├── .gitignore
├── CONTRIBUTING.md
├── Code-of-Conduct.md
├── LICENSE
├── OS.md
├── PULL_REQUEST_TEMPLATE.md
├── README.md
├── _resources
├── index.css
└── index.js
├── guides
├── Cloud_development
│ ├── Azure.md
│ ├── Firebase.md
│ ├── Heroku.md
│ ├── REST_API.md
│ └── ZEIT.md
├── DevOps
│ ├── Ansible.md
│ ├── Laravel.md
│ ├── Package_Manager.md
│ ├── Vagrant.md
│ ├── docker_intro.md
│ ├── grunt.md
│ └── kubernetes.md
├── Game Development
│ ├── Blender.md
│ ├── Game_Design_Elements.md
│ ├── Godot.md
│ ├── Unity.md
│ └── Unreal.md
├── Networking
│ ├── Blockchain.md
│ ├── IP_adresses.md
│ └── ISO-OSI Referent Model.md
├── Open_Source_Software
│ └── OpenSourceSoftware.md
├── Programming_Paradigm
│ ├── Functional_Programming.md
│ ├── OOP
│ │ ├── Prototypal_Inheritance.md
│ │ └── SOLID_design_principles
│ │ │ ├── Dependency_Inversion_Principle.md
│ │ │ ├── Interface_Segregation_Principle.md
│ │ │ ├── Liskov_Substitution_Principle.md
│ │ │ ├── Open-Closed_Principle.md
│ │ │ └── Single_Responsibility_Principle.md
│ └── parallelcomputing.md
├── Security
│ ├── RSA.md
│ ├── Steganography.md
│ ├── Wireshark.md
│ └── honeypot.md
├── Starters
│ ├── Creating_md_files.md
│ └── Vanilla_js.md
├── Testing
│ └── testing_pyramid.md
├── UI_design
│ └── vue_js.md
├── UX_design
│ ├── An-Introduction-To-AntiPatterns.md
│ ├── Fitts'_Law.md
│ └── Hick's_Law.md
├── Version_Control
│ ├── Git and PR.md
│ ├── Git.md
│ ├── GitHub.md
│ ├── GitHubSSH.md
│ ├── Mercurial.md
│ └── svn.md
├── Visual_design
│ ├── Architectural_Pattern
│ │ └── MVC.md
│ ├── Design_Language
│ │ └── Material_Design.md
│ ├── Wireframing
│ │ ├── Justinmind.md
│ │ └── Wireframing.md
│ └── color_theory
│ │ └── color_theory.md
├── Web_Containers
│ ├── Apache_Tomcat.md
│ ├── GlassFish.md
│ └── Progressive_Web_Apps.md
├── Web_Frameworks
│ ├── Angular.md
│ ├── CakePHP.md
│ ├── Drupal.md
│ ├── Flask.md
│ ├── Gitlab,Flask,Heroku.md
│ ├── Grails.md
│ ├── Next-js.md
│ ├── Next.js
│ ├── Phalcon.md
│ ├── Phoenix.md
│ ├── Pyramid.md
│ └── Semantic_Web.md
├── agile
│ ├── Code_Smell.md
│ ├── Dont_Repeat_Yourself.md
│ ├── How_To_Brainstorm.md
│ ├── MoSCoW.md
│ └── Software_Development_Life_Cycle.md
├── computation
│ └── Amdahl's_law.md
├── data_science
│ ├── Hidden Markov Model.md
│ ├── data_visualization
│ │ ├── D3.md
│ │ ├── DataHero.md
│ │ ├── Tableau.md
│ │ └── plotly.md
│ ├── deep_learning
│ │ ├── ANN.md
│ │ ├── Autoencoder.md
│ │ ├── CNN.md
│ │ ├── LSTM.md
│ │ ├── RNN.md
│ │ └── TensorFlow.md
│ ├── machine_learning
│ │ ├── Regression.md
│ │ └── classification_algorithms
│ │ │ ├── Decision_Tree_Classifier.md
│ │ │ ├── Logistic_Regression.md
│ │ │ ├── Naive_Bayes_Classifier.md
│ │ │ ├── Neural_Network.md
│ │ │ ├── Random_Forest.md
│ │ │ └── SVM.md
│ ├── miscellaneous
│ │ ├── Hadoop.md
│ │ └── Spark.md
│ └── natural_language_processing
│ │ ├── Text_Classification.md
│ │ ├── machine_translation.md
│ │ ├── morphology.md
│ │ ├── regular_expression.md
│ │ ├── semantic_parsing.md
│ │ ├── sentiment_analysis.md
│ │ ├── stemming_lemmatization.md
│ │ ├── synctatic_parsing.md
│ │ └── text_summarization.md
├── databases
│ ├── DBMS.md
│ ├── SQLAlchemy_intro.md
│ ├── database_keys.md
│ ├── mongodb.md
│ └── mysql.md
├── issue_tracking
│ ├── Bugzilla.md
│ └── Jira.md
├── logic
│ ├── Monty_Hall_Problem.md
│ ├── The_Dining_Philosophers_Problem.md
│ ├── The_Hardest_Logic_Puzzle_Ever.md
│ └── Turing_Test.md
├── python
│ └── django.md
└── web_development
│ ├── ES6.md
│ ├── NodeJS.md
│ ├── Reactjs.md
│ ├── WebAssembly.md
│ ├── itcss.md
│ └── svelte.md
└── index.html
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
2 | __pycache__/
3 | *.py[cod]
4 | *$py.class
5 |
6 | # C extensions
7 | *.so
8 |
9 | # Distribution / packaging
10 | .Python
11 | env/
12 | build/
13 | develop-eggs/
14 | dist/
15 | downloads/
16 | eggs/
17 | .eggs/
18 | lib/
19 | lib64/
20 | parts/
21 | sdist/
22 | var/
23 | wheels/
24 | *.egg-info/
25 | .installed.cfg
26 | *.egg
27 |
28 | # PyInstaller
29 | # Usually these files are written by a python script from a template
30 | # before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it.
31 | *.manifest
32 | *.spec
33 |
34 | # Installer logs
35 | pip-log.txt
36 | pip-delete-this-directory.txt
37 |
38 | # Unit test / coverage reports
39 | htmlcov/
40 | .tox/
41 | .coverage
42 | .coverage.*
43 | .cache
44 | nosetests.xml
45 | coverage.xml
46 | *.cover
47 | .hypothesis/
48 |
49 | # Translations
50 | *.mo
51 | *.pot
52 |
53 | # Django stuff:
54 | *.log
55 | local_settings.py
56 |
57 | # Flask stuff:
58 | instance/
59 | .webassets-cache
60 |
61 | # Scrapy stuff:
62 | .scrapy
63 |
64 | # Sphinx documentation
65 | docs/_build/
66 |
67 | # PyBuilder
68 | target/
69 |
70 | # Jupyter Notebook
71 | .ipynb_checkpoints
72 |
73 | # pyenv
74 | .python-version
75 |
76 | # celery beat schedule file
77 | celerybeat-schedule
78 |
79 | # SageMath parsed files
80 | *.sage.py
81 |
82 | # dotenv
83 | .env
84 |
85 | # virtualenv
86 | .venv
87 | venv/
88 | ENV/
89 |
90 | # Spyder project settings
91 | .spyderproject
92 | .spyproject
93 |
94 | # Rope project settings
95 | .ropeproject
96 |
97 | # mkdocs documentation
98 | /site
99 |
100 | # mypy
101 | .mypy_cache/
102 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/CONTRIBUTING.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Being a first-timer, contributing is awesome! :tada:
2 |
3 | But, of course there are some contributing rules: Like how filling out the comment part or how to make an appropriate pull request.
4 | The `CONTRIBUTING.md` file helps you out.
5 |
6 | Big projects have a big set of rules & regulations over how to contribute. But, since this project is for a first-timer,
7 | we will have as few rules as possible. :pizza:
8 |
9 | - Write your guide only in Markdown format.
10 | - Place your guide in an appropriate folder. Generally, the name of the folder can be taken from the label tag of the respective
11 | issue itself.
12 | - If you are writing an article for which an issue has not been defined, you are free to do it!
13 | - When making a PR, mention the issue you are solving or the name of the article.
14 | - **Do not COPY any article from Wikipedia/encyclopedia/book/blog**. The content of an article easily determines whether you have
15 | written it by yourself or copied it. Note: this is not the aim of this project.
16 | - If an article is found to be copied, the maintainer will comment on it as 'copied'.
17 | - While writing the PR please follow the PR template guidelines
18 | - The maintainer will review your PR within a week. **Do not review other contributor's PR unless said so by the maintainer
19 | himself**.
20 |
21 | **HAPPY CONTRIBUTING** :smile:
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Code-of-Conduct.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Contributor Covenant Code of Conduct
2 |
3 | ## Our Pledge
4 |
5 | In the interest of fostering an open and welcoming environment, we as contributors and maintainers pledge to making participation in our project and our community a harassment-free experience for everyone, regardless of age, body size, disability, ethnicity, gender identity and expression, level of experience, nationality, personal appearance, race, religion, or sexual identity and orientation.
6 |
7 | ## Our Standards
8 |
9 | Examples of behavior that contributes to creating a positive environment include:
10 |
11 | * Using welcoming and inclusive language
12 | * Being respectful of differing viewpoints and experiences
13 | * Gracefully accepting constructive criticism
14 | * Focusing on what is best for the community
15 | * Showing empathy towards other community members
16 |
17 | Examples of unacceptable behavior by participants include:
18 |
19 | * The use of sexualized language or imagery and unwelcome sexual attention or advances
20 | * Trolling, insulting or derogatory comments, and personal or political attacks
21 | * Public or private harassment
22 | * Publishing others' private information, such as a physical or electronic address, without explicit permission
23 | * Other conduct which could reasonably be considered inappropriate in a professional setting
24 |
25 | ## Our Responsibilities
26 |
27 | Project maintainers are responsible for clarifying the standards of acceptable behavior and are expected to take appropriate and fair corrective action in response to any instances of unacceptable behavior.
28 |
29 | Project maintainers have the right and responsibility to remove, edit, or reject comments, commits, code, wiki edits, issues, and other contributions that are not aligned to this Code of Conduct, as well as to ban, temporarily or permanently, any contributor for other behaviors that they deem inappropriate, threatening, offensive, or harmful.
30 |
31 | ## Scope
32 |
33 | This Code of Conduct applies both within project spaces and in public spaces when an individual is representing the project or its community. Examples of representing a project or community include using an official project e-mail address, posting via an official social media account, or acting as an appointed representative at an online or offline event. Representation of a project may be further defined and clarified by project maintainers.
34 |
35 | ## Enforcement
36 |
37 | Instances of abusive, harassing, or otherwise unacceptable behavior may be reported by contacting the project team. The project team will review and investigate all complaints, and will respond in a way that it deems appropriate to the circumstances. The project team is obligated to maintain confidentiality with regard to the reporter of an incident. Further details of specific enforcement policies may be posted separately.
38 |
39 | Project maintainers who do not follow or enforce the Code of Conduct in good faith may face temporary or permanent repercussions as determined by other members of the project's leadership.
40 |
41 | ## Attribution
42 |
43 | This Code of Conduct is adapted from the [Contributor Covenant][homepage], version 1.4, available at [http://contributor-covenant.org/version/1/4][version]
44 |
45 | [homepage]: http://contributor-covenant.org
46 | [version]: http://contributor-covenant.org/version/1/4/
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2017 Dhruv Apte
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/OS.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # What is an Operating System?
2 | An operating system acts as an intermediary between the user of a computer and the computer hardware. The purpose of an operating system is to provide an environment in which a user can execute programs in a convenient and efficient manner. It is thus a software that manages the computer hardware.
3 |
4 | ## Types of Operating Systems:
5 | 1. Batch OS
6 | 2. Multiprogrammed OS
7 | 3. Time sharing
8 | 4. Distributed
9 | 5. Real time
10 |
11 | An operating system must support the following tasks -
12 | 1. Process management
13 | 2. Main memory management
14 | 3. File management
15 | 4. I/O system management
16 | 5. Secondary storage management
17 | 6. Networking
18 | 7. Protection
19 | 8. Command Line Interpreter (CLI)
20 |
21 | ## Examples of Operating System are –
22 | * Windows
23 | * GNU/Linux
24 | * macOS (Macintosh), used for Apple’s personal computers and workstations (MacBook, iMac)
25 | * Android (Google’s Operating System for smartphones/tablets/smartwatches)
26 | * iOS (Apple’s OS for iPhone, iPad and iPod Touch)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/PULL_REQUEST_TEMPLATE.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | NOTE:
2 | - Please fill out the template below
3 |
4 | ## Did you read the instructions in the [README](https://github.com/the-ethan-hunt/first-timers-guide/blob/master/README.md)?
5 |
6 | > Y/N
7 |
8 | ## Have you read the instructions in [CONTRIBUTING](https://github.com/the-ethan-hunt/first-timers-guide/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md)?
9 |
10 | > Y/N
11 |
12 | ## Have you written this article by yourself? Have you taken inspiration from anywhere and then written it in your words?
13 |
14 | > [Write here. Be specific.]
15 |
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_resources/index.css:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | body {
2 | margin-left: 2%;
3 | margin-right: 2%;
4 | background-color: Khaki;
5 | }
6 |
7 | .topnav {
8 | overflow: hidden;
9 | position:static;
10 | }
11 |
12 | .search-container {
13 | float: right;
14 | }
15 |
16 | input[type=text] {
17 | padding: 6px;
18 | margin-top: 8px;
19 | font-size: 17px;
20 | border: none;
21 | }
22 |
23 | .search-container button {
24 | float: right;
25 | padding: 6px 10px;
26 | margin-top: 8px;
27 | margin-right: 16px;
28 | font-size: 17px;
29 | border: none;
30 | cursor: pointer;
31 | }
32 |
33 | .search-container button:hover {
34 | background: DimGray;
35 | }
36 |
37 | .links_header {
38 | margin: 0.5% 0 0 0;
39 | color: Yellow;
40 | }
41 |
42 | .main_header {
43 | position: absolute;
44 | left: 30%;
45 | top: 0;
46 | width: 40%;
47 | text-align: center;
48 | line-height: 30px;
49 | }
50 |
51 | #tempBG {
52 | width: 100%;
53 | height: 100%;
54 | top: 10%;
55 | opacity: 0.75;
56 | background-color: DimGray;
57 | z-index: 2;
58 | }
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_resources/index.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function disabler() {
2 | document.getElementById("tempBG").style.display = "none";
3 | }
4 |
5 | window.onload = function() {
6 | disabler();
7 | }
8 |
9 | document.onkeyup = function(keyPressed) {
10 | if (keyPressed.keyCode == 27) {
11 | disabler();
12 | } else if (keyPressed.keyCode == 13) {
13 | searchNow();
14 | }
15 | }
16 |
17 | function searchNow() {
18 | var searchText, mainList, l_elements, i, fetch_txt, tempString;
19 | document.getElementById("tempBG").style.display = "";
20 | searchText = document.getElementById("searchText");
21 | searchText = searchText.value.toUpperCase();
22 | mainList = document.getElementById("tempBG");
23 | l_elements = mainList.getElementsByTagName("li");
24 | for (i = 0; i < l_elements.length; i++) {
25 | fetch_txt = l_elements[i].getElementsByTagName("a")[0];
26 | tempString = fetch_txt.textContent;
27 | if (tempString.toUpperCase().indexOf(searchText) > -1) {
28 | l_elements[i].style.display = "";
29 | } else {
30 | l_elements[i].style.display = "none";
31 | }
32 | }
33 | }
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Cloud_development/Azure.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Azure
2 |
3 | Microsoft Azure is a platform as a service (PaaS) solution for building and hosting solutions using Microsoft’s products in their data centers. With the increase in cloud technology, developers can use Azure as a platform for building and deploying applications. It is easier to create programs with the help of tools provided by Azure. It is based on “pay as much as you use”.
4 |
5 | Azure was first released in February 1, 2010 as “Windows Azure” And later on March 25, 2014 it got renamed as “Microsoft Azure”.
6 | Microsoft Azure is reliable and secure. It is works on Virtualization technology, which allows it to use many virtual machines run at the same time.
7 |
8 | Azure provides a wide range of cloud services. Some of them are listed below: -
9 |
10 | • Storage Services
11 |
12 | • Analytics
13 |
14 | • Networking
15 |
16 | • Machine Learning
17 |
18 | • IoT
19 |
20 | Because of it’s features like - Flexibility, cost, applications, disaster recovery many companies like 3M, BMW, and GE are moving their workloads to Azure.
21 |
22 | ### Azure Account Registration
23 | 1. Visit https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/
24 | 1. Click on Free Account Link
25 | 1. Click Start Free
26 | 1. If you don't have a microsoft account, then create one
27 | 1. Enter your details, it will require Mobile Verification and a credit card.
28 | 1. To open Azure DashBoard visit https://portal.azure.com/
29 |
30 | You will get $200 in a free account for 30 days. You can use these credits to run services.
31 | Later you can purchase more.
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Cloud_development/Firebase.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Firebase
2 |
3 | [Firebase](https://firebase.google.com) is a development platform owned by Google (formerly known as *Firebase, Inc.* acquired in 2014) that enables programmers to build web and mobile applications faster. It is comprised of many functionalities such as:
4 | - [**Cloud Storage**](https://firebase.google.com/products/storage/) to simply serve resources like videos and photos.
5 | - [**Hosting**](https://firebase.google.com/products/hosting/) to deliver web assets easily by deploying static files (HTML, CSS, JS);
6 | - [**Cloud Functions**](https://firebase.google.com/products/functions/) to run server side code hassle-free.
7 |
8 | > For further details about their many other functionalities such as their **user engagement** tools (*analytics*, *invites* and so on), please follow this [link](https://firebase.google.com/products/).
9 | ***
10 | ## Install and develop with the [Firebase client](https://firebase.google.com/docs/cli/) locally:
11 | 1. [**NodeJS**](https://nodejs.org/en/download/) must be installed first.
12 | 2. Second, open a **command prompt** and run `npm i -g firebase-tools` (Patience will help for this step as there are lots of node modules being downloaded...).
13 | 3. Afterwards, by running this command: `firebase login`, you can log in to your Google account to access your Google projects (Email + password of the Google account).
14 | 4. Next, run `firebase init` in a project folder of your choice to start developing.
15 | 5. Use `firebase serve` to test the project locally ([**ngrok**](https://ngrok.com/download) shall come in handy to expose your local instance to the Web with HTTP tunnelling).
16 | 5. Finally, once you're done tinkering with your app, `firebase deploy` can be used to push your changes to Google's servers.
17 | ***
18 | ## There are 3 pricing plans:
19 | - **Spark Plan** which is mainly used for testing purposes and external network calls are disabled.
20 | - **Flame Plan** is a monthly fee plan with capped services.
21 | - **Blaze Plan** is a "pay-as-you-go" plan without any capping on use and allows several databases per project unlike the other plans.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Cloud_development/Heroku.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## What is Heroku ?
2 |
3 | Heroku is basically a cloud platform for running applications. To deploy an application your code needs to run on a server that will respond to request over the internet,but where does Heroku come in ? Well,Heroku will take your application and make it accesible on the internet with few simple commands.Heroku is a platform service for the developer to upload the code and make your application accesible to everyone, this is called a platform as a servive and is one kind of internet product available today along with infrastructure and software. As a service you might see this shortened to Paas,Iaas and Saas.What is special about paas product is that how simple they make it for you to host your application online.Heroku handles most of the details behind the scenes that are required for your application to run. To deploy your application on Heroku all you need is a few simple command line tools installed and your application code is ready to deploy services. Heroku handles all these background task for you making it much simpler for developers to release a live application. The Heroku platform supports development in Ruby on Rails, Java, Node.js, Python, Scala and Clojure.
4 |
5 | Heroku is a platform where you have the possibility to host your web apps on its remote servers. Supported Programming languages are: Python, PHP, Ruby, Go, Java and Node. It uses git as Version Control System just like GitHub and GitLab.
6 |
7 | ### Advantages of using Heroku
8 |
9 | - Heroku is easy to get started, you only need to install heroku ruby gem.
10 | - They having sufficient documentation to follow up.
11 | - Heroku is the cheapest option for a low traffic site.
12 | - Database integration is pretty simple with PostgreSQL.
13 |
14 |
15 | ### Disadvantages of using Heroku
16 |
17 | - You have to pay very high, once you decide to handle more traffic.
18 | - You have to manually scale your application on hight traffic.
19 | - You can't login to your server via SSH.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Cloud_development/REST_API.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Rest API or RESTful API
2 | Restful or REST API is architectural style of the web which is used in web services.Let us understand it in a layman language rather than reproducing the technical jargon .Before it we must understand what an API actually stands for
3 |
4 | ## What is an API ?
5 | API stands for application programming interface.It actually means that whenever we want to use a service provided by the server we get the service by actually calling their API which is exposed by the service provider.The best example to understand is that we can get the weather reports in our mobile weather app, we can use authenticaton using third party providers like google,facebook etc during sign up in many of the websites.So what actually we are doing is that we are using their code by requesting the server in a proper structure and server responds back with the data and thus all the communication takes place through these APIs
6 |
7 | ## Now what is REST then ...?
8 | REST stands for representational state transfer.It is nothing but an architecture style which is used for effective communication between the two machines than the traditional SOAP(Simple Object Access Protocol) services.It makes use of HTTP protocol for communication and thus is stateless.It is more popular because it uses various methods of HTTP protocol like GET to retrieve a resource ,PUT to change the state of or update a resource, which can be an object, file or block POST to create that resource and DELETE to remove it.The best part is we deal with the resources not command the resources through query strings
9 |
10 | The communication between the machines takes place in a structured format that uses either XML or JSON but latter is more popular because of the clean and more comprehensible structure.
11 |
12 | ## Now lets combine both
13 |
14 | Thus a REST API is only a newer way of communication through the concept of directly addressing the resource.It is more effective as it consumes less bandwidth and because of its stateless nature due to HTTP it is gaining more popularity in cloud services.
15 |
16 | ## Resources to learn further
17 | * https://searchmicroservices.techtarget.com/definition/RESTful-API
18 | * https://www.quora.com/What-is-a-REST-API
19 | * https://www.restapitutorial.com/
20 | * https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qVTAB8Z2VmA
21 | * https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q-BpqyOT3a8
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Cloud_development/ZEIT.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # ZEIT
2 | **[ZEIT](https://zeit.co/)** with their mission - "To Make Cloud Computing Accessible To Everyone", which allows developers to deploy their web projects with minimal effort and maintenance.
3 |
4 |
5 | ## What is ZEIT Now?
6 | **ZEIT Now** is a deployment tool by **ZEIT**. It’s a hands-down seamless way to launch your web applications, docker containers or even static websites to the cloud platform. Moreover, **ZEIT Now** is free (or Pay as you Grow plan) and light use even just for a beginner.
7 |
8 |
9 | ## Personal Domain
10 | **ZEIT Now** also allows developers to set up their projects to their custom domain (or a free .now.sh suffixed URL) along with free automatic SSL which puts a protective cover to shared encrypted data between the server and browser.
11 |
12 |
13 | ## Zero Config = Serverless
14 | **ZEIT Now** integrate directly with GitHub or GitLab as well. It allows developers to host static websites and web applications that deploy upon every push in branches or merge/pull requests to preview changes live. At the same time, it scales automatically, requires no orchestrate, operate and monitor, all with no configuration to the server. It also provides developers with a GUI(graphical symbols) or command-line(text only), to quickly spin up their projects on **ZEIT** platform.
15 |
16 |
17 | ## What can I deploy?
18 | - Any web framework/frontend stack of your choice.
19 | - API endpoints that query databases or web APIs that return dynamic data.
20 |
21 | ```
22 | Examples:
23 | - Node.js
24 | - Docker
25 | - Next.js
26 | - Gatsby
27 | - React, Vue, Angular
28 | - Go APIs
29 | ```
30 |
31 |
32 |
33 | ## Resources
34 | - [ZEIT Documentation](https://zeit.co/docs)
35 | - [ZEIT API Reference](https://zeit.co/docs/api)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/DevOps/Ansible.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Overview
2 |
3 | First of all DevOps is a working model that involves developers and operations to collaborate and improve productivity.DevOps consits of various tools and Ansible is one such tool.
4 |
5 | # What is Ansible ?
