies on learned positional embeddings.
8 |
9 | It might not be the best we can do.
10 |
11 | ## New Implementation: TODO
12 |
13 | Naturally, a pose is visual. It has spatiotemporal information, with a strong bias towards neighboring frames.
14 | Therefore, we should use a CNN to encode the pose.
15 |
16 | Using the `FastAndUglyPoseVisualizer`, we can visualize each of the pose's components independently as an `Nx64x64` monochrome video.
17 |
18 | 
19 | 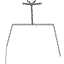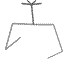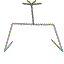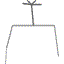
20 | 
21 | 
22 |
23 | The rational behind having each component as a separate video is that we want to cover as much as the video as possible, and avoid white space.
24 | To generate a video with hands and face clearly visible, we would need very high video resolution.
25 |
26 | While we can treat this as a `Nx64x64x4` tensor, it doesn't really makes sense to perform 4D convolutions.
27 | Instead, we can use a 3D CNN (`Nx64x64`), with multiple layers,
28 | to "compress" the `64x64` frames to a `256` dimensional vector, for example,
29 | and finally convolve over the `Nx256x4` tensor, or concatenate to `Nx1024` vectors, and encode them with a transformer.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/src/model/text_encoder.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from typing import List
2 |
3 | import torch
4 | from torch import nn
5 |
6 |
7 | class TextEncoderModel(nn.Module):
8 |
9 | def __init__(self,
10 | tokenizer,
11 | max_seq_size: int = 1000,
12 | hidden_dim: int = 128,
13 | num_layers: int = 2,
14 | dim_feedforward: int = 2048,
15 | encoder_heads=2):
16 | super().__init__()
17 |
18 | self.tokenizer = tokenizer
19 | self.max_seq_size = max_seq_size
20 |
21 | self.embedding = nn.Embedding(
22 | num_embeddings=len(tokenizer),
23 | embedding_dim=hidden_dim,
24 | padding_idx=tokenizer.pad_token_id,
25 | )
26 |
27 | self.positional_embedding = nn.Embedding(num_embeddings=max_seq_size, embedding_dim=hidden_dim)
28 |
29 | encoder_layer = nn.TransformerEncoderLayer(d_model=hidden_dim,
30 | nhead=encoder_heads,
31 | dim_feedforward=dim_feedforward,
32 | batch_first=True)
33 | self.encoder = nn.TransformerEncoder(encoder_layer, num_layers=num_layers)
34 |
35 | # Used to figure out the device of the model
36 | self.dummy_param = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(0))
37 |
38 | def forward(self, texts: List[str]):
39 | tokenized = self.tokenizer(texts, device=self.dummy_param.device)
40 | positional_embedding = self.positional_embedding(tokenized["positions"])
41 | embedding = self.embedding(tokenized["tokens_ids"]) + positional_embedding
42 |
43 | encoded = self.encoder(embedding, src_key_padding_mask=tokenized["attention_mask"])
44 |
45 | return {"data": encoded, "mask": tokenized["attention_mask"]}
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/video_to_pose/bin.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python
2 | import argparse
3 |
4 | import cv2
5 | from pose_format.utils.holistic import load_holistic
6 |
7 |
8 | def load_video_frames(cap: cv2.VideoCapture):
9 | while True:
10 | ret, frame = cap.read()
11 | if not ret:
12 | break
13 | yield cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
14 | cap.release()
15 |
16 |
17 | def pose_video(input_path: str, output_path: str, format: str):
18 | # Load video frames
19 | print('Loading video ...')
20 | cap = cv2.VideoCapture(input_path)
21 | width = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
22 | height = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
23 | fps = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))
24 | frames = load_video_frames(cap)
25 |
26 | # Perform pose estimation
27 | print('Estimating pose ...')
28 | if format == 'mediapipe':
29 | pose = load_holistic(frames,
30 | fps=fps,
31 | width=width,
32 | height=height,
33 | progress=True,
34 | additional_holistic_config={'model_complexity': 1})
35 | else:
36 | raise NotImplementedError('Pose format not supported')
37 |
38 | # Write
39 | print('Saving to disk ...')
40 | with open(output_path, "wb") as f:
41 | pose.write(f)
42 |
43 |
44 | def main():
45 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
46 | parser.add_argument('--format',
47 | choices=['mediapipe'],
48 | default='mediapipe',
49 | type=str,
50 | help='type of pose estimation to use')
51 | parser.add_argument('-i', required=True, type=str, help='path to input video file')
52 | parser.add_argument('-o', required=True, type=str, help='path to output pose file')
53 |
54 | args = parser.parse_args()
55 |
56 | pose_video(args.i, args.o, args.format)
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/src/model/schedule.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Taken from https://huggingface.co/blog/annotated-diffusion"""
2 |
3 | import torch
4 |
5 |
6 | def cosine_beta_schedule(timesteps, s=0.008):
7 | """
8 | cosine schedule as proposed in https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.09672
9 | """
10 | steps = timesteps + 1
11 | x = torch.linspace(0, timesteps, steps)
12 | alphas_cumprod = torch.cos(((x / timesteps) + s) / (1 + s) * torch.pi * 0.5)**2
13 | alphas_cumprod = alphas_cumprod / alphas_cumprod[0]
14 | betas = 1 - (alphas_cumprod[1:] / alphas_cumprod[:-1])
15 | return torch.clip(betas, 0.0001, 1)
16 |
17 |
18 | def linear_beta_schedule(timesteps):
19 | beta_start = 0.0001
20 | beta_end = 0.02
21 | return torch.linspace(beta_start, beta_end, timesteps)
22 |
23 |
24 | def quadratic_beta_schedule(timesteps):
25 | beta_start = 0.0001
26 | beta_end = 0.02
27 | return torch.linspace(beta_start**0.5, beta_end**0.5, timesteps)**2
28 |
29 |
30 | def sigmoid_beta_schedule(timesteps):
31 | beta_start = 0.0001
32 | beta_end = 0.02
33 | betas = torch.linspace(-6, 6, timesteps)
34 | return torch.sigmoid(betas) * (beta_end - beta_start) + beta_start
35 |
36 |
37 | def get_alphas(betas: torch.Tensor):
38 | """
39 | In train time at step n, we try to predict y from x_n = ((1-b_n)*x + b_n*y)
40 | In test time, we want to know how much to add to x for it to represent the next step's input.
41 | x_{n-1} + a_n*(y - a_{n-1}) = x_n
42 | (1-b_{n-1})*x + b_{n-1}*y + a_n*(y - ((1-b_{n-1})*x + b_{n-1}*y)) = (1-b_n)*x + b_n*y
43 | x - b_{n-1}*x + a_n*(1-b_{n-1})*(y-x) = x - b_n*x + b_n*y - b_{n-1}*y
44 | a_n*(1-b_{n-1})*(y-x) = - b_n*x + b_n*y - b_{n-1}*y + b_{n-1}*x
45 | a_n*(1-b_{n-1})*(y-x) = (b_n - b_{n-1})*(y-x)
46 | a_n = (b_n - b_{n-1}) / (1-b_{n-1})
47 | """
48 | alphas = []
49 | prev_beta = 0
50 | for beta in betas:
51 | alpha = (beta - prev_beta) / (1 - prev_beta)
52 | alphas.append(alpha)
53 | prev_beta = beta
54 | return torch.tensor(alphas)
55 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pose_to_text/tests/model_test.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import unittest
2 |
3 | import torch
4 | from joeynmt.vocabulary import Vocabulary
5 |
6 | from pose_to_text.batch import SignBatch
7 |
8 | from ..._shared.collator import collate_tensors
9 | from ..model import build_model
10 |
11 |
12 | class ModelTestCase(unittest.TestCase):
13 |
14 | def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
15 | super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
16 | self.pose_dim = (2, 2)
17 | self.seq_length = 5
18 |
19 | def model_setup(self):
20 | transformer_cfg = {
21 | "num_layers": 2,
22 | "num_heads": 2,
23 | "hidden_size": 10,
24 | "ff_size": 20,
25 | "dropout": 0.1,
26 | "emb_dropout": 0.1,
27 | "type": "transformer"
28 | }
29 | cfg = {
30 | "decoder": {
31 | **transformer_cfg, "embeddings": {
32 | "embedding_dim": 10
33 | }
34 | },
35 | "encoder": transformer_cfg,
36 | "pose_encoder": transformer_cfg,
37 | }
38 | model = build_model(pose_dims=self.pose_dim, cfg=cfg, trg_vocab=Vocabulary([]))
39 | model.log_parameters_list()
40 | model.loss_function = ("crossentropy", 0.0)
41 |
42 | return model
43 |
44 | def get_batch(self):
45 | return SignBatch(src=torch.rand(1, self.seq_length, *self.pose_dim),
46 | src_length=collate_tensors([self.seq_length]),
47 | trg=torch.zeros(1, self.seq_length, dtype=torch.long),
48 | trg_length=collate_tensors([self.seq_length]),
49 | device=torch.device("cpu"))
50 |
51 | def test_forward_expected_loss_finite(self):
52 | model = self.model_setup()
53 | batch = self.get_batch()
54 |
55 | loss = model(return_type="loss", **batch.__dict__)[0]
56 | self.assertNotEqual(float(loss), 0)
57 | self.assertTrue(torch.isfinite(loss))
58 |
59 |
60 | if __name__ == "__main__":
61 | unittest.main()
62 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/signwriting/signwriting.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import re
2 | from typing import List, Tuple, TypedDict
3 |
4 |
5 | class SignSymbol(TypedDict):
6 | symbol: str
7 | position: Tuple[int, int]
8 |
9 |
10 | class Sign(TypedDict):
11 | box: SignSymbol
12 | symbols: List[SignSymbol]
13 |
14 |
15 | def fsw_to_sign(fsw: str) -> Sign:
16 | box = re.match(r'([BLMR])(\d{3})x(\d{3})', fsw)
17 | box_symbol, x, y = box.groups() if box is not None else ("M", 500, 500)
18 |
19 | symbols = re.findall(r'(S[123][0-9a-f]{2}[0-5][0-9a-f])(\d{3})x(\d{3})', fsw)
20 |
21 | return {
22 | "box": {
23 | "symbol": box_symbol,
24 | "position": (int(x), int(y))
25 | },
26 | "symbols": [{
27 | "symbol": s[0],
28 | "position": (int(s[1]), int(s[2]))
29 | } for s in symbols]
30 | }
31 |
32 |
33 | def sign_to_fsw(sign: Sign) -> str:
34 | symbols = [sign["box"]] + sign["symbols"]
35 | symbols_str = [s["symbol"] + str(s["position"][0]) + 'x' + str(s["position"][1]) for s in symbols]
36 | return "".join(symbols_str)
37 |
38 |
39 | def all_ys(_sign):
40 | return [s["position"][1] for s in _sign["symbols"]]
41 |
42 |
43 | def join_signs(*fsws: str, spacing: int = 0):
44 | signs = [fsw_to_sign(fsw) for fsw in fsws]
45 | new_sign: Sign = {"box": {"symbol": "M", "position": (500, 500)}, "symbols": []}
46 |
47 | accumulative_offset = 0
48 |
49 | for sign in signs:
50 | sign_min_y = min(all_ys(sign))
51 | sign_offset_y = accumulative_offset + spacing - sign_min_y
52 | accumulative_offset += (sign["box"]["position"][1] - sign_min_y) + spacing # * 2
53 |
54 | new_sign["symbols"] += [{
55 | "symbol": s["symbol"],
56 | "position": (s["position"][0], s["position"][1] + sign_offset_y)
57 | } for s in sign["symbols"]]
58 |
59 | # Recenter around box center
60 | sign_middle = max(all_ys(new_sign)) // 2
61 |
62 | for symbol in new_sign["symbols"]:
63 | symbol["position"] = (symbol["position"][0],
64 | new_sign["box"]["position"][1] - sign_middle + symbol["position"][1])
65 |
66 | return sign_to_fsw(new_sign)
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/tokenizers/signwriting/signwriting_tokenizer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import re
2 | from itertools import chain
3 | from typing import List
4 |
5 | from ...signwriting.signwriting import SignSymbol, fsw_to_sign
6 | from ...tokenizers.base_tokenizer import BaseTokenizer
7 |
8 |
9 | class SignWritingTokenizer(BaseTokenizer):
10 |
11 | def __init__(self, starting_index=None, **kwargs):
12 | super().__init__(tokens=SignWritingTokenizer.tokens(), starting_index=starting_index, **kwargs)
13 |
14 | @staticmethod
15 | def tokens():
16 | box_symbols = ["B", "L", "M", "R"]
17 |
18 | base_symbols = ["S" + hex(i)[2:] + hex(j)[2:] for i in range(0x10, 0x38 + 1) for j in range(0x0, 0xf + 1)]
19 | base_symbols.remove("S38c")
20 | base_symbols.remove("S38d")
21 | base_symbols.remove("S38e")
22 | base_symbols.remove("S38f")
23 |
24 | rows = ["r" + hex(j)[2:] for j in range(0x0, 0xf + 1)]
25 | cols = ["c0", "c1", "c2", "c3", "c4", "c5"]
26 |
27 | positions = ["p" + str(p) for p in range(250, 750)]
28 |
29 | return list(chain.from_iterable([box_symbols, base_symbols, rows, cols, positions]))
30 |
31 | @staticmethod
32 | def tokenize_symbol(symbol: SignSymbol):
33 | if symbol["symbol"] in ["B", "L", "M", "R"]:
34 | yield symbol["symbol"]
35 | else:
36 | yield symbol["symbol"][:4] # Break symbol down
37 | num = int(symbol["symbol"][4:], 16)
38 | yield "c" + hex(num // 0x10)[2:]
39 | yield "r" + hex(num % 0x10)[2:]
40 |
41 | yield "p" + str(symbol["position"][0])
42 | yield "p" + str(symbol["position"][1])
43 |
44 | def text_to_tokens(self, text: str) -> List[str]:
45 | signs = [fsw_to_sign(f) for f in text.split(" ")]
46 | for sign in signs:
47 | yield from SignWritingTokenizer.tokenize_symbol(sign["box"])
48 | for symbol in sign["symbols"]:
49 | yield from SignWritingTokenizer.tokenize_symbol(symbol)
50 |
51 | def tokens_to_text(self, tokens: List[str]) -> str:
52 | tokenized = " ".join(tokens)
53 | tokenized = re.sub(r'p(\d*) p(\d*)', r'\1x\2', tokenized)
54 | tokenized = re.sub(r'c(\d)\d? r(.)', r'\1\2', tokenized)
55 | tokenized = re.sub(r'c(\d)\d?', r'\1 0', tokenized)
56 | tokenized = re.sub(r'r(.)', r'0\1', tokenized)
57 |
58 | tokenized = tokenized.replace(' ', '')
59 | tokenized = re.sub(r'(\d)M', r'\1 M', tokenized)
60 |
61 | return tokenized
62 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/tests/data_test.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import unittest
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 | import tensorflow as tf
5 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
6 |
7 | from _shared.collator import zero_pad_collator
8 | from _shared.pose_utils import fake_pose
9 | from _shared.tfds_dataset import ProcessedPoseDatum
10 | from text_to_pose.diffusion.src.data import TextPoseDataset, TextPoseDatum, process_datum
11 |
12 |
13 | def single_datum(num_frames) -> TextPoseDatum:
14 | return {"id": "test_id", "text": "test text", "pose": fake_pose(num_frames=num_frames), "length": 0}
15 |
16 |
17 | class DataTestCase(unittest.TestCase):
18 |
19 | def test_getting_single_item(self):
20 | datum = single_datum(num_frames=5)
21 | dataset = TextPoseDataset([datum])
22 | self.assertEqual(len(dataset), 1)
23 |
24 | pose = dataset[0]["pose"]
25 |
26 | self.assertEqual(pose["data"].shape, (5, 137, 2))
27 | self.assertEqual(pose["confidence"].shape, (5, 137))
28 | self.assertEqual(pose["length"].shape, tuple([1]))
29 | self.assertEqual(pose["inverse_mask"].shape, tuple([5]))
30 |
31 | def test_multiple_items_data_collation(self):
32 | dataset = TextPoseDataset([single_datum(num_frames=5), single_datum(num_frames=10)])
33 | self.assertEqual(len(dataset), 2)
34 |
35 | data_loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=2, collate_fn=zero_pad_collator)
36 | batch = next(iter(data_loader))
37 | pose = batch["pose"]
38 |
39 | self.assertEqual(pose["data"].shape, (2, 10, 137, 2))
40 | self.assertEqual(pose["confidence"].shape, (2, 10, 137))
41 | self.assertEqual(pose["length"].shape, tuple([2, 1]))
42 | self.assertEqual(pose["inverse_mask"].shape, tuple([2, 10]))
43 |
44 | def test_process_datum_not_prunes_not_zeros(self):
45 | pose = fake_pose(num_frames=100)
46 |
47 | hamnosys = tf.convert_to_tensor(np.array("abc"))
48 | datum: ProcessedPoseDatum = {"id": "test", "pose": pose, "tf_datum": {"hamnosys": hamnosys}}
49 |
50 | [processed_datum] = process_datum(datum)
51 | pose_data = processed_datum["pose"].body.data
52 |
53 | self.assertEqual(len(pose_data), 100)
54 |
55 | def test_process_datum_prunes_zeros(self):
56 | pose = fake_pose(num_frames=100)
57 | pose.body.confidence[:5] = 0
58 |
59 | hamnosys = tf.convert_to_tensor(np.array("abc"))
60 | datum: ProcessedPoseDatum = {"id": "test", "pose": pose, "tf_datum": {"hamnosys": hamnosys}}
61 |
62 | [processed_datum] = process_datum(datum)
