├── project
├── controllers
│ └── all_controller
│ │ ├── .idea
│ │ ├── .name
│ │ ├── .gitignore
│ │ ├── inspectionProfiles
│ │ │ ├── profiles_settings.xml
│ │ │ └── Project_Default.xml
│ │ ├── misc.xml
│ │ ├── modules.xml
│ │ ├── test3_controller.iml
│ │ └── runConfigurations
│ │ │ └── test3_controller.xml
│ │ ├── test_a_star.py
│ │ ├── pid.py
│ │ ├── point.py
│ │ ├── prm_with_pid_controller1.py
│ │ ├── pid_test.py
│ │ ├── test3_controller.py
│ │ ├── atf_with_pid_controller.py
│ │ ├── a_star_controller.py
│ │ ├── atf_controller.py
│ │ ├── dwa_controller.py
│ │ ├── 1030DWA
│ │ ├── dwa_controller.py
│ │ ├── new_MPCController.py
│ │ └── dwa.py
│ │ ├── prm_controller.py
│ │ ├── 人工势场.py
│ │ ├── prm_with_pid_controller.py
│ │ ├── a_star.py
│ │ ├── MPCController.py
│ │ ├── prm算法.py
│ │ └── dwa.py
└── worlds
│ ├── .prm1.wbproj
│ ├── .prm.wbproj
│ ├── .trace.wbproj
│ └── .empty.wbproj
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
└── .gitignore
/project/controllers/all_controller/.idea/.name:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | dwa_controller.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/.idea/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 默认忽略的文件
2 | /shelf/
3 | /workspace.xml
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/.idea/inspectionProfiles/profiles_settings.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/.idea/misc.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/.idea/modules.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/test_a_star.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from a_star import *
2 |
3 | if __name__ == '__main__':
4 | obstacle = [(2.1, 2.3), (3.5, 4.7), (9, 9)]
5 | env = Env(100, 100, obstacle)
6 |
7 | start_point = (-20.5, -20.6)
8 | goal_point = (20, 20)
9 |
10 | a_star = AStar(start_point, goal_point, env)
11 |
12 | path, _ = a_star.searching()
13 |
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/.idea/test3_controller.iml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/worlds/.prm1.wbproj:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Webots Project File version R2021a
2 | perspectives: 000000ff00000000fd00000003000000000000000000000000fc0100000001fb0000001a0044006f00630075006d0065006e0074006100740069006f006e0000000000ffffffff0000005400ffffff0000000100000124000004d0fc0200000001fb0000001400540065007800740045006400690074006f00720100000025000004d00000004400ffffff0000000300000f00000002c4fc0100000001fb0000001a0043006f006e0073006f006c00650041006c006c0041006c006c010000000000000f000000007a00ffffff00000dd6000004d000000001000000020000000100000008fc00000000
3 | simulationViewPerspectives: 000000ff0000000100000002000002af00000b210100000006010000000100
4 | sceneTreePerspectives: 000000ff00000001000000020000069f000000fc0100000006010000000200
5 | maximizedDockId: -1
6 | centralWidgetVisible: 1
7 | orthographicViewHeight: 1
8 | textFiles: -1
9 | consoles: Console:All:All
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/worlds/.prm.wbproj:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Webots Project File version R2021a
2 | perspectives: 000000ff00000000fd000000030000000000000320000003acfc0100000002fb0000001e00480074006d006c0052006f0062006f007400570069006e0064006f00770000000000000003200000000000000000fb0000001a0044006f00630075006d0065006e0074006100740069006f006e0000000000ffffffff0000005400ffffff000000010000029900000331fc0200000001fb0000001400540065007800740045006400690074006f0072000000001a000003310000004400ffffff0000000300000f00000000ebfc0100000001fb0000001a0043006f006e0073006f006c00650041006c006c0041006c006c010000000000000f000000007a00ffffff00000f00000006a900000001000000020000000100000008fc00000000
3 | simulationViewPerspectives: 000000ff00000001000000020000041f00000adb0100000006010000000100
4 | sceneTreePerspectives: 000000ff00000001000000020000010f000000fc0100000006010000000200
5 | maximizedDockId: -1
6 | centralWidgetVisible: 1
7 | orthographicViewHeight: 1
8 | textFiles: -1
9 | globalOptionalRendering: CoordinateSystem
10 | consoles: Console:All:All
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/.idea/inspectionProfiles/Project_Default.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/.idea/runConfigurations/test3_controller.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | BSD 3-Clause License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2023, thinkerhui
4 |
5 | Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
6 | modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
7 |
8 | 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this
9 | list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
10 |
11 | 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
12 | this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
13 | and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
14 |
15 | 3. Neither the name of the copyright holder nor the names of its
16 | contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from
17 | this software without specific prior written permission.
18 |
19 | THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"
20 | AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
21 | IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
22 | DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE
23 | FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
24 | DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
25 | SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
26 | CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY,
27 | OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
28 | OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Algorithm-program-of-Unmanned-Vehicle-Tracking-Obstacle-Avoidance-Software-and-Webots-platform-model
2 | ## 项目介绍与团队成员
3 | 这个仓库存放的是SSE,SYSU的《基于多模态数据融合的无人车自主循迹避障软件》大创项目在研究过程过研究和实现的5个算法(A*、PRM、DWA、APF和MPC)的程序以及它们在Webots平台上对应的控制器搭载适配。这个仓库还包括和Webots相关的世界(World),World里面有大创小组自主搭建的麦克纳姆轮小车模型。
4 |
5 | 本项目的目的是设计并实现一种智能无人车自主循迹和避障的程序,通过深入研究无人车从环境识别、路径规划到与运动控制的算法,并结合各种算法的具体特点和适用条件进行多模态数据融合的输入,提高无人车循迹和避障算法的性能和鲁棒性。
6 |
7 | 本项目的研究和探索将为基于多模态数据融合的循迹避障算法贡献理论观点、模型平台和实验数据,推动无人车在无人驾驶、物流运输等领域的应用落地和优化。
8 |
9 | 项目指导老师:陈建国 组长:吴仰晖 组员:李健文、梁竞冀、孙惠祥、张凯茗
10 |
11 | ## 仓库说明
12 | ### 目录构成
13 | ### 开始/运行
14 |
15 | ## 算法运行动态图展示
16 |
17 | PRM算法:
18 | 
19 |
20 | 实际上这里展现的是图搜索的过程,路径运行和下面的图差不多。
21 | 除了PRM,实际上项目在执行过程中还探索了针对狭窄通道问题的OBPRM算法:
22 |
23 | 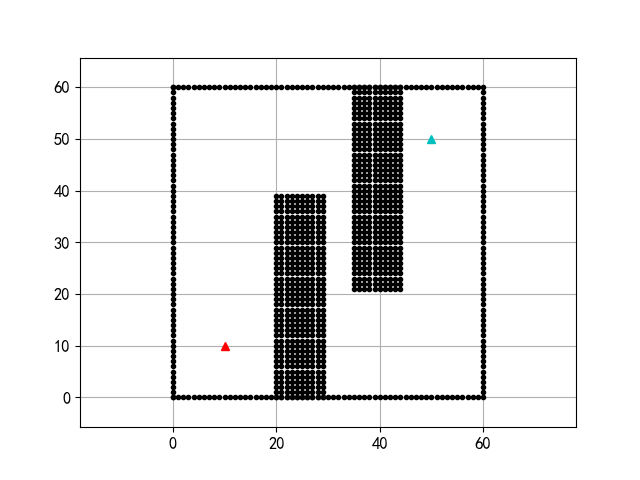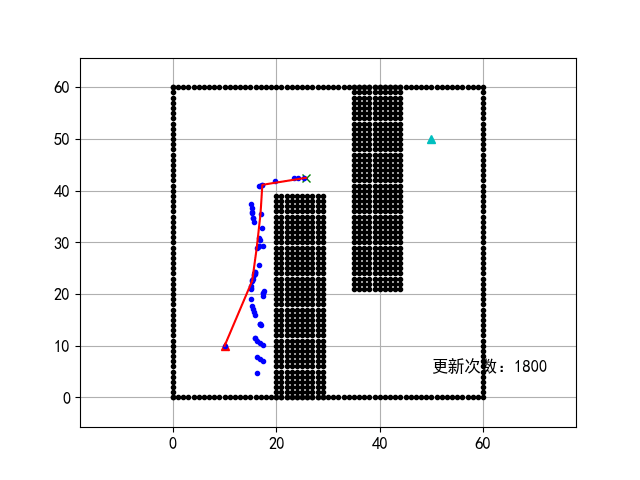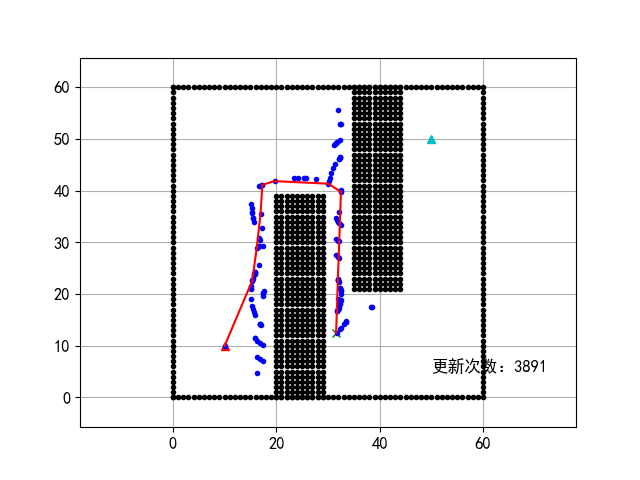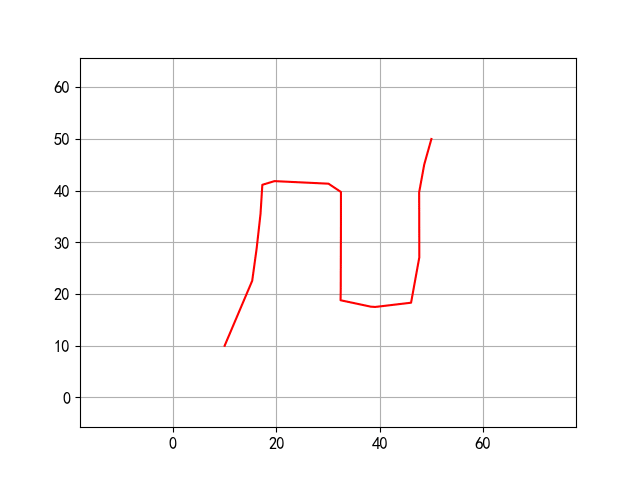
24 |
25 | A*算法动图:
26 | 
27 |
28 | APF算法动图:
29 |
30 | 
31 |
32 | DWA算法动图:
33 | 
34 |
35 | ## Webots仿真展示
36 |
37 | PRM算法Webots仿真录像:
38 |
39 | 
40 |
41 | APF算法Webots仿真录像:
42 |
43 | 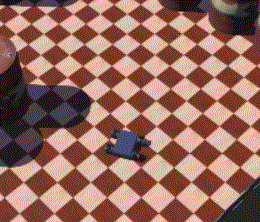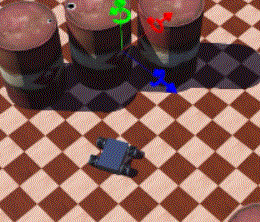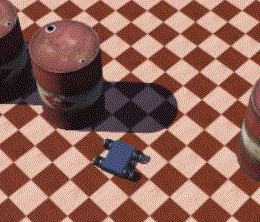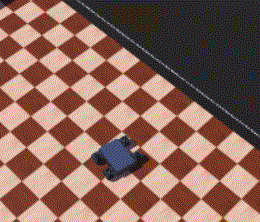
44 |
45 | DWA算法Webots仿真录像:
46 |
47 | 
48 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/worlds/.trace.wbproj:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Webots Project File version R2021a
2 | perspectives: 000000ff00000000fd000000030000000000000320000003ecfc0100000003fc00000000ffffffff0000000000fffffffc0200000001fb00000012005300630065006e0065005400720065006501000000000000039f0000000000000000fb0000001e00480074006d006c0052006f0062006f007400570069006e0064006f00770000000000000003200000000000000000fb0000001a0044006f00630075006d0065006e0074006100740069006f006e0000000000ffffffff0000005400ffffff000000010000028900000702fc0200000001fb0000001400540065007800740045006400690074006f0072010000002500000702000000d000ffffff0000000300000f0000000092fc0100000002fb0000000e0043006f006e0073006f006c006501000000000000073f0000000000000000fb0000001a0043006f006e0073006f006c00650041006c006c0041006c006c010000000000000f000000007a00ffffff00000c710000070200000004000000040000000100000008fc00000000
3 | simulationViewPerspectives: 000000ff00000001000000020000018b000003690100000006010000000101
4 | sceneTreePerspectives: 000000ff0000000100000002000000c0000001120100000006010000000201
5 | minimizedPerspectives: 000000ff00000000fd00000003000000000000016c00000469fc0200000001fb00000012005300630065006e006500540072006500650100000019000004690000018500ffffff000000010000022e0000036bfc0200000001fb0000001400540065007800740045006400690074006f007201000000190000036b000000ab00ffffff00000003000005cd000000f8fc0100000001fb0000000e0043006f006e0073006f006c00650100000172000005cd0000004e00ffffff000003990000036b00000004000000040000000100000008fc00000000
6 | maximizedDockId: -1
7 | centralWidgetVisible: 1
8 | orthographicViewHeight: 1
9 | textFiles: 0 "C:/Users/Administrator/AppData/Local/Programs/Webots/projects/default/controllers/sumo_supervisor/sumo_supervisor.py"
10 | globalOptionalRendering: CoordinateSystem
11 | consoles: Console:All:All
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/worlds/.empty.wbproj:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Webots Project File version R2021a
2 | perspectives: 000000ff00000000fd000000030000000000000320000003ecfc0100000003fc00000000ffffffff0000000000fffffffc0200000001fb00000012005300630065006e0065005400720065006501000000000000039f0000000000000000fb0000001e00480074006d006c0052006f0062006f007400570069006e0064006f00770000000000000003200000000000000000fb0000001a0044006f00630075006d0065006e0074006100740069006f006e0000000000ffffffff0000005400ffffff0000000100000289000006c6fc0200000001fb0000001400540065007800740045006400690074006f00720100000025000006c6000000d000ffffff0000000300000f00000000cefc0100000002fb0000000e0043006f006e0073006f006c006501000000000000073f0000000000000000fb0000001a0043006f006e0073006f006c00650041006c006c0041006c006c010000000000000f000000007a00ffffff00000c71000006c600000004000000040000000100000008fc00000000
3 | simulationViewPerspectives: 000000ff00000001000000020000018b000003690100000006010000000101
4 | sceneTreePerspectives: 000000ff0000000100000002000000c0000001120100000006010000000201
5 | minimizedPerspectives: 000000ff00000000fd00000003000000000000016c00000469fc0200000001fb00000012005300630065006e006500540072006500650100000019000004690000018500ffffff000000010000022e0000036bfc0200000001fb0000001400540065007800740045006400690074006f007201000000190000036b000000ab00ffffff00000003000005cd000000f8fc0100000001fb0000000e0043006f006e0073006f006c00650100000172000005cd0000004e00ffffff000003990000036b00000004000000040000000100000008fc00000000
6 | maximizedDockId: -1
7 | centralWidgetVisible: 1
8 | orthographicViewHeight: 1
9 | textFiles: 1 "controllers/my_controller/my_controller.cpp" "C:/Users/Administrator/AppData/Local/Programs/Webots/projects/default/controllers/sumo_supervisor/sumo_supervisor.py"
10 | globalOptionalRendering: CoordinateSystem
11 | consoles: Console:All:All
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/pid.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 吴仰晖创建 2023/09/26
2 | import math
3 |
4 | # Initialize PID controller constants 初始化PID控制器
5 | kp = 2.0 # Proportional gain
6 | ki = 0.1 # Integral gain
7 | kd = 0.2 # Derivative gain
8 | prev_error = 0.0
9 | integral = 0.0
10 | velocity = 6.0
11 |
12 |
13 | def init_global(kp1=2.0, ki1=0.1, kd1=0.2, velocity1=7.0):
14 | global kp, ki, kd,velocity
15 | kp = kp1
16 | ki = ki1
17 | kd = kd1
18 | velocity = velocity1
19 |
20 |
21 | def get(x_car, y_car, angle_car, x_target, y_target):
22 | global prev_error, integral
23 | heading = math.atan2(y_target - y_car, x_target - x_car)
24 | angle_delta = heading - angle_car
25 | if angle_delta < -3.1416:
26 | angle_delta = angle_delta + 2 * 3.141596
27 | elif angle_delta > 3.1416:
28 | angle_delta = angle_delta - 2 * 3.141596
29 | error = angle_delta
30 | if integral < 300:
31 | integral += error # 积分
32 | derivative = error - prev_error # 微分
33 | prev_error = error # 记录上一次的误差值
34 | # Calculate PID control output
35 | steering = kp * error + ki * integral + kd * derivative
36 | output = velocity * 0.5 + steering.__abs__()
37 | speed_forward = [velocity, velocity, velocity, velocity]
38 | speed_backward = [-output, -output, -output, -output]
39 | speed_leftward = [output, -output, output, -output]
40 | speed_rightward = [-output, output, -output, output]
41 | speed_leftCircle = [output, -output, -output, output]
42 | speed_rightCircle = [-output, output, output, -output]
43 | speed1 = [0] * 4
44 | speed2 = [0] * 4
45 | print("angle_diff:", angle_delta)
46 | if angle_delta < -0.00001:
47 | speed1 = speed_rightward.copy()
48 | elif angle_delta > 0.00001:
49 | speed1 = speed_leftward.copy()
50 | speed2 = speed_forward.copy()
51 | return [x + y for x, y in zip(speed1, speed2)]
52 |
53 |
54 | def reset_integral():
55 | global integral
56 | integral = 0.0
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/point.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from controller import Supervisor, Robot
2 | import sys
3 | import math
4 |
5 | robot = Supervisor()
6 | # Supervisor是一个特殊的机器人节点,记得要在webots把对应机器人节点的supervisor设置为true
7 | car = robot.getFromDef('robot')
8 | wheels_names = ["motor1", "motor2", "motor3", "motor4"]
9 | motors = [robot.getMotor(name) for name in wheels_names]
10 | for motor in motors:
11 | motor.setPosition(float('inf'))
12 | motor.setVelocity(0.0)
13 | speed1 = [0] * 4
14 | speed2 = [0] * 4
15 | velocity = 7.4 # max motor velocity div 2
16 | goalpoint = [[-1, -1], [-1, 1], [1, 1], [1, -1]]
17 | goalindex = 0
18 | speed_forward = [velocity, velocity, velocity, velocity]
19 | speed_backward = [-velocity, -velocity, -velocity, -velocity]
20 | speed_leftward = [velocity, -velocity, velocity, -velocity]
21 | speed_rightward = [-velocity, velocity, -velocity, velocity]
22 | speed_leftCircle = [velocity, -velocity, -velocity, velocity]
23 | speed_rightCircle = [-velocity, velocity, velocity, -velocity]
24 | timeStep = int(robot.getBasicTimeStep())
25 |
26 | while robot.step(timeStep) != -1:
27 | pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
28 | rotation = car.getField("rotation").getSFRotation()
29 | # print('pos:', pos)
30 | # print('rotation:', rotation)
31 | x = pos[0]
32 | y = pos[1]
33 | # 发现在这个webots世界中旋转角是顺时针增长的,和atan2的计算的角度相反(互为正负)
34 | angle = -rotation[3]
35 | heading = math.atan2(goalpoint[goalindex][1] - y, goalpoint[goalindex][0] - x)
36 | angle_delta = heading - angle
37 | # print('car angle:', angle)
38 | # print('obstacle angle:', heading)
39 | if angle_delta < -3.1416:
40 | angle_delta = angle_delta + 2 * 3.141596
41 | elif angle_delta > 3.1416:
42 | angle_delta = angle_delta - 2 * 3.141596
43 | # print("angle_diff:", angle_delta)
44 | if angle_delta < -0.05:
45 | speed1 = speed_rightward.copy()
46 | elif angle_delta > 0.05:
47 | speed1 = speed_leftward.copy()
48 | speed2 = speed_forward.copy()
49 | distance = math.sqrt((goalpoint[goalindex][0] - x) ** 2 + (goalpoint[goalindex][1] - y) ** 2)
50 | # print('nowgoal:', goalpoint[goalindex], " distance:", distance)
51 | if distance < 0.05:
52 | print("到达目标:", goalpoint[goalindex])
53 | if goalindex < 3:
54 | goalindex = goalindex + 1
55 | else:
56 | goalindex = 0
57 | print("向新目标前进:", goalpoint[goalindex])
58 | # set velocity
59 | for i in range(4):
60 | motors[i].setVelocity(speed1[i] + speed2[i])
61 |
62 | sys.stdout.flush()
63 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/prm_with_pid_controller1.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 吴仰晖创建 2023.9.24
2 | from controller import Supervisor, Robot
3 | import sys
4 | import math
5 | import prm算法 as prm
6 | import pid
7 | robot = Supervisor()
8 | # Supervisor是一个特殊的机器人节点,记得要在webots把对应机器人节点的supervisor设置为true
9 | car = robot.getFromDef('robot')
