├── models
├── __init__.py
├── vgg.py
├── wide_resnet.py
└── preresnet.py
├── .gitignore
├── LICENSE
├── utils.py
├── train.py
└── README.md
/models/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .preresnet import *
2 | from .vgg import *
3 | from .wide_resnet import *
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
2 | __pycache__/
3 | *.py[cod]
4 | *$py.class
5 |
6 | # C extensions
7 | *.so
8 |
9 | # Distribution / packaging
10 | .Python
11 | env/
12 | build/
13 | develop-eggs/
14 | dist/
15 | downloads/
16 | eggs/
17 | .eggs/
18 | lib/
19 | lib64/
20 | parts/
21 | sdist/
22 | var/
23 | *.egg-info/
24 | .installed.cfg
25 | *.egg
26 |
27 | # PyInstaller
28 | # Usually these files are written by a python script from a template
29 | # before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it.
30 | *.manifest
31 | *.spec
32 |
33 | # Installer images
34 | pip-log.txt
35 | pip-delete-this-directory.txt
36 |
37 | # Unit test / coverage reports
38 | htmlcov/
39 | .tox/
40 | .coverage
41 | .coverage.*
42 | .cache
43 | nosetests.xml
44 | coverage.xml
45 | *,cover
46 | .hypothesis/
47 |
48 | # Translations
49 | *.mo
50 | *.pot
51 |
52 | # Django stuff:
53 | *.log
54 |
55 | # Sphinx documentation
56 | docs/_build/
57 |
58 | # PyBuilder
59 | target/
60 |
61 | #Ipython Notebook
62 | .ipynb_checkpoints
63 |
64 | #Archives
65 | *.gz
66 |
67 | #Idea
68 | .idea*
69 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | BSD 2-Clause License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2018, Pavel Izmailov, Dmitrii Podoprikhin, Timur Garipov, Dmitry Vetrov, Andrew Gordon Wilson
4 | All rights reserved.
5 |
6 | Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
7 | modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
8 |
9 | * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this
10 | list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
11 |
12 | * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
13 | this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
14 | and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
15 |
16 | THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"
17 | AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
18 | IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
19 | DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE
20 | FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
21 | DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
22 | SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
23 | CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY,
24 | OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
25 | OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/vgg.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | VGG model definition
3 | ported from https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/master/torchvision/models/vgg.py
4 | """
5 |
6 | import math
7 | import torch.nn as nn
8 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
9 |
10 | __all__ = ['VGG16', 'VGG16BN', 'VGG19', 'VGG19BN']
11 |
12 |
13 | def make_layers(cfg, batch_norm=False):
14 | layers = list()
15 | in_channels = 3
16 | for v in cfg:
17 | if v == 'M':
18 | layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)]
19 | else:
20 | conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, v, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
21 | if batch_norm:
22 | layers += [conv2d, nn.BatchNorm2d(v), nn.ReLU(inplace=True)]
23 | else:
24 | layers += [conv2d, nn.ReLU(inplace=True)]
25 | in_channels = v
26 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
27 |
28 |
29 | cfg = {
30 | 16: [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
31 | 19: [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M',
32 | 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
33 | }
34 |
35 |
36 | class VGG(nn.Module):
37 | def __init__(self, num_classes=10, depth=16, batch_norm=False):
38 | super(VGG, self).__init__()
39 | self.features = make_layers(cfg[depth], batch_norm)
40 | self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
41 | nn.Dropout(),
42 | nn.Linear(512, 512),
43 | nn.ReLU(True),
44 | nn.Dropout(),
45 | nn.Linear(512, 512),
46 | nn.ReLU(True),
47 | nn.Linear(512, num_classes),
48 | )
49 |
50 | for m in self.modules():
51 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
52 | n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
53 | m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
54 | m.bias.data.zero_()
55 |
56 | def forward(self, x):
57 | x = self.features(x)
58 | x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
59 | x = self.classifier(x)
60 | return x
61 |
62 |
63 | class Base:
64 | base = VGG
65 | args = list()
66 | kwargs = dict()
67 | transform_train = transforms.Compose([
68 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
69 | transforms.RandomCrop(32, padding=4),
70 | transforms.ToTensor(),