63 | pose_data = processed_datum["pose"].body.data
64 |
65 | self.assertEqual(len(pose_data), 95)
66 |
67 |
68 | if __name__ == '__main__':
69 | unittest.main()
70 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/models/pose_encoder.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import torch
3 | from torch import nn
4 |
5 |
6 | # TODO @AmitMY - 3D normalize hand and face
7 | class PoseEncoderModel(nn.Module):
8 |
9 | def __init__(self,
10 | pose_dims: (int, int) = (137, 2),
11 | hidden_dim: int = 128,
12 | encoder_depth=4,
13 | encoder_heads=2,
14 | encoder_dim_feedforward=2048,
15 | max_seq_size: int = 1000,
16 | dropout=0.5):
17 | super().__init__()
18 |
19 | self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=dropout)
20 |
21 | self.max_seq_size = max_seq_size
22 | self.pose_dims = pose_dims
23 | self.pose_dim = int(np.prod(pose_dims))
24 |
25 | # Embedding layers
26 | self.positional_embeddings = nn.Embedding(num_embeddings=max_seq_size, embedding_dim=hidden_dim)
27 |
28 | self.pose_projection = nn.Linear(self.pose_dim, hidden_dim)
29 |
30 | # Encoder
31 | self.encoder_layer = nn.TransformerEncoderLayer(d_model=hidden_dim,
32 | nhead=encoder_heads,
33 | dim_feedforward=encoder_dim_feedforward,
34 | batch_first=True)
35 | self.pose_encoder = nn.TransformerEncoder(self.encoder_layer, num_layers=encoder_depth)
36 |
37 | def forward(self, pose, additional_sequence=None):
38 | """
39 |
40 | :param pose: Dictionary including "data" (torch.Tenosr: Batch, Length, Points, Dimensions) and
41 | "mask" (torch.BoolTensor: Batch, Length)
42 | :param additional_sequence: Dictionary including "data" (torch.Tenosr: Batch, Length, Embedding) and
43 | "mask" (torch.BoolTensor: Batch, Length)
44 | :return: torch.Tensor
45 | """
46 | # Repeat the first frame for initial prediction
47 | batch_size, seq_length, _, _ = pose["data"].shape
48 |
49 | pose_data = self.dropout(pose["data"])
50 |
51 | flat_pose_data = pose_data.reshape(batch_size, seq_length, -1)
52 |
53 | positions = torch.arange(0, seq_length, dtype=torch.int, device=pose_data.device)
54 | positional_embedding = self.positional_embeddings(positions)
55 |
56 | # Encode pose sequence
57 | embedding = self.pose_projection(flat_pose_data) + positional_embedding
58 | mask = pose["mask"]
59 |
60 | if additional_sequence is not None:
61 | embedding = torch.cat([embedding, additional_sequence["data"]], dim=1)
62 | mask = torch.cat([mask, additional_sequence["mask"]], dim=1)
63 |
64 | return self.pose_encoder(embedding, src_key_padding_mask=mask)
65 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/tokenizers/base_tokenizer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import annotations
2 |
3 | from typing import List
4 |
5 | import torch
6 |
7 | from ..collator.collator import zero_pad_collator
8 |
9 |
10 | class BaseTokenizer:
11 |
12 | def __init__(self,
13 | tokens: List[str],
14 | starting_index=None,
15 | init_token="[CLS]",
16 | eos_token="[SEP]",
17 | pad_token="[PAD]",
18 | unk_token="[UNK]"):
19 | if starting_index is None:
20 | starting_index = 4
21 |
22 | self.pad_token = pad_token
23 | self.bos_token = init_token
24 | self.eos_token = eos_token
25 | self.unk_token = unk_token
26 |
27 | self.i2s = {(i + starting_index): c for i, c in enumerate(tokens)}
28 | # Following the same ID scheme as JoeyNMT
29 | self.i2s[0] = self.unk_token
30 | self.i2s[1] = self.pad_token
31 | self.i2s[2] = self.bos_token
32 | self.i2s[3] = self.eos_token
33 | self.s2i = {c: i for i, c in self.i2s.items()}
34 |
35 | self.pad_token_id = self.s2i[self.pad_token]
36 | self.bos_token_id = self.s2i[self.bos_token]
37 | self.eos_token_id = self.s2i[self.eos_token]
38 | self.unk_token_id = self.s2i[self.unk_token]
39 |
40 | def __len__(self):
41 | return len(self.i2s)
42 |
43 | def vocab(self):
44 | return list(self.i2s.values())
45 |
46 | def text_to_tokens(self, text: str) -> List[str]:
47 | raise NotImplementedError()
48 |
49 | def tokens_to_text(self, tokens: List[str]) -> str:
50 | raise NotImplementedError()
51 |
52 | def tokenize(self, text: str, bos=False, eos=False):
53 | tokens = [self.s2i[c] for c in self.text_to_tokens(text)]
54 | if bos:
55 | tokens.insert(0, self.bos_token_id)
56 | if eos:
57 | tokens.append(self.eos_token_id)
58 |
59 | return tokens
60 |
61 | def detokenize(self, tokens: List[int]):
62 | if len(tokens) == 0:
63 | return ""
64 | if tokens[0] == self.bos_token_id:
65 | tokens = tokens[1:]
66 | if tokens[-1] == self.eos_token_id:
67 | tokens = tokens[:-1]
68 |
69 | try:
70 | padding_index = tokens.index(self.pad_token_id)
71 | tokens = tokens[:padding_index]
72 | except ValueError:
73 | pass
74 |
75 | return self.tokens_to_text([self.i2s[t] for t in tokens])
76 |
77 | def __call__(self, texts: List[str] | torch.Tensor, is_tokenized=False, device=None):
78 | if not is_tokenized:
79 | all_tokens = [self.tokenize(text) for text in texts]
80 | else:
81 | all_tokens = texts.tolist()
82 |
83 | tokens_batch = zero_pad_collator([{
84 | "tokens_ids": torch.tensor(tokens, dtype=torch.long, device=device),
85 | "attention_mask": torch.ones(len(tokens), dtype=torch.bool, device=device),
86 | "positions": torch.arange(0, len(tokens), dtype=torch.int, device=device)
87 | } for tokens in all_tokens])
88 | # In transformers, 1 is mask, not 0
89 | tokens_batch["attention_mask"] = torch.logical_not(tokens_batch["attention_mask"])
90 |
91 | return tokens_batch
92 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/tests/model_overfit_test.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import random
2 | import unittest
3 |
4 | import torch
5 |
6 | from _shared.models import PoseEncoderModel
7 |
8 | from _shared.tokenizers.dummy_tokenizer import DummyTokenizer
9 | from text_to_pose.diffusion.src.model.iterative_decoder import IterativeGuidedPoseGenerationModel
10 | from text_to_pose.diffusion.src.model.text_encoder import TextEncoderModel
11 |
12 |
13 | def get_batch(bsz=4):
14 | data_tensor = torch.tensor([[[1, 1]], [[2, 2]], [[3, 3]]], dtype=torch.float32)
15 | return {
16 | "text": ["text1"] * bsz,
17 | "pose": {
18 | "length": torch.tensor([3], dtype=torch.float32).expand(bsz, 1),
19 | "data": data_tensor.expand(bsz, *data_tensor.shape),
20 | "confidence": torch.ones([bsz, 3, 1]),
21 | "inverse_mask": torch.ones([bsz, 3]),
22 | },
23 | }
24 |
25 |
26 | class ModelOverfitTestCase(unittest.TestCase):
27 |
28 | def overfit_in_steps(self, steps: int):
29 | torch.manual_seed(42)
30 | random.seed(42)
31 |
32 | batch = get_batch()
33 |
34 | hidden_dim = 10
35 | max_seq_size = 10
36 |
37 | text_encoder = TextEncoderModel(tokenizer=DummyTokenizer(), hidden_dim=hidden_dim, dim_feedforward=10)
38 |
39 | pose_encoder = PoseEncoderModel(pose_dims=(1, 2),
40 | encoder_dim_feedforward=10,
41 | hidden_dim=hidden_dim,
42 | max_seq_size=max_seq_size)
43 |
44 | model = IterativeGuidedPoseGenerationModel(
45 | text_encoder=text_encoder,
46 | pose_encoder=pose_encoder,
47 | hidden_dim=hidden_dim,
48 | max_seq_size=max_seq_size,
49 | num_steps=steps,
50 | seq_len_loss_weight=1 # Make sure sequence length is well predicted
51 | )
52 |
53 | optimizer = model.configure_optimizers()
54 |
55 | model.train()
56 | torch.set_grad_enabled(True)
57 |
58 | # Simple training loop
59 | losses = []
60 | for _ in range(100):
61 | loss = model.training_step(batch)
62 | loss_float = float(loss.detach())
63 | losses.append(loss_float)
64 |
65 | optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients
66 | loss.backward() # backward
67 | optimizer.step() # update parameters
68 |
69 | print("losses", losses)
70 |
71 | model.eval()
72 |
73 | first_pose = batch["pose"]["data"][0, 0, :, :]
74 | with torch.no_grad():
75 | prediction = model.forward("text1", first_pose=first_pose)
76 |
77 | # Exhaust sequence
78 | final_seq = None
79 | for seq in prediction:
80 | final_seq = seq
81 | print("seq predicted", seq)
82 |
83 | self.assertEqual(final_seq.shape, (3, 1, 2))
84 | self.assertTrue(torch.all(torch.eq(torch.round(final_seq), batch["pose"]["data"][0])))
85 |
86 | def test_model_should_overfit_single_step(self):
87 | # Here, in training the model always sees the same sequence
88 | self.overfit_in_steps(steps=1)
89 |
90 | def test_model_should_overfit_multiple_steps(self):
91 | # Here, in training the model sees different sequences
92 | self.overfit_in_steps(steps=3)
93 |
94 |
95 | if __name__ == '__main__':
96 | unittest.main()
97 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/src/args.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import random
3 | from argparse import ArgumentParser
4 | from os import path
5 |
6 | import numpy as np
7 | import torch
8 |
9 | root_dir = path.dirname(path.realpath(__file__))
10 | parser = ArgumentParser()
11 |
12 | parser.add_argument('--no_wandb', type=bool, default=False, help='ignore wandb?')
13 | parser.add_argument('--config_file', type=str, default="", help='path to yaml config file')
14 |
15 | # Training Arguments
16 | parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=42, help='random seed')
17 | parser.add_argument('--num_gpus', type=int, default=1, help='how many gpus?')
18 | parser.add_argument('--batch_size', type=int, default=64, help='batch size')
19 | parser.add_argument('--max_epochs', type=int, default=2000, help='max number of epochs')
20 | parser.add_argument('--learning_rate', type=float, default=1e-4, help='optimizer learning rate')
21 |
22 | # Data Arguments
23 | parser.add_argument('--max_seq_size', type=int, default=200, help='input sequence size')
24 | parser.add_argument('--fps', type=int, default=None, help='fps to load')
25 | parser.add_argument('--pose',
26 | choices=['openpose', 'holistic'],
27 | default='holistic',
28 | help='which pose estimation model to use?')
29 | parser.add_argument(
30 | '--pose_components',
31 | type=list,
32 | default=["POSE_LANDMARKS", "LEFT_HAND_LANDMARKS", "RIGHT_HAND_LANDMARKS"], # , "FACE_LANDMARKS"
33 | help='what pose components to use?')
34 |
35 | # Model Arguments
36 | parser.add_argument('--noise_epsilon', type=float, default=1e-2, help='noise epsilon')
37 | parser.add_argument('--seq_len_loss_weight', type=float, default=2e-5, help='sequence length weight in loss')
38 | parser.add_argument('--smoothness_loss_weight', type=float, default=1e-3, help='smootheness weight in loss')
39 |
40 | parser.add_argument('--num_steps', type=int, default=100, help='number of pose refinement steps')
41 | parser.add_argument('--hidden_dim', type=int, default=512, help='encoder hidden dimension')
42 | parser.add_argument('--text_encoder_depth', type=int, default=2, help='number of layers for the text encoder')
43 | parser.add_argument('--pose_encoder_depth', type=int, default=4, help='number of layers for the pose encoder')
44 | parser.add_argument('--encoder_heads', type=int, default=8, help='number of heads for the encoder')
45 | parser.add_argument('--encoder_dim_feedforward', type=int, default=2048, help='size of encoder dim feedforward')
46 |
47 | # Prediction args
48 | parser.add_argument(
49 | "--guidance_param",
50 | default=2.5,
51 | type=float,
52 | help="For classifier-free sampling - specifies the s parameter, as defined in https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.14916.")
53 | parser.add_argument('--checkpoint', type=str, default=None, metavar='PATH', help="Checkpoint path for prediction")
54 | parser.add_argument('--output_dir',
55 | type=str,
56 | default="videos",
57 | metavar='PATH',
58 | help="output videos directory name "
59 | "inside model directory")
60 | parser.add_argument('--ffmpeg_path', type=str, default=None, metavar='PATH', help="Path for ffmpeg executable")
61 |
62 | args = parser.parse_args()
63 |
64 | # Set Seed
65 | if args.seed == 0: # Make seed random if 0
66 | args.seed = random.randint(0, 1000)
67 | torch.manual_seed(args.seed)
68 | np.random.seed(args.seed)
69 | random.seed(args.seed)
70 |
71 | # Set Available GPUs
72 | gpus = ["0", "1", "2", "3"]
73 | os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = ",".join(gpus[:args.num_gpus])
74 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/tfds_dataset.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import importlib
2 | from typing import Dict, List, TypedDict, Union
3 |
4 | import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
5 | from pose_format import Pose
6 | from pose_format.numpy.pose_body import NumPyPoseBody
7 | from pose_format.pose_header import PoseHeader
8 | from pose_format.utils.reader import BufferReader
9 | from sign_language_datasets.datasets.config import SignDatasetConfig
10 | from sign_language_datasets.datasets.dgs_corpus import DgsCorpusConfig
11 | from tqdm import tqdm
12 | import mediapipe as mp
13 |
14 | from .pose_utils import pose_hide_legs, pose_normalization_info
15 |
16 |
17 | mp_holistic = mp.solutions.holistic
18 | FACEMESH_CONTOURS_POINTS = [str(p) for p in sorted(set([p for p_tup in list(mp_holistic.FACEMESH_CONTOURS) for p in p_tup]))]
19 |
20 | class ProcessedPoseDatum(TypedDict):
21 | id: str
22 | pose: Union[Pose, Dict[str, Pose]]
23 | tf_datum: dict
24 |
25 |
26 | def get_tfds_dataset(name,
27 | poses="holistic",
28 | fps=25,
29 | split="train",
30 | components: List[str] = None,
31 | reduce_face=False,
32 | data_dir=None,
33 | version="1.0.0",
34 | filter_func=None):
35 | dataset_module = importlib.import_module("sign_language_datasets.datasets." + name + "." + name)
36 |
37 | config_kwargs = dict(
38 | name=poses + "-" + str(fps),
39 | version=version, # Specific version
40 | include_video=False, # Download and load dataset videos
41 | fps=fps, # Load videos at constant fps
42 | include_pose=poses)
43 |
44 | # Loading a dataset with custom configuration
45 | if name == "dgs_corpus":
46 | config = DgsCorpusConfig(**config_kwargs, split="3.0.0-uzh-document")
47 | else:
48 | config = SignDatasetConfig(**config_kwargs)
49 |
50 | tfds_dataset = tfds.load(name=name, builder_kwargs=dict(config=config), split=split, data_dir=data_dir)
51 |
52 | # pylint: disable=protected-access
53 | with open(dataset_module._POSE_HEADERS[poses], "rb") as buffer:
54 | pose_header = PoseHeader.read(BufferReader(buffer.read()))
55 |
56 | normalization_info = pose_normalization_info(pose_header)
57 | return [process_datum(datum, pose_header, normalization_info, components, reduce_face)
58 | for datum in tqdm(tfds_dataset, desc="Loading dataset")
59 | if filter_func is None or filter_func(datum)]
60 |
61 |
62 | def process_datum(datum,
63 | pose_header: PoseHeader,
64 | normalization_info,
65 | components: List[str] = None,
66 | reduce_face=False) -> ProcessedPoseDatum:
67 | tf_poses = {"": datum["pose"]} if "pose" in datum else datum["poses"]
68 | poses = {}
69 | for key, tf_pose in tf_poses.items():
70 | fps = int(tf_pose["fps"].numpy())
71 | pose_body = NumPyPoseBody(fps, tf_pose["data"].numpy(), tf_pose["conf"].numpy())
72 | pose = Pose(pose_header, pose_body)
73 |
74 | # Get subset of components if needed
75 | if reduce_face:
76 | pose = pose.get_components(components, {"FACE_LANDMARKS": FACEMESH_CONTOURS_POINTS})
77 | elif components and len(components) != len(pose_header.components):
78 | pose = pose.get_components(components)
79 |
80 | pose = pose.normalize(normalization_info)
81 | pose_hide_legs(pose)
82 | poses[key] = pose
83 |
84 | return {
85 | "id": datum["id"].numpy().decode('utf-8'),
86 | "pose": poses[""] if "pose" in datum else poses,
87 | "tf_datum": datum
88 | }
89 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 📝 ⇝ 🧏 Transcription [DEPRECATED]
2 |
3 | Repository for sign language transcription related models.
