# if not specified, defaults to "default"
912 | ```
913 |
914 | ⚠️ 以下方式只能用于对象构造器和对象请求,不能形成完整链路:
915 |
916 | ```ts {4-}
917 | import { Client } from "langsmith";
918 | import { LangChainTracer } from "langchain/callbacks";
919 |
920 | const client = new Client({ apiUrl: "https://api.smith.langchain.com", apiKey: "YOUR_API_KEY" });
921 | const tracer = new LangChainTracer({ projectName: "YOUR_PROJECT_NAME", client });
922 | ```
923 |
924 | ---
925 | level: 2
926 | ---
927 |
928 | # 如何自定义 Callback 处理器
929 |
930 | LangChain 支持通过实现基本回调处理程序接口来创建您自己的处理程序
931 |
932 | 自定义 Callback Handler 可以做一些比输出调试信息到控制台更复杂的事情,例如将事件发送到日志记录服务。作为示例,这里是一个记录到控制台的处理程序的 JS/TS 版本简单实现:
933 |
934 | ```ts {4-} {maxHeight:'70%'}
935 | import { BaseCallbackHandler } from "langchain/callbacks";
936 | import { Serialized } from "langchain/load/serializable";
937 | import { AgentAction, AgentFinish, ChainValues } from "langchain/schema";
938 |
939 | export class MyCallbackHandler extends BaseCallbackHandler {
940 | name = "MyCallbackHandler";
941 |
942 | async handleChainStart(chain: Serialized) {
943 | console.log(`Entering new ${chain.id} chain...`);
944 | }
945 |
946 | async handleChainEnd(_output: ChainValues) {
947 | console.log("Finished chain.");
948 | }
949 |
950 | async handleAgentAction(action: AgentAction) {
951 | console.log(action.log);
952 | }
953 |
954 | async handleToolEnd(output: string) {
955 | console.log(output);
956 | }
957 |
958 | async handleText(text: string) {
959 | console.log(text);
960 | }
961 |
962 | async handleAgentEnd(action: AgentFinish) {
963 | console.log(action.log);
964 | }
965 | }
966 | ```
967 |
968 | ---
969 | src: ../../pages/common/refs.md
970 | ---
971 |
972 | ---
973 | src: ../../pages/common/end.md
974 | ---
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/240106-langchain-status/src/package.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "private": true,
3 | "scripts": {
4 | "dev": "slidev",
5 | "build": "slidev build --base /240106-langchain-status/ --out ../../dist/240106-langchain-status",
6 | "export": "slidev export --dark --timeout 0 --output ../../pdfs/240106-langchain-status.pdf"
7 | },
8 | "devDependencies": {
9 | "@slidev/cli": "^0.46.1",
10 | "@slidev/theme-seriph": "^0.21.3"
11 | },
12 | "slidev": {
13 | "addons": [
14 | "../../addons/webup"
15 | ]
16 | }
17 | }
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/240106-langchain-status/src/slides.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | # See all frontmatter configurations: https://sli.dev/custom/#frontmatter-configures
3 | # theme id or package name, see also: https://sli.dev/themes/use.html
4 | theme: 'seriph'
5 | # titleTemplate for the webpage, `%s` will be replaced by the page's title
6 | titleTemplate: '%s|WebUP'
7 | # some information about the slides, markdown enabled
8 | info: |
9 | AGI 学习笔记,仅供个人学习使用
10 | # favicon, can be a local file path or URL
11 | favicon: https://files.codelife.cc/user-website-icon/20220523/5hyKeZxOknU2owAPvnSWD1388.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,limit_0,m_fill,w_25,h_25/quality,q_92/format,webp
12 | # enabled pdf downloading in SPA build, can also be a custom url
13 | download: 'https://github.com/webup/agi-talks/raw/master/pdfs/240106-langchain-status.pdf'
14 | # syntax highlighter, can be 'prism' or 'shiki'
15 | highlighter: 'shikiji'
16 | # controls whether texts in slides are selectable
17 | selectable: false
18 | # enable slide recording, can be boolean, 'dev' or 'build'
19 | record: 'build'
20 | # define transition between slides
21 | transition: fade
22 | # default frontmatter applies to all slides
23 | defaults:
24 |
25 | # slide configurations
26 | hideInToc: true
27 | layout: cover
28 | class: text-center
29 | background: https://source.unsplash.com/collection/94734566/1920x1080
30 | ---
31 |
32 | # LangChain 生态综述
33 |
34 | LangChain Ecosystem Walkthrough
35 |
36 |
37 |
38 | Press Space for next page
39 |
40 |
41 |
42 |
56 |
57 | ---
58 | hideInToc: true
59 | layout: intro
60 | ---
61 |
62 | # 张海立
63 |
64 |
65 | KubeSphere Ambassador, CNCF OpenFunction TOC Member
66 | 驭势科技 UISEE© 云平台研发总监,开源爱好者
67 | 云原生专注领域: Kubernetes, DevOps, FaaS, Observability
68 | AGI 专注领域:LangChain, RAG, Prompt Engineering, GenAI
69 |
70 |
71 |
72 |
73 |
74 |
75 |
76 |
77 |
78 |
79 |
80 |
 83 |
84 | ---
85 | layout: quote
86 | ---
87 |
88 | # 🗺️ 开局一张图
89 |
90 | 从 LangChain 生态全景(架构)图说起
91 |
92 | ---
93 | layout: iframe
94 | url: https://python.langchain.com/docs/get_started/introduction
95 | ---
96 |
97 | ---
98 | layout: iframe-right
99 | url: https://blog.langchain.dev/the-new-langchain-architecture-langchain-core-v0-1-langchain-community-and-a-path-to-langchain-v0-1/
100 | ---
101 |
102 | # 🦜️🔗 LangChain 类库
103 |
104 | 定位:本地构建 LLM 原型应用
105 |
106 | - langchain-core 包含了核心抽象和 [LangChain Expression Language](https://python.langchain.com/docs/expression_language/)(LCEL)
107 | - 版本已经达到 0.1, 未来的任何破坏性变更都会带来小版本升级(0.x)
108 | - 模块化的抽象为第三方集成提供标准接口
109 | - langchain-community 包含 [第三方集成](https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/providers)
110 | - 主要集成将被进一步拆分为独立软件包
111 | - 目前,LangChain 拥有近 700 个集成
112 | - langchain 包含了实际运用的 Chain、Agent 和 Retriever 流程策略
113 | - 官方计划 1/9 推出 0.1 稳定版本
114 |
115 | ---
116 | layout: iframe
117 | url: https://integrations.langchain.com/
118 | ---
119 |
120 | ---
121 | layout: iframe-right
122 | url: https://blog.langchain.dev/langchain-templates/
123 | ---
124 |
125 | # 🦜️🔗 LangChain 模板
126 |
127 | 定位:提供预制的可参考的 LLM 原型应用
128 |
129 | 通常配合 LangServe 一起使用(三步走):
130 |
131 | 1️⃣ 安装 `langchain-cli`
132 |
133 | ```sh
134 | pip install -U langchain-cli
135 | ```
136 |
137 | 2️⃣ (创建新项目)导入指定模版
138 |
139 | ```sh
140 | langchain app new my-app --package $PACKAGE_NAME
141 | langchain app add $PACKAGE_NAME
142 | # adding custom GitHub repo packages
143 | langchain app add --repo $OWNER/$REPO
144 | ```
145 |
146 | 3️⃣ 绑定 LangServe 服务端点(`server.py`)
147 |
148 | ```py
149 | add_routes(app, chain, path="/chain-path")
150 | ```
151 |
152 | 🚀 启动!`langchain serve`
153 |
154 | ---
155 | layout: iframe
156 | url: https://templates.langchain.com/
157 | ---
158 |
159 | ---
160 | layout: iframe-right
161 | url: https://blog.langchain.dev/introducing-langserve/
162 | ---
163 |
164 | # 🦜️🏓 LangServe 类库
165 |
166 | 定位:一键 REST 服务化 LLM 原型应用
167 |
168 |
169 |
170 | ---
171 | layout: iframe-right
172 | url: https://blog.langchain.dev/announcing-langsmith/
173 | ---
174 |
175 | # 🦜️⚒️ LangSmith 平台
176 |
177 | 定位:提供全生命周期的可观测能力
178 |
179 |
180 |
181 |
182 | ---
183 | layout: quote
184 | ---
185 |
186 | # 🌰 LangServe + LangSmith 演示
187 |
188 | Talk is cheap, show me the [code](https://github.com/webup/langserve-app-demo) or [data](https://smith.langchain.com/public/452ccafc-18e1-4314-885b-edd735f17b9d/d) or [whatever](https://chat.langchain.com/) 🤣
189 |
190 | ---
191 | src: ../../pages/common/end.md
192 | ---
193 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/240720-langchain-minio/src/index.html:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/240720-langchain-minio/src/package.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "private": true,
3 | "scripts": {
4 | "dev": "slidev",
5 | "build": "slidev build --base /240720-langchain-minio/ --out ../../dist/240720-langchain-minio",
6 | "export": "slidev export --dark --timeout 0 --output ../../pdfs/240720-langchain-minio.pdf"
7 | },
8 | "devDependencies": {
9 | "@slidev/cli": "^0.49.17",
10 | "@slidev/theme-seriph": "^0.25.0"
11 | },
12 | "slidev": {
13 | "addons": [
14 | "../addons/webup"
15 | ]
16 | }
17 | }
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/240720-langchain-minio/src/slides.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | theme: seriph
3 | titleTemplate: '%s|WebUP'
4 | background: https://s2.loli.net/2024/07/17/nU2EpACXOPoc3qh.png
