├── .gitmodules
├── entrypoints
├── __init__.py
└── curl.sh
├── xfuser
├── ray
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── pipeline
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ └── base_executor.py
│ └── worker
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── utils.py
│ │ └── worker_wrappers.py
├── model_executor
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── patch
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ └── unet_patch.py
│ ├── models
│ │ ├── customized
│ │ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ │ └── step_video_t2v
│ │ │ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ │ │ ├── linear.py
│ │ │ │ ├── attentions.py
│ │ │ │ └── rope.py
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ └── transformers
│ │ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ │ └── register.py
│ ├── cache
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ └── diffusers_adapters
│ │ │ ├── registry.py
│ │ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ │ └── flux.py
│ ├── layers
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── base_layer.py
│ │ ├── register.py
│ │ └── feedforward.py
│ ├── schedulers
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── base_scheduler.py
│ │ ├── register.py
│ │ ├── scheduling_ddpm.py
│ │ ├── scheduling_dpm_cogvideox.py
│ │ ├── scheduling_ddim_cogvideox.py
│ │ └── scheduling_ddim.py
│ ├── pipelines
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── pipeline_stable_diffusion_xl.py
│ │ └── register.py
│ └── base_wrapper.py
├── __version__.py
├── core
│ ├── utils
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ └── timer.py
│ ├── cache_manager
│ │ └── __init__.py
│ ├── long_ctx_attention
│ │ ├── ring
│ │ │ └── __init__.py
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ └── hybrid
│ │ │ └── __init__.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── fast_attention
│ │ └── __init__.py
│ └── distributed
│ │ └── __init__.py
├── config
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── diffusers.py
├── __init__.py
├── parallel.py
└── logger.py
├── .gitignore
├── pytest.ini
├── docs
├── methods
│ ├── cfg_parallel_zh.md
│ ├── cfg_parallel.md
│ ├── ditfastattn_zh.md
│ ├── ditfastattn.md
│ ├── parallel_vae.md
│ ├── usp.md
│ ├── hybrid_zh.md
│ ├── pipefusion.md
│ └── hybrid.md
├── performance
│ ├── latte_zh.md
│ ├── sana_zh.md
│ ├── sd3_zh.md
│ ├── latte.md
│ ├── pixart_alpha_legacy.md
│ ├── stepvideo_zh.md
│ ├── sana.md
│ ├── sd3.md
│ ├── hunyuanvideo.md
│ ├── stepvideo.md
│ ├── consisid_zh.md
│ ├── hunyuandit_zh.md
│ ├── cogvideo_zh.md
│ └── consisid.md
├── developer
│ ├── Http_Service.md
│ └── adding_models
│ │ ├── adding_model_cfg_usp.md
│ │ ├── readme.md
│ │ └── adding_model_cfg.py
└── fid
│ └── FID.md
├── .pre-commit-config.yaml
├── tests
├── context_parallel
│ ├── debug_tests.py
│ └── debug_flux_usp_example.py
├── parallel_test.py
├── core
│ └── test_envs.py
└── layers
│ └── feedforward_test.py
├── benchmark
├── run.sh
├── fid
│ ├── generate.sh
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── pixartalpha_generate.py
│ ├── flux_generate.py
│ └── compute_fid.py
└── usp_latency_test.py
├── docker
└── Dockerfile
├── examples
├── run_cogvideo.sh
├── run_hunyuan_video_usp.sh
├── ray
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── ray_pixartsigma_example.py
│ ├── ray_pixartalpha_example.py
│ ├── ray_hunyuandit_example.py