4 |
5 | Ideally pose based models should use a shared large-pose-language-model,
6 | able to encode arbitrary pose sequence lengths, and pre-trained on non-autoregressive reconstruction.
7 |
8 | - [_shared](_shared) - includes shared utilities for all models
9 | - [video_to_pose](video_to_pose) - performs pose estimation on a video
10 | - [pose_to_segments](pose_to_segments) - segments pose sequences
11 | - [text_to_pose](text_to_pose) - animates poses using text
12 | - [pose_to_text](pose_to_text) - generates text from poses
13 |
14 | ## Installation
15 |
16 | ```bash
17 | pip install git+https://github.com/sign-language-processing/transcription
18 | ```
19 |
20 | ## Development Setup
21 | ```bash
22 | # Update conda
23 |
24 | # Create environment
25 | conda create -y --name sign python=3.10
26 | conda activate sign
27 |
28 | # Install all dependencies, may cause a segmentation fault
29 | pip install .[dev]
30 |
31 | export PROTOCOL_BUFFERS_PYTHON_IMPLEMENTATION=python
32 | ```
33 |
34 |
35 | ## Example Usage: Video-to-Text
36 |
37 | Let's start with having a video file of a sign language sentence, word, or conversation.
38 |
39 | ```bash
40 | curl https://media.spreadthesign.com/video/mp4/13/93875.mp4 --output sign.mp4
41 | ```
42 |
43 | Next, we'll use `video_to_pose` to extract the human pose from the video.
44 |
45 | ```bash
46 | pip install mediapipe # depends on mediapipe
47 | video_to_pose -i sign.mp4 --format mediapipe -o sign.pose
48 | ```
49 |
50 | Now let's create an ELAN file with sign and sentence segments:
51 | (To demo this on a longer file, you can download a large pose file from [here](https://nlp.biu.ac.il/~amit/datasets/poses/holistic/dgs_corpus/1413451-11105600-11163240_a.pose))
52 |
53 | ```bash
54 | pip install pympi-ling # depends on pympi to create elan files
55 | pose_to_segments -i sign.pose -o sign.eaf --video sign.mp4
56 | ```
57 |
58 |
59 |
60 | Next Steps (TODO)
61 |
62 | After looking at the ELAN file, adjusting where needed, we'll transcribe every sign segment into HamNoSys or
63 | SignWriting:
64 |
65 | ```bash
66 | pose_to_text --notation=signwriting --pose=sign.pose --eaf=sign.eaf
67 | ```
68 |
69 | After looking at the ELAN file again, fixing any mistakes, we finally translate each sentence segment into spoken
70 | language text:
71 |
72 | ```bash
73 | text_to_text --sign_language=us --spoken_language=en --eaf=sign.eaf
74 | ```
75 |
76 |
77 |
78 |
79 | ## Example Usage: Text-to-Video
80 |
81 | Let's start with having a spoken language word, or sentence - "Hello World".
82 |
83 |
84 | Next Steps (TODO)
85 |
86 | First, we'll translate it into sign language text, in SignWriting format:
87 |
88 | ```bash
89 | text_to_text --spoken_language=en --sign_language=us \
90 | --notation=signwriting --text="Hello World" > sign.txt
91 | ```
92 |
93 | Next, we'll animate the sign language text into a pose sequence:
94 |
95 | ```bash
96 | text_to_pose --notation=signwriting --text=$(cat sign.txt) --pose=sign.pose
97 | ```
98 |
99 |
100 |
101 | Finally, we'll animate the pose sequence into a video:
102 |
103 | ```bash
104 | pip install git+https://github.com/sign-language-processing/pose-to-video
105 |
106 | # Using Pix2Pix
107 | wget -O pix2pix.h5 "https://firebasestorage.googleapis.com/v0/b/sign-mt-assets/o/models%2Fgenerator%2Fmodel.h5?alt=media"
108 | pose_to_video --type=pix2pix --model=pix2pix.h5 --pose=sign.pose --video=sign.mp4 --upscale
109 | ```
110 |
111 |
112 | Next Steps (TODO)
113 |
114 | ```bash
115 | # OR Using StyleGAN3
116 | pose_to_video --type=stylegan3 --pose=sign.pose --video=sign.mp4 --upscale
117 | # OR Using Mixamo
118 | pose_to_video --type=mixamo --pose=sign.pose --video=sign.mp4
119 | ```
120 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pose_to_text/train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import argparse
2 | import logging
3 | import shutil
4 | from pathlib import Path
5 |
6 | from joeynmt.helpers import load_config, log_cfg, make_logger, make_model_dir, set_seed
7 | from joeynmt.prediction import test
8 | from joeynmt.training import TrainManager
9 |
10 | from pose_to_text.dataset import get_dataset
11 | from pose_to_text.model import build_model
12 |
13 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
14 |
15 |
16 | def train(cfg_file: str, skip_test: bool = False) -> None:
17 | """
18 | Main training function. After training, also test on test data if given.
19 | :param cfg_file: path to configuration yaml file
20 | :param skip_test: whether a test should be run or not after training
21 | """
22 | # read config file
23 | cfg = load_config(Path(cfg_file))
24 |
25 | # make logger
26 | model_dir = make_model_dir(
27 | Path(cfg["training"]["model_dir"]),
28 | overwrite=cfg["training"].get("overwrite", False),
29 | )
30 | joeynmt_version = make_logger(model_dir, mode="train")
31 | if "joeynmt_version" in cfg:
32 | assert str(joeynmt_version) == str(
33 | cfg["joeynmt_version"]), (f"You are using JoeyNMT version {joeynmt_version}, "
34 | f'but {cfg["joeynmt_version"]} is expected in the given config.')
35 |
36 | # write all entries of config to the log
37 | log_cfg(cfg)
38 |
39 | # store copy of original training config in model dir
40 | shutil.copy2(cfg_file, (model_dir / "config.yaml").as_posix())
41 |
42 | # set the random seed
43 | set_seed(seed=cfg["training"].get("random_seed", 42))
44 |
45 | # load the data
46 | data_args = {
47 | "poses": cfg["data"]["pose"],
48 | "fps": cfg["data"]["fps"],
49 | "components": cfg["data"]["components"],
50 | "max_seq_size": cfg["data"]["max_seq_size"]
51 | }
52 | train_data = get_dataset(**data_args, split="train[50:]")
53 | dev_data = get_dataset(**data_args, split="train[:50]")
54 | test_data = dev_data
55 |
56 | trg_vocab = train_data.trg_vocab
57 |
58 | trg_vocab.to_file(model_dir / "trg_vocab.txt")
59 | if hasattr(train_data.tokenizer[train_data.trg_lang], "copy_cfg_file"):
60 | train_data.tokenizer[train_data.trg_lang].copy_cfg_file(model_dir)
61 |
62 | # build an encoder-decoder model
63 | _, num_pose_joints, num_pose_dims = train_data[0][0].shape
64 | model = build_model(pose_dims=(num_pose_joints, num_pose_dims), cfg=cfg["model"], trg_vocab=trg_vocab)
65 |
66 | # for training management, e.g. early stopping and model selection
67 | trainer = TrainManager(model=model, cfg=cfg)
68 |
69 | # train the model
70 | trainer.train_and_validate(train_data=train_data, valid_data=dev_data)
71 |
72 | if not skip_test:
73 | # predict with the best model on validation and test
74 | # (if test data is available)
75 |
76 | ckpt = model_dir / f"{trainer.stats.best_ckpt_iter}.ckpt"
77 | output_path = model_dir / f"{trainer.stats.best_ckpt_iter:08d}.hyps"
78 |
79 | datasets_to_test = {
80 | "dev": dev_data,
81 | "test": test_data,
82 | "src_vocab": None,
83 | "trg_vocab": trg_vocab,
84 | }
85 | test(
86 | cfg_file,
87 | ckpt=ckpt.as_posix(),
88 | output_path=output_path.as_posix(),
89 | datasets=datasets_to_test,
90 | )
91 | else:
92 | logger.info("Skipping test after training")
93 |
94 |
95 | if __name__ == "__main__":
96 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser("Joey-NMT")
97 | parser.add_argument(
98 | "--config",
99 | default="configs/default.yaml",
100 | type=str,
101 | help="Training configuration file (yaml).",
102 | )
103 | args = parser.parse_args()
104 | train(cfg_file=args.config)
105 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/tests/model_test.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import unittest
2 | from unittest.mock import MagicMock
3 |
4 | import torch
5 |
6 | from _shared.models import PoseEncoderModel
7 | from text_to_pose.diffusion.src.model import TextEncoderModel
8 |
9 | from _shared.tokenizers.dummy_tokenizer import DummyTokenizer
10 | from text_to_pose.diffusion.src.model.iterative_decoder import IterativeGuidedPoseGenerationModel
11 |
12 |
13 | class ModelTestCase(unittest.TestCase):
14 |
15 | def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
16 | super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
17 | self.pose_dim = (2, 2)
18 | self.seq_length = 5
19 | self.hidden_dim = 2
20 |
21 | def test_encode_text(self):
22 | text_encoder = TextEncoderModel(tokenizer=DummyTokenizer(), hidden_dim=self.hidden_dim)
23 | encoded_text = text_encoder(["test"])
24 | self.assertTrue(torch.all(torch.isfinite(encoded_text["data"])))
25 | self.assertTrue(torch.all(torch.eq(torch.zeros_like(encoded_text["mask"]), encoded_text["mask"])))
26 |
27 | def model_setup(self):
28 | pose_encoder = PoseEncoderModel(pose_dims=self.pose_dim,
29 | hidden_dim=self.hidden_dim,
30 | max_seq_size=self.seq_length)
31 |
32 | text_encoder = MagicMock(return_value={
33 | "data": torch.ones([1, 2, self.hidden_dim]),
34 | "mask": torch.zeros([1, 2], dtype=torch.bool),
35 | })
36 | model = IterativeGuidedPoseGenerationModel(text_encoder=text_encoder,
37 | pose_encoder=pose_encoder,
38 | hidden_dim=self.hidden_dim,
39 | max_seq_size=self.seq_length)
40 | model.log = MagicMock(return_value=True)
41 | return model
42 |
43 | def model_forward(self):
44 | model = self.model_setup()
45 | model.eval()
46 | with torch.no_grad():
47 | first_pose = torch.full(self.pose_dim, fill_value=2, dtype=torch.float)
48 | return model.forward("", first_pose, force_sequence_length=self.seq_length)
49 |
50 | def test_forward_yields_initial_pose_sequence(self):
51 | model_forward = self.model_forward()
52 |
53 | pose_sequence = next(model_forward)
54 | self.assertEqual(pose_sequence.shape, (self.seq_length, *self.pose_dim))
55 | self.assertTrue(torch.all(pose_sequence == 2))
56 |
57 | def test_forward_yields_many_pose_sequences(self):
58 | model_forward = self.model_forward()
59 |
60 | next(model_forward)
61 | pose_sequence = next(model_forward)
62 | self.assertEqual(pose_sequence.shape, (self.seq_length, *self.pose_dim))
63 | self.assertTrue(torch.all(torch.isfinite(pose_sequence)))
64 |
65 | def get_batch(self, confidence=1):
66 | return {
67 | "text": ["text1"],
68 | "pose": {
69 | "length": torch.tensor([self.seq_length], dtype=torch.float),
70 | "data": torch.ones([1, self.seq_length, *self.pose_dim], dtype=torch.float),
71 | "confidence": torch.full([1, self.seq_length, self.pose_dim[0]], fill_value=confidence),
72 | "inverse_mask": torch.ones([1, self.seq_length]),
73 | },
74 | }
75 |
76 | def test_training_step_expected_loss_zero(self):
77 | model = self.model_setup()
78 | model.seq_len_loss_weight = 0
79 | batch = self.get_batch(confidence=0)
80 |
81 | loss = float(model.training_step(batch))
82 | self.assertEqual(0, loss)
83 |
84 | def test_training_step_expected_loss_finite(self):
85 | model = self.model_setup()
86 | batch = self.get_batch(confidence=1)
87 |
88 | loss = model.training_step(batch)
89 | self.assertNotEqual(0, float(loss))
90 | self.assertTrue(torch.isfinite(loss))
91 |
92 |
93 | if __name__ == "__main__":
94 | unittest.main()
95 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/src/data.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from random import shuffle
2 | from typing import List, TypedDict
3 |
4 | import torch
5 | from pose_format import Pose
6 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
7 |
8 | from _shared.tfds_dataset import ProcessedPoseDatum, get_tfds_dataset
9 |
10 |
11 | class TextPoseDatum(TypedDict):
12 | id: str
13 | text: str
14 | pose: Pose
15 | length: int
16 |
17 |
18 | class TextPoseDataset(Dataset):
19 |
20 | def __init__(self, data: List[TextPoseDatum]):
21 | self.data = data
22 |
23 | def __len__(self):
24 | return len(self.data)
25 |
26 | def __getitem__(self, index):
27 | datum = self.data[index]
28 | pose = datum["pose"]
29 |
30 | torch_body = pose.body.torch()
31 | pose_length = len(torch_body.data)
32 |
33 | return {
34 | "id": datum["id"],
35 | "text": datum["text"],
36 | "pose": {
37 | "obj": pose,
38 | "data": torch_body.data.tensor[:, 0, :, :],
39 | "confidence": torch_body.confidence[:, 0, :],
40 | "length": torch.tensor([pose_length], dtype=torch.float),
41 | "inverse_mask": torch.ones(pose_length, dtype=torch.int8)
42 | }
43 | }
44 |
45 |
46 | def process_datum(datum: ProcessedPoseDatum) -> List[TextPoseDatum]:
47 | if "hamnosys" in datum["tf_datum"]:
48 | text = datum["tf_datum"]["hamnosys"].numpy().decode('utf-8').strip()
49 | else:
50 | text = ""
51 |
52 | if "pose" in datum:
53 | poses: List[Pose] = [datum["pose"]]
54 | elif "views" in datum:
55 | poses: List[Pose] = datum["views"]["pose"]
56 | else:
57 | raise ValueError("No pose found in datum")
58 |
59 | data = []
60 | for pose in poses:
61 | pose.body.data = pose.body.data[:, :, :, :3] # X,Y,Z
62 | # Prune all leading frames containing only zeros
63 | for i in range(len(pose.body.data)):
64 | if pose.body.confidence[i].sum() != 0:
65 | if i != 0:
66 | pose.body.data = pose.body.data[i:]
67 | pose.body.confidence = pose.body.confidence[i:]
68 | break
69 |
70 | data.append({"id": datum["id"], "text": text, "pose": pose, "length": max(len(pose.body.data), len(text) + 1)})
71 |
72 | return data
73 |
74 |
75 | # TODO use dgs_types by default
76 | def get_dataset(name="dicta_sign",
77 | poses="holistic",
78 | fps=25,
79 | split="train",
80 | components: List[str] = None,
81 | data_dir=None,
82 | max_seq_size=1000):
83 | print("Loading", name, "dataset...")
