├── StudyNotes.pdf
├── export_to_pdf.bat
├── story to remember contents.MD
├── General Tips.md
├── D8 - Software Development Security.md
├── printJS.bat
├── D4 - Communication and Network Security.md
├── D2 - Asset Security.md
├── README.md
├── D6 - Security Assessment and Testing.md
├── tricky definitions.md
├── D5 - Identity and Access Management.md
├── D3 - Security Architecture and Engineering.md
├── D7 - Security Operations.md
└── D1 - Security and Risk Management.md
/StudyNotes.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/so87/CISSP-Study-Guide/HEAD/StudyNotes.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/export_to_pdf.bat:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | @echo off
2 | for %%a in (*.pdf *.doc) do (
3 | call printJS.bat "%%~fa"
4 | )
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/story to remember contents.MD:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Short story to remember all of the contents of the CISSP material. If your brain can map information to long term memory locations then it will remember.
2 | #### This will only work for me because I'm remembering this happening in a long term memory location
3 | I walk outside my door to see the CIA. They have my DAD and want my (AAA). They recorded my statement so there was NONREPUDIATION.
4 | They said I didn't NEED TO KNOW anymore more information. There were legal issues to follow, but they had to remain COMPLIANT to the
5 | law. I then walked over to the stand where there was no DUE CARE or DUE DILIGENCE. they weren't thinking before acting, and they weren't
6 | even checking if anyone was stealing. There were no FORENSIC capabilities. All of our INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY could have been stolen, and
7 | our PRIVACY was gone. We had to scream at the church to get some INTERATIONAL COOPERATION so we could IMPORT more vegies. They are a
8 | THIRD PARTY so we had to take certain precautions. We followed import laws, but wrote ETHICS for everything they didn't cover.
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/General Tips.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # General Tips for Taking the Exam
2 |
3 | ## What skills does this test want you to know?
4 | This is an English test. This test is for a security manager. You have to analyze scope, time, and cost for most questions. Your goal is to reduce the risk
5 |
6 | ## Reading and understanding the question
7 | Read the question and answers twice. Skim the question and answers. Then go back and read it carefully. Argue with each of the answers. Does this answer work? It meets all requirements in question? Are any other answers more efficient for time and cost?
8 |
9 | ## Quantitative, Qualitative, nouns, verbs, processes, technologies
10 | If you have no idea what the answer is, you can generally eliminate at least two answers from the language in the question. The question could be asking for a technology, and two of the answers are processes. The test could want an action and 1 of the answers is a noun.
11 | * Accuracy = correct
12 | * Precision = consistent
13 |
14 | ## Human life and risk
15 | Human life is always the most important thing. Reducing risk is always the most important thing.
16 |
17 | ## Due Diligence
18 | Think before you Act. Ready, Aim, Fire Before taking action:
19 | * Understand business objectives
20 | * Review current security state
21 | * interview stakeholders
22 | * Identify owners/assets/values
23 | * Assess current controls
24 | * Analyze Impact/Exposure/Alternatives
25 | * Verify/Confirm reports
26 |
27 | ## Due Care
28 | Actions speak louder than words. For questions that require assurance:
29 | * Auditing
30 | * Monitoring
31 | * Interviewing
32 | * Assessing
33 | * Testing
34 | * Exercising
35 | * Training
36 |
37 | ## Process Management
38 | What phase is this question in? This will help set context
39 | 1. Plan
40 | 2. Do
41 | 3. Check
42 | 4. Act
43 | repeat
44 |
45 | ## Speed
46 | Take practices tests and time yourself. You need to take your time and not have to worry about rushing. You must be focused only on answering the questions. If you are taking too long on your practice tests, then adjust yourself. You are also not going to know several test questions, so do your best, eliminate as many as you can, and move on.
47 |
48 | ## Failure
49 | Now I'm not going to be your life coach, but your mind is capable of incredible things. I believe that you can learn anything as long as you don't put up any mental barriers or excuses for yourself. That being said, studying is hard, this test is hard, life is hard. You must appreciate all that you do in life, do your best, and be happy with it. Get back up and keep trying if this certification is your priority.
50 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/D8 - Software Development Security.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Software Development Security
2 |
3 | [Back to Home Page](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Study-Guide)
4 |
5 | ### Understand and integrate security in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
6 | 0. Feasibility
7 | 1. Project initialization
8 | 2. Requirements
9 | 3. Design
10 | 4. Develop
11 | 5. Test / Assess
12 | 6. Operate / Maintain
13 | 7. Dispose / Retire
14 | * Development methodologies - Waterfall, Sashim, Agile Software Dev
15 | * Maturity models - evaluating and improving the software development process
16 | * Operation and maintenance - the system is modified by the addition of hardware and software and by other events
17 | * Change management - tracks changes across an entire software development program.
18 | * Integrated product team - customer-facing group that focuses on the entire lifecyle of a product
19 |
20 | ### Identify and apply security controls in development environments
21 | * Security of the software environments - contractors must be DFARS compliant. There is a Application Security Assessment STIG to ensure developers are developing with secure methods. Development environment is highly compromisable so there must be monitoring, anti-virus, patching, and security controls/hardening
22 | * Configuration management as an aspect of secure coding - ensure automated builds with static code analysis on code base
23 | * Security of code repositories - must have stric permissions for accessing all of source code. have data loss prevention so users can't take all code that has been worked on
24 |
25 | ### Assess the effectiveness of software security
26 | * Auditing and logging of changes - must have proper version history and changes documented
27 | * Risk analysis and mitigation - Perform risk analysis. how often are vulnerabilities and bugs being commited. how long do they take to fix when in production?
28 |
29 | ### Assess security impact of acquired software
30 | There could be vulnerabilities and flaws in software that is acquired. There could even be malware or backdoors in them. There are various procurement tools to analyze the security of libraries or other products used
31 |
32 | ### Define and apply secure coding guidelines and standards
33 | * Security weaknesses and vulnerabilities at the source-code level - there should be static analysis done to test for vulnerabilities. Fixing pentesting and fuzzing findings are much more expensive than fixing a finding before commiting it back to master stream.
34 | * Security of application programming interfaces - test interfaces for abuse cases/fuzzing
35 | * Secure coding practices - ASD STIG, CERT SEI, OWASP Top 10, SANS Top 25
36 |
37 |
38 | [Back to Home Page](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Study-Guide)
39 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/printJS.bat:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | @if (@X)==(@Y) @end /* JScript comment
2 | @echo off
3 |
4 | cscript //E:JScript //nologo "%~f0" %*
5 |
6 | exit /b %errorlevel%
7 |
8 | @if (@X)==(@Y) @end JScript comment */
9 |
10 | //gets an information that normally is acquired by right click-details
11 | // can get image dimensions , media file play time and etc.