│ ├── ray_run.sh
│ ├── ray_flux_example.py
│ └── ray_sd3_example.py
├── run_multinodes.sh
├── run_consisid.sh
├── run_consisid_usp.sh
├── run_service.sh
├── run_fastditattn.sh
├── run.sh
├── latte_example.py
├── sana_sprint_example.py
├── pixartsigma_example.py
├── pixartalpha_example.py
├── sdxl_example.py
├── sd3_example.py
├── cogvideox_example.py
├── hunyuandit_example.py
├── zimage_example.py
└── sana_example.py
├── .github
└── workflows
│ └── python-publish.yml
└── setup.py
/.gitmodules:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/entrypoints/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/xfuser/ray/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/xfuser/model_executor/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/xfuser/ray/pipeline/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/xfuser/ray/worker/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/xfuser/model_executor/patch/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/xfuser/__version__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | __version__ = "0.4.5"
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/xfuser/model_executor/models/customized/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/xfuser/model_executor/models/customized/step_video_t2v/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/xfuser/core/utils/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .timer import gpu_timer_decorator
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/xfuser/core/cache_manager/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .cache_manager import CacheManager
2 |
3 | __all__ = [
4 | "CacheManager",
5 | ]
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/xfuser/model_executor/models/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .base_model import xFuserModelBaseWrapper
2 |
3 | __all__ = [
4 | "xFuserModelBaseWrapper"
5 | ]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/xfuser/model_executor/cache/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | adapted from https://github.com/ali-vilab/TeaCache.git
3 | adapted from https://github.com/chengzeyi/ParaAttention.git
4 | """
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .idea
2 | .DS_Store
3 | build
4 | __pycache__
5 | *.log
6 | *.txt
7 | results/
8 | profile/
9 | .vscode/
10 | xfuser.egg-info/
11 | dist/*
12 | *.mp4
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pytest.ini:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [pytest]
2 | log_format = %(asctime)s %(filename)s:%(lineno)d %(levelname)s %(message)s
3 | log_date_format = %Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S
4 | log_cli = true
5 | log_level = INFO
6 | addopts = --capture=tee-sys --verbose --color=auto --durations=0
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/xfuser/core/long_ctx_attention/ring/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .ring_flash_attn import (
2 | xdit_ring_flash_attn_func,
3 | xdit_sana_ring_flash_attn_func,
4 | )
5 |
6 | __all__ = [
7 | "xdit_ring_flash_attn_func",
8 | "xdit_sana_ring_flash_attn_func",
9 | ]
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/xfuser/core/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .cache_manager import CacheManager
2 | from .long_ctx_attention import xFuserLongContextAttention
3 | from .utils import gpu_timer_decorator
4 |
5 | __all__ = [
6 | "CacheManager",
