├── models
├── __init__.py
├── mnist_model.py
├── moiveRnn.py
└── resnet.py
├── data
└── README.md
├── checkpoint
└── README.md
├── .idea
├── .gitignore
├── encodings.xml
├── vcs.xml
├── other.xml
├── modules.xml
├── misc.xml
├── deployment.xml
├── DBA.iml
└── inspectionProfiles
│ └── Project_Default.xml
├── util
├── wordProcess.py
├── roc_plot.py
└── runutils.py
├── README.md
├── mnist_undercover_train.py
├── adversary
├── fgsm.py
├── jsma.py
└── cw.py
├── cifar_undercover_train.py
├── mnist_DBA.ipynb
└── cifar_DBA.ipynb
/models/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/data/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # store datas
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/checkpoint/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # store checkpoints
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Default ignored files
2 | /workspace.xml
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/encodings.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/vcs.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/other.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/modules.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/misc.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/deployment.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/DBA.iml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/inspectionProfiles/Project_Default.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/util/wordProcess.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import re
2 | import unicodedata
3 |
4 | class wordIndex(object):
5 | def __init__(self):
6 | self.count = 0
7 | self.word_to_idx = {}
8 | self.word_count = {}
9 |
10 | def add_word(self, word):
11 | if not word in self.word_to_idx:
12 | self.word_to_idx[word] = self.count
13 | self.word_count[word] = 1
14 | self.count += 1
15 | else:
16 | self.word_count[word] += 1
17 |
18 | def add_text(self, text):
19 | for word in text.split(' '):
20 | self.add_word(word)
21 |
22 |
23 | def normalizeString(s):
24 | s = s.lower().strip()
25 | s = re.sub(r"
", r" ", s)
26 | # s = re.sub(' +',' ',s)
27 | s = re.sub(r'(\W)(?=\1)', '', s)
28 | s = re.sub(r"([.!?])", r" \1", s)
29 | s = re.sub(r"[^a-zA-Z.!?]+", r" ", s)
30 |
31 | return s
32 |
33 |
34 | def limitDict(limit, classObj):
35 | dict1 = sorted(classObj.word_count.items(), key=lambda t: t[1], reverse=True)
36 | count = 0
37 | for x, y in dict1:
38 | if count >= limit - 1:
39 | classObj.word_to_idx[x] = limit
40 | else:
41 | classObj.word_to_idx[x] = count
42 |
43 | count += 1
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/mnist_model.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | import torch.nn.functional as F
3 |
4 | class MnistModel(nn.Module):
5 |
6 | def __init__(self):
7 | super(MnistModel, self).__init__()
8 | # input is 28x28
9 | # padding=2 for same padding
10 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, 5, padding=2)
11 | # feature map size is 14*14 by pooling
12 | # padding=2 for same padding
13 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 5, padding=2)
14 | # feature map size is 7*7 by pooling
15 | self.fc1 = nn.Linear(64 * 7 * 7, 1024)
16 | self.fc2 = nn.Linear(1024, 10)
17 |
18 | def forward(self, x, dba=False):
19 | x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv1(x)), 2)
20 | x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2)
21 | x = x.view(-1, 64 * 7 * 7) # reshape Variable
22 | h = self.fc1(x)
23 | x = F.relu(h)
24 | x = self.fc2(x)
25 | if dba:
26 | return x, h
27 | else:
28 | return x
29 | # return F.log_softmax(x, dim=-1)
30 |
31 |
32 | class MLP(nn.Module):
33 | def __init__(self):
34 | super(MLP, self).__init__()
35 | self.fc1 = nn.Linear(1024 * 4, 256)
36 | self.fc2 = nn.Linear(256, 2)
37 |
38 | def forward(self, x):
39 | x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
40 | x = self.fc2(x)
41 | return x
42 | # return F.log_softmax(x, dim=-1)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Detection by Attack: Detecting Adversarial Samples by Undercover Attack
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 | This repository includes the source code of the paper "Detection by Attack: Detecting Adversarial Samples by Undercover Attack". Please cite our paper when you use this program! 😍
5 |
6 | ```
7 | @inproceedings{zhou2020detection,
8 | title={Detection by attack: Detecting adversarial samples by undercover attack},
9 | author={Zhou, Qifei and Zhang, Rong and Wu, Bo and Li, Weiping and Mo, Tong},
10 | booktitle={European Symposium on Research in Computer Security},
11 | pages={146--164},
12 | year={2020},
13 | organization={Springer}
14 | }
15 | ```
16 |
17 | ## DBA overview
18 | 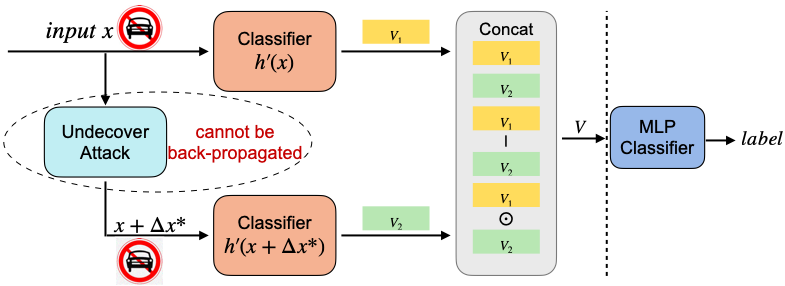
19 |
20 | The pipeline of our framework consists of two steps:
21 | 1. Injecting adversarial samples to train the classification model.
22 | 2. Training a simple multi-layer perceptron (MLP) classifier to judge whether the sample is adversarial.
23 |
24 | We take MNIST and CIFAR as examples: the mnist_undercover_train.py and cifar_undercover_train.py refer to the step one; the mnist_DBA.ipynb and cifar_DBA.ipynb refer to the step two.
25 |
26 | ## Report issues
27 | Please let us know if you encounter any problems.
28 |
29 | The contact email is qifeizhou@pku.edu.cn
30 |
31 |
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/util/roc_plot.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc
2 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
3 | import numpy as np
4 | import pandas as pd
5 |
6 | def roc_auc(labels, losses):
7 | fpt, tpt, thresholds = roc_curve(labels, losses)
8 | roc_auc = auc(fpt, tpt)
9 | plt.switch_backend('Agg')
10 | fig = plt.figure()
11 | lw = 2
12 | plt.plot(fpt, tpt, color='red',
13 | lw=lw, label='ROC curve (auc = %0.2f)' % roc_auc)
14 | plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='blue', lw=lw, linestyle='--')
15 | plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
16 | plt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])
17 | plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
18 | plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
19 | plt.title('adversarial detect roc curve')
20 | plt.legend(loc="lower right")
21 | fig.savefig('./output/roc.png', dpi=fig.dpi)
22 |
23 | return roc_auc
24 |
25 | def creterion_func(benign_losses, adv_losses):
26 | benign_losses = benign_losses[:]
27 | adv_losses = adv_losses[:]
28 | creterion = pd.DataFrame([benign_losses, adv_losses])
29 | creterion.to_csv('./output/creterion.csv', index=False)
30 | fig = plt.figure()
31 | plt.scatter(np.arange(len(benign_losses)), benign_losses, color='cornflowerblue', s=3, marker='o')
32 | plt.scatter(np.arange(len(adv_losses)), adv_losses, color='crimson', s=3, marker='*')
33 | plt.xticks([])
34 | fig.savefig('./output/creterion.png', dpi=400)
35 | plt.show()
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/moiveRnn.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | from torch.autograd import Variable
4 | from torch import optim
5 | import torch.nn.functional as F
6 | from settings import *
7 |
8 | class Model(torch.nn.Module):
9 | """
10 | we need to load init embed weights, because var_embeddings can not be trained!
11 | """
12 | def __init__(self, embedding_dim, hidden_dim, vocabLimit):
13 | super(Model, self).__init__()
14 | self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
15 | self.embeddings = nn.Embedding(vocabLimit + 1, embedding_dim)
16 | # self.lstm = nn.LSTM(embedding_dim, hidden_dim)
17 | # self.linearOut = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, 2)
18 | self.lstm = nn.LSTM(embedding_dim, hidden_dim, bidirectional=True)
19 | self.linearOut = nn.Linear(hidden_dim*2, 2)
20 |
21 | def forward(self, inputs, after_embedding=False, train=False):
22 | hidden = self.init_hidden()
23 | if not after_embedding:
24 | embeddings = self.embeddings(inputs).view(len(inputs), 1, -1)
25 | if train:
26 | var_embeddings = embeddings
27 | else:
28 | var_embeddings = Variable(embeddings, requires_grad=True)
29 | else:
30 | var_embeddings = inputs
31 | lstm_out, (hn, cn) = self.lstm(var_embeddings, hidden)
32 | x = hn.view(1, -1)
33 | x = self.linearOut(x)
34 | return x, var_embeddings
35 |
36 | def init_hidden(self):
37 | return (Variable(torch.zeros(2, 1, self.hidden_dim)).cuda(),
38 | Variable(torch.zeros(2, 1, self.hidden_dim)).cuda())
39 | # return (Variable(torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_dim)).cuda(,
40 | # Variable(torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_dim)).cuda()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/util/runutils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from operator import methodcaller
2 |
3 | import torch
4 | import torch.nn as nn
5 | from torch.autograd import Variable
6 | from settings import *
7 |
8 |
9 | def get_cuda_state(obj):
10 | """
11 | Get cuda state of any object.
12 |
13 | :param obj: an object (a tensor or an `torch.nn.Module`)
14 | :raise TypeError:
15 | :return: True if the object or the parameter set of the object
16 | is on GPU
17 | """
18 | if isinstance(obj, nn.Module):
19 | try:
20 | return next(obj.parameters()).is_cuda
21 | except StopIteration:
22 | return None
23 | elif hasattr(obj, 'is_cuda'):
24 | return obj.is_cuda
25 | else:
26 | raise TypeError('unrecognized type ({}) in args'.format(type(obj)))
27 |
28 |
29 | def is_cuda_consistent(*args):
30 | """
31 | See if the cuda states are consistent among variables (of type either
32 | tensors or torch.autograd.Variable). For example,
33 |
34 | import torch
35 | from torch.autograd import Variable
36 | import torch.nn as nn
37 |
38 | net = nn.Linear(512, 10)
39 | tensor = torch.rand(10, 10).cuda()
40 | assert not is_cuda_consistent(net=net, tensor=tensor)
41 |
42 | :param args: the variables to test
43 | :return: True if len(args) == 0 or the cuda states of all elements in args
44 | are consistent; False otherwise
45 | """
46 | result = dict()
47 | for v in args:
48 | cur_cuda_state = get_cuda_state(v)
49 | cuda_state = result.get('cuda', cur_cuda_state)
50 | if cur_cuda_state is not cuda_state:
51 | return False
52 | result['cuda'] = cur_cuda_state
53 | return True
54 |
55 | def make_cuda_consistent(refobj, *args):
56 | """
57 | Attempt to make the cuda states of args consistent with that of ``refobj``.