10 | wheels_names = ["motor1", "motor2", "motor3", "motor4"]
11 | motors = [robot.getMotor(name) for name in wheels_names]
12 | for motor in motors:
13 | motor.setPosition(float('inf'))
14 | motor.setVelocity(0.0)
15 | # 获取世界中的所有对象
16 | world = robot.getRoot()
17 | world_children = world.getField('children')
18 | n = world_children.getCount()
19 | print("This world contains nodes:", n)
20 | # 遍历所有对象,找到名字符合要求的Oilbarrel对象node并存入obstacle
21 | obstacle = []
22 | for i in range(n):
23 | obj = world_children.getMFNode(i)
24 | # print(obj.getTypeName())
25 | if obj.getTypeName() == "OilBarrel":
26 | print(obj.getField('name').getSFString())
27 | obstacle.append(obj.getField("translation").getSFVec3f())
28 | obstacle = [(x * 10, y * 10) for x, y, z in obstacle]
29 |
30 | velocity = 7 # max motor velocity div 2
31 | goalpoint = [45, 45]
32 | pathindex = 0
33 | timeStep = int(robot.getBasicTimeStep())
34 | pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
35 | pos = [x * 10 for x in pos]
36 | # 初始化prm算法
37 | # 地图中floor size=10,这里写100,也就是放大了10倍。
38 | prm.init_global(start_position_x=pos[0], start_position_y=pos[1], goal_position_x=goalpoint[0],
39 | goal_position_y=goalpoint[1], obstacle=obstacle, size_robot=2, x_range=100, y_range=100,
40 | n_sample=500, show_animat=False, n_knn=50, max_edge_len=10)
41 | # 运行prm算法
42 | rx, ry = prm.start()
43 | pathpoint = [(x, y) for x, y in zip(rx, ry)]
44 | pathpoint = pathpoint[::-1]
45 |
46 | # 初始化pid
47 |
48 |
49 | while robot.step(timeStep) != -1:
50 | rotation = car.getField("rotation").getSFRotation()
51 | # print('pos:', pos)
52 | # print('rotation:', rotation)
53 | pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
54 | pos = [x * 10 for x in pos]
55 | x = pos[0]
56 | y = pos[1]
57 | # 发现在这个webots世界中旋转角是顺时针增长的,和atan2的计算的角度相反(互为正负)
58 | angle = -rotation[3]
59 | distance = math.sqrt((pathpoint[pathindex][0] - x) ** 2 + (pathpoint[pathindex][1] - y) ** 2)
60 | print('nowgoal:', pathpoint[pathindex], " distance:", distance)
61 | if distance < 0.2:
62 | print("到达目标:", pathpoint[pathindex])
63 | pid.reset_integral()
64 | if pathindex < len(pathpoint):
65 | pathindex = pathindex + 1
66 | if pathindex == len(pathpoint):
67 | print("到达目标点")
68 | for i in range(4):
69 | motors[i].setVelocity(0)
70 | break
71 | speed = pid.get(x_car=x, y_car=y, angle_car=angle, x_target=pathpoint[pathindex][0], y_target=pathpoint[pathindex][1])
72 | # set velocity 实际上这里是
73 | for i in range(4):
74 | motors[i].setVelocity(speed[i])
75 |
76 | sys.stdout.flush()
77 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/pid_test.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from controller import Supervisor, Robot
2 | import sys
3 | import math
4 |
5 | robot = Supervisor()
6 | # Supervisor是一个特殊的机器人节点,记得要在webots把对应机器人节点的supervisor设置为true
7 | car = robot.getFromDef('robot')
8 | wheels_names = ["motor1", "motor2", "motor3", "motor4"]
9 | motors = [robot.getMotor(name) for name in wheels_names]
10 | # 获取世界中的所有对象
11 | world = robot.getRoot()
12 | world_children = world.getField('children')
13 | n = world_children.getCount()
14 | print("This world contains nodes:",n)
15 | # 遍历所有对象,找到名字符合要求的Oilbarrel对象node并存入obstacle
16 | obstacle = []
17 | for i in range(n):
18 | obj = world_children.getMFNode(i)
19 | # print(obj.getTypeName())
20 | if obj.getTypeName() == "OilBarrel":
21 | print(obj.getField('name').getSFString())
22 | obstacle.append(obj)
23 | for motor in motors:
24 | motor.setPosition(float('inf'))
25 | motor.setVelocity(0.0)
26 | speed1 = [0] * 4
27 | speed2 = [0] * 4
28 | velocity = 7.4 # max motor velocity div 2
29 | goalpoint = [[-1, -1], [-1, 1], [1, 1], [1, -1]]
30 | goalindex = 0
31 | speed_forward = [velocity, velocity, velocity, velocity]
32 | speed_backward = [-velocity, -velocity, -velocity, -velocity]
33 | speed_leftward = [velocity, -velocity, velocity, -velocity]
34 | speed_rightward = [-velocity, velocity, -velocity, velocity]
35 | speed_leftCircle = [velocity, -velocity, -velocity, velocity]
36 | speed_rightCircle = [-velocity, velocity, velocity, -velocity]
37 | timeStep = int(robot.getBasicTimeStep())
38 |
39 | while robot.step(timeStep) != -1:
40 | pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
41 | rotation = car.getField("rotation").getSFRotation()
42 | # print('pos:', pos)
43 | # print('rotation:', rotation)
44 | x = pos[0]
45 | y = pos[1]
46 | # 发现在这个webots世界中旋转角是顺时针增长的,和atan2的计算的角度相反(互为正负)
47 | angle = -rotation[3]
48 | heading = math.atan2(goalpoint[goalindex][1] - y, goalpoint[goalindex][0] - x)
49 | angle_delta = heading - angle
50 | # print('car angle:', angle)
51 | # print('obstacle angle:', heading)
52 | if angle_delta < -3.1416:
53 | angle_delta = angle_delta + 2 * 3.141596
54 | elif angle_delta > 3.1416:
55 | angle_delta = angle_delta - 2 * 3.141596
56 | # print("angle_diff:", angle_delta)
57 | if angle_delta < -0.05:
58 | speed1 = speed_rightward.copy()
59 | elif angle_delta > 0.05:
60 | speed1 = speed_leftward.copy()
61 | speed2 = speed_forward.copy()
62 | distance = math.sqrt((goalpoint[goalindex][0] - x) ** 2 + (goalpoint[goalindex][1] - y) ** 2)
63 | # print('nowgoal:', goalpoint[goalindex], " distance:", distance)
64 | if distance < 0.05:
65 | print("到达目标:",goalpoint[goalindex])
66 | if goalindex<3:
67 | goalindex = goalindex + 1
68 | else:
69 | goalindex = 0
70 | print("向新目标前进:",goalpoint[goalindex])
71 | # set velocity
72 | for i in range(4):
73 | motors[i].setVelocity(speed1[i] + speed2[i])
74 |
75 | sys.stdout.flush()
76 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/test3_controller.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from controller import Supervisor, Robot
2 | import sys
3 | import math
4 |
5 | robot = Supervisor()
6 | # Supervisor是一个特殊的机器人节点,记得要在webots把对应机器人节点的supervisor设置为true
7 | car = robot.getFromDef('robot')
8 | wheels_names = ["motor1", "motor2", "motor3", "motor4"]
9 | motors = [robot.getMotor(name) for name in wheels_names]
10 | # 获取世界中的所有对象
11 | world = robot.getRoot()
12 | world_children = world.getField('children')
13 | n = world_children.getCount()
14 | print("This world contains nodes:", n)
15 | # 遍历所有对象,找到名字符合要求的Oilbarrel对象node并存入obstacle
16 | obstacle = []
17 | for i in range(n):
18 | obj = world_children.getMFNode(i)
19 | # print(obj.getTypeName())
20 | if obj.getTypeName() == "OilBarrel":
21 | print(obj.getField('name').getSFString())
22 | obstacle.append(obj)
23 | for motor in motors:
24 | motor.setPosition(float('inf'))
25 | motor.setVelocity(0.0)
26 | speed1 = [0] * 4
27 | speed2 = [0] * 4
28 | velocity = 7.4 # max motor velocity div 2
29 | goalpoint = [[-1, -1], [-1, 1], [1, 1], [1, -1]]
30 | goalindex = 0
31 | speed_forward = [velocity, velocity, velocity, velocity]
32 | speed_backward = [-velocity, -velocity, -velocity, -velocity]
33 | speed_leftward = [velocity, -velocity, velocity, -velocity]
34 | speed_rightward = [-velocity, velocity, -velocity, velocity]
35 | speed_leftCircle = [velocity, -velocity, -velocity, velocity]
36 | speed_rightCircle = [-velocity, velocity, velocity, -velocity]
37 | timeStep = int(robot.getBasicTimeStep())
38 | print("timestep:", timeStep)
39 | # InertialUnit = robot.getInertialUnit("inertial unit")
40 | # print(InertialUnit.getRollPitchYaw())
41 | print(car.getVelocity())
42 | while robot.step(timeStep) != -1:
43 | pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
44 | rotation = car.getField("rotation").getSFRotation()
45 | # print('pos:', pos)
46 | # print('rotation:', rotation)
47 | x = pos[0]
48 | y = pos[1]
49 | # 发现在这个webots世界中旋转角是顺时针增长的,和atan2的计算的角度相反(互为正负)
50 | angle = -rotation[3]
51 | heading = math.atan2(goalpoint[goalindex][1] - y, goalpoint[goalindex][0] - x)
52 | angle_delta = heading - angle
53 | # print('car angle:', angle)
54 | # print('obstacle angle:', heading)
55 | if angle_delta < -3.1416:
56 | angle_delta = angle_delta + 2 * 3.141596
57 | elif angle_delta > 3.1416:
58 | angle_delta = angle_delta - 2 * 3.141596
59 | # print("angle_diff:", angle_delta)
60 | if angle_delta < -0.05:
61 | speed1 = speed_rightward.copy()
62 | elif angle_delta > 0.05:
63 | speed1 = speed_leftward.copy()
64 | speed2 = speed_forward.copy()
65 | distance = math.sqrt((goalpoint[goalindex][0] - x) ** 2 + (goalpoint[goalindex][1] - y) ** 2)
66 | # print('nowgoal:', goalpoint[goalindex], " distance:", distance)
67 | if distance < 0.05:
68 | print("到达目标:", goalpoint[goalindex])
69 | if goalindex < 3:
70 | goalindex = goalindex + 1
71 | else:
72 | goalindex = 0
73 | print("向新目标前进:", goalpoint[goalindex])
74 | # set velocity
75 | for i in range(4):
76 | motors[i].setVelocity(speed1[i] + speed2[i])
77 |
78 | sys.stdout.flush()
79 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/atf_with_pid_controller.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """atf_controller controller."""
2 | import sys
3 | import math
4 | import 人工势场 as atf
5 | import pid
6 | # You may need to import some classes of the controller module. Ex:
7 | # from controller import Robot, Motor, DistanceSensor
8 | from controller import Robot,Supervisor
9 |
10 | robot = Supervisor()
11 | # Supervisor是一个特殊的机器人节点,记得要在webots把对应机器人节点的supervisor设置为true
12 | car = robot.getFromDef('robot')
13 | wheels_names = ["motor1", "motor2", "motor3", "motor4"]
14 | motors = [robot.getMotor(name) for name in wheels_names]
15 | for motor in motors:
16 | motor.setPosition(float('inf'))
17 | motor.setVelocity(0.0)
18 | # 获取世界中的所有对象
19 | world = robot.getRoot()
20 | world_children = world.getField('children')
21 | n = world_children.getCount()
22 | print("This world contains nodes:", n)
23 | # 遍历所有对象,找到名字符合要求的Oilbarrel对象node并存入obstacle
24 | obstacle = []
25 | for i in range(n):
26 | obj = world_children.getMFNode(i)
27 | # print(obj.getTypeName())
28 | if obj.getTypeName() == "OilBarrel":
29 | print(obj.getField('name').getSFString())
30 | obstacle.append(obj.getField("translation").getSFVec3f())
31 | obstacle = [(x * 10, y * 10, z * 10) for x, y, z in obstacle]
32 | speed1 = [0] * 4
33 | speed2 = [0] * 4
34 | velocity = 5 # max motor velocity div 2
35 | goalpoint = [45, 45]
36 | pathindex = 0
37 | speed_forward = [velocity, velocity, velocity, velocity]
38 | speed_backward = [-velocity, -velocity, -velocity, -velocity]
39 | speed_leftward = [velocity, -velocity, velocity, -velocity]
40 | speed_rightward = [-velocity, velocity, -velocity, velocity]
41 | speed_leftCircle = [velocity, -velocity, -velocity, velocity]
42 | speed_rightCircle = [-velocity, velocity, velocity, -velocity]
43 | timeStep = int(robot.getBasicTimeStep())
44 | pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
45 | pos = [x * 10 for x in pos]
46 | # 初始化prm算法
47 | # 地图中floor size=10,这里写100,也就是放大了10倍。
48 | pathpoint = atf.start(pos[0],pos[1],goalpoint[0],goalpoint[1],obstacle)
49 | # 运行prm算法
50 | print('pathpoint:',pathpoint)
51 |
52 | while robot.step(timeStep) != -1:
53 | rotation = car.getField("rotation").getSFRotation()
54 | # print('pos:', pos)
55 | # print('rotation:', rotation)
56 | pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
57 | pos = [x * 10 for x in pos]
58 | x = pos[0]
59 | y = pos[1]
60 | # 发现在这个webots世界中旋转角是顺时针增长的,和atan2的计算的角度相反(互为正负)
61 | angle = -rotation[3]
62 | distance = math.sqrt((pathpoint[pathindex][0] - x) ** 2 + (pathpoint[pathindex][1] - y) ** 2)
63 | print('nowgoal:', pathpoint[pathindex], " distance:", distance)
64 | if distance < 0.2:
65 | print("到达目标:", pathpoint[pathindex])
66 | pid.reset_integral()
67 | if pathindex < len(pathpoint):
68 | pathindex = pathindex + 1
69 | if pathindex == len(pathpoint):
70 | print("到达目标点")
71 | for i in range(4):
72 | motors[i].setVelocity(0)
73 | break
74 | speed = pid.get(x_car=x, y_car=y, angle_car=angle, x_target=pathpoint[pathindex][0], y_target=pathpoint[pathindex][1])
75 | # set velocity 实际上这里是
76 | for i in range(4):
77 | motors[i].setVelocity(speed[i])
78 |
79 | sys.stdout.flush()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/a_star_controller.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from controller import Supervisor, Robot
2 | import sys
3 | import math
4 | from a_star import *
5 |
6 | robot = Supervisor()
7 | # Supervisor是一个特殊的机器人节点,记得要在webots把对应机器人节点的supervisor设置为true
8 | car = robot.getFromDef('robot')
9 | wheels_names = ["motor1", "motor2", "motor3", "motor4"]
10 | motors = [robot.getMotor(name) for name in wheels_names]
11 | for motor in motors:
12 | motor.setPosition(float('inf'))
13 | motor.setVelocity(0.0)
14 | # 获取世界中的所有对象
15 | world = robot.getRoot()
16 | world_children = world.getField('children')
17 | n = world_children.getCount()
18 | print("This world contains nodes:", n)
19 | # 遍历所有对象,找到名字符合要求的Oilbarrel对象node并存入obstacle
20 | obstacle = []
21 | for i in range(n):
22 | obj = world_children.getMFNode(i)
23 | if obj.getTypeName() == "OilBarrel":
24 | obstacle.append(obj.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()[:2]) # 只保留x, y两个坐标
25 | obstacle = [(x * 10, y * 10) for x, y in obstacle]
26 | speed1 = [0] * 4
27 | speed2 = [0] * 4
28 | velocity = 5 # max motor velocity div 2
29 | goal_point = (45, 45)
30 | path_index = 0
31 | speed_forward = [velocity, velocity, velocity, velocity]
32 | speed_backward = [-velocity, -velocity, -velocity, -velocity]
33 | speed_leftward = [velocity, -velocity, velocity, -velocity]
34 | speed_rightward = [-velocity, velocity, -velocity, velocity]
35 | speed_leftCircle = [velocity, -velocity, -velocity, velocity]
36 | speed_rightCircle = [-velocity, velocity, velocity, -velocity]
37 | timeStep = int(robot.getBasicTimeStep())
38 | pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
39 | pos = [x * 10 for x in pos]
40 | start_point = (pos[0], pos[1])
41 | # 若使用先验地图信息则先进行路径规划
42 | # 得到结果后再令机器人按照规划的结果行进即可
43 |
44 | # 运行a_star算法
45 | # create env
46 | print('start_point: ', start_point)
47 | print('obstacle: ', obstacle)
48 | env = Env(100, 100, obstacle)
49 |
50 | # a_star path planning
51 | a_star = AStar(start_point, goal_point, env, 2)
52 | path, _ = a_star.searching()
53 |
54 | # 此处为控制机器人按照路径行进
55 | while robot.step(timeStep) != -1:
56 | rotation = car.getField("rotation").getSFRotation()
57 | # print('pos:', pos)
58 | # print('rotation:', rotation)
59 | pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
60 | pos = [x * 10 for x in pos]
61 | x = pos[0]
62 | y = pos[1]
63 | # 发现在这个webots世界中旋转角是顺时针增长的,和atan2的计算的角度相反(互为正负)
64 | angle = -rotation[3]
65 | heading = math.atan2(path[path_index][1] - y, path[path_index][0] - x)
66 | angle_delta = heading - angle
67 | # print('car angle:', angle)
68 | # print('obstacle angle:', heading)
69 | if angle_delta < -3.1416:
70 | angle_delta = angle_delta + 2 * 3.141596
71 | elif angle_delta > 3.1416:
72 | angle_delta = angle_delta - 2 * 3.141596
73 | # print("angle_diff:", angle_delta)
74 | if angle_delta < -0.05:
75 | speed1 = speed_rightward.copy()
76 | elif angle_delta > 0.05:
77 | speed1 = speed_leftward.copy()
78 | speed2 = speed_forward.copy()
79 | distance = math.sqrt((path[path_index][0] - x) ** 2 + (path[path_index][1] - y) ** 2)
80 | print('now goal:', path[path_index], " distance:", distance)
81 | if distance < 0.05:
82 | print("到达目标:", path[path_index])
83 | if path_index < len(path):
84 | path_index = path_index + 1
85 | if path_index == len(path):
86 | print("到达目标点")
87 | break
88 | # set velocity
89 | for i in range(4):
90 | motors[i].setVelocity(speed1[i] + speed2[i])
91 |
92 | sys.stdout.flush()
93 |
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/atf_controller.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """atf_controller controller."""