7 | "xFuserLongContextAttention",
8 | "gpu_timer_decorator",
9 | ]
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/xfuser/core/long_ctx_attention/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .hybrid import (
2 | xFuserLongContextAttention,
3 | xFuserSanaLinearLongContextAttention,
4 | AttnType,)
5 |
6 | __all__ = [
7 | "xFuserLongContextAttention",
8 | "xFuserSanaLinearLongContextAttention",
9 | "AttnType",
10 | ]
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/xfuser/core/long_ctx_attention/hybrid/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .attn_layer import (
2 | xFuserLongContextAttention,
3 | xFuserSanaLinearLongContextAttention,
4 | AttnType,
5 | )
6 |
7 | __all__ = [
8 | "xFuserLongContextAttention",
9 | "xFuserSanaLinearLongContextAttention",
10 | "AttnType",
11 | ]
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/entrypoints/curl.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | curl -X POST "http://localhost:6000/generate" \
3 | -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
4 | -d '{
5 | "prompt": "a cute rabbit",
6 | "num_inference_steps": 50,
7 | "seed": 42,
8 | "cfg": 7.5,
9 | "save_disk_path": "/tmp"
10 | }'
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/methods/cfg_parallel_zh.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG) Parallel
2 |
3 | Classifier-Free Guidance通过提供更广泛的条件控制、减少训练负担、增强生成内容的质量和细节,以及提高模型的实用性和适应性,成为了扩散模型领域的一个重要进展技术。
4 |
5 | 对于一个输入prompt,使用CFG需要同时进行unconditional guide和text guide的生成 ,相当于输入DiT blocks的input latents batch_size = 2。CFG Parallel分离两个latents分别进行计算,在每个Diffusion Step forward完成后、Scheduler执行前Allgather一次latent space结果。它通信量远小于Pipefusion和Sequence Parallel。因此,使用CFG一定要使用CFG Parallel。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.pre-commit-config.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | repos:
2 | # Using this mirror lets us use mypyc-compiled black, which is about 2x faster
3 | - repo: https://github.com/psf/black-pre-commit-mirror
4 | rev: 24.2.0
5 | hooks:
6 | - id: black
7 | # It is recommended to specify the latest version of Python
8 | # supported by your project here, or alternatively use
9 | # pre-commit's default_language_version, see
10 | # https://pre-commit.com/#top_level-default_language_version
11 | language_version: python3.10
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/context_parallel/debug_tests.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import sys
3 | import subprocess
4 | import shlex
5 | from pathlib import Path
6 |
7 | wd: str = Path(__file__).parent.absolute()
8 | #os.environ["PYTHONPATH"] = f"{WD}:{os.getenv('PYTHONPATH', '')}"
9 | test_script: str = wd / "test_diffusers_adapters.py"
10 | model_test: str = "FluxPipelineTest"
11 | os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "0,1"
12 |
13 | cmd: str = (
14 | f"{sys.executable} -m pytest {test_script.as_posix()}::{model_test}"
15 | )
16 | cmd = shlex.split(cmd)
17 | print(cmd)
18 | subprocess.run(cmd, check=True)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/performance/latte_zh.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Latte性能
2 |
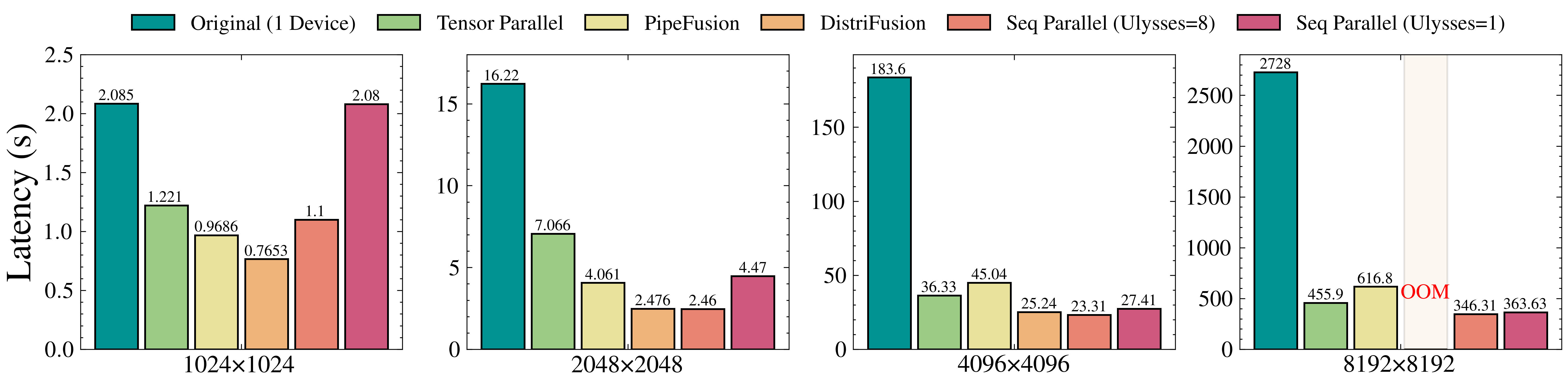
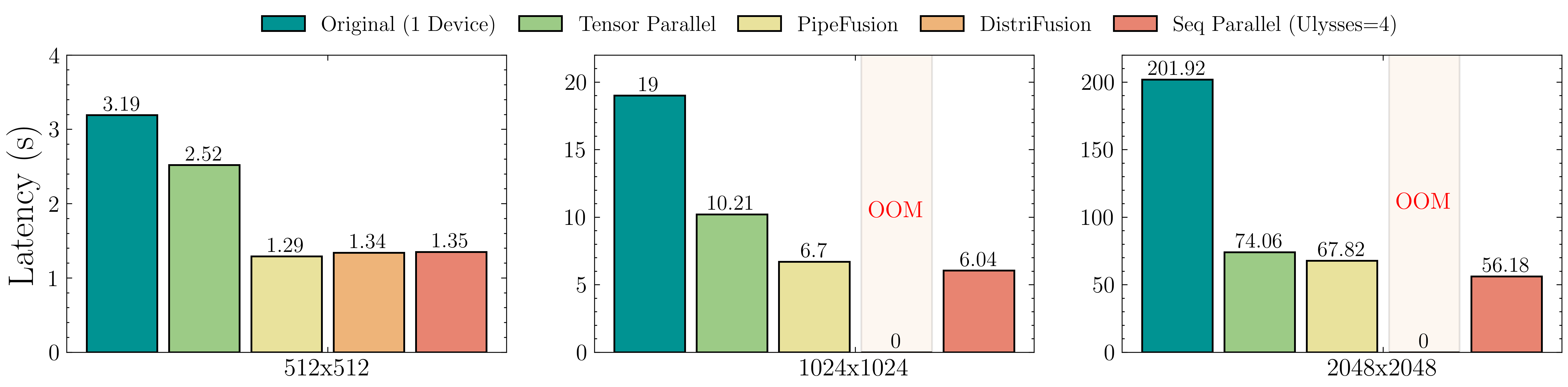
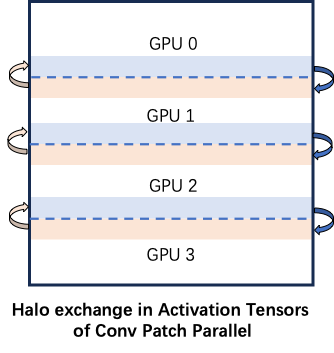
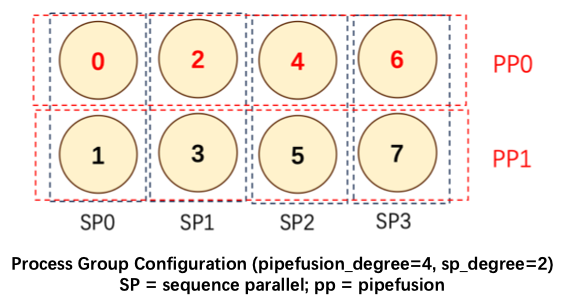
3 | Latte是文生视频模型,xDiT目前实现了USP方式对它进行并行推理加速。PipeFusion还在开发中。
4 |
5 | 在8xL20 (PCIe)的机器上,生成512x512x16视频的延迟表现如下图所示。
6 |
7 |
8 |

