├── basics
├── collections.py
├── zero_values.py
└── dictionary.py
├── dsa.jpeg
├── list
├── node.py
├── middle.py
├── delete_duplicates.py
├── swap_pairs.py
├── detect_cycle.py
├── find_intersection_node.py
├── odd_even_linked_list.py
├── linked_list_cycle_2.py
├── merge_two_sorted_list.py
├── reverse_linked_list.py
├── traverse.py
├── deep_coppy.py
├── is_palindrom.py
└── merge_sort.py
├── tree
├── tree_node.py
├── lowest_common_ancestor.py
├── maxdepth.py
├── mindepth.py
├── traverse.py
├── min_heap.py
└── README.md
├── sorting
├── bubblesort.py
├── quicksort.py
├── mergesort.py
└── radixsort.py
├── graph
├── README.md
├── minimum_spanning_tree.py
├── union_find.py
├── cycle_detection.py
└── shortest_reach.py
├── basics.md
├── array
├── target_sum.py
├── missing_number.py
├── duplicated_numbers.py
├── merge_sort.py
└── subarray_mins.py
├── stack:queue
├── max_sliding_window.py
└── jump_game_4.py
├── bfs
└── level_order_traverse_tree.py
├── matrix
└── enclaves.py
├── unionfind
└── unionfind.py
├── trie
└── trie.py
└── README.md
/basics/collections.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dsa.jpeg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/the-writer-dev/ace-interview/HEAD/dsa.jpeg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/list/node.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | class ListNode:
2 | def __init__(self, data):
3 | self.data = data
4 | self.next = None
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/basics/zero_values.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # zero values in python
2 |
3 | print(bool({}))
4 | print(bool(set()))
5 | print(bool([]))
6 | print(bool(None))
7 | print(bool(''))
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tree/tree_node.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | class TreeNode:
2 | def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
3 | self.val = val
4 | self.left = left
5 | self.right = right
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/list/middle.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # find the middle node of the given linked list
2 |
3 |
4 | def middle(head):
5 | slow = fast = head
6 | while fast and fast.next:
7 | fast = fast.next.next
8 | slow = slow.next
9 |
10 | return slow
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tree/lowest_common_ancestor.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | def lca(root, p, q):
2 | if root.left:
3 | l = lca(root.left, p, q)
4 | if root.right:
5 | r = lca(root.right, p, q)
6 |
7 | if l and r:
8 | return root
9 | return l or r
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/basics/dictionary.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | example = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': {'value2-1', 'value2-2'}}
2 |
3 | # difference between del vs pop
4 | # del does not return any value
5 | # pop does return pop value
6 |
7 | print(example)
8 | value1 = example.pop('key1')
9 | del example['key2']
10 |
11 | print(example)
12 |
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sorting/bubblesort.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | def bubblesort(arr):
2 | n = len(arr)
3 |
4 | for i in range(n):
5 | for j in range(n-i-1):
6 | if arr[j] > arr[j+1]:
7 | arr[j], arr[j+1] = arr[j+1], arr[j]
8 | return arr
9 |
10 | arr = [64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90]
11 | print(bubblesort(arr))
12 |
13 |
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/list/delete_duplicates.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # link: https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list/description/
3 | def deleteDuplicate(head):
4 | curr = head
5 | while curr:
6 | while curr.next and curr.val == curr.next.val:
7 | curr.next = curr.next.next
8 | curr = curr.next
9 | return head
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/graph/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## What is graph?
2 | A Graph is a non-linear data structure consisting of vertices and edges. You can think of a vertice as a node and edges as connections between nodes.
3 |
4 | 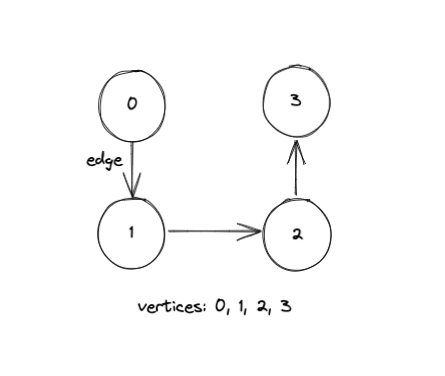
5 |
6 | ## Concepts
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/basics.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ### defaultdict
2 | defaultdict never raises a KeyError. It provides a default value for the key that does not exists.
3 |
4 | ```python
5 | from collections import defaultdict
6 | d = defaultdict(int)
7 |
8 | for letter in s:
9 | d[letter] += 1
10 |
11 | # iteration
12 | for k,v in d.items():
13 | print("{}: {}".format(k,v))
14 | ```
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/list/swap_pairs.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # link: https://leetcode.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/
2 |
3 | # idea: messing around the multiple pointers...