12 |
13 | //////
14 | FSOObj = new ActiveXObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject");
15 | var ARGS = WScript.Arguments;
16 | if (ARGS.Length < 1 ) {
17 | WScript.Echo("No file passed");
18 | WScript.Echo("Usage (prints with default printer a file if possible)");
19 | WScript.Echo(WScript.ScriptName + " file");
20 | WScript.Quit(1);
21 | }
22 | var filename=ARGS.Item(0);
23 | var objShell=new ActiveXObject("Shell.Application");
24 |
25 | /////
26 |
27 |
28 | //fso
29 | ExistsItem = function (path) {
30 | return FSOObj.FolderExists(path)||FSOObj.FileExists(path);
31 | }
32 |
33 | getFullPath = function (path) {
34 | return FSOObj.GetAbsolutePathName(path);
35 | }
36 | //
37 |
38 | //paths
39 | getParent = function(path){
40 | var splitted=path.split("\\");
41 | var result="";
42 | for (var s=0;s
4 | [To next domain! - D5 - Identity and Access Management](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D5%20-%20Identity%20and%20Access%20Management.md)
5 |
6 | ### Implement secure design principles in network architectures
7 | * Open System Interconnection (OSI) and Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) models
8 | Layers:
9 | 7. Application - Google chrome
10 | 6. Presentation - JPEG
11 | 5. Sessions - RPC
12 | 4. Transport - TCP/UDP
13 | 3. Network - IP Addressing
14 | 2. Data Link - MAC Address
15 | 1. Physical - Electrical/Optical Current
16 | Think of it like you are trying to send a package of cookies to someone else half way across the world.
17 |
18 | * Internet Protocol (IP) networking - DHCP on LAN. Lan connects to WAN. ISPs route traffic
19 | * Implications of multilayer protocols
20 | * Converged protocols - providing industrial controls, storage, voice, etc via Ethernet(tcp/udp)
21 | * Software-defined networks - seperates a router's control plane from data forwarding plane
22 | * Wireless networks - WEP, WPA, WPA2. 802.11 is the wireless standard
23 | Many varieties of EAP
24 | * LEAP : Cisco-proprietry, very bad
25 | * EAP-TLS : requires server/client certificates
26 | * EAP-TTLS : allows passwords for client-side authentication
27 | * PEAP : similar to EAP-TTLS, developed by cisco and microsoft
28 | * Firewalls - network segmentation
29 | * Packet Filter: no decisions. set list of allow rules
30 | * Stateful: slower but more secure. compare packets to previous ones.
31 | * Proxy: acts as middle man on network. does not give anything back if doesn't meet proxy rules
32 | * application-layer proxy: make decissions on like HTTP, and layers 3 and 4
33 | * VoIP - voice over IP
34 | * RTP for streaming
35 | * SRTP for secure communication
36 |
37 | ### Secure network components
38 | * Operation of hardware
39 | * Transmission media - properly encrypt media
40 | * Network Access Control (NAC) devices - 802.1X is port based network access control
41 | * Endpoint security - deep packet inspection. email filtering.
42 | * Content-distribution networks - series of distributed caching servers to imporve performance and lower latency. They find closest servers to you and go
43 |
44 | ### Implement secure communication channels according to design
45 | Figure out what type of security mechanisms are best for scenarios you get on the test
46 | * Voice
47 | * Multimedia collaboration
48 | * Remote access
49 | * Data communications
50 | * Virtualized networks
51 |
52 | [Back to Home Page](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-)
53 | [To next domain! - D5 - Identity and Access Management](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D5%20-%20Identity%20and%20Access%20Management.md)
54 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/D2 - Asset Security.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Asset Security
2 |
3 | [Back to Home Page](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-)
4 | [To next domain! - D3 - Security Architecture and Engineering](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D3%20-%20Security%20Architecture%20and%20Engineering.md)
5 |
6 |
7 | ### Identify and classify information and assets
8 | * Data classification - indicates the level of confidentiality, integrity, and availability protection that is required
9 | * Levels: Confidential > Private > Sensitive > Public
10 | * Asset Classification - ^^
11 |
12 | ### Determine and maintain information and asset ownership
13 | Primary information security roles include business or mission owners, data owners, system owners, custodians, and users. Each role has a different set of responsibilities in securing an organization's assets. There should be a plan in place to audit assets atleast every year
14 |
15 | ### Protect privacy
16 | * Data owners - The data/information owner is a manager responsible for ensuring that specific data is protected. Data sensitivity labels and the frequency of data backup is something they decide. They focus on data itself(electronic or paper format). Generally each line of business will have their own data owner. The data owner performs management duties, while custodians perform the hands-on protection of data.
17 |
18 | * Data processers - A data controller is someone who controls sensitive data, they own it. A data processor is someone that uses and reads that. An outsourced payroll company is an example of a data processor. Data processors manage payroll data, which is used to determine the amount to pay individual employees, on behalf of a data controller, such as an HR department.
19 |
20 | * Data remanence - Data that persists beyond noninvasive means to delete it. Though data remanence is sometimes used specifically to refer to residual data that persists on magnetic storage, remanence concerns go beyond just that of magnetic storage media.
21 |
22 | * Collection limitation - There should be limits to the collection of personal data. The subject must consent before this data is collected
23 |
24 | ### Ensure appropriate asset retention
25 | Information stops being useful after a certain amount of time. Sensitive data should have a retention time on it. There may be regulations or legal reasons why an organization may have to keep information for a long time.
26 |
27 | ### Determine data security controls
28 | * Understand data states - data is either at rest or in motion. Different controls apply to them.
29 |
30 | * Scoping and tailoring - scoping is deciding which standards will be carried out by organization. Tailoring is customizing that standard towards the organization (like implimenting subplimental controls)
31 |
32 | * Standards selection - pick the following: PCI-DSS, OCTAVE, ISO 17799, COBIT, ITIL
33 |
34 | * Data protection methods - network encryption, HDD and tape encryption, and transportation protection
35 |
36 | ### Establish information and asset handling requirements
37 | Need to have classification and need to know before accessing information or assets. There should be solid justification for accessing these things.
38 |
39 | [Back to Home Page](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-)
40 | [To next domain! - D3 - Security Architecture and Engineering](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D3%20-%20Security%20Architecture%20and%20Engineering.md)
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # UPDATE
2 | ## THIS REPOSITORY HAS BEEN MOVED TO THIS SITE: https://simonowens157.gitlab.io/cissp/
3 | * repo: https://gitlab.com/simonowens157/cissp/
4 |
5 | 
6 | This is study material for the 2018 CISSP Exam. There are links below to my
7 | notes on each domain, information about the exam, and other study tools.
8 | * Like this repository? Star it! Helps get this out to other people!
9 | * Want to contribute? Something incorrect? Make a change and push it back to me!
