get access to advanced cloud features like transparent bottomless object storage
5 |
don't waste time running high performance, highly available TimescaleDB and PostgreSQL in the cloud
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_consider-cloud.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | Timescale is a fully managed service with automatic backup and restore, high
3 | availability with replication, seamless scaling and resizing, and much more. You
4 | can try Timescale free for thirty days.
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_create-hypertable-energy.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import OldCreateHypertable from "versionContent/_partials/_old-api-create-hypertable.mdx";
2 | import HypertableIntro from "versionContent/_partials/_tutorials_hypertable_intro.mdx";
3 |
4 | ## Optimize time-series data in hypertables
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 | 1. To create a $HYPERTABLE to store the energy consumption data, call [CREATE TABLE][hypertable-create-table].
11 |
12 | ```sql
13 | CREATE TABLE "metrics"(
14 | created timestamp with time zone default now() not null,
15 | type_id integer not null,
16 | value double precision not null
17 | ) WITH (
18 | tsdb.hypertable,
19 | tsdb.partition_column='time'
20 | );
21 | ```
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 | [hypertable-create-table]: /api/:currentVersion:/hypertable/create_table/
29 | [indexing]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/schema-management/indexing/
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_data_model_metadata.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | You might also notice that the metadata fields are missing. Because this is a
3 | relational database, metadata can be stored in a secondary table and `JOIN`ed at
4 | query time. Learn more about [Timescale's support for `JOIN`s](#joins-with-relational-data).
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_datadog-data-exporter.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | 1. **In $CONSOLE, open [Exporters][console-integrations]**
4 | 1. **Click `New exporter`**
5 | 1. **Select `Metrics` for `Data type` and `Datadog` for provider**
6 |
7 | 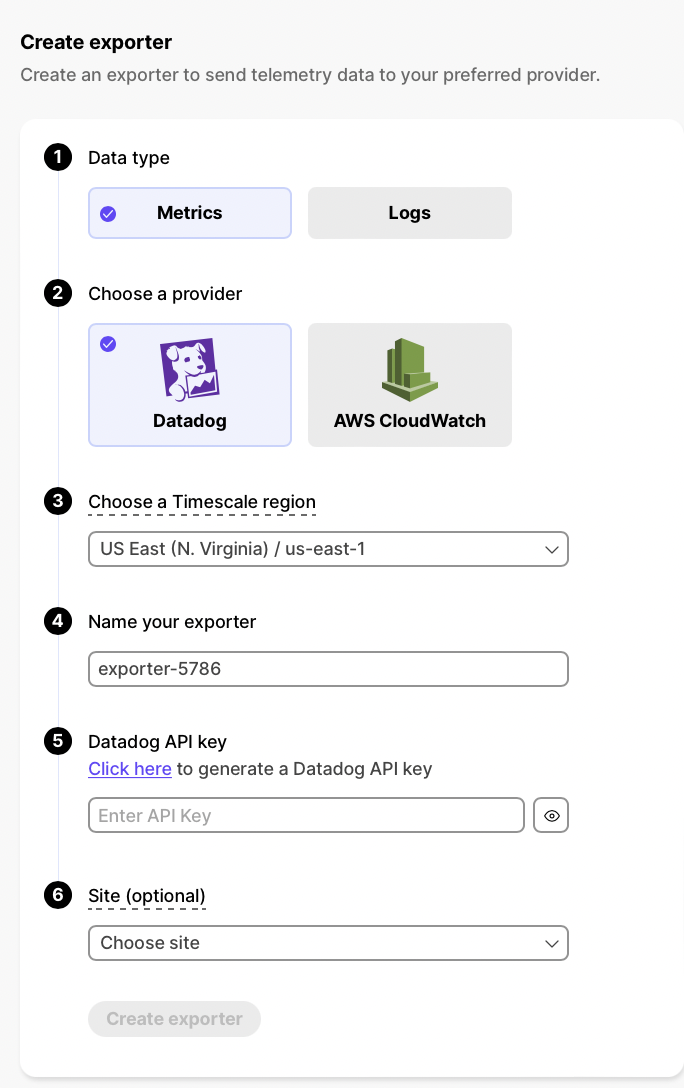
8 |
9 | 1. **Choose your AWS region and provide the API key**
10 |
11 | The AWS region must be the same for your $CLOUD_LONG exporter and the Datadog provider.
12 |
13 | 1. **Set `Site` to your Datadog region, then click `Create exporter`**
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 | [console-integrations]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/dashboard/integrations
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_deprecated.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | This section describes a feature that is deprecated on Timescale. We strongly
4 | recommend that you do not use this feature in a production environment. If you
5 | need more information, [contact us](https://www.timescale.com/contact/).
6 |
7 |
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_deprecated_2_18_0.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Old API since [TimescaleDB v2.18.0](https://github.com/timescale/timescaledb/releases/tag/2.18.0)
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_deprecated_2_20_0.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Old API since [TimescaleDB v2.20.0](https://github.com/timescale/timescaledb/releases/tag/2.20.0)
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_deprecated_2_21_0.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Deprecated since TimescaleDB v2.21.0
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_early_access.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Early access
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_early_access_2_18_0.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Early access: TimescaleDB v2.18.0
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_experimental-private-beta.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | This feature is experimental and offered as part of a private beta. Do not use
3 | this feature in production.
4 |
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_experimental-schema-upgrade.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | When you upgrade the `timescaledb` extension, the experimental schema is removed
3 | by default. To use experimental features after an upgrade, you need to add the
4 | experimental schema again.
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_experimental.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | Experimental features could have bugs. They might not be backwards compatible,
3 | and could be removed in future releases. Use these features at your own risk, and
4 | do not use any experimental features in production.
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_financial-industry-data-analysis.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | The financial industry is extremely data-heavy and relies on real-time and historical data for decision-making, risk assessment, fraud detection, and market analysis. Timescale simplifies management of these large volumes of data, while also providing you with meaningful analytical insights and optimizing storage costs.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_grafana-viz-prereqs.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Before you begin, make sure you have:
2 |
3 | * Created a [Timescale][cloud-login] service.
4 | * Installed a self-managed Grafana account, or signed up for
5 | [Grafana Cloud][install-grafana].
6 | * Ingested some data to your database. You can use the stock trade data from
7 | the [Getting Started Guide][gsg-data].
8 |
9 | The examples in this section use these variables and Grafana functions:
10 |
11 | * `$symbol`: a variable used to filter results by stock symbols.
12 | * `$__timeFrom()::timestamptz` & `$__timeTo()::timestamptz`:
13 | Grafana variables. You change the values of these variables by
14 | using the dashboard's date chooser when viewing your graph.
15 | * `$bucket_interval`: the interval size to pass to the `time_bucket`
16 | function when aggregating data.
17 |
18 | [install-grafana]: https://grafana.com/get/
19 | [gsg-data]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/
20 | [cloud-login]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_high-availability-setup.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | 1. In [Timescale Console][cloud-login], select the service to enable replication for.
4 | 1. Click `Operations`, then select `High availability`.
5 | 1. Choose your replication strategy, then click `Change configuration`.
6 |
7 | 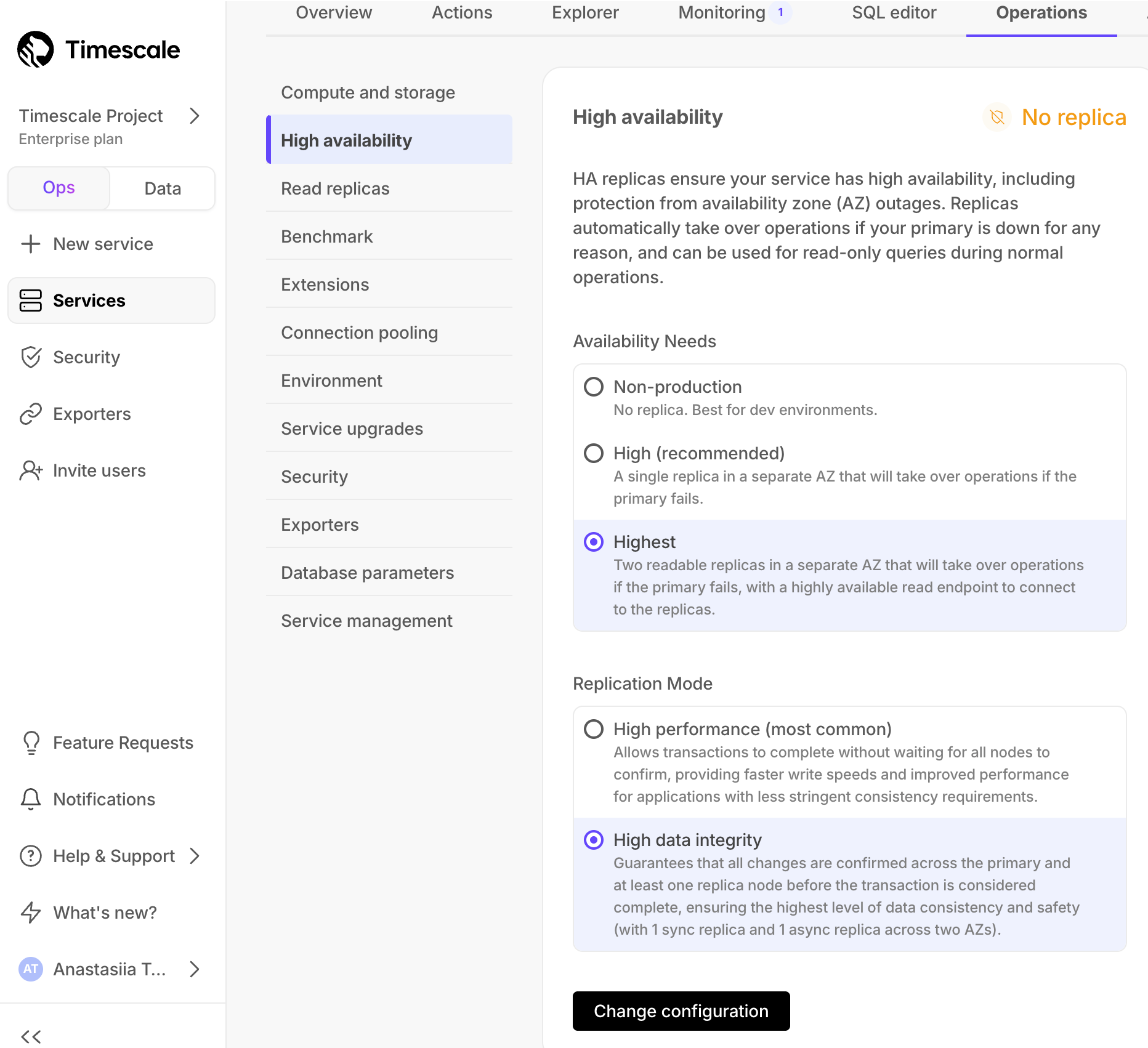
8 |
9 | 1. In `Change high availability configuration`, click `Change config`.
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 | [cloud-login]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_hypercore-conversion-overview.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | When you convert chunks from the rowstore to the columnstore, multiple records are grouped into a single row.
2 | The columns of this row hold an array-like structure that stores all the data. For example, data in the following
3 | rowstore chunk:
4 |
5 | | Timestamp | Device ID | Device Type | CPU |Disk IO|
6 | |---|---|---|---|---|
7 | |12:00:01|A|SSD|70.11|13.4|
8 | |12:00:01|B|HDD|69.70|20.5|
9 | |12:00:02|A|SSD|70.12|13.2|
10 | |12:00:02|B|HDD|69.69|23.4|
11 | |12:00:03|A|SSD|70.14|13.0|
12 | |12:00:03|B|HDD|69.70|25.2|
13 |
14 | Is converted and compressed into arrays in a row in the columnstore:
15 |
16 | |Timestamp|Device ID|Device Type|CPU|Disk IO|
17 | |-|-|-|-|-|
18 | |[12:00:01, 12:00:01, 12:00:02, 12:00:02, 12:00:03, 12:00:03]|[A, B, A, B, A, B]|[SSD, HDD, SSD, HDD, SSD, HDD]|[70.11, 69.70, 70.12, 69.69, 70.14, 69.70]|[13.4, 20.5, 13.2, 23.4, 13.0, 25.2]|
19 |
20 | Because a single row takes up less disk space, you can reduce your chunk size by more than 90%, and can also
21 | speed up your queries. This saves on storage costs, and keeps your queries operating at lightning speed.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_hypershift-alternatively.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | Alternatively, if you have data in an existing database, you can migrate it
3 | directly into your new Timescale database using hypershift. For more information
4 | about hypershift, including instructions for how to migrate your data, see the
5 | [hypershift documentation](https://docs.timescale.com/use-timescale/latest/migration/).
6 |
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_hypershift-intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | You can use hypershift to migrate existing PostgreSQL databases in one step, and
2 | enable compression and create hypertables instantly.
3 |
4 | Use Hypershift to migrate your data to Timescale from these sources:
5 |
6 | * Standard PostgreSQL databases
7 | * Amazon RDS databases
8 | * Other Timescale databases, including Managed Service for TimescaleDB, and
9 | self-hosted TimescaleDB
10 |
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_integration-debezium-cloud-config-service.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | 1. **Connect to your $SERVICE_LONG**
4 |
5 | For $CLOUD_LONG, open an [SQL editor][run-queries] in [$CONSOLE][open-console]. For self-hosted, use [`psql`][psql].
6 |
7 | 1. **Enable logical replication for your $SERVICE_LONG**
8 |
9 | 1. Run the following command to enable logical replication:
10 |
11 | ```sql
12 | ALTER SYSTEM SET wal_level = logical;
13 | SELECT pg_reload_conf();
14 | ```
15 |
16 | 1. Restart your $SERVICE_SHORT.
17 |
18 | 1. **Create a table**
19 |
20 | Create a table to test the integration. For example:
21 |
22 | ```sql
23 | CREATE TABLE sensor_data (
24 | id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
25 | device_id TEXT NOT NULL,
26 | temperature FLOAT NOT NULL,
27 | recorded_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT now()
28 | );
29 | ```
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_integration-prereqs-cloud-only.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | To follow the steps on this page:
3 |
4 | * Create a target [$SERVICE_LONG][create-service] with time-series and analytics enabled.
5 |
6 | You need your [connection details][connection-info].
7 |
8 |
9 | [create-service]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/services/
10 | [connection-info]: /integrations/:currentVersion:/find-connection-details/
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_integration-prereqs-self-only.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | To follow the steps on this page:
3 |
4 | * Create a target [self-hosted $TIMESCALE_DB][enable-timescaledb] instance.
5 |
6 |
7 | [enable-timescaledb]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/install/
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_integration-prereqs.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | To follow the steps on this page:
2 |
3 | * Create a target [$SERVICE_LONG][create-service] with time-series and analytics enabled.
4 |
5 | You need [your connection details][connection-info]. This procedure also
6 | works for [$SELF_LONG][enable-timescaledb].
7 |
8 | [create-service]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/services/
9 | [enable-timescaledb]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/install/
10 | [connection-info]: /integrations/:currentVersion:/find-connection-details/
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_kubernetes-prereqs.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | - Install [self-managed Kubernetes][kubernetes-install] or sign up for a Kubernetes [Turnkey Cloud Solution][kubernetes-managed].
2 | - Install [kubectl][kubectl] for command-line interaction with your cluster.
3 |
4 | [kubernetes-install]: https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/
5 | [kubectl]: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/
6 | [kubernetes-managed]: https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/production-environment/turnkey-solutions/
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_livesync-limitations.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | * Schema changes must be co-ordinated.
2 |
3 | Make compatible changes to the schema in your $SERVICE_LONG first, then make
4 | the same changes to the source PostgreSQL instance.
5 | * Ensure that the source $PG instance and the target $SERVICE_LONG have the same extensions installed.
6 |
7 | $LIVESYNC_CAP does not create extensions on the target. If the table uses column types from an extension,
8 | first create the extension on the target $SERVICE_LONG before syncing the table.
9 | * There is WAL volume growth on the source PostgreSQL instance during large table copy.
10 | * This works for PostgreSQL databases only as source. TimescaleDB is not yet supported.
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_dual_write_6e_turn_on_compression_policies.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ### 6e. Enable policies that compress data in the target hypertable
2 |
3 | In the following command, replace `` with the fully qualified table
4 | name of the target hypertable, for example `public.metrics`:
5 |
6 | ```bash
7 | psql -d $TARGET -f -v hypertable= - <<'EOF'
8 | SELECT public.alter_job(j.id, scheduled=>true)
9 | FROM _timescaledb_config.bgw_job j
10 | JOIN _timescaledb_catalog.hypertable h ON h.id = j.hypertable_id
11 | WHERE j.proc_schema IN ('_timescaledb_internal', '_timescaledb_functions')
12 | AND j.proc_name = 'policy_compression'
13 | AND j.id >= 1000
14 | AND format('%I.%I', h.schema_name, h.table_name)::text::regclass = :'hypertable'::text::regclass;
15 | EOF
16 | ```
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_dual_write_backfill_getting_help.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import OpenSupportRequest from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_open_support_request.mdx"
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 | If you get stuck, you can get help by either opening a support request, or take
6 | your issue to the `#migration` channel in the [community slack](https://slack.timescale.com/),
7 | where the developers of this migration method are there to help.
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_dual_write_step1.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import OpenSupportRequest from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_open_support_request.mdx"
2 |
3 | ## 1. Set up a target database instance in Timescale
4 |
5 | [Create a database service in Timescale][create-service].
6 |
7 | If you intend on migrating more than 400 GB, open a support request to
8 | ensure that enough disk is pre-provisioned on your Timescale instance.
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 | [create-service]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/services/
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_dual_write_step4.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## 4. Start application in dual-write mode
2 |
3 | With the target database set up, your application can now be started in
4 | dual-write mode.
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_dual_write_switch_production_workload.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Once you've validated that all the data is present, and that the target
2 | database can handle the production workload, the final step is to switch to the
3 | target database as your primary. You may want to continue writing to the source
4 | database for a period, until you are certain that the target database is
5 | holding up to all production traffic.
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_dual_write_validate_production_load.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Now that dual-writes have been in place for a while, the target database should
2 | be holding up to production write traffic. Now would be the right time to
3 | determine if the target database can serve all production traffic (both reads
4 | _and_ writes). How exactly this is done is application-specific and up to you
5 | to determine.
6 |
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_dump_awsrds.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import MigrateAWSRDSConnectIntermediary from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_awsrds_connect_intermediary.mdx";
2 | import MigrateAWSRDSMigrateData from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_awsrds_migrate_data_downtime.mdx";
3 | import MigrationValidateRestartApp from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_validate_and_restart_app.mdx";
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 | ## Migrate your data to your Timescale Cloud service
8 |
9 | To securely migrate data from your RDS instance:
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 | ## Validate your Timescale Cloud service and restart your app
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_explain_pg_dump_flags.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | - `--no-tablespaces` is required because Timescale does not support
2 | tablespaces other than the default. This is a known limitation.
3 |
4 | - `--no-owner` is required because Timescale's `tsdbadmin` user is not a
5 | superuser and cannot assign ownership in all cases. This flag means that
6 | everything is owned by the user used to connect to the target, regardless of
7 | ownership in the source. This is a known limitation.
8 |
9 | - `--no-privileges` is required because Timescale's `tsdbadmin` user is not a
10 | superuser and cannot assign privileges in all cases. This flag means that
11 | privileges assigned to other users must be reassigned in the target database
12 | as a manual clean-up task. This is a known limitation.
