├── .gitignore
├── LICENSE
└── README.md
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Binaries for programs and plugins
2 | *.exe
3 | *.exe~
4 | *.dll
5 | *.so
6 | *.dylib
7 |
8 | # Test binary, build with `go test -c`
9 | *.test
10 |
11 | # Output of the go coverage tool, specifically when used with LiteIDE
12 | *.out
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
2 | Version 3, 29 June 2007
3 |
4 | Copyright (C) 2007 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
5 | Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies
6 | of this license document, but changing it is not allowed.
7 |
8 | Preamble
9 |
10 | The GNU General Public License is a free, copyleft license for
11 | software and other kinds of works.
12 |
13 | The licenses for most software and other practical works are designed
14 | to take away your freedom to share and change the works. By contrast,
15 | the GNU General Public License is intended to guarantee your freedom to
16 | share and change all versions of a program--to make sure it remains free
17 | software for all its users. We, the Free Software Foundation, use the
18 | GNU General Public License for most of our software; it applies also to
19 | any other work released this way by its authors. You can apply it to
20 | your programs, too.
21 |
22 | When we speak of free software, we are referring to freedom, not
23 | price. Our General Public Licenses are designed to make sure that you
24 | have the freedom to distribute copies of free software (and charge for
25 | them if you wish), that you receive source code or can get it if you
26 | want it, that you can change the software or use pieces of it in new
27 | free programs, and that you know you can do these things.
28 |
29 | To protect your rights, we need to prevent others from denying you
30 | these rights or asking you to surrender the rights. Therefore, you have
31 | certain responsibilities if you distribute copies of the software, or if
32 | you modify it: responsibilities to respect the freedom of others.
33 |
34 | For example, if you distribute copies of such a program, whether
35 | gratis or for a fee, you must pass on to the recipients the same
36 | freedoms that you received. You must make sure that they, too, receive
37 | or can get the source code. And you must show them these terms so they
38 | know their rights.
39 |
40 | Developers that use the GNU GPL protect your rights with two steps:
41 | (1) assert copyright on the software, and (2) offer you this License
42 | giving you legal permission to copy, distribute and/or modify it.
43 |
44 | For the developers' and authors' protection, the GPL clearly explains
45 | that there is no warranty for this free software. For both users' and
46 | authors' sake, the GPL requires that modified versions be marked as
47 | changed, so that their problems will not be attributed erroneously to
48 | authors of previous versions.
49 |
50 | Some devices are designed to deny users access to install or run
51 | modified versions of the software inside them, although the manufacturer
52 | can do so. This is fundamentally incompatible with the aim of
53 | protecting users' freedom to change the software. The systematic
54 | pattern of such abuse occurs in the area of products for individuals to
55 | use, which is precisely where it is most unacceptable. Therefore, we
56 | have designed this version of the GPL to prohibit the practice for those
57 | products. If such problems arise substantially in other domains, we
58 | stand ready to extend this provision to those domains in future versions
59 | of the GPL, as needed to protect the freedom of users.
60 |
61 | Finally, every program is threatened constantly by software patents.
62 | States should not allow patents to restrict development and use of
63 | software on general-purpose computers, but in those that do, we wish to
64 | avoid the special danger that patents applied to a free program could
65 | make it effectively proprietary. To prevent this, the GPL assures that
66 | patents cannot be used to render the program non-free.
67 |
68 | The precise terms and conditions for copying, distribution and
69 | modification follow.
70 |
71 | TERMS AND CONDITIONS
72 |
73 | 0. Definitions.
74 |
75 | "This License" refers to version 3 of the GNU General Public License.
76 |
77 | "Copyright" also means copyright-like laws that apply to other kinds of
78 | works, such as semiconductor masks.
79 |
80 | "The Program" refers to any copyrightable work licensed under this
81 | License. Each licensee is addressed as "you". "Licensees" and
82 | "recipients" may be individuals or organizations.
83 |
84 | To "modify" a work means to copy from or adapt all or part of the work
85 | in a fashion requiring copyright permission, other than the making of an
86 | exact copy. The resulting work is called a "modified version" of the
87 | earlier work or a work "based on" the earlier work.
88 |
89 | A "covered work" means either the unmodified Program or a work based
90 | on the Program.
91 |
92 | To "propagate" a work means to do anything with it that, without
93 | permission, would make you directly or secondarily liable for
94 | infringement under applicable copyright law, except executing it on a
95 | computer or modifying a private copy. Propagation includes copying,
96 | distribution (with or without modification), making available to the
97 | public, and in some countries other activities as well.
98 |
99 | To "convey" a work means any kind of propagation that enables other
100 | parties to make or receive copies. Mere interaction with a user through
101 | a computer network, with no transfer of a copy, is not conveying.
102 |
103 | An interactive user interface displays "Appropriate Legal Notices"
104 | to the extent that it includes a convenient and prominently visible
105 | feature that (1) displays an appropriate copyright notice, and (2)
106 | tells the user that there is no warranty for the work (except to the
107 | extent that warranties are provided), that licensees may convey the
108 | work under this License, and how to view a copy of this License. If
109 | the interface presents a list of user commands or options, such as a
110 | menu, a prominent item in the list meets this criterion.
111 |
112 | 1. Source Code.
113 |
114 | The "source code" for a work means the preferred form of the work
115 | for making modifications to it. "Object code" means any non-source
116 | form of a work.
117 |
118 | A "Standard Interface" means an interface that either is an official
119 | standard defined by a recognized standards body, or, in the case of
120 | interfaces specified for a particular programming language, one that
121 | is widely used among developers working in that language.
122 |
123 | The "System Libraries" of an executable work include anything, other
124 | than the work as a whole, that (a) is included in the normal form of
125 | packaging a Major Component, but which is not part of that Major
126 | Component, and (b) serves only to enable use of the work with that
127 | Major Component, or to implement a Standard Interface for which an
128 | implementation is available to the public in source code form. A
129 | "Major Component", in this context, means a major essential component
130 | (kernel, window system, and so on) of the specific operating system
131 | (if any) on which the executable work runs, or a compiler used to
132 | produce the work, or an object code interpreter used to run it.
133 |
134 | The "Corresponding Source" for a work in object code form means all
135 | the source code needed to generate, install, and (for an executable
136 | work) run the object code and to modify the work, including scripts to
137 | control those activities. However, it does not include the work's
138 | System Libraries, or general-purpose tools or generally available free
139 | programs which are used unmodified in performing those activities but
140 | which are not part of the work. For example, Corresponding Source
141 | includes interface definition files associated with source files for
142 | the work, and the source code for shared libraries and dynamically
143 | linked subprograms that the work is specifically designed to require,
144 | such as by intimate data communication or control flow between those
145 | subprograms and other parts of the work.
146 |
147 | The Corresponding Source need not include anything that users
148 | can regenerate automatically from other parts of the Corresponding
149 | Source.
150 |
151 | The Corresponding Source for a work in source code form is that
152 | same work.
153 |
154 | 2. Basic Permissions.
155 |
156 | All rights granted under this License are granted for the term of
157 | copyright on the Program, and are irrevocable provided the stated
158 | conditions are met. This License explicitly affirms your unlimited
159 | permission to run the unmodified Program. The output from running a
160 | covered work is covered by this License only if the output, given its
161 | content, constitutes a covered work. This License acknowledges your
162 | rights of fair use or other equivalent, as provided by copyright law.
163 |
164 | You may make, run and propagate covered works that you do not
165 | convey, without conditions so long as your license otherwise remains
166 | in force. You may convey covered works to others for the sole purpose
167 | of having them make modifications exclusively for you, or provide you
168 | with facilities for running those works, provided that you comply with
169 | the terms of this License in conveying all material for which you do
170 | not control copyright. Those thus making or running the covered works
171 | for you must do so exclusively on your behalf, under your direction
172 | and control, on terms that prohibit them from making any copies of
173 | your copyrighted material outside their relationship with you.
174 |
175 | Conveying under any other circumstances is permitted solely under
176 | the conditions stated below. Sublicensing is not allowed; section 10
177 | makes it unnecessary.
178 |
179 | 3. Protecting Users' Legal Rights From Anti-Circumvention Law.
180 |
181 | No covered work shall be deemed part of an effective technological
182 | measure under any applicable law fulfilling obligations under article
183 | 11 of the WIPO copyright treaty adopted on 20 December 1996, or
184 | similar laws prohibiting or restricting circumvention of such
185 | measures.
186 |
187 | When you convey a covered work, you waive any legal power to forbid
188 | circumvention of technological measures to the extent such circumvention
189 | is effected by exercising rights under this License with respect to
190 | the covered work, and you disclaim any intention to limit operation or
191 | modification of the work as a means of enforcing, against the work's
192 | users, your or third parties' legal rights to forbid circumvention of
193 | technological measures.
194 |
195 | 4. Conveying Verbatim Copies.
196 |
197 | You may convey verbatim copies of the Program's source code as you
198 | receive it, in any medium, provided that you conspicuously and
199 | appropriately publish on each copy an appropriate copyright notice;
200 | keep intact all notices stating that this License and any
201 | non-permissive terms added in accord with section 7 apply to the code;
202 | keep intact all notices of the absence of any warranty; and give all
203 | recipients a copy of this License along with the Program.
204 |
205 | You may charge any price or no price for each copy that you convey,
206 | and you may offer support or warranty protection for a fee.
207 |
208 | 5. Conveying Modified Source Versions.
209 |
210 | You may convey a work based on the Program, or the modifications to
211 | produce it from the Program, in the form of source code under the
212 | terms of section 4, provided that you also meet all of these conditions:
213 |
214 | a) The work must carry prominent notices stating that you modified
215 | it, and giving a relevant date.
216 |
217 | b) The work must carry prominent notices stating that it is
218 | released under this License and any conditions added under section
219 | 7. This requirement modifies the requirement in section 4 to
220 | "keep intact all notices".
221 |
222 | c) You must license the entire work, as a whole, under this
223 | License to anyone who comes into possession of a copy. This
224 | License will therefore apply, along with any applicable section 7
225 | additional terms, to the whole of the work, and all its parts,
226 | regardless of how they are packaged. This License gives no
227 | permission to license the work in any other way, but it does not
228 | invalidate such permission if you have separately received it.
229 |
230 | d) If the work has interactive user interfaces, each must display
231 | Appropriate Legal Notices; however, if the Program has interactive
232 | interfaces that do not display Appropriate Legal Notices, your
233 | work need not make them do so.
234 |
235 | A compilation of a covered work with other separate and independent
236 | works, which are not by their nature extensions of the covered work,
237 | and which are not combined with it such as to form a larger program,
238 | in or on a volume of a storage or distribution medium, is called an
239 | "aggregate" if the compilation and its resulting copyright are not
240 | used to limit the access or legal rights of the compilation's users
241 | beyond what the individual works permit. Inclusion of a covered work
242 | in an aggregate does not cause this License to apply to the other
243 | parts of the aggregate.
244 |
245 | 6. Conveying Non-Source Forms.
246 |
247 | You may convey a covered work in object code form under the terms
248 | of sections 4 and 5, provided that you also convey the
249 | machine-readable Corresponding Source under the terms of this License,
250 | in one of these ways:
251 |
252 | a) Convey the object code in, or embodied in, a physical product
253 | (including a physical distribution medium), accompanied by the
254 | Corresponding Source fixed on a durable physical medium
255 | customarily used for software interchange.
256 |
257 | b) Convey the object code in, or embodied in, a physical product
258 | (including a physical distribution medium), accompanied by a
259 | written offer, valid for at least three years and valid for as
260 | long as you offer spare parts or customer support for that product
261 | model, to give anyone who possesses the object code either (1) a
262 | copy of the Corresponding Source for all the software in the
263 | product that is covered by this License, on a durable physical
264 | medium customarily used for software interchange, for a price no
265 | more than your reasonable cost of physically performing this
266 | conveying of source, or (2) access to copy the
267 | Corresponding Source from a network server at no charge.
268 |
269 | c) Convey individual copies of the object code with a copy of the
270 | written offer to provide the Corresponding Source. This
271 | alternative is allowed only occasionally and noncommercially, and
272 | only if you received the object code with such an offer, in accord
273 | with subsection 6b.
274 |
275 | d) Convey the object code by offering access from a designated
276 | place (gratis or for a charge), and offer equivalent access to the
277 | Corresponding Source in the same way through the same place at no
278 | further charge. You need not require recipients to copy the
279 | Corresponding Source along with the object code. If the place to
280 | copy the object code is a network server, the Corresponding Source
281 | may be on a different server (operated by you or a third party)
282 | that supports equivalent copying facilities, provided you maintain
283 | clear directions next to the object code saying where to find the
284 | Corresponding Source. Regardless of what server hosts the
285 | Corresponding Source, you remain obligated to ensure that it is
286 | available for as long as needed to satisfy these requirements.
287 |
288 | e) Convey the object code using peer-to-peer transmission, provided
289 | you inform other peers where the object code and Corresponding
290 | Source of the work are being offered to the general public at no
291 | charge under subsection 6d.
292 |
293 | A separable portion of the object code, whose source code is excluded
294 | from the Corresponding Source as a System Library, need not be
295 | included in conveying the object code work.
296 |
297 | A "User Product" is either (1) a "consumer product", which means any
298 | tangible personal property which is normally used for personal, family,
299 | or household purposes, or (2) anything designed or sold for incorporation
300 | into a dwelling. In determining whether a product is a consumer product,
301 | doubtful cases shall be resolved in favor of coverage. For a particular
302 | product received by a particular user, "normally used" refers to a
303 | typical or common use of that class of product, regardless of the status
304 | of the particular user or of the way in which the particular user
305 | actually uses, or expects or is expected to use, the product. A product
306 | is a consumer product regardless of whether the product has substantial
307 | commercial, industrial or non-consumer uses, unless such uses represent
308 | the only significant mode of use of the product.
309 |
310 | "Installation Information" for a User Product means any methods,
311 | procedures, authorization keys, or other information required to install
312 | and execute modified versions of a covered work in that User Product from
313 | a modified version of its Corresponding Source. The information must
314 | suffice to ensure that the continued functioning of the modified object
315 | code is in no case prevented or interfered with solely because
316 | modification has been made.
317 |
318 | If you convey an object code work under this section in, or with, or
319 | specifically for use in, a User Product, and the conveying occurs as
320 | part of a transaction in which the right of possession and use of the
321 | User Product is transferred to the recipient in perpetuity or for a
322 | fixed term (regardless of how the transaction is characterized), the
323 | Corresponding Source conveyed under this section must be accompanied
324 | by the Installation Information. But this requirement does not apply
325 | if neither you nor any third party retains the ability to install
326 | modified object code on the User Product (for example, the work has
327 | been installed in ROM).
328 |
329 | The requirement to provide Installation Information does not include a
330 | requirement to continue to provide support service, warranty, or updates
331 | for a work that has been modified or installed by the recipient, or for
332 | the User Product in which it has been modified or installed. Access to a
333 | network may be denied when the modification itself materially and
334 | adversely affects the operation of the network or violates the rules and
335 | protocols for communication across the network.
336 |
337 | Corresponding Source conveyed, and Installation Information provided,
338 | in accord with this section must be in a format that is publicly
339 | documented (and with an implementation available to the public in
340 | source code form), and must require no special password or key for
341 | unpacking, reading or copying.
342 |
343 | 7. Additional Terms.
344 |
345 | "Additional permissions" are terms that supplement the terms of this
346 | License by making exceptions from one or more of its conditions.
347 | Additional permissions that are applicable to the entire Program shall
348 | be treated as though they were included in this License, to the extent
349 | that they are valid under applicable law. If additional permissions
350 | apply only to part of the Program, that part may be used separately
351 | under those permissions, but the entire Program remains governed by
352 | this License without regard to the additional permissions.
353 |
354 | When you convey a copy of a covered work, you may at your option
355 | remove any additional permissions from that copy, or from any part of
356 | it. (Additional permissions may be written to require their own
357 | removal in certain cases when you modify the work.) You may place
358 | additional permissions on material, added by you to a covered work,
359 | for which you have or can give appropriate copyright permission.
360 |
361 | Notwithstanding any other provision of this License, for material you
362 | add to a covered work, you may (if authorized by the copyright holders of
363 | that material) supplement the terms of this License with terms:
364 |
365 | a) Disclaiming warranty or limiting liability differently from the
366 | terms of sections 15 and 16 of this License; or
367 |
368 | b) Requiring preservation of specified reasonable legal notices or
369 | author attributions in that material or in the Appropriate Legal
370 | Notices displayed by works containing it; or
371 |
372 | c) Prohibiting misrepresentation of the origin of that material, or
373 | requiring that modified versions of such material be marked in
374 | reasonable ways as different from the original version; or
375 |
376 | d) Limiting the use for publicity purposes of names of licensors or
377 | authors of the material; or
378 |
379 | e) Declining to grant rights under trademark law for use of some
380 | trade names, trademarks, or service marks; or
381 |
382 | f) Requiring indemnification of licensors and authors of that
383 | material by anyone who conveys the material (or modified versions of
384 | it) with contractual assumptions of liability to the recipient, for
385 | any liability that these contractual assumptions directly impose on
386 | those licensors and authors.
387 |
388 | All other non-permissive additional terms are considered "further
389 | restrictions" within the meaning of section 10. If the Program as you
390 | received it, or any part of it, contains a notice stating that it is
391 | governed by this License along with a term that is a further
392 | restriction, you may remove that term. If a license document contains
393 | a further restriction but permits relicensing or conveying under this
394 | License, you may add to a covered work material governed by the terms
395 | of that license document, provided that the further restriction does
396 | not survive such relicensing or conveying.
397 |
398 | If you add terms to a covered work in accord with this section, you
399 | must place, in the relevant source files, a statement of the
400 | additional terms that apply to those files, or a notice indicating
401 | where to find the applicable terms.
402 |
403 | Additional terms, permissive or non-permissive, may be stated in the
404 | form of a separately written license, or stated as exceptions;
405 | the above requirements apply either way.
406 |
407 | 8. Termination.
408 |
409 | You may not propagate or modify a covered work except as expressly
410 | provided under this License. Any attempt otherwise to propagate or
411 | modify it is void, and will automatically terminate your rights under
412 | this License (including any patent licenses granted under the third
413 | paragraph of section 11).
414 |
415 | However, if you cease all violation of this License, then your
416 | license from a particular copyright holder is reinstated (a)
417 | provisionally, unless and until the copyright holder explicitly and
418 | finally terminates your license, and (b) permanently, if the copyright
419 | holder fails to notify you of the violation by some reasonable means
420 | prior to 60 days after the cessation.
421 |
422 | Moreover, your license from a particular copyright holder is
423 | reinstated permanently if the copyright holder notifies you of the
424 | violation by some reasonable means, this is the first time you have
425 | received notice of violation of this License (for any work) from that
426 | copyright holder, and you cure the violation prior to 30 days after
427 | your receipt of the notice.
428 |
429 | Termination of your rights under this section does not terminate the
430 | licenses of parties who have received copies or rights from you under
431 | this License. If your rights have been terminated and not permanently
432 | reinstated, you do not qualify to receive new licenses for the same
433 | material under section 10.
434 |
435 | 9. Acceptance Not Required for Having Copies.
436 |
437 | You are not required to accept this License in order to receive or
438 | run a copy of the Program. Ancillary propagation of a covered work
439 | occurring solely as a consequence of using peer-to-peer transmission
440 | to receive a copy likewise does not require acceptance. However,
441 | nothing other than this License grants you permission to propagate or
442 | modify any covered work. These actions infringe copyright if you do
443 | not accept this License. Therefore, by modifying or propagating a
444 | covered work, you indicate your acceptance of this License to do so.
445 |
446 | 10. Automatic Licensing of Downstream Recipients.
447 |
448 | Each time you convey a covered work, the recipient automatically
449 | receives a license from the original licensors, to run, modify and
450 | propagate that work, subject to this License. You are not responsible
451 | for enforcing compliance by third parties with this License.
452 |
453 | An "entity transaction" is a transaction transferring control of an
454 | organization, or substantially all assets of one, or subdividing an
455 | organization, or merging organizations. If propagation of a covered
456 | work results from an entity transaction, each party to that
457 | transaction who receives a copy of the work also receives whatever
458 | licenses to the work the party's predecessor in interest had or could
459 | give under the previous paragraph, plus a right to possession of the
460 | Corresponding Source of the work from the predecessor in interest, if
461 | the predecessor has it or can get it with reasonable efforts.
462 |
463 | You may not impose any further restrictions on the exercise of the
464 | rights granted or affirmed under this License. For example, you may
465 | not impose a license fee, royalty, or other charge for exercise of
466 | rights granted under this License, and you may not initiate litigation
467 | (including a cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that
468 | any patent claim is infringed by making, using, selling, offering for
469 | sale, or importing the Program or any portion of it.
470 |
471 | 11. Patents.
472 |
473 | A "contributor" is a copyright holder who authorizes use under this
474 | License of the Program or a work on which the Program is based. The
475 | work thus licensed is called the contributor's "contributor version".
476 |
477 | A contributor's "essential patent claims" are all patent claims
478 | owned or controlled by the contributor, whether already acquired or
479 | hereafter acquired, that would be infringed by some manner, permitted
480 | by this License, of making, using, or selling its contributor version,
481 | but do not include claims that would be infringed only as a
482 | consequence of further modification of the contributor version. For
483 | purposes of this definition, "control" includes the right to grant
484 | patent sublicenses in a manner consistent with the requirements of
485 | this License.
486 |
487 | Each contributor grants you a non-exclusive, worldwide, royalty-free
488 | patent license under the contributor's essential patent claims, to
489 | make, use, sell, offer for sale, import and otherwise run, modify and
490 | propagate the contents of its contributor version.
491 |
492 | In the following three paragraphs, a "patent license" is any express
493 | agreement or commitment, however denominated, not to enforce a patent
494 | (such as an express permission to practice a patent or covenant not to
495 | sue for patent infringement). To "grant" such a patent license to a
496 | party means to make such an agreement or commitment not to enforce a
497 | patent against the party.
498 |
499 | If you convey a covered work, knowingly relying on a patent license,
500 | and the Corresponding Source of the work is not available for anyone
501 | to copy, free of charge and under the terms of this License, through a
502 | publicly available network server or other readily accessible means,
503 | then you must either (1) cause the Corresponding Source to be so
504 | available, or (2) arrange to deprive yourself of the benefit of the
505 | patent license for this particular work, or (3) arrange, in a manner
506 | consistent with the requirements of this License, to extend the patent
507 | license to downstream recipients. "Knowingly relying" means you have
508 | actual knowledge that, but for the patent license, your conveying the
509 | covered work in a country, or your recipient's use of the covered work
510 | in a country, would infringe one or more identifiable patents in that
511 | country that you have reason to believe are valid.
512 |
513 | If, pursuant to or in connection with a single transaction or
514 | arrangement, you convey, or propagate by procuring conveyance of, a
515 | covered work, and grant a patent license to some of the parties
516 | receiving the covered work authorizing them to use, propagate, modify
517 | or convey a specific copy of the covered work, then the patent license
518 | you grant is automatically extended to all recipients of the covered
519 | work and works based on it.
520 |
521 | A patent license is "discriminatory" if it does not include within
522 | the scope of its coverage, prohibits the exercise of, or is
523 | conditioned on the non-exercise of one or more of the rights that are
524 | specifically granted under this License. You may not convey a covered
525 | work if you are a party to an arrangement with a third party that is
526 | in the business of distributing software, under which you make payment
527 | to the third party based on the extent of your activity of conveying
528 | the work, and under which the third party grants, to any of the
529 | parties who would receive the covered work from you, a discriminatory
530 | patent license (a) in connection with copies of the covered work
531 | conveyed by you (or copies made from those copies), or (b) primarily
532 | for and in connection with specific products or compilations that
533 | contain the covered work, unless you entered into that arrangement,
534 | or that patent license was granted, prior to 28 March 2007.
535 |
536 | Nothing in this License shall be construed as excluding or limiting
537 | any implied license or other defenses to infringement that may
538 | otherwise be available to you under applicable patent law.
539 |
540 | 12. No Surrender of Others' Freedom.
541 |
542 | If conditions are imposed on you (whether by court order, agreement or
543 | otherwise) that contradict the conditions of this License, they do not
544 | excuse you from the conditions of this License. If you cannot convey a
545 | covered work so as to satisfy simultaneously your obligations under this
546 | License and any other pertinent obligations, then as a consequence you may
547 | not convey it at all. For example, if you agree to terms that obligate you
548 | to collect a royalty for further conveying from those to whom you convey
549 | the Program, the only way you could satisfy both those terms and this
550 | License would be to refrain entirely from conveying the Program.
551 |
552 | 13. Use with the GNU Affero General Public License.
553 |
554 | Notwithstanding any other provision of this License, you have
555 | permission to link or combine any covered work with a work licensed
556 | under version 3 of the GNU Affero General Public License into a single
557 | combined work, and to convey the resulting work. The terms of this
558 | License will continue to apply to the part which is the covered work,
559 | but the special requirements of the GNU Affero General Public License,
560 | section 13, concerning interaction through a network will apply to the
561 | combination as such.
562 |
563 | 14. Revised Versions of this License.
564 |
565 | The Free Software Foundation may publish revised and/or new versions of
566 | the GNU General Public License from time to time. Such new versions will
567 | be similar in spirit to the present version, but may differ in detail to
568 | address new problems or concerns.
569 |
570 | Each version is given a distinguishing version number. If the
571 | Program specifies that a certain numbered version of the GNU General
572 | Public License "or any later version" applies to it, you have the
573 | option of following the terms and conditions either of that numbered
574 | version or of any later version published by the Free Software
575 | Foundation. If the Program does not specify a version number of the
576 | GNU General Public License, you may choose any version ever published
577 | by the Free Software Foundation.
578 |
579 | If the Program specifies that a proxy can decide which future
580 | versions of the GNU General Public License can be used, that proxy's
581 | public statement of acceptance of a version permanently authorizes you
582 | to choose that version for the Program.
583 |
584 | Later license versions may give you additional or different
585 | permissions. However, no additional obligations are imposed on any
586 | author or copyright holder as a result of your choosing to follow a
587 | later version.
588 |
589 | 15. Disclaimer of Warranty.
590 |
591 | THERE IS NO WARRANTY FOR THE PROGRAM, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY
592 | APPLICABLE LAW. EXCEPT WHEN OTHERWISE STATED IN WRITING THE COPYRIGHT
593 | HOLDERS AND/OR OTHER PARTIES PROVIDE THE PROGRAM "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY
594 | OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
595 | THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
596 | PURPOSE. THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE OF THE PROGRAM
597 | IS WITH YOU. SHOULD THE PROGRAM PROVE DEFECTIVE, YOU ASSUME THE COST OF
598 | ALL NECESSARY SERVICING, REPAIR OR CORRECTION.
599 |
600 | 16. Limitation of Liability.
601 |
602 | IN NO EVENT UNLESS REQUIRED BY APPLICABLE LAW OR AGREED TO IN WRITING
603 | WILL ANY COPYRIGHT HOLDER, OR ANY OTHER PARTY WHO MODIFIES AND/OR CONVEYS
604 | THE PROGRAM AS PERMITTED ABOVE, BE LIABLE TO YOU FOR DAMAGES, INCLUDING ANY
605 | GENERAL, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE
606 | USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE PROGRAM (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO LOSS OF
607 | DATA OR DATA BEING RENDERED INACCURATE OR LOSSES SUSTAINED BY YOU OR THIRD
608 | PARTIES OR A FAILURE OF THE PROGRAM TO OPERATE WITH ANY OTHER PROGRAMS),
609 | EVEN IF SUCH HOLDER OR OTHER PARTY HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF
610 | SUCH DAMAGES.
611 |
612 | 17. Interpretation of Sections 15 and 16.
613 |
614 | If the disclaimer of warranty and limitation of liability provided
615 | above cannot be given local legal effect according to their terms,
616 | reviewing courts shall apply local law that most closely approximates
617 | an absolute waiver of all civil liability in connection with the
618 | Program, unless a warranty or assumption of liability accompanies a
619 | copy of the Program in return for a fee.
620 |
621 | END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
622 |
623 | How to Apply These Terms to Your New Programs
624 |
625 | If you develop a new program, and you want it to be of the greatest
626 | possible use to the public, the best way to achieve this is to make it
627 | free software which everyone can redistribute and change under these terms.
628 |
629 | To do so, attach the following notices to the program. It is safest
630 | to attach them to the start of each source file to most effectively
631 | state the exclusion of warranty; and each file should have at least
632 | the "copyright" line and a pointer to where the full notice is found.
633 |
634 |
635 | Copyright (C)
636 |
637 | This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
638 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
639 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
640 | (at your option) any later version.
641 |
642 | This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
643 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
644 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
645 | GNU General Public License for more details.
646 |
647 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
648 | along with this program. If not, see .
649 |
650 | Also add information on how to contact you by electronic and paper mail.
651 |
652 | If the program does terminal interaction, make it output a short
653 | notice like this when it starts in an interactive mode:
654 |
655 | Copyright (C)
656 | This program comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY; for details type `show w'.
657 | This is free software, and you are welcome to redistribute it
658 | under certain conditions; type `show c' for details.
659 |
660 | The hypothetical commands `show w' and `show c' should show the appropriate
661 | parts of the General Public License. Of course, your program's commands
662 | might be different; for a GUI interface, you would use an "about box".
663 |
664 | You should also get your employer (if you work as a programmer) or school,
665 | if any, to sign a "copyright disclaimer" for the program, if necessary.
666 | For more information on this, and how to apply and follow the GNU GPL, see
667 | .
668 |
669 | The GNU General Public License does not permit incorporating your program
670 | into proprietary programs. If your program is a subroutine library, you
671 | may consider it more useful to permit linking proprietary applications with
672 | the library. If this is what you want to do, use the GNU Lesser General
673 | Public License instead of this License. But first, please read
674 | .
675 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## GOPROXY简介
2 |  3 | 一款轻量级、功能强大、高性能的http代理、https代理、socks5代理、内网穿透代理服务器、ss代理、游戏盾、游戏代理,支持API代理认证。websocke代理、tcp代理、udp代理、socket代理、高仿服务器。支持正向代理、反向代理、透明代理、TCP内网穿透、UDP内网穿透、HTTP内网穿透、HTTPS内网穿透、https代理负载均衡、http代理负载均衡、socks5代理负载均衡、socket代理负载均衡、ss代理负载均衡、TCP/UDP端口映射、SSH中转、TLS加密传输、协议转换、防污染DNS代理,限速,限连接数。官方QQ交流群: 793015219。
4 |
5 | ---
6 |
7 | [](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/) []() [](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases) [](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases)
8 |
9 | ---
10 | ### [点击我观看视频教程](https://space.bilibili.com/472844633)
11 | - [点击下载](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases)
12 | - 如果上面不能正常下载,点击这里[镜像下载](https://www.host900.com/snail007/goproxy/)
13 | - [桌面版,控制面板ProxyAdmin](https://github.com/snail007/proxy_admin_free/blob/master/README_ZH.md)
14 | - [安卓全局代理版](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy-ss-plugin-android)
15 | - [安卓全能代理版](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy-android)
16 | - [安卓内网穿透客户端](https://github.com/snail007/lanass)
17 | - [SDK](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy-sdk)
18 | - [GORPOXY帮助手册](https://snail007.github.io/goproxy/manual/zh/)
19 | - [GORPOXY实战教程](https://snail007.github.io/goproxy)
20 | - [免费版VS商业版](https://snail007.github.io/goproxy/free_vs_commercial/)
21 |
22 | ## ProxyAdmin介绍预览
23 | goproxy提供的web控制面板 `ProxyAdmin` 是强大的代理服务工具 snail007/goproxy 的控制面板,运行了它,一秒让你的服务器变为强大的代理服务器,友好的交互界面,小白也能轻松上手,让你用起来得心应手,心情舒畅。
24 |
25 | 
26 |
27 | ### goproxy能干什么?
28 | - 链式代理,程序本身可以作为一级代理,如果设置了上级代理那么可以作为二级代理,乃至N级代理。
29 | - 通讯加密,如果程序不是一级代理,而且上级代理也是本程序,那么可以加密和上级代理之间的通讯,采用底层tls高强度加密,安全无特征。
30 | - 智能HTTP代理,HTTPS代理,SOCKS5代理,会自动判断访问的网站是否屏蔽,如果被屏蔽那么就会使用上级代理(前提是配置了上级代理)访问网站;如果访问的网站没有被屏蔽,为了加速访问,代理会直接访问网站,不使用上级代理。
31 | - 域名黑白名单,更加自由的控制网站的访问方式。
32 | - 跨平台性,无论你是widows,linux,还是mac,甚至是树莓派,都可以很好的运行proxy。
33 | - 多协议支持,支持HTTP(S),TCP,UDP,Websocket,SOCKS5代理。
34 | - TCP/UDP端口转发。
35 | - 游戏盾,游戏代理,高仿服务器。
36 | - 内网穿透,P2P传输,协议支持TCP和UDP,针对HTTP的优化穿透。
37 | - SSH中转,HTTP(S),SOCKS5代理支持SSH中转,上级Linux服务器不需要任何服务端,本地一个proxy即可开心上网。
38 | - [KCP](https://github.com/xtaci/kcp-go)协议支持,HTTP(S),SOCKS5代理支持KCP协议传输数据,降低延迟,提升浏览体验。
39 | - 动态选择上级代理,通过外部API,HTTP(S),SOCKS5,SPS代理可以实现基于用户或者IP的限速,连接数限制,动态获取上级。
40 | - 灵活的上级分配,HTTP(S),SOCKS5,SPS代理可以通过配置文件实现基于用户或者IP的限速,连接数限制,指定上级。
41 | - 反向代理,支持直接把域名解析到proxy监听的ip,然后proxy就会帮你代理访问需要访问的HTTP(S)网站。
42 | - 透明HTTP(S)代理,配合iptables,在网关直接把出去的80,443方向的流量转发到proxy,就能实现无感知的智能路由器代理。
43 | - 协议转换,可以把已经存在的HTTP(S)或SOCKS5或SS代理转换为一个端口同时支持HTTP(S)和SOCKS5和SS代理,转换后的SOCKS5和SS代理如果上级是SOCKS5代理,那么支持UDP功能,同时支持强大的级联认证功能。
44 | - 自定义底层加密传输,http(s)\sps\socks代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可。
45 | - 底层压缩高效传输,http(s)\sps\socks代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在加密之后还可以对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的。
46 | - 安全的DNS代理,可以通过本地的proxy提供的DNS代理服务器与上级代理加密通讯实现安全防污染的DNS查询。
47 | - 负载均衡,高可用,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS代理支持上级负载均衡和高可用,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
48 | - 指定出口IP,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS代理支持客户端用入口IP连接过来的,就用入口IP作为出口IP访问目标网站的功能。如果入口IP是内网IP,出口IP不会使用入口IP
49 | - 支持限速,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS\TCP代理支持限速。
50 | - 支持限连接数,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS\TCP代理支持限连接数。
51 | - SOCKS5代理支持级联认证。
52 | - 证书参数使用base64数据,默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
53 | - 支持客户端IP黑白名单,更加安全的控制客户端对代理服务的访问,如果黑白名单同时设置,那么只有白名单生效。socks/http(s)/sps/tcp/udp/dns/内网穿透bridge/内网穿透tbridge,都支持客户端IP黑白名单。
54 | - 端口范围批量监听,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS\TCP代理支持指定端口范围监听,避免启动过多进程,提高性能。
55 |
56 | ### 为什么需要它?
57 |
58 | - 当由于某某原因,我们不能访问我们在其它地方的服务,我们可以通过多个相连的proxy节点建立起一个安全的隧道访问我们的服务。
59 | - 微信接口本地开发,方便调试。
60 | - 远程访问内网机器。
61 | - 和小伙伴一起玩局域网游戏。
62 | - 以前只能在局域网玩的,现在可以在任何地方玩。
63 | - 替代圣剑内网通,显IP内网通,花生壳之类的工具。
64 | - ..。
65 |
66 |
67 | 本页手册适用于最新版goproxy,其他版本可能有的地方不再适用,请自己根据命令帮助使用。
68 |
69 |
70 | ### 加入组织
71 | [点击加入交流组织gitter](https://gitter.im/go-proxy/Lobby?utm_source=share-link&utm_medium=link&utm_campaign=share-link)
72 |
73 | [点击加入交流组织TG](https://t.me/snail007_goproxy)
74 |
75 | ## 下载安装 goproxy
76 |
77 | ### 快速安装 goproxy
78 |
79 | 0.如果你的VPS是linux64位的系统,那么只需要执行下面一句,就可以完成自动安装和配置.
80 |
81 | 提示:所有操作需要root权限。
82 |
83 | 免费版执行这个:
84 |
85 | ```shell
86 | curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/snail007/goproxy/master/install_auto.sh | bash
87 | ```
88 |
89 | 商业版执行这个:
90 |
91 | ```shell
92 | curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/snail007/goproxy/master/install_auto_commercial.sh | bash
93 | ```
94 |
95 | 安装完成,配置目录是/etc/proxy,更详细的使用方法请参考上面的手册目录,进一步了解你想要使用的功能。
96 | 如果安装失败或者你的vps不是linux64位系统,请按照下面的半自动步骤安装:
97 |
98 | ### 手动安装 goproxy
99 |
100 | 1.下载goproxy
101 |
102 | 下载地址:https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases/latest
103 |
104 | 下面以v7.9为例,如果有最新版,请使用最新版链接,注意替换下面的下载连接里面的版本号为最新版版本号。
105 |
106 | 免费版执行这个:
107 |
108 | ```shell
109 | cd /root/proxy/
110 | wget https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases/download/v7.9/proxy-linux-amd64.tar.gz
111 | ```
112 |
113 | 商业版执行这个:
114 |
115 | ```shell
116 | cd /root/proxy/
117 | wget https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases/download/v7.9/proxy-linux-amd64_commercial.tar.gz
118 | ```
119 |
120 | 2.下载自动安装脚本
121 |
122 | 免费版执行这个:
123 |
124 | ```shell
125 | cd /root/proxy/
126 | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/snail007/goproxy/master/install.sh
127 | chmod +x install.sh
128 | ./install.sh
129 | ```
130 |
131 | 商业版执行这个:
132 |
133 | ```shell
134 | cd /root/proxy/
135 | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/snail007/goproxy/master/install_commercial.sh
136 | chmod +x install_commercial.sh
137 | ./install_commercial.sh
138 | ```
139 |
140 | ## TODO
141 | - http,socks代理多个上级负载均衡?
142 | - http(s)代理增加pac支持?
143 | - 欢迎加群反馈..。
144 |
145 | ## License
146 | Proxy is licensed under GPLv3 license。
147 |
148 | ## Contact
149 | 官方QQ交流群: 793015219
150 |
151 | ## Donation
152 | 如果proxy帮助你解决了很多问题,你可以通过下面的捐赠更好的支持proxy。
153 |
3 | 一款轻量级、功能强大、高性能的http代理、https代理、socks5代理、内网穿透代理服务器、ss代理、游戏盾、游戏代理,支持API代理认证。websocke代理、tcp代理、udp代理、socket代理、高仿服务器。支持正向代理、反向代理、透明代理、TCP内网穿透、UDP内网穿透、HTTP内网穿透、HTTPS内网穿透、https代理负载均衡、http代理负载均衡、socks5代理负载均衡、socket代理负载均衡、ss代理负载均衡、TCP/UDP端口映射、SSH中转、TLS加密传输、协议转换、防污染DNS代理,限速,限连接数。官方QQ交流群: 793015219。
4 |
5 | ---
6 |
7 | [](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/) []() [](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases) [](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases)
8 |
9 | ---
10 | ### [点击我观看视频教程](https://space.bilibili.com/472844633)
11 | - [点击下载](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases)
12 | - 如果上面不能正常下载,点击这里[镜像下载](https://www.host900.com/snail007/goproxy/)
13 | - [桌面版,控制面板ProxyAdmin](https://github.com/snail007/proxy_admin_free/blob/master/README_ZH.md)
14 | - [安卓全局代理版](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy-ss-plugin-android)
15 | - [安卓全能代理版](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy-android)
16 | - [安卓内网穿透客户端](https://github.com/snail007/lanass)
17 | - [SDK](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy-sdk)
18 | - [GORPOXY帮助手册](https://snail007.github.io/goproxy/manual/zh/)
19 | - [GORPOXY实战教程](https://snail007.github.io/goproxy)
20 | - [免费版VS商业版](https://snail007.github.io/goproxy/free_vs_commercial/)
21 |
22 | ## ProxyAdmin介绍预览
23 | goproxy提供的web控制面板 `ProxyAdmin` 是强大的代理服务工具 snail007/goproxy 的控制面板,运行了它,一秒让你的服务器变为强大的代理服务器,友好的交互界面,小白也能轻松上手,让你用起来得心应手,心情舒畅。
24 |
25 | 
26 |
27 | ### goproxy能干什么?
28 | - 链式代理,程序本身可以作为一级代理,如果设置了上级代理那么可以作为二级代理,乃至N级代理。
29 | - 通讯加密,如果程序不是一级代理,而且上级代理也是本程序,那么可以加密和上级代理之间的通讯,采用底层tls高强度加密,安全无特征。
30 | - 智能HTTP代理,HTTPS代理,SOCKS5代理,会自动判断访问的网站是否屏蔽,如果被屏蔽那么就会使用上级代理(前提是配置了上级代理)访问网站;如果访问的网站没有被屏蔽,为了加速访问,代理会直接访问网站,不使用上级代理。
31 | - 域名黑白名单,更加自由的控制网站的访问方式。
32 | - 跨平台性,无论你是widows,linux,还是mac,甚至是树莓派,都可以很好的运行proxy。
33 | - 多协议支持,支持HTTP(S),TCP,UDP,Websocket,SOCKS5代理。
34 | - TCP/UDP端口转发。
35 | - 游戏盾,游戏代理,高仿服务器。
36 | - 内网穿透,P2P传输,协议支持TCP和UDP,针对HTTP的优化穿透。
37 | - SSH中转,HTTP(S),SOCKS5代理支持SSH中转,上级Linux服务器不需要任何服务端,本地一个proxy即可开心上网。
38 | - [KCP](https://github.com/xtaci/kcp-go)协议支持,HTTP(S),SOCKS5代理支持KCP协议传输数据,降低延迟,提升浏览体验。
39 | - 动态选择上级代理,通过外部API,HTTP(S),SOCKS5,SPS代理可以实现基于用户或者IP的限速,连接数限制,动态获取上级。
40 | - 灵活的上级分配,HTTP(S),SOCKS5,SPS代理可以通过配置文件实现基于用户或者IP的限速,连接数限制,指定上级。
41 | - 反向代理,支持直接把域名解析到proxy监听的ip,然后proxy就会帮你代理访问需要访问的HTTP(S)网站。
42 | - 透明HTTP(S)代理,配合iptables,在网关直接把出去的80,443方向的流量转发到proxy,就能实现无感知的智能路由器代理。
43 | - 协议转换,可以把已经存在的HTTP(S)或SOCKS5或SS代理转换为一个端口同时支持HTTP(S)和SOCKS5和SS代理,转换后的SOCKS5和SS代理如果上级是SOCKS5代理,那么支持UDP功能,同时支持强大的级联认证功能。
44 | - 自定义底层加密传输,http(s)\sps\socks代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可。
45 | - 底层压缩高效传输,http(s)\sps\socks代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在加密之后还可以对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的。
46 | - 安全的DNS代理,可以通过本地的proxy提供的DNS代理服务器与上级代理加密通讯实现安全防污染的DNS查询。
47 | - 负载均衡,高可用,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS代理支持上级负载均衡和高可用,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
48 | - 指定出口IP,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS代理支持客户端用入口IP连接过来的,就用入口IP作为出口IP访问目标网站的功能。如果入口IP是内网IP,出口IP不会使用入口IP
49 | - 支持限速,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS\TCP代理支持限速。
50 | - 支持限连接数,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS\TCP代理支持限连接数。
51 | - SOCKS5代理支持级联认证。
52 | - 证书参数使用base64数据,默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
53 | - 支持客户端IP黑白名单,更加安全的控制客户端对代理服务的访问,如果黑白名单同时设置,那么只有白名单生效。socks/http(s)/sps/tcp/udp/dns/内网穿透bridge/内网穿透tbridge,都支持客户端IP黑白名单。
54 | - 端口范围批量监听,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS\TCP代理支持指定端口范围监听,避免启动过多进程,提高性能。
55 |
56 | ### 为什么需要它?
57 |
58 | - 当由于某某原因,我们不能访问我们在其它地方的服务,我们可以通过多个相连的proxy节点建立起一个安全的隧道访问我们的服务。
59 | - 微信接口本地开发,方便调试。
60 | - 远程访问内网机器。
61 | - 和小伙伴一起玩局域网游戏。
62 | - 以前只能在局域网玩的,现在可以在任何地方玩。
63 | - 替代圣剑内网通,显IP内网通,花生壳之类的工具。
64 | - ..。
65 |
66 |
67 | 本页手册适用于最新版goproxy,其他版本可能有的地方不再适用,请自己根据命令帮助使用。
68 |
69 |
70 | ### 加入组织
71 | [点击加入交流组织gitter](https://gitter.im/go-proxy/Lobby?utm_source=share-link&utm_medium=link&utm_campaign=share-link)
72 |
73 | [点击加入交流组织TG](https://t.me/snail007_goproxy)
74 |
75 | ## 下载安装 goproxy
76 |
77 | ### 快速安装 goproxy
78 |
79 | 0.如果你的VPS是linux64位的系统,那么只需要执行下面一句,就可以完成自动安装和配置.
80 |
81 | 提示:所有操作需要root权限。
82 |
83 | 免费版执行这个:
84 |
85 | ```shell
86 | curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/snail007/goproxy/master/install_auto.sh | bash
87 | ```
88 |
89 | 商业版执行这个:
90 |
91 | ```shell
92 | curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/snail007/goproxy/master/install_auto_commercial.sh | bash
93 | ```
94 |
95 | 安装完成,配置目录是/etc/proxy,更详细的使用方法请参考上面的手册目录,进一步了解你想要使用的功能。
96 | 如果安装失败或者你的vps不是linux64位系统,请按照下面的半自动步骤安装:
97 |
98 | ### 手动安装 goproxy
99 |
100 | 1.下载goproxy
101 |
102 | 下载地址:https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases/latest
103 |
104 | 下面以v7.9为例,如果有最新版,请使用最新版链接,注意替换下面的下载连接里面的版本号为最新版版本号。
105 |
106 | 免费版执行这个:
107 |
108 | ```shell
109 | cd /root/proxy/
110 | wget https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases/download/v7.9/proxy-linux-amd64.tar.gz
111 | ```
112 |
113 | 商业版执行这个:
114 |
115 | ```shell
116 | cd /root/proxy/
117 | wget https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases/download/v7.9/proxy-linux-amd64_commercial.tar.gz
118 | ```
119 |
120 | 2.下载自动安装脚本
121 |
122 | 免费版执行这个:
123 |
124 | ```shell
125 | cd /root/proxy/
126 | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/snail007/goproxy/master/install.sh
127 | chmod +x install.sh
128 | ./install.sh
129 | ```
130 |
131 | 商业版执行这个:
132 |
133 | ```shell
134 | cd /root/proxy/
135 | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/snail007/goproxy/master/install_commercial.sh
136 | chmod +x install_commercial.sh
137 | ./install_commercial.sh
138 | ```
139 |
140 | ## TODO
141 | - http,socks代理多个上级负载均衡?
142 | - http(s)代理增加pac支持?
143 | - 欢迎加群反馈..。
144 |
145 | ## License
146 | Proxy is licensed under GPLv3 license。
147 |
148 | ## Contact
149 | 官方QQ交流群: 793015219
150 |
151 | ## Donation
152 | 如果proxy帮助你解决了很多问题,你可以通过下面的捐赠更好的支持proxy。
153 |  154 |
154 |  155 |
156 | ### 源代码申明
157 |
158 | 本项目作者发现大量的开发者基于本项目进行二次开发或使用大量本项目核心代码而不遵循GPLv3协议,这严重违背了本项目使用GPLv3开源协议的初衷,鉴于这种情况,本项目采取源代码延迟发布策略,在一定程度上遏制这些不尊重开源,不尊重他人劳动成果的行为。
159 | 本项目会持续更新迭代,持续发布全平台的二进制程序,给大家提供强大便捷的代理工具。
160 | 如果你有定制,商业需求请发邮件至`arraykeys@gmail.com`
161 |
162 | ## goproxy使用手册
163 |
164 |
165 | ## 首次使用必看!
166 |
167 | ### 1. 环境
168 |
169 | 该手册教程,默认系统是linux,程序是proxy;所有操作需要root权限;
170 |
171 | 如果你的是windows,请使用windows版本的proxy.exe即可。
172 |
173 | ### 2. 使用配置文件
174 |
175 | 接下来的教程都是通过命令行参数介绍使用方法,也可以通过读取配置文件获取参数。
176 |
177 | 具体格式是通过@符号指定配置文件,例如:./proxy @configfile.txt
178 |
179 | configfile.txt里面的格式是,第一行是子命令名称,第二行开始一行一个参数,
180 |
181 | 格式:`参数 参数值`,没有参数值的直接写参数,比如:--nolog
182 |
183 | 比如configfile.txt内容如下:
184 |
185 | ```shell
186 | http
187 | -t tcp
188 | -p :33080
189 | --forever
190 | ```
191 |
192 | ### 3. 调试输出
193 |
194 | 默认情况下,日志输出的信息不包含文件行数,某些情况下为了排除程序问题,快速定位问题,
195 |
196 | 可以使用--debug参数,输出代码行数和毫秒时间。
197 |
198 | ### 4. 使用日志文件
199 |
200 | 默认情况下,日志是直接在控制台显示出来的,如果要保存到文件,可以使用--log参数,
201 |
202 | 比如: --log proxy.log,日志就会输出到proxy.log方便排除问题。
203 |
204 |
205 | ### 5. 生成加密通讯需要的证书文件
206 |
207 | http(s)代理、tcp代理、udp代理、socks5代理、内网穿透等功能和上级通讯的时候,为了安全我们采用TLS加密通讯,当然可以选择不加密通信通讯,本教程所有和上级通讯都采用加密,需要证书文件。
208 |
209 | ***所有端必须使用相同的proxy.crt和proxy.key***
210 |
211 | 1.通过下面的命令生成自签名的证书和key文件。
212 | `./proxy keygen -C proxy`
213 | 会在当前程序目录下面生成证书文件proxy.crt和key文件proxy.key。
214 |
215 | 2.通过下面的命令生,使用自签名证书proxy.crt和key文件proxy.key签发新证书:goproxy.crt和goproxy.key。
216 | `./proxy keygen -s -C proxy -c goproxy`
217 | 会在当前程序目录下面生成证书文件goproxy.crt和key文件goproxy.key。
218 |
219 | 3.默认情况下证书的里面的域名是随机的,可以使用`-n test.com`参数指定。
220 |
221 | 4.更多用法:`proxy keygen --help`。
222 |
223 | ### 6. 后台运行
224 |
225 | 默认执行proxy之后,如果要保持proxy运行,不能关闭命令行。
226 |
227 | 如果想在后台运行proxy,命令行可以关闭,只需要在命令最后加上--daemon参数即可。
228 |
229 | 比如:
230 |
231 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --daemon`
232 |
233 | ### 7. 守护运行
234 | 守护运行参数--forever,比如: `proxy http --forever` ,
235 |
236 | proxy会fork子进程,然后监控子进程,如果子进程异常退出,5秒后重启子进程。
237 |
238 | 该参数配合后台运行参数--daemon和日志参数--log,可以保障proxy一直在后台执行不会因为意外退出,
239 |
240 | 而且可以通过日志文件看到proxy的输出日志内容。
241 |
242 | 比如: `proxy http -p ":9090" --forever --log proxy.log --daemon`
243 |
244 | ### 8. 安全建议
245 |
246 | 当VPS在nat设备后面,vps上网卡IP都是内网IP,这个时候可以通过-g参数添加vps的外网ip防止死循环。
247 |
248 | 假设你的vps外网ip是23.23.23.23,下面命令通过-g参数设置23.23.23.23
249 |
250 | `./proxy http -g "23.23.23.23"`
251 |
252 | ### 9. 负载均衡和高可用
253 |
254 | HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS代理支持上级负载均衡和高可用,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
255 |
256 | 负载均衡策略支持5种,可以通过`--lb-method`参数指定:
257 |
258 | roundrobin 轮流使用
259 |
260 | leastconn 使用最小连接数的
261 |
262 | leasttime 使用连接时间最小的
263 |
264 | hash 使用根据客户端地址计算出一个固定上级
265 |
266 | weight 根据每个上级的权重和连接数情况,选择出一个上级
267 |
268 | 提示:
269 |
270 | 负载均衡检查时间间隔可以通过`--lb-retrytime`设置,单位毫秒
271 |
272 | 负载均衡连接超时时间可以通过`--lb-timeout`设置,单位毫秒
273 |
274 | 如果负载均衡策略是权重(weight),-P格式为:2.2.2.2:3880?w=1,1就是权重,大于0的整数。
275 |
276 | 如果负载均衡策略是hash,默认是根据客户端地址选择上级,可以通过开关`--lb-hashtarget`使用访问的目标地址选择上级。
277 |
278 |
279 | ### 10. 代理跳板跳转
280 |
281 | http(s)代理,SPS代理,内网穿透,tcp代理都支持通过中间第三方代理连接上级,
282 |
283 | 参数是:--jumper,所有格式如下:
284 |
285 | ```text
286 | http://username:password@host:port
287 | http://host:port
288 | https://username:password@host:port
289 | https://host:port
290 | socks5://username:password@host:port
291 | socks5://host:port
292 | socks5s://username:password@host:port
293 | socks5s://host:port
294 | ss://method:password@host:port
295 | ```
296 |
297 | http,socks5代表的是普通的http和socks5代理。
298 |
299 | https,socks5s代表的是通过tls保护的http和socks5代理,
300 |
301 | 也就是http代理 over TLS , socks over TLS。
302 |
303 | ### 11. 域名黑白名单
304 |
305 | socks/http(s)/sps代理都支持域名黑白名单。
306 |
307 | 用--stop参数指定一个域名黑名单列表文件,那么当用户连接文件里面这些域名的时候连接就会被断开。
308 |