2 | import sys
3 | import math
4 | import 人工势场 as atf
5 | # You may need to import some classes of the controller module. Ex:
6 | # from controller import Robot, Motor, DistanceSensor
7 | from controller import Robot,Supervisor
8 |
9 | robot = Supervisor()
10 | # Supervisor是一个特殊的机器人节点,记得要在webots把对应机器人节点的supervisor设置为true
11 | car = robot.getFromDef('robot')
12 | wheels_names = ["motor1", "motor2", "motor3", "motor4"]
13 | motors = [robot.getMotor(name) for name in wheels_names]
14 | for motor in motors:
15 | motor.setPosition(float('inf'))
16 | motor.setVelocity(0.0)
17 | # 获取世界中的所有对象
18 | world = robot.getRoot()
19 | world_children = world.getField('children')
20 | n = world_children.getCount()
21 | print("This world contains nodes:", n)
22 | # 遍历所有对象,找到名字符合要求的Oilbarrel对象node并存入obstacle
23 | obstacle = []
24 | for i in range(n):
25 | obj = world_children.getMFNode(i)
26 | # print(obj.getTypeName())
27 | if obj.getTypeName() == "OilBarrel":
28 | print(obj.getField('name').getSFString())
29 | obstacle.append(obj.getField("translation").getSFVec3f())
30 | obstacle = [(x * 10, y * 10, z * 10) for x, y, z in obstacle]
31 | speed1 = [0] * 4
32 | speed2 = [0] * 4
33 | velocity = 7 # max motor velocity div 2
34 | goalpoint = [45, 45]
35 | pathindex = 0
36 | speed_forward = [velocity, velocity, velocity, velocity]
37 | speed_backward = [-velocity, -velocity, -velocity, -velocity]
38 | speed_leftward = [velocity, -velocity, velocity, -velocity]
39 | speed_rightward = [-velocity, velocity, -velocity, velocity]
40 | speed_leftCircle = [velocity, -velocity, -velocity, velocity]
41 | speed_rightCircle = [-velocity, velocity, velocity, -velocity]
42 | timeStep = int(robot.getBasicTimeStep())
43 | pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
44 | pos = [x * 10 for x in pos]
45 | # 初始化prm算法
46 | # 地图中floor size=10,这里写100,也就是放大了10倍。
47 | pathpoint = atf.start(pos[0],pos[1],goalpoint[0],goalpoint[1],obstacle)
48 | # 运行prm算法
49 | print('pathpoint:',pathpoint)
50 |
51 | while robot.step(timeStep) != -1:
52 | rotation = car.getField("rotation").getSFRotation()
53 | # print('pos:', pos)
54 | # print('rotation:', rotation)
55 | pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
56 | pos = [x * 10 for x in pos]
57 | x = pos[0]
58 | y = pos[1]
59 | # 发现在这个webots世界中旋转角是顺时针增长的,和atan2的计算的角度相反(互为正负)
60 | angle = -rotation[3]
61 | heading = math.atan2(pathpoint[pathindex][1] - y, pathpoint[pathindex][0] - x)
62 | angle_delta = heading - angle
63 | # print('car angle:', angle)
64 | # print('obstacle angle:', heading)
65 | if angle_delta < -3.1416:
66 | angle_delta = angle_delta + 2 * 3.141596
67 | elif angle_delta > 3.1416:
68 | angle_delta = angle_delta - 2 * 3.141596
69 | # print("angle_diff:", angle_delta)
70 | print(angle_delta)
71 | if angle_delta < -0.0001:
72 | speed1 = speed_rightward.copy()
73 | elif angle_delta > 0.0001:
74 | speed1 = speed_leftward.copy()
75 | speed2 = speed_forward.copy()
76 | distance = math.sqrt((pathpoint[pathindex][0] - x) ** 2 + (pathpoint[pathindex][1] - y) ** 2)
77 | print('nowgoal:', pathpoint[pathindex], " distance:", distance)
78 | if distance < 1:
79 | print("到达目标:", pathpoint[pathindex])
80 | if pathindex < len(pathpoint):
81 | pathindex = pathindex + 1
82 | if pathindex == len(pathpoint):
83 | print("到达目标点")
84 | break
85 | # set velocity
86 | for i in range(4):
87 | motors[i].setVelocity(speed1[i] + speed2[i])
88 |
89 | sys.stdout.flush()
90 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/dwa_controller.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 |
3 | from controller import Supervisor, Robot
4 | import sys
5 | import math
6 | import prm算法 as prm
7 | import dwa
8 |
9 | robot = Supervisor()
10 | robot.getSynchronization()
11 | # Supervisor是一个特殊的机器人节点,记得要在webots把对应机器人节点的supervisor设置为true
12 | car = robot.getFromDef('robot')
13 | wheels_names = ["motor1", "motor2", "motor3", "motor4"]
14 | motors = [robot.getMotor(name) for name in wheels_names]
15 | for motor in motors:
16 | motor.setPosition(float('inf'))
17 | motor.setVelocity(0.0)
18 | # 小车车身属性
19 | a = 0.15
20 | b = 0.1
21 | wheel_radius = 0.05
22 | # 获取世界中的所有对象
23 | world = robot.getRoot()
24 | world_children = world.getField('children')
25 | n = world_children.getCount()
26 | print("This world contains nodes:", n)
27 | # 遍历所有对象,找到名字符合要求的Oilbarrel对象node并存入obstacle
28 | obstacle = []
29 | for i in range(n):
30 | obj = world_children.getMFNode(i)
31 | # print(obj.getTypeName())
32 | if obj.getTypeName() == "OilBarrel":
33 | # print(obj.getField('name').getSFString())
34 | obstacle.append(obj.getField("translation").getSFVec3f())
35 | obstacle = [[x, y] for x, y, z in obstacle]
36 | print(obstacle)
37 | obstacle = np.array(obstacle)
38 |
39 | speed1 = [0] * 4
40 |
41 | velocity = 7 # max motor velocity div 2
42 | # goalpoint为设立的目标点
43 | goalpoint = [4.0, 4.0]
44 | timeStep = int(robot.getBasicTimeStep())
45 | print("timeStep:", timeStep)
46 | rotation = car.getField("rotation").getSFRotation()
47 | angle = -rotation[3]
48 | pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
49 | # 初始化dwa算法
50 | dwa_object = dwa.init(obstacle, goalpoint)
51 | now_velocity = 0
52 | while robot.step(timeStep) != -1:
53 | # 其实这里有个瑕疵,就是这while的一个timestep内其实是没有发出指令的
54 | rotation = car.getField("rotation").getSFRotation() # 获取小车的旋转角度,我们实际只要用到围绕z轴的旋转角度,也就是rotation[3]
55 | pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f() # 获取小车当前位置,我们要用到x坐标pos[0],y坐标pos[1]
56 | # print('pos:', pos)
57 | # print('rotation:', rotation)
58 | # getVelocity()返回一个正好包含6个值的向量。前三个分别是x、y和z方向上的线速度。后三个分别是围绕x、y和z轴的角速度。
59 | now_velocity = car.getVelocity()
60 | # 计算当前线速度大小
61 | linear_velocity = math.sqrt(now_velocity[0] ** 2 + now_velocity[1] ** 2)
62 | x = pos[0]
63 | y = pos[1]
64 | # now_state是获取到的当前的小车的状态,从左往右依次是:x坐标,y坐标,小车朝向角度,线速度大小,绕z轴的角速度大小
65 | now_state = np.array([pos[0], pos[1], -rotation[3], linear_velocity, now_velocity[5]])
66 | u, predicted_trajectory = dwa_object.dwa_control(now_state, goalpoint, obstacle)
67 | # 预测十步轨迹,把这十步轨迹用完
68 | # 这里的配置和dwa的相关参数有关
69 | # 例如:timestep在这里是32ms,然后dwa的dt可以设为32ms的十倍也就是320ms,然后predict_time设为3.2s,这样就预测10步(实际上不止10步,有12步)
70 | # 我们在下面的for循环把这十步走完,就是设置轮子的速度
71 | for i in range(10):
72 | v = predicted_trajectory[i][3]
73 | w = predicted_trajectory[i][4]
74 | # 通过速度和角速度计算出每个轮子的控制速度
75 | v1 = v - w * (a + b)
76 | v2 = v - w * (a + b)
77 | v3 = v + w * (a + b)
78 | v4 = v + w * (a + b)
79 | # 要注意和真实模拟世界的轮子对应
80 | speed1 = [v1, v2, v3, v4]
81 | # 要注意我们计算的应该是角速度 v=w*r w=v/r
82 | speed1 = [x / wheel_radius for x in speed1]
83 | print(speed1)
84 | # print("control:",u," predicted_trajectory:",predicted_trajectory)
85 | # 取预测轨迹的最后一个点作为当前的目标状态
86 | goal_state = predicted_trajectory[-1]
87 | # speed2 = speed_forward.copy()
88 | print('nowgoal:', (goal_state[0], goal_state[1]))
89 | for i in range(4):
90 | motors[i].setVelocity(speed1[i])
91 | robot.step(timeStep * 10)
92 |
93 | sys.stdout.flush()
94 | for i in range(4):
95 | motors[i].setVelocity(0)
96 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/1030DWA/dwa_controller.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 |
3 | from controller import Supervisor, Robot
4 | import sys
5 | import math
6 | import prm算法 as prm
7 | import dwa
8 |
9 | robot = Supervisor()
10 | robot.getSynchronization()
11 | # Supervisor是一个特殊的机器人节点,记得要在webots把对应机器人节点的supervisor设置为true
12 | car = robot.getFromDef('robot')
13 | wheels_names = ["motor1", "motor2", "motor3", "motor4"]
14 | motors = [robot.getMotor(name) for name in wheels_names]
15 | for motor in motors:
16 | motor.setPosition(float('inf'))
17 | motor.setVelocity(0.0)
18 | # 小车车身属性
19 | a = 0.15
20 | b = 0.1
21 | wheel_radius = 0.05
22 | # 获取世界中的所有对象
23 | world = robot.getRoot()
24 | world_children = world.getField('children')
25 | n = world_children.getCount()
26 | print("This world contains nodes:", n)
27 | # 遍历所有对象,找到名字符合要求的Oilbarrel对象node并存入obstacle
28 | obstacle = []
29 | for i in range(n):
30 | obj = world_children.getMFNode(i)
31 | # print(obj.getTypeName())
32 | if obj.getTypeName() == "OilBarrel":
33 | # print(obj.getField('name').getSFString())
34 | obstacle.append(obj.getField("translation").getSFVec3f())
35 | obstacle = [[x, y] for x, y, z in obstacle]
36 | print(obstacle)
37 | obstacle = np.array(obstacle)
38 |
39 | speed1 = [0] * 4
40 |
41 | velocity = 7 # max motor velocity div 2
42 | # goalpoint为设立的目标点
43 | goalpoint = [4.0, 4.0]
44 | timeStep = int(robot.getBasicTimeStep())
45 | print("timeStep:", timeStep)
46 | rotation = car.getField("rotation").getSFRotation()
47 | angle = -rotation[3]
48 | pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
49 | # 初始化dwa算法
50 | dwa_object = dwa.init(obstacle, goalpoint)
51 | now_velocity = 0
52 | while robot.step(timeStep) != -1:
53 | # 其实这里有个瑕疵,就是这while的一个timestep内其实是没有发出指令的
54 | rotation = car.getField("rotation").getSFRotation() # 获取小车的旋转角度,我们实际只要用到围绕z轴的旋转角度,也就是rotation[3]
55 | pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f() # 获取小车当前位置,我们要用到x坐标pos[0],y坐标pos[1]
56 | # print('pos:', pos)
57 | # print('rotation:', rotation)
58 | # getVelocity()返回一个正好包含6个值的向量。前三个分别是x、y和z方向上的线速度。后三个分别是围绕x、y和z轴的角速度。
59 | now_velocity = car.getVelocity()
60 | # 计算当前线速度大小
61 | linear_velocity = math.sqrt(now_velocity[0] ** 2 + now_velocity[1] ** 2)
62 | x = pos[0]
63 | y = pos[1]
64 | # now_state是获取到的当前的小车的状态,从左往右依次是:x坐标,y坐标,小车朝向角度,线速度大小,绕z轴的角速度大小
65 | now_state = np.array([pos[0], pos[1], -rotation[3], linear_velocity, now_velocity[5]])
66 | u, predicted_trajectory = dwa_object.dwa_control(now_state, goalpoint, obstacle)
67 | # 预测十步轨迹,把这十步轨迹用完
68 | # 这里的配置和dwa的相关参数有关
69 | # 例如:timestep在这里是32ms,然后dwa的dt可以设为32ms的十倍也就是320ms,然后predict_time设为3.2s,这样就预测10步(实际上不止10步,有12步)
70 | # 我们在下面的for循环把这十步走完,就是设置轮子的速度
71 | for i in range(10):
72 | v = predicted_trajectory[i][3]
73 | w = predicted_trajectory[i][4]
74 | # 通过速度和角速度计算出每个轮子的控制速度
75 | v1 = v - w * (a + b)
76 | v2 = v - w * (a + b)
77 | v3 = v + w * (a + b)
78 | v4 = v + w * (a + b)
79 | # 要注意和真实模拟世界的轮子对应
80 | speed1 = [v1, v2, v3, v4]
81 | # 要注意我们计算的应该是角速度 v=w*r w=v/r
82 | speed1 = [x / wheel_radius for x in speed1]
83 | print(speed1)
84 | # print("control:",u," predicted_trajectory:",predicted_trajectory)
85 | # 取预测轨迹的最后一个点作为当前的目标状态
86 | goal_state = predicted_trajectory[-1]
87 | # speed2 = speed_forward.copy()
88 | print('nowgoal:', (goal_state[0], goal_state[1]))
89 | for i in range(4):
90 | motors[i].setVelocity(speed1[i])
91 | robot.step(timeStep * 10)
92 |
93 | sys.stdout.flush()
94 | for i in range(4):
95 | motors[i].setVelocity(0)
96 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/prm_controller.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from controller import Supervisor, Robot
2 | import sys
3 | import math
4 | import prm算法 as prm
5 |
6 | robot = Supervisor()
7 | # Supervisor是一个特殊的机器人节点,记得要在webots把对应机器人节点的supervisor设置为true
8 | car = robot.getFromDef('robot')
9 | wheels_names = ["motor1", "motor2", "motor3", "motor4"]
10 | motors = [robot.getMotor(name) for name in wheels_names]
11 | for motor in motors:
12 | motor.setPosition(float('inf'))
13 | motor.setVelocity(0.0)
14 | # 获取世界中的所有对象
15 | world = robot.getRoot()
16 | world_children = world.getField('children')
17 | n = world_children.getCount()
18 | print("This world contains nodes:", n)
19 | # 遍历所有对象,找到名字符合要求的Oilbarrel对象node并存入obstacle
20 | obstacle = []
21 | for i in range(n):
22 | obj = world_children.getMFNode(i)
23 | # print(obj.getTypeName())
24 | if obj.getTypeName() == "OilBarrel":
25 | print(obj.getField('name').getSFString())
26 | obstacle.append(obj.getField("translation").getSFVec3f())
27 | obstacle = [(x * 10, y * 10, z * 10) for x, y, z in obstacle]
28 | speed1 = [0] * 4
29 | speed2 = [0] * 4
30 | velocity = 5 # max motor velocity div 2
31 | goalpoint = [45, 45]
32 | pathindex = 0
33 | speed_forward = [velocity, velocity, velocity, velocity]
34 | speed_backward = [-velocity, -velocity, -velocity, -velocity]
35 | speed_leftward = [velocity, -velocity, velocity, -velocity]
36 | speed_rightward = [-velocity, velocity, -velocity, velocity]
37 | speed_leftCircle = [velocity, -velocity, -velocity, velocity]
38 | speed_rightCircle = [-velocity, velocity, velocity, -velocity]
39 | timeStep = int(robot.getBasicTimeStep())
40 |
41 | pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
42 | pos = [x * 10 for x in pos]
43 | # 初始化prm算法
44 | # 地图中floor size=10,这里写100,也就是放大了10倍。
45 | prm.init_global(start_position_x=pos[0], start_position_y=pos[1], goal_position_x=goalpoint[0],
46 | goal_position_y=goalpoint[1], obstacle=obstacle, size_robot=2, x_range=100, y_range=100,
47 | n_sample=500, show_animat=False, n_knn=50,max_edge_len=10)
48 | # 运行prm算法
49 | rx,ry = prm.start()
50 | pathpoint = [(x, y) for x, y in zip(rx, ry)]
51 | pathpoint = pathpoint[::-1]
52 |
53 | while robot.step(timeStep) != -1:
54 | rotation = car.getField("rotation").getSFRotation()
55 | # print('pos:', pos)
56 | # print('rotation:', rotation)
57 | pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
58 | linear_velocity = car.getField
59 | pos = [x * 10 for x in pos]
60 | x = pos[0]
61 | y = pos[1]
62 | # 发现在这个webots世界中旋转角是顺时针增长的,和atan2的计算的角度相反(互为正负)
63 | angle = -rotation[3]
64 | heading = math.atan2(pathpoint[pathindex][1] - y, pathpoint[pathindex][0] - x)
65 | angle_delta = heading - angle
66 | # print('car angle:', angle)
67 | # print('obstacle angle:', heading)
68 | if angle_delta < -3.1416:
69 | angle_delta = angle_delta + 2 * 3.141596
70 | elif angle_delta > 3.1416:
71 | angle_delta = angle_delta - 2 * 3.141596
72 | # print("angle_diff:", angle_delta)
73 | if angle_delta < -0.01:
74 | speed1 = speed_rightward.copy()
75 | elif angle_delta > 0.01:
76 | speed1 = speed_leftward.copy()
77 | speed2 = speed_forward.copy()
78 | distance = math.sqrt((pathpoint[pathindex][0] - x) ** 2 + (pathpoint[pathindex][1] - y) ** 2)
79 | print('nowgoal:', pathpoint[pathindex], " distance:", distance)
80 | if distance < 0.05:
81 | print("到达目标:", pathpoint[pathindex])
82 | if pathindex < len(pathpoint):
83 | pathindex = pathindex + 1
84 | if pathindex == len(pathpoint):
85 | print("到达目标点")
86 | break
87 | # set velocity
88 | for i in range(4):
89 | motors[i].setVelocity(speed1[i] + speed2[i])
90 |
91 | sys.stdout.flush()
92 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
2 | __pycache__/
3 | *.py[cod]
4 | *$py.class
5 |
6 | # C extensions
7 | *.so
8 |
9 | # Distribution / packaging
10 | .Python
11 | build/
12 | develop-eggs/
13 | dist/
14 | downloads/
15 | eggs/
16 | .eggs/
17 | lib/
18 | lib64/
19 | parts/
20 | sdist/
21 | var/
22 | wheels/
23 | share/python-wheels/
24 | *.egg-info/
25 | .installed.cfg
26 | *.egg
27 | MANIFEST
28 |
29 | # PyInstaller
30 | # Usually these files are written by a python script from a template
31 | # before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it.
32 | *.manifest
33 | *.spec
34 |
35 | # Installer logs
36 | pip-log.txt
37 | pip-delete-this-directory.txt
38 |
39 | # Unit test / coverage reports
40 | htmlcov/
41 | .tox/
42 | .nox/
43 | .coverage
44 | .coverage.*
45 | .cache
46 | nosetests.xml
47 | coverage.xml
48 | *.cover
49 | *.py,cover
50 | .hypothesis/
51 | .pytest_cache/
52 | cover/
53 |
54 | # Translations
55 | *.mo
56 | *.pot
57 |
58 | # Django stuff:
59 | *.log
60 | local_settings.py
61 | db.sqlite3
62 | db.sqlite3-journal
63 |
64 | # Flask stuff:
65 | instance/
66 | .webassets-cache
67 |
68 | # Scrapy stuff:
69 | .scrapy
70 |
71 | # Sphinx documentation
72 | docs/_build/
73 |
74 | # PyBuilder
75 | .pybuilder/
76 | target/
77 |
78 | # Jupyter Notebook
79 | .ipynb_checkpoints
80 |
81 | # IPython
82 | profile_default/
83 | ipython_config.py
84 |
85 | # pyenv
86 | # For a library or package, you might want to ignore these files since the code is
87 | # intended to run in multiple environments; otherwise, check them in:
88 | # .python-version
89 |
90 | # pipenv
91 | # According to pypa/pipenv#598, it is recommended to include Pipfile.lock in version control.
92 | # However, in case of collaboration, if having platform-specific dependencies or dependencies
93 | # having no cross-platform support, pipenv may install dependencies that don't work, or not
94 | # install all needed dependencies.
95 | #Pipfile.lock
96 |
97 | # poetry
98 | # Similar to Pipfile.lock, it is generally recommended to include poetry.lock in version control.
99 | # This is especially recommended for binary packages to ensure reproducibility, and is more
100 | # commonly ignored for libraries.
101 | # https://python-poetry.org/docs/basic-usage/#commit-your-poetrylock-file-to-version-control
102 | #poetry.lock
103 |
104 | # pdm
105 | # Similar to Pipfile.lock, it is generally recommended to include pdm.lock in version control.
106 | #pdm.lock
107 | # pdm stores project-wide configurations in .pdm.toml, but it is recommended to not include it
108 | # in version control.
109 | # https://pdm.fming.dev/#use-with-ide
110 | .pdm.toml
111 |
112 | # PEP 582; used by e.g. github.com/David-OConnor/pyflow and github.com/pdm-project/pdm
113 | __pypackages__/
114 |
115 | # Celery stuff
116 | celerybeat-schedule
117 | celerybeat.pid
118 |
119 | # SageMath parsed files
120 | *.sage.py
121 |
122 | # Environments
123 | .env
124 | .venv
125 | env/
126 | venv/
127 | ENV/
128 | env.bak/
129 | venv.bak/
130 |
131 | # Spyder project settings
132 | .spyderproject
133 | .spyproject
134 |
135 | # Rope project settings
136 | .ropeproject
137 |
138 | # mkdocs documentation
139 | /site
140 |
141 | # mypy
142 | .mypy_cache/
143 | .dmypy.json
144 | dmypy.json
145 |
146 | # Pyre type checker
147 | .pyre/
148 |
149 | # pytype static type analyzer
150 | .pytype/
151 |
152 | # Cython debug symbols
153 | cython_debug/
154 |
155 | # PyCharm
156 | # JetBrains specific template is maintained in a separate JetBrains.gitignore that can
157 | # be found at https://github.com/github/gitignore/blob/main/Global/JetBrains.gitignore
158 | # and can be added to the global gitignore or merged into this file. For a more nuclear
159 | # option (not recommended) you can uncomment the following to ignore the entire idea folder.