84 | data = get_tfds_dataset(name=name, poses=poses, fps=fps, split=split, components=components, data_dir=data_dir)
85 |
86 | data = [d for datum in data for d in process_datum(datum)]
87 | data = [d for d in data if d["length"] < max_seq_size]
88 |
89 | return TextPoseDataset(data)
90 |
91 |
92 | def get_datasets(poses="holistic", fps=25, split="train", components: List[str] = None, max_seq_size=1000):
93 | dicta_sign = get_dataset(name="dicta_sign",
94 | poses=poses,
95 | fps=fps,
96 | split=split,
97 | components=components,
98 | max_seq_size=max_seq_size)
99 | # dgs_types = get_dataset(name="dgs_types", poses=poses, fps=fps, split=split, components=components,
100 | # max_seq_size=max_seq_size)
101 | autsl = get_dataset(name="autsl",
102 | poses=poses,
103 | fps=fps,
104 | split=split,
105 | components=components,
106 | max_seq_size=max_seq_size)
107 |
108 | all_data = dicta_sign.data + autsl.data
109 | return TextPoseDataset(all_data)
110 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pose_to_text/dataset.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import logging
2 | from itertools import chain
3 | from typing import List, Tuple
4 |
5 | import torch
6 | from joeynmt.constants import BOS_TOKEN, EOS_TOKEN, PAD_ID, PAD_TOKEN, UNK_TOKEN
7 | from joeynmt.datasets import BaseDataset
8 | from joeynmt.vocabulary import Vocabulary
9 |
10 | from pose_to_text.batch import SignBatch
11 | from text_to_pose.diffusion.src.data import TextPoseDataset
12 | from text_to_pose.diffusion.src.data import get_dataset as get_single_dataset
13 |
14 | from .._shared.collator import collate_tensors
15 | from .._shared.tokenizers import SignLanguageTokenizer
16 |
17 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
18 | CPU_DEVICE = torch.device("cpu")
19 |
20 |
21 | class PoseTextDataset(BaseDataset):
22 |
23 | def __init__(self, dataset: TextPoseDataset, split: str, has_trg: bool = True, random_subset=0):
24 | trg_lang = "signed"
25 | src_lang = "poses"
26 |
27 | special_tokens = {
28 | "init_token": BOS_TOKEN,
29 | "eos_token": EOS_TOKEN,
30 | "pad_token": PAD_TOKEN,
31 | "unk_token": UNK_TOKEN
32 | }
33 |
34 | super().__init__(path=None,
35 | src_lang=src_lang,
36 | trg_lang=trg_lang,
37 | has_trg=has_trg,
38 | split=split,
39 | random_subset=random_subset,
40 | tokenizer={
41 | src_lang: None,
42 | trg_lang: SignLanguageTokenizer(**special_tokens),
43 | },
44 | sequence_encoder={
45 | src_lang: lambda x: x,
46 | trg_lang: lambda x: x,
47 | })
48 |
49 | self.dataset = dataset
50 |
51 | # Model needs to know how many classes for softmax
52 | self.trg_vocab = Vocabulary(self.tokenizer[self.trg_lang].vocab())
53 |
54 | def __len__(self):
55 | return len(self.dataset)
56 |
57 | @property
58 | def src(self) -> List[str]:
59 | """get detokenized preprocessed data in src language."""
60 | # For compatibility with Joey
61 | return ["" for _ in self.dataset.data]
62 |
63 | @property
64 | def trg(self) -> List[str]:
65 | """get detokenized preprocessed data in trg language."""
66 | # For bleu calculation
67 | return [" ".join(self.tokenizer[self.trg_lang].text_to_tokens(datum["text"])) for datum in self.dataset.data]
68 |
69 | def __getitem__(self, idx) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
70 | datum = self.dataset[idx]
71 | src = datum["pose"]["data"]
72 | trg = self.tokenizer[self.trg_lang].tokenize(datum["text"], bos=True, eos=True)
73 | trg = torch.tensor(trg, dtype=torch.long)
74 | return src, trg
75 |
76 | def collate_fn(
77 | self,
78 | batch: List[Tuple],
79 | pad_index: int = PAD_ID,
80 | device: torch.device = CPU_DEVICE,
81 | ) -> SignBatch:
82 | src, trg = zip(*batch)
83 | src_length = [len(s) for s in src]
84 | trg_length = [len(s) for s in trg]
85 |
86 | return SignBatch(
87 | src=collate_tensors(src),
88 | src_length=collate_tensors(src_length),
89 | trg=collate_tensors(trg, pad_value=pad_index),
90 | trg_length=collate_tensors(trg_length),
91 | device=device,
92 | pad_index=pad_index,
93 | has_trg=self.has_trg,
94 | is_train=self.split == "train",
95 | )
96 |
97 |
98 | def get_dataset(split_name="train", **kwargs):
99 | datasets = [
100 | get_single_dataset(name="dicta_sign", **kwargs),
101 | # get_single_dataset(name="sign2mint", **kwargs)
102 | ]
103 |
104 | all_data = list(chain.from_iterable([d.data for d in datasets]))
105 | return PoseTextDataset(TextPoseDataset(all_data), split=split_name)
106 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pose_to_text/model.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from typing import Tuple
2 |
3 | import torch
4 | from joeynmt.constants import PAD_TOKEN
5 | from joeynmt.decoders import Decoder, TransformerDecoder
6 | from joeynmt.embeddings import Embeddings
7 | from joeynmt.encoders import Encoder, TransformerEncoder
8 | from joeynmt.helpers import ConfigurationError
9 | from joeynmt.initialization import initialize_model
10 | from joeynmt.model import Model as JoeyNMTModel
11 | from joeynmt.vocabulary import Vocabulary
12 | from torch import Tensor
13 |
14 | from .._shared.models.pose_encoder import PoseEncoderModel
15 |
16 |
17 | class PoseToTextModel(JoeyNMTModel):
18 |
19 | def __init__(self, pose_encoder: PoseEncoderModel, encoder: Encoder, decoder: Decoder, trg_embed: Embeddings,
20 | trg_vocab: Vocabulary):
21 | # Setup fake "src" parameters
22 | src_vocab = Vocabulary([])
23 | src_embed = Embeddings(vocab_size=len(src_vocab), padding_idx=src_vocab.lookup(PAD_TOKEN))
24 | super().__init__(encoder=encoder,
25 | decoder=decoder,
26 | src_embed=src_embed,
27 | trg_embed=trg_embed,
28 | src_vocab=src_vocab,
29 | trg_vocab=trg_vocab)
30 |
31 | self.pose_encoder = pose_encoder
32 |
33 | def _encode(self, src: Tensor, src_length: Tensor, src_mask: Tensor, **unused_kwargs) \
34 | -> (Tensor, Tensor):
35 | # Encode pose using the universal pose encoder
36 | pose_mask = torch.logical_not(torch.squeeze(src_mask, dim=1))
37 | pose_encoding = self.pose_encoder({"data": src, "mask": pose_mask})
38 |
39 | # Encode using additional custom JoeyNMT encoder
40 | return self.encoder(pose_encoding, src_length, src_mask)
41 |
42 | def to(self, *args, **kwargs):
43 | super().to(*args, **kwargs)
44 | # TODO figure out why this is not happening by default
45 | self.pose_encoder.to(*args, **kwargs)
46 | return self
47 |
48 |
49 | def build_model(pose_dims: Tuple[int, int], cfg: dict, trg_vocab: Vocabulary) -> PoseToTextModel:
50 | trg_padding_idx = trg_vocab.lookup(PAD_TOKEN)
51 |
52 | # Embeddings
53 | trg_embed = Embeddings(**cfg["decoder"]["embeddings"], vocab_size=len(trg_vocab), padding_idx=trg_padding_idx)
54 |
55 | # Build encoder
56 | assert cfg["encoder"]["type"] == "transformer", "Only transformer encoder is supported"
57 | encoder = TransformerEncoder(**cfg["encoder"])
58 |
59 | # Build decoder
60 | assert cfg["decoder"]["type"] == "transformer", "Only transformer decoder is supported"
61 | decoder = TransformerDecoder(**cfg["decoder"],
62 | encoder=encoder,
63 | vocab_size=len(trg_vocab),
64 | emb_size=trg_embed.embedding_dim)
65 |
66 | pose_encoder = PoseEncoderModel(pose_dims=pose_dims,
67 | dropout=cfg["pose_encoder"]["dropout"],
68 | hidden_dim=cfg["pose_encoder"]["hidden_size"],
69 | encoder_depth=cfg["pose_encoder"]["num_layers"],
70 | encoder_heads=cfg["pose_encoder"]["num_heads"],
71 | encoder_dim_feedforward=cfg["pose_encoder"]["ff_size"])
72 |
73 | model = PoseToTextModel(pose_encoder=pose_encoder,
74 | encoder=encoder,
75 | decoder=decoder,
76 | trg_embed=trg_embed,
77 | trg_vocab=trg_vocab)
78 |
79 | # tie softmax layer with trg embeddings
80 | if cfg.get("tied_softmax", False):
81 | if trg_embed.lut.weight.shape == model.decoder.output_layer.weight.shape:
82 | # (also) share trg embeddings and softmax layer:
83 | model.decoder.output_layer.weight = trg_embed.lut.weight
84 | else:
85 | raise ConfigurationError("For tied_softmax, the decoder embedding_dim and decoder hidden_size "
86 | "must be the same. The decoder must be a Transformer.")
87 |
88 | # custom initialization of model parameters
89 | initialize_model(model=model, cfg=cfg, src_padding_idx=None, trg_padding_idx=trg_padding_idx)
90 |
91 | return model
92 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/tokenizers/signwriting/test_signwriting_tokenizer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import unittest
2 |
3 | from .signwriting_tokenizer import SignWritingTokenizer
4 |
5 |
6 | class TokenizeCase(unittest.TestCase):
7 |
8 | def test_tokenization_single_sign(self):
9 | tokenizer = SignWritingTokenizer()
10 |
11 | fsw = 'M123x456S1f720487x492S1f720487x492'
12 | tokens = list(tokenizer.text_to_tokens(fsw))
13 | self.assertEqual(tokens,
14 | ['M', 'p123', 'p456', 'S1f7', 'c2', 'r0', 'p487', 'p492', 'S1f7', 'c2', 'r0', 'p487', 'p492'])
15 |
16 | def test_tokenization_no_box(self):
17 | tokenizer = SignWritingTokenizer()
18 |
19 | fsw = 'S38800464x496'
20 | tokens = list(tokenizer.text_to_tokens(fsw))
21 | self.assertEqual(tokens, ['M', 'p500', 'p500', 'S388', 'c0', 'r0', 'p464', 'p496'])
22 |
23 | def test_tokenization_multiple_signs(self):
24 | tokenizer = SignWritingTokenizer()
25 |
26 | fsw = 'M123x456S1f720487x492 M124x456S1f210488x493'
27 | tokens = list(tokenizer.text_to_tokens(fsw))
28 | self.assertEqual(tokens, [
29 | 'M', 'p123', 'p456', 'S1f7', 'c2', 'r0', 'p487', 'p492', 'M', 'p124', 'p456', 'S1f2', 'c1', 'r0', 'p488',
30 | 'p493'
31 | ])
32 |
33 | def test_not_failing_for_r_box(self):
34 | tokenizer = SignWritingTokenizer()
35 |
36 | # pylint: disable=line-too-long
37 | fsw = 'M528x518S15a37473x494S1f010488x503S26507515x483 M524x515S1dc20476x485S18720506x486 S38800464x496 M521x576S10021478x555S10029457x555S22a07495x535S22a11461x535S30a00480x483S36d01479x516 M511x590S1f720489x410S1fb20494x554S10120494x429S10e20494x461S17620494x494S16d20494x513S1f720489x536S14a20494x575 M527x561S20302486x439S20300491x456S2890f491x474S22a14473x546S15a40513x514S15a48473x514S22a04514x546 S38700463x496 R521x536S11541471x509S1150a449x511S22a04472x488S36d01479x465 R518x542S1d441493x482S1d437493x517S22a00499x459S22105483x493 R519x515S1ce18481x485S1ce10497x485S2fb06498x500 R518x612S2ff00482x483S10010487x512S15a30485x565S11541487x585S26500503x569 S38700463x496 M562x527S36d01480x516S32107478x483S15a37539x488S15a37517x488 M521x516S20500480x505S10043491x484 M562x518S15a56522x485S18221537x467S26501517x451S22101535x468S2ff00482x483 M525x527S10041504x497S2d60e476x474 M533x518S2b700514x459S15a10521x486S2ff00482x483 S38800464x496 M562x527S36d01480x516S32107478x483S15a37539x488S15a37517x488 M533x518S2ff00482x483S15a10521x484S2b700514x454 M568x528S10149521x459S10142538x447S2be14526x490S2be04548x477S32107482x483 M517x517S10018483x487S10002487x484 M525x527S10041504x497S2d60e476x474 M526x522S10018475x483S26505513x509S10641490x479 M560x518S1f721516x469S1f70f471x468S2ff00482x483S22a17489x460S22a07534x460S14c10537x427S14c18500x432S32107482x483 S38900464x493 M562x527S36d01480x516S32107478x483S15a37539x488S15a37517x488 M533x518S2ff00482x483S15a10521x484S2b700514x454 M518x642S2ff00482x483S10000487x512S15a20494x570S15a56490x630S37800499x596 M522x516S15a37498x489S15a31499x488S2e800479x484 M530x516S10012500x485S18518470x490S2e734494x491 M520x517S20500480x506S10043490x484 S38800464x496' # noqa: E501
38 | self.assertTrue(isinstance(tokenizer.tokenize(fsw), list))
39 |
40 | def test_tokenization_into_ids(self):
41 | tokenizer = SignWritingTokenizer()
42 |
43 | tokens = ['M', 'p251', 'p456', 'S1f7', 'c2', 'r0', 'p487', 'p492']
44 | ids = [tokenizer.s2i[t] for t in tokens]
45 | self.assertEqual([6, 683, 888, 255, 678, 660, 919, 924], ids)
46 |
47 |
48 | class DetokenizeCase(unittest.TestCase):
49 |
50 | def test_detokenization_single_sign(self):
51 | tokenizer = SignWritingTokenizer()
52 |
53 | tokens = ['M', 'p251', 'p456', 'S1f7', 'c2', 'r0', 'p487', 'p492', 'S1f7', 'c2', 'r0', 'p487', 'p492']
54 | fsw = tokenizer.tokens_to_text(tokens)
55 | self.assertEqual(fsw, 'M251x456S1f720487x492S1f720487x492')
56 |
57 | def test_detokenization_multiple_signs(self):
58 | tokenizer = SignWritingTokenizer()
59 |
60 | tokens = [
61 | 'M', 'p251', 'p456', 'S1f7', 'c2', 'r0', 'p487', 'p492', 'M', 'p124', 'p456', 'S1f2', 'c1', 'r0', 'p488',
62 | 'p493'
63 | ]
64 | fsw = tokenizer.tokens_to_text(tokens)
65 | self.assertEqual(fsw, 'M251x456S1f720487x492 M124x456S1f210488x493')
66 |
67 |
68 | if __name__ == '__main__':
69 | unittest.main()
70 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/IDEA.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # SignDiffusion - A Generic Framework for Sign Language Animation
2 |
3 | ## Introduction
4 |
5 | Building on the success of Ham2Pose @shalev2022ham2pose, which animates HamNoSys notation into pose sequences, we propose a generic framework that supports various conditioning, including HamNoSys, SignWriting, and generic text. The goal is to improve sign language animation by addressing the limitations of the Ham2Pose approach and developing a more generic and flexible framework.
6 |
7 | ## Objectives
8 |
9 | 1. Improve the diffusion process used in Ham2Pose.
10 | 2. Enhance the training method for scalability.
11 | 3. Optimize model evaluation using appropriate metrics.
12 | 4. Utilize both parallel and monolingual pose data for training.
13 | 5. Implement a better sequence length prediction method.
14 | 6. Conduct hyperparameter tuning using WANDB sweeps.