58 | If any element of args is a Variable and the cuda state of the element is
59 | inconsistent with ``refobj``, raise ValueError, since changing the cuda state
60 | of a Variable involves rewrapping it in a new Variable, which changes the
61 | semantics of the code.
62 |
63 | :param refobj: either the referential object or the cuda state of the
64 | referential object
65 | :param args: the variables to test
66 | :return: tuple of the same data as ``args`` but on the same device as
67 | ``refobj``
68 | """
69 | ref_cuda_state = refobj if type(refobj) is bool else get_cuda_state(refobj)
70 | if ref_cuda_state is None:
71 | raise ValueError('cannot determine the cuda state of `refobj` ({})'
72 | .format(refobj))
73 |
74 | result_args = list()
75 | for v in args:
76 | cuda_state = get_cuda_state(v)
77 | if cuda_state != ref_cuda_state:
78 | v = v.cuda()
79 | result_args.append(v)
80 | return tuple(result_args)
81 |
82 | def predict(net, inputs):
83 | """
84 | Predict labels. The cuda state of `net` decides that of the returned
85 | prediction tensor.
86 |
87 | :param net: the network
88 | :param inputs: the input tensor (non Variable), of dimension [B x C x W x H]
89 | :return: prediction tensor (LongTensor), of dimension [B]
90 | """
91 | inputs = make_cuda_consistent(net, inputs)[0]
92 | inputs_var = Variable(inputs)
93 | outputs_var = net(inputs_var)
94 | predictions = torch.max(outputs_var.data, dim=1)[1]
95 | return predictions
96 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnist_undercover_train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import torch
3 | import torch.nn as nn
4 | import torch.optim as optim
5 | import torchvision
6 | from torch.autograd import Variable
7 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
8 | from models.mnist_model import MnistModel
9 | from adversary.fgsm import Attack
10 |
11 |
12 | def undercover_attack(UndercoverAttack, x, y_true, eps=1/255):
13 | x = Variable(x.to(device), requires_grad=True)
14 | y_true = Variable(y_true.to(device), requires_grad=False)
15 | x_adv = UndercoverAttack.fgsm(x, y_true, False, eps)
16 | return x_adv
17 |
18 |
19 | def train(epochs):
20 | print('==> Preparing data..')
21 | transform_train = transforms.Compose([
22 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
23 | transforms.ToTensor(),
24 | ])
25 |
26 | trainset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=True, download=True, transform=transform_train)
27 | trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=256, shuffle=True,
28 | num_workers=4)
29 | # Model
30 | print('==> Building model..')
31 | net = MnistModel()
32 | net = net.to(device)
33 | UndercoverAttack = Attack(net, nn.functional.cross_entropy)
34 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
35 | optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=1e-3, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=5e-4)
36 |
37 | net.train()
38 | best_acc = 0.0
39 | for epoch in range(epochs):
40 | train_loss = 0
41 | correct, total = 0, 0
42 | for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(trainloader):
43 | inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)
44 | optimizer.zero_grad()
45 | outputs = net(inputs)
46 | _, predicted = outputs.max(1)
47 | total += targets.size(0)
48 | correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item()
49 |
50 | x_adv = undercover_attack(UndercoverAttack, inputs, targets, eps=0.15)
51 | adv_outputs = net(x_adv)
52 |
53 | loss1 = criterion(outputs, targets)
54 | loss2 = criterion(adv_outputs, targets)
55 | loss = loss1 + loss2 * 0.8
56 | train_loss += loss.item()
57 | loss.backward()
58 | optimizer.step()
59 | acc = 1.0 * correct / total
60 | print('epoch: %d, train loss: %.2f, train acc: %.4f' % (epoch, train_loss, acc))
61 | if acc > best_acc:
62 | best_acc = acc
63 | state = {
64 | 'net': net.state_dict(),
65 | 'acc': acc,
66 | 'epoch': epoch,
67 | }
68 | if not os.path.isdir('checkpoint'):
69 | os.mkdir('checkpoint')
70 | torch.save(state, MNIST_CKPT)
71 |
72 |
73 | def test():
74 | # Data
75 | print('==> Preparing data..')
76 | transform_test = transforms.Compose([
77 | transforms.ToTensor(),
78 | ])
79 | testset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=False, download=True, transform=transform_test)
80 | testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testset, batch_size=256, shuffle=False,
81 | num_workers=4)
82 |
83 | # Model
84 | print('==> Building model..')
85 | net = MnistModel()
86 | net = net.to(device)
87 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
88 | checkpoint = torch.load(MNIST_CKPT)
89 | net.load_state_dict(checkpoint['net'])
90 |
91 | net.eval()
92 | test_loss = 0
93 | correct, total = 0, 0
94 |
95 | with torch.no_grad():
96 | for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(testloader):
97 | inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)
98 | outputs = net(inputs)
99 | loss = criterion(outputs, targets)
100 |
101 | test_loss += loss.item()
102 | _, predicted = outputs.max(1)
103 | total += targets.size(0)
104 | correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item()
105 | acc = 1.0 * correct / total
106 | print('test loss: %.2f, test acc: %.4f' % (test_loss, acc))
107 |
108 |
109 | if __name__ == '__main__':
110 | MNIST_CKPT = './checkpoint/mnist_undercover.pth'
111 | device = 'cuda:1' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
112 |
113 | # train(50)
114 | test()
115 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/resnet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | import torch.nn.functional as F
3 |
4 |
5 | class PreActBlock(nn.Module):
6 | '''Pre-activation version of the BasicBlock.'''
7 | expansion = 1
8 |
9 | def __init__(self, in_planes, planes, stride=1):
10 | super(PreActBlock, self).__init__()
11 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
12 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
13 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
14 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
15 |
16 | if stride != 1 or in_planes != self.expansion*planes:
17 | self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
18 | nn.Conv2d(in_planes, self.expansion*planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False)
19 | )
20 |
21 | def forward(self, x):
22 | out = F.relu(self.bn1(x))
23 | shortcut = self.shortcut(out) if hasattr(self, 'shortcut') else x
24 | out = self.conv1(out)
25 | out = self.conv2(F.relu(self.bn2(out)))
26 | out += shortcut
27 | return out
28 |
29 |
30 | class PreActBottleneck(nn.Module):
31 | '''Pre-activation version of the original Bottleneck module.'''
32 | expansion = 4
33 |
34 | def __init__(self, in_planes, planes, stride=1):
35 | super(PreActBottleneck, self).__init__()
36 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
37 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
38 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
39 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
40 | self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
41 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(planes, self.expansion*planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
42 |
43 | if stride != 1 or in_planes != self.expansion*planes:
44 | self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
45 | nn.Conv2d(in_planes, self.expansion*planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False)
46 | )
47 |
48 | def forward(self, x):
49 | out = F.relu(self.bn1(x))
50 | shortcut = self.shortcut(out) if hasattr(self, 'shortcut') else x
51 | out = self.conv1(out)
52 | out = self.conv2(F.relu(self.bn2(out)))
53 | out = self.conv3(F.relu(self.bn3(out)))
54 | out += shortcut
55 | return out
56 |
57 |
58 | class PreActResNet(nn.Module):
59 | def __init__(self, block, num_blocks, num_classes=10):
60 | super(PreActResNet, self).__init__()
61 | self.in_planes = 64
62 |
63 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
64 | self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, num_blocks[0], stride=1)
65 | self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, num_blocks[1], stride=2)
66 | self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, num_blocks[2], stride=2)
67 | self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, num_blocks[3], stride=2)
68 | self.linear1 = nn.Linear(512*block.expansion, 512)
69 | self.linear2 = nn.Linear(512, num_classes)
70 |
71 | def _make_layer(self, block, planes, num_blocks, stride):
72 | strides = [stride] + [1]*(num_blocks-1)
73 | layers = []
74 | for stride in strides:
75 | layers.append(block(self.in_planes, planes, stride))
76 | self.in_planes = planes * block.expansion
77 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
78 |
79 | def forward(self, x, dba=False):
80 | out = self.conv1(x)
81 | out = self.layer1(out)
82 | out = self.layer2(out)
83 | out = self.layer3(out)
84 | out = self.layer4(out)
85 | out = F.avg_pool2d(out, 4)
86 | out = out.view(out.size(0), -1)
87 | h = self.linear1(out)
88 | out = self.linear2(h)
89 |
90 | if dba:
91 | return out, h
92 | else:
93 | return out
94 | # out = F.log_softmax(out, dim=1)
95 |
96 | def PreActResNet18():
97 | return PreActResNet(PreActBlock, [2,2,2,2])
98 |
99 |
100 | class MLP(nn.Module):
101 | def __init__(self):
102 | super(MLP, self).__init__()
103 | self.fc1 = nn.Linear(512 * 4, 256)
104 | self.fc2 = nn.Linear(256, 2)
105 |
106 | def forward(self, x):
107 | x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
108 | x = self.fc2(x)
109 | return x
110 |
111 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adversary/fgsm.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """fgsm.py"""
2 | import torch
3 | from torch.autograd import Variable
4 | import numpy as np
5 | from settings import *
6 | import torch.nn.functional as F
7 |
8 | class Attack(object):
9 | def __init__(self, classify_net, criterion):
10 | self.net = classify_net
11 | self.criterion = criterion
12 |
13 | def fgsm(self, x, y, targeted=False, eps=8/255, x_val_min=0, x_val_max=1):