160 | #.idea/
161 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/人工势场.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
3 | import copy
4 | from celluloid import Camera # 保存动图时用,pip install celluloid
5 |
6 | def start(start_x,start_y,goal_x,goal_y,obstacle):
7 | ## 初始化车的参数
8 | #d = 3.5 # 道路标准宽度
9 |
10 | #W = 1.8 # 汽车宽度
11 |
12 | #L = 4.7 # 车长
13 |
14 | #P0 = np.array([0, - d / 2, 1, 1]) # 车辆起点位置,分别代表x,y,vx,vy
15 |
16 | P0 = np.array([start_x, start_y, 0, 0])
17 |
18 | Pg = np.array([goal_x, goal_y, 0, 0]) # 目标位置
19 |
20 | # 障碍物位置
21 |
22 | Pobs = []
23 | for ob in obstacle:
24 | p = [ob[0],ob[1],0,0]
25 | Pobs.append(p)
26 | Pobs = np.array(Pobs)
27 | P = np.vstack((Pg, Pobs)) # 将目标位置和障碍物位置合放在一起,即是将Pg加入到Pobs的最后
28 |
29 | Eta_att = 15 # 引力的增益系数
30 |
31 | Eta_rep_ob = 150 # 斥力的增益系数
32 |
33 | #Eta_rep_edge = 50 # 道路边界斥力的增益系数
34 |
35 | d0 = 100 # 障碍影响的最大距离
36 |
37 | num = P.shape[0] # 障碍与目标总计个数,即P有多少行
38 |
39 | len_step = 1 # 步长
40 |
41 | n = 2
42 |
43 | Num_iter = 500 # 最大循环迭代次数
44 |
45 | path = [] # 保存车走过的每个点的坐标
46 | delta = np.zeros((num, 2)) # 保存车辆当前位置与障碍物的方向向量,方向指向车辆;以及保存车辆当前位置与目标点的方向向量,方向指向目标点
47 | dists = [] # 保存车辆当前位置与障碍物的距离以及车辆当前位置与目标点的距离
48 | unite_vec = np.zeros((num, 2)) # 保存车辆当前位置与障碍物的单位方向向量,方向指向车辆;以及保存车辆当前位置与目标点的单位方向向量,方向指向目标点
49 |
50 | F_rep_ob = np.zeros((len(Pobs), 2)) # 存储每一个障碍到车辆的斥力,带方向
51 |
52 | ## ***************初始化结束,开始主体循环******************
53 | Pi = P0[0:2] # 当前车辆位置
54 |
55 | # count=0
56 | for i in range(Num_iter):
57 | if ((Pi[0] - Pg[0]) ** 2 + (Pi[1] - Pg[1]) ** 2) ** 0.5 < 1:
58 | break #判断车辆是否一开始就在目标点附近
59 | dists = []
60 | path.append(Pi)
61 | # print(count)
62 | # count+=1
63 | # 计算车辆当前位置与障碍物的单位方向向量
64 | for j in range(len(Pobs)):
65 | delta[j] = Pi[0:2] - Pobs[j, 0:2]
66 | dists.append(np.linalg.norm(delta[j]))
67 | unite_vec[j] = delta[j] / dists[j]
68 | # 计算车辆当前位置与目标的单位方向向量
69 | delta[len(Pobs)] = Pg[0:2] - Pi[0:2]
70 | dists.append(np.linalg.norm(delta[len(Pobs)]))
71 | unite_vec[len(Pobs)] = delta[len(Pobs)] / dists[len(Pobs)]
72 |
73 | ## 计算引力
74 | F_att = Eta_att * dists[len(Pobs)] * unite_vec[len(Pobs)]
75 |
76 | ## 计算斥力
77 | # 在原斥力势场函数增加目标调节因子(即车辆至目标距离),以使车辆到达目标点后斥力也为0
78 | for j in range(len(Pobs)):
79 | if dists[j] >= d0:
80 | F_rep_ob[j] = np.array([0, 0])
81 | else:
82 | # 障碍物的斥力1,方向由障碍物指向车辆
83 | F_rep_ob1_abs = Eta_rep_ob * \
84 | (1 / dists[j] - 1 / d0) * \
85 | (dists[len(Pobs)]) ** n / dists[j] ** 2 # 斥力大小
86 | F_rep_ob1 = F_rep_ob1_abs * unite_vec[j] # 斥力向量
87 | # 障碍物的斥力2,方向由车辆指向目标点
88 | F_rep_ob2_abs = n / 2 * Eta_rep_ob * \
89 | (1 / dists[j] - 1 / d0) ** 2 * \
90 | (dists[len(Pobs)]) ** (n - 1) # 斥力大小
91 | F_rep_ob2 = F_rep_ob2_abs * unite_vec[len(Pobs)] # 斥力向量
92 | # 改进后的障碍物合斥力计算
93 | F_rep_ob[j] = F_rep_ob1 + F_rep_ob2
94 | '''
95 | # 增加道路边界斥力势场,根据车辆当前位置,选择对应的斥力函数
96 | if Pi[1] > - d + W / 2 and Pi[1] <= - d / 2:
97 | F_rep_edge = [0, Eta_rep_edge * v *
98 | np.exp(-d / 2 - Pi[1])] # 下道路边界区域斥力势场,方向指向y轴正向
99 | elif Pi[1] > - d / 2 and Pi[1] <= - W / 2:
100 | F_rep_edge = np.array([0, 1 / 3 * Eta_rep_edge * Pi[1] ** 2])
101 | elif Pi[1] > W / 2 and Pi[1] <= d / 2:
102 | F_rep_edge = np.array([0, - 1 / 3 * Eta_rep_edge * Pi[1] ** 2])
103 | elif Pi[1] > d / 2 and Pi[1] <= d - W / 2:
104 | F_rep_edge = np.array([0, Eta_rep_edge * v * (np.exp(Pi[1] - d / 2))])
105 | '''
106 | ## 计算合力和方向
107 | #F_rep = np.sum(F_rep_ob, axis=0) + F_rep_edge
108 |
109 | F_sum = F_att + np.sum(F_rep_ob, axis=0)
110 |
111 | UnitVec_Fsum = 1 / np.linalg.norm(F_sum) * F_sum
112 | # 计算车的下一步位置
113 | Pi = copy.deepcopy(Pi + len_step * UnitVec_Fsum)
114 | # Pi[0:2] = Pi[0:2] + len_step * UnitVec_Fsum
115 | # print(Pi)
116 |
117 | path.append(Pg[0:2]) # 最后把目标点也添加进路径中
118 | path = np.array(path) # 转为numpy
119 | return path
120 |
121 |
122 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/prm_with_pid_controller.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 吴仰晖创建 2023.9.24
2 | from controller import Supervisor, Robot
3 | import sys
4 | import math
5 | import prm算法 as prm
6 |
7 | robot = Supervisor()
8 | # Supervisor是一个特殊的机器人节点,记得要在webots把对应机器人节点的supervisor设置为true
9 | car = robot.getFromDef('robot')
10 | wheels_names = ["motor1", "motor2", "motor3", "motor4"]
11 | motors = [robot.getMotor(name) for name in wheels_names]
12 | for motor in motors:
13 | motor.setPosition(float('inf'))
14 | motor.setVelocity(0.0)
15 | # 获取世界中的所有对象
16 | world = robot.getRoot()
17 | world_children = world.getField('children')
18 | n = world_children.getCount()
19 | print("This world contains nodes:", n)
20 | # 遍历所有对象,找到名字符合要求的Oilbarrel对象node并存入obstacle
21 | obstacle = []
22 | for i in range(n):
23 | obj = world_children.getMFNode(i)
24 | # print(obj.getTypeName())
25 | if obj.getTypeName() == "OilBarrel":
26 | print(obj.getField('name').getSFString())
27 | obstacle.append(obj.getField("translation").getSFVec3f())
28 | obstacle = [(x * 10, y * 10) for x, y, z in obstacle]
29 | speed1 = [0] * 4
30 | speed2 = [0] * 4
31 | velocity = 7 # max motor velocity div 2
32 | goalpoint = [40, 40]
33 | pathindex = 0
34 | timeStep = int(robot.getBasicTimeStep())
35 | pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
36 | pos = [x * 10 for x in pos]
37 | # 初始化prm算法
38 | # 地图中floor size=10,这里写100,也就是放大了10倍。
39 | prm.init_global(start_position_x=pos[0], start_position_y=pos[1], goal_position_x=goalpoint[0],
40 | goal_position_y=goalpoint[1], obstacle=obstacle, size_robot=2, x_range=100, y_range=100,
41 | n_sample=500, show_animat=False, n_knn=50, max_edge_len=10)
42 | # 运行prm算法
43 | rx, ry = prm.start()
44 | pathpoint = [(x, y) for x, y in zip(rx, ry)]
45 | pathpoint = pathpoint[::-1]
46 |
47 | # Initialize PID controller constants 初始化PID
48 | kp = 2.0 # Proportional gain
49 | ki = 0.1 # Integral gain
50 | kd = 0.2 # Derivative gain
51 | prev_error = 0.0
52 | integral = 0.0
53 |
54 | while robot.step(timeStep) != -1:
55 | rotation = car.getField("rotation").getSFRotation()
56 | # print('pos:', pos)
57 | # print('rotation:', rotation)
58 | pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
59 | pos = [x * 10 for x in pos]
60 | x = pos[0]
61 | y = pos[1]
62 | # 发现在这个webots世界中旋转角是顺时针增长的,和atan2的计算的角度相反(互为正负)
63 | angle = -rotation[3]
64 | heading = math.atan2(pathpoint[pathindex][1] - y, pathpoint[pathindex][0] - x)
65 | # angle_delta是目前小车的方向和目标方向之间的差值
66 | angle_delta = heading - angle
67 | # print('car angle:', angle)
68 | # print('obstacle angle:', heading)
69 | if angle_delta < -3.1416:
70 | angle_delta = angle_delta + 2 * 3.141596
71 | elif angle_delta > 3.1416:
72 | angle_delta = angle_delta - 2 * 3.141596
73 |
74 | error = angle_delta # 误差
75 | if integral < 500:
76 | integral += error # 积分
77 | derivative = error - prev_error # 微分
78 | prev_error = error # 记录上一次的误差值
79 |
80 | # Calculate PID control output
81 | steering = kp * error + ki * integral + kd * derivative
82 | output = velocity*0.5 + steering.__abs__()
83 | speed_forward = [velocity, velocity, velocity, velocity]
84 | speed_backward = [-output, -output, -output, -output]
85 | speed_leftward = [output, -output, output, -output]
86 | speed_rightward = [-output, output, -output, output]
87 | speed_leftCircle = [output, -output, -output, output]
88 | speed_rightCircle = [-output, output, output, -output]
89 | # speed = [0] * 4
90 | # # Update wheel speeds
91 | # speed[0] = velocity - steering
92 | # speed[1] = velocity + steering
93 | # speed[2] = velocity - steering
94 | # speed[3] = velocity + steering
95 | print("angle_diff:", angle_delta)
96 | if angle_delta < -0.00001:
97 | speed1 = speed_rightward.copy()
98 | elif angle_delta > 0.00001:
99 | speed1 = speed_leftward.copy()
100 | # speed1 = speed_leftward.copy()
101 | speed2 = speed_forward.copy()
102 | distance = math.sqrt((pathpoint[pathindex][0] - x) ** 2 + (pathpoint[pathindex][1] - y) ** 2)
103 | print('nowgoal:', pathpoint[pathindex], " distance:", distance)
104 | if distance < 0.2:
105 | print("到达目标:", pathpoint[pathindex])
106 | # prev_error = 0
107 | integral = 0
108 | if pathindex < len(pathpoint):
109 | pathindex = pathindex + 1
110 | if pathindex == len(pathpoint):
111 | print("到达目标点")
112 | break
113 | # set velocity 实际上这里是
114 | for i in range(4):
115 | motors[i].setVelocity(speed1[i] + speed2[i])
116 | # Set wheel velocities
117 | # for i in range(4):
118 | # motors[i].setVelocity(speed[i])
119 |
120 | sys.stdout.flush()
121 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/a_star.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | import heapq
3 |
4 |
5 | class Env:
6 | def __init__(self, x_range, y_range, obstacle):
7 | self.x_range = x_range # size of background
8 | self.y_range = y_range
9 | self.motions = [(-1, 0), (-1, 1), (0, 1), (1, 1),
10 | (1, 0), (1, -1), (0, -1), (-1, -1)]
11 | # 将浮点数取整
12 | self.obstacle = [tuple(int(x) for x in tpl) for tpl in obstacle]
13 |
14 |
15 | class AStar:
16 | """
17 | AStar set the cost + heuristics as the priority
18 | """
19 |
20 | def __init__(self, s_start, s_goal, env, robot_size=2, heuristic_type="Euclidean"):
21 | self.s_start = (int(s_start[0]), int(s_start[1]))
22 | self.s_goal = (int(s_goal[0]), int(s_goal[1]))
23 | self.heuristic_type = heuristic_type
24 | self.robot_size = robot_size
25 |
26 | self.Env = env # class Env
27 |
28 | self.u_set = self.Env.motions # feasible input set
29 | self.obstacle = self.Env.obstacle # position of obstacles
30 |
31 | self.OPEN = [] # priority queue / OPEN set
32 | self.CLOSED = [] # CLOSED set / VISITED order
33 | self.PARENT = dict() # recorded parent
34 | self.g = dict() # cost to come
35 | print('start-point: ', self.s_start)
36 | print('goal-point: ', self.s_goal)
37 | print('obstacle: ', self.obstacle)
38 |
39 | def searching(self):
40 | """
41 | A_star Searching.
42 | :return: path, visited order
43 | """
44 |
45 | self.PARENT[self.s_start] = self.s_start
46 | self.g[self.s_start] = 0
47 | self.g[self.s_goal] = math.inf
48 | heapq.heappush(self.OPEN,
49 | (self.f_value(self.s_start), self.s_start))
50 |
51 | while self.OPEN:
52 | _, s = heapq.heappop(self.OPEN)
53 | self.CLOSED.append(s)
54 |
55 | if s == self.s_goal: # stop condition
56 | break
57 |
58 | for s_n in self.get_neighbor(s):
59 | new_cost = self.g[s] + self.cost(s, s_n)
60 |
61 | if s_n not in self.g:
62 | self.g[s_n] = math.inf
63 |
64 | if new_cost < self.g[s_n]: # conditions for updating Cost
65 | self.g[s_n] = new_cost
66 | self.PARENT[s_n] = s
67 | heapq.heappush(self.OPEN, (self.f_value(s_n), s_n))
68 |
69 | print('a_star search done:')
70 | self.print_path()
71 | return self.extract_path(self.PARENT)[::-1], self.CLOSED
72 |
73 | def searching_repeated_astar(self, e):
74 | """
75 | repeated A*.
76 | :param e: weight of A*
77 | :return: path and visited order
78 | """
79 |
80 | path, visited = [], []
81 |
82 | while e >= 1:
83 | p_k, v_k = self.repeated_searching(self.s_start, self.s_goal, e)
84 | path.append(p_k)
85 | visited.append(v_k)
86 | e -= 0.5
87 |
88 | return path, visited
89 |
90 | def repeated_searching(self, s_start, s_goal, e):
91 | """
92 | run A* with weight e.
93 | :param s_start: starting state
94 | :param s_goal: goal state
95 | :param e: weight of a*
96 | :return: path and visited order.
97 | """
98 |
99 | g = {s_start: 0, s_goal: float("inf")}
100 | PARENT = {s_start: s_start}
101 | OPEN = []
102 | CLOSED = []
103 | heapq.heappush(OPEN,
104 | (g[s_start] + e * self.heuristic(s_start), s_start))
105 |
106 | while OPEN:
107 | _, s = heapq.heappop(OPEN)
108 | CLOSED.append(s)
109 |
110 | if self.is_in_target_range(s):
111 | break
112 |
113 | for s_n in self.get_neighbor(s):
114 | new_cost = g[s] + self.cost(s, s_n)
115 |
116 | if s_n not in g:
117 | g[s_n] = math.inf
118 |
119 | if new_cost < g[s_n]: # conditions for updating Cost
120 | g[s_n] = new_cost
121 | PARENT[s_n] = s
122 | heapq.heappush(OPEN, (g[s_n] + e * self.heuristic(s_n), s_n))
123 |
124 | return self.extract_path(PARENT), CLOSED
125 |
126 | def get_neighbor(self, s):
127 | """
128 | find neighbors of state s that not in obstacles.
129 | :param s: state
130 | :return: neighbors
131 | """
132 | neighbors = [(s[0] + u[0], s[1] + u[1]) for u in self.u_set]
133 | return neighbors
134 |
135 | def cost(self, s_start, s_goal):
136 | """
137 | Calculate Cost for this motion
138 | :param s_start: starting node
139 | :param s_goal: end node
140 | :return: Cost for this motion
141 | :note: Cost function could be more complicate!
142 | """
143 |
144 | if self.is_collision(s_start, s_goal):
145 | return math.inf
146 |
147 | return math.hypot(s_goal[0] - s_start[0], s_goal[1] - s_start[1])
148 |
149 | def is_collision(self, s_start, s_end):
150 | """
151 | check if the line segment (s_start, s_end) is collision.
152 | :param s_start: start node
153 | :param s_end: end node
154 | :return: True: is collision / False: not collision
155 | """
156 |
157 | if s_start in self.obstacle or s_end in self.obstacle:
158 | return True
159 |
160 | if s_start[0] != s_end[0] and s_start[1] != s_end[1]:
161 | if s_end[0] - s_start[0] == s_start[1] - s_end[1]:
162 | s1 = (min(s_start[0], s_end[0]), min(s_start[1], s_end[1]))
163 | s2 = (max(s_start[0], s_end[0]), max(s_start[1], s_end[1]))
164 | else:
165 | s1 = (min(s_start[0], s_end[0]), max(s_start[1], s_end[1]))
166 | s2 = (max(s_start[0], s_end[0]), min(s_start[1], s_end[1]))
167 |
168 | if s1 in self.obstacle or s2 in self.obstacle:
169 | return True
170 |
171 | return False
172 |
173 | def f_value(self, s):
174 | """
175 | f = g + h. (g: Cost to come, h: heuristic value)
176 | :param s: current state
177 | :return: f
178 | """
179 |
180 | return self.g[s] + self.heuristic(s)
181 |
182 | def extract_path(self, PARENT):
183 | """
184 | Extract the path based on the PARENT set.
185 | :return: The planning path
186 | """
187 |
188 | path = [self.s_goal]
189 | s = self.s_goal
190 |
191 | while True:
192 | s = PARENT[s]
193 | path.append(s)
194 |
195 | if s == self.s_start:
196 | break
197 |
198 | return list(path)
199 |
200 | def heuristic(self, s):
201 | """
202 | Calculate heuristic.
203 | :param s: current node (state)
204 | :return: heuristic function value
205 | """
206 |
207 | heuristic_type = self.heuristic_type # heuristic type
208 | goal = self.s_goal # goal node
209 |
210 | if heuristic_type == "manhattan":
211 | return abs(goal[0] - s[0]) + abs(goal[1] - s[1])
212 | else:
213 | return math.hypot(goal[0] - s[0], goal[1] - s[1])
214 |
215 | def is_in_target_range(self, s):
216 | """
217 | Check if a node is within the target range.