10 |
11 | # Domain Study Guides and Notes
12 | [Domain 1: Security and Risk Management](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D1%20-%20Security%20and%20Risk%20Management.md)
13 |
14 | [Domain 2: Asset Security](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D2%20-%20Asset%20Security.md)
15 |
16 | [Domain 3: Security Architecture and Engineering](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D3%20-%20Security%20Architecture%20and%20Engineering.md)
17 |
18 | [Domain 4: Communication and Network Security](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D4%20-%20Communication%20and%20Network%20Security.md)
19 |
20 | [Domain 5: Identity and Access Management (IAM)](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D5%20-%20Identity%20and%20Access%20Management.md)
21 |
22 | [Domain 6: Security Assessment and Testing](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D6%20-%20Security%20Assessment%20and%20Testing.md)
23 |
24 | [Domain 7: Security Operations](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D7%20-%20Security%20Operations.md)
25 |
26 | [Domain 8: Software Development Security](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D8%20-%20Software%20Development%20Security.md)
27 |
28 | [Another great study guide with definitions and pictures](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Study-Guide/blob/master/StudyNotes.pdf) Thanks Scott Gibbsons for sharing!
29 |
30 | # About the exam:
31 | Need 5 years expierence for certification. Get associate if less than that.
32 | 3 hours
33 | 100-150 Multiple Choice Questions
34 | 70% to pass
35 | All domains 10-15% of score
36 | [Official Information](https://www.isc2.org/Certifications/-/media/CC72396FD9F34D3AAF073BF2AADB185C.ashx)
37 |
38 | # Study Tools:
39 | [General Tips](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Study-Guide/blob/master/General%20Tips.md)
40 | [Free Government Training](https://fedvte.usalearning.gov/)
41 | [Book](https://www.amazon.com/CISSP-All-One-Guide-Seventh/dp/0071849270/ref=sr_1_6?s=books&ie=UTF8&qid=1525371721&sr=1-6&keywords=cissp)
42 | [Video Course(cybrary)](https://www.cybrary.it/course/cissp/)
43 | [More Free Videos](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JWqd_qaR81g&list=PLEiEAq2VkUUId6PKW0fpJdBRJO5MFQ8VM)
44 | [Video Questions](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JywLANSd-1E&list=PLfuKjbmP_JpVtQSl9AL7PPIxrim6K8q0r)
45 | [Flash cards](https://quizlet.com/2519918/cissp-practice-flash-cards/)
46 | [Pratice Tests](https://www.amazon.com/CISSP-Official-ISC-Practice-Tests/dp/1119475929/ref=mt_paperback?_encoding=UTF8&me=&qid=1532002117)
47 | [Review on Exam](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eLYbFtS7G9E)
48 | [Learning how to learn.](https://www.amazon.com/Unlimited-Memory-Advanced-Strategies-Productive-ebook/dp/B00I3QS1XQ/ref=sr_1_3_sspa?s=books&ie=UTF8&qid=1540590777&sr=1-3-spons&keywords=learning+how+to+learn&psc=1) If you are going to spend 200 hours learning you might as well take 10 to do it right?
49 | [Tricky definitions I've missed on practice tests](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Study-Guide/blob/master/tricky%20definitions.md)
50 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/D6 - Security Assessment and Testing.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Security Assessment and Testing
2 |
3 | [Back to Home Page](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-)
4 | [To next domain! - D7 - Security Operations](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D7%20-%20Security%20Operations.md)
5 |
6 | ### Definitions
7 | * War Dialing - technique to automatically scan a list of telephone numbers
8 | * Pentesting Methodology
9 | * Planning
10 | * Reconnaissance
11 | * Scanning(enumeration)
12 | * Vulnerability Assessment
13 | * Exploitation
14 | * Reporting
15 | * Unit Testing - low level, functions, procedures, or objects
16 | * Installation Testing - seeing if it installs and can run
17 | * Integration Testing - multiple components together. say there is unit test for head lights and one for turn signal. integration test would be making sure they both work at same time
18 | * Regression Testing - testing updates, modifications, or patches
19 | * Acceptance Testing - ensuring it meets standards and requirements
20 | * Fuzzing - black-box testing that submits random, malformed data to see if it will crash
21 | * Dynamic Analysis - giving program inputs to test all paths for bugs, weaknesses, vulnerabilities, etc
22 | * Static Analysis - analyzing the source for for bugs, weaknesses, vulnerabilities, style, etc
23 | * Risk = Threat X Vulnerability
24 |
25 | ### Design and validate assessment, test, and audit strategies
26 | Pentesting and active assessments. Once you create something, look for weaknesses or abuse cases
27 | * Internal - usually done by checking logs, scanning internal network with vulnerability scanner, checking camera coverage, etc
28 | * External - analyzing firewall rules, IDS/IPS, endpoint protection, fences, gates, etc
29 | * Third-party - paying another organization to test your security for you
30 |
31 | ### Conduct security control testing
32 | * Vulnerability assessment - describes a ton of weaknesses in the system. Doesn't exploit anything
33 | * Penetration testing - chaining together weaknesses to see what is possible. Puts theirselves in place of attackers to see what they could do
34 | * Log reviews - manually reviewing logs or setting up log analysis tool/filter i.e. splunk
35 | * Synthetic transactions - building scripts to simulate normal activities. this is capture a baseline and simulate traffic
36 | * Code review and testing - manual review, static analysis, and dynamic analysis. all three should be used
37 | * Misuse case testing - writing security tests. could write a security test to ensure the server redirects you, or that all passwords hashes used are strong
38 | * Test coverage analysis - sees how much code you are testing or covering with dynamic analysis
39 | * Interface testing - testing functionality of interface. ensuring user can't see any weird files, error messages, or anything unneccessary.
40 |
41 | ### Collect security process data (e.g., technical and administrative)
42 | * Account management - user accounts should be monitored, permissions checked, and passwords automatically changed
43 | * Management review and approval - weaknesses and risk should always be taken to management before acting. determine what the best plan forward and how much risk they want to accept.
44 | * Key performance and risk indicators - *no idea what this means..*
45 | * Backup verification data - Information used to verify and manage should be backed up
46 | * Training and awareness - everyone should have to take frequent awarness training and their training should be tracked
47 | * Disaster Recovery (DR) and Business Continuity (BC) - there should be plans in place for what to do when bad things happen. Is a Hot site, cold site needed? Should everything be completely redundant?
48 |
49 | ### Analyze test output and generate report
50 | * Policies and Procedures
51 | * Security Personel Training
52 | * Change Management
53 | * Architectural Reviews
54 | * Vulnerability Reports
55 | * Metrics reports on security
56 | * Metrics reports on IT and remediation
57 | * Pentest Reports
58 |
59 | ### Conduct or facilitate security audits
60 | Same thing as the first title in this section, except you are doing this for real now.