14 | x_adv = Variable(x.data, requires_grad=True)
15 | h_adv = self.net(x_adv)
16 | if targeted:
17 | cost = -self.criterion(h_adv, y)
18 | else:
19 | cost = self.criterion(h_adv, y)
20 |
21 | self.net.zero_grad()
22 | if x_adv.grad is not None:
23 | x_adv.grad.data.fill_(0)
24 | cost.backward()
25 |
26 | x_adv = x_adv + eps*x_adv.grad.sign_()
27 | x_adv = torch.clamp(x_adv, x_val_min, x_val_max)
28 | return x_adv
29 |
30 | """
31 | BIM_b
32 | """
33 | def i_fgsm(self, x, y, targeted=False, eps=8/255, alpha=1/255, iteration=1, x_val_min=0, x_val_max=1):
34 | x_adv = Variable(x.data, requires_grad=True)
35 | for i in range(iteration):
36 | h_adv = self.net(x_adv)
37 |
38 | if targeted:
39 | cost = -self.criterion(h_adv, y)
40 | else:
41 | cost = self.criterion(h_adv, y)
42 |
43 | self.net.zero_grad()
44 | if x_adv.grad is not None:
45 | x_adv.grad.data.fill_(0)
46 | cost.backward()
47 |
48 | x_adv = x_adv + alpha*x_adv.grad.sign_()
49 | x_adv = where(x_adv > x-eps, x_adv, x-eps)
50 | x_adv = where(x_adv < x+eps, x_adv, x+eps)
51 | x_adv = torch.clamp(x_adv, x_val_min, x_val_max)
52 | x_adv = Variable(x_adv.data, requires_grad=True)
53 | return x_adv
54 |
55 | def i_fgsm_a(self, x, y, targeted=False, eps=8 / 255, alpha=1 / 255, iteration=1, x_val_min=0, x_val_max=1,
56 | confidence=0.5):
57 | x_adv = Variable(x.data, requires_grad=True)
58 | for i in range(iteration):
59 | h_adv = self.net(x_adv)
60 | probs, predicted = F.softmax(h_adv, dim=-1).max(1)
61 | flag = (predicted != y).detach().cpu().numpy().astype(bool) & \
62 | (probs >= confidence).detach().cpu().numpy().astype(bool)
63 |
64 | if targeted:
65 | cost = -self.criterion(h_adv, y)
66 | else:
67 | cost = self.criterion(h_adv, y)
68 |
69 | self.net.zero_grad()
70 | if x_adv.grad is not None:
71 | x_adv.grad.data.fill_(0)
72 | cost.backward()
73 | # examples which have been misclassified won't update
74 | modify = alpha*x_adv.grad.sign_().detach().cpu().numpy()
75 | modify[flag] = 0
76 |
77 | x_adv = x_adv + torch.from_numpy(modify).cuda()
78 | x_adv = where(x_adv > x-eps, x_adv, x-eps)
79 | x_adv = where(x_adv < x+eps, x_adv, x+eps)
80 | x_adv = torch.clamp(x_adv, x_val_min, x_val_max)
81 | x_adv = Variable(x_adv.data, requires_grad=True)
82 | return x_adv
83 |
84 |
85 | class Attack_MOVIE(object):
86 | def __init__(self, classify_net, criterion):
87 | self.net = classify_net
88 | self.criterion = criterion
89 |
90 | def fgsm(self, x, y, targeted=False, eps=8/255):
91 | x_adv = Variable(x.data, requires_grad=True)
92 | h_adv, _ = self.net(x_adv, after_embedding=True)
93 | if targeted:
94 | cost = -self.criterion(h_adv, y)
95 | else:
96 | cost = self.criterion(h_adv, y)
97 |
98 | self.net.zero_grad()
99 | if x_adv.grad is not None:
100 | x_adv.grad.data.fill_(0)
101 | cost.backward()
102 |
103 | x_adv = x_adv + eps*x_adv.grad.sign_()
104 | return x_adv
105 |
106 |
107 | def where(cond, x, y):
108 | """
109 | code from :
110 | https://discuss.pytorch.org/t/how-can-i-do-the-operation-the-same-as-np-where/1329/8
111 | """
112 | cond = cond.float()
113 | return (cond*x) + ((1-cond)*y)
114 |
115 |
116 | def ShannonEntropy(logits, soft_label):
117 | pred_probs = F.softmax(logits, dim=-1)
118 | H = torch.sum(torch.mul(soft_label, torch.log(soft_label/pred_probs)), dim=-1)
119 | return H
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/cifar_undercover_train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import torch
3 | import torch.nn as nn
4 | import torch.optim as optim
5 | import torchvision
6 | from torch.autograd import Variable
7 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
8 | from models.resnet import PreActResNet18
9 | from adversary.fgsm import Attack
10 |
11 |
12 | def undercover_attack(UndercoverAttack, x, y_true, eps=1/255):
13 | x = Variable(x.to(device), requires_grad=True)
14 | y_true = Variable(y_true.to(device), requires_grad=False)
15 | x_adv = UndercoverAttack.fgsm(x, y_true, False, eps)
16 | return x_adv
17 |
18 |
19 | def train(epochs):
20 | print('==> Preparing data..')
21 | transform_train = transforms.Compose([
22 | transforms.RandomCrop(32, padding=4),
23 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
24 | transforms.ToTensor(),
25 | ])
26 |
27 | trainset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True, download=True, transform=transform_train)
28 | trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=256, shuffle=True,
29 | num_workers=4)
30 | # Model
31 | print('==> Building model..')
32 | best_acc = 0.0
33 | start_epoch = 0
34 | net = PreActResNet18().to(device)
35 | # checkpoint = torch.load(CIFAR_CKPT, map_location=torch.device(device))
36 | # net.load_state_dict(checkpoint['net'])
37 | # start_epoch = int(checkpoint['epoch'])
38 | # best_acc = float(checkpoint['acc'])
39 |
40 | UndercoverAttack = Attack(net, nn.functional.cross_entropy)
41 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
42 | optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=1e-3, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=5e-4)
43 | scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=40, gamma=0.1)
44 |
45 | net.train()
46 | for epoch in range(start_epoch, epochs):
47 | train_loss = 0
48 | correct, total = 0, 0
49 | for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(trainloader):
50 | inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)
51 | optimizer.zero_grad()
52 | outputs = net(inputs)
53 | _, predicted = outputs.max(1)
54 | total += targets.size(0)
55 | correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item()
56 |
57 | x_adv = undercover_attack(UndercoverAttack, inputs, targets, eps=0.15)
58 | adv_outputs = net(x_adv)
59 |
60 | loss1 = criterion(outputs, targets)
61 | loss2 = criterion(adv_outputs, targets)
62 | loss = loss1 + loss2 * 0.8
63 | train_loss += loss.item()
64 | loss.backward()
65 | optimizer.step()
66 | scheduler.step(epoch)
67 | acc = 1.0 * correct / total
68 | print('epoch: %d, train loss: %.2f, train acc: %.4f' % (epoch, train_loss, acc))
69 | if acc > best_acc:
70 | best_acc = acc
71 | state = {
72 | 'net': net.state_dict(),
73 | 'acc': acc,
74 | 'epoch': epoch,
75 | }
76 | if not os.path.isdir('checkpoint'):
77 | os.mkdir('checkpoint')
78 | torch.save(state, CIFAR_CKPT)
79 |
80 |
81 | def test():
82 | # Data
83 | print('==> Preparing data..')
84 | transform_test = transforms.Compose([
85 | transforms.ToTensor(),
86 | ])
87 | testset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False, download=True, transform=transform_test)
88 | testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testset, batch_size=256, shuffle=False,
89 | num_workers=4)
90 |
91 | # Model
92 | print('==> Building model..')
93 | net = PreActResNet18().to(device)
94 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
95 | checkpoint = torch.load(CIFAR_CKPT)
96 | net.load_state_dict(checkpoint['net'])
97 |
98 | net.eval()
99 | test_loss = 0
100 | correct, total = 0, 0
101 |
102 | with torch.no_grad():
103 | for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(testloader):
104 | inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)
105 | outputs = net(inputs)
106 | loss = criterion(outputs, targets)
107 |
108 | test_loss += loss.item()
109 | _, predicted = outputs.max(1)
110 | total += targets.size(0)
111 | correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item()
112 | acc = 1.0 * correct / total
113 | print('test loss: %.2f, test acc: %.4f' % (test_loss, acc))
114 |
115 |
116 | if __name__ == '__main__':
117 | CIFAR_CKPT = './checkpoint/cifar_undercover.pth'
118 | device = 'cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
119 |
120 | train(150)
121 | test()
122 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnist_DBA.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "code",
5 | "execution_count": 1,
6 | "metadata": {},
7 | "outputs": [],
8 | "source": [
9 | "import numpy as np\n",
10 | "import torch\n",
11 | "import adversary.cw as cw\n",
12 | "from adversary.jsma import SaliencyMapMethod\n",
13 | "from adversary.fgsm import Attack\n",
14 | "import torchvision\n",
15 | "import torch.nn.functional as F\n",
16 | "import torch.utils.data as Data\n",
17 | "from models.mnist_model import MnistModel, MLP\n",
18 | "from torchvision import transforms\n",
19 | "\n",
20 | "%reload_ext autoreload\n",
21 | "%autoreload 2"
22 | ]
23 | },
24 | {
25 | "cell_type": "code",
26 | "execution_count": 3,
27 | "metadata": {},
28 | "outputs": [
29 | {
30 | "data": {
31 | "text/plain": [
32 | "'cuda:1'"
33 | ]
34 | },
35 | "execution_count": 3,
36 | "metadata": {},
37 | "output_type": "execute_result"
38 | }
39 | ],
40 | "source": [
41 | "MNIST_UNDERCOVER_CKPT = './checkpoint/mnist_undercover.pth'\n",
42 | "device = 'cuda:1' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'\n",
43 | "device"
44 | ]
45 | },
46 | {
47 | "cell_type": "code",
48 | "execution_count": 4,
49 | "metadata": {},
50 | "outputs": [
51 | {
52 | "data": {
53 | "text/plain": [
54 | ""
55 | ]
56 | },
57 | "execution_count": 4,
58 | "metadata": {},
59 | "output_type": "execute_result"
60 | }
61 | ],
62 | "source": [
63 | "transform_test = transforms.Compose([\n",
64 | " transforms.ToTensor(),\n",
65 | "])\n",
66 | "\n",
67 | "mlp = MLP().to(device)\n",
68 | "criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()\n",
69 | "optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(mlp.parameters(), lr=1e-3, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=5e-4)\n",
70 | "\n",
71 | "\n",
72 | "undercoverNet = MnistModel().to(device)\n",
73 | "checkpoint = torch.load(MNIST_UNDERCOVER_CKPT, map_location=torch.device(device))\n",
74 | "undercoverNet.load_state_dict(checkpoint['net'])"
75 | ]
76 | },
77 | {
78 | "cell_type": "code",
79 | "execution_count": 5,
80 | "metadata": {},
81 | "outputs": [],
82 | "source": [
83 | "trainset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=True, download=True, transform=transform_test)\n",
84 | "trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=512, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)\n",