6 |
7 | Ansible is a Redhat tool for automating configuration using YAML as programming language and ssh as communication.
8 |
9 | # How does Ansible work ?
10 |
11 | First your admin client connects to your target service via ssh you do not need to setup any agents on the machine,all you need is peyten and a user that can log in and execute a script.Then ansible starts gathering facts about the machine,this can be checked like what operating system is installed,what services are running,what packages are installed etc and then ansible is going to run a palybook on the server,for example it can assign a webserver role that would install nginx and some firewall rules,it can also run any kind of tasks like deleting a temp folder.Finally you can use variables to make your deployments dynamic and reusable.For example you could set up a database connection string in your configuaration files depending on the enviornment you deploy in.
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/DevOps/Laravel.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## The PHP Framework For Web Artisans
2 |
3 | [**Laravel**][1] is a free, open-source and considered as one of the most popular [PHP][2] web framework with expressive syntax. Laravel attempts to take the pain out of development by easing common tasks used in the majority of web projects! It provides great tools following [MVC][3] architectural pattern right out of the window to help us build robust web application.
4 |
5 | 
6 |
7 | **Taylor Otwell** created this elegant framework with it's first beta being released on June 9, 2011.
8 |
9 | ## Laravel Framework For Web Development
10 |
11 | Whether you are a seasoned PHP developer or just starting out; a basic understanding of PHP is a prerequisite for getting acquainted with this particular framework but of course the important question:
12 |
13 | > Why should you care?
14 |
15 | Well, here are top 7 reasons why Laravel is a better choice for your web development requirements when it comes choosing a PHP framework:
16 |
17 | 1. **Security** - offers [CSRF][4] for supervising POST & GET request
18 | 2. **Emerging Platform** - featured on Google trends as it's popularity increases
19 | 3. **Template** - consists light-weight templates for creating impressive layouts
20 | 4. **Concise Programming** - learn Laravel for developing optimized solutions on [Laracasts][5]
21 | 5. **Model View Controller Support** - leads to elegant overall performance, better documentation and offer multiple functionalities.
22 | 6. **Built-in Project Environment** - project management becomes easier with [Artisan][6]
23 | 7. **Ready Made Applications** - availability of ready-made applications
24 |
25 | #### Get Started
26 |
27 | So, if you feel like it's worth a shot, just dive in! Here's a list of resources that might help you get started:
28 |
29 | - [**Laravel Docs 5.6**][7] (check out the official documentation)
30 | - [**Laravel Repository**][8] (build an application using Laravel 5)
31 | - [**Laravel Tutorial**][9] (install & configure Laravel for creating a simple blog)
32 | - [**PHP Tutorial**][10] (for revising key concepts)
33 | - [**Laravel Playlist - Traversy Media**][11] (excellent youtube resource for beginners)
34 | - [**Laracasts**][5] (the best Laravel & PHP screencasts)
35 |
36 | ## Open Source Contribution
37 |
38 | Being open-source, anyone can contribute to the betterment of **Laravel's** features. For further info, visit [here][12]
39 |
40 | [1]: https://laravel.com/
41 | [2]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PHP
42 | [3]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Model%E2%80%93view%E2%80%93controller
43 | [4]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cross-site_request_forgery
44 | [5]: https://laracasts.com/
45 | [6]: https://laravel.com/docs/5.6/artisan
46 | [7]: https://laravel.com/docs/5.6
47 | [8]: https://github.com/laravel/laravel
48 | [9]: https://medium.com/laravel-myanmar/tutorials-laravel-blog-f066f2e59588
49 | [10]: https://www.w3schools.com/pHP/default.asp
50 | [11]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EU7PRmCpx-0&list=PLillGF-RfqbYhQsN5WMXy6VsDMKGadrJ-
51 | [12]: https://github.com/laravel/framework
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/DevOps/Vagrant.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Vagrant
2 | Vagrant is open source tool for working with virtual environments.Vagrant acts as a wrapper for virtual environment configuration which is too tedious to do and thus provides an easy and efficient solution to manage VMs(virtual machines).It provides a command line interface with its own custom configuration and automates task with a few commands.One thing to always keep in mind is that it is not a replacement of VM but an efficient solution built over top of virtualization setup.
3 |
4 | # Installing Vagrant
5 | Vagarant is open source project which is available for all the platforms.You can easily download it from their official download [page](https://www.vagrantup.com/downloads.html).It is also available as repo in the package manager for various linux distribution like fedora,ubuntu
6 | For fedora distribution you can run
7 | ```
8 | sudo dnf install vagrant
9 | ```
10 | For ubuntu distribution use can run the following command into your terminal
11 | ```
12 | sudo apt-get install vagrant
13 | ```
14 | But remember the version can be outdated on these default package mangers. So the best approach is to head over to the official download page given above.The github repo of the vagrant can be vistied from [here](https://github.com/hashicorp/vagrant).The best way to learn vagrant is try your hand by installing it on your own system .You can also learn from invaluable [documentation](https://www.vagrantup.com/docs/) provided by the Hashicorp team.
15 |
16 | # Why should one choose it ?
17 | There are many reason to use vagrant. It is very helpful in setting up the environment which is same for development and production so that there would be not any excuse thereafter with a developer that ***it does work on my machine***.It is very helpful to set up the environment which works same on all the machines irrespective of the different host machines so therefore there would be no chaos for different OS, or different softwares among differnet devs.It consist of interpreter for text based environment in the form of vagrant files which contains all the confurigations for the setup.If for some reason the virtual machine corrupts the vagrant file can be shared with the others so that it will be easy for them to run the setup again within less time rather than completely reinstalling the OS and the necessary tools again to build the environment.
18 |
19 | # Basic Terminologies
20 | Vagrant comes with a command line interface which helps to set up the virtual environments and it provides an abstraction over the different commands and configurations of the different VM tools as it does them internally on its own.
21 |
22 | The basic terms can be understood from here
23 |
24 | * Box: Boxes are the packaged vagrant environments typically a virtual machines
25 | * Provider: A provider is the location in which the virtual environment runs. It can be local, remote, or even a docker container.The default local environment is virtual box(as it is free) but ofcourse it can be configured for other hypervisors.
26 | * Provisioner: A provisioner is a tool to set up the virtual environment, which can be a shell script, but we can use also other provisioning tools like chef,puppet and ansible.
27 |
28 | # Basic Vagrant Commands and their descriptions
29 | * vagrant ssh SSH into virtual machine.
30 | * vagrant up. Start virtual machine.
31 | * vagrant share. Share your virtual machine to the world via a temporary and unique url.
32 | * vagrant halt. Halts virtual machine.
33 | * vagrant destroy. Destroy your virtual machine
34 | * vagrant provision Reconfigure the virtual machine after a source code change.
35 | * vagrant reload Reload the environment again.
36 |
37 | # References
38 | https://opensource.com/resources/vagrant
39 | https://www.vagrantup.com/docs/cli/
40 | https://www.drupal.org/node/2008794
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/DevOps/docker_intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Overview
2 |
3 | Docker is used by developers pretty much everywhere now, and chances are you will require it if you plan to contribute to Open Source. This article aims at introducing Docker in the simplest way possible.
4 |
5 | ### Need for Docker
6 |
7 | Why do developers need Docker?
8 | Before Docker was introduced, there used to be major discrepancies when a developer's code was deployed in production, which was essentially caused due to difference in computing environments. This led to wastage of a lot of time and effort.
9 | Also, organizations which worked on microservice architecture found it very costly to develop their software because each microservice would require a different Virtual Machine to run on top of the base OS. This caused a lot of wastage of resources such as RAM, processor and disk space.
10 |
11 | ### How does Docker work?
12 |
13 | Docker deploys a separate *container* for **each** microservice on top of a **single** Virtual Machine. Actually, Docker containers are lightweight alternatives to Virtual Machines. One important thing to note here is that you do not need to pre-allocate any RAM to any of the containers; each container allocates as much RAM as that microservice requires, to itself.
14 |
15 | ### Docker Workflow
16 |
17 | The developer writes code into an easy-to-write Docker file. This Docker file creates an *image*. Containers are just run-time instances of these Docker images. The image is pushed to Docker hub, an online repository from which others can pull them and set up the containers in their own machines.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/DevOps/grunt.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## OVERVIEW
2 |
3 | Grunt,the javascript task runner written in Node.js,is used to automate tasks that are performed in routine manner.Automation tools are used to lessen the workload by doing the assigned tasks faster with better precision.Grunt mainly helps in debugging code, concatenating and minifying CSS and JavaScript files, compressing images and applying changes to a server or files on the server.These tasks may sound simple but they may be time consuming,if we are working on large projects,upon using grunt such tasks can be performed easily and at a faster pace.
4 |
5 | Popular companies that makes use of grunt includes Twitter,Adobe,Mordernizr,Bitovi,jQuery.
6 | For example,a process is set up that compresses jpg files,as the process starts all images having EXIF(Exchangeable image file format) data are removed from the project and are compressed.If Grunt is properly installed and configured, the image compression task code would look similar to the following:
7 |
8 |
9 | imagemin: {
10 | jpgs: {
11 | options: {
12 | progressive: true
13 | },
14 | files: [{
15 | expand: true,
16 | cwd: 'src/img',
17 | src: ['*.jpg'],
18 | dest: 'images/'
19 | }]
20 | }
21 | }
22 | While this task could have been done easily but Grunt does it automatically in a fraction of seconds.
23 |
24 | Grunt makes use of plugins in order to accomplish any task.One of the striking features of Grunt is,it can accomplish multiple tasks at the same time.
25 |
26 | [Complete guide for Grunt installtion](https://gruntjs.com/installing-grunt)
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Game Development/Blender.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Blender
2 |
3 | Blender is open-source software which has a wide range of applications in game development and animation.
4 |
5 | The game engine is supported by online forums, which allow individuals to download graphics designed by other people, making Blender simpler for beginners to get started with.
6 |
7 | If you did want to customize your own graphics, it is also possible to use the rendering tools to design these so they are fit for purpose. For beginners, this may involve changing textures on objects. For instance, by adding a texture to a plane, one could make a pond, with a water pattern, or simply a block of colour to represent water.
8 |
9 | While Blender is compatible with Python, game logic is usually determined using the graphical user interface the software provides. This allows users to associate controls with actions. For example, one could specify that when the up arrow is pressed, the avatar should move forward one step and the sound of a footstep should be triggered.
10 |
11 | In Blender, it is possible to package together all of the files used in the game (such as sound files and graphics) in order to make the game transportable.
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Game Development/Game_Design_Elements.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Elements of Game Design
2 | Here are some questions you should answer when designing a game, as explained by game designer [Tracy Fullerton](https://www.tracyfullerton.com/):
3 |
4 | ## Players
5 | What form does the player assume when playing this game? Do they play alone or with others? If they compete with other players, do they compete as an individual or as part of a team?
6 |
7 | E.g. Mario Party - you can play as different characters from the Mario Universe and compete with other players as an individual.
8 |
9 | ## Objectives/goals
10 | What is the #1 rule to winning the game? What conditions cause the player to win - or lose - the game? How do the player's actions lead to these conditions?
11 |
12 | E.g. Mario Party - Collect the most stars to win. Collect the stars by stealing from others or earning enough coins to buy them.
13 |
14 | ## Procedures
15 | What are the core mechanics (verbs) of the game? What types/patterns of play are allowed by the rules defined?
16 |
17 | E.g. Mario Party - Take turns rolling the die to move around the board, play minigames, and collect items.
18 |
19 | ## Rules
20 | How is the game played with defined challenges, actions, goals, and termination conditions? How can the environment, objects, and NPCs hinder or benefit the player?
21 |
22 | E.g. Mario Party - Star spaces may move when an event is triggered or an item is used. In minigames, a player may die if they fall into a pit or are hit by fire.
23 |
24 | ## Conflicts
25 | How do the procedures and rules make it difficult for the player to achieve their goal(s)? In other words, how do they challenge the player?
26 |
27 | E.g. Mario Party - The environment may have physical barriers to prevent you from getting to the star. Other players can gain items that will sabotage your attempts to get the most stars.
28 |
29 | ## Boundaries
30 | How do you separate the game world from everything outside of the game? How do you feel like you're in a game?
31 |
32 | E.g. Mario Party - You can only move on the spaces within the board and not walk off of the board.
33 |
34 | ## Outcome
35 | What outcomes can the player have? How many ways can they win or lose? Can the player actually "win" or "lose"?
36 |
37 | E.g. Mario Party - The player with the most stars wins, and the others lose. If more than one player has the same number of stars, then the player with the most coins wins.
38 |
39 | You can read more in Fullerton's [Game Design Workshop Book](https://books.google.com/books?id=GELLBQAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover#v=onepage&q&f=false).
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Game Development/Godot.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## What is a Game Engine?
2 |
3 | A game engine is a software development environment designed for people to build video games.Developers use them to create games for consoles, mobile devices, and personal computers.Godot is one such game engine.The process of game development is often economized, in large part, by reusing/adapting the same game engine to create different games or to make it easier to port games to multiple platforms.
4 |
5 | In general a game engine provides you a framework where you can focus on making game and you dont have to write the code to do all the underlying things. It has a rendering engine that produces the graphics in 2D or 3D.
6 |
7 | ## GODOT
8 |
9 | Godot is a 2D and 3D cross-platform compatible game engine released as open source software under the MIT license. It was initially developed for several companies in Latin America before its public release.The development environment runs on Windows, macOS, Linux, BSD and Haiku (both 32 and 64-bit) and can create games targeting PC, console, mobile and web platforms and Godot is completely free.
10 |
11 | Godot has
12 |
13 | - two separate 2D and 3D engines.
14 | - a complete editor to create your levels.
15 | - code editor with embedded docs and autocompletion.
16 | - animation editor with 2D rigging.
17 | - visual programming for designers.
18 | - shader editors,both text and graph-based.
19 |
20 | In Godot exports are available for PC and mobile. In order to export to a console you need a license and a development kit from the manufracturer and thats the reason why these exports are not available for everyone.
21 |
22 | ### NODE
23 |
24 | Everything in Godot is a node.A node might be anything,it might be a sprite,an animation,a sound.Every node has a name and it has all sorts of properties that define what it is and how it works. It has callback functions which are ways to make a node react to things. You can send commands to the nodes.Basically nodes are the base bricks with which Godot games are developed.Nodes display the required information as text, but editing is done via the Inspector.
25 |
26 | A node is extendable that is you can make a node do more things.Nodes are arranged in a tree which means that every node is going to have only one parent but any node can have any number of children.Any tree of nodes grouped together in a Godot is called a Scene.Nodes and Scenes are fundamental to how you build everything in Godot.
27 |
28 |
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Game Development/Unity.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Unity
2 |
3 | 
4 |
5 |
6 | Unity is a popular 2D and 3D game development engine that offers both free and paid models. It is used in both independent and large scale game development.
7 |
8 | ## Interface
9 | Unity has a customizable workspace that allows users to move windows around. The GUI is user friendly and utilizes graphical icons in addition to text to represent core functions. Key features include a live viewport and real time game preview without needing to build the entire project.
10 |
11 | ## Engine
12 | The engine is based on a drag and drop component system where each object can be fully customized through attributes associated with each component. Custom functions are often supported through script components, which are written in C# or Javascript (documentation can be found on the Unity website). Additional scripts and assets can be downloaded from the well populated Asset Store. Assets can vary from models and animation to full multiplayer frameworks and in game systems. This allows users to customize and rapidly prototype their project from a barebone starting point.
13 |
14 | Asset support is relatively robust in the engine, supporting almost any 3D file format including .blend files, which is especially popular in low budget or independent projects. Materials, textures, or animations can be imported or created from within the editor's file browser. Although scripts can be written in any editor, Visual Studio and Monodevelop are integrated with Unity to be default text editors.
15 |
16 | As of the latest release, Unity supports a variety of platforms (most notably mobile) and is known for its ease of cross platform development.
17 |
18 | ## Community
19 | Due to being free to use for a long time, Unity has become an extremely common tool for independent or small developers. Unity also has been the engine for several high profile successes such as Cities: Skylines, Kerbal Space Program, and Hearthstone. The large community and ease of access makes it easy to find documentation and tutorials to learn the engine.
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Game Development/Unreal.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Unreal
2 | 
3 |
4 | Unreal is a popular 2D and 3D game development engine that offers both free and paid models. It is used in both independent and large scale game development.
5 |
6 | ## Interface
7 | Unreal has a customizable workspace that allows users to move windows around, although many windows will open externally. The GUI is user friendly and utilizes graphical icons in addition to text to represent core functions. Key features include a live viewport and in game preview with a build.
8 |
9 | ## Engine
10 | The engine utilizes a node based blueprints system to support game functionality, materials, scripting. To script, C++ is supported however the engine primarily focuses on its node based blueprints script. Additional scripts and assets can be downloaded from the Asset Store, but it is not as rich as Unity. Unreal engine starts with a greater amount of graphical post processing. This makes projects in Unreal look great out of the box, however adding objects or changing light parameters will require a build before running, similar to a coding pipeline.
11 |
12 | Asset support is decent in the engine, supporting almost any 3D file format but not .blend files natively. Materials, textures, or animations can be created or modified from within the specific windows also using a node based system. Unreal is a long time supporter of Physically Based Rendering (PBR) so their node based material editor looks great and is similar to other pipelines that use node editors (like Blender). As a result of including high quality graphics in the default engine, Unreal trades barebone customization for AAA graphics.
13 |
14 | As of the latest release, Unreal engine supports several platforms but is heavily geared towards PC or powerful consoles.
15 |
16 | ## Community
17 | For a long time, Unreal was divided into the professional Unreal Engine and the hobbyist Unreal Development Kit. Prior to UDK, Unreal was mostly known for being a proprietary engine that was used to make the Unreal Tournament series. The limited accessibility early on and less lightweight starting point led to a slower growth in users. Popular game releases such as Fortnite, Rocket League, and Batman Arkham series have revitalized independent and small developer interest.
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Networking/Blockchain.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Blockchain
2 |
3 | The [**blockchain**][1] is an open, distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way. In 2008, [Satoshi Nakamoto][2] invented it to serve as the public transaction ledger of the [cryptocurrency][3]. Many people think of blockchain as the technology that powers [bitcoin][4]. While the original purpose of blockchain is to power bitcoin, still it is capable of so much more. In fact, blockchain is shorthand for a whole suite of distributed ledger technologies that can be programmed to record and track anything of value!
4 |
5 | 
6 |
7 | **BUT!**… we already have processes in place to track data. What’s so special about **Blockchain**?
8 |
9 | ###### Let’s break down the reasons why blockchain technology stands to revolutionalize the way we interact with each other!
10 |
11 | #### 1. The way it tracks and stores data
12 |
13 | Blockchain stores information in a so-called called blocks which are linked together in a chronological fashion to form a continuous line vis-a-vis **the metaphorical chain of blocks**! If we make a change to the information recorded in a particular block, we don't have to rewrite it. Instead, the change is stored in a new block registering that particular data and time permanently. Sounds familiar? That's because blockchain is based on the centuries-old method of the general financial ledger. But unlike the age-old ledger method, blockchain was designed to be decentralized and distributed across a large [peer-to-peer][5] (**P2P**) network of computers which reduces the ability for data tampering!
14 |
15 | #### 2. It creates trust in the data
16 |
17 | Before adding a block to the chain a few things must happen. First, a cryptographic puzzle must be solved thus creating the block. Secondly, the computer that solves the puzzle shares the solution to all the other computers on the network. This is called [proof-of-work][6]. The P2P network will then verify this proof-of-work and if correct, the block will be added to the chain. The combination of these complex math puzzles and verification by end users build the foundation for trusting each and every block on the chain. Because the network does the trust building for us we now have the opportunity to interact directly with our data in real-time.
18 |
19 | #### 3. No more intermediaries
20 |
21 | Currently, when doing business with one another, we don’t show the other person our financial or business records. Instead, we rely on trusted intermediaries, such as a bank or a lawyer, to view our records and keep that information confidential. These intermediaries build trust between the parties and are able to verify! But blockchain cut out the intermediaries as we now know all blocks added to the chain have been verified to be true and can’t be tampered with! This type of trusted P2P interaction with our data can revolutionize the way we access, verify and transact with one another because blockchain can be implemented in many different ways as its a type of technology, and not a single network. Some blockchain can be completely public and open to everyone to view and access while others are limited to a group of authorized users such as your company, a group of banks or government agencies. And there are hybrid public-private blockchains too.
22 |
23 | ## Applications
24 |
25 | Some of the most crucial applications of blockchain technology are as follows:
26 |
27 | - **Cryptocurrency**
28 | - **Financial Services**
29 | - **Smart Property**
30 | - **Smart Contracts**
31 |
32 | ------------
33 |
34 | [1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blockchain
35 | [2]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Satoshi_Nakamoto
36 | [3]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cryptocurrency
37 | [4]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bitcoin
38 | [5]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peer-to-peer
39 | [6]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proof-of-work_system
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Networking/IP_adresses.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # The IPv4 address format
2 | These addresses consist of 32 bits and are in the form of octets (groups of 8 bits) represented decimally and separated by a dot.
3 | An example IPv4 address may look like this: `192.168.0.1` with a *subnet mask* of `255.255.255.0`.
4 |
5 | The subnet mask specifies which part of the address is used for specifying the *network* we are addressing (bits are set to `1`), and the rest is used for the *host* (bits are set to `0`). Therefore, in order to extract the network part of the address, we only have to apply a *bitwise AND* operation on the address using the mask.
6 |
7 | The example address and mask look like this in binary, and after the AND operation:
8 | ```
9 | 11000000.10101000.00000000.00000001
10 | 11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000
11 | -----------------------------------
12 | 11000000.10101000.00000000.00000000
13 | ```
14 | Thus we have determined that the network address is simply `192.168.0.0`. This way we can easily tell if another address is on the same network as our device.
15 |
16 | The example address and mask can be alternatively represented in CIDR notation as `192.168.0.1/24`, where `24` is the number of *consecutive bits set to 1* starting from the most important (leftmost) bit.
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Networking/ISO-OSI Referent Model.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # ISO-OSI Referent Model
2 |
3 | The ISO - OSI model is one of the first referent models developed by the International Standards Organization as the first move towards standardizations of protocols used in computer networks. ISO - OSI connects with open systems (systems open for communication with other systems)and exchanges data.
4 |
5 | 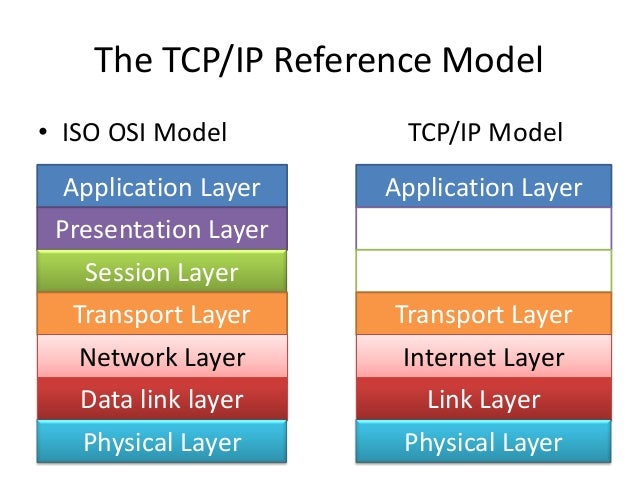
6 |
7 | ## Layers
8 |
9 | The ISO - OSI referent model started out with 7 different layers, each offering different services. Today, that number is reduced to five.
10 |
11 | ### Physical
12 |
13 | The Physical layer moves the bits between physically connnected end systems. The standards here define multiple coding schemes for bit representation, connector shapes and size and bit-level synchronization.
14 | On the internet, it is associated towards technologies that move bits over wired, wireless, satellite and other types of links.
15 |
16 | ### Data Layer
17 |
18 | The Data layer establishes reliable communication over a given link. Here you will find different protocols, which are the first software layers in the ISO-OSI model.
19 | This layer introduces the concept of a frame - a set of bits that belong together. Alongside that, this layer is very dependent on the physical layer, and they're often grouped together in the hardware.
20 |
21 | ### Network Layer
22 |
23 | The Network layer transfers data from the source to the desired destination. It does this by logically connecting a set of links, calculating and forming a route for the two systems to communicate.
24 | On the internet, this layer is provided with the Internet Protocol (IP), providing path abstraction, packet formatting, routing and unique IP addresses, among others.