309 | 用--only参数指定一个域名白名单列表文件,那么当用户连接文件里面这些域名之外的域名的时候连接就会被断开。
310 |
311 | 如果同时设置了--stop和--only,那么只有--only会起作用。
312 |
313 | 黑白域名名单文件内容格式如下:
314 |
315 | ```text
316 | **.baidu.com
317 | *.taobao.com
318 | a.com
319 | 192.168.1.1
320 | 192.168.*.*
321 | ?.qq.com
322 | ```
323 |
324 | 说明:
325 |
326 | 1.一行一个域名,域名写法支持通配符`*`和`?`,`*`代表任意个字符,`?`代表一个任意字符,
327 |
328 | 2.`**.baidu.com` 匹配无论是多少级所有后缀是`.baidu.com`的域名。
329 |
330 | 3.`*.taobao.com` 匹配后缀是`.taobao.com`的三级域名。
331 |
332 | 4.还可以直接是IP地址。
333 |
334 | 5.`#`开头的为注释。
335 |
336 | ### 12. 客户端IP黑白名单
337 |
338 | socks/http(s)/sps/tcp/udp/dns/内网穿透bridge/内网穿透tbridge,都支持客户端IP黑白名单。
339 |
340 | 用--ip-deny参数指定一个客户端IP黑名单列表文件,那么当用户的IP在这个文件里面的时候连接就会被断开。
341 |
342 | 用--ip-allow参数指定一个客户端IP白名单列表文件,那么当用户的IP不在这个文件里面的时候连接就会被断开。
343 |
344 | 如果同时设置了--ip-deny和--ip-allow,那么只有--ip-allow会起作用。
345 |
346 | 客户端IP黑白名单文件内容格式如下:
347 |
348 | ```text
349 | 192.168.1.1
350 | 192.168.*.*
351 | 192.168.1?.*
352 | ```
353 |
354 | 说明:
355 |
356 | 1.一行一个域名,域名写法支持通配符`*`和`?`,`*`代表任意个字符,`?`代表一个任意字符。
357 |
358 | 2.`#`开头的为注释。
359 |
360 | ### 13. 协议加载文件
361 |
362 | proxy的各种代理功能里面很多地方都有参数设置一个文件,比如:--blocked 指定一个直接走上级的域名列表文件,参数值是文件的路径,
363 |
364 | 如果参数支持协议加载文件,那么文件路径不仅可以是文件路径,还可以是:
365 |
366 | a.“base64://”开头的base64编码的上面说明的文件内容,比如:base64://ajfpoajsdfa=
367 |
368 | b.”str://“开头的英文逗号分割的多个,比如:str://xxx,yyy
369 |
370 | proxy的blocked,direct,stop,only,hosts,resolve.rules,rewriter.rules,ip.allow,ip.deny 文件支持协议加载。
371 |
372 | ## 1.HTTP代理
373 |
374 | ### 1.1.普通一级HTTP代理
375 |
376 | 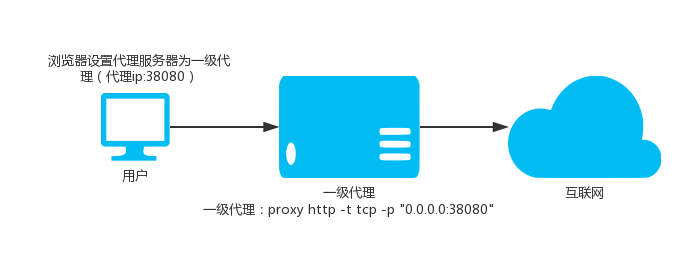
377 |
378 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080"`
379 |
380 | -p参数支持的写法:
381 |
382 | ```text
383 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
384 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
385 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
386 | ```
387 |
388 | ### 1.2.普通二级HTTP代理
389 |
390 | 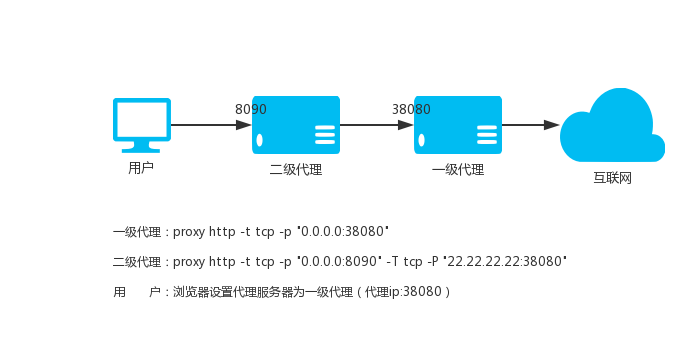
391 |
392 | 使用本地端口8090,假设上级HTTP代理是`22.22.22.22:8080`
393 |
394 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" `
395 |
396 | 我们还可以指定网站域名的黑白名单文件,一行一个域名,匹配规则是最右匹配,比如:baidu.com,匹配的是*.*.baidu.com,黑名单的域名直接走上级代理,白名单的域名不走上级代理。
397 |
398 | `./proxy http -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" -b blocked.txt -d direct.txt`
399 |
400 | ### 1.3.HTTP二级代理(加密)
401 |
402 | > 注意: 后面二级代理使用的`proxy.crt`和`proxy.key`应与一级代理一致
403 |
404 | 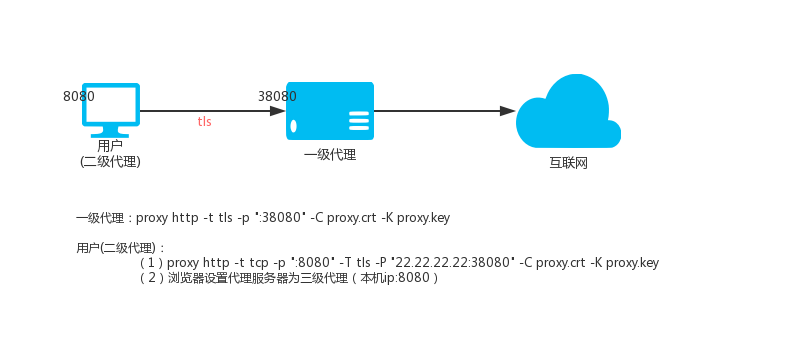
405 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
406 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
407 |
408 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
409 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
410 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080。
411 |
412 | 二级HTTP代理(本地windows)
413 | `./proxy.exe http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
414 | 然后设置你的windos系统中,需要通过代理上网的程序的代理为http模式,地址为:127.0.0.1,端口为:8080,程序即可通过加密通道通过vps上网。
415 |
416 | ### 1.4.HTTP三级代理(加密)
417 | 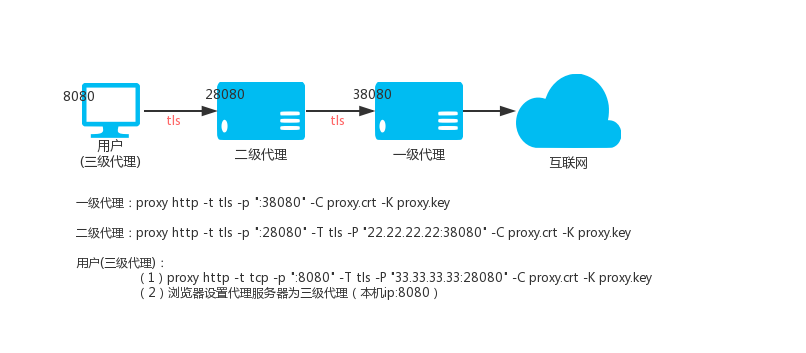
418 | 一级HTTP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
419 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
420 | 二级HTTP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
421 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
422 | 三级HTTP代理(本地)
423 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
424 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问一级HTTP代理上面的代理端口38080。
425 |
426 | ### 1.5.Basic认证,API认证
427 |
428 | 请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
429 |
430 | ### 1.6.HTTP代理流量强制走上级HTTP代理
431 | 默认情况下,proxy会智能判断一个网站域名是否无法访问,如果无法访问才走上级HTTP代理.通过--always可以使全部HTTP代理流量强制走上级HTTP代理。
432 | `./proxy http --always -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
433 |
434 | ### 1.7.HTTP(S)通过SSH中转
435 | 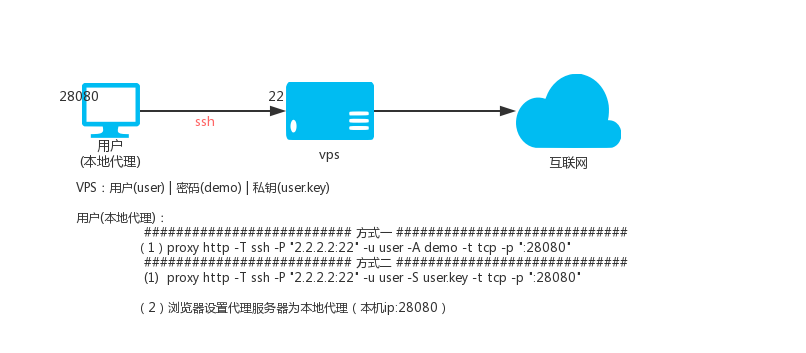
436 | 说明:ssh中转的原理是利用了ssh的转发功能,就是你连接上ssh之后,可以通过ssh代理访问目标地址。
437 | 假设有:vps
438 | - IP是2.2.2.2, ssh端口是22, ssh用户名是:user, ssh用户密码是:demo
439 | - 用户user的ssh私钥名称是user.key
440 |
441 | #### *1.7.1 ssh用户名和密码的方式*
442 | 本地HTTP(S)代理28080端口,执行:
443 | `./proxy http -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -D demo -t tcp -p ":28080"`
444 | #### *1.7.2 ssh用户名和密钥的方式*
445 | 本地HTTP(S)代理28080端口,执行:
446 | `./proxy http -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -S user.key -t tcp -p ":28080"`
447 |
448 | ### 1.8.KCP协议传输
449 | 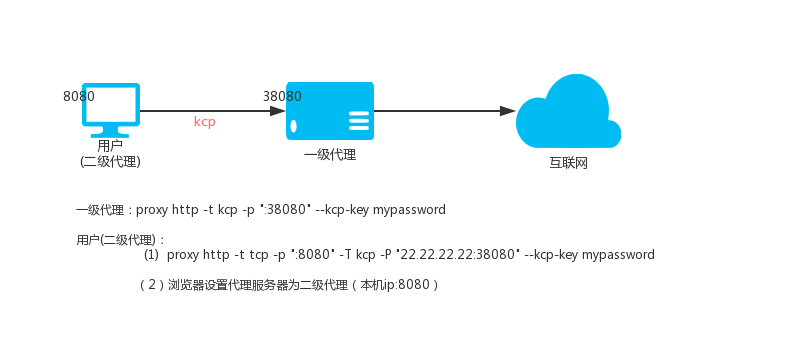
450 | KCP协议需要--kcp-key参数设置一个密码用于加密解密数据
451 |
452 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
453 | `./proxy http -t kcp -p ":38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
454 |
455 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
456 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T kcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
457 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080,数据通过kcp协议传输,注意kcp走的是udp协议协议,所以防火墙需放开38080的udp协议。
458 |
459 | ### 1.9 HTTP(S)反向代理
460 | 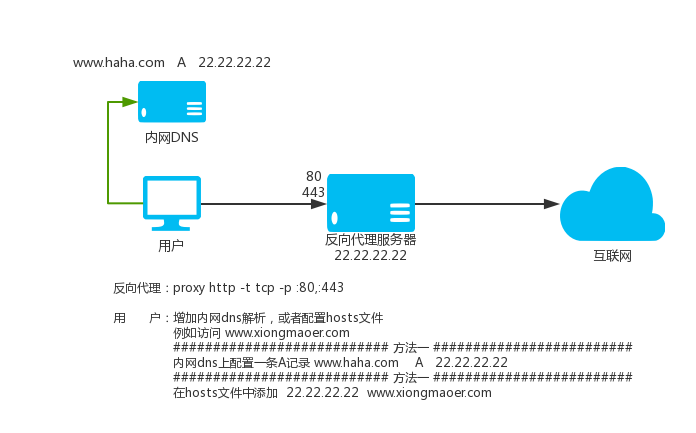
461 | proxy不仅支持在其他软件里面通过设置代理的方式,为其他软件提供代理服务,而且支持直接把请求的网站域名解析到proxy监听的ip上,然后proxy监听80和443端口,那么proxy就会自动为你代理访问需要访问的HTTP(S)网站。
462 |
463 | 使用方式:
464 | 在"最后一级proxy代理"的机器上,因为proxy要伪装成所有网站,网站默认的端口HTTP是80,HTTPS是443,让proxy监听80和443端口即可.参数-p多个地址用逗号分割。
465 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :80,:443`
466 |
467 | 这个命令就在机器上启动了一个proxy代理,同时监听80和443端口,既可以当作普通的代理使用,也可以直接把需要代理的域名解析到这个机器的IP上。
468 |
469 | 如果有上级代理那么参照上面教程设置上级即可,使用方式完全一样。
470 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :80,:443 -T tls -P "2.2.2.2:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
471 |
472 | 注意:
473 | proxy所在的服务器的DNS解析结果不能受到自定义的解析影响,不然就死循环了,proxy代理最好指定`--dns 8.8.8.8`参数。
474 |
475 | ### 1.10 HTTP(S)透明代理
476 | 该模式需要具有一定的网络基础,相关概念不懂的请自行搜索解决。
477 | 假设proxy现在在路由器上运行,启动命令如下:
478 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :33080 -T tls -P "2.2.2.2:33090" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
479 |
480 | 然后添加iptables规则,下面是参考规则:
481 | ```shell
482 | #上级proxy服务端服务器IP地址:
483 | proxy_server_ip=2.2.2.2
484 |
485 | #路由器运行proxy监听的端口:
486 | proxy_local_port=33080
487 |
488 | #下面的就不用修改了
489 | #create a new chain named PROXY
490 | iptables -t nat -N PROXY
491 |
492 | # Ignore your PROXY server's addresses
493 | # It's very IMPORTANT, just be careful。
494 |
495 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d $proxy_server_ip -j RETURN
496 |
497 | # Ignore LANs IP address
498 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 0.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
499 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 10.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
500 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 127.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
501 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 169.254.0.0/16 -j RETURN
502 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 172.16.0.0/12 -j RETURN
503 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 192.168.0.0/16 -j RETURN
504 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 224.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
505 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 240.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
506 |
507 | # Anything to port 80 443 should be redirected to PROXY's local port
508 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
509 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp --dport 443 -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
510 |
511 | # Apply the rules to nat client
512 | iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -j PROXY
513 | # Apply the rules to localhost
514 | iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp -j PROXY
515 | ```
516 | - 清空整个链 iptables -F 链名比如iptables -t nat -F PROXY
517 | - 删除指定的用户自定义链 iptables -X 链名 比如 iptables -t nat -X PROXY
518 | - 从所选链中删除规则 iptables -D 链名 规则详情 比如 iptables -t nat -D PROXY -d 223.223.192.0/255.255.240.0 -j RETURN
519 |
520 | ### 1.11 自定义DNS
521 | --dns-address和--dns-ttl参数,用于自己指定proxy访问域名的时候使用的dns(--dns-address)
522 | 以及解析结果缓存时间(--dns-ttl)秒数,避免系统dns对proxy的干扰,另外缓存功能还能减少dns解析时间提高访问速度。
523 | 比如:
524 | `./proxy http -p ":33080" --dns-address "8.8.8.8:53" --dns-ttl 300`
525 |
526 | ### 1.12 自定义加密
527 | proxy的http(s)代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义
528 | 加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可,
529 | 加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
530 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以,下面分别用二级,三级为例:
531 |
532 | 二级实例
533 |
534 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
535 | `proxy http -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
536 | 本地二级执行:
537 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
538 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
539 |
540 |
541 | 三级实例
542 |
543 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
544 | `proxy http -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
545 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
546 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
547 | 本地三级执行:
548 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
549 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
550 |
551 | ### 1.13 压缩传输
552 | proxy的http(s)代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以对数据进行压缩,
553 | 也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,
554 | 一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
555 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据,下面分别用二级,三级为例:
556 |
557 | 二级实例
558 |
559 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
560 | `proxy http -t tcp -m -p :7777`
561 | 本地二级执行:
562 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
563 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
564 |
565 |
566 | 三级实例
567 |
568 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
569 | `proxy http -t tcp -m -p :7777`
570 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
571 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
572 | 本地三级执行:
573 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
574 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
575 |
576 | ### 1.14 负载均衡
577 |
578 | HTTP(S)代理支持上级负载均衡,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
579 |
580 | `proxy http --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080`
581 |
582 | ### 1.14.1 设置重试间隔和超时时间
583 |
584 | `proxy http --lb-method=leastconn --lb-retrytime 300 --lb-timeout 300 -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -t tcp -p :33080`
585 |
586 | ### 1.14.2 设置权重
587 |
588 | `proxy http --lb-method=weight -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -P 2.1.1.1:33080?w=2 -P 3.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -t tcp -p :33080`
589 |
590 | ### 1.14.3 使用目标地址选择上级
591 |
592 | `proxy http --lb-hashtarget --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -t tcp -p :33080`
593 |
594 | ### 1.15 限速
595 |
596 | 限速100K,通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
597 |
598 | `proxy http -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -l 100K`
599 |
600 | ### 1.16 指定出口IP
601 |
602 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作,此时代理会尝试不绑定IP去访问目标,同时日志会提示。
603 |
604 | `proxy http -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 --bind-listen`
605 |
606 | ### 1.17 证书参数使用base64数据
607 |
608 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
609 |
610 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
611 |
612 | ### 1.18 智能模式
613 | 智能模式设置,可以是intelligent|direct|parent三者之一。
614 | 默认是:intelligent。
615 | 每个值的含义如下:
616 | `--intelligent=direct`,不在blocked里面的目标都直连。
617 | `--intelligent=parent`,不在direct里面的目标都走上级。
618 | `--intelligent=intelligent`,blocked和direct里面都没有的目标,智能判断是否使用上级访问目标。
619 |
620 | ### 1.19 查看帮助
621 | `./proxy help http`
622 |
623 | ## 2.TCP代理
624 |
625 | ### 2.1 普通一级TCP代理
626 | 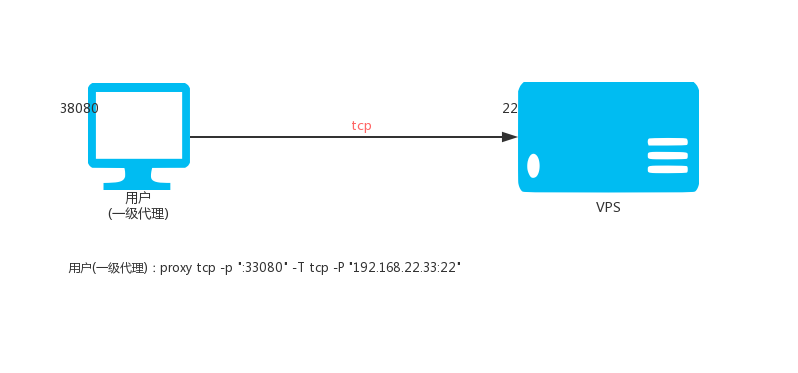
627 | 本地执行:
628 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22"`
629 | 那么访问本地33080端口就是访问192.168.22.33的22端口。
630 |
631 | `-p`参数支持的写法:
632 |
633 | ```text
634 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
635 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
636 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
637 | ```
638 |
639 | 如果本地监听端口数量大于1,那么将会连接与本地端口一致的对应上级端口,忽略`-P`里面的端口。
640 |
641 | 如果需要所有端口进来的连接,都连接到上级指定端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`。
642 |
643 | 比如:
644 |
645 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080-33085" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:0"`
646 |
647 | 那么`33080`端口进来的连接,将会连接192.168.22.33的`33080`端口,其它端口以此类推,本地和上级端口一致,此时参数`-P`里面的端口用`0`。
648 |
649 | 如果想无论是`33080`,`33081`等端口进来的连接都连接到192.168.22.33的`22`端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`
650 |
651 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080-33085" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --lock-port`
652 |
653 |
654 | ### 2.2 普通二级TCP代理
655 | 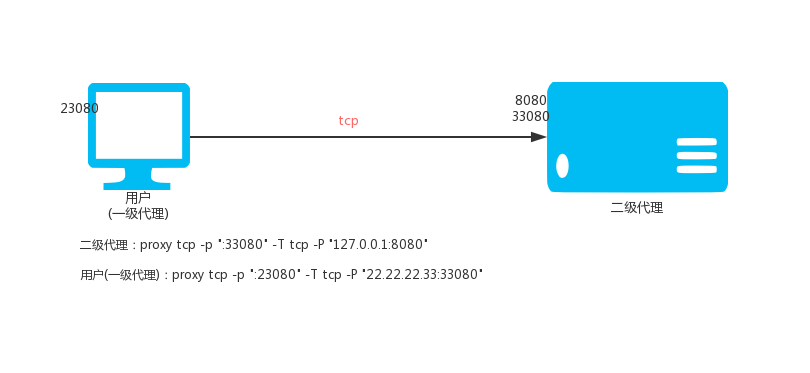
656 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
657 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "127.0.0.1:8080"`
658 | 本地执行:
659 | `./proxy tcp -p ":23080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.33:33080"`
660 | 那么访问本地23080端口就是访问22.22.22.33的8080端口。
661 |
662 | ### 2.3 普通三级TCP代理
663 | 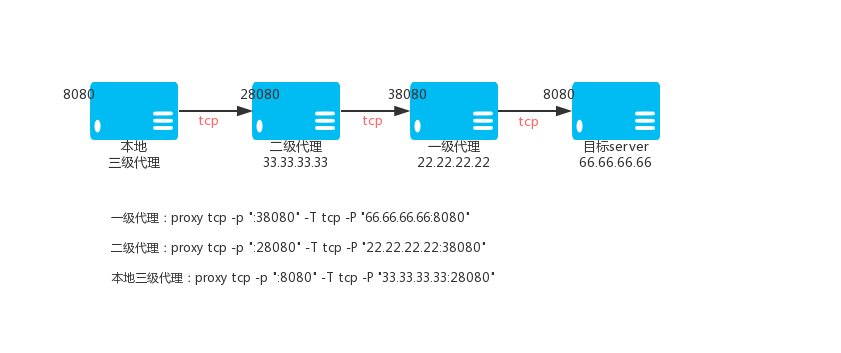
664 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
665 | `./proxy tcp -p ":38080" -T tcp -P "66.66.66.66:8080"`
666 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
667 | `./proxy tcp -p ":28080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080"`
668 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
669 | `./proxy tcp -p ":8080" -T tcp -P "33.33.33.33:28080"`
670 | 那么访问本地8080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问66.66.66.66的8080端口。
671 |
672 | ### 2.4 加密二级TCP代理
673 | 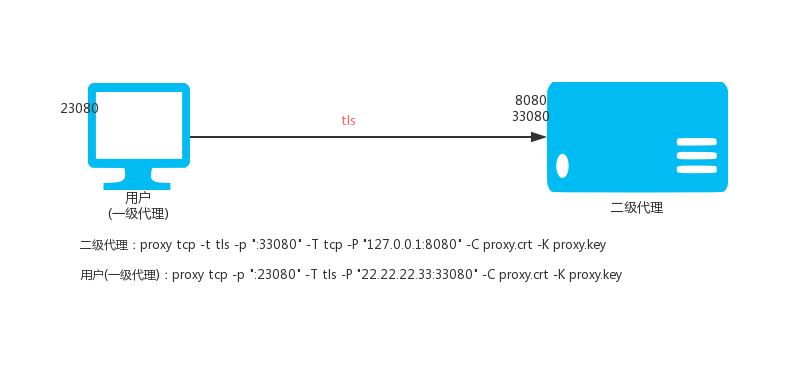
674 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
675 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "127.0.0.1:8080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
676 | 本地执行:
677 | `./proxy tcp -p ":23080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.33:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
678 | 那么访问本地23080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问22.22.22.33的8080端口。
679 |
680 | ### 2.5 加密三级TCP代理
681 | 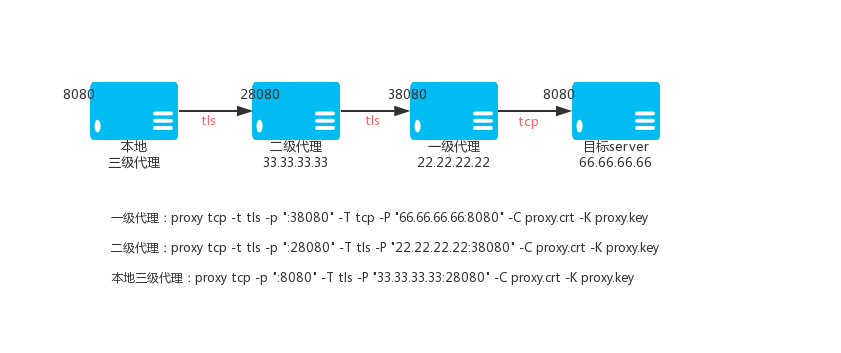
682 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
683 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":38080" -T tcp -P "66.66.66.66:8080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
684 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
685 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
686 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
687 | `./proxy tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
688 | 那么访问本地8080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问66.66.66.66的8080端口。
689 |
690 | ### 2.6 通过代理连接上级
691 | 有时候proxy所在的网络不能直接访问外网,需要通过一个https或者socks5代理才能上网,那么这个时候
692 | -J参数就可以帮助你让proxy的tcp端口映射的时候通过https或者socks5代理去连接上级-P,将外部端口映射到本地。
693 | -J参数格式如下:
694 |
695 | https代理写法:
696 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
697 | https://username:password@host:port
698 | 代理不需要认证
699 | https://host:port
700 |
701 | socks5代理写法:
702 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
703 | socks5://username:password@host:port
704 | 代理不需要认证
705 | socks5://host:port
706 |
707 | host:代理的IP或者域名
708 | port:代理的端口
709 |
710 | ### 2.7 指定`出口IP`
711 | 当TCP代理当上级类型(参数:-T)是tcp当时候,支持指定`出口IP`。使用`--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作,此时代理会尝试不绑定IP去访问目标,同时日志会提示。
712 |
713 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" -B`
714 |
715 | ### 2.8 限速,限制连接数
716 |
717 | 参数`--max-conns`可以限制每个端口的最大连接数。
718 | 比如限制每个端口最多1000个连接数:
719 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --max-conns 1000`
720 | 参数`--rate-limit`可以限制每个tcp连接的速率。
721 | 比如限制每个tcp连接速率为100k/s:
722 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --rate-limit 100k`
723 |
724 | ### 2.9 查看帮助
725 | `./proxy help tcp`
726 |
727 | ## 3.UDP代理
728 |
729 | ### 3.1.普通一级UDP代理
730 | 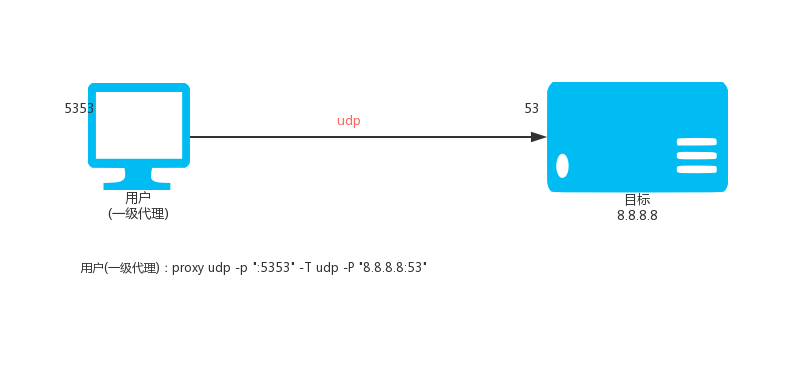
731 | 本地执行:
732 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
733 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
734 |
735 | `-p`参数支持的写法:
736 |
737 | ```text
738 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
739 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
740 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
741 | ```
742 |
743 | 如果本地监听端口数量大于1,那么将会连接与本地端口一致的对应上级端口,忽略`-P`里面的端口。
744 |
745 | 如果需要所有端口进来的连接,都连接到上级指定端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`。
746 |
747 | 比如:
748 |
749 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080-33085" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:0"`
750 |
751 | 那么`33080`端口进来的连接,将会连接192.168.22.33的`33080`端口,其它端口以此类推,本地和上级端口一致,此时参数`-P`里面的端口用`0`。
752 |
753 | 如果想无论是`33080`,`33081`等端口进来的连接都连接到192.168.22.33的`2222`端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`
754 |
755 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080-33085" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:2222" --lock-port`
756 |
757 | ### 3.2.普通二级UDP代理
758 | 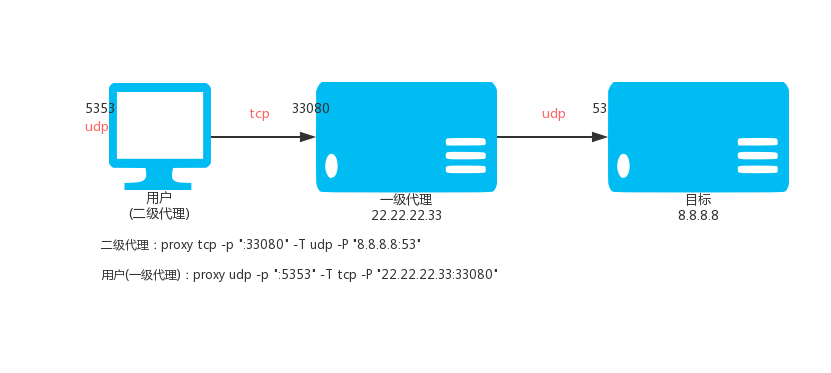
759 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
760 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
761 | 本地执行:
762 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.33:33080"`
763 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是通过TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
764 |
765 | ### 3.3.普通三级UDP代理
766 | 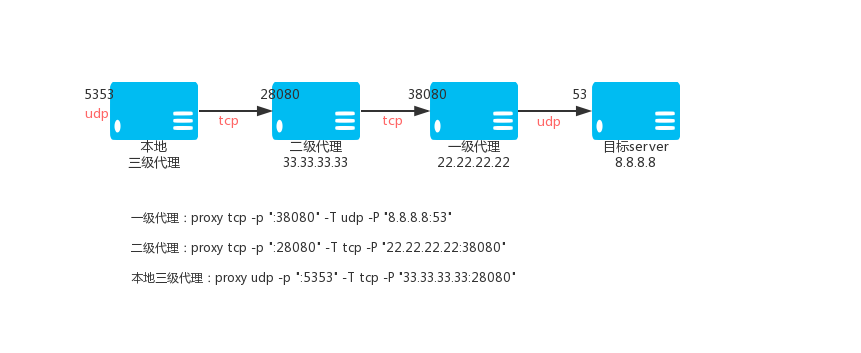
767 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
768 | `./proxy tcp -p ":38080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
769 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
770 | `./proxy tcp -p ":28080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080"`
771 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
772 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tcp -P "33.33.33.33:28080"`
773 | 那么访问本地5353端口就是通过TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的53端口。
774 |
775 | ### 3.4.加密二级UDP代理
776 | 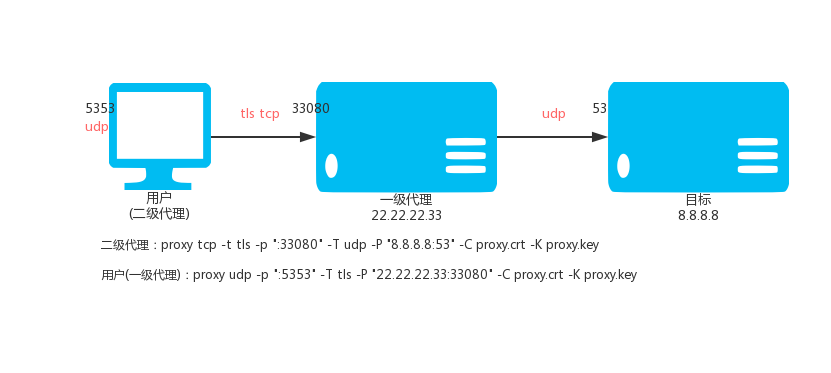
777 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
778 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":33080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
779 | 本地执行:
780 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tls -P "22.22.22.33:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
781 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是通过加密TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
782 |
783 | ### 3.5.加密三级UDP代理
784 | 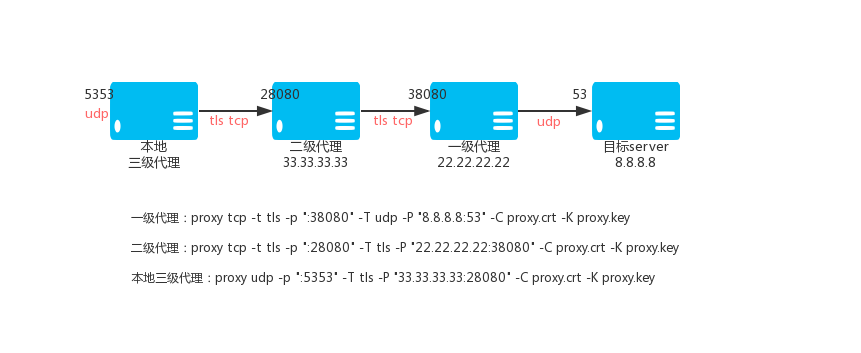
785 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
786 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":38080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
787 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
788 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
789 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
790 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
791 | 那么访问本地5353端口就是通过加密TCP隧道,通过VPS_01访问8.8.8.8的53端口。
792 |
793 | ### 3.6 指定`出口IP`
794 | 当UDP代理当上级类型(参数:-T)是udp当时候,支持指定`出口IP`。使用`--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作。
795 |
796 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:2222" -B`
797 |
798 | ### 3.7 查看帮助
799 | `./proxy help udp`
800 |
801 | ## 4.内网穿透
802 | ### 4.1、原理说明
803 | 内网穿透,分为两个版本,“多链接版本”和“多路复用版本”,一般像web服务这种不是长时间连接的服务建议用“多链接版本”,如果是要保持长时间连接建议使用“多路复用版本”。
804 | 1. 多链接版本,对应的子命令是tserver,tclient,tbridge。
805 | 1. 多路复用版本,对应的子命令是server,client,bridge。
806 | 1. 多链接版本和多路复用版本的参数和使用方式完全一样。
807 | 1. 多路复用版本的server,client可以开启压缩传输,参数是--c。
808 | 1. server,client要么都开启压缩,要么都不开启,不能只开一个。
809 |
810 | 下面的教程以“多路复用版本”为例子,说明使用方法。
811 | 内网穿透由三部分组成:client端,server端,bridge端;client和server主动连接bridge端进行桥接。
812 |
813 | ### 4.2、TCP普通用法
814 | 背景:
815 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口
816 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
817 |
818 | 需求:
819 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的28080端口访问到公司机器A的80端口
820 |
821 | 步骤:
822 | 1. 在vps上执行
823 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
824 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
825 |
826 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
827 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
828 |
829 | 1. 完成
830 |
831 | ### 4.3、微信接口本地开发
832 | 背景:
833 | - 自己的笔记本提供了nginx服务80端口
834 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
835 |
836 | 需求:
837 | 在微信的开发帐号的网页回调接口配置里面填写地址:http://22.22.22.22/calback.php
838 | 然后就可以访问到笔记本的80端口下面的calback.php,如果需要绑定域名,可以用自己的域名
839 | 比如:wx-dev.xxx.com解析到22.22.22.22,然后在自己笔记本的nginx里
840 | 配置域名wx-dev.xxx.com到具体的目录即可。
841 |
842 |
843 | 步骤:
844 | 1. 在vps上执行,确保vps的80端口没被其它程序占用。
845 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
846 | `./proxy server -r ":80@:80" -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
847 |
848 | 1. 在自己笔记本上面执行
849 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
850 |
851 | 1. 完成
852 |
853 | ### 4.4、UDP普通用法
854 | 背景:
855 | - 公司机器A提供了DNS解析服务,UDP:53端口
856 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
857 |
858 | 需求:
859 | 在家里能够通过设置本地dns为22.22.22.22,使用公司机器A进行域名解析服务。
860 |
861 | 步骤:
862 | 1. 在vps上执行
863 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
864 | `./proxy server --udp -r ":53@:53" -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
865 |
866 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
867 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
868 |
869 | 1. 完成
870 |
871 | ### 4.5、高级用法一
872 | 背景:
873 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口
874 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
875 |
876 | 需求:
877 | 为了安全,不想在VPS上能够访问到公司机器A,在家里能够通过访问本机的28080端口,
878 | 通过加密隧道访问到公司机器A的80端口。
879 |
880 | 步骤:
881 | 1. 在vps上执行
882 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
883 |
884 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
885 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
886 |
887 | 1. 在家里电脑上执行
888 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
889 |
890 | 1. 完成
891 |
892 | ### 4.6、高级用法二
893 | 提示:
894 | 如果同时有多个client连接到同一个bridge,需要指定不同的key,可以通过--k参数设定,--k可以是任意唯一字符串,
895 | 只要在同一个bridge上唯一即可。
896 | server连接到bridge的时候,如果同时有多个client连接到同一个bridge,需要使用--k参数选择client。
897 | 暴露多个端口重复-r参数即可.-r格式是:"本地IP:本地端口@clientHOST:client端口"。
898 |
899 | 背景:
900 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口,ftp服务21端口
901 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
902 |
903 | 需求:
904 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的28080端口访问到公司机器A的80端口
905 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的29090端口访问到公司机器A的21端口
906 |
907 | 步骤:
908 | 1. 在vps上执行
909 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
910 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -r ":29090@:21" --k test -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
911 |
912 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
913 | `./proxy client --k test -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
914 |
915 | 1. 完成
916 |
917 | ### 4.7.server的-r参数
918 | -r完整格式是:`PROTOCOL://LOCAL_IP:LOCAL_PORT@[CLIENT_KEY]CLIENT_LOCAL_HOST:CLIENT_LOCAL_PORT`
919 |
920 | 4.7.1.协议PROTOCOL:tcp、udp、ptcp、pudp。
921 | 比如: `-r "udp://:10053@:53" -r "tcp://:10800@:1080" -r ":8080@:80"`
922 | 如果指定了--udp参数,PROTOCOL默认为udp,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`默认为udp;
923 | 如果没有指定--udp参数,PROTOCOL默认为tcp,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`默认为tcp;
924 |
925 | 4.7.2.CLIENT_KEY:默认是default。
926 | 比如: -r "udp://:10053@[test1]:53" -r "tcp://:10800@[test2]:1080" -r ":8080@:80"
927 | 如果指定了--k参数,比如--k test,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`CLIENT_KEY默认为test;
928 | 如果没有指定--k参数,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`CLIENT_KEY默认为default;
929 |
930 | 4.7.3.LOCAL_IP为空默认是:`0.0.0.0`,CLIENT_LOCAL_HOST为空默认是:`127.0.0.1`;
931 |
932 | ### 4.8.server和client通过代理连接bridge
933 | 有时候server或者client所在的网络不能直接访问外网,需要通过一个https或者socks5代理才能上网,那么这个时候
934 | -J参数就可以帮助你让server或者client通过https或者socks5代理去连接bridge。
935 | -J参数格式如下:
936 |
937 | https代理写法:
938 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
939 | https://username:password@host:port
940 | 代理不需要认证
941 | https://host:port
942 |
943 | socks5代理写法:
944 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
945 | socks5://username:password@host:port
946 | 代理不需要认证
947 | socks5://host:port
948 |
949 | host:代理的IP或者域名
950 | port:代理的端口
951 |
952 | ### 4.9.内网穿透HTTP服务
953 |
954 | 通常HTTP请求客户端会使用server的ip和端口去设置HOST字段,但是与期望的后端实际HOST不一样,这样就造成了tcp是通的,
955 | 但后端依赖HOST字段定位虚拟主机就不能工作.现在用--http-host参数强制设置http头部的HOST字段值为后端实际的
956 | 域名和端口即可轻松解决。
957 |
958 | `server`的--http-host参数格式如下:
959 |
960 | `--http-host www.test.com:80@2200`,如果server监听多个端口,只需要重复`--http-host`参数设置每个端口的HOST即可。
961 |
962 | 实例:
963 |
964 | 比如client本地nginx,127.0.0.1:80提供了web服务,其中绑定了一个域名`local.com`。
965 |
966 | 那么server的启动参数可以如下:
967 |
968 | `proxy server -P :30000 -r :2500@127.0.0.1:80 --http-host local.com@2500`
969 |
970 | 解释:
971 |
972 | `-r :2500@127.0.0.1:80` 和 `--http-host local.com:80@2500` 里面的2500端口是server本地监听的端口
973 |
974 | 当使用http协议请求server的ip:2500端口的时候,http的头部HOST字段就会被设置为`local.com`。
975 |
976 | ### 4.10 关于流量统计
977 |
978 | 如果单独启动一个server对接上级是proxy-admin控制面板,需要在上级控制面板里面新建一个映射,获得个映射规则的ID,
979 |
980 | 然后启动server的时候加上参数 --server-id=映射规则的ID 才能统计到流量。
981 |
982 | ### 4.11 关于p2p
983 | 内网穿透支持在server和client网络情况满足的情况下,server和client之间通过p2p直接连接,开启方法是:
984 |
985 | 在启动bridge,server,client到时候都加上`--p2p`参数即可。server的-r参数可以针对端口是否启用p2p(ptcp和pudp)。
986 |
987 | 如果server和client之间p2p打洞失败,那么会自动切换使用bridge中转传输数据。
988 |
989 | ### 4.12 客户端key白名单
990 | 内网穿透bridge可以设置客户端key白名单,参数是--client-keys,格式可以是:
991 |
992 | a.文件名,文件内容一行一个客户端key只能包含数字字母下划线,也就是客户端启动参数--k的值,只有客户端key在此白名单的客户端才能连接。# 开头的行,为注释。
993 |
994 | b.“base64://”开头的base64编码的上面a说明的文件内容,比如:base64://ajfpoajsdfa=
995 |
996 | c.”str://“开头的英文逗号分割的多个key,比如:str://default,company,school
997 |
998 | 默认是空,允许所有key。
999 |
1000 | ### 4.13 网络NAT类型判断
1001 |
1002 | nat类型判断,方便查看网络是否支持p2p,可以执行:`proxy tools -a nattype`
1003 |
1004 | ### 4.14 查看帮助
1005 | `./proxy help bridge`
1006 | `./proxy help server`
1007 | `./proxy help client`
1008 |
1009 | ## 5.SOCKS5代理
1010 | 提示:
1011 |
1012 | SOCKS5代理,支持CONNECT,UDP协议,不支持BIND,支持用户名密码认证。
1013 |
1014 | ***如果你的VPS是阿里云,腾讯云这种VPS,就是ifconfig看不见你的公网IP,只能看见内网IP,***
1015 |
1016 | ***那么需要加上`-g VPS公网IP`参数,SOCKS5代理的UDP功能才能正常工作。***
1017 |
1018 | ### 5.1 普通SOCKS5代理
1019 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080"`
1020 |
1021 | -p参数支持的写法:
1022 |
1023 | ```text
1024 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
1025 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
1026 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
1027 | ```
1028 |
1029 | ### 5.2.普通二级SOCKS5代理
1030 | 
1031 | 使用本地端口8090,假设上级SOCKS5代理是`22.22.22.22:8080`
1032 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" `
1033 | 我们还可以指定网站域名的黑白名单文件,一行一个域名,匹配规则是最右匹配,比如:baidu.com,匹配的是*.*.baidu.com,黑名单的域名域名直接走上级代理,白名单的域名不走上级代理;如果域名即在黑名单又在白名单中,那么黑名单起作用。
1034 | `./proxy socks -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" -b blocked.txt -d direct.txt`
1035 |
1036 | ### 5.3.SOCKS二级代理(加密)
1037 | 
1038 | 一级SOCKS代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
1039 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1040 |
1041 | 二级SOCKS代理(本地Linux)
1042 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1043 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080。
1044 |
1045 | 二级SOCKS代理(本地windows)
1046 | `./proxy.exe socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1047 | 然后设置你的windos系统中,需要通过代理上网的程序的代理为socks5模式,地址为:127.0.0.1,端口为:8080,程序即可通过加密通道通过vps上网。
1048 |
1049 | ### 5.4.SOCKS三级代理(加密)
1050 | 
1051 | 一级SOCKS代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
1052 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1053 | 二级SOCKS代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
1054 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1055 | 三级SOCKS代理(本地)
1056 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1057 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问一级SOCKS代理上面的代理端口38080。
1058 |
1059 | ### 5.5.SOCKS代理流量强制走上级SOCKS代理
1060 | 默认情况下,proxy会智能判断一个网站域名是否无法访问,如果无法访问才走上级SOCKS代理.通过--always可以使全部SOCKS代理流量强制走上级SOCKS代理。
1061 | `./proxy socks --always -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1062 |
1063 | ### 5.6.SOCKS通过SSH中转
1064 | 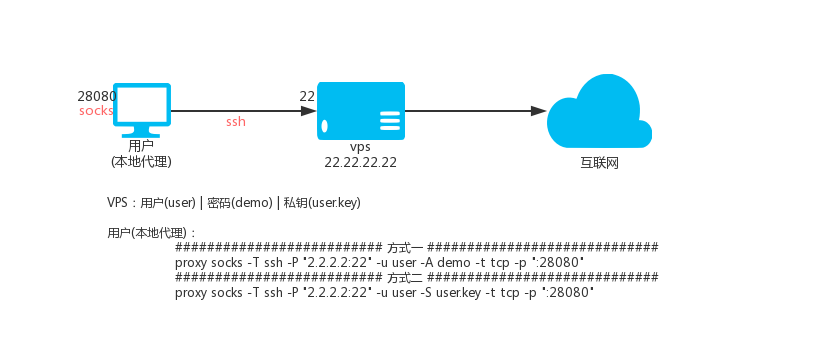
1065 | 说明:ssh中转的原理是利用了ssh的转发功能,就是你连接上ssh之后,可以通过ssh代理访问目标地址。
1066 | 假设有:vps
1067 | - IP是2.2.2.2, ssh端口是22, ssh用户名是:user, ssh用户密码是:demo
1068 | - 用户user的ssh私钥名称是user.key
1069 |
1070 | #### *5.6.1 ssh用户名和密码的方式*
1071 | 本地SOCKS5代理28080端口,执行:
1072 | `./proxy socks -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -D demo -t tcp -p ":28080"`
1073 | #### *5.6.2 ssh用户名和密钥的方式*
1074 | 本地SOCKS5代理28080端口,执行:
1075 | `./proxy socks -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -S user.key -t tcp -p ":28080"`
1076 |
1077 | 那么访问本地的28080端口就是通过VPS访问目标地址。
1078 |
1079 | ### 5.7.认证
1080 | 对于socks5代理协议我们可以进行用户名密码认证,认证的用户名和密码可以在命令行指定
1081 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1" -a "user2:pass2"`
1082 | 多个用户,重复-a参数即可。
1083 | 也可以放在文件中,格式是一行一个"用户名:密码",然后用-F指定。
1084 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":33080" -F auth-file.txt`
1085 |
1086 | ### 5.8.KCP协议传输
1087 | KCP协议需要--kcp-key参数设置一个密码用于加密解密数据
1088 |
1089 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
1090 | `./proxy socks -t kcp -p ":38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
1091 |
1092 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
1093 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T kcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
1094 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080,数据通过kcp协议传输。
1095 |
1096 | ### 5.9.自定义DNS
1097 | --dns-address和--dns-ttl参数,用于自己指定proxy访问域名的时候使用的dns(--dns-address)
1098 | 以及解析结果缓存时间(--dns-ttl)秒数,避免系统dns对proxy的干扰,另外缓存功能还能减少dns解析时间提高访问速度。
1099 | 比如:
1100 | `./proxy socks -p ":33080" --dns-address "8.8.8.8:53" --dns-ttl 300`
1101 |
1102 | ### 5.10 自定义加密
1103 | proxy的socks代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可,
1104 | 加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
1105 |
1106 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以。
1107 |
1108 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
1109 |
1110 | 二级实例
1111 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1112 | `proxy socks -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
1113 | 本地二级执行:
1114 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
1115 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
1116 |
1117 |
1118 | 三级实例
1119 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1120 | `proxy socks -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
1121 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
1122 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
1123 | 本地三级执行:
1124 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
1125 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
1126 |
1127 | ### 5.11 压缩传输
1128 | proxy的socks代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以
1129 | 对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,
1130 | 一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
1131 |
1132 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据。
1133 |
1134 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
1135 |
1136 | 二级实例
1137 |
1138 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1139 | `proxy socks -t tcp -m -p :7777`
1140 | 本地二级执行:
1141 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
1142 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
1143 |
1144 |
1145 | 三级实例
1146 |
1147 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1148 | `proxy socks -t tcp -m -p :7777`
1149 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
1150 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
1151 | 本地三级执行:
1152 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
1153 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
1154 |
1155 |
1156 | ### 5.12 负载均衡
1157 |
1158 | SOCKS代理支持上级负载均衡,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
1159 |
1160 | `proxy socks --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
1161 |
1162 | ### 5.12.1 设置重试间隔和超时时间
1163 |
1164 | `proxy socks --lb-method=leastconn --lb-retrytime 300 --lb-timeout 300 -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
1165 |
1166 | ### 5.12.2 设置权重
1167 |
1168 | `proxy socks --lb-method=weight -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -P 2.1.1.1:33080?w=2 -P 3.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -p :33080 -t tcp`
1169 |
1170 | ### 5.12.3 使用目标地址选择上级
1171 |
1172 | `proxy socks --lb-hashtarget --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
1173 |
1174 | ### 5.13 限速
1175 |
1176 | 限速100K,通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
1177 |
1178 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -l 100K`
1179 |
1180 | ### 5.14 指定`出口IP`
1181 |
1182 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果`入口IP`是内网IP,`出口IP`不会使用`入口IP`。
1183 |
1184 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 --bind-listen`
1185 |
1186 | ### 5.15 级联认证
1187 |
1188 | SOCKS5支持级联认证,-A可以设置上级认证信息。
1189 |
1190 | 上级:
1191 |
1192 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -a user:pass`
1193 |
1194 | 本地:
1195 |
1196 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -A user:pass -t tcp -p :33080`
1197 |
1198 | 请更多认证细节,请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
1199 |
1200 | ### 5.16 证书参数使用base64数据
1201 |
1202 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
1203 |
1204 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
1205 |
1206 |
1207 | ### 5.17 智能模式
1208 | 智能模式设置,可以是intelligent|direct|parent三者之一。
1209 | 默认是:intelligent。
1210 | 每个值的含义如下:
1211 | `--intelligent=direct`,不在blocked里面的目标都直连。
1212 | `--intelligent=parent`,不在direct里面的目标都走上级。
1213 | `--intelligent=intelligent`,blocked和direct里面都没有的目标,智能判断是否使用上级访问目标。
1214 |
1215 | ### 5.18 固定UDP功能端口
1216 |
1217 | 默认情况下socks5的UDP功能的端口号,proxy是按着`rfc1982草案`要求,使用协议握手过程中随机指定,不需要提前指定。
1218 |
1219 | 但是某些情况下,需要固定UDP功能端口,可以通过参数`--udp-port 端口号`用来固定UDP功能的端口号,比如:
1220 |
1221 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --udp-port 38080`
1222 |
1223 | ### 5.19 查看帮助
1224 | `./proxy help socks`
1225 |
1226 | ## 6.SPS协议转换
1227 |
1228 | ### 6.1 功能介绍
1229 | 代理协议转换使用的是sps子命令,sps本身不提供代理功能,只是接受代理请求"转换并转发"给已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理或者ss代理;sps可以把已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理或ss代理转换为一个端口同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的代理,而且http(s)代理支持正向代理和反向代理(SNI),转换后的SOCKS5代理,当上级是SOCKS5或者SS时仍然支持UDP功能;另外对于已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理,支持tls、tcp、kcp三种模式,支持链式连接,也就是可以多个sps结点层级连接构建加密通道。
1230 |
1231 | `ss`功能支持的加密方法为:aes-128-cfb , aes-128-ctr , aes-128-gcm , aes-192-cfb , aes-192-ctr , aes-192-gcm , aes-256-cfb , aes-256-ctr , aes-256-gcm , bf-cfb , cast5-cfb , chacha20 , chacha20-ietf , chacha20-ietf-poly1305 , des-cfb , rc4-md5 , rc4-md5-6 , salsa20 , xchacha20
1232 |
1233 | 本地监听端口-p参数支持的写法:
1234 |
1235 | ```text
1236 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
1237 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
1238 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
1239 | ```
1240 |
1241 | ### 6.2 HTTP(S)转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
1242 | 假设已经存在一个普通的http(s)代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1243 | 命令如下:
1244 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1245 |
1246 | 假设已经存在一个tls的http(s)代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,tls需要证书文件,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1247 | 命令如下:
1248 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1249 |
1250 | 假设已经存在一个kcp的http(s)代理(密码是:demo123):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1251 | 命令如下:
1252 | `./proxy sps -S http -T kcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 --kcp-key demo123 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1253 |
1254 | ### 6.3 SOCKS5转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
1255 | 假设已经存在一个普通的socks5代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1256 | 命令如下:
1257 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1258 |
1259 | 假设已经存在一个tls的socks5代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,tls需要证书文件,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1260 | 命令如下:
1261 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T tls -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1262 |
1263 | 假设已经存在一个kcp的socks5代理(密码是:demo123):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1264 | 命令如下:
1265 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T kcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 --kcp-key demo123 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1266 |
1267 | ### 6.4 SS转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
1268 | SPS上级和本地支持ss协议,上级可以是SPS或者标准的ss服务。
1269 | SPS本地默认提供HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS三种代理,当上级是SOCKS5时转换后的SOCKS5和SS支持UDP功能。
1270 | 假设已经存在一个普通的SS或者SPS代理(开启了ss,加密方式:aes-256-cfb,密码:demo):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,转换后的ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1271 | 命令如下:
1272 | `./proxy sps -S ss -H aes-256-cfb -J pass -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`。
1273 |
1274 | ### 6.5 链式连接
1275 | 
1276 | 上面提过多个sps结点可以层级连接构建加密通道,假设有如下vps和家里的pc电脑。
1277 | vps01:2.2.2.2
1278 | vps02:3.3.3.3
1279 | 现在我们想利用pc和vps01和vps02构建一个加密通道,本例子用tls加密也可以用kcp,在pc上访问本地18080端口就是访问vps01的本地8080端口。
1280 | 首先在vps01(2.2.2.2)上我们运行一个只有本地可以访问的http(s)代理,执行:
1281 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p 127.0.0.1:8080`
1282 |
1283 | 然后在vps01(2.2.2.2)上运行一个sps结点,执行:
1284 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tls -p :8081 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1285 |
1286 | 然后在vps02(3.3.3.3)上运行一个sps结点,执行:
1287 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:8081 -t tls -p :8082 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1288 |
1289 | 然后在pc上运行一个sps结点,执行:
1290 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 3.3.3.3:8082 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1291 |
1292 | 完成。
1293 |
1294 | ### 6.6 监听多个端口
1295 | 一般情况下监听一个端口就可以,不过如果作为反向代理需要同时监听80和443两个端口,那么-p参数是支持的,
1296 | 格式是:`-p 0.0.0.0:80,0.0.0.0:443`,多个绑定用逗号分隔即可。
1297 |
1298 | ### 6.7 认证功能
1299 | sps支持http(s)\socks5代理认证,可以级联认证,有四个重要的信息:
1300 | 1:用户发送认证信息`user-auth`。
1301 | 2:设置的本地认证信息`local-auth`。
1302 | 3:设置的连接上级使用的认证信息`parent-auth`。
1303 | 4:最终发送给上级的认证信息`auth-info-to-parent`。
1304 | 他们的情况关系如下:
1305 |
1306 | | user-auth | local-auth | parent-auth | auth-info-to-paren
1307 | | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------
1308 | | 有/没有 | 有 | 有 | 来自parent-auth
1309 | | 有/没有 | 没有 | 有 | 来自parent-auth
1310 | | 有/没有 | 有 | 没有 | 无
1311 | | 没有 | 没有 | 没有 | 无
1312 | | 有 | 没有 | 没有 | 来自user-auth
1313 |
1314 | 对于sps代理我们可以进行用户名密码认证,认证的用户名和密码可以在命令行指定
1315 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1:0:0:" -a "user2:pass2:0:0:"`
1316 | 多个用户,重复-a参数即可。
1317 | 也可以放在文件中,格式是一行一个`用户名:密码:连接数:速率:上级`,然后用-F指定。
1318 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -F auth-file.txt`
1319 |
1320 | 如果上级有认证,下级可以通过-A参数设置认证信息,比如:
1321 | 上级:`./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1:0:0:" -a "user2:pass2:0:0:"`
1322 | 下级:`./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -A "user1:pass1" -t tcp -p ":33080" `
1323 |
1324 | 请更多认证细节,请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
1325 |
1326 | ### 6.8 多个上级
1327 |
1328 | 如果存在多个上级,可以通过多个-P指定。
1329 |
1330 | 比如:
1331 |
1332 | `proxy sps -P http://127.0.0.1:3100 -P socks5://127.0.0.1:3200`
1333 |
1334 | `-P`完整格式如下:
1335 |
1336 | `protocol://a:b@2.2.2.2:33080#1`
1337 |
1338 | 下面对每部分进行解释:
1339 |
1340 | `protocol://` 是协议类型,可能的类型以及含有如下:
1341 |
1342 | ```text
1343 | http 等价于 -S http -T tcp
1344 | https 等价于 -S http -T tls --parent-tls-single , 也就是http(s)代理 over TLS
1345 | https2 等价于 -S http -T tls
1346 | socks5 等价于 -S socks -T tcp
1347 | socks5s 等价于 -S socks -T tls --parent-tls-single , 也就是socks over TLS
1348 | socks5s2 等价于 -S socks -T tls
1349 | ss 等价于 -S ss -T tcp
1350 | httpws 等价于 -S http -T ws
1351 | httpwss 等价于 -S http -T wss
1352 | socks5ws 等价于 -S socks -T ws
1353 | socks5wss 等价于 -S socks -T wss
1354 | ```
1355 |
1356 | `a:b`是代理认证的用户名密码,如果是ss,`a`是加密方法,`b`是密码,没有用户名密码可以留空比如:`http://2.2.2.2:33080`,如果用户名和密码保护特殊符号可以使用urlencode进行编码。
1357 |
1358 | `2.2.2.2:33080`是上级地址,格式是:`IP(或域名):端口`,如果底层是ws/wss协议还可以带上路径,比如:`2.2.2.2:33080/ws`;
1359 | 还能通过附加查询参数`m`和`k`设置`ws\wss`的`加密方法`和`密码`,比如:`2.2.2.2:33080/ws?m=aes-192-cfb&k=password`
1360 |
1361 | `#1`多个上级的负载均衡是权重策略时候,设置的权重,很少用到。
1362 |
1363 | ### 6.9 自定义加密
1364 | proxy的sps代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行
1365 | 自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义
1366 | 一个密码即可,加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
1367 |
1368 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以。
1369 |
1370 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
1371 |
1372 | 假设已经存在一个http(s)代理:`6.6.6.6:6666`
1373 |
1374 | 二级实例
1375 |
1376 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1377 | `proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 6.6.6.6:6666 -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
1378 | 本地二级执行:
1379 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
1380 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
1381 |
1382 |
1383 | 三级实例
1384 |
1385 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1386 | `proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 6.6.6.6:6666 -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
1387 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
1388 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
1389 | 本地三级执行:
1390 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
1391 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
1392 |
1393 | ### 6.10 压缩传输
1394 | proxy的sps代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以
1395 | 对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,
1396 | 一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
1397 |
1398 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据。
1399 |
1400 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
1401 |
1402 | 二级实例
1403 |
1404 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1405 | `proxy sps -t tcp -m -p :7777`
1406 | 本地二级执行:
1407 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
1408 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
1409 |
1410 |
1411 | 三级实例
1412 |
1413 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1414 | `proxy sps -t tcp -m -p :7777`
1415 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
1416 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
1417 | 本地三级执行:
1418 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
1419 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
1420 |
1421 | ### 6.11 禁用协议
1422 | SPS默认情况下一个端口支持http(s)和socks5两种代理协议,我们可以通过参数禁用某个协议
1423 | 比如:
1424 | 1.禁用HTTP(S)代理功能只保留SOCKS5代理功能,参数:`--disable-http`。
1425 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080 --disable-http`
1426 |
1427 | 1.禁用SOCKS5代理功能只保留HTTP(S)代理功能,参数:`--disable-socks`。
1428 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080 --disable-http`
1429 |
1430 | ### 6.12 限速
1431 |
1432 | 假设存在SOCKS5上级:
1433 |
1434 | `proxy socks -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -z password -t tcp`
1435 |
1436 | sps下级,限速100K
1437 |
1438 | `proxy sps -S socks -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -T tcp -Z password -l 100K -t tcp -p :33080`
1439 |
1440 | 通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
1441 |
1442 | ### 6.13 指定`出口IP`
1443 |
1444 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果`入口IP`是内网IP,`出口IP`不会使用`入口IP`。
1445 |
1446 | `proxy sps -S socks -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -T tcp -Z password -l 100K -t tcp --bind-listen -p :33080`
1447 |
1448 | ### 6.14 证书参数使用base64数据
1449 |
1450 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
1451 |
1452 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
1453 |
1454 | ### 6.15 独立服务
1455 | sps功能不强制指定一个上级,当上级为空,sps本身即可完成完整的代理功能.如果指定了上级那么就和之前一样使用上级连接目标。
1456 | 下面这个命令,就是一键开启http(s)\ss\socks服务。
1457 | `./proxy sps -p :33080`
1458 |
1459 | ### 6.16 目标重定向
1460 | sps功能提供的http(s)\socks5\ss代理功能,客户端通过sps代理去连接指定的“目标”,这个“目标”一般是网站也可能是任意的tcp地址,
1461 | 网站”目标“一般是foo.com:80,foo.com:443,sps支持使用--rewrite参数指定一个“目标”重定向规则文件,对目标进行重定向,客户端是无感知的,
1462 | 比如你对“目标”:demo.com:80重定向到192.168.0.12:80,那么客户端访问网站demo.com,其实访问的是192.168.0.12提供的网站服务。
1463 | “目标”重定向规则文件示例:
1464 |
1465 | ```text
1466 | # example
1467 | www.a.com:80 10.0.0.2:8080
1468 | **.b.com:80 10.0.0.2:80
1469 | 192.168.0.11:80 10.0.0.2:8080
1470 | ```
1471 |
1472 | ### 6.17 固定UDP功能端口
1473 |
1474 | 默认情况下sps的socks5的UDP功能的端口号是按着`rfc1982草案`要求,使用协议握手过程中随机指定,不需要提前指定。
1475 |
1476 | 但是某些情况下,需要固定UDP功能端口,可以通过参数`--udp-port 端口号`用来固定UDP功能的端口号,比如:
1477 |
1478 | `./proxy sps -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --udp-port 38081`
1479 |
1480 | 需要注意的是,sps的ss功能也有UDP功能,而且ss的UDP端口和tcp端口是一样的,所以要避免socks5的UDP端口和ss的UDP端口冲突,
1481 |
1482 | 要指定和tcp端口不一样的端口。
1483 |
1484 | ### 6.18 iptables 透明代理
1485 | sps模式支持Linux系统的iptables转发支持,也就是通常所说的iptables透明代理,如果在网关设备上进行iptables透明代理,那么对通过网关联网的设备就能实现无感知的代理。
1486 |
1487 | 启动命令实例:
1488 |
1489 | `./proxy sps --redir -p :8888 -P httpws://1.1.1.1:33080`
1490 |
1491 | 这里假设存在一个http的上级代理1.1.1.1:33080,使用ws传输数据。
1492 |
1493 | 然后添加iptables规则,下面是参考规则:
1494 | ```shell
1495 | #上级proxy服务端服务器IP地址:
1496 | proxy_server_ip=1.1.1.1
1497 |
1498 | #路由器运行proxy监听的端口:
1499 | proxy_local_port=33080
1500 |
1501 | #下面的就不用修改了
1502 | #create a new chain named PROXY
1503 | iptables -t nat -N PROXY
1504 |
1505 | # Ignore your PROXY server's addresses
1506 | # It's very IMPORTANT, just be careful。
1507 |
1508 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d $proxy_server_ip -j RETURN
1509 |
1510 | # Ignore LANs IP address
1511 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 0.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
1512 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 10.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
1513 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 127.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
1514 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 169.254.0.0/16 -j RETURN
1515 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 172.16.0.0/12 -j RETURN
1516 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 192.168.0.0/16 -j RETURN
1517 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 224.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
1518 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 240.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
1519 |
1520 | # Anything to port 80 443 should be redirected to PROXY's local port
1521 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
1522 | # Apply the rules to nat client
1523 | iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -j PROXY
1524 | # Apply the rules to localhost
1525 | iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp -j PROXY
1526 | ```
1527 | - 清空整个链 iptables -F 链名比如iptables -t nat -F PROXY
1528 | - 删除指定的用户自定义链 iptables -X 链名 比如 iptables -t nat -X PROXY
1529 | - 从所选链中删除规则 iptables -D 链名 规则详情 比如 iptables -t nat -D PROXY -d 223.223.192.0/255.255.240.0 -j RETURN
1530 |
1531 | ### 6.19 查看帮助
1532 |
1533 | `./proxy help sps`
1534 |
1535 | ## 7.KCP配置
1536 |
1537 | ### 7.1 配置介绍
1538 | proxy的很多功能都支持kcp协议,凡是使用了kcp协议的功能都支持这里介绍的配置参数。
1539 | 所以这里统一对KCP配置参数进行介绍。
1540 |
1541 | ### 7.2 详细配置
1542 | 所有的KCP配置参数共有17个,你可以都不用设置,他们都有默认值,如果为了或者最好的效果,
1543 | 就需要自己根据自己根据网络情况对参数进行配置。由于kcp配置很复杂需要一定的网络基础知识,
1544 | 如果想获得kcp参数更详细的配置和解说,请自行搜索。每个参数的命令行名称以及默认值和简单的功能说明如下:
1545 | ```
1546 | --kcp-key="secrect" pre-shared secret between client and server
1547 | --kcp-method="aes" encrypt/decrypt method, can be: aes, aes-128, aes-192, salsa20, blowfish,
1548 | twofish, cast5, 3des, tea, xtea, xor, sm4, none
1549 | --kcp-mode="fast" profiles: fast3, fast2, fast, normal, manual
1550 | --kcp-mtu=1350 set maximum transmission unit for UDP packets
1551 | --kcp-sndwnd=1024 set send window size(num of packets)
1552 | --kcp-rcvwnd=1024 set receive window size(num of packets)
1553 | --kcp-ds=10 set reed-solomon erasure coding - datashard
1554 | --kcp-ps=3 set reed-solomon erasure coding - parityshard
1555 | --kcp-dscp=0 set DSCP(6bit)
1556 | --kcp-nocomp disable compression
1557 | --kcp-acknodelay be carefull! flush ack immediately when a packet is received
1558 | --kcp-nodelay=0 be carefull!
1559 | --kcp-interval=50 be carefull!
1560 | --kcp-resend=0 be carefull!
1561 | --kcp-nc=0 be carefull! no congestion
1562 | --kcp-sockbuf=4194304 be carefull!
1563 | --kcp-keepalive=10 be carefull!
1564 | ```
1565 | 提示:
1566 | 参数:--kcp-mode中的四种fast3, fast2, fast, normal模式,
1567 | 相当于设置了下面四个参数:
1568 | normal:`--nodelay=0 --interval=40 --resend=2 --nc=1`
1569 | fast :`--nodelay=0 --interval=30 --resend=2 --nc=1`
1570 | fast2:`--nodelay=1 --interval=20 --resend=2 --nc=1`
1571 | fast3:`--nodelay=1 --interval=10 --resend=2 --nc=1`
1572 |
1573 | ## 8.安全DNS
1574 |
1575 | ### 8.1 介绍
1576 | 众所周知DNS是UDP端口53提供的服务,但是随着网络的发展一些知名DNS服务器也支持TCP方式dns查询,比如谷歌的8.8.8.8,proxy的DNS防污染服务器原理就是在本地启动一个proxy的DNS代理服务器,它用TCP的方式通过上级代理进行dns查询。如果它和上级代理通讯采用加密的方式,那么就可以进行安全无污染的DNS解析,还支持独立服务,并发解析,支持增强的hosts文件功能支持灵活的并发解析转发。
1577 |
1578 | dns解析顺序:
1579 | 1.使用参数--hosts解析。
1580 | 2.要解析的域名在1中没有找到,就使用参数--forward规则解析。
1581 | 3.要解析的域名在1和2中都没有找到,就使用默认--default解析,--default默认行为参数值有三种:proxy,direct,system。
1582 | 三种参数值解释如下:
1583 | proxy:通过上级去连接-q参数指定的dns服务器去解析域名。
1584 | direct:通过本地网络去连接-q参数指定的dns服务器去解析域名。
1585 | system:通过系统dns去解析域名。
1586 |
1587 | 提示:
1588 | --hosts 参数指定的host文件格式和系统hosts文件一致,而且域名支持通配符,可以参考hosts文件。
1589 | --forward 参数指定的解析转发规则文件,格式可以参考resolve.rules文件,域名支持通配符,支持为每个域名指定多个dns服务器并发解析,谁最快解析成功就用谁的解析结果。
1590 | -q 参数可以指定多个远程dns服务器,执行并发解析谁最快解析成功就用谁的解析结果,默认是:1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8,9.9.9.9,多个用逗号分割,
1591 | 比如还可以带端口:1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8#53,9.9.9.9
1592 |
1593 | 如果独立服务,不需要上级:
1594 | 可以执行:
1595 | `proxy dns --default system -p :5353`
1596 | or
1597 | `proxy dns --default direct -p :5353`
1598 |
1599 | ### 8.2 使用示例
1600 |
1601 | #### 8.2.1 普通HTTP(S)上级代理
1602 |
1603 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1604 | 本地执行:
1605 | `proxy dns -S http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1606 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了DNS解析功能。
1607 |
1608 | #### 8.2.2 普通SOCKS5上级代理
1609 |
1610 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1611 | 本地执行:
1612 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1613 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了DNS解析功能。
1614 |
1615 | #### 8.2.3 TLS加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
1616 |
1617 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1618 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1619 | `proxy http -t tls -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :33080`
1620 | 本地执行:
1621 | `proxy dns -S http -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :53`
1622 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1623 |
1624 | #### 8.2.4 TLS加密的SOCKS5上级代理
1625 |
1626 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1627 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1628 | `proxy socks -t tls -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :33080`
1629 | 本地执行:
1630 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :53`
1631 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1632 |
1633 | #### 8.2.5 KCP加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
1634 |
1635 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1636 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1637 | `proxy http -t kcp -p :33080`
1638 | 本地执行:
1639 | `proxy dns -S http -T kcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1640 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1641 |
1642 | #### 8.2.6 KCP加密的SOCKS5上级代理
1643 |
1644 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1645 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1646 | `proxy socks -t kcp -p :33080`
1647 | 本地执行:
1648 | `proxy dns -S socks -T kcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1649 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1650 |
1651 | #### 8.2.7 自定义加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
1652 |
1653 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1654 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1655 | `proxy http -t tcp -p :33080 -z password`
1656 | 本地执行:
1657 | `proxy dns -S http -T tcp -Z password -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1658 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1659 |
1660 | #### 8.2.8 自定义加密的SOCKS5上级代理
1661 |
1662 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1663 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1664 | `proxy socks -t kcp -p :33080 -z password`
1665 | 本地执行:
1666 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tcp -Z password -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1667 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1668 |
1669 | ## 9.API认证,限速,控制连接数
1670 |
1671 | proxy的http(s)/socks5/sps代理功能,支持通过API控制用户对代理对访问。
1672 |
1673 | ### 通过API可以干什么?
1674 |
1675 | - 用户维度,控制单个连接速率,控制最大连接数。
1676 | - IP维度,控制单个连接速率,控制最大连接数。
1677 | - 动态上级,可以根据用户或者客户端IP,动态的从API获取其上级,支持http(s)/socks5/ss上级。
1678 | - 认证每一个连接,无论是否要求客户端认证。
1679 | - 缓存认证结果,时间可以设置,减轻API压力。
1680 |
1681 | #### 具体使用
1682 | proxy的http(s)/socks5/sps代理API功能,通过`--auth-url`和`--auth-nouser`和`--auth-cache`三个参数控制。
1683 | 参数`--auth-url`是HTTP API接口地址,客户端连接的时候,proxy会GET方式请求这url,带上下面参数,如果返回HTTP状态码204,代表认证成功,其它情况认为认证失败。
1684 |
1685 | 一个完整的请求API的示例:
1686 | `http://test.com/auth.php?user=a&pass=b&client_addr=127.0.0.1:49892&local_addr=127.0.0.1:8100&target=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.baidu.com&service=http&sps=0`
1687 |
1688 | #### 参数说明
1689 | `user和pass` 当代理开启了认证功能,这里就是客户端提供的用户名和密码。
1690 | `client_addr` 客户端访问代理时的用的地址,格式IP:端口。
1691 | `local_addr` 客户端访问的代理地址,格式IP:端口。
1692 | `service` 代理类型,分为:http、socks。
1693 | `sps` 代理是否是sps提供的,1:是,0:否。
1694 | `target` 客户端要访问的目标,如果是http(s)代理,target是访问的具体url;如果是socks5代理,target是空。
1695 |
1696 | #### 示例
1697 | 假设--auth-url http://127.0.0.1:333/auth.php 指向了一个php接口地址.