218 | :param s: the node to check
219 | :return: True if the node is within the target range, False otherwise
220 | """
221 | distance = math.hypot(self.s_goal[0] - s[0], self.s_goal[1] - s[1])
222 | return distance <= self.robot_size
223 |
224 | def print_path(self):
225 | path = self.extract_path(self.PARENT)[::-1]
226 | for i in range(0, len(path), 10):
227 | group = path[i:i + 10]
228 | print('a_star path planning:', group)
229 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/1030DWA/new_MPCController.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 |
3 | from scipy import sparse
4 |
5 | from controller import Supervisor, Robot
6 | import sys
7 | import numpy as np
8 | import time
9 | import osqp
10 | from scipy.spatial import KDTree
11 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
12 |
13 | v_d = 7.4 # 速度
14 | dt = 0.16 # 每一步的时间
15 | sim_steps = 500 # 步数(参考轨迹图像可能会短,但不影响循迹)
16 | wheel_radius = 0.05
17 |
18 |
19 | # 控制小车移动
20 | def move(v1, v2, v3, v4):
21 | newv = [v1, v2, v3, v4]
22 | speed = newv.copy()
23 | # set velocity
24 | for i in range(4):
25 | motors[i].setVelocity(speed[i])
26 | robot.step(timeStep * 5)
27 | return
28 |
29 |
30 | # 生成参考轨迹
31 | def load_ref_traj():
32 | ref_traj = np.zeros((sim_steps, 5)) # 参考轨迹列表,sim_steps行5列
33 |
34 | for i in range(sim_steps): # 用参数方程的形式给出期望的轨迹,是直线
35 | ref_traj[i, 0] = v_d * i * dt # x方向的期望值,期望是以v_d的速度在x方向做匀速直线运动
36 | ref_traj[i, 1] = -1.0 # y方向的期望值,期望在y=1的直线上运动
37 | ref_traj[i, 2] = 0.0 # 车身和x轴方向的偏移量
38 | ref_traj[i, 3] = v_d # 小车速度,匀速运动
39 | ref_traj[i, 4] = 0 # 车前轮的偏角,期望不转弯
40 |
41 | return ref_traj
42 |
43 |
44 | robot = Supervisor()
45 | # Supervisor是一个特殊的机器人节点,记得要在webots把对应机器人节点的supervisor设置为true
46 | car = robot.getFromDef('robot')
47 |
48 | wheels_names = ["motor1", "motor2", "motor3", "motor4"]
49 | motors = [robot.getMotor(name) for name in wheels_names]
50 | for motor in motors:
51 | motor.setPosition(float('inf'))
52 | motor.setVelocity(0.0)
53 |
54 | speed1 = [0] * 4
55 | speed2 = [0] * 4
56 | stop = [0] * 4
57 |
58 |
59 | # 基于车辆运动学模型实现一个简单的仿真环境
60 | class UGV_model:
61 | def __init__(self, x0, y0, theta0, a, b, T): # a是到车身坐标系X轴距离,b是到Y轴距离
62 | self.x = x0 # X
63 | self.y = y0 # Y
64 | self.theta = theta0 # 小车的朝向(与大地坐标系的x轴的夹角)
65 | self.a = a # 到x轴距离
66 | self.b = b # 到y轴距离
67 | self.k = a + b
68 | self.dt = T # decision time periodic-决策周期时间
69 |
70 | def update(self, v1, v2, v3, v4): # update ugv's state-更新小车状态
71 | # 小车状态的变化量
72 | dx = wheel_radius * (v1 + v2 + v3 + v4) / 4 # x方向速度
73 | dy = wheel_radius * (-v1 + v2 - v3 + v4) / 4 # y方向速度
74 | dv = wheel_radius * (v1 + v2 + v3 + v4) / 4
75 | dtheta = (-v1 - v2 + v3 + v4) / (4 * self.k) # 角度变化
76 | print("v1:%f v2:%f v3:%f v4:%f" % (v1, v2, v3, v4))
77 | print("dv:%f dtheta:%f" % (dv, dtheta))
78 | # self.x = self.x + dv * math.cos(self.theta) * self.dt
79 | # self.y = self.y + dv * math.sin(self.theta) * self.dt
80 | self.x += dx * self.dt
81 | self.y += dy * self.dt
82 | self.theta += dtheta * self.dt
83 |
84 | def plot_duration(self): # 画图像的函数
85 | plt.scatter(self.x, self.y, color='r')
86 | plt.axis([-5, 10, -4, 4])
87 |
88 | plt.pause(0.001)
89 |
90 |
91 | class MPCController: # MPC控制器设计
92 | def __init__(self, a, b, dt):
93 | self.a = a # 到x轴距离
94 | self.b = b # 到y轴距离
95 | self.k = a + b
96 |
97 | self.Nx = 3 # 状态量个数
98 | self.Nu = 4 # 控制量个数
99 |
100 | self.Nc = 5 # 控制时域
101 | self.Np = 30 # 预测时域
102 |
103 | self.T = dt
104 |
105 | def Solve(self, x, u_pre, ref_traj):
106 | # 寻找参考轨迹上的最近的参考点,以k-d树的方法去寻找
107 | tree = KDTree(ref_traj[:, :2])
108 | nearest_ref_info = tree.query(x[:2])
109 | nearest_ref_x = ref_traj[nearest_ref_info[1]]
110 |
111 | # 计算H和F矩阵,就是目标函数的第一、二项的系数矩阵
112 | # 计算线性时变的一个参数A
113 | a = np.array([
114 | [1.0, 0, 0],
115 | [0, 1.0, 0],
116 | [0, 0, 1.0]
117 | ])
118 |
119 | # 计算B
120 | b = np.array([
121 | [self.T / 4, self.T / 4, self.T / 4, self.T / 4],
122 | [-self.T / 4, self.T / 4, -self.T / 4, self.T / 4],
123 | [-self.T / (4 * self.k), -self.T / (4 * self.k),
124 | self.T / (4 * self.k), self.T / (4 * self.k)]
125 | ])
126 | b = b * wheel_radius
127 |
128 | # 计算tildeA
129 | A = np.zeros([self.Nx + self.Nu, self.Nx + self.Nu])
130 | A[0: self.Nx, 0: self.Nx] = a
131 | A[0: self.Nx, self.Nx:] = b
132 | A[self.Nx:, self.Nx:] = np.eye(self.Nu)
133 |
134 | # 计算tildeB
135 | B = np.zeros([self.Nx + self.Nu, self.Nu])
136 | B[0: self.Nx, :] = b
137 | B[self.Nx:, :] = np.eye(self.Nu)
138 |
139 | C = np.array([[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
140 | [0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
141 | [0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
142 |
143 | theta = np.zeros([self.Np * self.Nx, self.Nc * self.Nu])
144 | phi = np.zeros([self.Np * self.Nx, self.Nu + self.Nx])
145 | tmp = C
146 |
147 | # 计算θ值和φ值
148 | for i in range(1, self.Np + 1): # i从1到Np
149 | phi[self.Nx * (i - 1): self.Nx * i] = np.dot(tmp, A)
150 |
151 | tmp_c = np.zeros([self.Nx, self.Nc * self.Nu])
152 | tmp_c[:, 0: self.Nu] = np.dot(tmp, B)
153 |
154 | if i > 1:
155 | tmp_c[:, self.Nu:] = theta[self.Nx * (i - 2): self.Nx * (i - 1), 0: -self.Nu]
156 |
157 | theta[self.Nx * (i - 1): self.Nx * i, :] = tmp_c
158 |
159 | tmp = np.dot(tmp, A)
160 |
161 | Q = np.eye(self.Nx * self.Np) # 权重Q
162 |
163 | R = 5.0 * np.eye(self.Nu * self.Nc) # 权重R
164 |
165 | rho = 10 # 松弛因子的权重值
166 |
167 | H = np.zeros((self.Nu * self.Nc + 1, self.Nu * self.Nc + 1))
168 | H[0: self.Nu * self.Nc, 0: self.Nu * self.Nc] = np.dot(np.dot(theta.transpose(), Q), theta) + R
169 | H[-1: -1] = rho # 加入权重值
170 |
171 | # 计算状态量ξ
172 | kesi = np.zeros((self.Nx + self.Nu, 1))
173 | diff_x = x - nearest_ref_x[:3]
174 | diff_x = diff_x.reshape(-1, 1) # 数据转换成1列
175 | kesi[: self.Nx, :] = diff_x
176 | diff_u = u_pre.reshape(-1, 1)
177 | kesi[self.Nx:, :] = diff_u
178 |
179 | F = np.zeros((1, self.Nu * self.Nc + 1))
180 | F_1 = 2 * np.dot(np.dot(np.dot(phi, kesi).transpose(), Q), theta)
181 | F[0, 0: self.Nu * self.Nc] = F_1
182 |
183 | # constraints-设置车速度和加速度的阈值
184 | umin = np.array([[-14.8], [-14.8], [-14.8], [-14.8]])
185 | umax = np.array([[14.8], [14.8], [14.8], [14.8]])
186 |
187 | delta_umin = np.array([[-7.4], [-7.4], [-7.4], [-7.4]])
188 | delta_umax = np.array([[7.4], [7.4], [7.4], [7.4]])
189 |
190 | # 计算A_I和约束条件
191 | A_t = np.zeros((self.Nc, self.Nc))
192 | for row in range(self.Nc): # 初始化下三角矩阵
193 | for col in range(self.Nc):
194 | if row >= col:
195 | A_t[row, col] = 1.0
196 |
197 | A_I = np.kron(A_t, np.eye(self.Nu))
198 |
199 | A_cons = np.zeros((self.Nc * self.Nu, self.Nc * self.Nu + 1))
200 | A_cons[0: self.Nc * self.Nu, 0: self.Nc * self.Nu] = A_I
201 |
202 | U_t = np.kron(np.ones((self.Nc, 1)), u_pre.reshape(-1, 1))
203 |
204 | U_min = np.kron(np.ones((self.Nc, 1)), umin)
205 | U_max = np.kron(np.ones((self.Nc, 1)), umax)
206 |
207 | LB = U_min - U_t
208 | UB = U_max - U_t
209 |
210 | delta_Umin = np.kron(np.ones((self.Nc, 1)), delta_umin)
211 | delta_Umax = np.kron(np.ones((self.Nc, 1)), delta_umax)
212 |
213 | delta_Umin = np.vstack((delta_Umin, [0]))
214 | delta_Umax = np.vstack((delta_Umax, [rho]))
215 |
216 | A_1_cons = np.eye(self.Nc * self.Nu + 1, self.Nc * self.Nu + 1)
217 |
218 | A_cons = np.vstack((A_cons, A_1_cons))
219 |
220 | LB = np.vstack((LB, delta_Umin))
221 | UB = np.vstack((UB, delta_Umax))
222 |
223 | # Create an OSQP object
224 | prob = osqp.OSQP()
225 |
226 | H = sparse.csc_matrix(H)
227 | A_cons = sparse.csc_matrix(A_cons) # 压缩稀疏矩阵
228 |
229 | # Setup workspace
230 | prob.setup(H, F.transpose(), A_cons, LB, UB)
231 |
232 | res = prob.solve()
233 |
234 | # Check solver status
235 | if res.info.status != 'solved':
236 | raise ValueError('OSQP did not solve the problem!')
237 |
238 | u_cur = u_pre + res.x[0: self.Nu]
239 | return u_cur, res.x[0: self.Nu]
240 |
241 |
242 | # pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
243 | pos = np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0]) # 小车的起始位置,表示x位置,y位置和起始偏角
244 | pre_u = np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]) # 小车当前的控制量
245 |
246 | a = 0.15
247 | b = 0.1
248 |
249 | ref_traj = load_ref_traj()
250 | plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))
251 | plt.plot(ref_traj[:, 0], ref_traj[:, 1], '-.b', linewidth=5.0)
252 |
253 | history_us = np.array([])
254 | history_delta_us = np.array([])
255 |
256 | # 开始运动
257 | timeStep = int(robot.getBasicTimeStep())
258 |
259 | t1 = time.time()
260 | ugv = UGV_model(pos[0], pos[1], pos[2], a, b, dt)
261 | controller = MPCController(a, b, dt)
262 |
263 | while robot.step(timeStep) != -1 and sim_steps > 0:
264 | # new_pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
265 | # pos = np.array([new_pos[0],
266 | # -new_pos[1],
267 | # -car.getField("rotation").getSFRotation()[3]])
268 | # for i in range(4):
269 | # pre_u[i] = motors[i].getVelocity()
270 | pos = [ugv.x, ugv.y, ugv.theta]
271 | # print(pre_u)
272 | u_cur, delta_u_cur = controller.Solve(pos, pre_u, ref_traj)
273 | abs_u = [v_d, v_d, v_d, v_d] + u_cur
274 | # print(abs_u)
275 |
276 | # move(abs_u[0], abs_u[1], abs_u[2], abs_u[3]) # 驱动小车
277 | ugv.update(abs_u[0], abs_u[1], abs_u[2], abs_u[3]) # 更新模型
278 |
279 | ugv.plot_duration() # 画图
280 |
281 | history_us = np.append(history_us, abs_u)
282 | if len(history_delta_us) == 0:
283 | history_delta_us = np.array([u_cur])
284 | else:
285 | history_delta_us = np.vstack((history_delta_us, u_cur))
286 |
287 | rpos = pos + np.array([wheel_radius * (abs_u[0] + abs_u[1] + abs_u[2] + abs_u[3]) / 4 * dt,
288 | wheel_radius * (-abs_u[0] + abs_u[1] - abs_u[2] + abs_u[3]) / 4 * dt,
289 | wheel_radius * (-abs_u[0] - abs_u[1] + abs_u[2] + abs_u[3]) / 4 * (a + b) * dt])
290 |
291 | print('车的参考位置%s' % rpos)
292 | print('车现在的位置%s' % pos)
293 | pre_u = u_cur
294 | sim_steps -= 1
295 |
296 | for i in range(4):
297 | motors[i].setVelocity(stop[i])
298 | t2 = time.time()
299 | print('程序运行时间:%s秒' % (t2 - t1))
300 | # plt.show()
301 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/MPCController.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from scipy import sparse
2 |
3 | from controller import Supervisor, Robot
4 | import sys
5 | import numpy as np
6 | import time
7 | import osqp
8 | from scipy.spatial import KDTree
9 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
10 |
11 | v_d = 7.4 # 速度
12 | dt = 0.5 # 每一步的时间
13 | sim_steps = 100 # 步数(参考轨迹图像可能会短,但不影响循迹)
14 |
15 |
16 | # 控制小车移动
17 | def move(v1, v2, v3, v4):
18 | newv = [1.5 * v1, 1.5 * v2, 1.5 * v3, 1.5 * v4]
19 | speed = newv.copy()
20 | # set velocity
21 | for i in range(4):
22 | motors[i].setVelocity(speed[i])
23 | sys.stdout.flush()
24 | return
25 |
26 |
27 | # 生成参考轨迹
28 | def load_ref_traj():
29 | ref_traj = np.zeros((sim_steps, 5)) # 参考轨迹列表,sim_steps行5列
30 |
31 | for i in range(sim_steps): # 用参数方程的形式给出期望的轨迹,是直线
32 | ref_traj[i, 0] = v_d * i * dt # x方向的期望值,期望是以v_d的速度在x方向做匀速直线运动
33 | ref_traj[i, 1] = 1 # y方向的期望值,期望在y=1的直线上运动
34 | ref_traj[i, 2] = 0.0 # 车身和x轴方向的偏移量
35 | ref_traj[i, 3] = v_d # 小车速度,匀速运动
36 | ref_traj[i, 4] = 0 # 车前轮的偏角,期望不转弯
37 |
38 | return ref_traj
39 |
40 |
41 | robot = Supervisor()
42 | # Supervisor是一个特殊的机器人节点,记得要在webots把对应机器人节点的supervisor设置为true
43 | car = robot.getFromDef('robot')
44 |
45 | wheels_names = ["motor1", "motor2", "motor3", "motor4"]
46 | motors = [robot.getMotor(name) for name in wheels_names]
47 | for motor in motors:
48 | motor.setPosition(float('inf'))
49 | motor.setVelocity(0.0)
50 |
51 | speed1 = [0] * 4
52 | speed2 = [0] * 4
53 | stop = [0] * 4
54 |
55 | # 小车动作控制
56 | speed_forward = [v_d, v_d, v_d, v_d]
57 | speed_backward = [-v_d, -v_d, -v_d, -v_d]
58 | speed_leftward = [v_d, -v_d, v_d, -v_d]
59 | speed_rightward = [-v_d, v_d, -v_d, v_d]
60 | speed_leftCircle = [v_d, -v_d, -v_d, v_d]
61 | speed_rightCircle = [-v_d, v_d, v_d, -v_d]
62 |
63 |
64 | # 基于车辆运动学模型实现一个简单的仿真环境
65 | class UGV_model:
66 | def __init__(self, x0, y0, theta0, a, b, T): # a是到车身坐标系X轴距离,b是到Y轴距离
67 | self.x = x0 # X
68 | self.y = y0 # Y
69 | self.theta = theta0 # 小车的朝向(与大地坐标系的x轴的夹角)
70 | self.a = a # 到x轴距离
71 | self.b = b # 到y轴距离
72 | self.k = a + b
73 | self.dt = T # decision time periodic-决策周期时间
74 |
75 | def update(self, v1, v2, v3, v4): # update ugv's state-更新小车状态
76 | # 小车状态的变化量
77 | dx = (v1 + v2 + v3 + v4) / 4 # x方向速度
78 | dy = (-v1 + v2 - v3 + v4) / 4 # y方向速度
79 | dtheta = (-v1 - v2 + v3 + v4) / (4 * self.k) # 角度变化
80 |
81 | self.x += dx * self.dt
82 | self.y += dy * self.dt
83 | self.theta += dtheta * self.dt
84 |
85 | def plot_duration(self): # 画图像的函数
86 | plt.scatter(self.x, self.y, color='r')
87 | plt.axis([-5, 400, -4, 4])
88 |
89 | plt.pause(0.008)
90 |
91 |
92 | class MPCController: # MPC控制器设计
93 | def __init__(self, a, b, dt):
94 | self.a = a # 到x轴距离
95 | self.b = b # 到y轴距离
96 | self.k = a + b
97 |
98 | self.Nx = 3 # 状态量个数
99 | self.Nu = 4 # 控制量个数
100 |
101 | self.Nc = 5 # 控制时域
102 | self.Np = 30 # 预测时域
103 |
104 | self.T = dt
105 |
106 | def Solve(self, x, u_pre, ref_traj):
107 | """
108 | Solve函数
109 | 它有三个输入参数:
110 | x,u_pre和ref_traj。
111 | x是一个包含当前状态的向量(x,y,yaw),x为x坐标,y为y坐标,yaw为小车当前朝向
112 | u_pre是上一时刻的控制输入(,
113 | ref_traj是一个包含参考轨迹的矩阵。
114 | """
115 | # 寻找参考轨迹上的最近距离的参考点,以k-d树的方法去寻找
116 | tree = KDTree(ref_traj[:, :2]) # 将参考轨迹中的前两列(即x和y坐标)作为输入数据,构建KD树
117 | nearest_ref_info = tree.query(x[:2]) # 使用k-d树中的查询功能来寻找距离当前状态最近的点
118 | nearest_ref_x = ref_traj[nearest_ref_info[1]] # tree.query会返回两个数组,第一个是包含最近邻居距离的数组,第二个是包含最近邻居索引的数组
119 |
120 | # 计算H和F矩阵,就是目标函数的第一、二项的系数矩阵
121 | # 计算线性时变的一个参数A
122 | # a和b分别是线性时变系统模型中的状态转移矩阵和控制输入矩阵
123 | a = np.array([
124 | [1.0, 0, 0],
125 | [0, 1.0, 0],
126 | [0, 0, 1.0]
127 | ])
128 | # 计算B
129 | b = np.array([
130 | [self.T / 4, self.T / 4, self.T / 4, self.T / 4],
131 | [-self.T / 4, self.T / 4, -self.T / 4, self.T / 4],
132 | [-self.T / (4 * self.k), -self.T / (4 * self.k),
133 | self.T / (4 * self.k), self.T / (4 * self.k)]
134 | ])
135 |
136 | # A和B分别是离散时间系统模型中的状态转移矩阵和控制输入矩阵
137 | # 计算tildeA
138 | A = np.zeros([self.Nx + self.Nu, self.Nx + self.Nu])
139 | A[0: self.Nx, 0: self.Nx] = a
140 | A[0: self.Nx, self.Nx:] = b
141 | A[self.Nx:, self.Nx:] = np.eye(self.Nu)
142 |
143 | # 计算tildeB
144 | B = np.zeros([self.Nx + self.Nu, self.Nu])
145 | B[0: self.Nx, :] = b
146 | B[self.Nx:, :] = np.eye(self.Nu)
147 |
148 | C = np.array([[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
149 | [0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
150 | [0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
151 |
152 | # theta和phi分别是目标函数中$x_k - x_{ref}$和$u_k$的系数矩阵。
153 | theta = np.zeros([self.Np * self.Nx, self.Nc * self.Nu])
154 | phi = np.zeros([self.Np * self.Nx, self.Nu + self.Nx])
155 | tmp = C # tmp是一个临时变量,用来存储C乘以A或B的结果。
156 |
157 | # 计算θ值和φ值
158 | # theta和phi的计算是基于预测步长Np和控制步长Nc的,
159 | # 它们分别表示了在未来Np个时刻内,状态变量和控制变量与参考状态和零向量的差值。
160 | for i in range(1, self.Np + 1): # i从1到Np。通过循环得到theta和phi矩阵
161 | phi[self.Nx * (i - 1): self.Nx * i] = np.dot(tmp, A)
162 |
163 | tmp_c = np.zeros([self.Nx, self.Nc * self.Nu])
164 | tmp_c[:, 0: self.Nu] = np.dot(tmp, B)
165 |
166 | if i > 1:
167 | tmp_c[:, self.Nu:] = theta[self.Nx * (i - 2): self.Nx * (i - 1), 0: -self.Nu]
168 |
169 | theta[self.Nx * (i - 1): self.Nx * i, :] = tmp_c
170 |
171 | tmp = np.dot(tmp, A)
172 |
173 | Q = np.eye(self.Nx * self.Np) # 权重Q,Q是一个对角矩阵,对角元素代表了对应状态变量的权重
174 |
175 | R = 5.0 * np.eye(self.Nu * self.Nc) # 权重R,R也是一个对角矩阵,对角元素代表了对应控制量的权重
176 |
177 | rho = 10 # rho是一个松弛因子的权重值,它表示了对松弛变量的惩罚程度。松弛变量是为了处理不等式约束而引入的一个辅助变量。
178 |
179 | #
180 | H = np.zeros((self.Nu * self.Nc + 1, self.Nu * self.Nc + 1))
181 | H[0: self.Nu * self.Nc, 0: self.Nu * self.Nc] = np.dot(np.dot(theta.transpose(), Q), theta) + R
182 | H[-1: -1] = rho # 加入权重值
183 |
184 | # 计算状态量ξ
185 | kesi = np.zeros((self.Nx + self.Nu, 1))
186 | diff_x = x - nearest_ref_x[:3]
187 | diff_x = diff_x.reshape(-1, 1) # 数据转换成1列
188 | kesi[: self.Nx, :] = diff_x
189 | diff_u = u_pre.reshape(-1, 1)
190 | kesi[self.Nx:, :] = diff_u
191 |
192 | F = np.zeros((1, self.Nu * self.Nc + 1))
193 | F_1 = 2 * np.dot(np.dot(np.dot(phi, kesi).transpose(), Q), theta)
194 | F[0, 0: self.Nu * self.Nc] = F_1
195 |
196 | # constraints-设置车速度和加速度的阈值
197 | umin = np.array([[-14.8], [-14.8], [-14.8], [-14.8]])
198 | umax = np.array([[14.8], [14.8], [14.8], [14.8]])
199 |
200 | delta_umin = np.array([[-2], [-2], [-2], [-2]])
201 | delta_umax = np.array([[2], [2], [2], [2]])
202 |
203 | # 计算A_I和约束条件
204 | A_t = np.zeros((self.Nc, self.Nc))
205 | for row in range(self.Nc): # 初始化下三角矩阵
206 | for col in range(self.Nc):
207 | if row >= col:
208 | A_t[row, col] = 1.0
209 |
210 | A_I = np.kron(A_t, np.eye(self.Nu))
211 |
212 | A_cons = np.zeros((self.Nc * self.Nu, self.Nc * self.Nu + 1))
213 | A_cons[0: self.Nc * self.Nu, 0: self.Nc * self.Nu] = A_I
214 |
215 | U_t = np.kron(np.ones((self.Nc, 1)), u_pre.reshape(-1, 1))
216 |
217 | U_min = np.kron(np.ones((self.Nc, 1)), umin)
218 | U_max = np.kron(np.ones((self.Nc, 1)), umax)
219 |
220 | LB = U_min - U_t
221 | UB = U_max - U_t
222 |
223 | delta_Umin = np.kron(np.ones((self.Nc, 1)), delta_umin)
224 | delta_Umax = np.kron(np.ones((self.Nc, 1)), delta_umax)
225 |
226 | delta_Umin = np.vstack((delta_Umin, [0]))
227 | delta_Umax = np.vstack((delta_Umax, [rho]))
228 |
229 | A_1_cons = np.eye(self.Nc * self.Nu + 1, self.Nc * self.Nu + 1)
230 |
231 | A_cons = np.vstack((A_cons, A_1_cons))
232 |
233 | LB = np.vstack((LB, delta_Umin))
234 | UB = np.vstack((UB, delta_Umax))
235 |
236 | # Create an OSQP object
237 | prob = osqp.OSQP()
238 |
239 | H = sparse.csc_matrix(H)
240 | A_cons = sparse.csc_matrix(A_cons) # 压缩稀疏矩阵
241 |
242 | # Setup workspace
243 | prob.setup(H, F.transpose(), A_cons, LB, UB)
244 |
245 | res = prob.solve()
246 |
247 | # Check solver status
248 | if res.info.status != 'solved':
249 | raise ValueError('OSQP did not solve the problem!')