25 |
26 | ### Transport Layer
27 |
28 | The Transport layer provides reliable end-to-end communication between the systems. It creates an abstraction of error-controlled, flow-controlled and multiplexed end-to-end link.
29 | On the internet, there are two protocols for the transport layer: TCP and UDP. TCP provides error-control, flow-control and multiplexing, while UDP only provides multiplexing.
30 |
31 | ### Application Layer
32 |
33 | The Application layer is the last one in the ISO-OSI model and is consisted of a set of applications that use the network in order to exchange information.
34 | Some of the most known ones are FTP, SMTP and DNS
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Open_Source_Software/OpenSourceSoftware.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Open Source Software
2 |
3 | Open Source Software is software governed by an [Open Source Initiative (OSI)](https://opensource.org) approved license. It is sometimes referred to as Free Software (free as in freedom, not as in no-cost). Proprietary Software is usually a commercial software where the source code is kept secret. Open source software however makes the source code public and requires free sharing and redistribution.
4 |
5 | The OSI approved licenses also have [additional requirements](https://opensource.org/osd-annotated), including in part:
6 | * The ability to make derived works
7 | * Guidelines for maintaining the integrity of the author’s source code
8 | * Prohibition of discrimination against both persons, groups, and fields of endeavor
9 | * Rules for the distribution of license, as well as rules for technological neutrality and for preventing licensing restriction for specific products or systems
10 |
11 | The three most popular open source licenses are:
12 | 1. [MIT License](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT) (the license selected by First-Timers-Only)
13 | 2. [GNU General Public License (GPL 2.0)](https://opensource.org/licenses/GPL-2.0)
14 | 3. [Apache License 2.0](https://opensource.org/licenses/Apache-2.0)
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Programming_Paradigm/OOP/SOLID_design_principles/Dependency_Inversion_Principle.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Dependency Inversion Principle
2 | The Dependency Inversion Principle states that high level modules should not depend on low level modules; both should depend on abstractions. In addition, abstractions should not depend on details, details should depend upon abstractions. This concept is difficult to explain in 150 words, but I'll do my best. Programmers typically make the mistake of tightly coupling their classes together. For example, clicking a button fires an event, which creates a new instance of a class in which a method is called, which in turn creates a new instance of another class which has a method that calls a database. All entities involved- the UI,classes, and methods- are dependant on the database, either directly or transitively. This makes maintenance difficult, since coupling will only increase as more features are added.
3 |
4 | However, by taking the same chain of events and instead calling to a method of an interface, we can eliminate coupling because we don't know what object we are calling. All that we know is that there is something out there that implements that interface's method. The new keyword isn't anywhere to be found. This is a technique called dependency injection. By eliminating this dependency, we can easily swap and replace different elements as we see fit. The referenced website below has links that go into greater detail and examples.
5 |
6 | ## References
7 | - [DevIQ] (https://deviq.com/dependency-inversion-principle/)
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Programming_Paradigm/OOP/SOLID_design_principles/Interface_Segregation_Principle.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Interface Segregation Principle
2 | The Interface Segregation Principle states that clients should not be forced to depend on methods that they do not use. In practice, this means that we should write interfaces that will be fully implemented. Rather than having large interfaces that have more functionality than what a class needs, it is preferable to have multiple smaller interfaces. That way if more functionality is needed, the interfaces can be stitched together, or perhaps an interface with more specific functionality can inherit from a more general interface.
3 |
4 | Smaller interfaces are important because they are easier to implement fully, and thus satisfy the Liskov Substitution Principle. This will prevent clutter and unncessary type checking as the scope of the project expands. Smaller interfaces are also more flexible, as smaller parts of a larger whole can be implemented in more unique ways.
5 |
6 | ## References
7 | - [DevIQ] (https://deviq.com/interface-segregation-principle/)
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Programming_Paradigm/OOP/SOLID_design_principles/Liskov_Substitution_Principle.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Liskov Substitution Principle
2 | The Liskov Substitution Principle states that subtypes must be substitutable for their base types. This means that when dealing with inheritance, we should look beyond the traditional "IS-A" relationship and try to establish an "IS-SUBSTITUTABLE-FOR" relationship as well. Violations of this principle lead to unnecessary type checking and conditional logic that quickly becomes unmaintainable as the project increases in size.
3 |
4 | A good example of a violation of this principle can be shown by creating a class Rectangle, and another class inheriting from Rectangle called Square. A Square IS-A Rectangle, and we can implement it by setting width equal to height as soon as it is instantiated. This is correct logic, however a Rectangle has the inherant property that width and height are two independant values. So this implementation of Square is NOT "SUBSTITUTABLE-FOR" Rectangle. This becomes an issue if we have a method that takes a rectangle and sets its height and width values to two different numbers. Passing in a square will return two of the same numbers, which is probably not what the user expected. Issues can also arise from only partially implementing an interface, tying Liscov Substitution closely with the Interface Segregation Principle.
5 |
6 | ## References
7 | - [DevIQ] (https://deviq.com/liskov-substitution-principle/)
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Programming_Paradigm/OOP/SOLID_design_principles/Open-Closed_Principle.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Open/Closed Principle
2 | The Open/Closed Principle states that software entities should be open for extension, but closed for modification. Software entities include classes, methods, etc. In practice, this principle suggests that we write entities whose behavior can be changed without changing its internal structure. A good real world analogy to this is that a person doesn't need brain surgery to put on a hat.
3 |
4 | In the same way, a method shouldn't have values hard-coded into its structure. If the values change, then the method would have to be "opened up" and changed as well. However, if we pass in the values as parameters, the method can stay the same, but it's behavior can be changed given different parameter values. To go back to the hat analogy, if a person needs a new hat, they just get a new hat, not a new head. This ultimately results in lower coupling for our entities, as well as improving encapsulation.
5 |
6 | ## References
7 | - [DevIQ] (https://deviq.com/open-closed-principle/)
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Programming_Paradigm/OOP/SOLID_design_principles/Single_Responsibility_Principle.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Single Responsibility Principle
2 | The Single Responsibility Principle states that a class should only have one reason to change. In other words, each class should do one thing. While this may seem trivial for small tasks, adhering to this principle preserves modularity as projects increase in size and scope.
3 |
4 | This principle was originally described by Robert C. Martin in "Principles, Patterns, and Practices of Agile Software Development". Martin wrote that we should defined the responsibility of a class as a "reason for change". If there are multiple reasons that a class should change, it has multiple responsibilities, and thus more dependencies and more "overlapping" among classes. If there is high overlap, then classes that depend on the changed class could break as a result and will need to be reexamined, increasing overhead. This notion of minimal overlap is called "low coupling". The lower the coupling between classes, the less dependencies, and the more modular the code. This is essential to agile development, as we should design around the asssumption the change will occur.
5 |
6 | ## References
7 | - [DevIQ] (https://deviq.com/single-responsibility-principle/)
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Programming_Paradigm/parallelcomputing.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## OVERVIEW:
2 |
3 | Parallel computing is the process in which execution of a number of computational processes are carried out simultaneously.Large problems are divided into small problems and further are executed simultaneously.
4 |
5 | ### DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PARALLEL AND SERIAL COMPUTING:
6 | In Serial computing a single task is completed one at a time and all other tasks are run by the processor in a sequence,a problem is broken into a discrete set of instructions which are executed one after the other.
7 | Any operating system running on the single processor is an example of the In serial operating system, an operating system runs on a single processor and completes one task at a given time. For e.g Pentium 3 and Pentium 4.
8 | In parallel computing we make use of multiple resources in order to solve a computational problem. In parallel computing a problem is broken into discrete parts that can be solved simultaneously, these parts are further broken down into series of instructions and instructions from different parts are executed simultaneously on different CPUs.For e.g. MATLAB.
9 | ### DIFFERENT FORMS OF PARALLEL COMPUTING:
10 | There are several different forms of parallel computing: bit-level, instruction-level, data, and task parallelism.
11 | - Bit-level parallelism involves dividing the bits of the processed task to be processed by different processors.
12 | - Instruction-level parallelism is done mainly on hardware level and it includes any architecture that does more than one instruction in single CPU.
13 | - Data parallelism involves execution of multiple data units, or an array in the same time by applying the same operation to them.
14 | - Task parallelism comes into play when the tasks are divided among the processors to be processed simultaneously. Dot net framework example of task parallelism is the thread
15 |
16 | [RESOURCES ON PARALLEL COMPUTING](http://web.eecs.umich.edu/~qstout/parlinks.html)
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Security/RSA.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # RSA
2 |
3 | What is RSA? RSA is a widely used public-key cryptosystem which can encrypt messages that are hard to 'break'. RSA uses an ecryption key
4 | that anyone can see but also uses a decryption key that is kept private. The reason why RSA is hard to crack is because of the impracticality
5 | of the factorization of two HUGE prime numbers. Did you know that RSA is an acryonym made of the initial letters of the people who designed
6 | the algorithm.
7 |
8 | ## How it works
9 |
10 | 2 Random distinct prime numbers are generated (p,q). The user MUST have their message as a base 10 number. Calculate n by the product of
11 | the generated prime numbers. Choose any number coprime to 780. This is e, the public key. At this point, m^e (mod n) is c, the cipher text.
12 | Calculate phi(n) = lcm(p-1,q-1). Calculate the private key d = e(mod phi(n)). Now, to decrypt the message, c^d mod n = m.
13 |
14 | As you've probably deduced, figuring out the two distince prime numbers will make cracking very simple.
15 |
16 | Using large, distinct prime numbers makes RSA almost uncrackable.
17 |
18 | ## Variables involved
19 |
20 | - m - plain message
21 | - c - cipher text (encrypted)
22 | - e - Any number coprime to 780
23 | - d - Modular multiplicative inverse of e(mod phi(n))
24 | - n - The product of p and q
25 | - p - Random prime number
26 | - q - Random prime number
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Security/Steganography.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Steganography is a process of hiding data behind an image or text. It is a form of cryptography, which is basically hiding some meaningful text in another text(which may be meaningful or not). The advantage of Steganography over cryptography is that the data which is hidden inside of an image doesn't attract user's attention as the cover is just an image or something we see in day-to-day basis.
2 | The first recorded use of the term was in 1499 by Johannes Trithemius in his Steganographia, a treatise on cryptography and steganography, disguised as a book on magic. Generally, the hidden messages appear to be (or be part of) something else: images, articles, shopping lists, or some other cover text.
3 | Steganography has been used for a long time and thus, it has developed various physical, as well as technical methods to implement it.
4 | Some physical methods include the following:
5 | 1) Hidden messages within a wax tablet: in ancient Greece, people wrote messages on wood and covered it with wax that bore an innocent covering message.
6 | 2) Hidden messages on paper written in secret inks, under other messages or on the blank parts of other messages.
7 | 3) Messages written in Morse code on yarn and then knitted into a piece of clothing worn by a courier.
8 | Some digital methods include:
9 | 1) Concealing messages within the lowest bits of noisy images or sound files.
10 | 2) Concealing data within encrypted data or within random data. The message to conceal is encrypted, then used to overwrite part of a much larger block of encrypted data or a block of random data (an unbreakable cipher like the one-time pad generates ciphertexts that look perfectly random without the private key).
11 | Steganography is what really an interesting practise. Imagine the number of steganographic images you have seen till now but you didn't have the slightest idea that it's a cover or what's hiding behind it and you simply ignored it!
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Security/Wireshark.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Wireshark
2 |
3 | Wireshark is an open-source tool for analyzing data packets, as well as helping to profile network traffic. It is used for many reasons such as troubleshooting, security, education and analysis. Since it can also be used for eavesdropping, you must make sure you have permission from the network administrator to run this software, and if it's to be used in an organization, it should be clearly explained within their privacy policy. From data packets we can find out much information, such as the transmit time, destination, protocol type and source of the traffic.
4 |
5 |
6 | ### Key Features
7 |
8 | * Capture live data, save for later to analyze
9 | * Various filters to find exactly what you are looking for from captured data
10 | * Abundance of settings to live capture exactly what you need
11 | * "Sniff" data packets to search for any potential security issues
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Security/honeypot.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## OVERVIEW
2 |
3 | A Honeypot is a network connected computer system which is a trap designed to attract various attackers and deviate them from unauthorised access to information systems.Honeypots are designed in order to engage them,deviate them and collect information regarding the attackers.Honeyspots aim at logging all the activities of the attacker in order to track their location and study their behaviour.They are easy to equip but they contain technology risks which includes firewall penetration,broken encryption methods and failures to detect attack against system that are not honeypot systems.
4 |
5 | ## TYPES OF HONEYPOTS
6 |
7 | Honeypots are of two types namely:
8 |
9 | - Production Honeypots:
10 |
11 | Production Honeypots are used in corporate world in order to collect information about the motives of the intruder and diverting and reducing risk of attacks on overall network.
12 |
13 | - Research Honeypots
14 | Research Honeypots are used by non profit organisations for the purpose of researching the motives of hackers.
15 |
16 | ## SETUP YOUR OWN HONEYPOT:
17 | Upon exploring the world of honeypots we come across a good number of varities which includes Honeyd,kippo and Dionaea.Configuring and installing each of them would be pretty hectic but honeydrive configurs and installs all these honaypots,hence it is discussed below.
18 | HONEYDRIVE:THE HONEYPOT PARADISE
19 | Honeydrive is honeypot paradise.It is a linux distribution which comes with 15 different honeypots preconfigured and a set of more than 30 forensic tools.
20 | 1 – Download HoneyDrive [here](https://sourceforge.net/projects/honeydrive/).
21 | 2 – Double click on the .ova file.
22 | 3 – Now your VirtualBox will start and will automatically install the new virtual machine with the pre-built guest additions.
23 | 4 – Once the installation process is finished, you will have your HoneyDrive up and running.
24 |
25 | Apart from identifying hackers,Honey pot developers are more interested in getting access to minds of hacker which further motivates them build more secure systems.
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Starters/Creating_md_files.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Creating Markdown Files
2 | =======================
3 |
4 | For those of you who are #super# new to coding you might find that there are very simple and common things that just you are just learning about. For me a Markdown file was one that was new to me.
5 |
6 | A markdown file is a type of text file that allows for simple and non-intrusive formatting so that it can be read both as a plain text document and a formatted document.
7 |
8 | To create a .md file open a front end IDE platform like Atom and create a new file with the .md extension. The next step is to familurize yourself with some of the formatting. I found the documentation on this site https://daringfireball.net/projects/markdown/basics. An example of some of the formatting can be seen in a text editor below.
9 |
10 | Best of Luck, and keep on coding!
11 |
12 |
13 | ### examples below ###
14 | credit goes to daringfireball.net
15 |
16 | A First Level Header
17 | ====================
18 |
19 | A Second Level Header
20 | ---------------------
21 |
22 | Now is the time for all good men to come to
23 | the aid of their country. This is just a
24 | regular paragraph.
25 |
26 | The quick brown fox jumped over the lazy
27 | dog's back.
28 |
29 | ### Header 3
30 |
31 | > This is a blockquote.
32 | >
33 | > This is the second paragraph in the blockquote.
34 | >
35 | > ## This is an H2 in a blockquote
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Starters/Vanilla_js.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Overview:
2 | The term Vanilla in english is termed as *"anything having no special or extra features"*. Vanilla javascript is basically plain old JavaScript. It's a fast and lightweight framework, which enables one to build incredible and powerful web applications. It is a framework which makes use of JavaScript without any libraries but it sacrifices code legibility and features in order to achieve better performance and simplicity.
3 |
4 | #### When should you use Vanilla JavaScript?
5 | Vanilla JavaScript is suitable for simple web applications or [static websites](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Static_web_page).
6 | #### How to get started using Vanilla Javascript:
7 | In order to use JavaScript, you'll need to create a HTML file, and include a script tag in the body of your document:
8 | ``
9 |
10 | **Your HTML file should look a little something like this:**
11 | ```html
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 | ```
24 | **Here is an example JavaScript file to get you started (place this in the same folder as your HTML file (name it vanilla.js):**
25 | This script will simply generates a random number when a button is pressed.
26 | ```js
27 | // Save our target element to the variable 'textbox'.
28 | const textbox = document.getElementById('random');
29 |
30 | // Defines our function to edit the textbox.
31 | function generateRandomNumber() {
32 | // This changes the 'inner text' of the element.
33 | textbox.innerText = Math.floor(Math.random() * 10);
34 |
35 | /* Math.floor will round the number, while Math.random will
36 | generate a number between 0 and 1, so we multiply it by 10 to
37 | get a bigger number that is less than or equal to 10. */
38 | }
39 | ```
40 | #### Resources to learn Vanilla JavaScript:
41 | **Interactive:**
42 | [Codecademy - JavaScript Courses](https://www.codecademy.com/catalog/language/javascript)
43 | **Articles:**
44 | [MDN Web Docs - JavaScript Basics](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Learn/Getting_started_with_the_web/JavaScript_basics)
45 | [w3schools - JavaScript Tutorial](https://www.w3schools.com/js/)
46 | [Best Resources to Learn Vanilla JavaScript from Scratch - Jake Rocheleau](https://designmodo.com/learn-vanilla-javascript/)
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Testing/testing_pyramid.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | **The Testing Pyramid**
2 |
3 | Testing is always going to be an important part of any project, whether your team actually has any QA staff or not. Following the concept of the testing pyramid will help your team to find defects deep in the code sooner.
4 |
5 | The concept of the testing pyramid from a QA perspective is that you want to test as far down the pyramid as you can. The further down the pyramid you start testing, the deeper into the code you are.
6 |
7 | **The Bottom of the Pyramid**
8 |
9 | This would be where developers (or testers who can program and understand the code) would write unit tests for the code. This is testing the code at its deepest level.
10 |
11 | **The Middle of the Pyramid**
12 |
13 | This would be where you can test at an API level using any tool of your choice,such as Postman. This is testing the integration, making sure the API integration works as expected, etc. This is typically done by testers.
14 |
15 | **The Top of the Pyramid**
16 |
17 | This would be where you would be testing the UI of an application. This would also where you can do UX tests, testing the application as a user would. At this level you can do a mix of manual testing and automation for any area that makes sense.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/UX_design/An-Introduction-To-AntiPatterns.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # AntiPatterns
2 |
3 | Introduction
4 |
5 | Frequently while learning software engineering, you will hear many terms that may be new to you. One term that will be used is AntiPatterns. An AntiPattern is a solution to a problem that is considered counterproductive. That is not to say it is not a solution, but rather a better solution exists. Being able to identify AntiPatterns will aide a developer in creating efficient and flexible code.
6 |
7 |
8 | ## An Example
9 | **Scenario**: A recent release brought a bug to the surface. Management is very displeased and demands immediate action.
10 | **Response**: You identify the issue and apply a *quick-fix solution* that is rather *inflexible*. Your change will not allow for changes within that block to occur without causing further issues.
11 |
12 |
13 | This is an example of the BandAid AntiPattern. The developer applies the quickest and easiest fix, rather than exploring to find the best solution. This will most likely result in recusion. To avoid falling victim to the BandAid, the developer should explore possible solutions and find the most flexible and least dependent solution possible. There are many AntiPatterns and they should be an area of study for continuous improvement. There are even language specific AntiPatterns.
14 |
15 |
16 | ### [Click Here](http://wiki.c2.com/?AntiPatternsCatalog) to review a list of AntiPatterns.
17 |
18 |
19 | ### Further Readings on the subject of AntiPatterns:
20 | [https://sourcemaking.com/antipatterns/software-development-antipatterns](https://sourcemaking.com/antipatterns/software-development-antipatterns)
21 | [https://sahandsaba.com/nine-anti-patterns-every-programmer-should-be-aware-of-with-examples.html](https://sahandsaba.com/nine-anti-patterns-every-programmer-should-be-aware-of-with-examples.html)
22 |
23 |
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/UX_design/Fitts'_Law.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Fitts' Law
2 |
3 | Fitts' Law is a scientific model that predicts the speed of the act of pointing, whether it be with a finger or with a point device such as a mouse. Specifically, it states that the time to move from where a person is pointing to a target location is a function of the ratio of the distance to the target and the target's width.
4 |
5 | While Fitts' Law was developed in the mid-1950's, it is used significantly in modern UI/UX design. In this application, it encourages neutral placement and shorter distances between commonly used elements as well as appropriate sizing of said elements.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/UX_design/Hick's_Law.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Hick's Law
2 |
3 | Hick's Law is a principle of design that states that the time for a human to take a decision is based on the number of possibilities it has, and increases logarithmically.
4 | It is part of a study on Computer-Human interaction, where we study human patterns and actions to have a better understanding of the end user when building software.
5 | The importance of the field is rising nowadays, with software developers having in mind the importance of delivering the software the user needs, and understanding what he needs is often really hard.
6 |
7 | Hick's Law has some exceptions and can be studied on differente IQ's and stimulus to differente results, but for the most part, it is a important principle of design.
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Version_Control/Git and PR.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Git has been one of the most famous Version control application in this century.
2 | It works like taking screenshot of project which you are working on and storing it like every version control.
3 | Git works on local machine and remote servers like github.
4 | we follow a particular protocol in using git
5 | **Pull requests**
6 | (Basic)(working only in master branch)
7 | 1. It is a kind of request you make to the owner of the project when you have contributed to his/her project and want that contribution to be shown.
8 | First,we fork the repository.
9 | Second we clone repository into local systems.
10 | Then we configure git into our local system using config commands(assuming git is already installed).
11 | Next we add the file using 'git add' command.
12 | We then make our desirable changes and then we 'commit' it .
13 | then we push the file back to our remote server using 'git push origin master',where origin is repository name and master is the master branch.
14 | Then we send a pull request to the owner of the project.
15 |
16 | SLOC
17 | git config –global user.email “[email address]”
18 | git config –global user.name “[name]”
19 | git clone https://github.com/the-ethan-hunt/first-timers-guide.git
20 | git add "filename"
21 | git commit -m “[ Type in the commit message]”
22 | git push
23 |
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Version_Control/Git.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Git
2 |
3 | [Git](https://git-scm.com/) is a free and open source version control system. It tracks changes to specific versions of code so that previous versions can be recalled and reinstated at a later date. It also makes it easy for multiple people to work on the same files without the risk of overwriting others’ work or losing files.
4 |
5 | Git runs at the command line or through a git interface on your local machine. It keeps track of and maintains files in something called a ***repository*** or ***repo***. A key feature of Git is the ability to make branches. A ***branch*** is a separate copy of the source code that allows a user to try new features and implement code without directly affecting the master branch. When a branch has successfully implemented a revision, it can be ***merged*** back into the master branch. The revision is then officially a part of the original project.
6 |
7 | There are also Repository Management Services which store and share Git repositories online. The most popular are:
8 | * [GitHub](/guides/Version_Control/GitHub.md)
9 | * [Bitbucket](https://bitbucket.org/)
10 | * [GitLab](https://about.gitlab.com/)
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Version_Control/GitHub.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # GitHub
2 |
3 | [GitHub](https://github.com/) is the most popular hosting and version control system for source code and [Git](/guides/Version_Control/Git.md) repositories online. In addition to features of Git such as branching and merging, GitHub also provides its own unique features. Some of these features include:
4 | * Issue Tracking
5 | * Documentation and Wikis
6 | * Detailed Code Reviews and Commit History
7 | * Insights: Special analytics detailing project traffic, trends, etc.
8 |
9 | GitHub can be used in collaboration with Git on your local machine, through its graphical user interface [GitHub Desktop]( https://desktop.github.com/), or entirely through the browser. It offers both private and public repositories. A private repository is a safe way to back-up your files, and a public repository opens up your code to be reviewed by the community. Making your source code public on GitHub allows for people from all over the world to collaborate on your project. As a result, GitHub is frequently used to host open-source projects.
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Version_Control/GitHubSSH.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # GitHub Secure Shell
2 |
3 | #### What is SSH?
4 |
5 | _Secure Shell (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network._ [wikipedia][1]
6 |
7 | **In a nutshell, SSH protocol allows connecting to and authenticating remote servers and services. This protocol requires ssh keys which facilitates connecting to Github without providing username and password credentials.**
8 |
9 |
10 | #### Do I have existing SSH keys?
11 | It is always good practice to look before you leap.
12 |
13 | ##### To check:
14 | At the command line type the following:
15 | ```
16 | $ ls -al ~/.ssh
17 | ```
18 | Note: **DO NOT ENTER** __*$*__ it simply signifies that you are at the command line.