1698 | auth.php内容如下:
1699 |
1700 | ```php
1701 | 注意: 后面二级代理使用的`proxy.crt`和`proxy.key`应与一级代理一致
2041 |
2042 | 
2043 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
2044 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2045 |
2046 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
2047 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2048 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080。
2049 |
2050 | 二级HTTP代理(本地windows)
2051 | `./proxy.exe http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2052 | 然后设置你的windos系统中,需要通过代理上网的程序的代理为http模式,地址为:127.0.0.1,端口为:8080,程序即可通过加密通道通过vps上网。
2053 |
2054 | ### 1.4.HTTP三级代理(加密)
2055 | 
2056 | 一级HTTP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2057 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2058 | 二级HTTP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2059 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2060 | 三级HTTP代理(本地)
2061 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2062 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问一级HTTP代理上面的代理端口38080。
2063 |
2064 | ### 1.5.Basic认证,API认证
2065 |
2066 | 请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
2067 |
2068 | ### 1.6.HTTP代理流量强制走上级HTTP代理
2069 | 默认情况下,proxy会智能判断一个网站域名是否无法访问,如果无法访问才走上级HTTP代理.通过--always可以使全部HTTP代理流量强制走上级HTTP代理。
2070 | `./proxy http --always -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2071 |
2072 | ### 1.7.HTTP(S)通过SSH中转
2073 | 
2074 | 说明:ssh中转的原理是利用了ssh的转发功能,就是你连接上ssh之后,可以通过ssh代理访问目标地址。
2075 | 假设有:vps
2076 | - IP是2.2.2.2, ssh端口是22, ssh用户名是:user, ssh用户密码是:demo
2077 | - 用户user的ssh私钥名称是user.key
2078 |
2079 | #### *1.7.1 ssh用户名和密码的方式*
2080 | 本地HTTP(S)代理28080端口,执行:
2081 | `./proxy http -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -D demo -t tcp -p ":28080"`
2082 | #### *1.7.2 ssh用户名和密钥的方式*
2083 | 本地HTTP(S)代理28080端口,执行:
2084 | `./proxy http -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -S user.key -t tcp -p ":28080"`
2085 |
2086 | ### 1.8.KCP协议传输
2087 | 
2088 | KCP协议需要--kcp-key参数设置一个密码用于加密解密数据
2089 |
2090 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
2091 | `./proxy http -t kcp -p ":38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
2092 |
2093 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
2094 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T kcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
2095 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080,数据通过kcp协议传输,注意kcp走的是udp协议协议,所以防火墙需放开38080的udp协议。
2096 |
2097 | ### 1.9 HTTP(S)反向代理
2098 | 
2099 | proxy不仅支持在其他软件里面通过设置代理的方式,为其他软件提供代理服务,而且支持直接把请求的网站域名解析到proxy监听的ip上,然后proxy监听80和443端口,那么proxy就会自动为你代理访问需要访问的HTTP(S)网站。
2100 |
2101 | 使用方式:
2102 | 在"最后一级proxy代理"的机器上,因为proxy要伪装成所有网站,网站默认的端口HTTP是80,HTTPS是443,让proxy监听80和443端口即可.参数-p多个地址用逗号分割。
2103 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :80,:443`
2104 |
2105 | 这个命令就在机器上启动了一个proxy代理,同时监听80和443端口,既可以当作普通的代理使用,也可以直接把需要代理的域名解析到这个机器的IP上。
2106 |
2107 | 如果有上级代理那么参照上面教程设置上级即可,使用方式完全一样。
2108 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :80,:443 -T tls -P "2.2.2.2:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2109 |
2110 | 注意:
2111 | proxy所在的服务器的DNS解析结果不能受到自定义的解析影响,不然就死循环了,proxy代理最好指定`--dns 8.8.8.8`参数。
2112 |
2113 | ### 1.10 HTTP(S)透明代理
2114 | 该模式需要具有一定的网络基础,相关概念不懂的请自行搜索解决。
2115 | 假设proxy现在在路由器上运行,启动命令如下:
2116 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :33080 -T tls -P "2.2.2.2:33090" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2117 |
2118 | 然后添加iptables规则,下面是参考规则:
2119 | ```shell
2120 | #上级proxy服务端服务器IP地址:
2121 | proxy_server_ip=2.2.2.2
2122 |
2123 | #路由器运行proxy监听的端口:
2124 | proxy_local_port=33080
2125 |
2126 | #下面的就不用修改了
2127 | #create a new chain named PROXY
2128 | iptables -t nat -N PROXY
2129 |
2130 | # Ignore your PROXY server's addresses
2131 | # It's very IMPORTANT, just be careful。
2132 |
2133 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d $proxy_server_ip -j RETURN
2134 |
2135 | # Ignore LANs IP address
2136 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 0.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
2137 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 10.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
2138 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 127.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
2139 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 169.254.0.0/16 -j RETURN
2140 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 172.16.0.0/12 -j RETURN
2141 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 192.168.0.0/16 -j RETURN
2142 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 224.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
2143 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 240.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
2144 |
2145 | # Anything to port 80 443 should be redirected to PROXY's local port
2146 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
2147 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp --dport 443 -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
2148 |
2149 | # Apply the rules to nat client
2150 | iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -j PROXY
2151 | # Apply the rules to localhost
2152 | iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp -j PROXY
2153 | ```
2154 | - 清空整个链 iptables -F 链名比如iptables -t nat -F PROXY
2155 | - 删除指定的用户自定义链 iptables -X 链名 比如 iptables -t nat -X PROXY
2156 | - 从所选链中删除规则 iptables -D 链名 规则详情 比如 iptables -t nat -D PROXY -d 223.223.192.0/255.255.240.0 -j RETURN
2157 |
2158 | ### 1.11 自定义DNS
2159 | --dns-address和--dns-ttl参数,用于自己指定proxy访问域名的时候使用的dns(--dns-address)
2160 | 以及解析结果缓存时间(--dns-ttl)秒数,避免系统dns对proxy的干扰,另外缓存功能还能减少dns解析时间提高访问速度。
2161 | 比如:
2162 | `./proxy http -p ":33080" --dns-address "8.8.8.8:53" --dns-ttl 300`
2163 |
2164 | ### 1.12 自定义加密
2165 | proxy的http(s)代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义
2166 | 加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可,
2167 | 加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
2168 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以,下面分别用二级,三级为例:
2169 |
2170 | 二级实例
2171 |
2172 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2173 | `proxy http -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
2174 | 本地二级执行:
2175 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
2176 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
2177 |
2178 |
2179 | 三级实例
2180 |
2181 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2182 | `proxy http -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
2183 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
2184 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
2185 | 本地三级执行:
2186 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
2187 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
2188 |
2189 | ### 1.13 压缩传输
2190 | proxy的http(s)代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以对数据进行压缩,
2191 | 也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,
2192 | 一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
2193 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据,下面分别用二级,三级为例:
2194 |
2195 | 二级实例
2196 |
2197 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2198 | `proxy http -t tcp -m -p :7777`
2199 | 本地二级执行:
2200 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
2201 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
2202 |
2203 |
2204 | 三级实例
2205 |
2206 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2207 | `proxy http -t tcp -m -p :7777`
2208 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
2209 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
2210 | 本地三级执行:
2211 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
2212 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
2213 |
2214 | ### 1.14 负载均衡
2215 |
2216 | HTTP(S)代理支持上级负载均衡,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
2217 |
2218 | `proxy http --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080`
2219 |
2220 | ### 1.14.1 设置重试间隔和超时时间
2221 |
2222 | `proxy http --lb-method=leastconn --lb-retrytime 300 --lb-timeout 300 -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -t tcp -p :33080`
2223 |
2224 | ### 1.14.2 设置权重
2225 |
2226 | `proxy http --lb-method=weight -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -P 2.1.1.1:33080?w=2 -P 3.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -t tcp -p :33080`
2227 |
2228 | ### 1.14.3 使用目标地址选择上级
2229 |
2230 | `proxy http --lb-hashtarget --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -t tcp -p :33080`
2231 |
2232 | ### 1.15 限速
2233 |
2234 | 限速100K,通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
2235 |
2236 | `proxy http -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -l 100K`
2237 |
2238 | ### 1.16 指定出口IP
2239 |
2240 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作,此时代理会尝试不绑定IP去访问目标,同时日志会提示。
2241 |
2242 | `proxy http -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 --bind-listen`
2243 |
2244 | ### 1.17 证书参数使用base64数据
2245 |
2246 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
2247 |
2248 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
2249 |
2250 | ### 1.18 智能模式
2251 | 智能模式设置,可以是intelligent|direct|parent三者之一。
2252 | 默认是:intelligent。
2253 | 每个值的含义如下:
2254 | `--intelligent=direct`,不在blocked里面的目标都直连。
2255 | `--intelligent=parent`,不在direct里面的目标都走上级。
2256 | `--intelligent=intelligent`,blocked和direct里面都没有的目标,智能判断是否使用上级访问目标。
2257 |
2258 | ### 1.19 查看帮助
2259 | `./proxy help http`
2260 |
2261 | ## 2.TCP代理
2262 |
2263 | ### 2.1 普通一级TCP代理
2264 | 
2265 | 本地执行:
2266 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22"`
2267 | 那么访问本地33080端口就是访问192.168.22.33的22端口。
2268 |
2269 | `-p`参数支持的写法:
2270 |
2271 | ```text
2272 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
2273 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
2274 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
2275 | ```
2276 |
2277 | 如果本地监听端口数量大于1,那么将会连接与本地端口一致的对应上级端口,忽略`-P`里面的端口。
2278 |
2279 | 如果需要所有端口进来的连接,都连接到上级指定端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`。
2280 |
2281 | 比如:
2282 |
2283 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080-33085" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:0"`
2284 |
2285 | 那么`33080`端口进来的连接,将会连接192.168.22.33的`33080`端口,其它端口以此类推,本地和上级端口一致,此时参数`-P`里面的端口用`0`。
2286 |
2287 | 如果想无论是`33080`,`33081`等端口进来的连接都连接到192.168.22.33的`22`端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`
2288 |
2289 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080-33085" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --lock-port`
2290 |
2291 |
2292 | ### 2.2 普通二级TCP代理
2293 | 
2294 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
2295 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "127.0.0.1:8080"`
2296 | 本地执行:
2297 | `./proxy tcp -p ":23080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.33:33080"`
2298 | 那么访问本地23080端口就是访问22.22.22.33的8080端口。
2299 |
2300 | ### 2.3 普通三级TCP代理
2301 | 
2302 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2303 | `./proxy tcp -p ":38080" -T tcp -P "66.66.66.66:8080"`
2304 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2305 | `./proxy tcp -p ":28080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080"`
2306 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
2307 | `./proxy tcp -p ":8080" -T tcp -P "33.33.33.33:28080"`
2308 | 那么访问本地8080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问66.66.66.66的8080端口。
2309 |
2310 | ### 2.4 加密二级TCP代理
2311 | 
2312 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
2313 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "127.0.0.1:8080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2314 | 本地执行:
2315 | `./proxy tcp -p ":23080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.33:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2316 | 那么访问本地23080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问22.22.22.33的8080端口。
2317 |
2318 | ### 2.5 加密三级TCP代理
2319 | 
2320 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2321 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":38080" -T tcp -P "66.66.66.66:8080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2322 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2323 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2324 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
2325 | `./proxy tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2326 | 那么访问本地8080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问66.66.66.66的8080端口。
2327 |
2328 | ### 2.6 通过代理连接上级
2329 | 有时候proxy所在的网络不能直接访问外网,需要通过一个https或者socks5代理才能上网,那么这个时候
2330 | -J参数就可以帮助你让proxy的tcp端口映射的时候通过https或者socks5代理去连接上级-P,将外部端口映射到本地。
2331 | -J参数格式如下:
2332 |
2333 | https代理写法:
2334 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
2335 | https://username:password@host:port
2336 | 代理不需要认证
2337 | https://host:port
2338 |
2339 | socks5代理写法:
2340 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
2341 | socks5://username:password@host:port
2342 | 代理不需要认证
2343 | socks5://host:port
2344 |
2345 | host:代理的IP或者域名
2346 | port:代理的端口
2347 |
2348 | ### 2.7 指定`出口IP`
2349 | 当TCP代理当上级类型(参数:-T)是tcp当时候,支持指定`出口IP`。使用`--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作,此时代理会尝试不绑定IP去访问目标,同时日志会提示。
2350 |
2351 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" -B`
2352 |
2353 | ### 2.8 限速,限制连接数
2354 |
2355 | 参数`--max-conns`可以限制每个端口的最大连接数。
2356 | 比如限制每个端口最多1000个连接数:
2357 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --max-conns 1000`
2358 | 参数`--rate-limit`可以限制每个tcp连接的速率。
2359 | 比如限制每个tcp连接速率为100k/s:
2360 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --rate-limit 100k`
2361 |
2362 | ### 2.9 查看帮助
2363 | `./proxy help tcp`
2364 |
2365 | ## 3.UDP代理
2366 |
2367 | ### 3.1.普通一级UDP代理
2368 | 
2369 | 本地执行:
2370 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
2371 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
2372 |
2373 | `-p`参数支持的写法:
2374 |
2375 | ```text
2376 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
2377 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
2378 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
2379 | ```
2380 |
2381 | 如果本地监听端口数量大于1,那么将会连接与本地端口一致的对应上级端口,忽略`-P`里面的端口。
2382 |
2383 | 如果需要所有端口进来的连接,都连接到上级指定端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`。
2384 |
2385 | 比如:
2386 |
2387 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080-33085" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:0"`
2388 |
2389 | 那么`33080`端口进来的连接,将会连接192.168.22.33的`33080`端口,其它端口以此类推,本地和上级端口一致,此时参数`-P`里面的端口用`0`。
2390 |
2391 | 如果想无论是`33080`,`33081`等端口进来的连接都连接到192.168.22.33的`2222`端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`
2392 |
2393 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080-33085" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:2222" --lock-port`
2394 |
2395 | ### 3.2.普通二级UDP代理
2396 | 
2397 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
2398 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
2399 | 本地执行:
2400 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.33:33080"`
2401 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是通过TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
2402 |
2403 | ### 3.3.普通三级UDP代理
2404 | 
2405 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2406 | `./proxy tcp -p ":38080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
2407 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2408 | `./proxy tcp -p ":28080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080"`
2409 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
2410 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tcp -P "33.33.33.33:28080"`
2411 | 那么访问本地5353端口就是通过TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的53端口。
2412 |
2413 | ### 3.4.加密二级UDP代理
2414 | 
2415 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
2416 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":33080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2417 | 本地执行:
2418 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tls -P "22.22.22.33:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2419 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是通过加密TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
2420 |
2421 | ### 3.5.加密三级UDP代理
2422 | 
2423 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2424 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":38080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2425 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2426 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2427 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
2428 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2429 | 那么访问本地5353端口就是通过加密TCP隧道,通过VPS_01访问8.8.8.8的53端口。
2430 |
2431 | ### 3.6 指定`出口IP`
2432 | 当UDP代理当上级类型(参数:-T)是udp当时候,支持指定`出口IP`。使用`--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作。
2433 |
2434 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:2222" -B`
2435 |
2436 | ### 3.7 查看帮助
2437 | `./proxy help udp`
2438 |
2439 | ## 4.内网穿透
2440 | ### 4.1、原理说明
2441 | 内网穿透,分为两个版本,“多链接版本”和“多路复用版本”,一般像web服务这种不是长时间连接的服务建议用“多链接版本”,如果是要保持长时间连接建议使用“多路复用版本”。
2442 | 1. 多链接版本,对应的子命令是tserver,tclient,tbridge。
2443 | 1. 多路复用版本,对应的子命令是server,client,bridge。
2444 | 1. 多链接版本和多路复用版本的参数和使用方式完全一样。
2445 | 1. 多路复用版本的server,client可以开启压缩传输,参数是--c。
2446 | 1. server,client要么都开启压缩,要么都不开启,不能只开一个。
2447 |
2448 | 下面的教程以“多路复用版本”为例子,说明使用方法。
2449 | 内网穿透由三部分组成:client端,server端,bridge端;client和server主动连接bridge端进行桥接。
2450 |
2451 | ### 4.2、TCP普通用法
2452 | 背景:
2453 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口
2454 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2455 |
2456 | 需求:
2457 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的28080端口访问到公司机器A的80端口
2458 |
2459 | 步骤:
2460 | 1. 在vps上执行
2461 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2462 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2463 |
2464 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
2465 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2466 |
2467 | 1. 完成
2468 |
2469 | ### 4.3、微信接口本地开发
2470 | 背景:
2471 | - 自己的笔记本提供了nginx服务80端口
2472 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2473 |
2474 | 需求:
2475 | 在微信的开发帐号的网页回调接口配置里面填写地址:http://22.22.22.22/calback.php
2476 | 然后就可以访问到笔记本的80端口下面的calback.php,如果需要绑定域名,可以用自己的域名
2477 | 比如:wx-dev.xxx.com解析到22.22.22.22,然后在自己笔记本的nginx里
2478 | 配置域名wx-dev.xxx.com到具体的目录即可。
2479 |
2480 |
2481 | 步骤:
2482 | 1. 在vps上执行,确保vps的80端口没被其它程序占用。
2483 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2484 | `./proxy server -r ":80@:80" -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2485 |
2486 | 1. 在自己笔记本上面执行
2487 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2488 |
2489 | 1. 完成
2490 |
2491 | ### 4.4、UDP普通用法
2492 | 背景:
2493 | - 公司机器A提供了DNS解析服务,UDP:53端口
2494 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2495 |
2496 | 需求:
2497 | 在家里能够通过设置本地dns为22.22.22.22,使用公司机器A进行域名解析服务。
2498 |
2499 | 步骤:
2500 | 1. 在vps上执行
2501 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2502 | `./proxy server --udp -r ":53@:53" -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2503 |
2504 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
2505 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2506 |
2507 | 1. 完成
2508 |
2509 | ### 4.5、高级用法一
2510 | 背景:
2511 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口
2512 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2513 |
2514 | 需求:
2515 | 为了安全,不想在VPS上能够访问到公司机器A,在家里能够通过访问本机的28080端口,
2516 | 通过加密隧道访问到公司机器A的80端口。
2517 |
2518 | 步骤:
2519 | 1. 在vps上执行
2520 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2521 |
2522 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
2523 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2524 |
2525 | 1. 在家里电脑上执行
2526 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2527 |
2528 | 1. 完成
2529 |
2530 | ### 4.6、高级用法二
2531 | 提示:
2532 | 如果同时有多个client连接到同一个bridge,需要指定不同的key,可以通过--k参数设定,--k可以是任意唯一字符串,
2533 | 只要在同一个bridge上唯一即可。
2534 | server连接到bridge的时候,如果同时有多个client连接到同一个bridge,需要使用--k参数选择client。
2535 | 暴露多个端口重复-r参数即可.-r格式是:"本地IP:本地端口@clientHOST:client端口"。
2536 |
2537 | 背景:
2538 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口,ftp服务21端口
2539 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2540 |
2541 | 需求:
2542 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的28080端口访问到公司机器A的80端口
2543 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的29090端口访问到公司机器A的21端口
2544 |
2545 | 步骤:
2546 | 1. 在vps上执行
2547 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2548 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -r ":29090@:21" --k test -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2549 |
2550 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
2551 | `./proxy client --k test -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2552 |
2553 | 1. 完成
2554 |
2555 | ### 4.7.server的-r参数
2556 | -r完整格式是:`PROTOCOL://LOCAL_IP:LOCAL_PORT@[CLIENT_KEY]CLIENT_LOCAL_HOST:CLIENT_LOCAL_PORT`
2557 |
2558 | 4.7.1.协议PROTOCOL:tcp、udp、ptcp、pudp。
2559 | 比如: `-r "udp://:10053@:53" -r "tcp://:10800@:1080" -r ":8080@:80"`
2560 | 如果指定了--udp参数,PROTOCOL默认为udp,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`默认为udp;
2561 | 如果没有指定--udp参数,PROTOCOL默认为tcp,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`默认为tcp;
2562 |
2563 | 4.7.2.CLIENT_KEY:默认是default。
2564 | 比如: -r "udp://:10053@[test1]:53" -r "tcp://:10800@[test2]:1080" -r ":8080@:80"
2565 | 如果指定了--k参数,比如--k test,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`CLIENT_KEY默认为test;
2566 | 如果没有指定--k参数,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`CLIENT_KEY默认为default;
2567 |
2568 | 4.7.3.LOCAL_IP为空默认是:`0.0.0.0`,CLIENT_LOCAL_HOST为空默认是:`127.0.0.1`;
2569 |
2570 | ### 4.8.server和client通过代理连接bridge
2571 | 有时候server或者client所在的网络不能直接访问外网,需要通过一个https或者socks5代理才能上网,那么这个时候
2572 | -J参数就可以帮助你让server或者client通过https或者socks5代理去连接bridge。
2573 | -J参数格式如下:
2574 |
2575 | https代理写法:
2576 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
2577 | https://username:password@host:port
2578 | 代理不需要认证
2579 | https://host:port
2580 |
2581 | socks5代理写法:
2582 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
2583 | socks5://username:password@host:port
2584 | 代理不需要认证
2585 | socks5://host:port
2586 |
2587 | host:代理的IP或者域名
2588 | port:代理的端口
2589 |
2590 | ### 4.9.内网穿透HTTP服务
2591 |
2592 | 通常HTTP请求客户端会使用server的ip和端口去设置HOST字段,但是与期望的后端实际HOST不一样,这样就造成了tcp是通的,
2593 | 但后端依赖HOST字段定位虚拟主机就不能工作.现在用--http-host参数强制设置http头部的HOST字段值为后端实际的
2594 | 域名和端口即可轻松解决。
2595 |
2596 | `server`的--http-host参数格式如下:
2597 |
2598 | `--http-host www.test.com:80@2200`,如果server监听多个端口,只需要重复`--http-host`参数设置每个端口的HOST即可。
2599 |
2600 | 实例:
2601 |
2602 | 比如client本地nginx,127.0.0.1:80提供了web服务,其中绑定了一个域名`local.com`。
2603 |
2604 | 那么server的启动参数可以如下:
2605 |
2606 | `proxy server -P :30000 -r :2500@127.0.0.1:80 --http-host local.com@2500`
2607 |
2608 | 解释:
2609 |
2610 | `-r :2500@127.0.0.1:80` 和 `--http-host local.com:80@2500` 里面的2500端口是server本地监听的端口
2611 |
2612 | 当使用http协议请求server的ip:2500端口的时候,http的头部HOST字段就会被设置为`local.com`。
2613 |
2614 | ### 4.10 关于流量统计
2615 |
2616 | 如果单独启动一个server对接上级是proxy-admin控制面板,需要在上级控制面板里面新建一个映射,获得个映射规则的ID,
2617 |
2618 | 然后启动server的时候加上参数 --server-id=映射规则的ID 才能统计到流量。
2619 |
2620 | ### 4.11 关于p2p
2621 | 内网穿透支持在server和client网络情况满足的情况下,server和client之间通过p2p直接连接,开启方法是:
2622 |
2623 | 在启动bridge,server,client到时候都加上`--p2p`参数即可。server的-r参数可以针对端口是否启用p2p(ptcp和pudp)。
2624 |
2625 | 如果server和client之间p2p打洞失败,那么会自动切换使用bridge中转传输数据。
2626 |
2627 | ### 4.12 客户端key白名单
2628 | 内网穿透bridge可以设置客户端key白名单,参数是--client-keys,格式可以是:
2629 |
2630 | a.文件名,文件内容一行一个客户端key只能包含数字字母下划线,也就是客户端启动参数--k的值,只有客户端key在此白名单的客户端才能连接。# 开头的行,为注释。
2631 |
2632 | b.“base64://”开头的base64编码的上面a说明的文件内容,比如:base64://ajfpoajsdfa=
2633 |
2634 | c.”str://“开头的英文逗号分割的多个key,比如:str://default,company,school
2635 |
2636 | 默认是空,允许所有key。
2637 |
2638 | ### 4.13 网络NAT类型判断
2639 |
2640 | nat类型判断,方便查看网络是否支持p2p,可以执行:`proxy tools -a nattype`
2641 |
2642 | ### 4.14 查看帮助
2643 | `./proxy help bridge`
2644 | `./proxy help server`
2645 | `./proxy help client`
2646 |
2647 | ## 5.SOCKS5代理
2648 | 提示:
2649 |
2650 | SOCKS5代理,支持CONNECT,UDP协议,不支持BIND,支持用户名密码认证。
2651 |
2652 | ***如果你的VPS是阿里云,腾讯云这种VPS,就是ifconfig看不见你的公网IP,只能看见内网IP,***
2653 |
2654 | ***那么需要加上`-g VPS公网IP`参数,SOCKS5代理的UDP功能才能正常工作。***
2655 |
2656 | ### 5.1 普通SOCKS5代理
2657 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080"`
2658 |
2659 | -p参数支持的写法:
2660 |
2661 | ```text
2662 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
2663 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
2664 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
2665 | ```
2666 |
2667 | ### 5.2.普通二级SOCKS5代理
2668 | 
2669 | 使用本地端口8090,假设上级SOCKS5代理是`22.22.22.22:8080`
2670 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" `
2671 | 我们还可以指定网站域名的黑白名单文件,一行一个域名,匹配规则是最右匹配,比如:baidu.com,匹配的是*.*.baidu.com,黑名单的域名域名直接走上级代理,白名单的域名不走上级代理;如果域名即在黑名单又在白名单中,那么黑名单起作用。
2672 | `./proxy socks -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" -b blocked.txt -d direct.txt`
2673 |
2674 | ### 5.3.SOCKS二级代理(加密)
2675 | 
2676 | 一级SOCKS代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
2677 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2678 |
2679 | 二级SOCKS代理(本地Linux)
2680 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2681 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080。
2682 |
2683 | 二级SOCKS代理(本地windows)
2684 | `./proxy.exe socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2685 | 然后设置你的windos系统中,需要通过代理上网的程序的代理为socks5模式,地址为:127.0.0.1,端口为:8080,程序即可通过加密通道通过vps上网。
2686 |
2687 | ### 5.4.SOCKS三级代理(加密)
2688 | 
2689 | 一级SOCKS代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2690 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2691 | 二级SOCKS代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2692 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2693 | 三级SOCKS代理(本地)
2694 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2695 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问一级SOCKS代理上面的代理端口38080。
2696 |
2697 | ### 5.5.SOCKS代理流量强制走上级SOCKS代理
2698 | 默认情况下,proxy会智能判断一个网站域名是否无法访问,如果无法访问才走上级SOCKS代理.通过--always可以使全部SOCKS代理流量强制走上级SOCKS代理。
2699 | `./proxy socks --always -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2700 |
2701 | ### 5.6.SOCKS通过SSH中转
2702 | 
2703 | 说明:ssh中转的原理是利用了ssh的转发功能,就是你连接上ssh之后,可以通过ssh代理访问目标地址。
2704 | 假设有:vps
2705 | - IP是2.2.2.2, ssh端口是22, ssh用户名是:user, ssh用户密码是:demo
2706 | - 用户user的ssh私钥名称是user.key
2707 |
2708 | #### *5.6.1 ssh用户名和密码的方式*
2709 | 本地SOCKS5代理28080端口,执行:
2710 | `./proxy socks -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -D demo -t tcp -p ":28080"`
2711 | #### *5.6.2 ssh用户名和密钥的方式*
2712 | 本地SOCKS5代理28080端口,执行:
2713 | `./proxy socks -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -S user.key -t tcp -p ":28080"`
2714 |
2715 | 那么访问本地的28080端口就是通过VPS访问目标地址。
2716 |
2717 | ### 5.7.认证
2718 | 对于socks5代理协议我们可以进行用户名密码认证,认证的用户名和密码可以在命令行指定
2719 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1" -a "user2:pass2"`
2720 | 多个用户,重复-a参数即可。
2721 | 也可以放在文件中,格式是一行一个"用户名:密码",然后用-F指定。
2722 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":33080" -F auth-file.txt`
2723 |
2724 | ### 5.8.KCP协议传输
2725 | KCP协议需要--kcp-key参数设置一个密码用于加密解密数据
2726 |
2727 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
2728 | `./proxy socks -t kcp -p ":38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
2729 |
2730 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
2731 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T kcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
2732 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080,数据通过kcp协议传输。
2733 |
2734 | ### 5.9.自定义DNS
2735 | --dns-address和--dns-ttl参数,用于自己指定proxy访问域名的时候使用的dns(--dns-address)
2736 | 以及解析结果缓存时间(--dns-ttl)秒数,避免系统dns对proxy的干扰,另外缓存功能还能减少dns解析时间提高访问速度。
2737 | 比如:
2738 | `./proxy socks -p ":33080" --dns-address "8.8.8.8:53" --dns-ttl 300`
2739 |
2740 | ### 5.10 自定义加密
2741 | proxy的socks代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可,
2742 | 加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
2743 |
2744 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以。
2745 |
2746 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
2747 |
2748 | 二级实例
2749 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2750 | `proxy socks -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
2751 | 本地二级执行:
2752 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
2753 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
2754 |
2755 |
2756 | 三级实例
2757 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2758 | `proxy socks -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
2759 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
2760 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
2761 | 本地三级执行:
2762 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
2763 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
2764 |
2765 | ### 5.11 压缩传输
2766 | proxy的socks代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以
2767 | 对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,
2768 | 一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
2769 |
2770 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据。
2771 |
2772 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
2773 |
2774 | 二级实例
2775 |
2776 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2777 | `proxy socks -t tcp -m -p :7777`
2778 | 本地二级执行:
2779 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
2780 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
2781 |
2782 |
2783 | 三级实例
2784 |
2785 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2786 | `proxy socks -t tcp -m -p :7777`
2787 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
2788 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
2789 | 本地三级执行:
2790 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
2791 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
2792 |
2793 |
2794 | ### 5.12 负载均衡
2795 |
2796 | SOCKS代理支持上级负载均衡,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
2797 |
2798 | `proxy socks --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
2799 |
2800 | ### 5.12.1 设置重试间隔和超时时间
2801 |
2802 | `proxy socks --lb-method=leastconn --lb-retrytime 300 --lb-timeout 300 -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
2803 |
2804 | ### 5.12.2 设置权重
2805 |
2806 | `proxy socks --lb-method=weight -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -P 2.1.1.1:33080?w=2 -P 3.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -p :33080 -t tcp`
2807 |
2808 | ### 5.12.3 使用目标地址选择上级
2809 |
2810 | `proxy socks --lb-hashtarget --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
2811 |
2812 | ### 5.13 限速
2813 |
2814 | 限速100K,通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
2815 |
2816 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -l 100K`
2817 |
2818 | ### 5.14 指定`出口IP`
2819 |
2820 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果`入口IP`是内网IP,`出口IP`不会使用`入口IP`。
2821 |
2822 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 --bind-listen`
2823 |
2824 | ### 5.15 级联认证
2825 |
2826 | SOCKS5支持级联认证,-A可以设置上级认证信息。
2827 |
2828 | 上级:
2829 |
2830 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -a user:pass`
2831 |
2832 | 本地:
2833 |
2834 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -A user:pass -t tcp -p :33080`
2835 |
2836 | 请更多认证细节,请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
2837 |
2838 | ### 5.16 证书参数使用base64数据
2839 |
2840 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
2841 |
2842 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
2843 |
2844 |
2845 | ### 5.17 智能模式
2846 | 智能模式设置,可以是intelligent|direct|parent三者之一。
2847 | 默认是:intelligent。
2848 | 每个值的含义如下:
2849 | `--intelligent=direct`,不在blocked里面的目标都直连。
2850 | `--intelligent=parent`,不在direct里面的目标都走上级。
2851 | `--intelligent=intelligent`,blocked和direct里面都没有的目标,智能判断是否使用上级访问目标。
2852 |
2853 | ### 5.18 固定UDP功能端口
2854 |
2855 | 默认情况下socks5的UDP功能的端口号,proxy是按着`rfc1982草案`要求,使用协议握手过程中随机指定,不需要提前指定。
2856 |
2857 | 但是某些情况下,需要固定UDP功能端口,可以通过参数`--udp-port 端口号`用来固定UDP功能的端口号,比如:
2858 |
2859 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --udp-port 38080`
2860 |
2861 | ### 5.19 查看帮助
2862 | `./proxy help socks`
2863 |
2864 | ## 6.SPS协议转换
2865 |
2866 | ### 6.1 功能介绍
2867 | 代理协议转换使用的是sps子命令,sps本身不提供代理功能,只是接受代理请求"转换并转发"给已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理或者ss代理;sps可以把已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理或ss代理转换为一个端口同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的代理,而且http(s)代理支持正向代理和反向代理(SNI),转换后的SOCKS5代理,当上级是SOCKS5或者SS时仍然支持UDP功能;另外对于已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理,支持tls、tcp、kcp三种模式,支持链式连接,也就是可以多个sps结点层级连接构建加密通道。
2868 |
2869 | `ss`功能支持的加密方法为:aes-128-cfb , aes-128-ctr , aes-128-gcm , aes-192-cfb , aes-192-ctr , aes-192-gcm , aes-256-cfb , aes-256-ctr , aes-256-gcm , bf-cfb , cast5-cfb , chacha20 , chacha20-ietf , chacha20-ietf-poly1305 , des-cfb , rc4-md5 , rc4-md5-6 , salsa20 , xchacha20
2870 |
2871 | 本地监听端口-p参数支持的写法:
2872 |
2873 | ```text
2874 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
2875 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
2876 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
2877 | ```
2878 |
2879 | ### 6.2 HTTP(S)转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
2880 | 假设已经存在一个普通的http(s)代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2881 | 命令如下:
2882 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2883 |
2884 | 假设已经存在一个tls的http(s)代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,tls需要证书文件,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2885 | 命令如下:
2886 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2887 |
2888 | 假设已经存在一个kcp的http(s)代理(密码是:demo123):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2889 | 命令如下:
2890 | `./proxy sps -S http -T kcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 --kcp-key demo123 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2891 |
2892 | ### 6.3 SOCKS5转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
2893 | 假设已经存在一个普通的socks5代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2894 | 命令如下:
2895 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2896 |
2897 | 假设已经存在一个tls的socks5代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,tls需要证书文件,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2898 | 命令如下:
2899 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T tls -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2900 |
2901 | 假设已经存在一个kcp的socks5代理(密码是:demo123):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2902 | 命令如下:
2903 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T kcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 --kcp-key demo123 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2904 |
2905 | ### 6.4 SS转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
2906 | SPS上级和本地支持ss协议,上级可以是SPS或者标准的ss服务。
2907 | SPS本地默认提供HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS三种代理,当上级是SOCKS5时转换后的SOCKS5和SS支持UDP功能。
2908 | 假设已经存在一个普通的SS或者SPS代理(开启了ss,加密方式:aes-256-cfb,密码:demo):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,转换后的ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2909 | 命令如下:
2910 | `./proxy sps -S ss -H aes-256-cfb -J pass -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`。
2911 |
2912 | ### 6.5 链式连接
2913 | 
2914 | 上面提过多个sps结点可以层级连接构建加密通道,假设有如下vps和家里的pc电脑。
2915 | vps01:2.2.2.2
2916 | vps02:3.3.3.3
2917 | 现在我们想利用pc和vps01和vps02构建一个加密通道,本例子用tls加密也可以用kcp,在pc上访问本地18080端口就是访问vps01的本地8080端口。
2918 | 首先在vps01(2.2.2.2)上我们运行一个只有本地可以访问的http(s)代理,执行:
2919 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p 127.0.0.1:8080`
2920 |
2921 | 然后在vps01(2.2.2.2)上运行一个sps结点,执行:
2922 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tls -p :8081 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2923 |
2924 | 然后在vps02(3.3.3.3)上运行一个sps结点,执行:
2925 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:8081 -t tls -p :8082 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2926 |
2927 | 然后在pc上运行一个sps结点,执行:
2928 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 3.3.3.3:8082 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2929 |
2930 | 完成。
2931 |
2932 | ### 6.6 监听多个端口
2933 | 一般情况下监听一个端口就可以,不过如果作为反向代理需要同时监听80和443两个端口,那么-p参数是支持的,
2934 | 格式是:`-p 0.0.0.0:80,0.0.0.0:443`,多个绑定用逗号分隔即可。
2935 |
2936 | ### 6.7 认证功能
2937 | sps支持http(s)\socks5代理认证,可以级联认证,有四个重要的信息:
2938 | 1:用户发送认证信息`user-auth`。
2939 | 2:设置的本地认证信息`local-auth`。
2940 | 3:设置的连接上级使用的认证信息`parent-auth`。
2941 | 4:最终发送给上级的认证信息`auth-info-to-parent`。
2942 | 他们的情况关系如下:
2943 |
2944 | | user-auth | local-auth | parent-auth | auth-info-to-paren
2945 | | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------
2946 | | 有/没有 | 有 | 有 | 来自parent-auth
2947 | | 有/没有 | 没有 | 有 | 来自parent-auth
2948 | | 有/没有 | 有 | 没有 | 无
2949 | | 没有 | 没有 | 没有 | 无
2950 | | 有 | 没有 | 没有 | 来自user-auth
2951 |
2952 | 对于sps代理我们可以进行用户名密码认证,认证的用户名和密码可以在命令行指定
2953 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1:0:0:" -a "user2:pass2:0:0:"`
2954 | 多个用户,重复-a参数即可。
2955 | 也可以放在文件中,格式是一行一个`用户名:密码:连接数:速率:上级`,然后用-F指定。
2956 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -F auth-file.txt`
2957 |
2958 | 如果上级有认证,下级可以通过-A参数设置认证信息,比如:
2959 | 上级:`./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1:0:0:" -a "user2:pass2:0:0:"`
2960 | 下级:`./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -A "user1:pass1" -t tcp -p ":33080" `
2961 |
2962 | 请更多认证细节,请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
2963 |
2964 | ### 6.8 多个上级
2965 |
2966 | 如果存在多个上级,可以通过多个-P指定。
2967 |
2968 | 比如:
2969 |
2970 | `proxy sps -P http://127.0.0.1:3100 -P socks5://127.0.0.1:3200`
2971 |
2972 | `-P`完整格式如下:
2973 |
2974 | `protocol://a:b@2.2.2.2:33080#1`
2975 |
2976 | 下面对每部分进行解释:
2977 |
2978 | `protocol://` 是协议类型,可能的类型以及含有如下:
2979 |
2980 | ```text
2981 | http 等价于 -S http -T tcp
2982 | https 等价于 -S http -T tls --parent-tls-single , 也就是http(s)代理 over TLS
2983 | https2 等价于 -S http -T tls
2984 | socks5 等价于 -S socks -T tcp
2985 | socks5s 等价于 -S socks -T tls --parent-tls-single , 也就是socks over TLS
2986 | socks5s2 等价于 -S socks -T tls
2987 | ss 等价于 -S ss -T tcp
2988 | httpws 等价于 -S http -T ws
2989 | httpwss 等价于 -S http -T wss
2990 | socks5ws 等价于 -S socks -T ws
2991 | socks5wss 等价于 -S socks -T wss
2992 | ```
2993 |
2994 | `a:b`是代理认证的用户名密码,如果是ss,`a`是加密方法,`b`是密码,没有用户名密码可以留空比如:`http://2.2.2.2:33080`,如果用户名和密码保护特殊符号可以使用urlencode进行编码。
2995 |
2996 | `2.2.2.2:33080`是上级地址,格式是:`IP(或域名):端口`,如果底层是ws/wss协议还可以带上路径,比如:`2.2.2.2:33080/ws`;
2997 | 还能通过附加查询参数`m`和`k`设置`ws\wss`的`加密方法`和`密码`,比如:`2.2.2.2:33080/ws?m=aes-192-cfb&k=password`
2998 |
2999 | `#1`多个上级的负载均衡是权重策略时候,设置的权重,很少用到。
3000 |
3001 | ### 6.9 自定义加密
3002 | proxy的sps代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行
3003 | 自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义
3004 | 一个密码即可,加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
3005 |
3006 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以。
3007 |
3008 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
3009 |
3010 | 假设已经存在一个http(s)代理:`6.6.6.6:6666`
3011 |
3012 | 二级实例
3013 |
3014 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
3015 | `proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 6.6.6.6:6666 -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
3016 | 本地二级执行:
3017 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
3018 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
3019 |
3020 |
3021 | 三级实例
3022 |
3023 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
3024 | `proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 6.6.6.6:6666 -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
3025 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
3026 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
3027 | 本地三级执行:
3028 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
3029 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
3030 |
3031 | ### 6.10 压缩传输
3032 | proxy的sps代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以
3033 | 对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,
3034 | 一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
3035 |
3036 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据。
3037 |
3038 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
3039 |
3040 | 二级实例
3041 |
3042 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
3043 | `proxy sps -t tcp -m -p :7777`
3044 | 本地二级执行:
3045 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
3046 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
3047 |
3048 |
3049 | 三级实例
3050 |
3051 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
3052 | `proxy sps -t tcp -m -p :7777`
3053 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
3054 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
3055 | 本地三级执行:
3056 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
3057 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
3058 |
3059 | ### 6.11 禁用协议
3060 | SPS默认情况下一个端口支持http(s)和socks5两种代理协议,我们可以通过参数禁用某个协议
3061 | 比如:
3062 | 1.禁用HTTP(S)代理功能只保留SOCKS5代理功能,参数:`--disable-http`。
3063 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080 --disable-http`
3064 |
3065 | 1.禁用SOCKS5代理功能只保留HTTP(S)代理功能,参数:`--disable-socks`。
3066 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080 --disable-http`
3067 |
3068 | ### 6.12 限速
3069 |
3070 | 假设存在SOCKS5上级:
3071 |
3072 | `proxy socks -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -z password -t tcp`
3073 |
3074 | sps下级,限速100K
3075 |
3076 | `proxy sps -S socks -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -T tcp -Z password -l 100K -t tcp -p :33080`
3077 |
3078 | 通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
3079 |
3080 | ### 6.13 指定`出口IP`
3081 |
3082 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果`入口IP`是内网IP,`出口IP`不会使用`入口IP`。
3083 |
3084 | `proxy sps -S socks -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -T tcp -Z password -l 100K -t tcp --bind-listen -p :33080`
3085 |
3086 | ### 6.14 证书参数使用base64数据
3087 |
3088 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
3089 |
3090 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
3091 |
3092 | ### 6.15 独立服务
3093 | sps功能不强制指定一个上级,当上级为空,sps本身即可完成完整的代理功能.如果指定了上级那么就和之前一样使用上级连接目标。
3094 | 下面这个命令,就是一键开启http(s)\ss\socks服务。
3095 | `./proxy sps -p :33080`
3096 |
3097 | ### 6.16 目标重定向
3098 | sps功能提供的http(s)\socks5\ss代理功能,客户端通过sps代理去连接指定的“目标”,这个“目标”一般是网站也可能是任意的tcp地址,
3099 | 网站”目标“一般是foo.com:80,foo.com:443,sps支持使用--rewrite参数指定一个“目标”重定向规则文件,对目标进行重定向,客户端是无感知的,
3100 | 比如你对“目标”:demo.com:80重定向到192.168.0.12:80,那么客户端访问网站demo.com,其实访问的是192.168.0.12提供的网站服务。
3101 | “目标”重定向规则文件示例:
3102 |
3103 | ```text
3104 | # example
3105 | www.a.com:80 10.0.0.2:8080
3106 | **.b.com:80 10.0.0.2:80
3107 | 192.168.0.11:80 10.0.0.2:8080
3108 | ```
3109 |
3110 | ### 6.17 固定UDP功能端口
3111 |
3112 | 默认情况下sps的socks5的UDP功能的端口号是按着`rfc1982草案`要求,使用协议握手过程中随机指定,不需要提前指定。
3113 |
3114 | 但是某些情况下,需要固定UDP功能端口,可以通过参数`--udp-port 端口号`用来固定UDP功能的端口号,比如:
3115 |
3116 | `./proxy sps -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --udp-port 38081`
3117 |
3118 | 需要注意的是,sps的ss功能也有UDP功能,而且ss的UDP端口和tcp端口是一样的,所以要避免socks5的UDP端口和ss的UDP端口冲突,
3119 |
3120 | 要指定和tcp端口不一样的端口。
3121 |
3122 | ### 6.18 iptables 透明代理
3123 | sps模式支持Linux系统的iptables转发支持,也就是通常所说的iptables透明代理,如果在网关设备上进行iptables透明代理,那么对通过网关联网的设备就能实现无感知的代理。
3124 |
3125 | 启动命令实例:
3126 |
3127 | `./proxy sps --redir -p :8888 -P httpws://1.1.1.1:33080`
3128 |
3129 | 这里假设存在一个http的上级代理1.1.1.1:33080,使用ws传输数据。
3130 |
3131 | 然后添加iptables规则,下面是参考规则:
3132 | ```shell
3133 | #上级proxy服务端服务器IP地址:
3134 | proxy_server_ip=1.1.1.1
3135 |
3136 | #路由器运行proxy监听的端口:
3137 | proxy_local_port=33080
3138 |
3139 | #下面的就不用修改了
3140 | #create a new chain named PROXY
3141 | iptables -t nat -N PROXY
3142 |
3143 | # Ignore your PROXY server's addresses
3144 | # It's very IMPORTANT, just be careful。
3145 |
3146 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d $proxy_server_ip -j RETURN
3147 |
3148 | # Ignore LANs IP address
3149 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 0.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
3150 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 10.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
3151 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 127.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
3152 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 169.254.0.0/16 -j RETURN
3153 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 172.16.0.0/12 -j RETURN
3154 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 192.168.0.0/16 -j RETURN
3155 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 224.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
3156 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 240.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
3157 |
3158 | # Anything to port 80 443 should be redirected to PROXY's local port
3159 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
3160 | # Apply the rules to nat client
3161 | iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -j PROXY
3162 | # Apply the rules to localhost
3163 | iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp -j PROXY
3164 | ```
3165 | - 清空整个链 iptables -F 链名比如iptables -t nat -F PROXY
3166 | - 删除指定的用户自定义链 iptables -X 链名 比如 iptables -t nat -X PROXY
3167 | - 从所选链中删除规则 iptables -D 链名 规则详情 比如 iptables -t nat -D PROXY -d 223.223.192.0/255.255.240.0 -j RETURN
3168 |
3169 | ### 6.19 查看帮助
3170 |
3171 | `./proxy help sps`
3172 |
3173 | ## 7.KCP配置
3174 |
3175 | ### 7.1 配置介绍
3176 | proxy的很多功能都支持kcp协议,凡是使用了kcp协议的功能都支持这里介绍的配置参数。
3177 | 所以这里统一对KCP配置参数进行介绍。
3178 |
3179 | ### 7.2 详细配置
3180 | 所有的KCP配置参数共有17个,你可以都不用设置,他们都有默认值,如果为了或者最好的效果,
3181 | 就需要自己根据自己根据网络情况对参数进行配置。由于kcp配置很复杂需要一定的网络基础知识,
3182 | 如果想获得kcp参数更详细的配置和解说,请自行搜索。每个参数的命令行名称以及默认值和简单的功能说明如下:
3183 | ```
3184 | --kcp-key="secrect" pre-shared secret between client and server
3185 | --kcp-method="aes" encrypt/decrypt method, can be: aes, aes-128, aes-192, salsa20, blowfish,
3186 | twofish, cast5, 3des, tea, xtea, xor, sm4, none
3187 | --kcp-mode="fast" profiles: fast3, fast2, fast, normal, manual
3188 | --kcp-mtu=1350 set maximum transmission unit for UDP packets
3189 | --kcp-sndwnd=1024 set send window size(num of packets)
3190 | --kcp-rcvwnd=1024 set receive window size(num of packets)
3191 | --kcp-ds=10 set reed-solomon erasure coding - datashard
3192 | --kcp-ps=3 set reed-solomon erasure coding - parityshard
3193 | --kcp-dscp=0 set DSCP(6bit)
3194 | --kcp-nocomp disable compression
3195 | --kcp-acknodelay be carefull! flush ack immediately when a packet is received
3196 | --kcp-nodelay=0 be carefull!
3197 | --kcp-interval=50 be carefull!
3198 | --kcp-resend=0 be carefull!
3199 | --kcp-nc=0 be carefull! no congestion
3200 | --kcp-sockbuf=4194304 be carefull!
3201 | --kcp-keepalive=10 be carefull!
3202 | ```
3203 | 提示:
3204 | 参数:--kcp-mode中的四种fast3, fast2, fast, normal模式,
3205 | 相当于设置了下面四个参数:
3206 | normal:`--nodelay=0 --interval=40 --resend=2 --nc=1`
3207 | fast :`--nodelay=0 --interval=30 --resend=2 --nc=1`
3208 | fast2:`--nodelay=1 --interval=20 --resend=2 --nc=1`
3209 | fast3:`--nodelay=1 --interval=10 --resend=2 --nc=1`
3210 |
3211 | ## 8.安全DNS
3212 |
3213 | ### 8.1 介绍
3214 | 众所周知DNS是UDP端口53提供的服务,但是随着网络的发展一些知名DNS服务器也支持TCP方式dns查询,比如谷歌的8.8.8.8,proxy的DNS防污染服务器原理就是在本地启动一个proxy的DNS代理服务器,它用TCP的方式通过上级代理进行dns查询。如果它和上级代理通讯采用加密的方式,那么就可以进行安全无污染的DNS解析,还支持独立服务,并发解析,支持增强的hosts文件功能支持灵活的并发解析转发。
3215 |
3216 | dns解析顺序:
3217 | 1.使用参数--hosts解析。
3218 | 2.要解析的域名在1中没有找到,就使用参数--forward规则解析。
3219 | 3.要解析的域名在1和2中都没有找到,就使用默认--default解析,--default默认行为参数值有三种:proxy,direct,system。
3220 | 三种参数值解释如下:
3221 | proxy:通过上级去连接-q参数指定的dns服务器去解析域名。
3222 | direct:通过本地网络去连接-q参数指定的dns服务器去解析域名。
3223 | system:通过系统dns去解析域名。
3224 |
3225 | 提示:
3226 | --hosts 参数指定的host文件格式和系统hosts文件一致,而且域名支持通配符,可以参考hosts文件。
3227 | --forward 参数指定的解析转发规则文件,格式可以参考resolve.rules文件,域名支持通配符,支持为每个域名指定多个dns服务器并发解析,谁最快解析成功就用谁的解析结果。
3228 | -q 参数可以指定多个远程dns服务器,执行并发解析谁最快解析成功就用谁的解析结果,默认是:1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8,9.9.9.9,多个用逗号分割,
3229 | 比如还可以带端口:1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8#53,9.9.9.9
3230 |
3231 | 如果独立服务,不需要上级:
3232 | 可以执行:
3233 | `proxy dns --default system -p :5353`
3234 | or
3235 | `proxy dns --default direct -p :5353`
3236 |
3237 | ### 8.2 使用示例
3238 |
3239 | #### 8.2.1 普通HTTP(S)上级代理
3240 |
3241 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3242 | 本地执行:
3243 | `proxy dns -S http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3244 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了DNS解析功能。
3245 |
3246 | #### 8.2.2 普通SOCKS5上级代理
3247 |
3248 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3249 | 本地执行:
3250 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3251 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了DNS解析功能。
3252 |
3253 | #### 8.2.3 TLS加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
3254 |
3255 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3256 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3257 | `proxy http -t tls -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :33080`
3258 | 本地执行:
3259 | `proxy dns -S http -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :53`
3260 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3261 |
3262 | #### 8.2.4 TLS加密的SOCKS5上级代理
3263 |
3264 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3265 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3266 | `proxy socks -t tls -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :33080`
3267 | 本地执行:
3268 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :53`
3269 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3270 |
3271 | #### 8.2.5 KCP加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
3272 |
3273 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3274 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3275 | `proxy http -t kcp -p :33080`
3276 | 本地执行:
3277 | `proxy dns -S http -T kcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3278 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3279 |
3280 | #### 8.2.6 KCP加密的SOCKS5上级代理
3281 |
3282 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3283 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3284 | `proxy socks -t kcp -p :33080`
3285 | 本地执行:
3286 | `proxy dns -S socks -T kcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3287 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3288 |
3289 | #### 8.2.7 自定义加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
3290 |
3291 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3292 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3293 | `proxy http -t tcp -p :33080 -z password`
3294 | 本地执行:
3295 | `proxy dns -S http -T tcp -Z password -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3296 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3297 |
3298 | #### 8.2.8 自定义加密的SOCKS5上级代理
3299 |
3300 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3301 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3302 | `proxy socks -t kcp -p :33080 -z password`
3303 | 本地执行:
3304 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tcp -Z password -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3305 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3306 |
3307 | ## 9.API认证,限速,控制连接数
3308 |
3309 | proxy的http(s)/socks5/sps代理功能,支持通过API控制用户对代理对访问。
3310 |
3311 | ### 通过API可以干什么?
3312 |
3313 | - 用户维度,控制单个连接速率,控制最大连接数。
3314 | - IP维度,控制单个连接速率,控制最大连接数。
3315 | - 动态上级,可以根据用户或者客户端IP,动态的从API获取其上级,支持http(s)/socks5/ss上级。
3316 | - 认证每一个连接,无论是否要求客户端认证。
3317 | - 缓存认证结果,时间可以设置,减轻API压力。
3318 |
3319 | #### 具体使用
3320 | proxy的http(s)/socks5/sps代理API功能,通过`--auth-url`和`--auth-nouser`和`--auth-cache`三个参数控制。
3321 | 参数`--auth-url`是HTTP API接口地址,客户端连接的时候,proxy会GET方式请求这url,带上下面参数,如果返回HTTP状态码204,代表认证成功,其它情况认为认证失败。
3322 |
3323 | 一个完整的请求API的示例:
3324 | `http://test.com/auth.php?user=a&pass=b&client_addr=127.0.0.1:49892&local_addr=127.0.0.1:8100&target=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.baidu.com&service=http&sps=0`
3325 |
3326 | #### 参数说明
3327 | `user和pass` 当代理开启了认证功能,这里就是客户端提供的用户名和密码。
3328 | `client_addr` 客户端访问代理时的用的地址,格式IP:端口。
3329 | `local_addr` 客户端访问的代理地址,格式IP:端口。
3330 | `service` 代理类型,分为:http、socks。
3331 | `sps` 代理是否是sps提供的,1:是,0:否。
3332 | `target` 客户端要访问的目标,如果是http(s)代理,target是访问的具体url;如果是socks5代理,target是空。
3333 |
3334 | #### 示例
3335 | 假设--auth-url http://127.0.0.1:333/auth.php 指向了一个php接口地址.
3336 | auth.php内容如下:
3337 |
3338 | ```php
3339 |
155 |
156 | ### 源代码申明
157 |
158 | 本项目作者发现大量的开发者基于本项目进行二次开发或使用大量本项目核心代码而不遵循GPLv3协议,这严重违背了本项目使用GPLv3开源协议的初衷,鉴于这种情况,本项目采取源代码延迟发布策略,在一定程度上遏制这些不尊重开源,不尊重他人劳动成果的行为。
159 | 本项目会持续更新迭代,持续发布全平台的二进制程序,给大家提供强大便捷的代理工具。
160 | 如果你有定制,商业需求请发邮件至`arraykeys@gmail.com`
161 |
162 | ## goproxy使用手册
163 |
164 |
165 | ## 首次使用必看!
166 |
167 | ### 1. 环境
168 |
169 | 该手册教程,默认系统是linux,程序是proxy;所有操作需要root权限;
170 |
171 | 如果你的是windows,请使用windows版本的proxy.exe即可。
172 |
173 | ### 2. 使用配置文件
174 |
175 | 接下来的教程都是通过命令行参数介绍使用方法,也可以通过读取配置文件获取参数。
176 |
177 | 具体格式是通过@符号指定配置文件,例如:./proxy @configfile.txt
178 |
179 | configfile.txt里面的格式是,第一行是子命令名称,第二行开始一行一个参数,
180 |
181 | 格式:`参数 参数值`,没有参数值的直接写参数,比如:--nolog
182 |
183 | 比如configfile.txt内容如下:
184 |
185 | ```shell
186 | http
187 | -t tcp
188 | -p :33080
189 | --forever
190 | ```
191 |
192 | ### 3. 调试输出
193 |
194 | 默认情况下,日志输出的信息不包含文件行数,某些情况下为了排除程序问题,快速定位问题,
195 |
196 | 可以使用--debug参数,输出代码行数和毫秒时间。
197 |
198 | ### 4. 使用日志文件
199 |
200 | 默认情况下,日志是直接在控制台显示出来的,如果要保存到文件,可以使用--log参数,
201 |
202 | 比如: --log proxy.log,日志就会输出到proxy.log方便排除问题。
203 |
204 |
205 | ### 5. 生成加密通讯需要的证书文件
206 |
207 | http(s)代理、tcp代理、udp代理、socks5代理、内网穿透等功能和上级通讯的时候,为了安全我们采用TLS加密通讯,当然可以选择不加密通信通讯,本教程所有和上级通讯都采用加密,需要证书文件。
208 |
209 | ***所有端必须使用相同的proxy.crt和proxy.key***
210 |
211 | 1.通过下面的命令生成自签名的证书和key文件。
212 | `./proxy keygen -C proxy`
213 | 会在当前程序目录下面生成证书文件proxy.crt和key文件proxy.key。
214 |
215 | 2.通过下面的命令生,使用自签名证书proxy.crt和key文件proxy.key签发新证书:goproxy.crt和goproxy.key。
216 | `./proxy keygen -s -C proxy -c goproxy`
217 | 会在当前程序目录下面生成证书文件goproxy.crt和key文件goproxy.key。
218 |
219 | 3.默认情况下证书的里面的域名是随机的,可以使用`-n test.com`参数指定。
220 |
221 | 4.更多用法:`proxy keygen --help`。
222 |
223 | ### 6. 后台运行
224 |
225 | 默认执行proxy之后,如果要保持proxy运行,不能关闭命令行。
226 |
227 | 如果想在后台运行proxy,命令行可以关闭,只需要在命令最后加上--daemon参数即可。
228 |
229 | 比如:
230 |
231 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --daemon`
232 |
233 | ### 7. 守护运行
234 | 守护运行参数--forever,比如: `proxy http --forever` ,
235 |
236 | proxy会fork子进程,然后监控子进程,如果子进程异常退出,5秒后重启子进程。
237 |
238 | 该参数配合后台运行参数--daemon和日志参数--log,可以保障proxy一直在后台执行不会因为意外退出,
239 |
240 | 而且可以通过日志文件看到proxy的输出日志内容。
241 |
242 | 比如: `proxy http -p ":9090" --forever --log proxy.log --daemon`
243 |
244 | ### 8. 安全建议
245 |
246 | 当VPS在nat设备后面,vps上网卡IP都是内网IP,这个时候可以通过-g参数添加vps的外网ip防止死循环。
247 |
248 | 假设你的vps外网ip是23.23.23.23,下面命令通过-g参数设置23.23.23.23
249 |
250 | `./proxy http -g "23.23.23.23"`
251 |
252 | ### 9. 负载均衡和高可用
253 |
254 | HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS代理支持上级负载均衡和高可用,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
255 |
256 | 负载均衡策略支持5种,可以通过`--lb-method`参数指定:
257 |
258 | roundrobin 轮流使用
259 |
260 | leastconn 使用最小连接数的
261 |
262 | leasttime 使用连接时间最小的
263 |
264 | hash 使用根据客户端地址计算出一个固定上级
265 |
266 | weight 根据每个上级的权重和连接数情况,选择出一个上级
267 |
268 | 提示:
269 |
270 | 负载均衡检查时间间隔可以通过`--lb-retrytime`设置,单位毫秒
271 |
272 | 负载均衡连接超时时间可以通过`--lb-timeout`设置,单位毫秒
273 |
274 | 如果负载均衡策略是权重(weight),-P格式为:2.2.2.2:3880?w=1,1就是权重,大于0的整数。
275 |
276 | 如果负载均衡策略是hash,默认是根据客户端地址选择上级,可以通过开关`--lb-hashtarget`使用访问的目标地址选择上级。
277 |
278 |
279 | ### 10. 代理跳板跳转
280 |
281 | http(s)代理,SPS代理,内网穿透,tcp代理都支持通过中间第三方代理连接上级,
282 |
283 | 参数是:--jumper,所有格式如下:
284 |
285 | ```text
286 | http://username:password@host:port
287 | http://host:port
288 | https://username:password@host:port
289 | https://host:port
290 | socks5://username:password@host:port
291 | socks5://host:port
292 | socks5s://username:password@host:port
293 | socks5s://host:port
294 | ss://method:password@host:port
295 | ```
296 |
297 | http,socks5代表的是普通的http和socks5代理。
298 |
299 | https,socks5s代表的是通过tls保护的http和socks5代理,
300 |
301 | 也就是http代理 over TLS , socks over TLS。
302 |
303 | ### 11. 域名黑白名单
304 |
305 | socks/http(s)/sps代理都支持域名黑白名单。
306 |
307 | 用--stop参数指定一个域名黑名单列表文件,那么当用户连接文件里面这些域名的时候连接就会被断开。
308 |
309 | 用--only参数指定一个域名白名单列表文件,那么当用户连接文件里面这些域名之外的域名的时候连接就会被断开。
310 |
311 | 如果同时设置了--stop和--only,那么只有--only会起作用。
312 |
313 | 黑白域名名单文件内容格式如下:
314 |
315 | ```text
316 | **.baidu.com
317 | *.taobao.com
318 | a.com
319 | 192.168.1.1
320 | 192.168.*.*
321 | ?.qq.com
322 | ```
323 |
324 | 说明:
325 |
326 | 1.一行一个域名,域名写法支持通配符`*`和`?`,`*`代表任意个字符,`?`代表一个任意字符,
327 |
328 | 2.`**.baidu.com` 匹配无论是多少级所有后缀是`.baidu.com`的域名。
329 |
330 | 3.`*.taobao.com` 匹配后缀是`.taobao.com`的三级域名。
331 |
332 | 4.还可以直接是IP地址。
333 |
334 | 5.`#`开头的为注释。
335 |
336 | ### 12. 客户端IP黑白名单
337 |
338 | socks/http(s)/sps/tcp/udp/dns/内网穿透bridge/内网穿透tbridge,都支持客户端IP黑白名单。
339 |
340 | 用--ip-deny参数指定一个客户端IP黑名单列表文件,那么当用户的IP在这个文件里面的时候连接就会被断开。
341 |
342 | 用--ip-allow参数指定一个客户端IP白名单列表文件,那么当用户的IP不在这个文件里面的时候连接就会被断开。
343 |
344 | 如果同时设置了--ip-deny和--ip-allow,那么只有--ip-allow会起作用。
345 |
346 | 客户端IP黑白名单文件内容格式如下:
347 |
348 | ```text
349 | 192.168.1.1
350 | 192.168.*.*
351 | 192.168.1?.*
352 | ```
353 |
354 | 说明:
355 |
356 | 1.一行一个域名,域名写法支持通配符`*`和`?`,`*`代表任意个字符,`?`代表一个任意字符。
357 |
358 | 2.`#`开头的为注释。
359 |
360 | ### 13. 协议加载文件
361 |
362 | proxy的各种代理功能里面很多地方都有参数设置一个文件,比如:--blocked 指定一个直接走上级的域名列表文件,参数值是文件的路径,
363 |
364 | 如果参数支持协议加载文件,那么文件路径不仅可以是文件路径,还可以是:
365 |
366 | a.“base64://”开头的base64编码的上面说明的文件内容,比如:base64://ajfpoajsdfa=
367 |
368 | b.”str://“开头的英文逗号分割的多个,比如:str://xxx,yyy
369 |
370 | proxy的blocked,direct,stop,only,hosts,resolve.rules,rewriter.rules,ip.allow,ip.deny 文件支持协议加载。
371 |
372 | ## 1.HTTP代理
373 |
374 | ### 1.1.普通一级HTTP代理
375 |
376 | 
377 |
378 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080"`
379 |
380 | -p参数支持的写法:
381 |
382 | ```text
383 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
384 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
385 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
386 | ```
387 |
388 | ### 1.2.普通二级HTTP代理
389 |
390 | 
391 |
392 | 使用本地端口8090,假设上级HTTP代理是`22.22.22.22:8080`
393 |
394 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" `
395 |
396 | 我们还可以指定网站域名的黑白名单文件,一行一个域名,匹配规则是最右匹配,比如:baidu.com,匹配的是*.*.baidu.com,黑名单的域名直接走上级代理,白名单的域名不走上级代理。
397 |
398 | `./proxy http -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" -b blocked.txt -d direct.txt`
399 |
400 | ### 1.3.HTTP二级代理(加密)
401 |
402 | > 注意: 后面二级代理使用的`proxy.crt`和`proxy.key`应与一级代理一致
403 |
404 | 
405 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
406 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
407 |
408 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
409 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
410 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080。
411 |
412 | 二级HTTP代理(本地windows)
413 | `./proxy.exe http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
414 | 然后设置你的windos系统中,需要通过代理上网的程序的代理为http模式,地址为:127.0.0.1,端口为:8080,程序即可通过加密通道通过vps上网。
415 |
416 | ### 1.4.HTTP三级代理(加密)
417 | 
418 | 一级HTTP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
419 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
420 | 二级HTTP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
421 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
422 | 三级HTTP代理(本地)
423 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
424 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问一级HTTP代理上面的代理端口38080。
425 |
426 | ### 1.5.Basic认证,API认证
427 |
428 | 请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
429 |
430 | ### 1.6.HTTP代理流量强制走上级HTTP代理
431 | 默认情况下,proxy会智能判断一个网站域名是否无法访问,如果无法访问才走上级HTTP代理.通过--always可以使全部HTTP代理流量强制走上级HTTP代理。
432 | `./proxy http --always -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
433 |
434 | ### 1.7.HTTP(S)通过SSH中转
435 | 
436 | 说明:ssh中转的原理是利用了ssh的转发功能,就是你连接上ssh之后,可以通过ssh代理访问目标地址。
437 | 假设有:vps
438 | - IP是2.2.2.2, ssh端口是22, ssh用户名是:user, ssh用户密码是:demo
439 | - 用户user的ssh私钥名称是user.key
440 |
441 | #### *1.7.1 ssh用户名和密码的方式*
442 | 本地HTTP(S)代理28080端口,执行:
443 | `./proxy http -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -D demo -t tcp -p ":28080"`
444 | #### *1.7.2 ssh用户名和密钥的方式*
445 | 本地HTTP(S)代理28080端口,执行:
446 | `./proxy http -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -S user.key -t tcp -p ":28080"`
447 |
448 | ### 1.8.KCP协议传输
449 | 
450 | KCP协议需要--kcp-key参数设置一个密码用于加密解密数据
451 |
452 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
453 | `./proxy http -t kcp -p ":38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
454 |
455 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
456 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T kcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
457 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080,数据通过kcp协议传输,注意kcp走的是udp协议协议,所以防火墙需放开38080的udp协议。
458 |
459 | ### 1.9 HTTP(S)反向代理
460 | 
461 | proxy不仅支持在其他软件里面通过设置代理的方式,为其他软件提供代理服务,而且支持直接把请求的网站域名解析到proxy监听的ip上,然后proxy监听80和443端口,那么proxy就会自动为你代理访问需要访问的HTTP(S)网站。
462 |
463 | 使用方式:
464 | 在"最后一级proxy代理"的机器上,因为proxy要伪装成所有网站,网站默认的端口HTTP是80,HTTPS是443,让proxy监听80和443端口即可.参数-p多个地址用逗号分割。
465 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :80,:443`
466 |
467 | 这个命令就在机器上启动了一个proxy代理,同时监听80和443端口,既可以当作普通的代理使用,也可以直接把需要代理的域名解析到这个机器的IP上。
468 |
469 | 如果有上级代理那么参照上面教程设置上级即可,使用方式完全一样。
470 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :80,:443 -T tls -P "2.2.2.2:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
471 |
472 | 注意:
473 | proxy所在的服务器的DNS解析结果不能受到自定义的解析影响,不然就死循环了,proxy代理最好指定`--dns 8.8.8.8`参数。
474 |
475 | ### 1.10 HTTP(S)透明代理
476 | 该模式需要具有一定的网络基础,相关概念不懂的请自行搜索解决。
477 | 假设proxy现在在路由器上运行,启动命令如下:
478 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :33080 -T tls -P "2.2.2.2:33090" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
479 |
480 | 然后添加iptables规则,下面是参考规则:
481 | ```shell
482 | #上级proxy服务端服务器IP地址:
483 | proxy_server_ip=2.2.2.2
484 |
485 | #路由器运行proxy监听的端口:
486 | proxy_local_port=33080
487 |
488 | #下面的就不用修改了
489 | #create a new chain named PROXY
490 | iptables -t nat -N PROXY
491 |
492 | # Ignore your PROXY server's addresses
493 | # It's very IMPORTANT, just be careful。
494 |
495 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d $proxy_server_ip -j RETURN
496 |
497 | # Ignore LANs IP address
498 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 0.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
499 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 10.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
500 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 127.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
501 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 169.254.0.0/16 -j RETURN
502 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 172.16.0.0/12 -j RETURN
503 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 192.168.0.0/16 -j RETURN
504 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 224.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
505 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 240.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
506 |
507 | # Anything to port 80 443 should be redirected to PROXY's local port
508 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
509 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp --dport 443 -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
510 |
511 | # Apply the rules to nat client
512 | iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -j PROXY
513 | # Apply the rules to localhost
514 | iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp -j PROXY
515 | ```
516 | - 清空整个链 iptables -F 链名比如iptables -t nat -F PROXY
517 | - 删除指定的用户自定义链 iptables -X 链名 比如 iptables -t nat -X PROXY
518 | - 从所选链中删除规则 iptables -D 链名 规则详情 比如 iptables -t nat -D PROXY -d 223.223.192.0/255.255.240.0 -j RETURN
519 |
520 | ### 1.11 自定义DNS
521 | --dns-address和--dns-ttl参数,用于自己指定proxy访问域名的时候使用的dns(--dns-address)
522 | 以及解析结果缓存时间(--dns-ttl)秒数,避免系统dns对proxy的干扰,另外缓存功能还能减少dns解析时间提高访问速度。
523 | 比如:
524 | `./proxy http -p ":33080" --dns-address "8.8.8.8:53" --dns-ttl 300`
525 |
526 | ### 1.12 自定义加密
527 | proxy的http(s)代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义
528 | 加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可,
529 | 加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
530 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以,下面分别用二级,三级为例:
531 |
532 | 二级实例
533 |
534 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
535 | `proxy http -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
536 | 本地二级执行:
537 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
538 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
539 |
540 |
541 | 三级实例
542 |
543 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
544 | `proxy http -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
545 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
546 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
547 | 本地三级执行:
548 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
549 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
550 |
551 | ### 1.13 压缩传输
552 | proxy的http(s)代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以对数据进行压缩,
553 | 也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,
554 | 一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
555 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据,下面分别用二级,三级为例:
556 |
557 | 二级实例
558 |
559 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
560 | `proxy http -t tcp -m -p :7777`
561 | 本地二级执行:
562 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
563 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
564 |
565 |
566 | 三级实例
567 |
568 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
569 | `proxy http -t tcp -m -p :7777`
570 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
571 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
572 | 本地三级执行:
573 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
574 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
575 |
576 | ### 1.14 负载均衡
577 |
578 | HTTP(S)代理支持上级负载均衡,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
579 |
580 | `proxy http --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080`
581 |
582 | ### 1.14.1 设置重试间隔和超时时间
583 |
584 | `proxy http --lb-method=leastconn --lb-retrytime 300 --lb-timeout 300 -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -t tcp -p :33080`
585 |
586 | ### 1.14.2 设置权重
587 |
588 | `proxy http --lb-method=weight -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -P 2.1.1.1:33080?w=2 -P 3.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -t tcp -p :33080`
589 |
590 | ### 1.14.3 使用目标地址选择上级
591 |
592 | `proxy http --lb-hashtarget --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -t tcp -p :33080`
593 |
594 | ### 1.15 限速
595 |
596 | 限速100K,通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
597 |
598 | `proxy http -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -l 100K`
599 |
600 | ### 1.16 指定出口IP
601 |
602 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作,此时代理会尝试不绑定IP去访问目标,同时日志会提示。
603 |
604 | `proxy http -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 --bind-listen`
605 |
606 | ### 1.17 证书参数使用base64数据
607 |
608 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
609 |
610 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
611 |
612 | ### 1.18 智能模式
613 | 智能模式设置,可以是intelligent|direct|parent三者之一。
614 | 默认是:intelligent。
615 | 每个值的含义如下:
616 | `--intelligent=direct`,不在blocked里面的目标都直连。
617 | `--intelligent=parent`,不在direct里面的目标都走上级。
618 | `--intelligent=intelligent`,blocked和direct里面都没有的目标,智能判断是否使用上级访问目标。
619 |
620 | ### 1.19 查看帮助
621 | `./proxy help http`
622 |
623 | ## 2.TCP代理
624 |
625 | ### 2.1 普通一级TCP代理
626 | 
627 | 本地执行:
628 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22"`
629 | 那么访问本地33080端口就是访问192.168.22.33的22端口。
630 |
631 | `-p`参数支持的写法:
632 |
633 | ```text
634 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
635 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
636 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
637 | ```
638 |
639 | 如果本地监听端口数量大于1,那么将会连接与本地端口一致的对应上级端口,忽略`-P`里面的端口。
640 |
641 | 如果需要所有端口进来的连接,都连接到上级指定端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`。
642 |
643 | 比如:
644 |
645 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080-33085" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:0"`
646 |
647 | 那么`33080`端口进来的连接,将会连接192.168.22.33的`33080`端口,其它端口以此类推,本地和上级端口一致,此时参数`-P`里面的端口用`0`。
648 |
649 | 如果想无论是`33080`,`33081`等端口进来的连接都连接到192.168.22.33的`22`端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`
650 |
651 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080-33085" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --lock-port`
652 |
653 |
654 | ### 2.2 普通二级TCP代理
655 | 
656 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
657 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "127.0.0.1:8080"`
658 | 本地执行:
659 | `./proxy tcp -p ":23080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.33:33080"`
660 | 那么访问本地23080端口就是访问22.22.22.33的8080端口。
661 |
662 | ### 2.3 普通三级TCP代理
663 | 
664 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
665 | `./proxy tcp -p ":38080" -T tcp -P "66.66.66.66:8080"`
666 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
667 | `./proxy tcp -p ":28080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080"`
668 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
669 | `./proxy tcp -p ":8080" -T tcp -P "33.33.33.33:28080"`
670 | 那么访问本地8080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问66.66.66.66的8080端口。
671 |
672 | ### 2.4 加密二级TCP代理
673 | 
674 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
675 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "127.0.0.1:8080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
676 | 本地执行:
677 | `./proxy tcp -p ":23080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.33:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
678 | 那么访问本地23080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问22.22.22.33的8080端口。
679 |
680 | ### 2.5 加密三级TCP代理
681 | 
682 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
683 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":38080" -T tcp -P "66.66.66.66:8080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
684 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
685 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
686 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
687 | `./proxy tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
688 | 那么访问本地8080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问66.66.66.66的8080端口。
689 |
690 | ### 2.6 通过代理连接上级
691 | 有时候proxy所在的网络不能直接访问外网,需要通过一个https或者socks5代理才能上网,那么这个时候
692 | -J参数就可以帮助你让proxy的tcp端口映射的时候通过https或者socks5代理去连接上级-P,将外部端口映射到本地。
693 | -J参数格式如下:
694 |
695 | https代理写法:
696 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
697 | https://username:password@host:port
698 | 代理不需要认证
699 | https://host:port
700 |
701 | socks5代理写法:
702 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
703 | socks5://username:password@host:port
704 | 代理不需要认证
705 | socks5://host:port
706 |
707 | host:代理的IP或者域名
708 | port:代理的端口
709 |
710 | ### 2.7 指定`出口IP`
711 | 当TCP代理当上级类型(参数:-T)是tcp当时候,支持指定`出口IP`。使用`--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作,此时代理会尝试不绑定IP去访问目标,同时日志会提示。
712 |
713 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" -B`
714 |
715 | ### 2.8 限速,限制连接数
716 |
717 | 参数`--max-conns`可以限制每个端口的最大连接数。
718 | 比如限制每个端口最多1000个连接数:
719 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --max-conns 1000`
720 | 参数`--rate-limit`可以限制每个tcp连接的速率。
721 | 比如限制每个tcp连接速率为100k/s:
722 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --rate-limit 100k`
723 |
724 | ### 2.9 查看帮助
725 | `./proxy help tcp`
726 |
727 | ## 3.UDP代理
728 |
729 | ### 3.1.普通一级UDP代理
730 | 
731 | 本地执行:
732 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
733 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
734 |
735 | `-p`参数支持的写法:
736 |
737 | ```text
738 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
739 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
740 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
741 | ```
742 |
743 | 如果本地监听端口数量大于1,那么将会连接与本地端口一致的对应上级端口,忽略`-P`里面的端口。
744 |
745 | 如果需要所有端口进来的连接,都连接到上级指定端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`。
746 |
747 | 比如:
748 |
749 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080-33085" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:0"`
750 |
751 | 那么`33080`端口进来的连接,将会连接192.168.22.33的`33080`端口,其它端口以此类推,本地和上级端口一致,此时参数`-P`里面的端口用`0`。
752 |
753 | 如果想无论是`33080`,`33081`等端口进来的连接都连接到192.168.22.33的`2222`端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`
754 |
755 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080-33085" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:2222" --lock-port`
756 |
757 | ### 3.2.普通二级UDP代理
758 | 
759 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
760 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
761 | 本地执行:
762 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.33:33080"`
763 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是通过TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
764 |
765 | ### 3.3.普通三级UDP代理
766 | 
767 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
768 | `./proxy tcp -p ":38080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
769 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
770 | `./proxy tcp -p ":28080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080"`
771 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
772 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tcp -P "33.33.33.33:28080"`
773 | 那么访问本地5353端口就是通过TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的53端口。
774 |
775 | ### 3.4.加密二级UDP代理
776 | 
777 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
778 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":33080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
779 | 本地执行:
780 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tls -P "22.22.22.33:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
781 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是通过加密TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
782 |
783 | ### 3.5.加密三级UDP代理
784 | 
785 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
786 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":38080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
787 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
788 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
789 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
790 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
791 | 那么访问本地5353端口就是通过加密TCP隧道,通过VPS_01访问8.8.8.8的53端口。
792 |
793 | ### 3.6 指定`出口IP`
794 | 当UDP代理当上级类型(参数:-T)是udp当时候,支持指定`出口IP`。使用`--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作。
795 |
796 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:2222" -B`
797 |
798 | ### 3.7 查看帮助
799 | `./proxy help udp`
800 |
801 | ## 4.内网穿透
802 | ### 4.1、原理说明
803 | 内网穿透,分为两个版本,“多链接版本”和“多路复用版本”,一般像web服务这种不是长时间连接的服务建议用“多链接版本”,如果是要保持长时间连接建议使用“多路复用版本”。
804 | 1. 多链接版本,对应的子命令是tserver,tclient,tbridge。
805 | 1. 多路复用版本,对应的子命令是server,client,bridge。
806 | 1. 多链接版本和多路复用版本的参数和使用方式完全一样。
807 | 1. 多路复用版本的server,client可以开启压缩传输,参数是--c。
808 | 1. server,client要么都开启压缩,要么都不开启,不能只开一个。
809 |
810 | 下面的教程以“多路复用版本”为例子,说明使用方法。
811 | 内网穿透由三部分组成:client端,server端,bridge端;client和server主动连接bridge端进行桥接。
812 |
813 | ### 4.2、TCP普通用法
814 | 背景:
815 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口
816 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
817 |
818 | 需求:
819 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的28080端口访问到公司机器A的80端口
820 |
821 | 步骤:
822 | 1. 在vps上执行
823 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
824 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
825 |
826 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
827 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
828 |
829 | 1. 完成
830 |
831 | ### 4.3、微信接口本地开发
832 | 背景:
833 | - 自己的笔记本提供了nginx服务80端口
834 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
835 |
836 | 需求:
837 | 在微信的开发帐号的网页回调接口配置里面填写地址:http://22.22.22.22/calback.php
838 | 然后就可以访问到笔记本的80端口下面的calback.php,如果需要绑定域名,可以用自己的域名
839 | 比如:wx-dev.xxx.com解析到22.22.22.22,然后在自己笔记本的nginx里
840 | 配置域名wx-dev.xxx.com到具体的目录即可。
841 |
842 |
843 | 步骤:
844 | 1. 在vps上执行,确保vps的80端口没被其它程序占用。
845 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
846 | `./proxy server -r ":80@:80" -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
847 |
848 | 1. 在自己笔记本上面执行
849 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
850 |
851 | 1. 完成
852 |
853 | ### 4.4、UDP普通用法
854 | 背景:
855 | - 公司机器A提供了DNS解析服务,UDP:53端口
856 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
857 |
858 | 需求:
859 | 在家里能够通过设置本地dns为22.22.22.22,使用公司机器A进行域名解析服务。
860 |
861 | 步骤:
862 | 1. 在vps上执行
863 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
864 | `./proxy server --udp -r ":53@:53" -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
865 |
866 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
867 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
868 |
869 | 1. 完成
870 |
871 | ### 4.5、高级用法一
872 | 背景:
873 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口
874 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
875 |
876 | 需求:
877 | 为了安全,不想在VPS上能够访问到公司机器A,在家里能够通过访问本机的28080端口,
878 | 通过加密隧道访问到公司机器A的80端口。
879 |
880 | 步骤:
881 | 1. 在vps上执行
882 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
883 |
884 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
885 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
886 |
887 | 1. 在家里电脑上执行
888 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
889 |
890 | 1. 完成
891 |
892 | ### 4.6、高级用法二
893 | 提示:
894 | 如果同时有多个client连接到同一个bridge,需要指定不同的key,可以通过--k参数设定,--k可以是任意唯一字符串,
895 | 只要在同一个bridge上唯一即可。
896 | server连接到bridge的时候,如果同时有多个client连接到同一个bridge,需要使用--k参数选择client。
897 | 暴露多个端口重复-r参数即可.-r格式是:"本地IP:本地端口@clientHOST:client端口"。
898 |
899 | 背景:
900 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口,ftp服务21端口
901 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
902 |
903 | 需求:
904 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的28080端口访问到公司机器A的80端口
905 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的29090端口访问到公司机器A的21端口
906 |
907 | 步骤:
908 | 1. 在vps上执行