71 | transforms.Normalize((0.485, 0.456, 0.406), (0.229, 0.224, 0.225))
72 | ])
73 |
74 | transform_test = transforms.Compose([
75 | transforms.ToTensor(),
76 | transforms.Normalize((0.485, 0.456, 0.406), (0.229, 0.224, 0.225))
77 | ])
78 |
79 |
80 | class VGG16(Base):
81 | pass
82 |
83 |
84 | class VGG16BN(Base):
85 | kwargs = {'batch_norm': True}
86 |
87 |
88 | class VGG19(Base):
89 | kwargs = {'depth': 19}
90 |
91 |
92 | class VGG19BN(Base):
93 | kwargs = {'depth': 19, 'batch_norm': True}
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/wide_resnet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | WideResNet model definition
3 | ported from https://github.com/meliketoy/wide-resnet.pytorch/blob/master/networks/wide_resnet.py
4 | """
5 |
6 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
7 | import torch.nn as nn
8 | import torch.nn.init as init
9 | import torch.nn.functional as F
10 | import math
11 |
12 | __all__ = ['WideResNet28x10']
13 |
14 |
15 | def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
16 | return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=True)
17 |
18 |
19 | def conv_init(m):
20 | classname = m.__class__.__name__
21 | if classname.find('Conv') != -1:
22 | init.xavier_uniform(m.weight, gain=math.sqrt(2))
23 | init.constant(m.bias, 0)
24 | elif classname.find('BatchNorm') != -1:
25 | init.constant(m.weight, 1)
26 | init.constant(m.bias, 0)
27 |
28 |
29 | class WideBasic(nn.Module):
30 | def __init__(self, in_planes, planes, dropout_rate, stride=1):
31 | super(WideBasic, self).__init__()
32 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
33 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, planes, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=True)
34 | self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate)
35 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
36 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=True)
37 |
38 | self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
39 | if stride != 1 or in_planes != planes:
40 | self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
41 | nn.Conv2d(in_planes, planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=True),
42 | )
43 |
44 | def forward(self, x):
45 | out = self.dropout(self.conv1(F.relu(self.bn1(x))))
46 | out = self.conv2(F.relu(self.bn2(out)))
47 | out += self.shortcut(x)
48 |
49 | return out
50 |
51 |
52 | class WideResNet(nn.Module):
53 | def __init__(self, num_classes=10, depth=28, widen_factor=10, dropout_rate=0.):
54 | super(WideResNet, self).__init__()
55 | self.in_planes = 16
56 |
57 | assert ((depth - 4) % 6 == 0), 'Wide-resnet depth should be 6n+4'
58 | n = (depth - 4) / 6
59 | k = widen_factor
60 |
61 | nstages = [16, 16 * k, 32 * k, 64 * k]
62 |
63 | self.conv1 = conv3x3(3, nstages[0])
64 | self.layer1 = self._wide_layer(WideBasic, nstages[1], n, dropout_rate, stride=1)
65 | self.layer2 = self._wide_layer(WideBasic, nstages[2], n, dropout_rate, stride=2)
66 | self.layer3 = self._wide_layer(WideBasic, nstages[3], n, dropout_rate, stride=2)
67 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(nstages[3], momentum=0.9)
68 | self.linear = nn.Linear(nstages[3], num_classes)
69 |
70 | def _wide_layer(self, block, planes, num_blocks, dropout_rate, stride):
71 | strides = [stride] + [1] * int(num_blocks - 1)
72 | layers = []
73 |
74 | for stride in strides:
75 | layers.append(block(self.in_planes, planes, dropout_rate, stride))
76 | self.in_planes = planes
77 |
78 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
79 |
80 | def forward(self, x):
81 | out = self.conv1(x)
82 | out = self.layer1(out)
83 | out = self.layer2(out)
84 | out = self.layer3(out)
85 | out = F.relu(self.bn1(out))
86 | out = F.avg_pool2d(out, 8)
87 | out = out.view(out.size(0), -1)
88 | out = self.linear(out)
89 |
90 | return out
91 |
92 |
93 | class WideResNet28x10:
94 | base = WideResNet
95 | args = list()
96 | kwargs = {'depth': 28, 'widen_factor': 10}
97 | transform_train = transforms.Compose([
98 | transforms.RandomCrop(32, padding=4),
99 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
100 | transforms.ToTensor(),
101 | transforms.Normalize((0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465), (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010)),
102 | ])
103 | transform_test = transforms.Compose([
104 | transforms.ToTensor(),
105 | transforms.Normalize((0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465), (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010)),
106 | ])
107 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import torch
3 |
4 |
5 | def adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, lr):
6 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
7 | param_group['lr'] = lr
8 | return lr
9 |
10 |
11 | def save_checkpoint(dir, epoch, **kwargs):
12 | state = {
13 | 'epoch': epoch,
14 | }