4 |
5 |
6 | def swapPairs(head):
7 | dummy = ListNode(None, head)
8 | prev, cur = dummy, head
9 | while cur and cur.next:
10 | prev.next = cur.next
11 | cur.next = cur.next.next
12 | prev.next.next = cur
13 | prev, cur = cur, cur.next
14 | return dummy.next
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/list/detect_cycle.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # link: https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/description/
2 |
3 | # idea: assume they are on the circular track.
4 | # if one is twice as fast as the other one, it will catch the other one at some point
5 | def hasCycle(head):
6 | fast = slow = head
7 | while fast and fast.next:
8 | slow = slow.next
9 | fast = fast.next.next
10 | if slow == fast:
11 | return True
12 | return False
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/list/find_intersection_node.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # link: https://leetcode.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/description/
2 |
3 | # idea: concatenate two linked list -> (a+b) and (b+a)
4 | # if a and b has intersection, we return that node
5 | # else we return null
6 | def find_intersection(a, b):
7 | if a == None or b == None:
8 | return None
9 |
10 | while a != b:
11 | a = a.next if a else b
12 | b = b.next if b else a
13 | return a
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tree/maxdepth.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from tree_node import TreeNode
2 |
3 | root = TreeNode(1)
4 | root.left = TreeNode(2)
5 | root.right = TreeNode(3)
6 | root.left.left = TreeNode(4)
7 |
8 |
9 | def max_depth(root):
10 | def dfs(root):
11 | if root == None:
12 | return 0
13 | else:
14 | l = dfs(root.left)
15 | r = dfs(root.right)
16 | return max(l, r) + 1
17 | return dfs(root)
18 |
19 |
20 | d = max_depth(root)
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/list/odd_even_linked_list.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # link: https://leetcode.com/problems/odd-even-linked-list/
2 |
3 |
4 | def oddEvenList(head):
5 | odd = even = head
6 | eHead = head.next
7 |
8 | while even and even.next:
9 | # jump to next odd index nodes
10 | odd.next = odd.next.next
11 |
12 | # jump to next even index nodes
13 | even.next = even.next.next
14 | odd = odd.next
15 | even = even.next
16 |
17 | odd.next = eHead
18 | return head
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/list/linked_list_cycle_2.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # link: https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/
2 |
3 | # the idea is discussed in /graph/cycle_detection.py
4 | def detectCycle(self, head):
5 | slow, fast = head, head
6 | while fast and fast.next:
7 | slow = slow.next
8 | fast = fast.next.next
9 | if slow == fast:
10 | slow = head
11 | while slow != fast:
12 | slow = slow.next
13 | fast = fast.next
14 | return slow
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tree/mindepth.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from tree_node import TreeNode
2 |
3 | root = TreeNode(3)
4 | root.left = TreeNode(9)
5 | root.right = TreeNode(1)
6 | root.left.left = TreeNode(4)
7 | root.left.left.left = TreeNode(6)
8 |
9 |
10 | def min_depth(root):
11 | if not root:
12 | return 0
13 | if None in [root.left, root.right]:
14 | return max(min_depth(root.left), min_depth(root.right)) + 1
15 | else:
16 | return min(min_depth(root.left), min_depth(root.right)) + 1
17 |
18 |
19 | d = min_depth(root)
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/array/target_sum.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # find the all pairs that sum to k
2 | # this is a tweaked question of two sum link -> https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum/
3 | from collections import defaultdict
4 |
5 | nums = [2,6,3,9,11,0]
6 | k = 9
7 | def target_sum(nums, k):
8 | h = defaultdict(int)
9 | res = []
10 | for i in range(len(nums)):
11 | if nums[i] in h:
12 | res.append({nums[h[nums[i]]], nums[i]})
13 | else:
14 | h[k-nums[i]] = i
15 |
16 | return res
17 |
18 | print(target_sum(nums, k))
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/list/merge_two_sorted_list.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from node import ListNode
2 |
3 | # merge two sorted linked list in one sorted linked list
4 |
5 |