909 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
910 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -r ":29090@:21" --k test -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
911 |
912 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
913 | `./proxy client --k test -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
914 |
915 | 1. 完成
916 |
917 | ### 4.7.server的-r参数
918 | -r完整格式是:`PROTOCOL://LOCAL_IP:LOCAL_PORT@[CLIENT_KEY]CLIENT_LOCAL_HOST:CLIENT_LOCAL_PORT`
919 |
920 | 4.7.1.协议PROTOCOL:tcp、udp、ptcp、pudp。
921 | 比如: `-r "udp://:10053@:53" -r "tcp://:10800@:1080" -r ":8080@:80"`
922 | 如果指定了--udp参数,PROTOCOL默认为udp,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`默认为udp;
923 | 如果没有指定--udp参数,PROTOCOL默认为tcp,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`默认为tcp;
924 |
925 | 4.7.2.CLIENT_KEY:默认是default。
926 | 比如: -r "udp://:10053@[test1]:53" -r "tcp://:10800@[test2]:1080" -r ":8080@:80"
927 | 如果指定了--k参数,比如--k test,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`CLIENT_KEY默认为test;
928 | 如果没有指定--k参数,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`CLIENT_KEY默认为default;
929 |
930 | 4.7.3.LOCAL_IP为空默认是:`0.0.0.0`,CLIENT_LOCAL_HOST为空默认是:`127.0.0.1`;
931 |
932 | ### 4.8.server和client通过代理连接bridge
933 | 有时候server或者client所在的网络不能直接访问外网,需要通过一个https或者socks5代理才能上网,那么这个时候
934 | -J参数就可以帮助你让server或者client通过https或者socks5代理去连接bridge。
935 | -J参数格式如下:
936 |
937 | https代理写法:
938 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
939 | https://username:password@host:port
940 | 代理不需要认证
941 | https://host:port
942 |
943 | socks5代理写法:
944 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
945 | socks5://username:password@host:port
946 | 代理不需要认证
947 | socks5://host:port
948 |
949 | host:代理的IP或者域名
950 | port:代理的端口
951 |
952 | ### 4.9.内网穿透HTTP服务
953 |
954 | 通常HTTP请求客户端会使用server的ip和端口去设置HOST字段,但是与期望的后端实际HOST不一样,这样就造成了tcp是通的,
955 | 但后端依赖HOST字段定位虚拟主机就不能工作.现在用--http-host参数强制设置http头部的HOST字段值为后端实际的
956 | 域名和端口即可轻松解决。
957 |
958 | `server`的--http-host参数格式如下:
959 |
960 | `--http-host www.test.com:80@2200`,如果server监听多个端口,只需要重复`--http-host`参数设置每个端口的HOST即可。
961 |
962 | 实例:
963 |
964 | 比如client本地nginx,127.0.0.1:80提供了web服务,其中绑定了一个域名`local.com`。
965 |
966 | 那么server的启动参数可以如下:
967 |
968 | `proxy server -P :30000 -r :2500@127.0.0.1:80 --http-host local.com@2500`
969 |
970 | 解释:
971 |
972 | `-r :2500@127.0.0.1:80` 和 `--http-host local.com:80@2500` 里面的2500端口是server本地监听的端口
973 |
974 | 当使用http协议请求server的ip:2500端口的时候,http的头部HOST字段就会被设置为`local.com`。
975 |
976 | ### 4.10 关于流量统计
977 |
978 | 如果单独启动一个server对接上级是proxy-admin控制面板,需要在上级控制面板里面新建一个映射,获得个映射规则的ID,
979 |
980 | 然后启动server的时候加上参数 --server-id=映射规则的ID 才能统计到流量。
981 |
982 | ### 4.11 关于p2p
983 | 内网穿透支持在server和client网络情况满足的情况下,server和client之间通过p2p直接连接,开启方法是:
984 |
985 | 在启动bridge,server,client到时候都加上`--p2p`参数即可。server的-r参数可以针对端口是否启用p2p(ptcp和pudp)。
986 |
987 | 如果server和client之间p2p打洞失败,那么会自动切换使用bridge中转传输数据。
988 |
989 | ### 4.12 客户端key白名单
990 | 内网穿透bridge可以设置客户端key白名单,参数是--client-keys,格式可以是:
991 |
992 | a.文件名,文件内容一行一个客户端key只能包含数字字母下划线,也就是客户端启动参数--k的值,只有客户端key在此白名单的客户端才能连接。# 开头的行,为注释。
993 |
994 | b.“base64://”开头的base64编码的上面a说明的文件内容,比如:base64://ajfpoajsdfa=
995 |
996 | c.”str://“开头的英文逗号分割的多个key,比如:str://default,company,school
997 |
998 | 默认是空,允许所有key。
999 |
1000 | ### 4.13 网络NAT类型判断
1001 |
1002 | nat类型判断,方便查看网络是否支持p2p,可以执行:`proxy tools -a nattype`
1003 |
1004 | ### 4.14 查看帮助
1005 | `./proxy help bridge`
1006 | `./proxy help server`
1007 | `./proxy help client`
1008 |
1009 | ## 5.SOCKS5代理
1010 | 提示:
1011 |
1012 | SOCKS5代理,支持CONNECT,UDP协议,不支持BIND,支持用户名密码认证。
1013 |
1014 | ***如果你的VPS是阿里云,腾讯云这种VPS,就是ifconfig看不见你的公网IP,只能看见内网IP,***
1015 |
1016 | ***那么需要加上`-g VPS公网IP`参数,SOCKS5代理的UDP功能才能正常工作。***
1017 |
1018 | ### 5.1 普通SOCKS5代理
1019 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080"`
1020 |
1021 | -p参数支持的写法:
1022 |
1023 | ```text
1024 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
1025 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
1026 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
1027 | ```
1028 |
1029 | ### 5.2.普通二级SOCKS5代理
1030 | 
1031 | 使用本地端口8090,假设上级SOCKS5代理是`22.22.22.22:8080`
1032 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" `
1033 | 我们还可以指定网站域名的黑白名单文件,一行一个域名,匹配规则是最右匹配,比如:baidu.com,匹配的是*.*.baidu.com,黑名单的域名域名直接走上级代理,白名单的域名不走上级代理;如果域名即在黑名单又在白名单中,那么黑名单起作用。
1034 | `./proxy socks -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" -b blocked.txt -d direct.txt`
1035 |
1036 | ### 5.3.SOCKS二级代理(加密)
1037 | 
1038 | 一级SOCKS代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
1039 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1040 |
1041 | 二级SOCKS代理(本地Linux)
1042 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1043 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080。
1044 |
1045 | 二级SOCKS代理(本地windows)
1046 | `./proxy.exe socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1047 | 然后设置你的windos系统中,需要通过代理上网的程序的代理为socks5模式,地址为:127.0.0.1,端口为:8080,程序即可通过加密通道通过vps上网。
1048 |
1049 | ### 5.4.SOCKS三级代理(加密)
1050 | 
1051 | 一级SOCKS代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
1052 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1053 | 二级SOCKS代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
1054 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1055 | 三级SOCKS代理(本地)
1056 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1057 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问一级SOCKS代理上面的代理端口38080。
1058 |
1059 | ### 5.5.SOCKS代理流量强制走上级SOCKS代理
1060 | 默认情况下,proxy会智能判断一个网站域名是否无法访问,如果无法访问才走上级SOCKS代理.通过--always可以使全部SOCKS代理流量强制走上级SOCKS代理。
1061 | `./proxy socks --always -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1062 |
1063 | ### 5.6.SOCKS通过SSH中转
1064 | 
1065 | 说明:ssh中转的原理是利用了ssh的转发功能,就是你连接上ssh之后,可以通过ssh代理访问目标地址。
1066 | 假设有:vps
1067 | - IP是2.2.2.2, ssh端口是22, ssh用户名是:user, ssh用户密码是:demo
1068 | - 用户user的ssh私钥名称是user.key
1069 |
1070 | #### *5.6.1 ssh用户名和密码的方式*
1071 | 本地SOCKS5代理28080端口,执行:
1072 | `./proxy socks -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -D demo -t tcp -p ":28080"`
1073 | #### *5.6.2 ssh用户名和密钥的方式*
1074 | 本地SOCKS5代理28080端口,执行:
1075 | `./proxy socks -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -S user.key -t tcp -p ":28080"`
1076 |
1077 | 那么访问本地的28080端口就是通过VPS访问目标地址。
1078 |
1079 | ### 5.7.认证
1080 | 对于socks5代理协议我们可以进行用户名密码认证,认证的用户名和密码可以在命令行指定
1081 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1" -a "user2:pass2"`
1082 | 多个用户,重复-a参数即可。
1083 | 也可以放在文件中,格式是一行一个"用户名:密码",然后用-F指定。
1084 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":33080" -F auth-file.txt`
1085 |
1086 | ### 5.8.KCP协议传输
1087 | KCP协议需要--kcp-key参数设置一个密码用于加密解密数据
1088 |
1089 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
1090 | `./proxy socks -t kcp -p ":38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
1091 |
1092 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
1093 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T kcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
1094 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080,数据通过kcp协议传输。
1095 |
1096 | ### 5.9.自定义DNS
1097 | --dns-address和--dns-ttl参数,用于自己指定proxy访问域名的时候使用的dns(--dns-address)
1098 | 以及解析结果缓存时间(--dns-ttl)秒数,避免系统dns对proxy的干扰,另外缓存功能还能减少dns解析时间提高访问速度。
1099 | 比如:
1100 | `./proxy socks -p ":33080" --dns-address "8.8.8.8:53" --dns-ttl 300`
1101 |
1102 | ### 5.10 自定义加密
1103 | proxy的socks代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可,
1104 | 加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
1105 |
1106 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以。
1107 |
1108 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
1109 |
1110 | 二级实例
1111 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1112 | `proxy socks -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
1113 | 本地二级执行:
1114 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
1115 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
1116 |
1117 |
1118 | 三级实例
1119 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1120 | `proxy socks -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
1121 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
1122 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
1123 | 本地三级执行:
1124 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
1125 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
1126 |
1127 | ### 5.11 压缩传输
1128 | proxy的socks代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以
1129 | 对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,
1130 | 一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
1131 |
1132 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据。
1133 |
1134 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
1135 |
1136 | 二级实例
1137 |
1138 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1139 | `proxy socks -t tcp -m -p :7777`
1140 | 本地二级执行:
1141 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
1142 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
1143 |
1144 |
1145 | 三级实例
1146 |
1147 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1148 | `proxy socks -t tcp -m -p :7777`
1149 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
1150 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
1151 | 本地三级执行:
1152 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
1153 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
1154 |
1155 |
1156 | ### 5.12 负载均衡
1157 |
1158 | SOCKS代理支持上级负载均衡,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
1159 |
1160 | `proxy socks --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
1161 |
1162 | ### 5.12.1 设置重试间隔和超时时间
1163 |
1164 | `proxy socks --lb-method=leastconn --lb-retrytime 300 --lb-timeout 300 -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
1165 |
1166 | ### 5.12.2 设置权重
1167 |
1168 | `proxy socks --lb-method=weight -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -P 2.1.1.1:33080?w=2 -P 3.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -p :33080 -t tcp`
1169 |
1170 | ### 5.12.3 使用目标地址选择上级
1171 |
1172 | `proxy socks --lb-hashtarget --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
1173 |
1174 | ### 5.13 限速
1175 |
1176 | 限速100K,通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
1177 |
1178 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -l 100K`
1179 |
1180 | ### 5.14 指定`出口IP`
1181 |
1182 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果`入口IP`是内网IP,`出口IP`不会使用`入口IP`。
1183 |
1184 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 --bind-listen`
1185 |
1186 | ### 5.15 级联认证
1187 |
1188 | SOCKS5支持级联认证,-A可以设置上级认证信息。
1189 |
1190 | 上级:
1191 |
1192 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -a user:pass`
1193 |
1194 | 本地:
1195 |
1196 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -A user:pass -t tcp -p :33080`
1197 |
1198 | 请更多认证细节,请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
1199 |
1200 | ### 5.16 证书参数使用base64数据
1201 |
1202 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
1203 |
1204 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
1205 |
1206 |
1207 | ### 5.17 智能模式
1208 | 智能模式设置,可以是intelligent|direct|parent三者之一。
1209 | 默认是:intelligent。
1210 | 每个值的含义如下:
1211 | `--intelligent=direct`,不在blocked里面的目标都直连。
1212 | `--intelligent=parent`,不在direct里面的目标都走上级。
1213 | `--intelligent=intelligent`,blocked和direct里面都没有的目标,智能判断是否使用上级访问目标。
1214 |
1215 | ### 5.18 固定UDP功能端口
1216 |
1217 | 默认情况下socks5的UDP功能的端口号,proxy是按着`rfc1982草案`要求,使用协议握手过程中随机指定,不需要提前指定。
1218 |
1219 | 但是某些情况下,需要固定UDP功能端口,可以通过参数`--udp-port 端口号`用来固定UDP功能的端口号,比如:
1220 |
1221 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --udp-port 38080`
1222 |
1223 | ### 5.19 查看帮助
1224 | `./proxy help socks`
1225 |
1226 | ## 6.SPS协议转换
1227 |
1228 | ### 6.1 功能介绍
1229 | 代理协议转换使用的是sps子命令,sps本身不提供代理功能,只是接受代理请求"转换并转发"给已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理或者ss代理;sps可以把已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理或ss代理转换为一个端口同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的代理,而且http(s)代理支持正向代理和反向代理(SNI),转换后的SOCKS5代理,当上级是SOCKS5或者SS时仍然支持UDP功能;另外对于已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理,支持tls、tcp、kcp三种模式,支持链式连接,也就是可以多个sps结点层级连接构建加密通道。
1230 |
1231 | `ss`功能支持的加密方法为:aes-128-cfb , aes-128-ctr , aes-128-gcm , aes-192-cfb , aes-192-ctr , aes-192-gcm , aes-256-cfb , aes-256-ctr , aes-256-gcm , bf-cfb , cast5-cfb , chacha20 , chacha20-ietf , chacha20-ietf-poly1305 , des-cfb , rc4-md5 , rc4-md5-6 , salsa20 , xchacha20
1232 |
1233 | 本地监听端口-p参数支持的写法:
1234 |
1235 | ```text
1236 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
1237 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
1238 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
1239 | ```
1240 |
1241 | ### 6.2 HTTP(S)转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
1242 | 假设已经存在一个普通的http(s)代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1243 | 命令如下:
1244 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1245 |
1246 | 假设已经存在一个tls的http(s)代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,tls需要证书文件,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1247 | 命令如下:
1248 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1249 |
1250 | 假设已经存在一个kcp的http(s)代理(密码是:demo123):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1251 | 命令如下:
1252 | `./proxy sps -S http -T kcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 --kcp-key demo123 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1253 |
1254 | ### 6.3 SOCKS5转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
1255 | 假设已经存在一个普通的socks5代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1256 | 命令如下:
1257 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1258 |
1259 | 假设已经存在一个tls的socks5代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,tls需要证书文件,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1260 | 命令如下:
1261 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T tls -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1262 |
1263 | 假设已经存在一个kcp的socks5代理(密码是:demo123):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1264 | 命令如下:
1265 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T kcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 --kcp-key demo123 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1266 |
1267 | ### 6.4 SS转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
1268 | SPS上级和本地支持ss协议,上级可以是SPS或者标准的ss服务。
1269 | SPS本地默认提供HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS三种代理,当上级是SOCKS5时转换后的SOCKS5和SS支持UDP功能。
1270 | 假设已经存在一个普通的SS或者SPS代理(开启了ss,加密方式:aes-256-cfb,密码:demo):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,转换后的ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1271 | 命令如下:
1272 | `./proxy sps -S ss -H aes-256-cfb -J pass -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`。
1273 |
1274 | ### 6.5 链式连接
1275 | 
1276 | 上面提过多个sps结点可以层级连接构建加密通道,假设有如下vps和家里的pc电脑。
1277 | vps01:2.2.2.2
1278 | vps02:3.3.3.3
1279 | 现在我们想利用pc和vps01和vps02构建一个加密通道,本例子用tls加密也可以用kcp,在pc上访问本地18080端口就是访问vps01的本地8080端口。
1280 | 首先在vps01(2.2.2.2)上我们运行一个只有本地可以访问的http(s)代理,执行:
1281 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p 127.0.0.1:8080`
1282 |
1283 | 然后在vps01(2.2.2.2)上运行一个sps结点,执行:
1284 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tls -p :8081 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1285 |
1286 | 然后在vps02(3.3.3.3)上运行一个sps结点,执行:
1287 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:8081 -t tls -p :8082 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1288 |
1289 | 然后在pc上运行一个sps结点,执行:
1290 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 3.3.3.3:8082 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1291 |
1292 | 完成。
1293 |
1294 | ### 6.6 监听多个端口
1295 | 一般情况下监听一个端口就可以,不过如果作为反向代理需要同时监听80和443两个端口,那么-p参数是支持的,
1296 | 格式是:`-p 0.0.0.0:80,0.0.0.0:443`,多个绑定用逗号分隔即可。
1297 |
1298 | ### 6.7 认证功能
1299 | sps支持http(s)\socks5代理认证,可以级联认证,有四个重要的信息:
1300 | 1:用户发送认证信息`user-auth`。
1301 | 2:设置的本地认证信息`local-auth`。
1302 | 3:设置的连接上级使用的认证信息`parent-auth`。
1303 | 4:最终发送给上级的认证信息`auth-info-to-parent`。
1304 | 他们的情况关系如下:
1305 |
1306 | | user-auth | local-auth | parent-auth | auth-info-to-paren
1307 | | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------
1308 | | 有/没有 | 有 | 有 | 来自parent-auth
1309 | | 有/没有 | 没有 | 有 | 来自parent-auth
1310 | | 有/没有 | 有 | 没有 | 无
1311 | | 没有 | 没有 | 没有 | 无
1312 | | 有 | 没有 | 没有 | 来自user-auth
1313 |
1314 | 对于sps代理我们可以进行用户名密码认证,认证的用户名和密码可以在命令行指定
1315 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1:0:0:" -a "user2:pass2:0:0:"`
1316 | 多个用户,重复-a参数即可。
1317 | 也可以放在文件中,格式是一行一个`用户名:密码:连接数:速率:上级`,然后用-F指定。
1318 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -F auth-file.txt`
1319 |
1320 | 如果上级有认证,下级可以通过-A参数设置认证信息,比如:
1321 | 上级:`./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1:0:0:" -a "user2:pass2:0:0:"`
1322 | 下级:`./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -A "user1:pass1" -t tcp -p ":33080" `
1323 |
1324 | 请更多认证细节,请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
1325 |
1326 | ### 6.8 多个上级
1327 |
1328 | 如果存在多个上级,可以通过多个-P指定。
1329 |
1330 | 比如:
1331 |
1332 | `proxy sps -P http://127.0.0.1:3100 -P socks5://127.0.0.1:3200`
1333 |
1334 | `-P`完整格式如下:
1335 |
1336 | `protocol://a:b@2.2.2.2:33080#1`
1337 |
1338 | 下面对每部分进行解释:
1339 |
1340 | `protocol://` 是协议类型,可能的类型以及含有如下:
1341 |
1342 | ```text
1343 | http 等价于 -S http -T tcp
1344 | https 等价于 -S http -T tls --parent-tls-single , 也就是http(s)代理 over TLS
1345 | https2 等价于 -S http -T tls
1346 | socks5 等价于 -S socks -T tcp
1347 | socks5s 等价于 -S socks -T tls --parent-tls-single , 也就是socks over TLS
1348 | socks5s2 等价于 -S socks -T tls
1349 | ss 等价于 -S ss -T tcp
1350 | httpws 等价于 -S http -T ws
1351 | httpwss 等价于 -S http -T wss
1352 | socks5ws 等价于 -S socks -T ws
1353 | socks5wss 等价于 -S socks -T wss
1354 | ```
1355 |
1356 | `a:b`是代理认证的用户名密码,如果是ss,`a`是加密方法,`b`是密码,没有用户名密码可以留空比如:`http://2.2.2.2:33080`,如果用户名和密码保护特殊符号可以使用urlencode进行编码。
1357 |
1358 | `2.2.2.2:33080`是上级地址,格式是:`IP(或域名):端口`,如果底层是ws/wss协议还可以带上路径,比如:`2.2.2.2:33080/ws`;
1359 | 还能通过附加查询参数`m`和`k`设置`ws\wss`的`加密方法`和`密码`,比如:`2.2.2.2:33080/ws?m=aes-192-cfb&k=password`
1360 |
1361 | `#1`多个上级的负载均衡是权重策略时候,设置的权重,很少用到。
1362 |
1363 | ### 6.9 自定义加密
1364 | proxy的sps代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行
1365 | 自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义
1366 | 一个密码即可,加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
1367 |
1368 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以。
1369 |
1370 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
1371 |
1372 | 假设已经存在一个http(s)代理:`6.6.6.6:6666`
1373 |
1374 | 二级实例
1375 |
1376 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1377 | `proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 6.6.6.6:6666 -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
1378 | 本地二级执行:
1379 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
1380 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
1381 |
1382 |
1383 | 三级实例
1384 |
1385 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1386 | `proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 6.6.6.6:6666 -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
1387 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
1388 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
1389 | 本地三级执行:
1390 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
1391 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
1392 |
1393 | ### 6.10 压缩传输
1394 | proxy的sps代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以
1395 | 对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,
1396 | 一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
1397 |
1398 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据。
1399 |
1400 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
1401 |
1402 | 二级实例
1403 |
1404 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1405 | `proxy sps -t tcp -m -p :7777`
1406 | 本地二级执行:
1407 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
1408 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
1409 |
1410 |
1411 | 三级实例
1412 |
1413 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1414 | `proxy sps -t tcp -m -p :7777`
1415 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
1416 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
1417 | 本地三级执行:
1418 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
1419 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
1420 |
1421 | ### 6.11 禁用协议
1422 | SPS默认情况下一个端口支持http(s)和socks5两种代理协议,我们可以通过参数禁用某个协议
1423 | 比如:
1424 | 1.禁用HTTP(S)代理功能只保留SOCKS5代理功能,参数:`--disable-http`。
1425 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080 --disable-http`
1426 |
1427 | 1.禁用SOCKS5代理功能只保留HTTP(S)代理功能,参数:`--disable-socks`。
1428 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080 --disable-http`
1429 |
1430 | ### 6.12 限速
1431 |
1432 | 假设存在SOCKS5上级:
1433 |
1434 | `proxy socks -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -z password -t tcp`
1435 |
1436 | sps下级,限速100K
1437 |
1438 | `proxy sps -S socks -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -T tcp -Z password -l 100K -t tcp -p :33080`
1439 |
1440 | 通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
1441 |
1442 | ### 6.13 指定`出口IP`
1443 |
1444 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果`入口IP`是内网IP,`出口IP`不会使用`入口IP`。
1445 |
1446 | `proxy sps -S socks -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -T tcp -Z password -l 100K -t tcp --bind-listen -p :33080`
1447 |
1448 | ### 6.14 证书参数使用base64数据
1449 |
1450 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
1451 |
1452 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
1453 |
1454 | ### 6.15 独立服务
1455 | sps功能不强制指定一个上级,当上级为空,sps本身即可完成完整的代理功能.如果指定了上级那么就和之前一样使用上级连接目标。
1456 | 下面这个命令,就是一键开启http(s)\ss\socks服务。
1457 | `./proxy sps -p :33080`
1458 |
1459 | ### 6.16 目标重定向
1460 | sps功能提供的http(s)\socks5\ss代理功能,客户端通过sps代理去连接指定的“目标”,这个“目标”一般是网站也可能是任意的tcp地址,
1461 | 网站”目标“一般是foo.com:80,foo.com:443,sps支持使用--rewrite参数指定一个“目标”重定向规则文件,对目标进行重定向,客户端是无感知的,
1462 | 比如你对“目标”:demo.com:80重定向到192.168.0.12:80,那么客户端访问网站demo.com,其实访问的是192.168.0.12提供的网站服务。
1463 | “目标”重定向规则文件示例:
1464 |
1465 | ```text
1466 | # example
1467 | www.a.com:80 10.0.0.2:8080
1468 | **.b.com:80 10.0.0.2:80
1469 | 192.168.0.11:80 10.0.0.2:8080
1470 | ```
1471 |
1472 | ### 6.17 固定UDP功能端口
1473 |
1474 | 默认情况下sps的socks5的UDP功能的端口号是按着`rfc1982草案`要求,使用协议握手过程中随机指定,不需要提前指定。
1475 |
1476 | 但是某些情况下,需要固定UDP功能端口,可以通过参数`--udp-port 端口号`用来固定UDP功能的端口号,比如:
1477 |
1478 | `./proxy sps -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --udp-port 38081`
1479 |
1480 | 需要注意的是,sps的ss功能也有UDP功能,而且ss的UDP端口和tcp端口是一样的,所以要避免socks5的UDP端口和ss的UDP端口冲突,
1481 |
1482 | 要指定和tcp端口不一样的端口。
1483 |
1484 | ### 6.18 iptables 透明代理
1485 | sps模式支持Linux系统的iptables转发支持,也就是通常所说的iptables透明代理,如果在网关设备上进行iptables透明代理,那么对通过网关联网的设备就能实现无感知的代理。
1486 |
1487 | 启动命令实例:
1488 |
1489 | `./proxy sps --redir -p :8888 -P httpws://1.1.1.1:33080`
1490 |
1491 | 这里假设存在一个http的上级代理1.1.1.1:33080,使用ws传输数据。
1492 |
1493 | 然后添加iptables规则,下面是参考规则:
1494 | ```shell
1495 | #上级proxy服务端服务器IP地址:
1496 | proxy_server_ip=1.1.1.1
1497 |
1498 | #路由器运行proxy监听的端口:
1499 | proxy_local_port=33080
1500 |
1501 | #下面的就不用修改了
1502 | #create a new chain named PROXY
1503 | iptables -t nat -N PROXY
1504 |
1505 | # Ignore your PROXY server's addresses
1506 | # It's very IMPORTANT, just be careful。
1507 |
1508 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d $proxy_server_ip -j RETURN
1509 |
1510 | # Ignore LANs IP address
1511 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 0.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
1512 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 10.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
1513 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 127.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
1514 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 169.254.0.0/16 -j RETURN
1515 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 172.16.0.0/12 -j RETURN
1516 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 192.168.0.0/16 -j RETURN
1517 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 224.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
1518 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 240.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
1519 |
1520 | # Anything to port 80 443 should be redirected to PROXY's local port
1521 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
1522 | # Apply the rules to nat client
1523 | iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -j PROXY
1524 | # Apply the rules to localhost
1525 | iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp -j PROXY
1526 | ```
1527 | - 清空整个链 iptables -F 链名比如iptables -t nat -F PROXY
1528 | - 删除指定的用户自定义链 iptables -X 链名 比如 iptables -t nat -X PROXY
1529 | - 从所选链中删除规则 iptables -D 链名 规则详情 比如 iptables -t nat -D PROXY -d 223.223.192.0/255.255.240.0 -j RETURN
1530 |
1531 | ### 6.19 查看帮助
1532 |
1533 | `./proxy help sps`
1534 |
1535 | ## 7.KCP配置
1536 |
1537 | ### 7.1 配置介绍
1538 | proxy的很多功能都支持kcp协议,凡是使用了kcp协议的功能都支持这里介绍的配置参数。
1539 | 所以这里统一对KCP配置参数进行介绍。
1540 |
1541 | ### 7.2 详细配置
1542 | 所有的KCP配置参数共有17个,你可以都不用设置,他们都有默认值,如果为了或者最好的效果,
1543 | 就需要自己根据自己根据网络情况对参数进行配置。由于kcp配置很复杂需要一定的网络基础知识,
1544 | 如果想获得kcp参数更详细的配置和解说,请自行搜索。每个参数的命令行名称以及默认值和简单的功能说明如下:
1545 | ```
1546 | --kcp-key="secrect" pre-shared secret between client and server
1547 | --kcp-method="aes" encrypt/decrypt method, can be: aes, aes-128, aes-192, salsa20, blowfish,
1548 | twofish, cast5, 3des, tea, xtea, xor, sm4, none
1549 | --kcp-mode="fast" profiles: fast3, fast2, fast, normal, manual
1550 | --kcp-mtu=1350 set maximum transmission unit for UDP packets
1551 | --kcp-sndwnd=1024 set send window size(num of packets)
1552 | --kcp-rcvwnd=1024 set receive window size(num of packets)
1553 | --kcp-ds=10 set reed-solomon erasure coding - datashard
1554 | --kcp-ps=3 set reed-solomon erasure coding - parityshard
1555 | --kcp-dscp=0 set DSCP(6bit)
1556 | --kcp-nocomp disable compression
1557 | --kcp-acknodelay be carefull! flush ack immediately when a packet is received
1558 | --kcp-nodelay=0 be carefull!
1559 | --kcp-interval=50 be carefull!
1560 | --kcp-resend=0 be carefull!
1561 | --kcp-nc=0 be carefull! no congestion
1562 | --kcp-sockbuf=4194304 be carefull!
1563 | --kcp-keepalive=10 be carefull!
1564 | ```
1565 | 提示:
1566 | 参数:--kcp-mode中的四种fast3, fast2, fast, normal模式,
1567 | 相当于设置了下面四个参数:
1568 | normal:`--nodelay=0 --interval=40 --resend=2 --nc=1`
1569 | fast :`--nodelay=0 --interval=30 --resend=2 --nc=1`
1570 | fast2:`--nodelay=1 --interval=20 --resend=2 --nc=1`
1571 | fast3:`--nodelay=1 --interval=10 --resend=2 --nc=1`
1572 |
1573 | ## 8.安全DNS
1574 |
1575 | ### 8.1 介绍
1576 | 众所周知DNS是UDP端口53提供的服务,但是随着网络的发展一些知名DNS服务器也支持TCP方式dns查询,比如谷歌的8.8.8.8,proxy的DNS防污染服务器原理就是在本地启动一个proxy的DNS代理服务器,它用TCP的方式通过上级代理进行dns查询。如果它和上级代理通讯采用加密的方式,那么就可以进行安全无污染的DNS解析,还支持独立服务,并发解析,支持增强的hosts文件功能支持灵活的并发解析转发。
1577 |
1578 | dns解析顺序:
1579 | 1.使用参数--hosts解析。
1580 | 2.要解析的域名在1中没有找到,就使用参数--forward规则解析。
1581 | 3.要解析的域名在1和2中都没有找到,就使用默认--default解析,--default默认行为参数值有三种:proxy,direct,system。
1582 | 三种参数值解释如下:
1583 | proxy:通过上级去连接-q参数指定的dns服务器去解析域名。
1584 | direct:通过本地网络去连接-q参数指定的dns服务器去解析域名。
1585 | system:通过系统dns去解析域名。
1586 |
1587 | 提示:
1588 | --hosts 参数指定的host文件格式和系统hosts文件一致,而且域名支持通配符,可以参考hosts文件。
1589 | --forward 参数指定的解析转发规则文件,格式可以参考resolve.rules文件,域名支持通配符,支持为每个域名指定多个dns服务器并发解析,谁最快解析成功就用谁的解析结果。
1590 | -q 参数可以指定多个远程dns服务器,执行并发解析谁最快解析成功就用谁的解析结果,默认是:1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8,9.9.9.9,多个用逗号分割,
1591 | 比如还可以带端口:1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8#53,9.9.9.9
1592 |
1593 | 如果独立服务,不需要上级:
1594 | 可以执行:
1595 | `proxy dns --default system -p :5353`
1596 | or
1597 | `proxy dns --default direct -p :5353`
1598 |
1599 | ### 8.2 使用示例
1600 |
1601 | #### 8.2.1 普通HTTP(S)上级代理
1602 |
1603 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1604 | 本地执行:
1605 | `proxy dns -S http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1606 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了DNS解析功能。
1607 |
1608 | #### 8.2.2 普通SOCKS5上级代理
1609 |
1610 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1611 | 本地执行:
1612 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1613 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了DNS解析功能。
1614 |
1615 | #### 8.2.3 TLS加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
1616 |
1617 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1618 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1619 | `proxy http -t tls -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :33080`
1620 | 本地执行:
1621 | `proxy dns -S http -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :53`
1622 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1623 |
1624 | #### 8.2.4 TLS加密的SOCKS5上级代理
1625 |
1626 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1627 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1628 | `proxy socks -t tls -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :33080`
1629 | 本地执行:
1630 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :53`
1631 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1632 |
1633 | #### 8.2.5 KCP加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
1634 |
1635 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1636 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1637 | `proxy http -t kcp -p :33080`
1638 | 本地执行:
1639 | `proxy dns -S http -T kcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1640 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1641 |
1642 | #### 8.2.6 KCP加密的SOCKS5上级代理
1643 |
1644 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1645 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1646 | `proxy socks -t kcp -p :33080`
1647 | 本地执行:
1648 | `proxy dns -S socks -T kcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1649 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1650 |
1651 | #### 8.2.7 自定义加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
1652 |
1653 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1654 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1655 | `proxy http -t tcp -p :33080 -z password`
1656 | 本地执行:
1657 | `proxy dns -S http -T tcp -Z password -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1658 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1659 |
1660 | #### 8.2.8 自定义加密的SOCKS5上级代理
1661 |
1662 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1663 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1664 | `proxy socks -t kcp -p :33080 -z password`
1665 | 本地执行:
1666 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tcp -Z password -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1667 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1668 |
1669 | ## 9.API认证,限速,控制连接数
1670 |
1671 | proxy的http(s)/socks5/sps代理功能,支持通过API控制用户对代理对访问。
1672 |
1673 | ### 通过API可以干什么?
1674 |
1675 | - 用户维度,控制单个连接速率,控制最大连接数。
1676 | - IP维度,控制单个连接速率,控制最大连接数。
1677 | - 动态上级,可以根据用户或者客户端IP,动态的从API获取其上级,支持http(s)/socks5/ss上级。
1678 | - 认证每一个连接,无论是否要求客户端认证。
1679 | - 缓存认证结果,时间可以设置,减轻API压力。
1680 |
1681 | #### 具体使用
1682 | proxy的http(s)/socks5/sps代理API功能,通过`--auth-url`和`--auth-nouser`和`--auth-cache`三个参数控制。
1683 | 参数`--auth-url`是HTTP API接口地址,客户端连接的时候,proxy会GET方式请求这url,带上下面参数,如果返回HTTP状态码204,代表认证成功,其它情况认为认证失败。
1684 |
1685 | 一个完整的请求API的示例:
1686 | `http://test.com/auth.php?user=a&pass=b&client_addr=127.0.0.1:49892&local_addr=127.0.0.1:8100&target=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.baidu.com&service=http&sps=0`
1687 |
1688 | #### 参数说明
1689 | `user和pass` 当代理开启了认证功能,这里就是客户端提供的用户名和密码。
1690 | `client_addr` 客户端访问代理时的用的地址,格式IP:端口。
1691 | `local_addr` 客户端访问的代理地址,格式IP:端口。
1692 | `service` 代理类型,分为:http、socks。
1693 | `sps` 代理是否是sps提供的,1:是,0:否。
1694 | `target` 客户端要访问的目标,如果是http(s)代理,target是访问的具体url;如果是socks5代理,target是空。
1695 |
1696 | #### 示例
1697 | 假设--auth-url http://127.0.0.1:333/auth.php 指向了一个php接口地址.
1698 | auth.php内容如下:
1699 |
1700 | ```php
1701 | 注意: 后面二级代理使用的`proxy.crt`和`proxy.key`应与一级代理一致
2041 |
2042 | 
2043 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
2044 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2045 |
2046 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
2047 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2048 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080。
2049 |
2050 | 二级HTTP代理(本地windows)
2051 | `./proxy.exe http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2052 | 然后设置你的windos系统中,需要通过代理上网的程序的代理为http模式,地址为:127.0.0.1,端口为:8080,程序即可通过加密通道通过vps上网。
2053 |
2054 | ### 1.4.HTTP三级代理(加密)
2055 | 
2056 | 一级HTTP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2057 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2058 | 二级HTTP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2059 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2060 | 三级HTTP代理(本地)
2061 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2062 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问一级HTTP代理上面的代理端口38080。
2063 |
2064 | ### 1.5.Basic认证,API认证
2065 |
2066 | 请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
2067 |
2068 | ### 1.6.HTTP代理流量强制走上级HTTP代理
2069 | 默认情况下,proxy会智能判断一个网站域名是否无法访问,如果无法访问才走上级HTTP代理.通过--always可以使全部HTTP代理流量强制走上级HTTP代理。
2070 | `./proxy http --always -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2071 |
2072 | ### 1.7.HTTP(S)通过SSH中转
2073 | 
2074 | 说明:ssh中转的原理是利用了ssh的转发功能,就是你连接上ssh之后,可以通过ssh代理访问目标地址。
2075 | 假设有:vps
2076 | - IP是2.2.2.2, ssh端口是22, ssh用户名是:user, ssh用户密码是:demo
2077 | - 用户user的ssh私钥名称是user.key
2078 |
2079 | #### *1.7.1 ssh用户名和密码的方式*
2080 | 本地HTTP(S)代理28080端口,执行:
2081 | `./proxy http -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -D demo -t tcp -p ":28080"`
2082 | #### *1.7.2 ssh用户名和密钥的方式*
2083 | 本地HTTP(S)代理28080端口,执行:
2084 | `./proxy http -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -S user.key -t tcp -p ":28080"`
2085 |
2086 | ### 1.8.KCP协议传输
2087 | 
2088 | KCP协议需要--kcp-key参数设置一个密码用于加密解密数据
2089 |
2090 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
2091 | `./proxy http -t kcp -p ":38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
2092 |
2093 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
2094 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T kcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
2095 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080,数据通过kcp协议传输,注意kcp走的是udp协议协议,所以防火墙需放开38080的udp协议。
2096 |
2097 | ### 1.9 HTTP(S)反向代理
2098 | 
2099 | proxy不仅支持在其他软件里面通过设置代理的方式,为其他软件提供代理服务,而且支持直接把请求的网站域名解析到proxy监听的ip上,然后proxy监听80和443端口,那么proxy就会自动为你代理访问需要访问的HTTP(S)网站。
2100 |
2101 | 使用方式:
2102 | 在"最后一级proxy代理"的机器上,因为proxy要伪装成所有网站,网站默认的端口HTTP是80,HTTPS是443,让proxy监听80和443端口即可.参数-p多个地址用逗号分割。
2103 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :80,:443`
2104 |
2105 | 这个命令就在机器上启动了一个proxy代理,同时监听80和443端口,既可以当作普通的代理使用,也可以直接把需要代理的域名解析到这个机器的IP上。
2106 |
2107 | 如果有上级代理那么参照上面教程设置上级即可,使用方式完全一样。
2108 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :80,:443 -T tls -P "2.2.2.2:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2109 |
2110 | 注意:
2111 | proxy所在的服务器的DNS解析结果不能受到自定义的解析影响,不然就死循环了,proxy代理最好指定`--dns 8.8.8.8`参数。
2112 |
2113 | ### 1.10 HTTP(S)透明代理
2114 | 该模式需要具有一定的网络基础,相关概念不懂的请自行搜索解决。
2115 | 假设proxy现在在路由器上运行,启动命令如下:
2116 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :33080 -T tls -P "2.2.2.2:33090" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2117 |
2118 | 然后添加iptables规则,下面是参考规则:
2119 | ```shell
2120 | #上级proxy服务端服务器IP地址:
2121 | proxy_server_ip=2.2.2.2
2122 |
2123 | #路由器运行proxy监听的端口:
2124 | proxy_local_port=33080
2125 |
2126 | #下面的就不用修改了
2127 | #create a new chain named PROXY
2128 | iptables -t nat -N PROXY
2129 |
2130 | # Ignore your PROXY server's addresses
2131 | # It's very IMPORTANT, just be careful。
2132 |
2133 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d $proxy_server_ip -j RETURN
2134 |
2135 | # Ignore LANs IP address
2136 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 0.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
2137 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 10.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
2138 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 127.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
2139 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 169.254.0.0/16 -j RETURN
2140 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 172.16.0.0/12 -j RETURN
2141 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 192.168.0.0/16 -j RETURN
2142 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 224.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
2143 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 240.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
2144 |
2145 | # Anything to port 80 443 should be redirected to PROXY's local port
2146 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
2147 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp --dport 443 -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
2148 |
2149 | # Apply the rules to nat client
2150 | iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -j PROXY
2151 | # Apply the rules to localhost
2152 | iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp -j PROXY
2153 | ```
2154 | - 清空整个链 iptables -F 链名比如iptables -t nat -F PROXY
2155 | - 删除指定的用户自定义链 iptables -X 链名 比如 iptables -t nat -X PROXY
2156 | - 从所选链中删除规则 iptables -D 链名 规则详情 比如 iptables -t nat -D PROXY -d 223.223.192.0/255.255.240.0 -j RETURN
2157 |
2158 | ### 1.11 自定义DNS
2159 | --dns-address和--dns-ttl参数,用于自己指定proxy访问域名的时候使用的dns(--dns-address)
2160 | 以及解析结果缓存时间(--dns-ttl)秒数,避免系统dns对proxy的干扰,另外缓存功能还能减少dns解析时间提高访问速度。
2161 | 比如:
2162 | `./proxy http -p ":33080" --dns-address "8.8.8.8:53" --dns-ttl 300`
2163 |
2164 | ### 1.12 自定义加密
2165 | proxy的http(s)代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义
2166 | 加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可,
2167 | 加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
2168 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以,下面分别用二级,三级为例:
2169 |
2170 | 二级实例
2171 |
2172 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2173 | `proxy http -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
2174 | 本地二级执行:
2175 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
2176 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
2177 |
2178 |
2179 | 三级实例
2180 |
2181 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2182 | `proxy http -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
2183 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
2184 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
2185 | 本地三级执行:
2186 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
2187 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
2188 |
2189 | ### 1.13 压缩传输
2190 | proxy的http(s)代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以对数据进行压缩,
2191 | 也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,
2192 | 一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
2193 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据,下面分别用二级,三级为例:
2194 |
2195 | 二级实例
2196 |
2197 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2198 | `proxy http -t tcp -m -p :7777`
2199 | 本地二级执行:
2200 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
2201 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
2202 |
2203 |
2204 | 三级实例
2205 |
2206 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2207 | `proxy http -t tcp -m -p :7777`
2208 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
2209 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
2210 | 本地三级执行:
2211 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
2212 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
2213 |
2214 | ### 1.14 负载均衡
2215 |
2216 | HTTP(S)代理支持上级负载均衡,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
2217 |
2218 | `proxy http --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080`
2219 |
2220 | ### 1.14.1 设置重试间隔和超时时间
2221 |
2222 | `proxy http --lb-method=leastconn --lb-retrytime 300 --lb-timeout 300 -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -t tcp -p :33080`
2223 |
2224 | ### 1.14.2 设置权重
2225 |
2226 | `proxy http --lb-method=weight -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -P 2.1.1.1:33080?w=2 -P 3.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -t tcp -p :33080`
2227 |
2228 | ### 1.14.3 使用目标地址选择上级
2229 |
2230 | `proxy http --lb-hashtarget --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -t tcp -p :33080`
2231 |
2232 | ### 1.15 限速
2233 |
2234 | 限速100K,通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
2235 |
2236 | `proxy http -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -l 100K`
2237 |
2238 | ### 1.16 指定出口IP
2239 |
2240 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作,此时代理会尝试不绑定IP去访问目标,同时日志会提示。
2241 |
2242 | `proxy http -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 --bind-listen`
2243 |
2244 | ### 1.17 证书参数使用base64数据
2245 |
2246 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
2247 |
2248 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
2249 |
2250 | ### 1.18 智能模式
2251 | 智能模式设置,可以是intelligent|direct|parent三者之一。
2252 | 默认是:intelligent。
2253 | 每个值的含义如下:
2254 | `--intelligent=direct`,不在blocked里面的目标都直连。
2255 | `--intelligent=parent`,不在direct里面的目标都走上级。
2256 | `--intelligent=intelligent`,blocked和direct里面都没有的目标,智能判断是否使用上级访问目标。
2257 |
2258 | ### 1.19 查看帮助
2259 | `./proxy help http`
2260 |
2261 | ## 2.TCP代理
2262 |
2263 | ### 2.1 普通一级TCP代理
2264 | 
2265 | 本地执行:
2266 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22"`
2267 | 那么访问本地33080端口就是访问192.168.22.33的22端口。
2268 |
2269 | `-p`参数支持的写法:
2270 |
2271 | ```text
2272 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
2273 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
2274 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
2275 | ```
2276 |
2277 | 如果本地监听端口数量大于1,那么将会连接与本地端口一致的对应上级端口,忽略`-P`里面的端口。
2278 |
2279 | 如果需要所有端口进来的连接,都连接到上级指定端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`。
2280 |
2281 | 比如:
2282 |
2283 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080-33085" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:0"`
2284 |
2285 | 那么`33080`端口进来的连接,将会连接192.168.22.33的`33080`端口,其它端口以此类推,本地和上级端口一致,此时参数`-P`里面的端口用`0`。
2286 |
2287 | 如果想无论是`33080`,`33081`等端口进来的连接都连接到192.168.22.33的`22`端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`
2288 |
2289 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080-33085" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --lock-port`
2290 |
2291 |
2292 | ### 2.2 普通二级TCP代理
2293 | 
2294 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
2295 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "127.0.0.1:8080"`
2296 | 本地执行:
2297 | `./proxy tcp -p ":23080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.33:33080"`
2298 | 那么访问本地23080端口就是访问22.22.22.33的8080端口。
2299 |
2300 | ### 2.3 普通三级TCP代理
2301 | 
2302 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2303 | `./proxy tcp -p ":38080" -T tcp -P "66.66.66.66:8080"`
2304 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2305 | `./proxy tcp -p ":28080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080"`
2306 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
2307 | `./proxy tcp -p ":8080" -T tcp -P "33.33.33.33:28080"`
2308 | 那么访问本地8080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问66.66.66.66的8080端口。
2309 |
2310 | ### 2.4 加密二级TCP代理
2311 | 
2312 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
2313 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "127.0.0.1:8080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2314 | 本地执行:
2315 | `./proxy tcp -p ":23080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.33:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2316 | 那么访问本地23080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问22.22.22.33的8080端口。
2317 |
2318 | ### 2.5 加密三级TCP代理
2319 | 
2320 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2321 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":38080" -T tcp -P "66.66.66.66:8080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2322 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2323 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2324 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
2325 | `./proxy tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2326 | 那么访问本地8080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问66.66.66.66的8080端口。
2327 |
2328 | ### 2.6 通过代理连接上级
2329 | 有时候proxy所在的网络不能直接访问外网,需要通过一个https或者socks5代理才能上网,那么这个时候
2330 | -J参数就可以帮助你让proxy的tcp端口映射的时候通过https或者socks5代理去连接上级-P,将外部端口映射到本地。
2331 | -J参数格式如下:
2332 |
2333 | https代理写法:
2334 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
2335 | https://username:password@host:port
2336 | 代理不需要认证
2337 | https://host:port
2338 |
2339 | socks5代理写法:
2340 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
2341 | socks5://username:password@host:port
2342 | 代理不需要认证
2343 | socks5://host:port
2344 |
2345 | host:代理的IP或者域名
2346 | port:代理的端口
2347 |
2348 | ### 2.7 指定`出口IP`
2349 | 当TCP代理当上级类型(参数:-T)是tcp当时候,支持指定`出口IP`。使用`--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作,此时代理会尝试不绑定IP去访问目标,同时日志会提示。
2350 |
2351 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" -B`
2352 |
2353 | ### 2.8 限速,限制连接数
2354 |
2355 | 参数`--max-conns`可以限制每个端口的最大连接数。
2356 | 比如限制每个端口最多1000个连接数:
2357 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --max-conns 1000`
2358 | 参数`--rate-limit`可以限制每个tcp连接的速率。
2359 | 比如限制每个tcp连接速率为100k/s:
2360 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --rate-limit 100k`
2361 |
2362 | ### 2.9 查看帮助
2363 | `./proxy help tcp`
2364 |
2365 | ## 3.UDP代理
2366 |
2367 | ### 3.1.普通一级UDP代理
2368 | 
2369 | 本地执行:
2370 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
2371 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
2372 |
2373 | `-p`参数支持的写法:
2374 |
2375 | ```text
2376 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
2377 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
2378 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
2379 | ```
2380 |
2381 | 如果本地监听端口数量大于1,那么将会连接与本地端口一致的对应上级端口,忽略`-P`里面的端口。
2382 |
2383 | 如果需要所有端口进来的连接,都连接到上级指定端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`。
2384 |
2385 | 比如:
2386 |
2387 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080-33085" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:0"`
2388 |
2389 | 那么`33080`端口进来的连接,将会连接192.168.22.33的`33080`端口,其它端口以此类推,本地和上级端口一致,此时参数`-P`里面的端口用`0`。
2390 |
2391 | 如果想无论是`33080`,`33081`等端口进来的连接都连接到192.168.22.33的`2222`端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`
2392 |
2393 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080-33085" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:2222" --lock-port`
2394 |
2395 | ### 3.2.普通二级UDP代理
2396 | 
2397 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
2398 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
2399 | 本地执行:
2400 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.33:33080"`
2401 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是通过TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
2402 |
2403 | ### 3.3.普通三级UDP代理
2404 | 
2405 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2406 | `./proxy tcp -p ":38080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
2407 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2408 | `./proxy tcp -p ":28080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080"`
2409 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
2410 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tcp -P "33.33.33.33:28080"`
2411 | 那么访问本地5353端口就是通过TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的53端口。
2412 |
2413 | ### 3.4.加密二级UDP代理
2414 | 
2415 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
2416 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":33080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2417 | 本地执行:
2418 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tls -P "22.22.22.33:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2419 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是通过加密TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
2420 |
2421 | ### 3.5.加密三级UDP代理
2422 | 
2423 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2424 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":38080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2425 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2426 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2427 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
2428 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2429 | 那么访问本地5353端口就是通过加密TCP隧道,通过VPS_01访问8.8.8.8的53端口。
2430 |
2431 | ### 3.6 指定`出口IP`
2432 | 当UDP代理当上级类型(参数:-T)是udp当时候,支持指定`出口IP`。使用`--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作。
2433 |
2434 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:2222" -B`
2435 |
2436 | ### 3.7 查看帮助
2437 | `./proxy help udp`
2438 |
2439 | ## 4.内网穿透
2440 | ### 4.1、原理说明
2441 | 内网穿透,分为两个版本,“多链接版本”和“多路复用版本”,一般像web服务这种不是长时间连接的服务建议用“多链接版本”,如果是要保持长时间连接建议使用“多路复用版本”。
2442 | 1. 多链接版本,对应的子命令是tserver,tclient,tbridge。
2443 | 1. 多路复用版本,对应的子命令是server,client,bridge。
2444 | 1. 多链接版本和多路复用版本的参数和使用方式完全一样。
2445 | 1. 多路复用版本的server,client可以开启压缩传输,参数是--c。
2446 | 1. server,client要么都开启压缩,要么都不开启,不能只开一个。
2447 |
2448 | 下面的教程以“多路复用版本”为例子,说明使用方法。
2449 | 内网穿透由三部分组成:client端,server端,bridge端;client和server主动连接bridge端进行桥接。
2450 |
2451 | ### 4.2、TCP普通用法
2452 | 背景:
2453 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口
2454 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2455 |
2456 | 需求:
2457 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的28080端口访问到公司机器A的80端口
2458 |
2459 | 步骤:
2460 | 1. 在vps上执行
2461 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2462 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2463 |
2464 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
2465 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2466 |
2467 | 1. 完成
2468 |
2469 | ### 4.3、微信接口本地开发
2470 | 背景:
2471 | - 自己的笔记本提供了nginx服务80端口
2472 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2473 |
2474 | 需求:
2475 | 在微信的开发帐号的网页回调接口配置里面填写地址:http://22.22.22.22/calback.php
2476 | 然后就可以访问到笔记本的80端口下面的calback.php,如果需要绑定域名,可以用自己的域名
2477 | 比如:wx-dev.xxx.com解析到22.22.22.22,然后在自己笔记本的nginx里
2478 | 配置域名wx-dev.xxx.com到具体的目录即可。
2479 |
2480 |
2481 | 步骤:
2482 | 1. 在vps上执行,确保vps的80端口没被其它程序占用。
2483 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2484 | `./proxy server -r ":80@:80" -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2485 |
2486 | 1. 在自己笔记本上面执行
2487 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2488 |
2489 | 1. 完成
2490 |
2491 | ### 4.4、UDP普通用法
2492 | 背景:
2493 | - 公司机器A提供了DNS解析服务,UDP:53端口
2494 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2495 |
2496 | 需求:
2497 | 在家里能够通过设置本地dns为22.22.22.22,使用公司机器A进行域名解析服务。
2498 |
2499 | 步骤:
2500 | 1. 在vps上执行
2501 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2502 | `./proxy server --udp -r ":53@:53" -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2503 |
2504 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
2505 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2506 |
2507 | 1. 完成
2508 |
2509 | ### 4.5、高级用法一
2510 | 背景:
2511 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口
2512 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2513 |
2514 | 需求:
2515 | 为了安全,不想在VPS上能够访问到公司机器A,在家里能够通过访问本机的28080端口,
2516 | 通过加密隧道访问到公司机器A的80端口。
2517 |
2518 | 步骤:
2519 | 1. 在vps上执行
2520 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2521 |
2522 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
2523 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2524 |
2525 | 1. 在家里电脑上执行
2526 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2527 |
2528 | 1. 完成
2529 |
2530 | ### 4.6、高级用法二
2531 | 提示:
2532 | 如果同时有多个client连接到同一个bridge,需要指定不同的key,可以通过--k参数设定,--k可以是任意唯一字符串,
2533 | 只要在同一个bridge上唯一即可。
2534 | server连接到bridge的时候,如果同时有多个client连接到同一个bridge,需要使用--k参数选择client。
2535 | 暴露多个端口重复-r参数即可.-r格式是:"本地IP:本地端口@clientHOST:client端口"。
2536 |
2537 | 背景:
2538 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口,ftp服务21端口
2539 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2540 |
2541 | 需求:
2542 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的28080端口访问到公司机器A的80端口
2543 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的29090端口访问到公司机器A的21端口
2544 |
2545 | 步骤:
2546 | 1. 在vps上执行
2547 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2548 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -r ":29090@:21" --k test -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2549 |
2550 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
2551 | `./proxy client --k test -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2552 |
2553 | 1. 完成
2554 |
2555 | ### 4.7.server的-r参数
2556 | -r完整格式是:`PROTOCOL://LOCAL_IP:LOCAL_PORT@[CLIENT_KEY]CLIENT_LOCAL_HOST:CLIENT_LOCAL_PORT`
2557 |
2558 | 4.7.1.协议PROTOCOL:tcp、udp、ptcp、pudp。
2559 | 比如: `-r "udp://:10053@:53" -r "tcp://:10800@:1080" -r ":8080@:80"`
2560 | 如果指定了--udp参数,PROTOCOL默认为udp,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`默认为udp;
2561 | 如果没有指定--udp参数,PROTOCOL默认为tcp,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`默认为tcp;
2562 |
2563 | 4.7.2.CLIENT_KEY:默认是default。
2564 | 比如: -r "udp://:10053@[test1]:53" -r "tcp://:10800@[test2]:1080" -r ":8080@:80"
2565 | 如果指定了--k参数,比如--k test,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`CLIENT_KEY默认为test;
2566 | 如果没有指定--k参数,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`CLIENT_KEY默认为default;
2567 |
2568 | 4.7.3.LOCAL_IP为空默认是:`0.0.0.0`,CLIENT_LOCAL_HOST为空默认是:`127.0.0.1`;
2569 |
2570 | ### 4.8.server和client通过代理连接bridge
2571 | 有时候server或者client所在的网络不能直接访问外网,需要通过一个https或者socks5代理才能上网,那么这个时候
2572 | -J参数就可以帮助你让server或者client通过https或者socks5代理去连接bridge。
2573 | -J参数格式如下:
2574 |
2575 | https代理写法:
2576 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
2577 | https://username:password@host:port
2578 | 代理不需要认证
2579 | https://host:port
2580 |
2581 | socks5代理写法:
2582 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
2583 | socks5://username:password@host:port
2584 | 代理不需要认证
2585 | socks5://host:port
2586 |
2587 | host:代理的IP或者域名
2588 | port:代理的端口
2589 |
2590 | ### 4.9.内网穿透HTTP服务
2591 |
2592 | 通常HTTP请求客户端会使用server的ip和端口去设置HOST字段,但是与期望的后端实际HOST不一样,这样就造成了tcp是通的,
2593 | 但后端依赖HOST字段定位虚拟主机就不能工作.现在用--http-host参数强制设置http头部的HOST字段值为后端实际的
2594 | 域名和端口即可轻松解决。
2595 |
2596 | `server`的--http-host参数格式如下:
2597 |
2598 | `--http-host www.test.com:80@2200`,如果server监听多个端口,只需要重复`--http-host`参数设置每个端口的HOST即可。
2599 |
2600 | 实例:
2601 |
2602 | 比如client本地nginx,127.0.0.1:80提供了web服务,其中绑定了一个域名`local.com`。
2603 |
2604 | 那么server的启动参数可以如下:
2605 |
2606 | `proxy server -P :30000 -r :2500@127.0.0.1:80 --http-host local.com@2500`
2607 |
2608 | 解释:
2609 |
2610 | `-r :2500@127.0.0.1:80` 和 `--http-host local.com:80@2500` 里面的2500端口是server本地监听的端口
2611 |
2612 | 当使用http协议请求server的ip:2500端口的时候,http的头部HOST字段就会被设置为`local.com`。
2613 |
2614 | ### 4.10 关于流量统计
2615 |
2616 | 如果单独启动一个server对接上级是proxy-admin控制面板,需要在上级控制面板里面新建一个映射,获得个映射规则的ID,
2617 |
2618 | 然后启动server的时候加上参数 --server-id=映射规则的ID 才能统计到流量。
2619 |
2620 | ### 4.11 关于p2p
2621 | 内网穿透支持在server和client网络情况满足的情况下,server和client之间通过p2p直接连接,开启方法是:
2622 |
2623 | 在启动bridge,server,client到时候都加上`--p2p`参数即可。server的-r参数可以针对端口是否启用p2p(ptcp和pudp)。
2624 |
2625 | 如果server和client之间p2p打洞失败,那么会自动切换使用bridge中转传输数据。
2626 |
2627 | ### 4.12 客户端key白名单
2628 | 内网穿透bridge可以设置客户端key白名单,参数是--client-keys,格式可以是:
2629 |
2630 | a.文件名,文件内容一行一个客户端key只能包含数字字母下划线,也就是客户端启动参数--k的值,只有客户端key在此白名单的客户端才能连接。# 开头的行,为注释。
2631 |
2632 | b.“base64://”开头的base64编码的上面a说明的文件内容,比如:base64://ajfpoajsdfa=
2633 |
2634 | c.”str://“开头的英文逗号分割的多个key,比如:str://default,company,school
2635 |
2636 | 默认是空,允许所有key。
2637 |
2638 | ### 4.13 网络NAT类型判断
2639 |
2640 | nat类型判断,方便查看网络是否支持p2p,可以执行:`proxy tools -a nattype`
2641 |
2642 | ### 4.14 查看帮助
2643 | `./proxy help bridge`
2644 | `./proxy help server`
2645 | `./proxy help client`
2646 |
2647 | ## 5.SOCKS5代理
2648 | 提示:
2649 |
2650 | SOCKS5代理,支持CONNECT,UDP协议,不支持BIND,支持用户名密码认证。
2651 |
2652 | ***如果你的VPS是阿里云,腾讯云这种VPS,就是ifconfig看不见你的公网IP,只能看见内网IP,***
2653 |
2654 | ***那么需要加上`-g VPS公网IP`参数,SOCKS5代理的UDP功能才能正常工作。***
2655 |
2656 | ### 5.1 普通SOCKS5代理
2657 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080"`
2658 |
2659 | -p参数支持的写法:
2660 |
2661 | ```text
2662 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
2663 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
2664 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
2665 | ```
2666 |
2667 | ### 5.2.普通二级SOCKS5代理
2668 | 
2669 | 使用本地端口8090,假设上级SOCKS5代理是`22.22.22.22:8080`
2670 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" `
2671 | 我们还可以指定网站域名的黑白名单文件,一行一个域名,匹配规则是最右匹配,比如:baidu.com,匹配的是*.*.baidu.com,黑名单的域名域名直接走上级代理,白名单的域名不走上级代理;如果域名即在黑名单又在白名单中,那么黑名单起作用。
2672 | `./proxy socks -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" -b blocked.txt -d direct.txt`
2673 |
2674 | ### 5.3.SOCKS二级代理(加密)
2675 | 
2676 | 一级SOCKS代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
2677 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2678 |
2679 | 二级SOCKS代理(本地Linux)
2680 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2681 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080。
2682 |
2683 | 二级SOCKS代理(本地windows)
2684 | `./proxy.exe socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2685 | 然后设置你的windos系统中,需要通过代理上网的程序的代理为socks5模式,地址为:127.0.0.1,端口为:8080,程序即可通过加密通道通过vps上网。
2686 |
2687 | ### 5.4.SOCKS三级代理(加密)
2688 | 
2689 | 一级SOCKS代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2690 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2691 | 二级SOCKS代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2692 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2693 | 三级SOCKS代理(本地)
2694 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2695 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问一级SOCKS代理上面的代理端口38080。
2696 |
2697 | ### 5.5.SOCKS代理流量强制走上级SOCKS代理
2698 | 默认情况下,proxy会智能判断一个网站域名是否无法访问,如果无法访问才走上级SOCKS代理.通过--always可以使全部SOCKS代理流量强制走上级SOCKS代理。
2699 | `./proxy socks --always -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2700 |
2701 | ### 5.6.SOCKS通过SSH中转
2702 | 
2703 | 说明:ssh中转的原理是利用了ssh的转发功能,就是你连接上ssh之后,可以通过ssh代理访问目标地址。
2704 | 假设有:vps
2705 | - IP是2.2.2.2, ssh端口是22, ssh用户名是:user, ssh用户密码是:demo
2706 | - 用户user的ssh私钥名称是user.key
2707 |
2708 | #### *5.6.1 ssh用户名和密码的方式*
2709 | 本地SOCKS5代理28080端口,执行:
2710 | `./proxy socks -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -D demo -t tcp -p ":28080"`
2711 | #### *5.6.2 ssh用户名和密钥的方式*
2712 | 本地SOCKS5代理28080端口,执行:
2713 | `./proxy socks -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -S user.key -t tcp -p ":28080"`
2714 |
2715 | 那么访问本地的28080端口就是通过VPS访问目标地址。
2716 |
2717 | ### 5.7.认证
2718 | 对于socks5代理协议我们可以进行用户名密码认证,认证的用户名和密码可以在命令行指定
2719 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1" -a "user2:pass2"`
2720 | 多个用户,重复-a参数即可。
2721 | 也可以放在文件中,格式是一行一个"用户名:密码",然后用-F指定。
2722 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":33080" -F auth-file.txt`
2723 |
2724 | ### 5.8.KCP协议传输
2725 | KCP协议需要--kcp-key参数设置一个密码用于加密解密数据
2726 |
2727 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
2728 | `./proxy socks -t kcp -p ":38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
2729 |
2730 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
2731 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T kcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
2732 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080,数据通过kcp协议传输。
2733 |
2734 | ### 5.9.自定义DNS
2735 | --dns-address和--dns-ttl参数,用于自己指定proxy访问域名的时候使用的dns(--dns-address)
2736 | 以及解析结果缓存时间(--dns-ttl)秒数,避免系统dns对proxy的干扰,另外缓存功能还能减少dns解析时间提高访问速度。
2737 | 比如:
2738 | `./proxy socks -p ":33080" --dns-address "8.8.8.8:53" --dns-ttl 300`
2739 |
2740 | ### 5.10 自定义加密
2741 | proxy的socks代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可,
2742 | 加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
2743 |
2744 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以。
2745 |
2746 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
2747 |
2748 | 二级实例
2749 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2750 | `proxy socks -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
2751 | 本地二级执行:
2752 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
2753 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
2754 |
2755 |
2756 | 三级实例
2757 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2758 | `proxy socks -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
2759 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
2760 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
2761 | 本地三级执行:
2762 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
2763 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
2764 |
2765 | ### 5.11 压缩传输
2766 | proxy的socks代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以
2767 | 对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,
2768 | 一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
2769 |
2770 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据。
2771 |
2772 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
2773 |
2774 | 二级实例
2775 |
2776 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2777 | `proxy socks -t tcp -m -p :7777`
2778 | 本地二级执行:
2779 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
2780 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
2781 |
2782 |
2783 | 三级实例
2784 |
2785 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2786 | `proxy socks -t tcp -m -p :7777`
2787 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
2788 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
2789 | 本地三级执行:
2790 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
2791 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
2792 |
2793 |
2794 | ### 5.12 负载均衡
2795 |
2796 | SOCKS代理支持上级负载均衡,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
2797 |
2798 | `proxy socks --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
2799 |
2800 | ### 5.12.1 设置重试间隔和超时时间
2801 |
2802 | `proxy socks --lb-method=leastconn --lb-retrytime 300 --lb-timeout 300 -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
2803 |
2804 | ### 5.12.2 设置权重
2805 |
2806 | `proxy socks --lb-method=weight -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -P 2.1.1.1:33080?w=2 -P 3.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -p :33080 -t tcp`
2807 |
2808 | ### 5.12.3 使用目标地址选择上级
2809 |
2810 | `proxy socks --lb-hashtarget --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
2811 |
2812 | ### 5.13 限速
2813 |
2814 | 限速100K,通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
2815 |
2816 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -l 100K`
2817 |
2818 | ### 5.14 指定`出口IP`
2819 |
2820 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果`入口IP`是内网IP,`出口IP`不会使用`入口IP`。
2821 |
2822 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 --bind-listen`
2823 |
2824 | ### 5.15 级联认证
2825 |
2826 | SOCKS5支持级联认证,-A可以设置上级认证信息。
2827 |
2828 | 上级:
2829 |
2830 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -a user:pass`
2831 |
2832 | 本地:
2833 |
2834 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -A user:pass -t tcp -p :33080`
2835 |
2836 | 请更多认证细节,请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
2837 |
2838 | ### 5.16 证书参数使用base64数据
2839 |
2840 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
2841 |
2842 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
2843 |
2844 |
2845 | ### 5.17 智能模式
2846 | 智能模式设置,可以是intelligent|direct|parent三者之一。
2847 | 默认是:intelligent。
2848 | 每个值的含义如下:
2849 | `--intelligent=direct`,不在blocked里面的目标都直连。
2850 | `--intelligent=parent`,不在direct里面的目标都走上级。
2851 | `--intelligent=intelligent`,blocked和direct里面都没有的目标,智能判断是否使用上级访问目标。
2852 |
2853 | ### 5.18 固定UDP功能端口
2854 |
2855 | 默认情况下socks5的UDP功能的端口号,proxy是按着`rfc1982草案`要求,使用协议握手过程中随机指定,不需要提前指定。
2856 |
2857 | 但是某些情况下,需要固定UDP功能端口,可以通过参数`--udp-port 端口号`用来固定UDP功能的端口号,比如:
2858 |
2859 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --udp-port 38080`
2860 |
2861 | ### 5.19 查看帮助
2862 | `./proxy help socks`
2863 |
2864 | ## 6.SPS协议转换
2865 |
2866 | ### 6.1 功能介绍
2867 | 代理协议转换使用的是sps子命令,sps本身不提供代理功能,只是接受代理请求"转换并转发"给已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理或者ss代理;sps可以把已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理或ss代理转换为一个端口同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的代理,而且http(s)代理支持正向代理和反向代理(SNI),转换后的SOCKS5代理,当上级是SOCKS5或者SS时仍然支持UDP功能;另外对于已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理,支持tls、tcp、kcp三种模式,支持链式连接,也就是可以多个sps结点层级连接构建加密通道。
2868 |
2869 | `ss`功能支持的加密方法为:aes-128-cfb , aes-128-ctr , aes-128-gcm , aes-192-cfb , aes-192-ctr , aes-192-gcm , aes-256-cfb , aes-256-ctr , aes-256-gcm , bf-cfb , cast5-cfb , chacha20 , chacha20-ietf , chacha20-ietf-poly1305 , des-cfb , rc4-md5 , rc4-md5-6 , salsa20 , xchacha20
2870 |
2871 | 本地监听端口-p参数支持的写法:
2872 |
2873 | ```text
2874 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
2875 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
2876 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
2877 | ```
2878 |
2879 | ### 6.2 HTTP(S)转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
2880 | 假设已经存在一个普通的http(s)代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2881 | 命令如下:
2882 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2883 |
2884 | 假设已经存在一个tls的http(s)代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,tls需要证书文件,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2885 | 命令如下:
2886 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2887 |
2888 | 假设已经存在一个kcp的http(s)代理(密码是:demo123):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2889 | 命令如下:
2890 | `./proxy sps -S http -T kcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 --kcp-key demo123 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2891 |
2892 | ### 6.3 SOCKS5转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
2893 | 假设已经存在一个普通的socks5代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2894 | 命令如下:
2895 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2896 |
2897 | 假设已经存在一个tls的socks5代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,tls需要证书文件,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2898 | 命令如下:
2899 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T tls -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2900 |
2901 | 假设已经存在一个kcp的socks5代理(密码是:demo123):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2902 | 命令如下:
2903 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T kcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 --kcp-key demo123 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2904 |
2905 | ### 6.4 SS转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
2906 | SPS上级和本地支持ss协议,上级可以是SPS或者标准的ss服务。
2907 | SPS本地默认提供HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS三种代理,当上级是SOCKS5时转换后的SOCKS5和SS支持UDP功能。
2908 | 假设已经存在一个普通的SS或者SPS代理(开启了ss,加密方式:aes-256-cfb,密码:demo):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,转换后的ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2909 | 命令如下:
2910 | `./proxy sps -S ss -H aes-256-cfb -J pass -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`。
2911 |
2912 | ### 6.5 链式连接
2913 | 
2914 | 上面提过多个sps结点可以层级连接构建加密通道,假设有如下vps和家里的pc电脑。
2915 | vps01:2.2.2.2
2916 | vps02:3.3.3.3
2917 | 现在我们想利用pc和vps01和vps02构建一个加密通道,本例子用tls加密也可以用kcp,在pc上访问本地18080端口就是访问vps01的本地8080端口。
2918 | 首先在vps01(2.2.2.2)上我们运行一个只有本地可以访问的http(s)代理,执行:
2919 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p 127.0.0.1:8080`
2920 |
2921 | 然后在vps01(2.2.2.2)上运行一个sps结点,执行:
2922 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tls -p :8081 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2923 |
2924 | 然后在vps02(3.3.3.3)上运行一个sps结点,执行:
2925 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:8081 -t tls -p :8082 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2926 |
2927 | 然后在pc上运行一个sps结点,执行:
2928 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 3.3.3.3:8082 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2929 |
2930 | 完成。
2931 |
2932 | ### 6.6 监听多个端口
2933 | 一般情况下监听一个端口就可以,不过如果作为反向代理需要同时监听80和443两个端口,那么-p参数是支持的,
2934 | 格式是:`-p 0.0.0.0:80,0.0.0.0:443`,多个绑定用逗号分隔即可。
2935 |
2936 | ### 6.7 认证功能
2937 | sps支持http(s)\socks5代理认证,可以级联认证,有四个重要的信息:
2938 | 1:用户发送认证信息`user-auth`。
2939 | 2:设置的本地认证信息`local-auth`。
2940 | 3:设置的连接上级使用的认证信息`parent-auth`。
2941 | 4:最终发送给上级的认证信息`auth-info-to-parent`。
2942 | 他们的情况关系如下:
2943 |
2944 | | user-auth | local-auth | parent-auth | auth-info-to-paren
2945 | | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------
2946 | | 有/没有 | 有 | 有 | 来自parent-auth
2947 | | 有/没有 | 没有 | 有 | 来自parent-auth
2948 | | 有/没有 | 有 | 没有 | 无
2949 | | 没有 | 没有 | 没有 | 无
2950 | | 有 | 没有 | 没有 | 来自user-auth
2951 |
2952 | 对于sps代理我们可以进行用户名密码认证,认证的用户名和密码可以在命令行指定
2953 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1:0:0:" -a "user2:pass2:0:0:"`
2954 | 多个用户,重复-a参数即可。
2955 | 也可以放在文件中,格式是一行一个`用户名:密码:连接数:速率:上级`,然后用-F指定。
2956 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -F auth-file.txt`
2957 |
2958 | 如果上级有认证,下级可以通过-A参数设置认证信息,比如:
2959 | 上级:`./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1:0:0:" -a "user2:pass2:0:0:"`
2960 | 下级:`./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -A "user1:pass1" -t tcp -p ":33080" `
2961 |
2962 | 请更多认证细节,请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
2963 |
2964 | ### 6.8 多个上级
2965 |
2966 | 如果存在多个上级,可以通过多个-P指定。
2967 |
2968 | 比如:
2969 |
2970 | `proxy sps -P http://127.0.0.1:3100 -P socks5://127.0.0.1:3200`
2971 |
2972 | `-P`完整格式如下:
2973 |
2974 | `protocol://a:b@2.2.2.2:33080#1`
2975 |
2976 | 下面对每部分进行解释:
2977 |
2978 | `protocol://` 是协议类型,可能的类型以及含有如下:
2979 |
2980 | ```text
2981 | http 等价于 -S http -T tcp
2982 | https 等价于 -S http -T tls --parent-tls-single , 也就是http(s)代理 over TLS
2983 | https2 等价于 -S http -T tls
2984 | socks5 等价于 -S socks -T tcp
2985 | socks5s 等价于 -S socks -T tls --parent-tls-single , 也就是socks over TLS
2986 | socks5s2 等价于 -S socks -T tls
2987 | ss 等价于 -S ss -T tcp
2988 | httpws 等价于 -S http -T ws
2989 | httpwss 等价于 -S http -T wss
2990 | socks5ws 等价于 -S socks -T ws
2991 | socks5wss 等价于 -S socks -T wss
2992 | ```
2993 |
2994 | `a:b`是代理认证的用户名密码,如果是ss,`a`是加密方法,`b`是密码,没有用户名密码可以留空比如:`http://2.2.2.2:33080`,如果用户名和密码保护特殊符号可以使用urlencode进行编码。
2995 |
2996 | `2.2.2.2:33080`是上级地址,格式是:`IP(或域名):端口`,如果底层是ws/wss协议还可以带上路径,比如:`2.2.2.2:33080/ws`;
2997 | 还能通过附加查询参数`m`和`k`设置`ws\wss`的`加密方法`和`密码`,比如:`2.2.2.2:33080/ws?m=aes-192-cfb&k=password`
2998 |
2999 | `#1`多个上级的负载均衡是权重策略时候,设置的权重,很少用到。
3000 |
3001 | ### 6.9 自定义加密
3002 | proxy的sps代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行
3003 | 自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义
3004 | 一个密码即可,加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
3005 |
3006 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以。
3007 |
3008 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
3009 |
3010 | 假设已经存在一个http(s)代理:`6.6.6.6:6666`
3011 |
3012 | 二级实例
3013 |
3014 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
3015 | `proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 6.6.6.6:6666 -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
3016 | 本地二级执行:
3017 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
3018 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
3019 |
3020 |
3021 | 三级实例
3022 |
3023 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
3024 | `proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 6.6.6.6:6666 -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
3025 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
3026 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
3027 | 本地三级执行:
3028 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
3029 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
3030 |
3031 | ### 6.10 压缩传输
3032 | proxy的sps代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以
3033 | 对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,
3034 | 一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
3035 |
3036 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据。
3037 |
3038 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
3039 |
3040 | 二级实例
3041 |
3042 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
3043 | `proxy sps -t tcp -m -p :7777`
3044 | 本地二级执行:
3045 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
3046 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
3047 |
3048 |
3049 | 三级实例
3050 |
3051 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
3052 | `proxy sps -t tcp -m -p :7777`
3053 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
3054 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
3055 | 本地三级执行:
3056 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
3057 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
3058 |
3059 | ### 6.11 禁用协议
3060 | SPS默认情况下一个端口支持http(s)和socks5两种代理协议,我们可以通过参数禁用某个协议
3061 | 比如:
3062 | 1.禁用HTTP(S)代理功能只保留SOCKS5代理功能,参数:`--disable-http`。
3063 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080 --disable-http`
3064 |
3065 | 1.禁用SOCKS5代理功能只保留HTTP(S)代理功能,参数:`--disable-socks`。
3066 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080 --disable-http`
3067 |
3068 | ### 6.12 限速
3069 |
3070 | 假设存在SOCKS5上级:
3071 |
3072 | `proxy socks -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -z password -t tcp`
3073 |
3074 | sps下级,限速100K
3075 |
3076 | `proxy sps -S socks -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -T tcp -Z password -l 100K -t tcp -p :33080`
3077 |
3078 | 通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
3079 |
3080 | ### 6.13 指定`出口IP`
3081 |
3082 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果`入口IP`是内网IP,`出口IP`不会使用`入口IP`。
3083 |
3084 | `proxy sps -S socks -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -T tcp -Z password -l 100K -t tcp --bind-listen -p :33080`
3085 |
3086 | ### 6.14 证书参数使用base64数据
3087 |
3088 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
3089 |
3090 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
3091 |
3092 | ### 6.15 独立服务
3093 | sps功能不强制指定一个上级,当上级为空,sps本身即可完成完整的代理功能.如果指定了上级那么就和之前一样使用上级连接目标。
3094 | 下面这个命令,就是一键开启http(s)\ss\socks服务。
3095 | `./proxy sps -p :33080`
3096 |
3097 | ### 6.16 目标重定向
3098 | sps功能提供的http(s)\socks5\ss代理功能,客户端通过sps代理去连接指定的“目标”,这个“目标”一般是网站也可能是任意的tcp地址,
3099 | 网站”目标“一般是foo.com:80,foo.com:443,sps支持使用--rewrite参数指定一个“目标”重定向规则文件,对目标进行重定向,客户端是无感知的,
3100 | 比如你对“目标”:demo.com:80重定向到192.168.0.12:80,那么客户端访问网站demo.com,其实访问的是192.168.0.12提供的网站服务。
3101 | “目标”重定向规则文件示例:
3102 |
3103 | ```text
3104 | # example
3105 | www.a.com:80 10.0.0.2:8080
3106 | **.b.com:80 10.0.0.2:80
3107 | 192.168.0.11:80 10.0.0.2:8080
3108 | ```
3109 |
3110 | ### 6.17 固定UDP功能端口
3111 |
3112 | 默认情况下sps的socks5的UDP功能的端口号是按着`rfc1982草案`要求,使用协议握手过程中随机指定,不需要提前指定。
3113 |
3114 | 但是某些情况下,需要固定UDP功能端口,可以通过参数`--udp-port 端口号`用来固定UDP功能的端口号,比如:
3115 |
3116 | `./proxy sps -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --udp-port 38081`
3117 |
3118 | 需要注意的是,sps的ss功能也有UDP功能,而且ss的UDP端口和tcp端口是一样的,所以要避免socks5的UDP端口和ss的UDP端口冲突,
3119 |
3120 | 要指定和tcp端口不一样的端口。
3121 |
3122 | ### 6.18 iptables 透明代理
3123 | sps模式支持Linux系统的iptables转发支持,也就是通常所说的iptables透明代理,如果在网关设备上进行iptables透明代理,那么对通过网关联网的设备就能实现无感知的代理。
3124 |
3125 | 启动命令实例:
3126 |
3127 | `./proxy sps --redir -p :8888 -P httpws://1.1.1.1:33080`
3128 |
3129 | 这里假设存在一个http的上级代理1.1.1.1:33080,使用ws传输数据。
3130 |
3131 | 然后添加iptables规则,下面是参考规则:
3132 | ```shell
3133 | #上级proxy服务端服务器IP地址:
3134 | proxy_server_ip=1.1.1.1
3135 |
3136 | #路由器运行proxy监听的端口:
3137 | proxy_local_port=33080
3138 |
3139 | #下面的就不用修改了
3140 | #create a new chain named PROXY
3141 | iptables -t nat -N PROXY
3142 |
3143 | # Ignore your PROXY server's addresses
3144 | # It's very IMPORTANT, just be careful。
3145 |
3146 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d $proxy_server_ip -j RETURN
3147 |
3148 | # Ignore LANs IP address
3149 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 0.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
3150 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 10.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
3151 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 127.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
3152 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 169.254.0.0/16 -j RETURN
3153 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 172.16.0.0/12 -j RETURN
3154 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 192.168.0.0/16 -j RETURN
3155 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 224.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
3156 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 240.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
3157 |
3158 | # Anything to port 80 443 should be redirected to PROXY's local port
3159 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
3160 | # Apply the rules to nat client
3161 | iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -j PROXY
3162 | # Apply the rules to localhost
3163 | iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp -j PROXY
3164 | ```
3165 | - 清空整个链 iptables -F 链名比如iptables -t nat -F PROXY
3166 | - 删除指定的用户自定义链 iptables -X 链名 比如 iptables -t nat -X PROXY
3167 | - 从所选链中删除规则 iptables -D 链名 规则详情 比如 iptables -t nat -D PROXY -d 223.223.192.0/255.255.240.0 -j RETURN
3168 |
3169 | ### 6.19 查看帮助
3170 |
3171 | `./proxy help sps`
3172 |
3173 | ## 7.KCP配置
3174 |
3175 | ### 7.1 配置介绍
3176 | proxy的很多功能都支持kcp协议,凡是使用了kcp协议的功能都支持这里介绍的配置参数。
3177 | 所以这里统一对KCP配置参数进行介绍。
3178 |
3179 | ### 7.2 详细配置
3180 | 所有的KCP配置参数共有17个,你可以都不用设置,他们都有默认值,如果为了或者最好的效果,
3181 | 就需要自己根据自己根据网络情况对参数进行配置。由于kcp配置很复杂需要一定的网络基础知识,
3182 | 如果想获得kcp参数更详细的配置和解说,请自行搜索。每个参数的命令行名称以及默认值和简单的功能说明如下:
3183 | ```
3184 | --kcp-key="secrect" pre-shared secret between client and server
3185 | --kcp-method="aes" encrypt/decrypt method, can be: aes, aes-128, aes-192, salsa20, blowfish,
3186 | twofish, cast5, 3des, tea, xtea, xor, sm4, none
3187 | --kcp-mode="fast" profiles: fast3, fast2, fast, normal, manual
3188 | --kcp-mtu=1350 set maximum transmission unit for UDP packets
3189 | --kcp-sndwnd=1024 set send window size(num of packets)
3190 | --kcp-rcvwnd=1024 set receive window size(num of packets)
3191 | --kcp-ds=10 set reed-solomon erasure coding - datashard
3192 | --kcp-ps=3 set reed-solomon erasure coding - parityshard
3193 | --kcp-dscp=0 set DSCP(6bit)
3194 | --kcp-nocomp disable compression
3195 | --kcp-acknodelay be carefull! flush ack immediately when a packet is received
3196 | --kcp-nodelay=0 be carefull!