61 | * Internal
62 | * External
63 | * Third-party
64 |
65 | [Back to Home Page](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-)
66 | [To next domain! - D7 - Security Operations](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D7%20-%20Security%20Operations.md)
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tricky definitions.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Definitions I've forgotten on practice tests
2 | * RPO - recovery point objective: identifies the maximum amount of data, measured in time, that may be lost during a recovery effort
3 | * RTO - recovery time objective: the amount of time expected to return an IT service to operation after failure
4 | * MTD - maximum tolerable down time: longest amount of time that an IT service may be unavailable without causing serious damage
5 | * SLA - service level agreement: written contracts that document service expectations
6 | * Device finger printing via web portal - requires user authentication and gather lots of data to uniquely identify devices
7 | * Data owner - responsible for classification of data
8 | * pulverizing - best way to comply remove data so that it doesn't leak
9 | * TACAS+ - cisco proprietary protocol. Improvement of radius
10 | * Most refquent target of account management reviews are highly privileged accounts
11 | * Biometrics
12 | * type 1 - valid subject not authenticated
13 | * type 2 - invalid subject is authenticatd
14 | * type 3/4 - not associated with biometric
15 | * Keys
16 | * Primary - uniquely identifies a row
17 | * Foreign - uniquely identifies a row and matches to another table
18 | * Referential - not a database key
19 | * fire extinguishers - this makes me so mad that we have to memorize these types
20 | * A - Fires that involve solid or organic materials, such as wood, plastics, paper, textiles, or coal
21 | * B - Fires that involve flammable liquids, such as gasoline, petroleum oil, paint, or diesel
22 | * C - Fires that involve flammable gases, such as propane, butane, or methane
23 | * D - Fires that involve combustible metals, such as magnesium, lithium, sodium, potassium, titanium, or aluminium
24 | * E - electrical
25 | * F - cooking
26 | * Risk indicators - can provide useful information for organizational planning and a deeper understading of how organizations view risk. Do not handle security response.
27 | * FERPA - protects privacy information of students
28 | * Digital Millennium Copyright act - protects IPS from activities of their customers
29 | * Preservation - Ensure that informatoin related to the matter at hand is protected against alteration or deletion
30 | * Multitasking - handles multiple processes on a single processor by switching them using OS
31 | * Multi-programming - requires modifications of underlying applications
32 | * Incident response phases
33 | * Detection - most important step is to realize that there is a problem. Must have a machine analyzing network, as well as a person to filter false positives.
34 | * Response - need to determine an appropriate response. analyize all of the material before making a decision
35 | * Mitigation - contain the incident. act on the situation to reduce damage and to keep the situation in a manageable state
36 | * Reporting - summary of incident, indicators, related incidents, actions taken, chain of custody, impact assessment, identity, and next steps to be taken. assess obligations under laws, regulations, and procedures on how to communicate to
37 | * Recovery - trying to get the asset to a known good state
38 | * Remediation - need to make sure attack or failure is not successful again. patch the issue, and figure out if this could happen again in future
39 | * Lessons learned - what happened, what did we learn, any mistakes, what was good, can we do better next time, is there a good plan in place to deal with this in the future?
40 | * Authentication and authorization web languages
41 | * SPML - an OASIS developed markup languaged to provide service, user, and resource prvisioning between organizations
42 | * SAML - used to exchange user authentication and authorization data
43 | * XACML - used to describe access controls
44 | * SOAP - like REST but has security in mind. Outlines how web service information is exchanged. When requesting access, a SOAP body contains a SAML request or response inside of it
45 | * REST - Representation State Transfer. an approach that uses HTTP protocol to access and manipulate text without keeping track of any data(or state)
46 | * OAUTH - open standard for authorization(not authentication) to third parties. Like when you authenticate with facebook, you can then authorize it to go off and manage your photos. Facebook could access your photos until you tell it not to anymore
47 | * Primary storage - ram is primary storage. secondary storage is hdds, solid state, and optical drives
48 | Whoa.. just got 11/24 on a practice test...
49 | * SIEM helps provide automated analysis and monitoring of logs and security events. not syslog.
50 | * Requiring authentication provides accountability be ensuring actions taken can be tracked to a specific user
51 | * PAT - port address translation allows a network to use any IP address set inside without causing a conclict with the public internet
52 | * LT2p navtively supports non-IP protocols. PPTP, L2F, and IPSec are all IP protocols
53 | * Parrallel test - team activates the disaster recovery site for testing but primary site remains untouched
54 | * 3DES can use 2 or 3 keys
55 | * RFC 1918 is range of 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255
56 | * passive monitoring is : network tap or span port. active monitoring relies on sythetic or previously recorded traffic.
57 | * RSA requiresly only two keys for each user... fucking duh. even if you have 10,000,000 people, they each just need a public and private key to be able to talk to everyone. they go and get the other persons public key before sending messages.
58 |
59 |
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/D5 - Identity and Access Management.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Identity and Access Management (IAM)
2 |
3 | [Back to Home Page](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-)
4 | [To next domain! - D6 - Security Assessment and Testing](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D6%20-%20Security%20Assessment%20and%20Testing.md)
5 |
6 | ### Control physical and logical access to assets
7 | Access is controled by setting up rules and procedures for access. If you are going to use the object, there should only be one/two ways to get to it. You must confirm someones identitiy by having them prove: Something they know, something they have, or something they are.
8 | * Information
9 | * Systems
10 | * Devices
11 | * Facilities
12 |
13 | ### Manage identification and authentication of people, devices, and services
14 | * Identity management implementation
15 | * Single/multi-factor authentication - in multi-factor authentication, you must provide two of three different forms of identity
16 | * Accountability - beng able to audit a system and demonstrate the actions of subjects
17 | * Session management - providing the user some type of token that they use to acquire resources and identity them with. They don't need to re-authenticate everytime they want to access something
18 | * Registration and proofing of identity - when signing up for a service you may be asked for PII, personal questions about your pas that would be difficult for other to figure out, and information that is unique to you like your email.
19 | * Federated Identity Management (FIM) - setup a trust relationship between two companies so they can share authentication information
20 | * Credential management systems - keeps passwords encrypted and safe from unauthorized access. allows passwords services read permissions to the hashes that need to authenticate someones password
21 |
22 | ### Integrate identity as a third-party service
23 | * On-premise - generally most identifications with information systems are on premise
24 | * Cloud - Identity as a service (IDaaS)
25 | * Federated - doing SSO at a much larger scale. doing it across organizations
26 |
27 | ### Implement and manage authorization mechanisms
28 | * Role Based Access Control (RBAC) - define roles in your organization(nurse, janitor, IT, manager) and give them default permissions
29 | * Rule-based access control - series of rules, restrictions, and filters for accessing objects
30 | * Mandatory Access Control (MAC) - system-enforced based on a subject's clearance and object's labels
31 | * Discretionary Access Control (DAC) - give full control of objects they created or given access to
32 | * Attribute Based Access Control (ABAC) - "IF" "then" access control. lots of policies combined together
33 |
34 | ### Manage the identity and access provisioning lifecycle
35 | * User access review - users can slowly keep gaining privileges over time. need to review them and take away when they are longer need those roles/permissions/resources. This is authorization creep
36 | * System account access review - samething?