6 | def merge(l1, l2):
7 | curr = dummy = ListNode(-1)
8 | while l1 and l2:
9 | if l1.val < l2.val:
10 | curr.next = ListNode(l1.val)
11 | curr, l1 = curr.next, l1.next
12 | else:
13 | curr.next = ListNode(l2.val)
14 | curr, l2 = curr.next, l2.next
15 | if l1 or l2:
16 | curr.next = l1 or l2
17 |
18 | return dummy.next
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/array/missing_number.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # link: https://leetcode.com/problems/missing-number/submissions/
2 |
3 | # idea
4 | # example = [3,0,1] -> ans = 2
5 | # example = [1,2,3] -> ans = 4
6 |
7 | # in perfect array, nor operation on both index and values
8 | # the bit will be 0, which we should return the border value
9 | # in imperfect array,
10 | # the bit will be the value we miss
11 |
12 | def missingNumber(self, nums):
13 | # bit manipulation
14 | # nor operation
15 | bit = len(nums)
16 | for i in range(len(nums)):
17 | bit ^= nums[i]
18 | bit ^= i
19 |
20 | return bit
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/array/duplicated_numbers.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # link: https://leetcode.com/problems/find-the-duplicate-number/
2 |
3 | # the idea is discussed in /graph/cycle_detection.py
4 |
5 |
6 | def findDuplicate(nums):
7 | if len(nums) < 2:
8 | return -1
9 |
10 | slow = nums[0]
11 | fast = nums[nums[0]]
12 |
13 | while slow != fast:
14 | slow = nums[slow]
15 | fast = nums[nums[fast]]
16 |
17 | slow = 0
18 | while slow != fast:
19 | slow = nums[slow]
20 | fast = nums[fast]
21 |
22 | return slow
23 |
24 |
25 | nums = [1, 3, 4, 2, 2]
26 | print(findDuplicate(nums))
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/stack:queue/max_sliding_window.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # link: https://leetcode.com/problems/sliding-window-maximum/
2 |
3 | # idea
4 | # use the monotonic deque
5 |
6 | # analysis: O(n)/ O(n)
7 | from collections import deque
8 | def max_sliding_window(nums, k):
9 | q = deque()
10 | res = []
11 | for i in range(len(nums)):
12 | while q and nums[q[-1]] <= nums[i]:
13 | q.pop()
14 | q.append(i)
15 |
16 | if i-q[0] == k:
17 | q.popleft()
18 |
19 | if i >= k-1:
20 | res.append(nums[q[0]])
21 | return res
22 |
23 | nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7]
24 | k = 3
25 |
26 | print(max_sliding_window(nums,k))
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/array/merge_sort.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | def mergeSort(arr):
2 | if len(arr) > 1:
3 | mid = len(arr) // 2
4 | l = arr[:mid]
5 | r = arr[mid:]
6 |
7 | mergeSort(l)
8 | mergeSort(r)
9 |
10 | i = j = k = 0
11 | while i < len(l) and j < len(r):
12 | if l[i] < r[j]:
13 | arr[k] = l[i]
14 | i += 1
15 | else:
16 | arr[k] = r[j]
17 | j += 1
18 | k += 1
19 |
20 | while i < len(l):
21 | arr[k] = l[i]
22 | i += 1
23 | k += 1
24 | while j < len(r):
25 | arr[k] = r[j]
26 | j += 1
27 | k += 1
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/list/reverse_linked_list.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from node import ListNode
2 | from traverse import traverse
3 |
4 |
5 | head = ListNode(1)
6 | head.next = ListNode(2)
7 | head.next.next = ListNode(3)
8 | head.next.next.next = ListNode(4)
9 |
10 | # reverse the linked list
11 | # recursion
12 |
13 |
14 | def reverse_itr(head):
15 | prev = None
16 | while head:
17 | curr = head
18 | head = head.next
19 | curr.next = prev
20 | prev = curr
21 | return prev
22 |
23 |
24 | def reverse_rec(node, prev=None):
25 | if not node:
26 | return prev
27 | n = node.next
28 | node.next = prev
29 | return reverse_rec(n, node)
30 |
31 |
32 | traverse(reverse_rec(head))
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/list/traverse.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from node import ListNode
2 |
3 |
4 | def traverse(head):
5 | curr = head
6 | while curr:
7 | print(curr.data)
8 | curr = curr.next
9 |
10 |
11 | def insert(head, data, pos):
12 | new = ListNode(data)
13 | if pos == 0:
14 | new.next = head
15 | head = new
16 | return
17 |
18 | prev = head
19 | for _ in range(pos-1):
20 | prev = prev.next
21 | new.next = prev.next
22 | prev.next = new
23 |
24 |
25 | def delete(head, pos):
26 | if pos == 0:
27 | head = head.next
28 | return
29 | prev = head
30 | for _ in range(pos-1):
31 | prev = prev.next