5 | favicon: https://files.codelife.cc/user-website-icon/20220523/5hyKeZxOknU2owAPvnSWD1388.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,limit_0,m_fill,w_25,h_25/quality,q_92/format,webp
6 | download: 'https://github.com/webup/agi-talks/raw/master/pdfs/240720-langchain-minio.pdf'
7 | class: text-center
8 | highlighter: shiki
9 | lineNumbers: false
10 | selectable: false
11 | info: |
12 | LangChain 与 MinIO:基于 GenAI 的数据管理可行性探索
13 | drawings:
14 | persist: false
15 | transition: slide-left
16 | title: LangChain 与 MinIO 的创新之旅
17 | ---
18 |
19 | # LangChain 🤝 MinIO
20 |
21 | 基于 GenAI 的数据管理可行性探索
22 |
23 | ---
24 | layout: intro
25 | ---
26 |
27 | # 张海立
28 |
29 |
83 |
84 | ---
85 | layout: quote
86 | ---
87 |
88 | # 🗺️ 开局一张图
89 |
90 | 从 LangChain 生态全景(架构)图说起
91 |
92 | ---
93 | layout: iframe
94 | url: https://python.langchain.com/docs/get_started/introduction
95 | ---
96 |
97 | ---
98 | layout: iframe-right
99 | url: https://blog.langchain.dev/the-new-langchain-architecture-langchain-core-v0-1-langchain-community-and-a-path-to-langchain-v0-1/
100 | ---
101 |
102 | # 🦜️🔗 LangChain 类库
103 |
104 | 定位:本地构建 LLM 原型应用
105 |
106 | - langchain-core 包含了核心抽象和 [LangChain Expression Language](https://python.langchain.com/docs/expression_language/)(LCEL)
107 | - 版本已经达到 0.1, 未来的任何破坏性变更都会带来小版本升级(0.x)
108 | - 模块化的抽象为第三方集成提供标准接口
109 | - langchain-community 包含 [第三方集成](https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/providers)
110 | - 主要集成将被进一步拆分为独立软件包
111 | - 目前,LangChain 拥有近 700 个集成
112 | - langchain 包含了实际运用的 Chain、Agent 和 Retriever 流程策略
113 | - 官方计划 1/9 推出 0.1 稳定版本
114 |
115 | ---
116 | layout: iframe
117 | url: https://integrations.langchain.com/
118 | ---
119 |
120 | ---
121 | layout: iframe-right
122 | url: https://blog.langchain.dev/langchain-templates/
123 | ---
124 |
125 | # 🦜️🔗 LangChain 模板
126 |
127 | 定位:提供预制的可参考的 LLM 原型应用
128 |
129 | 通常配合 LangServe 一起使用(三步走):
130 |
131 | 1️⃣ 安装 `langchain-cli`
132 |
133 | ```sh
134 | pip install -U langchain-cli
135 | ```
136 |
137 | 2️⃣ (创建新项目)导入指定模版
138 |
139 | ```sh
140 | langchain app new my-app --package $PACKAGE_NAME
141 | langchain app add $PACKAGE_NAME
142 | # adding custom GitHub repo packages
143 | langchain app add --repo $OWNER/$REPO
144 | ```
145 |
146 | 3️⃣ 绑定 LangServe 服务端点(`server.py`)
147 |
148 | ```py
149 | add_routes(app, chain, path="/chain-path")
150 | ```
151 |
152 | 🚀 启动!`langchain serve`
153 |
154 | ---
155 | layout: iframe
156 | url: https://templates.langchain.com/
157 | ---
158 |
159 | ---
160 | layout: iframe-right
161 | url: https://blog.langchain.dev/introducing-langserve/
162 | ---
163 |
164 | # 🦜️🏓 LangServe 类库
165 |
166 | 定位:一键 REST 服务化 LLM 原型应用
167 |
168 |
169 |
170 | ---
171 | layout: iframe-right
172 | url: https://blog.langchain.dev/announcing-langsmith/
173 | ---
174 |
175 | # 🦜️⚒️ LangSmith 平台
176 |
177 | 定位:提供全生命周期的可观测能力
178 |
179 |
180 |
181 |
182 | ---
183 | layout: quote
184 | ---
185 |
186 | # 🌰 LangServe + LangSmith 演示
187 |
188 | Talk is cheap, show me the [code](https://github.com/webup/langserve-app-demo) or [data](https://smith.langchain.com/public/452ccafc-18e1-4314-885b-edd735f17b9d/d) or [whatever](https://chat.langchain.com/) 🤣
189 |
190 | ---
191 | src: ../../pages/common/end.md
192 | ---
193 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/240720-langchain-minio/src/index.html:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/240720-langchain-minio/src/package.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "private": true,
3 | "scripts": {
4 | "dev": "slidev",
5 | "build": "slidev build --base /240720-langchain-minio/ --out ../../dist/240720-langchain-minio",
6 | "export": "slidev export --dark --timeout 0 --output ../../pdfs/240720-langchain-minio.pdf"
7 | },
8 | "devDependencies": {
9 | "@slidev/cli": "^0.49.17",
10 | "@slidev/theme-seriph": "^0.25.0"
11 | },
12 | "slidev": {
13 | "addons": [
14 | "../addons/webup"
15 | ]
16 | }
17 | }
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/240720-langchain-minio/src/slides.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | theme: seriph
3 | titleTemplate: '%s|WebUP'
4 | background: https://s2.loli.net/2024/07/17/nU2EpACXOPoc3qh.png
5 | favicon: https://files.codelife.cc/user-website-icon/20220523/5hyKeZxOknU2owAPvnSWD1388.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,limit_0,m_fill,w_25,h_25/quality,q_92/format,webp
6 | download: 'https://github.com/webup/agi-talks/raw/master/pdfs/240720-langchain-minio.pdf'
7 | class: text-center
8 | highlighter: shiki
9 | lineNumbers: false
10 | selectable: false
11 | info: |
12 | LangChain 与 MinIO:基于 GenAI 的数据管理可行性探索
13 | drawings:
14 | persist: false
15 | transition: slide-left
16 | title: LangChain 与 MinIO 的创新之旅
17 | ---
18 |
19 | # LangChain 🤝 MinIO
20 |
21 | 基于 GenAI 的数据管理可行性探索
22 |
23 | ---
24 | layout: intro
25 | ---
26 |
27 | # 张海立
28 |
29 |
30 | KubeSphere Ambassador, CNCF OpenFunction TOC Member
31 |
《LangChain 实战》作者,开源爱好者和布道师
32 | 云原生专注领域:Kubernetes, DevOps, FaaS, Observability
33 | GenAI 专注领域:LangChain, RAG, Evaluation, Prompt + Flow Engineering
34 |
37 |
38 |
39 |
40 |
41 |
42 |
43 |
44 |
45 |
 48 |
49 | ---
50 |
51 | # 引言:重塑 AI 应用中的数据交互模式
52 | 在当今的 AI 应用开发中,如何让用户以更自然、更直观的方式与复杂的数据存储系统交互,是一个关键挑战
53 |
54 | 自然语言交互的力量
55 | - LangChain 使开发者能够构建允许用户通过自然语言与 MinIO 等专业数据存储系统交互的应用
56 | - 这极大地简化了用户操作,使得复杂的数据管理变得直观易懂
57 |
58 | 开发效率的跃升
59 | - 通过 LangChain,开发者可以快速构建智能数据管理接口,它提供了连接 AI 模型和数据存储的简洁框架
60 | - 这大幅缩短了开发周期,使得从概念到上线的过程更加顺畅
61 |
62 | 用户体验的质的提升
63 | - 借助 LangChain 的能力,用户无需学习复杂的查询语言或了解底层存储结构,就能轻松管理和检索数据
64 | - 这为非技术用户打开了数据分析的大门
65 |
66 | ---
67 | layout: image-right
68 | image: https://s2.loli.net/2024/07/17/kNQHM3Fdoc4Uqrz.png
69 | backgroundSize: 28em
70 | ---
71 |
72 | # GenAI 应用开发的助手
73 |
74 | LangChain 提供了一套全面的工具和框架
75 |
76 | - RAG(检索增强生成)
77 | - 集成外部知识源,大幅提升信息检索能力
78 | - 感知上下文,提高输出准确性和相关性
79 |
80 | - Agent(智能代理)
81 | - 构建能自主决策和执行任务的 LLM 实体
82 | - 灵活调用多种工具和 API,处理复杂请求
83 |
84 | - Evaluation(评测评估)
85 | - 提供评估框架,帮助开发者持续优化流程
86 | - 自定义评估指标,确保输出符合领域需求
87 |
88 |
89 | ---
90 |
91 |
48 |
49 | ---
50 |
51 | # 引言:重塑 AI 应用中的数据交互模式
52 | 在当今的 AI 应用开发中,如何让用户以更自然、更直观的方式与复杂的数据存储系统交互,是一个关键挑战
53 |
54 | 自然语言交互的力量
55 | - LangChain 使开发者能够构建允许用户通过自然语言与 MinIO 等专业数据存储系统交互的应用
56 | - 这极大地简化了用户操作,使得复杂的数据管理变得直观易懂
57 |
58 | 开发效率的跃升
59 | - 通过 LangChain,开发者可以快速构建智能数据管理接口,它提供了连接 AI 模型和数据存储的简洁框架
60 | - 这大幅缩短了开发周期,使得从概念到上线的过程更加顺畅
61 |
62 | 用户体验的质的提升
63 | - 借助 LangChain 的能力,用户无需学习复杂的查询语言或了解底层存储结构,就能轻松管理和检索数据
64 | - 这为非技术用户打开了数据分析的大门
65 |
66 | ---
67 | layout: image-right
68 | image: https://s2.loli.net/2024/07/17/kNQHM3Fdoc4Uqrz.png
69 | backgroundSize: 28em
70 | ---
71 |
72 | # GenAI 应用开发的助手
73 |
74 | LangChain 提供了一套全面的工具和框架
75 |
76 | - RAG(检索增强生成)
77 | - 集成外部知识源,大幅提升信息检索能力
78 | - 感知上下文,提高输出准确性和相关性
79 |
80 | - Agent(智能代理)
81 | - 构建能自主决策和执行任务的 LLM 实体
82 | - 灵活调用多种工具和 API,处理复杂请求
83 |
84 | - Evaluation(评测评估)
85 | - 提供评估框架,帮助开发者持续优化流程
86 | - 自定义评估指标,确保输出符合领域需求
87 |
88 |
89 | ---
90 |
91 |
92 |
99 |
{{ item.icon }}
100 |
{{ item.title }}
101 |
{{ item.description }}
102 |
103 |
125 |
126 | ###### 以下内容因为时间关系不做演示
127 |
128 | - 设计提示工程:迭代调优提示模板,确保 Agent 能准确理解用户意图,并执行相应的 MinIO 操作
129 | - 测试和优化:通过多轮测试和反馈,不断优化 Agent 性能和用户体验,提高系统的可靠性和效率
130 |
131 |
132 | ---
133 |
134 | # 1️⃣ 设置 MinIO 客户端
135 |
136 | MinIO 提供了多语言的开发框架,如 Python、JavaScript、Go 等
137 |
138 | ```python {1-5|8-|all}
139 | from minio import Minio
140 |
141 | # 首先初始化 MinIO 客户端
142 | # play.min.io 是一个公共测试服务器,在生产环境中请替换为您自己的服务器
143 | minio_client = Minio('play.min.io:443', access_key='minioadmin', secret_key='minioadmin', secure=True)
144 |
145 |
146 | # 接下来检查指定 bucket 是否存在,如果不存在则创建
147 | bucket_name = "test"
148 |
149 | try:
150 | # 检查 bucket 是否存在
151 | if not minio_client.bucket_exists(bucket_name):
152 | # 如果 bucket 不存在,则创建
153 | minio_client.make_bucket(bucket_name)
154 | print(f"Bucket '{bucket_name}' created successfully.")
155 | else:
156 | print(f"Bucket '{bucket_name}' already exists.")