85 | "trainiter = iter(trainloader)\n",
86 | "\n",
87 | "testset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=False, download=True, transform=transform_test)\n",
88 | "testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testset, batch_size=512, shuffle=False, num_workers=4)\n",
89 | "testiter = iter(testloader)"
90 | ]
91 | },
92 | {
93 | "cell_type": "markdown",
94 | "metadata": {},
95 | "source": [
96 | "# Take BIM attack as an example"
97 | ]
98 | },
99 | {
100 | "cell_type": "code",
101 | "execution_count": 6,
102 | "metadata": {},
103 | "outputs": [],
104 | "source": [
105 | "undercover_gradient_attacker = Attack(undercoverNet, F.cross_entropy)"
106 | ]
107 | },
108 | {
109 | "cell_type": "code",
110 | "execution_count": 7,
111 | "metadata": {},
112 | "outputs": [],
113 | "source": [
114 | "# construct bim adversarial samples\n",
115 | "# --------------------train---------------------\n",
116 | "normal_samples, adversarial_samples = [], []\n",
117 | "for x, y in trainloader:\n",
118 | " x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)\n",
119 | " y_pred = undercoverNet(x).argmax(dim=1)\n",
120 | " \n",
121 | " eps = 0.3\n",
122 | " x_adv = undercover_gradient_attacker.i_fgsm(x, y, eps=eps, alpha=1/255, iteration=int(min(eps*255 + 4, 1.25*eps*255)))\n",
123 | " y_pred_adv = undercoverNet(x_adv).argmax(dim=1)\n",
124 | " selected = (y == y_pred) & (y != y_pred_adv)\n",
125 | " normal_samples.append(x[selected].detach().cpu())\n",
126 | " adversarial_samples.append(x_adv[selected].detach().cpu())\n",
127 | "# break\n",
128 | "\n",
129 | "normal_x = torch.cat(normal_samples, dim=0)\n",
130 | "adversarial_x = torch.cat(adversarial_samples, dim=0)\n",
131 | "normal_y = torch.zeros(normal_x.shape[0]).long()\n",
132 | "adversarial_y = torch.ones(adversarial_x.shape[0]).long()\n",
133 | "\n",
134 | "dba_trainloader = Data.DataLoader(Data.TensorDataset(torch.cat([normal_x, adversarial_x], dim=0),\n",
135 | " torch.cat([normal_y, adversarial_y], dim=0)), \n",
136 | " batch_size=512, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)\n",
137 | "dba_trainiter = iter(dba_trainloader)\n",
138 | "\n",
139 | "# ----------------test---------------------\n",
140 | "normal_samples, adversarial_samples = [], []\n",
141 | "for x, y in testloader:\n",
142 | " x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)\n",
143 | " y_pred = undercoverNet(x).argmax(dim=1)\n",
144 | " \n",
145 | " eps = 0.3\n",
146 | " x_adv = undercover_gradient_attacker.i_fgsm(x, y, eps=eps, alpha=1/255, iteration=int(min(eps*255 + 4, 1.25*eps*255)))\n",
147 | " y_pred_adv = undercoverNet(x_adv).argmax(dim=1)\n",
148 | " selected = (y == y_pred) & (y != y_pred_adv)\n",
149 | " normal_samples.append(x[selected].detach().cpu())\n",
150 | " adversarial_samples.append(x_adv[selected].detach().cpu())\n",
151 | "# break\n",
152 | "\n",
153 | "normal_x = torch.cat(normal_samples, dim=0)\n",
154 | "adversarial_x = torch.cat(adversarial_samples, dim=0)\n",
155 | "normal_y = torch.zeros(normal_x.shape[0]).long()\n",
156 | "adversarial_y = torch.ones(adversarial_x.shape[0]).long()\n",
157 | "\n",
158 | "dba_testloader = Data.DataLoader(Data.TensorDataset(torch.cat([normal_x, adversarial_x], dim=0),\n",
159 | " torch.cat([normal_y, adversarial_y], dim=0)), \n",
160 | " batch_size=1024, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)\n",
161 | "dba_testiter = iter(dba_testloader)"
162 | ]
163 | },
164 | {
165 | "cell_type": "code",
166 | "execution_count": 8,
167 | "metadata": {},
168 | "outputs": [],
169 | "source": [
170 | "# train the mlp\n",
171 | "epochs = 10\n",
172 | "for i in range(epochs):\n",
173 | " for x, y in dba_trainloader:\n",
174 | " optimizer.zero_grad()\n",
175 | " x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)\n",
176 | " _, V1 = undercoverNet(x, dba=True)\n",
177 | " undercover_adv = undercover_gradient_attacker.fgsm(x, y, False, 1/255)\n",
178 | " _, V2 = undercoverNet(undercover_adv, dba=True)\n",
179 | " V = torch.cat([V1, V2, V1 - V2, V1 * V2], axis=-1)\n",
180 | " y_pred = mlp(V)\n",
181 | " loss = criterion(y_pred, y)\n",
182 | " loss.backward()\n",
183 | " optimizer.step()"
184 | ]
185 | },
186 | {
187 | "cell_type": "code",
188 | "execution_count": 9,
189 | "metadata": {},
190 | "outputs": [
191 | {
192 | "name": "stdout",
193 | "output_type": "stream",
194 | "text": [
195 | "0.997010144153764\n"
196 | ]
197 | }
198 | ],
199 | "source": [
200 | "# test\n",
201 | "total, correct = 0, 0\n",
202 | "for x, y in dba_testloader:\n",
203 | " x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)\n",
204 | " _, V1 = undercoverNet(x, dba=True)\n",
205 | " undercover_adv = undercover_gradient_attacker.fgsm(x, y, False, 1/255)\n",
206 | " _, V2 = undercoverNet(undercover_adv, dba=True)\n",
207 | " V = torch.cat([V1, V2, V1 - V2, V1 * V2], axis=-1)\n",
208 | " y_pred = mlp(V).argmax(dim=1)\n",
209 | " \n",
210 | " total += y.size(0)\n",
211 | " correct += y_pred.eq(y).sum().item()\n",
212 | "print(correct / total)"
213 | ]
214 | },
215 | {
216 | "cell_type": "code",
217 | "execution_count": null,
218 | "metadata": {},
219 | "outputs": [],
220 | "source": []
221 | },
222 | {
223 | "cell_type": "code",
224 | "execution_count": null,
225 | "metadata": {},
226 | "outputs": [],
227 | "source": []
228 | },
229 | {
230 | "cell_type": "code",
231 | "execution_count": null,
232 | "metadata": {},
233 | "outputs": [],
234 | "source": []
235 | },
236 | {
237 | "cell_type": "code",
238 | "execution_count": null,
239 | "metadata": {},
240 | "outputs": [],
241 | "source": []
242 | },
243 | {
244 | "cell_type": "code",
245 | "execution_count": null,
246 | "metadata": {},
247 | "outputs": [],
248 | "source": []
249 | },
250 | {
251 | "cell_type": "code",
252 | "execution_count": null,
253 | "metadata": {},
254 | "outputs": [],
255 | "source": []
256 | },
257 | {
258 | "cell_type": "code",
259 | "execution_count": null,
260 | "metadata": {},
261 | "outputs": [],
262 | "source": []
263 | },
264 | {
265 | "cell_type": "code",
266 | "execution_count": null,
267 | "metadata": {},
268 | "outputs": [],
269 | "source": []
270 | },
271 | {
272 | "cell_type": "code",
273 | "execution_count": null,
274 | "metadata": {},
275 | "outputs": [],
276 | "source": []
277 | }
278 | ],
279 | "metadata": {
280 | "kernelspec": {
281 | "display_name": "Python 3",
282 | "language": "python",
283 | "name": "python3"
284 | },
285 | "language_info": {
286 | "codemirror_mode": {
287 | "name": "ipython",
288 | "version": 3
289 | },
290 | "file_extension": ".py",
291 | "mimetype": "text/x-python",
292 | "name": "python",
293 | "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
294 | "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
295 | "version": "3.7.6"
296 | }
297 | },
298 | "nbformat": 4,
299 | "nbformat_minor": 2
300 | }
301 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/cifar_DBA.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "code",
5 | "execution_count": 1,
6 | "metadata": {},
7 | "outputs": [],
8 | "source": [
9 | "import numpy as np\n",
10 | "import torch\n",
11 | "import adversary.cw as cw\n",
12 | "from adversary.jsma import SaliencyMapMethod\n",
13 | "from adversary.fgsm import Attack\n",
14 | "import torchvision\n",
15 | "import torch.nn.functional as F\n",
16 | "import torch.utils.data as Data\n",
17 | "from models.resnet import PreActResNet18, MLP\n",
18 | "from torchvision import transforms\n",
19 | "\n",
20 | "%reload_ext autoreload\n",
21 | "%autoreload 2"
22 | ]
23 | },
24 | {
25 | "cell_type": "code",
26 | "execution_count": 2,
27 | "metadata": {},
28 | "outputs": [
29 | {
30 | "data": {
31 | "text/plain": [
32 | "'cuda:1'"
33 | ]
34 | },
35 | "execution_count": 2,
36 | "metadata": {},
37 | "output_type": "execute_result"
38 | }
39 | ],
40 | "source": [
41 | "CIFAR_UNDERCOVER_CKPT = './checkpoint/cifar_undercover.pth'\n",
42 | "device = 'cuda:1' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'\n",
43 | "device"
44 | ]
45 | },
46 | {
47 | "cell_type": "code",
48 | "execution_count": 10,
49 | "metadata": {},
50 | "outputs": [
51 | {
52 | "data": {
53 | "text/plain": [
54 | ""
55 | ]
56 | },
57 | "execution_count": 10,
58 | "metadata": {},
59 | "output_type": "execute_result"
60 | }
61 | ],
62 | "source": [
63 | "transform_test = transforms.Compose([\n",
64 | " transforms.ToTensor(),\n",
65 | "])\n",
66 | "\n",
67 | "mlp = MLP().to(device)\n",
68 | "criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()\n",
69 | "optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(mlp.parameters(), lr=1e-3, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=5e-4)\n",
70 | "\n",
71 | "\n",
72 | "undercoverNet = PreActResNet18().to(device)\n",
73 | "checkpoint = torch.load(CIFAR_UNDERCOVER_CKPT, map_location=torch.device(device))\n",
74 | "undercoverNet.load_state_dict(checkpoint['net'])"
75 | ]
76 | },
77 | {
78 | "cell_type": "code",
79 | "execution_count": 4,
80 | "metadata": {},
81 | "outputs": [
82 | {
83 | "name": "stdout",
84 | "output_type": "stream",
85 | "text": [
86 | "Files already downloaded and verified\n",
87 | "Files already downloaded and verified\n"
88 | ]
89 | }
90 | ],
91 | "source": [
92 | "trainset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True, download=True, transform=transform_test)\n",
93 | "trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=512, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)\n",
94 | "trainiter = iter(trainloader)\n",
95 | "\n",
96 | "testset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False, download=True, transform=transform_test)\n",
97 | "testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testset, batch_size=512, shuffle=False, num_workers=4)\n",
98 | "testiter = iter(testloader)"
99 | ]
100 | },
101 | {
102 | "cell_type": "markdown",
103 | "metadata": {},
104 | "source": [
105 | "# Take BIM attack as an example"
106 | ]
107 | },
108 | {
109 | "cell_type": "code",
110 | "execution_count": 5,
111 | "metadata": {},