32 | prev.next = prev.next.next
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sorting/quicksort.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # analysis: O(n^2)
2 |
3 | def partition(arr, low, high):
4 | i = (low - 1)
5 | pivot = arr[high]
6 | print("i {} and pivot {}".format(i, pivot))
7 | for j in range(low, high):
8 | if arr[j] <= pivot:
9 | i = i + 1
10 | arr[i], arr[j] = arr[j], arr[i]
11 | arr[i+1],arr[high] = arr[high],arr[i+1]
12 | return (i+1)
13 |
14 | def quicksort(arr, start, end):
15 | if start >= end:
16 | return arr
17 | pivotIndex = partition(arr, start, end)
18 |
19 | quicksort(arr, start, pivotIndex - 1)
20 | quicksort(arr, pivotIndex + 1, end)
21 |
22 | return arr
23 |
24 | arr = [4,8,7,2,11,1,3]
25 | print(quicksort(arr, 0, len(arr)-1))
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/graph/minimum_spanning_tree.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # link:
2 | import union_find
3 |
4 |
5 | def minCostConnectPoints(self, points: List[List[int]]) -> int:
6 | def manhattanDist(p1, p2):
7 | return abs(p1[0] - p2[0]) + abs(p1[1] - p2[1])
8 |
9 | edges = []
10 | n = len(points)
11 | for i in range(n):
12 | for j in range(i + 1, n):
13 | edges.append([manhattanDist(points[i], points[j]), i, j])
14 |
15 | edges.sort() # Sort increasing order by dist
16 | uf = union_find.UnionFind(n)
17 | ans = 0
18 | for d, u, v in edges:
19 | if uf.union(u, v):
20 | ans += d
21 | n -= 1
22 | if n == 1:
23 | break # a bit optimize when we found enough n-1 edges!
24 | return ans
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/stack:queue/jump_game_4.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # link: https://leetcode.com/problems/jump-game-vi/
2 |
3 | # idea
4 | # similar to max sliding window problem
5 | # note that the first element and the last element should be always included in the calculation
6 |
7 | # analysis: O(n)/ O(n)
8 | from collections import deque
9 | def max_result(nums, k):
10 | q = deque()
11 | for i in range(len(nums)):
12 | nums[i] += nums[q[0]] if len(q) else 0
13 | while q and nums[i] >= nums[q[-1]]: q.pop() # remove elements which are smaller than the current input
14 | if q and i - q[0] == k: q.popleft() # remove expired elements which are earlier than the (i-k)th element
15 | q.append(i)
16 | return nums[-1]
17 |
18 | nums = [1,-1,-2,4,-7,3]
19 | k = 2
20 |
21 | print(max_result(nums,k))
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/graph/union_find.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | class UnionFind:
2 | # initially each node is its parent and rank is 1
3 | def __init__(self, N):
4 | self.parents = [n for n in range(N)]
5 | self.ranks = [1 for _ in range(N)]
6 |
7 | # path compression
8 | # complexity: O(log n)
9 | def find(self, u):
10 | while u != self.parents[u]:
11 | self.parents[u] = self.parents[self.parents[u]]
12 | u = self.parents[u]
13 | return u
14 |
15 | # union by rank
16 | # complex: O(log n)
17 | def union(self, u, v):
18 | if self.ranks[u] < self.ranks[v]:
19 | self.parents[u] = v
20 | elif self.ranks[u] > self.ranks[v]:
21 | self.parents[v] = u
22 | else:
23 | self.parents[v] = u
24 | self.ranks[u] += 1
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sorting/mergesort.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | def mergeSort(arr):
2 | if len(arr) < 2:
3 | return arr
4 |
5 | mid = len(arr) // 2
6 | left = mergeSort(arr[0:mid])
7 | right = mergeSort(arr[mid:])
8 |
9 | return merge(left, right)
10 |
11 | # unlike JS, list has no popleft thus we need indicies to iterate through
12 | def merge(l, r):
13 | res = []
14 | i = 0
15 | j = 0
16 | while i < len(l)and j < len(r):
17 | if l[i] < r[j]:
18 | res.append(l[i])
19 | i += 1
20 | else:
21 | res.append(r[j])
22 | j += 1
23 |
24 | while i < len(l) :
25 | res.append(l[i])
26 | i += 1
27 | while j < len(r):
28 | res.append(r[j])
29 | j += 1
30 |
31 | return res
32 |
33 | arr = [4,8,7,2,11,1,3]
34 | print(mergeSort(arr))
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/list/deep_coppy.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # link: https://leetcode.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/description/
2 |
3 | import collections
4 |
5 |
6 | class RandomNode:
7 | def __init__(self, x: int, next: "Node" = None, random: "Node" = None):
8 | self.val = int(x)