157 | except S3Error as err:
158 | print(f"Error encountered: {err}")
159 | ```
160 |
161 | ---
162 |
163 | # 2️⃣ 创建自定义 MinIO 工具
164 |
165 | 这些自定义工具允许我们的 LangChain 代理与 MinIO 存储进行精确而高效的交互
166 |
167 | ```python {4-16|18-|all}{maxHeight:'400px'}
168 | from langchain.agents import tool
169 | import io
170 |
171 | @tool
172 | def upload_file_to_minio(bucket_name: str, object_name: str, data_bytes: bytes):
173 | """
174 | 将文件上传到 MinIO
175 |
176 | 参数:
177 | bucket_name (str):目标存储桶的名称,用于组织和管理对象存储中的文件
178 | object_name (str):在存储桶中创建的对象名称,代表文件在 MinIO 中的唯一标识
179 | data_bytes (bytes):要上传的文件的原始字节数据,确保数据完整性和安全传输
180 | """
181 | data_stream = io.BytesIO(data_bytes)
182 | minio_client.put_object(bucket_name, object_name, data_stream, length=len(data_bytes))
183 | return f"文件 {object_name} 成功上传到桶 {bucket_name}。上传过程确保了数据的完整性和安全性。"
184 |
185 | @tool
186 | def list_objects_in_minio_bucket(file_info):
187 | """
188 | 列出 MinIO 桶中的对象,提供存储内容的全面概览
189 |
190 | 期望 file_info 字典包含'bucket_name'键,指定要查询的存储桶
191 | 返回包含'ObjectKey'和'Size'键的字典列表,详细展示每个对象的名称和大小信息
192 | """
193 | bucket_name = file_info['bucket_name']
194 | response = minio_client.list_objects(bucket_name)
195 | return [{'ObjectKey': obj.object_name, 'Size': obj.size} for obj in response]
196 | ```
197 |
198 | ---
199 |
200 | # 3️⃣ 实现 MinIO Agent
201 |
202 | 功能目标:基于用户输入执行精确的 MinIO 操作,实现 AI 与云存储的无缝集成
203 |
204 | ```python {7-12|14-19|21-|all}{maxHeight:'400px'}
205 | from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
206 | from langchain.agents.format_scratchpad.openai_tools import format_to_openai_tool_messages
207 | from langchain.agents.output_parsers.openai_tools import OpenAIToolsAgentOutputParser
208 | from langchain_core.messages import MessagesPlaceholder
209 | from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableLambda
210 |
211 | # 定义提示模板
212 | prompt_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
213 | ("system", "您是一个配备先进文件管理能力的 AI 助手,能够精确理解用户需求并高效执行复杂的数据操作任务。"),
214 | ("user", "{input}"),
215 | MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="agent_scratchpad"),
216 | ])
217 |
218 | # 绑定工具
219 | upload_file_runnable = RunnableLambda(upload_file_to_minio)
220 | list_objects_runnable = RunnableLambda(list_objects_in_minio_bucket)
221 |
222 | tools = [upload_file_to_minio, list_objects_in_minio_bucket]
223 | llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
224 |
225 | # 创建代理
226 | agent = (
227 | {
228 | "input": lambda x: x["input"],
229 | "agent_scratchpad": lambda x: format_to_openai_tool_messages(x["intermediate_steps"]),
230 | }
231 | | prompt_template
232 | | llm_with_tools
233 | | OpenAIToolsAgentOutputParser()
234 | )
235 |
236 | # 初始化代理执行器
237 | agent_executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent, tools=tools, verbose=True)
238 | ```
239 |
240 | ---
241 | layout: two-cols-header
242 | ---
243 |
244 | # 4️⃣ 用 LangServe 创建应用服务
245 |
246 | 将 MinIO Agent 作为 REST API 端点暴露在微服务的 /minio 路径
247 |
248 | ::left::
249 |
250 | ```python
251 | from fastapi import FastAPI
252 | from langserve import add_routes
253 |
254 | # 初始化 FastAPI 应用
255 | app = FastAPI(
256 | title="MinIO 智能数据管理 API",
257 | version="1.0",
258 | )
259 |
260 | # 添加 LangServe 路由
261 | add_routes(
262 | app,
263 | agent_executor.with_config(
264 | {"run_name": "minio_data_agent"}
265 | ),
266 | path="/minio"
267 | )
268 |
269 | # 这段代码设置了一个集成 LangServe 的 FastAPI 服务器
270 | # 使得 LLM 驱动的 MinIO 操作可以通过 HTTP 请求轻松调用
271 | ```
272 |
273 | ::right::
274 |
275 | - 自动 API 生成:LangServe 能够自动为 LangChain 应用创建 RESTful API 端点,大大简化了从开发到部署的过程,加速了 AI 服务的上线和迭代
276 |
277 | - 内置模式验证:提供强大的输入输出验证机制,确保数据的一致性和安全性,有效防止因数据格式错误导致的系统故障
278 |
279 | - 无缝集成:与现有 LangChain 代码完美兼容,使得开发者能够轻松将复杂的 LLM 应用转化为可部署的微服务,提高开发效率
280 |
281 | - 监控和日志:无缝集成 LangSmith 的监控和日志功能,便于开发者跟踪服务性能,快速定位和解决问题
282 |
283 | ---
284 | layout: iframe-right
285 | url: https://langserve-launch-example-vz4y4ooboq-uc.a.run.app/docs
286 | ---
287 |
288 | # 调用 MinIO Agent
289 |
290 | 通过 LangServe SDK 调用 REST API 端点
291 |
292 | ```python
293 | from langserve import RemoteRunnable
294 |
295 | # 连接到已部署的 API
296 | remote_runnable = RemoteRunnable(
297 | "http://localhost:8000/minio/"
298 | )
299 |
300 | # 向代理发送请求
301 | response = remote_runnable.invoke({
302 | "input": "请列出桶中的所有文件,并计算它们的总大小"
303 | })
304 |
305 | print(response)
306 | # 输出 Agent 与 MinIO 交互后的详细响应
307 | # 包括文件列表和总大小统计
308 | ```
309 |
310 | ---
311 | layout: iframe
312 | url: https://smith.langchain.com/public/99e01003-c745-48c3-8563-7f6d7967772d/r
313 | ---
314 |
315 | ---
316 | layout: iframe-right
317 | url: https://blog.langchain.dev/langgraph-cloud/
318 | ---
319 |
320 | # 未来展望:LangGraph 助力复杂云原生应用
321 |
322 | - 复杂工作流编排:LangGraph 允许开发者设计和实现复杂的多步骤 LLM 工作流,能够处理需要多个阶段决策和执行的复杂任务
323 |
324 | - 状态管理优化:通过图结构管理应用状态,使得长期运行的 LLM 任务能够更加稳定和可靠,提高了系统的鲁棒性
325 |
326 | - 并行处理支持:能够设计并执行并行任务,大大提高了复杂应用的处理效率,特别适合需要多任务协同的云原生环境
327 |
328 | - 可视化和调试:提供工作流程的可视化工具,更直观地设计和调试复杂的 LLM 应用逻辑
329 |
330 |
331 | ---
332 | layout: iframe
333 | url: //player.bilibili.com/player.html?isOutside=true&aid=1206121699&bvid=BV1vf421z7cp&cid=1603007386&p=1&autoplay=0
334 | ---
335 |
336 |
337 | ---
338 | layout: cover
339 | class: text-center
340 | background: https://s2.loli.net/2024/07/17/nU2EpACXOPoc3qh.png
341 | ---
342 |
343 | # 感谢聆听 🙏
344 |
345 | 有问题吗?让我们一起讨论!
346 |
347 | [LangChain 文档](https://python.langchain.com/docs/get_started/introduction.html) | [MinIO 文档](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html) | [KubeSphere 文档](https://kubesphere.com.cn/documents/)
348 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/301-langchain-chatdoc/src/index.html:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/301-langchain-chatdoc/src/package.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "private": true,
3 | "scripts": {
4 | "dev": "slidev",
5 | "build": "slidev build --base /301-langchain-chatdoc/ --out ../../dist/301-langchain-chatdoc",
6 | "export": "slidev export --dark --timeout 0 --output ../../pdfs/301-langchain-chatdoc.pdf"
7 | },
8 | "devDependencies": {
9 | "@slidev/cli": "^0.43.7",
10 | "@slidev/theme-seriph": "^0.21.3"
11 | },
12 | "slidev": {
13 | "addons": [
14 | "../../addons/webup"
15 | ]
16 | }
17 | }
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/301-langchain-chatdoc/src/slides.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | # See all frontmatter configurations: https://sli.dev/custom/#frontmatter-configures
3 | # theme id or package name, see also: https://sli.dev/themes/use.html
4 | theme: 'seriph'
5 | # titleTemplate for the webpage, `%s` will be replaced by the page's title
6 | titleTemplate: '%s|WebUP'
7 | # some information about the slides, markdown enabled
8 | info: |
9 | AGI 学习笔记,仅供个人学习使用
10 | # favicon, can be a local file path or URL
11 | favicon: https://files.codelife.cc/user-website-icon/20220523/5hyKeZxOknU2owAPvnSWD1388.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,limit_0,m_fill,w_25,h_25/quality,q_92/format,webp
12 | # enabled pdf downloading in SPA build, can also be a custom url
13 | download: 'https://github.com/webup/agi-talks/raw/master/pdfs/301-langchain-chatdoc.pdf'
14 | # syntax highlighter, can be 'prism' or 'shiki'
15 | highlighter: 'shiki'
16 | # controls whether texts in slides are selectable
17 | selectable: false
18 | # enable slide recording, can be boolean, 'dev' or 'build'
19 | record: 'build'
20 | # define transition between slides
21 | transition: fade
22 | # default frontmatter applies to all slides
23 | defaults:
24 |
25 | # slide configurations
26 | hideInToc: true
27 | layout: cover
28 | class: text-center
29 | background: https://source.unsplash.com/collection/94734566/1920x1080
30 | ---
31 |
32 | # Chat LangChain 应用解析
33 |
34 | [Chat LangChain](https://chat.langchain.com/) Walkthrough
35 |
36 |
37 |
38 | Press Space for next page
39 |
40 |
41 |
42 |
56 |
57 | ---
58 | src: ../../pages/common/series.md
59 | ---
60 |
61 | ---
62 | src: ../../pages/common/toc.md
63 | ---
64 |
65 | ---
66 | layout: iframe
67 | url: https://chat.langchain.com
68 | ---
69 |
70 | ---
71 | layout: iframe-right
72 | url: https://blog.langchain.dev/building-chat-langchain-2/
73 | ---
74 |
75 | # Chat LangChain 🦜️🔗
76 |
77 | 基于 LC 开发的 LC Python 文档查询应用
78 |
79 | 项目代码构成:
80 |
81 | - [前端](https://github.com/langchain-ai/chat-langchain/tree/master/chat-langchain):[Next.js LangChain Starter](https://github.com/vercel/ai/tree/main/examples/next-langchain)
82 | - 使用 [Next.js](https://nextjs.org/)、LangChain 和 [Vercel AI SDK](https://sdk.vercel.ai/) 构建 AI 驱动的聊天应用程序的入门模板
83 | - [后端](https://github.com/langchain-ai/chat-langchain/blob/master/main.py):[LangChain Python](https://github.com/langchain-ai/langchain) SDK + [FastAPI](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/)
84 |
85 |
86 |
87 | 核心技术摘要:
88 |
89 | - RAG(Retrieval Augumented Generation)
90 | - [LCEL](https://python.langchain.com/docs/expression_language/)(LangChain Expression Language)
91 | - 基于 [LangChain Indexing API](https://python.langchain.com/docs/modules/data_connection/indexing) 的持续更新
92 | - 基于 [LangSmith](https://smith.langchain.com/) 的追踪、监控、评估
93 |
94 | ---
95 | layout: image-right
96 | image: https://communitykeeper-media.s3.amazonaws.com/media/images/Complete.original.png
97 | ---
98 |
99 | # RAG 核心流程回顾
100 |
101 | [How do domain-specific chatbots work?](https://scriv.ai/guides/retrieval-augmented-generation-overview/) 👉
102 |
103 | 建立私域数据索引(Indexing)
104 |
105 | 1⃣️ 读取 / 加载私域数据
106 |
107 | 2⃣️ 数据预处理及存储
108 |
109 | 3⃣️ 持续数据索引及存储
110 |
111 |
112 |
113 | 执行私域数据问答(Retrieval & Generation)
114 |
115 | 4⃣️ 基于用户提问的数据检索
116 |
117 | 5⃣️ 基于检索内容的应答生成
118 |
119 | ---
120 | layout: two-cols-header
121 | ---
122 |
123 | # 1⃣️ 读取 / 加载私域数据
124 |
125 | 💡 [ingest.py#L81-L84](https://github.com/langchain-ai/chat-langchain/blob/3de16f8318abce7e88dc1da5444d9fb067a46200/ingest.py#L81-L84)|首先通过抓取相关文档网页来加载为 `Document`
126 |
127 | ::left::
128 |
129 | ```python
130 | docs = SitemapLoader(
131 | "https://python.langchain.com/sitemap.xml",
132 | filter_urls=["https://python.langchain.com/"],
133 | parsing_function=langchain_docs_extractor,
134 | default_parser="lxml",
135 | bs_kwargs={
136 | "parse_only": SoupStrainer(
137 | name=("article", "title", "html", "lang", "content")
138 | ),
139 | },
140 | meta_function=metadata_extractor,
141 | ).load()
142 | ```
143 |
144 | - 使用 [`SitemapLoader`](https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/document_loaders/sitemap) 从站点地图 XML 中抓取所有链接
145 | - 很多工作都是由 [langchain_docs_extractor](https://github.com/langchain-ai/chat-langchain/blob/3de16f8318abce7e88dc1da5444d9fb067a46200/parser.py) 方法完成的