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_from_timescaledb_version.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | It is very important that the version of the TimescaleDB extension is the same
2 | in the source and target databases. This requires upgrading the TimescaleDB
3 | extension in the source database before migrating.
4 |
5 | You can determine the version of TimescaleDB in the target database with the
6 | following command:
7 |
8 | ```bash
9 | psql $TARGET -c "SELECT extversion FROM pg_extension WHERE extname = 'timescaledb';"
10 | ```
11 |
12 | To update the TimescaleDB extension in your source database, first ensure that
13 | the desired version is installed from your package repository. Then you can
14 | upgrade the extension with the following query:
15 |
16 | ```bash
17 | psql $SOURCE -c "ALTER EXTENSION timescaledb UPDATE TO '';"
18 | ```
19 |
20 | For more information and guidance, consult the [Upgrade TimescaleDB] page.
21 |
22 | [Upgrade TimescaleDB]: https://docs.timescale.com/self-hosted/latest/upgrades/
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_import_setup_connection_strings_parquet.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | This variable hold the connection information for the target Timescale Cloud service.
2 |
3 | In Terminal on the source machine, set the following:
4 |
5 | ```bash
6 | export TARGET=postgres://tsdbadmin:@:/tsdb?sslmode=require
7 | ```
8 | You find the connection information for your Timescale Cloud service in the configuration file you
9 | downloaded when you created the service.
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_live_migrate_data.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import MigrateData from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_live_run_live_migration.mdx";
2 | import CleanupData from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_live_run_cleanup.mdx";
3 |
4 | ## Migrate your data, then start downtime
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 | [modify-parameters]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion/configuration/customize-configuration/#modify-basic-parameters
12 | [mst-portal]: https://portal.managed.timescale.com/login
13 | [tsc-portal]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/
14 | [configure-instance-parameters]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion/configuration/customize-configuration/#configure-database-parameters
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_live_migrate_data_timescaledb.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import MigrateDataTimescaleDB from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_live_run_live_migration_timescaledb.mdx";
2 |
3 |
4 | ## Migrate your data, then start downtime
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_live_migration_cleanup.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | To clean up resources associated with live migration, use the following command:
2 |
3 | ```sh
4 | docker run --rm -it --name live-migration-clean \
5 | -e PGCOPYDB_SOURCE_PGURI=$SOURCE \
6 | -e PGCOPYDB_TARGET_PGURI=$TARGET \
7 | --pid=host \
8 | -v ~/live-migration:/opt/timescale/ts_cdc \
9 | timescale/live-migration:latest clean --prune
10 | ```
11 |
12 | The `--prune` flag is used to delete temporary files in the `~/live-migration` directory
13 | that were needed for the migration process. It's important to note that executing the
14 | `clean` command means you cannot resume the interrupted live migration.
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_live_run_cleanup.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 1. **Validate the migrated data**
2 |
3 | The contents of both databases should be the same. To check this you could compare
4 | the number of rows, or an aggregate of columns. However, the best validation method
5 | depends on your app.
6 |
7 | 1. **Stop app downtime**
8 |
9 | Once you are confident that your data is successfully replicated, configure your apps
10 | to use your Timescale Cloud service.
11 |
12 | 1. **Cleanup resources associated with live-migration from your migration machine**
13 |
14 | This command removes all resources and temporary files used in the migration process.
15 | When you run this command, you can no longer resume live-migration.
16 |
17 | ```shell
18 | docker run --rm -it --name live-migration-clean \
19 | -e PGCOPYDB_SOURCE_PGURI=$SOURCE \
20 | -e PGCOPYDB_TARGET_PGURI=$TARGET \
21 | --pid=host \
22 | -v ~/live-migration:/opt/timescale/ts_cdc \
23 | timescale/live-migration:latest clean --prune
24 | ```
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_live_run_cleanup_postgres.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 1. **Validate the migrated data**
2 |
3 | The contents of both databases should be the same. To check this you could compare
4 | the number of rows, or an aggregate of columns. However, the best validation method
5 | depends on your app.
6 |
7 | 1. **Stop app downtime**
8 |
9 | Once you are confident that your data is successfully replicated, configure your apps
10 | to use your Timescale Cloud service.
11 |
12 | 1. **Cleanup resources associated with live-migration from your migration machine**
13 |
14 | This command removes all resources and temporary files used in the migration process.
15 | When you run this command, you can no longer resume live-migration.
16 |
17 | ```shell
18 | docker run --rm -it --name live-migration-clean \
19 | -e PGCOPYDB_SOURCE_PGURI=$SOURCE \
20 | -e PGCOPYDB_TARGET_PGURI=$TARGET \
21 | --pid=host \
22 | -v ~/live-migration:/opt/timescale/ts_cdc \
23 | timescale/live-migration:latest1 clean --prune
24 | ```
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_live_setup_connection_strings.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | These variables hold the connection information for the source database and target Timescale Cloud service.
2 | In Terminal on your migration machine, set the following:
3 |
4 | ```bash
5 | export SOURCE="postgres://:@:/"
6 | export TARGET="postgres://tsdbadmin:@:/tsdb?sslmode=require"
7 | ```
8 | You find the connection information for your Timescale Cloud service in the configuration file you
9 | downloaded when you created the service.
10 |
11 |
12 | Avoid using connection strings that route through connection poolers like PgBouncer or similar tools. This tool requires a direct connection to the database to function properly.
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_live_setup_environment.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import SetupConnectionStrings from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_live_setup_connection_strings.mdx";
2 | import MigrationSetupDBConnectionTimescaleDB from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_set_up_align_db_extensions_timescaledb.mdx";
3 | import TuneSourceDatabase from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_live_tune_source_database.mdx";
4 |
5 |
6 | ## Set your connection strings
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 | ## Align the version of TimescaleDB on the source and target
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 | ## Tune your source database
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 | [modify-parameters]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion/configuration/customize-configuration/#modify-basic-parameters
25 | [mst-portal]: https://portal.managed.timescale.com/login
26 | [tsc-portal]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/
27 | [configure-instance-parameters]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion/configuration/customize-configuration/#configure-database-parameters
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_live_setup_environment_awsrds.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import SetupConnectionStrings from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_live_setup_connection_strings.mdx";
2 | import MigrationSetupDBConnectionPostgresql from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_set_up_align_db_extensions_postgres_based.mdx";
3 | import TuneSourceDatabaseAWSRDS from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_live_tune_source_database_awsrds.mdx";
4 |
5 | ## Set your connection strings
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 | ## Align the extensions on the source and target
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 | ## Tune your source database
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 | [modify-parameters]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/configuration/customize-configuration/#modify-basic-parameters
26 | [mst-portal]: https://portal.managed.timescale.com/login
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_live_setup_environment_mst.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import SetupConnectionStrings from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_live_setup_connection_strings.mdx";
2 | import MigrationSetupDBConnectionTimescaleDB from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_set_up_align_db_extensions_timescaledb.mdx";
3 | import TuneSourceDatabaseMST from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_live_tune_source_database_mst.mdx";
4 |
5 | ## Set your connection strings
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 | ## Align the version of TimescaleDB on the source and target
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 | ## Tune your source database
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 | [modify-parameters]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/configuration/customize-configuration/#modify-basic-parameters
26 | [mst-portal]: https://portal.managed.timescale.com/login
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_live_setup_environment_postgres.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import SetupConnectionStrings from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_live_setup_connection_strings.mdx";
2 | import MigrationSetupDBConnectionPostgresql from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_set_up_align_db_extensions_postgres_based.mdx";
3 | import TuneSourceDatabasePostgres from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_live_tune_source_database_postgres.mdx";
4 |
5 |
6 | ## Set your connection strings
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 | ## Align the extensions on the source and target
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 | ## Tune your source database
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 | [modify-parameters]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion/configuration/customize-configuration/#modify-basic-parameters
27 | [mst-portal]: https://portal.managed.timescale.com/login
28 | [tsc-portal]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/
29 | [configure-instance-parameters]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion/configuration/customize-configuration/#configure-database-parameters
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_live_tune_source_database_mst.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import EnableReplication from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_live_setup_enable_replication.mdx";
2 |
3 | 1. **Enable live-migration to replicate `DELETE` and`UPDATE` operations**
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 | [mst-portal]: https://portal.managed.timescale.com/login
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_live_validate_data.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import CleanupData from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_live_run_cleanup.mdx";
2 |
3 | ## Validate your data, then restart your app
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 | [modify-parameters]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion/configuration/customize-configuration/#modify-basic-parameters
11 | [mst-portal]: https://portal.managed.timescale.com/login
12 | [tsc-portal]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/
13 | [configure-instance-parameters]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion/configuration/customize-configuration/#configure-database-parameters
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_open_support_request.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | You can open a support request directly from the [Timescale console][support-link],
2 | or by email to [support@timescale.com](mailto:support@timescale.com).
3 |
4 | [support-link]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/dashboard/support
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_pg_dump_do_not_recommend_for_large_migration.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | If you want to migrate more than 400GB of data, create a [Timescale Console support request](https://console.cloud.timescale.com/dashboard/support), or
4 | send us an email at [support@timescale.com](mailto:support@timescale.com) saying how much data you want to migrate. We will pre-provision
5 | your Timescale Cloud instance for you.
6 |
7 |
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_pg_dump_minimal_downtime.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | For minimal downtime, run the migration commands from a machine with a low-latency,
2 | high-throughput link to the source and target databases. If you are using an AWS
3 | EC2 instance to run the migration commands, use one in the same region as your target
4 | Timescale Cloud instance.
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_post_data_dump_source_schema.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import ExplainPgDumpFlags from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_explain_pg_dump_flags.mdx";
2 |
3 | ```shell
4 | pg_dump -d "$SOURCE" \
5 | --format=plain \
6 | --quote-all-identifiers \
7 | --no-tablespaces \
8 | --no-owner \
9 | --no-privileges \
10 | --section=post-data \
11 | --file=post-data-dump.sql \
12 | --snapshot=$(cat /tmp/pgcopydb/snapshot)
13 | ```
14 |
15 | - `--section=post-data` is used to dump post-data items include definitions of
16 | indexes, triggers, rules, and constraints other than validated check
17 | constraints.
18 |
19 | - `--snapshot` is used to specified the synchronized [snapshot][snapshot] when
20 | making a dump of the database.
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 | [snapshot]: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/functions-admin.html#FUNCTIONS-SNAPSHOT-SYNCHRONIZATION
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_pre_data_dump_source_schema.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import ExplainPgDumpFlags from "versionContent/_partials/_migrate_explain_pg_dump_flags.mdx";
2 |
3 | ```sh
4 | pg_dump -d "$SOURCE" \
5 | --format=plain \
6 | --quote-all-identifiers \
7 | --no-tablespaces \
8 | --no-owner \
9 | --no-privileges \
10 | --section=pre-data \
11 | --file=pre-data-dump.sql \
12 | --snapshot=$(cat /tmp/pgcopydb/snapshot)
13 | ```
14 |
15 | - `--section=pre-data` is used to dump only the definition of tables,
16 | sequences, check constraints and inheritance hierarchy. It excludes
17 | indexes, foreign key constraints, triggers and rules.
18 |
19 | - `--snapshot` is used to specified the synchronized [snapshot][snapshot] when
20 | making a dump of the database.
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 | [snapshot]: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/functions-admin.html#FUNCTIONS-SNAPSHOT-SYNCHRONIZATION
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_set_up_database_first_steps.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 1. **Take the applications that connect to the source database offline**
2 |
3 | The duration of the migration is proportional to the amount of data stored in your database. By
4 | disconnection your app from your database you avoid and possible data loss.
5 |
6 | 1. **Set your connection strings**
7 |
8 | These variables hold the connection information for the source database and target Timescale Cloud service:
9 |
10 | ```bash
11 | export SOURCE="postgres://:@:/"
12 | export TARGET="postgres://tsdbadmin:@:/tsdb?sslmode=require"
13 | ```
14 | You find the connection information for your Timescale Cloud Service in the configuration file you
15 | downloaded when you created the service.
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_set_up_source_and_target.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | For the sake of convenience, connection strings to the source and target
3 | databases are referred to as `$SOURCE` and `$TARGET` throughout this guide.
4 |
5 | This can be set in your shell, for example:
6 |
7 | ```bash
8 | export SOURCE="postgres://:@:/"
9 | export TARGET="postgres://:@:/"
10 | ```
11 |
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_source_target_note.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | In the context of migrations, your existing production database is referred to
3 | as the "source" database, while the new Timescale database that you intend to
4 | migrate your data to is referred to as the "target" database.
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_using_parallel_copy.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | ### Restoring data into Timescale with timescaledb-parallel-copy
4 |
5 | 1. At the command prompt, install `timescaledb-parallel-copy`:
6 |
7 | ```bash
8 | go get github.com/timescale/timescaledb-parallel-copy/cmd/timescaledb-parallel-copy
9 | ```
10 |
11 | 1. Use `timescaledb-parallel-copy` to import data into
12 | your Timescale database. Set `` to twice the number of CPUs in your
13 | database. For example, if you have 4 CPUs, `` should be `8`.
14 |
15 | ```bash
16 | timescaledb-parallel-copy \
17 | --connection "host= \
18 | user=tsdbadmin password= \
19 | port= \
20 | dbname=tsdb \
21 | sslmode=require
22 | " \
23 | --table \
24 | --file .csv \
25 | --workers \
26 | --reporting-period 30s
27 | ```
28 |
29 | Repeat for each table and hypertable you want to migrate.
30 |
31 |
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_using_postgres_copy.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | ### Restoring data into Timescale with COPY
4 |
5 | 1. Connect to your Timescale database:
6 |
7 | ```sql
8 | psql "postgres://tsdbadmin:@:/tsdb?sslmode=require"
9 | ```
10 |
11 | 1. Restore the data to your Timescale database:
12 |
13 | ```sql
14 | \copy FROM '.csv' WITH (FORMAT CSV);
15 | ```
16 |
17 | Repeat for each table and hypertable you want to migrate.
18 |
19 |
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_migrate_validate_and_restart_app.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 1. Update the table statistics.
2 |
3 | ```bash
4 | psql $TARGET -c "ANALYZE;"
5 | ```
6 |
7 | 1. Verify the data in the target Timescale Cloud service.
8 |
9 | Check that your data is correct, and returns the results that you expect,
10 |
11 | 1. Enable any Timescale Cloud features you want to use.
12 |
13 | Migration from PostgreSQL moves the data only. Now manually enable Timescale Cloud features like
14 | [hypertables][about-hypertables], [hypercore][data-compression] or [data retention][data-retention]
15 | while your database is offline.
16 |
17 | 1. Reconfigure your app to use the target database, then restart it.
18 |
19 |
20 | [about-hypertables]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/hypertables/
21 | [data-compression]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/hypercore/
22 | [data-retention]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/data-retention/about-data-retention/
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_mst-intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Managed Service for TimescaleDB (MST) is [TimescaleDB](https://github.com/timescale/timescaledb) hosted on Azure and GCP.
2 | MST is offered in partnership with Aiven.
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_multi-node-deprecation.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | [Multi-node support is sunsetted][multi-node-deprecation].
4 |
5 | TimescaleDB v2.13 is the last release that includes multi-node support for PostgreSQL
6 | versions 13, 14, and 15.
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 | [multi-node-deprecation]: https://github.com/timescale/timescaledb/blob/main/docs/MultiNodeDeprecation.md
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_old-api-create-hypertable.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | If you are self-hosting $TIMESCALE_DB v2.19.3 and below, create a [$PG relational table][pg-create-table],
2 | then convert it using [create_hypertable][create_hypertable]. You then enable $HYPERCORE with a call
3 | to [ALTER TABLE][alter_table_hypercore].
4 |
5 |
6 | [pg-create-table]: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/sql-createtable.html
7 | [create_hypertable]: /api/:currentVersion:/hypertable/create_hypertable/
8 | [alter_table_hypercore]: /api/:currentVersion:/hypercore/alter_table/
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_plan_upgrade.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | - Install the PostgreSQL client tools on your migration machine. This includes `psql`, and `pg_dump`.
3 | - Read [the release notes][relnotes] for the version of TimescaleDB that you are upgrading to.
4 | - [Perform a backup][backup] of your database. While Timescale
5 | upgrades are performed in-place, upgrading is an intrusive operation. Always
6 | make sure you have a backup on hand, and that the backup is readable in the
7 | case of disaster.
8 |
9 | [relnotes]: https://github.com/timescale/timescaledb/releases
10 | [upgrade-pg]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/upgrade-pg/#upgrade-your-postgresql-instance
11 | [backup]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/backup-and-restore/
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_preloaded-data.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | If you have been provided with a pre-loaded dataset on your Timescale service,
3 | go directly to the
4 | [queries section](https://docs.timescale.com/tutorials/latest/nyc-taxi-geospatial/plot-nyc/).
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_prereqs-cloud-and-self.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | To follow the procedure on this page you need to:
2 |
3 | * Create a [target $SERVICE_LONG][create-service].
4 |
5 | This procedure also works for [self-hosted $TIMESCALE_DB][enable-timescaledb].
6 |
7 | [create-service]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/services/
8 | [enable-timescaledb]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/install/
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_prereqs-cloud-no-connection.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | To follow the steps on this page:
2 |
3 | * Create a target [$SERVICE_LONG][create-service] with time-series and analytics enabled.
4 |
5 | [create-service]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/services/
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_prereqs-cloud-only.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | To follow the steps on this page:
2 |
3 | * Create a target [$SERVICE_LONG][create-service] with time-series and analytics enabled.
4 |
5 | You need your [connection details][connection-info].
6 |
7 |
8 | [create-service]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/services/
9 | [connection-info]: /integrations/:currentVersion:/find-connection-details/
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_psql-installation-homebrew.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | #### Installing psql using Homebrew
4 |
5 | 1. Install `psql`:
6 |
7 | ```bash
8 | brew install libpq
9 | ```
10 |
11 | 1. Update your path to include the `psql` tool.
12 |
13 | ```bash
14 | brew link --force libpq
15 | ```
16 |
17 | On Intel chips, the symbolic link is added to `/usr/local/bin`. On Apple
18 | Silicon, the symbolic link is added to `/opt/homebrew/bin`.
19 |
20 |
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_psql-installation-macports.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | #### Installing psql using MacPorts
4 |
5 | 1. Install the latest version of `libpqxx`:
6 |
7 | ```bash
8 | sudo port install libpqxx
9 | ```
10 |
11 | 1. [](#)View the files that were installed by `libpqxx`:
12 |
13 | ```bash
14 | port contents libpqxx
15 | ```
16 |
17 |
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_psql-installation-windows.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Install psql on Windows
2 |
3 | The `psql` tool is installed by default on Windows systems when you install
4 | PostgreSQL, and this is the most effective way to install the tool. These
5 | instructions use the interactive installer provided by PostgreSQL and
6 | EnterpriseDB.
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 | ### Installing psql on Windows
11 |
12 | 1. Download and run the PostgreSQL installer from
13 | [www.enterprisedb.com][windows-installer].
14 | 1. In the `Select Components` dialog, check `Command Line Tools`, along with
15 | any other components you want to install, and click `Next`.
16 | 1. Complete the installation wizard to install the package.
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 | [windows-installer]: https://www.postgresql.org/download/windows/
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_quickstart-intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Easily integrate your app with $CLOUD_LONG. Use your favorite programming language to connect to your
2 | $SERVICE_LONG, create and manage hypertables, then ingest and query data.