19 |
20 | The above lists the files in a directory named **.ssh**, if they exist. The following are default file names:
21 |
22 | > id_dsa.pub
23 | id_ecdsa.pub
24 | id_ed25519.pub
25 | id_rsa.pub
26 |
27 | #### Keys to the kingdom
28 | 1. Execute this command adding your Github **email address** to **create a key pair**:
29 |
30 | `$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_email@example.com"
31 | `
32 |
33 | 2. Press **Enter** to save the file to the default location when prompted. You have the option to save the file elsewhere.
34 |
35 | 3. Type in a **passphrase** or **opt out** by leaving it empty when prompted.
36 |
37 | 4. Confirm you **passphrase**.
38 |
39 | #### Add keys via ssh-agent
40 | 1. `
41 | $ eval "$(ssh-agent -s)" `
42 |
43 | You should see something like:
44 |
45 | `Agent pid xxxxx`
46 |
47 | That starts a **ssh-agent** background process.
48 |
49 | 2. If your OS is _macOS Sierra 10.12.2_ or later update your **_~/.ssh/config_** file with the following:
50 |
51 | ```
52 | Host *
53 | AddKeysToAgent yes
54 | UseKeychain yes
55 | IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa
56 | ```
57 | See [GitHub][2] for more details.
58 |
59 | 3. Add keys and store phrase to key chain.
60 | ```
61 | $ ssh-add -K ~/.ssh/id_rsa
62 | ```
63 | If you get an error see [ssh-add:illegal option -K.][3]
64 |
65 |
66 | #### Add SSH key to GitHub
67 | 1. View the contents of your public key.
68 |
69 | ```
70 | $ cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
71 | ```
72 | 2. **Copy** the entire **key**.
73 |
74 | 3. **Login** in to **GitHub**.
75 |
76 | 4. Click on you **profile photo**.
77 |
78 | 5. Go to **settings**.
79 |
80 | 6. In the **left sidebar** click **SSH and GPG Keys**.
81 |
82 | 7. Choose **New SSH key** or **Add SSH key**.
83 |
84 | 8. Use the **_Title_** field to name your key.
85 |
86 | 9. **Paste** the key into the **_Key_** field.
87 |
88 | 10. Click **ADD SSH Key**.
89 |
90 | 11. **Confirm** your **password** if required.
91 |
92 | You now have a secure **SSH** connection. You can forget about having to supply pesky username and password credentials.
93 |
94 | WORTHY NOTE: The **https** protocol is less secure than SSH but, it is easier to configure and less likely to be blocked by a firewall or proxy. This means that the remote **clone URLs** work everywhere.
95 |
96 |
97 | [1]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secure_Shell
98 | [2]:https://help.github.com/articles/generating-a-new-ssh-key-and-adding-it-to-the-ssh-agent/
99 | [3]:https://help.github.com/articles/error-ssh-add-illegal-option-k/
100 |
101 | # Resources
102 | [WIkipedia - Secure Shell](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secure_Shell)
103 |
104 | [GitHub - Generate SSH Key](https://help.github.com/articles/generating-a-new-ssh-key-and-adding-it-to-the-ssh-agent/)
105 |
106 | [GitHub - option -K Error](https://help.github.com/articles/error-ssh-add-illegal-option-k/)
107 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Version_Control/Mercurial.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Mercurial
2 | Mercurial is one of the distributed version control system available today.If you are not aware of what a distributed version control is refer to [this](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Distributed_version_control). The most commonly used Micrsoft Windows uses it. It is also used in developing various other linux distributions including FreeBSD and even macOS.
3 |
4 | ## Installation
5 | Mercurial is available for all platforms. To download it visit their official download [page](https://www.mercurial-scm.org/downloads). It provides all the necessary information and guide for download and installion.
6 |
7 | ## Where shall I learn mercurial?
8 | The best resource to learn is the official [guide](https://www.mercurial-scm.org/guide). It will take you as a noob and will you make you pro.
9 |
10 | ## Features
11 | * design goals include high performance and scalability,
12 | * robust handling of both plain text and binary files
13 | * advanced branching and merging capabilities
14 | * easy transition from earlier version control e.g SVN
15 |
16 | ## More stuff to grasp
17 | Mercurial is available both in command line and as well graphical user interface.For GUI you need to download various extensions.[TortoiseHg](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TortoiseHg) is one of the popularly used extensions while there are many others IDE as well.
18 |
19 | ## Git vs Mercurial
20 | ### Pros of git
21 | 1. git stores commits using an commit hash while mercurial does maintain only logs appended in the disk thus the unique commit hash in git being immutable results in a cleaner history.
22 | 2. git provides more safety feature to prevent destructive actions when one tries to rewrite history.
23 | 3. With git it is easier to go back to earlier commits and do relevant changes than mercurial.
24 | 4. Branching in git is much better and killer feature as we don't need to clone the repo again for each new branch as in case of mercurial.
25 | 5. No staging area in mercurial although the feature is available in the form of extensions but it is not fully fledged like that of git
26 | and lot more...
27 |
28 | For more informaiton you can visit this [page](https://www.atlassian.com/blog/git/git-vs-mercurial-why-git)
29 |
30 | ## Want more resources ??
31 | * Mercurial Extensions - https://www.mercurial-scm.org/wiki/UsingExtensions
32 | * Mercurial Tutorial - https://www.mercurial-scm.org/wiki/Tutorial
33 |
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Visual_design/Architectural_Pattern/MVC.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## What is MVC?
2 |
3 | [**MVC**][1] is an architectural pattern commonly used for developing user interfaces that divides an application into three components viz **Model**, **View** & **Controller**.
4 |
5 | 
6 |
7 | - **Model** represents business logic & maintains the data of the application.
8 | - **View** displays the application’s user interface using the model data.
9 | - **Controller** handles the user request & renders the appropriate view with the model data as a response.
10 |
11 | ## So... What MVC really is!
12 |
13 | Let us consider implementing MVC in Game Development. So, how about designing a game where 2 players fight in a combat where each one has a **Strike** & a **Life** bar. Now, if one player attacks, then the opponent's **Life** decrements by 1 unit. When **Life** equals 0, the player dies! The question is how do we develop this simple game with MVC paradigm.
14 |
15 | Now, almost every game has three basic elements -
16 | - **State** (Model?)
17 | - **Interface** (View?)
18 | - **Gameplay** (Controller?)
19 |
20 | It seems intuitive enough that for each iteration of the game a state must be preserved. Also, when we talk about the state it means a data-model. Gameplay enables specific ways in which players interact with a game & that can be addressed by a controller object which updates the interface for every state as present in the model. By the way, the game view takes care of the visual interface.
21 |
22 | Let us consider, **Model** holds an initial state in which both players' **Strike** & **Life** counts are equal to 0 & 10 respectively!
23 | - 1st Iteration: Player1 strikes Player2, now **Controller** uses the **Model** object to alter the state of the game in which Player1 has **Strike** count 1 & Player2 has **Life** count 9! Ultimately **View** updates the UI with this newly generated data from the **Model** with the help of **Controller**.
24 | - 2nd Iteration: ...
25 | - 3rd Iteration: ...
26 | .
27 | .
28 | .
29 | And the game ends with having **Controller** either reset the game or exit it depending on user request. (**SPOILER**: PLayer2 Wins!)
30 |
31 | This was nothing but a trivial example as for how to implement MVC architecture into an application!
32 |
33 | ## But... Why MVC?
34 |
35 | The fundamental reason for adopting MVC principles into a development workflow is to have **seperation of concerns**. Well, during traditional approach of programming, the code was written into a single file which creates lack of maintainability, testability as well as scalability of the application. With MVC, you create applications that separate the different aspects of the application while providing a loose coupling between these elements.
36 |
37 | ###### Pros
38 |
39 | MVC encourages simultaneous development from multiple developers because of the separation of responsibilities which in turn increases the scalability of the product. The very nature of the MVC architecture is such that there is low coupling among models, views or controllers.
40 |
41 | ###### Cons
42 |
43 | MVC design navigation can be complex because it introduces new layers of abstraction. So, decomposing a feature into three components causes scattering. Thus, requiring developers to maintain the consistency of multiple representations at once!
44 |
45 | [1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Model%E2%80%93view%E2%80%93controller
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Visual_design/Design_Language/Material_Design.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Quantum Paper
2 |
3 | [**Material Design**][1] is a design language developed by Google & inspired by the physical world and its textures, including how they reflect light and cast shadows. Material surfaces reimagine the mediums of paper and ink. It represents visual principles of good design with the innovation of technology and science. While developing this design, it was codenamed '**Quantum Paper**'.
4 |
5 | > Material Design is a unified system that combines theory, resources, and tools for crafting digital experiences.
6 | Here, **Material** is the metaphor! Designers from Google refer to it as 'Quantum Paper'.
7 |
8 | 
9 |
10 | Google announced **Material Design** on June 25, 2014, at the [Google I/O][2] conference. Expanding upon the 'card' motifs that debuted in Google Now, **Material Design** makes more liberal use of grid-based layouts, responsive animations and transitions, padding, and depth effects such as lighting and shadows. Google developed Material Design to create a consistent visual language for all of their products viz. Gmail, Google Drive, Youtube, Hangouts, Photos, etc.
11 |
12 | # Design Principles
13 |
14 | The design philosophy simply began with creating a robust, minimal UI that utilises both **space** and **time** as elements of design. The history of GUI’s has been one of trying to replicate something recognisable to us in the physical world & Material Design simply builds on top of that!
15 |
16 | 
17 |
18 | ###### *Space*
19 |
20 | - Each element occupies its own space on the **z axis**, giving us the impression that they actually exist beyond the pane of glass, inside the device. Like little sheets of paper sliding over each other. Material Design is not re-inventing the wheel. Instead it simply provides a set of rules that govern the spaces in which elements can live.
21 |
22 | 
23 |
24 | ###### *Time*
25 |
26 | - Humans don’t just experience states of a device, they experience the transition between states too. A sudden event would be jarring but only adding animation won't do the job. It’s not that simple. Animation needs to feel real as well as authentic.
27 |
28 | # Implementation
29 |
30 | The best way to implement this elegant, seamless design is to choose a framework that supports it so as to add a layer of abstraction & make things simple! Let's talk about web apps:
31 |
32 | > [Materialize][3] is a responsive front-end component library similar to Bootstrap. It offers everything that Bootstrap has to offer, but the difference is that Materialize follows material design principles.
33 |
34 | Here’s a list of features that Materialize offers:
35 |
36 | - Grid Based Layout
37 | - Tables
38 | - Badges, Buttons, Breadcrumbs
39 | - Carousel, Cards, Chips, Collections, Colors
40 | - Footer, Forms
41 | - Modals
42 | - Navbar
43 | - Shadow
44 | - And a lot more!
45 |
46 | ### When To Use Material Design?
47 |
48 | There's no right or wrong scenario for applying the relevant design principles. It solely depends on the product that you're building. However, Material design only becomes constricting when designers fail to stay true to their own brands. Use the concepts to enhance your own unique design style to get the most benefit effective digital design philosophy.
49 |
50 | For more info on Material Design, visit [here][4]. You can also check the [video][5] by Google Designers team!
51 |
52 | ------------
53 |
54 | [1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Material_Design
55 | [2]: https://www.google.com/events/io
56 | [3]: https://materializecss.com/
57 | [4]: https://material.io
58 | [5]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rrT6v5sOwJg
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Visual_design/Wireframing/Justinmind.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Justinmind
2 |
3 | Justinmind is a high-fidelity wireframing/prototyping tool that allows developers to plan what their mobile app/website will look like. Unlike low-fidelity tools, Justinmind allows for the creation of a wireframe that will look, feel and operate just like the final product. It is useful for beginners as it does not require any coding knowledge, and is as simple as drag-and-drop whichever feature to the spot on the design you would like it to go.
4 |
5 |
6 | ### Key Features
7 |
8 | * Widget libraries and the ability to download more
9 | * Share your wireframe via your account
10 | * Give feedback on shared wireframes
11 | * Zero coding knowledge required
12 | * Mobile gesture compatible (Swipe left or right, tap the screen etc)
13 | * Test your created wireframe on your own device
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Visual_design/Wireframing/Wireframing.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Wireframing
2 |
3 | Wireframing is a process undertaken during the early development stages of a website and/or mobile application and is basically a blueprint, enabling a developer to plan what their creation will look like. It will include all the various content and features the page will have, and this is usually done after the user requirements have been gathered and analyzed.
4 |
5 | ## Types of Wireframe
6 |
7 | ### Low-fidelity
8 |
9 | These are both quick and easy to create, and can be edited/updated without much issue as they are kept relatively simple and straightforward. This can be done with pen and paper.
10 |
11 | ### High-fidelity
12 |
13 | These are more representative of how the final website/app will look and are more detailed than low-fidelity wireframes. They also allow for interactive functions to be included, such as menu buttons and linking to other pages. There are various tools that can be used to create these, such as Justinmind.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Visual_design/color_theory/color_theory.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Overview
2 |
3 | Color theory is a combination of science and art of color. It explains how humans perceive color, how colors mix, match or clash and various ways in which colors can be classified and used.
4 |
5 | # RGB Color Model
6 | This model uses the primary colors red,green and blue in different proportions to create all the necessary colors.When you mix red,green and blue colors to their full extent i.e 100% the resultant color is white and when they are mixed to their lowest degree the resultant color is black. So basically you start with black and as you add lights of various colors you get white. Thus RGB color model is also called as additive color model. Colors are much more vibrant in case of rgb as compared to cmyk.
7 |
8 | # CMYK Color Model
9 |
10 | This model uses the colors cyan, magenta, yellow and black in various amounts to create all of the necessary colors. When you mix cyan magenta and yellow to their full extent i.e 100% the resultant color is black thus as you remove or subtract (absorb) various proportions of these colors you get a variety of different colors ,thus CMYK model is also called as subtractive color model .
11 |
12 | # HEX CODE
13 |
14 | Colors can also be represented using hexadecimal values also called as hex code.The code starts with a hash sign (#) and is followed by six hex values or three hex value pairs for example #AFD645. You can get hex codes for various colors [here]("https://htmlcolorcodes.com/"). Hex codes are generally used for html pages.
15 |
16 | # COLOR WHEEL
17 |
18 | A color wheel primarily consists of 6 parts. There are three primary colors red,blue and yellow.Colors formed by mixing primary colors are called secondary colors .
19 |
20 | - Red + Yellow = Orange (thus orange goes between red and yellow in the color wheel)
21 | - Blue + Yellow = Green (thus green goes between blue and yellow in the color wheel)
22 | - Blue + Red = Purple (thus purple goes between blue and red in the color wheel)
23 |
24 | Thus each primary color has a secondary color to compliment it and as explained above they are represented across each other on the color wheel.
25 |
26 | Colors in the upper part of the wheel are called as warm colors (red,orange,yellow) and can be used to represent sun or fire similarly colors in the lower part of the wheel are called as cool colors (blue,green,purple)
27 |
28 | warm and cool colors are also used to represent feelings,for example to express anger one can use warm colors and to express sadness one can use cool colors.
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Web_Containers/Apache_Tomcat.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Apache Tomcat
2 |
3 | ## What is Tomcat ?
4 | If you are new to Java programming, you might have heard about Tomcat, but what exactly does it mean? After learning core Java, if you want to go into the business world, if you want to work on websites or suppose you want to make your own web application using Java, then of course you have to work on servlets. What is a servlet? If you are familiar with websites or the web world you must have heard about HTTP(hyper text transfer protocol). If you want to provide a web service or any static content using HTML or maybe you just want to send data from a server to a client, you need a server and that server is HTTP. So if you want to make a static website you need a HTTP server but to make it dynamic we need servlets. So we use HTTP only for fetching data but if you want to send dynamic data then you need a servlet. Thus, we need a HTTP server where you will run your servlets. Tomcat will combine your HTTP server and servlet to give you one server. Effectively, Tomcat is a HTTP server and a servlet container. Tomcat has got Apache license and is handled by Apache Software Foundation(ASF). Tomcat is not the only server available in the market there are other servers available as well.
5 |
6 | Tomcat is the result of an open collaboration of developers and is available from the Apache website in both binary and source versions. Tomcat can be used as either a standalone product with its own internal web server or together with other web servers, including Apache, Netscape Enterprise Server, Microsoft Internet Information Server (IIS) and Microsoft Personal Web Server. Tomcat requires a Java Runtime Enterprise Environment that conforms to JRE 1.1 or later.
7 |
8 |
9 | ## Useful Links
10 | - [Apache Tomcat official Website](http://tomcat.apache.org/)
11 | - [Steps to setup and install Apache Tomcat Server](https://crunchify.com/step-by-step-guide-to-setup-and-install-apache-tomcat-server-in-eclipse-development-environment-ide/)
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Web_Containers/GlassFish.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Sun Microsystem had a plan to open source its application server and that plan was implemented through Project GlassFish, which was announced at JavaOne 2005. Initially Sun and Oracle Corporation became the main source code donors for this project. As a result of this effort, we have a freely available, open source, Java EE-compatible application server that is quickly growing in popularity.
2 |
3 | GlassFish is an Application Server which can also be used as a Web Server(Http Server). A web Server involves handling HTTP requests (usually from browsers). It is different from the popular software Apache Tomcat which is a Servlet Container meaning that it can handle servlets & JSP code. An Application Server GlassFish in this case means that it can manage Java EE applications, usually both servlet/JavaServerPages(JSP) and EJBs(Enterprise JavaBeans). You can use GlassFish for efficient Java EE enterprise applications.
4 |
5 | Glassfish can be utilized under the the folowing licenses a. Common Development & Distribution(CCDL)
6 | b. GNU General public license(GPL)
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Web_Frameworks/Angular.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Angular
2 |
3 | Angular is a Javascript framework that is used to build client side applications. It is Developed & Maintained by Google.
4 | It is mainly used for Single Page Application SPAs, where the whole page doesn't reload again and again to generate the view.
5 | Angular make use of Typescript language, which is a superscript of javascript (.ts).
6 | As per now the latest version is Angular6. Google team has decided to upgrade the version twice a year.
7 |
8 | ### Why Angular?
9 | * Angular follows modular approach.
10 | * It uses making of components which can be reusable.
11 | * Angular allow Quicker and fast Development (using routings, templates and other features)
12 | * Angular can help in unit testing of code easily.
13 |
14 | #### Prerequisites
15 | HTML, CSS , JS, TypeScript
16 |
17 | ### Angular Installation
18 | For any Angular Project You will need few things installed on your machine beforehand. These are:-
19 | 1. Node.js
20 | 1. Npm
21 | 1. Angular CLI - It is a command line interface which can be used to perform different operations
22 | * To install angular CLI write- `npm install -g @angular/cli`
23 |
24 | ### Create Angular Project
25 | Follow these commands in you terminal
26 | * `ng new my_app_name` // it creates all the neccessary files for angular project.
27 | * `cd my_app_name`
28 | * `ng serve` // runs the server default on http://localhost:4200
29 |
30 |
31 | #### Building Blocks
32 | There are few main building blocks in Angular.
33 | * **Modules** -
34 | These actually seperates our application logic and are used by app to manage feature area.
35 | There is atleast one module in every angular app - rootModule called as AppModule.
36 |
37 | * **Components** -
38 | Components are the class which interacts with templates and generate logic or data for the view.
39 | There is atleast one component in Angular - AppComponent
40 | * **Templates** -
41 | Templates are used by components to render the output on browser. It Defines the UI with HTML
42 | * **Metadata** -
43 | It tells how to process a class depending on decorators.
44 | Decorators are defined by angular they starts with `@` . They describe behaviour of the class.
45 | e.g @Component -> it means this class will be a component
46 | * **Data Binding** -
47 | Data Binding is used by component and templates to exchange data.
48 | If in template anywhere the value of a variable(firstName) changes, it will automatically detected by component and vice-versa.
49 | * **Directives** -
50 | These are angular attributes used for rendering in a specific way.
51 | There are some predefined directives like ngIf, ngClass.
52 | E.g If you want to loop through array use ngFor directive
53 | * **Services** -
54 | These seperate business logic of Application. eg- fetch data from server.
55 | It's good practice to maintain business logic in service class.
56 | * **Dependency Injection** -
57 | They are used by components to inject services.
58 | It is done with the use of a constructor.
59 | Before creating service, we have to specify that this service is injectable with decorator `@Injectable()`
60 |
61 | Learning these will help you to get a firm understanding of angular.
62 | To know more about them Follow the link https://angular.io/guide/architecture
63 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Web_Frameworks/CakePHP.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # CakePHP
2 |
3 | CakePHP is a MVC Framework written in PHP. The major difference between 3.0 and 2.0 version of CakePHP is 3.0 is object oriented (uses class and objects).
4 | It has lots of features which can be used in fast development with less code and builds complex applications faster than plain PHP.
5 |
6 | It need Composer which is a Dependency Manager for PHP. Install **Composer** first in your desired directory with command-
7 |
8 | php -r "copy('https://getcomposer.org/installer', 'composer-setup.php');"
9 |
10 | php -r "if (hash_file('SHA384', 'composer-setup.php') === '544e09ee996cdf60ece3804abc52599c22b1f40f4323403c44d44fdfdd586475ca9813a858088ffbc1f233e9b180f061') { echo 'Installer verified'; } else { echo 'Installer corrupt'; unlink('composer-setup.php'); } echo PHP_EOL;"
11 |
12 | php composer-setup.php
13 |
14 | Now You have composer.phar in your directory.
15 |
16 | ### CakePHP Installation
17 |
18 | Make sure you have Apache Server, PhP 7.2 , and *mbstring PHP extension , intl PHP extension* are enabled in php.ini file.
19 |
20 | Run this command -
21 | php composer.phar create-project --prefer-dist cakephp/app my_app_name
22 |
23 | It will create lots of files and folders of cakephp framework,in vendor folder one is autoload.php which automatically loads all the files of framework.
24 |
25 |
26 | ### Files/Directory Structure
27 |
28 | * bin - it handles console commands
29 | * config - configuration of our application
30 | * app.php - setup database , email configuration.
31 | * bootstrap.php - components of our app
32 | * routes.php - specifies the routes in our app
33 | * logs - contains logs file generated by app.
34 | * plugins - it has plugins stored of the framwork.
35 | * src - It is the main directory. It has Controller, Model , View , (Templates) where we will write our code most of the time.
36 | * vendor - this is created by composer which have framework files.
37 | * webroot - This is the root folder. It has css, img, js files.
38 |
39 | The webServer first get into .htaccess which makes flow of program to webroot folder from there it spread to other part of our app.
40 |
41 | ### To Run Project
42 |
43 | change directory inside your App folder
44 |
45 | run command - bin/cake server
46 |
47 | That's it. Your Server is ready on localhost:8765
48 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Web_Frameworks/Drupal.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Drupal
2 | [Drupal](https://www.drupal.org/home) is a content management system which supports as a backend service in websites. It is a framework written in php and provides a support to millions of people and organizations to build and maintain their websites.The best part of it is that it is free and open source with a rich and supportive community.Many top businesses and government organizations use Drupal, like Red Cross, Harvard, The Economist, BBC, NBC News, Whole Foods, Cisco, Twitter, and many more.We use it everyday without being aware of it. It is a product which is released under [GNU Public licence](https://www.drupal.org/about/licensing).The github repo of the drupal can be found [here](https://github.com/drupal).You can visit and see the source code and feel free to use it.
3 |
4 | # Installation
5 | Drupal can be easily downloaded from its [official website](https://www.drupal.org/download). It is available for all platforms.Rather than reinventing the wheel of providing instructions to download ,you can simply visit the above link and download it.
6 |
7 | # Lets Learn Drupal
8 | Drupal provides various training programs to learn and get [certified](https://www.acquia.com/customer-success/learning-services/acquia-certification-program-overview).There are various programs available you can visit the [website](https://www.drupal.org/training) for more information.The latest version is drupal 8. It also has a rich [documentation](https://www.drupal.org/docs/8) for everyone and it is very helpful for self learners to get familiarised with it in an easy go.
9 |
10 | # Why Drupal ?
11 | * Provide simple Web-based tools so that users can publish content directly to the website
12 | * Smoothen and boost the process even the website becomes heavy.
13 | * Control content author. As a web manager, you will able to control what is created, how the content is edited, formatted and reviewed.