146 | - 这是一个很棒的自定义 HTML -> 文本解析器
147 |
148 |
149 |
150 | ::right::
151 |
152 | ```python
153 | api_ref = RecursiveUrlLoader(
154 | "https://api.python.langchain.com/en/latest/",
155 | max_depth=8,
156 | extractor=simple_extractor,
157 | prevent_outside=True,
158 | use_async=True,
159 | check_response_status=True,
160 | exclude_dirs=(
161 | "https://api.python.langchain.com/en/latest/_sources",
162 | "https://api.python.langchain.com/en/latest/_modules",
163 | ),
164 | ).load()
165 | ```
166 |
167 | - 使用 [`RecursiveURLLoader`](https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/document_loaders/recursive_url) 加载 API 参考文档
168 | - 这些文档内容没有非常有用的站点地图
169 | - 它可以从页面递归加载子链接到一定深度
170 |
171 | ---
172 |
173 | # 2⃣️ 数据预处理及存储
174 |
175 | 💡 [ingest.py#L86-L114](https://github.com/langchain-ai/chat-langchain/blob/3de16f8318abce7e88dc1da5444d9fb067a46200/ingest.py#L86-L114)|下面我们把文档切片并向量化后存入 Weaviate 向量存储中
176 |
177 | ```python
178 | docs_transformed = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=4000, chunk_overlap=200).split_documents(docs + api_ref)
179 | ```
180 |
181 | - 使用一个简单的 [`RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter`](https://python.langchain.com/docs/modules/data_connection/document_transformers/text_splitters/recursive_text_splitter) 将内容划分为大约大小相等的块,切分原因:
182 | - 帮助提高检索性能:如果相关文档还包含大量不相关信息,相似性搜索可能会错过相关文档
183 | - 使我们不必担心检索到的文档是否适合模型的上下文窗口(如 `gpt-3.5-turbo` 默认是 4K 容量)
184 |
185 |
186 |
187 | ```python
188 | client = weaviate.Client(url=WEAVIATE_URL, auth_client_secret=weaviate.AuthApiKey(api_key=WEAVIATE_API_KEY))
189 |
190 | vectorstore = Weaviate(
191 | client=client,
192 | index_name=WEAVIATE_DOCS_INDEX_NAME,
193 | text_key="text",
194 | embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings(chunk_size=200),
195 | by_text=False,
196 | attributes=["source", "title"],
197 | )
198 | ```
199 |
200 | - 使用 [`OpenAIEmbeddings`](https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/text_embedding/openai) 进行向量化处理并存储到 [Weaviate](https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/vectorstores/weaviate) 向量存储中
201 |
202 | ---
203 |
204 | # 3⃣️ 持续数据索引及存储
205 |
206 | 💡 [ingest.py#L116-L127](https://github.com/langchain-ai/chat-langchain/blob/3de16f8318abce7e88dc1da5444d9fb067a46200/ingest.py#L116-L127)|我们通过管理索引记录让我们不必每次都从头开始重新索引所有文档
207 |
208 | ```python
209 | record_manager = SQLRecordManager(
210 | f"weaviate/{WEAVIATE_DOCS_INDEX_NAME}", db_url=RECORD_MANAGER_DB_URL
211 | )
212 | record_manager.create_schema()
213 |
214 | indexing_stats = index(
215 | transformed_docs,
216 | record_manager,
217 | vectorstore,
218 | cleanup="full",
219 | source_id_key="source",
220 | )
221 | ```
222 |
223 | - 我们使用 [LangChain Indexing API](https://python.langchain.com/docs/modules/data_connection/indexing) 将任何来源的文档加载到向量存储中并保持同步
224 | - 它使用 `RecordManager` 来跟踪对任何向量存储的写入,并处理来自同一源的文档的重复数据删除和清理
225 | - 目前的实现中使用了 [Supabase](https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/providers/supabase) PostgreSQL 作为后台的 `SQLRecordManager`
226 | - 并使用 [GitHub Action](https://github.com/langchain-ai/chat-langchain/blob/3de16f8318abce7e88dc1da5444d9fb067a46200/.github/workflows/update-index.yml#L21-L27) 定时触发,番外参考:[Syncing data sources to vector stores](https://blog.langchain.dev/syncing-data-sources-to-vector-stores/)
227 |
228 | ---
229 | layout: image
230 | image: https://blog.langchain.dev/content/images/size/w1000/2023/09/langchain-overview-5.png
231 | ---
232 |
233 | ---
234 |
235 | # 4⃣️ 基于用户提问的数据检索
236 |
237 | 💡 [main.py#L107-L127](https://github.com/langchain-ai/chat-langchain/blob/3de16f8318abce7e88dc1da5444d9fb067a46200/main.py#L115-L126)|准备好用户的提问,构建数据检索的链路
238 |
239 | ```python
240 | condense_question_chain = (
241 | PromptTemplate.from_template(REPHRASE_TEMPLATE)
242 | | llm
243 | | StrOutputParser()
244 | ).with_config(
245 | run_name="CondenseQuestion",
246 | )
247 | retriever_chain = condense_question_chain | retriever
248 | ```
249 |
250 | - 我们讲用户提出的问题与当前聊天会话中过去的消息结合起来,并编写一个独立的搜索查询
251 | - 🌰 如果用户询问 “我如何使用 Anthropic LLM” 并接着问 “Vertex AI 怎么样”,我们可以将最后一个问题重写为 “我如何使用 Vertex AI LLM” 并使用它来查询检索器而不是 “Vertex AI 怎么样”
252 | - 💡 可以在 [LangChain Hub](https://smith.langchain.com/hub/bagatur/chat-langchain-rephrase) 中和调试用于改写问题的提示词
253 |
254 | ---
255 | layout: iframe
256 | url: https://smith.langchain.com/hub/bagatur/chat-langchain-rephrase?organizationId=e9dbe5e8-c426-4df0-a8a3-da8a1fc82968
257 | ---
258 |
259 | ---
260 |
261 | # 5⃣️ 基于检索内容的应答生成
262 |
263 | 💡 [main.py#L138-L164](https://github.com/langchain-ai/chat-langchain/blob/3de16f8318abce7e88dc1da5444d9fb067a46200/main.py#L138-L164)|最后我们将原始问题、聊天历史记录和检索到的上下文传递给大语言模型继续应答生成
264 |
265 | ```python {1-7|8-14|16-|all}
266 | _context = RunnableMap(
267 | {
268 | "context": retriever_chain | format_docs,
269 | "question": itemgetter("question"),
270 | "chat_history": itemgetter("chat_history"),
271 | }
272 | ).with_config(run_name="RetrieveDocs")
273 | prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
274 | [
275 | ("system", RESPONSE_TEMPLATE),
276 | MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="chat_history"),
277 | ("human", "{question}"),
278 | ]
279 | )
280 |
281 | response_synthesizer = (prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()).with_config(
282 | run_name="GenerateResponse",
283 | )
284 | answer_chain = _context | response_synthesizer
285 | ```
286 |
287 | - 问答链的 [提示词](https://smith.langchain.com/hub/bagatur/chat-langchain-response) 中会提示 LLM 输出引用来源,目的是:1) 尝试减轻幻觉,2) 让用户能够自行探索相关文档
288 |
289 | ---
290 | layout: iframe
291 | url: https://smith.langchain.com/hub/bagatur/chat-langchain-response
292 | ---
293 |
294 | ---
295 |
296 | # 🔀 输出增强:流式输出
297 |
298 | 💡 [main.py#L204-L220](https://github.com/langchain-ai/chat-langchain/blob/3de16f8318abce7e88dc1da5444d9fb067a46200/main.py#L204-L220)|我们还希望最小化用户首次获得应答文本的时间,或者说 “打字机” 输出效果
299 |
300 | ```python
301 | stream = answer_chain.astream_log(
302 | {
303 | "question": question,
304 | "chat_history": converted_chat_history,
305 | },
306 | config={"metadata": metadata},
307 | include_names=["FindDocs"],
308 | include_tags=["FindDocs"],
309 | )
310 | return StreamingResponse(
311 | transform_stream_for_client(stream),
312 | headers={"Content-Type": "text/event-stream"},
313 | )
314 | ```
315 |
316 | - 我们使用 [`astream_log`](https://python.langchain.com/docs/expression_language/interface#async-stream-intermediate-steps) 方法将来自问答链的响应异步地流式地传输到 Web 客户端
317 | - `astream_log` 的优点是除了流式传输最终响应之外,还可以实时地流式输出中间步骤中产生的内容
318 | - 由于我们使用 LangChain [Runnables](https://python.langchain.com/docs/expression_language/) 构建了问答链,流式传输可以自然应用到链路中所有的输出内容
319 |
320 | ---
321 | layout: image
322 | image: https://blog.langchain.dev/content/images/2023/09/ezgif.com-gif-maker.gif
323 | ---
324 |
325 | ---
326 |
327 | # 🎦 监控增强:聚合指标
328 |
329 | 应用上线之后,我们希望聚合和监控相关指标,以便我们可以跟踪应用程序的运行情况
330 |
331 | 通过接入 LangSmith,我们可以检查首次 Token 时间指标(TTFT)
332 | - TTFT:Time-to-First-Token
333 | - 该指标捕获 “将查询发送到聊天机器人应用” 与 “将第一个响应令牌发送回用户” 之间的延迟
334 |
335 | 我们可以监控跟踪中何时出现任何错误,以确保我们的聊天机器人按预期运行
336 | - Success Rate 指标:聚合链路调用状态 —— 成功、失败、阻塞(Pending)
337 |
338 | 我们还可以记录用户反馈并保存到 LangSmith 中
339 |
340 | ```python
341 | client.create_feedback(run_id, "user_score", score=score)
342 |
343 | client.update_feedback(feedback_id, score=score, comment=comment)
344 |
345 | ```
346 |
347 | ---
348 | layout: none
349 | ---
350 |
351 | 
352 | 
353 |
354 | ---
355 | src: ../../pages/common/refs.md
356 | ---
357 |
358 | ---
359 | src: ../../pages/common/end.md
360 | ---
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/302-langserve/src/index.html:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/302-langserve/src/package.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "private": true,
3 | "scripts": {
4 | "dev": "slidev",
5 | "build": "slidev build --base /302-langserve/ --out ../../dist/302-langserve",
6 | "export": "slidev export --dark --timeout 0 --output ../../pdfs/302-langserve.pdf"
7 | },
8 | "devDependencies": {
9 | "@slidev/cli": "^0.43.7",
10 | "@slidev/theme-seriph": "^0.21.3"
11 | },
12 | "slidev": {
13 | "addons": [
14 | "../../addons/webup"
15 | ]
16 | }
17 | }
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/302-langserve/src/slides.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | # See all frontmatter configurations: https://sli.dev/custom/#frontmatter-configures
3 | # theme id or package name, see also: https://sli.dev/themes/use.html
4 | theme: 'seriph'
5 | # titleTemplate for the webpage, `%s` will be replaced by the page's title
6 | titleTemplate: '%s|WebUP'
7 | # some information about the slides, markdown enabled
8 | info: |
9 | AGI 学习笔记,仅供个人学习使用
10 | # favicon, can be a local file path or URL
11 | favicon: https://files.codelife.cc/user-website-icon/20220523/5hyKeZxOknU2owAPvnSWD1388.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,limit_0,m_fill,w_25,h_25/quality,q_92/format,webp
12 | # enabled pdf downloading in SPA build, can also be a custom url
13 | download: 'https://github.com/webup/agi-talks/raw/master/pdfs/302-langserve.pdf'
14 | # syntax highlighter, can be 'prism' or 'shiki'
15 | highlighter: 'shiki'
16 | # controls whether texts in slides are selectable
17 | selectable: false
18 | # enable slide recording, can be boolean, 'dev' or 'build'
19 | record: 'build'
20 | # define transition between slides
21 | transition: fade
22 | # default frontmatter applies to all slides
23 | defaults:
24 |
25 | # slide configurations
26 | hideInToc: true
27 | layout: cover
28 | class: text-center
29 | background: https://source.unsplash.com/collection/94734566/1920x1080
30 | ---
31 |
32 | # LangServe: Serve LangChain
33 |
34 | LangServe Intro and Walkthrough
35 |
36 |
37 |
38 | Press Space for next page
39 |
40 |
41 |
42 |
56 |
57 | ---
58 | src: ../../pages/common/series.md
59 | ---
60 |
61 | ---
62 | src: ../../pages/common/toc.md
63 | ---
64 |
65 | ---
66 | layout: iframe
67 | url: https://embeds.onemodel.app/d/iframe/955y5DDdxGVRezQ2ZzVL718O7iuBgmQepg1aXLS7I6JvFP793OV9GySY5UoZ
68 | ---
69 |
70 | ---
71 | layout: iframe
72 | url: //player.bilibili.com/player.html?aid=492239144&bvid=BV1oN41147Ak&cid=1301106610&p=1
73 | ---
74 |
75 | ---
76 | layout: iframe-right
77 | url: https://blog.langchain.dev/introducing-langserve/
78 | ---
79 |
80 | # LangServe 之诞生
81 |
82 |
83 |
84 | ---
85 | layout: two-cols-header
86 | ---
87 |
88 | # 使用 LangServe 构建生产可用的 Web API
89 |
90 | Building Production-Ready Web APIs with LangServe
91 |
92 | ::left::
93 |
94 | `my_package/chain.py`:
95 |
96 | ```py {7-}
97 | """A conversational retrieval chain."""