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_real-time-aggregates.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | In $TIMESCALE_DB v2.13 and later, real-time aggregates are **DISABLED** by default. In earlier versions, real-time aggregates are **ENABLED** by default; when you create a continuous aggregate, queries to that view include the results from the most recent raw data.
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_release_notification.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | To be notified about the latest releases, in [Github](https://github.com/timescale/timescaledb)
4 | click `Watch` > `Custom`, then enable `Releases`.
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_selfhosted_cta.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | Deploy a Timescale service in the cloud. We tune your database for performance and handle scalability, high availability, backups and management so you can relax.
3 |
4 |
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_selfhosted_production_alert.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | The following instructions are for development and testing installations. For a production environment, we strongly recommend
4 | that you implement the following, many of which you can achieve using PostgreSQL tooling.
5 |
6 | - Incremental backup and database snapshots, with efficient point-in-time recovery.
7 | - High availability replication, ideally with nodes across multiple availability zones.
8 | - Automatic failure detection with fast restarts, for both non-replicated and replicated deployments.
9 | - Asynchronous replicas for scaling reads when needed.
10 | - Connection poolers for scaling client connections.
11 | - Zero-down-time minor version and extension upgrades.
12 | - Forking workflows for major version upgrades and other feature testing.
13 | - Monitoring and observability.
14 |
15 | Deploying for production? With a $SERVICE_LONG we tune your database for performance and handle scalability, high
16 | availability, backups and management so you can relax.
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_since_2_18_0.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Since [TimescaleDB v2.18.0](https://github.com/timescale/timescaledb/releases/tag/2.18.0)
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_since_2_20_0.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Since [TimescaleDB v2.20.0](https://github.com/timescale/timescaledb/releases/tag/2.20.0)
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_tiered-storage-billing.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | $COMPANY charges only for the storage that your data occupies in S3 in the Apache Parquet format, regardless of whether it was compressed in $CLOUD_LONG before tiering. There are no additional expenses, such as data transfer or compute.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_timescale-intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | $COMPANY extends $PG for all of your resource-intensive production workloads, so you
2 | can build faster, scale further, and stay under budget.
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_timescaledb.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | TimescaleDB is an extension for PostgreSQL that enables time-series workloads,
2 | increasing ingest, query, storage and analytics performance.
3 |
4 | Best practice is to run TimescaleDB in a [Timescale Service](https://console.cloud.timescale.com/signup), but if you want to
5 | self-host you can run TimescaleDB yourself.
6 |
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_tutorials_hypertable_intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import HypercoreIntroShort from "versionContent/_partials/_hypercore-intro-short.mdx";
2 |
3 | Time-series data represents the way a system, process, or behavior changes over time. $HYPERTABLE_CAPs enable
4 | $TIMESCALE_DB to work efficiently with time-series data. $HYPERTABLE_CAPs are $PG tables that automatically partition
5 | your time-series data by time. Each $HYPERTABLE is made up of child tables called chunks. Each chunk is assigned a range
6 | of time, and only contains data from that range. When you run a query, $TIMESCALE_DB identifies the correct chunk and
7 | runs the query on it, instead of going through the entire table.
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 | Because $TIMESCALE_DB is 100% $PG, you can use all the standard PostgreSQL tables, indexes, stored
12 | procedures, and other objects alongside your $HYPERTABLEs. This makes creating and working with $HYPERTABLEs similar
13 | to standard $PG.
14 |
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_usage-based-storage-intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | $CLOUD_LONG charges are based on the amount of storage you use. You don't pay for
2 | fixed storage size, and you don't need to worry about scaling disk size as your
3 | data grows—we handle it all for you. To reduce your data costs further,
4 | combine [$HYPERCORE][hypercore], a [data retention policy][data-retention], and
5 | [tiered storage][data-tiering].
6 |
7 | [hypercore]: /api/:currentVersion:/hypercore/
8 | [data-retention]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/data-retention/
9 | [data-tiering]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/data-tiering/
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_use-case-setup-blockchain-dataset.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | import CreateHypertableBlockchain from "versionContent/_partials/_create-hypertable-blockchain.mdx";
4 | import AddDataBlockchain from "versionContent/_partials/_add-data-blockchain.mdx";
5 | import IntegrationPrereqs from "versionContent/_partials/_integration-prereqs.mdx";
6 |
7 | # Ingest data into a $SERVICE_LONG
8 |
9 | This tutorial uses a dataset that contains Bitcoin blockchain data for
10 | the past five days, in a $HYPERTABLE named `transactions`.
11 |
12 | ## Prerequisites
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_vpc-limitations.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | * You **can attach**:
2 | * Up to 50 Customer $VPCs to a Peering $VPC.
3 | * A $SERVICE_LONG to a single Peering $VPC at a time.
4 | The $SERVICE_SHORT and the Peering $VPC must be in the same AWS region. However, you can peer a Customer $VPC and a Peering $VPC that are in different regions.
5 | * Multiple $SERVICE_LONGs to the same Peering $VPC.
6 | * You **cannot attach** a $SERVICE_LONG to multiple Peering $VPCs at the same time.
7 |
8 | The number of Peering $VPCs you can create in your project depends on your [$PRICING_PLAN][pricing-plans].
9 | If you need another Peering $VPC, either contact [support@timescale.com](mailto:support@timescale.com) or change your $PRICING_PLAN in [$CONSOLE][console-login].
10 |
11 | [console-login]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/
12 | [pricing-plans]: /about/:currentVersion:/pricing-and-account-management/
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_partials/_where-to-next.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | What next? [Try the main features offered by Timescale][try-timescale-features], see the [use case tutorials][tutorials],
2 | interact with the data in your $SERVICE_LONG using [your favorite programming language][connect-with-code], integrate
3 | your $SERVICE_LONG with a range of [third-party tools][integrations], plain old [Use Timescale][use-timescale], or dive
4 | into [the API][use-the-api].
5 |
6 | [tutorials]: /tutorials/:currentVersion:/
7 | [integrations]: /integrations/:currentVersion:/
8 | [connect-with-code]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/start-coding-with-timescale/
9 | [use-the-api]: /api/:currentVersion:/
10 | [use-timescale]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/
11 | [try-timescale-features]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/try-key-features-timescale-products/
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_queries/getting-started-cagg-tesla.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | SELECT * FROM stock_candlestick_daily
2 | WHERE symbol='TSLA'
3 | ORDER BY day DESC
4 | LIMIT 10;
5 |
6 | -- Output
7 |
8 | day | symbol | high | open | close | low
9 | -----------------------+--------+----------+----------+----------+----------
10 | 2023-07-31 00:00:00+00 | TSLA | 269 | 266.42 | 266.995 | 263.8422
11 | 2023-07-28 00:00:00+00 | TSLA | 267.4 | 259.32 | 266.8 | 258.06
12 | 2023-07-27 00:00:00+00 | TSLA | 269.98 | 268.3 | 256.8 | 241.5539
13 | 2023-07-26 00:00:00+00 | TSLA | 271.5168 | 265.48 | 265.3283 | 258.0418
14 | 2023-07-25 00:00:00+00 | TSLA | 270.22 | 267.5099 | 264.55 | 257.21
15 | 2023-07-20 00:00:00+00 | TSLA | 267.58 | 267.34 | 260.6 | 247.4588
16 | 2023-07-14 00:00:00+00 | TSLA | 285.27 | 277.29 | 281.7 | 264.7567
17 | 2023-07-13 00:00:00+00 | TSLA | 290.0683 | 274.07 | 277.4509 | 270.6127
18 | 2023-07-12 00:00:00+00 | TSLA | 277.68 | 271.26 | 272.94 | 258.0418
19 | 2023-07-11 00:00:00+00 | TSLA | 271.44 | 270.83 | 269.8303 | 266.3885
20 | (10 rows)
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_queries/getting-started-cagg.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | SELECT * FROM stock_candlestick_daily
2 | ORDER BY day DESC, symbol
3 | LIMIT 10;
4 |
5 | -- Output
6 |
7 | day | symbol | high | open | close | low
8 | -----------------------+--------+----------+--------+----------+----------
9 | 2023-07-31 00:00:00+00 | AAPL | 196.71 | 195.9 | 196.1099 | 195.2699
10 | 2023-07-31 00:00:00+00 | ABBV | 151.25 | 151.25 | 148.03 | 148.02
11 | 2023-07-31 00:00:00+00 | ABNB | 154.95 | 153.43 | 152.95 | 151.65
12 | 2023-07-31 00:00:00+00 | ABT | 113 | 112.4 | 111.49 | 111.44
13 | 2023-07-31 00:00:00+00 | ADBE | 552.87 | 536.74 | 550.835 | 536.74
14 | 2023-07-31 00:00:00+00 | AMAT | 153.9786 | 152.5 | 151.84 | 150.52
15 | 2023-07-31 00:00:00+00 | AMD | 114.57 | 113.47 | 113.15 | 112.35
16 | 2023-07-31 00:00:00+00 | AMGN | 237 | 236.61 | 233.6 | 233.515
17 | 2023-07-31 00:00:00+00 | AMT | 191.69 | 189.75 | 190.55 | 188.97
18 | 2023-07-31 00:00:00+00 | AMZN | 133.89 | 132.42 | 133.055 | 132.32
19 | (10 rows)
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_queries/getting-started-crypto-cagg.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | SELECT * FROM assets_candlestick_daily
2 | ORDER BY day DESC, symbol
3 | LIMIT 10;
4 |
5 | -- Output
6 |
7 | day | symbol | high | open | close | low
8 | -----------------------+--------+----------+--------+----------+----------
9 | 2025-01-30 00:00:00+00 | ADA/USD | 0.9708 | 0.9396 | 0.9607 | 0.9365
10 | 2025-01-30 00:00:00+00 | ATOM/USD | 6.114 | 5.825 | 6.063 | 5.776
11 | 2025-01-30 00:00:00+00 | AVAX/USD | 34.1 | 32.8 | 33.95 | 32.44
12 | 2025-01-30 00:00:00+00 | BNB/USD | 679.3 | 668.12 | 677.81 | 666.08
13 | 2025-01-30 00:00:00+00 | BTC/USD | 105595.65 | 103735.84 | 105157.21 | 103298.84
14 | 2025-01-30 00:00:00+00 | CRO/USD | 0.13233 | 0.12869 | 0.13138 | 0.12805
15 | 2025-01-30 00:00:00+00 | DAI/USD | 1 | 1 | 0.9999 | 0.99989998
16 | 2025-01-30 00:00:00+00 | DOGE/USD | 0.33359 | 0.32392 | 0.33172 | 0.32231
17 | 2025-01-30 00:00:00+00 | DOT/USD | 6.01 | 5.779 | 6.004 | 5.732
18 | 2025-01-30 00:00:00+00 | ETH/USD | 3228.9 | 3113.36 | 3219.25 | 3092.92
19 | (10 rows)
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_queries/getting-started-crypto-srt-orderby.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | SELECT * FROM crypto_ticks srt
2 | WHERE symbol='ETH/USD'
3 | ORDER BY time DESC
4 | LIMIT 10;
5 |
6 | -- Output
7 |
8 | time | symbol | price | day_volume
9 | -----------------------+--------+----------+------------
10 | 2025-01-30 12:05:09+00 | ETH/USD | 3219.25 | 39425
11 | 2025-01-30 12:05:00+00 | ETH/USD | 3219.26 | 39425
12 | 2025-01-30 12:04:42+00 | ETH/USD | 3219.26 | 39459
13 | 2025-01-30 12:04:33+00 | ETH/USD | 3219.91 | 39458
14 | 2025-01-30 12:04:15+00 | ETH/USD | 3219.6 | 39458
15 | 2025-01-30 12:04:06+00 | ETH/USD | 3220.68 | 39458
16 | 2025-01-30 12:03:57+00 | ETH/USD | 3220.68 | 39483
17 | 2025-01-30 12:03:48+00 | ETH/USD | 3220.12 | 39483
18 | 2025-01-30 12:03:20+00 | ETH/USD | 3219.79 | 39482
19 | 2025-01-30 12:03:11+00 | ETH/USD | 3220.06 | 39472
20 | (10 rows)
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_queries/getting-started-srt-4-days.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | SELECT * FROM stocks_real_time srt
2 | LIMIT 10;
3 |
4 | -- Output
5 |
6 | time | symbol | price | day_volume
7 | -----------------------+--------+----------+------------
8 | 2023-07-31 16:32:16+00 | PEP | 187.755 | 1618189
9 | 2023-07-31 16:32:16+00 | TSLA | 268.275 | 51902030
10 | 2023-07-31 16:32:16+00 | INTC | 36.035 | 22736715
11 | 2023-07-31 16:32:15+00 | CHTR | 402.27 | 626719
12 | 2023-07-31 16:32:15+00 | TSLA | 268.2925 | 51899210
13 | 2023-07-31 16:32:15+00 | AMD | 113.72 | 29136618
14 | 2023-07-31 16:32:15+00 | NVDA | 467.72 | 13951198
15 | 2023-07-31 16:32:15+00 | AMD | 113.72 | 29137753
16 | 2023-07-31 16:32:15+00 | RTX | 87.74 | 4295687
17 | 2023-07-31 16:32:15+00 | RTX | 87.74 | 4295907
18 | (10 rows)
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_queries/getting-started-srt-aggregation.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | SELECT
2 | time_bucket('1 day', time) AS bucket,
3 | symbol,
4 | max(price) AS high,
5 | first(price, time) AS open,
6 | last(price, time) AS close,
7 | min(price) AS low
8 | FROM stocks_real_time srt
9 | WHERE time > now() - INTERVAL '1 week'
10 | GROUP BY bucket, symbol
11 | ORDER BY bucket, symbol
12 | LIMIT 10;
13 |
14 | -- Output
15 |
16 | day | symbol | high | open | close | low
17 | -----------------------+--------+--------------+----------+----------+--------------
18 | 2023-06-07 00:00:00+00 | AAPL | 179.25 | 178.91 | 179.04 | 178.17
19 | 2023-06-07 00:00:00+00 | ABNB | 117.99 | 117.4 | 117.9694 | 117
20 | 2023-06-07 00:00:00+00 | AMAT | 134.8964 | 133.73 | 134.8964 | 133.13
21 | 2023-06-07 00:00:00+00 | AMD | 125.33 | 124.11 | 125.13 | 123.82
22 | 2023-06-07 00:00:00+00 | AMZN | 127.45 | 126.22 | 126.69 | 125.81
23 | ...
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_queries/getting-started-srt-bucket-first-last.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | SELECT time_bucket('1 hour', time) AS bucket,
2 | first(price,time),
3 | last(price, time)
4 | FROM stocks_real_time srt
5 | WHERE time > now() - INTERVAL '4 days'
6 | GROUP BY bucket;
7 |
8 | -- Output
9 |
10 | bucket | first | last
11 | ------------------------+--------+--------
12 | 2023-08-07 08:00:00+00 | 88.75 | 182.87
13 | 2023-08-07 09:00:00+00 | 140.85 | 35.16
14 | 2023-08-07 10:00:00+00 | 182.89 | 52.58
15 | 2023-08-07 11:00:00+00 | 86.69 | 255.15
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_queries/getting-started-srt-candlestick.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | SELECT
2 | time_bucket('1 day', "time") AS day,
3 | symbol,
4 | max(price) AS high,
5 | first(price, time) AS open,
6 | last(price, time) AS close,
7 | min(price) AS low
8 | FROM stocks_real_time srt
9 | GROUP BY day, symbol
10 | ORDER BY day DESC, symbol
11 | LIMIT 10;
12 |
13 | -- Output
14 |
15 | day | symbol | high | open | close | low
16 | -----------------------+--------+--------------+----------+----------+--------------
17 | 2023-06-07 00:00:00+00 | AAPL | 179.25 | 178.91 | 179.04 | 178.17
18 | 2023-06-07 00:00:00+00 | ABNB | 117.99 | 117.4 | 117.9694 | 117
19 | 2023-06-07 00:00:00+00 | AMAT | 134.8964 | 133.73 | 134.8964 | 133.13
20 | 2023-06-07 00:00:00+00 | AMD | 125.33 | 124.11 | 125.13 | 123.82
21 | 2023-06-07 00:00:00+00 | AMZN | 127.45 | 126.22 | 126.69 | 125.81
22 | ...
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_queries/getting-started-srt-first-last.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | SELECT symbol, first(price,time), last(price, time)
2 | FROM stocks_real_time srt
3 | WHERE time > now() - INTERVAL '4 days'
4 | GROUP BY symbol
5 | ORDER BY symbol
6 | LIMIT 10;
7 |
8 | -- Output
9 |
10 | symbol | first | last
11 | -------+----------+----------
12 | AAPL | 179.0507 | 179.04
13 | ABNB | 118.83 | 117.9694
14 | AMAT | 133.55 | 134.8964
15 | AMD | 122.6476 | 125.13
16 | AMZN | 126.5599 | 126.69
17 | ...
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_queries/getting-started-srt-orderby.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | SELECT * FROM stocks_real_time srt
2 | WHERE symbol='TSLA'
3 | ORDER BY time DESC
4 | LIMIT 10;
5 |
6 | -- Output
7 |
8 | time | symbol | price | day_volume
9 | -----------------------+--------+----------+------------
10 | 2025-01-30 00:51:00+00 | TSLA | 405.32 | NULL
11 | 2025-01-30 00:41:00+00 | TSLA | 406.05 | NULL
12 | 2025-01-30 00:39:00+00 | TSLA | 406.25 | NULL
13 | 2025-01-30 00:32:00+00 | TSLA | 406.02 | NULL
14 | 2025-01-30 00:32:00+00 | TSLA | 406.10 | NULL
15 | 2025-01-30 00:25:00+00 | TSLA | 405.95 | NULL
16 | 2025-01-30 00:24:00+00 | TSLA | 406.04 | NULL
17 | 2025-01-30 00:24:00+00 | TSLA | 406.04 | NULL
18 | 2025-01-30 00:22:00+00 | TSLA | 406.38 | NULL
19 | 2025-01-30 00:21:00+00 | TSLA | 405.77 | NULL
20 | (10 rows)
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_queries/getting-started-week-average.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | SELECT
2 | time_bucket('1 day', time) AS bucket,
3 | symbol,
4 | avg(price)
5 | FROM stocks_real_time srt
6 | WHERE time > now() - INTERVAL '1 week'
7 | GROUP BY bucket, symbol
8 | ORDER BY bucket, symbol
9 | LIMIT 10;
10 |
11 | -- Output
12 |
13 | bucket | symbol | avg
14 | -----------------------+--------+--------------------
15 | 2023-06-01 00:00:00+00 | AAPL | 179.3242530284364
16 | 2023-06-01 00:00:00+00 | ABNB | 112.05498586371293
17 | 2023-06-01 00:00:00+00 | AMAT | 134.41263567849518
18 | 2023-06-01 00:00:00+00 | AMD | 119.43332772033834
19 | 2023-06-01 00:00:00+00 | AMZN | 122.3446364966392
20 | ...
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_queries/test.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | SELECT time,
2 | symbol,
3 | price
4 | FROM stocks_real_time
5 | ORDER BY time DESC
6 | LIMIT 10;
7 |
8 | -- Output
9 |
10 | here | is | some | fake | data
11 | -----|----|------|------|-----
12 | 25 | 2 | yes | no | 1.25
13 | 25 | 2 | yes | no | 1.25
14 | 25 | 2 | yes | no | 1.25
15 | 25 | 2 | yes | no | 1.25
16 | 25 | 2 | yes | no | 1.25
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_troubleshooting/caggs-hypertable-retention-policy-not-applying.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Hypertable retention policy isn't applying to continuous aggregates
3 | section: troubleshooting
4 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
5 | topics: [continuous aggregates, data retention]
6 | apis:
7 | - [data retention, add_retention_policy()]
8 | keywords: [continuous aggregates, data retention]
9 | tags: [continuous aggregates, data retention]
10 | ---
11 |
12 |
20 |
21 | A retention policy set on a hypertable does not apply to any continuous
22 | aggregates made from the hypertable. This allows you to set different retention
23 | periods for raw and summarized data. To apply a retention policy to a continuous
24 | aggregate, set the policy on the continuous aggregate itself.