250 |
251 | u_cur = u_pre + res.x[0: self.Nu]
252 | return u_cur, res.x[0: self.Nu]
253 |
254 |
255 | # pos = car.getField("translation").getSFVec3f()
256 | pos = np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0]) # 小车的起始位置,表示x位置,y位置和起始偏角
257 | pre_u = np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]) # 小车当前的控制量
258 |
259 | # 小车车身参数
260 | a = 0.15
261 | b = 0.1
262 |
263 | ref_traj = load_ref_traj()
264 | plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))
265 | plt.plot(ref_traj[:, 0], ref_traj[:, 1], '-.b', linewidth=5.0)
266 |
267 | history_us = np.array([])
268 | history_delta_us = np.array([])
269 |
270 | # 开始运动
271 | timeStep = int(robot.getBasicTimeStep())
272 |
273 | t1 = time.time()
274 | ugv = UGV_model(pos[0], pos[1], pos[2], a, b, dt)
275 | controller = MPCController(a, b, dt)
276 |
277 | while robot.step(timeStep) != -1 and sim_steps > 0:
278 |
279 | # 计算控制量
280 | u_cur, delta_u_cur = controller.Solve(pos, pre_u, ref_traj)
281 | abs_u = [v_d, v_d, v_d, v_d] + u_cur
282 | print(abs_u)
283 |
284 | # 更新模型
285 | ugv.update(abs_u[0], abs_u[1], abs_u[2], abs_u[3]) # 更新模型
286 | move(abs_u[0], abs_u[1], abs_u[2], abs_u[3]) # 驱动小车
287 | ugv.plot_duration() # 画图
288 |
289 | # 记录控制量
290 | history_us = np.append(history_us, abs_u)
291 | if len(history_delta_us) == 0:
292 | history_delta_us = np.array([u_cur])
293 | else:
294 | history_delta_us = np.vstack((history_delta_us, u_cur))
295 |
296 | # 更新位置
297 | pos = pos + np.array([(abs_u[0] + abs_u[1] + abs_u[2] + abs_u[3]) / 4 * dt,
298 | (-abs_u[0] + abs_u[1] - abs_u[2] + abs_u[3]) / 4 * dt,
299 | (-abs_u[0] - abs_u[1] + abs_u[2] + abs_u[3]) / 4 * (a + b) * dt])
300 |
301 | # 更新前一次控制量
302 | pre_u = u_cur
303 | sim_steps -= 1
304 |
305 | for i in range(4):
306 | motors[i].setVelocity(stop[i])
307 | t2 = time.time()
308 | print('程序运行时间:%s秒' % (t2 - t1))
309 | plt.show()
310 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/prm算法.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 吴仰晖创建 2023/04/21
2 | import math
3 |
4 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
5 | import numpy as np
6 | from celluloid import Camera # 保存动图时用,pip install celluloid
7 | from scipy.spatial import KDTree
8 |
9 | plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei', 'FangSong'] # 汉字字体,优先使用楷体,如果找不到楷体,则使用黑体
10 | plt.rcParams['font.size'] = 12 # 字体大小
11 | plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 正常显示负号
12 |
13 | # parameter
14 | N_SAMPLE = 200 # 采样点数目,即随机点集V的大小
15 | N_KNN = 30 # 一个采样点的领域点个数
16 | MAX_EDGE_LEN = 30.0 # [m] Maximum edge length 边的最大长度
17 | MAP_MAX_LENGTH = 60.0 # [m] Map maximum length
18 | MAP_MAX_WIDTH = 60.0 # [m] Map maximum width
19 | show_animation = True # 生成动画的开关
20 |
21 | '''
22 | 下面是设置障碍物,
23 | ox[]用来存障碍物的x坐标
24 | oy[]用来存障碍物的y坐标
25 | '''
26 | ox = []
27 | oy = []
28 |
29 | # start and goal position
30 | # (sx,sy)为开始位置坐标,(gx,gy)为目标地点坐标,robot_size为机器人半径
31 | sx = 10.0 # [m]
32 | sy = 10.0 # [m]
33 | gx = 50.0 # [m]
34 | gy = 50.0 # [m]
35 | robot_size = 2.5 # [m]
36 |
37 |
38 | # 初始化函数
39 | def init_global(start_position_x, start_position_y, goal_position_x, goal_position_y, obstacle, size_robot=2.5,
40 | x_range=100,
41 | y_range=100, n_sample=200,
42 | max_edge_len=30, show_animat=True, n_knn=30):
43 | global ox, oy, N_SAMPLE, N_KNN, MAX_EDGE_LEN, MAP_MAX_LENGTH, MAP_MAX_WIDTH
44 | global show_animation, sx, sy, gx, gy, robot_size
45 | N_SAMPLE = n_sample
46 | N_KNN = n_knn
47 | MAX_EDGE_LEN = max_edge_len
48 | MAP_MAX_LENGTH = x_range
49 | MAP_MAX_WIDTH = y_range
50 | show_animation = show_animat
51 | # 设置开始位置
52 | sx = start_position_x
53 | sy = start_position_y
54 | # 设置目标位置
55 | gx = goal_position_x
56 | gy = goal_position_y
57 | # 设置机器人半径
58 | robot_size = size_robot
59 |
60 | # 生成地图边界,相对于中心坐标
61 | # 生成地图上边界
62 | for i in range(-MAP_MAX_LENGTH // 2, MAP_MAX_LENGTH // 2):
63 | ox.append(i)
64 | oy.append(MAP_MAX_WIDTH / 2.0)
65 |
66 | # 生成地图右边界
67 | for i in range(-MAP_MAX_WIDTH // 2, MAP_MAX_WIDTH // 2):
68 | ox.append(MAP_MAX_LENGTH / 2.0)
69 | oy.append(i)
70 |
71 | # 生成地图下边界
72 | for i in range(-MAP_MAX_LENGTH // 2, MAP_MAX_LENGTH // 2):
73 | ox.append(i)
74 | oy.append(-MAP_MAX_WIDTH / 2.0)
75 |
76 | # 生成地图左边界
77 | for i in range(-MAP_MAX_WIDTH // 2, MAP_MAX_WIDTH // 2):
78 | ox.append(-MAP_MAX_LENGTH / 2.0)
79 | oy.append(i)
80 |
81 | # 生成障碍物及其半径范围内的点
82 | for i in obstacle:
83 | obs_radius = 3
84 | obs_x = i[0]
85 | obs_y = i[1]
86 | for angle in range(0, 360, 10): # 以10度为间隔生成点
87 | # 将角度转换为弧度
88 | angle_rad = math.radians(angle)
89 | # 计算点的坐标
90 | point_x = obs_x + obs_radius * math.cos(angle_rad)
91 | point_y = obs_y + obs_radius * math.sin(angle_rad)
92 |
93 | # 将生成的点添加到障碍物周围
94 | ox.append(point_x)
95 | oy.append(point_y)
96 |
97 |
98 | """
99 | kd-tree用于快速查找nearest-neighbor
100 |
101 | query(self, x[, k, eps, p, distance_upper_bound]): 查询kd-tree附近的邻居
102 |
103 |
104 | """
105 |
106 |
107 | class Node:
108 | """
109 | Node class for dijkstra search
110 | 点类
111 | """
112 |
113 | def __init__(self, x, y, cost, parent_index):
114 | self.x = x
115 | self.y = y
116 | self.cost = cost # 每条边权值总和,或者说到达该点所的代价
117 | self.parent_index = parent_index # 上一个点是啥,也就是从哪个点到达该点的
118 |
119 | # 用来打印/显示该点的信息(坐标、代价、连接的上一个点)
120 | def __str__(self):
121 | return str(self.x) + "," + str(self.y) + "," + \
122 | str(self.cost) + "," + str(self.parent_index)
123 |
124 |
125 | def prm_planning(start_x, start_y, goal_x, goal_y, obstacle_x_list, obstacle_y_list, robot_radius, *, camara=None,
126 | rng=None):
127 | """
128 | Run probabilistic road map planning
129 |
130 | :param start_x: start x position
131 | :param start_y: start y position
132 | (start_x,start_y)表示开始的坐标
133 | :param goal_x: goal x position
134 | :param goal_y: goal y position
135 | (goal_x,goal_y)表示目标的坐标
136 | :param obstacle_x_list: obstacle x positions
137 | :param obstacle_y_list: obstacle y positions
138 | (obstacle_x_list[n],obstacle_y_list[n])表示第n+1个障碍物的坐标
139 | :param robot_radius: robot radius 机器人的半径
140 | :param rng: 随机数构造器
141 | :return:
142 | """
143 | obstacle_kd_tree = KDTree(np.vstack((obstacle_x_list, obstacle_y_list)).T)
144 | # 采样点集生成
145 | sample_x, sample_y = sample_points(start_x, start_y, goal_x, goal_y,
146 | robot_radius,
147 | obstacle_x_list, obstacle_y_list,
148 | obstacle_kd_tree, rng)
149 | if show_animation:
150 | plt.plot(sample_x, sample_y, ".b")
151 |
152 | # 生成概率路图
153 | road_map = generate_road_map(sample_x, sample_y, robot_radius, obstacle_kd_tree)
154 | # 使用迪杰斯特拉规划路径
155 | rx, ry = dijkstra_planning(
156 | start_x, start_y, goal_x, goal_y, road_map, sample_x, sample_y, camara)
157 |
158 | return rx, ry
159 |
160 |
161 | def is_collision(sx, sy, gx, gy, rr, obstacle_kd_tree):
162 | """判断是否发生碰撞,true碰撞,false不碰
163 | rr: 机器人半径
164 | """
165 | x = sx
166 | y = sy
167 | dx = gx - sx
168 | dy = gy - sy
169 | yaw = math.atan2(gy - sy, gx - sx) # 计算角度
170 | d = math.hypot(dx, dy) # 计算距离
171 |
172 | if d >= MAX_EDGE_LEN: # 如果大于规定的边的长度,那么认为其碰撞,也就是不在这两点连边(实际上MAX_EDGE_LEN是构建路图的邻域的半径)
173 | return True
174 |
175 | D = rr
176 | n_step = round(d / D)
177 | # 判断走在这两个点之间的边会不会发生碰撞
178 | for i in range(n_step):
179 | dist, _ = obstacle_kd_tree.query([x, y]) # 查询kd-tree附近的邻居
180 | if dist <= rr:
181 | return True # collision
182 | # 每次移动D实际不能确保100%筛选出不会碰撞边?
183 | x += D * math.cos(yaw)
184 | y += D * math.sin(yaw)
185 |
186 | # goal point check
187 | dist, _ = obstacle_kd_tree.query([gx, gy])
188 | if dist <= rr:
189 | return True # collision
190 |
191 | return False # OK
192 |
193 |
194 | def generate_road_map(sample_x, sample_y, rr, obstacle_kd_tree):
195 | """
196 | 概率路图生成
197 |
198 | sample_x: [m] x positions of sampled points
199 | sample_y: [m] y positions of sampled points
200 | robot_radius: Robot Radius[m]
201 | obstacle_kd_tree: KDTree object of obstacles
202 | """
203 |
204 | road_map = []
205 | n_sample = len(sample_x)
206 | # vstack()会将(N,)的数组转化为(1,N)的数组,再加上.T(转置),这里就是将sample_x和sample_y转化为以[sample_x,sample_y]为元素的数组
207 | sample_kd_tree = KDTree(np.vstack((sample_x, sample_y)).T)
208 | # vstack会把
209 | for (i, ix, iy) in zip(range(n_sample), sample_x, sample_y):
210 | # (i,ix,iy)中i是采样点的序号,ix和iy分别是采样点的x和y坐标值
211 | # 对采样点击V中的每个点q,选择k个邻域点,这里k=n_sample是遍历所有的点?实际是按距离排序返回点集
212 | dists, indexes = sample_kd_tree.query([ix, iy], k=n_sample)
213 | edge_id = []
214 | # indexes返回的k个最邻近采样点的序号,由于第一个肯定是自己,for从1开始
215 | for ii in range(1, len(indexes)):
216 | nx = sample_x[indexes[ii]]
217 | ny = sample_y[indexes[ii]]
218 | # 对每个领域点$q'$进行判断,如果$q$和$q'$尚未形成路径,则将其连接形成路径并进行碰撞检测,若无碰撞,则保留该路径。
219 | if not is_collision(ix, iy, nx, ny, rr, obstacle_kd_tree):
220 | edge_id.append(indexes[ii])
221 |
222 | if len(edge_id) >= N_KNN: # 如果邻域点够了,不停止加入
223 | break
224 |
225 | road_map.append(edge_id)
226 | # 下面的函数用于画出路图的所有边
227 | # plot_road_map(road_map, sample_x, sample_y)
228 |
229 | return road_map
230 |
231 |
232 | def dijkstra_planning(sx, sy, gx, gy, road_map, sample_x, sample_y, camara):
233 | """
234 | s_x: start x position [m]
235 | s_y: start y position [m]
236 | goal_x: goal x position [m]
237 | goal_y: goal y position [m]
238 | obstacle_x_list: x position list of Obstacles [m]
239 | obstacle_y_list: y position list of Obstacles [m]
240 | robot_radius: robot radius [m]
241 | road_map: 构建好的路图 [m]
242 | sample_x: 采样点集x [m]
243 | sample_y: 采样点集y [m]
244 |
245 | @return: Two lists of path coordinates ([x1, x2, ...], [y1, y2, ...]), empty list when no path was found
246 | """
247 | # 初始化开始点与目标点
248 | start_node = Node(sx, sy, 0.0, -1)
249 | goal_node = Node(gx, gy, 0.0, -1)
250 | # 使用字典的方式构造开闭集合
251 | # openList表由待考察的节点(也就是与已经考察的节点关联但未考察的节点)组成, closeList表由已经考察过的节点组成。
252 | open_set, closed_set = dict(), dict()
253 | open_set[len(road_map) - 2] = start_node
254 |
255 | path_found = True
256 | num_sum = 0
257 | # 步骤与A星算法一致
258 | while True:
259 | # 如果open_set是空的
260 | if not open_set:
261 | print("Cannot find path")
262 | path_found = False
263 | break
264 | # 从未考察的节点中选取到达花费最小点加入,其中key参数为排序关键字
265 | c_id = min(open_set, key=lambda o: open_set[o].cost)
266 | current = open_set[c_id]
267 |
268 | # show graph 画图,每考察两个点画1个X?已考察的点的个数是偶数时画点
269 | if show_animation and len(closed_set.keys()) % 5 == 0:
270 | # for stopping simulation with the esc key.
271 | plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect(
272 | 'key_release_event',
273 | lambda event: [exit(0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])
274 | # 在当前考察的点画一个绿色(green)的X
275 | plt.plot(current.x, current.y, "xg")
276 | plt.pause(0.001)
277 | # 画出当前的路径图
278 | plot_shortest_road(current, closed_set, camara, sample_x, sample_y, num_sum)
279 | if camara != None:
280 | """Capture current state of the figure."""
281 | camara.snap()
282 | # 如果c_id是目标点那么说明已经找到了路径!
283 | # 目标点在road_map的最后一个road_map[len-1],开始点在road_map的倒数第二road_map[len-2]
284 | # 这样的位置缘于生成采样点sample_point和生成路图generate_road_map
285 | if c_id == (len(road_map) - 1):
286 | print("goal is found!")
287 | goal_node.parent_index = current.parent_index
288 | goal_node.cost = current.cost
289 | break
290 |
291 | # Remove the item from the open set
292 | del open_set[c_id]
293 | # Add it to the closed set
294 | closed_set[c_id] = current
295 |
296 | # expand search grid based on motion model
297 | # 以下是更新路径的关键部分,遍历与c_id关联的所有边/点
298 | for i in range(len(road_map[c_id])):
299 | num_sum = num_sum + 1
300 | n_id = road_map[c_id][i]
301 | dx = sample_x[n_id] - current.x
302 | dy = sample_y[n_id] - current.y
303 | d = math.hypot(dx, dy) # 计算从current点(c_id点)到n_id点的距离,记为d
304 | node = Node(sample_x[n_id], sample_y[n_id],
305 | current.cost + d, c_id)
306 |
307 | # 如果n_id点在已经考察过的点里,那么这条边(c_id,n_id)也一定考察过,跳过
308 | if n_id in closed_set:
309 | continue
310 | # Otherwise if it is already in the open set
311 | if n_id in open_set:
312 | # 如果当前记录的到达n_id的代价 大于 经current点到n_id的代价,那么更新!
313 | if open_set[n_id].cost > node.cost:
314 | open_set[n_id].cost = node.cost
315 | open_set[n_id].parent_index = c_id
316 | # 如果不在open_set,说明这个点与之前所有已经考察的节点都不关联!所以无须比较,直接更新
317 | else:
318 | open_set[n_id] = node
319 |
320 | # 如果找不到路径,返回两个空集
321 | if path_found is False:
322 | return [], []
323 |
324 | # generate final course
325 | # 根据close_set的信息生成路径,从目标点‘回溯’
326 | rx, ry = [goal_node.x], [goal_node.y]
327 | parent_index = goal_node.parent_index
328 | while parent_index != -1:
329 | n = closed_set[parent_index]
330 | rx.append(n.x)
331 | ry.append(n.y)
332 | parent_index = n.parent_index
333 |
334 | return rx, ry
335 |
336 |
337 | def plot_shortest_road(current, closed_set, camara, sample_x, sample_y, num_sum):
338 | plt.text(50, 5, f'更新次数:{num_sum}', fontsize=12)
339 | # 画出地图
340 | if show_animation:
341 | plt.plot(ox, oy, ".k") # 显示障碍物,用黑点表示
342 | plt.plot(sx, sy, "^r") # 显示开始位置,用红三角表示
343 | plt.plot(gx, gy, "^c") # 显示目标地点,用蓝三角表示
344 | # 画出当前已经考察过的点
345 | for i in closed_set:
346 | plt.plot(sample_x[i], sample_y[i], '.b')
347 | rx, ry = [current.x], [current.y]
348 | parent_index = current.parent_index
349 | while parent_index != -1:
350 | n = closed_set[parent_index]
351 | rx.append(n.x)
352 | ry.append(n.y)
353 | parent_index = n.parent_index
354 | if show_animation:
355 | plt.plot(rx, ry, "-r") # 给路径点连线
356 | plt.pause(0.001)
357 |
358 |
359 | def sample_points(sx, sy, gx, gy, rr, ox, oy, obstacle_kd_tree, rng):
360 | # 采样点集生成
361 |
362 | # 这里其实是确定采样的区域(矩形)大小
363 | max_x = max(ox)
364 | max_y = max(oy)
365 | min_x = min(ox)
366 | min_y = min(oy)
367 |
368 | sample_x, sample_y = [], []
369 |
370 | # 如果没有传入随机生成器,就采用默认的(PCG64) 位生成器构造的随机生成器
371 | if rng is None:
372 | rng = np.random.default_rng()
373 | # 随机采样,直到采样点的数量足够
374 | while len(sample_x) <= N_SAMPLE:
375 | '''rng.random()返回[0.0,1.0)的随机浮点数
376 | 所以下面两条语句可以生成在区域内的随机坐标
377 | '''
378 | tx = (rng.random() * (max_x - min_x)) + min_x
379 | ty = (rng.random() * (max_y - min_y)) + min_y
380 |
381 | # 查询离随机点(tx, ty)最近的障碍点的距离
382 | dist, index = obstacle_kd_tree.query([tx, ty])
383 |
384 | '''
385 | 如果机器人与最近的障碍点的距离大于半径,说明没有碰撞.
386 | 则将这个无碰撞的点加入采样点集中。
387 | '''
388 | if dist >= rr:
389 | sample_x.append(tx)
390 | sample_y.append(ty)
391 | # 别忘了起点和目标点也要放入采样点中!
392 | sample_x.append(sx)
393 | sample_y.append(sy)
394 | sample_x.append(gx)
395 | sample_y.append(gy)
396 |
397 | return sample_x, sample_y
398 |
399 |
400 | def plot_road_map(road_map, sample_x, sample_y): # pragma: no cover
401 |
402 | for i, _ in enumerate(road_map):
403 | for ii in range(len(road_map[i])):
404 | ind = road_map[i][ii]
405 |
406 | plt.plot([sample_x[i], sample_x[ind]],
407 | [sample_y[i], sample_y[ind]], "-k")
408 |
409 |
410 | def start(rng=None):
411 | print(" start!!")