98 |
99 | from langchain.chains import ConversationalRetrievalChain
100 | from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
101 | from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
102 | from langchain.vectorstores import FAISS
103 |
104 | vectorstore = FAISS.from_texts(
105 | ["cats like fish", "dogs like sticks"],
106 | embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings()
107 | )
108 | retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
109 |
110 | model = ChatOpenAI()
111 |
112 | chain = ConversationalRetrievalChain.from_llm(model, retriever)
113 | ```
114 |
115 | 任意构建一个 Chain(完全可以是基于 [LCEL](https://python.langchain.com/docs/expression_language/) 构建)
116 |
117 | Build a Chain as you like (especially via LCEL)
118 |
119 | ::right::
120 |
121 | `my_package/server.py`:
122 |
123 | ```py {8-}
124 | #!/usr/bin/env python
125 | """A server for the chain above."""
126 |
127 | from fastapi import FastAPI
128 | from langserve import add_routes
129 |
130 | from my_package.chain import chain
131 |
132 | app = FastAPI(title="Retrieval App")
133 |
134 | add_routes(app, chain)
135 |
136 | if __name__ == "__main__":
137 | import uvicorn
138 |
139 | uvicorn.run(app, host="localhost", port=8000)
140 | ```
141 |
142 | 通过 `add_routes` 方法把 Chain 注册到 Web 服务
143 |
144 | Register chain to web server via add_routes
145 |
146 | ---
147 | layout: iframe-right
148 | url: https://replit.com/@webup/langserve-replit-template?embed=true
149 | ---
150 |
151 | # LangServe Replit 模板
152 |
153 | [LangServe Replit Template](https://github.com/langchain-ai/langserve-replit-template)
154 |
155 | 该模板展示了如何使用 LangServe 将 LangChain Expression Language Runnable 部署为一组 HTTP 端点到 [Replit](https://replit.com/) 上,并支持流和批处理
156 |
157 | This template shows how to deploy a LangChain Expression Language Runnable as a set of HTTP endpoints with stream and batch support using LangServe onto Replit.
158 |
159 | ###### Notice
160 |
161 | 在运行示例前,需要通过左下角的 `Tools > Secrets` 来设置 `OPENAI_API_KEY`
162 | Need to set an OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable by going under Tools > Secrets in the bottom left corner
163 |
164 | ---
165 | layout: iframe-right
166 | url: https://langserve-launch-example-vz4y4ooboq-uc.a.run.app/docs
167 | ---
168 |
169 | # LangServe 特性概览
170 |
171 | LangServe Endpoints and Features
172 |
173 | 📚 `//docs` 通过 [Swagger UI](https://swagger.io/tools/swagger-ui/) 展示和调试 API
174 |
175 | //docs endpoint serves API docs with Swagger UI
176 |
177 | 📞 4 个“写”端点用于调用 Chain:`/invoke`,`/batch`,`/stream`,`/stream_log`
178 |
179 | 4 endpoints to call your chain in various approaches
180 |
181 | 🔍 2 个“读”端点用于获取 Chain 的输入输出结构:`/input_schema`,`/output_schema`
182 |
183 | 2 endpoints to retrieve input and output schemas (Pydantic models) auto-generated from the structure of the chain
184 |
185 | 📂 支持在同一服务的不同路径下托管多个 Chain
186 |
187 | Support for hosting multiple chains in the same server under separate paths, e.g. /chat/invoke, /say/invoke
188 |
189 | ---
190 |
191 | # 调用 LangServe 端点接口的多种方式
192 |
193 | Calling hosted chain from various clients
194 |
195 | ```py
196 | from langserve import RemoteRunnable
197 |
198 | pirate_chain = RemoteRunnable("https://your_url.repl.co/chat/")
199 |
200 | pirate_chain.invoke({"question": "how are you?"})
201 | await pirate_chain.ainvoke({"question": "how are you?"})
202 | ```
203 |
204 |
205 |
206 | ```js
207 | import { RemoteRunnable } from "langchain/runnables/remote"; // Introduced in LangChain.js 0.0.166+
208 |
209 | const pirateChain = new RemoteRunnable({ url: `https://your_url.repl.co/chat/` });
210 | const result = await pirateChain.invoke({ "question": "what did i just say my name was?" });
211 | ```
212 |
213 |
214 |
215 | ```sh
216 | curl --location --request POST 'https://your_url.repl.co/chat/invoke' \
217 | --header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
218 | --data-raw '{
219 | "input": { "question": "what did i just say my name was?" }
220 | }'
221 | ```
222 |
223 | ---
224 |
225 | # LCEL 对于 LangServe 的重要支撑
226 |
227 | The journey to build LangServe really started when LCEL and the Runnable protocol launched
228 |
229 | ###### Streaming Capacity
230 |
231 | 🌊 一流的流式传输支持:使用 LCEL 时,您可以获得最佳的首次 Token 时间;正在尝试支持 [流式 JSON 解析器](https://twitter.com/LangChainAI/status/1709690468030914584)
232 |
233 | First-class support for streaming: build your chains with LCEL you get the best possible time-to-first-token, streaming JSON parser is WIP
234 |
235 | 🔍 流式输出中间结果:添加了对 [流式输出中间结果](https://python.langchain.com/docs/expression_language/interface#async-stream-intermediate-steps) 的支持,并且在每个 LangServe 服务上都可用
236 |
237 | Accessing intermediate results: added support for streaming intermediate results, and it’s available on every LangServe server
238 |
239 |
240 |
241 | ###### Control Flow
242 |
243 | ⚡️ 优化的并行执行:只要 LCEL 链具有 [可以并行执行](https://python.langchain.com/docs/expression_language/how_to/map) 的步骤,就会在同步和异步接口中自动并行执行此操作
244 |
245 | Optimized parallel execution: whenever LCEL chains have steps that can be executed in parallel, will do it in both sync and async interfaces
246 |
247 | 🔁 支持重试和回退:为 LCEL 链的增加了 [重试和回退](https://python.langchain.com/docs/expression_language/how_to/fallbacks) 的支持;目前正在努力添加对重试/回退的流支持
248 |
249 | Retries and fallbacks: added support for any part of your LCEL chain; currently working on adding streaming support for retries/fallback
250 |
251 | ---
252 | src: ../../pages/common/refs.md
253 | ---
254 |
255 | ---
256 | src: ../../pages/common/end.md
257 | ---
258 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # AGI 应用实践
2 |
3 | > 面向开源社区的 AGI 学习笔记,专注 LangChain、提示工程、大语言模型开放接口的介绍和实践经验分享。
4 |
5 | ## AGI Overview
6 |
7 | - [101:AGI 提示工程指北](https://agi-talks.vercel.app/101-prompt-engineering/)
8 | - [102:OpenAI API 浅出](https://agi-talks.vercel.app/102-openai-api/)
9 | - [103:LangChain Hub 提示词面面观](https://agi-talks.vercel.app/103-prompt-landscape/)
10 |
11 | ## LangChain in Action
12 |
13 | - [201:LangChain 功能模块解析(上篇)](https://agi-talks.vercel.app/201-langchain-modules/)
14 | - [202:LangChain 功能模块解析(中篇)](https://agi-talks.vercel.app/202-langchain-chains/)
15 | - [203:LangChain 功能模块解析(下篇)](https://agi-talks.vercel.app/203-langchain-agents/)
16 | - [301:LangChain 实战 - Chat LangChain 应用解析](https://agi-talks.vercel.app/301-langchain-chatdoc)
17 | - [302:LangServe - 部署 LangChain 最佳方式](https://agi-talks.vercel.app/302-langserve)
18 |
19 | ## 论坛 / 社区分享
20 |
21 | - 2024.07.20 @ Shanghai:[LangChain 与 MinIO:基于 GenAI 的数据管理可行性探索](https://agi-talks.vercel.app/240720-langchain-minio/) 📍 [KubeSphere x OpenCSG Meetup](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/YB1M3oTR2NIrdOovoquEBA)
22 | - 2024.01.06:[LangChain 生态发展解读](https://agi-talks.vercel.app/240106-langchain-status/)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/addons/webup/.npmignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | node_modules
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/addons/webup/components/B.vue:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/addons/webup/components/NPM.vue:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
8 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/addons/webup/components/PB.vue:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/addons/webup/components/T.vue:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/addons/webup/components/Val.vue:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
8 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/addons/webup/components/Version.vue:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/addons/webup/components/Wiki.vue:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
8 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/addons/webup/package.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "name": "slidev-addon-webup",
3 | "version": "0.1.0",
4 | "keywords": [
5 | "slidev",
6 | "slidev-addon"
7 | ],
8 | "engines": {
9 | "slidev": ">=0.32.0"
10 | }
11 | }
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/langchain-biweekly/src/index.html:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/langchain-biweekly/src/package.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "private": true,
3 | "scripts": {
4 | "dev": "slidev",
5 | "build": "slidev build --base /langchain-biweekly/ --out ../../dist/langchain-biweekly",
6 | "export": "slidev export --dark --timeout 0 --output ../../pdfs/langchain-biweekly.pdf"
7 | },
8 | "devDependencies": {
9 | "@slidev/cli": "^0.49.17",
10 | "@slidev/theme-seriph": "^0.25.0"
11 | },
12 | "slidev": {
13 | "addons": [
14 | "../addons/webup"
15 | ]
16 | }
17 | }
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/netlify.toml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [build.environment]
2 | NODE_VERSION = "18"
3 | PLAYWRIGHT_BROWSERS_PATH = "0"
4 |
5 | [build]
6 | publish = "dist"
7 | command = "npm run build"
8 |
9 | [[redirects]]
10 | from = "/101-prompt-engineering/*"
11 | to = "/101-prompt-engineering/index.html"
12 | status = 200
13 |
14 | [[redirects]]
15 | from = "/102-openai-api/*"
16 | to = "/102-openai-api/index.html"
17 | status = 200
18 |
19 | [[redirects]]
20 | from = "/201-langchain-modules/*"
21 | to = "/201-langchain-modules/index.html"
22 | status = 200
23 |
24 | [[redirects]]
25 | from = "/202-langchain-chains/*"
26 | to = "/202-langchain-chains/index.html"
27 | status = 200
28 |
29 | [[redirects]]
30 | from = "/203-langchain-agents/*"
31 | to = "/203-langchain-agents/index.html"
32 | status = 200
33 |
34 | [[redirects]]
35 | from = "/301-langchain-chatdoc/*"
36 | to = "/301-langchain-chatdoc/index.html"
37 | status = 200
38 |
39 | [[redirects]]
40 | from = "/302-langserve/*"
41 | to = "/302-langserve/index.html"
42 | status = 200
43 |
44 | [[redirects]]
45 | from = "/240106-langchain-status/*"
46 | to = "/240106-langchain-status/index.html"
47 | status = 200
48 |
49 | [[redirects]]
50 | from = "/240720-langchain-minio/*"
51 | to = "/240720-langchain-minio/index.html"
52 | status = 200
53 |
54 | [[redirects]]
55 | from = "/langchain-biweekly/*"
56 | to = "/langchain-biweekly/index.html"
57 | status = 200
58 |
59 | [[redirects]]
60 | from = "/"
61 | to = "https://github.com/webup/agi-talks"
62 | status = 302
63 | force = true
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/package.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "private": true,
3 | "scripts": {
4 | "build": "rimraf dist && pnpm -r run build",
5 | "export": "pnpm -r run export",
6 | "serve:netlify": "netlify dev",
7 | "serve:vercel": "vercel dev"
8 | },
9 | "devDependencies": {
10 | "@iconify-json/ant-design": "^1.1.16",
11 | "@iconify-json/mdi": "^1.1.67",
12 | "netlify-cli": "^17.33.4",
13 | "playwright-chromium": "^1.45.2",
14 | "pnpm": "^9.5.0",
15 | "rimraf": "^6.0.1",
16 | "vercel": "^35.0.2"
17 | }
18 | }
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pages/common/end.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | layout: quote
3 | class: text-center
4 | hideInToc: true
5 | ---
6 |
7 | # 感谢聆听 ❤️
8 |
9 | [webup](https://github.com/webup) | [serviceup](https://www.yuque.com/serviceup)
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pages/common/refs.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | hideInToc: true
3 | ---
4 | # 参考资料
5 |
6 | 本教程在制作过程中参考和引用了以下资料(排名不分先后)的内容,特此鸣谢!