9 | self.next = next
10 | self.random = random
11 |
12 |
13 | def deep_copy(head):
14 | dic = collections.defaultdict(lambda: RandomNode(0))
15 |
16 | # in case a node's random pointer refers to None
17 | dic[None] = None
18 | curr = head
19 |
20 | # while iterating, default dict will create a randome node with next and random set to none
21 | while curr:
22 | dic[curr].val = curr.val
23 | dic[curr].next = dic[curr.next]
24 | dic[curr].random = dic[curr.random]
25 | curr = curr.next
26 |
27 | return dic[head]
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/graph/cycle_detection.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # in graph
2 | # if a cycle exists, we can detect the cycle in 2 steps
3 | # 1. slow and fast pointer, which slow advances one node each unit of time while fast advances two nodes each unit of time
4 | # so, the fast will catch up the slow
5 | # 2. put either slow and fast pointer to the first position of the graph
6 | # advance both one node each unit of time and the meeting point is the starting point of the cycle
7 |
8 | # proof
9 | # let's say slow travels only x + y and fast travels x + y + z + y where they meet at y
10 | # fast is fast as twice as slow, so the equation would be 2 (x + y) = x + 2y + z => x = z hence moving one pointer
11 | # to the first point of graph works
12 |
13 | # related topic (you can find either in this repo or Leetcode)
14 | # linked list cycle
15 | # linked list cycle 2
16 | # duplicated numbers
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/list/is_palindrom.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # link: https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list/description/
2 |
3 | # idea: move the first pointer to the mid
4 | # while moving the first pointer to last node, reverse the second pointer to the first node
5 |
6 |
7 | def isPalindrome(head):
8 | slow, fast, prev = head, head, None
9 | while fast and fast.next:
10 | slow, fast = slow.next, fast.next.next
11 |
12 | prev, prev.next, slow = slow, None, slow.next
13 |
14 | # reverse the last half of linked list
15 | while slow:
16 | slow.next, prev, slow = prev, slow, slow.next
17 |
18 | fast, slow = head, prev
19 |
20 | # check the first half of linked list and last half of linked list
21 | while slow:
22 | if fast.val != slow.val:
23 | return False
24 | fast, slow = fast.next, slow.next
25 | return True
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/bfs/level_order_traverse_tree.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from collections import deque
2 | from collections import defaultdict
3 |
4 |
5 | class Graph:
6 | def __init__(self):
7 | self.graph = defaultdict(list)
8 |
9 | def addEdge(self, u, v):
10 | self.graph[u].append(v)
11 |
12 | def bfs(self, s):
13 | visited = [False] * (max(self.graph) + 1)
14 | q = deque([s])
15 | visited[s] = True
16 |
17 | while q:
18 | c = q.popleft()
19 | print(c)
20 | for v in self.graph[s]:
21 | if visited[v] == False:
22 | q.append(v)
23 | visited[v] = True
24 |
25 |
26 | g = Graph()
27 | g.addEdge(0, 1)
28 | g.addEdge(0, 2)
29 | g.addEdge(0, 3)
30 | g.addEdge(1, 0)
31 | g.addEdge(2, 0)
32 | g.addEdge(2, 3)
33 | g.addEdge(3, 0)
34 | g.addEdge(3, 2)
35 |
36 | g.bfs(0)
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sorting/radixsort.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # utilize the auxiliary arr to reduce the time complexity
2 | # analysis: O(n+k)/O(max(arr))
3 | def countingsort(arr, place):
4 | size = len(arr)
5 | output = [0] * size
6 |
7 | count = [0] * 10
8 | for i in range(0, size):
9 | count[arr[i]] += 1
10 |
11 | for i in range(1, 10):
12 | count[i] += count[i-1]
13 |
14 | i = size - 1
15 | while i >= 0:
16 | index = arr[i] // place
17 | output[count[index % 10]-1] = arr[i]
18 | count[index % 10] -= 1
19 | i -= 1
20 | for i in range(size):
21 | arr[i] = output[i]
22 |
23 | def radixsort(arr):
24 | max_element = max(arr)
25 | place = 1
26 | while max_element // place > 0:
27 | countingsort(arr, place)
28 | place *= 10
29 |
30 | arr = [4, 2, 2, 8, 3, 3, 1]
31 | radixsort(arr)
32 |
33 | print(arr)
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/list/merge_sort.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # link: https://leetcode.com/problems/sort-list/description/
2 |
3 |
4 | def mergeSort(head):
5 | # divide input in halves