3197 | --kcp-interval=50 be carefull!
3198 | --kcp-resend=0 be carefull!
3199 | --kcp-nc=0 be carefull! no congestion
3200 | --kcp-sockbuf=4194304 be carefull!
3201 | --kcp-keepalive=10 be carefull!
3202 | ```
3203 | 提示:
3204 | 参数:--kcp-mode中的四种fast3, fast2, fast, normal模式,
3205 | 相当于设置了下面四个参数:
3206 | normal:`--nodelay=0 --interval=40 --resend=2 --nc=1`
3207 | fast :`--nodelay=0 --interval=30 --resend=2 --nc=1`
3208 | fast2:`--nodelay=1 --interval=20 --resend=2 --nc=1`
3209 | fast3:`--nodelay=1 --interval=10 --resend=2 --nc=1`
3210 |
3211 | ## 8.安全DNS
3212 |
3213 | ### 8.1 介绍
3214 | 众所周知DNS是UDP端口53提供的服务,但是随着网络的发展一些知名DNS服务器也支持TCP方式dns查询,比如谷歌的8.8.8.8,proxy的DNS防污染服务器原理就是在本地启动一个proxy的DNS代理服务器,它用TCP的方式通过上级代理进行dns查询。如果它和上级代理通讯采用加密的方式,那么就可以进行安全无污染的DNS解析,还支持独立服务,并发解析,支持增强的hosts文件功能支持灵活的并发解析转发。
3215 |
3216 | dns解析顺序:
3217 | 1.使用参数--hosts解析。
3218 | 2.要解析的域名在1中没有找到,就使用参数--forward规则解析。
3219 | 3.要解析的域名在1和2中都没有找到,就使用默认--default解析,--default默认行为参数值有三种:proxy,direct,system。
3220 | 三种参数值解释如下:
3221 | proxy:通过上级去连接-q参数指定的dns服务器去解析域名。
3222 | direct:通过本地网络去连接-q参数指定的dns服务器去解析域名。
3223 | system:通过系统dns去解析域名。
3224 |
3225 | 提示:
3226 | --hosts 参数指定的host文件格式和系统hosts文件一致,而且域名支持通配符,可以参考hosts文件。
3227 | --forward 参数指定的解析转发规则文件,格式可以参考resolve.rules文件,域名支持通配符,支持为每个域名指定多个dns服务器并发解析,谁最快解析成功就用谁的解析结果。
3228 | -q 参数可以指定多个远程dns服务器,执行并发解析谁最快解析成功就用谁的解析结果,默认是:1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8,9.9.9.9,多个用逗号分割,
3229 | 比如还可以带端口:1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8#53,9.9.9.9
3230 |
3231 | 如果独立服务,不需要上级:
3232 | 可以执行:
3233 | `proxy dns --default system -p :5353`
3234 | or
3235 | `proxy dns --default direct -p :5353`
3236 |
3237 | ### 8.2 使用示例
3238 |
3239 | #### 8.2.1 普通HTTP(S)上级代理
3240 |
3241 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3242 | 本地执行:
3243 | `proxy dns -S http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3244 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了DNS解析功能。
3245 |
3246 | #### 8.2.2 普通SOCKS5上级代理
3247 |
3248 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3249 | 本地执行:
3250 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3251 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了DNS解析功能。
3252 |
3253 | #### 8.2.3 TLS加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
3254 |
3255 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3256 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3257 | `proxy http -t tls -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :33080`
3258 | 本地执行:
3259 | `proxy dns -S http -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :53`
3260 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3261 |
3262 | #### 8.2.4 TLS加密的SOCKS5上级代理
3263 |
3264 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3265 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3266 | `proxy socks -t tls -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :33080`
3267 | 本地执行:
3268 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :53`
3269 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3270 |
3271 | #### 8.2.5 KCP加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
3272 |
3273 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3274 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3275 | `proxy http -t kcp -p :33080`
3276 | 本地执行:
3277 | `proxy dns -S http -T kcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3278 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3279 |
3280 | #### 8.2.6 KCP加密的SOCKS5上级代理
3281 |
3282 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3283 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3284 | `proxy socks -t kcp -p :33080`
3285 | 本地执行:
3286 | `proxy dns -S socks -T kcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3287 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3288 |
3289 | #### 8.2.7 自定义加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
3290 |
3291 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3292 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3293 | `proxy http -t tcp -p :33080 -z password`
3294 | 本地执行:
3295 | `proxy dns -S http -T tcp -Z password -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3296 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3297 |
3298 | #### 8.2.8 自定义加密的SOCKS5上级代理
3299 |
3300 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3301 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3302 | `proxy socks -t kcp -p :33080 -z password`
3303 | 本地执行:
3304 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tcp -Z password -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3305 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3306 |
3307 | ## 9.API认证,限速,控制连接数
3308 |
3309 | proxy的http(s)/socks5/sps代理功能,支持通过API控制用户对代理对访问。
3310 |
3311 | ### 通过API可以干什么?
3312 |
3313 | - 用户维度,控制单个连接速率,控制最大连接数。
3314 | - IP维度,控制单个连接速率,控制最大连接数。
3315 | - 动态上级,可以根据用户或者客户端IP,动态的从API获取其上级,支持http(s)/socks5/ss上级。
3316 | - 认证每一个连接,无论是否要求客户端认证。
3317 | - 缓存认证结果,时间可以设置,减轻API压力。
3318 |
3319 | #### 具体使用
3320 | proxy的http(s)/socks5/sps代理API功能,通过`--auth-url`和`--auth-nouser`和`--auth-cache`三个参数控制。
3321 | 参数`--auth-url`是HTTP API接口地址,客户端连接的时候,proxy会GET方式请求这url,带上下面参数,如果返回HTTP状态码204,代表认证成功,其它情况认为认证失败。
3322 |
3323 | 一个完整的请求API的示例:
3324 | `http://test.com/auth.php?user=a&pass=b&client_addr=127.0.0.1:49892&local_addr=127.0.0.1:8100&target=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.baidu.com&service=http&sps=0`
3325 |
3326 | #### 参数说明
3327 | `user和pass` 当代理开启了认证功能,这里就是客户端提供的用户名和密码。
3328 | `client_addr` 客户端访问代理时的用的地址,格式IP:端口。
3329 | `local_addr` 客户端访问的代理地址,格式IP:端口。
3330 | `service` 代理类型,分为:http、socks。
3331 | `sps` 代理是否是sps提供的,1:是,0:否。
3332 | `target` 客户端要访问的目标,如果是http(s)代理,target是访问的具体url;如果是socks5代理,target是空。
3333 |
3334 | #### 示例
3335 | 假设--auth-url http://127.0.0.1:333/auth.php 指向了一个php接口地址.
3336 | auth.php内容如下:
3337 |
3338 | ```php
3339 |  3 | 一款轻量级、功能强大、高性能的http代理、https代理、socks5代理、内网穿透代理服务器、ss代理、游戏盾、游戏代理,支持API代理认证。websocke代理、tcp代理、udp代理、socket代理、高仿服务器。支持正向代理、反向代理、透明代理、TCP内网穿透、UDP内网穿透、HTTP内网穿透、HTTPS内网穿透、https代理负载均衡、http代理负载均衡、socks5代理负载均衡、socket代理负载均衡、ss代理负载均衡、TCP/UDP端口映射、SSH中转、TLS加密传输、协议转换、防污染DNS代理,限速,限连接数。官方QQ交流群: 793015219。
4 |
5 | ---
6 |
7 | [](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/) []() [](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases) [](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases)
8 |
9 | ---
10 | ### [点击我观看视频教程](https://space.bilibili.com/472844633)
11 | - [点击下载](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases)
12 | - 如果上面不能正常下载,点击这里[镜像下载](https://www.host900.com/snail007/goproxy/)
13 | - [桌面版,控制面板ProxyAdmin](https://github.com/snail007/proxy_admin_free/blob/master/README_ZH.md)
14 | - [安卓全局代理版](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy-ss-plugin-android)
15 | - [安卓全能代理版](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy-android)
16 | - [安卓内网穿透客户端](https://github.com/snail007/lanass)
17 | - [SDK](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy-sdk)
18 | - [GORPOXY帮助手册](https://snail007.github.io/goproxy/manual/zh/)
19 | - [GORPOXY实战教程](https://snail007.github.io/goproxy)
20 | - [免费版VS商业版](https://snail007.github.io/goproxy/free_vs_commercial/)
21 |
22 | ## ProxyAdmin介绍预览
23 | goproxy提供的web控制面板 `ProxyAdmin` 是强大的代理服务工具 snail007/goproxy 的控制面板,运行了它,一秒让你的服务器变为强大的代理服务器,友好的交互界面,小白也能轻松上手,让你用起来得心应手,心情舒畅。
24 |
25 | 
26 |
27 | ### goproxy能干什么?
28 | - 链式代理,程序本身可以作为一级代理,如果设置了上级代理那么可以作为二级代理,乃至N级代理。
29 | - 通讯加密,如果程序不是一级代理,而且上级代理也是本程序,那么可以加密和上级代理之间的通讯,采用底层tls高强度加密,安全无特征。
30 | - 智能HTTP代理,HTTPS代理,SOCKS5代理,会自动判断访问的网站是否屏蔽,如果被屏蔽那么就会使用上级代理(前提是配置了上级代理)访问网站;如果访问的网站没有被屏蔽,为了加速访问,代理会直接访问网站,不使用上级代理。
31 | - 域名黑白名单,更加自由的控制网站的访问方式。
32 | - 跨平台性,无论你是widows,linux,还是mac,甚至是树莓派,都可以很好的运行proxy。
33 | - 多协议支持,支持HTTP(S),TCP,UDP,Websocket,SOCKS5代理。
34 | - TCP/UDP端口转发。
35 | - 游戏盾,游戏代理,高仿服务器。
36 | - 内网穿透,P2P传输,协议支持TCP和UDP,针对HTTP的优化穿透。
37 | - SSH中转,HTTP(S),SOCKS5代理支持SSH中转,上级Linux服务器不需要任何服务端,本地一个proxy即可开心上网。
38 | - [KCP](https://github.com/xtaci/kcp-go)协议支持,HTTP(S),SOCKS5代理支持KCP协议传输数据,降低延迟,提升浏览体验。
39 | - 动态选择上级代理,通过外部API,HTTP(S),SOCKS5,SPS代理可以实现基于用户或者IP的限速,连接数限制,动态获取上级。
40 | - 灵活的上级分配,HTTP(S),SOCKS5,SPS代理可以通过配置文件实现基于用户或者IP的限速,连接数限制,指定上级。
41 | - 反向代理,支持直接把域名解析到proxy监听的ip,然后proxy就会帮你代理访问需要访问的HTTP(S)网站。
42 | - 透明HTTP(S)代理,配合iptables,在网关直接把出去的80,443方向的流量转发到proxy,就能实现无感知的智能路由器代理。
43 | - 协议转换,可以把已经存在的HTTP(S)或SOCKS5或SS代理转换为一个端口同时支持HTTP(S)和SOCKS5和SS代理,转换后的SOCKS5和SS代理如果上级是SOCKS5代理,那么支持UDP功能,同时支持强大的级联认证功能。
44 | - 自定义底层加密传输,http(s)\sps\socks代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可。
45 | - 底层压缩高效传输,http(s)\sps\socks代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在加密之后还可以对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的。
46 | - 安全的DNS代理,可以通过本地的proxy提供的DNS代理服务器与上级代理加密通讯实现安全防污染的DNS查询。
47 | - 负载均衡,高可用,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS代理支持上级负载均衡和高可用,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
48 | - 指定出口IP,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS代理支持客户端用入口IP连接过来的,就用入口IP作为出口IP访问目标网站的功能。如果入口IP是内网IP,出口IP不会使用入口IP
49 | - 支持限速,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS\TCP代理支持限速。
50 | - 支持限连接数,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS\TCP代理支持限连接数。
51 | - SOCKS5代理支持级联认证。
52 | - 证书参数使用base64数据,默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
53 | - 支持客户端IP黑白名单,更加安全的控制客户端对代理服务的访问,如果黑白名单同时设置,那么只有白名单生效。socks/http(s)/sps/tcp/udp/dns/内网穿透bridge/内网穿透tbridge,都支持客户端IP黑白名单。
54 | - 端口范围批量监听,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS\TCP代理支持指定端口范围监听,避免启动过多进程,提高性能。
55 |
56 | ### 为什么需要它?
57 |
58 | - 当由于某某原因,我们不能访问我们在其它地方的服务,我们可以通过多个相连的proxy节点建立起一个安全的隧道访问我们的服务。
59 | - 微信接口本地开发,方便调试。
60 | - 远程访问内网机器。
61 | - 和小伙伴一起玩局域网游戏。
62 | - 以前只能在局域网玩的,现在可以在任何地方玩。
63 | - 替代圣剑内网通,显IP内网通,花生壳之类的工具。
64 | - ..。
65 |
66 |
67 | 本页手册适用于最新版goproxy,其他版本可能有的地方不再适用,请自己根据命令帮助使用。
68 |
69 |
70 | ### 加入组织
71 | [点击加入交流组织gitter](https://gitter.im/go-proxy/Lobby?utm_source=share-link&utm_medium=link&utm_campaign=share-link)
72 |
73 | [点击加入交流组织TG](https://t.me/snail007_goproxy)
74 |
75 | ## 下载安装 goproxy
76 |
77 | ### 快速安装 goproxy
78 |
79 | 0.如果你的VPS是linux64位的系统,那么只需要执行下面一句,就可以完成自动安装和配置.
80 |
81 | 提示:所有操作需要root权限。
82 |
83 | 免费版执行这个:
84 |
85 | ```shell
86 | curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/snail007/goproxy/master/install_auto.sh | bash
87 | ```
88 |
89 | 商业版执行这个:
90 |
91 | ```shell
92 | curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/snail007/goproxy/master/install_auto_commercial.sh | bash
93 | ```
94 |
95 | 安装完成,配置目录是/etc/proxy,更详细的使用方法请参考上面的手册目录,进一步了解你想要使用的功能。
96 | 如果安装失败或者你的vps不是linux64位系统,请按照下面的半自动步骤安装:
97 |
98 | ### 手动安装 goproxy
99 |
100 | 1.下载goproxy
101 |
102 | 下载地址:https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases/latest
103 |
104 | 下面以v7.9为例,如果有最新版,请使用最新版链接,注意替换下面的下载连接里面的版本号为最新版版本号。
105 |
106 | 免费版执行这个:
107 |
108 | ```shell
109 | cd /root/proxy/
110 | wget https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases/download/v7.9/proxy-linux-amd64.tar.gz
111 | ```
112 |
113 | 商业版执行这个:
114 |
115 | ```shell
116 | cd /root/proxy/
117 | wget https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases/download/v7.9/proxy-linux-amd64_commercial.tar.gz
118 | ```
119 |
120 | 2.下载自动安装脚本
121 |
122 | 免费版执行这个:
123 |
124 | ```shell
125 | cd /root/proxy/
126 | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/snail007/goproxy/master/install.sh
127 | chmod +x install.sh
128 | ./install.sh
129 | ```
130 |
131 | 商业版执行这个:
132 |
133 | ```shell
134 | cd /root/proxy/
135 | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/snail007/goproxy/master/install_commercial.sh
136 | chmod +x install_commercial.sh
137 | ./install_commercial.sh
138 | ```
139 |
140 | ## TODO
141 | - http,socks代理多个上级负载均衡?
142 | - http(s)代理增加pac支持?
143 | - 欢迎加群反馈..。
144 |
145 | ## License
146 | Proxy is licensed under GPLv3 license。
147 |
148 | ## Contact
149 | 官方QQ交流群: 793015219
150 |
151 | ## Donation
152 | 如果proxy帮助你解决了很多问题,你可以通过下面的捐赠更好的支持proxy。
153 |
3 | 一款轻量级、功能强大、高性能的http代理、https代理、socks5代理、内网穿透代理服务器、ss代理、游戏盾、游戏代理,支持API代理认证。websocke代理、tcp代理、udp代理、socket代理、高仿服务器。支持正向代理、反向代理、透明代理、TCP内网穿透、UDP内网穿透、HTTP内网穿透、HTTPS内网穿透、https代理负载均衡、http代理负载均衡、socks5代理负载均衡、socket代理负载均衡、ss代理负载均衡、TCP/UDP端口映射、SSH中转、TLS加密传输、协议转换、防污染DNS代理,限速,限连接数。官方QQ交流群: 793015219。
4 |
5 | ---
6 |
7 | [](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/) []() [](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases) [](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases)
8 |
9 | ---
10 | ### [点击我观看视频教程](https://space.bilibili.com/472844633)
11 | - [点击下载](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases)
12 | - 如果上面不能正常下载,点击这里[镜像下载](https://www.host900.com/snail007/goproxy/)
13 | - [桌面版,控制面板ProxyAdmin](https://github.com/snail007/proxy_admin_free/blob/master/README_ZH.md)
14 | - [安卓全局代理版](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy-ss-plugin-android)
15 | - [安卓全能代理版](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy-android)
16 | - [安卓内网穿透客户端](https://github.com/snail007/lanass)
17 | - [SDK](https://github.com/snail007/goproxy-sdk)
18 | - [GORPOXY帮助手册](https://snail007.github.io/goproxy/manual/zh/)
19 | - [GORPOXY实战教程](https://snail007.github.io/goproxy)
20 | - [免费版VS商业版](https://snail007.github.io/goproxy/free_vs_commercial/)
21 |
22 | ## ProxyAdmin介绍预览
23 | goproxy提供的web控制面板 `ProxyAdmin` 是强大的代理服务工具 snail007/goproxy 的控制面板,运行了它,一秒让你的服务器变为强大的代理服务器,友好的交互界面,小白也能轻松上手,让你用起来得心应手,心情舒畅。
24 |
25 | 
26 |
27 | ### goproxy能干什么?
28 | - 链式代理,程序本身可以作为一级代理,如果设置了上级代理那么可以作为二级代理,乃至N级代理。
29 | - 通讯加密,如果程序不是一级代理,而且上级代理也是本程序,那么可以加密和上级代理之间的通讯,采用底层tls高强度加密,安全无特征。
30 | - 智能HTTP代理,HTTPS代理,SOCKS5代理,会自动判断访问的网站是否屏蔽,如果被屏蔽那么就会使用上级代理(前提是配置了上级代理)访问网站;如果访问的网站没有被屏蔽,为了加速访问,代理会直接访问网站,不使用上级代理。
31 | - 域名黑白名单,更加自由的控制网站的访问方式。
32 | - 跨平台性,无论你是widows,linux,还是mac,甚至是树莓派,都可以很好的运行proxy。
33 | - 多协议支持,支持HTTP(S),TCP,UDP,Websocket,SOCKS5代理。
34 | - TCP/UDP端口转发。
35 | - 游戏盾,游戏代理,高仿服务器。
36 | - 内网穿透,P2P传输,协议支持TCP和UDP,针对HTTP的优化穿透。
37 | - SSH中转,HTTP(S),SOCKS5代理支持SSH中转,上级Linux服务器不需要任何服务端,本地一个proxy即可开心上网。
38 | - [KCP](https://github.com/xtaci/kcp-go)协议支持,HTTP(S),SOCKS5代理支持KCP协议传输数据,降低延迟,提升浏览体验。
39 | - 动态选择上级代理,通过外部API,HTTP(S),SOCKS5,SPS代理可以实现基于用户或者IP的限速,连接数限制,动态获取上级。
40 | - 灵活的上级分配,HTTP(S),SOCKS5,SPS代理可以通过配置文件实现基于用户或者IP的限速,连接数限制,指定上级。
41 | - 反向代理,支持直接把域名解析到proxy监听的ip,然后proxy就会帮你代理访问需要访问的HTTP(S)网站。
42 | - 透明HTTP(S)代理,配合iptables,在网关直接把出去的80,443方向的流量转发到proxy,就能实现无感知的智能路由器代理。
43 | - 协议转换,可以把已经存在的HTTP(S)或SOCKS5或SS代理转换为一个端口同时支持HTTP(S)和SOCKS5和SS代理,转换后的SOCKS5和SS代理如果上级是SOCKS5代理,那么支持UDP功能,同时支持强大的级联认证功能。
44 | - 自定义底层加密传输,http(s)\sps\socks代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可。
45 | - 底层压缩高效传输,http(s)\sps\socks代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在加密之后还可以对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的。
46 | - 安全的DNS代理,可以通过本地的proxy提供的DNS代理服务器与上级代理加密通讯实现安全防污染的DNS查询。
47 | - 负载均衡,高可用,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS代理支持上级负载均衡和高可用,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
48 | - 指定出口IP,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS代理支持客户端用入口IP连接过来的,就用入口IP作为出口IP访问目标网站的功能。如果入口IP是内网IP,出口IP不会使用入口IP
49 | - 支持限速,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS\TCP代理支持限速。
50 | - 支持限连接数,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS\TCP代理支持限连接数。
51 | - SOCKS5代理支持级联认证。
52 | - 证书参数使用base64数据,默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
53 | - 支持客户端IP黑白名单,更加安全的控制客户端对代理服务的访问,如果黑白名单同时设置,那么只有白名单生效。socks/http(s)/sps/tcp/udp/dns/内网穿透bridge/内网穿透tbridge,都支持客户端IP黑白名单。
54 | - 端口范围批量监听,HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS\TCP代理支持指定端口范围监听,避免启动过多进程,提高性能。
55 |
56 | ### 为什么需要它?
57 |
58 | - 当由于某某原因,我们不能访问我们在其它地方的服务,我们可以通过多个相连的proxy节点建立起一个安全的隧道访问我们的服务。
59 | - 微信接口本地开发,方便调试。
60 | - 远程访问内网机器。
61 | - 和小伙伴一起玩局域网游戏。
62 | - 以前只能在局域网玩的,现在可以在任何地方玩。
63 | - 替代圣剑内网通,显IP内网通,花生壳之类的工具。
64 | - ..。
65 |
66 |
67 | 本页手册适用于最新版goproxy,其他版本可能有的地方不再适用,请自己根据命令帮助使用。
68 |
69 |
70 | ### 加入组织
71 | [点击加入交流组织gitter](https://gitter.im/go-proxy/Lobby?utm_source=share-link&utm_medium=link&utm_campaign=share-link)
72 |
73 | [点击加入交流组织TG](https://t.me/snail007_goproxy)
74 |
75 | ## 下载安装 goproxy
76 |
77 | ### 快速安装 goproxy
78 |
79 | 0.如果你的VPS是linux64位的系统,那么只需要执行下面一句,就可以完成自动安装和配置.
80 |
81 | 提示:所有操作需要root权限。
82 |
83 | 免费版执行这个:
84 |
85 | ```shell
86 | curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/snail007/goproxy/master/install_auto.sh | bash
87 | ```
88 |
89 | 商业版执行这个:
90 |
91 | ```shell
92 | curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/snail007/goproxy/master/install_auto_commercial.sh | bash
93 | ```
94 |
95 | 安装完成,配置目录是/etc/proxy,更详细的使用方法请参考上面的手册目录,进一步了解你想要使用的功能。
96 | 如果安装失败或者你的vps不是linux64位系统,请按照下面的半自动步骤安装:
97 |
98 | ### 手动安装 goproxy
99 |
100 | 1.下载goproxy
101 |
102 | 下载地址:https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases/latest
103 |
104 | 下面以v7.9为例,如果有最新版,请使用最新版链接,注意替换下面的下载连接里面的版本号为最新版版本号。
105 |
106 | 免费版执行这个:
107 |
108 | ```shell
109 | cd /root/proxy/
110 | wget https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases/download/v7.9/proxy-linux-amd64.tar.gz
111 | ```
112 |
113 | 商业版执行这个:
114 |
115 | ```shell
116 | cd /root/proxy/
117 | wget https://github.com/snail007/goproxy/releases/download/v7.9/proxy-linux-amd64_commercial.tar.gz
118 | ```
119 |
120 | 2.下载自动安装脚本
121 |
122 | 免费版执行这个:
123 |
124 | ```shell
125 | cd /root/proxy/
126 | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/snail007/goproxy/master/install.sh
127 | chmod +x install.sh
128 | ./install.sh
129 | ```
130 |
131 | 商业版执行这个:
132 |
133 | ```shell
134 | cd /root/proxy/
135 | wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/snail007/goproxy/master/install_commercial.sh
136 | chmod +x install_commercial.sh
137 | ./install_commercial.sh
138 | ```
139 |
140 | ## TODO
141 | - http,socks代理多个上级负载均衡?
142 | - http(s)代理增加pac支持?
143 | - 欢迎加群反馈..。
144 |
145 | ## License
146 | Proxy is licensed under GPLv3 license。
147 |
148 | ## Contact
149 | 官方QQ交流群: 793015219
150 |
151 | ## Donation
152 | 如果proxy帮助你解决了很多问题,你可以通过下面的捐赠更好的支持proxy。
153 |  154 |
154 |  155 |
156 | ### 源代码申明
157 |
158 | 本项目作者发现大量的开发者基于本项目进行二次开发或使用大量本项目核心代码而不遵循GPLv3协议,这严重违背了本项目使用GPLv3开源协议的初衷,鉴于这种情况,本项目采取源代码延迟发布策略,在一定程度上遏制这些不尊重开源,不尊重他人劳动成果的行为。
159 | 本项目会持续更新迭代,持续发布全平台的二进制程序,给大家提供强大便捷的代理工具。
160 | 如果你有定制,商业需求请发邮件至`arraykeys@gmail.com`
161 |
162 | ## goproxy使用手册
163 |
164 |
165 | ## 首次使用必看!
166 |
167 | ### 1. 环境
168 |
169 | 该手册教程,默认系统是linux,程序是proxy;所有操作需要root权限;
170 |
171 | 如果你的是windows,请使用windows版本的proxy.exe即可。
172 |
173 | ### 2. 使用配置文件
174 |
175 | 接下来的教程都是通过命令行参数介绍使用方法,也可以通过读取配置文件获取参数。
176 |
177 | 具体格式是通过@符号指定配置文件,例如:./proxy @configfile.txt
178 |
179 | configfile.txt里面的格式是,第一行是子命令名称,第二行开始一行一个参数,
180 |
181 | 格式:`参数 参数值`,没有参数值的直接写参数,比如:--nolog
182 |
183 | 比如configfile.txt内容如下:
184 |
185 | ```shell
186 | http
187 | -t tcp
188 | -p :33080
189 | --forever
190 | ```
191 |
192 | ### 3. 调试输出
193 |
194 | 默认情况下,日志输出的信息不包含文件行数,某些情况下为了排除程序问题,快速定位问题,
195 |
196 | 可以使用--debug参数,输出代码行数和毫秒时间。
197 |
198 | ### 4. 使用日志文件
199 |
200 | 默认情况下,日志是直接在控制台显示出来的,如果要保存到文件,可以使用--log参数,
201 |
202 | 比如: --log proxy.log,日志就会输出到proxy.log方便排除问题。
203 |
204 |
205 | ### 5. 生成加密通讯需要的证书文件
206 |
207 | http(s)代理、tcp代理、udp代理、socks5代理、内网穿透等功能和上级通讯的时候,为了安全我们采用TLS加密通讯,当然可以选择不加密通信通讯,本教程所有和上级通讯都采用加密,需要证书文件。
208 |
209 | ***所有端必须使用相同的proxy.crt和proxy.key***
210 |
211 | 1.通过下面的命令生成自签名的证书和key文件。
212 | `./proxy keygen -C proxy`
213 | 会在当前程序目录下面生成证书文件proxy.crt和key文件proxy.key。
214 |
215 | 2.通过下面的命令生,使用自签名证书proxy.crt和key文件proxy.key签发新证书:goproxy.crt和goproxy.key。
216 | `./proxy keygen -s -C proxy -c goproxy`
217 | 会在当前程序目录下面生成证书文件goproxy.crt和key文件goproxy.key。
218 |
219 | 3.默认情况下证书的里面的域名是随机的,可以使用`-n test.com`参数指定。
220 |
221 | 4.更多用法:`proxy keygen --help`。
222 |
223 | ### 6. 后台运行
224 |
225 | 默认执行proxy之后,如果要保持proxy运行,不能关闭命令行。
226 |
227 | 如果想在后台运行proxy,命令行可以关闭,只需要在命令最后加上--daemon参数即可。
228 |
229 | 比如:
230 |
231 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --daemon`
232 |
233 | ### 7. 守护运行
234 | 守护运行参数--forever,比如: `proxy http --forever` ,
235 |
236 | proxy会fork子进程,然后监控子进程,如果子进程异常退出,5秒后重启子进程。
237 |
238 | 该参数配合后台运行参数--daemon和日志参数--log,可以保障proxy一直在后台执行不会因为意外退出,
239 |
240 | 而且可以通过日志文件看到proxy的输出日志内容。
241 |
242 | 比如: `proxy http -p ":9090" --forever --log proxy.log --daemon`
243 |
244 | ### 8. 安全建议
245 |
246 | 当VPS在nat设备后面,vps上网卡IP都是内网IP,这个时候可以通过-g参数添加vps的外网ip防止死循环。
247 |
248 | 假设你的vps外网ip是23.23.23.23,下面命令通过-g参数设置23.23.23.23
249 |
250 | `./proxy http -g "23.23.23.23"`
251 |
252 | ### 9. 负载均衡和高可用
253 |
254 | HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS代理支持上级负载均衡和高可用,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
255 |
256 | 负载均衡策略支持5种,可以通过`--lb-method`参数指定:
257 |
258 | roundrobin 轮流使用
259 |
260 | leastconn 使用最小连接数的
261 |
262 | leasttime 使用连接时间最小的
263 |
264 | hash 使用根据客户端地址计算出一个固定上级
265 |
266 | weight 根据每个上级的权重和连接数情况,选择出一个上级
267 |
268 | 提示:
269 |
270 | 负载均衡检查时间间隔可以通过`--lb-retrytime`设置,单位毫秒
271 |
272 | 负载均衡连接超时时间可以通过`--lb-timeout`设置,单位毫秒
273 |
274 | 如果负载均衡策略是权重(weight),-P格式为:2.2.2.2:3880?w=1,1就是权重,大于0的整数。
275 |
276 | 如果负载均衡策略是hash,默认是根据客户端地址选择上级,可以通过开关`--lb-hashtarget`使用访问的目标地址选择上级。
277 |
278 |
279 | ### 10. 代理跳板跳转
280 |
281 | http(s)代理,SPS代理,内网穿透,tcp代理都支持通过中间第三方代理连接上级,
282 |
283 | 参数是:--jumper,所有格式如下:
284 |
285 | ```text
286 | http://username:password@host:port
287 | http://host:port
288 | https://username:password@host:port
289 | https://host:port
290 | socks5://username:password@host:port
291 | socks5://host:port
292 | socks5s://username:password@host:port
293 | socks5s://host:port
294 | ss://method:password@host:port
295 | ```
296 |
297 | http,socks5代表的是普通的http和socks5代理。
298 |
299 | https,socks5s代表的是通过tls保护的http和socks5代理,
300 |
301 | 也就是http代理 over TLS , socks over TLS。
302 |
303 | ### 11. 域名黑白名单
304 |
305 | socks/http(s)/sps代理都支持域名黑白名单。
306 |
307 | 用--stop参数指定一个域名黑名单列表文件,那么当用户连接文件里面这些域名的时候连接就会被断开。
308 |
309 | 用--only参数指定一个域名白名单列表文件,那么当用户连接文件里面这些域名之外的域名的时候连接就会被断开。
310 |
311 | 如果同时设置了--stop和--only,那么只有--only会起作用。
312 |
313 | 黑白域名名单文件内容格式如下:
314 |
315 | ```text
316 | **.baidu.com
317 | *.taobao.com
318 | a.com
319 | 192.168.1.1
320 | 192.168.*.*
321 | ?.qq.com
322 | ```
323 |
324 | 说明:
325 |
326 | 1.一行一个域名,域名写法支持通配符`*`和`?`,`*`代表任意个字符,`?`代表一个任意字符,
327 |
328 | 2.`**.baidu.com` 匹配无论是多少级所有后缀是`.baidu.com`的域名。
329 |
330 | 3.`*.taobao.com` 匹配后缀是`.taobao.com`的三级域名。
331 |
332 | 4.还可以直接是IP地址。
333 |
334 | 5.`#`开头的为注释。
335 |
336 | ### 12. 客户端IP黑白名单
337 |
338 | socks/http(s)/sps/tcp/udp/dns/内网穿透bridge/内网穿透tbridge,都支持客户端IP黑白名单。
339 |
340 | 用--ip-deny参数指定一个客户端IP黑名单列表文件,那么当用户的IP在这个文件里面的时候连接就会被断开。
341 |
342 | 用--ip-allow参数指定一个客户端IP白名单列表文件,那么当用户的IP不在这个文件里面的时候连接就会被断开。
343 |
344 | 如果同时设置了--ip-deny和--ip-allow,那么只有--ip-allow会起作用。
345 |
346 | 客户端IP黑白名单文件内容格式如下:
347 |
348 | ```text
349 | 192.168.1.1
350 | 192.168.*.*
351 | 192.168.1?.*
352 | ```
353 |
354 | 说明:
355 |
356 | 1.一行一个域名,域名写法支持通配符`*`和`?`,`*`代表任意个字符,`?`代表一个任意字符。
357 |
358 | 2.`#`开头的为注释。
359 |
360 | ### 13. 协议加载文件
361 |
362 | proxy的各种代理功能里面很多地方都有参数设置一个文件,比如:--blocked 指定一个直接走上级的域名列表文件,参数值是文件的路径,
363 |
364 | 如果参数支持协议加载文件,那么文件路径不仅可以是文件路径,还可以是:
365 |
366 | a.“base64://”开头的base64编码的上面说明的文件内容,比如:base64://ajfpoajsdfa=
367 |
368 | b.”str://“开头的英文逗号分割的多个,比如:str://xxx,yyy
369 |
370 | proxy的blocked,direct,stop,only,hosts,resolve.rules,rewriter.rules,ip.allow,ip.deny 文件支持协议加载。
371 |
372 | ## 1.HTTP代理
373 |
374 | ### 1.1.普通一级HTTP代理
375 |
376 | 
377 |
378 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080"`
379 |
380 | -p参数支持的写法:
381 |
382 | ```text
383 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
384 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
385 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
386 | ```
387 |
388 | ### 1.2.普通二级HTTP代理
389 |
390 | 
391 |
392 | 使用本地端口8090,假设上级HTTP代理是`22.22.22.22:8080`
393 |
394 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" `
395 |
396 | 我们还可以指定网站域名的黑白名单文件,一行一个域名,匹配规则是最右匹配,比如:baidu.com,匹配的是*.*.baidu.com,黑名单的域名直接走上级代理,白名单的域名不走上级代理。
397 |
398 | `./proxy http -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" -b blocked.txt -d direct.txt`
399 |
400 | ### 1.3.HTTP二级代理(加密)
401 |
402 | > 注意: 后面二级代理使用的`proxy.crt`和`proxy.key`应与一级代理一致
403 |
404 | 
405 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
406 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
407 |
408 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
409 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
410 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080。
411 |
412 | 二级HTTP代理(本地windows)
413 | `./proxy.exe http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
414 | 然后设置你的windos系统中,需要通过代理上网的程序的代理为http模式,地址为:127.0.0.1,端口为:8080,程序即可通过加密通道通过vps上网。
415 |
416 | ### 1.4.HTTP三级代理(加密)
417 | 
418 | 一级HTTP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
419 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
420 | 二级HTTP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
421 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
422 | 三级HTTP代理(本地)
423 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
424 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问一级HTTP代理上面的代理端口38080。
425 |
426 | ### 1.5.Basic认证,API认证
427 |
428 | 请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
429 |
430 | ### 1.6.HTTP代理流量强制走上级HTTP代理
431 | 默认情况下,proxy会智能判断一个网站域名是否无法访问,如果无法访问才走上级HTTP代理.通过--always可以使全部HTTP代理流量强制走上级HTTP代理。
432 | `./proxy http --always -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
433 |
434 | ### 1.7.HTTP(S)通过SSH中转
435 | 
436 | 说明:ssh中转的原理是利用了ssh的转发功能,就是你连接上ssh之后,可以通过ssh代理访问目标地址。
437 | 假设有:vps
438 | - IP是2.2.2.2, ssh端口是22, ssh用户名是:user, ssh用户密码是:demo
439 | - 用户user的ssh私钥名称是user.key
440 |
441 | #### *1.7.1 ssh用户名和密码的方式*
442 | 本地HTTP(S)代理28080端口,执行:
443 | `./proxy http -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -D demo -t tcp -p ":28080"`
444 | #### *1.7.2 ssh用户名和密钥的方式*
445 | 本地HTTP(S)代理28080端口,执行:
446 | `./proxy http -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -S user.key -t tcp -p ":28080"`
447 |
448 | ### 1.8.KCP协议传输
449 | 
450 | KCP协议需要--kcp-key参数设置一个密码用于加密解密数据
451 |
452 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
453 | `./proxy http -t kcp -p ":38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
454 |
455 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
456 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T kcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
457 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080,数据通过kcp协议传输,注意kcp走的是udp协议协议,所以防火墙需放开38080的udp协议。
458 |
459 | ### 1.9 HTTP(S)反向代理
460 | 
461 | proxy不仅支持在其他软件里面通过设置代理的方式,为其他软件提供代理服务,而且支持直接把请求的网站域名解析到proxy监听的ip上,然后proxy监听80和443端口,那么proxy就会自动为你代理访问需要访问的HTTP(S)网站。
462 |
463 | 使用方式:
464 | 在"最后一级proxy代理"的机器上,因为proxy要伪装成所有网站,网站默认的端口HTTP是80,HTTPS是443,让proxy监听80和443端口即可.参数-p多个地址用逗号分割。
465 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :80,:443`
466 |
467 | 这个命令就在机器上启动了一个proxy代理,同时监听80和443端口,既可以当作普通的代理使用,也可以直接把需要代理的域名解析到这个机器的IP上。
468 |
469 | 如果有上级代理那么参照上面教程设置上级即可,使用方式完全一样。
470 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :80,:443 -T tls -P "2.2.2.2:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
471 |
472 | 注意:
473 | proxy所在的服务器的DNS解析结果不能受到自定义的解析影响,不然就死循环了,proxy代理最好指定`--dns 8.8.8.8`参数。
474 |
475 | ### 1.10 HTTP(S)透明代理
476 | 该模式需要具有一定的网络基础,相关概念不懂的请自行搜索解决。
477 | 假设proxy现在在路由器上运行,启动命令如下:
478 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :33080 -T tls -P "2.2.2.2:33090" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
479 |
480 | 然后添加iptables规则,下面是参考规则:
481 | ```shell
482 | #上级proxy服务端服务器IP地址:
483 | proxy_server_ip=2.2.2.2
484 |
485 | #路由器运行proxy监听的端口:
486 | proxy_local_port=33080
487 |
488 | #下面的就不用修改了
489 | #create a new chain named PROXY
490 | iptables -t nat -N PROXY
491 |
492 | # Ignore your PROXY server's addresses
493 | # It's very IMPORTANT, just be careful。
494 |
495 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d $proxy_server_ip -j RETURN
496 |
497 | # Ignore LANs IP address
498 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 0.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
499 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 10.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
500 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 127.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
501 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 169.254.0.0/16 -j RETURN
502 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 172.16.0.0/12 -j RETURN
503 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 192.168.0.0/16 -j RETURN
504 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 224.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
505 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 240.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
506 |
507 | # Anything to port 80 443 should be redirected to PROXY's local port
508 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
509 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp --dport 443 -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
510 |
511 | # Apply the rules to nat client
512 | iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -j PROXY
513 | # Apply the rules to localhost
514 | iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp -j PROXY
515 | ```
516 | - 清空整个链 iptables -F 链名比如iptables -t nat -F PROXY
517 | - 删除指定的用户自定义链 iptables -X 链名 比如 iptables -t nat -X PROXY
518 | - 从所选链中删除规则 iptables -D 链名 规则详情 比如 iptables -t nat -D PROXY -d 223.223.192.0/255.255.240.0 -j RETURN
519 |
520 | ### 1.11 自定义DNS
521 | --dns-address和--dns-ttl参数,用于自己指定proxy访问域名的时候使用的dns(--dns-address)
522 | 以及解析结果缓存时间(--dns-ttl)秒数,避免系统dns对proxy的干扰,另外缓存功能还能减少dns解析时间提高访问速度。
523 | 比如:
524 | `./proxy http -p ":33080" --dns-address "8.8.8.8:53" --dns-ttl 300`
525 |
526 | ### 1.12 自定义加密
527 | proxy的http(s)代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义
528 | 加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可,
529 | 加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
530 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以,下面分别用二级,三级为例:
531 |
532 | 二级实例
533 |
534 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
535 | `proxy http -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
536 | 本地二级执行:
537 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
538 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
539 |
540 |
541 | 三级实例
542 |
543 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
544 | `proxy http -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
545 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
546 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
547 | 本地三级执行:
548 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
549 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
550 |
551 | ### 1.13 压缩传输
552 | proxy的http(s)代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以对数据进行压缩,
553 | 也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,
554 | 一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
555 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据,下面分别用二级,三级为例:
556 |
557 | 二级实例
558 |
559 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
560 | `proxy http -t tcp -m -p :7777`
561 | 本地二级执行:
562 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
563 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
564 |
565 |
566 | 三级实例
567 |
568 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
569 | `proxy http -t tcp -m -p :7777`
570 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
571 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
572 | 本地三级执行:
573 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
574 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
575 |
576 | ### 1.14 负载均衡
577 |
578 | HTTP(S)代理支持上级负载均衡,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
579 |
580 | `proxy http --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080`
581 |
582 | ### 1.14.1 设置重试间隔和超时时间
583 |
584 | `proxy http --lb-method=leastconn --lb-retrytime 300 --lb-timeout 300 -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -t tcp -p :33080`
585 |
586 | ### 1.14.2 设置权重
587 |
588 | `proxy http --lb-method=weight -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -P 2.1.1.1:33080?w=2 -P 3.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -t tcp -p :33080`
589 |
590 | ### 1.14.3 使用目标地址选择上级
591 |
592 | `proxy http --lb-hashtarget --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -t tcp -p :33080`
593 |
594 | ### 1.15 限速
595 |
596 | 限速100K,通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
597 |
598 | `proxy http -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -l 100K`
599 |
600 | ### 1.16 指定出口IP
601 |
602 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作,此时代理会尝试不绑定IP去访问目标,同时日志会提示。
603 |
604 | `proxy http -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 --bind-listen`
605 |
606 | ### 1.17 证书参数使用base64数据
607 |
608 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
609 |
610 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
611 |
612 | ### 1.18 智能模式
613 | 智能模式设置,可以是intelligent|direct|parent三者之一。
614 | 默认是:intelligent。
615 | 每个值的含义如下:
616 | `--intelligent=direct`,不在blocked里面的目标都直连。
617 | `--intelligent=parent`,不在direct里面的目标都走上级。
618 | `--intelligent=intelligent`,blocked和direct里面都没有的目标,智能判断是否使用上级访问目标。
619 |
620 | ### 1.19 查看帮助
621 | `./proxy help http`
622 |
623 | ## 2.TCP代理
624 |
625 | ### 2.1 普通一级TCP代理
626 | 
627 | 本地执行:
628 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22"`
629 | 那么访问本地33080端口就是访问192.168.22.33的22端口。
630 |
631 | `-p`参数支持的写法:
632 |
633 | ```text
634 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
635 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
636 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
637 | ```
638 |
639 | 如果本地监听端口数量大于1,那么将会连接与本地端口一致的对应上级端口,忽略`-P`里面的端口。
640 |
641 | 如果需要所有端口进来的连接,都连接到上级指定端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`。
642 |
643 | 比如:
644 |
645 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080-33085" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:0"`
646 |
647 | 那么`33080`端口进来的连接,将会连接192.168.22.33的`33080`端口,其它端口以此类推,本地和上级端口一致,此时参数`-P`里面的端口用`0`。
648 |
649 | 如果想无论是`33080`,`33081`等端口进来的连接都连接到192.168.22.33的`22`端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`
650 |
651 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080-33085" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --lock-port`
652 |
653 |
654 | ### 2.2 普通二级TCP代理
655 | 
656 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
657 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "127.0.0.1:8080"`
658 | 本地执行:
659 | `./proxy tcp -p ":23080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.33:33080"`
660 | 那么访问本地23080端口就是访问22.22.22.33的8080端口。
661 |
662 | ### 2.3 普通三级TCP代理
663 | 
664 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
665 | `./proxy tcp -p ":38080" -T tcp -P "66.66.66.66:8080"`
666 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
667 | `./proxy tcp -p ":28080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080"`
668 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
669 | `./proxy tcp -p ":8080" -T tcp -P "33.33.33.33:28080"`
670 | 那么访问本地8080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问66.66.66.66的8080端口。
671 |
672 | ### 2.4 加密二级TCP代理
673 | 
674 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
675 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "127.0.0.1:8080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
676 | 本地执行:
677 | `./proxy tcp -p ":23080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.33:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
678 | 那么访问本地23080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问22.22.22.33的8080端口。
679 |
680 | ### 2.5 加密三级TCP代理
681 | 
682 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
683 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":38080" -T tcp -P "66.66.66.66:8080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
684 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
685 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
686 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
687 | `./proxy tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
688 | 那么访问本地8080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问66.66.66.66的8080端口。
689 |
690 | ### 2.6 通过代理连接上级
691 | 有时候proxy所在的网络不能直接访问外网,需要通过一个https或者socks5代理才能上网,那么这个时候
692 | -J参数就可以帮助你让proxy的tcp端口映射的时候通过https或者socks5代理去连接上级-P,将外部端口映射到本地。
693 | -J参数格式如下:
694 |
695 | https代理写法:
696 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
697 | https://username:password@host:port
698 | 代理不需要认证
699 | https://host:port
700 |
701 | socks5代理写法:
702 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
703 | socks5://username:password@host:port
704 | 代理不需要认证
705 | socks5://host:port
706 |
707 | host:代理的IP或者域名
708 | port:代理的端口
709 |
710 | ### 2.7 指定`出口IP`
711 | 当TCP代理当上级类型(参数:-T)是tcp当时候,支持指定`出口IP`。使用`--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作,此时代理会尝试不绑定IP去访问目标,同时日志会提示。
712 |
713 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" -B`
714 |
715 | ### 2.8 限速,限制连接数
716 |
717 | 参数`--max-conns`可以限制每个端口的最大连接数。
718 | 比如限制每个端口最多1000个连接数:
719 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --max-conns 1000`
720 | 参数`--rate-limit`可以限制每个tcp连接的速率。
721 | 比如限制每个tcp连接速率为100k/s:
722 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --rate-limit 100k`
723 |
724 | ### 2.9 查看帮助
725 | `./proxy help tcp`
726 |
727 | ## 3.UDP代理
728 |
729 | ### 3.1.普通一级UDP代理
730 | 
731 | 本地执行:
732 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
733 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
734 |
735 | `-p`参数支持的写法:
736 |
737 | ```text
738 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
739 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
740 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
741 | ```
742 |
743 | 如果本地监听端口数量大于1,那么将会连接与本地端口一致的对应上级端口,忽略`-P`里面的端口。
744 |
745 | 如果需要所有端口进来的连接,都连接到上级指定端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`。
746 |
747 | 比如:
748 |
749 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080-33085" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:0"`
750 |
751 | 那么`33080`端口进来的连接,将会连接192.168.22.33的`33080`端口,其它端口以此类推,本地和上级端口一致,此时参数`-P`里面的端口用`0`。
752 |
753 | 如果想无论是`33080`,`33081`等端口进来的连接都连接到192.168.22.33的`2222`端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`
754 |
755 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080-33085" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:2222" --lock-port`
756 |
757 | ### 3.2.普通二级UDP代理
758 | 
759 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
760 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
761 | 本地执行:
762 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.33:33080"`
763 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是通过TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
764 |
765 | ### 3.3.普通三级UDP代理
766 | 
767 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
768 | `./proxy tcp -p ":38080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
769 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
770 | `./proxy tcp -p ":28080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080"`
771 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
772 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tcp -P "33.33.33.33:28080"`
773 | 那么访问本地5353端口就是通过TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的53端口。
774 |
775 | ### 3.4.加密二级UDP代理
776 | 
777 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
778 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":33080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
779 | 本地执行:
780 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tls -P "22.22.22.33:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
781 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是通过加密TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
782 |
783 | ### 3.5.加密三级UDP代理
784 | 
785 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
786 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":38080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
787 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
788 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
789 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
790 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
791 | 那么访问本地5353端口就是通过加密TCP隧道,通过VPS_01访问8.8.8.8的53端口。
792 |
793 | ### 3.6 指定`出口IP`
794 | 当UDP代理当上级类型(参数:-T)是udp当时候,支持指定`出口IP`。使用`--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作。
795 |
796 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:2222" -B`
797 |
798 | ### 3.7 查看帮助
799 | `./proxy help udp`
800 |
801 | ## 4.内网穿透
802 | ### 4.1、原理说明
803 | 内网穿透,分为两个版本,“多链接版本”和“多路复用版本”,一般像web服务这种不是长时间连接的服务建议用“多链接版本”,如果是要保持长时间连接建议使用“多路复用版本”。
804 | 1. 多链接版本,对应的子命令是tserver,tclient,tbridge。
805 | 1. 多路复用版本,对应的子命令是server,client,bridge。
806 | 1. 多链接版本和多路复用版本的参数和使用方式完全一样。
807 | 1. 多路复用版本的server,client可以开启压缩传输,参数是--c。
808 | 1. server,client要么都开启压缩,要么都不开启,不能只开一个。
809 |
810 | 下面的教程以“多路复用版本”为例子,说明使用方法。
811 | 内网穿透由三部分组成:client端,server端,bridge端;client和server主动连接bridge端进行桥接。
812 |
813 | ### 4.2、TCP普通用法
814 | 背景:
815 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口
816 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
817 |
818 | 需求:
819 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的28080端口访问到公司机器A的80端口
820 |
821 | 步骤:
822 | 1. 在vps上执行
823 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
824 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
825 |
826 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
827 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
828 |
829 | 1. 完成
830 |
831 | ### 4.3、微信接口本地开发
832 | 背景:
833 | - 自己的笔记本提供了nginx服务80端口
834 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
835 |
836 | 需求:
837 | 在微信的开发帐号的网页回调接口配置里面填写地址:http://22.22.22.22/calback.php
838 | 然后就可以访问到笔记本的80端口下面的calback.php,如果需要绑定域名,可以用自己的域名
839 | 比如:wx-dev.xxx.com解析到22.22.22.22,然后在自己笔记本的nginx里
840 | 配置域名wx-dev.xxx.com到具体的目录即可。
841 |
842 |
843 | 步骤:
844 | 1. 在vps上执行,确保vps的80端口没被其它程序占用。
845 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
846 | `./proxy server -r ":80@:80" -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
847 |
848 | 1. 在自己笔记本上面执行
849 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
850 |
851 | 1. 完成
852 |
853 | ### 4.4、UDP普通用法
854 | 背景:
855 | - 公司机器A提供了DNS解析服务,UDP:53端口
856 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
857 |
858 | 需求:
859 | 在家里能够通过设置本地dns为22.22.22.22,使用公司机器A进行域名解析服务。
860 |
861 | 步骤:
862 | 1. 在vps上执行
863 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
864 | `./proxy server --udp -r ":53@:53" -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
865 |
866 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
867 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
868 |
869 | 1. 完成
870 |
871 | ### 4.5、高级用法一
872 | 背景:
873 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口
874 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
875 |
876 | 需求:
877 | 为了安全,不想在VPS上能够访问到公司机器A,在家里能够通过访问本机的28080端口,
878 | 通过加密隧道访问到公司机器A的80端口。
879 |
880 | 步骤:
881 | 1. 在vps上执行
882 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
883 |
884 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
885 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
886 |
887 | 1. 在家里电脑上执行
888 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
889 |
890 | 1. 完成
891 |
892 | ### 4.6、高级用法二
893 | 提示:
894 | 如果同时有多个client连接到同一个bridge,需要指定不同的key,可以通过--k参数设定,--k可以是任意唯一字符串,
895 | 只要在同一个bridge上唯一即可。
896 | server连接到bridge的时候,如果同时有多个client连接到同一个bridge,需要使用--k参数选择client。
897 | 暴露多个端口重复-r参数即可.-r格式是:"本地IP:本地端口@clientHOST:client端口"。
898 |
899 | 背景:
900 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口,ftp服务21端口
901 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
902 |
903 | 需求:
904 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的28080端口访问到公司机器A的80端口
905 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的29090端口访问到公司机器A的21端口
906 |
907 | 步骤:
908 | 1. 在vps上执行
909 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
910 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -r ":29090@:21" --k test -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
911 |
912 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
913 | `./proxy client --k test -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
914 |
915 | 1. 完成
916 |
917 | ### 4.7.server的-r参数
918 | -r完整格式是:`PROTOCOL://LOCAL_IP:LOCAL_PORT@[CLIENT_KEY]CLIENT_LOCAL_HOST:CLIENT_LOCAL_PORT`
919 |
920 | 4.7.1.协议PROTOCOL:tcp、udp、ptcp、pudp。
921 | 比如: `-r "udp://:10053@:53" -r "tcp://:10800@:1080" -r ":8080@:80"`
922 | 如果指定了--udp参数,PROTOCOL默认为udp,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`默认为udp;
923 | 如果没有指定--udp参数,PROTOCOL默认为tcp,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`默认为tcp;
924 |
925 | 4.7.2.CLIENT_KEY:默认是default。
926 | 比如: -r "udp://:10053@[test1]:53" -r "tcp://:10800@[test2]:1080" -r ":8080@:80"
927 | 如果指定了--k参数,比如--k test,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`CLIENT_KEY默认为test;
928 | 如果没有指定--k参数,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`CLIENT_KEY默认为default;
929 |
930 | 4.7.3.LOCAL_IP为空默认是:`0.0.0.0`,CLIENT_LOCAL_HOST为空默认是:`127.0.0.1`;
931 |
932 | ### 4.8.server和client通过代理连接bridge
933 | 有时候server或者client所在的网络不能直接访问外网,需要通过一个https或者socks5代理才能上网,那么这个时候
934 | -J参数就可以帮助你让server或者client通过https或者socks5代理去连接bridge。
935 | -J参数格式如下:
936 |
937 | https代理写法:
938 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
939 | https://username:password@host:port
940 | 代理不需要认证
941 | https://host:port
942 |
943 | socks5代理写法:
944 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
945 | socks5://username:password@host:port
946 | 代理不需要认证
947 | socks5://host:port
948 |
949 | host:代理的IP或者域名
950 | port:代理的端口
951 |
952 | ### 4.9.内网穿透HTTP服务
953 |
954 | 通常HTTP请求客户端会使用server的ip和端口去设置HOST字段,但是与期望的后端实际HOST不一样,这样就造成了tcp是通的,
955 | 但后端依赖HOST字段定位虚拟主机就不能工作.现在用--http-host参数强制设置http头部的HOST字段值为后端实际的
956 | 域名和端口即可轻松解决。
957 |
958 | `server`的--http-host参数格式如下:
959 |
960 | `--http-host www.test.com:80@2200`,如果server监听多个端口,只需要重复`--http-host`参数设置每个端口的HOST即可。
961 |
962 | 实例:
963 |
964 | 比如client本地nginx,127.0.0.1:80提供了web服务,其中绑定了一个域名`local.com`。
965 |
966 | 那么server的启动参数可以如下:
967 |
968 | `proxy server -P :30000 -r :2500@127.0.0.1:80 --http-host local.com@2500`
969 |
970 | 解释:
971 |
972 | `-r :2500@127.0.0.1:80` 和 `--http-host local.com:80@2500` 里面的2500端口是server本地监听的端口
973 |
974 | 当使用http协议请求server的ip:2500端口的时候,http的头部HOST字段就会被设置为`local.com`。
975 |
976 | ### 4.10 关于流量统计
977 |
978 | 如果单独启动一个server对接上级是proxy-admin控制面板,需要在上级控制面板里面新建一个映射,获得个映射规则的ID,
979 |
980 | 然后启动server的时候加上参数 --server-id=映射规则的ID 才能统计到流量。
981 |
982 | ### 4.11 关于p2p
983 | 内网穿透支持在server和client网络情况满足的情况下,server和client之间通过p2p直接连接,开启方法是:
984 |
985 | 在启动bridge,server,client到时候都加上`--p2p`参数即可。server的-r参数可以针对端口是否启用p2p(ptcp和pudp)。
986 |
987 | 如果server和client之间p2p打洞失败,那么会自动切换使用bridge中转传输数据。
988 |
989 | ### 4.12 客户端key白名单
990 | 内网穿透bridge可以设置客户端key白名单,参数是--client-keys,格式可以是:
991 |
992 | a.文件名,文件内容一行一个客户端key只能包含数字字母下划线,也就是客户端启动参数--k的值,只有客户端key在此白名单的客户端才能连接。# 开头的行,为注释。
993 |
994 | b.“base64://”开头的base64编码的上面a说明的文件内容,比如:base64://ajfpoajsdfa=
995 |
996 | c.”str://“开头的英文逗号分割的多个key,比如:str://default,company,school
997 |
998 | 默认是空,允许所有key。
999 |
1000 | ### 4.13 网络NAT类型判断
1001 |
1002 | nat类型判断,方便查看网络是否支持p2p,可以执行:`proxy tools -a nattype`
1003 |
1004 | ### 4.14 查看帮助
1005 | `./proxy help bridge`
1006 | `./proxy help server`
1007 | `./proxy help client`
1008 |
1009 | ## 5.SOCKS5代理
1010 | 提示:
1011 |
1012 | SOCKS5代理,支持CONNECT,UDP协议,不支持BIND,支持用户名密码认证。
1013 |
1014 | ***如果你的VPS是阿里云,腾讯云这种VPS,就是ifconfig看不见你的公网IP,只能看见内网IP,***
1015 |
1016 | ***那么需要加上`-g VPS公网IP`参数,SOCKS5代理的UDP功能才能正常工作。***
1017 |
1018 | ### 5.1 普通SOCKS5代理
1019 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080"`
1020 |
1021 | -p参数支持的写法:
1022 |
1023 | ```text
1024 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
1025 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
1026 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
1027 | ```
1028 |
1029 | ### 5.2.普通二级SOCKS5代理
1030 | 
1031 | 使用本地端口8090,假设上级SOCKS5代理是`22.22.22.22:8080`
1032 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" `
1033 | 我们还可以指定网站域名的黑白名单文件,一行一个域名,匹配规则是最右匹配,比如:baidu.com,匹配的是*.*.baidu.com,黑名单的域名域名直接走上级代理,白名单的域名不走上级代理;如果域名即在黑名单又在白名单中,那么黑名单起作用。
1034 | `./proxy socks -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" -b blocked.txt -d direct.txt`
1035 |
1036 | ### 5.3.SOCKS二级代理(加密)
1037 | 
1038 | 一级SOCKS代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
1039 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1040 |
1041 | 二级SOCKS代理(本地Linux)
1042 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1043 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080。
1044 |
1045 | 二级SOCKS代理(本地windows)
1046 | `./proxy.exe socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1047 | 然后设置你的windos系统中,需要通过代理上网的程序的代理为socks5模式,地址为:127.0.0.1,端口为:8080,程序即可通过加密通道通过vps上网。
1048 |
1049 | ### 5.4.SOCKS三级代理(加密)
1050 | 
1051 | 一级SOCKS代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
1052 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1053 | 二级SOCKS代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
1054 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1055 | 三级SOCKS代理(本地)
1056 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1057 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问一级SOCKS代理上面的代理端口38080。
1058 |
1059 | ### 5.5.SOCKS代理流量强制走上级SOCKS代理
1060 | 默认情况下,proxy会智能判断一个网站域名是否无法访问,如果无法访问才走上级SOCKS代理.通过--always可以使全部SOCKS代理流量强制走上级SOCKS代理。
1061 | `./proxy socks --always -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1062 |
1063 | ### 5.6.SOCKS通过SSH中转
1064 | 
1065 | 说明:ssh中转的原理是利用了ssh的转发功能,就是你连接上ssh之后,可以通过ssh代理访问目标地址。
1066 | 假设有:vps
1067 | - IP是2.2.2.2, ssh端口是22, ssh用户名是:user, ssh用户密码是:demo
1068 | - 用户user的ssh私钥名称是user.key
1069 |
1070 | #### *5.6.1 ssh用户名和密码的方式*
1071 | 本地SOCKS5代理28080端口,执行:
1072 | `./proxy socks -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -D demo -t tcp -p ":28080"`
1073 | #### *5.6.2 ssh用户名和密钥的方式*
1074 | 本地SOCKS5代理28080端口,执行:
1075 | `./proxy socks -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -S user.key -t tcp -p ":28080"`
1076 |
1077 | 那么访问本地的28080端口就是通过VPS访问目标地址。
1078 |
1079 | ### 5.7.认证
1080 | 对于socks5代理协议我们可以进行用户名密码认证,认证的用户名和密码可以在命令行指定
1081 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1" -a "user2:pass2"`
1082 | 多个用户,重复-a参数即可。
1083 | 也可以放在文件中,格式是一行一个"用户名:密码",然后用-F指定。
1084 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":33080" -F auth-file.txt`
1085 |
1086 | ### 5.8.KCP协议传输
1087 | KCP协议需要--kcp-key参数设置一个密码用于加密解密数据
1088 |
1089 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
1090 | `./proxy socks -t kcp -p ":38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
1091 |
1092 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
1093 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T kcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
1094 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080,数据通过kcp协议传输。
1095 |
1096 | ### 5.9.自定义DNS
1097 | --dns-address和--dns-ttl参数,用于自己指定proxy访问域名的时候使用的dns(--dns-address)
1098 | 以及解析结果缓存时间(--dns-ttl)秒数,避免系统dns对proxy的干扰,另外缓存功能还能减少dns解析时间提高访问速度。
1099 | 比如:
1100 | `./proxy socks -p ":33080" --dns-address "8.8.8.8:53" --dns-ttl 300`
1101 |
1102 | ### 5.10 自定义加密
1103 | proxy的socks代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可,
1104 | 加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
1105 |
1106 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以。
1107 |
1108 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
1109 |
1110 | 二级实例
1111 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1112 | `proxy socks -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
1113 | 本地二级执行:
1114 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
1115 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
1116 |
1117 |
1118 | 三级实例
1119 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1120 | `proxy socks -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
1121 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
1122 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
1123 | 本地三级执行:
1124 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
1125 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
1126 |
1127 | ### 5.11 压缩传输
1128 | proxy的socks代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以
1129 | 对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,
1130 | 一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
1131 |
1132 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据。
1133 |
1134 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
1135 |
1136 | 二级实例
1137 |
1138 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1139 | `proxy socks -t tcp -m -p :7777`
1140 | 本地二级执行:
1141 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
1142 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
1143 |
1144 |
1145 | 三级实例
1146 |
1147 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1148 | `proxy socks -t tcp -m -p :7777`
1149 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
1150 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
1151 | 本地三级执行:
1152 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
1153 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
1154 |
1155 |
1156 | ### 5.12 负载均衡
1157 |
1158 | SOCKS代理支持上级负载均衡,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
1159 |
1160 | `proxy socks --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
1161 |
1162 | ### 5.12.1 设置重试间隔和超时时间
1163 |
1164 | `proxy socks --lb-method=leastconn --lb-retrytime 300 --lb-timeout 300 -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
1165 |
1166 | ### 5.12.2 设置权重
1167 |
1168 | `proxy socks --lb-method=weight -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -P 2.1.1.1:33080?w=2 -P 3.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -p :33080 -t tcp`
1169 |
1170 | ### 5.12.3 使用目标地址选择上级
1171 |
1172 | `proxy socks --lb-hashtarget --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
1173 |
1174 | ### 5.13 限速
1175 |
1176 | 限速100K,通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
1177 |
1178 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -l 100K`
1179 |
1180 | ### 5.14 指定`出口IP`
1181 |
1182 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果`入口IP`是内网IP,`出口IP`不会使用`入口IP`。
1183 |
1184 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 --bind-listen`
1185 |
1186 | ### 5.15 级联认证
1187 |
1188 | SOCKS5支持级联认证,-A可以设置上级认证信息。
1189 |
1190 | 上级:
1191 |
1192 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -a user:pass`
1193 |
1194 | 本地:
1195 |
1196 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -A user:pass -t tcp -p :33080`
1197 |
1198 | 请更多认证细节,请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
1199 |
1200 | ### 5.16 证书参数使用base64数据
1201 |
1202 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
1203 |
1204 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
1205 |
1206 |
1207 | ### 5.17 智能模式
1208 | 智能模式设置,可以是intelligent|direct|parent三者之一。
1209 | 默认是:intelligent。
1210 | 每个值的含义如下:
1211 | `--intelligent=direct`,不在blocked里面的目标都直连。
1212 | `--intelligent=parent`,不在direct里面的目标都走上级。
1213 | `--intelligent=intelligent`,blocked和direct里面都没有的目标,智能判断是否使用上级访问目标。
1214 |
1215 | ### 5.18 固定UDP功能端口
1216 |
1217 | 默认情况下socks5的UDP功能的端口号,proxy是按着`rfc1982草案`要求,使用协议握手过程中随机指定,不需要提前指定。
1218 |
1219 | 但是某些情况下,需要固定UDP功能端口,可以通过参数`--udp-port 端口号`用来固定UDP功能的端口号,比如:
1220 |
1221 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --udp-port 38080`
1222 |
1223 | ### 5.19 查看帮助
1224 | `./proxy help socks`
1225 |
1226 | ## 6.SPS协议转换
1227 |
1228 | ### 6.1 功能介绍
1229 | 代理协议转换使用的是sps子命令,sps本身不提供代理功能,只是接受代理请求"转换并转发"给已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理或者ss代理;sps可以把已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理或ss代理转换为一个端口同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的代理,而且http(s)代理支持正向代理和反向代理(SNI),转换后的SOCKS5代理,当上级是SOCKS5或者SS时仍然支持UDP功能;另外对于已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理,支持tls、tcp、kcp三种模式,支持链式连接,也就是可以多个sps结点层级连接构建加密通道。
1230 |
1231 | `ss`功能支持的加密方法为:aes-128-cfb , aes-128-ctr , aes-128-gcm , aes-192-cfb , aes-192-ctr , aes-192-gcm , aes-256-cfb , aes-256-ctr , aes-256-gcm , bf-cfb , cast5-cfb , chacha20 , chacha20-ietf , chacha20-ietf-poly1305 , des-cfb , rc4-md5 , rc4-md5-6 , salsa20 , xchacha20
1232 |
1233 | 本地监听端口-p参数支持的写法:
1234 |
1235 | ```text
1236 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
1237 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
1238 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
1239 | ```
1240 |
1241 | ### 6.2 HTTP(S)转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
1242 | 假设已经存在一个普通的http(s)代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1243 | 命令如下:
1244 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1245 |
1246 | 假设已经存在一个tls的http(s)代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,tls需要证书文件,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1247 | 命令如下:
1248 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1249 |
1250 | 假设已经存在一个kcp的http(s)代理(密码是:demo123):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1251 | 命令如下:
1252 | `./proxy sps -S http -T kcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 --kcp-key demo123 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1253 |
1254 | ### 6.3 SOCKS5转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
1255 | 假设已经存在一个普通的socks5代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1256 | 命令如下:
1257 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1258 |
1259 | 假设已经存在一个tls的socks5代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,tls需要证书文件,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1260 | 命令如下:
1261 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T tls -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1262 |
1263 | 假设已经存在一个kcp的socks5代理(密码是:demo123):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1264 | 命令如下:
1265 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T kcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 --kcp-key demo123 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1266 |
1267 | ### 6.4 SS转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
1268 | SPS上级和本地支持ss协议,上级可以是SPS或者标准的ss服务。
1269 | SPS本地默认提供HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS三种代理,当上级是SOCKS5时转换后的SOCKS5和SS支持UDP功能。
1270 | 假设已经存在一个普通的SS或者SPS代理(开启了ss,加密方式:aes-256-cfb,密码:demo):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,转换后的ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1271 | 命令如下:
1272 | `./proxy sps -S ss -H aes-256-cfb -J pass -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`。
1273 |
1274 | ### 6.5 链式连接
1275 | 
1276 | 上面提过多个sps结点可以层级连接构建加密通道,假设有如下vps和家里的pc电脑。
1277 | vps01:2.2.2.2
1278 | vps02:3.3.3.3
1279 | 现在我们想利用pc和vps01和vps02构建一个加密通道,本例子用tls加密也可以用kcp,在pc上访问本地18080端口就是访问vps01的本地8080端口。
1280 | 首先在vps01(2.2.2.2)上我们运行一个只有本地可以访问的http(s)代理,执行:
1281 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p 127.0.0.1:8080`
1282 |
1283 | 然后在vps01(2.2.2.2)上运行一个sps结点,执行:
1284 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tls -p :8081 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1285 |
1286 | 然后在vps02(3.3.3.3)上运行一个sps结点,执行:
1287 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:8081 -t tls -p :8082 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1288 |
1289 | 然后在pc上运行一个sps结点,执行:
1290 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 3.3.3.3:8082 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1291 |
1292 | 完成。
1293 |
1294 | ### 6.6 监听多个端口
1295 | 一般情况下监听一个端口就可以,不过如果作为反向代理需要同时监听80和443两个端口,那么-p参数是支持的,
1296 | 格式是:`-p 0.0.0.0:80,0.0.0.0:443`,多个绑定用逗号分隔即可。
1297 |
1298 | ### 6.7 认证功能
1299 | sps支持http(s)\socks5代理认证,可以级联认证,有四个重要的信息:
1300 | 1:用户发送认证信息`user-auth`。
1301 | 2:设置的本地认证信息`local-auth`。
1302 | 3:设置的连接上级使用的认证信息`parent-auth`。
1303 | 4:最终发送给上级的认证信息`auth-info-to-parent`。
1304 | 他们的情况关系如下:
1305 |
1306 | | user-auth | local-auth | parent-auth | auth-info-to-paren
1307 | | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------
1308 | | 有/没有 | 有 | 有 | 来自parent-auth
1309 | | 有/没有 | 没有 | 有 | 来自parent-auth
1310 | | 有/没有 | 有 | 没有 | 无
1311 | | 没有 | 没有 | 没有 | 无
1312 | | 有 | 没有 | 没有 | 来自user-auth
1313 |
1314 | 对于sps代理我们可以进行用户名密码认证,认证的用户名和密码可以在命令行指定
1315 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1:0:0:" -a "user2:pass2:0:0:"`
1316 | 多个用户,重复-a参数即可。
1317 | 也可以放在文件中,格式是一行一个`用户名:密码:连接数:速率:上级`,然后用-F指定。
1318 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -F auth-file.txt`
1319 |
1320 | 如果上级有认证,下级可以通过-A参数设置认证信息,比如:
1321 | 上级:`./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1:0:0:" -a "user2:pass2:0:0:"`
1322 | 下级:`./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -A "user1:pass1" -t tcp -p ":33080" `
1323 |
1324 | 请更多认证细节,请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
1325 |
1326 | ### 6.8 多个上级
1327 |
1328 | 如果存在多个上级,可以通过多个-P指定。
1329 |
1330 | 比如:
1331 |
1332 | `proxy sps -P http://127.0.0.1:3100 -P socks5://127.0.0.1:3200`
1333 |
1334 | `-P`完整格式如下:
1335 |
1336 | `protocol://a:b@2.2.2.2:33080#1`
1337 |
1338 | 下面对每部分进行解释:
1339 |
1340 | `protocol://` 是协议类型,可能的类型以及含有如下:
1341 |
1342 | ```text