7 |
8 | ###### 视频资料
9 |
10 | - [Short Courses | Learn Generative AI from DeepLearning.AI](https://www.deeplearning.ai/short-courses/)
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 | ###### 图文资料
15 |
16 | - [Core Concepts | 🦜️🔗 LangChain](https://docs.langchain.com/)
17 | - [JS/TS Docs](https://js.langchain.com/), [Python Docs](https://python.langchain.com/), [LangSmith Docs](https://docs.smith.langchain.com/)
18 | - LangChain [Blog](https://blog.langchain.dev/), [Release Notes](https://blog.langchain.dev/tag/release-notes/)
19 | - [入门:Prompts(提示词)|通往 AGI 之路](https://ywh1bkansf.feishu.cn/wiki/Q5mXww4rriujFFkFQOzc8uIsnah?table=tbldSgFt2xNUDNAz&view=vewo2g2ktO)
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 | ###### 代码资料
24 |
25 | - [openai/openai-cookbook: Examples and guides for using the OpenAI API](https://github.com/openai/openai-cookbook)
26 | - [datawhalechina/prompt-engineering-for-developers: 吴恩达大模型系列课程中文版](https://github.com/datawhalechina/prompt-engineering-for-developers)
27 | - [slidevjs/slidev: Presentation Slides for Developers](https://github.com/slidevjs/slidev)
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pages/common/series.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | hideInToc: true
3 | ---
4 |
5 | # 《AGI 应用实践》系列教程
6 |
7 | ###### AGI Overview
8 |
9 | - [101:AGI 提示工程指北](https://agi-talks.vercel.app/101-prompt-engineering/)
10 | - [102:OpenAI API 浅出](https://agi-talks.vercel.app/102-openai-api/)
11 | - [103:LangChain Hub 提示词面面观](https://agi-talks.vercel.app/103-prompt-landscape/)
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 | ###### LangChain in Action
16 |
17 | - [201:LangChain 功能模块解析(上篇)](https://agi-talks.vercel.app/201-langchain-modules/)
18 | - [202:LangChain 功能模块解析(中篇)](https://agi-talks.vercel.app/202-langchain-chains/)
19 | - [203:LangChain 功能模块解析(下篇)](https://agi-talks.vercel.app/203-langchain-agents/)
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 | - [301:LangChain 实战 - Chat LangChain 应用解析](https://agi-talks.vercel.app/301-langchain-chatdoc)
24 | - [302:LangServe - 部署 LangChain 最佳方式](https://agi-talks.vercel.app/302-langserve)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pages/common/toc.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | hideInToc: true
3 | ---
4 |
5 | # 教程大纲
6 |
7 |
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pages/playground/langchain.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | hideInToc: true
3 | ---
4 |
5 | # 演示环境准备
6 |
7 | 基于 [Val Town](https://www.val.town/) 平台,调用 LangChain 来实现 LLM 应用流程
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 | 💡 官方也提供 [Python](https://python.langchain.com/) 类库,以及庞大的社区 [Integrations](https://integrations.langchain.com/)(实名羡慕啊 🍋)
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pages/playground/openai.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 演示环境准备
2 |
3 | 基于 [Val Town](https://www.val.town/) 平台,调用 OpenAI 来执行人机对话
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 | 💡 官方也提供 [Python](https://github.com/openai/openai-python) 类库;[社区类库](https://platform.openai.com/docs/libraries/community-libraries) 支持多种编程语言(但请谨慎使用 ⚠️)
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pdfs/101-prompt-engineering.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/webup/agi-talks/bd464647b1b77cdd7a7cf03598d2bb11261b72a4/pdfs/101-prompt-engineering.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pdfs/102-openai-api.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/webup/agi-talks/bd464647b1b77cdd7a7cf03598d2bb11261b72a4/pdfs/102-openai-api.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pdfs/201-langchain-modules.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/webup/agi-talks/bd464647b1b77cdd7a7cf03598d2bb11261b72a4/pdfs/201-langchain-modules.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pdfs/202-langchain-chains.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/webup/agi-talks/bd464647b1b77cdd7a7cf03598d2bb11261b72a4/pdfs/202-langchain-chains.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pdfs/203-langchain-agents.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/webup/agi-talks/bd464647b1b77cdd7a7cf03598d2bb11261b72a4/pdfs/203-langchain-agents.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pdfs/240106-langchain-status.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/webup/agi-talks/bd464647b1b77cdd7a7cf03598d2bb11261b72a4/pdfs/240106-langchain-status.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pdfs/240720-langchain-minio.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/webup/agi-talks/bd464647b1b77cdd7a7cf03598d2bb11261b72a4/pdfs/240720-langchain-minio.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pdfs/302-langserve.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/webup/agi-talks/bd464647b1b77cdd7a7cf03598d2bb11261b72a4/pdfs/302-langserve.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pdfs/langchain-biweekly.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/webup/agi-talks/bd464647b1b77cdd7a7cf03598d2bb11261b72a4/pdfs/langchain-biweekly.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pnpm-workspace.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | packages:
2 | - '*/src'
3 | - 'addons/*'
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/styles/component.css:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .slidev-code {
2 | @apply mt-4;
3 | }
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/styles/layout.css:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .grid-cols-2 {
2 | @apply gap-x-5;
3 | }
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/vercel.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "rewrites": [
3 | { "source": "/101-prompt-engineering/(.*)", "destination": "/101-prompt-engineering/index.html" },
4 | { "source": "/102-openai-api/(.*)", "destination": "/102-openai-api/index.html" },
5 | { "source": "/201-langchain-modules/(.*)", "destination": "/201-langchain-modules/index.html" },
6 | { "source": "/202-langchain-chains/(.*)", "destination": "/202-langchain-chains/index.html" },
7 | { "source": "/203-langchain-agents/(.*)", "destination": "/203-langchain-agents/index.html" },
8 | { "source": "/301-langchain-chatdoc/(.*)", "destination": "/301-langchain-chatdoc/index.html" },
9 | { "source": "/302-langserve/(.*)", "destination": "/302-langserve/index.html" },
10 | { "source": "/240106-langchain-status/(.*)", "destination": "/240106-langchain-status/index.html" },
11 | { "source": "/240720-langchain-minio/(.*)", "destination": "/240720-langchain-minio/index.html" },
12 | { "source": "/(.*)", "destination": "/langchain-biweekly/index.html" }
13 | ]
14 | }
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 235 |
236 |
235 |
236 |  235 |
236 |
235 |
236 | 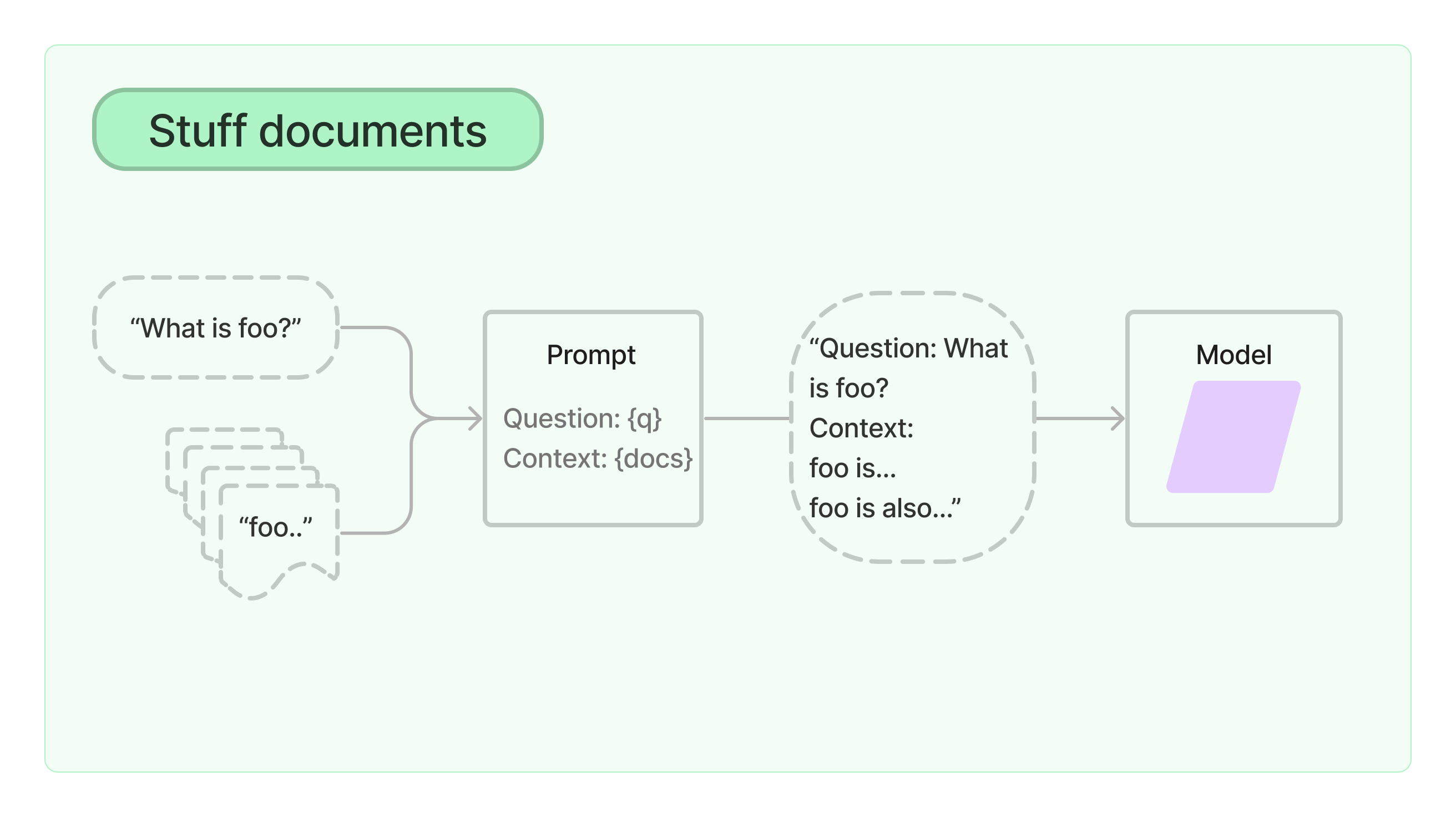 654 |