112 | "outputs": [],
113 | "source": [
114 | "undercover_gradient_attacker = Attack(undercoverNet, F.cross_entropy)"
115 | ]
116 | },
117 | {
118 | "cell_type": "code",
119 | "execution_count": 6,
120 | "metadata": {},
121 | "outputs": [],
122 | "source": [
123 | "# construct bim adversarial samples\n",
124 | "# --------------------train---------------------\n",
125 | "normal_samples, adversarial_samples = [], []\n",
126 | "for x, y in trainloader:\n",
127 | " x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)\n",
128 | " y_pred = undercoverNet(x).argmax(dim=1)\n",
129 | " \n",
130 | " eps = 0.3\n",
131 | " x_adv = undercover_gradient_attacker.i_fgsm(x, y, eps=eps, alpha=1/255, iteration=int(min(eps*255 + 4, 1.25*eps*255)))\n",
132 | " y_pred_adv = undercoverNet(x_adv).argmax(dim=1)\n",
133 | " selected = (y == y_pred) & (y != y_pred_adv)\n",
134 | " normal_samples.append(x[selected].detach().cpu())\n",
135 | " adversarial_samples.append(x_adv[selected].detach().cpu())\n",
136 | "# break\n",
137 | "\n",
138 | "normal_x = torch.cat(normal_samples, dim=0)\n",
139 | "adversarial_x = torch.cat(adversarial_samples, dim=0)\n",
140 | "normal_y = torch.zeros(normal_x.shape[0]).long()\n",
141 | "adversarial_y = torch.ones(adversarial_x.shape[0]).long()\n",
142 | "\n",
143 | "dba_trainloader = Data.DataLoader(Data.TensorDataset(torch.cat([normal_x, adversarial_x], dim=0),\n",
144 | " torch.cat([normal_y, adversarial_y], dim=0)), \n",
145 | " batch_size=256, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)\n",
146 | "dba_trainiter = iter(dba_trainloader)\n",
147 | "\n",
148 | "# ----------------test---------------------\n",
149 | "normal_samples, adversarial_samples = [], []\n",
150 | "for x, y in testloader:\n",
151 | " x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)\n",
152 | " y_pred = undercoverNet(x).argmax(dim=1)\n",
153 | " \n",
154 | " eps = 0.3\n",
155 | " x_adv = undercover_gradient_attacker.i_fgsm(x, y, eps=eps, alpha=1/255, iteration=int(min(eps*255 + 4, 1.25*eps*255)))\n",
156 | " y_pred_adv = undercoverNet(x_adv).argmax(dim=1)\n",
157 | " selected = (y == y_pred) & (y != y_pred_adv)\n",
158 | " normal_samples.append(x[selected].detach().cpu())\n",
159 | " adversarial_samples.append(x_adv[selected].detach().cpu())\n",
160 | "# break\n",
161 | "\n",
162 | "normal_x = torch.cat(normal_samples, dim=0)\n",
163 | "adversarial_x = torch.cat(adversarial_samples, dim=0)\n",
164 | "normal_y = torch.zeros(normal_x.shape[0]).long()\n",
165 | "adversarial_y = torch.ones(adversarial_x.shape[0]).long()\n",
166 | "\n",
167 | "dba_testloader = Data.DataLoader(Data.TensorDataset(torch.cat([normal_x, adversarial_x], dim=0),\n",
168 | " torch.cat([normal_y, adversarial_y], dim=0)), \n",
169 | " batch_size=256, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)\n",
170 | "dba_testiter = iter(dba_testloader)"
171 | ]
172 | },
173 | {
174 | "cell_type": "code",
175 | "execution_count": null,
176 | "metadata": {},
177 | "outputs": [],
178 | "source": []
179 | },
180 | {
181 | "cell_type": "code",
182 | "execution_count": 11,
183 | "metadata": {},
184 | "outputs": [],
185 | "source": [
186 | "# train the mlp\n",
187 | "epochs = 10\n",
188 | "for i in range(epochs):\n",
189 | " for x, y in dba_trainloader:\n",
190 | " optimizer.zero_grad()\n",
191 | " x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)\n",
192 | " _, V1 = undercoverNet(x, dba=True)\n",
193 | " undercover_adv = undercover_gradient_attacker.fgsm(x, y, False, 1/255)\n",
194 | " _, V2 = undercoverNet(undercover_adv, dba=True)\n",
195 | " V = torch.cat([V1, V2, V1 - V2, V1 * V2], axis=-1)\n",
196 | " y_pred = mlp(V)\n",
197 | " loss = criterion(y_pred, y)\n",
198 | " loss.backward()\n",
199 | " optimizer.step()"
200 | ]
201 | },
202 | {
203 | "cell_type": "code",
204 | "execution_count": 12,
205 | "metadata": {},
206 | "outputs": [
207 | {
208 | "name": "stdout",
209 | "output_type": "stream",
210 | "text": [
211 | "0.9993314018275017\n"
212 | ]
213 | }
214 | ],
215 | "source": [
216 | "# test\n",
217 | "total, correct = 0, 0\n",
218 | "for x, y in dba_testloader:\n",
219 | " x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)\n",
220 | " _, V1 = undercoverNet(x, dba=True)\n",
221 | " undercover_adv = undercover_gradient_attacker.fgsm(x, y, False, 1/255)\n",
222 | " _, V2 = undercoverNet(undercover_adv, dba=True)\n",
223 | " V = torch.cat([V1, V2, V1 - V2, V1 * V2], axis=-1)\n",
224 | " y_pred = mlp(V).argmax(dim=1)\n",
225 | " \n",
226 | " total += y.size(0)\n",
227 | " correct += y_pred.eq(y).sum().item()\n",
228 | "print(correct / total)"
229 | ]
230 | },
231 | {
232 | "cell_type": "code",
233 | "execution_count": null,
234 | "metadata": {},
235 | "outputs": [],
236 | "source": []
237 | },
238 | {
239 | "cell_type": "code",
240 | "execution_count": null,
241 | "metadata": {},
242 | "outputs": [],
243 | "source": []
244 | },
245 | {
246 | "cell_type": "code",
247 | "execution_count": null,
248 | "metadata": {},
249 | "outputs": [],
250 | "source": []
251 | },
252 | {
253 | "cell_type": "code",
254 | "execution_count": null,
255 | "metadata": {},
256 | "outputs": [],
257 | "source": []
258 | },
259 | {
260 | "cell_type": "code",
261 | "execution_count": null,
262 | "metadata": {},
263 | "outputs": [],
264 | "source": []
265 | },
266 | {
267 | "cell_type": "code",
268 | "execution_count": null,
269 | "metadata": {},
270 | "outputs": [],
271 | "source": []
272 | },
273 | {
274 | "cell_type": "code",
275 | "execution_count": null,
276 | "metadata": {},
277 | "outputs": [],
278 | "source": []
279 | },
280 | {
281 | "cell_type": "code",
282 | "execution_count": null,
283 | "metadata": {},
284 | "outputs": [],
285 | "source": []
286 | },
287 | {
288 | "cell_type": "code",
289 | "execution_count": null,
290 | "metadata": {},
291 | "outputs": [],
292 | "source": []
293 | }
294 | ],
295 | "metadata": {
296 | "kernelspec": {
297 | "display_name": "Python 3",
298 | "language": "python",
299 | "name": "python3"
300 | },
301 | "language_info": {
302 | "codemirror_mode": {
303 | "name": "ipython",
304 | "version": 3
305 | },
306 | "file_extension": ".py",
307 | "mimetype": "text/x-python",
308 | "name": "python",
309 | "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
310 | "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
311 | "version": "3.7.6"
312 | }
313 | },
314 | "nbformat": 4,
315 | "nbformat_minor": 2
316 | }
317 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adversary/jsma.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Referential implementation: cleverhans tensorflow
3 | """
4 | import torch
5 | import torch.nn.functional as F
6 | import torch.nn as nn
7 | import numpy as np
8 | from settings import *
9 | from torch.autograd import Variable
10 |
11 | class SaliencyMapMethod(object):
12 | """
13 | The Jacobian-based Saliency Map Method (Papernot et al. 2016).
14 | Paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1511.07528.pdf
15 | :param model: pytorch model
16 | :param kwargs: passed through to super constructor
17 | """
18 |
19 | def __init__(self, model, **kwargs):
20 | super(SaliencyMapMethod, self).__init__()
21 | self.model = model
22 |
23 | self.theta = kwargs['theta']
24 | self.gamma = kwargs['gamma']
25 | self.clip_min = kwargs['clip_min']
26 | self.clip_max = kwargs['clip_max']
27 | self.nb_classes = kwargs['nb_classes']
28 | self.confidence = 0.5
29 |
30 | def generate(self, x, y=None, y_target=None, confidence=0.5):
31 | """
32 | :param x: The model's inputs.
33 | :return:
34 | """
35 | self.confidence = confidence
36 | self.y = y
37 | self.y_target = y_target
38 | # Create random targets if y_target not provided
39 | if self.y_target is None:
40 | from random import randint
41 |
42 | def random_targets(gt):
43 | result = gt.copy()
44 | for i in range(len(gt)):
45 | rand_num = randint(0, self.nb_classes-1)
46 | while rand_num == result[i]:
47 | rand_num = randint(0, self.nb_classes - 1)
48 | result[i] = rand_num
49 | return result
50 |
51 | labels = self.get_or_guess_labels(x)
52 | self.y_target = torch.from_numpy(random_targets(labels.cpu().numpy())).cuda()
53 |
54 | x_adv = jsma_symbolic(
55 | x,
56 | model=self.model,
57 | y_target=self.y_target,
58 | theta=self.theta,
59 | gamma=self.gamma,
60 | clip_min=self.clip_min,
61 | clip_max=self.clip_max,
62 | nb_classes=self.nb_classes,
63 | confidence=self.confidence)
64 | return x_adv
65 |
66 | def get_or_guess_labels(self, x):
67 | if self.y is not None:
68 | labels = self.y
69 | else:
70 | outputs = self.model(x)
71 | _, labels = outputs.max(1)
72 | return labels
73 |
74 | def jsma_symbolic(x, y_target, model, theta, gamma, clip_min, clip_max, nb_classes, confidence=0.5):
75 | """
76 | :param x: the input tensor
77 | :param y_target: the target tensor
78 | :param model: a pytorch model object.
79 | :param theta: delta for each feature adjustment
80 | :param gamma: a float between 0 - 1 indicating the maximum distortion
81 | percentage
82 | :param clip_min: minimum value for components of the example returned
83 | :param clip_max: maximum value for components of the example returned
84 | :return: a tensor for the adversarial example
85 | """
86 | nb_features = int(np.prod(x.size()[1:]))
87 |
88 | max_iters = np.floor(nb_features * gamma / 2)
89 | # print('max_iters: ', max_iters)
90 | increase = bool(theta > 0)
91 |
92 | tmp = np.ones((nb_features, nb_features), int)
93 | np.fill_diagonal(tmp, 0)
94 | zero_diagonal = torch.from_numpy(tmp).float().cuda()
95 |
96 | # Compute our initial search domain. We optimize the initial search domain
97 | # by removing all features that are already at their maximum values (if
98 | # increasing input features---otherwise, at their minimum value).x
99 | if increase:
100 | search_domain = (x < clip_max).float().reshape(-1, nb_features)
101 | else:
102 | search_domain = (x > clip_min).float().reshape(-1, nb_features)
103 |
104 | # Loop variables
105 | # x_in: the tensor that holds the latest adversarial outputs that are in
106 | # progress.