15 |
16 | ## Proposed Solutions
17 |
18 | | Category | Problem | Proposed Solution |
19 | |-------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
20 | | Diffusion Process | Directly predicting $T_{i-1}$ from step $T_i$, instead of predicting $T_0$ and sampling $T_{i-1}$ from it. | Following a standard diffusion process: sampling a step $T_i$, noising the pose to that step, and predicting $T_0$. |
21 | | Training Method | Training by looping over all steps for a single example, not scalable to many diffusion steps. | Sampling a step for each iteration during training. |
22 | | Model Evaluation | Stopping model training based on the loss, not the proposed metrics. | Calculating the DTW-MJE metric and stopping training when it stops improving. |
23 | | Training Data | Only using parallel corpora for training, missing monolingual pose data. | Using both parallel and monolingual pose data for training. |
24 | | Sequence Length | Predicting sequence length as a number using regression, leading to average predictions. | Learning to predict a sequence length distribution (mu, std) and sampling from it. |
25 | | Hyperparameter | No hyper-parameter search | We perform hyperparameter tuning using WANDB sweeps. |
26 |
27 | ## Datasets
28 |
29 | We use the following datasets for training our model:
30 |
31 | | Dataset | Citation | Notation | Number of Videos | Video Length (mean ± std) |
32 | |-----------------|------------------------------------|--------------|------------------|---------------------------|
33 | | Sign2MINT | | SignWriting | \fix{@@} | \fix{@@ ± @@} |
34 | | DictaSign | @dataset:matthes2012dicta | HamNoSys | \fix{@@} | \fix{@@ ± @@} |
35 | | DGS_Types | @dataset:hanke-etal-2020-extending | HamNoSys | \fix{@@} | \fix{@@ ± @@} |
36 | | AUTSL | @dataset:sincan2020autsl | | \fix{@@} | \fix{@@ ± @@} |
37 |
38 | ## Evaluation
39 |
40 | ### Quantitative Evaluation
41 |
42 | We evaluate our model using the DTW-MJE metric, as proposed in @huang2021towards. We assess the model on multiple datasets using the distance metric:
43 |
44 | - Sign2MINT (parallel SignWriting and Poses)
45 | - DictaSign (parallel HamNoSys and Poses), comparing with Ham2Pose
46 | - DGS_Types (parallel HamNoSys and Poses), comparing with Ham2Pose
47 |
48 | ### Qualitative Evaluation
49 |
50 | We include a figure with two subfigures:
51 |
52 | 1. SignWriting example, original Pose Sequence, and predicted Pose Sequence
53 | 2. HamNoSys example, original Pose Sequence, and predicted Pose Sequence
54 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Diffusion
2 |
3 | This is a non-autoregressive pose sequence generator. Starting from a bad pose sequence, we would like to iteratively
4 | refine it, by predicting for each frame the desired change.
5 |
6 | For pretraining, this model can learn to refine any pose sequence, regardless of the text input.
7 | In fine-tuning, the refinement process is conditioned on the text input.
8 |
9 |
10 | ## Training
11 |
12 | ```bash
13 | python -m text_to_pose.diffusion.src.train
14 | ```
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 | -
20 | -
21 | -
22 | -
23 | -
24 | -
25 | -
26 | -
27 | -
28 | -
29 | -
30 | -
31 |
32 | #### Pseudo code:
33 |
34 | ```python
35 | text_embedding = embed(text)
36 | sequence_length = predict_length(text_embedding)
37 | initial_pose_sequence = initial_frame.repeat(sequence_length)
38 | for i in reversed(range(num_steps)):
39 | yield initial_pose_sequence
40 | refinement = predict_change(text_embedding, initial_pose_sequence)
41 | step_size = get_step_size(i)
42 | initial_pose_sequence += step_size * refinement
43 | ```
44 |
45 | ## Advantages:
46 |
47 | 1. Non-autoregressive, and therefore extremely fast (10 refinements, with batch size 32 in 0.15 seconds)
48 | 2. Controllable number of refinements - can try to refine the sequence in 1 step, or let it run for 1000
49 | 3. Controllable appearance - you control the appearance of the output by supplying the first pose
50 | 4. Composable - given multiple sequences to be generated and composed, use the last frame of each sequence to predict
51 | the next one
52 | 5. Consistent - always predicts all keypoints, including the hands
53 | 6. Can be used to correct a pose sequence with missing frames/keypoints
54 |
55 |
56 | ## Extra details
57 |
58 | - Model tests, including overfitting, and continuous integration
59 | - We remove the legs because they are not informative
60 | - For experiment management we use WANDB
61 | - Training works on CPU and GPU (90% util)
62 | - Multiple-GPUs not tested
63 |
64 |
65 |
66 | Instead of predicting the noise as formulated by Ho et al. (2020) `Jonathan Ho, Ajay Jain, and Pieter Abbeel. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. Advances in
67 | Neural Information Processing Systems, 33:6840–6851, 2020.`,
68 | we follow Ramesh et al. (2022) `Aditya Ramesh, Prafulla Dhariwal, Alex Nichol, Casey Chu, and Mark Chen. Hierarchical textconditional image generation with clip latents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.06125, 2022.`
69 | and predict the signal itself, i.e., `xˆ0 = G(xt, t, c)`.
70 |
71 | ## Inference types
72 |
73 | In every time step `t` we predict the clean sample `x_0 = Model(x_t, t, c)` and noise it back to `x_{t−1}`.
74 |
75 | Normal
76 |
77 | Or
78 |
79 | Guidance free
80 | ```
81 | unconditional = Model(x_t, t, ∅)
82 | conditional = Model(x_t, t, c)
83 | Model_f(x_t, t, c) = unconditional + s * (conditional - unconditional)
84 | ```
85 |
86 | ## Example
87 |
88 | Given the following never-seen HamNoSys text sequence:
89 |
90 | 
91 |
92 | We predict the number of frames to generate (77) which is close to the reference number (66).
93 |
94 | We use the first reference frame, expanded 77 times as a starting sequence to be refined iteratively.
95 |
96 | | | Reference | Predicted | Predicted |
97 | |----------------|--------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
98 | | Frames | 66 | 77 | 77 |
99 | | Starting Frame | N/A | From [494_GSL](https://www.sign-lang.uni-hamburg.de/dicta-sign/portal/concepts/gsl/494.mp4) | From [118_LSF](https://www.sign-lang.uni-hamburg.de/dicta-sign/portal/concepts/lsf/118.mp4) |
100 | | Pose |  |  |  |
101 |
102 | With the following [training](https://wandb.ai/amit_my/text-to-pose/runs/392fs203) loss curve:
103 |
104 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/src/train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 |
3 | import pytorch_lightning as pl
4 | from pytorch_lightning.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint
5 | from pytorch_lightning.loggers import WandbLogger
6 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
7 |
8 | from _shared.collator import zero_pad_collator
9 | from _shared.models import PoseEncoderModel
10 | from _shared.tokenizers import HamNoSysTokenizer
11 |
12 | from text_to_pose.diffusion.src.args import args
13 | from .data import get_datasets, get_dataset
14 | from text_to_pose.diffusion.src.model.iterative_decoder import IterativeGuidedPoseGenerationModel
15 | from text_to_pose.diffusion.src.model.text_encoder import TextEncoderModel
16 |
17 | if __name__ == '__main__':
18 | LOGGER = None
19 | if not args.no_wandb:
20 | LOGGER = WandbLogger(project="text-to-pose", log_model=False, offline=False)
21 | if LOGGER.experiment.sweep_id is None:
22 | LOGGER.log_hyperparams(args)
23 |
24 | train_dataset = get_datasets(poses=args.pose,
25 | fps=args.fps,
26 | components=args.pose_components,
27 | max_seq_size=args.max_seq_size,
28 | split="train[5:]")
29 | train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True, collate_fn=zero_pad_collator)
30 |
31 | # validation_dataset = get_datasets(poses=args.pose,
32 | # fps=args.fps,
33 | # components=args.pose_components,
34 | # max_seq_size=args.max_seq_size,
35 | # split="train[:10]")
36 |
37 | validation_dataset = get_dataset(poses=args.pose,
38 | fps=args.fps,
39 | components=args.pose_components,
40 | max_seq_size=args.max_seq_size,
41 | split="train[:10]")
42 | validation_loader = DataLoader(validation_dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size, collate_fn=zero_pad_collator)
43 |
44 | # # TODO remove, this tests ovefitting
45 | # train_dataset = validation_dataset
46 | # train_loader = validation_loader
47 |
48 | _, num_pose_joints, num_pose_dims = train_dataset[0]["pose"]["data"].shape
49 |
50 | pose_encoder = PoseEncoderModel(pose_dims=(num_pose_joints, num_pose_dims),
51 | hidden_dim=args.hidden_dim,
52 | encoder_depth=args.pose_encoder_depth,
53 | encoder_heads=args.encoder_heads,
54 | encoder_dim_feedforward=args.encoder_dim_feedforward,
55 | max_seq_size=args.max_seq_size,
56 | dropout=0)
57 |
58 | text_encoder = TextEncoderModel(tokenizer=HamNoSysTokenizer(),
59 | max_seq_size=args.max_seq_size,
60 | hidden_dim=args.hidden_dim,
61 | num_layers=args.text_encoder_depth,
62 | dim_feedforward=args.encoder_dim_feedforward,
63 | encoder_heads=args.encoder_heads)
64 |
65 | # Model Arguments
66 | model_args = dict(pose_encoder=pose_encoder,
67 | text_encoder=text_encoder,
68 | hidden_dim=args.hidden_dim,
69 | learning_rate=args.learning_rate,
70 | seq_len_loss_weight=args.seq_len_loss_weight,
71 | smoothness_loss_weight=args.smoothness_loss_weight,
72 | noise_epsilon=args.noise_epsilon,
73 | num_steps=args.num_steps)
74 |
75 | if args.checkpoint is not None:
76 | model = IterativeGuidedPoseGenerationModel.load_from_checkpoint(args.checkpoint, **model_args)
77 | else:
78 | model = IterativeGuidedPoseGenerationModel(**model_args)
79 |
80 | callbacks = []
81 | if LOGGER is not None:
82 | os.makedirs("models", exist_ok=True)
83 |
84 | callbacks.append(
85 | ModelCheckpoint(dirpath="models/" + LOGGER.experiment.name,
86 | filename="model",
87 | verbose=True,
88 | save_top_k=1,
89 | monitor='validation_dtw_mje',
90 | mode='min'))
91 |
92 | trainer = pl.Trainer(max_epochs=5000,
93 | logger=LOGGER,
94 | callbacks=callbacks,
95 | check_val_every_n_epoch=1,
96 | accelerator='gpu',
97 | devices=args.num_gpus)
98 |
99 | trainer.fit(model, train_dataloaders=train_loader, val_dataloaders=validation_loader)
100 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pose_to_text/IDEA.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Automatic Transcription of Sign Languages Using SignWriting
2 |
3 | ## Introduction
4 |
5 | Sign languages are rich and diverse forms of communication, yet their transcription and documentation face challenges
6 | due to the lack of standardized writing systems.
7 | SignWriting, a unique notation system, seeks to universally represent sign languages in written form, as 2D pictographs.
8 | This research proposal aims to develop an automatic transcription system for sign
9 | languages using SignWriting notation. The system will take a video of a single sign in sign language as input and
10 | generate SignWriting as output.
11 |
12 | ## Literature Review
13 |
14 | ### SignWriting
15 |
16 | Valerie Sutton introduced SignWriting in 1974 as a visual script designed to represent sign languages. This script
17 | captures the movements, facial expressions, and body positions unique to each sign. SignWriting has found applications
18 | in education, research, and daily communication within the deaf community.
19 |
20 | ## Sign Language Datasets
21 |
22 | 1. Sign2MINT: A lexicon of German Sign Language (DGS) that focuses on natural science subjects, featuring 5,263 videos
23 | with SignWriting transcriptions.
24 | 2. SignSuisse: A Swiss Sign Language Lexicon that covers all three Swiss sign languages: Swiss-German Sign Language (
25 | DSGS), Langue des Signes Française (LSF), and Lingua Italiana dei Segni (LIS). Approximately 5,000 LSF videos include
26 | SignWriting transcriptions in SignBank.
27 |
28 | ## Methodology
29 |
30 | The proposed research will utilize the Neural Machine Translation (NMT) framework to model the problem as a
31 | sequence-to-sequence task, using JoeyNMT 2.2.0 for experimentation.
32 |
33 | ### Data Representation
34 |
35 | 1. Input: Videos will be preprocessed with the MediaPipe framework to extract 3D skeletal poses. While these poses have
36 | limitations and do not capture the full range of a sign, they serve as a compromise for avoiding video input.
37 | 2. Output: Formal SignWriting in ASCII (FSW), e.g., "M518x529S14c20481x471S27106503x489"
38 |
39 | ### Data Preprocessing
40 |
41 | Outputs will be tokenized to separate shape, orientation, and position, e.g., "M 518 x 529 S14c 2 0 481 x 471 S271 0 6
42 | 503 x 489". Predictable symbols, such as "M" and "x," will be removed to create a more compact sequence: "518 529 S14c 2
43 | 0 481 471 S271 0 6 503 489".
44 |
45 | ### Experiments
46 |
47 | #### Input Experiments
48 |
49 | - Use poses as they are.
50 | - Pose Sequence Length Reduction: As the input pose sequence length often exceeds the output length, poses unchanged
51 | from the previous frame will be removed. Optical flow calculations and threshold checks will be used for this purpose.
52 | - Hand and Face Normalization: To emphasize the importance of hand and face shapes, 3D hand and face normalization will
53 | be included in the experiments. The face will be replaced with a normalized face, and 3D normalized hands will be
54 | added alongside the original hands.
55 |
56 | #### Output Experiments
57 |
58 | 1. Embedding-based token representation: At every step of the decoder, we represent input tokens using an embedding matrix.
59 | 2. Image-based token representation: Instead of inputting embeddings for each token in the decoder, the sequence up to
60 | that point will be drawn into an image. This method employs the same number of tokens but represents them as images
61 | instead of embeddings.
62 | 3. Token prediction without history: The self-attention in the decoder will be removed, and images will be "colored"
63 | based on the next predicted token. The decoder will receive the input sequence and the last image, predicting a token
64 | without considering the prediction history. This approach may improve robustness and memory efficiency, as there is
65 | no need to review the prediction history. During training, all images will be produced, while only the final image
66 | will be generated during testing.
67 |
68 | ### Quality Metrics
69 |
70 | SignCLIPScore: We use SignCLIP to measure the similarity between the input pose sequence and output SignWriting.
71 | (Just like CLIPScore for images (https://arxiv.org/pdf/2104.08718.pdf))
72 |
73 | ## Conclusion
74 |
75 | The proposed research seeks to develop an automatic transcription system for sign languages using SignWriting notation.
76 | By leveraging the NMT framework and conducting various input and output preprocessing experiments, this project will
77 | contribute to the advancement of sign language transcription technology. The outcomes of the experiments will be
78 | compared and analyzed to determine the most effective method for automatic transcription using SignWriting.
79 |
80 |
81 | ```latex
82 | \documentclass{article}
83 | \usepackage{booktabs}
84 | \usepackage{multirow}
85 | \usepackage{makecell}
86 |
87 | \begin{document}
88 |
89 | \begin{table}[h!]
90 | \centering
91 | \begin{tabular}{@{}llccc@{}}
92 | \toprule
93 | \multirow{2}{*}{\textbf{Input Experiment}} & \multirow{2}{*}{\textbf{Output Experiment}} & \multicolumn{3}{c}{\textbf{Results}} \\
94 | \cmidrule(lr){3-5}
95 | & & \textbf{Metric 1} & \textbf{Metric 2} & \textbf{Metric 3} \\
96 | \midrule
97 | \multirow{3}{*}{As is} & Embedding-based & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
98 | & Image-based & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
99 | & No history & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
100 | \midrule
101 | \multirow{3}{*}{+ Length Reduction} & Embedding-based & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
102 | & Image-based & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
103 | & No history & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
104 | \midrule
105 | \multirow{3}{*}{+ Normalization} & Embedding-based & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
106 | & Image-based & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
107 | & No history & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
108 | \midrule
109 | \multirow{3}{*}{\makecell{+ Length Reduction\\+ Normalization}} & Embedding-based & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
110 | & Image-based & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
111 | & No history & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
112 | \bottomrule
113 | \end{tabular}
114 | \caption{Results of Input and Output Experiments}
115 | \label{table:results}
116 | \end{table}
117 |
118 | \end{document}
119 | ```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pose_to_text/IDEA-CLIP.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # SignCLIP: Contrastive Pre-training for Phonetic Sign Language Understanding
2 |
3 | ## Introduction
4 |
5 | Sign languages are rich and diverse forms of communication, yet their transcription and documentation face challenges
6 | due to the lack of standardized writing systems.
7 | SignWriting, a unique notation system, seeks to universally represent sign languages in written form, as 2D pictographs.
8 | Similarly, HamNoSys, is a phonetic transcription system that writes signs as a sequence of symbols.
9 | This research proposal aims to develop an automatic transcription system for sign
10 | languages using SignWriting notation. The system will take a video of a single sign in sign language as input and
11 | generate SignWriting as output.
12 |
13 | ## Literature Review
14 |
15 | ### SignWriting
16 |
17 | Valerie Sutton introduced SignWriting in 1974 as a visual script designed to represent sign languages. This script
18 | captures the movements, facial expressions, and body positions unique to each sign. SignWriting has found applications
19 | in education, research, and daily communication within the deaf community.