1343 | http 等价于 -S http -T tcp
1344 | https 等价于 -S http -T tls --parent-tls-single , 也就是http(s)代理 over TLS
1345 | https2 等价于 -S http -T tls
1346 | socks5 等价于 -S socks -T tcp
1347 | socks5s 等价于 -S socks -T tls --parent-tls-single , 也就是socks over TLS
1348 | socks5s2 等价于 -S socks -T tls
1349 | ss 等价于 -S ss -T tcp
1350 | httpws 等价于 -S http -T ws
1351 | httpwss 等价于 -S http -T wss
1352 | socks5ws 等价于 -S socks -T ws
1353 | socks5wss 等价于 -S socks -T wss
1354 | ```
1355 |
1356 | `a:b`是代理认证的用户名密码,如果是ss,`a`是加密方法,`b`是密码,没有用户名密码可以留空比如:`http://2.2.2.2:33080`,如果用户名和密码保护特殊符号可以使用urlencode进行编码。
1357 |
1358 | `2.2.2.2:33080`是上级地址,格式是:`IP(或域名):端口`,如果底层是ws/wss协议还可以带上路径,比如:`2.2.2.2:33080/ws`;
1359 | 还能通过附加查询参数`m`和`k`设置`ws\wss`的`加密方法`和`密码`,比如:`2.2.2.2:33080/ws?m=aes-192-cfb&k=password`
1360 |
1361 | `#1`多个上级的负载均衡是权重策略时候,设置的权重,很少用到。
1362 |
1363 | ### 6.9 自定义加密
1364 | proxy的sps代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行
1365 | 自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义
1366 | 一个密码即可,加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
1367 |
1368 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以。
1369 |
1370 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
1371 |
1372 | 假设已经存在一个http(s)代理:`6.6.6.6:6666`
1373 |
1374 | 二级实例
1375 |
1376 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1377 | `proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 6.6.6.6:6666 -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
1378 | 本地二级执行:
1379 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
1380 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
1381 |
1382 |
1383 | 三级实例
1384 |
1385 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1386 | `proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 6.6.6.6:6666 -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
1387 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
1388 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
1389 | 本地三级执行:
1390 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
1391 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
1392 |
1393 | ### 6.10 压缩传输
1394 | proxy的sps代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以
1395 | 对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,
1396 | 一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
1397 |
1398 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据。
1399 |
1400 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
1401 |
1402 | 二级实例
1403 |
1404 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1405 | `proxy sps -t tcp -m -p :7777`
1406 | 本地二级执行:
1407 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
1408 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
1409 |
1410 |
1411 | 三级实例
1412 |
1413 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1414 | `proxy sps -t tcp -m -p :7777`
1415 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
1416 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
1417 | 本地三级执行:
1418 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
1419 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
1420 |
1421 | ### 6.11 禁用协议
1422 | SPS默认情况下一个端口支持http(s)和socks5两种代理协议,我们可以通过参数禁用某个协议
1423 | 比如:
1424 | 1.禁用HTTP(S)代理功能只保留SOCKS5代理功能,参数:`--disable-http`。
1425 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080 --disable-http`
1426 |
1427 | 1.禁用SOCKS5代理功能只保留HTTP(S)代理功能,参数:`--disable-socks`。
1428 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080 --disable-http`
1429 |
1430 | ### 6.12 限速
1431 |
1432 | 假设存在SOCKS5上级:
1433 |
1434 | `proxy socks -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -z password -t tcp`
1435 |
1436 | sps下级,限速100K
1437 |
1438 | `proxy sps -S socks -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -T tcp -Z password -l 100K -t tcp -p :33080`
1439 |
1440 | 通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
1441 |
1442 | ### 6.13 指定`出口IP`
1443 |
1444 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果`入口IP`是内网IP,`出口IP`不会使用`入口IP`。
1445 |
1446 | `proxy sps -S socks -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -T tcp -Z password -l 100K -t tcp --bind-listen -p :33080`
1447 |
1448 | ### 6.14 证书参数使用base64数据
1449 |
1450 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
1451 |
1452 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
1453 |
1454 | ### 6.15 独立服务
1455 | sps功能不强制指定一个上级,当上级为空,sps本身即可完成完整的代理功能.如果指定了上级那么就和之前一样使用上级连接目标。
1456 | 下面这个命令,就是一键开启http(s)\ss\socks服务。
1457 | `./proxy sps -p :33080`
1458 |
1459 | ### 6.16 目标重定向
1460 | sps功能提供的http(s)\socks5\ss代理功能,客户端通过sps代理去连接指定的“目标”,这个“目标”一般是网站也可能是任意的tcp地址,
1461 | 网站”目标“一般是foo.com:80,foo.com:443,sps支持使用--rewrite参数指定一个“目标”重定向规则文件,对目标进行重定向,客户端是无感知的,
1462 | 比如你对“目标”:demo.com:80重定向到192.168.0.12:80,那么客户端访问网站demo.com,其实访问的是192.168.0.12提供的网站服务。
1463 | “目标”重定向规则文件示例:
1464 |
1465 | ```text
1466 | # example
1467 | www.a.com:80 10.0.0.2:8080
1468 | **.b.com:80 10.0.0.2:80
1469 | 192.168.0.11:80 10.0.0.2:8080
1470 | ```
1471 |
1472 | ### 6.17 固定UDP功能端口
1473 |
1474 | 默认情况下sps的socks5的UDP功能的端口号是按着`rfc1982草案`要求,使用协议握手过程中随机指定,不需要提前指定。
1475 |
1476 | 但是某些情况下,需要固定UDP功能端口,可以通过参数`--udp-port 端口号`用来固定UDP功能的端口号,比如:
1477 |
1478 | `./proxy sps -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --udp-port 38081`
1479 |
1480 | 需要注意的是,sps的ss功能也有UDP功能,而且ss的UDP端口和tcp端口是一样的,所以要避免socks5的UDP端口和ss的UDP端口冲突,
1481 |
1482 | 要指定和tcp端口不一样的端口。
1483 |
1484 | ### 6.18 iptables 透明代理
1485 | sps模式支持Linux系统的iptables转发支持,也就是通常所说的iptables透明代理,如果在网关设备上进行iptables透明代理,那么对通过网关联网的设备就能实现无感知的代理。
1486 |
1487 | 启动命令实例:
1488 |
1489 | `./proxy sps --redir -p :8888 -P httpws://1.1.1.1:33080`
1490 |
1491 | 这里假设存在一个http的上级代理1.1.1.1:33080,使用ws传输数据。
1492 |
1493 | 然后添加iptables规则,下面是参考规则:
1494 | ```shell
1495 | #上级proxy服务端服务器IP地址:
1496 | proxy_server_ip=1.1.1.1
1497 |
1498 | #路由器运行proxy监听的端口:
1499 | proxy_local_port=33080
1500 |
1501 | #下面的就不用修改了
1502 | #create a new chain named PROXY
1503 | iptables -t nat -N PROXY
1504 |
1505 | # Ignore your PROXY server's addresses
1506 | # It's very IMPORTANT, just be careful。
1507 |
1508 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d $proxy_server_ip -j RETURN
1509 |
1510 | # Ignore LANs IP address
1511 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 0.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
1512 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 10.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
1513 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 127.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
1514 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 169.254.0.0/16 -j RETURN
1515 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 172.16.0.0/12 -j RETURN
1516 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 192.168.0.0/16 -j RETURN
1517 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 224.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
1518 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 240.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
1519 |
1520 | # Anything to port 80 443 should be redirected to PROXY's local port
1521 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
1522 | # Apply the rules to nat client
1523 | iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -j PROXY
1524 | # Apply the rules to localhost
1525 | iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp -j PROXY
1526 | ```
1527 | - 清空整个链 iptables -F 链名比如iptables -t nat -F PROXY
1528 | - 删除指定的用户自定义链 iptables -X 链名 比如 iptables -t nat -X PROXY
1529 | - 从所选链中删除规则 iptables -D 链名 规则详情 比如 iptables -t nat -D PROXY -d 223.223.192.0/255.255.240.0 -j RETURN
1530 |
1531 | ### 6.19 查看帮助
1532 |
1533 | `./proxy help sps`
1534 |
1535 | ## 7.KCP配置
1536 |
1537 | ### 7.1 配置介绍
1538 | proxy的很多功能都支持kcp协议,凡是使用了kcp协议的功能都支持这里介绍的配置参数。
1539 | 所以这里统一对KCP配置参数进行介绍。
1540 |
1541 | ### 7.2 详细配置
1542 | 所有的KCP配置参数共有17个,你可以都不用设置,他们都有默认值,如果为了或者最好的效果,
1543 | 就需要自己根据自己根据网络情况对参数进行配置。由于kcp配置很复杂需要一定的网络基础知识,
1544 | 如果想获得kcp参数更详细的配置和解说,请自行搜索。每个参数的命令行名称以及默认值和简单的功能说明如下:
1545 | ```
1546 | --kcp-key="secrect" pre-shared secret between client and server
1547 | --kcp-method="aes" encrypt/decrypt method, can be: aes, aes-128, aes-192, salsa20, blowfish,
1548 | twofish, cast5, 3des, tea, xtea, xor, sm4, none
1549 | --kcp-mode="fast" profiles: fast3, fast2, fast, normal, manual
1550 | --kcp-mtu=1350 set maximum transmission unit for UDP packets
1551 | --kcp-sndwnd=1024 set send window size(num of packets)
1552 | --kcp-rcvwnd=1024 set receive window size(num of packets)
1553 | --kcp-ds=10 set reed-solomon erasure coding - datashard
1554 | --kcp-ps=3 set reed-solomon erasure coding - parityshard
1555 | --kcp-dscp=0 set DSCP(6bit)
1556 | --kcp-nocomp disable compression
1557 | --kcp-acknodelay be carefull! flush ack immediately when a packet is received
1558 | --kcp-nodelay=0 be carefull!
1559 | --kcp-interval=50 be carefull!
1560 | --kcp-resend=0 be carefull!
1561 | --kcp-nc=0 be carefull! no congestion
1562 | --kcp-sockbuf=4194304 be carefull!
1563 | --kcp-keepalive=10 be carefull!
1564 | ```
1565 | 提示:
1566 | 参数:--kcp-mode中的四种fast3, fast2, fast, normal模式,
1567 | 相当于设置了下面四个参数:
1568 | normal:`--nodelay=0 --interval=40 --resend=2 --nc=1`
1569 | fast :`--nodelay=0 --interval=30 --resend=2 --nc=1`
1570 | fast2:`--nodelay=1 --interval=20 --resend=2 --nc=1`
1571 | fast3:`--nodelay=1 --interval=10 --resend=2 --nc=1`
1572 |
1573 | ## 8.安全DNS
1574 |
1575 | ### 8.1 介绍
1576 | 众所周知DNS是UDP端口53提供的服务,但是随着网络的发展一些知名DNS服务器也支持TCP方式dns查询,比如谷歌的8.8.8.8,proxy的DNS防污染服务器原理就是在本地启动一个proxy的DNS代理服务器,它用TCP的方式通过上级代理进行dns查询。如果它和上级代理通讯采用加密的方式,那么就可以进行安全无污染的DNS解析,还支持独立服务,并发解析,支持增强的hosts文件功能支持灵活的并发解析转发。
1577 |
1578 | dns解析顺序:
1579 | 1.使用参数--hosts解析。
1580 | 2.要解析的域名在1中没有找到,就使用参数--forward规则解析。
1581 | 3.要解析的域名在1和2中都没有找到,就使用默认--default解析,--default默认行为参数值有三种:proxy,direct,system。
1582 | 三种参数值解释如下:
1583 | proxy:通过上级去连接-q参数指定的dns服务器去解析域名。
1584 | direct:通过本地网络去连接-q参数指定的dns服务器去解析域名。
1585 | system:通过系统dns去解析域名。
1586 |
1587 | 提示:
1588 | --hosts 参数指定的host文件格式和系统hosts文件一致,而且域名支持通配符,可以参考hosts文件。
1589 | --forward 参数指定的解析转发规则文件,格式可以参考resolve.rules文件,域名支持通配符,支持为每个域名指定多个dns服务器并发解析,谁最快解析成功就用谁的解析结果。
1590 | -q 参数可以指定多个远程dns服务器,执行并发解析谁最快解析成功就用谁的解析结果,默认是:1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8,9.9.9.9,多个用逗号分割,
1591 | 比如还可以带端口:1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8#53,9.9.9.9
1592 |
1593 | 如果独立服务,不需要上级:
1594 | 可以执行:
1595 | `proxy dns --default system -p :5353`
1596 | or
1597 | `proxy dns --default direct -p :5353`
1598 |
1599 | ### 8.2 使用示例
1600 |
1601 | #### 8.2.1 普通HTTP(S)上级代理
1602 |
1603 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1604 | 本地执行:
1605 | `proxy dns -S http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1606 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了DNS解析功能。
1607 |
1608 | #### 8.2.2 普通SOCKS5上级代理
1609 |
1610 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1611 | 本地执行:
1612 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1613 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了DNS解析功能。
1614 |
1615 | #### 8.2.3 TLS加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
1616 |
1617 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1618 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1619 | `proxy http -t tls -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :33080`
1620 | 本地执行:
1621 | `proxy dns -S http -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :53`
1622 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1623 |
1624 | #### 8.2.4 TLS加密的SOCKS5上级代理
1625 |
1626 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1627 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1628 | `proxy socks -t tls -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :33080`
1629 | 本地执行:
1630 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :53`
1631 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1632 |
1633 | #### 8.2.5 KCP加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
1634 |
1635 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1636 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1637 | `proxy http -t kcp -p :33080`
1638 | 本地执行:
1639 | `proxy dns -S http -T kcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1640 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1641 |
1642 | #### 8.2.6 KCP加密的SOCKS5上级代理
1643 |
1644 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1645 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1646 | `proxy socks -t kcp -p :33080`
1647 | 本地执行:
1648 | `proxy dns -S socks -T kcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1649 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1650 |
1651 | #### 8.2.7 自定义加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
1652 |
1653 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1654 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1655 | `proxy http -t tcp -p :33080 -z password`
1656 | 本地执行:
1657 | `proxy dns -S http -T tcp -Z password -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1658 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1659 |
1660 | #### 8.2.8 自定义加密的SOCKS5上级代理
1661 |
1662 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1663 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1664 | `proxy socks -t kcp -p :33080 -z password`
1665 | 本地执行:
1666 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tcp -Z password -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1667 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1668 |
1669 | ## 9.API认证,限速,控制连接数
1670 |
1671 | proxy的http(s)/socks5/sps代理功能,支持通过API控制用户对代理对访问。
1672 |
1673 | ### 通过API可以干什么?
1674 |
1675 | - 用户维度,控制单个连接速率,控制最大连接数。
1676 | - IP维度,控制单个连接速率,控制最大连接数。
1677 | - 动态上级,可以根据用户或者客户端IP,动态的从API获取其上级,支持http(s)/socks5/ss上级。
1678 | - 认证每一个连接,无论是否要求客户端认证。
1679 | - 缓存认证结果,时间可以设置,减轻API压力。
1680 |
1681 | #### 具体使用
1682 | proxy的http(s)/socks5/sps代理API功能,通过`--auth-url`和`--auth-nouser`和`--auth-cache`三个参数控制。
1683 | 参数`--auth-url`是HTTP API接口地址,客户端连接的时候,proxy会GET方式请求这url,带上下面参数,如果返回HTTP状态码204,代表认证成功,其它情况认为认证失败。
1684 |
1685 | 一个完整的请求API的示例:
1686 | `http://test.com/auth.php?user=a&pass=b&client_addr=127.0.0.1:49892&local_addr=127.0.0.1:8100&target=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.baidu.com&service=http&sps=0`
1687 |
1688 | #### 参数说明
1689 | `user和pass` 当代理开启了认证功能,这里就是客户端提供的用户名和密码。
1690 | `client_addr` 客户端访问代理时的用的地址,格式IP:端口。
1691 | `local_addr` 客户端访问的代理地址,格式IP:端口。
1692 | `service` 代理类型,分为:http、socks。
1693 | `sps` 代理是否是sps提供的,1:是,0:否。
1694 | `target` 客户端要访问的目标,如果是http(s)代理,target是访问的具体url;如果是socks5代理,target是空。
1695 |
1696 | #### 示例
1697 | 假设--auth-url http://127.0.0.1:333/auth.php 指向了一个php接口地址.
1698 | auth.php内容如下:
1699 |
1700 | ```php
1701 | 注意: 后面二级代理使用的`proxy.crt`和`proxy.key`应与一级代理一致
2041 |
2042 | 
2043 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
2044 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2045 |
2046 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
2047 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2048 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080。
2049 |
2050 | 二级HTTP代理(本地windows)
2051 | `./proxy.exe http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2052 | 然后设置你的windos系统中,需要通过代理上网的程序的代理为http模式,地址为:127.0.0.1,端口为:8080,程序即可通过加密通道通过vps上网。
2053 |
2054 | ### 1.4.HTTP三级代理(加密)
2055 | 
2056 | 一级HTTP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2057 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2058 | 二级HTTP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2059 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2060 | 三级HTTP代理(本地)
2061 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2062 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问一级HTTP代理上面的代理端口38080。
2063 |
2064 | ### 1.5.Basic认证,API认证
2065 |
2066 | 请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
2067 |
2068 | ### 1.6.HTTP代理流量强制走上级HTTP代理
2069 | 默认情况下,proxy会智能判断一个网站域名是否无法访问,如果无法访问才走上级HTTP代理.通过--always可以使全部HTTP代理流量强制走上级HTTP代理。
2070 | `./proxy http --always -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2071 |
2072 | ### 1.7.HTTP(S)通过SSH中转
2073 | 
2074 | 说明:ssh中转的原理是利用了ssh的转发功能,就是你连接上ssh之后,可以通过ssh代理访问目标地址。
2075 | 假设有:vps
2076 | - IP是2.2.2.2, ssh端口是22, ssh用户名是:user, ssh用户密码是:demo
2077 | - 用户user的ssh私钥名称是user.key
2078 |
2079 | #### *1.7.1 ssh用户名和密码的方式*
2080 | 本地HTTP(S)代理28080端口,执行:
2081 | `./proxy http -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -D demo -t tcp -p ":28080"`
2082 | #### *1.7.2 ssh用户名和密钥的方式*
2083 | 本地HTTP(S)代理28080端口,执行:
2084 | `./proxy http -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -S user.key -t tcp -p ":28080"`
2085 |
2086 | ### 1.8.KCP协议传输
2087 | 
2088 | KCP协议需要--kcp-key参数设置一个密码用于加密解密数据
2089 |
2090 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
2091 | `./proxy http -t kcp -p ":38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
2092 |
2093 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
2094 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T kcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
2095 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080,数据通过kcp协议传输,注意kcp走的是udp协议协议,所以防火墙需放开38080的udp协议。
2096 |
2097 | ### 1.9 HTTP(S)反向代理
2098 | 
2099 | proxy不仅支持在其他软件里面通过设置代理的方式,为其他软件提供代理服务,而且支持直接把请求的网站域名解析到proxy监听的ip上,然后proxy监听80和443端口,那么proxy就会自动为你代理访问需要访问的HTTP(S)网站。
2100 |
2101 | 使用方式:
2102 | 在"最后一级proxy代理"的机器上,因为proxy要伪装成所有网站,网站默认的端口HTTP是80,HTTPS是443,让proxy监听80和443端口即可.参数-p多个地址用逗号分割。
2103 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :80,:443`
2104 |
2105 | 这个命令就在机器上启动了一个proxy代理,同时监听80和443端口,既可以当作普通的代理使用,也可以直接把需要代理的域名解析到这个机器的IP上。
2106 |
2107 | 如果有上级代理那么参照上面教程设置上级即可,使用方式完全一样。
2108 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :80,:443 -T tls -P "2.2.2.2:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2109 |
2110 | 注意:
2111 | proxy所在的服务器的DNS解析结果不能受到自定义的解析影响,不然就死循环了,proxy代理最好指定`--dns 8.8.8.8`参数。
2112 |
2113 | ### 1.10 HTTP(S)透明代理
2114 | 该模式需要具有一定的网络基础,相关概念不懂的请自行搜索解决。
2115 | 假设proxy现在在路由器上运行,启动命令如下:
2116 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :33080 -T tls -P "2.2.2.2:33090" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2117 |
2118 | 然后添加iptables规则,下面是参考规则:
2119 | ```shell
2120 | #上级proxy服务端服务器IP地址:
2121 | proxy_server_ip=2.2.2.2
2122 |
2123 | #路由器运行proxy监听的端口:
2124 | proxy_local_port=33080
2125 |
2126 | #下面的就不用修改了
2127 | #create a new chain named PROXY
2128 | iptables -t nat -N PROXY
2129 |
2130 | # Ignore your PROXY server's addresses
2131 | # It's very IMPORTANT, just be careful。
2132 |
2133 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d $proxy_server_ip -j RETURN
2134 |
2135 | # Ignore LANs IP address
2136 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 0.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
2137 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 10.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
2138 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 127.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
2139 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 169.254.0.0/16 -j RETURN
2140 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 172.16.0.0/12 -j RETURN
2141 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 192.168.0.0/16 -j RETURN
2142 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 224.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
2143 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 240.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
2144 |
2145 | # Anything to port 80 443 should be redirected to PROXY's local port
2146 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
2147 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp --dport 443 -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
2148 |
2149 | # Apply the rules to nat client
2150 | iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -j PROXY
2151 | # Apply the rules to localhost
2152 | iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp -j PROXY
2153 | ```
2154 | - 清空整个链 iptables -F 链名比如iptables -t nat -F PROXY
2155 | - 删除指定的用户自定义链 iptables -X 链名 比如 iptables -t nat -X PROXY
2156 | - 从所选链中删除规则 iptables -D 链名 规则详情 比如 iptables -t nat -D PROXY -d 223.223.192.0/255.255.240.0 -j RETURN
2157 |
2158 | ### 1.11 自定义DNS
2159 | --dns-address和--dns-ttl参数,用于自己指定proxy访问域名的时候使用的dns(--dns-address)
2160 | 以及解析结果缓存时间(--dns-ttl)秒数,避免系统dns对proxy的干扰,另外缓存功能还能减少dns解析时间提高访问速度。
2161 | 比如:
2162 | `./proxy http -p ":33080" --dns-address "8.8.8.8:53" --dns-ttl 300`
2163 |
2164 | ### 1.12 自定义加密
2165 | proxy的http(s)代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义
2166 | 加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可,
2167 | 加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
2168 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以,下面分别用二级,三级为例:
2169 |
2170 | 二级实例
2171 |
2172 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2173 | `proxy http -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
2174 | 本地二级执行:
2175 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
2176 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
2177 |
2178 |
2179 | 三级实例
2180 |
2181 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2182 | `proxy http -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
2183 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
2184 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
2185 | 本地三级执行:
2186 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
2187 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
2188 |
2189 | ### 1.13 压缩传输
2190 | proxy的http(s)代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以对数据进行压缩,
2191 | 也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,
2192 | 一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
2193 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据,下面分别用二级,三级为例:
2194 |
2195 | 二级实例
2196 |
2197 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2198 | `proxy http -t tcp -m -p :7777`
2199 | 本地二级执行:
2200 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
2201 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
2202 |
2203 |
2204 | 三级实例
2205 |
2206 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2207 | `proxy http -t tcp -m -p :7777`
2208 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
2209 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
2210 | 本地三级执行:
2211 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
2212 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
2213 |
2214 | ### 1.14 负载均衡
2215 |
2216 | HTTP(S)代理支持上级负载均衡,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
2217 |
2218 | `proxy http --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080`
2219 |
2220 | ### 1.14.1 设置重试间隔和超时时间
2221 |
2222 | `proxy http --lb-method=leastconn --lb-retrytime 300 --lb-timeout 300 -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -t tcp -p :33080`
2223 |
2224 | ### 1.14.2 设置权重
2225 |
2226 | `proxy http --lb-method=weight -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -P 2.1.1.1:33080?w=2 -P 3.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -t tcp -p :33080`
2227 |
2228 | ### 1.14.3 使用目标地址选择上级
2229 |
2230 | `proxy http --lb-hashtarget --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -t tcp -p :33080`
2231 |
2232 | ### 1.15 限速
2233 |
2234 | 限速100K,通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
2235 |
2236 | `proxy http -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -l 100K`
2237 |
2238 | ### 1.16 指定出口IP
2239 |
2240 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作,此时代理会尝试不绑定IP去访问目标,同时日志会提示。
2241 |
2242 | `proxy http -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 --bind-listen`
2243 |
2244 | ### 1.17 证书参数使用base64数据
2245 |
2246 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
2247 |
2248 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
2249 |
2250 | ### 1.18 智能模式
2251 | 智能模式设置,可以是intelligent|direct|parent三者之一。
2252 | 默认是:intelligent。
2253 | 每个值的含义如下:
2254 | `--intelligent=direct`,不在blocked里面的目标都直连。
2255 | `--intelligent=parent`,不在direct里面的目标都走上级。
2256 | `--intelligent=intelligent`,blocked和direct里面都没有的目标,智能判断是否使用上级访问目标。
2257 |
2258 | ### 1.19 查看帮助
2259 | `./proxy help http`
2260 |
2261 | ## 2.TCP代理
2262 |
2263 | ### 2.1 普通一级TCP代理
2264 | 
2265 | 本地执行:
2266 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22"`
2267 | 那么访问本地33080端口就是访问192.168.22.33的22端口。
2268 |
2269 | `-p`参数支持的写法:
2270 |
2271 | ```text
2272 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
2273 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
2274 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
2275 | ```
2276 |
2277 | 如果本地监听端口数量大于1,那么将会连接与本地端口一致的对应上级端口,忽略`-P`里面的端口。
2278 |
2279 | 如果需要所有端口进来的连接,都连接到上级指定端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`。
2280 |
2281 | 比如:
2282 |
2283 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080-33085" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:0"`
2284 |
2285 | 那么`33080`端口进来的连接,将会连接192.168.22.33的`33080`端口,其它端口以此类推,本地和上级端口一致,此时参数`-P`里面的端口用`0`。
2286 |
2287 | 如果想无论是`33080`,`33081`等端口进来的连接都连接到192.168.22.33的`22`端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`
2288 |
2289 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080-33085" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --lock-port`
2290 |
2291 |
2292 | ### 2.2 普通二级TCP代理
2293 | 
2294 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
2295 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "127.0.0.1:8080"`
2296 | 本地执行:
2297 | `./proxy tcp -p ":23080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.33:33080"`
2298 | 那么访问本地23080端口就是访问22.22.22.33的8080端口。
2299 |
2300 | ### 2.3 普通三级TCP代理
2301 | 
2302 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2303 | `./proxy tcp -p ":38080" -T tcp -P "66.66.66.66:8080"`
2304 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2305 | `./proxy tcp -p ":28080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080"`
2306 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
2307 | `./proxy tcp -p ":8080" -T tcp -P "33.33.33.33:28080"`
2308 | 那么访问本地8080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问66.66.66.66的8080端口。
2309 |
2310 | ### 2.4 加密二级TCP代理
2311 | 
2312 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
2313 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "127.0.0.1:8080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2314 | 本地执行:
2315 | `./proxy tcp -p ":23080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.33:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2316 | 那么访问本地23080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问22.22.22.33的8080端口。
2317 |
2318 | ### 2.5 加密三级TCP代理
2319 | 
2320 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2321 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":38080" -T tcp -P "66.66.66.66:8080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2322 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2323 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2324 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
2325 | `./proxy tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2326 | 那么访问本地8080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问66.66.66.66的8080端口。
2327 |
2328 | ### 2.6 通过代理连接上级
2329 | 有时候proxy所在的网络不能直接访问外网,需要通过一个https或者socks5代理才能上网,那么这个时候
2330 | -J参数就可以帮助你让proxy的tcp端口映射的时候通过https或者socks5代理去连接上级-P,将外部端口映射到本地。
2331 | -J参数格式如下:
2332 |
2333 | https代理写法:
2334 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
2335 | https://username:password@host:port
2336 | 代理不需要认证
2337 | https://host:port
2338 |
2339 | socks5代理写法:
2340 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
2341 | socks5://username:password@host:port
2342 | 代理不需要认证
2343 | socks5://host:port
2344 |
2345 | host:代理的IP或者域名
2346 | port:代理的端口
2347 |
2348 | ### 2.7 指定`出口IP`
2349 | 当TCP代理当上级类型(参数:-T)是tcp当时候,支持指定`出口IP`。使用`--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作,此时代理会尝试不绑定IP去访问目标,同时日志会提示。
2350 |
2351 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" -B`
2352 |
2353 | ### 2.8 限速,限制连接数
2354 |
2355 | 参数`--max-conns`可以限制每个端口的最大连接数。
2356 | 比如限制每个端口最多1000个连接数:
2357 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --max-conns 1000`
2358 | 参数`--rate-limit`可以限制每个tcp连接的速率。
2359 | 比如限制每个tcp连接速率为100k/s:
2360 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --rate-limit 100k`
2361 |
2362 | ### 2.9 查看帮助
2363 | `./proxy help tcp`
2364 |
2365 | ## 3.UDP代理
2366 |
2367 | ### 3.1.普通一级UDP代理
2368 | 
2369 | 本地执行:
2370 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
2371 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
2372 |
2373 | `-p`参数支持的写法:
2374 |
2375 | ```text
2376 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
2377 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
2378 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
2379 | ```
2380 |
2381 | 如果本地监听端口数量大于1,那么将会连接与本地端口一致的对应上级端口,忽略`-P`里面的端口。
2382 |
2383 | 如果需要所有端口进来的连接,都连接到上级指定端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`。
2384 |
2385 | 比如:
2386 |
2387 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080-33085" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:0"`
2388 |
2389 | 那么`33080`端口进来的连接,将会连接192.168.22.33的`33080`端口,其它端口以此类推,本地和上级端口一致,此时参数`-P`里面的端口用`0`。
2390 |
2391 | 如果想无论是`33080`,`33081`等端口进来的连接都连接到192.168.22.33的`2222`端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`
2392 |
2393 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080-33085" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:2222" --lock-port`
2394 |
2395 | ### 3.2.普通二级UDP代理
2396 | 
2397 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
2398 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
2399 | 本地执行:
2400 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.33:33080"`
2401 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是通过TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
2402 |
2403 | ### 3.3.普通三级UDP代理
2404 | 
2405 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2406 | `./proxy tcp -p ":38080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
2407 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2408 | `./proxy tcp -p ":28080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080"`
2409 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
2410 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tcp -P "33.33.33.33:28080"`
2411 | 那么访问本地5353端口就是通过TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的53端口。
2412 |
2413 | ### 3.4.加密二级UDP代理
2414 | 
2415 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
2416 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":33080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2417 | 本地执行:
2418 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tls -P "22.22.22.33:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2419 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是通过加密TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
2420 |
2421 | ### 3.5.加密三级UDP代理
2422 | 
2423 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2424 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":38080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2425 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2426 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2427 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
2428 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2429 | 那么访问本地5353端口就是通过加密TCP隧道,通过VPS_01访问8.8.8.8的53端口。
2430 |
2431 | ### 3.6 指定`出口IP`
2432 | 当UDP代理当上级类型(参数:-T)是udp当时候,支持指定`出口IP`。使用`--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作。
2433 |
2434 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:2222" -B`
2435 |
2436 | ### 3.7 查看帮助
2437 | `./proxy help udp`
2438 |
2439 | ## 4.内网穿透
2440 | ### 4.1、原理说明
2441 | 内网穿透,分为两个版本,“多链接版本”和“多路复用版本”,一般像web服务这种不是长时间连接的服务建议用“多链接版本”,如果是要保持长时间连接建议使用“多路复用版本”。
2442 | 1. 多链接版本,对应的子命令是tserver,tclient,tbridge。
2443 | 1. 多路复用版本,对应的子命令是server,client,bridge。
2444 | 1. 多链接版本和多路复用版本的参数和使用方式完全一样。
2445 | 1. 多路复用版本的server,client可以开启压缩传输,参数是--c。
2446 | 1. server,client要么都开启压缩,要么都不开启,不能只开一个。
2447 |
2448 | 下面的教程以“多路复用版本”为例子,说明使用方法。
2449 | 内网穿透由三部分组成:client端,server端,bridge端;client和server主动连接bridge端进行桥接。
2450 |
2451 | ### 4.2、TCP普通用法
2452 | 背景:
2453 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口
2454 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2455 |
2456 | 需求:
2457 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的28080端口访问到公司机器A的80端口
2458 |
2459 | 步骤:
2460 | 1. 在vps上执行
2461 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2462 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2463 |
2464 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
2465 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2466 |
2467 | 1. 完成
2468 |
2469 | ### 4.3、微信接口本地开发
2470 | 背景:
2471 | - 自己的笔记本提供了nginx服务80端口
2472 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2473 |
2474 | 需求:
2475 | 在微信的开发帐号的网页回调接口配置里面填写地址:http://22.22.22.22/calback.php
2476 | 然后就可以访问到笔记本的80端口下面的calback.php,如果需要绑定域名,可以用自己的域名
2477 | 比如:wx-dev.xxx.com解析到22.22.22.22,然后在自己笔记本的nginx里
2478 | 配置域名wx-dev.xxx.com到具体的目录即可。
2479 |
2480 |
2481 | 步骤:
2482 | 1. 在vps上执行,确保vps的80端口没被其它程序占用。
2483 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2484 | `./proxy server -r ":80@:80" -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2485 |
2486 | 1. 在自己笔记本上面执行
2487 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2488 |
2489 | 1. 完成
2490 |
2491 | ### 4.4、UDP普通用法
2492 | 背景:
2493 | - 公司机器A提供了DNS解析服务,UDP:53端口
2494 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2495 |
2496 | 需求:
2497 | 在家里能够通过设置本地dns为22.22.22.22,使用公司机器A进行域名解析服务。
2498 |
2499 | 步骤:
2500 | 1. 在vps上执行
2501 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2502 | `./proxy server --udp -r ":53@:53" -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2503 |
2504 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
2505 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2506 |
2507 | 1. 完成
2508 |
2509 | ### 4.5、高级用法一
2510 | 背景:
2511 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口
2512 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2513 |
2514 | 需求:
2515 | 为了安全,不想在VPS上能够访问到公司机器A,在家里能够通过访问本机的28080端口,
2516 | 通过加密隧道访问到公司机器A的80端口。
2517 |
2518 | 步骤:
2519 | 1. 在vps上执行
2520 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2521 |
2522 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
2523 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2524 |
2525 | 1. 在家里电脑上执行
2526 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2527 |
2528 | 1. 完成
2529 |
2530 | ### 4.6、高级用法二
2531 | 提示:
2532 | 如果同时有多个client连接到同一个bridge,需要指定不同的key,可以通过--k参数设定,--k可以是任意唯一字符串,
2533 | 只要在同一个bridge上唯一即可。
2534 | server连接到bridge的时候,如果同时有多个client连接到同一个bridge,需要使用--k参数选择client。
2535 | 暴露多个端口重复-r参数即可.-r格式是:"本地IP:本地端口@clientHOST:client端口"。
2536 |
2537 | 背景:
2538 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口,ftp服务21端口
2539 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2540 |
2541 | 需求:
2542 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的28080端口访问到公司机器A的80端口
2543 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的29090端口访问到公司机器A的21端口
2544 |
2545 | 步骤:
2546 | 1. 在vps上执行
2547 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2548 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -r ":29090@:21" --k test -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2549 |
2550 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
2551 | `./proxy client --k test -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2552 |
2553 | 1. 完成
2554 |
2555 | ### 4.7.server的-r参数
2556 | -r完整格式是:`PROTOCOL://LOCAL_IP:LOCAL_PORT@[CLIENT_KEY]CLIENT_LOCAL_HOST:CLIENT_LOCAL_PORT`
2557 |
2558 | 4.7.1.协议PROTOCOL:tcp、udp、ptcp、pudp。
2559 | 比如: `-r "udp://:10053@:53" -r "tcp://:10800@:1080" -r ":8080@:80"`
2560 | 如果指定了--udp参数,PROTOCOL默认为udp,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`默认为udp;
2561 | 如果没有指定--udp参数,PROTOCOL默认为tcp,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`默认为tcp;
2562 |
2563 | 4.7.2.CLIENT_KEY:默认是default。
2564 | 比如: -r "udp://:10053@[test1]:53" -r "tcp://:10800@[test2]:1080" -r ":8080@:80"
2565 | 如果指定了--k参数,比如--k test,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`CLIENT_KEY默认为test;
2566 | 如果没有指定--k参数,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`CLIENT_KEY默认为default;
2567 |
2568 | 4.7.3.LOCAL_IP为空默认是:`0.0.0.0`,CLIENT_LOCAL_HOST为空默认是:`127.0.0.1`;
2569 |
2570 | ### 4.8.server和client通过代理连接bridge
2571 | 有时候server或者client所在的网络不能直接访问外网,需要通过一个https或者socks5代理才能上网,那么这个时候
2572 | -J参数就可以帮助你让server或者client通过https或者socks5代理去连接bridge。
2573 | -J参数格式如下:
2574 |
2575 | https代理写法:
2576 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
2577 | https://username:password@host:port
2578 | 代理不需要认证
2579 | https://host:port
2580 |
2581 | socks5代理写法:
2582 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
2583 | socks5://username:password@host:port
2584 | 代理不需要认证
2585 | socks5://host:port
2586 |
2587 | host:代理的IP或者域名
2588 | port:代理的端口
2589 |
2590 | ### 4.9.内网穿透HTTP服务
2591 |
2592 | 通常HTTP请求客户端会使用server的ip和端口去设置HOST字段,但是与期望的后端实际HOST不一样,这样就造成了tcp是通的,
2593 | 但后端依赖HOST字段定位虚拟主机就不能工作.现在用--http-host参数强制设置http头部的HOST字段值为后端实际的
2594 | 域名和端口即可轻松解决。
2595 |
2596 | `server`的--http-host参数格式如下:
2597 |
2598 | `--http-host www.test.com:80@2200`,如果server监听多个端口,只需要重复`--http-host`参数设置每个端口的HOST即可。
2599 |
2600 | 实例:
2601 |
2602 | 比如client本地nginx,127.0.0.1:80提供了web服务,其中绑定了一个域名`local.com`。
2603 |
2604 | 那么server的启动参数可以如下:
2605 |
2606 | `proxy server -P :30000 -r :2500@127.0.0.1:80 --http-host local.com@2500`
2607 |
2608 | 解释:
2609 |
2610 | `-r :2500@127.0.0.1:80` 和 `--http-host local.com:80@2500` 里面的2500端口是server本地监听的端口
2611 |
2612 | 当使用http协议请求server的ip:2500端口的时候,http的头部HOST字段就会被设置为`local.com`。
2613 |
2614 | ### 4.10 关于流量统计
2615 |
2616 | 如果单独启动一个server对接上级是proxy-admin控制面板,需要在上级控制面板里面新建一个映射,获得个映射规则的ID,
2617 |
2618 | 然后启动server的时候加上参数 --server-id=映射规则的ID 才能统计到流量。
2619 |
2620 | ### 4.11 关于p2p
2621 | 内网穿透支持在server和client网络情况满足的情况下,server和client之间通过p2p直接连接,开启方法是:
2622 |
2623 | 在启动bridge,server,client到时候都加上`--p2p`参数即可。server的-r参数可以针对端口是否启用p2p(ptcp和pudp)。
2624 |
2625 | 如果server和client之间p2p打洞失败,那么会自动切换使用bridge中转传输数据。
2626 |
2627 | ### 4.12 客户端key白名单
2628 | 内网穿透bridge可以设置客户端key白名单,参数是--client-keys,格式可以是:
2629 |
2630 | a.文件名,文件内容一行一个客户端key只能包含数字字母下划线,也就是客户端启动参数--k的值,只有客户端key在此白名单的客户端才能连接。# 开头的行,为注释。
2631 |
2632 | b.“base64://”开头的base64编码的上面a说明的文件内容,比如:base64://ajfpoajsdfa=
2633 |
2634 | c.”str://“开头的英文逗号分割的多个key,比如:str://default,company,school
2635 |
2636 | 默认是空,允许所有key。
2637 |
2638 | ### 4.13 网络NAT类型判断
2639 |
2640 | nat类型判断,方便查看网络是否支持p2p,可以执行:`proxy tools -a nattype`
2641 |
2642 | ### 4.14 查看帮助
2643 | `./proxy help bridge`
2644 | `./proxy help server`
2645 | `./proxy help client`
2646 |
2647 | ## 5.SOCKS5代理
2648 | 提示:
2649 |
2650 | SOCKS5代理,支持CONNECT,UDP协议,不支持BIND,支持用户名密码认证。
2651 |
2652 | ***如果你的VPS是阿里云,腾讯云这种VPS,就是ifconfig看不见你的公网IP,只能看见内网IP,***
2653 |
2654 | ***那么需要加上`-g VPS公网IP`参数,SOCKS5代理的UDP功能才能正常工作。***
2655 |
2656 | ### 5.1 普通SOCKS5代理
2657 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080"`
2658 |
2659 | -p参数支持的写法:
2660 |
2661 | ```text
2662 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
2663 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
2664 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
2665 | ```
2666 |
2667 | ### 5.2.普通二级SOCKS5代理
2668 | 
2669 | 使用本地端口8090,假设上级SOCKS5代理是`22.22.22.22:8080`
2670 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" `
2671 | 我们还可以指定网站域名的黑白名单文件,一行一个域名,匹配规则是最右匹配,比如:baidu.com,匹配的是*.*.baidu.com,黑名单的域名域名直接走上级代理,白名单的域名不走上级代理;如果域名即在黑名单又在白名单中,那么黑名单起作用。
2672 | `./proxy socks -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" -b blocked.txt -d direct.txt`
2673 |
2674 | ### 5.3.SOCKS二级代理(加密)
2675 | 
2676 | 一级SOCKS代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
2677 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2678 |
2679 | 二级SOCKS代理(本地Linux)
2680 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2681 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080。
2682 |
2683 | 二级SOCKS代理(本地windows)
2684 | `./proxy.exe socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2685 | 然后设置你的windos系统中,需要通过代理上网的程序的代理为socks5模式,地址为:127.0.0.1,端口为:8080,程序即可通过加密通道通过vps上网。
2686 |
2687 | ### 5.4.SOCKS三级代理(加密)
2688 | 
2689 | 一级SOCKS代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2690 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2691 | 二级SOCKS代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2692 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2693 | 三级SOCKS代理(本地)
2694 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2695 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问一级SOCKS代理上面的代理端口38080。
2696 |
2697 | ### 5.5.SOCKS代理流量强制走上级SOCKS代理
2698 | 默认情况下,proxy会智能判断一个网站域名是否无法访问,如果无法访问才走上级SOCKS代理.通过--always可以使全部SOCKS代理流量强制走上级SOCKS代理。
2699 | `./proxy socks --always -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2700 |
2701 | ### 5.6.SOCKS通过SSH中转
2702 | 
2703 | 说明:ssh中转的原理是利用了ssh的转发功能,就是你连接上ssh之后,可以通过ssh代理访问目标地址。
2704 | 假设有:vps
2705 | - IP是2.2.2.2, ssh端口是22, ssh用户名是:user, ssh用户密码是:demo
2706 | - 用户user的ssh私钥名称是user.key
2707 |
2708 | #### *5.6.1 ssh用户名和密码的方式*
2709 | 本地SOCKS5代理28080端口,执行:
2710 | `./proxy socks -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -D demo -t tcp -p ":28080"`
2711 | #### *5.6.2 ssh用户名和密钥的方式*
2712 | 本地SOCKS5代理28080端口,执行:
2713 | `./proxy socks -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -S user.key -t tcp -p ":28080"`
2714 |
2715 | 那么访问本地的28080端口就是通过VPS访问目标地址。
2716 |
2717 | ### 5.7.认证
2718 | 对于socks5代理协议我们可以进行用户名密码认证,认证的用户名和密码可以在命令行指定
2719 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1" -a "user2:pass2"`
2720 | 多个用户,重复-a参数即可。
2721 | 也可以放在文件中,格式是一行一个"用户名:密码",然后用-F指定。
2722 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":33080" -F auth-file.txt`
2723 |
2724 | ### 5.8.KCP协议传输
2725 | KCP协议需要--kcp-key参数设置一个密码用于加密解密数据
2726 |
2727 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
2728 | `./proxy socks -t kcp -p ":38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
2729 |
2730 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
2731 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T kcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
2732 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080,数据通过kcp协议传输。
2733 |
2734 | ### 5.9.自定义DNS
2735 | --dns-address和--dns-ttl参数,用于自己指定proxy访问域名的时候使用的dns(--dns-address)
2736 | 以及解析结果缓存时间(--dns-ttl)秒数,避免系统dns对proxy的干扰,另外缓存功能还能减少dns解析时间提高访问速度。
2737 | 比如:
2738 | `./proxy socks -p ":33080" --dns-address "8.8.8.8:53" --dns-ttl 300`
2739 |
2740 | ### 5.10 自定义加密
2741 | proxy的socks代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可,
2742 | 加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
2743 |
2744 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以。
2745 |
2746 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
2747 |
2748 | 二级实例
2749 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2750 | `proxy socks -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
2751 | 本地二级执行:
2752 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
2753 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
2754 |
2755 |
2756 | 三级实例
2757 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2758 | `proxy socks -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
2759 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
2760 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
2761 | 本地三级执行:
2762 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
2763 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
2764 |
2765 | ### 5.11 压缩传输
2766 | proxy的socks代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以
2767 | 对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,
2768 | 一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
2769 |
2770 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据。
2771 |
2772 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
2773 |
2774 | 二级实例
2775 |
2776 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2777 | `proxy socks -t tcp -m -p :7777`
2778 | 本地二级执行:
2779 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
2780 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
2781 |
2782 |
2783 | 三级实例
2784 |
2785 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2786 | `proxy socks -t tcp -m -p :7777`
2787 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
2788 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
2789 | 本地三级执行:
2790 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
2791 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
2792 |
2793 |
2794 | ### 5.12 负载均衡
2795 |
2796 | SOCKS代理支持上级负载均衡,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
2797 |
2798 | `proxy socks --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
2799 |
2800 | ### 5.12.1 设置重试间隔和超时时间
2801 |
2802 | `proxy socks --lb-method=leastconn --lb-retrytime 300 --lb-timeout 300 -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
2803 |
2804 | ### 5.12.2 设置权重
2805 |
2806 | `proxy socks --lb-method=weight -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -P 2.1.1.1:33080?w=2 -P 3.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -p :33080 -t tcp`
2807 |
2808 | ### 5.12.3 使用目标地址选择上级
2809 |
2810 | `proxy socks --lb-hashtarget --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
2811 |
2812 | ### 5.13 限速
2813 |
2814 | 限速100K,通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
2815 |
2816 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -l 100K`
2817 |
2818 | ### 5.14 指定`出口IP`
2819 |
2820 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果`入口IP`是内网IP,`出口IP`不会使用`入口IP`。
2821 |
2822 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 --bind-listen`
2823 |
2824 | ### 5.15 级联认证
2825 |
2826 | SOCKS5支持级联认证,-A可以设置上级认证信息。
2827 |
2828 | 上级:
2829 |
2830 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -a user:pass`
2831 |
2832 | 本地:
2833 |
2834 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -A user:pass -t tcp -p :33080`
2835 |
2836 | 请更多认证细节,请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
2837 |
2838 | ### 5.16 证书参数使用base64数据
2839 |
2840 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
2841 |
2842 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
2843 |
2844 |
2845 | ### 5.17 智能模式
2846 | 智能模式设置,可以是intelligent|direct|parent三者之一。
2847 | 默认是:intelligent。
2848 | 每个值的含义如下:
2849 | `--intelligent=direct`,不在blocked里面的目标都直连。
2850 | `--intelligent=parent`,不在direct里面的目标都走上级。
2851 | `--intelligent=intelligent`,blocked和direct里面都没有的目标,智能判断是否使用上级访问目标。
2852 |
2853 | ### 5.18 固定UDP功能端口
2854 |
2855 | 默认情况下socks5的UDP功能的端口号,proxy是按着`rfc1982草案`要求,使用协议握手过程中随机指定,不需要提前指定。
2856 |
2857 | 但是某些情况下,需要固定UDP功能端口,可以通过参数`--udp-port 端口号`用来固定UDP功能的端口号,比如:
2858 |
2859 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --udp-port 38080`
2860 |
2861 | ### 5.19 查看帮助
2862 | `./proxy help socks`
2863 |
2864 | ## 6.SPS协议转换
2865 |
2866 | ### 6.1 功能介绍
2867 | 代理协议转换使用的是sps子命令,sps本身不提供代理功能,只是接受代理请求"转换并转发"给已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理或者ss代理;sps可以把已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理或ss代理转换为一个端口同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的代理,而且http(s)代理支持正向代理和反向代理(SNI),转换后的SOCKS5代理,当上级是SOCKS5或者SS时仍然支持UDP功能;另外对于已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理,支持tls、tcp、kcp三种模式,支持链式连接,也就是可以多个sps结点层级连接构建加密通道。
2868 |
2869 | `ss`功能支持的加密方法为:aes-128-cfb , aes-128-ctr , aes-128-gcm , aes-192-cfb , aes-192-ctr , aes-192-gcm , aes-256-cfb , aes-256-ctr , aes-256-gcm , bf-cfb , cast5-cfb , chacha20 , chacha20-ietf , chacha20-ietf-poly1305 , des-cfb , rc4-md5 , rc4-md5-6 , salsa20 , xchacha20
2870 |
2871 | 本地监听端口-p参数支持的写法:
2872 |
2873 | ```text
2874 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
2875 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
2876 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
2877 | ```
2878 |
2879 | ### 6.2 HTTP(S)转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
2880 | 假设已经存在一个普通的http(s)代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2881 | 命令如下:
2882 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2883 |
2884 | 假设已经存在一个tls的http(s)代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,tls需要证书文件,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2885 | 命令如下:
2886 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2887 |
2888 | 假设已经存在一个kcp的http(s)代理(密码是:demo123):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2889 | 命令如下:
2890 | `./proxy sps -S http -T kcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 --kcp-key demo123 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2891 |
2892 | ### 6.3 SOCKS5转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
2893 | 假设已经存在一个普通的socks5代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2894 | 命令如下:
2895 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2896 |
2897 | 假设已经存在一个tls的socks5代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,tls需要证书文件,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2898 | 命令如下:
2899 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T tls -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2900 |
2901 | 假设已经存在一个kcp的socks5代理(密码是:demo123):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2902 | 命令如下:
2903 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T kcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 --kcp-key demo123 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2904 |
2905 | ### 6.4 SS转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
2906 | SPS上级和本地支持ss协议,上级可以是SPS或者标准的ss服务。
2907 | SPS本地默认提供HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS三种代理,当上级是SOCKS5时转换后的SOCKS5和SS支持UDP功能。
2908 | 假设已经存在一个普通的SS或者SPS代理(开启了ss,加密方式:aes-256-cfb,密码:demo):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,转换后的ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2909 | 命令如下:
2910 | `./proxy sps -S ss -H aes-256-cfb -J pass -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`。
2911 |
2912 | ### 6.5 链式连接
2913 | 
2914 | 上面提过多个sps结点可以层级连接构建加密通道,假设有如下vps和家里的pc电脑。
2915 | vps01:2.2.2.2
2916 | vps02:3.3.3.3
2917 | 现在我们想利用pc和vps01和vps02构建一个加密通道,本例子用tls加密也可以用kcp,在pc上访问本地18080端口就是访问vps01的本地8080端口。
2918 | 首先在vps01(2.2.2.2)上我们运行一个只有本地可以访问的http(s)代理,执行:
2919 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p 127.0.0.1:8080`
2920 |
2921 | 然后在vps01(2.2.2.2)上运行一个sps结点,执行:
2922 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tls -p :8081 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2923 |
2924 | 然后在vps02(3.3.3.3)上运行一个sps结点,执行:
2925 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:8081 -t tls -p :8082 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2926 |
2927 | 然后在pc上运行一个sps结点,执行:
2928 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 3.3.3.3:8082 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2929 |
2930 | 完成。
2931 |
2932 | ### 6.6 监听多个端口
2933 | 一般情况下监听一个端口就可以,不过如果作为反向代理需要同时监听80和443两个端口,那么-p参数是支持的,
2934 | 格式是:`-p 0.0.0.0:80,0.0.0.0:443`,多个绑定用逗号分隔即可。
2935 |
2936 | ### 6.7 认证功能
2937 | sps支持http(s)\socks5代理认证,可以级联认证,有四个重要的信息:
2938 | 1:用户发送认证信息`user-auth`。
2939 | 2:设置的本地认证信息`local-auth`。
2940 | 3:设置的连接上级使用的认证信息`parent-auth`。
2941 | 4:最终发送给上级的认证信息`auth-info-to-parent`。
2942 | 他们的情况关系如下:
2943 |
2944 | | user-auth | local-auth | parent-auth | auth-info-to-paren
2945 | | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------
2946 | | 有/没有 | 有 | 有 | 来自parent-auth
2947 | | 有/没有 | 没有 | 有 | 来自parent-auth
2948 | | 有/没有 | 有 | 没有 | 无
2949 | | 没有 | 没有 | 没有 | 无
2950 | | 有 | 没有 | 没有 | 来自user-auth
2951 |
2952 | 对于sps代理我们可以进行用户名密码认证,认证的用户名和密码可以在命令行指定
2953 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1:0:0:" -a "user2:pass2:0:0:"`
2954 | 多个用户,重复-a参数即可。
2955 | 也可以放在文件中,格式是一行一个`用户名:密码:连接数:速率:上级`,然后用-F指定。
2956 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -F auth-file.txt`
2957 |
2958 | 如果上级有认证,下级可以通过-A参数设置认证信息,比如:
2959 | 上级:`./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1:0:0:" -a "user2:pass2:0:0:"`
2960 | 下级:`./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -A "user1:pass1" -t tcp -p ":33080" `
2961 |
2962 | 请更多认证细节,请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
2963 |
2964 | ### 6.8 多个上级
2965 |
2966 | 如果存在多个上级,可以通过多个-P指定。
2967 |
2968 | 比如:
2969 |
2970 | `proxy sps -P http://127.0.0.1:3100 -P socks5://127.0.0.1:3200`
2971 |
2972 | `-P`完整格式如下:
2973 |
2974 | `protocol://a:b@2.2.2.2:33080#1`
2975 |
2976 | 下面对每部分进行解释:
2977 |
2978 | `protocol://` 是协议类型,可能的类型以及含有如下:
2979 |
2980 | ```text
2981 | http 等价于 -S http -T tcp
2982 | https 等价于 -S http -T tls --parent-tls-single , 也就是http(s)代理 over TLS
2983 | https2 等价于 -S http -T tls
2984 | socks5 等价于 -S socks -T tcp
2985 | socks5s 等价于 -S socks -T tls --parent-tls-single , 也就是socks over TLS
2986 | socks5s2 等价于 -S socks -T tls
2987 | ss 等价于 -S ss -T tcp
2988 | httpws 等价于 -S http -T ws
2989 | httpwss 等价于 -S http -T wss
2990 | socks5ws 等价于 -S socks -T ws
2991 | socks5wss 等价于 -S socks -T wss
2992 | ```
2993 |
2994 | `a:b`是代理认证的用户名密码,如果是ss,`a`是加密方法,`b`是密码,没有用户名密码可以留空比如:`http://2.2.2.2:33080`,如果用户名和密码保护特殊符号可以使用urlencode进行编码。
2995 |
2996 | `2.2.2.2:33080`是上级地址,格式是:`IP(或域名):端口`,如果底层是ws/wss协议还可以带上路径,比如:`2.2.2.2:33080/ws`;
2997 | 还能通过附加查询参数`m`和`k`设置`ws\wss`的`加密方法`和`密码`,比如:`2.2.2.2:33080/ws?m=aes-192-cfb&k=password`
2998 |
2999 | `#1`多个上级的负载均衡是权重策略时候,设置的权重,很少用到。
3000 |
3001 | ### 6.9 自定义加密
3002 | proxy的sps代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行
3003 | 自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义
3004 | 一个密码即可,加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
3005 |
3006 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以。
3007 |
3008 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
3009 |
3010 | 假设已经存在一个http(s)代理:`6.6.6.6:6666`
3011 |
3012 | 二级实例
3013 |
3014 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
3015 | `proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 6.6.6.6:6666 -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
3016 | 本地二级执行:
3017 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
3018 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
3019 |
3020 |
3021 | 三级实例
3022 |
3023 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
3024 | `proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 6.6.6.6:6666 -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
3025 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
3026 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
3027 | 本地三级执行:
3028 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
3029 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
3030 |
3031 | ### 6.10 压缩传输
3032 | proxy的sps代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以
3033 | 对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,
3034 | 一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
3035 |
3036 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据。
3037 |
3038 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
3039 |
3040 | 二级实例
3041 |
3042 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
3043 | `proxy sps -t tcp -m -p :7777`
3044 | 本地二级执行:
3045 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
3046 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
3047 |
3048 |
3049 | 三级实例
3050 |
3051 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
3052 | `proxy sps -t tcp -m -p :7777`
3053 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
3054 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
3055 | 本地三级执行:
3056 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
3057 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
3058 |
3059 | ### 6.11 禁用协议
3060 | SPS默认情况下一个端口支持http(s)和socks5两种代理协议,我们可以通过参数禁用某个协议
3061 | 比如:
3062 | 1.禁用HTTP(S)代理功能只保留SOCKS5代理功能,参数:`--disable-http`。
3063 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080 --disable-http`
3064 |
3065 | 1.禁用SOCKS5代理功能只保留HTTP(S)代理功能,参数:`--disable-socks`。
3066 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080 --disable-http`
3067 |
3068 | ### 6.12 限速
3069 |
3070 | 假设存在SOCKS5上级:
3071 |
3072 | `proxy socks -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -z password -t tcp`
3073 |
3074 | sps下级,限速100K
3075 |
3076 | `proxy sps -S socks -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -T tcp -Z password -l 100K -t tcp -p :33080`
3077 |
3078 | 通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
3079 |
3080 | ### 6.13 指定`出口IP`
3081 |
3082 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果`入口IP`是内网IP,`出口IP`不会使用`入口IP`。
3083 |
3084 | `proxy sps -S socks -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -T tcp -Z password -l 100K -t tcp --bind-listen -p :33080`
3085 |
3086 | ### 6.14 证书参数使用base64数据
3087 |
3088 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
3089 |
3090 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
3091 |
3092 | ### 6.15 独立服务
3093 | sps功能不强制指定一个上级,当上级为空,sps本身即可完成完整的代理功能.如果指定了上级那么就和之前一样使用上级连接目标。
3094 | 下面这个命令,就是一键开启http(s)\ss\socks服务。
3095 | `./proxy sps -p :33080`
3096 |
3097 | ### 6.16 目标重定向
3098 | sps功能提供的http(s)\socks5\ss代理功能,客户端通过sps代理去连接指定的“目标”,这个“目标”一般是网站也可能是任意的tcp地址,
3099 | 网站”目标“一般是foo.com:80,foo.com:443,sps支持使用--rewrite参数指定一个“目标”重定向规则文件,对目标进行重定向,客户端是无感知的,
3100 | 比如你对“目标”:demo.com:80重定向到192.168.0.12:80,那么客户端访问网站demo.com,其实访问的是192.168.0.12提供的网站服务。
3101 | “目标”重定向规则文件示例:
3102 |
3103 | ```text
3104 | # example
3105 | www.a.com:80 10.0.0.2:8080
3106 | **.b.com:80 10.0.0.2:80
3107 | 192.168.0.11:80 10.0.0.2:8080
3108 | ```
3109 |
3110 | ### 6.17 固定UDP功能端口
3111 |
3112 | 默认情况下sps的socks5的UDP功能的端口号是按着`rfc1982草案`要求,使用协议握手过程中随机指定,不需要提前指定。
3113 |
3114 | 但是某些情况下,需要固定UDP功能端口,可以通过参数`--udp-port 端口号`用来固定UDP功能的端口号,比如:
3115 |
3116 | `./proxy sps -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --udp-port 38081`
3117 |
3118 | 需要注意的是,sps的ss功能也有UDP功能,而且ss的UDP端口和tcp端口是一样的,所以要避免socks5的UDP端口和ss的UDP端口冲突,
3119 |
3120 | 要指定和tcp端口不一样的端口。
3121 |
3122 | ### 6.18 iptables 透明代理
3123 | sps模式支持Linux系统的iptables转发支持,也就是通常所说的iptables透明代理,如果在网关设备上进行iptables透明代理,那么对通过网关联网的设备就能实现无感知的代理。
3124 |
3125 | 启动命令实例:
3126 |
3127 | `./proxy sps --redir -p :8888 -P httpws://1.1.1.1:33080`
3128 |
3129 | 这里假设存在一个http的上级代理1.1.1.1:33080,使用ws传输数据。
3130 |
3131 | 然后添加iptables规则,下面是参考规则:
3132 | ```shell
3133 | #上级proxy服务端服务器IP地址:
3134 | proxy_server_ip=1.1.1.1
3135 |
3136 | #路由器运行proxy监听的端口:
3137 | proxy_local_port=33080
3138 |
3139 | #下面的就不用修改了
3140 | #create a new chain named PROXY
3141 | iptables -t nat -N PROXY
3142 |
3143 | # Ignore your PROXY server's addresses
3144 | # It's very IMPORTANT, just be careful。
3145 |
3146 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d $proxy_server_ip -j RETURN
3147 |
3148 | # Ignore LANs IP address
3149 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 0.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
3150 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 10.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
3151 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 127.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
3152 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 169.254.0.0/16 -j RETURN
3153 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 172.16.0.0/12 -j RETURN
3154 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 192.168.0.0/16 -j RETURN
3155 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 224.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
3156 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 240.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
3157 |
3158 | # Anything to port 80 443 should be redirected to PROXY's local port
3159 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
3160 | # Apply the rules to nat client
3161 | iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -j PROXY
3162 | # Apply the rules to localhost
3163 | iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp -j PROXY
3164 | ```
3165 | - 清空整个链 iptables -F 链名比如iptables -t nat -F PROXY
3166 | - 删除指定的用户自定义链 iptables -X 链名 比如 iptables -t nat -X PROXY
3167 | - 从所选链中删除规则 iptables -D 链名 规则详情 比如 iptables -t nat -D PROXY -d 223.223.192.0/255.255.240.0 -j RETURN
3168 |
3169 | ### 6.19 查看帮助
3170 |
3171 | `./proxy help sps`
3172 |
3173 | ## 7.KCP配置
3174 |
3175 | ### 7.1 配置介绍
3176 | proxy的很多功能都支持kcp协议,凡是使用了kcp协议的功能都支持这里介绍的配置参数。
3177 | 所以这里统一对KCP配置参数进行介绍。
3178 |
3179 | ### 7.2 详细配置
3180 | 所有的KCP配置参数共有17个,你可以都不用设置,他们都有默认值,如果为了或者最好的效果,
3181 | 就需要自己根据自己根据网络情况对参数进行配置。由于kcp配置很复杂需要一定的网络基础知识,
3182 | 如果想获得kcp参数更详细的配置和解说,请自行搜索。每个参数的命令行名称以及默认值和简单的功能说明如下:
3183 | ```
3184 | --kcp-key="secrect" pre-shared secret between client and server
3185 | --kcp-method="aes" encrypt/decrypt method, can be: aes, aes-128, aes-192, salsa20, blowfish,
3186 | twofish, cast5, 3des, tea, xtea, xor, sm4, none
3187 | --kcp-mode="fast" profiles: fast3, fast2, fast, normal, manual
3188 | --kcp-mtu=1350 set maximum transmission unit for UDP packets
3189 | --kcp-sndwnd=1024 set send window size(num of packets)
3190 | --kcp-rcvwnd=1024 set receive window size(num of packets)
3191 | --kcp-ds=10 set reed-solomon erasure coding - datashard
3192 | --kcp-ps=3 set reed-solomon erasure coding - parityshard
3193 | --kcp-dscp=0 set DSCP(6bit)
3194 | --kcp-nocomp disable compression
3195 | --kcp-acknodelay be carefull! flush ack immediately when a packet is received
3196 | --kcp-nodelay=0 be carefull!