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_troubleshooting/caggs-migrate-permissions.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Permissions error when migrating a continuous aggregate
3 | section: troubleshooting
4 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
5 | topics: [continuous aggregates]
6 | apis:
7 | - [continuous aggregates, cagg_migrate()]
8 | keywords: [continuous aggregates]
9 | tags: [continuous aggregates, migrate]
10 | ---
11 |
12 | import CaggMigratePermissions from 'versionContent/_partials/_caggs-migrate-permissions.mdx';
13 |
14 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_troubleshooting/caggs-queries-fail.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Queries fail when defining continuous aggregates but work on regular tables
3 | section: troubleshooting
4 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
5 | topics: [continuous aggregates]
6 | apis:
7 | - [continuous aggregates, CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW (Continuous Aggregate)]
8 | keywords: [continuous aggregates]
9 | tags: [continuous aggregates, query]
10 | ---
11 |
12 | import CaggsFunctionSupport from 'versionContent/_partials/_caggs-function-support.mdx';
13 |
14 | Continuous aggregates do not work on all queries. For example, TimescaleDB does not support window functions on
15 | continuous aggregates. If you use an unsupported function, you see the following error:
16 |
17 | ```sql
18 | ERROR: invalid continuous aggregate view
19 | SQL state: 0A000
20 | ```
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 | [postgres-parallel-agg]: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/parallel-plans.html#PARALLEL-AGGREGATION
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_troubleshooting/compression-inefficient-chunk-interval.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Inefficient `compress_chunk_time_interval` configuration
3 | section: troubleshooting
4 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
5 | topics: [compression, hypercore]
6 | errors:
7 | - language: text
8 | message: |-
9 | compress_chunk_time_interval configured and primary dimension not first column in compress_orderby.
10 | consider setting "" as first compress_orderby column
11 | keywords: [compression, alter_table]
12 | tags: [compression, alter_table]
13 | ---
14 |
15 | When you configure `compress_chunk_time_interval` but do not set the primary dimension as the first column in `compress_orderby`, $TIMESCALE_DB decompresses chunks before merging. This makes merging less efficient. Set the primary dimension of the chunk as the first column in `compress_orderby` to improve efficiency.
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_troubleshooting/mst/forgotten-password.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Reset password
3 | section: troubleshooting
4 | products: [mst]
5 | topics: [security]
6 | keywords: [password]
7 | tags: [alter]
8 | ---
9 |
10 | It happens to us all, you want to login to MST Console, and the password is somewhere
11 | next to your keys, wherever they are.
12 |
13 | To reset your password:
14 |
15 | 1. Open [MST Portal][mst-login].
16 | 2. Click `Forgot password`.
17 | 3. Enter your email address, then click `Reset password`.
18 |
19 | A secure reset password link is sent to the email associated with this account. Click the link
20 | and update your password.
21 |
22 |
23 | [mst-login]:https://portal.managed.timescale.com/login
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_troubleshooting/self-hosted/pg_dump-errors.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Errors occur when running `pg_dump`
3 | section: troubleshooting
4 | products: [self_hosted]
5 | topics: [backups]
6 | errors:
7 | - language: bash
8 | message: |-
9 | pg_dump: NOTICE: hypertable data are in the chunks, no data will be copied
10 | DETAIL: Data for hypertables are stored in the chunks of a hypertable so COPY TO of a hypertable will not copy any data.
11 | HINT: Use "COPY (SELECT * FROM ) TO ..." to copy all data in hypertable, or copy each chunk individually.
12 | keywords: [backups, restore]
13 | ---
14 |
15 |
23 | You might see the errors above when running `pg_dump`. You can safely ignore
24 | these. Your hypertable data is still accurately copied.
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_troubleshooting/self-hosted/pg_restore-errors.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Errors occur after restoring from file dump
3 | section: troubleshooting
4 | products: [self_hosted]
5 | topics: [backups]
6 | errors:
7 | - language: bash
8 | message: |-
9 | org.postgresql.util.PSQLException: ERROR: invalid INSERT on the root table of hypertable "_hyper_1_10_chunk.
10 | keywords: [backups, restore]
11 | ---
12 |
13 |
21 | You might see the errors above when running `pg_restore`. When loading from a
22 | logical dump make sure that you set `timescaledb.restoring` to true before loading
23 | the dump.
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_troubleshooting/self-hosted/update-error-third-party-tool.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Error updating TimescaleDB when using a third-party PostgreSQL admin tool
3 | products: [self_hosted]
4 | topics: [upgrades]
5 | keywords: [updates, third-party tools]
6 | ---
7 |
8 |
16 |
17 | The update command `ALTER EXTENSION timescaledb UPDATE` must be the first command
18 | executed upon connection to a database. Some admin tools execute commands before
19 | this, which can disrupt the process. Try manually updating the database with
20 | `psql`. For instructions, see the [updating guide][update].
21 |
22 | [update]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/upgrades/
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_troubleshooting/self-hosted/windows-install-library-not-loaded.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Error loading the timescaledb extension
3 | section: troubleshooting
4 | products: [self_hosted]
5 | topics: [Install]
6 | errors:
7 | - language: sql
8 | message: |-
9 | ERROR: could not load library "C:/Program Files/PostgreSQL/16/lib/timescaledb-2.14.2.dll": The specified module could not be found.
10 | keywords: [install]
11 | tags: [install]
12 | ---
13 |
14 | If you see a message saying that $PG cannot load the $TIMESCALE_DB library `timescaledb-.dll`, start a new psql
15 | session to your self-hosted instance and create the `timescaledb` extension as the first command:
16 |
17 | ```bash
18 | psql -X -d "postgres://:@:/" -c "CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS timescaledb;"
19 | ```
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_troubleshooting/slow-tiering-chunks.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Slow tiering of chunks
3 | section: troubleshooting
4 | products: [cloud]
5 | topics: [data tiering]
6 | keywords: [tiered storage]
7 | tags: [tiered storage]
8 | ---
9 |
10 |
11 |
19 |
20 | Chunks are tiered asynchronously. Chunks are selected to be tiered to the object storage tier one at a time ordered by their enqueue time.
21 |
22 | To see the chunks waiting to be tiered query the `timescaledb_osm.chunks_queued_for_tiering` view
23 |
24 | ```sql
25 | select count(*) from timescaledb_osm.chunks_queued_for_tiering
26 | ```
27 |
28 | Processing all the chunks in the queue may take considerable time if a large quantity of data is being migrated to the object storage tier.
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/_tutorials/deprecated.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | []
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/about/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: About Timescale products
3 | excerpt: Learn about Timescale Cloud and TimescaleDB, including pricing, release notes, feature overview, and contribution guidelines
4 | products: [cloud, self_hosted, mst]
5 | ---
6 |
7 | # About Timescale
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/.templates/hyperfunctions/examples.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: ()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | # Example 1
7 |
8 | Extended examples that use multiple hyperfunctions from the group go here.
9 |
10 | ### Example 2
11 |
12 | Each example should be preceded by a heading level 3 that briefly describes
13 | what the example does.
14 |
15 | ## Some other section
16 |
17 | If you need to add another freeform section to the end of the page, for example
18 | some discussion about Advanced Usage or an algorithm explanation, put it down
19 | here under a heading level 2. That ensures it shows up as a top-level section in
20 | the Table of Contents.
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/.templates/hyperfunctions/intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: ()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Freeform text that goes at the very top of the page, describing why you would
7 | use this group of functions.
8 |
9 | No need to put a title, that is auto-generated, just start writing paragraphs.
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/candlestick_agg/close.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: close()
3 | excerpt: Get the closing price from a candlestick aggregate
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | tags: [hyperfunctions, finance, candlestick, close]
6 | api:
7 | license: community
8 | type: function
9 | experimental: false
10 | toolkit: true
11 | version:
12 | experimental: 1.12.0
13 | stable: 1.14.0
14 | hyperfunction:
15 | family: financial analysis
16 | type: accessor
17 | aggregates:
18 | - candlestick_agg()
19 | api_details:
20 | summary: Get the closing price from a candlestick aggregate.
21 | signatures:
22 | - language: sql
23 | code: |
24 | close(
25 | candlestick Candlestick
26 | ) RETURNS DOUBLE PRECISION
27 | parameters:
28 | required:
29 | - name: candlestick
30 | type: Candlestick
31 | description: Candlestick aggregate
32 | returns:
33 | - column: close
34 | type: DOUBLE PRECISION
35 | description: The closing price
36 | ---
37 |
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/candlestick_agg/close_time.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: close_time()
3 | excerpt: Get the timestamp corresponding to the closing time from a candlestick aggregate
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | tags: [hyperfunctions, finance, candlestick, close]
6 | api:
7 | license: community
8 | type: function
9 | experimental: false
10 | toolkit: true
11 | version:
12 | experimental: 1.12.0
13 | stable: 1.14.0
14 | hyperfunction:
15 | family: financial analysis
16 | type: accessor
17 | aggregates:
18 | - candlestick_agg()
19 | api_details:
20 | summary: Get the timestamp corresponding to the closing time from a candlestick aggregate.
21 | signatures:
22 | - language: sql
23 | code: |
24 | close_time(
25 | candlestick Candlestick
26 | ) RETURNS TIMESTAMPTZ
27 | parameters:
28 | required:
29 | - name: candlestick
30 | type: Candlestick
31 | description: Candlestick aggregate
32 | returns:
33 | - column: close_time
34 | type: TIMESTAMPTZ
35 | description: The time at which the closing price occurred
36 | ---
37 |
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/candlestick_agg/high.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: high()
3 | excerpt: Get the high price from a candlestick aggregate
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | tags: [hyperfunctions, finance, candlestick, high]
6 | api:
7 | license: community
8 | type: function
9 | experimental: false
10 | toolkit: true
11 | version:
12 | experimental: 1.12.0
13 | stable: 1.14.0
14 | hyperfunction:
15 | family: financial analysis
16 | type: accessor
17 | aggregates:
18 | - candlestick_agg()
19 | api_details:
20 | summary: Get the high price from a candlestick aggregate.
21 | signatures:
22 | - language: sql
23 | code: |
24 | high(
25 | candlestick Candlestick
26 | ) RETURNS DOUBLE PRECISION
27 | parameters:
28 | required:
29 | - name: candlestick
30 | type: Candlestick
31 | description: Candlestick aggregate
32 | returns:
33 | - column: high
34 | type: DOUBLE PRECISION
35 | description: The high price
36 | ---
37 |
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/candlestick_agg/high_time.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: high_time()
3 | excerpt: Get the timestamp corresponding to the high time from a candlestick aggregate
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | tags: [hyperfunctions, finance, candlestick, high]
6 | api:
7 | license: community
8 | type: function
9 | experimental: false
10 | toolkit: true
11 | version:
12 | experimental: 1.12.0
13 | stable: 1.14.0
14 | hyperfunction:
15 | family: financial analysis
16 | type: accessor
17 | aggregates:
18 | - candlestick_agg()
19 | api_details:
20 | summary: Get the timestamp corresponding to the high time from a candlestick aggregate.
21 | signatures:
22 | - language: sql
23 | code: |
24 | high_time(
25 | candlestick Candlestick
26 | ) RETURNS TIMESTAMPTZ
27 | parameters:
28 | required:
29 | - name: candlestick
30 | type: Candlestick
31 | description: Candlestick aggregate
32 | returns:
33 | - column: high_time
34 | type: TIMESTAMPTZ
35 | description: The first time at which the high price occurred
36 | ---
37 |
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/candlestick_agg/intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: candlestick_agg()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Perform analysis of financial asset data. These specialized hyperfunctions make
7 | it easier to write financial analysis queries that involve candlestick data.
8 |
9 | They help you answer questions such as:
10 |
11 | * What are the opening and closing prices of these stocks?
12 | * When did the highest price occur for this stock?
13 |
14 | This function group uses the [two-step aggregation][two-step-aggregation]
15 | pattern. In addition to the usual aggregate function,
16 | [`candlestick_agg`][candlestick_agg], it also includes the pseudo-aggregate
17 | function `candlestick`. `candlestick_agg` produces a candlestick aggregate from
18 | raw tick data, which can then be used with the accessor and rollup functions in
19 | this group. `candlestick` takes pre-aggregated data and transforms it into the
20 | same format that `candlestick_agg` produces. This allows you to use the
21 | accessors and rollups with existing candlestick data.
22 |
23 | [candlestick_agg]: #candlestick_agg
24 | [two-step-aggregation]: #two-step-aggregation
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/candlestick_agg/low.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: low()
3 | excerpt: Get the low price from a candlestick aggregate
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | tags: [hyperfunctions, finance, candlestick, low]
6 | api:
7 | license: community
8 | type: function
9 | experimental: false
10 | toolkit: true
11 | version:
12 | experimental: 1.12.0
13 | stable: 1.14.0
14 | hyperfunction:
15 | family: financial analysis
16 | type: accessor
17 | aggregates:
18 | - candlestick_agg()
19 | api_details:
20 | summary: Get the low price from a candlestick aggregate.
21 | signatures:
22 | - language: sql
23 | code: |
24 | low(
25 | candlestick Candlestick
26 | ) RETURNS DOUBLE PRECISION
27 | parameters:
28 | required:
29 | - name: candlestick
30 | type: Candlestick
31 | description: Candlestick aggregate
32 | returns:
33 | - column: low
34 | type: DOUBLE PRECISION
35 | description: The low price
36 | ---
37 |
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/candlestick_agg/low_time.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: low_time()
3 | excerpt: Get the timestamp corresponding to the low time from a candlestick aggregate
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | tags: [hyperfunctions, finance, candlestick, low]
6 | api:
7 | license: community
8 | type: function
9 | experimental: false
10 | toolkit: true
11 | version:
12 | experimental: 1.12.0
13 | stable: 1.14.0
14 | hyperfunction:
15 | family: financial analysis
16 | type: accessor
17 | aggregates:
18 | - candlestick_agg()
19 | api_details:
20 | summary: Get the timestamp corresponding to the low time from a candlestick aggregate.
21 | signatures:
22 | - language: sql
23 | code: |
24 | low_time(
25 | candlestick Candlestick
26 | ) RETURNS TIMESTAMPTZ
27 | parameters:
28 | required:
29 | - name: candlestick
30 | type: Candlestick
31 | description: Candlestick aggregate
32 | returns:
33 | - column: low_time
34 | type: TIMESTAMPTZ
35 | description: The first time at which the low price occurred
36 | ---
37 |
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/candlestick_agg/open.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: open()
3 | excerpt: Get the opening price from a candlestick aggregate
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | tags: [hyperfunctions, finance, candlestick, open]
6 | api:
7 | license: community
8 | type: function
9 | experimental: false
10 | toolkit: true
11 | version:
12 | experimental: 1.12.0
13 | stable: 1.14.0
14 | hyperfunction:
15 | family: financial analysis
16 | type: accessor
17 | aggregates:
18 | - candlestick_agg()
19 | api_details:
20 | summary: Get the opening price from a candlestick aggregate.
21 | signatures:
22 | - language: sql
23 | code: |
24 | open(
25 | candlestick Candlestick
26 | ) RETURNS DOUBLE PRECISION
27 | parameters:
28 | required:
29 | - name: candlestick
30 | type: Candlestick
31 | description: Candlestick aggregate
32 | returns:
33 | - column: open
34 | type: DOUBLE PRECISION
35 | description: The opening price
36 | ---
37 |
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/candlestick_agg/open_time.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: open_time()
3 | excerpt: Get the timestamp corresponding to the open time from a candlestick aggregate
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | tags: [hyperfunctions, finance, candlestick, open]
6 | api:
7 | license: community
8 | type: function
9 | experimental: false
10 | toolkit: true
11 | version:
12 | experimental: 1.12.0
13 | stable: 1.14.0
14 | hyperfunction:
15 | family: financial analysis
16 | type: accessor
17 | aggregates:
18 | - candlestick_agg()
19 | api_details:
20 | summary: Get the timestamp corresponding to the open time from a candlestick aggregate.
21 | signatures:
22 | - language: sql
23 | code: |
24 | open_time(
25 | candlestick Candlestick
26 | ) RETURNS TIMESTAMPTZ
27 | parameters:
28 | required:
29 | - name: candlestick
30 | type: Candlestick
31 | description: Candlestick aggregate
32 | returns:
33 | - column: open_time
34 | type: TIMESTAMPTZ
35 | description: The time at which the opening price occurred
36 | ---
37 |
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/candlestick_agg/volume.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: volume()
3 | excerpt: Get the total volume from a candlestick aggregate
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | tags: [hyperfunctions, finance, candlestick, volume]
6 | api:
7 | license: community
8 | type: function
9 | experimental: false
10 | toolkit: true
11 | version:
12 | experimental: 1.12.0
13 | stable: 1.14.0
14 | hyperfunction:
15 | family: financial analysis
16 | type: accessor
17 | aggregates:
18 | - candlestick_agg()
19 | api_details:
20 | summary: Get the total volume from a candlestick aggregate.
21 | signatures:
22 | - language: sql
23 | code: |
24 | volume(
25 | candlestick Candlestick
26 | ) RETURNS DOUBLE PRECISION
27 | parameters:
28 | required:
29 | - name: candlestick
30 | type: Candlestick
31 | description: Candlestick aggregate
32 | returns:
33 | - column: volume
34 | type: DOUBLE PRECISION
35 | description: Total volume of trades within the period
36 | ---
37 |
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/compact_state_agg/intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: compact_state_agg()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Given a system or value that switches between discrete states, aggregate the
7 | amount of time spent in each state. For example, you can use the `compact_state_agg`
8 | functions to track how much time a system spends in `error`, `running`, or
9 | `starting` states.
10 |
11 | `compact_state_agg` is designed to work with a relatively small number of states. It
12 | might not perform well on datasets where states are mostly distinct between
13 | rows.
14 |
15 | If you need to track when each state is entered and exited, use the
16 | [`state_agg`][state_agg] functions. If you need to track the liveness of a
17 | system based on a heartbeat signal, consider using the
18 | [`heartbeat_agg`][heartbeat_agg] functions.
19 |
20 | [heartbeat_agg]: /api/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/state-tracking/heartbeat_agg/
21 | [state_agg]: /api/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/state-tracking/state_agg/
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/count_min_sketch/intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: count_min_sketch()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Count the number of times a value appears in a column, using the probabilistic
7 | [`count-min sketch`][count-min-sketch] data structure and its associated
8 | algorithms. For applications where a small error rate is tolerable, this can
9 | result in huge savings in both CPU time and memory, especially for large
10 | datasets.
11 |
12 | [count-min-sketch]: http://dimacs.rutgers.edu/~graham/pubs/papers/cm-full.pdf
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/counter_agg/intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: counter_agg()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Analyze data whose values are designed to monotonically increase, and where any
7 | decreases are treated as resets. The `counter_agg` functions simplify this task,
8 | which can be difficult to do in pure SQL.
9 |
10 | If it's possible for your readings to decrease as well as increase, use [`gauge_agg`][gauge_agg]
11 | instead.