37 | * Provisioning and deprovisioning - need to have policies and guides in place to review people, give them permissions, and take them away after certain key events
38 |
39 | ### Definition of Existing Services
40 | what is it used for? what does it provide?
41 | * Directory services - allows an admin to configure and manage how identification, authentication, authorization, and access control take place within the network and on individual systems.
42 | * Active Directory - A database that is a directory service. allows user access control functionality and network resources. like some users can only view certain files, use printer, etc
43 | * LDAP - a protocol used to query the directory services database. this is how subjects and applications find out if they can AAA a user, because LDAP queries their database information.
44 | * Domain Controller - hosts Active Directory
45 | * CA - users don't trust each other, but they do trust certificate authority. CA vouches for individuals identities by using digital certificates.
46 | * Samba - directory services for linux. Domain controller for linux
47 | * SSO - subject may authenticate once, then access multiple systems. Authenication, authorization, and accountabilitiy.
48 | * SAML - an XML standard that allows the exchange of authentication and authorization to be shared between security domains. Ex, your business uses Gmail and SAML. when a user goes to login, they are directed to your SSO server, which has access and password rules. SAML is the request and response to/from SSO server. REST requests will exlicit an HTML, XML, or JSON response. Example operations are GET,POST,PUT,DELETE
49 | * REST - Representation State Transfer. an approach that uses HTTP protocol to access and manipulate text without keeping track of any data(or state)
50 | * SOAP - like REST but has security in mind. Outlines how web service information is exchanged. When requesting access, a SOAP body contains a SAML request or response inside of it
51 | * JSON - JavaScript Object Notation is a lightweight data format
52 | * OAUTH - open standard for authorization(not authentication) to third parties. Like when you authenticate with facebook, you can then authorize it to go off and manage your photos. Facebook could access your photos until you tell it not to anymore
53 | * Kerberos - Authentication protocol. works in client/server model. SSO for distributed environment. symmetric key encryption that doesn't send any passwords over the network. has a session key. has a key distribution center that holds all users keys. a challenge packet is sent to user for their user name, and if they enter password right, the challenge is decrypted. session keys are created for each session greated.
54 | * One time pad - can't be cracked. requireds a preshared key that is same size or longer than message being sent
55 | * RADIUS - provides client/server authentication and audits remote users.
56 | * TACACS - basically same as RADIUS but uses TCP. Seems more secure than RADIUS.
57 | * Biometrics - a way to authenticate a user. won't match perfectly all the time, so if more restrict will have more false positives.
58 |
59 |
60 | [Back to Home Page](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-)
61 | [To next domain! - D6 - Security Assessment and Testing](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D6%20-%20Security%20Assessment%20and%20Testing.md)
62 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/D3 - Security Architecture and Engineering.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Security Architecture and Engineering
2 |
3 | [Back to Home Page](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-)
4 | [To next domain! - D4 - Communication and Networking Security](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D4%20-%20Communication%20and%20Network%20Security.md)
5 |
6 | ### Implement and manage engineering processes using secure design principles
7 | Designing and managing secure computer systems breaks out into 4 layers: hardware, kernel and device drivers, operating system, applications. Perimeter defenses is physical security. There should be multiple layers of defense at each component that needs to be protected.
8 |
9 | ### Understand the fundamental concepts of security models
10 | * Access control and least privilege - Bella-lapadula model
11 | * Complex environments - Lattice-based access control
12 | * Integirty - Biba Model, Clark-Wilson
13 | * Conflict of Interest - Chinese Wall Model
14 |
15 | ### Select controls based upon systems security requirements
16 | [NIST document for selecing controls](https://csrc.nist.gov/CSRC/media/Projects/Risk-Management/documents/select/faq-Select-step2.pdf)
17 | Generally a framework is used to categorize the information system or business, and then it will tell you which controls or standards are applicable.
18 |
19 | ### Understand security capabilities of information systems (e.g., memory protection, Trusted Platform Module (TPM), encryption/decryption)
20 | * Access control - ring model is used. Ring 3 is user, ring 0 is Kernel.
21 | * Memory Protection - prevents a program from affecting the integrity, availability, and confidentiality from another
22 | * TPM - a processor at harware level that allows computer to do cryptographic operations. If TPM, can do secure boot and full disk encryption
23 | * Encryption - can provide confidentiality and integrity depending on type of cryptography used
24 |
25 | ### Assess and mitigate the vulnerabilities of security architectures, designs, and solution elements
26 | * Client-based systems - when user downloads content or has a vulnerable browser on a malicious website
27 | * Server-based systems - clients attacking systems accepting connections/commands
28 | * Database systems - data mining, polyinstantiation, inference and aggregation
29 | * Cryptographic systems - weak IV, key size, key exchange, or symetric encryption algorithm used. good crypto is mathematically difficult
30 | * Industrial Control Systems (ICS) - generic term that refers to anything from a thermostat to a chemical processing monitor
31 | * Cloud-based systems - A company that stands up several servers for outsourcing. Pay them money to get the below examples
32 | * Infrastructure as a Service(IaaS)=Linux Server Hosting
33 | * Platform as a Service(PaaS)=Web Service hosting
34 | * Software as a Service(SaaS)=Web mail
35 | * Distributed systems - use lots of devices that aren't necessarly high performance. think Docker swarm or beowolf cluster
36 | * Internet of Things (IoT) - embedded systems that do only set few things. Smart TV, fridge, thermostat, etc. often built on linux kernel, has libraries that alow basic functionality like ping, store data, and query APIs.
37 |
38 | ### Assess and mitigate vulnerabilities in web-based systems
39 | ##### Types of code run in web browsers
40 | * Applets - small pieces of mobile code embedded in web browsers to display content. executables that are run locally. write them in java.
41 | * Java script - scripts that can be embedded in web pages to make your browser do certain things. everyone uses java script
42 | * DOM/CSS - There are DOM/CSS vulnerabilities you have to watch out for. attackers can inject their own code here.
43 | * ActiveX - same as applets but use digital certificates instead of sandbox like java. microsoft only
44 | ##### Want to fix?
45 | * Look at OWASP. See if any of your web app is vulnerable of the things. scan it with OWASP ZAP.
46 | * Update hosting software. use secure libraries. follow OWASP rules. use a static analysis tool. run OWASP zap on it. update web browser.
47 | ##### Types of Vulns?