412 | fig = plt.figure(1)
413 |
414 | camara = Camera(fig) # 保存动图时使用
415 | # camara = None
416 |
417 | if show_animation:
418 | plt.plot(ox, oy, ".k") # 显示障碍物,用黑点表示
419 | plt.plot(sx, sy, "^r") # 显示开始位置,用红三角表示
420 | plt.plot(gx, gy, "^c") # 显示目标地点,用蓝三角表示
421 | plt.grid(True)
422 | plt.axis("equal")
423 | if camara is not None:
424 | camara.snap()
425 | # 运行prm路径规划算法,得到路径点集
426 | rx, ry = prm_planning(sx, sy, gx, gy, ox, oy, robot_size, camara=camara, rng=rng)
427 | # 如果rx为空,说明找不到路径
428 | # assert rx, 'Cannot found path'
429 | return rx, ry
430 | if show_animation:
431 | plt.plot(rx, ry, "-r") # 给路径点连线
432 | plt.pause(0.001)
433 | if camara is not None: # 保存动图
434 | camara.snap()
435 | animation = camara.animate()
436 | animation.save('trajectory.gif', fps=10)
437 | plt.savefig("result.png") # 保存图片
438 | plt.show()
439 |
440 |
441 | if __name__ == '__main__':
442 | start()
443 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/1030DWA/dwa.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 吴仰晖创建 2023/10/22
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
4 | import copy
5 | from celluloid import Camera # 保存动图时用,pip install celluloid
6 | import math
7 |
8 |
9 | class Config:
10 | """
11 | simulation parameter class
12 | """
13 |
14 | def __init__(self, obstacle=None, goal=None):
15 | # robot parameter
16 | # 线速度边界
17 | if goal is None:
18 | goal = []
19 | if obstacle is None:
20 | obstacle = []
21 | self.v_max = 0.74 # [m/s] 最大(前进)线速度
22 | self.v_min = -0.74 # [m/s] 最小速度/最大(后退线速度)
23 | # 角速度边
24 | self.w_max = 40.0 * math.pi / 180.0 # [rad/s]
25 | self.w_min = -40.0 * math.pi / 180.0 # [rad/s]
26 | # 线加速度和角加速度最大值
27 | self.a_vmax = 0.5 # [m/ss]
28 | self.a_wmax = 40.0 * math.pi / 180.0 # [rad/ss]
29 | # 采样分辨率
30 | # 通过调低这里的分辨率,可以提高计算速度,但是会降低轨迹的平滑度
31 | # 低分辨率也让webots更加流畅
32 | self.v_sample = 0.05 # [m/s]
33 | self.w_sample = 1.0 * math.pi / 180.0 # [rad/s]
34 | # 离散时间
35 | self.dt = 0.32 # [s] Time tick for motion prediction
36 | # 轨迹推算时间长度
37 | self.predict_time = 3.2 # [s]
38 | # 轨迹评价函数系数
39 | self.alpha = 0.15
40 | self.beta = 1.0
41 | self.gamma = 1.0
42 |
43 | # Also used to check if goal is reached in both types
44 | self.robot_radius = 0.48 # [m] for collision check
45 |
46 | self.judge_distance = 10 # 若与障碍物的最小距离大于阈值(例如这里设置的阈值为robot_radius+0.2),则设为一个较大的常值
47 |
48 | # 障碍物位置 [x(m) y(m), ....]
49 | # self.ob = np.array([[-1, -1],
50 | # [0, 2],
51 | # [4.0, 2.0],
52 | # [5.0, 4.0],
53 | # [5.0, 5.0],
54 | # [5.0, 6.0],
55 | # [5.0, 9.0],
56 | # [8.0, 9.0],
57 | # [7.0, 9.0],
58 | # [8.0, 10.0],
59 | # [9.0, 11.0],
60 | # [12.0, 13.0],
61 | # [12.0, 12.0],
62 | # [15.0, 15.0],
63 | # [13.0, 13.0]
64 | # ])
65 | # 发现考虑少了障碍物的半径,在dwa中可以不用采用生成一圈的办法,只要增加judge_distance即可
66 | # obstacle = [[0.8572527545203357, -2.2172098729958623], [-0.6741852076368721, -4.6115193149832585],
67 | # [-0.7621386866002345, -3.9535764656708983], [-0.8369834345404434, -3.261055588337847],
68 | # [-1.010366856626901, -2.4959208871676766], [0.2098959999999998, -0.46027808659712655],
69 | # [2.959102826085521, -1.111275406277689], [2.0699852866327326, 0.6001139296402963],
70 | # [1.7621899882463656, 1.3538201247028991], [1.4825232582087984, 2.041558184052668],
71 | # [-0.15357100000000012, 2.8364377319986698], [-3.6503399999826605, 0.029938400947660367],
72 | # [-3.060002753141268, 1.9307752017999635], [-4.491749999600772, -2.273028797129561],
73 | # [-3.7846899998194625, -2.2760496178222844], [-0.9226689999550016, 0.2762752351882738],
74 | # [-2.56802998958373, -0.7738599262186142], [-0.292953, -0.016882052974691777]]
75 | # obstacle = [[-1, -1],
76 | # [0, 2],
77 | # [4.0, 2.0],
78 | # [5.0, 4.0],
79 | # [5.0, 5.0],
80 | # [5.0, 6.0],
81 | # [5.0, 9.0],
82 | # [8.0, 9.0],
83 | # [7.0, 9.0],
84 | # [8.0, 10.0],
85 | # [9.0, 11.0],
86 | # [12.0, 13.0],
87 | # [12.0, 12.0],
88 | # [15.0, 15.0],
89 | # [13.0, 13.0]
90 | # ]
91 | # 遍历列表中的每个坐标,并将其四舍五入到两位小数
92 | # obstacle = [[round(x, 2), round(y, 2)] for x, y in obstacle]
93 | # 等比放大两倍
94 | # obstacle = [[x * 2, y * 2] for x, y in obstacle]
95 | self.ob = obstacle.copy() # 注意这里不要self.ob = obstacle,否则二者指向的是同一个对象,所以下面会陷入死循环
96 | # ob_num = 0
97 | # # 生成障碍物及其半径范围内的点
98 | # for i in obstacle:
99 | # obs_radius = 0.6
100 | # obs_x = i[0]
101 | # obs_y = i[1]
102 | # for angle in range(0, 360, 36): # 以10度为间隔生成点
103 | # # 将角度转换为弧度
104 | # angle_rad = math.radians(angle)
105 | # # 计算点的坐标
106 | # point_x = obs_x + obs_radius * math.cos(angle_rad)
107 | # point_y = obs_y + obs_radius * math.sin(angle_rad)
108 | #
109 | # # 将生成的点添加到障碍物周围
110 | # print("ob_num:",ob_num)
111 | # ob_num += 1
112 | # self.ob.append([point_x,point_y])
113 | self.ob = np.array(self.ob)
114 | # self.ob = obstacle
115 | # 目标点位置
116 | # self.target = np.array([13, 10])
117 | # self.target = np.array([10, 6])
118 | self.target = goal
119 |
120 |
121 | class DWA:
122 | def __init__(self, config) -> None:
123 | """初始化
124 | Args:
125 | config (_type_): 参数类
126 | """
127 | self.dt = config.dt
128 | self.v_min = config.v_min
129 | self.w_min = config.w_min
130 | self.v_max = config.v_max
131 | self.w_max = config.w_max
132 | self.predict_time = config.predict_time
133 | self.a_vmax = config.a_vmax
134 | self.a_wmax = config.a_wmax
135 | self.v_sample = config.v_sample # 线速度采样分辨率
136 | self.w_sample = config.w_sample # 角速度采样分辨率
137 | self.alpha = config.alpha
138 | self.beta = config.beta
139 | self.gamma = config.gamma
140 | self.radius = config.robot_radius
141 | self.judge_distance = config.judge_distance
142 | # cal_num用来统计计算复杂度
143 | self.cal_num = 0
144 |
145 | def dwa_control(self, state, goal, obstacle):
146 | """滚动窗口算法入口
147 | Args:
148 | state (_type_): 机器人当前状态--[x,y,yaw,v,w]
149 | goal (_type_): 目标点位置,[x,y]
150 | obstacle (_type_): 障碍物位置,dim:[num_ob,2]
151 | Returns:
152 | _type_: 控制量、轨迹(便于绘画)
153 | trajectory [[x,y,yaw,v,w],2] 2维list,
154 | """
155 | control, trajectory = self.trajectory_evaluation(state, goal, obstacle)
156 | return control, trajectory #
157 |
158 | def cal_dynamic_window_vel(self, v, w, state, obstacle):
159 | """速度采样,得到速度空间窗口
160 | Args:
161 | v (_type_): 当前时刻线速度
162 | w (_type_): 当前时刻角速度
163 | state (_type_): 当前机器人状态
164 | obstacle (_type_): 障碍物位置
165 | Returns:
166 | [v_low,v_high,w_low,w_high]: 最终采样后的速度空间
167 | """
168 | Vm = self.__cal_vel_limit()
169 | Vd = self.__cal_accel_limit(v, w)
170 | Va = self.__cal_obstacle_limit(state, obstacle)
171 | a = max([Vm[0], Vd[0], Va[0]])
172 | b = min([Vm[1], Vd[1], Va[1]])
173 | c = max([Vm[2], Vd[2], Va[2]])
174 | d = min([Vm[3], Vd[3], Va[3]])
175 | return [a, b, c, d]
176 |
177 | def __cal_vel_limit(self):
178 | """计算速度边界限制Vm
179 | Returns:
180 | _type_: 速度边界限制后的速度空间Vm
181 | """
182 | return [self.v_min, self.v_max, self.w_min, self.w_max]
183 |
184 | def __cal_accel_limit(self, v, w):
185 | """计算加速度限制Vd
186 | Args:
187 | v (_type_): 当前时刻线速度
188 | w (_type_): 当前时刻角速度
189 | Returns:
190 | _type_:考虑加速度时的速度空间Vd
191 | """
192 | v_low = v - self.a_vmax * self.dt
193 | v_high = v + self.a_vmax * self.dt
194 | w_low = w - self.a_wmax * self.dt
195 | w_high = w + self.a_wmax * self.dt
196 | return [v_low, v_high, w_low, w_high]
197 |
198 | def __cal_obstacle_limit(self, state, obstacle):
199 | """环境障碍物限制Va
200 | Args:
201 | state (_type_): 当前机器人状态
202 | obstacle (_type_): 障碍物位置
203 | Returns:
204 | _type_: 某一时刻移动机器人不与周围障碍物发生碰撞的速度空间Va
205 | """
206 | v_low = self.v_min
207 | v_high = np.sqrt(2 * self._dist(state, obstacle) * self.a_vmax)
208 | w_low = self.w_min
209 | w_high = np.sqrt(2 * self._dist(state, obstacle) * self.a_wmax)
210 | return [v_low, v_high, w_low, w_high]
211 |
212 | def trajectory_predict(self, state_init, v, w):
213 | """轨迹推算
214 | Args:
215 | state_init (_type_): 当前状态---x,y,yaw,v,w
216 | v (_type_): 当前时刻线速度
217 | w (_type_): 当前时刻角速度
218 | Returns:
219 | _type_: _description_
220 | """
221 | state = np.array(state_init)
222 | trajectory = state
223 | time = 0
224 | # 在预测时间段内,不断进行轨迹推算
225 | while time <= self.predict_time:
226 | x = KinematicModel(state, [v, w], self.dt) # 运动学模型
227 | trajectory = np.vstack((trajectory, x))
228 | time += self.dt
229 | self.cal_num += 1
230 | return trajectory
231 |
232 | def trajectory_evaluation(self, state, goal, obstacle):
233 | """轨迹评价函数,评价越高,轨迹越优
234 | Args:
235 | state (_type_): 当前状态---x,y,yaw,v,w
236 | dynamic_window_vel (_type_): 采样的速度空间窗口---[v_low,v_high,w_low,w_high]
237 | goal (_type_): 目标点位置,[x,y]
238 | obstacle (_type_): 障碍物位置,dim:[num_ob,2]
239 | Returns:
240 | _type_: 最优控制量、最优轨迹
241 | control_opt:[v,w] 最优控制量包含速度v和角速度w
242 | """
243 | G_max = -float('inf') # 最优评价
244 | trajectory_opt = state # 最优轨迹
245 | control_opt = [0., 0.] # 最优控制
246 | dynamic_window_vel = self.cal_dynamic_window_vel(state[3], state[4], state, obstacle) # 第1步--计算速度空间
247 |
248 | # sum_heading,sum_dist,sum_vel = 0,0,0 # 统计全部采样轨迹的各个评价之和,便于评价的归一化
249 | # # 在本次实验中,不进行归一化也可实现该有的效果。
250 | # for v in np.arange(dynamic_window_vel[0],dynamic_window_vel[1],self.v_sample):
251 | # for w in np.arange(dynamic_window_vel[2], dynamic_window_vel[3], self.w_sample):
252 | # trajectory = self.trajectory_predict(state, v, w)
253 |
254 | # heading_eval = self.alpha*self.__heading(trajectory,goal)
255 | # dist_eval = self.beta*self.__dist(trajectory,obstacle)
256 | # vel_eval = self.gamma*self.__velocity(trajectory)
257 | # sum_vel+=vel_eval
258 | # sum_dist+=dist_eval
259 | # sum_heading +=heading_eval
260 |
261 | # 在速度空间中按照预先设定的分辨率采样
262 | sum_heading, sum_dist, sum_vel = 1, 1, 1 # 不进行归一化
263 | for v in np.arange(dynamic_window_vel[0], dynamic_window_vel[1], self.v_sample):
264 | for w in np.arange(dynamic_window_vel[2], dynamic_window_vel[3], self.w_sample):
265 |
266 | trajectory = self.trajectory_predict(state, v, w) # 第2步--轨迹推算
267 |
268 | # 这个__heading是当前采样速度下产生的轨迹终点位置方向与目标点连线的夹角的误差
269 | heading_eval = self.alpha * self.__heading(trajectory, goal) / sum_heading
270 | # heading_eval = 0
271 | # 表示当前速度下对应模拟轨迹与障碍物之间的最近距离
272 | # 距离越大,轨迹就越优
273 | # 当距离大于阈值,它就会设为一个比较大的值
274 | dist_eval = self.beta * self.__dist(trajectory, obstacle) / sum_dist
275 | # dist_eval = 0
276 | #
277 | vel_eval = self.gamma * self.__velocity(trajectory) / sum_vel
278 | # vel_eval = 0
279 | # print("heading_eval:",heading_eval," dist_eval:",dist_eval," vel_eval:",vel_eval)
280 | G = heading_eval + dist_eval + vel_eval # 第3步--轨迹评价
281 |
282 | if G_max <= G:
283 | G_max = G
284 | trajectory_opt = trajectory
285 | control_opt = [v, w]
286 |
287 | return control_opt, trajectory_opt
288 |
289 | def _dist(self, state, obstacle):
290 | """计算当前移动机器人距离障碍物最近的几何距离
291 | Args:
292 | state (_type_): 当前机器人状态
293 | obstacle (_type_): 障碍物位置
294 | Returns:
295 | _type_: 移动机器人距离障碍物最近的几何距离
296 | """
297 | ox = obstacle[:, 0]
298 | oy = obstacle[:, 1]
299 | dx = state[0, None] - ox[:, None]
300 | dy = state[1, None] - oy[:, None]
301 | r = np.hypot(dx, dy)
302 | return np.min(r)
303 |
304 | def __dist(self, trajectory, obstacle):
305 | """距离评价函数
306 | 表示当前速度下对应模拟轨迹与障碍物之间的最近距离;
307 | 如果没有障碍物或者最近距离大于设定的阈值,那么就将其值设为一个较大的常数值。
308 | Args:
309 | trajectory (_type_): 轨迹,dim:[n,5]
310 |
311 | obstacle (_type_): 障碍物位置,dim:[num_ob,2]
312 | Returns:
313 | _type_: _description_
314 | """
315 | ox = obstacle[:, 0]
316 | oy = obstacle[:, 1]
317 | dx = trajectory[:, 0] - ox[:, None]
318 | dy = trajectory[:, 1] - oy[:, None]
319 | r = np.hypot(dx, dy)
320 | return np.min(r) if np.array(r < self.radius+0.1).any() else self.judge_distance
321 |
322 | def __heading(self, trajectory, goal):
323 | """方位角评价函数
324 | 评估在当前采样速度下产生的轨迹终点位置方向与目标点连线的夹角的误差
325 | Args:
326 | trajectory (_type_): 轨迹,dim:[n,5]
327 | goal (_type_): 目标点位置[x,y]
328 | Returns:
329 | cost_type_: 方位角评价数值
330 | 误差越大,cost越小
331 | """
332 | dx = goal[0] - trajectory[-1, 0]
333 | dy = goal[1] - trajectory[-1, 1]
334 | error_angle = math.atan2(dy, dx)
335 | cost_angle = error_angle - trajectory[-1, 2]
336 | cost = math.pi - abs(cost_angle)
337 |
338 | return cost
339 |
340 | def __velocity(self, trajectory):
341 | """速度评价函数, 表示当前的速度大小,可以用模拟轨迹末端位置的线速度的大小来表示
342 | Args:
343 | trajectory (_type_): 轨迹,dim:[n,5]
344 | Returns:
345 | _type_: 速度评价
346 | """
347 | return trajectory[-1, 3]
348 |
349 |
350 | def KinematicModel(state, control, dt):
351 | """机器人运动学模型
352 | Args:
353 | state (_type_): 状态量---x,y,yaw,v,w
354 | control (_type_): 控制量---v,w,线速度和角速度
355 | dt (_type_): 离散时间
356 | Returns:
357 | _type_: 下一步的状态 x,y,yaw,v,w
358 | """
359 | # 我们是麦克纳姆轮的小车,但是用这个运动学模型问题也不大
360 | state[0] += control[0] * math.cos(state[2]) * dt
361 | state[1] += control[0] * math.sin(state[2]) * dt
362 | state[2] += control[1] * dt
363 | state[3] = control[0]
364 | state[4] = control[1]
365 |
366 | return state
367 |
368 |
369 | def plot_arrow(x, y, yaw, length=0.5, width=0.1): # pragma: no cover
370 | plt.arrow(x, y, length * math.cos(yaw), length * math.sin(yaw),
371 | head_length=width, head_width=width)
372 | plt.plot(x, y)
373 |
374 |
375 | def plot_robot(x, y, yaw, config): # pragma: no cover
376 | circle = plt.Circle((x, y), config.robot_radius, color="b")
377 | plt.gcf().gca().add_artist(circle)
378 | out_x, out_y = (np.array([x, y]) +
379 | np.array([np.cos(yaw), np.sin(yaw)]) * config.robot_radius)
380 | plt.plot([x, out_x], [y, out_y], "-k")
381 |
382 |
383 | def init(ob, target):
384 | dwa = DWA(Config(ob, target))
385 | return dwa
386 |
387 |
388 | def main(config):
389 | start_position = [0, 5]
390 | # initial state [x(m), y(m), yaw(rad), v(m/s), omega(rad/s)]
391 | # 初始状态 x 包含机器人的初始位置和速度信息,以及朝向。
392 | # x 是一个包含五个元素的NumPy数组,
393 | # 分别表示x坐标、y坐标、朝向角度、线速度(速度大小),和角速度(转向速度)
394 | x = np.array([start_position[0], start_position[1], -math.pi , 0.0, 0.0])
395 | # goal position [x(m), y(m)]
396 | # goal 是目标位置的坐标,这是机器人要尝试到达的位置。
397 | goal = config.target
398 |
399 | # input [forward speed, yaw_rate]
400 | # trajectory 是一个NumPy数组,用于存储机器人的轨迹,它最初包含机器人的初始状态
401 | trajectory = np.array(x)
402 | # ob 是一组障碍物的位置
403 | ob = config.ob
404 | # 创建了一个 DWA 对象 dwa,用于执行动态窗口法(Dynamic Window Approach)的路径规划。
405 | dwa = DWA(config)
406 | fig = plt.figure(1)
407 | camera = Camera(fig)
408 | while True:
409 | #
410 | u, predicted_trajectory = dwa.dwa_control(x, goal, ob)
411 | # print(predicted_trajectory)
412 | x = KinematicModel(x, u, config.dt) # simulate robot
413 | trajectory = np.vstack((trajectory, x)) # store state history
414 |
415 | plt.cla()
416 | # for stopping simulation with the esc key.
417 | plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect(
418 | 'key_release_event',
419 | lambda event: [exit(0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])
420 | plt.plot(predicted_trajectory[:, 0], predicted_trajectory[:, 1], "-g")
421 | plt.plot(x[0], x[1], "xr")
422 | plt.plot(goal[0], goal[1], "xb")
423 | plt.plot(ob[:, 0], ob[:, 1], "ok")
424 | plot_robot(x[0], x[1], x[2], config)
425 | plot_arrow(x[0], x[1], x[2])
426 | plt.text(0, 0, f'Calculation Count: {dwa.cal_num}', fontsize=12, color='red') # 添加文本标签
427 | plt.axis("equal")
428 | plt.grid(True)
429 | plt.pause(0.00001)
430 |
431 | # check reaching goal
432 | dist_to_goal = math.hypot(x[0] - goal[0], x[1] - goal[1])
433 | if dist_to_goal <= config.robot_radius:
434 | print("Goal!!")