12 |
13 | [gauge_agg]: /api/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/counters-and-gauges/gauge_agg/
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/counter_agg/rollup.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: rollup()
3 | excerpt: Combine multiple counter aggregates
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | api:
6 | license: community
7 | type: function
8 | toolkit: true
9 | experimental: false
10 | version:
11 | experimental: 0.3.0
12 | stable: 1.3.0
13 | hyperfunction:
14 | family: counters and gauges
15 | type: rollup
16 | aggregates:
17 | - counter_agg()
18 | api_details:
19 | summary: |
20 | This function combines multiple counter aggregates into one. This can be used
21 | to combine aggregates from adjacent intervals into one larger interval,
22 | such as rolling daily aggregates into a weekly or monthly aggregate.
23 | signatures:
24 | - language: sql
25 | code: |
26 | rollup(
27 | cs CounterSummary
28 | ) RETURNS CounterSummary
29 | parameters:
30 | required:
31 | - name: cs
32 | type: CounterSummary
33 | description: A counter aggregate created using [`counter_agg`](#counter_agg)
34 | returns:
35 | - column: counter_agg
36 | type: CounterSummary
37 | description: A new counter aggregate created by combining the input counter aggregates
38 | ---
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/downsampling-intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: downsampling
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Downsample your data to visualize trends while preserving fewer data points.
7 | Downsampling replaces a set of values with a much smaller set that is highly
8 | representative of the original data. This is particularly useful for graphing
9 | applications.
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/freq_agg/intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: freq_agg()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Get the most common elements of a set and their relative frequency. The
7 | estimation uses the [SpaceSaving][spacingsaving-algorithm] algorithm.
8 |
9 | This group of functions contains two aggregate functions, which let you set the
10 | cutoff for keeping track of a value in different ways. [`freq_agg`](#freq_agg)
11 | allows you to specify a minimum frequency, and [`mcv_agg`](#mcv_agg) allows
12 | you to specify the target number of values to keep.
13 |
14 | To estimate the absolute number of times a value appears, use [`count_min_sketch`][count_min_sketch].
15 |
16 | [count_min_sketch]: /api/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/frequency-analysis/count_min_sketch/
17 | [spacingsaving-algorithm]: https://www.cse.ust.hk/~raywong/comp5331/References/EfficientComputationOfFrequentAndTop-kElementsInDataStreams.pdf
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/gauge_agg/intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: gauge_agg()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Analyze data coming from gauges. Unlike counters, gauges can decrease as well as
7 | increase.
8 |
9 | If your value can only increase, use [`counter_agg`][counter_agg] instead to
10 | appropriately account for resets.
11 |
12 | [counter_agg]: /api/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/counters-and-gauges/counter_agg/
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/gauge_agg/rollup.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: rollup()
3 | excerpt: Combine multiple gauge aggregates
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | api:
6 | license: community
7 | type: function
8 | toolkit: true
9 | experimental: true
10 | version:
11 | experimental: 1.6.0
12 | hyperfunction:
13 | family: counters and gauges
14 | type: rollup
15 | aggregates:
16 | - gauge_agg()
17 | api_details:
18 | summary: |
19 | This function combines multiple gauge aggregates into one. This can be used
20 | to combine aggregates from adjacent intervals into one larger interval,
21 | such as rolling daily aggregates into a weekly or monthly aggregate.
22 | signatures:
23 | - language: sql
24 | code: |
25 | rollup(
26 | cs GaugeSummary
27 | ) RETURNS GaugeSummary
28 | parameters:
29 | required:
30 | - name: cs
31 | type: GaugeSummary
32 | description: A gauge aggregate created using [`gauge_agg`](#gauge_agg)
33 | returns:
34 | - column: gauge_agg
35 | type: GaugeSummary
36 | description: A new gauge aggregate created by combining the input gauge aggregates
37 | ---
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/heartbeat_agg/intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: heartbeat_agg()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Given a series of timestamped heartbeats and a liveness interval, determine the
7 | overall liveness of a system. This aggregate can be used to report total uptime
8 | or downtime as well as report the time ranges where the system was live or dead.
9 |
10 | It's also possible to combine multiple heartbeat aggregates to determine the
11 | overall health of a service. For example, the heartbeat aggregates from a
12 | primary and standby server could be combined to see if there was ever a window
13 | where both machines were down at the same time.
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/hyperloglog/intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: hyperloglog()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Estimate the number of distinct values in a dataset. This is also known as
7 | cardinality estimation. For large datasets and datasets with high cardinality
8 | (many distinct values), this can be much more efficient in both CPU and memory
9 | than an exact count using `count(DISTINCT)`.
10 |
11 | The estimation uses the [`hyperloglog++`][hyperloglog] algorithm. If you aren't
12 | sure what parameters to set for the `hyperloglog`, try using the
13 | [`approx_count_distinct`][approx_count_distinct] aggregate, which sets some
14 | reasonable default values.
15 |
16 | [approx_count_distinct]: #approx_count_distinct
17 | [hyperloglog]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HyperLogLog
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/max_n/examples.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: max_n()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | ### Get the 10 largest transactions from a table of stock trades
7 |
8 | This example assumes that you have a table of stock trades in this format:
9 |
10 | ```sql
11 | CREATE TABLE stock_sales(
12 | ts TIMESTAMPTZ,
13 | symbol TEXT,
14 | price FLOAT,
15 | volume INT
16 | );
17 | ```
18 |
19 | You can query for the 10 largest transactions each day:
20 |
21 | ```sql
22 | WITH t as (
23 | SELECT
24 | time_bucket('1 day'::interval, ts) as day,
25 | max_n(price * volume, 10) AS daily_max
26 | FROM stock_sales
27 | GROUP BY time_bucket('1 day'::interval, ts)
28 | )
29 | SELECT
30 | day, as_array(daily_max)
31 | FROM t;
32 | ```
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/max_n/intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: max_n()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Get the N largest values from a column.
7 |
8 | The `max_n()` functions give the same results as the regular SQL query `SELECT
9 | ... ORDER BY ... LIMIT n`. But unlike the SQL query, they can be composed and
10 | combined like other aggregate hyperfunctions.
11 |
12 | To get the N smallest values, use [`min_n()`][min_n]. To get the N largest
13 | values with accompanying data, use [`max_n_by()`][max_n_by].
14 |
15 | [max_n_by]: /api/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/minimum-and-maximum/max_n_by/
16 | [min_n]: /api/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/minimum-and-maximum/min_n/
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/max_n/rollup.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: rollup()
3 | excerpt: Combine multiple MaxN aggregates
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | tags: [hyperfunctions, toolkit, maximum]
6 | api:
7 | license: community
8 | type: function
9 | toolkit: true
10 | version:
11 | experimental: 1.12.0
12 | stable: 1.16.0
13 | hyperfunction:
14 | family: minimum and maximum
15 | type: rollup
16 | aggregates:
17 | - max_n()
18 | api_details:
19 | summary: |
20 | This aggregate combines the aggregates generated by other `max_n`
21 | aggregates. Combined with an accessor, it returns the maximum values found
22 | across all the aggregated data.
23 | signatures:
24 | - language: sql
25 | code: |
26 | rollup(
27 | agg MaxN
28 | ) MaxN
29 | parameters:
30 | required:
31 | - name: agg
32 | type: MaxN
33 | description: The aggregates being combined
34 | returns:
35 | - column: rollup
36 | type: MaxN
37 | description: >
38 | An aggregate over all of the contributing values.
39 | ---
40 |
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/max_n_by/examples.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: max_n_by()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | This example assumes that you have a table of stock trades in this format:
7 |
8 | ```sql
9 | CREATE TABLE stock_sales(
10 | ts TIMESTAMPTZ,
11 | symbol TEXT,
12 | price FLOAT,
13 | volume INT
14 | );
15 | ```
16 |
17 | Find the 10 largest transactions in the table, what time they occurred, and what
18 | symbol was being traded:
19 |
20 | ```sql
21 | SELECT
22 | (data).time,
23 | (data).symbol,
24 | value AS transaction
25 | FROM
26 | into_values((
27 | SELECT max_n_by(price * volume, stock_sales, 10)
28 | FROM stock_sales
29 | ),
30 | NULL::stock_sales);
31 | ```
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/max_n_by/intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: max_n_by()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Get the N largest values from a column, with an associated piece of data per
7 | value. For example, you can return an accompanying column, or the full row.
8 |
9 | The `max_n_by()` functions give the same results as the regular SQL query
10 | `SELECT ... ORDER BY ... LIMIT n`. But unlike the SQL query, they can be
11 | composed and combined like other aggregate hyperfunctions.
12 |
13 | To get the N smallest values with accompanying data, use
14 | [`min_n_by()`][min_n_by]. To get the N largest values without accompanying data,
15 | use [`max_n()`][max_n].
16 |
17 | [max_n]: /api/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/minimum-and-maximum/max_n/
18 | [min_n_by]: /api/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/minimum-and-maximum/min_n_by/
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/max_n_by/rollup.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: rollup()
3 | excerpt: Combine multiple MaxNBy aggregates
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | tags: [hyperfunctions, toolkit, maximum]
6 | api:
7 | license: community
8 | type: function
9 | toolkit: true
10 | version:
11 | experimental: 1.12.0
12 | stable: 1.16.0
13 | hyperfunction:
14 | family: minimum and maximum
15 | type: rollup
16 | aggregates:
17 | - max_n_by()
18 | api_details:
19 | summary: |
20 | This aggregate combines the aggregates generated by other max_n_by
21 | aggregates and returns the maximum values, with associated data, found
22 | across all the aggregated data.
23 | signatures:
24 | - language: sql
25 | code: |
26 | rollup(
27 | agg MaxNBy
28 | ) MaxNBy
29 | parameters:
30 | required:
31 | - name: agg
32 | type: MaxNBy
33 | description: The aggregates being combined
34 | returns:
35 | - column: rollup
36 | type: MaxNBy
37 | description: >
38 | An aggregate over all of the contributing values.
39 | ---
40 |
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/min_n/examples.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: min_n()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | This example assumes that you have a table of stock trades in this format:
7 |
8 | ```sql
9 | CREATE TABLE stock_sales(
10 | ts TIMESTAMPTZ,
11 | symbol TEXT,
12 | price FLOAT,
13 | volume INT
14 | );
15 | ```
16 |
17 | You can query for the 10 smallest transactions each day:
18 |
19 | ```sql
20 | WITH t as (
21 | SELECT
22 | time_bucket('1 day'::interval, ts) as day,
23 | min_n(price * volume, 10) AS daily_min
24 | FROM stock_sales
25 | GROUP BY time_bucket('1 day'::interval, ts)
26 | )
27 | SELECT
28 | day, as_array(daily_max)
29 | FROM t;
30 | ```
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/min_n/intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: min_n()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Get the N smallest values from a column.
7 |
8 | The `min_n()` functions give the same results as the regular SQL query `SELECT
9 | ... ORDER BY ... LIMIT n`. But unlike the SQL query, they can be composed and
10 | combined like other aggregate hyperfunctions.
11 |
12 | To get the N largest values, use [`max_n()`][max_n]. To get the N smallest
13 | values with accompanying data, use [`min_n_by()`][min_n_by].
14 |
15 | [max_n]: /api/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/minimum-and-maximum/max_n/
16 | [min_n_by]: /api/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/minimum-and-maximum/min_n_by/
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/min_n/rollup.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: rollup()
3 | excerpt: Combine multiple MinN aggregates
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | tags: [hyperfunctions, toolkit, minimum]
6 | api:
7 | license: community
8 | type: function
9 | toolkit: true
10 | version:
11 | experimental: 1.12.0
12 | stable: 1.16.0
13 | hyperfunction:
14 | family: minimum and maximum
15 | type: rollup
16 | aggregates:
17 | - min_n()
18 | api_details:
19 | summary: |
20 | This aggregate combines the aggregates generated by other `min_n`
21 | aggregates and returns the minimum values found across all the
22 | aggregated data.
23 | signatures:
24 | - language: sql
25 | code: |
26 | rollup(
27 | agg MinN
28 | ) MinN
29 | parameters:
30 | required:
31 | - name: agg
32 | type: MinN
33 | description: The aggregates being combined
34 | returns:
35 | - column: rollup
36 | type: MinN
37 | description: >
38 | An aggregate over all of the contributing values.
39 | ---
40 |
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/min_n_by/examples.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: min_n_by()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | This example assumes that you have a table of stock trades in this format:
7 |
8 | ```sql
9 | CREATE TABLE stock_sales(
10 | ts TIMESTAMPTZ,
11 | symbol TEXT,
12 | price FLOAT,
13 | volume INT
14 | );
15 | ```
16 |
17 | Find the 10 smallest transactions in the table, what time they occurred, and
18 | what symbol was being traded.
19 |
20 | ```sql
21 | SELECT
22 | (data).time,
23 | (data).symbol,
24 | value AS transaction
25 | FROM
26 | into_values((
27 | SELECT min_n_by(price * volume, stock_sales, 10)
28 | FROM stock_sales
29 | ),
30 | NULL::stock_sales);
31 | ```
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/min_n_by/intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: min_n_by()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Get the N smallest values from a column, with an associated piece of data per
7 | value. For example, you can return an accompanying column, or the full row.
8 |
9 | The `min_n_by()` functions give the same results as the regular SQL query
10 | `SELECT ... ORDER BY ... LIMIT n`. But unlike the SQL query, they can be
11 | composed and combined like other aggregate hyperfunctions.
12 |
13 | To get the N largest values with accompanying data, use
14 | [`max_n_by()`][max_n_by]. To get the N smallest values without accompanying
15 | data, use [`min_n()`][min_n].
16 |
17 | [max_n_by]: /api/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/minimum-and-maximum/max_n_by/
18 | [min_n]: /api/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/minimum-and-maximum/min_n/
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/min_n_by/rollup.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: rollup()
3 | excerpt: Combine multiple MinNBy aggregates
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | tags: [hyperfunctions, toolkit, minimum]
6 | api:
7 | license: community
8 | type: function
9 | toolkit: true
10 | version:
11 | experimental: 1.12.0
12 | stable: 1.16.0
13 | hyperfunction:
14 | family: minimum and maximum
15 | type: rollup
16 | aggregates:
17 | - min_n_by()
18 | api_details:
19 | summary: |
20 | This aggregate combines the aggregates generated by other min_n_by
21 | aggregates and returns the minimum values and associated data found
22 | across all the aggregated data.
23 | signatures:
24 | - language: sql
25 | code: |
26 | rollup(
27 | agg MinNBy
28 | ) MinNBy
29 | parameters:
30 | required:
31 | - name: agg
32 | type: MinNBy
33 | description: The aggregates being combined
34 | returns:
35 | - column: rollup
36 | type: MinNBy
37 | description: >
38 | An aggregate over all of the contributing values.
39 | ---
40 |
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/saturating-math-intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: saturating math
4 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
5 | ---
6 |
7 | The saturating math hyperfunctions help you perform saturating math on integers.
8 | In saturating math, the final result is bounded. If the result of a normal
9 | mathematical operation exceeds either the minimum or maximum bound, the result
10 | of the corresponding saturating math operation is capped at the bound. For
11 | example, `2 + (-3) = -1`. But in a saturating math function with a lower bound
12 | of `0`, such as [`saturating_add_pos`](#saturating_add_pos), the result is `0`.
13 |
14 | You can use saturating math to make sure your results don't overflow the allowed
15 | range of integers, or to force a result to be greater than or equal to zero.
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/saturating_add_pos.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: saturating_add_pos()
3 | excerpt: Adds two numbers, saturating at 0 for the minimum bound
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | api:
6 | license: community
7 | type: function
8 | toolkit: true
9 | experimental: true
10 | version:
11 | experimental: 1.8.0
12 | hyperfunction:
13 | family: saturating math
14 | type: function
15 | api_details:
16 | summary: The `saturating_add_pos` function adds two numbers, saturating at 0 and 2,147,483,647 instead of overflowing.
17 | signatures:
18 | - language: sql
19 | code: |
20 | saturating_add_pos(
21 | x INT,
22 | y INT
23 | ) RETURNS INT
24 | parameters:
25 | required:
26 | - name: x
27 | type: INT
28 | description: An integer to add to `y`
29 | - name: y
30 | type: INT
31 | description: An integer to add to `x`
32 | returns:
33 | - column: saturating_add_pos
34 | type: INT
35 | description: The result of `x + y`, saturating at 0 for the minimum bound.
36 | ---
37 |
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/saturating_multiply.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: saturating_mul()
3 | excerpt: Multiples two numbers, saturating at the 32-bit integer bounds instead of overflowing
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | api:
6 | license: community
7 | type: function
8 | toolkit: true
9 | experimental: true
10 | version:
11 | experimental: 1.8.0
12 | hyperfunction:
13 | family: saturating math
14 | type: function
15 | api_details:
16 | summary: The `saturating_mul` function multiples two numbers, saturating at -2,147,483,648 and 2,147,483,647 instead of overflowing.
17 | signatures:
18 | - language: sql
19 | code: |
20 | saturating_mul(
21 | x INT,
22 | y INT
23 | ) RETURNS INT
24 | parameters:
25 | required:
26 | - name: x
27 | type: INT
28 | description: An integer to multiply with `y`
29 | - name: y
30 | type: INT
31 | description: An integer to multiply with `x`
32 | returns:
33 | - column: saturating_mul
34 | type: INT
35 | description: The result of `x * y`, saturating at the numeric bounds instead of overflowing. The numeric bounds are the upper and lower bounds of the 32-bit signed integers.
36 | ---
37 |
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/saturating_sub_pos.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: saturating_sub_pos()
3 | excerpt: Subtracts one number from another, saturating at 0 for the minimum bound
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | api:
6 | license: community
7 | type: function
8 | toolkit: true
9 | experimental: true
10 | version:
11 | experimental: 1.8.0
12 | hyperfunction:
13 | family: saturating math
14 | type: function
15 | api_details:
16 | summary: The `saturating_sub_pos` subtracts the second number from the first, saturating at 0 and 2,147,483,647 instead of overflowing.
17 | signatures:
18 | - language: sql
19 | code: |
20 | saturating_sub_pos(
21 | x INT,
22 | y INT
23 | ) RETURNS INT
24 | parameters:
25 | required:
26 | - name: x
27 | type: INT
28 | description: An integer for `y` to subtract from
29 | - name: y
30 | type: INT
31 | description: An integer to subtract from `x`
32 | returns:
33 | - column: saturating_sub_pos
34 | type: INT
35 | description: The result of `x - y`, saturating at 0 for the minimum bound.
36 | ---
37 |
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/state_agg/intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: state_agg()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Given a system or value that switches between discrete states, track transitions
7 | between the states. For example, you can use `state_agg` to create a state
8 | of state transitions, or to calculate the durations of states. `state_agg`
9 | extends the capabilities of [`compact_state_agg`][compact_state_agg].
10 |
11 | `state_agg` is designed to work with a relatively small number of states. It
12 | might not perform well on datasets where states are mostly distinct between
13 | rows.
14 |
15 | Because `state_agg` tracks more information, it uses more memory than
16 | `compact_state_agg`. If you want to minimize memory use and don't need to query the
17 | timestamps of state transitions, consider using [`compact_state_agg`][compact_state_agg]
18 | instead.