10 |
15 |

17 |
12 |
14 |
20 |
22 |
9 |

11 |
16 |

18 |
9 |
10 |
15 |
16 |
21 |
22 |
27 |
29 |
11 |

13 |
18 |

20 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
19 |
20 |
28 |
29 |
8 |
10 |
10 |
12 |
28 |
30 |
41 |
43 |
50 |
52 |
60 |
62 |
69 |
71 |
10 |
12 |
17 |
19 |
24 |
26 |
30 |

32 |
40 |
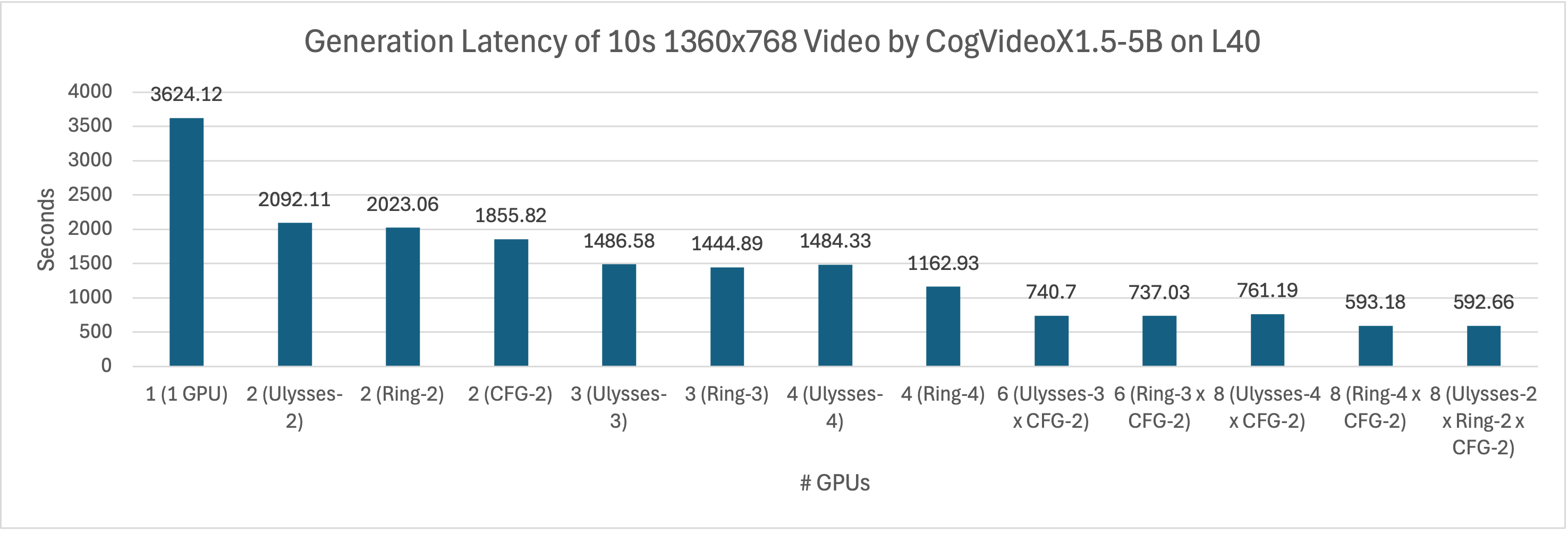
42 |
48 |
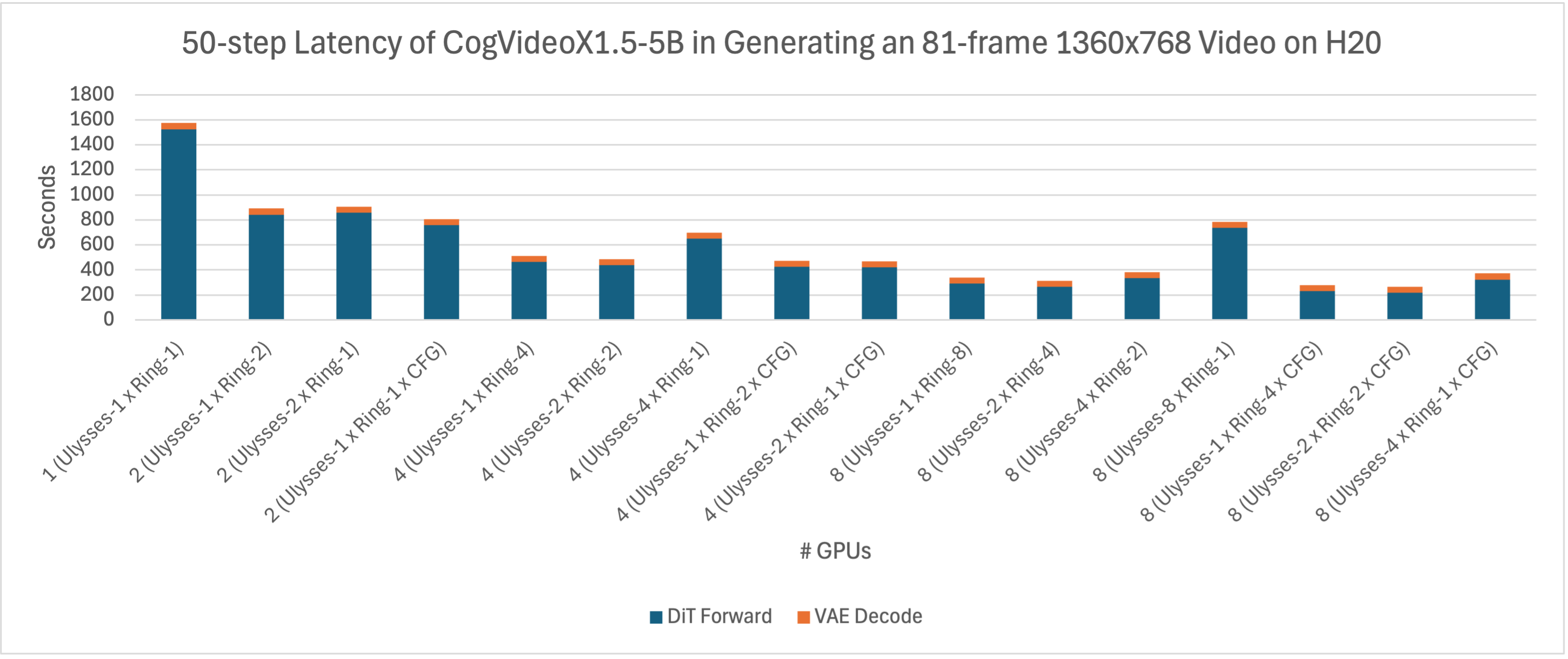
50 |
54 |
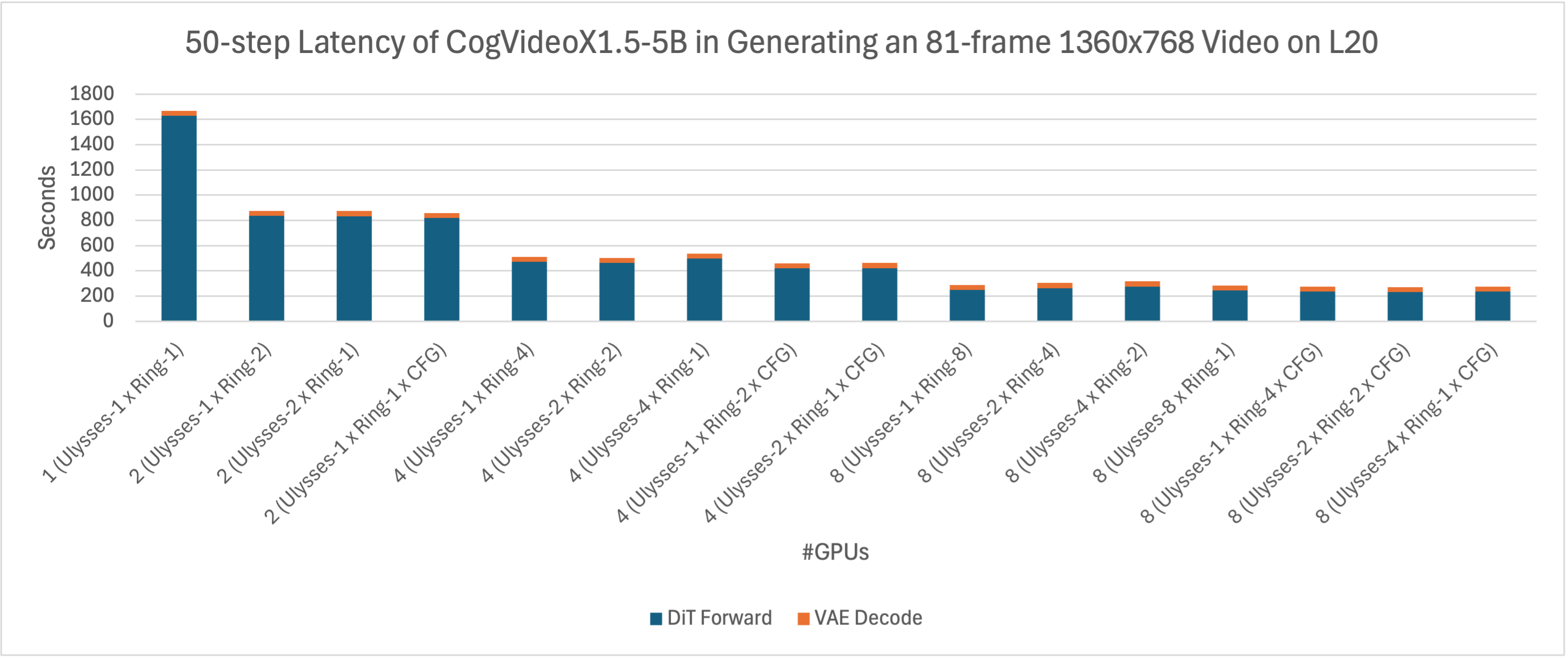
56 |
11 |

12 |
28 |

29 |
35 |

36 |
14 |

15 |
24 |

25 |
30 |

31 |
 10 |
10 |  10 |
10 |  17 |
17 |  14 |
14 |  22 |
22 |  11 |
11 |  18 |
18 |  10 |
10 |  16 |
16 |  22 |
22 |  29 |
29 |  13 |
13 |  20 |
20 |  12 |
12 |  14 |
14 |  20 |
20 |  29 |
29 |  10 |
10 |  12 |
12 |  30 |
30 |  43 |
43 |  52 |
52 |  62 |
62 |  71 |
71 |  12 |
12 |  19 |
19 |  26 |
26 |  32 |
32 |  42 |
42 |  50 |
50 |  56 |
56 |  12 |
12 |  29 |
29 |  36 |
36 |  15 |
15 |  25 |
25 |  31 |
31 |