14 |
15 | # Uses of Drupal
16 | * Personal or corporate Web sites
17 | * Blogs, art, portfolio, music, multimedia sites
18 | * Forums
19 | * E-commerce sites
20 | * Social networking sites
21 | and a lot more ...
22 |
23 | # Some live examples
24 | * Sapanarts: http://www.sapanarts.org/
25 | * Twitter developer community: http://dev.twitter.com
26 | * Zynga https://zynga.com/
27 | etc
28 |
29 | # References
30 | * https://www.drupal.org/docs/8
31 | * https://www.weebpal.com/blog/what-is-drupal-and-why-is-drupal-right-choice
32 | * https://drupalize.me/
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Web_Frameworks/Flask.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Flask
2 | flask is modern light weight web framework which is written in python.Since it does not require any tools or libraries (external) therefore it is also termed as microframework. It does not have its own components therefore it is light weight. By component we can understand in terms of data abstraction layer,form validation etc which you can see in Django if you are a hard code django lover till now .The core functionality is available from pre-existing libraries but if we want to extend the functionality we can easily do so with the help of extensions.There are many extensions which are available to add them to core flask ,few of them including form validaton,Object relational mappers etc.
3 | ## Installation
4 | To install flask just open up your terminal or command prompt (in case of windows users) and type the following command
5 | ```python
6 | pip install Flask
7 | ```
8 | If you want to experience and hack the latest release you can just head over to this [link](https://pypi.org/project/Flask/1.0.2/)
9 | To update your package just type the following command
10 | ```python
11 | pip install -U Flask
12 | ```
13 | The github repo of the flask can be found [here](https://github.com/pallets/flask).Feel free to contribute if you are interested.
14 | The flask [documentation](http://flask.pocoo.org/docs/1.0/) is well maintained and if you are looking for a guide to learn it then this is the best start.
15 | ## Some more stuffs to grab
16 | * Advantages of using extensions lies behind the fact that these third party extensions are continuously updated rather than core libraries
17 | * Scaling of complex applications is quick and easy in flask
18 | * It is based on two projects Jinja and Werkzeug
19 | ## Flask vs Django
20 | To choose Flask over Django or vice versa ,you need to be pretty familiar about them a little more ,so rather than reinventing the wheel you can visit the [link](https://www.codementor.io/garethdwyer/flask-vs-django-why-flask-might-be-better-4xs7mdf8v#quick-comparison) and learn more about them and after reading this you can decide which one to choose for your next web application.
21 | ## References
22 | * https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flask_(web_framework)
23 | * http://flask.pocoo.org/
24 |
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Web_Frameworks/Gitlab,Flask,Heroku.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Integrating GitLab CI/CD, Flask, and Heroku
2 |
3 | This tutorial assumes you already have a working flask application within a virtual environment and have your code hosted on GitLab. Also ensure you have Gunicorn installed. You can install it from ```pip install gunicorn```.
4 |
5 | ## Getting Ready
6 |
7 | Run ```pip freeze > requirements.txt``` to grab all the requirements for running your application.
8 |
9 | Create a ```Procfile``` file. Inside, place the following code ```web: gunicorn :``` where app-name is usually “app”.
10 |
11 | Push everything to GitLab.
12 |
13 | ## Connecting Everything
14 |
15 | Create a new Heroku application. Using a short name will make later steps easier.
16 |
17 | Create a new file in your app root called ```.gitlab-ci.yaml```.
18 |
19 | Here is a cookie-cutter example of a GitLab CI/CD config:
20 | ```yaml
21 | [app.py file name]:
22 | script:
23 | — apt-get update -qy
24 | — apt-get install -y python-dev python-pip
25 | — pip install -r requirements.txt
26 |
27 | production:
28 | type: deploy
29 | script:
30 | — apt-get update -qy
31 | — apt-get install -y ruby-dev
32 | — gem install dpl
33 | — dpl — provider=heroku — app=[Heroku App Name] — api-key=$HEROKU_SECRET_KEY
34 | only:
35 | — master
36 | ```
37 |
38 | Now swap out ```[app.py file name]``` with your file name and ```[Heroku App Name]``` with the name of your heroku app.
39 |
40 | To set the HEROKU_SECRET_KEY,
41 | * Get your Heroku API key from https://dashboard.heroku.com/account.
42 |
43 | * Within GitLab, go to **Settings → CI / CD → Secret variables**.
44 |
45 | * Create a new variable and set the **Variable key** to **HEROKU_SECRET_KEY** and the **Variable Value** to your **Heroku API Key**.
46 |
47 | * Set the protected switch to **ON**.
48 |
49 | Push the changes to GitLab.
50 |
51 | ## Conclusion
52 |
53 | Now that everything is all setup, head over to your Heroku app URL and enjoy the fruits of your labour.
54 |
55 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Web_Frameworks/Grails.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Grails
2 | Grails is a full stack MVC framework for building web application on the java platform.
3 | Grails is an open source and is maintained by spring source and later by VMware.
4 |
5 | Grails itself has scripting language that ties all these pieces together, called Groovy.
6 | Groovy is java compatible language (similar to java) that gives java many modern features of python, ruby, Perl.
7 |
8 | It uses "coding by convention" paradigm which provides developer an easy environment to create application but hides most of its technical functionality from the developer.
9 |
10 | ## Architecture
11 | We need java virtual machine, java language and java SDK.
12 | Strength of grails is the package of model-view-controller components that comes with it.
13 | * Spring framework is core controller for grails.
14 | * Hibernate is used for building data models and communicating with DB.
15 | * Sitemash is template framework used by views.
16 | * Grails is based on all these frameworks and groovy combine them all.
17 |
18 |
19 | 
20 |
21 | ## Installation
22 |
23 | **Prerequisites:-** groovy and jdk
24 |
25 | 1. download grails from the website - https://grails.org/
26 | 1. unzip the folder and paste into C: drive
27 | 1. add grails folder's bin directory to the path in environment variables of system.
28 | 1. This completes installation of grails. To check type `grails -version` and you will see the version number.
29 |
30 | There is an easy way of automated installation of grails using SDKMAN.
31 | Follow this official link of grails installation http://grails.org/download.html using SDKMAN.
32 |
33 |
34 | ### What is MVC
35 | * Model - It is java object which stores our data that can be passed to view or controller for processing.
36 |
37 | * Controller - It basically handles requests from front-end, kind of process the data. Controller can be created with command `create-controller` from terminal.
38 |
39 | * View - To render a model, we need views. HTML, CSS, AJAX are used to build views in grails.
40 |
41 | ### Building first grails application
42 |
43 | `grails create-app myFirstApp`
44 |
45 | `cd myFirstApp` change directory to our app
46 |
47 | `grails run-app` this will start a server at http://localhost:8080/
48 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Web_Frameworks/Next-js.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## OVERVIEW:
2 |
3 | Nuxt.js is a free and open source web application framework which is based on Vue.js, Node.js, Express.js, Webpack and Babel.js.Its main feature is UI rendering while abstracting away the client/server distribution.This framework is used for creating universal applications.Now the question arises-What are Universal aaplications? An universal app is a mix between client side and server side app. To be an universal app the application must use the same code both on client and server side to render the application components.
4 | Our goal is to create a framework flexible enough that you can use it as a main project base or in addition to your current project based on Node.js.
5 |
6 | Nuxt.js presets all the features that are needed to make your development of a Vue.js Application Server Rendered more enjoyable. It also consists of another deployment feature called nuxt generate which helps in building a static generated Vue.js Application.
7 |
8 | #### FEATURES OF NUXT.JS:
9 | - Write Vue Files (*.vue)
10 | - Automatic Code Splitting
11 | - Server-Side Rendering
12 | - Powerful Routing System with Asynchronous Data
13 | - Static File Serving
14 | - ES6/ES7 Transpilation
15 | - Bundling and minifying of your JS & CSS
16 | - Hot module replacement in Development
17 | - Pre-processor: Sass, Less, Stylus, etc.
18 | - HTTP/2 push headers ready
19 | - Extending with Modular architecture
20 |
21 | #### INSTALLATION:
22 | Install it with vue-cli:
23 |
24 | **$ vue init nuxt-community/starter-template {project-name}**
25 |
26 | If vue-cli is not installed,install it with **npm install -g @vue/cli @vue/cli-init**
27 |
28 | followed by the other dependencies:
29 |
30 | **$ cd {project-name}**
31 |
32 | **$ npm install**
33 |
34 | and launch the project with:
35 |
36 | .**$ npm run dev**
37 |
38 | The application is now running on http://localhost:3000.
39 |
40 | #### LEARN NUXT.JS:
41 |
42 | [NUXT.JS TUTORIALS](https://frontendmasters.com/courses/vue/introducing-nuxt-js/)
43 |
44 | [KNOW MORE ABOUT NUXT.JS](https://scotch.io/tutorials/build-a-server-side-rendered-vue-app-with-nuxtjs)
45 |
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Web_Frameworks/Next.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Next.js
2 | Next.js is javascript framework which is basically designed for server side rendering of the content.It is used to simplify the application development using javascript.It is a React based framework therefore used along with React to develop web apps in a matter of few hours. It saves a lot of developer efforts and time.
3 |
4 | In building javascript applications which require client side routing and other actions required to be done at client side, and one more problem arose that of SEO because javacript need to be loaded before content and this could result in increase in page loading time.The solution to both of those problems is server rendering, also called static pre-rendering.
5 |
6 | ## Installation
7 | Next.js is a cross platform framework i.e available for Linux, Mac and Windows.It is available on both npm as well as on yarn package manager.To download it just run the following command.You can choose the either one.
8 | ```
9 | npm install --save next react react-dom
10 | ```
11 | ```
12 | yarn add next react react-dom
13 | ```
14 | The github repo of the same can be reached from [here](https://github.com/zeit/next.js/).
15 |
16 | ## Resources to learn
17 | There are bunch of resources available on the web but the documentation is a full fledged resource.It provides you complete in depth knowledge of the tool.You can reach out the [documentation[(https://nextjs.org/docs/#setup) to learn it.There are few more resources which you can head over them as well.Few ones provided below
18 | * https://nextjs.org/learn/
19 | * https://flaviocopes.com/nextjs/
20 | * https://hackernoon.com/next-js-react-server-side-rendering-done-right-f9700078a3b6
21 | * https://medium.freecodecamp.org/use-react-with-next-js-framework-and-how-it-made-my-life-easier-4280b643451
22 |
23 | ## Some more stuff to grab off
24 | * It is a product of [Zeit](https://zeit.co/blog/next)
25 | * It’s advertised by its creators as a zero-configuration, single-command toolchain for React apps.
26 | * Its combination with React makes it skyrocketing and thus it is increasingly used now rather than React alone.
27 | * Application building is as simple as that in case of webapps build using php
28 | * It provides a common structure that allows you to easily build a frontend React application, and transparently handle server-side rendering for you.
29 |
30 | ## References
31 | * https://nextjs.org/docs/#setup
32 | * https://flaviocopes.com/nextjs/
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Web_Frameworks/Phalcon.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # PHALCON:
2 | Phalcon is an open source,high performance and one of the most popular PHP web framework delivered as an extension of C but written in Zephir (its a compiler written in PHP to convert Zephir language into C extension).
3 |
4 | ### WHY USE PHALCON?
5 | Phalcon is an extension to the PHP itself so it is installed on the server like any other PHP extension and hence is faster.It has well designed features and framework and can handle more HTTP requests per second than comparable frameworks written in PHP.It also aims at reducing resource usage,hence is prefered over other frameworks.The compiled nature of Phalcon offers extraordinary performance that outperforms all other frameworks measured in certain benchmarks.
6 |
7 | ### PHALCON INSTALLATION
8 | Phalcon needs PHP to run. Its loosely coupled design (system in which each of its components has, or makes use of,little or no knowledge of the definitions of other separate components) allows developers to install Phalcon and use its functionality without additional extensions.
9 |
10 | #### PHP INSTALLATION:
11 | Install a web server on your own PC, and then install PHP and MySQL
12 |
13 | [INSTALLING PHP](http://php.net/downloads.php)
14 |
15 | [INSTALLING MYSQL](https://www.tutorialspoint.com/mysql/mysql-installation.htm)
16 |
17 | [INSTALLING PHALCON ON WINDOWS,LINUX,MAC](https://docs.phalconphp.com/zh/3.3/installation)
18 |
19 | [MORE ABOUT PHALCON](https://docs.phalconphp.com/zh/3.2/tutorial-base)
20 |
21 | [PHALCON TUTORIALS FOR BEGINNERS](https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/getting-started-with-phalcon-a-php-framework-part-2)
22 |
23 | [LEARN PHALCON FROM SCRATCH](https://www.eduonix.com/learn-phalcon-php-framework-from-scratch)
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Web_Frameworks/Phoenix.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Phoenix
2 | [Phoenix](http://phoenixframework.org/) is a framework written in Elixir which implements the server-side MVC pattern. It is built for web development.It is a good option today in the market.The website of the phoenix says **A productive web framework that does not compromise speed and maintainability**.This is true in fact because earlier developers had a myth either speed or quality both can not go hand in hand one need to compromise the either but phoenix breaks the myth and therefore it carved its name among the most popular and fastest web frameworks.Phoenix is a modern web framework that helps building APIs and web applications easy. It’s built with [Elixir](https://elixir-lang.org/) and runs on Erlang VM .It has excellent support for handling very large numbers of simultaneous users.
3 |
4 | # Installaion
5 | The link for the installation is [here](https://hexdocs.pm/phoenix/installation.html#content).Phoenix has been provided with rich set of guides to understand the workflow.The link to the [documentation](https://hexdocs.pm/phoenix/Phoenix.html) is here.If you fallen in love with it at the very first sight you can also contribute to it [here](https://github.com/phoenixframework/phoenix).
6 |
7 | # What about learning Phoenix?
8 | There are dozens of resources available on the web.The best is if one can scratch the surface with some good tutorials isn't? There are few resources available one is [head start guide](www.phoenixforrailsdevelopers.com) and this is also a [good book](https://pragprog.com/book/phoenix/programming-phoenix).
9 |
10 | # Some More Resources
11 | [Phoenix is not Rails](https://dockyard.com/blog/2015/11/18/phoenix-is-not-rails)
12 | [Architecture of WhatsApp](http://highscalability.com/blog/2014/2/26/the-whatsapp-architecture-facebook-bought-for-19-billion.html)
13 |
14 | # References
15 | https://blog.carbonfive.com/2016/04/19/elixir-and-phoenix-the-future-of-web-apis-and-apps/
16 | http://phoenixframework.org/
17 | https://medium.com/@elviovicosa/5-reasons-you-should-use-phoenix-instead-of-rails-in-your-next-project-504b4d83c48e
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/Web_Frameworks/Pyramid.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Pyramid
2 | Pyramid is python web framework used to create web applications. It is mostly used in projects that require flexibility, scalability and speed compared to django,flask or others.It is a product of pylons project.Another coolest thing in pyramid is that it is open source.It is also called down to earth framework because of its structure and it is clearly visible from its logo as well.
3 |
4 | ## Installation
5 | For installing python it is necessary to have python3 installed on the system.The best is when you have the latest version.If you don't have the latest version of python you can visit the [python official website](https://www.python.org/) to download it.
6 |
7 | After installing python3 there is no much tedious task to install pyramid
8 | First create a virtual environment into your project directory.It is useful so that you don't need to install the packages system wide. To download pyramid for all platforms and guide for how to create virtual environment just head over to this [link](https://docs.pylonsproject.org/projects/pyramid/en/latest/narr/install.html). It provides detailed instructions related to installation on all the platforms.
9 | The github repo of pyramid can be visited from [here](https://github.com/Pylons/pyramid).If you want to contribute to the project then you are welcome to do so as it is very great and welcoming community.
10 |
11 | ## Learning Resources
12 | The Pylon community has provided very rich [documentation](https://docs.pylonsproject.org/projects/pyramid/en/latest/narr/introduction.html#).If you want to get your hands dirty with the framework it is the first and best step to proceed.
13 |
14 | ## Why Pyramid is Unique ?
15 | * It allows you to become productive quickly
16 | * Using it we can build single-file applications
17 | * Many others including static assets,configuration,interactive development and
18 | munch more
19 |
20 | ## References
21 | * https://docs.pylonsproject.org/projects/pyramid/en/latest/narr/introduction.html
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/agile/Code_Smell.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | > ** "Code Smell is a term used by [agile][1] programmers."** - [wikipedia][2]
2 |
3 | ## Wait, how can a code smell?
4 |
5 | In [computer programming][3], a code smell may refer to anything unusual in the source code of a program that probably indicates a deeper problem. The term was popularised by [Kent Beck][4] on [WardsWiki][5] in the late 1990s. Duplicate code, too many comments or long classes can be considered as a code smell however exact definition is subjective & varies by language, developer, and community. And yes, we are not talking about a literal smell which is obvious! Consider expert programmers having this hypothetical nose in their brain such that, once they see code that indicates the violation of fundamental design principles and negatively impacts design quality, seeks to take proper action based on their gut feeling that something might be wrong! The code may not be technically incorrect and does not prevent the program from running instead it may include weaknesses that may slow down the development process or increase the risks of bugs and failures in the future. In a nutshell, a code smell is a metaphorical smell and not necessarily bugs!
6 |
7 | ## How about code refactoring!
8 |
9 | - ##### The Perfect Deodorant
10 | According to [Martin Fowler][6], in his book **Refactoring: Improving the Design of Existing Code**, popularized the term **code smell** quite a bit that it certainly gained traction in the agile community in particular. Bad code smells can be an indicator of factors that contribute to technical debt. [Robert C. Martin][7] (popularly known as **Uncle Bob**) calls a list of code smells a "value system" for software craftsmanship. Now, avoidance of bad code smells lead to elegant design principles. That is where code refactoring comes in & it is done to remove code smells where it is refactored into small, controlled steps, and the resulting design is examined for further code smells that in turn indicates the need for more refactoring.
11 |
12 | ------------
13 |
14 | [1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Agile_software_development
15 | [2]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Code_smell
16 | [3]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_programming
17 | [4]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kent_Beck
18 | [5]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/WardsWiki
19 | [6]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Martin_Fowler
20 | [7]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Robert_Cecil_Martin
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/agile/Dont_Repeat_Yourself.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # DRY
2 |
3 | [**Don't Repeat Yourself**][1] (DRY) is a principle of software development aimed at reducing repetition of software patterns; it states that **duplication in logic** should be eliminated via abstraction & **duplication in a process** should be eliminated via automation.
4 |
5 | > "Every piece of knowledge must have a single, unambiguous, authoritative representation within a system".
6 |
7 | -- [The Pragmatic Programmer][2], a book by **Andy Hunt** and **Dave Thomas**
8 |
9 | ###### WET
10 |
11 | - Violations of **DRY** are typically referred to as **WET** solutions, which is commonly taken to stand for either `write everything twice`, `we enjoy typing` or `waste everyone's time`.
12 |
13 | ## How To Achieve DRYness!
14 |
15 | While building a large software project, we often are overwhelmed by the overall complexity. A basic strategy for reducing such complexity is to divide both the **logic** & **process** into parts that are simpler. Any complex system can be broken down into components, where each component may represent its own subsystem that adheres to some specific functionality!
16 |
17 | > When you find yourself writing code that is similar or equal to something you've written before, take a moment to think about what you're doing and **don't repeat yourself**!
18 |
19 | In a nut-shell, if you have the same code in more than one place, you need to extract this into a single location, as adding additional, unnecessary code to a codebase increases the amount of work required to maintain and extend the software in the future.
20 |
21 | 
22 |
23 | Duplicate code adds to technical debt! Whether the duplication arises from poor understanding of how to apply abstraction or due to spaghetti code, it eventually decreases the quality of the code. Duplication in a process can also be automated by eliminating manual testing, manual build, integration processes, etc. whenever possible through the use of automation!
24 |
25 | ------------
26 |
27 | [1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Don%27t_repeat_yourself
28 | [2]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Pragmatic_Programmer
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/agile/How_To_Brainstorm.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # How to do a brainstorming
2 |
3 | Before starting a brainstorming session everybody should agree to theses rules:
4 |
5 | - Quantity then quality - tell all your thoughts and ideas - even the most foolish ones are welcome, no self censorship
6 | - Be scandalous, funny, wild, creative
7 | - Build your ideas on other people’s ideas
8 | - No judgment, no evaluation, no critics - discussion comes later
9 | - Show and read your post-its for everybody
10 |
11 | ## How do we do the brainstorming ?
12 |
13 | - On remote : Meet/skype/TeamViewer/orwhatever + screenshare of your Trello Board / OrWhatEverYouUse
14 | - Onsite : Juste a wall and post-its
15 | - You create as many cards as you want to (you can propose silent brainstorming for some minutes)
16 | - Then each participant reads the post-it and explains his/her thoughts.
17 |
18 | ## What 2 Do ?
19 |
20 | - Then you can create up to 6 categories where to put / organize the trello cards or post-its.
21 | - Dot-Voting : Everybody has three votes and then you choose the three favorit categories
22 | - Choose concret actions for each category, give a maintainer and a date
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/agile/MoSCoW.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | The MoSCoW method is a way for a group of people to prioritize and organize requirements for a project. MoSCoW is an acronym which stands for Must have, Should have, Could have and Won’t have.
2 |
3 | Must Have:
4 | These are the parts of the project that absolutely must be included. They are non-negotiable requirements that must be included so that, if the project was made of all 'Must Have' components, the project would be successful.
5 |
6 | Should Have:
7 | These are requirements that are important, however they come in second priority to the 'Must Have' requirements. If there is time, these requirements will most likely be added.
8 |
9 | Could Have:
10 | These are requirements that would be nice to have, however it is more than likely that there will not be enough time to include them.
11 |
12 | Won’t Have:
13 | These requirements could be added at a future date but are not crucial to the success of the project at this time.
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/agile/Software_Development_Life_Cycle.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## SDLC
2 |
3 | [**SDLC**][1] or **Software Development Life Cycle** is a methodical approach performed at each step in the software development process. It's a structure followed by a development team of any organization to help increase productivity efficiently while sustaining stability!
4 |
5 | ## Phases
6 |
7 | SDLC model comprises of mainly 6 phases viz.
8 |
9 | 1. **Analysis** - *gathering requirement from the client, determining project's scope*
10 |
11 | 2. **Design** - *specifying system requirements, defining overall system architecture*
12 |
13 | 3. **Implementation** - *writing the code according to design specifications*
14 |
15 | 4. **Testing** - *fixing bugs, testing various modules, performing [STLC][2]*
16 |
17 | 5. **Deployment** - *publishing software for customer usage*
18 |
19 | 6. **Maintenance** - *continuous evaluation of the system in terms of its performance*
20 |
21 | ## Types
22 |
23 | SDLC again has 6 models like so.
24 |
25 | 1. **Waterfall Model**
26 | 2. **V-Shaped Model**
27 | 3. **Evolutionary Prototyping Model**
28 | 4. **Spiral Method (SDM)**
29 | 5. **Iterative and Incremental Method**
30 | 6. **Agile development**
31 |
32 | ## Why implement SDLC?
33 |
34 | First of all, let's clarify a misunderstood concept, you simply don't implement SDLC for writing a [hello world][3] program. SDLC is basically a process followed in software projects where each phase generates output required by the next phase in the life cycle. Requirements are translated into design. Code is produced according to the design. Testing should be done on a developed product based on requirement. Deployment should be done once the testing was completed. Once the product is available, it needs maintenance!
35 |
36 | ## STLC
37 |
38 | > [Software Testing][4] is a process of executing a program or application with the intent of finding the software bugs.
39 |
40 | **Testing** is one of the significant phase of **SDLC** since it's the last step before deployment of any software. As a result, it has its own dedicated [**Software Testing Life Cycle**][2] (**STLC**) for following proper paradigms in order to rectify buggy codes.
41 |
42 | STLC comprises of following phases:
43 |
44 | - Requirement Analysis
45 | - Test Planning
46 | - Test Case Development
47 | - Environment Setup
48 | - Test Execution
49 | - Test Cycle Closure
50 |
51 | Here's an article talking a bit about SDLC & STLC -
52 |
53 | - https://medium.com/@testautomation/software-testing-life-cycle-vs-software-development-life-cycle-76bd7cbaf28e
54 |
55 | [1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Systems_development_life_cycle
56 | [2]: https://www.softwaretestingclass.com/software-testing-life-cycle-stlc/
57 | [3]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/%22Hello,_World!%22_program
58 | [4]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_testing
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/computation/Amdahl's_law.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## What is Amdahl's law?