15 | state.update(kwargs)
16 | filepath = os.path.join(dir, 'checkpoint-%d.pt' % epoch)
17 | torch.save(state, filepath)
18 |
19 |
20 | def train_epoch(loader, model, criterion, optimizer):
21 | loss_sum = 0.0
22 | correct = 0.0
23 |
24 | model.train()
25 |
26 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(loader):
27 | input = input.cuda(async=True)
28 | target = target.cuda(async=True)
29 | input_var = torch.autograd.Variable(input)
30 | target_var = torch.autograd.Variable(target)
31 |
32 | output = model(input_var)
33 | loss = criterion(output, target_var)
34 |
35 | optimizer.zero_grad()
36 | loss.backward()
37 | optimizer.step()
38 |
39 | loss_sum += loss.data[0] * input.size(0)
40 | pred = output.data.max(1, keepdim=True)[1]
41 | correct += pred.eq(target_var.data.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
42 |
43 | return {
44 | 'loss': loss_sum / len(loader.dataset),
45 | 'accuracy': correct / len(loader.dataset) * 100.0,
46 | }
47 |
48 |
49 | def eval(loader, model, criterion):
50 | loss_sum = 0.0
51 | correct = 0.0
52 |
53 | model.eval()
54 |
55 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(loader):
56 | input = input.cuda(async=True)
57 | target = target.cuda(async=True)
58 | input_var = torch.autograd.Variable(input)
59 | target_var = torch.autograd.Variable(target)
60 |
61 | output = model(input_var)
62 | loss = criterion(output, target_var)
63 |
64 | loss_sum += loss.data[0] * input.size(0)
65 | pred = output.data.max(1, keepdim=True)[1]
66 | correct += pred.eq(target_var.data.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
67 |
68 | return {
69 | 'loss': loss_sum / len(loader.dataset),
70 | 'accuracy': correct / len(loader.dataset) * 100.0,
71 | }
72 |
73 |
74 | def moving_average(net1, net2, alpha=1):
75 | for param1, param2 in zip(net1.parameters(), net2.parameters()):
76 | param1.data *= (1.0 - alpha)
77 | param1.data += param2.data * alpha
78 |
79 |
80 | def _check_bn(module, flag):
81 | if issubclass(module.__class__, torch.nn.modules.batchnorm._BatchNorm):
82 | flag[0] = True
83 |
84 |
85 | def check_bn(model):
86 | flag = [False]
87 | model.apply(lambda module: _check_bn(module, flag))
88 | return flag[0]
89 |
90 |
91 | def reset_bn(module):
92 | if issubclass(module.__class__, torch.nn.modules.batchnorm._BatchNorm):
93 | module.running_mean = torch.zeros_like(module.running_mean)
94 | module.running_var = torch.ones_like(module.running_var)
95 |
96 |
97 | def _get_momenta(module, momenta):
98 | if issubclass(module.__class__, torch.nn.modules.batchnorm._BatchNorm):
99 | momenta[module] = module.momentum
100 |
101 |
102 | def _set_momenta(module, momenta):
103 | if issubclass(module.__class__, torch.nn.modules.batchnorm._BatchNorm):
104 | module.momentum = momenta[module]
105 |
106 |
107 | def bn_update(loader, model):
108 | """
109 | BatchNorm buffers update (if any).
110 | Performs 1 epochs to estimate buffers average using train dataset.
111 |
112 | :param loader: train dataset loader for buffers average estimation.
113 | :param model: model being update
114 | :return: None
115 | """
116 | if not check_bn(model):
117 | return
118 | model.train()
119 | momenta = {}
120 | model.apply(reset_bn)
121 | model.apply(lambda module: _get_momenta(module, momenta))
122 | n = 0
123 | for input, _ in loader:
124 | input = input.cuda(async=True)
125 | input_var = torch.autograd.Variable(input)
126 | b = input_var.data.size(0)
127 |
128 | momentum = b / (n + b)
129 | for module in momenta.keys():
130 | module.momentum = momentum
131 |
132 | model(input_var)
133 | n += b
134 |
135 | model.apply(lambda module: _set_momenta(module, momenta))
136 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/preresnet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | PreResNet model definition
3 | ported from https://github.com/bearpaw/pytorch-classification/blob/master/models/cifar/preresnet.py
4 | """
5 |
6 | import torch.nn as nn
7 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
8 | import math
9 |
10 | __all__ = ['PreResNet110', 'PreResNet164']
11 |
12 |
13 | def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
14 | return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
15 | padding=1, bias=False)
16 |
17 |
18 | class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
19 | expansion = 1
20 |
21 | def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None):
22 | super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
23 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(inplanes)
24 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
25 | self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
26 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
27 | self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
28 | self.downsample = downsample
29 | self.stride = stride
30 |
31 | def forward(self, x):
32 | residual = x
33 |
34 | out = self.bn1(x)