19 |
20 | [compact_state_agg]: /api/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/state-tracking/compact_state_agg/
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/stats_agg-one-variable/examples.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: stats_agg() (one variable)
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Create a statistical aggregate to summarize daily statistical data about the
7 | variable `val1`. Use the statistical aggregate to calculate average, standard
8 | deviation, and skewness of the variable:
9 |
10 | ```sql
11 | WITH t as (
12 | SELECT
13 | time_bucket('1 day'::interval, ts) as dt,
14 | stats_agg(val1) AS stats1D
15 | FROM foo
16 | WHERE id = 'bar'
17 | GROUP BY time_bucket('1 day'::interval, ts)
18 | )
19 | SELECT
20 | average(stats1D),
21 | stddev(stats1D),
22 | skewness(stats1D)
23 | FROM t;
24 | ```
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/stats_agg-one-variable/intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: stats_agg() (one variable)
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Perform common statistical analyses, such as calculating averages and standard
7 | deviations, using this group of functions. These functions are similar to the
8 | [PostgreSQL statistical aggregates][pg-stats-aggs], but they include more
9 | features and are easier to use in [continuous aggregates][caggs] and window
10 | functions.
11 |
12 | These functions work on one-dimensional data. To work with two-dimensional data,
13 | for example to perform linear regression, see [the two-dimensional `stats_agg`
14 | functions][stats_agg-2d].
15 |
16 | [caggs]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/continuous-aggregates/
17 | [pg-stats-aggs]:
18 | https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/functions-aggregate.html#FUNCTIONS-AGGREGATE-STATISTICS-TABLE
19 | [stats_agg-2d]: /api/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/statistical-and-regression-analysis/stats_agg-two-variables/
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/stats_agg-two-variables/examples.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: stats_agg() (two variables)
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Create a statistical aggregate that summarizes daily statistical data about two
7 | variables, `val2` and `val1`, where `val2` is the dependent variable and `val1`
8 | is the independent variable. Use the statistical aggregate to calculate the
9 | average of the dependent variable and the slope of the linear-regression fit:
10 |
11 | ```sql
12 | WITH t as (
13 | SELECT
14 | time_bucket('1 day'::interval, ts) as dt,
15 | stats_agg(val2, val1) AS stats2D,
16 | FROM foo
17 | WHERE id = 'bar'
18 | GROUP BY time_bucket('1 day'::interval, ts)
19 | )
20 | SELECT
21 | average_x(stats2D),
22 | slope(stats2D)
23 | FROM t;
24 | ```
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/stats_agg-two-variables/intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: stats_agg() (two variables)
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Perform linear regression analysis, for example to calculate correlation
7 | coefficient and covariance, on two-dimensional data. You can also calculate
8 | common statistics, such as average and standard deviation, on each dimension
9 | separately. These functions are similar to the [PostgreSQL statistical
10 | aggregates][pg-stats-aggs], but they include more features and are easier to use
11 | in [continuous aggregates][caggs] and window functions. The linear regressions
12 | are based on the standard least-squares fitting method.
13 |
14 | These functions work on two-dimensional data. To work with one-dimensional data,
15 | for example to calculate the average and standard deviation of a single
16 | variable, see [the one-dimensional `stats_agg` functions][stats_agg-1d].
17 |
18 | [caggs]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/continuous-aggregates/
19 | [pg-stats-aggs]:
20 | https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/functions-aggregate.html#FUNCTIONS-AGGREGATE-STATISTICS-TABLE
21 | [stats_agg-1d]: /api/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/statistical-and-regression-analysis/stats_agg-one-variable/
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/tdigest/examples.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: tdigest()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | ### Aggregate and roll up percentile data to calculate daily percentiles
7 |
8 | Create an hourly continuous aggregate that contains a percentile aggregate:
9 |
10 | ```sql
11 | CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW foo_hourly
12 | WITH (timescaledb.continuous)
13 | AS SELECT
14 | time_bucket('1 h'::interval, ts) as bucket,
15 | tdigest(value) as tdigest
16 | FROM foo
17 | GROUP BY 1;
18 | ```
19 |
20 | You can use accessors to query directly from the continuous aggregate for
21 | hourly data. You can also roll the hourly data up into daily buckets, then
22 | calculate approximate percentiles:
23 |
24 | ```sql
25 | SELECT
26 | time_bucket('1 day'::interval, bucket) as bucket,
27 | approx_percentile(0.95, rollup(tdigest)) as p95,
28 | approx_percentile(0.99, rollup(tdigest)) as p99
29 | FROM foo_hourly
30 | GROUP BY 1;
31 | ```
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/tdigest/rollup.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: rollup()
3 | excerpt: Roll up multiple `tdigest`s
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | api:
6 | license: community
7 | type: function
8 | toolkit: true
9 | version:
10 | experimental: 0.3.0
11 | stable: 1.0.0
12 | hyperfunction:
13 | family: percentile approximation
14 | type: rollup
15 | aggregates:
16 | - tdigest()
17 | api_details:
18 | summary: >
19 | Combine multiple intermediate `tdigest` aggregates, produced by `tdigest`,
20 | into a single intermediate `tdigest` aggregate. For example, you can use
21 | `rollup` to combine `tdigest`s from 15-minute buckets into daily buckets.
22 | signatures:
23 | - language: sql
24 | code: |
25 | rollup(
26 | digest TDigest
27 | ) RETURNS TDigest
28 | parameters:
29 | required:
30 | - name: digest
31 | type: TDigest
32 | description: The `tdigest`s to roll up.
33 | returns:
34 | - column: rollup
35 | type: TDigest
36 | description: >
37 | A new `tdigest` created by combining the input `tdigests`.
38 | ---
39 |
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/time_bucket_gapfill/intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: time_bucket_gapfill()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Aggregate data by time interval, while filling in gaps of missing data.
7 |
8 | `time_bucket_gapfill` works similarly to [`time_bucket`][time_bucket], but adds
9 | gapfilling capabilities. The other functions in this group must be used in the
10 | same query as `time_bucket_gapfill`. They control how missing values are treated.
11 |
12 |
13 | `time_bucket_gapfill` must be used as a top-level expression in a query or
14 | subquery. You cannot, for example, nest `time_bucket_gapfill` in another
15 | function (such as `round(time_bucket_gapfill(...))`), or cast the result of the
16 | gapfilling call. If you need to cast, you can use `time_bucket_gapfill` in a
17 | subquery, and let the outer query do the type cast.
18 |
19 |
20 | [time_bucket]: /api/latest/hyperfunctions/time_bucket/
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/time_weight/intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | section: hyperfunction
3 | subsection: time_weight()
4 | ---
5 |
6 | Calculate time-weighted summary statistics, such as averages (means) and
7 | integrals. Time weighting is used when data is unevenly sampled over time. In
8 | that case, a straight average gives misleading results, as it biases towards
9 | more frequently sampled values.
10 |
11 | For example, a sensor might silently spend long periods of time in a steady
12 | state, and send data only when a significant change occurs. The regular mean
13 | counts the steady-state reading as only a single point, whereas a time-weighted
14 | mean accounts for the long period of time spent in the steady state. In essence,
15 | the time-weighted mean takes an integral over time, then divides by the elapsed
16 | time.
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/_hyperfunctions/uddsketch/rollup.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: rollup()
3 | excerpt: Roll up multiple `uddsketch`es
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | api:
6 | license: community
7 | type: function
8 | toolkit: true
9 | version:
10 | experimental: 0.3.0
11 | stable: 1.0.0
12 | hyperfunction:
13 | family: percentile approximation
14 | type: rollup
15 | aggregates:
16 | - uddsketch()
17 | api_details:
18 | summary: >
19 | Combine multiple intermediate `uddsketch` aggregates, produced by
20 | `uddsketch`, into a single intermediate `uddsketch` aggregate. For example,
21 | you can use `rollup` to combine `uddsketch`es from 15-minute buckets into
22 | daily buckets.
23 | signatures:
24 | - language: sql
25 | code: |
26 | rollup(
27 | sketch UddSketch
28 | ) RETURNS UddSketch
29 | parameters:
30 | required:
31 | - name: sketch
32 | type: UddSketch
33 | description: The `uddsketch` aggregates to roll up.
34 | returns:
35 | - column: rollup
36 | type: UddSketch
37 | description: >
38 | A new `uddsketch` aggregate created by combining the input `uddsketch`
39 | aggregates.
40 | ---
41 |
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/configuration.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Configuration
3 | excerpt: Use the default PostgreSQL server configuration settings for your Timescale Cloud service, or customize them as needed
4 | keywords: [configure]
5 | products: [self_hosted]
6 | ---
7 |
8 | # Configuration
9 |
10 | By default, TimescaleDB uses the default PostgreSQL server configuration
11 | settings. You can also change both PostgreSQL and TimescaleDB configuration
12 | settings yourself. For a list of settings, see the
13 | [configuration how-to guide][configuration-how-to].
14 |
15 | [configuration-how-to]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/configuration/about-configuration/
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/continuous-aggregates/hypertable_detailed_size.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: hypertable_detailed_size()
3 | excerpt: Get detailed information about disk space used by a hypertable
4 | topics: [hypertables]
5 | keywords: [hypertables, information]
6 | tags: [statistics, size, disk space]
7 | api:
8 | license: apache
9 | type: function
10 | products: [cloud, self_hosted, mst]
11 | ---
12 |
13 | import HypertableDetailedSize from "versionContent/_partials/_hypertable-detailed-size-api.mdx";
14 |
15 |
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/continuous-aggregates/hypertable_size.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: hypertable_size()
3 | excerpt: Get the total disk space used by a hypertable
4 | topics: [hypertables]
5 | keywords: [hypertables, information]
6 | tags: [disk space, size]
7 | api:
8 | license: apache
9 | type: function
10 | products: [cloud, self_hosted, mst]
11 | ---
12 |
13 | import HypertableSize from "versionContent/_partials/_hypertable-size-api.mdx";
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/continuous-aggregates/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Continuous aggregates
3 | excerpt: Timescale Cloud API reference for calculating continuous aggregates on your data. Includes SQL functions and views related to creating, altering, and dropping continuous aggregates
4 | keywords: [hypertables, chunks]
5 | products: [cloud, self_hosted, mst]
6 | ---
7 |
8 | import CaggsIntro from "versionContent/_partials/_caggs-intro.mdx";
9 |
10 | # Continuous aggregates
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 | For more information about using continuous aggregates, see the documentation in [Use Timescale][cagg-docs].
15 |
16 | [cagg-docs]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/continuous-aggregates/
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/data-retention/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Data retention
3 | excerpt: Timescale Cloud API reference for data retention. Includes SQL functions for adding and removing data retention policies that run on a schedule that you define
4 | keywords: [data retention, delete]
5 | tags: [drop]
6 | products: [cloud, self_hosted, mst]
7 | ---
8 |
9 | # Data Retention Community
10 |
11 | An intrinsic part of time-series data is that new data is accumulated and old
12 | data is rarely, if ever, updated. This means that the relevance of the data
13 | diminishes over time. It is therefore often desirable to delete old data to save
14 | disk space.
15 |
16 | With TimescaleDB, you can manually remove old chunks of data or implement
17 | policies using these APIs.
18 |
19 | For more information about creating a data retention policy, see the
20 | [data retention section][data-retention-howto].
21 |
22 | [data-retention-howto]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/data-retention/create-a-retention-policy/
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/data-retention/remove_retention_policy.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: remove_retention_policy()
3 | excerpt: Remove a retention policy from a hypertable
4 | topics: [data retention, jobs]
5 | keywords: [data retention, policies, remove]
6 | tags: [delete, drop]
7 | api:
8 | license: community
9 | type: function
10 | products: [cloud, self_hosted, mst]
11 | ---
12 |
13 | # remove_retention_policy() Community
14 |
15 | Remove a policy to drop chunks of a particular hypertable.
16 |
17 | ## Required arguments
18 |
19 | |Name|Type|Description|
20 | |---|---|---|
21 | | `relation` | REGCLASS | Name of the hypertable or continuous aggregate from which to remove the policy |
22 |
23 | ## Optional arguments
24 |
25 | |Name|Type|Description|
26 | |---|---|---|
27 | | `if_exists` | BOOLEAN | Set to true to avoid throwing an error if the policy does not exist. Defaults to false.|
28 |
29 | ## Sample usage
30 |
31 | ```sql
32 | SELECT remove_retention_policy('conditions');
33 | ```
34 |
35 | Removes the existing data retention policy for the `conditions` table.
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/days_in_month.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: days_in_month()
3 | excerpt: Calculates days in month given a timestamptz
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | keywords: [hyperfunctions, Toolkit, normalization]
6 | api:
7 | license: community
8 | type: function
9 | toolkit: true
10 | version:
11 | experimental: 1.6.0
12 | stable: 1.16.0
13 | hyperfunction:
14 | type: one-step operation
15 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
16 | ---
17 |
18 | # days_in_month()
19 |
20 | Given a timestamptz, returns how many days are in that month.
21 |
22 | ### Required arguments
23 |
24 | |Name|Type|Description|
25 | |-|-|-|
26 | |`date`|`TIMESTAMPTZ`|Timestamp to use to calculate how many days in the month|
27 |
28 | ### Sample usage
29 |
30 | Calculate how many days in the month of January 1, 2022:
31 |
32 | ```sql
33 | SELECT days_in_month('2021-01-01 00:00:00+03'::timestamptz)
34 | ```
35 |
36 | The output looks like this:
37 |
38 | ```sql
39 | days_in_month
40 | ----------------------
41 | 31
42 | ```
43 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/distributed-hypertables/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Distributed hypertables ( Sunsetted v2.14.x )
3 | excerpt: Sunsetted v2.14.x. Timescale Cloud API reference for dealing with distributed hypertables
4 | keywords: [distributed hypertables]
5 | seo:
6 | robots: noindex
7 | ---
8 |
9 | import MultiNodeDeprecation from "versionContent/_partials/_multi-node-deprecation.mdx";
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 | # Distributed hypertables ( Sunsetted v2.14.x) Community
14 |
15 | Distributed hypertables are an extension of regular hypertables, available when
16 | using a [multi-node installation][getting-started-multi-node] of TimescaleDB.
17 | Distributed hypertables provide the ability to store data chunks across multiple
18 | data nodes for better scale-out performance.
19 |
20 | Most management APIs used with regular hypertable chunks also work with distributed
21 | hypertables as documented in this section. There are a number of APIs for
22 | specifically dealing with data nodes and a special API for executing SQL commands
23 | on data nodes.
24 |
25 | [getting-started-multi-node]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/multinode-timescaledb/
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/downsample.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Downsample
3 | excerpt: Downsample data to a smaller, representative subset
4 | keywords: [downsample, hyperfunctions, Toolkit]
5 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
6 | ---
7 |
8 | # Downsample
9 |
10 | This section includes functions used to downsample data. Downsampling
11 | is used to replace a set of values with a much smaller set that is highly
12 | representative of the original data. This is particularly useful for
13 | graphing applications.
14 |
15 | Some hyperfunctions are included in the default TimescaleDB product. For
16 | additional hyperfunctions, you need to install the
17 | [Timescale Toolkit][install-toolkit] PostgreSQL extension.
18 |
19 |
24 |
25 | [install-toolkit]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/tooling/install-toolkit/
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/frequency-analysis.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Frequency analysis
3 | excerpt: Measure how often values occur in a dataset
4 | keywords: [frequency, hyperfunctions, Toolkit]
5 | ---
6 |
7 | # Frequency analysis
8 |
9 | This section includes frequency aggregate APIs, which find the most common elements out of a set of
10 | vastly more varied values.
11 |
12 | For these hyperfunctions, you need to install the [TimescaleDB Toolkit][install-toolkit] PostgreSQL extension.
13 |
14 |
19 |
20 | [install-toolkit]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/tooling/install-toolkit/
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/gapfilling-interpolation.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Gapfilling and interpolation
3 | excerpt: Fill in gaps for unevenly collected data
4 | keywords: [gapfilling, interpolate, hyperfunctions, Toolkit]
5 | ---
6 |
7 | # Gapfilling and interpolation
8 |
9 | This section contains functions related to gapfilling and interpolation. You can
10 | use a gapfilling function to create additional rows of data in any gaps,
11 | ensuring that the returned rows are in chronological order, and contiguous. For
12 | more information about gapfilling and interpolation functions, see the
13 | [hyperfunctions documentation][hyperfunctions-gapfilling].
14 |
15 | Some hyperfunctions are included in the default TimescaleDB product. For
16 | additional hyperfunctions, you need to install the
17 | [Timescale Toolkit][install-toolkit] PostgreSQL extension.
18 |
19 |
24 |
25 | [hyperfunctions-gapfilling]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/gapfilling-interpolation/
26 | [install-toolkit]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/tooling/install-toolkit/
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/hyperfunctions.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Hyperfunctions
3 | excerpt: The full list of hyperfunctions available in Timescale Cloud, with required arguments, returns, and complete use examples
4 | keywords: [hyperfunctions, Toolkit]
5 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
6 | ---
7 |
8 | # Hyperfunctions
9 |
10 | Timescale hyperfunctions are a specialized set of functions that allow you to
11 | analyze time-series data. You can use hyperfunctions to analyze anything you
12 | have stored as time-series data, including IoT devices, IT systems, marketing
13 | analytics, user behavior, financial metrics, and cryptocurrency.
14 |
15 | Some hyperfunctions are included by default in Timescale. For
16 | additional hyperfunctions, you need to install the
17 | [Timescale Toolkit][install-toolkit] PostgreSQL extension.
18 |
19 | For more information, see the [hyperfunctions
20 | documentation][hyperfunctions-howto].
21 |
22 |
25 |
26 | [hyperfunctions-howto]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/
27 | [install-toolkit]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/tooling/install-toolkit/
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/hypertable/detach_tablespaces.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: detach_tablespaces()
3 | excerpt: Detach all tablespaces from a hypertable
4 | topics: [hypertables]
5 | keywords: [tablespaces, hypertables, detach]
6 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
7 | api:
8 | license: apache
9 | type: function
10 | ---
11 |
12 | # detach_tablespaces()
13 |
14 | Detach all tablespaces from a hypertable. After issuing this command
15 | on a hypertable, it no longer has any tablespaces attached to
16 | it. New chunks are instead placed in the database's default
17 | tablespace.
18 |
19 | ## Required arguments
20 |
21 | |Name|Type|Description|
22 | |---|---|---|
23 | | `hypertable` | REGCLASS | Hypertable to detach a the tablespace from.|
24 |
25 | ## Sample usage
26 |
27 | Detach all tablespaces from the hypertable `conditions`:
28 |
29 | ```sql
30 | SELECT detach_tablespaces('conditions');
31 | ```
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/hypertable/hypertable_detailed_size.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: hypertable_detailed_size()
3 | excerpt: Get detailed information about disk space used by a hypertable
4 | topics: [hypertables]
5 | keywords: [hypertables, information]
6 | tags: [statistics, size, disk space]
7 | api:
8 | license: apache
9 | type: function
10 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
11 | ---
12 |
13 | import HypertableDetailedSize from "versionContent/_partials/_hypertable-detailed-size-api.mdx";
14 |
15 |
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/hypertable/hypertable_size.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: hypertable_size()
3 | excerpt: Get the total disk space used by a hypertable
4 | topics: [hypertables]
5 | keywords: [hypertables, information]
6 | tags: [disk space, size]
7 | api:
8 | license: apache
9 | type: function
10 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
11 | ---
12 |
13 | import HypertableSize from "versionContent/_partials/_hypertable-size-api.mdx";
14 |
15 |
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/hypertable/remove_reorder_policy.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: remove_reorder_policy()
3 | excerpt: Remove a reorder policy from a hypertable
4 | topics: [hypertables, jobs]
5 | keywords: [reorder, policies, remove]
6 | tags: [delete, drop]
7 | api:
8 | license: community
9 | type: function
10 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
11 | ---
12 |
13 | # remove_reorder_policy() Community
14 |
15 | Remove a policy to reorder a particular hypertable.