2 | In advanced computer architecture, Amdahl’s law is a formula used to determine the maximum improvement possible by improving a particular part of a system.
3 | Amdahl's law is a law which administers the speedup of using parallel processors on a problem in comparision with using only one serial processor.
4 |
5 | Let's take a real life example to get a clear understanding of the law:
6 | - Suppose there are three friends A, B, and C who go to the same school.
7 | All three decide to meet at the school gate every day before entering the school together. Friend A goes to school by bike, B makes use of bicycle in order to reach school, and C goes by foot. In this situation A and B take much less time compared to C. Hence no matter how fast A and B reach the school gate they both need to wait for C in order to enter the school together. This means that in order to accelerate the overall process, you need to concentrate on improving the performance of C much more than the other two, as C takes much more time compared to the other two to reach the same destination.
8 |
9 | Amdahl's law is mainly used in parallel computing to predict the theoretical speedup when multiple processors are used.. Different forms of parallel computing: bit-level, instruction-level, data, and task parallelism.
10 | Amdahl's law can be written as:
11 |
12 | Slatency (s)= 1/((1-p)+(p/s))
13 |
14 | - Slatency is the measure of maximum possible improvement in theoretical speedup of the execution of the whole task.
15 | - s is the speedup of the part of the task that gets benifited from improved system resources.
16 | - p is the proportion of execution time that the part benifiting from improved resources originally occupied.
17 |
18 | If N tends to infinity then the maximum speedup tends to 1/(1-P).
19 |
20 | [MORE ABOUT AMDAHL'S LAW](http://tutorials.jenkov.com/java-concurrency/amdahls-law.html)
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/Hidden Markov Model.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Hidden Markov Model (HMM)
2 |
3 | Hidden Markov Model is a statistical model which generates models based on a set of input sequence.These sets of input sequence are called as states represented as s1,s2,s3.....sn.
4 | Each state is associated with a probability distribution .
5 |
6 | In HMM the system being modelled is assumed to be a Markov chain with unobserved hidden states. In simpler Markov models like a Markov chain the state is directly visible to the observer and thus the state transition probabilities are the only parameters. In a hidden markov model the state is not directly visible but the output dependent on the state is visible .Each state has a probability distribution over the possible output tokens therefore the sequence of tokens generated gives some information about the sequence of states .The adjective hidden refers to the state sequence through which the model passes,not to the parameters of the model,the model is still referred to a hidden markov model even if these parameters are known exactly.Hidden markov models are specially known for their application in speech,gesture,handwriting recoginition etc. A hidden markov model can be considered as a generalization of a hidden model where the hidden variables which control the mixture component to be selected for each observation are related to a markov process rather than independent of each other.Hidden markov models have been generalized to pairwise markov models and triplet markov models which allow consideration of more complex data structures.
7 |
8 | The requirement for HMM is Markov Property Satisfaction. Markov property is a property which is memory less. It is called memory less because Markov model considers only one state at a time.This model is a relatively simple way to model sequential data. A hidden Markov model implies that the Markov Model underlying the data is hidden or unknown to you. More specifically, you only know observational data and not information about the states. In other words, there’s a specific type of model that produces the data (a Markov Model) but you don’t know what processes are producing it. You basically use your knowledge of Markov Models to make an educated guess about the model’s structure.
9 |
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/data_visualization/D3.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## D3.js, What!
2 |
3 | [**D3.js**][1] (**Data-Driven Documents**) is a JavaScript library for producing dynamic, interactive data visualizations in web browsers. **D3.js** API contains various methods which can be grouped into the following logical units - *Selections*, *Transitions*, *Arrays*, *Math*, *Color*, *Scales*, *SVG*, *Time*, *Layouts*, *Geography*, *Geometry*, *Behaviors*.
4 |
5 | 
6 |
7 | **D3.js** helps you visualize data by combining powerful visualization and interaction techniques with a data-driven approach to [DOM][2] manipulation. It also provides full capabilities of modern browsers by designing the right visual interface for your data.
8 |
9 | **D3.js** version 1.0.0 was released back in 18 February 2011.
10 |
11 | ## Why, D3.js?
12 |
13 | > **D3** does not introduce a new visual representation. Unlike **Processing**, **Raphaël**, or **Protovis**, *D3's* vocabulary of graphical marks comes directly from web standards: HTML, SVG, and CSS - https://d3js.org/
14 |
15 | ###### Get Started
16 |
17 | There are over [20,000+][3] **D3.js** examples you could learn from, but you never know how approachable any given one will be! So, the question is - how do we build up our visualization from first principles? As you've probably seen, D3's API is massive, so lets call out a few of the utilities that will be particularly helpful early on:
18 |
19 | - **d3-scale**
20 |
21 | 
22 |
23 | - **d3-shape**
24 |
25 | 
26 |
27 | - **d3-selection**
28 |
29 | 
30 |
31 | - **d3-collection**
32 |
33 | 
34 |
35 | - **d3-hierarchy**
36 |
37 | 
38 |
39 | - **d3-zoom**
40 |
41 | 
42 |
43 | - **d3-force**
44 |
45 | 
46 |
47 | So, with just some basic knowledge of latest HTML5 features such as SVG, Canvas you can dive into a world where library like **D3.js** bring data to life!
48 |
49 | ##### Contribution
50 |
51 | - https://github.com/d3/
52 |
53 | ------------
54 |
55 | [1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/D3.js
56 | [2]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Document_Object_Model
57 | [3]: http://blockbuilder.org/search
58 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/data_visualization/DataHero.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # DataHero
2 |
3 | DataHero is a data visualization tool that enables users to immediately link to cloud-hosted services and import data and generate powerful visuals. It is so easy to use that it doesn’t require an IT team to set up and get running.
4 | DataHero comes with a built-in data decoder that automatically performs data classification and normalization and creates a uniform data repository that is easily accessible and yet secure.
5 |
6 | DataHero provides one with the world’s first total self-service data visualization and data dashboard solution that transforms siloed data into highly actionable insights.
7 | The software has pre-built connectors that instantly links to multiple cloud-based services, software, and applications like Marketo, Salesforce, MailChimp, Shopify, Box, and more. This functionality ensures that you are able to connect to services that matter to your business and operations. The connection is quick and easy and you only have to use your credentials to get instant access to the data you need.
8 |
9 | DataHero is equipped with a highly powerful and advanced data classification engine that automates data classification and normalization.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/data_visualization/Tableau.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # DATA VISUALIZATION
2 |
3 | It is basically a process of visually showing information.People have a tendency to gain insights from data quicker using visuals.Data visualization is typically achieved by extracting data from the underlying IT system. This data is generally in the form of numbers, statistics and overall activity. The data is processed using data visualization software and is displayed on the system's dashboard.
4 |
5 | It is generally done to assist IT administrators in getting quick, visual and easy-to-understand insight into the performance of the underlying system. Most IT performance monitoring applications use data visualization techniques to provide statistical insight of performance of the monitored system.
6 |
7 | # TABLEAU
8 |
9 | Tableau is a data visualization tool created by tableau software.Tableau is a software tool that basically connects easily to several data sources. It allows for rapid insights by pouring data into dashboards that look amazing and are also interactive.Recreation takes minute and can be done with simple drag and drops of data fields.Tableau is a type of tool that you can pick up right away and start exploring in built dashboards all on your own.However it has some advance capabilities that requires experience and training.Tableau is a software that helps you percieve and understand your data quickly and easily.
10 |
11 | ## Tableau Software Products
12 | There are mainly five main products
13 | - Tableau desktop
14 | - Tableau server
15 | - Tableau online
16 | - Tableau reader
17 | - Tableau public
18 |
19 | Tableau public and Tableau reader are actually free to use. Both Tableau server and Tableau desktop come with a 14 day fully functional free trial period.Tableau desktop comes in both professional and personal edition and Tableau online is available for an annual subscription for a single user and it scales to support thousands of users.
20 |
21 | # Resources to learn Tableau
22 |
23 | 1) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jj6-0cvcNEA
24 | 2) https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLWPirh4EWFpGXTBu8ldLZGJCUeTMBpJFK
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/data_visualization/plotly.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Plotly
2 |
3 | # Introduction
4 | Plotly from the name it gives clear indication of it what it provides.The logical breakdown of the name tells something which is related to plotting something(i.e graphs charts or visual graphics) isn't ?.A formal description of plotly is described as follows
5 |
6 | # Description
7 | Plotly is one of the data visualization and data analytics tools.It is built on top of data visualization library D3.js, HTML and CSS. It is developed using Python and Django. It is compatible with a number of languages/ tools: R, Python, MATLAB, Perl, Julia, Arduino. Plotly provides online graphing and statistics tools for individuals and collaborations .It also offers scientific graphing libraries for Python, R, MATLAB, Perl, Julia, and REST.The github repo of plotly is found [here](https://github.com/plotly).
8 |
9 | It provides six main features
10 | ### Dash -
11 | Dash is a Open Source Python library for creating reactive, Web-based applications
12 | ### plotly.js and plotly.py
13 | plotly.js and plotly.py are high-level, declarative charting libraries. They ship with over 30 chart types, including scientific charts, 3D graphs, statistical charts, SVG maps, financial charts, and more.
14 | ### falcon-sql-client
15 | Falcon is a free, open-source SQL editor with inline data visualization.
16 | ### react-plotly.js
17 | A plotly.js React component from Plotly. The basis of Plotly's React component suite.
18 | ### react-chart-editor
19 | Customizable React-based editor panel for Plotly charts, Part of Plotly's React Component Suite for building data visualization Web apps and products.
20 |
21 | # Get hands on with learning
22 | Here are few referral links which provide a good documentation for learning
23 | 1. [Analytics Vidhya](https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2017/01/beginners-guide-to-create-beautiful-interactive-data-visualizations-using-plotly-in-r-and-python/)
24 | 2. [Plotly](https://plot.ly/)
25 | 3. [What is plotly?](https://bookdown.org/paulcbauer/idv2/7-plotly-in-r.html)
26 | 4. [Plotly wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plotly)
27 |
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/deep_learning/ANN.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/the-ethan-hunt/first-timers-guide/815c822f0a7f802ab5b7932aaab174d1b7e588dc/guides/data_science/deep_learning/ANN.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/deep_learning/Autoencoder.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/the-ethan-hunt/first-timers-guide/815c822f0a7f802ab5b7932aaab174d1b7e588dc/guides/data_science/deep_learning/Autoencoder.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/deep_learning/CNN.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/the-ethan-hunt/first-timers-guide/815c822f0a7f802ab5b7932aaab174d1b7e588dc/guides/data_science/deep_learning/CNN.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/deep_learning/LSTM.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/the-ethan-hunt/first-timers-guide/815c822f0a7f802ab5b7932aaab174d1b7e588dc/guides/data_science/deep_learning/LSTM.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/deep_learning/RNN.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/the-ethan-hunt/first-timers-guide/815c822f0a7f802ab5b7932aaab174d1b7e588dc/guides/data_science/deep_learning/RNN.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/machine_learning/Regression.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Regression
2 | Towards **Machine Learning** and **Data Science** *Regression* is the first topic to be ~~learned~~ *Mastered* . In the following we will try to introduce you about Regression and its basic types:
3 | #### What is Regression?
4 | Regression is basically a statistical approach to find the relationship between variables. In machine learning, this is used to predict the outcome of an event based on the relationship between variables obtained from the data-set.
5 | More precisely:
6 | There are two type of variables
7 | * Dependent variable
8 | * Independent variables
9 |
10 | Now we can say that Regression use a linear function to _predict_ the dependent variable.
11 |
12 | ## Types Of Regression
13 | ##### Linear Regression
14 | Linear Regression establishes a relationship between dependent(y) variable and one or more independent variables(x) using a best fit straight line (also known as regression line).
15 | ```y = mx + c```
16 | Now we can predict the ```y``` with respect to independent variable ```x```.
17 | It is a **Simple Linear Regression**.
18 | If there are more than one Independent variables ```y = x1 +x2 + x3``` then it is called **Multiple Linear Regression**.
19 |
20 | ##### Polynomial Regression
21 | A regression equation is a polynomial regression equation if the power of independent variable is more than 1. The equation below represents a polynomial equation:
22 | ```y = ax + bx^2```
23 | In this type the Best fit line is not a straight line, It is a curve that fit the data-points.
24 |
25 | ##### Logistic Regression
26 | Logistic regression is used to find the probability of event=Success and event=Failure. We should use logistic regression when the dependent variable is binary (0/ 1, True/ False, Yes/ No) in nature. Here the value of Y ranges from 0 to 1.
27 |
28 | ##### Stepwise Regression
29 | This form of regression is used when we deal with multiple independent variables. In this technique, the selection of independent variables is done with the help of an automatic process, which involve no human intervention.
30 | The aim of this technique is to maximize the prediction power with minimum number of independent variables. It is one of the method to handle higher dimension data set.
31 |
32 |
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/machine_learning/classification_algorithms/Decision_Tree_Classifier.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Decision Tree Classifier
2 |
3 | [**Decision Tree Classifier**][1] belongs to the family of supervised learning algorithms. Unlike other supervised learning algorithms, decision tree algorithm can be used for solving both classification problems as well as regression problems too. It uses a **tree-like** model for visually & explicitly representing decisions and decision making!
4 |
5 | ## how the decision tree looks like!
6 |
7 | Let's consider the classic [Titanic Data Set][2] for predicting if a passenger will survive or not! This is a basic example for a model that uses only 3 features from the data set, namely **sex**, **age** & **sibsp** (i.e. no. of siblings or spouses aboard the ship) as shown below:
8 |
9 | 
10 |
11 | So, a decision tree always exists in an upside-down manner with its root at the top where the black bold text represents a **condition** based on which the tree splits into branches. Now, those branch end which doesn't split anymore tends to provide us with a **decision** (or leaf)! There should be a lot of emphasis on the selection of features as that is what makes a well-structured decision tree.
12 |
13 | > This methodology is more commonly known as **learning decision tree from data** and the above tree is called **Classification Tree** as the target is to classify passenger as 'survived' or 'died'.
14 |
15 | #### Pros
16 |
17 | - Simple to understand, interpret, visualize
18 | - Perform feature selection implicitly
19 | - Can handle multi-output problems
20 |
21 | #### Cons
22 |
23 | - Can cause [overfitting][3] i.e. creates over-complex trees
24 | - Small variations in the data may generate a completely different tree
25 | - Improper balancing of data set prior to fitting may create biased trees
26 |
27 | ------------
28 |
29 | [1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decision_tree_learning
30 | [2]: https://www.kaggle.com/c/titanic
31 | [3]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Overfitting
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/machine_learning/classification_algorithms/Logistic_Regression.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Logistic Regression
2 |
3 | [**Logistic Regression**][1] is a statistical model which identifies itself as one of the most used **Machine Learning** algorithms for binary classification. Despite its name, it is not an algorithm for regression problems i.e. predicting a continuous outcome. Instead, Logistic Regression provides a discrete binary outcome between one thing or another! That's why it falls under the group of the classification algorithm.
4 |
5 | ## how it works...
6 |
7 | Logistic Regression measures the relationship between the dependent variable (**label**) and the one or more independent variables (**features**), by estimating probabilities using its underlying logistic function vis-a-vis sigmoid function.
8 |
9 | 
10 |
11 | > The Sigmoid-Function is an S-shaped curve that can take any real-valued number and map it into a value between the range of 0 and 1, but never exactly at those limits.
12 |
13 | Lastly, these values between 0 and 1 will then be transformed into either 0 or 1 using a threshold classifier.
14 |
15 | ## when to use it...
16 |
17 | Clearly, Logistic Regression isn't the same thing as Linear Regression as the former one provides a discrete outcome whereas the latter one gives a continuous outcome. An example of a continuous outcome would be a model that predicts the value of a house. A discrete outcome will always be one thing (having cancer) or another (not having cancer).
18 |
19 | Logistic Regression separates the input space into two regions with a linear boundary; therefore it is required that a given data must be linearly separable as shown below:
20 |
21 | 
22 |
23 | In a nutshell, one should think about using logistic regression when the dependent variable aka **label** takes on only two values!
24 |
25 | [1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Logistic_regression
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/machine_learning/classification_algorithms/Naive_Bayes_Classifier.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Naive Bayes Classifier
2 |
3 | **Naive Bayes** is a simple but surprisingly powerful algorithm for predictive modeling whereas [Naive Bayes Classifiers][1] are a family of 'probabilistic classifiers' based on applying Bayes' theorem. The use of [Bayes' Theorem][2] in the classifier's decision rule is trivial, but Naive Bayes is not necessarily a Bayesian method. The whole concept of Naive Bayes classification revolves around **maximum likelihood** & it serves as a foundation for many other supervised machine learning algorithms!
4 |
5 | ###### Some of the applications are --
6 |
7 | - Real-time Prediction
8 | - Text classification
9 | - Spam Filtering
10 | - Recommendation System
11 |
12 | ## Bayes' Theorem
13 |
14 | Bayes’ Theorem is useful when working with conditional probabilities, because it provides us with a way to reverse them. Here's the mathematical formula:
15 |
16 | 
17 |
18 | ###### Being Naive!
19 |
20 | After calculating the probabilities for every factor, **Naive Bayes Classifier** then selects the outcome with the highest probability. This classifier assumes that every pair of features being classified is independent of each other. Hence the word '**naive**'!
21 |
22 | ## Interpretations of Naive Bayes
23 |
24 | > The different Naive Bayes classifiers differ mainly by the assumptions they make regarding the distribution of P(A | B)
25 |
26 | - **Gaussian Naive Bayes** -- In Gaussian Naive Bayes, continuous values associated with each feature are assumed to be distributed according to a Gaussian distribution aka Normal distribution. Plotting a graph for such a distribution provides a bell shaped curve symmetric about the mean of the feature values!
27 |
28 | - **Multinomial Naive Bayes** -- Feature vectors represent the frequencies with which certain events have been generated by a multinomial distribution. This is the event model typically used for document classification.
29 |
30 | - **Bernoulli Naive Bayes** -- Bernoulli Naive Bayes is for independent binary features only. Like the multinomial model, this model is also popular for document classification tasks; where we treat a feature as if binary-constructed viz. whether a word occurs in a document or not!
31 |
32 | ------------
33 |
34 | [1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Naive_Bayes_classifier
35 | [2]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bayes%27_theorem
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/machine_learning/classification_algorithms/Neural_Network.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Neural Network
2 |
3 | ###### Brief History
4 |
5 | [Artificial Neural Network][1] (or **ANN**) is one of the most fundamental machine learning algorithm that tends to mimic the human brain's thinking process for decision-making. Traditional explicit programming does computation with absolute certainties such as `2 + 2 = 4` but computations involved in **image classification**, **speech recognition**, **sentiment classification** are much more likely to be based on probability! In light of this realization, [Warren McCulloch][2] and [Walter Pitts][3] (1943) created a computational model called 'threshold logic' based on statistical learning. Their work evolved eventually and led to the rise of Neural Networks, enabling computers to really think and solve problems that were once thought impossible!
6 |
7 | ###### Introducing ANN!
8 |
9 | The development of ANN have been key to teaching computers to think & understand the world in the way that humans do. Simply put, a neural network is a graph of nodes (**artificial neurons**) which mimic the neurons in a biological brain, connected by weighted edges (**synapses**) as shown below:
10 |
11 | 
12 |
13 | ## How Machines Think!
14 |
15 | ###### Introducing ANN
16 |
17 | An ANN can have multiple layers aka [multilayer perceptron][4] where each one tries to abstract the overall complexity of the previous layer. In the above figure we have an input layer, an output layer & two hidden layers!
18 |
19 | Let’s go into detail about some of the components of ANN:
20 |
21 | - **Neuron** -- An artificial neuron is a mathematical function that can receive multiple inputs and gives a single output representing the result of the computation
22 | - **Weights** -- All the connections of a neural network is assigned an arbitrary value at the initial stage viz. a weight
23 | - **Propagation Function** -- This function computes the input of a neuron in the next layer based on the outputs of predecessor neurons by leveraging the forward propagation stage of training
24 | - **Learning Rule** -- This function modifies the weights of the connection by leveraging backward propagation stage of training
25 |
26 | 
27 |
28 | > For every iteration, a neural network tries to reduce the error in the output by adjusting the weights of each connection by implementing backward propagation in order to attain the optimum solution. This is what we call **learning**!
29 |
30 | Now, the bigger & more diverse the data-set is for training a neural network, the better the model becomes in classifications. In case of classification, neural networks are mainly of 4 kinds viz. [Autoencoder][5], [Probabilistic][6], [Time delay][7] & [Convolutional][8].
31 |
32 | ------------
33 |
34 | [1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_neural_network
35 | [2]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Warren_McCulloch
36 | [3]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Walter_Pitts
37 | [4]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multilayer_perceptron
38 | [5]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autoencoder
39 | [6]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Probabilistic_neural_network
40 | [7]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Time_delay_neural_network
41 | [8]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Convolutional_neural_network
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/machine_learning/classification_algorithms/Random_Forest.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Random Forest
2 |
3 | [**Random Forest**][1] is an [ensemble][2] supervised learning algorithm and capable of performing both regression and classification tasks. The Random Forest Classifier creates a so-called **forest** with a number of [decision trees][3] as shown below:
4 |
5 | 
6 |
7 | ## How does Random Forest work?
8 |
9 | The Random Forest algorithm uses Bagging (**B**ootstrap **Agg**regat**ing**) for splitting the dataset into chunks so as to fit those with separate decision trees. In case of bagging, we train each decision tree on a different sample of data and also the sampling of dataset happens with replacement. Here, each decision tree acts as a base learner. This results in ensemble learning. The general idea of the ensemble methods is that a combination of learning models increases the overall result.
10 |
11 | > **Random Forest Classifier** creates a set of decision trees from the randomly selected subset of a training set. It then aggregates the votes from different decision trees to decide the final class of the test object.
12 |
13 | ###### Let’s take an example:
14 |
15 | Suppose, we have a training dataset : `[X1, X2, X3, … X10]`
16 | Random forest may create three decision trees taking the input from subset using bagging as shown below:
17 |
18 | 
19 |
20 | Finally, it predicts the outcome based on the majority of votes (in case of classification) or aggregation (in case of regression) from each of the decision trees made!
21 |
22 | ## Advantages
23 |
24 | - Random Forest algorithm avoids overfitting
25 | - The same algorithm can be used for both classification and regression
26 | - Improves feature engineering by identifying the most important features
27 |
28 | ## Disadvantages of Random Forest
29 |
30 | - Difficult to interpret due to the randomness
31 | - Computationally expensive compared to a decision tree
32 |
33 | ------------
34 |
35 | [1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Random_forest
36 | [2]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ensemble_learning
37 | [3]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decision_tree_learning
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/machine_learning/classification_algorithms/SVM.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # SVM
2 |
3 | [**Support Vector Machines**][1], in short **SVM**, are defined as supervised machine learning models for both classification as well as regression problems. **SVM** falls under the category of classification algorithms that allows a computer to take a set of data and classify it into two groups. What's unique about **SVM** is its benefit of maximizing the margin (or space) between the two groups to allow for new observation that the computer has not seen before to be better classified. This learning model can solve both linear and non-linear problems and work well for many practical problems!
4 |
5 | ## Support Vectors
6 |
7 | Support Vectors are closest data points about which the classifier would distinguish among classes. These vectors determine the orientation of the line suitable for maximized separation as shown below:
8 |
9 | 
10 |
11 | SVM gets its name from these support vectors that are ultimately supporting the model vectors by providing sufficient information to the computer as all other points have no effect on the model or predictions.
12 |
13 | ## Kernel Trick
14 |
15 | [Kernel Trick][2] enables SVM to be interpreted in higher dimensional spaces. It is even very effective on data sets where the number of dimensions is greater than the number of samples. SVM can classify both the linear and non-linear data!
16 |
17 | ###### How does this work?
18 |
19 | For humans the above image seems pretty intuitive. We just draw a line to separate the different labeled classes from each other. But how does SVM solve this problem?