654 |  655 |
656 | ---
657 | level: 3
658 | ---
659 |
660 | # 层叠递进的 Refine 模式
661 |
662 | - 对于每个文档,它将所有非文档输入、当前文档以及最新的中间答案传递给 LLM 链以获得新的答案
663 | - 由于 Refine 链一次仅将单个文档传递给 LLM,因此很适合需要分析的文档数量多于模型上下文的任务
664 | - 明显的缺点是:将比 Stuff 文档链进行更多的 LLM 调用;当文档频繁地互相交叉引用时很可能表现不佳
665 |
666 | 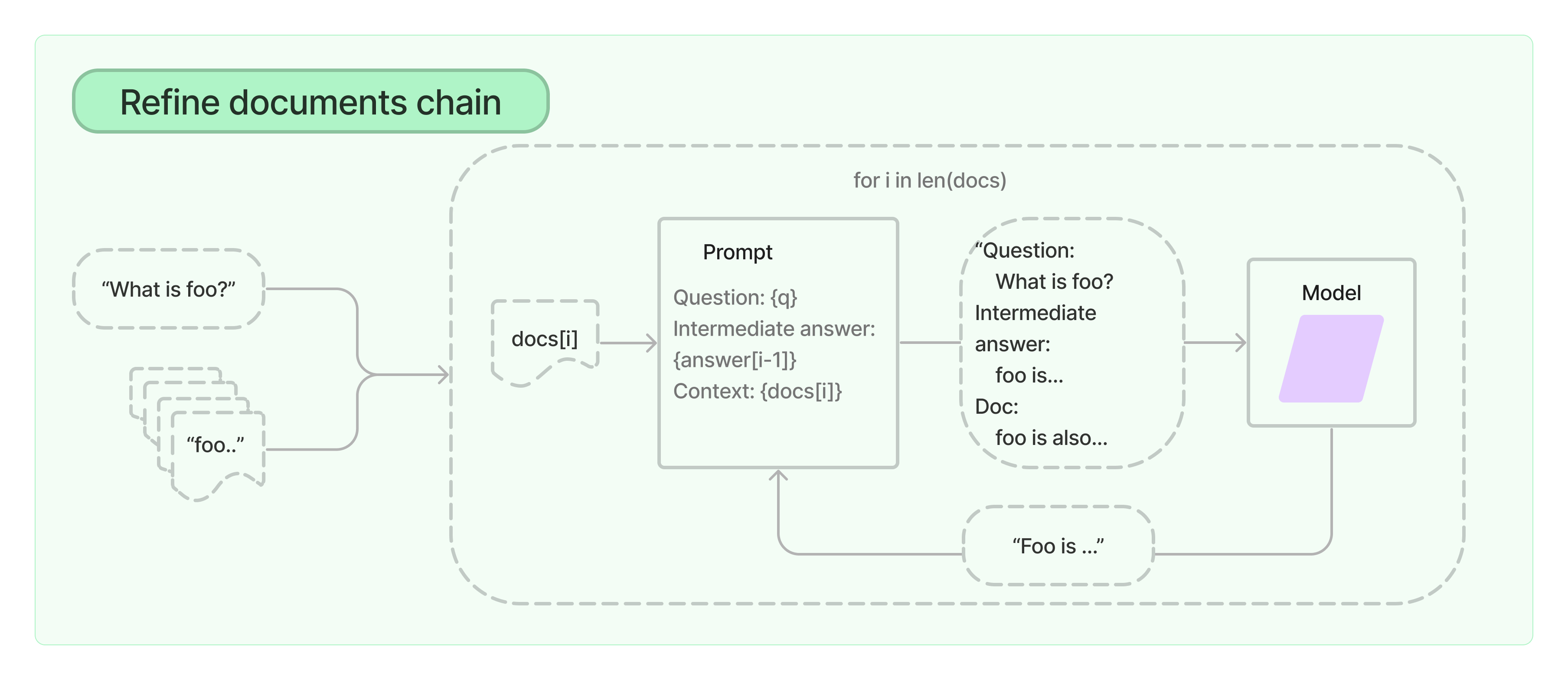
667 |
668 | ---
669 | level: 3
670 | ---
671 |
672 | # 🌰 Refine 文档链的二阶段提示词应用
673 |
674 | ```ts {8-18|20-34|36-39|all} {maxHeight:'90%'}
675 | import { loadQARefineChain } from "langchain/chains";
676 | import { OpenAI } from "langchain/llms/openai";
677 | import { TextLoader } from "langchain/document_loaders/fs/text";
678 | import { MemoryVectorStore } from "langchain/vectorstores/memory";
679 | import { OpenAIEmbeddings } from "langchain/embeddings/openai";
680 | import { PromptTemplate } from "langchain/prompts";
681 |
682 | /* 最终提问时使用的提示词 */
683 | export const questionPromptTemplateString = `Context information is below.
684 | ---------------------
685 | {context}
686 | ---------------------
687 | Given the context information and no prior knowledge, answer the question: {question}`;
688 |
689 | const questionPrompt = new PromptTemplate({
690 | inputVariables: ["context", "question"],
691 | template: questionPromptTemplateString,
692 | });
693 |
694 | /* 中间 Refine 过程使用的提示词 */
695 | const refinePromptTemplateString = `The original question is as follows: {question}
696 | We have provided an existing answer: {existing_answer}
697 | We have the opportunity to refine the existing answer
698 | (only if needed) with some more context below.
699 | ------------
700 | {context}
701 | ------------
702 | Given the new context, refine the original answer to better answer the question.
703 | You must provide a response, either original answer or refined answer.`;
704 |
705 | const refinePrompt = new PromptTemplate({
706 | inputVariables: ["question", "existing_answer", "context"],
707 | template: refinePromptTemplateString,
708 | });
709 |
710 | /* 构建 Refine 文档链,并导入两份提示词模板 */
711 | const embeddings = new OpenAIEmbeddings();
712 | const model = new OpenAI({ temperature: 0 });
713 | const chain = loadQARefineChain(model, { questionPrompt, refinePrompt });
714 |
715 | // Load the documents and create the vector store
716 | const loader = new TextLoader("./state_of_the_union.txt");
717 | const docs = await loader.loadAndSplit();
718 | const store = await MemoryVectorStore.fromDocuments(docs, embeddings);
719 |
720 | // Select the relevant documents
721 | const question = "What did the president say about Justice Breyer";
722 | const relevantDocs = await store.similaritySearch(question);
723 |
724 | const res = await chain.call({ input_documents: relevantDocs, question });
725 | ```
726 |
727 | ---
728 | level: 2
729 | ---
730 |
731 | # 四套应用疏通途:Retrieval QA
732 |
733 | [Retrieval QA Chain](https://js.langchain.com/docs/modules/chains/popular/vector_db_qa) 通过从检索器检索文档,然后使用文档工具链,根据检索到的文档回答问题
734 |
735 | ```ts {18-22|24-|all} {maxHeight:'85%'}
736 | import { OpenAI } from "langchain/llms/openai";
737 | import { RetrievalQAChain, loadQAStuffChain } from "langchain/chains";
738 | import { HNSWLib } from "langchain/vectorstores/hnswlib";
739 | import { OpenAIEmbeddings } from "langchain/embeddings/openai";
740 | import { RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter } from "langchain/text_splitter";
741 | import { PromptTemplate } from "langchain/prompts";
742 | import * as fs from "fs";
743 |
744 | const promptTemplate = `Use the following pieces of context to answer the question at the end. If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know, don't try to make up an answer.
745 |
746 | {context}
747 |
748 | Question: {question}
749 | Answer in Italian:`;
750 | const prompt = PromptTemplate.fromTemplate(promptTemplate);
751 | const model = new OpenAI({});
752 |
753 | /* 构建文档检索器 */
754 | const text = fs.readFileSync("state_of_the_union.txt", "utf8");
755 | const textSplitter = new RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter({ chunkSize: 1000 });
756 | const docs = await textSplitter.createDocuments([text]);
757 | const vectorStore = await HNSWLib.fromDocuments(docs, new OpenAIEmbeddings());
758 |
759 | /* 构建基于 Stuff 文档链和自定义提示词的 Retrieval QA Chain */
760 | const chain = new RetrievalQAChain({
761 | combineDocumentsChain: loadQAStuffChain(model, { prompt }),
762 | retriever: vectorStore.asRetriever(),
763 | returnSourceDocuments: true, // 要求一并返回原始文档
764 | });
765 | const res = await chain.call({ query: "What did the president say about Justice Breyer?" });
766 | ```
767 |
768 | ---
769 | level: 2
770 | ---
771 |
772 | # 四套应用疏通途:Conversational Retrieval QA
773 |
774 | [Conversational Retrieval QA Chain](https://js.langchain.com/docs/modules/chains/popular/chat_vector_db) 建立在 Retrieval QA Chain 的基础上,并接入 Memory 组件
775 |
776 | 它首先将聊天历史记录和问题组合成一个独立的问题,然后将检索得到的文档和问题传递给问答链以返回响应
777 |
778 | ```ts {35-49|51-|all} {maxHeight:'75%'}
779 | import { ChatOpenAI } from "langchain/chat_models/openai";
780 | import { ConversationalRetrievalQAChain } from "langchain/chains";
781 | import { HNSWLib } from "langchain/vectorstores/hnswlib";
782 | import { OpenAIEmbeddings } from "langchain/embeddings/openai";
783 | import { BufferMemory } from "langchain/memory";
784 |
785 | const CUSTOM_QUESTION_GENERATOR_CHAIN_PROMPT = `Given the following conversation and a follow up question, return the conversation history excerpt that includes any relevant context to the question if it exists and rephrase the follow up question to be a standalone question.
786 | Chat History:
787 | {chat_history}
788 | Follow Up Input: {question}
789 | Your answer should follow the following format:
790 | \`\`\`
791 | Use the following pieces of context to answer the users question.
792 | If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know, don't try to make up an answer.
793 | ----------------
794 |
655 |
656 | ---
657 | level: 3
658 | ---
659 |
660 | # 层叠递进的 Refine 模式
661 |
662 | - 对于每个文档,它将所有非文档输入、当前文档以及最新的中间答案传递给 LLM 链以获得新的答案
663 | - 由于 Refine 链一次仅将单个文档传递给 LLM,因此很适合需要分析的文档数量多于模型上下文的任务
664 | - 明显的缺点是:将比 Stuff 文档链进行更多的 LLM 调用;当文档频繁地互相交叉引用时很可能表现不佳
665 |
666 | 
667 |
668 | ---
669 | level: 3
670 | ---
671 |
672 | # 🌰 Refine 文档链的二阶段提示词应用
673 |
674 | ```ts {8-18|20-34|36-39|all} {maxHeight:'90%'}
675 | import { loadQARefineChain } from "langchain/chains";
676 | import { OpenAI } from "langchain/llms/openai";
677 | import { TextLoader } from "langchain/document_loaders/fs/text";
678 | import { MemoryVectorStore } from "langchain/vectorstores/memory";
679 | import { OpenAIEmbeddings } from "langchain/embeddings/openai";
680 | import { PromptTemplate } from "langchain/prompts";
681 |
682 | /* 最终提问时使用的提示词 */
683 | export const questionPromptTemplateString = `Context information is below.