48 | * Web hosting software vulns
49 | * hard coded credentials
50 | * inpropper permissions and redirects
51 | * badauthentication
52 | * bad session management
53 | * bad encryption
54 | * SQL injection
55 | * cross site scripting (XSS)
56 | * cross site forgery requests
57 | * local/remote file inclusion
58 | * API information disclosure
59 |
60 | ### Assess and mitigate vulnerabilities in mobile systems
61 | Mobile devices are actually a real problem. Should manage them with "mobile device manager" to push policies out. Can also remotely wipe them, and put full disk encryption on them.
62 |
63 | ### Assess and mitigate vulnerabilities in embedded devices
64 | Should see what track the device flows across the network. See if you can connect to any ports. See if they have any CVEs or a security program for their products.
65 |
66 | ### Apply cryptography
67 | [OWASP CHEATSHEET LINK](https://www.owasp.org/index.php/Key_Management_Cheat_Sheet)
68 | * Cryptographic life cycle (e.g., key management, algorithm selection)
69 | * key management: how are you going to store all of your private/public keys? are there backups? who do you trust
70 | * algorithm selection: need to know if you need CIA? Speed? How much strength do you need?
71 | * Cryptographic methods (e.g., symmetric, asymmetric, elliptic curves)
72 | * symmetric: one key that encrypts and decrpts
73 | * asymmetric: each person has their own public and private key. Private decrypts, public encrypts
74 | * elliptic cures: a type of math model used to gennerate commputationally difficult private/public key pairs
75 | * Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) - leverages all three forms of encryption to provide and manage digital certificates. Users have confidentiality, integrity, non-repudiation
76 | * Key management practices: Have certificate authority for managaging and signing certificates
77 | * Digital signatures - uniquely represents who someone is
78 | * Non-repudiation - can't deny that you did something
79 | * Integrity (e.g., hashing) - proving that the data hasn't been altered
80 | * Understand methods of cryptanalytic attacks - analyzing initilzation vectors, key exchanges, symmetric encryption, etc for weaknesses that could be exploited
81 | * Digital Rights Management (DRM) - systematic approach for protecting digital rights
82 |
83 | ### Apply security principles to site and facility design
84 | Need to know about physical security like: doors, locks, walls, fences, lights, guards, badges, gates, man traps, sensors, alarms, seucrely failing, emergency protocols.
85 |
86 | ### Implement site and facility security controls
87 | * Wiring closets/intermediate distribution facilities -
88 | * Server rooms/data centers - could need shielded racks, cabling, seperation of equipment, locks, temperator monitors
89 | * Media storage facilities - encryption
90 | * Evidence storage - classification and access control
91 | * Restricted and work area security
92 | * Utilities and Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC)
93 | * Environmental issues
94 | * Fire prevention, detection, and suppression - know which fire extenguishers put out different fires
95 |
96 |
97 | [Back to Home Page](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-)
98 | [To next domain! - D4 - Communication and Networking Security](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D4%20-%20Communication%20and%20Network%20Security.md)
99 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/D7 - Security Operations.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Security Operations
2 |
3 | [Back to Home Page](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Study-Guide)
4 | [To next domain! - D8 - Software Development Security](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Study-Guide/blob/master/D8%20-%20Software%20Development%20Security.md)
5 |
6 | # Understand and support investigations, Evidence collection, and handling
7 | This is pretty generic. Make sure you confirm something is a problem before taking any actions. If something needs to be acted upon, contain it first(unplug ethernet or put up crime scene tape), and use procedures (write blocks or gloves to keep integrity of the object you are assessing). Forensics focuses on the legality of conducting an investigation.
8 | * Reporting and documentation
9 | * Investigative techniques
10 | * Digital forensics tools, tactics, and procedures
11 |
12 | # Understand requirements for investigation types
13 | I've never seen these questions asked in practice tests so I wouldn't worry about them. They are also not covered in the 2 different CISSP books I have...
14 | * Administrative
15 | * Criminal
16 | * Civil
17 | * Regulatory
18 | * Industry standards
19 |
20 | # Conduct logging and monitoring activities
21 | * Intrusion detection and prevention - detections looks for actions and reports, while prevention takes action. There are network based and host based.
22 | * Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) - Security Information and Event Management. Most should provide traffic analysis, analyze logs, scan the network with a vulnerability scanner, and report actions/info via email, phone, etc.
23 | * Continuous monitoring - this is a strategy. NIST 800-137 provides a plan for implimenting continuous monitoring that provides visibility of assets, awarness of threats/vulns, and security controls deployed.
24 | * Egress monitoring - monitoring traffic leaving your network
25 |
26 | # Securely provisioning resources
27 | * Asset inventory - tracking: hardware, software, programs installed
28 | * Asset management - updating software, replacing hardware, adding functionality, removing functionality, tracking their location
29 | * Configuration management - process of establishing and maintaining consistent baselines of all of the systems. get baselines of everything
30 |
31 | # Understand and apply foundational security operations concepts
32 | * Need-to-know/least privileges - A user should have a need to know to access particular resources, and least privilege should be implemented to ensure she only accesses the resources she has a need to know.
33 | * Separation of duties and responsibilities - Separation of duties is put into place to ensure that one entity cannot carry out a critical task alone.
34 | * Privileged account management - privilege kreep tends to happen over time. need to ensure there is great justification always to have administrative privileges. administrative actions are logged.
35 | * Job rotation - Rotation of duties enables a company to have more than one person trained in a position and can uncover fraudulent activities
36 | * Information lifecycle - flow of information. overtime information becomes less useful and less sensitive. if someone stole your credit card info for your current one it would be bad, but one you had 15 years ago wouldn't really matter that much.
37 | * Service Level Agreements (SLA) - helps decide what type of availability technology is appropriate.
38 |
39 | # Apply resource protection techniques
40 | Apply deterrents, monitoring, and protectin to keep assets undamaged and unstolen. Put in GPS tracking, bag inspections, and scanners
41 | * Media management
42 | * Hardware and software asset management
43 |
44 | ### Conduct incident management
45 | * Detection - most important step is to realize that there is a problem. Must have a machine analyzing network, as well as a person to filter false positives.
46 | * Response - need to determine an appropriate response. analyize all of the material before making a decision
47 | * Mitigation - contain the incident. act on the situation to reduce damage and to keep the situation in a manageable state
48 | * Reporting - summary of incident, indicators, related incidents, actions taken, chain of custody, impact assessment, identity, and next steps to be taken
49 | * Recovery - trying to get the asset to a known good state
50 | * Remediation - need to make sure attack or failure is not successful again. patch the issue, and figure out if this could happen again in future
51 | * Lessons learned - what happened, what did we learn, any mistakes, what was good, can we do better next time, is there a good plan in place to deal with this in the future?