20 | Similarly, HamNoSys, is a phonetic transcription system that writes signs as a sequence of symbols.
21 |
22 | ## Sign Language Datasets
23 |
24 | 1. Sign2MINT: A lexicon of German Sign Language (DGS) that focuses on natural science subjects, featuring 5,263 videos
25 | with SignWriting transcriptions.
26 | 2. SignSuisse: A Swiss Sign Language Lexicon that covers all three Swiss sign languages: Swiss-German Sign Language (
27 | DSGS), Langue des Signes Française (LSF), and Lingua Italiana dei Segni (LIS). Approximately 5,000 LSF videos include
28 | SignWriting transcriptions in SignBank.
29 | 3. DictaSign Lexicon: A dictionary of 1000+ concepts with a sign language equivalent in four languages:
30 | British Sign Language (BSL), German Sign Language (DGS), Greek Sign Language (GSL) and French Sign Language (LSF).
31 | Each concept is represented by a video of a sign, and a HamNoSys transcription.
32 | 4. MeineDGS Types: A lexicon of \fix{@@} signs in DGS, with HamNoSys transcriptions.
33 | 5. ChicagoFSWild: An American Sign Language (ASL) fingerspelling dataset, with synthetic SignWriting transcriptions.
34 |
35 | ##
36 |
37 |
38 | ## Methodology
39 |
40 | The proposed research will utilize the Neural Machine Translation (NMT) framework to model the problem as a
41 | sequence-to-sequence task, using JoeyNMT 2.2.0 for experimentation.
42 |
43 | ### Data Representation
44 |
45 | 1. Input: Videos will be preprocessed with the MediaPipe framework to extract 3D skeletal poses. While these poses have
46 | limitations and do not capture the full range of a sign, they serve as a compromise for avoiding video input.
47 | 2. Output: Formal SignWriting in ASCII (FSW), e.g., "M518x529S14c20481x471S27106503x489"
48 |
49 | ### Data Preprocessing
50 |
51 | Outputs will be tokenized to separate shape, orientation, and position, e.g., "M 518 x 529 S14c 2 0 481 x 471 S271 0 6
52 | 503 x 489". Predictable symbols, such as "M" and "x," will be removed to create a more compact sequence: "518 529 S14c 2
53 | 0 481 471 S271 0 6 503 489".
54 |
55 | ### Experiments
56 |
57 | #### Input Experiments
58 |
59 | - Use poses as they are.
60 | - Pose Sequence Length Reduction: As the input pose sequence length often exceeds the output length, poses unchanged
61 | from the previous frame will be removed. Optical flow calculations and threshold checks will be used for this purpose.
62 | - Hand and Face Normalization: To emphasize the importance of hand and face shapes, 3D hand and face normalization will
63 | be included in the experiments. The face will be replaced with a normalized face, and 3D normalized hands will be
64 | added alongside the original hands.
65 |
66 | #### Output Experiments
67 |
68 | 1. Embedding-based token representation: At every step of the decoder, we represent input tokens using an embedding matrix.
69 | 2. Image-based token representation: Instead of inputting embeddings for each token in the decoder, the sequence up to
70 | that point will be drawn into an image. This method employs the same number of tokens but represents them as images
71 | instead of embeddings.
72 | 3. Token prediction without history: The self-attention in the decoder will be removed, and images will be "colored"
73 | based on the next predicted token. The decoder will receive the input sequence and the last image, predicting a token
74 | without considering the prediction history. This approach may improve robustness and memory efficiency, as there is
75 | no need to review the prediction history. During training, all images will be produced, while only the final image
76 | will be generated during testing.
77 |
78 | ## Conclusion
79 |
80 | The proposed research seeks to develop an automatic transcription system for sign languages using SignWriting notation.
81 | By leveraging the NMT framework and conducting various input and output preprocessing experiments, this project will
82 | contribute to the advancement of sign language transcription technology. The outcomes of the experiments will be
83 | compared and analyzed to determine the most effective method for automatic transcription using SignWriting.
84 |
85 |
86 | ```latex
87 | \documentclass{article}
88 | \usepackage{booktabs}
89 | \usepackage{multirow}
90 | \usepackage{makecell}
91 |
92 | \begin{document}
93 |
94 | \begin{table}[h!]
95 | \centering
96 | \begin{tabular}{@{}llccc@{}}
97 | \toprule
98 | \multirow{2}{*}{\textbf{Input Experiment}} & \multirow{2}{*}{\textbf{Output Experiment}} & \multicolumn{3}{c}{\textbf{Results}} \\
99 | \cmidrule(lr){3-5}
100 | & & \textbf{Metric 1} & \textbf{Metric 2} & \textbf{Metric 3} \\
101 | \midrule
102 | \multirow{3}{*}{As is} & Embedding-based & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
103 | & Image-based & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
104 | & No history & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
105 | \midrule
106 | \multirow{3}{*}{+ Length Reduction} & Embedding-based & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
107 | & Image-based & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
108 | & No history & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
109 | \midrule
110 | \multirow{3}{*}{+ Normalization} & Embedding-based & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
111 | & Image-based & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
112 | & No history & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
113 | \midrule
114 | \multirow{3}{*}{\makecell{+ Length Reduction\\+ Normalization}} & Embedding-based & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
115 | & Image-based & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
116 | & No history & @@ & @@ & @@ \\
117 | \bottomrule
118 | \end{tabular}
119 | \caption{Results of Input and Output Experiments}
120 | \label{table:results}
121 | \end{table}
122 |
123 | \end{document}
124 | ```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pose_to_text/configs/default.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: "toy_experiment" # name of experiment
2 | joeynmt_version: "2.2.0" # joeynmt version
3 |
4 | data:
5 | pose: "holistic"
6 | components:
7 | - "POSE_LANDMARKS"
8 | - "LEFT_HAND_LANDMARKS"
9 | - "RIGHT_HAND_LANDMARKS"
10 | fps: 25
11 | max_seq_size: 1000
12 | writing: "signwriting" # "signwriting" or "text"
13 |
14 | testing: # specify which inference algorithm to use for testing (for validation it's always greedy decoding)
15 | n_best: 1 # n_best size, must be smaller than or equal to beam_size
16 | beam_size: 5 # size of the beam for beam search
17 | beam_alpha: 1.0 # length penalty for beam search
18 | batch_size: 1024 # mini-batch size for evaluation
19 | batch_type: "token" # evaluation batch type ("sentence", default) or tokens ("token")
20 | eval_metrics: [ "bleu", "chrf" ]# validation metric, default: "bleu", other options: "chrf", "token_accuracy", "sequence_accuracy"
21 | max_output_length: 50 # maximum output length for decoding, default: None. If set to None, allow sentences of max 1.5*src length
22 | min_output_length: 1 # minimum output length for decoding, default: 1.
23 | return_prob: "none" # whether to return probabilities of references ("ref") or hypotheses ("hyp"). default: "none".
24 | return_attention: False # whether to return attention scores, default: False. (enabled if --save_attention flag is set.)
25 | generate_unk: True # whether to generate unk token
26 | no_repeat_ngram_size: 1 # ngram size to prohibit repetition, default -1. If set to -1, no blocker applied.
27 | repetition_penalty: -1 # repetition penalty, default: -1. If set to -1, no penalty applied.
28 | sacrebleu_cfg: # sacrebleu options
29 | whitespace: False # `whitespace` option in sacrebleu.metrics.CHRF() class (default: False)
30 | tokenize: "13a" # `tokenize` option in sacrebleu.metrics.BLEU() class (default: 13a)
31 |
32 | training: # specify training details here
33 | random_seed: 42 # set this seed to make training deterministic
34 | optimizer: "adam" # choices: "sgd", "adam", "adadelta", "adagrad", "rmsprop", default is SGD
35 | adam_betas: [ 0.9, 0.98 ] # beta parameters for Adam. These are the defaults. Typically these are different for Transformer models.
36 | learning_rate: 0.001 # initial learning rate, default: 3.0e-4
37 | learning_rate_min: 0.00000001 # stop learning when learning rate is reduced below this threshold, default: 1.0e-8
38 | #learning_rate_factor: 1 # factor for Noam scheduler (used with Transformer)
39 | learning_rate_warmup: 4000 # warmup steps for Noam scheduler (used with Transformer)
40 | # clip_grad_val: 0 # clip the gradients to this value when they exceed it, optional
41 | clip_grad_norm: 1.0 # norm clipping instead of value clipping
42 | weight_decay: 0. # l2 regularization, default: 0
43 | loss: "crossentropy" # loss type, default: "crossentropy"
44 | label_smoothing: 0.1 # label smoothing: reference tokens will have 1-label_smoothing probability instead of 1, rest of probability mass is uniformly distributed over the rest of the vocabulary, default: 0.0 (off)
45 | batch_size: 8192 # mini-batch size as number of sentences (when batch_type is "sentence"; default) or total number of tokens (when batch_type is "token"). When you use more than 1 GPUs, the actual batch size per device will be: batch_size // n_gpu.
46 | batch_type: "token" # create batches with sentences ("sentence", default) or tokens ("token")
47 | batch_multiplier: 1 # increase the effective batch size with values >1 to batch_multiplier*batch_size without increasing memory consumption by making updates only every batch_multiplier batches
48 | normalization: "tokens" # loss normalization of a mini-batch, default: "batch" (by number of sequences in batch), other options: "tokens" (by number of tokens in batch), "none" (don't normalize, sum up loss)
49 | scheduling: "warmupinversesquareroot" # learning rate scheduling, optional, if not specified stays constant, options: "plateau", "exponential", "decaying", "noam" (for Transformer), "warmupexponentialdecay", "warmupinversesquareroot"
50 | patience: 5 # specific to plateau scheduler: wait for this many validations without improvement before decreasing the learning rate
51 | decrease_factor: 0.5 # specific to plateau & exponential scheduler: decrease the learning rate by this factor
52 | epochs: 100 # train for this many epochs (will be reset in resumed process)
53 | updates: 36000 # train for this many updates (won't be reset in resumed process)
54 | validation_freq: 1000 # validate after this many updates (number of mini-batches), default: 1000
55 | logging_freq: 100 # log the training progress after this many updates, default: 100
56 | early_stopping_metric: "ppl" # when a new high score on this metric is achieved, a checkpoint is written, when "eval_metric" (default) is maximized, when "loss" or "ppl" is minimized
57 | model_dir: "toy_transformer" # directory where models and validation results are stored, required
58 | overwrite: True # overwrite existing model directory, default: False. Do not set to True unless for debugging!
59 | shuffle: True # shuffle the training data, default: True
60 | use_cuda: True # use CUDA for acceleration on GPU, required. Set to False when working on CPU.
61 | fp16: False # whether to use 16-bit half-precision training (through NVIDIA apex) instead of 32-bit training.
62 | print_valid_sents: [ 0, 1, 2, 3 ] # print this many validation sentences during each validation run, default: [0, 1, 2]
63 | keep_best_ckpts: 3 # keep this many of the best checkpoints, if -1: all of them, default: 5
64 |
65 | model: # specify your model architecture here
66 | initializer: "xavier_normal"
67 | bias_initializer: "zeros"
68 | init_gain: 1.0
69 | embed_initializer: "xavier_normal"
70 | embed_init_gain: 1.0
71 | tied_embeddings: False
72 | tied_softmax: False
73 | pose_encoder:
74 | hidden_size: 512
75 | ff_size: 512
76 | num_layers: 1
77 | num_heads: 4
78 | dropout: 0.1
79 | embeddings:
80 | embedding_dim: 272 # 1 point less than default
81 | encoder:
82 | type: "transformer"
83 | num_layers: 6
84 | num_heads: 8
85 | embeddings:
86 | embedding_dim: 512
87 | scale: True
88 | dropout: 0.1
89 | # typically ff_size = 4 x hidden_size
90 | hidden_size: 512
91 | ff_size: 2048
92 | dropout: 0.1
93 | layer_norm: "post"
94 | decoder:
95 | type: "transformer"
96 | num_layers: 6
97 | num_heads: 8
98 | embeddings:
99 | embedding_dim: 512
100 | scale: True
101 | dropout: 0.1
102 | # typically ff_size = 4 x hidden_size
103 | hidden_size: 512
104 | ff_size: 2048
105 | dropout: 0.1
106 | layer_norm: "post"
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_shared/pose_utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from typing import Tuple
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 | from numpy import ma
5 | from pose_format import Pose
6 | from pose_format.numpy import NumPyPoseBody
7 | from pose_format.pose_header import PoseHeader, PoseHeaderDimensions
8 | from pose_format.utils.normalization_3d import PoseNormalizer
9 | from pose_format.utils.openpose import OpenPose_Components
10 |
11 |
12 | def pose_hide_legs(pose: Pose):
13 | if pose.header.components[0].name == "POSE_LANDMARKS":
14 | point_names = ["KNEE", "ANKLE", "HEEL", "FOOT_INDEX"]
15 | # pylint: disable=protected-access
16 | points = [
17 | pose.header._get_point_index("POSE_LANDMARKS", side + "_" + n)
18 | for n in point_names
19 | for side in ["LEFT", "RIGHT"]
20 | ]
21 | pose.body.data[:, :, points, :] = 0
22 | pose.body.confidence[:, :, points] = 0
23 | elif pose.header.components[0].name == "pose_keypoints_2d":
24 | point_names = ["Hip", "Knee", "Ankle", "BigToe", "SmallToe", "Heel"]
25 | # pylint: disable=protected-access
26 | points = [
27 | pose.header._get_point_index("pose_keypoints_2d", side + n)
28 | for n in point_names
29 | for side in ["L", "R"]
30 | ]
31 | pose.body.data[:, :, points, :] = 0
32 | pose.body.confidence[:, :, points] = 0
33 | else:
34 | raise ValueError("Unknown pose header schema for hiding legs")
35 |
36 |
37 | def pose_shoulders(pose_header: PoseHeader):
38 | if pose_header.components[0].name == "POSE_LANDMARKS":
39 | return ("POSE_LANDMARKS", "RIGHT_SHOULDER"), ("POSE_LANDMARKS", "LEFT_SHOULDER")
40 |
41 | if pose_header.components[0].name == "BODY_135":
42 | return ("BODY_135", "RShoulder"), ("BODY_135", "LShoulder")
43 |
44 | if pose_header.components[0].name == "pose_keypoints_2d":
45 | return ("pose_keypoints_2d", "RShoulder"), ("pose_keypoints_2d", "LShoulder")
46 |
47 | raise ValueError("Unknown pose header schema for normalization")
48 |
49 |
50 | def hands_indexes(pose_header: PoseHeader):
51 | if pose_header.components[0].name == "POSE_LANDMARKS":
52 | return [pose_header._get_point_index("LEFT_HAND_LANDMARKS", "MIDDLE_FINGER_MCP"),
53 | pose_header._get_point_index("RIGHT_HAND_LANDMARKS", "MIDDLE_FINGER_MCP")]
54 |
55 | if pose_header.components[0].name == "pose_keypoints_2d":
56 | return [pose_header._get_point_index("hand_left_keypoints_2d", "M_CMC"),
57 | pose_header._get_point_index("hand_right_keypoints_2d", "M_CMC")]
58 |
59 |
60 | def pose_normalization_info(pose_header: PoseHeader):
61 | (c1, p1), (c2, p2) = pose_shoulders(pose_header)
62 | return pose_header.normalization_info(p1=(c1, p1), p2=(c2, p2))
63 |
64 |
65 | def hands_components(pose_header: PoseHeader):
66 | if pose_header.components[0].name in ["POSE_LANDMARKS", "LEFT_HAND_LANDMARKS", "RIGHT_HAND_LANDMARKS"]:
67 | return ("LEFT_HAND_LANDMARKS", "RIGHT_HAND_LANDMARKS"), \
68 | ("WRIST", "PINKY_MCP", "INDEX_FINGER_MCP"), \
69 | ("WRIST", "MIDDLE_FINGER_MCP")
70 |
71 | if pose_header.components[0].name in ["pose_keypoints_2d", "hand_left_keypoints_2d", "hand_right_keypoints_2d"]:
72 | return ("hand_left_keypoints_2d", "hand_right_keypoints_2d"), \
73 | ("BASE", "P_CMC", "I_CMC"), \
74 | ("BASE", "M_CMC")
75 |
76 | raise ValueError("Unknown pose header")
77 |
78 |
79 | def normalize_component_3d(pose, component_name: str, plane: Tuple[str, str, str], line: Tuple[str, str]):
80 | hand_pose = pose.get_components([component_name])
81 | plane = hand_pose.header.normalization_info(p1=(component_name, plane[0]),
82 | p2=(component_name, plane[1]),
83 | p3=(component_name, plane[2]))