684 | ---------------------
685 | {context}
686 | ---------------------
687 | Given the context information and no prior knowledge, answer the question: {question}`;
688 |
689 | const questionPrompt = new PromptTemplate({
690 | inputVariables: ["context", "question"],
691 | template: questionPromptTemplateString,
692 | });
693 |
694 | /* 中间 Refine 过程使用的提示词 */
695 | const refinePromptTemplateString = `The original question is as follows: {question}
696 | We have provided an existing answer: {existing_answer}
697 | We have the opportunity to refine the existing answer
698 | (only if needed) with some more context below.
699 | ------------
700 | {context}
701 | ------------
702 | Given the new context, refine the original answer to better answer the question.
703 | You must provide a response, either original answer or refined answer.`;
704 |
705 | const refinePrompt = new PromptTemplate({
706 | inputVariables: ["question", "existing_answer", "context"],
707 | template: refinePromptTemplateString,
708 | });
709 |
710 | /* 构建 Refine 文档链,并导入两份提示词模板 */
711 | const embeddings = new OpenAIEmbeddings();
712 | const model = new OpenAI({ temperature: 0 });
713 | const chain = loadQARefineChain(model, { questionPrompt, refinePrompt });
714 |
715 | // Load the documents and create the vector store
716 | const loader = new TextLoader("./state_of_the_union.txt");
717 | const docs = await loader.loadAndSplit();
718 | const store = await MemoryVectorStore.fromDocuments(docs, embeddings);
719 |
720 | // Select the relevant documents
721 | const question = "What did the president say about Justice Breyer";
722 | const relevantDocs = await store.similaritySearch(question);
723 |
724 | const res = await chain.call({ input_documents: relevantDocs, question });
725 | ```
726 |
727 | ---
728 | level: 2
729 | ---
730 |
731 | # 四套应用疏通途:Retrieval QA
732 |
733 | [Retrieval QA Chain](https://js.langchain.com/docs/modules/chains/popular/vector_db_qa) 通过从检索器检索文档,然后使用文档工具链,根据检索到的文档回答问题
734 |
735 | ```ts {18-22|24-|all} {maxHeight:'85%'}
736 | import { OpenAI } from "langchain/llms/openai";
737 | import { RetrievalQAChain, loadQAStuffChain } from "langchain/chains";
738 | import { HNSWLib } from "langchain/vectorstores/hnswlib";
739 | import { OpenAIEmbeddings } from "langchain/embeddings/openai";
740 | import { RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter } from "langchain/text_splitter";
741 | import { PromptTemplate } from "langchain/prompts";
742 | import * as fs from "fs";
743 |
744 | const promptTemplate = `Use the following pieces of context to answer the question at the end. If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know, don't try to make up an answer.
745 |
746 | {context}
747 |
748 | Question: {question}
749 | Answer in Italian:`;
750 | const prompt = PromptTemplate.fromTemplate(promptTemplate);
751 | const model = new OpenAI({});
752 |
753 | /* 构建文档检索器 */
754 | const text = fs.readFileSync("state_of_the_union.txt", "utf8");
755 | const textSplitter = new RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter({ chunkSize: 1000 });
756 | const docs = await textSplitter.createDocuments([text]);
757 | const vectorStore = await HNSWLib.fromDocuments(docs, new OpenAIEmbeddings());
758 |
759 | /* 构建基于 Stuff 文档链和自定义提示词的 Retrieval QA Chain */
760 | const chain = new RetrievalQAChain({
761 | combineDocumentsChain: loadQAStuffChain(model, { prompt }),
762 | retriever: vectorStore.asRetriever(),
763 | returnSourceDocuments: true, // 要求一并返回原始文档
764 | });
765 | const res = await chain.call({ query: "What did the president say about Justice Breyer?" });
766 | ```
767 |
768 | ---
769 | level: 2
770 | ---
771 |
772 | # 四套应用疏通途:Conversational Retrieval QA
773 |
774 | [Conversational Retrieval QA Chain](https://js.langchain.com/docs/modules/chains/popular/chat_vector_db) 建立在 Retrieval QA Chain 的基础上,并接入 Memory 组件
775 |
776 | 它首先将聊天历史记录和问题组合成一个独立的问题,然后将检索得到的文档和问题传递给问答链以返回响应
777 |
778 | ```ts {35-49|51-|all} {maxHeight:'75%'}
779 | import { ChatOpenAI } from "langchain/chat_models/openai";
780 | import { ConversationalRetrievalQAChain } from "langchain/chains";
781 | import { HNSWLib } from "langchain/vectorstores/hnswlib";
782 | import { OpenAIEmbeddings } from "langchain/embeddings/openai";
783 | import { BufferMemory } from "langchain/memory";
784 |
785 | const CUSTOM_QUESTION_GENERATOR_CHAIN_PROMPT = `Given the following conversation and a follow up question, return the conversation history excerpt that includes any relevant context to the question if it exists and rephrase the follow up question to be a standalone question.
786 | Chat History:
787 | {chat_history}
788 | Follow Up Input: {question}
789 | Your answer should follow the following format:
790 | \`\`\`
791 | Use the following pieces of context to answer the users question.
792 | If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know, don't try to make up an answer.
793 | ----------------
794 |  83 |
84 | ---
85 | layout: quote
86 | ---
87 |
88 | # 🗺️ 开局一张图
89 |
90 | 从 LangChain 生态全景(架构)图说起
91 |
92 | ---
93 | layout: iframe
94 | url: https://python.langchain.com/docs/get_started/introduction
95 | ---
96 |
97 | ---
98 | layout: iframe-right
99 | url: https://blog.langchain.dev/the-new-langchain-architecture-langchain-core-v0-1-langchain-community-and-a-path-to-langchain-v0-1/
100 | ---
101 |
102 | # 🦜️🔗 LangChain 类库
103 |
104 | 定位:本地构建 LLM 原型应用
105 |
106 | - langchain-core 包含了核心抽象和 [LangChain Expression Language](https://python.langchain.com/docs/expression_language/)(LCEL)
107 | - 版本已经达到 0.1, 未来的任何破坏性变更都会带来小版本升级(0.x)
108 | - 模块化的抽象为第三方集成提供标准接口
109 | - langchain-community 包含 [第三方集成](https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/providers)
110 | - 主要集成将被进一步拆分为独立软件包
111 | - 目前,LangChain 拥有近 700 个集成
112 | - langchain 包含了实际运用的 Chain、Agent 和 Retriever 流程策略
113 | - 官方计划 1/9 推出 0.1 稳定版本
114 |
115 | ---
116 | layout: iframe
117 | url: https://integrations.langchain.com/
118 | ---
119 |
120 | ---
121 | layout: iframe-right
122 | url: https://blog.langchain.dev/langchain-templates/
123 | ---
124 |
125 | # 🦜️🔗 LangChain 模板
126 |
127 | 定位:提供预制的可参考的 LLM 原型应用
128 |
129 | 通常配合 LangServe 一起使用(三步走):
130 |
131 | 1️⃣ 安装 `langchain-cli`
132 |
133 | ```sh
134 | pip install -U langchain-cli
135 | ```
136 |
137 | 2️⃣ (创建新项目)导入指定模版
138 |
139 | ```sh
140 | langchain app new my-app --package $PACKAGE_NAME
141 | langchain app add $PACKAGE_NAME
142 | # adding custom GitHub repo packages
143 | langchain app add --repo $OWNER/$REPO
144 | ```
145 |
146 | 3️⃣ 绑定 LangServe 服务端点(`server.py`)
147 |
148 | ```py
149 | add_routes(app, chain, path="/chain-path")
150 | ```
151 |
152 | 🚀 启动!`langchain serve`
153 |
154 | ---
155 | layout: iframe
156 | url: https://templates.langchain.com/
157 | ---
158 |
159 | ---
160 | layout: iframe-right
161 | url: https://blog.langchain.dev/introducing-langserve/
162 | ---
163 |
164 | # 🦜️🏓 LangServe 类库
165 |
166 | 定位:一键 REST 服务化 LLM 原型应用
83 |
84 | ---
85 | layout: quote
86 | ---
87 |
88 | # 🗺️ 开局一张图
89 |
90 | 从 LangChain 生态全景(架构)图说起
91 |
92 | ---
93 | layout: iframe
94 | url: https://python.langchain.com/docs/get_started/introduction
95 | ---
96 |
97 | ---
98 | layout: iframe-right
99 | url: https://blog.langchain.dev/the-new-langchain-architecture-langchain-core-v0-1-langchain-community-and-a-path-to-langchain-v0-1/
100 | ---
101 |
102 | # 🦜️🔗 LangChain 类库
103 |
104 | 定位:本地构建 LLM 原型应用
105 |
106 | - langchain-core 包含了核心抽象和 [LangChain Expression Language](https://python.langchain.com/docs/expression_language/)(LCEL)
107 | - 版本已经达到 0.1, 未来的任何破坏性变更都会带来小版本升级(0.x)
108 | - 模块化的抽象为第三方集成提供标准接口
109 | - langchain-community 包含 [第三方集成](https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/providers)
110 | - 主要集成将被进一步拆分为独立软件包
111 | - 目前,LangChain 拥有近 700 个集成
112 | - langchain 包含了实际运用的 Chain、Agent 和 Retriever 流程策略
113 | - 官方计划 1/9 推出 0.1 稳定版本
114 |
115 | ---
116 | layout: iframe
117 | url: https://integrations.langchain.com/
118 | ---
119 |
120 | ---
121 | layout: iframe-right
122 | url: https://blog.langchain.dev/langchain-templates/
123 | ---
124 |
125 | # 🦜️🔗 LangChain 模板
126 |
127 | 定位:提供预制的可参考的 LLM 原型应用
128 |
129 | 通常配合 LangServe 一起使用(三步走):
130 |
131 | 1️⃣ 安装 `langchain-cli`
132 |
133 | ```sh
134 | pip install -U langchain-cli
135 | ```
136 |
137 | 2️⃣ (创建新项目)导入指定模版
138 |
139 | ```sh
140 | langchain app new my-app --package $PACKAGE_NAME
141 | langchain app add $PACKAGE_NAME
142 | # adding custom GitHub repo packages
143 | langchain app add --repo $OWNER/$REPO
144 | ```
145 |
146 | 3️⃣ 绑定 LangServe 服务端点(`server.py`)
147 |
148 | ```py
149 | add_routes(app, chain, path="/chain-path")
150 | ```
151 |
152 | 🚀 启动!`langchain serve`
153 |
154 | ---
155 | layout: iframe
156 | url: https://templates.langchain.com/
157 | ---
158 |
159 | ---
160 | layout: iframe-right
161 | url: https://blog.langchain.dev/introducing-langserve/
162 | ---
163 |
164 | # 🦜️🏓 LangServe 类库
165 |
166 | 定位:一键 REST 服务化 LLM 原型应用  48 |
49 | ---
50 |
51 | # 引言:重塑 AI 应用中的数据交互模式
52 | 在当今的 AI 应用开发中,如何让用户以更自然、更直观的方式与复杂的数据存储系统交互,是一个关键挑战
53 |
54 |
48 |
49 | ---
50 |
51 | # 引言:重塑 AI 应用中的数据交互模式
52 | 在当今的 AI 应用开发中,如何让用户以更自然、更直观的方式与复杂的数据存储系统交互,是一个关键挑战
53 |
54 |