20 |
21 | 
22 |
23 | Well, the SVM want to find so-called maximum-margin hyperplane which iterates anything from n-dimensional space into higher ones so as to classify them properly. This is what we call **Kernel Trick**! In case of a non-linear data set SVM cannot simply draw a linear hyperplane. Therefore Support Vector Machines use the Kernel Trick.
24 |
25 | > Kernel Trick equips SVM with the ability to build a classification model for non-linear data sets
26 |
27 | 
28 | **Kernel Trick in Action**
29 |
30 | ## Implementation
31 |
32 | Well, SVM is capable of doing both classification and regression. The benefit is that you can capture much more complex relationships between your data points without having to perform difficult transformations on your own. The downside is that the training time is much longer as it's much more computationally intensive.
33 |
34 | Further advantages of Support Vector Machines are the memory efficiency, speed and general accuracy in comparison to other classification methods like k-nearest neighbor or deep neural networks in some particular cases!
35 |
36 | ------------
37 |
38 | [1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Support_vector_machine
39 | [2]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kernel_method
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/miscellaneous/Hadoop.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## What is Big Data ?
2 |
3 | Any piece of information can be considered as data and thus it can be of various sizes.
4 | The data size today is increasing tremendously and thus to process and manage such huge volume of data, different Big Data technologies comes into play.
5 |
6 | The Big Data consits of the 5V's as follows:-
7 |
8 | 1) Volume
9 | 2) Variety
10 | 3) Velocity
11 | 4) Value
12 | 5) Veracity
13 |
14 | ## Problems Faced with Big Data
15 | The problems with Big Data are as follows :-
16 | 1) Storage.
17 | 2) Processing data having complex structure.
18 | 3) Bringing huge amount of data to computation until becomes a bottleneck.
19 |
20 | ## Hadoop - A Solution to Problems of Big Data
21 |
22 | Hadoop is a framework that allows you to store and process huge data in parallel and distributed fashion. Hadoop has the following two components:-
23 | 1) HDFS(storage) - It allows to dump any kind of data across the cluster.It is a distributed file system .It divides input data into smaller chunks and store it.It stores any kind of data and no schema validation is done while dumping the data,that is whenever you dump data you do not need to specify a schema for it.
24 |
25 | 2) MapReduce(Processing)-It allows parallel processing of the data stored in HDFS.It is basically a software framework which helps in writing applications that processes large data sets using distributed and parallel algorithms inside hadoop enviornment.It consists of two parts as folows:-
26 | - Map part-A block of data is read and processed to produce a key value pair.
27 |
28 | - Reduce part -The output of the Map job is the input to the Reduce part.It recieves these key value pairs from multiple map jobs and it aggregates these intermediate key value pairs as a final output.
29 |
30 |
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/miscellaneous/Spark.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Overview
2 | Organizations need data to make intelligent decisions. Cheap compute and storage has allowed organizations to accumulate massive amounts of data. Algorithms and scientific methods need to be applied to this data, which may be structured or unstructured, to derive insights. This is considered as data science. Modern tools and frameworks are required to accomplish this.
3 |
4 | ## Introduction to Apache Spark
5 | Apache spark is an open source Big Data processing framework that is built for this purpose. It is a very powerful and efficient data processing platform originally created at UC Berkley. Spark is a cluster-computing framework, which means it uses multiple computers to process its workloads. It is independent of Hadoop, but uses Hadoop's Distributed File System (HDFS). Spark also replaces Hadoop's "Map/Reduce" framework with its own data processing framework. It supports development in multiple languages (Java, Scala, Python and R) in a uniform manner. Spark has a number of libraries and modules that make it a robust ecosystem for Big Data processing.
6 |
7 | ## High Performance
8 | What makes it fast? First, Spark is capable of using both memory and disk for processing. Spark can string together dependent tasks (chaining) in memory while minimizing writes to the disk. When the output of one task has to be handed as input to the next task, it doesn't always have to write it to disk. Second it uses a sophisticated concept called Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG). DAG is used to organize and sequence tasks, determine which tasks can be run in parallel, when to use memory only and when to write to disk, etc. Similar to Hadoop Map / Reduce, Spark can handle batch workloads very well, but is also built to handle machine-based learning and streaming workloads. So it is good for processing web clicks in real time for instance.
9 |
10 | ## RDD - Spark's Foundational Data Structure
11 | Spark uses a data structure called RDD. It is an immutable (unchangeable) collection of objects which is distributed across multiple nodes in the cluster. RDD is:
12 |
13 |
14 | 1. Resilient - It is able to self-recover damaged partitions or from node failures
15 | 1. Distributed - It is distributed across multiple nodes
16 | 1. Dataset - It holds the data which could be database records, a text file, a CSV file, etc.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/natural_language_processing/Text_Classification.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Let's Dive In
2 |
3 | **Text Classification** is a problem in computer science in which the task is to assign a text document to one or more classes or categories. This may be done manually or automatically. In the 21st century, web pages, emails, science journals, e-books, learning content, news and social media are all full of textual data. The idea is to create, analyze and report information fast. This is when automated text classification comes up for faster development! [Machine Learning][1] can be implemented to automate these tasks making the whole process super-fast and efficient.
4 |
5 | ## Supervised Text Classification
6 |
7 | This classification technique is based on metrics by defining features and labels for a certain text document. It works on training and testing principle. We feed labeled data to the machine learning algorithm for training. During the testing phase, the algorithm is fed with unobserved data and classifies them into categories based on the training phase. It basically tries to mimic the human human learning.
8 |
9 | #### Examples --
10 |
11 | - Email Spam Filtering
12 |
13 | ## Unsupervised Text Classification
14 |
15 | This classification technique doesn't require labeled input while training data sets instead the algorithms try to discover natural structure in data by identifying similar patterns and structures in the data points and groups them into clusters. This technique is [language-agnostic][2] since it can operate on any textual data without the need to be explicitly labeled and can generate insights from such data. It also follows **Train Once , Test Anywhere** paradigm!
16 |
17 | #### Examples --
18 |
19 | - Sentiment Analysis
20 |
21 | ## One Application?
22 |
23 | [Natural Language Processing][3]
24 |
25 | ## How about Implementation!
26 |
27 | There are plenty of great resources out there to help you get started in the domain of text classification. Here's [one][4] as a token of appreciation for reading this article!
28 |
29 | [1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Machine_learning
30 | [2]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Language-agnostic
31 | [3]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Natural_language_processing
32 | [4]: https://towardsdatascience.com/machine-learning-nlp-text-classification-using-scikit-learn-python-and-nltk-c52b92a7c73a
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/natural_language_processing/machine_translation.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Machine translation is a part of natural language processing that deals with the process of translating a source language text into a target language. Researchers have been working on the problem of machine translation for decades, and it’s considered one of the earliest pursuits in computer science. However, given the difficulties associated with parts of language like assumptions, relations, expectations and conditions, achieving high quality machine translation results has proven to be an elusive goal.
2 |
3 | The process of completing a machine translation starts with analysis of a text input. Sentence are analyzed and often classified based on the degree of difficulty of translation. Often, looking at sentences as individual instances isn’t sufficient, due to the inter-connected nature of adjacent sentences and ideas that are carried from one sentence to another. Common knowledge, as well as more localized knowledge (especially specific to the country or countries where the source language is spoken) may be necessary to achieve high quality results.
4 |
5 | Deformatting and reformatting may also be necessary, since the source material may contain charts and diagrams that don’t require translation. Analysis and transfer are also essential. Morphological analysis is carried out to determine and tag the parts of speech, while semantic analysis determines if a word is a subject or an object. This analysis allows for an accurate transfer of a sentence to a target natural language. This is closely tied to the process of parsing and tagging, where tagging identifies the linguistic properties of each word, and parsing looks at their relation to each other.
6 |
7 | One emerging area of machine translation is example-based machine translation (EBMT), where existing translations are used as the basis for new translations of similar texts or topics. This process involves three stages, matching, alignment, and recombination. In the matching stage, examples are found that will contribute to the translation on the basis of the similarity of the input. In a process known as sequence comparison, matching can occur by comparing each character of the texts. During sequence comparison, tags may be added to parts of speech as they are identified, shortening the length of time necessary to create a final translated product. During the alignment phase, EBMT algorithms identify the pieces of the corresponding translation that are to be used. This is carried out using a bilingual dictionary, or via comparison with other examples. Finally, during recombination, the algorithms work to ensure that the reusable pieces identified are put together in a sensible way that aligns with natural language.
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/natural_language_processing/morphology.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | In order to understand morphology in the context of Natural Language Processing, one must first understand the concept of a morpheme. In linguistics, a morpheme represents the smallest unit of a language. Morphemes are not necessarily words, though in some instances a word may be a morpheme, however a morpheme doesn’t have to be “freestanding” in the same way that a word is. For example, the word “unbreakable” is comprised of three morphemes – un- (a bound morpheme that signifies “not”), -break- (the root, a free morpheme), and –able (a free morpheme signifying “can be done”). Morphology is simply the study of the structure of a word as a composition of morphemes, and is related to the rules of word formation.
2 |
3 | Morphological Analysis is important for a number of reasons. One reason is for the purposes of information retrieval – a query for cats should return matches for both cat and cats. Another is for language modeling. Once we have seen the word “itemize”, we can predict the word “itemized”. Morphological analysis is also essential for machine translation. The Spanish word gato corresponds to the English word cat. Further, morphological analysis is highly variable across languages, due to the amount of variation in each language itself.
4 |
5 | Morphological processes can be used to form new words. In derivation, a stem plus an affix are joined to example. For example, friend + ly = friendly, and unfriendly + ness = unfriendliness. In compounding, two stems are joined together. For example, the two stems wheel and chair form the compound word wheelchair.
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/natural_language_processing/regular_expression.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Regular Expression
2 | Regular expressions (also known as RegEx or RegExp) is used to match characters in a string based on some patterns.The definition just described seems little tricky to some,so let us understand it with an example.
3 | Let us consider a string which stores url of your favourite website i.e string s = "https://www.google.com" and suppose you are given a pattern which is string regex = "https" (remember i am writting regex pattern just like a normal string, actually syntax is explained later).Now suppose if you want to check if the above pattern of characters is present in the string or not.In the above case the answer is yes.
4 |
5 | Another use case which all of us might have experienced is that when we signup for any portal or forum etc we are required to choose a password with some constraints.This constraints are basically held behind with regular expression.
6 |
7 | Now we have scratched the surface but remember it is only the tip of the iceberg rest it yet to hack into it.
8 |
9 | ## I'm too excited now ,from where shall i learn it??
10 |
11 | There are thousands(or even more) of tutorials available on the web if you just search for it.I shall reference down few of them which one might find useful in getting a good start and enjoy the learning experience.
12 |
13 | [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Regular_expression)
14 | [Regular expressions in depth](https://www.regular-expressions.info/)
15 | [Regular expression using javascript - 1]()
16 | [Regular expression using javascript -2](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Guide/Regular_Expressions)
17 | [Regular Expression CheatSheet](https://medium.com/factory-mind/regex-tutorial-a-simple-cheatsheet-by-examples-649dc1c3f285)
18 | and much more...
19 |
20 | ## Purpose
21 | Regular expressions are used in search engines,search and replace dialogs of word processors and text editors.Many programming languages provide regex capabilities, built-in or via libraries.
22 |
23 | # Regular Expression in Lexical Analyzer
24 | The following guide will explain how to use regular expression in lexical analysis.Basically regular expression is used to make scanners which is helpful in finding the tokens from the input string.We can even make more complex scanner to even parse the XML documents.A detailed guided can be found below
25 |
26 | [Using Regular Expressions in lexical Analyzer](http://effbot.org/zone/xml-scanner.htm)
27 |
28 | ## Conclusion
29 | This is just a beginner guide to regular expression and is only a kickstart.More is yet to go through
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/natural_language_processing/semantic_parsing.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Semantic parsing is the process of mapping natural language into component parts, with the intention of translating the text into a logical form that a machine can understand. One example of this is translating a search engine query into a SQL query, which can then be used to search a database. While there are similarities between semantic parsing and machine translation, the two processes differ in one important way – while in machine translation the target output is human readable, in semantic parsing the target output is machine readable.
2 |
3 | In semantic parsing development and research, there are four major models, with most instances using one or a combination of the models. These models are the Compositional Semantic Model, the Translation Model, Rule Extraction, and the Probabilistic Model. In the Compositional Semantic Model, algorithms generate compositional meaning representations such as logical forms and functional representations. These representations form the backbone of machine language. This process essentially transforms grammar structures into logical ones. The Translation Model works to map text inputs to representations structures like context-free grammar, which are recursive rules used to generate patterns of strings. Because context-free grammar applies defined rules to the text and translates it into a logical form, it is then easier to convert into a final, machine-readable product.
4 |
5 | In Rule Extraction, algorithms find the candidate translation rules. One method of doing this is through the construction of SILT trees, or trees for the Semantic Interpretation by Learning Transformations. SILT uses pattern-based transformation rules to map phrases in natural language to productions in machine-languages. In the Probabilistic Model, a variety of techniques are applied to learn and find the best translations. One such technique is known as semantic-based Probabilistic Context Free Grammar (PCFG). PCFG takes context-free grammar techniques one step further by associating rules with probabilities that are derived through annotated training data. The probabilistic data is then used in the case of multiple translation possibilities – the final selection can be made based on the overall probability of a parse tree for a given statement.
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/natural_language_processing/sentiment_analysis.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Sentiment analysis refers to the process of machines trying to do something humans find difficult much of the time – interpreting the emotion or feeling behind a body of text. In conversation, most people are very good at gauging sentiment, especially given the availability of cues such as facial expressions and vocal intonation. However, even the most emotionally intelligent person can have difficulties understanding the sentiments behind words when they are transmitted via a chat box on a computer. So how is it possible to train a machine to perform sentiment analysis accurately and reliably?
2 |
3 | Sentiment analysis is a Natural Language Processing technique that is generally done through something called deep learning. During the process of deep learning, engineers “teach” machines to recognize emotion in text by pairing examples of natural language with labels such as “negative” or “positive”. Internet forums and social media are popular sources of teaching material. Applications of this technology range, and include customer service, educational, and investing. For example, imagine your chatbot can infer your customer is frustrated and escalate their ticket, or you can make predictions about a stock price based on the way it’s being discussed in online forums.
4 |
5 | The accuracy of sentiment analysis is generally measured based on two criteria, polarity and degree. Polarity looks at whether a piece of text is positive or negative. Degree looks at how positive or negative it is. This measure is less clear, as even among people there can be disagreement over the degree of a piece of text. Ratings websites (such as those used to assign ratings to movies) provide one way to measure accuracy. Not only do users write reviews, but they also assign numerical or star scores to accompany them. This gives researchers the opportunity to pair a piece of text with a positive or negative rating.
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/natural_language_processing/stemming_lemmatization.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Stemming and Lemmatization
2 | ==========================
3 | An essential part of language is the use of different forms of a word, such as translate, translates, and translating.
4 | There are also derivations of words that carry similar meanings, for example multiply and multiplication.
5 |
6 | The goal of both stemming and lemmatization is to reduce inflectional forms and/or derivationally related forms of a word to a common base form. This is extremely useful for applications such as querying a search engine. For example, while a user may query the engine for childrens jackets, results returned for keywords child jacket could be equally as relevant to the user.
7 |
8 |
9 | The reduction may look something like this:
10 |
11 |
12 | am, are, is -> be
13 |
14 |
15 | cat, cats, cat’s, cats’ -> cat
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 | While both stemming and lemmatization share the goal of “normalizing” words to a common base form, they differ in how they attempt to achieve it.
21 |
22 |
23 | **Stemming:** heuristically removes the affixes of a word, to get to its stem (root). The end result is the non-changing portion of a word is returned. For example, the stem of amusing, amusement, and amused would be amus.
24 |
25 |
26 | Algorithms used for stemming include lookup tables and suffix-stripping algorithms. The most common algorithm used for stemming is the Porter stemming algorithm.
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 | **Lemmatization:** morphological analysis of a word that returns its lemma, a normalized form of a set of morphologically related forms chosen by convention. The result is that typically inflectional endings are removed and the dictionary form of a word is returned. For example, the word “better” has “good” as its lemma. The use of lemmatizers is more common than the user of stemmers, and typically returns more accurate results.
32 |
33 |
34 | Algorithms used for lemmatization can be based on dictionary lookups, Levenshtein distances, and other techniques.
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/natural_language_processing/synctatic_parsing.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Syntactic Parsing
2 |
3 | Syntactic parsing is the process of analysing words for grammar and arranging them such that the relationship between them is
4 | shown. Its attributes include dependency and part of speech tags-
5 | - Dependency is analysis of binary relations between 2 lexical items or words. Each relation is represented in the form of triplets(
6 | relation,governor,dependent)
7 |
8 | - Part of Speech tagging or POS tagging - This helps in identifying each word of the sentenceas a noun,pronoun,adjective and so on.
9 | It is used to improve word features and converting a word to its base(for example swimming,swam are derived from same word, swim).
10 | It can also be used to removed stopwords(repeatable words that are not required for analysis like 'the','if' etc)
11 |
12 | Motivations for syntactic parsing include machine translation, speech recognition, grammar checking, relation extraction, and question answering.
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/data_science/natural_language_processing/text_summarization.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | The goal of text summarization is to create a concise, accurate, and sensible summary of a longer piece of text. This is a difficult problem, because in order to create a summary of the important information, one must truly understand the point of the text. Text summarizers are essential because there is too much information in the world to summarize manually, and summaries allow us to reduce reading time, make selecting documents easier while researching, and contribute to the results of other algorithms, such as those used to answer questions. Examples of summaries are widespread, and include newspaper headlines, meeting minutes, movie previews, and sound bites.
2 |
3 | There are two main methods of creating summaries, extractive and abstractive. Extractive involves taking phrases or sentences directly from the source text to create a summary. Abstractive summarization is more challenging, as it involves generating entirely new phrases and sentences in an attempt to capture the meaning of the original document. Generally, regardless of the method used, the process of summarizing text using Natural Language Processing starts with interpreting the text as a whole. From there, the relevant information is extracted and condensed. Finally, the summary representation is presented to the reader in fluent, natural language.
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/databases/DBMS.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Database Management System
2 |
3 | A database management system (DBMS) is a collection of interrelated data and a set of programs to access those data. The collection of data, usually referred to as the database, contains inter-related information. The primary goal of a DBMS is to provide a way to store and retrieve database information that is both convenient and efficient.
4 |
5 | As opposed to the traditional file system used to manage data using files in hard disk, database management systems help overcome a number of issues such as -
6 | * Data redundancy and inconsistency
7 | * Difficulty in accessing data
8 | * Atomicity problems
9 | * Integrity problems
10 | * Concurrent access anomalies
11 | * Security problems
12 |
13 | ### Database Languages
14 |
15 | A database system provides a **data-definition language** to specify the database schema and a **data-manipulation language** to express database queries and updates. In practice, the data-definition and data-manipulation languages are not two separate languages; instead they simply form parts of a single database language, such as the widely used SQL.
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/databases/SQLAlchemy_intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # SQLAlchemy introduction
2 |
3 | If you are working with Python and need database integration in your project, SQLAlchemy is a widely used and trusted tool for doing so. SQLAlchemy is a Python SQL toolkit which basically provides SQL functionality in **pythonic** code.
4 | You could always say why not write raw SQL queries as Python strings and work with those? Well, there are certain disadvantages to that approach. SQL queries with python strings could get really messy and that too, really quickly.
5 | SQLAlchemy has several advantages over this approach. It makes the code cleaner and more secure. Most importantly,
6 | you can think of database structure in terms of objects and their attributes instead of the traditional columns and tables.
7 | With this, we can introduce the term ORM. SQLAlchemy is an ORM, namely an **Object Relational Mapper**. This means that this toolkit transfers *low level database logic* ( columns and tables ) into *higher level entities such as objects* which are more compliant with object oriented programming languages like Python or Java.
8 | This way when you get back a query result, you need not worry about working with columns or rows in the traditional way. Rather, that can be returned as a query *object* which will have certain properties and functions of its own like a normal object, which can be used to work with the query result in a manner we are much more familiar with.
9 | SQLAlchemy can be thought of as being made up of two major components: SQLAlchemy Core and ORM. The ORM is built on the core. However, you have the flexibility to use each of these as your application requires and according to the level of abstraction you prefer to have.
10 | A very simple example would be:
11 | A raw SQL statement would look something like this:
12 | ``` INSERT INTO students (name, ID, date_of_birth) VALUES ("Peter", 32, "20/1/2000") ```
13 |
14 | whereas using SQLAlchemy it would look something like this:
15 | ``` students.insert().values(name="Peter", ID=32, date_of_birth="20/1/2000")```
16 |
17 | We can clearly observe that the second statement looks a lot more like what we are familiar with and this is only the very basic level in which this can be used. There are several other features and advantages which one can use.
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/databases/database_keys.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Database keys
2 |
3 | A key is a collection of attributes (columns) with the ability to distinguish between different database entries (rows). This is most commonly referred to as a **superkey**, and no two entries can have the exact same values across all the attributes of the superkey.
4 |
5 | A **candidate key** is a superkey, but without all the extra attributes. This means that if we decided to omit an attribute, we would no longer be able to identify a single entry just by comparing the values in those specific columns.
6 |
7 | When creating a database table, we often have to specify which attributes will be used by the database as a unique identifier for our data. These *chosen* attributes are called the **primary key** and belong to one of the candidate keys.
8 |
9 | We might also have an attribute in our table which is a primary key in another table. This is called a **foreign key**. Specifying a foreign key constraint (rule) is a good way to make sure that entries from multiple tables are consistent.
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/databases/mongodb.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## OVERVIEW:
2 |
3 | MongoDB is a free and open-source cross-platform document-oriented database program (stores data as a "document" inside a collection) written in C++. It is a leading NoSQL database which works on terminologies that include database,collection and document. It is currently used by thousands of top organizations like Source Forge, Craigslist,eBay, Viacom, Foursquare and The New York Times
4 | ### CORE COMPONENTS OF MongoDB:
5 | **Mongod:** It handles data requests,manages data access and performs background data management operations.
6 |
7 | **Mongos:** It determines the location of the data in shard cluster in order to complete commanded operations.
8 |
9 | **Mongo:** It provides an interface to test queries and operation in the databases directly.
10 | ### KEY FEATURES OF MongoDB:
11 | #### SHARDING IN MongoDB:
12 | One of the most extinguishing features of MongoDB is the process of sharding.It is the process of storing data records across multiple machines.Upon increasing the data size a single machine may not be able to store data,here comes the concept of sharding.It's an attempt of MongoDB to meet the demands of data growth.
13 | #### REPLICATION IN MongoDB:
14 | Replication is the process of keeping identical copies of data on multiple servers to keep applications running and data safe.
15 | #### DIFFERENCE BETWEEN SHARDING AND REPLICATION:
16 | The shard provides the ability to partition the data and store it across multiple servers.So the resources are not limited to a single machine. Replication on the other hand, is a duplicate copy of the data in full to be used in case of hardware failure.
17 | ### OTHER FEATURES OF MongoDB
18 | Document-oriented,File storage,Server-side JavaScript execution,Capped collections
19 |
20 | ### ADVANTAGES OF USING MongoDB
21 |
22 | It finds application in Bigdata,Datahub,Mobile Infrastructure Development,User Data Management.
23 | One doesn't need much time to design database.
24 | It is scalable and consistent in nature It offers us freedom to run anywhere.
25 |
26 |
27 | [MongoDB INSTALLATION ON WINDOWS](https://www.guru99.com/installation-configuration-mongodb.html#1)
28 |
29 | [MongoDB TUTORIALS](https://www.guru99.com/mongodb-tutorials.html)
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/databases/mysql.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## OVERVIEW:
2 |
3 | MySQL is an open-source database management system, commonly installed as part of the popular LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP/Python/Perl) stack. It uses a relational database and SQL (Structured Query Language) to manage its data.
4 |
5 | The short version of the installation is simple: update your package index, install the mysql-server package, and then run the included security script.
6 |
7 | ### STEPS FOR INSTALLING MySQL in LINUX:
8 |
9 | #### Step 1: INSTALLING MySQL
10 | To install it, simply update the package index on your server and install the default package with `apt-get.`
11 |
12 | `sudo apt-get update`
13 | `sudo apt-get install mysql-server`
14 |
15 | You'll be prompted to create a root password during the installation. Choose a secure one and make sure you remember it, because you'll need it later. Next, we'll finish configuring MySQL.