84 | line = hand_pose.header.normalization_info(p1=(component_name, line[0]),
85 | p2=(component_name, line[1]))
86 | normalizer = PoseNormalizer(plane=plane, line=line)
87 | normalized_hand = normalizer(hand_pose.body.data)
88 |
89 | # Add normalized hand to pose
90 | pose.body.data = ma.concatenate([pose.body.data, normalized_hand], axis=2).astype(np.float32)
91 | pose.body.confidence = np.concatenate([pose.body.confidence, hand_pose.body.confidence], axis=2)
92 |
93 |
94 | def normalize_hands_3d(pose: Pose, left_hand=True, right_hand=True):
95 | (left_hand_component, right_hand_component), plane, line = hands_components(pose.header)
96 | if left_hand:
97 | normalize_component_3d(pose, left_hand_component, plane, line)
98 | if right_hand:
99 | normalize_component_3d(pose, right_hand_component, plane, line)
100 |
101 |
102 | def fake_pose(num_frames: int, fps=25, dims=2, components=OpenPose_Components):
103 | dimensions = PoseHeaderDimensions(width=1, height=1, depth=1)
104 | header = PoseHeader(version=0.1, dimensions=dimensions, components=components)
105 |
106 | total_points = header.total_points()
107 | data = np.random.randn(num_frames, 1, total_points, dims)
108 | confidence = np.random.randn(num_frames, 1, total_points)
109 | masked_data = ma.masked_array(data)
110 |
111 | body = NumPyPoseBody(fps=int(fps), data=masked_data, confidence=confidence)
112 |
113 | return Pose(header, body)
114 |
115 |
116 | def correct_wrist(pose: Pose, hand: str) -> Pose:
117 | wrist_index = pose.header._get_point_index(f'{hand}_HAND_LANDMARKS', 'WRIST')
118 | wrist = pose.body.data[:, :, wrist_index]
119 | wrist_conf = pose.body.confidence[:, :, wrist_index]
120 |
121 | body_wrist_index = pose.header._get_point_index('POSE_LANDMARKS', f'{hand}_WRIST')
122 | body_wrist = pose.body.data[:, :, body_wrist_index]
123 | body_wrist_conf = pose.body.confidence[:, :, body_wrist_index]
124 |
125 | new_wrist_data = ma.where(wrist.data == 0, body_wrist, wrist)
126 | new_wrist_conf = ma.where(wrist_conf == 0, body_wrist_conf, wrist_conf)
127 |
128 | pose.body.data[:, :, body_wrist_index] = ma.masked_equal(new_wrist_data, 0)
129 | pose.body.confidence[:, :, body_wrist_index] = new_wrist_conf
130 | return pose
131 |
132 |
133 | def correct_wrists(pose: Pose) -> Pose:
134 | pose = correct_wrist(pose, 'LEFT')
135 | pose = correct_wrist(pose, 'RIGHT')
136 | return pose
137 |
138 |
139 | def reduce_holistic(pose: Pose) -> Pose:
140 | if pose.header.components[0].name != "POSE_LANDMARKS":
141 | return pose
142 |
143 | import mediapipe as mp
144 | points_set = set([p for p_tup in list(mp.solutions.holistic.FACEMESH_CONTOURS) for p in p_tup])
145 | face_contours = [str(p) for p in sorted(points_set)]
146 |
147 | ignore_names = [
148 | "EAR", "NOSE", "MOUTH", "EYE", # Face
149 | "THUMB", "PINKY", "INDEX", # Hands
150 | "KNEE", "ANKLE", "HEEL", "FOOT_INDEX" # Feet
151 | ]
152 |
153 | body_component = [c for c in pose.header.components if c.name == 'POSE_LANDMARKS'][0]
154 | body_no_face_no_hands = [p for p in body_component.points if all([i not in p for i in ignore_names])]
155 |
156 | components = [c.name for c in pose.header.components if c.name != 'POSE_WORLD_LANDMARKS']
157 | return pose.get_components(components, {
158 | "FACE_LANDMARKS": face_contours,
159 | "POSE_LANDMARKS": body_no_face_no_hands
160 | })
161 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/src/pred.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import shutil
3 | from typing import List
4 |
5 | import torch
6 | from pose_format import Pose
7 | from pose_format.numpy.pose_body import NumPyPoseBody
8 | from pose_format.pose_header import PoseHeader
9 | from pose_format.pose_visualizer import PoseVisualizer
10 |
11 | from _shared.models import PoseEncoderModel
12 | from _shared.pose_utils import pose_hide_legs, pose_normalization_info
13 | from _shared.tokenizers import HamNoSysTokenizer
14 |
15 | from text_to_pose.diffusion.src.args import args
16 | from .data import get_datasets
17 | from text_to_pose.diffusion.src.model.iterative_decoder import IterativeGuidedPoseGenerationModel
18 | from text_to_pose.diffusion.src.model.text_encoder import TextEncoderModel
19 |
20 | os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "" # Only use CPU
21 |
22 |
23 | def visualize_pose(pose: Pose, pose_name: str):
24 | normalization_info = pose_normalization_info(pose.header)
25 |
26 | # Normalize pose
27 | pose = pose.normalize(normalization_info, scale_factor=100)
28 | pose.focus()
29 |
30 | # Draw original pose
31 | visualizer = PoseVisualizer(pose, thickness=2)
32 | visualizer.save_video(os.path.join(args.output_dir, pose_name), visualizer.draw(), custom_ffmpeg=args.ffmpeg_path)
33 |
34 |
35 | def visualize_poses(_id: str, text: str, poses: List[Pose]) -> str:
36 | lengths = " / ".join([str(len(p.body.data)) for p in poses])
37 | html_tags = f"{_id}: {text} ({lengths})
(original / pred / pred + length / cfg)
"
38 |
39 | for k, pose in enumerate(poses):
40 | pose_name = f"{_id}_{k}.mp4"
41 | visualize_pose(pose, pose_name)
42 | html_tags += f""
43 |
44 | return html_tags
45 |
46 |
47 | def data_to_pose(pose_body: NumPyPoseBody, pose_header: PoseHeader):
48 | predicted_pose = Pose(header=pose_header, body=pose_body)
49 | pose_hide_legs(predicted_pose)
50 | return predicted_pose
51 |
52 |
53 | if __name__ == '__main__':
54 | if args.checkpoint is None:
55 | raise ValueError("Must specify `checkpoint`")
56 | if args.output_dir is None:
57 | raise ValueError("Must specify `output_dir`")
58 | if args.ffmpeg_path is None:
59 | raise ValueError("Must specify `ffmpeg_path`")
60 |
61 | os.makedirs(args.output_dir, exist_ok=True)
62 |
63 | dataset = get_datasets(poses=args.pose,
64 | fps=args.fps,
65 | components=args.pose_components,
66 | max_seq_size=args.max_seq_size,
67 | split="train[:10]")
68 |
69 | _, num_pose_joints, num_pose_dims = dataset[0]["pose"]["data"].shape
70 | pose_header = dataset.data[0]["pose"].header
71 |
72 | pose_encoder = PoseEncoderModel(pose_dims=(num_pose_joints, num_pose_dims),
73 | hidden_dim=args.hidden_dim,
74 | encoder_depth=args.pose_encoder_depth,
75 | encoder_heads=args.encoder_heads,
76 | encoder_dim_feedforward=args.encoder_dim_feedforward,
77 | max_seq_size=args.max_seq_size,
78 | dropout=0)
79 |
80 | text_encoder = TextEncoderModel(tokenizer=HamNoSysTokenizer(),
81 | max_seq_size=args.max_seq_size,
82 | hidden_dim=args.hidden_dim,
83 | num_layers=args.text_encoder_depth,
84 | dim_feedforward=args.encoder_dim_feedforward,
85 | encoder_heads=args.encoder_heads)
86 |
87 | # Model Arguments
88 | model_args = dict(pose_encoder=pose_encoder,
89 | text_encoder=text_encoder,
90 | hidden_dim=args.hidden_dim,
91 | learning_rate=args.learning_rate,
92 | noise_epsilon=args.noise_epsilon,
93 | num_steps=args.num_steps)
94 |
95 | model = IterativeGuidedPoseGenerationModel.load_from_checkpoint(args.checkpoint, **model_args)
96 | model.eval()
97 |
98 | html = []
99 |
100 | with torch.no_grad():
101 | for datum in dataset:
102 | pose_data = datum["pose"]["data"]
103 | first_pose = pose_data[0]
104 | sequence_length = pose_data.shape[0]
105 | # datum["text"] = ""
106 | fps = 25 if args.fps is None else args.fps
107 | pred_normal = model.forward(text=datum["text"], first_pose=first_pose)
108 | pred_normal_body = model.forward_to_body(pred_normal, fps=fps)
109 | pred_len = model.forward(text=datum["text"], first_pose=first_pose, force_sequence_length=sequence_length)
110 | pred_len_body = model.forward_to_body(pred_len, fps=fps)
111 | pred_cfg = model.forward(text=datum["text"], first_pose=first_pose, classifier_free_guidance=2.5)
112 | pred_cfg_body = model.forward_to_body(pred_cfg, fps=fps)
113 |
114 | html.append(
115 | visualize_poses(_id=datum["id"],
116 | text=datum["text"],
117 | poses=[
118 | datum["pose"]["obj"],
119 | data_to_pose(pred_normal_body, pose_header),
120 | data_to_pose(pred_len_body, pose_header),
121 | data_to_pose(pred_cfg_body, pose_header)
122 | ]))
123 |
124 | # # Iterative change
125 | # datum = dataset[12] # dataset[0] starts with an empty frame
126 | # first_pose = datum["pose"]["data"][0]
127 | # seq_iter = model.forward(text=datum["text"], first_pose=first_pose, step_size=1)
128 | #
129 | # data = torch.stack([next(seq_iter) for i in range(1000)], dim=1)
130 | # data = data[:, ::100, :, :]
131 | #
132 | # conf = torch.ones_like(data[:, :, :, 0])
133 | # pose_body = NumPyPoseBody(args.fps, data.numpy(), conf.numpy())
134 | # predicted_pose = Pose(pose_header, pose_body)
135 | # pose_hide_legs(predicted_pose)
136 | # predicted_pose.focus()
137 | # # shift poses
138 | # for i in range(predicted_pose.body.data.shape[1] - 1):
139 | # max_x = np.max(predicted_pose.body.data[:, i, :, 0])
140 | # predicted_pose.body.data[:, i + 1, :, 0] += max_x
141 | #
142 | # html.append(visualize_poses(_id=datum["id"] + "_iterative",
143 | # text=datum["text"],
144 | # poses=[datum["pose"]["obj"], predicted_pose]))
145 |
146 | with open(os.path.join(args.output_dir, "index.html"), "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
147 | f.write(
148 | "")
149 | f.write("
".join(html))
150 |
151 | shutil.copyfile(text_encoder.tokenizer.font_path, os.path.join(args.output_dir, "HamNoSys.ttf"))
152 | """
153 | python -m text_to_pose.diffusion.src.pred \
154 | --checkpoint=/home/nlp/amit/sign-language/transcription/models/fine-eon-128/model.ckpt \
155 | --ffmpeg_path=/home/nlp/amit/libs/anaconda3/envs/transcription/bin/ffmpeg \
156 | --output_dir=/home/nlp/amit/WWW/tmp/ham2pose/
157 | """
158 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_text/video_to_text_idea.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Surprising Applications of Video-to-Text in Sign Language Translation
2 |
3 | ## Introduction:
4 |
5 | Sign Language, a vital mode of communication for the deaf has for too long been inadequately served by the limited available translation methods.
6 | This research proposal aims to explore innovative,
7 | technology-aided improvements in the translation between signed languages, represented in SignWriting, and spoken languages.
8 | Our study diverges from the traditional approach and proposes to utilize a more visually-focused technique which mirrors the human process of reading SignWriting as a sequence of images rather than a conventional text.
9 |
10 | Previously, Jiang et al. (2023) laid down a significant foundation in this field, with their work on translating SignWriting using specialized parsing and factorized machine translation.
11 | Building upon this work, we strive to integrate SignWriting into large pre-trained language models in a more natural and holistic manner.
12 | We propose a comparison between using a text-based SignWriting encoder to an image-based encoder that leverages Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) or a Vision Transformer (ViT).
13 | The image-based encoders treat each sign as either a single token (in the case of CNNs) or as 32 tokens (in the case of ViT), offering a radically different approach to encoding SignWriting.
14 |
15 | To accomplish this, we will utilize BLIP-2 (Li et al. 2023) and, based on VideoBLIP (Yu et al. 2023), we will encode a sequence of images as an input.
16 | To decode, we will employ the advanced and highly effective encoder-decoder-based LLM, FLAN-T5-XL, by fine-tuning Salesforce/blip2-flan-t5-xl.
17 |
18 | We assert that image-based encoding of SignWriting provides a more effective and versatile method for translating sign languages when compared to traditional text-based encoding.
19 | Through this research, we aim to provide compelling evidence to substantiate our theory, which, if confirmed, could pave the way for a significant breakthrough in sign language translation technologies.
20 |
21 | ## Related Work:
22 |
23 | Jiang et al. (2023) explore text-to-text sign to spoken language translation, with SignWriting as the chosen sign language notation system. Despite SignWriting usually represented in 2D, they use the 1D Formal SignWriting specification and propose a neural factored machine translation approach to encode sequences of the SignWriting graphemes as well as their position in the 2D space. They verify the proposed approach on the SignBank dataset in both a bilingual setup (American Sign Language to English) and two multilingual setups (4 and 21 signed-to-spoken language pairs, respectively). They apply several low-resource machine translation techniques used to improve spoken language translation to similarly improve the performance of sign language translation. Their findings validate the use of an intermediate text representation for signed language translation, and pave the way for including sign language translation in natural language processing research.
24 |
25 | Yu et al. (2023) propose VideoBLIP, a video-to-text translation model that leverages the BLIP-2 architecture.
26 | They encode a sequence of images using the BLIP image encoder, and flatten them into a single sequence of image patch tokens.
27 | Trained end-to-end, their model can generate texts based on videos.
28 |
29 | Li et al. (2023) propose BLIP-2, a new architecture for image-to-text translation.
30 | They propose a generic and efficient pretraining strategy that bootstraps vision-language pre-training from
31 | off-the-shelf frozen pre-trained image encoders and frozen large language models.
32 |
33 | The Bergamot project developed pipelines for fast, local, multilingual machine translation models.
34 | Based on marian, they developed a pipeline for training and quantizing models.
35 | This only supports text-to-text translation, and expects a shared source-target vocabulary, and a huge amount of data.
36 |
37 | ## Methodology:
38 |
39 | Our approach to SignWriting translation involves a novel paradigm that interprets SignWriting as a series of images, akin to the human reading process.
40 | The methodology employed to bring this concept to fruition is detailed as follows:
41 | By following these steps, our research aims to shed light on the unexpected and untapped potential of video-to-text and image-based methodologies in sign language translation.
42 |
43 |
44 | ### Dataset Preparation:
45 | We will utilize the SignBank dataset, which includes a diverse array of signed languages represented in SignWriting.
46 | As per the requirements of our model, the dataset will be prepared by converting the 1D Formal SignWriting specification into 2D images.
47 |
48 | In addition to the SignBank dataset, we have undertaken a manual data collection effort to further strengthen our model.
49 | We have annotated fingerspelling letters and numbers in 22^[American, Brazilian, British, Chinese, Danish, Flemish, French, French Belgian, German, Honduran, Irish, Israeli, Italian, Japanese, Mexican, Nicaraguan, Norwegian, Portuguese, Spanish, Swedish, Swiss German, and Thai.] different signed languages.
50 | The fingerspelling is mostly taken from: https://www.signwriting.org/forums/software/fingkeys/fkey001.html
51 | The transcribed was mostly performed by Sutthikhun Phaengphongsai, paid by `sign.mt ltd`.
52 | To make our model robust to fingerspelling, we have artificially generated 10K words from wordslist^[https://github.com/imsky/wordlists]
53 | and 4K numbers sampled from 0 to 10^9.
54 | and numbers in the aforementioned signed languages deterministically.
55 |
56 | ### Dataset cleaning
57 | We note that the SignBank dataset contains many issues, and is not immidiately fit for machine translation
58 | It includes SignWriting entries with text that is not parallel, or multiple terms where only some of them are parallel
59 | (for example, it includes a chapter and page number for a book, but not the text, or a word and its definition).
60 |
61 | We manually correct at least 5 entries per puddle. Some puddles are somewhat formulaic, and we can correct many entries at once using rules.
62 | In the appendix, we include the rules we used.
63 |
64 | Then, we use ChatGPT on all of the text entries, and implement two pseudo-functions:
65 |
66 | `clean(#number-of-signs, language-code, terms)` that takes the number of signs, language code, and existing terms, and returns a clean version of the terms that are parallel.