35 | out = self.relu(out)
36 | out = self.conv1(out)
37 |
38 | out = self.bn2(out)
39 | out = self.relu(out)
40 | out = self.conv2(out)
41 |
42 | if self.downsample is not None:
43 | residual = self.downsample(x)
44 |
45 | out += residual
46 |
47 | return out
48 |
49 |
50 | class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
51 | expansion = 4
52 |
53 | def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None):
54 | super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
55 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(inplanes)
56 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
57 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
58 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
59 | padding=1, bias=False)
60 | self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
61 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes * 4, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
62 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
63 | self.downsample = downsample
64 | self.stride = stride
65 |
66 | def forward(self, x):
67 | residual = x
68 |
69 | out = self.bn1(x)
70 | out = self.relu(out)
71 | out = self.conv1(out)
72 |
73 | out = self.bn2(out)
74 | out = self.relu(out)
75 | out = self.conv2(out)
76 |
77 | out = self.bn3(out)
78 | out = self.relu(out)
79 | out = self.conv3(out)
80 |
81 | if self.downsample is not None:
82 | residual = self.downsample(x)
83 |
84 | out += residual
85 |
86 | return out
87 |
88 |
89 | class PreResNet(nn.Module):
90 |
91 | def __init__(self, num_classes=10, depth=110):
92 | super(PreResNet, self).__init__()
93 | if depth >= 44:
94 | assert (depth - 2) % 9 == 0, 'depth should be 9n+2'
95 | n = (depth - 2) // 9
96 | block = Bottleneck
97 | else:
98 | assert (depth - 2) % 6 == 0, 'depth should be 6n+2'
99 | n = (depth - 2) // 6
100 | block = BasicBlock
101 |
102 |
103 | self.inplanes = 16
104 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, padding=1,
105 | bias=False)
106 | self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 16, n)
107 | self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 32, n, stride=2)
108 | self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 64, n, stride=2)
109 | self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(64 * block.expansion)
110 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
111 | self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(8)
112 | self.fc = nn.Linear(64 * block.expansion, num_classes)
113 |
114 | for m in self.modules():
115 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
116 | n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
117 | m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
118 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
119 | m.weight.data.fill_(1)
120 | m.bias.data.zero_()
121 |
122 | def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1):
123 | downsample = None
124 | if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
125 | downsample = nn.Sequential(
126 | nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
127 | kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
128 | )
129 |
130 | layers = list()
131 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
132 | self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
133 | for i in range(1, blocks):
134 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
135 |
136 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
137 |
138 | def forward(self, x):
139 | x = self.conv1(x)
140 |
141 | x = self.layer1(x) # 32x32
142 | x = self.layer2(x) # 16x16
143 | x = self.layer3(x) # 8x8
144 | x = self.bn(x)
145 | x = self.relu(x)
146 |
147 | x = self.avgpool(x)
148 | x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
149 | x = self.fc(x)
150 |
151 | return x
152 |
153 |
154 | class PreResNet110:
155 | base = PreResNet
156 | args = list()
157 | kwargs = {'depth': 110}
158 | transform_train = transforms.Compose([
159 | transforms.RandomCrop(32, padding=4),
160 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
161 | transforms.ToTensor(),
162 | transforms.Normalize((0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465), (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010)),
163 | ])
164 | transform_test = transforms.Compose([
165 | transforms.ToTensor(),
166 | transforms.Normalize((0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465), (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010)),
167 | ])
168 |
169 | class PreResNet164:
170 | base = PreResNet
171 | args = list()
172 | kwargs = {'depth': 164}
173 | transform_train = transforms.Compose([
174 | transforms.RandomCrop(32, padding=4),
175 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
176 | transforms.ToTensor(),
177 | transforms.Normalize((0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465), (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010)),