107 | # y_in: the tensor for target labels
108 | # domain_in: the tensor that holds the latest search domain
109 | # cond_in: the boolean tensor to show if more iteration is needed for
110 | # generating adversarial samples
111 |
112 | def condition(x_in, y_in, domain_in, i_in, cond_in):
113 | # Repeat the loop until we have achieved misclassification or
114 | # reaches the maximum iterations
115 | return (i_in < max_iters) and cond_in
116 |
117 | def body(x_in, y_in, domain_in, i_in, cond_in):
118 | x_in = Variable(x_in.data, requires_grad=True)
119 | y_in_one_hot = torch.zeros(y_in.shape[0], nb_classes).scatter_(1, y_in.cpu().reshape(-1, 1).long(), 1).cuda()
120 | logits = model(x_in)
121 | # _, preds = logits.max(1)
122 | probs, preds = F.softmax(logits, dim=-1).max(1)
123 |
124 | # create the Jacobian
125 | grads = None
126 | for class_ind in range(nb_classes):
127 | model.zero_grad()
128 | logits[:, class_ind].sum().backward(retain_graph=True)
129 | derivatives = x_in.grad
130 | if class_ind == 0:
131 | grads = derivatives
132 | else:
133 | grads = torch.cat((grads, derivatives))
134 | grads = grads.reshape(nb_classes, -1, nb_features)
135 |
136 | # Compute the Jacobian components
137 | # To help with the computation later, reshape the target_class
138 | # and other_class to [nb_classes, -1, 1].
139 | # The last dimention is added to allow broadcasting later.
140 | target_class = y_in_one_hot.permute(1, 0).reshape(nb_classes, -1, 1)
141 | other_class = (target_class != 1).float()
142 |
143 | grads_target = torch.sum(grads * target_class, dim=0)
144 | grads_other = torch.sum(grads * other_class, dim=0)
145 |
146 | # Remove the already-used input features from the search space
147 | # Subtract 2 times the maximum value from those value so that
148 | # they won't be picked later
149 | increase_coef = (4 * int(increase) - 2) * (domain_in == 0).float()
150 |
151 | target_tmp = grads_target
152 | target_tmp -= increase_coef * torch.max(torch.abs(grads_target), dim=1, keepdim=True)[0]
153 | target_sum = target_tmp.reshape(-1, nb_features, 1) + target_tmp.reshape(-1, 1, nb_features)
154 |
155 | other_tmp = grads_other
156 | other_tmp -= increase_coef * torch.max(torch.abs(grads_other), dim=1, keepdim=True)[0]
157 | other_sum = other_tmp.reshape(-1, nb_features, 1) + other_tmp.reshape(-1, 1, nb_features)
158 |
159 | # Create a mask to only keep features that match conditions
160 | if increase:
161 | scores_mask = ((target_sum > 0) & (other_sum < 0))
162 | else:
163 | scores_mask = ((target_sum < 0) & (other_sum > 0))
164 |
165 | # Create a 2D numpy array of scores for each pair of candidate features
166 | scores = scores_mask.float() * (-target_sum * other_sum) * zero_diagonal
167 |
168 | # Extract the best two pixels
169 | best = torch.argmax(scores.reshape(-1, nb_features * nb_features), dim=1).cpu()
170 |
171 | p1 = np.mod(best, nb_features)
172 | p2 = np.floor_divide(best, nb_features)
173 | p1_one_hot = torch.zeros(y_in.shape[0], nb_features).scatter_(1, p1.reshape(-1,1).long(), 1).cuda()
174 | p2_one_hot = torch.zeros(y_in.shape[0], nb_features).scatter_(1, p2.reshape(-1,1).long(), 1).cuda()
175 |
176 | # Check if more modification is needed for each sample
177 | mod_not_done = (y_in != preds) & (probs >= confidence)
178 | cond = mod_not_done & (torch.sum(domain_in, dim=1) >= 2)
179 |
180 | #update the search domain
181 | cond_float = cond.reshape(-1, 1).float().cuda()
182 | to_mod = (p1_one_hot + p2_one_hot) * cond_float
183 |
184 | domain_out = domain_in - to_mod
185 |
186 | # Apply the modification to the images
187 | to_mod_reshape = to_mod.reshape([-1] + list(x_in.shape[1:]))
188 | if increase:
189 | x_out = torch.clamp(x_in + to_mod_reshape * theta, max=clip_max)
190 | else:
191 | x_out = torch.clamp(x_in - to_mod_reshape * theta, min=clip_min)
192 |
193 | # Increase the iterator, and check if all misclassifications are done
194 | i_out = i_in + 1
195 | cond_out = torch.sum(cond) != 0
196 |
197 | return x_out, y_in, domain_out, i_out, cond_out
198 |
199 | # Run loop to do JSMA
200 | x_adv, y_in, domain_out, i_out, cond_out = x, y_target, search_domain, 0, True
201 | conditions = condition(x_adv, y_in, domain_out, i_out, cond_out)
202 | while (conditions):
203 | x_adv, y_in, domain_out, i_out, cond_out = body(x_adv, y_in, domain_out, i_out, cond_out)
204 | conditions = condition(x_adv, y_in, domain_out, i_out, cond_out)
205 |
206 | return x_adv
207 |
208 | def jsma(x_in, y_in, model, nb_classes, max_iter=10, fix_iter=False, stop_confidence=0.5):
209 | """
210 | jacobian-based attack on RNNs
211 | :param x_in:
212 | :param y_in:
213 | :param model:
214 | :param nb_classes:
215 | :param max_iter:
216 | :param fix_iter:
217 | :return:
218 | """
219 | stop_confidence = 1 - stop_confidence
220 | criterion_none = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none')
221 | logits, embeddings = model(x_in)
222 | change_words = 0
223 | change_list = []
224 | changed = False
225 | while not changed and change_words < max_iter:
226 | change_words += 1
227 | # create the Jacobian
228 | grads = None
229 | for class_ind in range(nb_classes):
230 | model.zero_grad()
231 | logits[:, class_ind].sum().backward(retain_graph=True)
232 | derivatives = embeddings.grad.reshape(len(x_in), -1)
233 | derivatives = derivatives.sum(dim=1)
234 | if class_ind == 0:
235 | grads = derivatives
236 | else:
237 | grads = torch.cat((grads, derivatives))
238 | grads = grads.reshape(nb_classes, -1).cpu().numpy()
239 | gradsum = np.abs(grads[1-y_in,:]) * (-grads[y_in,:])
240 | max_index = np.argmax(gradsum)
241 | while max_index in change_list:
242 | gradsum[max_index] = -1
243 | max_index = np.argmax(gradsum)
244 | change_list.append(max_index)
245 | min_confidence = torch.nn.functional.softmax(logits, dim=1)[0, y_in]
246 | best_word = x_in[max_index]
247 | for i in range(50):
248 | x_in[max_index] = i
249 | logits, _ = model(x_in)
250 | confidence = torch.nn.functional.softmax(logits, dim=1)[0,y_in]
251 | if confidence < min_confidence:
252 | min_confidence = confidence
253 | best_word = i
254 | if confidence < stop_confidence: # for speed up, u can delete it
255 | break
256 | x_in[max_index] = best_word
257 | logits, _ = model(x_in)
258 | _, predicted = logits.max(1)
259 | changed = bool(predicted != y_in)
260 | if fix_iter:
261 | changed = False
262 | return changed, x_in, change_words, criterion_none(logits, torch.LongTensor([y_in]).cuda()).detach().cpu().numpy()[0]
263 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adversary/cw.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Carlini-Wagner attack (http://arxiv.org/abs/1608.04644).
3 |
4 | Referential implementation:
5 | - https://github.com/kkew3/pytorch-cw2
6 | - https://github.com/carlini/nn_robust_attacks.git (the original implementation)
7 | - https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-nips2017-attack-example.git
8 | """
9 | import operator as op
10 |
11 | from typing import Union, Tuple
12 |
13 | import numpy as np
14 | import torch
15 | import torch.nn as nn
16 | import torch.optim as optim
17 | from torch.autograd import Variable
18 | from settings import *
19 |
20 | import util.runutils as runutils
21 |
22 |
23 | def _var2numpy(var):
24 | """
25 | Make Variable to numpy array. No transposition will be made.
26 |
27 | :param var: Variable instance on whatever device
28 | :type var: Variable
29 | :return: the corresponding numpy array
30 | :rtype: np.ndarray
31 | """
32 | return var.data.cpu().numpy()
33 |
34 |
35 | def atanh(x, eps=1e-6):
36 | """
37 | The inverse hyperbolic tangent function, missing in pytorch.
38 |
39 | :param x: a tensor or a Variable
40 | :param eps: used to enhance numeric stability
41 | :return: :math:`\\tanh^{-1}{x}`, of the same type as ``x``
42 | """
43 | x = x * (1 - eps)
44 | return 0.5 * torch.log((1.0 + x) / (1.0 - x))
45 |
46 | def to_tanh_space(x, box):
47 | # type: (Union[Variable, torch.FloatTensor], Tuple[float, float]) -> Union[Variable, torch.FloatTensor]
48 | """
49 | Convert a batch of tensors to tanh-space. This method complements the
50 | implementation of the change-of-variable trick in terms of tanh.
51 |
52 | :param x: the batch of tensors, of dimension [B x C x H x W]
53 | :param box: a tuple of lower bound and upper bound of the box constraint
54 | :return: the batch of tensors in tanh-space, of the same dimension;
55 | the returned tensor is on the same device as ``x``
56 | """
57 | _box_mul = (box[1] - box[0]) * 0.5
58 | _box_plus = (box[1] + box[0]) * 0.5
59 | return atanh((x - _box_plus) / _box_mul)
60 |
61 | def from_tanh_space(x, box):
62 | # type: (Union[Variable, torch.FloatTensor], Tuple[float, float]) -> Union[Variable, torch.FloatTensor]
63 | """
64 | Convert a batch of tensors from tanh-space to oridinary image space.
65 | This method complements the implementation of the change-of-variable trick
66 | in terms of tanh.
67 |
68 | :param x: the batch of tensors, of dimension [B x C x H x W]
69 | :param box: a tuple of lower bound and upper bound of the box constraint
70 | :return: the batch of tensors in ordinary image space, of the same
71 | dimension; the returned tensor is on the same device as ``x``
72 | """
73 | _box_mul = (box[1] - box[0]) * 0.5
74 | _box_plus = (box[1] + box[0]) * 0.5
75 | return torch.tanh(x) * _box_mul + _box_plus
76 |
77 |
78 | class L2Adversary(object):
79 | """
80 | The L2 attack adversary. To enforce the box constraint, the
81 | change-of-variable trick using tanh-space is adopted.
82 |
83 | The loss function to optimize:
84 |
85 | .. math::
86 | \\|\\delta\\|_2^2 + c \\cdot f(x + \\delta)
87 |
88 | where :math:`f` is defined as
89 |
90 | .. math::
91 | f(x') = \\max\\{0, (\\max_{i \\ne t}{Z(x')_i} - Z(x')_t) \\cdot \\tau + \\kappa\\}
92 |
93 | where :math:`\\tau` is :math:`+1` if the adversary performs targeted attack;
94 | otherwise it's :math:`-1`.