3197 | --kcp-interval=50 be carefull!
3198 | --kcp-resend=0 be carefull!
3199 | --kcp-nc=0 be carefull! no congestion
3200 | --kcp-sockbuf=4194304 be carefull!
3201 | --kcp-keepalive=10 be carefull!
3202 | ```
3203 | 提示:
3204 | 参数:--kcp-mode中的四种fast3, fast2, fast, normal模式,
3205 | 相当于设置了下面四个参数:
3206 | normal:`--nodelay=0 --interval=40 --resend=2 --nc=1`
3207 | fast :`--nodelay=0 --interval=30 --resend=2 --nc=1`
3208 | fast2:`--nodelay=1 --interval=20 --resend=2 --nc=1`
3209 | fast3:`--nodelay=1 --interval=10 --resend=2 --nc=1`
3210 |
3211 | ## 8.安全DNS
3212 |
3213 | ### 8.1 介绍
3214 | 众所周知DNS是UDP端口53提供的服务,但是随着网络的发展一些知名DNS服务器也支持TCP方式dns查询,比如谷歌的8.8.8.8,proxy的DNS防污染服务器原理就是在本地启动一个proxy的DNS代理服务器,它用TCP的方式通过上级代理进行dns查询。如果它和上级代理通讯采用加密的方式,那么就可以进行安全无污染的DNS解析,还支持独立服务,并发解析,支持增强的hosts文件功能支持灵活的并发解析转发。
3215 |
3216 | dns解析顺序:
3217 | 1.使用参数--hosts解析。
3218 | 2.要解析的域名在1中没有找到,就使用参数--forward规则解析。
3219 | 3.要解析的域名在1和2中都没有找到,就使用默认--default解析,--default默认行为参数值有三种:proxy,direct,system。
3220 | 三种参数值解释如下:
3221 | proxy:通过上级去连接-q参数指定的dns服务器去解析域名。
3222 | direct:通过本地网络去连接-q参数指定的dns服务器去解析域名。
3223 | system:通过系统dns去解析域名。
3224 |
3225 | 提示:
3226 | --hosts 参数指定的host文件格式和系统hosts文件一致,而且域名支持通配符,可以参考hosts文件。
3227 | --forward 参数指定的解析转发规则文件,格式可以参考resolve.rules文件,域名支持通配符,支持为每个域名指定多个dns服务器并发解析,谁最快解析成功就用谁的解析结果。
3228 | -q 参数可以指定多个远程dns服务器,执行并发解析谁最快解析成功就用谁的解析结果,默认是:1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8,9.9.9.9,多个用逗号分割,
3229 | 比如还可以带端口:1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8#53,9.9.9.9
3230 |
3231 | 如果独立服务,不需要上级:
3232 | 可以执行:
3233 | `proxy dns --default system -p :5353`
3234 | or
3235 | `proxy dns --default direct -p :5353`
3236 |
3237 | ### 8.2 使用示例
3238 |
3239 | #### 8.2.1 普通HTTP(S)上级代理
3240 |
3241 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3242 | 本地执行:
3243 | `proxy dns -S http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3244 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了DNS解析功能。
3245 |
3246 | #### 8.2.2 普通SOCKS5上级代理
3247 |
3248 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3249 | 本地执行:
3250 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3251 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了DNS解析功能。
3252 |
3253 | #### 8.2.3 TLS加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
3254 |
3255 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3256 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3257 | `proxy http -t tls -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :33080`
3258 | 本地执行:
3259 | `proxy dns -S http -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :53`
3260 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3261 |
3262 | #### 8.2.4 TLS加密的SOCKS5上级代理
3263 |
3264 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3265 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3266 | `proxy socks -t tls -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :33080`
3267 | 本地执行:
3268 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :53`
3269 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3270 |
3271 | #### 8.2.5 KCP加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
3272 |
3273 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3274 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3275 | `proxy http -t kcp -p :33080`
3276 | 本地执行:
3277 | `proxy dns -S http -T kcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3278 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3279 |
3280 | #### 8.2.6 KCP加密的SOCKS5上级代理
3281 |
3282 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3283 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3284 | `proxy socks -t kcp -p :33080`
3285 | 本地执行:
3286 | `proxy dns -S socks -T kcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3287 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3288 |
3289 | #### 8.2.7 自定义加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
3290 |
3291 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3292 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3293 | `proxy http -t tcp -p :33080 -z password`
3294 | 本地执行:
3295 | `proxy dns -S http -T tcp -Z password -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3296 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3297 |
3298 | #### 8.2.8 自定义加密的SOCKS5上级代理
3299 |
3300 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3301 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3302 | `proxy socks -t kcp -p :33080 -z password`
3303 | 本地执行:
3304 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tcp -Z password -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3305 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3306 |
3307 | ## 9.API认证,限速,控制连接数
3308 |
3309 | proxy的http(s)/socks5/sps代理功能,支持通过API控制用户对代理对访问。
3310 |
3311 | ### 通过API可以干什么?
3312 |
3313 | - 用户维度,控制单个连接速率,控制最大连接数。
3314 | - IP维度,控制单个连接速率,控制最大连接数。
3315 | - 动态上级,可以根据用户或者客户端IP,动态的从API获取其上级,支持http(s)/socks5/ss上级。
3316 | - 认证每一个连接,无论是否要求客户端认证。
3317 | - 缓存认证结果,时间可以设置,减轻API压力。
3318 |
3319 | #### 具体使用
3320 | proxy的http(s)/socks5/sps代理API功能,通过`--auth-url`和`--auth-nouser`和`--auth-cache`三个参数控制。
3321 | 参数`--auth-url`是HTTP API接口地址,客户端连接的时候,proxy会GET方式请求这url,带上下面参数,如果返回HTTP状态码204,代表认证成功,其它情况认为认证失败。
3322 |
3323 | 一个完整的请求API的示例:
3324 | `http://test.com/auth.php?user=a&pass=b&client_addr=127.0.0.1:49892&local_addr=127.0.0.1:8100&target=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.baidu.com&service=http&sps=0`
3325 |
3326 | #### 参数说明
3327 | `user和pass` 当代理开启了认证功能,这里就是客户端提供的用户名和密码。
3328 | `client_addr` 客户端访问代理时的用的地址,格式IP:端口。
3329 | `local_addr` 客户端访问的代理地址,格式IP:端口。
3330 | `service` 代理类型,分为:http、socks。
3331 | `sps` 代理是否是sps提供的,1:是,0:否。
3332 | `target` 客户端要访问的目标,如果是http(s)代理,target是访问的具体url;如果是socks5代理,target是空。
3333 |
3334 | #### 示例
3335 | 假设--auth-url http://127.0.0.1:333/auth.php 指向了一个php接口地址.
3336 | auth.php内容如下:
3337 |
3338 | ```php
3339 |
155 |
156 | ### 源代码申明
157 |
158 | 本项目作者发现大量的开发者基于本项目进行二次开发或使用大量本项目核心代码而不遵循GPLv3协议,这严重违背了本项目使用GPLv3开源协议的初衷,鉴于这种情况,本项目采取源代码延迟发布策略,在一定程度上遏制这些不尊重开源,不尊重他人劳动成果的行为。
159 | 本项目会持续更新迭代,持续发布全平台的二进制程序,给大家提供强大便捷的代理工具。
160 | 如果你有定制,商业需求请发邮件至`arraykeys@gmail.com`
161 |
162 | ## goproxy使用手册
163 |
164 |
165 | ## 首次使用必看!
166 |
167 | ### 1. 环境
168 |
169 | 该手册教程,默认系统是linux,程序是proxy;所有操作需要root权限;
170 |
171 | 如果你的是windows,请使用windows版本的proxy.exe即可。
172 |
173 | ### 2. 使用配置文件
174 |
175 | 接下来的教程都是通过命令行参数介绍使用方法,也可以通过读取配置文件获取参数。
176 |
177 | 具体格式是通过@符号指定配置文件,例如:./proxy @configfile.txt
178 |
179 | configfile.txt里面的格式是,第一行是子命令名称,第二行开始一行一个参数,
180 |
181 | 格式:`参数 参数值`,没有参数值的直接写参数,比如:--nolog
182 |
183 | 比如configfile.txt内容如下:
184 |
185 | ```shell
186 | http
187 | -t tcp
188 | -p :33080
189 | --forever
190 | ```
191 |
192 | ### 3. 调试输出
193 |
194 | 默认情况下,日志输出的信息不包含文件行数,某些情况下为了排除程序问题,快速定位问题,
195 |
196 | 可以使用--debug参数,输出代码行数和毫秒时间。
197 |
198 | ### 4. 使用日志文件
199 |
200 | 默认情况下,日志是直接在控制台显示出来的,如果要保存到文件,可以使用--log参数,
201 |
202 | 比如: --log proxy.log,日志就会输出到proxy.log方便排除问题。
203 |
204 |
205 | ### 5. 生成加密通讯需要的证书文件
206 |
207 | http(s)代理、tcp代理、udp代理、socks5代理、内网穿透等功能和上级通讯的时候,为了安全我们采用TLS加密通讯,当然可以选择不加密通信通讯,本教程所有和上级通讯都采用加密,需要证书文件。
208 |
209 | ***所有端必须使用相同的proxy.crt和proxy.key***
210 |
211 | 1.通过下面的命令生成自签名的证书和key文件。
212 | `./proxy keygen -C proxy`
213 | 会在当前程序目录下面生成证书文件proxy.crt和key文件proxy.key。
214 |
215 | 2.通过下面的命令生,使用自签名证书proxy.crt和key文件proxy.key签发新证书:goproxy.crt和goproxy.key。
216 | `./proxy keygen -s -C proxy -c goproxy`
217 | 会在当前程序目录下面生成证书文件goproxy.crt和key文件goproxy.key。
218 |
219 | 3.默认情况下证书的里面的域名是随机的,可以使用`-n test.com`参数指定。
220 |
221 | 4.更多用法:`proxy keygen --help`。
222 |
223 | ### 6. 后台运行
224 |
225 | 默认执行proxy之后,如果要保持proxy运行,不能关闭命令行。
226 |
227 | 如果想在后台运行proxy,命令行可以关闭,只需要在命令最后加上--daemon参数即可。
228 |
229 | 比如:
230 |
231 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --daemon`
232 |
233 | ### 7. 守护运行
234 | 守护运行参数--forever,比如: `proxy http --forever` ,
235 |
236 | proxy会fork子进程,然后监控子进程,如果子进程异常退出,5秒后重启子进程。
237 |
238 | 该参数配合后台运行参数--daemon和日志参数--log,可以保障proxy一直在后台执行不会因为意外退出,
239 |
240 | 而且可以通过日志文件看到proxy的输出日志内容。
241 |
242 | 比如: `proxy http -p ":9090" --forever --log proxy.log --daemon`
243 |
244 | ### 8. 安全建议
245 |
246 | 当VPS在nat设备后面,vps上网卡IP都是内网IP,这个时候可以通过-g参数添加vps的外网ip防止死循环。
247 |
248 | 假设你的vps外网ip是23.23.23.23,下面命令通过-g参数设置23.23.23.23
249 |
250 | `./proxy http -g "23.23.23.23"`
251 |
252 | ### 9. 负载均衡和高可用
253 |
254 | HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS代理支持上级负载均衡和高可用,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
255 |
256 | 负载均衡策略支持5种,可以通过`--lb-method`参数指定:
257 |
258 | roundrobin 轮流使用
259 |
260 | leastconn 使用最小连接数的
261 |
262 | leasttime 使用连接时间最小的
263 |
264 | hash 使用根据客户端地址计算出一个固定上级
265 |
266 | weight 根据每个上级的权重和连接数情况,选择出一个上级
267 |
268 | 提示:
269 |
270 | 负载均衡检查时间间隔可以通过`--lb-retrytime`设置,单位毫秒
271 |
272 | 负载均衡连接超时时间可以通过`--lb-timeout`设置,单位毫秒
273 |
274 | 如果负载均衡策略是权重(weight),-P格式为:2.2.2.2:3880?w=1,1就是权重,大于0的整数。
275 |
276 | 如果负载均衡策略是hash,默认是根据客户端地址选择上级,可以通过开关`--lb-hashtarget`使用访问的目标地址选择上级。
277 |
278 |
279 | ### 10. 代理跳板跳转
280 |
281 | http(s)代理,SPS代理,内网穿透,tcp代理都支持通过中间第三方代理连接上级,
282 |
283 | 参数是:--jumper,所有格式如下:
284 |
285 | ```text
286 | http://username:password@host:port
287 | http://host:port
288 | https://username:password@host:port
289 | https://host:port
290 | socks5://username:password@host:port
291 | socks5://host:port
292 | socks5s://username:password@host:port
293 | socks5s://host:port
294 | ss://method:password@host:port
295 | ```
296 |
297 | http,socks5代表的是普通的http和socks5代理。
298 |
299 | https,socks5s代表的是通过tls保护的http和socks5代理,
300 |
301 | 也就是http代理 over TLS , socks over TLS。
302 |
303 | ### 11. 域名黑白名单
304 |
305 | socks/http(s)/sps代理都支持域名黑白名单。
306 |
307 | 用--stop参数指定一个域名黑名单列表文件,那么当用户连接文件里面这些域名的时候连接就会被断开。
308 |
309 | 用--only参数指定一个域名白名单列表文件,那么当用户连接文件里面这些域名之外的域名的时候连接就会被断开。
310 |
311 | 如果同时设置了--stop和--only,那么只有--only会起作用。
312 |
313 | 黑白域名名单文件内容格式如下:
314 |
315 | ```text
316 | **.baidu.com
317 | *.taobao.com
318 | a.com
319 | 192.168.1.1
320 | 192.168.*.*
321 | ?.qq.com
322 | ```
323 |
324 | 说明:
325 |
326 | 1.一行一个域名,域名写法支持通配符`*`和`?`,`*`代表任意个字符,`?`代表一个任意字符,
327 |
328 | 2.`**.baidu.com` 匹配无论是多少级所有后缀是`.baidu.com`的域名。
329 |
330 | 3.`*.taobao.com` 匹配后缀是`.taobao.com`的三级域名。
331 |
332 | 4.还可以直接是IP地址。
333 |
334 | 5.`#`开头的为注释。
335 |
336 | ### 12. 客户端IP黑白名单
337 |
338 | socks/http(s)/sps/tcp/udp/dns/内网穿透bridge/内网穿透tbridge,都支持客户端IP黑白名单。
339 |
340 | 用--ip-deny参数指定一个客户端IP黑名单列表文件,那么当用户的IP在这个文件里面的时候连接就会被断开。
341 |
342 | 用--ip-allow参数指定一个客户端IP白名单列表文件,那么当用户的IP不在这个文件里面的时候连接就会被断开。
343 |
344 | 如果同时设置了--ip-deny和--ip-allow,那么只有--ip-allow会起作用。
345 |
346 | 客户端IP黑白名单文件内容格式如下:
347 |
348 | ```text
349 | 192.168.1.1
350 | 192.168.*.*
351 | 192.168.1?.*
352 | ```
353 |
354 | 说明:
355 |
356 | 1.一行一个域名,域名写法支持通配符`*`和`?`,`*`代表任意个字符,`?`代表一个任意字符。
357 |
358 | 2.`#`开头的为注释。
359 |
360 | ### 13. 协议加载文件
361 |
362 | proxy的各种代理功能里面很多地方都有参数设置一个文件,比如:--blocked 指定一个直接走上级的域名列表文件,参数值是文件的路径,
363 |
364 | 如果参数支持协议加载文件,那么文件路径不仅可以是文件路径,还可以是:
365 |
366 | a.“base64://”开头的base64编码的上面说明的文件内容,比如:base64://ajfpoajsdfa=
367 |
368 | b.”str://“开头的英文逗号分割的多个,比如:str://xxx,yyy
369 |
370 | proxy的blocked,direct,stop,only,hosts,resolve.rules,rewriter.rules,ip.allow,ip.deny 文件支持协议加载。
371 |
372 | ## 1.HTTP代理
373 |
374 | ### 1.1.普通一级HTTP代理
375 |
376 | 
377 |
378 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080"`
379 |
380 | -p参数支持的写法:
381 |
382 | ```text
383 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
384 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
385 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
386 | ```
387 |
388 | ### 1.2.普通二级HTTP代理
389 |
390 | 
391 |
392 | 使用本地端口8090,假设上级HTTP代理是`22.22.22.22:8080`
393 |
394 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" `
395 |
396 | 我们还可以指定网站域名的黑白名单文件,一行一个域名,匹配规则是最右匹配,比如:baidu.com,匹配的是*.*.baidu.com,黑名单的域名直接走上级代理,白名单的域名不走上级代理。
397 |
398 | `./proxy http -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" -b blocked.txt -d direct.txt`
399 |
400 | ### 1.3.HTTP二级代理(加密)
401 |
402 | > 注意: 后面二级代理使用的`proxy.crt`和`proxy.key`应与一级代理一致
403 |
404 | 
405 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
406 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
407 |
408 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
409 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
410 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080。
411 |
412 | 二级HTTP代理(本地windows)
413 | `./proxy.exe http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
414 | 然后设置你的windos系统中,需要通过代理上网的程序的代理为http模式,地址为:127.0.0.1,端口为:8080,程序即可通过加密通道通过vps上网。
415 |
416 | ### 1.4.HTTP三级代理(加密)
417 | 
418 | 一级HTTP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
419 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
420 | 二级HTTP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
421 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
422 | 三级HTTP代理(本地)
423 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
424 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问一级HTTP代理上面的代理端口38080。
425 |
426 | ### 1.5.Basic认证,API认证
427 |
428 | 请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
429 |
430 | ### 1.6.HTTP代理流量强制走上级HTTP代理
431 | 默认情况下,proxy会智能判断一个网站域名是否无法访问,如果无法访问才走上级HTTP代理.通过--always可以使全部HTTP代理流量强制走上级HTTP代理。
432 | `./proxy http --always -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
433 |
434 | ### 1.7.HTTP(S)通过SSH中转
435 | 
436 | 说明:ssh中转的原理是利用了ssh的转发功能,就是你连接上ssh之后,可以通过ssh代理访问目标地址。
437 | 假设有:vps
438 | - IP是2.2.2.2, ssh端口是22, ssh用户名是:user, ssh用户密码是:demo
439 | - 用户user的ssh私钥名称是user.key
440 |
441 | #### *1.7.1 ssh用户名和密码的方式*
442 | 本地HTTP(S)代理28080端口,执行:
443 | `./proxy http -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -D demo -t tcp -p ":28080"`
444 | #### *1.7.2 ssh用户名和密钥的方式*
445 | 本地HTTP(S)代理28080端口,执行:
446 | `./proxy http -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -S user.key -t tcp -p ":28080"`
447 |
448 | ### 1.8.KCP协议传输
449 | 
450 | KCP协议需要--kcp-key参数设置一个密码用于加密解密数据
451 |
452 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
453 | `./proxy http -t kcp -p ":38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
454 |
455 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
456 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T kcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
457 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080,数据通过kcp协议传输,注意kcp走的是udp协议协议,所以防火墙需放开38080的udp协议。
458 |
459 | ### 1.9 HTTP(S)反向代理
460 | 
461 | proxy不仅支持在其他软件里面通过设置代理的方式,为其他软件提供代理服务,而且支持直接把请求的网站域名解析到proxy监听的ip上,然后proxy监听80和443端口,那么proxy就会自动为你代理访问需要访问的HTTP(S)网站。
462 |
463 | 使用方式:
464 | 在"最后一级proxy代理"的机器上,因为proxy要伪装成所有网站,网站默认的端口HTTP是80,HTTPS是443,让proxy监听80和443端口即可.参数-p多个地址用逗号分割。
465 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :80,:443`
466 |
467 | 这个命令就在机器上启动了一个proxy代理,同时监听80和443端口,既可以当作普通的代理使用,也可以直接把需要代理的域名解析到这个机器的IP上。
468 |
469 | 如果有上级代理那么参照上面教程设置上级即可,使用方式完全一样。
470 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :80,:443 -T tls -P "2.2.2.2:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
471 |
472 | 注意:
473 | proxy所在的服务器的DNS解析结果不能受到自定义的解析影响,不然就死循环了,proxy代理最好指定`--dns 8.8.8.8`参数。
474 |
475 | ### 1.10 HTTP(S)透明代理
476 | 该模式需要具有一定的网络基础,相关概念不懂的请自行搜索解决。
477 | 假设proxy现在在路由器上运行,启动命令如下:
478 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :33080 -T tls -P "2.2.2.2:33090" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
479 |
480 | 然后添加iptables规则,下面是参考规则:
481 | ```shell
482 | #上级proxy服务端服务器IP地址:
483 | proxy_server_ip=2.2.2.2
484 |
485 | #路由器运行proxy监听的端口:
486 | proxy_local_port=33080
487 |
488 | #下面的就不用修改了
489 | #create a new chain named PROXY
490 | iptables -t nat -N PROXY
491 |
492 | # Ignore your PROXY server's addresses
493 | # It's very IMPORTANT, just be careful。
494 |
495 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d $proxy_server_ip -j RETURN
496 |
497 | # Ignore LANs IP address
498 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 0.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
499 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 10.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
500 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 127.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
501 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 169.254.0.0/16 -j RETURN
502 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 172.16.0.0/12 -j RETURN
503 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 192.168.0.0/16 -j RETURN
504 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 224.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
505 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 240.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
506 |
507 | # Anything to port 80 443 should be redirected to PROXY's local port
508 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
509 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp --dport 443 -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
510 |
511 | # Apply the rules to nat client
512 | iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -j PROXY
513 | # Apply the rules to localhost
514 | iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp -j PROXY
515 | ```
516 | - 清空整个链 iptables -F 链名比如iptables -t nat -F PROXY
517 | - 删除指定的用户自定义链 iptables -X 链名 比如 iptables -t nat -X PROXY
518 | - 从所选链中删除规则 iptables -D 链名 规则详情 比如 iptables -t nat -D PROXY -d 223.223.192.0/255.255.240.0 -j RETURN
519 |
520 | ### 1.11 自定义DNS
521 | --dns-address和--dns-ttl参数,用于自己指定proxy访问域名的时候使用的dns(--dns-address)
522 | 以及解析结果缓存时间(--dns-ttl)秒数,避免系统dns对proxy的干扰,另外缓存功能还能减少dns解析时间提高访问速度。
523 | 比如:
524 | `./proxy http -p ":33080" --dns-address "8.8.8.8:53" --dns-ttl 300`
525 |
526 | ### 1.12 自定义加密
527 | proxy的http(s)代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义
528 | 加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可,
529 | 加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
530 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以,下面分别用二级,三级为例:
531 |
532 | 二级实例
533 |
534 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
535 | `proxy http -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
536 | 本地二级执行:
537 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
538 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
539 |
540 |
541 | 三级实例
542 |
543 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
544 | `proxy http -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
545 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
546 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
547 | 本地三级执行:
548 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
549 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
550 |
551 | ### 1.13 压缩传输
552 | proxy的http(s)代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以对数据进行压缩,
553 | 也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,
554 | 一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
555 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据,下面分别用二级,三级为例:
556 |
557 | 二级实例
558 |
559 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
560 | `proxy http -t tcp -m -p :7777`
561 | 本地二级执行:
562 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
563 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
564 |
565 |
566 | 三级实例
567 |
568 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
569 | `proxy http -t tcp -m -p :7777`
570 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
571 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
572 | 本地三级执行:
573 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
574 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
575 |
576 | ### 1.14 负载均衡
577 |
578 | HTTP(S)代理支持上级负载均衡,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
579 |
580 | `proxy http --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080`
581 |
582 | ### 1.14.1 设置重试间隔和超时时间
583 |
584 | `proxy http --lb-method=leastconn --lb-retrytime 300 --lb-timeout 300 -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -t tcp -p :33080`
585 |
586 | ### 1.14.2 设置权重
587 |
588 | `proxy http --lb-method=weight -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -P 2.1.1.1:33080?w=2 -P 3.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -t tcp -p :33080`
589 |
590 | ### 1.14.3 使用目标地址选择上级
591 |
592 | `proxy http --lb-hashtarget --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -t tcp -p :33080`
593 |
594 | ### 1.15 限速
595 |
596 | 限速100K,通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
597 |
598 | `proxy http -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -l 100K`
599 |
600 | ### 1.16 指定出口IP
601 |
602 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作,此时代理会尝试不绑定IP去访问目标,同时日志会提示。
603 |
604 | `proxy http -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 --bind-listen`
605 |
606 | ### 1.17 证书参数使用base64数据
607 |
608 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
609 |
610 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
611 |
612 | ### 1.18 智能模式
613 | 智能模式设置,可以是intelligent|direct|parent三者之一。
614 | 默认是:intelligent。
615 | 每个值的含义如下:
616 | `--intelligent=direct`,不在blocked里面的目标都直连。
617 | `--intelligent=parent`,不在direct里面的目标都走上级。
618 | `--intelligent=intelligent`,blocked和direct里面都没有的目标,智能判断是否使用上级访问目标。
619 |
620 | ### 1.19 查看帮助
621 | `./proxy help http`
622 |
623 | ## 2.TCP代理
624 |
625 | ### 2.1 普通一级TCP代理
626 | 
627 | 本地执行:
628 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22"`
629 | 那么访问本地33080端口就是访问192.168.22.33的22端口。
630 |
631 | `-p`参数支持的写法:
632 |
633 | ```text
634 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
635 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
636 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
637 | ```
638 |
639 | 如果本地监听端口数量大于1,那么将会连接与本地端口一致的对应上级端口,忽略`-P`里面的端口。
640 |
641 | 如果需要所有端口进来的连接,都连接到上级指定端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`。
642 |
643 | 比如:
644 |
645 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080-33085" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:0"`
646 |
647 | 那么`33080`端口进来的连接,将会连接192.168.22.33的`33080`端口,其它端口以此类推,本地和上级端口一致,此时参数`-P`里面的端口用`0`。
648 |
649 | 如果想无论是`33080`,`33081`等端口进来的连接都连接到192.168.22.33的`22`端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`
650 |
651 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080-33085" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --lock-port`
652 |
653 |
654 | ### 2.2 普通二级TCP代理
655 | 
656 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
657 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "127.0.0.1:8080"`
658 | 本地执行:
659 | `./proxy tcp -p ":23080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.33:33080"`
660 | 那么访问本地23080端口就是访问22.22.22.33的8080端口。
661 |
662 | ### 2.3 普通三级TCP代理
663 | 
664 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
665 | `./proxy tcp -p ":38080" -T tcp -P "66.66.66.66:8080"`
666 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
667 | `./proxy tcp -p ":28080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080"`
668 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
669 | `./proxy tcp -p ":8080" -T tcp -P "33.33.33.33:28080"`
670 | 那么访问本地8080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问66.66.66.66的8080端口。
671 |
672 | ### 2.4 加密二级TCP代理
673 | 
674 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
675 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "127.0.0.1:8080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
676 | 本地执行:
677 | `./proxy tcp -p ":23080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.33:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
678 | 那么访问本地23080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问22.22.22.33的8080端口。
679 |
680 | ### 2.5 加密三级TCP代理
681 | 
682 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
683 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":38080" -T tcp -P "66.66.66.66:8080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
684 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
685 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
686 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
687 | `./proxy tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
688 | 那么访问本地8080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问66.66.66.66的8080端口。
689 |
690 | ### 2.6 通过代理连接上级
691 | 有时候proxy所在的网络不能直接访问外网,需要通过一个https或者socks5代理才能上网,那么这个时候
692 | -J参数就可以帮助你让proxy的tcp端口映射的时候通过https或者socks5代理去连接上级-P,将外部端口映射到本地。
693 | -J参数格式如下:
694 |
695 | https代理写法:
696 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
697 | https://username:password@host:port
698 | 代理不需要认证
699 | https://host:port
700 |
701 | socks5代理写法:
702 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
703 | socks5://username:password@host:port
704 | 代理不需要认证
705 | socks5://host:port
706 |
707 | host:代理的IP或者域名
708 | port:代理的端口
709 |
710 | ### 2.7 指定`出口IP`
711 | 当TCP代理当上级类型(参数:-T)是tcp当时候,支持指定`出口IP`。使用`--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作,此时代理会尝试不绑定IP去访问目标,同时日志会提示。
712 |
713 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" -B`
714 |
715 | ### 2.8 限速,限制连接数
716 |
717 | 参数`--max-conns`可以限制每个端口的最大连接数。
718 | 比如限制每个端口最多1000个连接数:
719 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --max-conns 1000`
720 | 参数`--rate-limit`可以限制每个tcp连接的速率。
721 | 比如限制每个tcp连接速率为100k/s:
722 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --rate-limit 100k`
723 |
724 | ### 2.9 查看帮助
725 | `./proxy help tcp`
726 |
727 | ## 3.UDP代理
728 |
729 | ### 3.1.普通一级UDP代理
730 | 
731 | 本地执行:
732 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
733 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
734 |
735 | `-p`参数支持的写法:
736 |
737 | ```text
738 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
739 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
740 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
741 | ```
742 |
743 | 如果本地监听端口数量大于1,那么将会连接与本地端口一致的对应上级端口,忽略`-P`里面的端口。
744 |
745 | 如果需要所有端口进来的连接,都连接到上级指定端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`。
746 |
747 | 比如:
748 |
749 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080-33085" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:0"`
750 |
751 | 那么`33080`端口进来的连接,将会连接192.168.22.33的`33080`端口,其它端口以此类推,本地和上级端口一致,此时参数`-P`里面的端口用`0`。
752 |
753 | 如果想无论是`33080`,`33081`等端口进来的连接都连接到192.168.22.33的`2222`端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`
754 |
755 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080-33085" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:2222" --lock-port`
756 |
757 | ### 3.2.普通二级UDP代理
758 | 
759 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
760 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
761 | 本地执行:
762 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.33:33080"`
763 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是通过TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
764 |
765 | ### 3.3.普通三级UDP代理
766 | 
767 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
768 | `./proxy tcp -p ":38080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
769 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
770 | `./proxy tcp -p ":28080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080"`
771 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
772 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tcp -P "33.33.33.33:28080"`
773 | 那么访问本地5353端口就是通过TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的53端口。
774 |
775 | ### 3.4.加密二级UDP代理
776 | 
777 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
778 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":33080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
779 | 本地执行:
780 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tls -P "22.22.22.33:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
781 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是通过加密TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
782 |
783 | ### 3.5.加密三级UDP代理
784 | 
785 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
786 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":38080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
787 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
788 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
789 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
790 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
791 | 那么访问本地5353端口就是通过加密TCP隧道,通过VPS_01访问8.8.8.8的53端口。
792 |
793 | ### 3.6 指定`出口IP`
794 | 当UDP代理当上级类型(参数:-T)是udp当时候,支持指定`出口IP`。使用`--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作。
795 |
796 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:2222" -B`
797 |
798 | ### 3.7 查看帮助
799 | `./proxy help udp`
800 |
801 | ## 4.内网穿透
802 | ### 4.1、原理说明
803 | 内网穿透,分为两个版本,“多链接版本”和“多路复用版本”,一般像web服务这种不是长时间连接的服务建议用“多链接版本”,如果是要保持长时间连接建议使用“多路复用版本”。
804 | 1. 多链接版本,对应的子命令是tserver,tclient,tbridge。
805 | 1. 多路复用版本,对应的子命令是server,client,bridge。
806 | 1. 多链接版本和多路复用版本的参数和使用方式完全一样。
807 | 1. 多路复用版本的server,client可以开启压缩传输,参数是--c。
808 | 1. server,client要么都开启压缩,要么都不开启,不能只开一个。
809 |
810 | 下面的教程以“多路复用版本”为例子,说明使用方法。
811 | 内网穿透由三部分组成:client端,server端,bridge端;client和server主动连接bridge端进行桥接。
812 |
813 | ### 4.2、TCP普通用法
814 | 背景:
815 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口
816 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
817 |
818 | 需求:
819 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的28080端口访问到公司机器A的80端口
820 |
821 | 步骤:
822 | 1. 在vps上执行
823 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
824 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
825 |
826 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
827 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
828 |
829 | 1. 完成
830 |
831 | ### 4.3、微信接口本地开发
832 | 背景:
833 | - 自己的笔记本提供了nginx服务80端口
834 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
835 |
836 | 需求:
837 | 在微信的开发帐号的网页回调接口配置里面填写地址:http://22.22.22.22/calback.php
838 | 然后就可以访问到笔记本的80端口下面的calback.php,如果需要绑定域名,可以用自己的域名
839 | 比如:wx-dev.xxx.com解析到22.22.22.22,然后在自己笔记本的nginx里
840 | 配置域名wx-dev.xxx.com到具体的目录即可。
841 |
842 |
843 | 步骤:
844 | 1. 在vps上执行,确保vps的80端口没被其它程序占用。
845 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
846 | `./proxy server -r ":80@:80" -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
847 |
848 | 1. 在自己笔记本上面执行
849 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
850 |
851 | 1. 完成
852 |
853 | ### 4.4、UDP普通用法
854 | 背景:
855 | - 公司机器A提供了DNS解析服务,UDP:53端口
856 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
857 |
858 | 需求:
859 | 在家里能够通过设置本地dns为22.22.22.22,使用公司机器A进行域名解析服务。
860 |
861 | 步骤:
862 | 1. 在vps上执行
863 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
864 | `./proxy server --udp -r ":53@:53" -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
865 |
866 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
867 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
868 |
869 | 1. 完成
870 |
871 | ### 4.5、高级用法一
872 | 背景:
873 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口
874 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
875 |
876 | 需求:
877 | 为了安全,不想在VPS上能够访问到公司机器A,在家里能够通过访问本机的28080端口,
878 | 通过加密隧道访问到公司机器A的80端口。
879 |
880 | 步骤:
881 | 1. 在vps上执行
882 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
883 |
884 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
885 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
886 |
887 | 1. 在家里电脑上执行
888 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
889 |
890 | 1. 完成
891 |
892 | ### 4.6、高级用法二
893 | 提示:
894 | 如果同时有多个client连接到同一个bridge,需要指定不同的key,可以通过--k参数设定,--k可以是任意唯一字符串,
895 | 只要在同一个bridge上唯一即可。
896 | server连接到bridge的时候,如果同时有多个client连接到同一个bridge,需要使用--k参数选择client。
897 | 暴露多个端口重复-r参数即可.-r格式是:"本地IP:本地端口@clientHOST:client端口"。
898 |
899 | 背景:
900 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口,ftp服务21端口
901 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
902 |
903 | 需求:
904 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的28080端口访问到公司机器A的80端口
905 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的29090端口访问到公司机器A的21端口
906 |
907 | 步骤:
908 | 1. 在vps上执行
909 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
910 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -r ":29090@:21" --k test -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
911 |
912 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
913 | `./proxy client --k test -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
914 |
915 | 1. 完成
916 |
917 | ### 4.7.server的-r参数
918 | -r完整格式是:`PROTOCOL://LOCAL_IP:LOCAL_PORT@[CLIENT_KEY]CLIENT_LOCAL_HOST:CLIENT_LOCAL_PORT`
919 |
920 | 4.7.1.协议PROTOCOL:tcp、udp、ptcp、pudp。
921 | 比如: `-r "udp://:10053@:53" -r "tcp://:10800@:1080" -r ":8080@:80"`
922 | 如果指定了--udp参数,PROTOCOL默认为udp,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`默认为udp;
923 | 如果没有指定--udp参数,PROTOCOL默认为tcp,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`默认为tcp;
924 |
925 | 4.7.2.CLIENT_KEY:默认是default。
926 | 比如: -r "udp://:10053@[test1]:53" -r "tcp://:10800@[test2]:1080" -r ":8080@:80"
927 | 如果指定了--k参数,比如--k test,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`CLIENT_KEY默认为test;
928 | 如果没有指定--k参数,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`CLIENT_KEY默认为default;
929 |
930 | 4.7.3.LOCAL_IP为空默认是:`0.0.0.0`,CLIENT_LOCAL_HOST为空默认是:`127.0.0.1`;
931 |
932 | ### 4.8.server和client通过代理连接bridge
933 | 有时候server或者client所在的网络不能直接访问外网,需要通过一个https或者socks5代理才能上网,那么这个时候
934 | -J参数就可以帮助你让server或者client通过https或者socks5代理去连接bridge。
935 | -J参数格式如下:
936 |
937 | https代理写法:
938 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
939 | https://username:password@host:port
940 | 代理不需要认证
941 | https://host:port
942 |
943 | socks5代理写法:
944 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
945 | socks5://username:password@host:port
946 | 代理不需要认证
947 | socks5://host:port
948 |
949 | host:代理的IP或者域名
950 | port:代理的端口
951 |
952 | ### 4.9.内网穿透HTTP服务
953 |
954 | 通常HTTP请求客户端会使用server的ip和端口去设置HOST字段,但是与期望的后端实际HOST不一样,这样就造成了tcp是通的,
955 | 但后端依赖HOST字段定位虚拟主机就不能工作.现在用--http-host参数强制设置http头部的HOST字段值为后端实际的
956 | 域名和端口即可轻松解决。
957 |
958 | `server`的--http-host参数格式如下:
959 |
960 | `--http-host www.test.com:80@2200`,如果server监听多个端口,只需要重复`--http-host`参数设置每个端口的HOST即可。
961 |
962 | 实例:
963 |
964 | 比如client本地nginx,127.0.0.1:80提供了web服务,其中绑定了一个域名`local.com`。
965 |
966 | 那么server的启动参数可以如下:
967 |
968 | `proxy server -P :30000 -r :2500@127.0.0.1:80 --http-host local.com@2500`
969 |
970 | 解释:
971 |
972 | `-r :2500@127.0.0.1:80` 和 `--http-host local.com:80@2500` 里面的2500端口是server本地监听的端口
973 |
974 | 当使用http协议请求server的ip:2500端口的时候,http的头部HOST字段就会被设置为`local.com`。
975 |
976 | ### 4.10 关于流量统计
977 |
978 | 如果单独启动一个server对接上级是proxy-admin控制面板,需要在上级控制面板里面新建一个映射,获得个映射规则的ID,
979 |
980 | 然后启动server的时候加上参数 --server-id=映射规则的ID 才能统计到流量。
981 |
982 | ### 4.11 关于p2p
983 | 内网穿透支持在server和client网络情况满足的情况下,server和client之间通过p2p直接连接,开启方法是:
984 |
985 | 在启动bridge,server,client到时候都加上`--p2p`参数即可。server的-r参数可以针对端口是否启用p2p(ptcp和pudp)。
986 |
987 | 如果server和client之间p2p打洞失败,那么会自动切换使用bridge中转传输数据。
988 |
989 | ### 4.12 客户端key白名单
990 | 内网穿透bridge可以设置客户端key白名单,参数是--client-keys,格式可以是:
991 |
992 | a.文件名,文件内容一行一个客户端key只能包含数字字母下划线,也就是客户端启动参数--k的值,只有客户端key在此白名单的客户端才能连接。# 开头的行,为注释。
993 |
994 | b.“base64://”开头的base64编码的上面a说明的文件内容,比如:base64://ajfpoajsdfa=
995 |
996 | c.”str://“开头的英文逗号分割的多个key,比如:str://default,company,school
997 |
998 | 默认是空,允许所有key。
999 |
1000 | ### 4.13 网络NAT类型判断
1001 |
1002 | nat类型判断,方便查看网络是否支持p2p,可以执行:`proxy tools -a nattype`
1003 |
1004 | ### 4.14 查看帮助
1005 | `./proxy help bridge`
1006 | `./proxy help server`
1007 | `./proxy help client`
1008 |
1009 | ## 5.SOCKS5代理
1010 | 提示:
1011 |
1012 | SOCKS5代理,支持CONNECT,UDP协议,不支持BIND,支持用户名密码认证。
1013 |
1014 | ***如果你的VPS是阿里云,腾讯云这种VPS,就是ifconfig看不见你的公网IP,只能看见内网IP,***
1015 |
1016 | ***那么需要加上`-g VPS公网IP`参数,SOCKS5代理的UDP功能才能正常工作。***
1017 |
1018 | ### 5.1 普通SOCKS5代理
1019 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080"`
1020 |
1021 | -p参数支持的写法:
1022 |
1023 | ```text
1024 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
1025 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
1026 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
1027 | ```
1028 |
1029 | ### 5.2.普通二级SOCKS5代理
1030 | 
1031 | 使用本地端口8090,假设上级SOCKS5代理是`22.22.22.22:8080`
1032 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" `
1033 | 我们还可以指定网站域名的黑白名单文件,一行一个域名,匹配规则是最右匹配,比如:baidu.com,匹配的是*.*.baidu.com,黑名单的域名域名直接走上级代理,白名单的域名不走上级代理;如果域名即在黑名单又在白名单中,那么黑名单起作用。
1034 | `./proxy socks -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" -b blocked.txt -d direct.txt`
1035 |
1036 | ### 5.3.SOCKS二级代理(加密)
1037 | 
1038 | 一级SOCKS代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
1039 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1040 |
1041 | 二级SOCKS代理(本地Linux)
1042 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1043 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080。
1044 |
1045 | 二级SOCKS代理(本地windows)
1046 | `./proxy.exe socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1047 | 然后设置你的windos系统中,需要通过代理上网的程序的代理为socks5模式,地址为:127.0.0.1,端口为:8080,程序即可通过加密通道通过vps上网。
1048 |
1049 | ### 5.4.SOCKS三级代理(加密)
1050 | 
1051 | 一级SOCKS代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
1052 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1053 | 二级SOCKS代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
1054 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1055 | 三级SOCKS代理(本地)
1056 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1057 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问一级SOCKS代理上面的代理端口38080。
1058 |
1059 | ### 5.5.SOCKS代理流量强制走上级SOCKS代理
1060 | 默认情况下,proxy会智能判断一个网站域名是否无法访问,如果无法访问才走上级SOCKS代理.通过--always可以使全部SOCKS代理流量强制走上级SOCKS代理。
1061 | `./proxy socks --always -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1062 |
1063 | ### 5.6.SOCKS通过SSH中转
1064 | 
1065 | 说明:ssh中转的原理是利用了ssh的转发功能,就是你连接上ssh之后,可以通过ssh代理访问目标地址。
1066 | 假设有:vps
1067 | - IP是2.2.2.2, ssh端口是22, ssh用户名是:user, ssh用户密码是:demo
1068 | - 用户user的ssh私钥名称是user.key
1069 |
1070 | #### *5.6.1 ssh用户名和密码的方式*
1071 | 本地SOCKS5代理28080端口,执行:
1072 | `./proxy socks -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -D demo -t tcp -p ":28080"`
1073 | #### *5.6.2 ssh用户名和密钥的方式*
1074 | 本地SOCKS5代理28080端口,执行:
1075 | `./proxy socks -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -S user.key -t tcp -p ":28080"`
1076 |
1077 | 那么访问本地的28080端口就是通过VPS访问目标地址。
1078 |
1079 | ### 5.7.认证
1080 | 对于socks5代理协议我们可以进行用户名密码认证,认证的用户名和密码可以在命令行指定
1081 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1" -a "user2:pass2"`
1082 | 多个用户,重复-a参数即可。
1083 | 也可以放在文件中,格式是一行一个"用户名:密码",然后用-F指定。
1084 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":33080" -F auth-file.txt`
1085 |
1086 | ### 5.8.KCP协议传输
1087 | KCP协议需要--kcp-key参数设置一个密码用于加密解密数据
1088 |
1089 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
1090 | `./proxy socks -t kcp -p ":38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
1091 |
1092 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
1093 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T kcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
1094 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080,数据通过kcp协议传输。
1095 |
1096 | ### 5.9.自定义DNS
1097 | --dns-address和--dns-ttl参数,用于自己指定proxy访问域名的时候使用的dns(--dns-address)
1098 | 以及解析结果缓存时间(--dns-ttl)秒数,避免系统dns对proxy的干扰,另外缓存功能还能减少dns解析时间提高访问速度。
1099 | 比如:
1100 | `./proxy socks -p ":33080" --dns-address "8.8.8.8:53" --dns-ttl 300`
1101 |
1102 | ### 5.10 自定义加密
1103 | proxy的socks代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可,
1104 | 加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
1105 |
1106 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以。
1107 |
1108 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
1109 |
1110 | 二级实例
1111 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1112 | `proxy socks -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
1113 | 本地二级执行:
1114 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
1115 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
1116 |
1117 |
1118 | 三级实例
1119 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1120 | `proxy socks -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
1121 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
1122 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
1123 | 本地三级执行:
1124 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
1125 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
1126 |
1127 | ### 5.11 压缩传输
1128 | proxy的socks代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以
1129 | 对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,
1130 | 一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
1131 |
1132 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据。
1133 |
1134 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
1135 |
1136 | 二级实例
1137 |
1138 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1139 | `proxy socks -t tcp -m -p :7777`
1140 | 本地二级执行:
1141 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
1142 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
1143 |
1144 |
1145 | 三级实例
1146 |
1147 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1148 | `proxy socks -t tcp -m -p :7777`
1149 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
1150 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
1151 | 本地三级执行:
1152 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
1153 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
1154 |
1155 |
1156 | ### 5.12 负载均衡
1157 |
1158 | SOCKS代理支持上级负载均衡,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
1159 |
1160 | `proxy socks --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
1161 |
1162 | ### 5.12.1 设置重试间隔和超时时间
1163 |
1164 | `proxy socks --lb-method=leastconn --lb-retrytime 300 --lb-timeout 300 -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
1165 |
1166 | ### 5.12.2 设置权重
1167 |
1168 | `proxy socks --lb-method=weight -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -P 2.1.1.1:33080?w=2 -P 3.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -p :33080 -t tcp`
1169 |
1170 | ### 5.12.3 使用目标地址选择上级
1171 |
1172 | `proxy socks --lb-hashtarget --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
1173 |
1174 | ### 5.13 限速
1175 |
1176 | 限速100K,通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
1177 |
1178 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -l 100K`
1179 |
1180 | ### 5.14 指定`出口IP`
1181 |
1182 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果`入口IP`是内网IP,`出口IP`不会使用`入口IP`。
1183 |
1184 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 --bind-listen`
1185 |
1186 | ### 5.15 级联认证
1187 |
1188 | SOCKS5支持级联认证,-A可以设置上级认证信息。
1189 |
1190 | 上级:
1191 |
1192 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -a user:pass`
1193 |
1194 | 本地:
1195 |
1196 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -A user:pass -t tcp -p :33080`
1197 |
1198 | 请更多认证细节,请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
1199 |
1200 | ### 5.16 证书参数使用base64数据
1201 |
1202 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
1203 |
1204 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
1205 |
1206 |
1207 | ### 5.17 智能模式
1208 | 智能模式设置,可以是intelligent|direct|parent三者之一。
1209 | 默认是:intelligent。
1210 | 每个值的含义如下:
1211 | `--intelligent=direct`,不在blocked里面的目标都直连。
1212 | `--intelligent=parent`,不在direct里面的目标都走上级。
1213 | `--intelligent=intelligent`,blocked和direct里面都没有的目标,智能判断是否使用上级访问目标。
1214 |
1215 | ### 5.18 固定UDP功能端口
1216 |
1217 | 默认情况下socks5的UDP功能的端口号,proxy是按着`rfc1982草案`要求,使用协议握手过程中随机指定,不需要提前指定。
1218 |
1219 | 但是某些情况下,需要固定UDP功能端口,可以通过参数`--udp-port 端口号`用来固定UDP功能的端口号,比如:
1220 |
1221 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --udp-port 38080`
1222 |
1223 | ### 5.19 查看帮助
1224 | `./proxy help socks`
1225 |
1226 | ## 6.SPS协议转换
1227 |
1228 | ### 6.1 功能介绍
1229 | 代理协议转换使用的是sps子命令,sps本身不提供代理功能,只是接受代理请求"转换并转发"给已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理或者ss代理;sps可以把已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理或ss代理转换为一个端口同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的代理,而且http(s)代理支持正向代理和反向代理(SNI),转换后的SOCKS5代理,当上级是SOCKS5或者SS时仍然支持UDP功能;另外对于已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理,支持tls、tcp、kcp三种模式,支持链式连接,也就是可以多个sps结点层级连接构建加密通道。
1230 |
1231 | `ss`功能支持的加密方法为:aes-128-cfb , aes-128-ctr , aes-128-gcm , aes-192-cfb , aes-192-ctr , aes-192-gcm , aes-256-cfb , aes-256-ctr , aes-256-gcm , bf-cfb , cast5-cfb , chacha20 , chacha20-ietf , chacha20-ietf-poly1305 , des-cfb , rc4-md5 , rc4-md5-6 , salsa20 , xchacha20
1232 |
1233 | 本地监听端口-p参数支持的写法:
1234 |
1235 | ```text
1236 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
1237 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
1238 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
1239 | ```
1240 |
1241 | ### 6.2 HTTP(S)转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
1242 | 假设已经存在一个普通的http(s)代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1243 | 命令如下:
1244 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1245 |
1246 | 假设已经存在一个tls的http(s)代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,tls需要证书文件,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1247 | 命令如下:
1248 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1249 |
1250 | 假设已经存在一个kcp的http(s)代理(密码是:demo123):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1251 | 命令如下:
1252 | `./proxy sps -S http -T kcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 --kcp-key demo123 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1253 |
1254 | ### 6.3 SOCKS5转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
1255 | 假设已经存在一个普通的socks5代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1256 | 命令如下:
1257 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1258 |
1259 | 假设已经存在一个tls的socks5代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,tls需要证书文件,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1260 | 命令如下:
1261 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T tls -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1262 |
1263 | 假设已经存在一个kcp的socks5代理(密码是:demo123):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1264 | 命令如下:
1265 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T kcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 --kcp-key demo123 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
1266 |
1267 | ### 6.4 SS转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
1268 | SPS上级和本地支持ss协议,上级可以是SPS或者标准的ss服务。
1269 | SPS本地默认提供HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS三种代理,当上级是SOCKS5时转换后的SOCKS5和SS支持UDP功能。
1270 | 假设已经存在一个普通的SS或者SPS代理(开启了ss,加密方式:aes-256-cfb,密码:demo):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,转换后的ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
1271 | 命令如下:
1272 | `./proxy sps -S ss -H aes-256-cfb -J pass -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`。
1273 |
1274 | ### 6.5 链式连接
1275 | 
1276 | 上面提过多个sps结点可以层级连接构建加密通道,假设有如下vps和家里的pc电脑。
1277 | vps01:2.2.2.2
1278 | vps02:3.3.3.3
1279 | 现在我们想利用pc和vps01和vps02构建一个加密通道,本例子用tls加密也可以用kcp,在pc上访问本地18080端口就是访问vps01的本地8080端口。
1280 | 首先在vps01(2.2.2.2)上我们运行一个只有本地可以访问的http(s)代理,执行:
1281 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p 127.0.0.1:8080`
1282 |
1283 | 然后在vps01(2.2.2.2)上运行一个sps结点,执行:
1284 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tls -p :8081 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1285 |
1286 | 然后在vps02(3.3.3.3)上运行一个sps结点,执行:
1287 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:8081 -t tls -p :8082 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1288 |
1289 | 然后在pc上运行一个sps结点,执行:
1290 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 3.3.3.3:8082 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
1291 |
1292 | 完成。
1293 |
1294 | ### 6.6 监听多个端口
1295 | 一般情况下监听一个端口就可以,不过如果作为反向代理需要同时监听80和443两个端口,那么-p参数是支持的,
1296 | 格式是:`-p 0.0.0.0:80,0.0.0.0:443`,多个绑定用逗号分隔即可。
1297 |
1298 | ### 6.7 认证功能
1299 | sps支持http(s)\socks5代理认证,可以级联认证,有四个重要的信息:
1300 | 1:用户发送认证信息`user-auth`。
1301 | 2:设置的本地认证信息`local-auth`。
1302 | 3:设置的连接上级使用的认证信息`parent-auth`。
1303 | 4:最终发送给上级的认证信息`auth-info-to-parent`。
1304 | 他们的情况关系如下:
1305 |
1306 | | user-auth | local-auth | parent-auth | auth-info-to-paren
1307 | | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------
1308 | | 有/没有 | 有 | 有 | 来自parent-auth
1309 | | 有/没有 | 没有 | 有 | 来自parent-auth
1310 | | 有/没有 | 有 | 没有 | 无
1311 | | 没有 | 没有 | 没有 | 无
1312 | | 有 | 没有 | 没有 | 来自user-auth
1313 |
1314 | 对于sps代理我们可以进行用户名密码认证,认证的用户名和密码可以在命令行指定
1315 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1:0:0:" -a "user2:pass2:0:0:"`
1316 | 多个用户,重复-a参数即可。
1317 | 也可以放在文件中,格式是一行一个`用户名:密码:连接数:速率:上级`,然后用-F指定。
1318 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -F auth-file.txt`
1319 |
1320 | 如果上级有认证,下级可以通过-A参数设置认证信息,比如:
1321 | 上级:`./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1:0:0:" -a "user2:pass2:0:0:"`
1322 | 下级:`./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -A "user1:pass1" -t tcp -p ":33080" `
1323 |
1324 | 请更多认证细节,请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
1325 |
1326 | ### 6.8 多个上级
1327 |
1328 | 如果存在多个上级,可以通过多个-P指定。
1329 |
1330 | 比如:
1331 |
1332 | `proxy sps -P http://127.0.0.1:3100 -P socks5://127.0.0.1:3200`
1333 |
1334 | `-P`完整格式如下:
1335 |
1336 | `protocol://a:b@2.2.2.2:33080#1`
1337 |
1338 | 下面对每部分进行解释:
1339 |
1340 | `protocol://` 是协议类型,可能的类型以及含有如下:
1341 |
1342 | ```text
1343 | http 等价于 -S http -T tcp
1344 | https 等价于 -S http -T tls --parent-tls-single , 也就是http(s)代理 over TLS
1345 | https2 等价于 -S http -T tls
1346 | socks5 等价于 -S socks -T tcp
1347 | socks5s 等价于 -S socks -T tls --parent-tls-single , 也就是socks over TLS
1348 | socks5s2 等价于 -S socks -T tls
1349 | ss 等价于 -S ss -T tcp
1350 | httpws 等价于 -S http -T ws
1351 | httpwss 等价于 -S http -T wss
1352 | socks5ws 等价于 -S socks -T ws
1353 | socks5wss 等价于 -S socks -T wss
1354 | ```
1355 |
1356 | `a:b`是代理认证的用户名密码,如果是ss,`a`是加密方法,`b`是密码,没有用户名密码可以留空比如:`http://2.2.2.2:33080`,如果用户名和密码保护特殊符号可以使用urlencode进行编码。
1357 |
1358 | `2.2.2.2:33080`是上级地址,格式是:`IP(或域名):端口`,如果底层是ws/wss协议还可以带上路径,比如:`2.2.2.2:33080/ws`;
1359 | 还能通过附加查询参数`m`和`k`设置`ws\wss`的`加密方法`和`密码`,比如:`2.2.2.2:33080/ws?m=aes-192-cfb&k=password`
1360 |
1361 | `#1`多个上级的负载均衡是权重策略时候,设置的权重,很少用到。
1362 |
1363 | ### 6.9 自定义加密
1364 | proxy的sps代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行
1365 | 自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义
1366 | 一个密码即可,加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
1367 |
1368 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以。
1369 |
1370 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
1371 |
1372 | 假设已经存在一个http(s)代理:`6.6.6.6:6666`
1373 |
1374 | 二级实例
1375 |
1376 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1377 | `proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 6.6.6.6:6666 -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
1378 | 本地二级执行:
1379 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
1380 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
1381 |
1382 |
1383 | 三级实例
1384 |
1385 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1386 | `proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 6.6.6.6:6666 -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
1387 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
1388 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
1389 | 本地三级执行:
1390 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
1391 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
1392 |
1393 | ### 6.10 压缩传输
1394 | proxy的sps代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以
1395 | 对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,
1396 | 一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
1397 |
1398 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据。
1399 |
1400 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
1401 |
1402 | 二级实例
1403 |
1404 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1405 | `proxy sps -t tcp -m -p :7777`
1406 | 本地二级执行:
1407 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
1408 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
1409 |
1410 |
1411 | 三级实例
1412 |
1413 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
1414 | `proxy sps -t tcp -m -p :7777`
1415 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
1416 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
1417 | 本地三级执行:
1418 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
1419 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
1420 |
1421 | ### 6.11 禁用协议
1422 | SPS默认情况下一个端口支持http(s)和socks5两种代理协议,我们可以通过参数禁用某个协议
1423 | 比如:
1424 | 1.禁用HTTP(S)代理功能只保留SOCKS5代理功能,参数:`--disable-http`。
1425 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080 --disable-http`
1426 |
1427 | 1.禁用SOCKS5代理功能只保留HTTP(S)代理功能,参数:`--disable-socks`。
1428 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080 --disable-http`
1429 |
1430 | ### 6.12 限速
1431 |
1432 | 假设存在SOCKS5上级:
1433 |
1434 | `proxy socks -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -z password -t tcp`
1435 |
1436 | sps下级,限速100K
1437 |
1438 | `proxy sps -S socks -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -T tcp -Z password -l 100K -t tcp -p :33080`
1439 |
1440 | 通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
1441 |
1442 | ### 6.13 指定`出口IP`
1443 |
1444 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果`入口IP`是内网IP,`出口IP`不会使用`入口IP`。
1445 |
1446 | `proxy sps -S socks -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -T tcp -Z password -l 100K -t tcp --bind-listen -p :33080`
1447 |
1448 | ### 6.14 证书参数使用base64数据
1449 |
1450 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
1451 |
1452 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
1453 |
1454 | ### 6.15 独立服务
1455 | sps功能不强制指定一个上级,当上级为空,sps本身即可完成完整的代理功能.如果指定了上级那么就和之前一样使用上级连接目标。
1456 | 下面这个命令,就是一键开启http(s)\ss\socks服务。
1457 | `./proxy sps -p :33080`
1458 |
1459 | ### 6.16 目标重定向
1460 | sps功能提供的http(s)\socks5\ss代理功能,客户端通过sps代理去连接指定的“目标”,这个“目标”一般是网站也可能是任意的tcp地址,
1461 | 网站”目标“一般是foo.com:80,foo.com:443,sps支持使用--rewrite参数指定一个“目标”重定向规则文件,对目标进行重定向,客户端是无感知的,
1462 | 比如你对“目标”:demo.com:80重定向到192.168.0.12:80,那么客户端访问网站demo.com,其实访问的是192.168.0.12提供的网站服务。
1463 | “目标”重定向规则文件示例:
1464 |
1465 | ```text
1466 | # example
1467 | www.a.com:80 10.0.0.2:8080
1468 | **.b.com:80 10.0.0.2:80
1469 | 192.168.0.11:80 10.0.0.2:8080
1470 | ```
1471 |
1472 | ### 6.17 固定UDP功能端口
1473 |
1474 | 默认情况下sps的socks5的UDP功能的端口号是按着`rfc1982草案`要求,使用协议握手过程中随机指定,不需要提前指定。
1475 |
1476 | 但是某些情况下,需要固定UDP功能端口,可以通过参数`--udp-port 端口号`用来固定UDP功能的端口号,比如:
1477 |
1478 | `./proxy sps -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --udp-port 38081`
1479 |
1480 | 需要注意的是,sps的ss功能也有UDP功能,而且ss的UDP端口和tcp端口是一样的,所以要避免socks5的UDP端口和ss的UDP端口冲突,
1481 |
1482 | 要指定和tcp端口不一样的端口。
1483 |
1484 | ### 6.18 iptables 透明代理
1485 | sps模式支持Linux系统的iptables转发支持,也就是通常所说的iptables透明代理,如果在网关设备上进行iptables透明代理,那么对通过网关联网的设备就能实现无感知的代理。
1486 |
1487 | 启动命令实例:
1488 |
1489 | `./proxy sps --redir -p :8888 -P httpws://1.1.1.1:33080`
1490 |
1491 | 这里假设存在一个http的上级代理1.1.1.1:33080,使用ws传输数据。
1492 |
1493 | 然后添加iptables规则,下面是参考规则:
1494 | ```shell
1495 | #上级proxy服务端服务器IP地址:
1496 | proxy_server_ip=1.1.1.1
1497 |
1498 | #路由器运行proxy监听的端口:
1499 | proxy_local_port=33080
1500 |
1501 | #下面的就不用修改了
1502 | #create a new chain named PROXY
1503 | iptables -t nat -N PROXY
1504 |
1505 | # Ignore your PROXY server's addresses
1506 | # It's very IMPORTANT, just be careful。
1507 |
1508 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d $proxy_server_ip -j RETURN
1509 |
1510 | # Ignore LANs IP address
1511 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 0.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
1512 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 10.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
1513 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 127.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
1514 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 169.254.0.0/16 -j RETURN
1515 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 172.16.0.0/12 -j RETURN
1516 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 192.168.0.0/16 -j RETURN
1517 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 224.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
1518 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 240.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
1519 |
1520 | # Anything to port 80 443 should be redirected to PROXY's local port
1521 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
1522 | # Apply the rules to nat client
1523 | iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -j PROXY
1524 | # Apply the rules to localhost
1525 | iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp -j PROXY
1526 | ```
1527 | - 清空整个链 iptables -F 链名比如iptables -t nat -F PROXY
1528 | - 删除指定的用户自定义链 iptables -X 链名 比如 iptables -t nat -X PROXY
1529 | - 从所选链中删除规则 iptables -D 链名 规则详情 比如 iptables -t nat -D PROXY -d 223.223.192.0/255.255.240.0 -j RETURN
1530 |
1531 | ### 6.19 查看帮助
1532 |
1533 | `./proxy help sps`
1534 |
1535 | ## 7.KCP配置
1536 |
1537 | ### 7.1 配置介绍
1538 | proxy的很多功能都支持kcp协议,凡是使用了kcp协议的功能都支持这里介绍的配置参数。
1539 | 所以这里统一对KCP配置参数进行介绍。
1540 |
1541 | ### 7.2 详细配置
1542 | 所有的KCP配置参数共有17个,你可以都不用设置,他们都有默认值,如果为了或者最好的效果,
1543 | 就需要自己根据自己根据网络情况对参数进行配置。由于kcp配置很复杂需要一定的网络基础知识,
1544 | 如果想获得kcp参数更详细的配置和解说,请自行搜索。每个参数的命令行名称以及默认值和简单的功能说明如下:
1545 | ```
1546 | --kcp-key="secrect" pre-shared secret between client and server
1547 | --kcp-method="aes" encrypt/decrypt method, can be: aes, aes-128, aes-192, salsa20, blowfish,
1548 | twofish, cast5, 3des, tea, xtea, xor, sm4, none
1549 | --kcp-mode="fast" profiles: fast3, fast2, fast, normal, manual
1550 | --kcp-mtu=1350 set maximum transmission unit for UDP packets
1551 | --kcp-sndwnd=1024 set send window size(num of packets)
1552 | --kcp-rcvwnd=1024 set receive window size(num of packets)
1553 | --kcp-ds=10 set reed-solomon erasure coding - datashard
1554 | --kcp-ps=3 set reed-solomon erasure coding - parityshard
1555 | --kcp-dscp=0 set DSCP(6bit)
1556 | --kcp-nocomp disable compression
1557 | --kcp-acknodelay be carefull! flush ack immediately when a packet is received
1558 | --kcp-nodelay=0 be carefull!