178 | ])
179 | transform_test = transforms.Compose([
180 | transforms.ToTensor(),
181 | transforms.Normalize((0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465), (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010)),
182 | ])
183 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import argparse
2 | import os
3 | import sys
4 | import time
5 | import torch
6 | import torch.nn.functional as F
7 | import torchvision
8 | import models
9 | import utils
10 | import tabulate
11 |
12 |
13 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='SGD/SWA training')
14 | parser.add_argument('--dir', type=str, default=None, required=True, help='training directory (default: None)')
15 |
16 | parser.add_argument('--dataset', type=str, default='CIFAR10', help='dataset name (default: CIFAR10)')
17 | parser.add_argument('--data_path', type=str, default=None, required=True, metavar='PATH',
18 | help='path to datasets location (default: None)')
19 | parser.add_argument('--batch_size', type=int, default=128, metavar='N', help='input batch size (default: 128)')
20 | parser.add_argument('--num_workers', type=int, default=4, metavar='N', help='number of workers (default: 4)')
21 | parser.add_argument('--model', type=str, default=None, required=True, metavar='MODEL',
22 | help='model name (default: None)')
23 |
24 | parser.add_argument('--resume', type=str, default=None, metavar='CKPT',
25 | help='checkpoint to resume training from (default: None)')
26 |
27 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=200, metavar='N', help='number of epochs to train (default: 200)')
28 | parser.add_argument('--save_freq', type=int, default=25, metavar='N', help='save frequency (default: 25)')
29 | parser.add_argument('--eval_freq', type=int, default=5, metavar='N', help='evaluation frequency (default: 5)')
30 | parser.add_argument('--lr_init', type=float, default=0.1, metavar='LR', help='initial learning rate (default: 0.01)')
31 | parser.add_argument('--momentum', type=float, default=0.9, metavar='M', help='SGD momentum (default: 0.9)')
32 | parser.add_argument('--wd', type=float, default=1e-4, help='weight decay (default: 1e-4)')
33 |
34 | parser.add_argument('--swa', action='store_true', help='swa usage flag (default: off)')
35 | parser.add_argument('--swa_start', type=float, default=161, metavar='N', help='SWA start epoch number (default: 161)')
36 | parser.add_argument('--swa_lr', type=float, default=0.05, metavar='LR', help='SWA LR (default: 0.05)')
37 | parser.add_argument('--swa_c_epochs', type=int, default=1, metavar='N',
38 | help='SWA model collection frequency/cycle length in epochs (default: 1)')
39 |
40 | parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=1, metavar='S', help='random seed (default: 1)')
41 |
42 | args = parser.parse_args()
43 |
44 | print('Preparing directory %s' % args.dir)
45 | os.makedirs(args.dir, exist_ok=True)
46 | with open(os.path.join(args.dir, 'command.sh'), 'w') as f:
47 | f.write(' '.join(sys.argv))
48 | f.write('\n')
49 |
50 | torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True
51 | torch.manual_seed(args.seed)
52 | torch.cuda.manual_seed(args.seed)
53 |
54 | print('Using model %s' % args.model)
55 | model_cfg = getattr(models, args.model)
56 |
57 | print('Loading dataset %s from %s' % (args.dataset, args.data_path))
58 | ds = getattr(torchvision.datasets, args.dataset)
59 | path = os.path.join(args.data_path, args.dataset.lower())
60 | train_set = ds(path, train=True, download=True, transform=model_cfg.transform_train)
61 | test_set = ds(path, train=False, download=True, transform=model_cfg.transform_test)
62 | loaders = {
63 | 'train': torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
64 | train_set,
65 | batch_size=args.batch_size,
66 | shuffle=True,
67 | num_workers=args.num_workers,
68 | pin_memory=True
69 | ),
70 | 'test': torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
71 | test_set,
72 | batch_size=args.batch_size,
73 | shuffle=False,
74 | num_workers=args.num_workers,
75 | pin_memory=True
76 | )
77 | }
78 | num_classes = max(train_set.train_labels) + 1
79 |
80 | print('Preparing model')
81 | model = model_cfg.base(*model_cfg.args, num_classes=num_classes, **model_cfg.kwargs)
82 | model.cuda()
83 |
84 |
85 | if args.swa:
86 | print('SWA training')
87 | swa_model = model_cfg.base(*model_cfg.args, num_classes=num_classes, **model_cfg.kwargs)
88 | swa_model.cuda()
89 | swa_n = 0
90 | else:
91 | print('SGD training')
92 |
93 |
94 | def schedule(epoch):
95 | t = (epoch) / (args.swa_start if args.swa else args.epochs)
96 | lr_ratio = args.swa_lr / args.lr_init if args.swa else 0.01
97 | if t <= 0.5:
98 | factor = 1.0
99 | elif t <= 0.9:
100 | factor = 1.0 - (1.0 - lr_ratio) * (t - 0.5) / 0.4
101 | else:
102 | factor = lr_ratio
103 | return args.lr_init * factor
104 |
105 |
106 | criterion = F.cross_entropy