95 |
96 | Usage::
97 |
98 | attacker = L2Adversary()
99 | # inputs: a batch of input tensors
100 | # targets: a batch of attack targets
101 | # model: the model to attack
102 | advx = attacker(model, inputs, targets)
103 |
104 |
105 | The change-of-variable trick
106 | ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
107 |
108 | Let :math:`a` be a proper affine transformation.
109 |
110 | 1. Given input :math:`x` in image space, map :math:`x` to "tanh-space" by
111 |
112 | .. math:: \\hat{x} = \\tanh^{-1}(a^{-1}(x))
113 |
114 | 2. Optimize an adversarial perturbation :math:`m` without constraint in the
115 | "tanh-space", yielding an adversarial example :math:`w = \\hat{x} + m`; and
116 |
117 | 3. Map :math:`w` back to the same image space as the one where :math:`x`
118 | resides:
119 |
120 | .. math::
121 | x' = a(\\tanh(w))
122 |
123 | where :math:`x'` is the adversarial example, and :math:`\\delta = x' - x`
124 | is the adversarial perturbation.
125 |
126 | Since the composition of affine transformation and hyperbolic tangent is
127 | strictly monotonic, $\\delta = 0$ if and only if $m = 0$.
128 |
129 | Symbols used in docstring
130 | +++++++++++++++++++++++++
131 |
132 | - ``B``: the batch size
133 | - ``C``: the number of channels
134 | - ``H``: the height
135 | - ``W``: the width
136 | - ``M``: the number of classes
137 | """
138 |
139 | def __init__(self, targeted=True, confidence=0.0, c_range=(1e-3, 1e10),
140 | search_steps=5, max_steps=1000, abort_early=True,
141 | box=(0, 1.), optimizer_lr=1e-3, init_rand=False):
142 | """
143 | :param targeted: ``True`` to perform targeted attack in ``self.run``
144 | method
145 | :type targeted: bool
146 | :param confidence: the confidence constant, i.e. the $\\kappa$ in paper
147 | :type confidence: float
148 | :param c_range: the search range of the constant :math:`c`; should be a
149 | tuple of form (lower_bound, upper_bound)
150 | :type c_range: Tuple[float, float]
151 | :param search_steps: the number of steps to perform binary search of
152 | the constant :math:`c` over ``c_range``
153 | :type search_steps: int
154 | :param max_steps: the maximum number of optimization steps for each
155 | constant :math:`c`
156 | :type max_steps: int
157 | :param abort_early: ``True`` to abort early in process of searching for
158 | :math:`c` when the loss virtually stops increasing
159 | :type abort_early: bool
160 | :param box: a tuple of lower bound and upper bound of the box
161 | :type box: Tuple[float, float]
162 | :param optimizer_lr: the base learning rate of the Adam optimizer used
163 | over the adversarial perturbation in clipped space
164 | :type optimizer_lr: float
165 | :param init_rand: ``True`` to initialize perturbation to small Gaussian;
166 | False is consistent with the original paper, where the
167 | perturbation is initialized to zero
168 | :type init_rand: bool
169 | :rtype: None
170 |
171 | Why to make ``box`` default to (-1., 1.) rather than (0., 1.)? TL;DR the
172 | domain of the problem in pytorch is [-1, 1] instead of [0, 1].
173 | According to Xiang Xu (samxucmu@gmail.com)::
174 |
175 | > The reason is that in pytorch a transformation is applied first
176 | > before getting the input from the data loader. So image in range [0,1]
177 | > will subtract some mean and divide by std. The normalized input image
178 | > will now be in range [-1,1]. For this implementation, clipping is
179 | > actually performed on the image after normalization, not on the
180 | > original image.
181 |
182 | Why to ``optimizer_lr`` default to 1e-2? The optimizer used in Carlini's
183 | code adopts 1e-2. In another pytorch implementation
184 | (https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-nips2017-attack-example.git),
185 | though, the learning rate is set to 5e-4.
186 | """
187 | if len(c_range) != 2:
188 | raise TypeError('c_range ({}) should be of form '
189 | 'tuple([lower_bound, upper_bound])'
190 | .format(c_range))
191 | if c_range[0] >= c_range[1]:
192 | raise ValueError('c_range lower bound ({}) is expected to be less '
193 | 'than c_range upper bound ({})'.format(*c_range))
194 | if len(box) != 2:
195 | raise TypeError('box ({}) should be of form '
196 | 'tuple([lower_bound, upper_bound])'
197 | .format(box))
198 | if box[0] >= box[1]:
199 | raise ValueError('box lower bound ({}) is expected to be less than '
200 | 'box upper bound ({})'.format(*box))
201 | self.targeted = targeted
202 | self.confidence = float(confidence)
203 | self.c_range = (float(c_range[0]), float(c_range[1]))
204 | self.binary_search_steps = search_steps
205 | self.max_steps = max_steps
206 | self.abort_early = abort_early
207 | self.ae_tol = 1e-4 # tolerance of early abort
208 | self.box = tuple(map(float, box)) # type: Tuple[float, float]
209 | self.optimizer_lr = optimizer_lr
210 |
211 | # `self.init_rand` is not in Carlini's code, it's an attempt in the
212 | # referencing pytorch implementation to improve the quality of attacks.
213 | self.init_rand = init_rand
214 |
215 | # Since the larger the `scale_const` is, the more likely a successful
216 | # attack can be found, `self.repeat` guarantees at least attempt the
217 | # largest scale_const once. Moreover, since the optimal criterion is the
218 | # L2 norm of the attack, and the larger `scale_const` is, the larger
219 | # the L2 norm is, thus less optimal, the last attempt at the largest
220 | # `scale_const` won't ruin the optimum ever found.
221 | self.repeat = (self.binary_search_steps >= 10)
222 |
223 | def __call__(self, model, inputs, targets, to_numpy=True):
224 | """
225 | Produce adversarial examples for ``inputs``.
226 |
227 | :param model: the model to attack
228 | :type model: nn.Module
229 | :param inputs: the original images tensor, of dimension [B x C x H x W].
230 | ``inputs`` can be on either CPU or GPU, but it will eventually be
231 | moved to the same device as the one the parameters of ``model``
232 | reside
233 | :type inputs: torch.FloatTensor
234 | :param targets: the original image labels, or the attack targets, of
235 | dimension [B]. If ``self.targeted`` is ``True``, then ``targets``
236 | is treated as the attack targets, otherwise the labels.
237 | ``targets`` can be on either CPU or GPU, but it will eventually
238 | be moved to the same device as the one the parameters of
239 | ``model`` reside
240 | :type targets: torch.LongTensor
241 | :param to_numpy: True to return an `np.ndarray`, otherwise,
242 | `torch.FloatTensor`
243 | :type to_numpy: bool
244 | :return: the adversarial examples on CPU, of dimension [B x C x H x W]
245 | """
246 | # sanity check
247 | assert isinstance(model, nn.Module)
248 | assert len(inputs.size()) == 4
249 | assert len(targets.size()) == 1
250 |
251 | # get a copy of targets in numpy before moving to GPU, used when doing
252 | # the binary search on `scale_const`
253 | targets_np = targets.clone().cpu().numpy() # type: np.ndarray
254 |
255 | # the type annotations here are used only for type hinting and do
256 | # not indicate the actual type (cuda or cpu); same applies to all codes
257 | # below
258 | inputs = runutils.make_cuda_consistent(model, inputs)[0] # type: # torch.FloatTensor
259 | targets = runutils.make_cuda_consistent(model, targets)[0] # type: # torch.FloatTensor
260 |
261 | # run the model a little bit to get the `num_classes`
262 | num_classes = model(Variable(inputs[0][None, :], requires_grad=False)).size(1) # type: int
263 | batch_size = inputs.size(0) # type: int
264 |
265 | # `lower_bounds_np`, `upper_bounds_np` and `scale_consts_np` are used
266 | # for binary search of each `scale_const` in the batch. The element-wise
267 | # inquality holds: lower_bounds_np < scale_consts_np <= upper_bounds_np
268 | lower_bounds_np = np.zeros(batch_size)
269 | upper_bounds_np = np.ones(batch_size) * self.c_range[1]
270 | scale_consts_np = np.ones(batch_size) * self.c_range[0]
271 |
272 | # Optimal attack to be found.
273 | # The three "placeholders" are defined as:
274 | # - `o_best_l2`: the least L2 norms
275 | # - `o_best_l2_ppred`: the perturbed predictions made by the adversarial
276 | # perturbations with the least L2 norms
277 | # - `o_best_advx`: the underlying adversarial example of
278 | # `o_best_l2_ppred`
279 | o_best_l2 = np.ones(batch_size) * np.inf
280 | o_best_l2_ppred = -np.ones(batch_size)
281 | o_best_advx = inputs.clone().cpu().numpy() # type: np.ndarray
282 |
283 | # convert `inputs` to tanh-space
284 | inputs_tanh = self._to_tanh_space(inputs) # type: torch.FloatTensor
285 | inputs_tanh_var = Variable(inputs_tanh, requires_grad=False)
286 |
287 | # the one-hot encoding of `targets`
288 | targets_oh = torch.zeros(targets.size() + (num_classes,)) # type: torch.FloatTensor
289 | targets_oh = runutils.make_cuda_consistent(model, targets_oh)[0]
290 | targets_oh.scatter_(1, targets.unsqueeze(1), 1.0)
291 | targets_oh_var = Variable(targets_oh, requires_grad=False)
292 |
293 | # the perturbation variable to optimize.
294 | # `pert_tanh` is essentially the adversarial perturbation in tanh-space.