52 |
53 | ### Operate and maintain detective and preventative measures
54 | * Firewalls - makes sure the right type of traffic is allowd in and out
55 | * Packet filtering - don't route, just accept or drop based on IP, packet type, port, etc
56 | * Circuit-level gateways - don't inspect packets, monitor TCP handhshake to see if session is legimate
57 | * Stateful - examine each packet and different sessions
58 | * application-level - like a proxy, affect performance, inspect packet and see if clients are trusted
59 | * Next-gen - packet inspection, stateful inspect, and deep packet inspection
60 | * Intrusion detection and prevention systems - need to make sure they are configured to detect real events, and that IPS actions done don't hurt business because of too many false positives
61 | * Whitelisting/blacklisting - white: allow certain applications. black: don't allow certain applications.
62 | * Third-party provided security services - pentest, monitoring, storage, physical, contracting to impliment security controls, etc
63 | * Sandboxing - run things in safe place so that if it is compromised it can't elevate privileges or effect systems around it
64 | * Honeypots/honeynets - attractive targets that alter the network admin someone is attacking things on network
65 | * Anti-malware - anti virus? local antivirus or network monitoring SIEMs can block traffic that is considered malicious
66 |
67 | ### Implement and support patch and vulnerability management
68 | * Everything should be patched regularly(daily or weekly) and there should be a plan for immediate patching if zero day comes out.
69 | * Look at the most concerning vulnerabilities first. look at what patches/solutions fix the most problems
70 | * have good network segmentation. if finance department is compromised, it should be hard for the attacker to pivot to software department
71 |
72 | ### Understand and participate in change management processes
73 | ##### Process
74 | 1. Identifying a change
75 | 2. Proposing a change
76 | 3. Assessing the risk associated with the change
77 | 4. Testing the change
78 | 5. Scheduling the change
79 | 6. Notifying impacted parties of the change
80 | 7. Implementing the change
81 | 8. Reporting results of the change implementation
82 | ##### Person
83 | 1. have closeout interview. sign NDA and other documents
84 | 2. security escort out of building
85 | 3. disable account
86 | 4. change passwords
87 |
88 |
89 | ### Implement recovery strategies
90 | * Backup storage strategies - how often do you do full packups? incremental packups? how long do you keep these? how long does it take to restore?
91 | * Recovery site strategies - hot, warm, cold sites. figure out what is absolutely needed when making a decision. obviously its nice to have a hot site, but is that the best for your $$$
92 | * Multiple processing sites -
93 | * System resilience, high availability, Quality of Service (QoS), and fault tolerance -
94 |
95 | ### Implement Disaster Recovery (DR) processes
96 | * Response - have a fast way to analyze the issue
97 | * Personnel - make sure trained personel are in charge and correct personel are alerted
98 | * Communications - super hard to always update necessary personel in status of whats going on
99 | * Assessment - assess if the current plan covers most all scenarios
100 | * Restoration - procedure for how to recover/restore from different failures? like if HD failes?
101 | * Training and awareness - peronsel should be properly trained and aware of what can happen
102 |
103 | ### Test Disaster Recovery Plans (DRP)
104 | * Read-through/tabletop
105 | * Walkthrough
106 | * Simulation
107 | * Parallel - test recovery of critical processing components at an alternate computing facility and recovery of system
108 | * Full interruption - what to do if businesses is completely interrupted
109 |
110 | ### Participate in Business Continuity (BC) planning and exercises
111 | Identitfy and prioritize critical IT systems and components. there are templates for this
112 |
113 | ### Implement and manage physical security
114 | * Perimeter security controls - fences, cameras, guards, lights, detectors
115 | * Internal security controls - man traps, RFID badge readers, RFID asset alarms, training, cameras, locks, and cameras
116 |
117 | ### Address personnel safety and security concerns
118 | * Travel - what material can they cary with them? how can they safely work? safe means of travel/escape?
119 | * Security training and awareness
120 | * Emergency management - what to do if asset is lost? stolen? in danager?
121 | * Duress - threats against someone to get them to do something against their better judgement
122 |
123 |
124 | [Back to Home Page](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Study-Guide)
125 | [To next domain! - D8 - Software Development Security](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Study-Guide/blob/master/D8%20-%20Software%20Development%20Security.md)
126 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/D1 - Security and Risk Management.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Security and Risk Management
2 |
3 | [Back to Home Page](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-)
4 | [To next domain! - D2 - Asset Security](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D2%20-%20Asset%20Security.md)
5 |
6 | ### Understand and apply concepts of confidentiality, integrity and availability
7 | #### Definitions and examples
8 | * Confidentiality - Making sure the right people can access the material. Data must be classified so the administrators knows exactly who should have access. Users must Identify themselves, authenticate, and then be given authorization before having access. Contents must be encrypted or restricted for users who don't do the above.
9 | * End to End symetric encryption holds confidentiality because only users with a key can see the data
10 | * File permissions only allow authorized users to view the contents
11 | * Integrity - Protected from changes
12 | * Hashing
13 | * Segregation of duties
14 | * approval checkpoints (SDLC)
15 | * RSA(uses HMC)
16 | * IPSec
17 | * Availability - Information is available to users when they need it
18 | * Not vulnerable to DOS
19 | * Has backups and redundancy to ensure no downtime
20 |
21 | #### How do they relate to each other?
22 | CIA TRIAD - You can't have maximum levels of everything
23 |
24 | 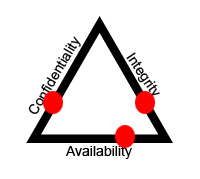 25 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 | ### Evaluate and apply security governance principles
29 | ##### English please?? - These are just defined roles, and processes for each role, to make sure executive management is informed about IT decisions being made. This makes sure that information is appropriately secured, communicated, documented, and budgeted for. It's like a questionaire. Look at ISO 27000 to get requimrents for which security frameworks you should impliment. Think of security frameworks as blue prints and governance principles(iso 27000 or togaf) as guides for how to draw blueprints.
30 | * Alignment of security function to business strategy, goals, mission, and objectives
31 | * Have to analyze cost of loss/thieft information, cost to impliment controls, and the benefit to organization by certain controls.
32 | * Organizational processes (e.g., acquisitions, divestitures, governance committees)
33 | * if the business changes at all, security needs to be involved in that changing process. apply frameworks to those processes.
34 | * Organizational roles and responsibilities
35 | * different job titles have to work with others and be aware of things. each job has a checklist of things to be concerend about. some positions will be reponsible for risk on certain decisions.
36 | * Security control frameworks
37 | * the blue prints to how security in the organization is done. ex. if you are going to label an area on a blueprint as a "bed room", it needs to meet certain requirements. certain frameworks need to be applied to your organization based off what you contain.
38 | * Due care/due diligence
39 | * legal perspective. What would a "reasonable person" due in the same circumstance if they were being responsible?
40 | ##### Difference between Process/architecture/framework/standard?
41 | * Process: A set up steps to accomplish a task.