107 | optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(
108 | model.parameters(),
109 | lr=args.lr_init,
110 | momentum=args.momentum,
111 | weight_decay=args.wd
112 | )
113 |
114 | start_epoch = 0
115 | if args.resume is not None:
116 | print('Resume training from %s' % args.resume)
117 | checkpoint = torch.load(args.resume)
118 | start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch']
119 | model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
120 | optimizer.load_state_dict(checkpoint['optimizer'])
121 | if args.swa:
122 | swa_state_dict = checkpoint['swa_state_dict']
123 | if swa_state_dict is not None:
124 | swa_model.load_state_dict(swa_state_dict)
125 | swa_n_ckpt = checkpoint['swa_n']
126 | if swa_n_ckpt is not None:
127 | swa_n = swa_n_ckpt
128 |
129 | columns = ['ep', 'lr', 'tr_loss', 'tr_acc', 'te_loss', 'te_acc', 'time']
130 | if args.swa:
131 | columns = columns[:-1] + ['swa_te_loss', 'swa_te_acc'] + columns[-1:]
132 | swa_res = {'loss': None, 'accuracy': None}
133 |
134 | utils.save_checkpoint(
135 | args.dir,
136 | start_epoch,
137 | state_dict=model.state_dict(),
138 | swa_state_dict=swa_model.state_dict() if args.swa else None,
139 | swa_n=swa_n if args.swa else None,
140 | optimizer=optimizer.state_dict()
141 | )
142 |
143 | for epoch in range(start_epoch, args.epochs):
144 | time_ep = time.time()
145 |
146 | lr = schedule(epoch)
147 | utils.adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, lr)
148 | train_res = utils.train_epoch(loaders['train'], model, criterion, optimizer)
149 | if epoch == 0 or epoch % args.eval_freq == args.eval_freq - 1 or epoch == args.epochs - 1:
150 | test_res = utils.eval(loaders['test'], model, criterion)
151 | else:
152 | test_res = {'loss': None, 'accuracy': None}
153 |
154 | if args.swa and (epoch + 1) >= args.swa_start and (epoch + 1 - args.swa_start) % args.swa_c_epochs == 0:
155 | utils.moving_average(swa_model, model, 1.0 / (swa_n + 1))
156 | swa_n += 1
157 | if epoch == 0 or epoch % args.eval_freq == args.eval_freq - 1 or epoch == args.epochs - 1:
158 | utils.bn_update(loaders['train'], swa_model)
159 | swa_res = utils.eval(loaders['test'], swa_model, criterion)
160 | else:
161 | swa_res = {'loss': None, 'accuracy': None}
162 |
163 | if (epoch + 1) % args.save_freq == 0:
164 | utils.save_checkpoint(
165 | args.dir,
166 | epoch + 1,
167 | state_dict=model.state_dict(),
168 | swa_state_dict=swa_model.state_dict() if args.swa else None,
169 | swa_n=swa_n if args.swa else None,
170 | optimizer=optimizer.state_dict()
171 | )
172 |
173 | time_ep = time.time() - time_ep
174 | values = [epoch + 1, lr, train_res['loss'], train_res['accuracy'], test_res['loss'], test_res['accuracy'], time_ep]
175 | if args.swa:
176 | values = values[:-1] + [swa_res['loss'], swa_res['accuracy']] + values[-1:]
177 | table = tabulate.tabulate([values], columns, tablefmt='simple', floatfmt='8.4f')
178 | if epoch % 40 == 0:
179 | table = table.split('\n')
180 | table = '\n'.join([table[1]] + table)
181 | else:
182 | table = table.split('\n')[2]
183 | print(table)
184 |
185 | if args.epochs % args.save_freq != 0:
186 | utils.save_checkpoint(
187 | args.dir,
188 | args.epochs,
189 | state_dict=model.state_dict(),
190 | swa_state_dict=swa_model.state_dict() if args.swa else None,
191 | swa_n=swa_n if args.swa else None,
192 | optimizer=optimizer.state_dict()
193 | )
194 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Stochastic Weight Averaging (SWA)
2 | This repository contains a PyTorch implementation of the Stochastic Weight Averaging (SWA) training method for DNNs from the paper
3 |
4 | [Averaging Weights Leads to Wider Optima and Better Generalization](https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.05407)
5 |
6 | by Pavel Izmailov, Dmitrii Podoprikhin, Timur Garipov, Dmitry Vetrov and Andrew Gordon Wilson.
7 |
8 | Note: as of August 2020, SWA is now a core optimizer in the PyTorch library, and can be immediately used by anyone with PyTorch, without needing an external repo, as easily SGD or Adam. Please see [this blog post](https://pytorch.org/blog/pytorch-1.6-now-includes-stochastic-weight-averaging/) introducing the native PyTorch implementation with examples.
9 |
10 | # Introduction
11 |
12 | SWA is a simple DNN training method that can be used as a drop-in replacement for SGD with improved generalization, faster convergence, and essentially no overhead. The key idea of SWA is to average multiple samples produced by SGD with a modified learning rate schedule. We use a constant or cyclical learning rate schedule that causes SGD to _explore_ the set of points in the weight space corresponding to high-performing networks. We observe that SWA converges more quickly than SGD, and to wider optima that provide higher test accuracy.
13 |
14 | In this repo we implement the constant learning rate schedule that we found to be most practical on CIFAR datasets.