16 |
17 | #### Step 2 — Configuring MySQL
18 | For fresh installations, you'll want to run the included security script. This changes some of the less secure default options for things like remote root logins and sample users. On older versions of MySQL, you needed to initialize the data directory manually as well, but this is done automatically now.
19 |
20 | Run the security script.
21 |
22 | `mysql_secure_installation`
23 |
24 | This will prompt you for the root password you created in Step 1. You can press `Y` and then `ENTER` to accept the defaults for all the subsequent questions, with the exception of the one that asks if you'd like to change the root password. You just set it in Step 1, so you don't have to change it now.
25 |
26 | #### Step 3 — Testing MySQL
27 | Regardless of how you installed it, MySQL should have started running automatically. To test this, check its status.
28 |
29 | `systemctl status mysql.service`
30 |
31 | If MySQL isn't running, you can start it with `sudo systemctl start mysql`.
32 |
33 | For an additional check, you can try connecting to the database using the mysqladmin tool, which is a client that lets you run administrative commands. For example, this command says to connect to MySQL as root (-u root), prompt for a password (-p), and return the version.
34 |
35 | `mysqladmin -p -u root version`
36 | ### OTHER FEATURES OF MongoDB
37 | Document-oriented,File storage,Server-side JavaScript execution,Capped collections
38 |
39 | ### ADVANTAGES OF USING MongoDB
40 |
41 | It finds application in Bigdata,Datahub,Mobile Infrastructure Development,User Data Management.
42 | One doesn't need much time to design database.
43 | It is scalable and consistent in nature It offers us freedom to run anywhere.
44 |
45 |
46 | [MySQL INSTALLATION ON OTHER OS](https://www.tutorialspoint.com/mysql/mysql-installation.htm)
47 |
48 | [MySQL TUTORIALS](https://www.w3schools.com/sql/)
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/issue_tracking/Bugzilla.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Bugzilla
2 |
3 | Bugzilla is a bugtracker and testing tool developed by the Mozilla project. It is written in *Perl*, uses MySQL and is licensed under Mozilla Public License.
4 |
5 | ## Why use Bugzilla ?
6 | You can use Bugzilla to track issues and bugs. Moreover, it is an open source tool and is free of cost. You can remove the bug or correct it by submitting a *patch* for review by mentors. It supports a robust, stable RDBMS back end.
7 | Bugzilla has a lot of features to offer:
8 |
9 | ## Features:
10 |
11 | ### Advanced search capabilities:
12 | Bugzilla not only offers a simple beginner-friendly bug search, that searches the full text of a bug but also, an advanced search, wherein the user can create any search he/she wants. The user can also have time-based searches and some specific queries, like the bug status.
13 |
14 | ### E-mail Notifications:
15 | The users have complete control over the notifications and emails sent by Bugzilla. You get an email about any change in Bugzilla and can enable\disable any notification that you get on a particular bug.
16 |
17 | ### Automatic Duplicate Bug Detection:
18 | When filing a bug in Bugzilla, as soon as you start typing a short summary for bug, it will automatically look for similar bugs in the system and allow the user to add themselves to the CC list of one of those bugs instead of filing a new one.
19 |
20 | ### Modify/file Bugs by e-mail:
21 | You can also send Bugzilla an email that will create a new bug, or will modify an existing bug and attach files to bugs.
22 |
23 | ### Time tracking:
24 | You can estimate how many hours a bug will take to fix, and then keep track of the hours you spend working on it. You can also set a deadline that a bug must be complete by.
25 |
26 | ### Strong security:
27 | Bugzilla protects against SQL Injection,Cross-Site Scripting and avoids information leaks. In case someone tries to guess your password and impersonate you, the account will be automatically locked after a few attempts.
28 |
29 | ### Customization:
30 | It makes the workflow completely customizable, you can add/edit the default list of bug statuses and resolutions. You can also add custom fields to your bug database, as per your organization's needs. You can also, define which groups of users can edit or see which bugs.
31 |
32 | ### Bug reporting:
33 | It has advanced reporting systems, to know how the bug database looks, you can create a table and use any search criteria to limit the bugs you want information on. You can move bugs, from an earlier version to the latest one or rather across installations.
34 |
35 | ## Links:
36 |
37 | Find more information at [https://www.bugzilla.org/features/](https://www.bugzilla.org/features/)
38 |
39 | Read it's [documentation](https://www.bugzilla.org/docs/)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/issue_tracking/Jira.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Jira
2 |
3 | Jira is a project management and issue tracking software developed by Atlassian, that can be used in the cloud, or self-hosted.
4 |
5 | ## Why use it?
6 |
7 | You can use Jira to track issues and bugs, but also to plan new features, get feedback and discuss issues, plan and track work, manage released and review performance.
8 |
9 | Using Jira to track bugs, issues, feature requests and planned enhancements helps developers by:
10 |
11 | * Reminding you what needs to be done
12 | * Prioritize issues in order of importance
13 | * Add extra information
14 | * Keep a record of the work being done to fix an issue
15 | * Discuss ideas
16 | * Keep track of who is working on what
17 |
18 | If you are working in a team, you can quickly see what stage a bug or new feature is at, by checking the issue. You can even subscribe to updates, and get an email notification when something changes.
19 |
20 | ## Features
21 |
22 | ### Issue Tracking
23 |
24 | The primary feature is to track your issues and bugs. Add an issue, and it can be assigned to someone in your team to fix. You can search, filter and comment on issues, and discuss how best to get them resolved.
25 |
26 | You can also use labels, status, and time tracking on issues.
27 |
28 | ### Planning
29 |
30 | You can use the board view to organise your issues into lists, or just to move issues along from planned, to in development, to completed. You can also use scrum style boards to set up a sprint and rank issues.
31 |
32 | Organising your issues in boards helps you see clearly what stage each issue is at towards getting resolved.
33 |
34 | ### Releases
35 |
36 | You can see what stage different versions of your software are at, in development or released. You can also maintain different versions at the same time, for different clients for example.
37 |
38 | ### Reports
39 |
40 | Report are available for a graphical overview, like charts and graphs.
41 |
42 | ## Pricing
43 |
44 | You can find out more about current pricing at [https://www.atlassian.com/software/jira/pricing](https://www.atlassian.com/software/jira/pricing)
45 |
46 | ## Links
47 |
48 | See some screenshots and information on features [https://www.atlassian.com/software/jira](https://www.atlassian.com/software/jira)
49 |
50 | Read the [documentation](https://confluence.atlassian.com/jirasoftwarecloud/jira-software-documentation-764477791.html)
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/logic/Monty_Hall_Problem.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Overview
2 | The **Monty Hall problem** is a probability puzzle credited to statistician [Steve Selvin](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Steve_Selvin), made famous by game show host Monty Hall. Steve published the puzzle and the solution in [The American Statistician](https://www.tandfonline.com/action/aboutThisJournal?journalCode=utas20), a scientific journal in 1975.
3 |
4 | ## The Puzzle
5 | Suppose that there are three doors. There is a car behind one of the doors, and goats behind the other two doors. You, as a contestant, do not know which door holds which. You are asked to pick a door. Let's say you pick door 1. The host, who knows what's behind each of the doors, opens one of the other doors, say door 3, to reveal a goat. Now you are given the option of switching your choice from door 1 to door 2. Does switching your choice increase your probability of winning the car?
6 |
7 | ## Controversy
8 | The solution provided by Steve in 1975 and later in 1990 by [Marilyn vos Savant](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marilyn_vos_Savant) generated a lot of controversy and made the puzzle famous throughout the world. A number of articles and papers were published on the puzzle. Mathematicians and PhDs provided formal proofs and computer simulations in support of the solution.
9 |
10 | ## Solution
11 | Consider the problem carefully. Your first choice, door 1, gives you a 1/3rd chance of winning the car. If you consider the other two doors as a set (door 2 and door 3), the chances of finding the car behind one of those doors is 2/3rd. Now the host opens one of those doors to reveal the goat. So the other door still retains the 2/3rd probability while your original choice has just a 1/3rd probability. So it is to your advantage to switch to door 2.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/logic/The_Dining_Philosophers_Problem.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Prologue
2 |
3 | **The Dining Philosophers Problem** is an abstract thought experiment often used in a [concurrent][1] algorithm to illustrate [synchronization][2] issues in computer science. The problem was originally formulated in 1965 by [Edsger Dijkstra][3].
4 |
5 | # Problem
6 |
7 | #### The Statement
8 |
9 | > Five philosophers sit at a round table with bowls of spaghetti. Forks are placed between each pair of adjacent philosophers. Each philosopher must alternately think and eat. However, one can only eat when they have both left and right forks. Each fork can be held by only one philosopher and so a philosopher can use the fork only if it is not being used by another philosopher. After an individual finishes eating, they need to put down both forks so that the forks become available to others. A philosopher can take the fork on their right or the one on their left as they become available, but cannot start eating before getting both forks.
10 |
11 | [][4]
12 |
13 | The problem is how to design a discipline of behavior such that no philosopher will starve!
14 |
15 | #### The Constraints
16 |
17 | - Eating is not limited by any space; an infinite supply and an infinite demand are assumed.
18 | - Each one can forever continue to alternate between eating and thinking.
19 | - No philosopher can know when others may want to eat or think.
20 |
21 | # Epilogue
22 |
23 | Suppose you construct a proposal like so:-
24 |
25 | 1. think until the left fork is available; when it is, pick it up;
26 | 2. think until the right fork is available; when it is, pick it up;
27 | 3. when both forks are held, eat for a fixed amount of time;
28 | 4. then, put the right fork down;
29 | 5. then, put the left fork down;
30 | 6. repeat from the beginning.
31 |
32 | Evidently, this attempted solution fails because it allows the system to reach a [deadlock][5] state, in which no progress is possible. You can improve upon it by including a timer but that too suffers from [livelock][6] & [starvation][7]!
33 |
34 | #### Solutions
35 |
36 | - **Resource Hierarchy Solution**, originally proposed by Dijkstra ([sample code][8]).
37 | - **Chandy/Misra Solution**, proposed by K. Mani Chandy & J. Misra in 1984.
38 |
39 | [1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Concurrency_(computer_science)
40 | [2]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Synchronization_(computer_science)
41 | [3]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edsger_W._Dijkstra
42 | [4]: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/7/7b/An_illustration_of_the_dining_philosophers_problem.png
43 | [5]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deadlock
44 | [6]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deadlock#Livelock
45 | [7]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Starvation_(computer_science)
46 | [8]: https://gist.github.com/davidjpfeiffer/2bda83fbba570592e4d46d5e47853d32
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/logic/The_Hardest_Logic_Puzzle_Ever.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Overview
2 |
3 | **The Hardest Logic Puzzle Ever** is a logic puzzle created by [Raymond Smullyan](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Raymond_Smullyan "Raymond Smullyan") and popularized by [George Boolos](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/George_Boolos "George Boolos"). This puzzle was published in [The Harvard Review of Philosophy](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Harvard_Review_of_Philosophy "The Harvard Review of Philosophy") in 1996 & is commonly known as *The Three Gods Riddle*.
4 |
5 | ## The Puzzle
6 |
7 | ### Statement :-
8 |
9 | > Three gods A, B, and C are called, in no particular order, True, False, and Random. True always speaks truly, False always speaks falsely, but whether Random speaks truly or falsely is a completely random matter. Your task is to determine the identities of A, B, and C by asking three yes-no questions; each question must be put to exactly one god. The gods understand English, but will answer all questions in their own language, in which the words for yes and no are da and ja, in some order. You do not know which word means which.
10 |
11 | ### Clarifications :-
12 |
13 | - You may ask three **yes** or **no** questions.
14 | - The Gods will answer either **da** or **ja** to each question.
15 | - In English, **da** or **ja** translates to **yes** or **no** but you do not know which is which!
16 | - Each question must be addressed to only one God.
17 | - You can address multiple questions to the same God.
18 | - You do not need to formulate the three questions simultaneously.
19 | - The response of God **Random** is equivalent to the outcome of the flip of a [fair coin](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fair_coin "fair coin")!
20 |
21 | ## Solution
22 |
23 | Let this problem sink in first & then try to come up with your own unique solution before referring to [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Hardest_Logic_Puzzle_Ever "Wikipedia") and [Youtube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LKvjIsyYng8 "Youtube")!
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/python/django.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## OVERVIEW
2 |
3 | Django,free and opensource web framework,which allows us to create secure and well maintained websites.Primary goal of django is to make the development of complex database driven websites easy.
4 | In order to write web applications in python directly basic requirements include:
5 |
6 | 1.Web server gateway interface.
7 |
8 | 2.Routing
9 |
10 | 3.SQL Interface
11 |
12 | 4.Template
13 |
14 | On the other hand Django includes all of the above mention features hence it becomes easy for one to write web application.One can focus on the designing part and writing of the web application without taking care of the above features.Various sites that use django includes Pinterest Public Broadcasting Service, Instagram, Mozilla, The Washington Times, Disqus, Bitbucket and Nextdoor.
15 |
16 |
17 | Django is fast,fully loaded,secure,scalable(can handle large increase in users,traffic on various sites) and versatile.Despite of the above stated advantages django is bad for large applications and it comes with tons of perbuilt features which may or maynot be used.
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 | ## RESOURCES TO LEARN DJANGO:
22 |
23 | [Django Girls Tutorial](https://tutorial.djangogirls.org/en/index.html)
24 |
25 | [How To Tango With Django 1.7](http://www.tangowithdjango.com/book17/)
26 |
27 | [Mastering Django for Django 1.8](https://mastering-django.thinkific.com/)
28 |
29 | [DJANGO INSTALLATION GUIDE](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/intro/install/)
30 |
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/web_development/ES6.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # ECMAScript 6
2 |
3 | ## Introduction
4 |
5 | ECMAScript 6 rolled out in 2015. Since it was the first major upgrade from ECMAScript 5, it brought along a lot of
6 | new and useful features with it. Currently, it isn't supported by a lot of browsers out there, and sometimes a complier
7 | is needed to translate ES 6 to ES 5.
8 |
9 | ## New Features
10 |
11 | + `let` and `const`keywords
12 | + Arrow functions
13 | ... and a lot more.
14 |
15 | ### `let` and `const` keywords
16 |
17 | With the `var` keyword, the enforcement of scopes of variables was pretty loose. For example -
18 |
19 | ```
20 | for(var i = 0;i<5;i++)
21 | console.log(i);
22 |
23 | console.log("After the loop, i is", i);
24 | ```
25 |
26 | Output-
27 |
28 | ```
29 | 0
30 | 1
31 | 2
32 | 3
33 | 4
34 | After the loop, i is 5
35 | ```
36 | On the other hand, if we try to run the following,
37 |
38 | ```
39 | for(let i = 0;i<5;i++)
40 | console.log(i);
41 |
42 | console.log("After the loop, i is", i);
43 | ```
44 | - we get an error message, since the variable `i` is available only inside the scope of the for loop. Clearly, this makes
45 | debugging a lot easier.
46 |
47 | We use `const` when we need to declare a constant whose value we do not want to change during program execution. The common
48 | convention is to put the names of constants in all uppercase letters with an underscore separating different words. For
49 | example-
50 |
51 | ```
52 | const ROOT_TWO = 1.414;
53 | ```
54 |
55 | ### Arrow functions
56 |
57 | Too often, we require single line functions that are consise and readable. For example -
58 |
59 | This-
60 | ```
61 | function sum(a,b){
62 | return a+b;
63 | }
64 |
65 | mySum = sum(10,5);
66 | ```
67 |
68 | - is unncecesarily lengthy for a function whose only job is to sum two numbers. So, now we have -
69 |
70 | ```
71 | sum = (a,b) => a+b;
72 |
73 | mySum = sum(a,b);
74 | ```
75 | However, it is worthwhile mentioning that arrow functions do not support the usage of the `this` keyword; nor can they
76 | be used as constructors. So, they're not suited to replace __all__ ES 5 functions.
77 |
78 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/web_development/NodeJS.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Node Js
2 |
3 | ## What is Node JS?
4 |
5 | **Node** JS is a runtime based on **Chrome's** V8 engine. People often confuse it with a framework or a language. But it's neither of them. Originally written by **[Ryan Dhal](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ryan_Dahl)** and later developed by **[Joyent, Inc](https://www.joyent.com/node-js/support)** was after 13 years of introduction to server-side programming using Javascript. What Ryan does is, he took out Chrome's V8 engine and wrapped it inside a C++ program.
6 | Node JS has the world's largest package ecosystem called **[npm](https://npmjs.org)**. NPM is a package manager built for using packages developed by other developers in a project. There are other package managers too. for example, yarn.
7 |
8 | ## *Out of the Box* modules
9 |
10 | Node JS comes with a few modules pre-installed. Here I am listing a few.
11 |
12 | `http`: http module is used to create http servers.
13 |
14 | `path`: As the name suggests, it's used for working with 'path'
15 |
16 | `os`: OS module is used to get the information of the system where we are running our app.
17 |
18 | So, these are a few modules with which you will work too frequently. Node JS isn't just limited in this modules. Using NPM or YARN, you can install a lot of modules and use them in your project.
19 |
20 | ## Frameworks
21 |
22 | Node JS comes with a lot of back-end frameworks. For example, for creating servers we will use **[Express.js](https://expressjs.com)** which is a framework for handling back-end tasks like routing etc. Express was built by **TJ Holowaychuk** who is one of the members of the core Node JS team.
23 | There are lots of other frameworks as well. Like **Hapi.js** for building APIs.
24 |
25 | ## Creating `http` server
26 |
27 | So, now we are gonna create our http server using the basic http module which ships with Node JS. And then we will create another server using Express JS.
28 |
29 | ### http server
30 |
31 | ```javascript
32 | const http = require('http');
33 |
34 | http.createServer(function (req, res) {
35 | res.write('Hello World!');
36 | res.end();
37 | }).listen(8080);
38 | ```
39 |
40 | Here, first, we required `http` module. Then we create a server object, `http.createServer`. createServer accepts a callback function which again accepts two arguments called `req, res`.
41 | `res` allows us to call another method 'write' using which we can write to the browser.
42 | At last, we are calling `listen()` to enable our app to listen to the port we specify.
43 | So, this is how we create an http server using the default http module.
44 |
45 | ### express server
46 |
47 | ```javascript
48 | const express = require('express');
49 | const app = express();
50 |
51 | app.get('/', (req, res) => {
52 | res.send('Hello World!');
53 | });
54 |
55 | app.listen(3000);
56 | ```
57 |
58 | First, install `express` using `npm install express` in your working directory or `npm instal -g express` for installing globally. `require()` it using `require()`. Now we have to call `express()` in another constant called `app`(or whatever you wanna name it). `app` gives us a method called `get` which performs a get request in a URL. `get` requires at least two parameters to work correctly, a path where it will perform get req and a callback function. Again callback function accepts two arguments `req` and `res`. req gives us a method called `send` which enables us to send data to the requested URL. Finally, we call `listen()` for listening to a specific port.
59 |
60 | So, this is how we create a basic server in Node Js.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/web_development/Reactjs.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # How to get started with React js quickly
2 |
3 | ## What is Reactjs ?
4 | ReactJS is an open-source JavaScript library used to build user interfaces specifically for single page applications.
5 |
6 | ## Step 1
7 |
8 | Install nodejs: go to [nodejs](https://nodejs.org/en/) website and install the application
9 |
10 | After installing nodejs go to Terminal/cmd and run `node -v` to check whether it's installed correctly or not(make sure to restart you computer before running the command)
11 |
12 | ## Step 2
13 |
14 | Open Terminal/cmd Run `npm install -g create-react-app`
15 | This command will install react on your workstation, -g flag means global i.e you will be able to create reactjs application throughout your operating system
16 |
17 | ## Step 3
18 |
19 | Run this command to create a reactjs app: `create-react-app app-name`
20 |
21 | To run the reactjs application: on terminal make sure you are inside the reactjs created application (cd app-name) and than run --> `npm start`
22 |
23 | After that open your browser and run `http://localhost:3000/`
24 | Now you are good to go, It will show welcome to reactjs template website which you can edit and then go to it's offical website if you want to learn more about [reactjs](https://reactjs.org/)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/web_development/WebAssembly.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Wasm
2 |
3 | [WebAssembly][1] (or Wasm) is a new portable, size as well as load-time efficient format suitable for compilation to the web. It is meant to execute code as nearly as fast as native machine code. Till now, we had been using [JavaScript][2] as the primary programming language in browsers for web development but it is not a compiled language and thus doesn't provide as much effieciency in terms of speed as compiled ones do! With WebAssembly, one can implement performance critical stuff & import it like a standard JavaScript module. Thus, WebAssembly is not meant to replace JS but to complement it wherever and whenever necessary.
4 |
5 | ## Pros
6 |
7 | #### Languages Supported
8 |
9 | - C/C++ (production ready support)
10 | - Rust (good support)
11 | - Java, C# (experimental support)
12 |
13 | #### Advantages
14 |
15 | - Efficient & Fast
16 | - Safe
17 | - Open & Debuggable
18 | - Open Web Platform
19 |
20 | ## And JS?
21 |
22 | **We need WebAssembly** because as flexible as JavaScript is, it’s still too hard to express many of the things we may want to in JavaScript, and the features we would need to make it easy might add complexity to a language that already confuses many users.
23 |
24 | ## Future
25 |
26 | Wasm is a Google, Microsoft, Apple & Mozilla initiave that is intended to build a faster web. It's all open source so hop in, just read the docs & get started. Here's some useful resources:
27 |
28 | - [Community Group][3]
29 | - [GitHub Repo][4]
30 |
31 |
32 | [1]: https://webassembly.org/
33 | [2]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/JavaScript
34 | [3]: https://www.w3.org/community/webassembly/
35 | [4]: https://github.com/WebAssembly
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/web_development/itcss.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ITCSS
2 | ======
3 | TCSS stands for Inverted Triangle CSS and it helps organize CSS by applying a structure that determines how specific to get with a specific component.
4 | Since ITCSS is mostly proprietary, no detailed rule book exists about its usage. Only a set of specific principles is at our disposal.
5 |
6 | Sections of ITCSS
7 | ==================
8 | Let’s take a quick look at each section of the inverted triangle moving from the top down to the tip.
9 |
10 | * Settings – Preprocessor variables and methods (no actual CSS output)
11 | * Tools – Mixins and functions (no actual CSS output)
12 | * Generic – CSS resets which might include Eric Meyer’s reset, Normalize.css, or your own batch of code
13 | * Elements – Single HTML element selectors without classes
14 | * Objects – Classes for page structure typically following the OOCSS methodology
15 | * Components – Aesthetic classes for styling any & all page elements (often combined with the structure of object classes)
16 | * Trumps – The most specific styles for overriding anything else in the triangle
17 |
18 | Conclusion
19 | ============
20 | Just as ITCSS doesn’t force you to use a certain naming conventions, it doesn’t force you to use all layers. Use a layer structure that works best for you while maintaining the ITCSS principles of generic to explicit, low to high specificity and far-reaching to localized.
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/guides/web_development/svelte.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # SVELTE Cybernetically enhanced web apps
2 |
3 | 
4 |
5 | ## WHAT EXACTLY SVELTE IS
6 |
7 | svelte got popular around 2019 with it's latest svelte 3 release.
8 | svelte is not a UI framework like angular or vue nor a library like UI react. Svelte is a compiler .svelte comes with a design pattern that is similar to vue.js design template. in production, svelte takes your code and makes a bundle.js file and other instruction files which does not have any extra code that is injected as other frameworks do. That bundle.js will be then shipped and execute on runtime. Because of that, svelte code is really small in size compared to other frameworks. with a small bundle size, svelte applications will load faster, enhancing the user experience.
9 |
10 | ## HELLO WORLD WITH SVELTE
11 |
12 | to get started with svelte install svelte template with npm
13 | ** make sure you have npm and nodejs installed before this step **
14 |
15 | ```
16 | npx degit sveltejs/template my-svelte-project
17 | ```
18 |
19 | now go to the cloned directory
20 |
21 | ```
22 | cd my-svelte-project
23 | ```
24 |
25 | now to install necessary dependencies
26 |
27 | ```
28 | npm install
29 | ```
30 |
31 | now to run the application
32 |
33 | ```
34 | npm run dev
35 |
36 | ```
37 |
38 | 
39 |
40 | there you have it, you successfully made hello world with svelte.
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------