67 | For example, `clean(1, "sl", ["Koreja (mednarodno)", "Korea"])` returns `["Koreja", "Korea"]`,
68 | And `clean(18, "en", ["Acts 04_27-31c", "James Orlow"])` returns `[]`
69 |
70 | `expand(language-code, terms)` that takes the language code and clean terms, and expands the terms to include paraphrases and correct capitalization.
71 | Since some of the terms in the data are in English, we ask the function to return both the language and english separately.
72 | For example, `expand("sv", ["tre"])` returns `{"sv": ["Tre", "3"], "en": ["Three"]}`
73 | And `expand("de", ["Vater", "father"])` returns `{"de": ["Vater", "Vati", "Papa", "Erzeuger"], "en": ["Father", "Dad", "Daddy"]}`
74 |
75 |
76 | ### Modelling Selection:
77 | We will employ two different types of image-based encoders - CNNs and ViTs.
78 | For the CNN-based approach, each sign will be treated as a single token, while the ViT-based approach will treat each sign as 32 tokens.
79 | Both encoders will be compared to a baseline model that uses a text-based SignWriting encoder.
80 |
81 | The image sequence generated will be encoded as input using the BLIP-2 (Li et al. 2023) model, leveraging its efficient vision-language pretraining strategy.
82 | We will further implement VideoBLIP's methodology (Yu et al. 2023), which allows us to flatten the encoded image sequence into a single sequence of image patch tokens.
83 |
84 | The encoded sequence will be fed into FLAN-T5-XL, a large language model fine-tuned based on Salesforce/blip2-flan-t5-xl.
85 | This model will act as our decoder and generate the translated text in the target spoken language.
86 |
87 | Finally, we also attempt a bergamot pipeline, which is a text-to-text translation, and the signwriting is encoded as text.
88 |
89 | ### Evaluation:
90 | The proposed models' performance will be evaluated by comparing the translated text to the ground truth in the target language using chrF scores.
91 | Comparative analysis between the models will be done to determine the efficacy of image-based encoding over traditional text-based encoding.
92 | Finally we compare to previous work (Jiang et al. 2023) on the SignBank dataset, using their public API.
93 |
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/text_to_pose/diffusion/src/model/iterative_decoder.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import random
2 | from typing import List, Iterator
3 |
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import pytorch_lightning as pl
6 | import torch
7 | import torch.nn.functional as F
8 | from pose_format import Pose
9 | from pose_format.numpy import NumPyPoseBody
10 | from pose_format.pose_visualizer import PoseVisualizer
11 | from torch import nn
12 | from wandb import Video
13 |
14 | from _shared.models.pose_encoder import PoseEncoderModel
15 |
16 | from .distribution import DistributionPredictionModel
17 | from .image_encoder import ImageEncoderModel
18 | from .masked_loss import masked_loss
19 | from .schedule import cosine_beta_schedule, get_alphas
20 | from .text_encoder import TextEncoderModel
21 | from ..metrics.dtw import dynamic_time_warping_mean_joint_error
22 | from ..metrics.mse import masked_mse
23 |
24 |
25 | class IterativeGuidedPoseGenerationModel(pl.LightningModule):
26 |
27 | def __init__(self,
28 | pose_encoder: PoseEncoderModel,
29 | text_encoder: TextEncoderModel = None,
30 | image_encoder: ImageEncoderModel = None,
31 | hidden_dim: int = 128,
32 | max_seq_size: int = 1000,
33 | learning_rate: float = 0.003,
34 | num_steps: int = 10,
35 | seq_len_loss_weight: float = 2e-5,
36 | smoothness_loss_weight: float = 1e-2,
37 | noise_epsilon: float = 1e-4,
38 | loss_type='l2'):
39 | super().__init__()
40 |
41 | self.noise_epsilon = noise_epsilon
42 | self.max_seq_size = max_seq_size
43 | self.num_steps = num_steps
44 | self.learning_rate = learning_rate
45 | self.loss_type = loss_type
46 | self.seq_len_loss_weight = seq_len_loss_weight
47 | self.smoothness_loss_weight = smoothness_loss_weight
48 |
49 | # Encoders
50 | self.pose_encoder = pose_encoder
51 | self.text_encoder = text_encoder
52 | self.image_encoder = image_encoder
53 |
54 | # Pose correction layer to fix missing joints
55 | self.pose_correction = nn.Sequential(
56 | nn.Linear(self.pose_encoder.pose_dim, self.pose_encoder.pose_dim),
57 | nn.SiLU(),
58 | nn.Linear(self.pose_encoder.pose_dim, self.pose_encoder.pose_dim),
59 | )
60 |
61 | # Embedding layers
62 | self.step_embedding = nn.Embedding(num_embeddings=num_steps, embedding_dim=hidden_dim)
63 |
64 | # Predict sequence length
65 | self.seq_length = DistributionPredictionModel(hidden_dim)
66 |
67 | # Predict pose difference
68 | self.pose_diff_projection = nn.Sequential(
69 | nn.Linear(hidden_dim, hidden_dim),
70 | nn.SiLU(),
71 | nn.Linear(hidden_dim, self.pose_encoder.pose_dim),
72 | )
73 |
74 | # Diffusion parameters
75 | self.betas = cosine_beta_schedule(self.num_steps) # Training time propotions
76 | self.alphas = get_alphas(self.betas) # Inference time steps
77 |
78 | def correct_pose(self, data: torch.FloatTensor):
79 | if self.training:
80 | _, keypoints, _ = data.shape
81 | # mask a block of keypoints
82 | keypoint_start = random.randint(0, keypoints - 1)
83 | keypoint_end = random.randint(keypoint_start, min(keypoints, keypoint_start + 21))
84 | data[:, keypoint_start:keypoint_end, :] = 0
85 |
86 | flat_pose = data.reshape(-1, self.pose_encoder.pose_dim)
87 | corrected_pose = self.pose_correction(flat_pose)
88 | if not self.training:
89 | flat_conf = (flat_pose != 0).float()
90 | corrected_pose = (1 - flat_conf) * corrected_pose + flat_conf * flat_pose
91 |
92 | return corrected_pose.reshape(data.shape)
93 |
94 | def refine_pose_sequence(self, pose_sequence, text_encoding, batch_step: torch.LongTensor):
95 | batch_size, seq_length, _, _ = pose_sequence["data"].shape
96 |
97 | step_embedding = self.step_embedding(batch_step).unsqueeze(1)
98 | step_mask = torch.zeros([step_embedding.shape[0], 1], dtype=torch.bool, device=self.device)
99 |
100 | additional_sequence = {
101 | "data": torch.cat([step_embedding, text_encoding["data"]], dim=1),
102 | "mask": torch.cat([step_mask, text_encoding["mask"]], dim=1)
103 | }
104 |
105 | pose_encoding = self.pose_encoder(pose=pose_sequence, additional_sequence=additional_sequence)
106 | pose_encoding = pose_encoding[:, :seq_length, :]
107 |
108 | # Predict desired change
109 | flat_pose_projection = self.pose_diff_projection(pose_encoding)
110 | predicted_diff = flat_pose_projection.reshape(batch_size, seq_length, *self.pose_encoder.pose_dims)
111 | return predicted_diff
112 |
113 | def get_step_proportion(self, step_num: int):
114 | # At the first step, n-1, we get 1 for noise and 0 for gold
115 | # At the last step, 0, we get a small number for noise, and a large one for gold
116 | return self.betas[step_num]
117 |
118 | def get_batch_step_proportion(self, batch_step: torch.LongTensor):
119 | steps = batch_step.tolist()
120 | sizes = [self.get_step_proportion(step) for step in steps]
121 | return torch.tensor(sizes, device=self.device, dtype=torch.float)
122 |
123 | def step_size(self, step_num: int):
124 | # Alphas in ascending order, but step size should be 1 when step_num=0
125 | return self.alphas[self.num_steps - step_num - 1]
126 |
127 | def batch_step_size(self, batch_step: torch.LongTensor):
128 | steps = batch_step.tolist()
129 | sizes = [self.step_size(step) for step in steps]
130 | return torch.tensor(sizes, device=self.device, dtype=torch.float)
131 |
132 | def forward(self,
133 | text: str,
134 | first_pose: torch.FloatTensor,
135 | force_sequence_length: int = None,
136 | classifier_free_guidance=None):
137 | assert first_pose.dim() == 2, "First pose should be a single pose, not a sequence"
138 | empty_text_encoding = self.text_encoder([""]) if classifier_free_guidance is not None else None
139 | text_encoding = self.text_encoder([text])
140 | sequence_length = self.seq_length(torch.mean(text_encoding["data"], dim=1))
141 | sequence_length = max(1, min(round(float(sequence_length)), self.max_seq_size))
142 | if force_sequence_length is not None:
143 | sequence_length = force_sequence_length
144 |
145 | # Add missing keypoints
146 | first_pose = self.correct_pose(first_pose)
147 |
148 | x_T = first_pose.expand(1, sequence_length, *self.pose_encoder.pose_dims)
149 | mask = torch.zeros([1, sequence_length], dtype=torch.bool, device=self.device)
150 |
151 | yield x_T[0]
152 |
153 | steps = torch.arange(self.num_steps, dtype=torch.long, device=self.device).unsqueeze(-1)
154 | steps_descending = (self.num_steps - 1) - steps
155 |
156 | x_t = x_T
157 | for step_num in steps_descending:
158 | pose_t = {"data": x_t, "mask": mask}
159 | conditional = self.refine_pose_sequence(pose_t, text_encoding, step_num)
160 |
161 | if classifier_free_guidance is not None:
162 | unconditional = self.refine_pose_sequence(pose_t, empty_text_encoding, step_num)
163 | x_0 = unconditional + classifier_free_guidance * (conditional - unconditional)
164 | else:
165 | x_0 = conditional
166 |
167 | yield x_0[0]
168 |
169 | if step_num > 0:
170 | # Now we need to noise the predicted sequence "back" to time t
171 | x_t = self.noise_pose_sequence(x_0, x_T, step_num - 1)
172 |
173 | def forward_to_body(self, forward_iterator: Iterator, fps=1):
174 | data = list(forward_iterator)[-1]
175 | data = torch.unsqueeze(data, 1).cpu()
176 | conf = torch.ones_like(data[:, :, :, 0])
177 | return NumPyPoseBody(fps, data.numpy(), conf.numpy())
178 |
179 | def noise_pose_sequence(self,
180 | x_0: torch.FloatTensor,
181 | x_T: torch.FloatTensor,
182 | batch_step: torch.LongTensor,
183 | deviation=0):
184 | noise_proportion = self.get_batch_step_proportion(batch_step).view(-1, 1, 1, 1)
185 | if deviation > 0:
186 | noise_proportion *= 1 + deviation * torch.randn_like(noise_proportion)
187 | noise_data = noise_proportion * x_T
188 | gold_data = (1 - noise_proportion) * x_0
189 | blend = noise_data + gold_data
190 | return blend
191 |
192 | def training_step(self, batch, *unused_args):
193 | return self.step(batch, *unused_args, steps=[-1])
194 |
195 | def validation_step(self, batch, *unused_args):
196 | for i, (pose, pose_data, text) in enumerate(zip(batch["pose"]["obj"], batch["pose"]["data"], batch["text"])):
197 | first_pose = pose_data[0]
198 | # TODO batch inference
199 | iterator = self.forward(text=text, first_pose=first_pose)
200 | pred_pose_body = self.forward_to_body(iterator)
201 | # Metrics
202 | dtw_mje = dynamic_time_warping_mean_joint_error(pose.body, pred_pose_body)
203 | self.log("validation_dtw_mje", dtw_mje)
204 |
205 | # Visualize and log video
206 | if i == 0:
207 | pred_pose = Pose(header=pose.header, body=pred_pose_body)
208 | pred_pose.body.data *= 50 # Scale up pose
209 | pred_pose.focus()
210 | frames = np.stack(list(PoseVisualizer(pred_pose, thickness=1).draw()))
211 | # Frames must be (time, channel, height, width)
212 | frames = np.transpose(frames, (0, 3, 1, 2))
213 | self.logger.experiment.log({"video": [Video(frames, fps=pose.body.fps)]})
214 |
215 | return self.step(batch, *unused_args, steps=list(range(self.num_steps)))
216 |
217 | def smoothness_loss(self, pose_sequence: torch.Tensor, confidence: torch.Tensor):
218 | shifted_pose = torch.roll(pose_sequence, 1, dims=1)
219 | shifted_confidence = torch.roll(confidence, 1, dims=1)
220 | confidence = confidence * shifted_confidence
221 | return masked_loss('l1', pose_sequence, shifted_pose, confidence=confidence, model_num_steps=self.num_steps)
222 |
223 | def step(self, batch, *unused_args, steps: List[int]):
224 | if self.training:
225 | # Randomly remove some text during training
226 | for i, text in enumerate(batch["text"]):
227 | if random.random() < 0.1:
228 | batch["text"][i] = ""
229 |
230 | text_encoding = self.text_encoder(batch["text"])
231 | pose = batch["pose"]
232 |
233 | # Calculate sequence length loss
234 | sequence_length = self.seq_length(torch.mean(text_encoding["data"], dim=1))
235 | sequence_length_loss = F.mse_loss(sequence_length, pose["length"])
236 |
237 | # Reconstruct missing keypoints from the first pose
238 | first_pose = pose["data"][:, 0]
239 | first_conf = pose["confidence"][:, 0]
240 | fixed_pose = self.correct_pose(first_pose)
241 | pose_reconstruction_loss = masked_loss(self.loss_type,
242 | first_pose,
243 | fixed_pose,
244 | confidence=first_conf,
245 | model_num_steps=1)
246 |
247 | # Repeat the first frame for initial prediction
248 | batch_size, pose_seq_length, _, _ = pose["data"].shape
249 | pose_sequence = {
250 | "data": torch.stack([first_pose] * pose_seq_length, dim=1),
251 | "mask": torch.logical_not(pose["inverse_mask"])
252 | }
253 |
254 | # In training, only one step is used. For validation, we use all steps
255 | refinement_loss = 0
256 | smoothness_loss = 0
257 | for step in steps:
258 | # Similar to diffusion, we will choose a random step number for every sample from the batch
259 | if step == -1:
260 | batch_step = torch.randint(low=0,
261 | high=self.num_steps,
262 | size=[batch_size],
263 | dtype=torch.long,
264 | device=self.device)
265 | else:
266 | # We want to make sure that we always use the same step number for validation loss calculation
267 | batch_step = torch.full([batch_size], fill_value=step, dtype=torch.long, device=self.device)
268 |
269 | # Let's randomly add noise based on the step
270 | deviation = self.noise_epsilon if self.training else 0
271 | pose_sequence["data"] = self.noise_pose_sequence(pose["data"],
272 | pose_sequence["data"],
273 | batch_step,
274 | deviation=deviation)
275 |
276 | if self.training: # multiply by just a little noise while training
277 | noise = 1 + torch.randn_like(pose_sequence["data"]) * self.noise_epsilon
278 | first_frame = pose_sequence["data"][:, 0]
279 | pose_sequence["data"] *= noise
280 | pose_sequence["data"][:, 0] = first_frame # First frame should never change
281 |
282 | # At every step, we apply loss to the predicted sequence to be exactly a full reproduction
283 | predicted_sequence = self.refine_pose_sequence(pose_sequence, text_encoding, batch_step)
284 |
285 | refinement_loss += masked_loss(self.loss_type,
286 | pose["data"],
287 | predicted_sequence,
288 | confidence=pose["confidence"],
289 | model_num_steps=self.num_steps)
290 |
291 | smoothness_loss += self.smoothness_loss(predicted_sequence, confidence=pose["confidence"])
292 |
293 | phase = "train" if self.training else "validation"
294 | self.log(f"{phase}_seq_length_loss", sequence_length_loss, batch_size=batch_size)
295 | self.log(f"{phase}_refinement_loss", refinement_loss, batch_size=batch_size)
296 | self.log(f"{phase}_smoothness_loss", smoothness_loss, batch_size=batch_size)
297 | self.log(f"{phase}_reconstruction_loss", pose_reconstruction_loss, batch_size=batch_size)
298 |
299 | loss = pose_reconstruction_loss + refinement_loss + \
300 | self.seq_len_loss_weight * sequence_length_loss + \
301 | self.smoothness_loss_weight * smoothness_loss
302 |
303 | # loss = refinement_loss + self.seq_len_loss_weight * sequence_length_loss
304 | self.log(f"{phase}_loss", loss, batch_size=batch_size)
305 |
306 | return loss
307 |
308 | def configure_optimizers(self):
309 | return torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=self.learning_rate)
310 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 12 |
12 |  12 |
12 |