15 |
16 |
17 |  18 |
18 |  19 |
19 | 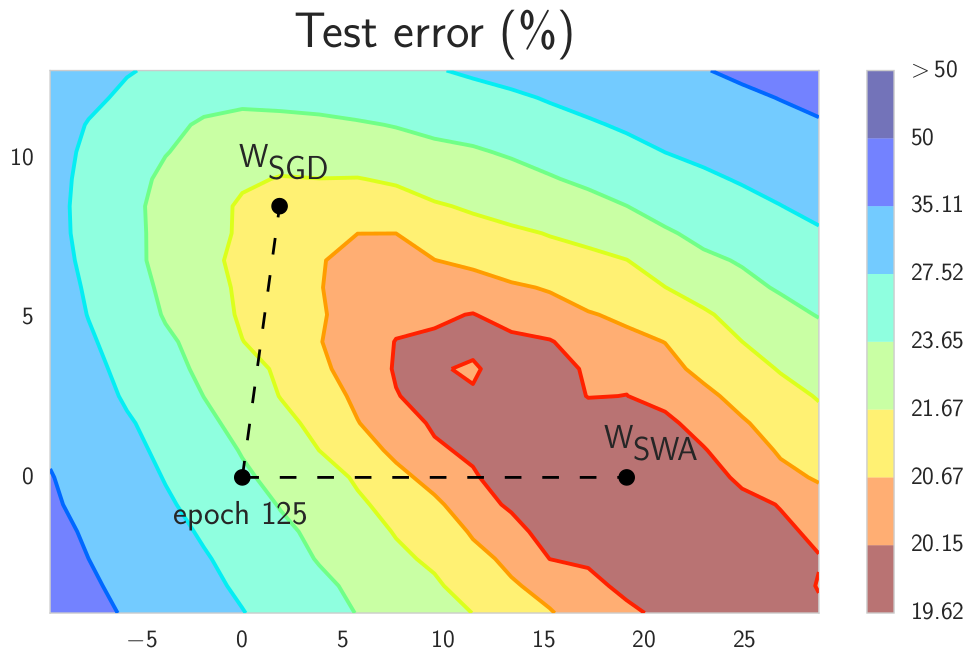 20 |
20 |
21 |
22 | Please cite our work if you find this approach useful in your research:
23 | ```bibtex
24 | @article{izmailov2018averaging,
25 | title={Averaging Weights Leads to Wider Optima and Better Generalization},
26 | author={Izmailov, Pavel and Podoprikhin, Dmitrii and Garipov, Timur and Vetrov, Dmitry and Wilson, Andrew Gordon},
27 | journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.05407},
28 | year={2018}
29 | }
30 | ```
31 |
32 |
33 | # Dependencies
34 | * [PyTorch](http://pytorch.org/)
35 | * [torchvision](https://github.com/pytorch/vision/)
36 | * [tabulate](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/tabulate/)
37 |
38 | # Usage
39 |
40 | The code in this repository implements both SWA and conventional SGD training, with examples on the CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets.
41 |
42 | To run SWA use the following command:
43 |
44 | ```bash
45 | python3 train.py --dir= \
46 | --dataset= \
47 | --data_path= \
48 | --model= \
49 | --epochs= \
50 | --lr_init= \
51 | --wd= \
52 | --swa \
53 | --swa_start= \
54 | --swa_lr=
55 | ```
56 |
57 | Parameters:
58 |
59 | * ```DIR``` — path to training directory where checkpoints will be stored
60 | * ```DATASET``` — dataset name [CIFAR10/CIFAR100] (default: CIFAR10)
61 | * ```PATH``` — path to the data directory
62 | * ```MODEL``` — DNN model name:
63 | - VGG16/VGG16BN/VGG19/VGG19BN
64 | - PreResNet110/PreResNet164
65 | - WideResNet28x10
66 | * ```EPOCHS``` — number of training epochs (default: 200)
67 | * ```LR_INIT``` — initial learning rate (default: 0.1)
68 | * ```WD``` — weight decay (default: 1e-4)
69 | * ```SWA_START``` — the number of epoch after which SWA will start to average models (default: 161)
70 | * ```SWA_LR``` — SWA learning rate (default: 0.05)
71 |
72 |
73 | To run conventional SGD training use the following command:
74 | ```bash
75 | python3 train.py --dir= \
76 | --dataset= \
77 | --data_path= \
78 | --model= \
79 | --epochs= \
80 | --lr_init= \
81 | --wd=
82 | ```
83 |
84 | ## Examples
85 |
86 | To reproduce the results from the paper run (we use same parameters for both CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 except for PreResNet):
87 | ```bash
88 | #VGG16
89 | python3 train.py --dir= --dataset=CIFAR100 --data_path= --model=VGG16 --epochs=200 --lr_init=0.05 --wd=5e-4 # SGD
90 | python3 train.py --dir= --dataset=CIFAR100 --data_path= --model=VGG16 --epochs=300 --lr_init=0.05 --wd=5e-4 --swa --swa_start=161 --swa_lr=0.01 # SWA 1.5 Budgets
91 |
92 | #PreResNet
93 | python3 train.py --dir= --dataset=CIFAR100 --data_path= --model=[PreResNet110 or PreResNet164] --epochs=150 --lr_init=0.1 --wd=3e-4 # SGD
94 | #CIFAR100
95 | python3 train.py --dir= --dataset=CIFAR100 --data_path= --model=[PreResNet110 or PreResNet164] --epochs=225 --lr_init=0.1 --wd=3e-4 --swa --swa_start=126 --swa_lr=0.05 # SWA 1.5 Budgets
96 | #CIFAR10