295 | # In Carlini's code it's denoted as `modifier`
296 | pert_tanh = torch.zeros(inputs.size()) # type: torch.FloatTensor
297 | if self.init_rand:
298 | nn.init.normal(pert_tanh, mean=0, std=1e-3)
299 | pert_tanh = runutils.make_cuda_consistent(model, pert_tanh)[0]
300 | pert_tanh_var = Variable(pert_tanh, requires_grad=True)
301 |
302 | optimizer = optim.Adam([pert_tanh_var], lr=self.optimizer_lr)
303 | for sstep in range(self.binary_search_steps):
304 | if self.repeat and sstep == self.binary_search_steps - 1:
305 | scale_consts_np = upper_bounds_np
306 | scale_consts = torch.from_numpy(np.copy(scale_consts_np)).float() # type: torch.FloatTensor
307 | scale_consts = runutils.make_cuda_consistent(model, scale_consts)[0]
308 | scale_consts_var = Variable(scale_consts, requires_grad=False)
309 | # print('Using scale consts:', list(scale_consts_np)) # FIXME
310 |
311 | # the minimum L2 norms of perturbations found during optimization
312 | best_l2 = np.ones(batch_size) * np.inf
313 | # the perturbed predictions corresponding to `best_l2`, to be used
314 | # in binary search of `scale_const`
315 | best_l2_ppred = -np.ones(batch_size)
316 | # previous (summed) batch loss, to be used in early stopping policy
317 | prev_batch_loss = np.inf # type: float
318 | for optim_step in range(self.max_steps):
319 | batch_loss, pert_norms_np, pert_outputs_np, advxs_np = \
320 | self._optimize(model, optimizer, inputs_tanh_var,
321 | pert_tanh_var, targets_oh_var,
322 | scale_consts_var)
323 | # if optim_step % 10 == 0: print('batch [{}] loss: {}'.format(optim_step, batch_loss)) # FIXME
324 |
325 | if self.abort_early and not optim_step % (self.max_steps // 10):
326 | if batch_loss > prev_batch_loss * (1 - self.ae_tol):
327 | break
328 | prev_batch_loss = batch_loss
329 |
330 | # update best attack found during optimization
331 | pert_predictions_np = np.argmax(pert_outputs_np, axis=1)
332 | comp_pert_predictions_np = np.argmax(
333 | self._compensate_confidence(pert_outputs_np,
334 | targets_np),
335 | axis=1)
336 | for i in range(batch_size):
337 | l2 = pert_norms_np[i]
338 | cppred = comp_pert_predictions_np[i]
339 | ppred = pert_predictions_np[i]
340 | tlabel = targets_np[i]
341 | ax = advxs_np[i]
342 | if self._attack_successful(cppred, tlabel):
343 | assert cppred == ppred
344 | if l2 < best_l2[i]:
345 | best_l2[i] = l2
346 | best_l2_ppred[i] = ppred
347 | if l2 < o_best_l2[i]:
348 | o_best_l2[i] = l2
349 | o_best_l2_ppred[i] = ppred
350 | o_best_advx[i] = ax
351 |
352 | # binary search of `scale_const`
353 | for i in range(batch_size):
354 | tlabel = targets_np[i]
355 | assert best_l2_ppred[i] == -1 or \
356 | self._attack_successful(best_l2_ppred[i], tlabel)
357 | assert o_best_l2_ppred[i] == -1 or \
358 | self._attack_successful(o_best_l2_ppred[i], tlabel)
359 | if best_l2_ppred[i] != -1:
360 | # successful; attempt to lower `scale_const` by halving it
361 | if scale_consts_np[i] < upper_bounds_np[i]:
362 | upper_bounds_np[i] = scale_consts_np[i]
363 | # `upper_bounds_np[i] == c_range[1]` implies no solution
364 | # found, i.e. upper_bounds_np[i] has never been updated by
365 | # scale_consts_np[i] until
366 | # `scale_consts_np[i] > 0.1 * c_range[1]`
367 | if upper_bounds_np[i] < self.c_range[1] * 0.1:
368 | scale_consts_np[i] = (lower_bounds_np[i] + upper_bounds_np[i]) / 2
369 | else:
370 | # failure; multiply `scale_const` by ten if no solution
371 | # found; otherwise do binary search
372 | if scale_consts_np[i] > lower_bounds_np[i]:
373 | lower_bounds_np[i] = scale_consts_np[i]
374 | if upper_bounds_np[i] < self.c_range[1] * 0.1:
375 | scale_consts_np[i] = (lower_bounds_np[i] + upper_bounds_np[i]) / 2
376 | else:
377 | scale_consts_np[i] *= 10
378 |
379 | if not to_numpy:
380 | o_best_advx = torch.from_numpy(o_best_advx).float().cuda()
381 | return o_best_advx
382 |
383 | def _optimize(self, model, optimizer, inputs_tanh_var, pert_tanh_var,
384 | targets_oh_var, c_var):
385 | """
386 | Optimize for one step.
387 |
388 | :param model: the model to attack
389 | :type model: nn.Module
390 | :param optimizer: the Adam optimizer to optimize ``modifier_var``
391 | :type optimizer: optim.Adam
392 | :param inputs_tanh_var: the input images in tanh-space
393 | :type inputs_tanh_var: Variable
394 | :param pert_tanh_var: the perturbation to optimize in tanh-space,
395 | ``pert_tanh_var.requires_grad`` flag must be set to True
396 | :type pert_tanh_var: Variable
397 | :param targets_oh_var: the one-hot encoded target tensor (the attack
398 | targets if self.targeted else image labels)
399 | :type targets_oh_var: Variable
400 | :param c_var: the constant :math:`c` for each perturbation of a batch,
401 | a Variable of FloatTensor of dimension [B]
402 | :type c_var: Variable
403 | :return: the batch loss, squared L2-norm of adversarial perturbations
404 | (of dimension [B]), the perturbed activations (of dimension
405 | [B]), the adversarial examples (of dimension [B x C x H x W])
406 | """
407 | # the adversarial examples in the image space
408 | # of dimension [B x C x H x W]
409 | advxs_var = self._from_tanh_space(inputs_tanh_var + pert_tanh_var) # type: Variable
410 | # the perturbed activation before softmax
411 | pert_outputs_var = model(advxs_var) # type: Variable
412 | # the original inputs
413 | inputs_var = self._from_tanh_space(inputs_tanh_var) # type: Variable
414 |
415 | perts_norm_var = torch.pow(advxs_var - inputs_var, 2)
416 | perts_norm_var = torch.sum(perts_norm_var.view(
417 | perts_norm_var.size(0), -1), 1)
418 |
419 | # In Carlini's code, `target_activ_var` is called `real`.
420 | # It should be a Variable of tensor of dimension [B], such that the
421 | # `target_activ_var[i]` is the final activation (right before softmax)
422 | # of the $t$th class, where $t$ is the attack target or the image label
423 | #
424 | # noinspection PyArgumentList
425 | target_activ_var = torch.sum(targets_oh_var * pert_outputs_var, 1)
426 | inf = 1e4 # sadly pytorch does not work with np.inf;
427 | # 1e4 is also used in Carlini's code
428 | # In Carlini's code, `maxother_activ_var` is called `other`.
429 | # It should be a Variable of tensor of dimension [B], such that the
430 | # `maxother_activ_var[i]` is the maximum final activation of all classes
431 | # other than class $t$, where $t$ is the attack target or the image
432 | # label.
433 | #
434 | # The assertion here ensures (sufficiently yet not necessarily) the
435 | # assumption behind the trick to get `maxother_activ_var` holds, that
436 | # $\max_{i \ne t}{o_i} \ge -\text{_inf}$, where $t$ is the target and
437 | # $o_i$ the $i$th element along axis=1 of `pert_outputs_var`.
438 | #
439 | # noinspection PyArgumentList
440 | assert (pert_outputs_var.max(1)[0] >= -inf).all(), 'assumption failed'
441 | # noinspection PyArgumentList
442 | maxother_activ_var = torch.max(((1 - targets_oh_var) * pert_outputs_var
443 | - targets_oh_var * inf), 1)[0]
444 |
445 | # Compute $f(x')$, where $x'$ is the adversarial example in image space.
446 | # The result `f_var` should be of dimension [B]
447 | if self.targeted:
448 | # if targeted, optimize to make `target_activ_var` larger than
449 | # `maxother_activ_var` by `self.confidence`
450 | #
451 | # noinspection PyArgumentList
452 | f_var = torch.clamp(maxother_activ_var - target_activ_var
453 | + self.confidence, min=0.0)
454 | else:
455 | # if not targeted, optimize to make `maxother_activ_var` larger than
456 | # `target_activ_var` (the ground truth image labels) by
457 | # `self.confidence`
458 | #
459 | # noinspection PyArgumentList
460 | f_var = torch.clamp(target_activ_var - maxother_activ_var
461 | + self.confidence, min=0.0)
462 | # the total loss of current batch, should be of dimension [1]
463 | batch_loss_var = torch.sum(perts_norm_var + c_var * f_var) # type: Variable
464 |
465 | # Do optimization for one step
466 | optimizer.zero_grad()
467 | batch_loss_var.backward()
468 | optimizer.step()
469 |
470 | # Make some records in python/numpy on CPU
471 | batch_loss = batch_loss_var.item() # type: float
472 | pert_norms_np = _var2numpy(perts_norm_var)
473 | pert_outputs_np = _var2numpy(pert_outputs_var)
474 | advxs_np = _var2numpy(advxs_var)
475 | return batch_loss, pert_norms_np, pert_outputs_np, advxs_np
476 |
477 | def _attack_successful(self, prediction, target):
478 | """
479 | See whether the underlying attack is successful.
480 |
481 | :param prediction: the prediction of the model on an input
482 | :type prediction: int
483 | :param target: either the attack target or the ground-truth image label
484 | :type target: int
485 | :return: ``True`` if the attack is successful
486 | :rtype: bool
487 | """
488 | if self.targeted:
489 | return prediction == target
490 | else:
491 | return prediction != target
492 |
493 | # noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
494 | def _compensate_confidence(self, outputs, targets):
495 | """
496 | Compensate for ``self.confidence`` and returns a new weighted sum
497 | vector.
498 |
499 | :param outputs: the weighted sum right before the last layer softmax
500 | normalization, of dimension [B x M]
501 | :type outputs: np.ndarray
502 | :param targets: either the attack targets or the real image labels,
503 | depending on whether or not ``self.targeted``, of dimension [B]
504 | :type targets: np.ndarray
505 | :return: the compensated weighted sum of dimension [B x M]
506 | :rtype: np.ndarray
507 | """
508 | outputs_comp = np.copy(outputs)
509 | rng = np.arange(targets.shape[0])
510 | if self.targeted:
511 | # for each image $i$:
512 | # if targeted, `outputs[i, target_onehot]` should be larger than
513 | # `max(outputs[i, ~target_onehot])` by `self.confidence`
514 | outputs_comp[rng, targets] -= self.confidence
515 | else:
516 | # for each image $i$:
517 | # if not targeted, `max(outputs[i, ~target_onehot]` should be larger
518 | # than `outputs[i, target_onehot]` (the ground truth image labels)
519 | # by `self.confidence`
520 | outputs_comp[rng, targets] += self.confidence
521 | return outputs_comp
522 |
523 | def _to_tanh_space(self, x):
524 | """
525 | Convert a batch of tensors to tanh-space.
526 |
527 | :param x: the batch of tensors, of dimension [B x C x H x W]
528 | :return: the batch of tensors in tanh-space, of the same dimension
529 | """
530 | return to_tanh_space(x, self.box)
531 |
532 | def _from_tanh_space(self, x):
533 | """
534 | Convert a batch of tensors from tanh-space to input space.
535 |
536 | :param x: the batch of tensors, of dimension [B x C x H x W]
537 | :return: the batch of tensors in tanh-space, of the same dimension;
538 | the returned tensor is on the same device as ``x``
539 | """
540 | return from_tanh_space(x, self.box)
541 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------