42 | * Architecture: specifies when and where to apply security controls. Describes interactions and roles
43 | * Framework: A set up processes with implimentation guidance
44 | * Standard: A set of requirements, roles, and controls/frameworks to impliment
45 |
46 | ### Determine compliance requirements
47 | ##### Governments are required to impliment NIST 800-53. Private sector is required to implimented COBIT. Many businesses end up implimenting part of each framework to meet its business objectives.
48 | Organizations operate in environments where laws, regulations, and compliance requirements must be met. Want to handle peoples cred cards? - must meet certain requirements and impliment certain frameworks. Want to be a defense contractor? - same as before.
49 | * Contractual, legal, industry standards, and regulatory requirements
50 | * one example is all federal agencies are required to ahere to FISMA. Gives list of requirements because they handle mission information as well as PIV.
51 | * Privacy requirements
52 | * Mitre has a good framework for dealing with privacy. You just need to identify what data you process and see if it applies in your TOGAF or other blueprint guidlines you are following.
53 |
54 |
55 | ### Understand legal and regulatory issues that pertain to information security in a global context
56 | * Cyber crimes and data breaches
57 | * Licensing and intellectual property requirements
58 | * Import/export controls
59 | * Trans-border data flow
60 | * Privacy
61 | ##### Difference between Criminal Law/Common Law/Private law/Civil Law/Federal Law/
62 | * Criminal Law: punished by jail, fine, or death
63 | * Common Law: jury makes decision. then judge decides punishment
64 | * Civil Law: a.k.a Tort Law: Non-criminal. Injured party seeks to be 'made whole' through financial means. ex. Money for pain, suffering
65 | * Private Law: deals with relations between individuals and institutions. Part of civil law
66 | * Federal Law: body of law consisting of a constitution, enacted laws, and the court decisions pertaining to them
67 |
68 | ### Understand, adhere to, and promote professional ethics
69 | * (ISC)² Code of Professional Ethics - be a nice boy or girl
70 | * Organizational code of ethics - basically that anything you invent/design/consult is for good. you do your due diligence
71 |
72 | ### Develop, document, and implement security policy, standards, procedures, and guidelines
73 | Examples below
74 | * Policy: write policy for people who use lab at work. no usb allow, need to take this training, etc etc
75 | * standards: FIPS 140-2 is a common cryptographic standard in the military. must do certain things to have your device certifed.
76 | * procedure: you are tasked with the job of writing a procedure for analyzing computers that may contain malware
77 | * guidlines: this is not mantatory and no penalties happen if not followed. ex. i give guidlines for how to configure SMB shares at work since there are no SMB STIGs we must follow.
78 |
79 | ### Identify, analyze, and prioritize Business Continuity (BC) requirements
80 | * Develop and document scope and plan
81 | * Business Impact Analysis (BIA) - process to determine and evaluate the potential effects of an interruption to critical business operations as a result of a disaster, accident or emergency. If a function went down, could the rest of the business function? Could customers still function? Could customers still purchase things?
82 |
83 | ### Contribute to and enforce personnel security policies and procedures
84 | * Candidate screening and hiring - talk to references. background check. credit history. criminal history. education. drug testing.
85 | * Employment agreements and policies - write policies that people can only use computers for work. NDA. mandatory vacations.
86 | * Onboarding and termination processes - make sure people are given least privilege. take away access, badge, account, change passwords.
87 | * Vendor, consultant, and contractor agreements and controls - your business has security requirements when dealing business with them. if their code is in yours, they must develop securely. their information systems that connect to yours must be hardened
88 | * Compliance policy requirements - PCI is a policy that makes sure you must follow various controls to deal with credit cards
89 | * Privacy policy requirements - FISMA regulates peoples PII info and that is appropriately controlled
90 |
91 | ### Understand and apply risk management concepts
92 | * Identify threats and vulnerabilities - NIST 800-30 defines threat sources. microsoft also has great threat model
93 | * Risk assessment/analysis - find all vulnerabilities and flaws in scope. prioritize them by level of effort to fix and the amount of risk of not fixing that.
94 | * Risk response - If you face risk, you can do one of the following things: avoid it, transfer it, mitigate it, or accept it
95 | * Countermeasure selection and implementation - If risk is identified, need to consider accountabilitiy, reliablility, dependencies, CIA, when implimenting a countermeasure. Think of solution to problem and other supplimental controls to help fix it. soemtimes you won't be able apply a patch to completely fix problem, so you will need some supplimental fixes (band aids)
96 | * Applicable types of controls (e.g., preventive, detective, corrective) - directive, deterrent, preventive, compensating, detective, corrective, recovery. a good plan usually contains most of the types of controls just listed. that is defense in depth
97 | * Security Control Assessment (SCA) -
98 | * Monitoring and measurement - make sure problems, vulnerabilities, failures are monitored. make sure metrics are recorded that document hours spent to fix and recover. cost from failure. for network, get IDS and log server. do bi-weekly analysis to determine information system failures and patterns
99 | * Asset valuation - conduct software and hardware inventories regularly and automatically
100 | * Reporting - document baseline. explain why something is a risk. how severe. provide a fix, supplimental fixes, level of effort to fix, and a mitigation for why this risk could potentially be accepted (if you think it should).
101 | * Continuous improvement - Six Sigma. record metrics on your processes. find bottlenecks. eliminate bottlenecks.
102 | * Risk frameworks - below is list of frameowkrs
103 | * ISACA
104 | * ISO 31000
105 | * ISO 2009
106 | * NIST RMF Framework
107 |
108 |
109 | ### Understand and apply threat modeling concepts and methodologies
110 | * Threat modeling methodologies - make scope, applicable attack vectors, vulnerabilities open, risks, and countermeasures. should result in architecture changes, remediation actions, and good data for a risk report
111 | * Threat modeling concepts - same as above
112 |
113 | ### Apply risk-based management concepts to the supply chain
114 | * Risks associated with hardware, software, and services - look at past CVEs
115 | * Third-party assessment and monitoring - the third party solutions you use could have vulnerabilities or back doors
116 | * Minimum security requirements - decide on requirements for your product. those, and only those things will be delivered. very hard.
117 | * Service-level requirements - requirements for a service from the client viewpoint, defining detailed service level targets and mutual responsibilities
118 |
119 | ### Establish and maintain a security awareness, education, and training program
120 | * Methods and techniques to present awareness and training - need to always train people constantly in security awarness or it doesn't work. always echo it. disaster recovery is always way more expensive.
121 | * Periodic content reviews - make sure as new responsibilities and processes arise that we have security training in mind for them. make sure we are being aware of current threats
122 | * Program effectiveness evaluation - track enforcement and enhancement of security initiatives. periodic walk throughs and quizes to make sure people are staying up to date
123 |
124 | [Back to Home Page](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-)
125 | [To next domain! - D2 - Asset Security](https://github.com/so87/CISSP-Cheat-Sheet-/blob/master/D2%20-%20Asset%20Security.md)
126 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 25 |
25 |  25 |
25 |