16 |
17 | ## Required arguments
18 |
19 | |Name|Type|Description|
20 | |---|---|---|
21 | | `hypertable` | REGCLASS | Name of the hypertable from which to remove the policy. |
22 |
23 | ## Optional arguments
24 |
25 | |Name|Type|Description|
26 | |---|---|---|
27 | | `if_exists` | BOOLEAN | Set to true to avoid throwing an error if the reorder_policy does not exist. A notice is issued instead. Defaults to false. |
28 |
29 | ## Sample usage
30 |
31 | ```sql
32 | SELECT remove_reorder_policy('conditions', if_exists => true);
33 | ```
34 |
35 | removes the existing reorder policy for the `conditions` table if it exists.
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/hypertable/show_tablespaces.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: show_tablespaces()
3 | excerpt: Show the tablespaces attached to a hypertable
4 | topics: [hypertables]
5 | keywords: [tablespaces, hypertables]
6 | tags: [show, get]
7 | api:
8 | license: apache
9 | type: function
10 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
11 | ---
12 |
13 | # show_tablespaces()
14 |
15 | Show the tablespaces attached to a hypertable.
16 |
17 | ## Required arguments
18 |
19 | |Name|Type|Description|
20 | |---|---|---|
21 | | `hypertable` | REGCLASS | Hypertable to show attached tablespaces for.|
22 |
23 | ## Sample usage
24 |
25 | ```sql
26 | SELECT * FROM show_tablespaces('conditions');
27 |
28 | show_tablespaces
29 | ------------------
30 | disk1
31 | disk2
32 | ```
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/hypertable/split_chunk.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: split_chunk()
3 | excerpt: Split a large chunk at a specific point in time.
4 | topics: [hypertables]
5 | keywords: [chunks, hypertables, split]
6 | api:
7 | license: community
8 | type: function
9 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
10 | ---
11 |
12 | # split_chunk() Community
13 |
14 | Split a large chunk at a specific point in time.
15 |
16 | ## Required arguments
17 |
18 | |Name|Type| Description |
19 | |---|---|----------------------------------|
20 | | `chunk` | REGCLASS | Name of the chunk to split. |
21 | | `split_at` | `TIMESTAMPTZ`| Timestamp to split the chunk at. |
22 |
23 |
24 | ## Returns
25 |
26 | This function returns void.
27 |
28 | ## Sample usage
29 |
30 | Split a chunk at a specific time:
31 |
32 | ```sql
33 | CALL split_chunk('chunk_1', split_at => '2025-03-01 00:00');
34 | ```
35 |
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: TimescaleDB API reference
3 | excerpt: See the full list of SQL functions and views that Timescale Cloud provides to help you interact with and manage your data
4 | keywords: [reference]
5 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
6 | ---
7 |
8 | # TimescaleDB API reference
9 |
10 | TimescaleDB provides many SQL functions and views to help you interact with and
11 | manage your data. See a full list below or search by keyword to find reference
12 | documentation for a specific API.
13 |
14 |
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/informational-views/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Information views
3 | excerpt: The full list of informational views available in Timescale Cloud. Informational views provide detailed information about the state of your data, hypertables, chunks, and any jobs or policies you have in place
4 | keywords: [information]
5 | tags: [statistics, background jobs, scheduled jobs, hypertables, continuous aggregates, compression]
6 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
7 | ---
8 |
9 | # Informational Views
10 | TimescaleDB makes complex database features like partitioning and data retention
11 | easy to use with our comprehensive APIs. TimescaleDB works hard to provide
12 | detailed information about the state of your data, hypertables, chunks, and any
13 | jobs or policies you have in place.
14 |
15 | These views provide the data and statistics you need to keep track of your
16 | database.
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/jobs-automation/delete_job.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: delete_job()
3 | excerpt: Delete a job from the automatic scheduler
4 | topics: [jobs]
5 | keywords: [jobs, delete]
6 | tags: [background jobs, scheduled jobs, automation framework]
7 | api:
8 | license: community
9 | type: function
10 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
11 | ---
12 |
13 | # delete_job() Community
14 |
15 | Delete a $JOB registered with the automation framework.
16 | This works for $JOBs as well as policies.
17 |
18 | If the $JOB is currently running, the process is terminated.
19 |
20 | ## Required arguments
21 |
22 | |Name|Type|Description|
23 | |---|---|---|
24 | |`job_id`| INTEGER | TimescaleDB background $JOB id |
25 |
26 | ## Sample usage
27 |
28 | Delete the $JOB with the $JOB id 1000:
29 |
30 | ```sql
31 | SELECT delete_job(1000);
32 | ```
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/jobs-automation/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Jobs
3 | excerpt: Timescale Cloud API reference for jobs. Includes SQL functions for adding, altering, deleting, and running a job
4 | keywords: [jobs]
5 | tags: [background jobs, scheduled jobs, automation framework]
6 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
7 | ---
8 |
9 | # $JOB_CAPs Community
10 |
11 | $JOB_CAPs allow you to run functions and procedures implemented in a
12 | language of your choice on a schedule within Timescale. This allows
13 | automatic periodic tasks that are not covered by existing policies and
14 | even enhancing existing policies with additional functionality.
15 |
16 | The following APIs and views allow you to manage the $JOBs that you create and
17 | get details around automatic $JOBs used by other TimescaleDB functions like
18 | continuous aggregation refresh policies and data retention policies. To view the
19 | policies that you set or the policies that already exist, see
20 | [informational views][informational-views].
21 |
22 | [informational-views]: /api/:currentVersion:/informational-views/jobs/
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/jobs-automation/run_job.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: run_job()
3 | excerpt: Manually run a job
4 | topics: [jobs]
5 | keywords: [jobs, run]
6 | tags: [background jobs, scheduled jobs, automation framework]
7 | api:
8 | license: community
9 | type: function
10 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
11 | ---
12 |
13 | # run_job() Community
14 |
15 | Run a previously registered $JOB in the current session.
16 | This works for $JOB as well as policies.
17 | Since `run_job` is implemented as stored procedure it cannot be executed
18 | inside a SELECT query but has to be executed with `CALL`.
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 | Any background worker $JOB can be run in the foreground when executed with
23 | `run_job`. You can use this with an increased log level to help debug problems.
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 | ## Required arguments
28 |
29 | |Name|Description|
30 | |---|---|
31 | |`job_id`| (INTEGER) TimescaleDB background $JOB ID |
32 |
33 | ## Sample usage
34 |
35 | Set log level shown to client to `DEBUG1` and run the $JOB with the $JOB ID 1000:
36 |
37 | ```sql
38 | SET client_min_messages TO DEBUG1;
39 | CALL run_job(1000);
40 | ```
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/month_normalize.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: month_normalize()
3 | excerpt: Normalize a monthly metric based on number of days in month
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | keywords: [hyperfunctions, Toolkit, normalization]
6 | api:
7 | license: community
8 | type: function
9 | toolkit: true
10 | version:
11 | experimental: 1.10.1
12 | stable: 1.16.0
13 | hyperfunction:
14 | type: one-step operation
15 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
16 | ---
17 |
18 | # month_normalize()
19 |
20 | Normalize the provided metric based on reference date and days.
21 |
22 | ### Required arguments
23 |
24 | |Name|Type|Description|
25 | |-|-|-|
26 | |`metric`|`float8`||
27 | |`reference_date`|`TIMESTAMPTZ`|Timestamp to normalize the metric with|
28 | |`days`|`float8`|Optional, defaults to 365.25/12 if none provided|
29 |
30 | ### Sample usage
31 |
32 | Get the normalized value for a metric of 1000, and a reference date of January
33 | 1, 2021:
34 |
35 | ```sql
36 | SELECT month_normalize(1000,'2021-01-01 00:00:00+03'::timestamptz)
37 | ```
38 |
39 | The output looks like this:
40 |
41 | ```sql
42 | month_normalize
43 | ----------------------
44 | 981.8548387096774
45 | ```
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/state-aggregates.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: State aggregates
3 | excerpt: Track time in states
4 | keywords: [states, hyperfunctions, Toolkit]
5 | ---
6 |
7 | # State aggregates
8 |
9 | This section includes functions used to measure the time spent in a relatively small number of states.
10 |
11 | For these hyperfunctions, you need to install the [TimescaleDB Toolkit][install-toolkit] PostgreSQL extension.
12 |
13 | ## Notes on compact_state_agg and state_agg
14 |
15 | `state_agg` supports all hyperfunctions that operate on CompactStateAggs, in addition
16 | to some additional functions that need a full state timeline.
17 |
18 | All `compact_state_agg` and `state_agg` hyperfunctions support both string (`TEXT`) and integer (`BIGINT`) states.
19 | You can't mix different types of states within a single aggregate.
20 | Integer states are useful when the state value is a foreign key representing a row in another table that stores all possible states.
21 |
22 | ## Hyperfunctions
23 |
24 |
29 |
30 | [install-toolkit]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/tooling/install-toolkit/
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/time-weighted-averages.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Time-weighted average functions
3 | excerpt: Calculate time-weighted averages for unevenly sampled data
4 | keywords: [time-weighted, average, hyperfunctions, Toolkit]
5 | tags: [mean]
6 | ---
7 |
8 | # Time-weighted average functions Toolkit
9 |
10 | This section contains functions related to time-weighted averages and integrals.
11 | Time weighted averages and integrals are commonly used in cases where a time
12 | series is not evenly sampled, so a traditional average gives misleading results.
13 | For more information about these functions, see the
14 | [hyperfunctions documentation][hyperfunctions-time-weight-average].
15 |
16 | Some hyperfunctions are included in the default TimescaleDB product. For
17 | additional hyperfunctions, you need to install the
18 | [Timescale Toolkit][install-toolkit] PostgreSQL extension.
19 |
20 |
25 |
26 | [hyperfunctions-time-weight-average]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/time-weighted-averages/
27 | [install-toolkit]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/tooling/install-toolkit/
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api/to_epoch.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | api_name: to_epoch()
3 | excerpt: Converts a date to a Unix epoch time
4 | topics: [hyperfunctions]
5 | keywords: [hyperfunctions, Toolkit, normalization]
6 | api:
7 | license: community
8 | type: function
9 | toolkit: true
10 | version:
11 | experimental: 1.6.0
12 | stable: 1.16.0
13 | hyperfunction:
14 | type: one-step operation
15 | ---
16 |
17 | # to_epoch()
18 |
19 | Given a timestamptz, returns the number of seconds since January 1, 1970 (the Unix epoch).
20 |
21 | ### Required arguments
22 |
23 | |Name|Type|Description|
24 | |-|-|-|
25 | |`date`|`TIMESTAMPTZ`|Timestamp to use to calculate epoch|
26 |
27 | ### Sample usage
28 |
29 | Convert a date to a Unix epoch time:
30 |
31 | ```sql
32 | SELECT to_epoch('2021-01-01 00:00:00+03'::timestamptz);
33 | ```
34 |
35 | The output looks like this:
36 |
37 | ```sql
38 | to_epoch
39 | ------------
40 | 1609448400
41 | ```
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/getting-started/page-index/page-index.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | module.exports = [
2 | {
3 | title: "Get started",
4 | href: "getting-started",
5 | defaultOpen: true,
6 | excerpt: "Get started with Timescale",
7 | children: [
8 | {
9 | title: "Try the key Timescale features",
10 | href: "try-key-features-timescale-products",
11 | excerpt:
12 | "Improve database performance with Hypertables, time bucketing, continuous aggregates, compression, data tiering, and high availability",
13 | },
14 | {
15 | title: "Start coding with Timescale",
16 | href: "start-coding-with-timescale",
17 | excerpt:
18 | "Integrate Timescale Cloud with your app using your preferred programming language",
19 | },
20 | {
21 | title: "Create a Timescale service",
22 | href: "services",
23 | excerpt: "Create a Timescale service and connect to it",
24 | },
25 | {
26 | title: "Run your queries from Timescale Console",
27 | href: "run-queries-from-console",
28 | excerpt: "Run your queries securely from inside Timescale Console",
29 | },
30 | ],
31 | },
32 | ];
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integrations/postgresql.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Integrate with PostgreSQL
3 | excerpt: Query any other PostgreSQL database or another Timescale Cloud service from your service by using PostgreSQL foreign data wrappers
4 | products: [cloud, self_hosted]
5 | keywords: [integrate, foreign data wrappers, fdw]
6 | tags: [change]
7 | ---
8 |
9 | import FDW from "versionContent/_partials/_foreign-data-wrappers.mdx";
10 |
11 | # Integrate PostgreSQL with $CLOUD_LONG
12 |
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integrations/prometheus.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Integrate Prometheus with Timescale Cloud
3 | excerpt: Prometheus is an open-source monitoring system with a modern alerting approach. Export telemetry metrics from your Timescale Cloud service to Prometheus
4 | products: [cloud, self_hosted]
5 | price_plans: [scale, enterprise]
6 | keywords: [integrate]
7 | ---
8 |
9 | import PrometheusIntegrate from "versionContent/_partials/_prometheus-integrate.mdx";
10 |
11 | # Integrate Prometheus with $CLOUD_LONG
12 |
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/lambda/regexRedirects.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | module.exports = [
2 | {
3 | from: /^\/v[0-1]\.[0-9]\/api/,
4 | to: "https://docs.timescale.com/api/latest/"
5 | },
6 | {
7 | from: /^\/v[0-1]\.[0-9]\/getting-started/,
8 | to: "https://docs.timescale.com/getting-started/latest/"
9 | },
10 | {
11 | from: /^\/use-timescale\/latest\/integrations(\/.*)?$/,
12 | to: (match) =>
13 | `https://docs.timescale.com/integrations/latest${match[1] || ""}`
14 | },
15 | {
16 | from: /^\/quick-start\/latest\/(\/.*)?$/,
17 | to: `https://docs.timescale.com/getting-started/latest/start-coding-with-timescale/`
18 | },
19 | {
20 | from: /^\/v[0-1]\.[0-9]\/tutorials/,
21 | to: "https://docs.timescale.com/tutorials/latest/"
22 | }
23 | ];
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mst/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Managed Service for TimescaleDB
3 | excerpt: Managed Service for TimescaleDB is TimescaleDB hosted on Azure and GCP, offered in partnership with Aiven. Learn all about creating an account and running services in it
4 | products: [mst]
5 | ---
6 |
7 | import MSTIntro from "versionContent/_partials/_mst-intro.mdx";
8 | import CloudMSTComparison from "versionContent/_partials/_cloud-mst-comparison.mdx";
9 |
10 | # Managed Service for TimescaleDB
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mst/integrations/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Integrations for Managed Service for TimescaleDB
3 | excerpt: Integrate Managed Service for TimescaleDB with other services
4 | products: [mst]
5 | ---
6 |
7 | # Integrations for Managed Service for TimescaleDB
8 |
9 | Managed Service for TimescaleDB integrates with the other tools you are already
10 | using. You can combine your Managed Service for TimescaleDB
11 | services with third party tools and build a complete cloud data platform.
12 |
13 | You can integrate Managed Service for TimescaleDB with:
14 |
15 | * [Grafana]
16 | * [Loggly]
17 | * [Datadog]
18 | * [Prometheus]
19 | * Syslog
20 | * External Elasticsearch
21 | * External OpenSearch
22 |
23 | [Grafana]: /mst/:currentVersion:/integrations/grafana-mst/
24 | [Loggly]: /mst/:currentVersion:/integrations/logging/
25 | [Datadog]: /mst/:currentVersion:/integrations/metrics-datadog/
26 | [Prometheus]: /mst/:currentVersion:/integrations/prometheus-mst/
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mst/migrate-to-cloud.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Migrate your Managed Service for TimescaleDB data to Timescale
3 | excerpt: Migrate a service in Managed Service for TimescaleDB to Timescale Cloud
4 | products: [mst, cloud]
5 | keywords: [data migration]
6 | ---
7 |
8 | # Migrate your Managed Service for TimescaleDB data to Timescale
9 |
10 | If you prefer Timescale's features, you can migrate your data from Managed
11 | Service for TimescaleDB to Timescale using the PostgreSQL `pg_backup` and
12 | `pg_restore` tools. To learn more about migration, see the
13 | [migration section][migration].
14 |
15 | [migration]: /migrate/:currentVersion:/
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/navigation/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Find a docs page
2 |
3 | Looking for information on something specific? There are several ways to find
4 | it:
5 |
6 | 1. For help with the [Cloud Console][cloud-console], try the [Cloud Console
7 | index][cloud-console-index].
8 | 1. For help on a specific topic, try browsing by [keyword][keywords].
9 | 1. Or try the [full search][search], which also returns results from the
10 | Timescale blog and forum.
11 |
12 | [cloud-console]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/
13 | [cloud-console-index]: /console/
14 | [keywords]: /keywords/
15 | [search]: /search/
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/navigation/page-index/page-index.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | module.exports = [
2 | {
3 | title: "Find a docs page",
4 | href: "navigation",
5 | excerpt: "Help tools for finding a docs page",
6 | filePath: "index.md",
7 | children: [
8 | {
9 | title: "Find by Console location",
10 | overrideHref: "/console",
11 | excerpt: "Browse topics by Timescale console location.",
12 | type: "placeholder",
13 | },
14 | {
15 | title: "Find by keyword",
16 | overrideHref: "/keywords",
17 | excerpt: "Browse topics by keywords.",
18 | type: "placeholder",
19 | },
20 | {
21 | title: "Full search",
22 | overrideHref: "/search/?query=timescale",
23 | excerpt: "Search Timescale docs, blog, and forum.",
24 | type: "placeholder",
25 | },
26 | ],
27 | },
28 | ];
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/node_modules/.yarn-integrity:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "systemParams": "darwin-arm64-93",
3 | "modulesFolders": [],
4 | "flags": [],
5 | "linkedModules": [
6 | "@petraui/icons"
7 | ],
8 | "topLevelPatterns": [],
9 | "lockfileEntries": {},
10 | "files": [],
11 | "artifacts": {}
12 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/package-lock.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "name": "timescale-docs",
3 | "version": "1.0.0",
4 | "lockfileVersion": 3,
5 | "requires": true,
6 | "packages": {
7 | "": {
8 | "name": "timescale-docs",
9 | "version": "1.0.0"
10 | }
11 | }
12 | }
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/package.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "name": "timescale-docs",
3 | "version": "1.0.0",
4 | "description": "Documentation for Timescale and related products",
5 | "scripts": {
6 | "template:hyperfunction": "node ./.helper-scripts/mkdir-hyperfn.mjs"
7 | }
8 | }
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/self-hosted/backup-and-restore/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Backup and restore
3 | excerpt: Back up and restore your TimescaleDB instance - use logical backup with `pg_dump` and `pg_restore` or physical backup with `pg_basebackup`
4 | products: [self_hosted]
5 | keywords: [backups, restore]
6 | tags: [recovery]
7 | ---
8 |
9 | import ConsiderCloud from "versionContent/_partials/_consider-cloud.mdx";
10 |
11 | # Backup and restore
12 |
13 | TimescaleDB takes advantage of the reliable backup and restore functionality
14 | provided by PostgreSQL. There are a few different mechanisms you can use to
15 | backup your self-hosted TimescaleDB database:
16 |
17 | * [Logical backup][logical-backups] with pg_dump and pg_restore.