97 | python3 train.py --dir= --dataset=CIFAR10 --data_path= --model=[PreResNet110 or PreResNet164] --epochs=225 --lr_init=0.1 --wd=3e-4 --swa --swa_start=126 --swa_lr=0.01 # SWA 1.5 Budgets
98 |
99 | #WideResNet28x10
100 | python3 train.py --dir= --dataset=CIFAR100 --data_path= --model=WideResNet28x10 --epochs=200 --lr_init=0.1 --wd=5e-4 # SGD
101 | python3 train.py --dir= --dataset=CIFAR100 --data_path= --model=WideResNet28x10 --epochs=300 --lr_init=0.1 --wd=5e-4 --swa --swa_start=161 --swa_lr=0.05 # SWA 1.5 Budgets
102 | ```
103 |
104 | # Results
105 |
106 | ## CIFAR-100
107 |
108 | Test accuracy (%) of SGD and SWA on CIFAR-100 for different training budgets. For each model the _Budget_ is defined as the number of epochs required to train the model with the conventional SGD procedure.
109 |
110 | | DNN (Budget) | SGD | SWA 1 Budget | SWA 1.25 Budgets | SWA 1.5 Budgets |
111 | | ------------------------- |:------------:|:------------:|:----------------:|:---------------:|
112 | | VGG16 (200) | 72.55 ± 0.10 | 73.91 ± 0.12 | 74.17 ± 0.15 | 74.27 ± 0.25 |
113 | | PreResNet110 (150) | 76.77 ± 0.38 | 78.75 ± 0.16 | 78.91 ± 0.29 | 79.10 ± 0.21 |
114 | | PreResNet164 (150) | 78.49 ± 0.36 | 79.77 ± 0.17 | 80.18 ± 0.23 | 80.35 ± 0.16 |
115 | | WideResNet28x10 (200) | 80.82 ± 0.23 | 81.46 ± 0.23 | 81.91 ± 0.27 | 82.15 ± 0.27 |
116 |
117 | Below we show the convergence plot for SWA and SGD with PreResNet164 on CIFAR-100 and the corresponding learning rates. The dashed line illustrates the accuracy of individual models averaged by SWA.
118 |
119 |
120 |  121 |
121 |
122 |
123 |
124 | ## CIFAR-10
125 |
126 | Test accuracy (%) of SGD and SWA on CIFAR-10 for different training budgets.
127 |
128 | | DNN (Budget) | SGD | SWA 1 Budget | SWA 1.25 Budgets | SWA 1.5 Budgets |
129 | | ------------------------- |:------------:|:------------:|:----------------:|:---------------:|
130 | | VGG16 (200) | 93.25 ± 0.16 | 93.59 ± 0.16 | 93.70 ± 0.22 | 93.64 ± 0.18 |
131 | | PreResNet110 (150) | 95.03 ± 0.05 | 95.51 ± 0.10 | 95.65 ± 0.03 | 95.82 ± 0.03 |
132 | | PreResNet164 (150) | 95.28 ± 0.10 | 95.56 ± 0.11 | 95.77 ± 0.04 | 95.83 ± 0.03 |
133 | | WideResNet28x10 (200) | 96.18 ± 0.11 | 96.45 ± 0.11 | 96.64 ± 0.08 | 96.79 ± 0.05 |
134 |
135 | # Other Implementations
136 |
137 | * Chainer Implementation: [github.com/chainer/models/tree/master/swa](https://github.com/chainer/models/tree/master/swa)
138 | * Keras/Tensorflow-Keras Implementation: [github.com/simon-larsson/keras-swa](https://github.com/simon-larsson/keras-swa)
139 | * PyTorch Contrib: [github.com/pytorch/contrib](https://github.com/pytorch/contrib)
140 |
141 | # References
142 |
143 | Provided model implementations were adapted from
144 | * VGG: [github.com/pytorch/vision/](https://github.com/pytorch/vision/)
145 | * PreResNet: [github.com/bearpaw/pytorch-classification](https://github.com/bearpaw/pytorch-classification)
146 | * WideResNet: [github.com/meliketoy/wide-resnet.pytorch](https://github.com/meliketoy/wide-resnet.pytorch)
147 |
148 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 18 |
18 |  19 |
19 |  20 |
20 |  18 |
18 |  19 |
19 |  20 |
20 |  121 |
121 |