6 | if not head or not head.next:
7 | return head
8 | fast, slow = head.next, head
9 | # find the middle node
10 | while fast and fast.next:
11 | fast = fast.next.next
12 | slow = slow.next
13 |
14 | nxt, slow.next = (slow.next,) = None
15 |
16 | # call the left sub and right sub
17 | l, r = mergeSort(head), mergeSort(nxt)
18 |
19 | # merge
20 | if not l or not r:
21 | return l or r
22 | dummy = curr = ListNode(0)
23 | while l and r:
24 | if l.val < r.val:
25 | curr.next = l
26 | l = l.next
27 | else:
28 | curr.next = r
29 | r = r.next
30 | curr = curr.next
31 | curr.next = l or r
32 | return dummy.next
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/array/subarray_mins.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # link: https://leetcode.com/problems/sum-of-subarray-minimums/
2 |
3 | def subarray_mins(arr):
4 | left = [x+1 for x in range(len(arr))]
5 | right = [len(arr) - x for x in range(len(arr))]
6 |
7 | p = []
8 | n = []
9 | for i in range(len(arr)):
10 | # previous less
11 | while p and p[-1][0] > arr[i]:
12 | p.pop()
13 | left[i] = i+1 if not p else i - p[-1][1]
14 | p.append([arr[i], i])
15 |
16 | # next less
17 | while n and n[-1][0] > arr[i]:
18 | x = n[-1]
19 | n.pop()
20 | right[x[1]] = i - x[1]
21 | n.append([arr[i], i])
22 |
23 | ans = 0
24 | mod = 10 ** 9 + 7
25 | for i in range(len(arr)):
26 | ans = (ans + arr[i]*left[i]*right[i]) % mod
27 | return ans
28 |
29 | arr = [3,7,8,4]
30 | print(subarray_mins(arr))
31 | arr = [2,9,7,3,4,6,1]
32 | print(subarray_mins(arr))
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tree/traverse.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import collections
2 | from tree_node import TreeNode
3 |
4 |
5 | root = TreeNode(1)
6 | root.left = TreeNode(2)
7 | root.right = TreeNode(3)
8 | root.left.left = TreeNode(4)
9 |
10 |
11 | def in_order(root):
12 | if root:
13 | in_order(root.left)
14 | print(root.val)
15 | in_order(root.right)
16 |
17 |
18 | def pre_order(root):
19 | if root:
20 | print(root.val)
21 | print(root.left)
22 | print(root.right)
23 |
24 |
25 | def post_order(root):
26 | if root:
27 | post_order(root.left)
28 | post_order(root.right)
29 | print(root.val)
30 |
31 |
32 | def level_order(root):
33 | if root == None:
34 | return
35 |
36 | q = collections.deque([root])
37 | while q:
38 | c = q.popleft()
39 | print(c.val)
40 | if c.left:
41 | q.append(c.left)
42 | if c.right:
43 | q.append(c.right)
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/matrix/enclaves.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # link: https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-enclaves/
2 |
3 | # idea
4 | # if land cells were totally surrounded by sea cells, add counts to the result
5 | # conversly, if lands were on the edge, we don't count -> clean these cells
6 | # use dfs to search through the cells
7 | def enclaves(grid):
8 | dirs = [[0,1], [0,-1], [1,0], [-1,0]]
9 |
10 | def search(i, j):
11 | # mark visited
12 | grid[i][j] = 0
13 | for d in dirs:
14 | x = i + d[0]
15 | y = j + d[1]
16 | if 0 <= x < len(grid) and 0 <= y < len(grid[0]) and grid[x][y] == 1:
17 | search(i,j)
18 |
19 | for i in range(len(grid)):
20 | for j in range(len(grid[0])):
21 | if grid[i][j] == 1 and (i == 0 or j == 0 or i == len(grid) or j == len(grid[0])):
22 | search(i,j)
23 |
24 | return sum(sum(grid,[]))
25 |
26 | cells = [[0,0,0,0],[1,0,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[0,0,0,0]]
27 | print(enclaves(cells))
28 |
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/unionfind/unionfind.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | class UnionFind:
2 | def __init__(self, n):
3 | self._parents = [node for node in range(n)]
4 | self._ranks = [1 for _ in range(n)]
5 |
6 | def union(self, u, v):
7 | root_u, root_v = self.find(u), self.find(v)
8 | if root_u == root_v:
9 | return
10 |
11 | if self._ranks[root_u] > self._ranks[root_v]:
12 | self._parents[root_v] = root_u
13 | elif self._ranks[root_u] < self._ranks[root_v]:
14 | self._parents[root_u] = root_v
15 | else:
16 | self._parents[root_u] = root_v
17 | self._ranks[root_v] += 1
18 |
19 | def find(self, u):
20 | while self._parents[u] != u:
21 | self._parents[u] = self._parents[self._parents[u]]
22 | u = self._parents[u]
23 | return u
24 |
25 | unionfind = UnionFind(5)
26 | print(unionfind._parents)