18 | * [Physical backup][physical-backups] with `pg_basebackup` or another tool.
19 | * _DEPRECATED_ [Ongoing physical backups][ongoing-physical-backups] using write-ahead log
20 | (WAL) archiving.
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 | [ongoing-physical-backups]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/backup-and-restore/docker-and-wale/
25 | [physical-backups]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/backup-and-restore/physical/
26 | [logical-backups]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/backup-and-restore/logical-backup/
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/self-hosted/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Self-hosted TimescaleDB
3 | excerpt: TimescaleDB is an extension for PostgreSQL that powers real-time analytics on time-series and event data, while also increasing ingest, query, and storage performance. Learn more about how to install and use it
4 | products: [self_hosted]
5 | tags: [self-hosted, about]
6 | ---
7 |
8 | import CTA from "versionContent/_partials/_selfhosted_cta.mdx";
9 | import TimescaleDB from "versionContent/_partials/_timescaledb.mdx";
10 |
11 | # Self-hosted TimescaleDB
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 | Self-hosted TimescaleDB is community supported. For additional help
17 | check out the friendly [Timescale community][community].
18 |
19 | If you'd prefer to pay for support then check out our [self-managed support][support].
20 |
21 | [self-hosted-install]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/install/
22 | [community]: https://www.timescale.com/community/
23 | [support]: https://www.timescale.com/self-managed-support/
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/self-hosted/install/self-hosted.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Install self-hosted TimescaleDB
3 | excerpt: Install a self-hosted, self-managed instance of TimescaleDB
4 | products: [self_hosted]
5 | keywords: [installation, self-hosted]
6 | ---
7 |
8 |
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/self-hosted/tooling/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Additional tooling
3 | excerpt: Get the most out of TimescaleDB with open-source tools that help you perform common tasks
4 | products: [self_hosted]
5 | ---
6 |
7 | # Additional tooling
8 |
9 | Get the most from TimescaleDB with open source tools that help you perform
10 | common tasks.
11 |
12 | * Automatically configure your TimescaleDB instance with
13 | [`timescaledb-tune`][tstune]
14 | * Install [TimescaleDB Toolkit][tstoolkit] to access more hyperfunctions and
15 | function pipelines
16 |
17 | [tscopy]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/ingest-data/about-timescaledb-parallel-copy
18 | [tstune]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/tooling/about-timescaledb-tune/
19 | [tstoolkit]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/tooling/install-toolkit/
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/self-hosted/uninstall/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Uninstall TimescaleDB
3 | excerpt: Uninstall TimescaleDB without uninstalling PostgreSQL
4 | products: [self_hosted]
5 | keywords: [Uninstall]
6 | ---
7 |
8 | # Uninstall TimescaleDB
9 |
10 | If you want to uninstall TimescaleDB because it does not meet your requirements,
11 | you can uninstall it without having to uninstall PostgreSQL.
12 |
13 | * [Learn how to uninstall][uninstall-timescaledb] TimescaleDB in macOS
14 |
15 | [uninstall-timescaledb]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/uninstall/
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorials/OLD_grafana/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Getting started with Grafana and TimescaleDB
3 | excerpt: Use Grafana to visualize time-series data stored in TimescaleDB
4 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
5 | keywords: [Grafana, visualizations, analytics]
6 | ---
7 |
8 | # Getting Started with Grafana and TimescaleDB
9 |
10 | [Grafana][grafana-website] is an open source analytics and monitoring tool that
11 | you can use visualize time-series data. Use these tutorials to:
12 |
13 | * Set up TimescaleDB and Grafana.
14 | * Create a Grafana dashboard and panel to visualize data in TimescaleDB.
15 | * Visualize Geospatial data in Grafana.
16 | * Use Grafana variables to filter and customize your visualizations.
17 | * Visualize missing data in Grafana using TimescaleDB features.
18 | * Set up Grafana alerts for Slack, PagerDuty, and other tools.
19 |
20 | ## Before you begin
21 |
22 | To complete this tutorial, you need at least some knowledge of SQL (structured
23 | query language). The tutorial walks you through each SQL command, but it is
24 | helpful if you've seen SQL before.
25 |
26 | [grafana-website]: https://www.grafana.com
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorials/OLD_grafana/visualizations/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Grafana visualizations
3 | excerpt: Learn how to create Grafana visualizations of time-series data
4 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
5 | keywords: [Grafana, visualization, analytics]
6 | ---
7 |
8 | # Grafana visualizations
9 |
10 | Learn how to create Grafana visualizations of time-series data.
11 |
12 | * Use time-series to graph data points in timed order.
13 | * Use histograms to graph the distribution of values in a set of
14 | data.
15 | * Use candlesticks to graph the open, high, low, and close
16 | values of financial assets.
17 | * Use bar charts to compare datasets between different categories.
18 | * Use pie charts to compare groups or categorized data.
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorials/_template/_advanced-tutorial.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Verb the widget tutorial - Advanced steps
3 | excerpt: Advanced steps to verb your widgets to achieve an outcome using the tool
4 | keywords: [noun, verb, tutorial]
5 | tags: [noun, noun]
6 | ---
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 | # Advanced steps
11 |
12 | Use this section to provide additional or extra things that readers can try with
13 | the dataset to further their understanding of the underlying topic.
14 |
15 | ## The first advanced step
16 |
17 | This should be the simplest of the advanced steps. Start by explaining which
18 | question the query answers. Then explain how the query is constructed, then
19 | provide the query in a code block.
20 |
21 | Provide example results of the query, using either a code block or, if more
22 | appropriate, an image.
23 |
24 | ## The second advanced step
25 |
26 | Continue to build on the first query you presented, providing more information,
27 | explaining the query, and continuing to explain which questions are being
28 | answered. Repeat as required.
29 |
30 | Include any reference-style links at the bottom of the page.
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorials/_template/_query-template.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Verb the widget tutorial - query the data
3 | excerpt: Query data to verb your widgets to achieve an outcome using the tool
4 | keywords: [noun, verb, tutorial]
5 | tags: [noun, noun]
6 | ---
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 | # Query the data
11 |
12 | Use this section to talk about the queries that readers can do on the dataset.
13 | Make sure you reference which questions are being answered by the queries.
14 |
15 | ## The first query
16 |
17 | This should be the simplest query. Start by explaining which question the query
18 | answers. Then explain how the query is constructed, then provide the query in a
19 | code block.
20 |
21 | Provide example results of the query, using either a code block or, if more
22 | appropriate, an image.
23 |
24 | ## The second query
25 |
26 | Continue to build on the first query you presented, providing more information,
27 | explaining the query, and continuing to explain which questions are being
28 | answered. Repeat as required.
29 |
30 | Include any reference-style links at the bottom of the page.
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorials/blockchain-analyze/blockchain-dataset.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Analyze the Bitcoin blockchain - set up dataset
3 | excerpt: Ingest and set up a sample dataset to run analytical queries on Bitcoin blockchain transactions with Timescale Cloud
4 | products: [cloud, self_hosted, mst]
5 | keywords: [intermediate, crypto, blockchain, Bitcoin, finance, analytics]
6 | layout_components: [next_prev_large]
7 | content_group: Analyze the Bitcoin blockchain
8 | ---
9 |
10 | import IngestData from "versionContent/_partials/_use-case-setup-blockchain-dataset.mdx";
11 | import GrafanaConnect from "versionContent/_partials/_grafana-connect.mdx";
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 | [satoshi-def]: https://www.pcmag.com/encyclopedia/term/satoshi
20 | [coinbase-def]: https://www.pcmag.com/encyclopedia/term/coinbase-transaction
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorials/blockchain-query/blockchain-dataset.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Query the Bitcoin blockchain - set up dataset
3 | excerpt: Ingest and set up a sample blockchain dataset to practice running analytical queries on it in Timescale Cloud
4 | products: [cloud, self_hosted, mst]
5 | keywords: [beginner, crypto, blockchain, Bitcoin, finance, analytics]
6 | layout_components: [next_prev_large]
7 | content_group: Query the Bitcoin blockchain
8 | ---
9 |
10 | import IngestData from "versionContent/_partials/_use-case-setup-blockchain-dataset.mdx";
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorials/cookbook.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Timescale cookbook
3 | excerpt: Browse code examples from the Timescale Cloud community that resolve common issues and provide solutions for non-standard tasks
4 | products: [cloud, self_hosted, mst]
5 | ---
6 |
7 | import IntegrationPrereqs from "versionContent/_partials/_integration-prereqs.mdx";
8 | import Hypertables from "versionContent/_partials/_cookbook-hypertables.mdx";
9 | import IOT from "versionContent/_partials/_cookbook-iot.mdx";
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 | # Timescale community cookbook
14 |
15 | This page contains suggestions from the [TimescaleDB Community](https://timescaledb.slack.com/) about how to resolve
16 | common issues. Use these code examples as guidance to work with your own data.
17 |
18 |
19 | ## Prerequisites
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 | [create-a-service]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/services/#create-a-timescale-cloud-service
30 | [connect-to-service]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/run-queries-from-console/
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/use-timescale/backup-restore/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Backup and restore
3 | excerpt: Timescale Cloud handles database backup and recovery for your services automatically, using the pgBackRest tool. Need more control? Set up point-in-time-recovery in Timescale Console
4 | products: [cloud]
5 | keywords: [backup, restore, pitr, point-in-time recovery]
6 | tags: [backup, restore, recovery, pitr]
7 | cloud_ui:
8 | path:
9 | - [services, :serviceId, operations, management]
10 | ---
11 |
12 | # Backup, restore, and PITR
13 |
14 | Timescale automatically handles backup and restore for all
15 | services using the `pgBackRest` tool. You don't need to perform
16 | backups for your Timescale service manually.
17 |
18 | Timescale also offers self-initiated point-in-time recovery (PITR) in Console.
19 |
20 | * [Backup and restore][backup-recovery] in Timescale
21 | * Performing a [point-in-time recovery][pitr] in Timescale
22 |
23 | [backup-recovery]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/backup-restore/backup-restore-cloud/
24 | [pitr]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/backup-restore/point-in-time-recovery/
25 |
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/use-timescale/compression/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Compression
3 | excerpt: With data compression, you can achieve a significant improvement in the performance of your analytical queries. Learn how to enable and benefit from data compression in Timescale Cloud
4 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
5 | keywords: [compression, hypertables]
6 | ---
7 | import Deprecated2180 from "versionContent/_partials/_deprecated_2_18_0.mdx";
8 | import UsageBasedStorage from "versionContent/_partials/_usage-based-storage-intro.mdx";
9 |
10 | # Compression (Replaced by [Hypercore][hypercore])
11 |
12 | Replaced by hypercore.
13 |
14 | Time-series data can be compressed to reduce the amount of storage required, and
15 | increase the speed of some queries. This is a cornerstone feature of
16 | Timescale. When new data is added to your database, it is in the form of
17 | uncompressed rows. Timescale uses a built-in job scheduler to convert this
18 | data to the form of compressed columns. This occurs across chunks of Timescale
19 | hypertables.
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 | [hypercore]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/hypercore/
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/use-timescale/configuration/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Configuration
3 | excerpt: Timescale Cloud includes additional configurable settings on top of standard PostgreSQL configuration. Learn what you can configure and how
4 | products: [cloud]
5 | keywords: [configuration, settings]
6 | ---
7 |
8 | # Configuration
9 |
10 | By default, Timescale uses the standard PostgreSQL server configuration
11 | settings. However, in some cases, these settings are not appropriate, especially
12 | if you have larger servers that use more hardware resources such as CPU, memory,
13 | and storage.
14 |
15 | This section contains information about tuning your Timescale database.
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/use-timescale/hypercore/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Hypercore
3 | excerpt: The Timescale hybrid row-columnar storage engine for real-time analytics, powered by time-series data
4 | products: [cloud, self_hosted]
5 | keywords: [hypercore, hypertable, compression, row-columnar storage]
6 | ---
7 |
8 | import UsageBasedStorage from "versionContent/_partials/_usage-based-storage-intro.mdx";
9 | import HypercoreIntro from "versionContent/_partials/_hypercore-intro.mdx";
10 |
11 | # $HYPERCORE_CAP
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 | In $CLOUD_LONG you only pay for what you use. Data converted to the $COLUMNSTORE is compressed, which
16 | immediately translates into cost savings.
17 |
18 | This section shows you how to:
19 |
20 | * [Optimize your data for real-time analytics][setup-hypercore]
21 | * [Improve query and upsert performance using secondary indexes][secondary-indexes]
22 |
23 | [setup-hypercore]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/hypercore/real-time-analytics-in-hypercore/
24 | [modify-data-in-hypercore]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/hypercore/modify-data-in-hypercore/
25 | [secondary-indexes]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/hypercore/secondary-indexes/
26 |
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/use-timescale/hyperfunctions/locf.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Last observation carried forward
3 | excerpt: Fill gaps in your data by carrying the last observation forward
4 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
5 | keywords: [hyperfunctions, Toolkit, gapfilling, interpolate, locf]
6 | ---
7 |
8 | # Last observation carried forward
9 |
10 | Last observation carried forward (LOCF) is a form of linear interpolation used
11 | to fill gaps in your data. It takes the last known value and uses it as a
12 | replacement for the missing data.
13 |
14 | For more information about gapfilling and interpolation API calls, see the
15 | [hyperfunction API documentation][hyperfunctions-api-gapfilling].
16 |
17 | [hyperfunctions-api-gapfilling]: /api/:currentVersion:/hyperfunctions/gapfilling/time_bucket_gapfill/
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/use-timescale/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Use Timescale
3 | excerpt: Create hypertables and continuous aggregates, compress your data, manage your projects, and use other features available in Timescale Cloud
4 | ---
5 |
6 | # Use Timescale
7 |
8 | This section contains information about using Timescale. If you're not sure how
9 | to find the information you need, try the [Find a docs page][find-docs] section.
10 |
11 | [find-docs]: /navigation/:currentVersion:/
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/use-timescale/ingest-data/ingest-kafka.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Ingest data using Kafka
3 | excerpt: Ingest data into your Timescale Cloud service using the PostgreSQL Kafka connector
4 | products: [cloud, self_hosted]
5 | keywords: [ingest, Kafka]
6 | tags: [insert]
7 | ---
8 |
9 | # PostgreSQL Kafka connector
10 |
11 | You can ingest data into a $SERVICE_LONG using the Kafka Connect
12 | [JDBC sink connector with a JDBC driver][postgresql-connector-kafka].
13 | To provide fault tolerance, and to ensure the connectors are running and continuously
14 | keeping up with changes in the database, you can distribute Kafka Connect.
15 |
16 |
17 | [postgresql-connector-kafka]: https://docs.confluent.io/kafka-connectors/jdbc/current/sink-connector/overview.html
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/use-timescale/limitations.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Limitations
3 | excerpt: Timescale Cloud features come with a few limitations that we are constantly working to remove. See the current and regularly updated list of limitations
4 | keywords: [hypertables, distributed hypertables]
5 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
6 | ---
7 |
8 | # Limitations
9 |
10 | While Timescale generally offers capabilities that go beyond what
11 | PostgreSQL offers, there are some limitations to using hypertables,
12 | and, in particular, distributed hypertables. This section documents
13 | the common limitations when using both regular and distributed
14 | hypertables.
15 |
16 | ## Hypertable limitations
17 |
18 | * Time dimensions (columns) used for partitioning cannot have NULL values.
19 | * Unique indexes must include all columns that are partitioning
20 | dimensions.
21 | * `UPDATE` statements that move values between partitions (chunks) are not
22 | supported. This includes upserts (`INSERT ... ON CONFLICT UPDATE`).
23 | * Foreign key constraints from a hypertable referencing another hypertable are not supported.
24 |
25 |
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/use-timescale/metrics-logging/metrics-to-prometheus.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Export metrics to Prometheus
3 | excerpt: Prometheus is an open-source monitoring system. Learn to integrate Prometheus with Timescale Cloud and export telemetry metrics of your service
4 | products: [cloud, self_hosted]
5 | price_plans: [scale, enterprise]
6 | keywords: [integration, metrics, Prometheus, alerting]
7 | tags: [telemetry, monitor]
8 | cloud_ui:
9 | path:
10 | - [integrations]
11 | - [services, :serviceId, operations, integrations]
12 | ---
13 |
14 | import PrometheusIntegrate from "versionContent/_partials/_prometheus-integrate.mdx";
15 |
16 | # Export metrics to Prometheus
17 |
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/use-timescale/metrics-logging/service-logs.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Service logs
3 | excerpt: Timescale Cloud enables you to view and download the 500 most recent entries in your service logs. Learn where to find them in Timescale Console
4 | products: [cloud]
5 | keywords: [logs, services]
6 | cloud_ui:
7 | path:
8 | - [services, :serviceId, logs]
9 | ---
10 |
11 | # Service logs
12 |
13 | From the `Services` page, click the service you are interested in and navigate
14 | to `Monitoring` > `Logs` tab. This section contains your service's logging data. Filter logs by type, date, and time.
15 |
16 | 
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/use-timescale/schema-management/foreign-data-wrappers.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Foreign data wrappers
3 | excerpt: Query other Timescale Cloud services or external PostgreSQL databases by using PostgreSQL foreign data wrappers
4 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
5 | keywords: [hypertables, schemas, alter]
6 | tags: [change]
7 | ---
8 |
9 | import FDW from "versionContent/_partials/_foreign-data-wrappers.mdx";
10 |
11 | # Foreign data wrappers
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/use-timescale/time-buckets/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: Time buckets
3 | excerpt: Data aggregation is a crucial part of real-time data analysis. Timescale Cloud time buckets enable you to aggregate data in hypertables by time interval. Learn to create and use time buckets in your service
4 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
5 | keywords: [time buckets]
6 | ---
7 |
8 | # Time buckets
9 |
10 | Time buckets enable you to aggregate data in [hypertables][create-hypertable] by time interval. For example, you can
11 | group data into 5-minute, 1-hour, and 3-day buckets to calculate summary values.
12 |
13 | * [Learn how time buckets work][about-time-buckets] in $CLOUD_LONG
14 | * [Use time buckets][use-time-buckets] to aggregate data
15 |
16 | [about-time-buckets]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/time-buckets/about-time-buckets/
17 | [use-time-buckets]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/time-buckets/use-time-buckets/
18 | [create-hypertable]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/hypertables/hypertable-crud/#create-a-hypertable
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/use-timescale/write-data/about-writing-data.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | title: About writing data
3 | excerpt: Writing data to Timescale Cloud services works the same way as writing data to regular PostgreSQL tables. Learn the basics of inserting, updating, upserting, and deleting data in your services using SQL
4 | products: [cloud, mst, self_hosted]
5 | keywords: [ingest]
6 | tags: [write]
7 | ---
8 |
9 | # About writing data
10 |
11 | Timescale supports writing data in the same way as PostgreSQL, using `INSERT`,
12 | `UPDATE`, `INSERT ... ON CONFLICT`, and `DELETE`.
13 |
14 |
15 | $CLOUD_LONG is optimized for running real-time analytics workloads on time-series data. For this reason, hypertables are optimized for
16 | inserts to the most recent time intervals. Inserting data with recent time
17 | values gives
18 | [excellent performance](https://www.timescale.com/blog/timescaledb-vs-6a696248104e/).
19 | However, if you need to make frequent updates to older time intervals, you
20 | might see lower write throughput.
21 |
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/yarn.lock:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # THIS IS AN AUTOGENERATED FILE. DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE DIRECTLY.
2 | # yarn lockfile v1
3 |
4 |
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------