1559 | --kcp-interval=50 be carefull!
1560 | --kcp-resend=0 be carefull!
1561 | --kcp-nc=0 be carefull! no congestion
1562 | --kcp-sockbuf=4194304 be carefull!
1563 | --kcp-keepalive=10 be carefull!
1564 | ```
1565 | 提示:
1566 | 参数:--kcp-mode中的四种fast3, fast2, fast, normal模式,
1567 | 相当于设置了下面四个参数:
1568 | normal:`--nodelay=0 --interval=40 --resend=2 --nc=1`
1569 | fast :`--nodelay=0 --interval=30 --resend=2 --nc=1`
1570 | fast2:`--nodelay=1 --interval=20 --resend=2 --nc=1`
1571 | fast3:`--nodelay=1 --interval=10 --resend=2 --nc=1`
1572 |
1573 | ## 8.安全DNS
1574 |
1575 | ### 8.1 介绍
1576 | 众所周知DNS是UDP端口53提供的服务,但是随着网络的发展一些知名DNS服务器也支持TCP方式dns查询,比如谷歌的8.8.8.8,proxy的DNS防污染服务器原理就是在本地启动一个proxy的DNS代理服务器,它用TCP的方式通过上级代理进行dns查询。如果它和上级代理通讯采用加密的方式,那么就可以进行安全无污染的DNS解析,还支持独立服务,并发解析,支持增强的hosts文件功能支持灵活的并发解析转发。
1577 |
1578 | dns解析顺序:
1579 | 1.使用参数--hosts解析。
1580 | 2.要解析的域名在1中没有找到,就使用参数--forward规则解析。
1581 | 3.要解析的域名在1和2中都没有找到,就使用默认--default解析,--default默认行为参数值有三种:proxy,direct,system。
1582 | 三种参数值解释如下:
1583 | proxy:通过上级去连接-q参数指定的dns服务器去解析域名。
1584 | direct:通过本地网络去连接-q参数指定的dns服务器去解析域名。
1585 | system:通过系统dns去解析域名。
1586 |
1587 | 提示:
1588 | --hosts 参数指定的host文件格式和系统hosts文件一致,而且域名支持通配符,可以参考hosts文件。
1589 | --forward 参数指定的解析转发规则文件,格式可以参考resolve.rules文件,域名支持通配符,支持为每个域名指定多个dns服务器并发解析,谁最快解析成功就用谁的解析结果。
1590 | -q 参数可以指定多个远程dns服务器,执行并发解析谁最快解析成功就用谁的解析结果,默认是:1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8,9.9.9.9,多个用逗号分割,
1591 | 比如还可以带端口:1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8#53,9.9.9.9
1592 |
1593 | 如果独立服务,不需要上级:
1594 | 可以执行:
1595 | `proxy dns --default system -p :5353`
1596 | or
1597 | `proxy dns --default direct -p :5353`
1598 |
1599 | ### 8.2 使用示例
1600 |
1601 | #### 8.2.1 普通HTTP(S)上级代理
1602 |
1603 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1604 | 本地执行:
1605 | `proxy dns -S http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1606 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了DNS解析功能。
1607 |
1608 | #### 8.2.2 普通SOCKS5上级代理
1609 |
1610 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1611 | 本地执行:
1612 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1613 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了DNS解析功能。
1614 |
1615 | #### 8.2.3 TLS加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
1616 |
1617 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1618 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1619 | `proxy http -t tls -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :33080`
1620 | 本地执行:
1621 | `proxy dns -S http -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :53`
1622 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1623 |
1624 | #### 8.2.4 TLS加密的SOCKS5上级代理
1625 |
1626 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1627 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1628 | `proxy socks -t tls -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :33080`
1629 | 本地执行:
1630 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :53`
1631 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1632 |
1633 | #### 8.2.5 KCP加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
1634 |
1635 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1636 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1637 | `proxy http -t kcp -p :33080`
1638 | 本地执行:
1639 | `proxy dns -S http -T kcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1640 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1641 |
1642 | #### 8.2.6 KCP加密的SOCKS5上级代理
1643 |
1644 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1645 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1646 | `proxy socks -t kcp -p :33080`
1647 | 本地执行:
1648 | `proxy dns -S socks -T kcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1649 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1650 |
1651 | #### 8.2.7 自定义加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
1652 |
1653 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1654 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1655 | `proxy http -t tcp -p :33080 -z password`
1656 | 本地执行:
1657 | `proxy dns -S http -T tcp -Z password -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1658 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1659 |
1660 | #### 8.2.8 自定义加密的SOCKS5上级代理
1661 |
1662 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
1663 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
1664 | `proxy socks -t kcp -p :33080 -z password`
1665 | 本地执行:
1666 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tcp -Z password -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
1667 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
1668 |
1669 | ## 9.API认证,限速,控制连接数
1670 |
1671 | proxy的http(s)/socks5/sps代理功能,支持通过API控制用户对代理对访问。
1672 |
1673 | ### 通过API可以干什么?
1674 |
1675 | - 用户维度,控制单个连接速率,控制最大连接数。
1676 | - IP维度,控制单个连接速率,控制最大连接数。
1677 | - 动态上级,可以根据用户或者客户端IP,动态的从API获取其上级,支持http(s)/socks5/ss上级。
1678 | - 认证每一个连接,无论是否要求客户端认证。
1679 | - 缓存认证结果,时间可以设置,减轻API压力。
1680 |
1681 | #### 具体使用
1682 | proxy的http(s)/socks5/sps代理API功能,通过`--auth-url`和`--auth-nouser`和`--auth-cache`三个参数控制。
1683 | 参数`--auth-url`是HTTP API接口地址,客户端连接的时候,proxy会GET方式请求这url,带上下面参数,如果返回HTTP状态码204,代表认证成功,其它情况认为认证失败。
1684 |
1685 | 一个完整的请求API的示例:
1686 | `http://test.com/auth.php?user=a&pass=b&client_addr=127.0.0.1:49892&local_addr=127.0.0.1:8100&target=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.baidu.com&service=http&sps=0`
1687 |
1688 | #### 参数说明
1689 | `user和pass` 当代理开启了认证功能,这里就是客户端提供的用户名和密码。
1690 | `client_addr` 客户端访问代理时的用的地址,格式IP:端口。
1691 | `local_addr` 客户端访问的代理地址,格式IP:端口。
1692 | `service` 代理类型,分为:http、socks。
1693 | `sps` 代理是否是sps提供的,1:是,0:否。
1694 | `target` 客户端要访问的目标,如果是http(s)代理,target是访问的具体url;如果是socks5代理,target是空。
1695 |
1696 | #### 示例
1697 | 假设--auth-url http://127.0.0.1:333/auth.php 指向了一个php接口地址.
1698 | auth.php内容如下:
1699 |
1700 | ```php
1701 | 注意: 后面二级代理使用的`proxy.crt`和`proxy.key`应与一级代理一致
2041 |
2042 | 
2043 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
2044 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2045 |
2046 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
2047 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2048 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080。
2049 |
2050 | 二级HTTP代理(本地windows)
2051 | `./proxy.exe http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2052 | 然后设置你的windos系统中,需要通过代理上网的程序的代理为http模式,地址为:127.0.0.1,端口为:8080,程序即可通过加密通道通过vps上网。
2053 |
2054 | ### 1.4.HTTP三级代理(加密)
2055 | 
2056 | 一级HTTP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2057 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2058 | 二级HTTP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2059 | `./proxy http -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2060 | 三级HTTP代理(本地)
2061 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2062 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问一级HTTP代理上面的代理端口38080。
2063 |
2064 | ### 1.5.Basic认证,API认证
2065 |
2066 | 请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
2067 |
2068 | ### 1.6.HTTP代理流量强制走上级HTTP代理
2069 | 默认情况下,proxy会智能判断一个网站域名是否无法访问,如果无法访问才走上级HTTP代理.通过--always可以使全部HTTP代理流量强制走上级HTTP代理。
2070 | `./proxy http --always -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2071 |
2072 | ### 1.7.HTTP(S)通过SSH中转
2073 | 
2074 | 说明:ssh中转的原理是利用了ssh的转发功能,就是你连接上ssh之后,可以通过ssh代理访问目标地址。
2075 | 假设有:vps
2076 | - IP是2.2.2.2, ssh端口是22, ssh用户名是:user, ssh用户密码是:demo
2077 | - 用户user的ssh私钥名称是user.key
2078 |
2079 | #### *1.7.1 ssh用户名和密码的方式*
2080 | 本地HTTP(S)代理28080端口,执行:
2081 | `./proxy http -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -D demo -t tcp -p ":28080"`
2082 | #### *1.7.2 ssh用户名和密钥的方式*
2083 | 本地HTTP(S)代理28080端口,执行:
2084 | `./proxy http -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -S user.key -t tcp -p ":28080"`
2085 |
2086 | ### 1.8.KCP协议传输
2087 | 
2088 | KCP协议需要--kcp-key参数设置一个密码用于加密解密数据
2089 |
2090 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
2091 | `./proxy http -t kcp -p ":38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
2092 |
2093 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
2094 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p ":8080" -T kcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
2095 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080,数据通过kcp协议传输,注意kcp走的是udp协议协议,所以防火墙需放开38080的udp协议。
2096 |
2097 | ### 1.9 HTTP(S)反向代理
2098 | 
2099 | proxy不仅支持在其他软件里面通过设置代理的方式,为其他软件提供代理服务,而且支持直接把请求的网站域名解析到proxy监听的ip上,然后proxy监听80和443端口,那么proxy就会自动为你代理访问需要访问的HTTP(S)网站。
2100 |
2101 | 使用方式:
2102 | 在"最后一级proxy代理"的机器上,因为proxy要伪装成所有网站,网站默认的端口HTTP是80,HTTPS是443,让proxy监听80和443端口即可.参数-p多个地址用逗号分割。
2103 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :80,:443`
2104 |
2105 | 这个命令就在机器上启动了一个proxy代理,同时监听80和443端口,既可以当作普通的代理使用,也可以直接把需要代理的域名解析到这个机器的IP上。
2106 |
2107 | 如果有上级代理那么参照上面教程设置上级即可,使用方式完全一样。
2108 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :80,:443 -T tls -P "2.2.2.2:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2109 |
2110 | 注意:
2111 | proxy所在的服务器的DNS解析结果不能受到自定义的解析影响,不然就死循环了,proxy代理最好指定`--dns 8.8.8.8`参数。
2112 |
2113 | ### 1.10 HTTP(S)透明代理
2114 | 该模式需要具有一定的网络基础,相关概念不懂的请自行搜索解决。
2115 | 假设proxy现在在路由器上运行,启动命令如下:
2116 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p :33080 -T tls -P "2.2.2.2:33090" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2117 |
2118 | 然后添加iptables规则,下面是参考规则:
2119 | ```shell
2120 | #上级proxy服务端服务器IP地址:
2121 | proxy_server_ip=2.2.2.2
2122 |
2123 | #路由器运行proxy监听的端口:
2124 | proxy_local_port=33080
2125 |
2126 | #下面的就不用修改了
2127 | #create a new chain named PROXY
2128 | iptables -t nat -N PROXY
2129 |
2130 | # Ignore your PROXY server's addresses
2131 | # It's very IMPORTANT, just be careful。
2132 |
2133 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d $proxy_server_ip -j RETURN
2134 |
2135 | # Ignore LANs IP address
2136 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 0.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
2137 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 10.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
2138 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 127.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
2139 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 169.254.0.0/16 -j RETURN
2140 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 172.16.0.0/12 -j RETURN
2141 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 192.168.0.0/16 -j RETURN
2142 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 224.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
2143 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 240.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
2144 |
2145 | # Anything to port 80 443 should be redirected to PROXY's local port
2146 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
2147 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp --dport 443 -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
2148 |
2149 | # Apply the rules to nat client
2150 | iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -j PROXY
2151 | # Apply the rules to localhost
2152 | iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp -j PROXY
2153 | ```
2154 | - 清空整个链 iptables -F 链名比如iptables -t nat -F PROXY
2155 | - 删除指定的用户自定义链 iptables -X 链名 比如 iptables -t nat -X PROXY
2156 | - 从所选链中删除规则 iptables -D 链名 规则详情 比如 iptables -t nat -D PROXY -d 223.223.192.0/255.255.240.0 -j RETURN
2157 |
2158 | ### 1.11 自定义DNS
2159 | --dns-address和--dns-ttl参数,用于自己指定proxy访问域名的时候使用的dns(--dns-address)
2160 | 以及解析结果缓存时间(--dns-ttl)秒数,避免系统dns对proxy的干扰,另外缓存功能还能减少dns解析时间提高访问速度。
2161 | 比如:
2162 | `./proxy http -p ":33080" --dns-address "8.8.8.8:53" --dns-ttl 300`
2163 |
2164 | ### 1.12 自定义加密
2165 | proxy的http(s)代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义
2166 | 加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可,
2167 | 加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
2168 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以,下面分别用二级,三级为例:
2169 |
2170 | 二级实例
2171 |
2172 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2173 | `proxy http -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
2174 | 本地二级执行:
2175 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
2176 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
2177 |
2178 |
2179 | 三级实例
2180 |
2181 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2182 | `proxy http -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
2183 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
2184 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
2185 | 本地三级执行:
2186 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
2187 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
2188 |
2189 | ### 1.13 压缩传输
2190 | proxy的http(s)代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以对数据进行压缩,
2191 | 也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,
2192 | 一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
2193 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据,下面分别用二级,三级为例:
2194 |
2195 | 二级实例
2196 |
2197 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2198 | `proxy http -t tcp -m -p :7777`
2199 | 本地二级执行:
2200 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
2201 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
2202 |
2203 |
2204 | 三级实例
2205 |
2206 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2207 | `proxy http -t tcp -m -p :7777`
2208 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
2209 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
2210 | 本地三级执行:
2211 | `proxy http -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
2212 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
2213 |
2214 | ### 1.14 负载均衡
2215 |
2216 | HTTP(S)代理支持上级负载均衡,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
2217 |
2218 | `proxy http --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080`
2219 |
2220 | ### 1.14.1 设置重试间隔和超时时间
2221 |
2222 | `proxy http --lb-method=leastconn --lb-retrytime 300 --lb-timeout 300 -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -t tcp -p :33080`
2223 |
2224 | ### 1.14.2 设置权重
2225 |
2226 | `proxy http --lb-method=weight -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -P 2.1.1.1:33080?w=2 -P 3.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -t tcp -p :33080`
2227 |
2228 | ### 1.14.3 使用目标地址选择上级
2229 |
2230 | `proxy http --lb-hashtarget --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -t tcp -p :33080`
2231 |
2232 | ### 1.15 限速
2233 |
2234 | 限速100K,通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
2235 |
2236 | `proxy http -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -l 100K`
2237 |
2238 | ### 1.16 指定出口IP
2239 |
2240 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作,此时代理会尝试不绑定IP去访问目标,同时日志会提示。
2241 |
2242 | `proxy http -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 --bind-listen`
2243 |
2244 | ### 1.17 证书参数使用base64数据
2245 |
2246 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
2247 |
2248 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
2249 |
2250 | ### 1.18 智能模式
2251 | 智能模式设置,可以是intelligent|direct|parent三者之一。
2252 | 默认是:intelligent。
2253 | 每个值的含义如下:
2254 | `--intelligent=direct`,不在blocked里面的目标都直连。
2255 | `--intelligent=parent`,不在direct里面的目标都走上级。
2256 | `--intelligent=intelligent`,blocked和direct里面都没有的目标,智能判断是否使用上级访问目标。
2257 |
2258 | ### 1.19 查看帮助
2259 | `./proxy help http`
2260 |
2261 | ## 2.TCP代理
2262 |
2263 | ### 2.1 普通一级TCP代理
2264 | 
2265 | 本地执行:
2266 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22"`
2267 | 那么访问本地33080端口就是访问192.168.22.33的22端口。
2268 |
2269 | `-p`参数支持的写法:
2270 |
2271 | ```text
2272 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
2273 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
2274 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
2275 | ```
2276 |
2277 | 如果本地监听端口数量大于1,那么将会连接与本地端口一致的对应上级端口,忽略`-P`里面的端口。
2278 |
2279 | 如果需要所有端口进来的连接,都连接到上级指定端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`。
2280 |
2281 | 比如:
2282 |
2283 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080-33085" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:0"`
2284 |
2285 | 那么`33080`端口进来的连接,将会连接192.168.22.33的`33080`端口,其它端口以此类推,本地和上级端口一致,此时参数`-P`里面的端口用`0`。
2286 |
2287 | 如果想无论是`33080`,`33081`等端口进来的连接都连接到192.168.22.33的`22`端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`
2288 |
2289 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080-33085" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --lock-port`
2290 |
2291 |
2292 | ### 2.2 普通二级TCP代理
2293 | 
2294 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
2295 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "127.0.0.1:8080"`
2296 | 本地执行:
2297 | `./proxy tcp -p ":23080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.33:33080"`
2298 | 那么访问本地23080端口就是访问22.22.22.33的8080端口。
2299 |
2300 | ### 2.3 普通三级TCP代理
2301 | 
2302 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2303 | `./proxy tcp -p ":38080" -T tcp -P "66.66.66.66:8080"`
2304 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2305 | `./proxy tcp -p ":28080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080"`
2306 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
2307 | `./proxy tcp -p ":8080" -T tcp -P "33.33.33.33:28080"`
2308 | 那么访问本地8080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问66.66.66.66的8080端口。
2309 |
2310 | ### 2.4 加密二级TCP代理
2311 | 
2312 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
2313 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "127.0.0.1:8080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2314 | 本地执行:
2315 | `./proxy tcp -p ":23080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.33:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2316 | 那么访问本地23080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问22.22.22.33的8080端口。
2317 |
2318 | ### 2.5 加密三级TCP代理
2319 | 
2320 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2321 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":38080" -T tcp -P "66.66.66.66:8080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2322 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2323 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2324 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
2325 | `./proxy tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2326 | 那么访问本地8080端口就是通过加密TCP隧道访问66.66.66.66的8080端口。
2327 |
2328 | ### 2.6 通过代理连接上级
2329 | 有时候proxy所在的网络不能直接访问外网,需要通过一个https或者socks5代理才能上网,那么这个时候
2330 | -J参数就可以帮助你让proxy的tcp端口映射的时候通过https或者socks5代理去连接上级-P,将外部端口映射到本地。
2331 | -J参数格式如下:
2332 |
2333 | https代理写法:
2334 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
2335 | https://username:password@host:port
2336 | 代理不需要认证
2337 | https://host:port
2338 |
2339 | socks5代理写法:
2340 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
2341 | socks5://username:password@host:port
2342 | 代理不需要认证
2343 | socks5://host:port
2344 |
2345 | host:代理的IP或者域名
2346 | port:代理的端口
2347 |
2348 | ### 2.7 指定`出口IP`
2349 | 当TCP代理当上级类型(参数:-T)是tcp当时候,支持指定`出口IP`。使用`--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作,此时代理会尝试不绑定IP去访问目标,同时日志会提示。
2350 |
2351 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" -B`
2352 |
2353 | ### 2.8 限速,限制连接数
2354 |
2355 | 参数`--max-conns`可以限制每个端口的最大连接数。
2356 | 比如限制每个端口最多1000个连接数:
2357 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --max-conns 1000`
2358 | 参数`--rate-limit`可以限制每个tcp连接的速率。
2359 | 比如限制每个tcp连接速率为100k/s:
2360 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T tcp -P "192.168.22.33:22" --rate-limit 100k`
2361 |
2362 | ### 2.9 查看帮助
2363 | `./proxy help tcp`
2364 |
2365 | ## 3.UDP代理
2366 |
2367 | ### 3.1.普通一级UDP代理
2368 | 
2369 | 本地执行:
2370 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
2371 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
2372 |
2373 | `-p`参数支持的写法:
2374 |
2375 | ```text
2376 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
2377 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
2378 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
2379 | ```
2380 |
2381 | 如果本地监听端口数量大于1,那么将会连接与本地端口一致的对应上级端口,忽略`-P`里面的端口。
2382 |
2383 | 如果需要所有端口进来的连接,都连接到上级指定端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`。
2384 |
2385 | 比如:
2386 |
2387 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080-33085" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:0"`
2388 |
2389 | 那么`33080`端口进来的连接,将会连接192.168.22.33的`33080`端口,其它端口以此类推,本地和上级端口一致,此时参数`-P`里面的端口用`0`。
2390 |
2391 | 如果想无论是`33080`,`33081`等端口进来的连接都连接到192.168.22.33的`2222`端口,可以加上参数`--lock-port`
2392 |
2393 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080-33085" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:2222" --lock-port`
2394 |
2395 | ### 3.2.普通二级UDP代理
2396 | 
2397 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
2398 | `./proxy tcp -p ":33080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
2399 | 本地执行:
2400 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.33:33080"`
2401 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是通过TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
2402 |
2403 | ### 3.3.普通三级UDP代理
2404 | 
2405 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2406 | `./proxy tcp -p ":38080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53"`
2407 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2408 | `./proxy tcp -p ":28080" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080"`
2409 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
2410 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tcp -P "33.33.33.33:28080"`
2411 | 那么访问本地5353端口就是通过TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的53端口。
2412 |
2413 | ### 3.4.加密二级UDP代理
2414 | 
2415 | VPS(IP:22.22.22.33)执行:
2416 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":33080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2417 | 本地执行:
2418 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tls -P "22.22.22.33:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2419 | 那么访问本地UDP:5353端口就是通过加密TCP隧道,通过VPS访问8.8.8.8的UDP:53端口。
2420 |
2421 | ### 3.5.加密三级UDP代理
2422 | 
2423 | 一级TCP代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2424 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":38080" -T udp -P "8.8.8.8:53" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2425 | 二级TCP代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2426 | `./proxy tcp -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2427 | 三级TCP代理(本地)
2428 | `./proxy udp -p ":5353" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2429 | 那么访问本地5353端口就是通过加密TCP隧道,通过VPS_01访问8.8.8.8的53端口。
2430 |
2431 | ### 3.6 指定`出口IP`
2432 | 当UDP代理当上级类型(参数:-T)是udp当时候,支持指定`出口IP`。使用`--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标的功能。如果绑定了不正确的IP会导致代理不能工作。
2433 |
2434 | `./proxy udp -p ":33080" -T udp -P "192.168.22.33:2222" -B`
2435 |
2436 | ### 3.7 查看帮助
2437 | `./proxy help udp`
2438 |
2439 | ## 4.内网穿透
2440 | ### 4.1、原理说明
2441 | 内网穿透,分为两个版本,“多链接版本”和“多路复用版本”,一般像web服务这种不是长时间连接的服务建议用“多链接版本”,如果是要保持长时间连接建议使用“多路复用版本”。
2442 | 1. 多链接版本,对应的子命令是tserver,tclient,tbridge。
2443 | 1. 多路复用版本,对应的子命令是server,client,bridge。
2444 | 1. 多链接版本和多路复用版本的参数和使用方式完全一样。
2445 | 1. 多路复用版本的server,client可以开启压缩传输,参数是--c。
2446 | 1. server,client要么都开启压缩,要么都不开启,不能只开一个。
2447 |
2448 | 下面的教程以“多路复用版本”为例子,说明使用方法。
2449 | 内网穿透由三部分组成:client端,server端,bridge端;client和server主动连接bridge端进行桥接。
2450 |
2451 | ### 4.2、TCP普通用法
2452 | 背景:
2453 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口
2454 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2455 |
2456 | 需求:
2457 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的28080端口访问到公司机器A的80端口
2458 |
2459 | 步骤:
2460 | 1. 在vps上执行
2461 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2462 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2463 |
2464 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
2465 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2466 |
2467 | 1. 完成
2468 |
2469 | ### 4.3、微信接口本地开发
2470 | 背景:
2471 | - 自己的笔记本提供了nginx服务80端口
2472 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2473 |
2474 | 需求:
2475 | 在微信的开发帐号的网页回调接口配置里面填写地址:http://22.22.22.22/calback.php
2476 | 然后就可以访问到笔记本的80端口下面的calback.php,如果需要绑定域名,可以用自己的域名
2477 | 比如:wx-dev.xxx.com解析到22.22.22.22,然后在自己笔记本的nginx里
2478 | 配置域名wx-dev.xxx.com到具体的目录即可。
2479 |
2480 |
2481 | 步骤:
2482 | 1. 在vps上执行,确保vps的80端口没被其它程序占用。
2483 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2484 | `./proxy server -r ":80@:80" -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2485 |
2486 | 1. 在自己笔记本上面执行
2487 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2488 |
2489 | 1. 完成
2490 |
2491 | ### 4.4、UDP普通用法
2492 | 背景:
2493 | - 公司机器A提供了DNS解析服务,UDP:53端口
2494 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2495 |
2496 | 需求:
2497 | 在家里能够通过设置本地dns为22.22.22.22,使用公司机器A进行域名解析服务。
2498 |
2499 | 步骤:
2500 | 1. 在vps上执行
2501 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2502 | `./proxy server --udp -r ":53@:53" -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2503 |
2504 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
2505 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2506 |
2507 | 1. 完成
2508 |
2509 | ### 4.5、高级用法一
2510 | 背景:
2511 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口
2512 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2513 |
2514 | 需求:
2515 | 为了安全,不想在VPS上能够访问到公司机器A,在家里能够通过访问本机的28080端口,
2516 | 通过加密隧道访问到公司机器A的80端口。
2517 |
2518 | 步骤:
2519 | 1. 在vps上执行
2520 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2521 |
2522 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
2523 | `./proxy client -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2524 |
2525 | 1. 在家里电脑上执行
2526 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2527 |
2528 | 1. 完成
2529 |
2530 | ### 4.6、高级用法二
2531 | 提示:
2532 | 如果同时有多个client连接到同一个bridge,需要指定不同的key,可以通过--k参数设定,--k可以是任意唯一字符串,
2533 | 只要在同一个bridge上唯一即可。
2534 | server连接到bridge的时候,如果同时有多个client连接到同一个bridge,需要使用--k参数选择client。
2535 | 暴露多个端口重复-r参数即可.-r格式是:"本地IP:本地端口@clientHOST:client端口"。
2536 |
2537 | 背景:
2538 | - 公司机器A提供了web服务80端口,ftp服务21端口
2539 | - 有VPS一个,公网IP:22.22.22.22
2540 |
2541 | 需求:
2542 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的28080端口访问到公司机器A的80端口
2543 | 在家里能够通过访问VPS的29090端口访问到公司机器A的21端口
2544 |
2545 | 步骤:
2546 | 1. 在vps上执行
2547 | `./proxy bridge -p ":33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2548 | `./proxy server -r ":28080@:80" -r ":29090@:21" --k test -P "127.0.0.1:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2549 |
2550 | 1. 在公司机器A上面执行
2551 | `./proxy client --k test -P "22.22.22.22:33080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2552 |
2553 | 1. 完成
2554 |
2555 | ### 4.7.server的-r参数
2556 | -r完整格式是:`PROTOCOL://LOCAL_IP:LOCAL_PORT@[CLIENT_KEY]CLIENT_LOCAL_HOST:CLIENT_LOCAL_PORT`
2557 |
2558 | 4.7.1.协议PROTOCOL:tcp、udp、ptcp、pudp。
2559 | 比如: `-r "udp://:10053@:53" -r "tcp://:10800@:1080" -r ":8080@:80"`
2560 | 如果指定了--udp参数,PROTOCOL默认为udp,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`默认为udp;
2561 | 如果没有指定--udp参数,PROTOCOL默认为tcp,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`默认为tcp;
2562 |
2563 | 4.7.2.CLIENT_KEY:默认是default。
2564 | 比如: -r "udp://:10053@[test1]:53" -r "tcp://:10800@[test2]:1080" -r ":8080@:80"
2565 | 如果指定了--k参数,比如--k test,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`CLIENT_KEY默认为test;
2566 | 如果没有指定--k参数,那么:`-r ":8080@:80"`CLIENT_KEY默认为default;
2567 |
2568 | 4.7.3.LOCAL_IP为空默认是:`0.0.0.0`,CLIENT_LOCAL_HOST为空默认是:`127.0.0.1`;
2569 |
2570 | ### 4.8.server和client通过代理连接bridge
2571 | 有时候server或者client所在的网络不能直接访问外网,需要通过一个https或者socks5代理才能上网,那么这个时候
2572 | -J参数就可以帮助你让server或者client通过https或者socks5代理去连接bridge。
2573 | -J参数格式如下:
2574 |
2575 | https代理写法:
2576 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
2577 | https://username:password@host:port
2578 | 代理不需要认证
2579 | https://host:port
2580 |
2581 | socks5代理写法:
2582 | 代理需要认证,用户名:username 密码:password
2583 | socks5://username:password@host:port
2584 | 代理不需要认证
2585 | socks5://host:port
2586 |
2587 | host:代理的IP或者域名
2588 | port:代理的端口
2589 |
2590 | ### 4.9.内网穿透HTTP服务
2591 |
2592 | 通常HTTP请求客户端会使用server的ip和端口去设置HOST字段,但是与期望的后端实际HOST不一样,这样就造成了tcp是通的,
2593 | 但后端依赖HOST字段定位虚拟主机就不能工作.现在用--http-host参数强制设置http头部的HOST字段值为后端实际的
2594 | 域名和端口即可轻松解决。
2595 |
2596 | `server`的--http-host参数格式如下:
2597 |
2598 | `--http-host www.test.com:80@2200`,如果server监听多个端口,只需要重复`--http-host`参数设置每个端口的HOST即可。
2599 |
2600 | 实例:
2601 |
2602 | 比如client本地nginx,127.0.0.1:80提供了web服务,其中绑定了一个域名`local.com`。
2603 |
2604 | 那么server的启动参数可以如下:
2605 |
2606 | `proxy server -P :30000 -r :2500@127.0.0.1:80 --http-host local.com@2500`
2607 |
2608 | 解释:
2609 |
2610 | `-r :2500@127.0.0.1:80` 和 `--http-host local.com:80@2500` 里面的2500端口是server本地监听的端口
2611 |
2612 | 当使用http协议请求server的ip:2500端口的时候,http的头部HOST字段就会被设置为`local.com`。
2613 |
2614 | ### 4.10 关于流量统计
2615 |
2616 | 如果单独启动一个server对接上级是proxy-admin控制面板,需要在上级控制面板里面新建一个映射,获得个映射规则的ID,
2617 |
2618 | 然后启动server的时候加上参数 --server-id=映射规则的ID 才能统计到流量。
2619 |
2620 | ### 4.11 关于p2p
2621 | 内网穿透支持在server和client网络情况满足的情况下,server和client之间通过p2p直接连接,开启方法是:
2622 |
2623 | 在启动bridge,server,client到时候都加上`--p2p`参数即可。server的-r参数可以针对端口是否启用p2p(ptcp和pudp)。
2624 |
2625 | 如果server和client之间p2p打洞失败,那么会自动切换使用bridge中转传输数据。
2626 |
2627 | ### 4.12 客户端key白名单
2628 | 内网穿透bridge可以设置客户端key白名单,参数是--client-keys,格式可以是:
2629 |
2630 | a.文件名,文件内容一行一个客户端key只能包含数字字母下划线,也就是客户端启动参数--k的值,只有客户端key在此白名单的客户端才能连接。# 开头的行,为注释。
2631 |
2632 | b.“base64://”开头的base64编码的上面a说明的文件内容,比如:base64://ajfpoajsdfa=
2633 |
2634 | c.”str://“开头的英文逗号分割的多个key,比如:str://default,company,school
2635 |
2636 | 默认是空,允许所有key。
2637 |
2638 | ### 4.13 网络NAT类型判断
2639 |
2640 | nat类型判断,方便查看网络是否支持p2p,可以执行:`proxy tools -a nattype`
2641 |
2642 | ### 4.14 查看帮助
2643 | `./proxy help bridge`
2644 | `./proxy help server`
2645 | `./proxy help client`
2646 |
2647 | ## 5.SOCKS5代理
2648 | 提示:
2649 |
2650 | SOCKS5代理,支持CONNECT,UDP协议,不支持BIND,支持用户名密码认证。
2651 |
2652 | ***如果你的VPS是阿里云,腾讯云这种VPS,就是ifconfig看不见你的公网IP,只能看见内网IP,***
2653 |
2654 | ***那么需要加上`-g VPS公网IP`参数,SOCKS5代理的UDP功能才能正常工作。***
2655 |
2656 | ### 5.1 普通SOCKS5代理
2657 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080"`
2658 |
2659 | -p参数支持的写法:
2660 |
2661 | ```text
2662 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
2663 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
2664 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
2665 | ```
2666 |
2667 | ### 5.2.普通二级SOCKS5代理
2668 | 
2669 | 使用本地端口8090,假设上级SOCKS5代理是`22.22.22.22:8080`
2670 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" `
2671 | 我们还可以指定网站域名的黑白名单文件,一行一个域名,匹配规则是最右匹配,比如:baidu.com,匹配的是*.*.baidu.com,黑名单的域名域名直接走上级代理,白名单的域名不走上级代理;如果域名即在黑名单又在白名单中,那么黑名单起作用。
2672 | `./proxy socks -p "0.0.0.0:8090" -T tcp -P "22.22.22.22:8080" -b blocked.txt -d direct.txt`
2673 |
2674 | ### 5.3.SOCKS二级代理(加密)
2675 | 
2676 | 一级SOCKS代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
2677 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2678 |
2679 | 二级SOCKS代理(本地Linux)
2680 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2681 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080。
2682 |
2683 | 二级SOCKS代理(本地windows)
2684 | `./proxy.exe socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2685 | 然后设置你的windos系统中,需要通过代理上网的程序的代理为socks5模式,地址为:127.0.0.1,端口为:8080,程序即可通过加密通道通过vps上网。
2686 |
2687 | ### 5.4.SOCKS三级代理(加密)
2688 | 
2689 | 一级SOCKS代理VPS_01,IP:22.22.22.22
2690 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2691 | 二级SOCKS代理VPS_02,IP:33.33.33.33
2692 | `./proxy socks -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2693 | 三级SOCKS代理(本地)
2694 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T tls -P "33.33.33.33:28080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2695 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问一级SOCKS代理上面的代理端口38080。
2696 |
2697 | ### 5.5.SOCKS代理流量强制走上级SOCKS代理
2698 | 默认情况下,proxy会智能判断一个网站域名是否无法访问,如果无法访问才走上级SOCKS代理.通过--always可以使全部SOCKS代理流量强制走上级SOCKS代理。
2699 | `./proxy socks --always -t tls -p ":28080" -T tls -P "22.22.22.22:38080" -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2700 |
2701 | ### 5.6.SOCKS通过SSH中转
2702 | 
2703 | 说明:ssh中转的原理是利用了ssh的转发功能,就是你连接上ssh之后,可以通过ssh代理访问目标地址。
2704 | 假设有:vps
2705 | - IP是2.2.2.2, ssh端口是22, ssh用户名是:user, ssh用户密码是:demo
2706 | - 用户user的ssh私钥名称是user.key
2707 |
2708 | #### *5.6.1 ssh用户名和密码的方式*
2709 | 本地SOCKS5代理28080端口,执行:
2710 | `./proxy socks -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -D demo -t tcp -p ":28080"`
2711 | #### *5.6.2 ssh用户名和密钥的方式*
2712 | 本地SOCKS5代理28080端口,执行:
2713 | `./proxy socks -T ssh -P "2.2.2.2:22" -u user -S user.key -t tcp -p ":28080"`
2714 |
2715 | 那么访问本地的28080端口就是通过VPS访问目标地址。
2716 |
2717 | ### 5.7.认证
2718 | 对于socks5代理协议我们可以进行用户名密码认证,认证的用户名和密码可以在命令行指定
2719 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1" -a "user2:pass2"`
2720 | 多个用户,重复-a参数即可。
2721 | 也可以放在文件中,格式是一行一个"用户名:密码",然后用-F指定。
2722 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":33080" -F auth-file.txt`
2723 |
2724 | ### 5.8.KCP协议传输
2725 | KCP协议需要--kcp-key参数设置一个密码用于加密解密数据
2726 |
2727 | 一级HTTP代理(VPS,IP:22.22.22.22)
2728 | `./proxy socks -t kcp -p ":38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
2729 |
2730 | 二级HTTP代理(本地Linux)
2731 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p ":8080" -T kcp -P "22.22.22.22:38080" --kcp-key mypassword`
2732 | 那么访问本地的8080端口就是访问VPS上面的代理端口38080,数据通过kcp协议传输。
2733 |
2734 | ### 5.9.自定义DNS
2735 | --dns-address和--dns-ttl参数,用于自己指定proxy访问域名的时候使用的dns(--dns-address)
2736 | 以及解析结果缓存时间(--dns-ttl)秒数,避免系统dns对proxy的干扰,另外缓存功能还能减少dns解析时间提高访问速度。
2737 | 比如:
2738 | `./proxy socks -p ":33080" --dns-address "8.8.8.8:53" --dns-ttl 300`
2739 |
2740 | ### 5.10 自定义加密
2741 | proxy的socks代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义一个密码即可,
2742 | 加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
2743 |
2744 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以。
2745 |
2746 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
2747 |
2748 | 二级实例
2749 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2750 | `proxy socks -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
2751 | 本地二级执行:
2752 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
2753 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
2754 |
2755 |
2756 | 三级实例
2757 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2758 | `proxy socks -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
2759 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
2760 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
2761 | 本地三级执行:
2762 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
2763 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
2764 |
2765 | ### 5.11 压缩传输
2766 | proxy的socks代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以
2767 | 对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,
2768 | 一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
2769 |
2770 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据。
2771 |
2772 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
2773 |
2774 | 二级实例
2775 |
2776 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2777 | `proxy socks -t tcp -m -p :7777`
2778 | 本地二级执行:
2779 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
2780 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
2781 |
2782 |
2783 | 三级实例
2784 |
2785 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
2786 | `proxy socks -t tcp -m -p :7777`
2787 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
2788 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
2789 | 本地三级执行:
2790 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
2791 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
2792 |
2793 |
2794 | ### 5.12 负载均衡
2795 |
2796 | SOCKS代理支持上级负载均衡,多个上级重复-P参数即可。
2797 |
2798 | `proxy socks --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
2799 |
2800 | ### 5.12.1 设置重试间隔和超时时间
2801 |
2802 | `proxy socks --lb-method=leastconn --lb-retrytime 300 --lb-timeout 300 -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
2803 |
2804 | ### 5.12.2 设置权重
2805 |
2806 | `proxy socks --lb-method=weight -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -P 2.1.1.1:33080?w=2 -P 3.1.1.1:33080?w=1 -p :33080 -t tcp`
2807 |
2808 | ### 5.12.3 使用目标地址选择上级
2809 |
2810 | `proxy socks --lb-hashtarget --lb-method=hash -T tcp -P 1.1.1.1:33080 -P 2.1.1.1:33080 -P 3.1.1.1:33080 -p :33080 -t tcp`
2811 |
2812 | ### 5.13 限速
2813 |
2814 | 限速100K,通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
2815 |
2816 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -l 100K`
2817 |
2818 | ### 5.14 指定`出口IP`
2819 |
2820 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果`入口IP`是内网IP,`出口IP`不会使用`入口IP`。
2821 |
2822 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 --bind-listen`
2823 |
2824 | ### 5.15 级联认证
2825 |
2826 | SOCKS5支持级联认证,-A可以设置上级认证信息。
2827 |
2828 | 上级:
2829 |
2830 | `proxy socks -t tcp -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -a user:pass`
2831 |
2832 | 本地:
2833 |
2834 | `proxy socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -A user:pass -t tcp -p :33080`
2835 |
2836 | 请更多认证细节,请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
2837 |
2838 | ### 5.16 证书参数使用base64数据
2839 |
2840 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
2841 |
2842 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
2843 |
2844 |
2845 | ### 5.17 智能模式
2846 | 智能模式设置,可以是intelligent|direct|parent三者之一。
2847 | 默认是:intelligent。
2848 | 每个值的含义如下:
2849 | `--intelligent=direct`,不在blocked里面的目标都直连。
2850 | `--intelligent=parent`,不在direct里面的目标都走上级。
2851 | `--intelligent=intelligent`,blocked和direct里面都没有的目标,智能判断是否使用上级访问目标。
2852 |
2853 | ### 5.18 固定UDP功能端口
2854 |
2855 | 默认情况下socks5的UDP功能的端口号,proxy是按着`rfc1982草案`要求,使用协议握手过程中随机指定,不需要提前指定。
2856 |
2857 | 但是某些情况下,需要固定UDP功能端口,可以通过参数`--udp-port 端口号`用来固定UDP功能的端口号,比如:
2858 |
2859 | `./proxy socks -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --udp-port 38080`
2860 |
2861 | ### 5.19 查看帮助
2862 | `./proxy help socks`
2863 |
2864 | ## 6.SPS协议转换
2865 |
2866 | ### 6.1 功能介绍
2867 | 代理协议转换使用的是sps子命令,sps本身不提供代理功能,只是接受代理请求"转换并转发"给已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理或者ss代理;sps可以把已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理或ss代理转换为一个端口同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的代理,而且http(s)代理支持正向代理和反向代理(SNI),转换后的SOCKS5代理,当上级是SOCKS5或者SS时仍然支持UDP功能;另外对于已经存在的http(s)代理或者socks5代理,支持tls、tcp、kcp三种模式,支持链式连接,也就是可以多个sps结点层级连接构建加密通道。
2868 |
2869 | `ss`功能支持的加密方法为:aes-128-cfb , aes-128-ctr , aes-128-gcm , aes-192-cfb , aes-192-ctr , aes-192-gcm , aes-256-cfb , aes-256-ctr , aes-256-gcm , bf-cfb , cast5-cfb , chacha20 , chacha20-ietf , chacha20-ietf-poly1305 , des-cfb , rc4-md5 , rc4-md5-6 , salsa20 , xchacha20
2870 |
2871 | 本地监听端口-p参数支持的写法:
2872 |
2873 | ```text
2874 | -p ":8081" 监听8081
2875 | -p ":8081,:8082" 监听8081和8082
2876 | -p ":8081,:8082,:9000-9999" 监听8081和8082以及9000,9001至9999,共1002个端口
2877 | ```
2878 |
2879 | ### 6.2 HTTP(S)转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
2880 | 假设已经存在一个普通的http(s)代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2881 | 命令如下:
2882 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2883 |
2884 | 假设已经存在一个tls的http(s)代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,tls需要证书文件,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2885 | 命令如下:
2886 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2887 |
2888 | 假设已经存在一个kcp的http(s)代理(密码是:demo123):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2889 | 命令如下:
2890 | `./proxy sps -S http -T kcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 --kcp-key demo123 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2891 |
2892 | ### 6.3 SOCKS5转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
2893 | 假设已经存在一个普通的socks5代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2894 | 命令如下:
2895 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2896 |
2897 | 假设已经存在一个tls的socks5代理:127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,tls需要证书文件,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2898 | 命令如下:
2899 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T tls -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2900 |
2901 | 假设已经存在一个kcp的socks5代理(密码是:demo123):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2902 | 命令如下:
2903 | `./proxy sps -S socks -T kcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 --kcp-key demo123 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`
2904 |
2905 | ### 6.4 SS转HTTP(S)+SOCKS5+SS
2906 | SPS上级和本地支持ss协议,上级可以是SPS或者标准的ss服务。
2907 | SPS本地默认提供HTTP(S)\SOCKS5\SPS三种代理,当上级是SOCKS5时转换后的SOCKS5和SS支持UDP功能。
2908 | 假设已经存在一个普通的SS或者SPS代理(开启了ss,加密方式:aes-256-cfb,密码:demo):127.0.0.1:8080,现在我们把它转为同时支持http(s)和socks5和ss的普通代理,转换后的本地端口为18080,转换后的ss加密方式:aes-192-cfb,ss密码:pass。
2909 | 命令如下:
2910 | `./proxy sps -S ss -H aes-256-cfb -J pass -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p :18080 -h aes-192-cfb -j pass`。
2911 |
2912 | ### 6.5 链式连接
2913 | 
2914 | 上面提过多个sps结点可以层级连接构建加密通道,假设有如下vps和家里的pc电脑。
2915 | vps01:2.2.2.2
2916 | vps02:3.3.3.3
2917 | 现在我们想利用pc和vps01和vps02构建一个加密通道,本例子用tls加密也可以用kcp,在pc上访问本地18080端口就是访问vps01的本地8080端口。
2918 | 首先在vps01(2.2.2.2)上我们运行一个只有本地可以访问的http(s)代理,执行:
2919 | `./proxy http -t tcp -p 127.0.0.1:8080`
2920 |
2921 | 然后在vps01(2.2.2.2)上运行一个sps结点,执行:
2922 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tls -p :8081 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2923 |
2924 | 然后在vps02(3.3.3.3)上运行一个sps结点,执行:
2925 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:8081 -t tls -p :8082 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2926 |
2927 | 然后在pc上运行一个sps结点,执行:
2928 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tls -P 3.3.3.3:8082 -t tcp -p :18080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key`
2929 |
2930 | 完成。
2931 |
2932 | ### 6.6 监听多个端口
2933 | 一般情况下监听一个端口就可以,不过如果作为反向代理需要同时监听80和443两个端口,那么-p参数是支持的,
2934 | 格式是:`-p 0.0.0.0:80,0.0.0.0:443`,多个绑定用逗号分隔即可。
2935 |
2936 | ### 6.7 认证功能
2937 | sps支持http(s)\socks5代理认证,可以级联认证,有四个重要的信息:
2938 | 1:用户发送认证信息`user-auth`。
2939 | 2:设置的本地认证信息`local-auth`。
2940 | 3:设置的连接上级使用的认证信息`parent-auth`。
2941 | 4:最终发送给上级的认证信息`auth-info-to-parent`。
2942 | 他们的情况关系如下:
2943 |
2944 | | user-auth | local-auth | parent-auth | auth-info-to-paren
2945 | | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------
2946 | | 有/没有 | 有 | 有 | 来自parent-auth
2947 | | 有/没有 | 没有 | 有 | 来自parent-auth
2948 | | 有/没有 | 有 | 没有 | 无
2949 | | 没有 | 没有 | 没有 | 无
2950 | | 有 | 没有 | 没有 | 来自user-auth
2951 |
2952 | 对于sps代理我们可以进行用户名密码认证,认证的用户名和密码可以在命令行指定
2953 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1:0:0:" -a "user2:pass2:0:0:"`
2954 | 多个用户,重复-a参数即可。
2955 | 也可以放在文件中,格式是一行一个`用户名:密码:连接数:速率:上级`,然后用-F指定。
2956 | `./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -F auth-file.txt`
2957 |
2958 | 如果上级有认证,下级可以通过-A参数设置认证信息,比如:
2959 | 上级:`./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -t tcp -p ":33080" -a "user1:pass1:0:0:" -a "user2:pass2:0:0:"`
2960 | 下级:`./proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 127.0.0.1:8080 -A "user1:pass1" -t tcp -p ":33080" `
2961 |
2962 | 请更多认证细节,请参考`9.API认证` 和 `10.本地认证`
2963 |
2964 | ### 6.8 多个上级
2965 |
2966 | 如果存在多个上级,可以通过多个-P指定。
2967 |
2968 | 比如:
2969 |
2970 | `proxy sps -P http://127.0.0.1:3100 -P socks5://127.0.0.1:3200`
2971 |
2972 | `-P`完整格式如下:
2973 |
2974 | `protocol://a:b@2.2.2.2:33080#1`
2975 |
2976 | 下面对每部分进行解释:
2977 |
2978 | `protocol://` 是协议类型,可能的类型以及含有如下:
2979 |
2980 | ```text
2981 | http 等价于 -S http -T tcp
2982 | https 等价于 -S http -T tls --parent-tls-single , 也就是http(s)代理 over TLS
2983 | https2 等价于 -S http -T tls
2984 | socks5 等价于 -S socks -T tcp
2985 | socks5s 等价于 -S socks -T tls --parent-tls-single , 也就是socks over TLS
2986 | socks5s2 等价于 -S socks -T tls
2987 | ss 等价于 -S ss -T tcp
2988 | httpws 等价于 -S http -T ws
2989 | httpwss 等价于 -S http -T wss
2990 | socks5ws 等价于 -S socks -T ws
2991 | socks5wss 等价于 -S socks -T wss
2992 | ```
2993 |
2994 | `a:b`是代理认证的用户名密码,如果是ss,`a`是加密方法,`b`是密码,没有用户名密码可以留空比如:`http://2.2.2.2:33080`,如果用户名和密码保护特殊符号可以使用urlencode进行编码。
2995 |
2996 | `2.2.2.2:33080`是上级地址,格式是:`IP(或域名):端口`,如果底层是ws/wss协议还可以带上路径,比如:`2.2.2.2:33080/ws`;
2997 | 还能通过附加查询参数`m`和`k`设置`ws\wss`的`加密方法`和`密码`,比如:`2.2.2.2:33080/ws?m=aes-192-cfb&k=password`
2998 |
2999 | `#1`多个上级的负载均衡是权重策略时候,设置的权重,很少用到。
3000 |
3001 | ### 6.9 自定义加密
3002 | proxy的sps代理在tcp之上可以通过tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,除此之外还支持在tls和kcp之后进行
3003 | 自定义加密,也就是说自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,内部采用AES256加密,使用的时候只需要自己定义
3004 | 一个密码即可,加密分为两个部分,一部分是本地(-z)是否加密解密,一部分是与上级(-Z)传输是否加密解密。
3005 |
3006 | 自定义加密要求两端都是proxy才可以。
3007 |
3008 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
3009 |
3010 | 假设已经存在一个http(s)代理:`6.6.6.6:6666`
3011 |
3012 | 二级实例
3013 |
3014 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
3015 | `proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 6.6.6.6:6666 -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
3016 | 本地二级执行:
3017 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -p :8080`
3018 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
3019 |
3020 |
3021 | 三级实例
3022 |
3023 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
3024 | `proxy sps -S http -T tcp -P 6.6.6.6:6666 -t tcp -z demo_password -p :7777`
3025 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
3026 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -Z demo_password -t tcp -z other_password -p :8888`
3027 | 本地三级执行:
3028 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -Z other_password -t tcp -p :8080`
3029 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级加密传输访问目标网站。
3030 |
3031 | ### 6.10 压缩传输
3032 | proxy的sps代理在tcp之上可以通过自定义加密和tls标准加密以及kcp协议加密tcp数据,在自定义加密之前还可以
3033 | 对数据进行压缩,也就是说压缩功能和自定义加密和tls|kcp是可以联合使用的,压缩分为两个部分,
3034 | 一部分是本地(-m)是否压缩传输,一部分是与上级(-M)传输是否压缩。
3035 |
3036 | 压缩要求两端都是proxy才可以,压缩也在一定程度上保护了(加密)数据。
3037 |
3038 | 下面分别用二级,三级为例:
3039 |
3040 | 二级实例
3041 |
3042 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
3043 | `proxy sps -t tcp -m -p :7777`
3044 | 本地二级执行:
3045 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:777 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
3046 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
3047 |
3048 |
3049 | 三级实例
3050 |
3051 | 一级vps(ip:2.2.2.2)上执行:
3052 | `proxy sps -t tcp -m -p :7777`
3053 | 二级vps(ip:3.3.3.3)上执行:
3054 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:7777 -M -t tcp -m -p :8888`
3055 | 本地三级执行:
3056 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080`
3057 | 这样通过本地代理8080访问网站的时候就是通过与上级压缩传输访问目标网站。
3058 |
3059 | ### 6.11 禁用协议
3060 | SPS默认情况下一个端口支持http(s)和socks5两种代理协议,我们可以通过参数禁用某个协议
3061 | 比如:
3062 | 1.禁用HTTP(S)代理功能只保留SOCKS5代理功能,参数:`--disable-http`。
3063 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080 --disable-http`
3064 |
3065 | 1.禁用SOCKS5代理功能只保留HTTP(S)代理功能,参数:`--disable-socks`。
3066 | `proxy sps -T tcp -P 3.3.3.3:8888 -M -t tcp -p :8080 --disable-http`
3067 |
3068 | ### 6.12 限速
3069 |
3070 | 假设存在SOCKS5上级:
3071 |
3072 | `proxy socks -p 2.2.2.2:33080 -z password -t tcp`
3073 |
3074 | sps下级,限速100K
3075 |
3076 | `proxy sps -S socks -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -T tcp -Z password -l 100K -t tcp -p :33080`
3077 |
3078 | 通过`-l`参数即可指定,比如:100K 2000K 1M . 0意味着无限制。
3079 |
3080 | ### 6.13 指定`出口IP`
3081 |
3082 | `--bind-listen`参数,就可以开启客户端用`入口IP`连接过来的,就用`入口IP`作为`出口IP`访问目标网站的功能。如果`入口IP`是内网IP,`出口IP`不会使用`入口IP`。
3083 |
3084 | `proxy sps -S socks -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -T tcp -Z password -l 100K -t tcp --bind-listen -p :33080`
3085 |
3086 | ### 6.14 证书参数使用base64数据
3087 |
3088 | 默认情况下-C,-K参数是crt证书和key文件的路径,
3089 |
3090 | 如果是base64://开头,那么就认为后面的数据是base64编码的,会解码后使用。
3091 |
3092 | ### 6.15 独立服务
3093 | sps功能不强制指定一个上级,当上级为空,sps本身即可完成完整的代理功能.如果指定了上级那么就和之前一样使用上级连接目标。
3094 | 下面这个命令,就是一键开启http(s)\ss\socks服务。
3095 | `./proxy sps -p :33080`
3096 |
3097 | ### 6.16 目标重定向
3098 | sps功能提供的http(s)\socks5\ss代理功能,客户端通过sps代理去连接指定的“目标”,这个“目标”一般是网站也可能是任意的tcp地址,
3099 | 网站”目标“一般是foo.com:80,foo.com:443,sps支持使用--rewrite参数指定一个“目标”重定向规则文件,对目标进行重定向,客户端是无感知的,
3100 | 比如你对“目标”:demo.com:80重定向到192.168.0.12:80,那么客户端访问网站demo.com,其实访问的是192.168.0.12提供的网站服务。
3101 | “目标”重定向规则文件示例:
3102 |
3103 | ```text
3104 | # example
3105 | www.a.com:80 10.0.0.2:8080
3106 | **.b.com:80 10.0.0.2:80
3107 | 192.168.0.11:80 10.0.0.2:8080
3108 | ```
3109 |
3110 | ### 6.17 固定UDP功能端口
3111 |
3112 | 默认情况下sps的socks5的UDP功能的端口号是按着`rfc1982草案`要求,使用协议握手过程中随机指定,不需要提前指定。
3113 |
3114 | 但是某些情况下,需要固定UDP功能端口,可以通过参数`--udp-port 端口号`用来固定UDP功能的端口号,比如:
3115 |
3116 | `./proxy sps -t tcp -p "0.0.0.0:38080" --udp-port 38081`
3117 |
3118 | 需要注意的是,sps的ss功能也有UDP功能,而且ss的UDP端口和tcp端口是一样的,所以要避免socks5的UDP端口和ss的UDP端口冲突,
3119 |
3120 | 要指定和tcp端口不一样的端口。
3121 |
3122 | ### 6.18 iptables 透明代理
3123 | sps模式支持Linux系统的iptables转发支持,也就是通常所说的iptables透明代理,如果在网关设备上进行iptables透明代理,那么对通过网关联网的设备就能实现无感知的代理。
3124 |
3125 | 启动命令实例:
3126 |
3127 | `./proxy sps --redir -p :8888 -P httpws://1.1.1.1:33080`
3128 |
3129 | 这里假设存在一个http的上级代理1.1.1.1:33080,使用ws传输数据。
3130 |
3131 | 然后添加iptables规则,下面是参考规则:
3132 | ```shell
3133 | #上级proxy服务端服务器IP地址:
3134 | proxy_server_ip=1.1.1.1
3135 |
3136 | #路由器运行proxy监听的端口:
3137 | proxy_local_port=33080
3138 |
3139 | #下面的就不用修改了
3140 | #create a new chain named PROXY
3141 | iptables -t nat -N PROXY
3142 |
3143 | # Ignore your PROXY server's addresses
3144 | # It's very IMPORTANT, just be careful。
3145 |
3146 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d $proxy_server_ip -j RETURN
3147 |
3148 | # Ignore LANs IP address
3149 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 0.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
3150 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 10.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
3151 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 127.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
3152 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 169.254.0.0/16 -j RETURN
3153 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 172.16.0.0/12 -j RETURN
3154 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 192.168.0.0/16 -j RETURN
3155 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 224.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
3156 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -d 240.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
3157 |
3158 | # Anything to port 80 443 should be redirected to PROXY's local port
3159 | iptables -t nat -A PROXY -p tcp -j REDIRECT --to-ports $proxy_local_port
3160 | # Apply the rules to nat client
3161 | iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -j PROXY
3162 | # Apply the rules to localhost
3163 | iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -p tcp -j PROXY
3164 | ```
3165 | - 清空整个链 iptables -F 链名比如iptables -t nat -F PROXY
3166 | - 删除指定的用户自定义链 iptables -X 链名 比如 iptables -t nat -X PROXY
3167 | - 从所选链中删除规则 iptables -D 链名 规则详情 比如 iptables -t nat -D PROXY -d 223.223.192.0/255.255.240.0 -j RETURN
3168 |
3169 | ### 6.19 查看帮助
3170 |
3171 | `./proxy help sps`
3172 |
3173 | ## 7.KCP配置
3174 |
3175 | ### 7.1 配置介绍
3176 | proxy的很多功能都支持kcp协议,凡是使用了kcp协议的功能都支持这里介绍的配置参数。
3177 | 所以这里统一对KCP配置参数进行介绍。
3178 |
3179 | ### 7.2 详细配置
3180 | 所有的KCP配置参数共有17个,你可以都不用设置,他们都有默认值,如果为了或者最好的效果,
3181 | 就需要自己根据自己根据网络情况对参数进行配置。由于kcp配置很复杂需要一定的网络基础知识,
3182 | 如果想获得kcp参数更详细的配置和解说,请自行搜索。每个参数的命令行名称以及默认值和简单的功能说明如下:
3183 | ```
3184 | --kcp-key="secrect" pre-shared secret between client and server
3185 | --kcp-method="aes" encrypt/decrypt method, can be: aes, aes-128, aes-192, salsa20, blowfish,
3186 | twofish, cast5, 3des, tea, xtea, xor, sm4, none
3187 | --kcp-mode="fast" profiles: fast3, fast2, fast, normal, manual
3188 | --kcp-mtu=1350 set maximum transmission unit for UDP packets
3189 | --kcp-sndwnd=1024 set send window size(num of packets)
3190 | --kcp-rcvwnd=1024 set receive window size(num of packets)
3191 | --kcp-ds=10 set reed-solomon erasure coding - datashard
3192 | --kcp-ps=3 set reed-solomon erasure coding - parityshard
3193 | --kcp-dscp=0 set DSCP(6bit)
3194 | --kcp-nocomp disable compression
3195 | --kcp-acknodelay be carefull! flush ack immediately when a packet is received
3196 | --kcp-nodelay=0 be carefull!
3197 | --kcp-interval=50 be carefull!
3198 | --kcp-resend=0 be carefull!
3199 | --kcp-nc=0 be carefull! no congestion
3200 | --kcp-sockbuf=4194304 be carefull!
3201 | --kcp-keepalive=10 be carefull!
3202 | ```
3203 | 提示:
3204 | 参数:--kcp-mode中的四种fast3, fast2, fast, normal模式,
3205 | 相当于设置了下面四个参数:
3206 | normal:`--nodelay=0 --interval=40 --resend=2 --nc=1`
3207 | fast :`--nodelay=0 --interval=30 --resend=2 --nc=1`
3208 | fast2:`--nodelay=1 --interval=20 --resend=2 --nc=1`
3209 | fast3:`--nodelay=1 --interval=10 --resend=2 --nc=1`
3210 |
3211 | ## 8.安全DNS
3212 |
3213 | ### 8.1 介绍
3214 | 众所周知DNS是UDP端口53提供的服务,但是随着网络的发展一些知名DNS服务器也支持TCP方式dns查询,比如谷歌的8.8.8.8,proxy的DNS防污染服务器原理就是在本地启动一个proxy的DNS代理服务器,它用TCP的方式通过上级代理进行dns查询。如果它和上级代理通讯采用加密的方式,那么就可以进行安全无污染的DNS解析,还支持独立服务,并发解析,支持增强的hosts文件功能支持灵活的并发解析转发。
3215 |
3216 | dns解析顺序:
3217 | 1.使用参数--hosts解析。
3218 | 2.要解析的域名在1中没有找到,就使用参数--forward规则解析。
3219 | 3.要解析的域名在1和2中都没有找到,就使用默认--default解析,--default默认行为参数值有三种:proxy,direct,system。
3220 | 三种参数值解释如下:
3221 | proxy:通过上级去连接-q参数指定的dns服务器去解析域名。
3222 | direct:通过本地网络去连接-q参数指定的dns服务器去解析域名。
3223 | system:通过系统dns去解析域名。
3224 |
3225 | 提示:
3226 | --hosts 参数指定的host文件格式和系统hosts文件一致,而且域名支持通配符,可以参考hosts文件。
3227 | --forward 参数指定的解析转发规则文件,格式可以参考resolve.rules文件,域名支持通配符,支持为每个域名指定多个dns服务器并发解析,谁最快解析成功就用谁的解析结果。
3228 | -q 参数可以指定多个远程dns服务器,执行并发解析谁最快解析成功就用谁的解析结果,默认是:1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8,9.9.9.9,多个用逗号分割,
3229 | 比如还可以带端口:1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8#53,9.9.9.9
3230 |
3231 | 如果独立服务,不需要上级:
3232 | 可以执行:
3233 | `proxy dns --default system -p :5353`
3234 | or
3235 | `proxy dns --default direct -p :5353`
3236 |
3237 | ### 8.2 使用示例
3238 |
3239 | #### 8.2.1 普通HTTP(S)上级代理
3240 |
3241 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3242 | 本地执行:
3243 | `proxy dns -S http -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3244 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了DNS解析功能。
3245 |
3246 | #### 8.2.2 普通SOCKS5上级代理
3247 |
3248 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3249 | 本地执行:
3250 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3251 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了DNS解析功能。
3252 |
3253 | #### 8.2.3 TLS加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
3254 |
3255 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3256 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3257 | `proxy http -t tls -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :33080`
3258 | 本地执行:
3259 | `proxy dns -S http -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :53`
3260 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3261 |
3262 | #### 8.2.4 TLS加密的SOCKS5上级代理
3263 |
3264 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3265 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3266 | `proxy socks -t tls -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :33080`
3267 | 本地执行:
3268 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tls -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -C proxy.crt -K proxy.key -p :53`
3269 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3270 |
3271 | #### 8.2.5 KCP加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
3272 |
3273 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3274 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3275 | `proxy http -t kcp -p :33080`
3276 | 本地执行:
3277 | `proxy dns -S http -T kcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3278 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3279 |
3280 | #### 8.2.6 KCP加密的SOCKS5上级代理
3281 |
3282 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3283 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3284 | `proxy socks -t kcp -p :33080`
3285 | 本地执行:
3286 | `proxy dns -S socks -T kcp -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3287 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3288 |
3289 | #### 8.2.7 自定义加密的HTTP(S)上级代理
3290 |
3291 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3292 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3293 | `proxy http -t tcp -p :33080 -z password`
3294 | 本地执行:
3295 | `proxy dns -S http -T tcp -Z password -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3296 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3297 |
3298 | #### 8.2.8 自定义加密的SOCKS5上级代理
3299 |
3300 | 假设有一个上级代理:2.2.2.2:33080
3301 | 上级代理执行的命令是:
3302 | `proxy socks -t kcp -p :33080 -z password`
3303 | 本地执行:
3304 | `proxy dns -S socks -T tcp -Z password -P 2.2.2.2:33080 -p :53`
3305 | 那么本地的UDP端口53就提供了安全防污染DNS解析功能。
3306 |
3307 | ## 9.API认证,限速,控制连接数
3308 |
3309 | proxy的http(s)/socks5/sps代理功能,支持通过API控制用户对代理对访问。
3310 |
3311 | ### 通过API可以干什么?
3312 |
3313 | - 用户维度,控制单个连接速率,控制最大连接数。
3314 | - IP维度,控制单个连接速率,控制最大连接数。
3315 | - 动态上级,可以根据用户或者客户端IP,动态的从API获取其上级,支持http(s)/socks5/ss上级。
3316 | - 认证每一个连接,无论是否要求客户端认证。
3317 | - 缓存认证结果,时间可以设置,减轻API压力。
3318 |
3319 | #### 具体使用
3320 | proxy的http(s)/socks5/sps代理API功能,通过`--auth-url`和`--auth-nouser`和`--auth-cache`三个参数控制。
3321 | 参数`--auth-url`是HTTP API接口地址,客户端连接的时候,proxy会GET方式请求这url,带上下面参数,如果返回HTTP状态码204,代表认证成功,其它情况认为认证失败。
3322 |
3323 | 一个完整的请求API的示例:
3324 | `http://test.com/auth.php?user=a&pass=b&client_addr=127.0.0.1:49892&local_addr=127.0.0.1:8100&target=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.baidu.com&service=http&sps=0`
3325 |
3326 | #### 参数说明
3327 | `user和pass` 当代理开启了认证功能,这里就是客户端提供的用户名和密码。
3328 | `client_addr` 客户端访问代理时的用的地址,格式IP:端口。
3329 | `local_addr` 客户端访问的代理地址,格式IP:端口。
3330 | `service` 代理类型,分为:http、socks。
3331 | `sps` 代理是否是sps提供的,1:是,0:否。
3332 | `target` 客户端要访问的目标,如果是http(s)代理,target是访问的具体url;如果是socks5代理,target是空。
3333 |
3334 | #### 示例
3335 | 假设--auth-url http://127.0.0.1:333/auth.php 指向了一个php接口地址.
3336 | auth.php内容如下:
3337 |
3338 | ```php
3339 |