435 | break
436 | # camera.snap()
437 |
438 | # print(x)
439 | # print(u)
440 |
441 | print("Done,calnum:", dwa.cal_num)
442 | plt.plot(trajectory[:, 0], trajectory[:, 1], "-r")
443 | plt.pause(0.00001)
444 | # camera.snap()
445 | # animation = camera.animate()
446 | # animation.save('trajectory.gif')
447 | plt.show()
448 |
449 |
450 | if __name__ == "__main__":
451 | main(Config())
452 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/project/controllers/all_controller/dwa.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 吴仰晖创建 2023/10/22
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
4 | import copy
5 | from celluloid import Camera # 保存动图时用,pip install celluloid
6 | import math
7 |
8 |
9 | class Config:
10 | """
11 | simulation parameter class
12 | """
13 |
14 | def __init__(self, obstacle=None, goal=None):
15 | # robot parameter
16 | # 线速度边界
17 | if goal is None:
18 | goal = []
19 | if obstacle is None:
20 | obstacle = []
21 | self.v_max = 0.74 # [m/s] 最大(前进)线速度
22 | self.v_min = -0.74 # [m/s] 最小速度/最大(后退线速度)
23 | # 角速度边界d
24 | self.w_max = 70.0 * math.pi / 180.0 # [rad/s]
25 | self.w_min = -70.0 * math.pi / 180.0 # [rad/s]
26 | # 线加速度和角加速度最大值
27 | self.a_vmax = 0.5 # [m/ss]
28 | self.a_wmax = 40.0 * math.pi / 180.0 # [rad/ss]
29 | # 采样分辨率
30 | # 通过调低这里的分辨率,可以提高计算速度,但是会降低轨迹的平滑度
31 | # 低分辨率也让webots更加流畅
32 | self.v_sample = 0.01 # [m/s]
33 | self.w_sample = 1.0 * math.pi / 180.0 # [rad/s]
34 | # 离散时间
35 | self.dt = 0.32 # [s] Time tick for motion prediction
36 | # 轨迹推算时间长度
37 | self.predict_time = 6.4 # [s]
38 | # 轨迹评价函数系数
39 | self.alpha = 0.2
40 | self.beta = 1.0
41 | self.gamma = 1.0
42 |
43 | # Also used to check if goal is reached in both types
44 | self.robot_radius = 0.48 # [m] for collision check
45 |
46 | self.judge_distance = 10 # 若与障碍物的最小距离大于阈值(例如这里设置的阈值为robot_radius+0.2),则设为一个较大的常值
47 |
48 | # 障碍物位置 [x(m) y(m), ....]
49 | # self.ob = np.array([[-1, -1],
50 | # [0, 2],
51 | # [4.0, 2.0],
52 | # [5.0, 4.0],
53 | # [5.0, 5.0],
54 | # [5.0, 6.0],
55 | # [5.0, 9.0],
56 | # [8.0, 9.0],
57 | # [7.0, 9.0],
58 | # [8.0, 10.0],
59 | # [9.0, 11.0],
60 | # [12.0, 13.0],
61 | # [12.0, 12.0],
62 | # [15.0, 15.0],
63 | # [13.0, 13.0]
64 | # ])
65 | # 发现考虑少了障碍物的半径,在dwa中可以不用采用生成一圈的办法,只要增加judge_distance即可
66 | # obstacle = [[0.8572527545203357, -2.2172098729958623], [-0.6741852076368721, -4.6115193149832585],
67 | # [-0.7621386866002345, -3.9535764656708983], [-0.8369834345404434, -3.261055588337847],
68 | # [-1.010366856626901, -2.4959208871676766], [0.2098959999999998, -0.46027808659712655],
69 | # [2.959102826085521, -1.111275406277689], [2.0699852866327326, 0.6001139296402963],
70 | # [1.7621899882463656, 1.3538201247028991], [1.4825232582087984, 2.041558184052668],
71 | # [-0.15357100000000012, 2.8364377319986698], [-3.6503399999826605, 0.029938400947660367],
72 | # [-3.060002753141268, 1.9307752017999635], [-4.491749999600772, -2.273028797129561],
73 | # [-3.7846899998194625, -2.2760496178222844], [-0.9226689999550016, 0.2762752351882738],
74 | # [-2.56802998958373, -0.7738599262186142], [-0.292953, -0.016882052974691777]]
75 | # obstacle = [[-1, -1],
76 | # [0, 2],
77 | # [4.0, 2.0],
78 | # [5.0, 4.0],
79 | # [5.0, 5.0],
80 | # [5.0, 6.0],
81 | # [5.0, 9.0],
82 | # [8.0, 9.0],
83 | # [7.0, 9.0],
84 | # [8.0, 10.0],
85 | # [9.0, 11.0],
86 | # [12.0, 13.0],
87 | # [12.0, 12.0],
88 | # [15.0, 15.0],
89 | # [13.0, 13.0]
90 | # ]
91 | # 遍历列表中的每个坐标,并将其四舍五入到两位小数
92 | # obstacle = [[round(x, 2), round(y, 2)] for x, y in obstacle]
93 | # 等比放大两倍
94 | # obstacle = [[x * 2, y * 2] for x, y in obstacle]
95 | self.ob = obstacle.copy() # 注意这里不要self.ob = obstacle,否则二者指向的是同一个对象,所以下面会陷入死循环
96 | # ob_num = 0
97 | # # 生成障碍物及其半径范围内的点
98 | # for i in obstacle:
99 | # obs_radius = 0.6
100 | # obs_x = i[0]
101 | # obs_y = i[1]
102 | # for angle in range(0, 360, 36): # 以10度为间隔生成点
103 | # # 将角度转换为弧度
104 | # angle_rad = math.radians(angle)
105 | # # 计算点的坐标
106 | # point_x = obs_x + obs_radius * math.cos(angle_rad)
107 | # point_y = obs_y + obs_radius * math.sin(angle_rad)
108 | #
109 | # # 将生成的点添加到障碍物周围
110 | # print("ob_num:",ob_num)
111 | # ob_num += 1
112 | # self.ob.append([point_x,point_y])
113 | self.ob = np.array(self.ob)
114 | # 生成地图边界,相对于中心坐标
115 | MAP_MAX_LENGTH = 10
116 | MAP_MAX_WIDTH = 10
117 | # 生成地图上边界
118 | for i in np.arange(-MAP_MAX_LENGTH // 2, MAP_MAX_LENGTH // 2,0.1):
119 | ox = i
120 | oy = MAP_MAX_LENGTH / 2.0
121 | self.ob = np.vstack((self.ob, [ox, oy]))
122 |
123 | # 生成地图右边界
124 | for i in np.arange(-MAP_MAX_WIDTH // 2, MAP_MAX_WIDTH // 2,0.1):
125 | ox = MAP_MAX_LENGTH / 2.0
126 | oy = i
127 | self.ob = np.vstack((self.ob, [ox, oy]))
128 |
129 | # 生成地图下边界
130 | for i in np.arange(-MAP_MAX_LENGTH // 2, MAP_MAX_LENGTH // 2,0.1):
131 | ox = i
132 | oy = -MAP_MAX_WIDTH / 2.0
133 | self.ob = np.vstack((self.ob, [ox, oy]))
134 | # 生成地图左边界
135 | for i in np.arange(-MAP_MAX_WIDTH // 2, MAP_MAX_WIDTH // 2,0.1):
136 | ox = -MAP_MAX_LENGTH / 2.0
137 | oy = i
138 | self.ob = np.vstack((self.ob, [ox, oy]))
139 |
140 | # self.ob = obstacle
141 | # 目标点位置
142 | # self.target = np.array([13, 10])
143 | # self.target = np.array([10, 6])
144 | self.target = goal
145 | plt.plot(self.ob[:, 0], self.ob[:, 1], ".k")
146 | plt.show()
147 |
148 | class DWA:
149 | def __init__(self, config) -> None:
150 | """初始化
151 | Args:
152 | config (_type_): 参数类
153 | """
154 | self.dt = config.dt
155 | self.v_min = config.v_min
156 | self.w_min = config.w_min
157 | self.v_max = config.v_max
158 | self.w_max = config.w_max
159 | self.predict_time = config.predict_time
160 | self.a_vmax = config.a_vmax
161 | self.a_wmax = config.a_wmax
162 | self.v_sample = config.v_sample # 线速度采样分辨率
163 | self.w_sample = config.w_sample # 角速度采样分辨率
164 | self.alpha = config.alpha
165 | self.beta = config.beta
166 | self.gamma = config.gamma
167 | self.radius = config.robot_radius
168 | self.judge_distance = config.judge_distance
169 | # cal_num用来统计计算复杂度
170 | self.cal_num = 0
171 |
172 | def dwa_control(self, state, goal, obstacle):
173 | """滚动窗口算法入口
174 | Args:
175 | state (_type_): 机器人当前状态--[x,y,yaw,v,w]
176 | goal (_type_): 目标点位置,[x,y]
177 | obstacle (_type_): 障碍物位置,dim:[num_ob,2]
178 | Returns:
179 | _type_: 控制量、轨迹(便于绘画)
180 | trajectory [[x,y,yaw,v,w],2] 2维list,
181 | """
182 | control, trajectory = self.trajectory_evaluation(state, goal, obstacle)
183 | return control, trajectory #
184 |
185 | def cal_dynamic_window_vel(self, v, w, state, obstacle):
186 | """速度采样,得到速度空间窗口
187 | Args:
188 | v (_type_): 当前时刻线速度
189 | w (_type_): 当前时刻角速度
190 | state (_type_): 当前机器人状态
191 | obstacle (_type_): 障碍物位置
192 | Returns:
193 | [v_low,v_high,w_low,w_high]: 最终采样后的速度空间
194 | """
195 | Vm = self.__cal_vel_limit()
196 | Vd = self.__cal_accel_limit(v, w)
197 | Va = self.__cal_obstacle_limit(state, obstacle)
198 | a = max([Vm[0], Vd[0], Va[0]])
199 | b = min([Vm[1], Vd[1], Va[1]])
200 | c = max([Vm[2], Vd[2], Va[2]])
201 | d = min([Vm[3], Vd[3], Va[3]])
202 | return [a, b, c, d]
203 |
204 | def __cal_vel_limit(self):
205 | """计算速度边界限制Vm
206 | Returns:
207 | _type_: 速度边界限制后的速度空间Vm
208 | """
209 | return [self.v_min, self.v_max, self.w_min, self.w_max]
210 |
211 | def __cal_accel_limit(self, v, w):
212 | """计算加速度限制Vd
213 | Args:
214 | v (_type_): 当前时刻线速度
215 | w (_type_): 当前时刻角速度
216 | Returns:
217 | _type_:考虑加速度时的速度空间Vd
218 | """
219 | v_low = v - self.a_vmax * self.dt
220 | v_high = v + self.a_vmax * self.dt
221 | w_low = w - self.a_wmax * self.dt
222 | w_high = w + self.a_wmax * self.dt
223 | return [v_low, v_high, w_low, w_high]
224 |
225 | def __cal_obstacle_limit(self, state, obstacle):
226 | """环境障碍物限制Va
227 | Args:
228 | state (_type_): 当前机器人状态
229 | obstacle (_type_): 障碍物位置
230 | Returns:
231 | _type_: 某一时刻移动机器人不与周围障碍物发生碰撞的速度空间Va
232 | """
233 | v_low = self.v_min
234 | v_high = np.sqrt(2 * self._dist(state, obstacle) * self.a_vmax)
235 | w_low = self.w_min
236 | w_high = np.sqrt(2 * self._dist(state, obstacle) * self.a_wmax)
237 | return [v_low, v_high, w_low, w_high]
238 |
239 | def trajectory_predict(self, state_init, v, w):
240 | """轨迹推算
241 | Args:
242 | state_init (_type_): 当前状态---x,y,yaw,v,w
243 | v (_type_): 当前时刻线速度
244 | w (_type_): 当前时刻角速度
245 | Returns:
246 | _type_: _description_
247 | """
248 | state = np.array(state_init)
249 | trajectory = state
250 | time = 0
251 | # 在预测时间段内,不断进行轨迹推算
252 | while time <= self.predict_time:
253 | x = KinematicModel(state, [v, w], self.dt) # 运动学模型
254 | trajectory = np.vstack((trajectory, x))
255 | time += self.dt
256 | self.cal_num += 1
257 | return trajectory
258 |
259 | def trajectory_evaluation(self, state, goal, obstacle):
260 | """轨迹评价函数,评价越高,轨迹越优
261 | Args:
262 | state (_type_): 当前状态---x,y,yaw,v,w
263 | dynamic_window_vel (_type_): 采样的速度空间窗口---[v_low,v_high,w_low,w_high]
264 | goal (_type_): 目标点位置,[x,y]
265 | obstacle (_type_): 障碍物位置,dim:[num_ob,2]
266 | Returns:
267 | _type_: 最优控制量、最优轨迹
268 | control_opt:[v,w] 最优控制量包含速度v和角速度w
269 | """
270 | G_max = -float('inf') # 最优评价
271 | trajectory_opt = state # 最优轨迹
272 | control_opt = [0., 0.] # 最优控制
273 | dynamic_window_vel = self.cal_dynamic_window_vel(state[3], state[4], state, obstacle) # 第1步--计算速度空间
274 |
275 | # sum_heading,sum_dist,sum_vel = 0,0,0 # 统计全部采样轨迹的各个评价之和,便于评价的归一化
276 | # # 在本次实验中,不进行归一化也可实现该有的效果。
277 | # for v in np.arange(dynamic_window_vel[0],dynamic_window_vel[1],self.v_sample):
278 | # for w in np.arange(dynamic_window_vel[2], dynamic_window_vel[3], self.w_sample):
279 | # trajectory = self.trajectory_predict(state, v, w)
280 |
281 | # heading_eval = self.alpha*self.__heading(trajectory,goal)
282 | # dist_eval = self.beta*self.__dist(trajectory,obstacle)
283 | # vel_eval = self.gamma*self.__velocity(trajectory)
284 | # sum_vel+=vel_eval
285 | # sum_dist+=dist_eval
286 | # sum_heading +=heading_eval
287 |
288 | # 在速度空间中按照预先设定的分辨率采样
289 | sum_heading, sum_dist, sum_vel = 1, 1, 1 # 不进行归一化
290 | for v in np.arange(dynamic_window_vel[0], dynamic_window_vel[1], self.v_sample):
291 | for w in np.arange(dynamic_window_vel[2], dynamic_window_vel[3], self.w_sample):
292 |
293 | trajectory = self.trajectory_predict(state, v, w) # 第2步--轨迹推算
294 |
295 | # 这个__heading是当前采样速度下产生的轨迹终点位置方向与目标点连线的夹角的误差
296 | heading_eval = self.alpha * self.__heading(trajectory, goal) / sum_heading
297 | # heading_eval = 0
298 | # 表示当前速度下对应模拟轨迹与障碍物之间的最近距离
299 | # 距离越大,轨迹就越优
300 | # 当距离大于阈值,它就会设为一个比较大的值
301 | dist_eval = self.beta * self.__dist(trajectory, obstacle) / sum_dist
302 | # dist_eval = 0
303 | #
304 | vel_eval = self.gamma * self.__velocity(trajectory) / sum_vel
305 | # vel_eval = 0
306 | # print("heading_eval:",heading_eval," dist_eval:",dist_eval," vel_eval:",vel_eval)
307 | G = heading_eval + dist_eval + vel_eval # 第3步--轨迹评价
308 |
309 | if G_max <= G:
310 | G_max = G
311 | trajectory_opt = trajectory
312 | control_opt = [v, w]
313 |
314 | return control_opt, trajectory_opt
315 |
316 | def _dist(self, state, obstacle):
317 | """计算当前移动机器人距离障碍物最近的几何距离
318 | Args:
319 | state (_type_): 当前机器人状态
320 | obstacle (_type_): 障碍物位置
321 | Returns:
322 | _type_: 移动机器人距离障碍物最近的几何距离
323 | """
324 | ox = obstacle[:, 0]
325 | oy = obstacle[:, 1]
326 | dx = state[0, None] - ox[:, None]
327 | dy = state[1, None] - oy[:, None]
328 | r = np.hypot(dx, dy)
329 | return np.min(r)
330 |
331 | def __dist(self, trajectory, obstacle):
332 | """距离评价函数
333 | 表示当前速度下对应模拟轨迹与障碍物之间的最近距离;
334 | 如果没有障碍物或者最近距离大于设定的阈值,那么就将其值设为一个较大的常数值。
335 | Args:
336 | trajectory (_type_): 轨迹,dim:[n,5]
337 |
338 | obstacle (_type_): 障碍物位置,dim:[num_ob,2]
339 | Returns:
340 | _type_: _description_
341 | """
342 | ox = obstacle[:, 0]
343 | oy = obstacle[:, 1]
344 | dx = trajectory[:, 0] - ox[:, None]
345 | dy = trajectory[:, 1] - oy[:, None]
346 | r = np.hypot(dx, dy)
347 | return np.min(r) if np.array(r < self.radius + 0.1).any() else self.judge_distance
348 |
349 | def __heading(self, trajectory, goal):
350 | """方位角评价函数
351 | 评估在当前采样速度下产生的轨迹终点位置方向与目标点连线的夹角的误差
352 | Args:
353 | trajectory (_type_): 轨迹,dim:[n,5]
354 | goal (_type_): 目标点位置[x,y]
355 | Returns:
356 | cost_type_: 方位角评价数值
357 | 误差越大,cost越小
358 | """
359 | dx = goal[0] - trajectory[-1, 0]
360 | dy = goal[1] - trajectory[-1, 1]
361 | error_angle = math.atan2(dy, dx)
362 | cost_angle = error_angle - trajectory[-1, 2]
363 | cost = math.pi - abs(cost_angle)
364 |
365 | return cost
366 |
367 | def __velocity(self, trajectory):
368 | """速度评价函数, 表示当前的速度大小,可以用模拟轨迹末端位置的线速度的大小来表示
369 | Args:
370 | trajectory (_type_): 轨迹,dim:[n,5]
371 | Returns:
372 | _type_: 速度评价
373 | """
374 | return trajectory[-1, 3]
375 |
376 |
377 | def KinematicModel(state, control, dt):
378 | """机器人运动学模型
379 | Args:
380 | state (_type_): 状态量---x,y,yaw,v,w
381 | control (_type_): 控制量---v,w,线速度和角速度
382 | dt (_type_): 离散时间
383 | Returns:
384 | _type_: 下一步的状态 x,y,yaw,v,w
385 | """
386 | # 我们是麦克纳姆轮的小车,但是用这个运动学模型问题也不大
387 | state[0] += control[0] * math.cos(state[2]) * dt
388 | state[1] += control[0] * math.sin(state[2]) * dt
389 | state[2] += control[1] * dt
390 | state[3] = control[0]
391 | state[4] = control[1]
392 |
393 | return state
394 |
395 |
396 | def plot_arrow(x, y, yaw, length=0.5, width=0.1): # pragma: no cover
397 | plt.arrow(x, y, length * math.cos(yaw), length * math.sin(yaw),
398 | head_length=width, head_width=width)
399 | plt.plot(x, y)
400 |
401 |
402 | def plot_robot(x, y, yaw, config): # pragma: no cover
403 | circle = plt.Circle((x, y), config.robot_radius, color="b")
404 | plt.gcf().gca().add_artist(circle)
405 | out_x, out_y = (np.array([x, y]) +
406 | np.array([np.cos(yaw), np.sin(yaw)]) * config.robot_radius)
407 | plt.plot([x, out_x], [y, out_y], "-k")
408 |
409 |
410 | def init(ob, target):
411 | dwa = DWA(Config(ob, target))
412 | return dwa
413 |
414 |
415 | def main(config):
416 | start_position = [0, 5]
417 | # initial state [x(m), y(m), yaw(rad), v(m/s), omega(rad/s)]
418 | # 初始状态 x 包含机器人的初始位置和速度信息,以及朝向。
419 | # x 是一个包含五个元素的NumPy数组,
420 | # 分别表示x坐标、y坐标、朝向角度、线速度(速度大小),和角速度(转向速度)
421 | x = np.array([start_position[0], start_position[1], -math.pi, 0.0, 0.0])
422 | # goal position [x(m), y(m)]
423 | # goal 是目标位置的坐标,这是机器人要尝试到达的位置。
424 | goal = config.target
425 |
426 | # input [forward speed, yaw_rate]
427 | # trajectory 是一个NumPy数组,用于存储机器人的轨迹,它最初包含机器人的初始状态
428 | trajectory = np.array(x)
429 | # ob 是一组障碍物的位置
430 | ob = config.ob
431 | # 创建了一个 DWA 对象 dwa,用于执行动态窗口法(Dynamic Window Approach)的路径规划。
432 | dwa = DWA(config)
433 | fig = plt.figure(1)
434 | camera = Camera(fig)
435 | while True:
436 | #
437 | u, predicted_trajectory = dwa.dwa_control(x, goal, ob)
438 | # print(predicted_trajectory)
439 | x = KinematicModel(x, u, config.dt) # simulate robot
440 | trajectory = np.vstack((trajectory, x)) # store state history
441 |
442 | plt.cla()
443 | # for stopping simulation with the esc key.
444 | plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect(
445 | 'key_release_event',
446 | lambda event: [exit(0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])
447 | plt.plot(predicted_trajectory[:, 0], predicted_trajectory[:, 1], "-g")
448 | plt.plot(x[0], x[1], "xr")
449 | plt.plot(goal[0], goal[1], "xb")
450 | plt.plot(ob[:, 0], ob[:, 1], "ok")
451 | plot_robot(x[0], x[1], x[2], config)
452 | plot_arrow(x[0], x[1], x[2])
453 | plt.text(0, 0, f'Calculation Count: {dwa.cal_num}', fontsize=12, color='red') # 添加文本标签
454 | plt.axis("equal")
455 | plt.grid(True)
456 | plt.pause(0.00001)
457 |
458 | # check reaching goal
459 | dist_to_goal = math.hypot(x[0] - goal[0], x[1] - goal[1])
460 | if dist_to_goal <= config.robot_radius:
461 | print("Goal!!")
462 | break
463 | # camera.snap()
464 | # print(x)
465 | # print(u)
466 |
467 | print("Done,calnum:", dwa.cal_num)
468 | plt.plot(trajectory[:, 0], trajectory[:, 1], "-r")
469 | plt.pause(0.00001)
470 | # camera.snap()
471 | # animation = camera.animate()
472 | # animation.save('trajectory.gif')
473 | plt.show()
474 |
475 |
476 | if __name__ == "__main__":
477 | main(Config())
478 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------