27 |
28 | unionfind.union(0,1)
29 | print(unionfind._parents)
30 |
31 | print(unionfind.find(1))
32 | print(unionfind.find(0))
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/graph/shortest_reach.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # link: https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/ctci-bfs-shortest-reach/problem
2 |
3 | # idea
4 | # build the graph
5 | # use bfs to search through and calculate the distances at each node
6 | from collections import defaultdict
7 |
8 | def shortest_reach(v, e, start):
9 | graph = defaultdict(dict)
10 |
11 | distances = [-1] * v
12 | for k, v in e:
13 | graph[k][v] = 1
14 | graph[v][k] = 1
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 | # why this weird 'start-1'? - normaly elements in arr start with 0 but given nodes start with 1
19 | distances[start-1] = 0
20 | q = [start]
21 | visited = {start}
22 | while q:
23 | level_size = len(q)
24 | for _ in range(level_size):
25 | n = q.pop(0)
26 | for neighbor in graph[n]:
27 | if neighbor not in visited:
28 | q.append(neighbor)
29 | visited.add(neighbor)
30 | distances[neighbor-1] = distances[n-1] + 6
31 |
32 | # return distances excluding the element of starting index
33 | return [distances[i] for i, x in enumerate(distances) if i not in [start-1]]
34 |
35 | e = [[1,2], [2,3], [3,4], [1,5]]
36 | print(shortest_reach(6, e, 2))
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tree/min_heap.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | class MinHeap:
2 | def __init__(self):
3 | self.q = []
4 |
5 | def push(self, item):
6 | self.q.append(item)
7 | self.shiftup(item)
8 |
9 | def pop(self):
10 | if len(self.q) == 1:
11 | return self.q.pop()
12 |
13 | pop_item = self.q[0]
14 | self.q[0] = self.q.pop()
15 | self.shiftdown()
16 | return pop_item
17 |
18 | def shiftup(self, item):
19 | pos = len(self.q) - 1
20 | while pos > 0:
21 | parent = (pos-1)//2
22 | if self.q[parent] > item:
23 | self.q[pos] = self.q[parent]
24 | else:
25 | break
26 | pos = parent
27 |
28 | self.q[pos] = item
29 |
30 | def shiftdown(self):
31 | pos = 0
32 | l_child = pos * 2 + 1
33 | while l_child < len(self.q):
34 | r_child = l_child + 1
35 | if r_child < len(self.q) and self.q[l_child] > self.q[r_child]:
36 | l_child = r_child
37 | if self.q[l_child] < self.q[pos]:
38 | self.q[l_child], self.q[pos] = self.q[pos], self.q[l_child]
39 | pos = l_child
40 | l_child = pos * 2 + 1
41 |
42 | def isleaf(self, pos):
43 | return pos*2 > len(self.q)
44 |
45 |
46 | heap = MinHeap()
47 | heap.push(2)
48 | heap.push(3)
49 | heap.push(5)
50 | heap.push(1)
51 | heap.push(7)
52 |
53 | print(heap.q)
54 | print(heap.pop())
55 | print(heap.q)
56 | print(heap.pop())
57 | print(heap.q)
58 | print(heap.pop())
59 | print(heap.q)
60 | print(heap.pop())
61 | print(heap.q)
62 | print(heap.pop())
63 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tree/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Tree Terminology
2 | - tree is data structure defined as a collection of nodes.
3 | - subtrees are descendants of a node
4 | - nodes have value and they are connected with edges
5 | - root has no parent node
6 | - parent node is immediate predecessor of a node
7 | - children nodes are all immediate successors of a node
8 | - leaf node has no children nodes
9 | - edge is a connection between one node to another
10 | - path is a number of successive edges from one node to another
11 | - depth of a node is the number of edges from the node to the tree's root node.
12 | - root node will have a depth of 0.
13 | - height of a node is the number of edges on the longest path from the node to a leaf.
14 | - leaf nodes will have a height of 0.
15 |
16 | ## Types of tree
17 | - binary tree: every node can have at most 2 children, left and right
18 | - complete tree: binary tree, which every level is completely filled, possibly except for the lowest level.
19 | - balanced tree: binary tree, which the height of the left and right subtree at any node differs at most by 1.
20 | - perfect tree: binary tree, which every internal node has exactly two child nodes and all the leaf nodes are at the same level.
21 | - binary search tree: left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys lesser than the node’s key. right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node’s key.
22 |
23 | ## Traverse
24 | Traversing nodes in tree is essential to solve any tree related problems. Make sure you know how to traverse in
25 | - In Order
26 | - Pre Order
27 | - Post Order
28 | - Level Order
29 |
30 | [Link](./traverse.py) for code
31 |
32 | ## Calculate the depth of the tree
33 |
34 | [Max Depth of Tree](./maxdepth.py)
35 | [Min Depth of Tree](./mindepth.py)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/trie/trie.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # trie operations
2 | # 1. insert a word into a trie
3 | # 2. searching for words using a prefix
4 |
5 | class TrieNode:
6 | def __init__(self, char):
7 | self.char = char
8 | self.is_end = False
9 | # count how many times a word was inserted
10 | self.counter = 0
11 | self.children = {}
12 |
13 | class Trie:
14 | def __init__(self):
15 | self.root = TrieNode("")
16 |
17 | def insert(self, word):
18 | n = self.root
19 |
20 | for char in word:
21 | if char in n.children:
22 | n = n.children[char]
23 | else:
24 | node = TrieNode(char)
25 | n.children[char] = node
26 | n = node
27 | n.is_end = True
28 | n.counter += 1
29 |
30 | def dfs(self, n, prefix):
31 | if n.is_end:
32 | self.output.append((prefix + n.char, n.counter))
33 |
34 | for child in n.children.values():
35 | self.dfs(child, prefix + n.char)
36 |
37 | def query(self, x):
38 | self.output = []
39 |
40 | n = self.root
41 | for char in x:
42 | if char in n.children:
43 | n = n.children[char]
44 | else:
45 | return []
46 |
47 | # currently n = 'w' -> 'h'
48 | # prefix should be 'w'
49 | self.dfs(n, x[:-1])
50 | return sorted(self.output, key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
51 | #
52 | # w
53 | # / | \
54 | # a o h
55 | # / \ | | \
56 | # s r r a e
57 | # | | \
58 | # d t r
59 | # \
60 | # e
61 |
62 | t = Trie()
63 | t.insert('was')
64 | t.insert('war')
65 | t.insert('word')
66 | t.insert('where')
67 | t.insert('where')
68 | t.insert('what')
69 |
70 | print(t.query('wh'))
71 | print(t.query('wht'))
72 |
73 |
74 |
75 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Ace-Interview
2 |
3 | 
4 |
5 | Hi, folks!
6 | I know many of you have struggled to wrap your head around data structure and algorithms to prepare for your next technical interviews and it is stressful, indeed!
7 | Plus, you may experience the knowledge you tried to push into your brain fade away after a few weeks. At least, that was me :)
8 |
9 |
10 | I realize that we can prepare these and pass the interviews successfully with the right system and strategies from the experience.
11 | Thus, I'm trying to compile all the knowledge/resources you need along with the system I devised. Wish this boosts your learning journey of this :wink:
12 |
13 | # Table of Content
14 | ## Data Structure
15 | ## Algorithms
16 |
17 | ## Strategy
18 | ### Pick up the right language
19 | When you choose the language for technical interview, you might want to choose what is most comfortable to you. Java, C++, Python, or JavaScript are popular ones. Yet, I want you to choose the Python, or JavaScript with following reasons.
20 |
21 | First, when you study problems, you will be stuck a lot. If you choose Rust, for example, you might find difficult time to find solutions. On the other hadn, you can easily find the resources for Python/JS.
22 |
23 | Second, Python/Js have simpler syntax. When you're under pressure, you might loose your memory for syntax. Given that most interviews wouldn't allow you to google, Python/Js can be a safe bet to you.
24 |
25 | Here's the example for creating simple list of integers in Python and Java
26 | ```python
27 | lst = []
28 | ```
29 |
30 | ```java
31 | List list = new ArrayList<>();
32 | ```
33 | Yet, if you're already super-familiar with Java/C++, ignore this and choose what you're most comfortable with.
34 |
35 |
36 | ### Manage your time
37 | If we're given unlimited time for solving problems, we can eventually figure things out. Unforutnately, that wouldn't happen. Admittedly, It can be stressful when you're short on time, yet we can still pass the interviews successfuly if we have the proper strategy laid out on how we should spend time.
38 |
39 | #### How to distribute your time
40 | - First 5 minutes
41 | - Explore what you were asked
42 | - Find the brute force solution first
43 | - Optimize if you have time left
44 | - BUD
45 | - data structure that can reduce your complexity
46 | - Complexity analysis
47 |
48 | ## System
49 |
50 | ## Question you should ask to your interviewer and team
51 | - What teams would you belong?
52 | - What do your team do?
53 | - What is the tech stack?
54 | - What would daily life look like as an engineer?
55 |
56 |
57 | ## Useful Links
58 | https://visualgo.net/en
59 | https://algorithm-visualizer.org/
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------