├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习100之模版.md
├── 1数据类型
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习12之密集向量和稀疏向量的生成.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习13之给向量打标签.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习15之创建分布式矩阵.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习16之分布式行矩阵的四种形式.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习14之从文本中读取带标签的数据,生成带label的向量.md
└── Spark中组件Mllib的学习3之用户相似度计算.md
├── 7特征提取和转换
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习53之HashingTF理解和使用.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习64之元素智能乘积ElementwiseProduct.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习60之归一化(Normalizer)Normalization using L^Inf distance.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习60之归一化(Normalizer)Normalization using L^Inf distance.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习59之归一化(Normalizer)Normalization using L2 distance.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习59之归一化(Normalizer)Normalization using L2 distance.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习58之归一化(Normalizer)Normalization using L1 distance.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习58之归一化(Normalizer)Normalization using L1 distance.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习53之Word2Vec简单实例.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习62之特征选择中的卡方选择器.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习52之TF-IDF学习.md
└── Spark中组件Mllib的学习54之word2Vec实例分析(text8数据集).md
├── 2基本统计
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习20之假设检验-卡方检验.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习17之colStats_以列为基础计算统计量的基本数据.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习21之随机数-RandomRDD产生.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习42之rowMatrix的QR分解.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习22之假设检验-卡方检验概念理解.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习19之分层抽样.md
└── Spark中组件Mllib的学习3之用户相似度计算.md
├── 8频繁项挖掘
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习67之关联规则AssociationRules.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习68之PrefixSpan.md
└── Spark中组件Mllib的学习66之FP-growth.md
├── 3分类和回归
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习24之线性回归1-小数据集.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习35之随机森林(entropy)进行分类.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习25之线性回归2-较大数据集(多元).md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习30之逻辑回归LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习34之决策树(使用entropy)_.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习26之逻辑回归-简单数据集,带预测.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习38之随机森林(使用variance)进行回归.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习36之决策树(使用variance)进行回归.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习33之决策树(使用Gini).md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习32之朴素贝叶斯分类器(伯努利朴素贝叶斯)_.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习31之朴素贝叶斯分类器(多项式朴素贝叶斯).md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习37之随机森林(Gini)进行分类.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习23之随机梯度下降(SGD).md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习40之梯度提升树(GBT)用于回归_.md
└── Spark中组件Mllib的学习41之保序回归(Isotonic regression).md
├── 9评估度量
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习73之回归问题的评估.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习71之对多标签分类进行评估.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习70之对多类分类结果进行评估Multiclass classification.md
└── Spark中组件Mllib的学习72之RankingSystem进行评估.md
├── 6降维
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习49之奇异值分解SVD(Singular value decomposition).md
└── Spark中组件Mllib的学习50之主成份分析PCA.md
├── 5聚类
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习46之Power iteration clustering.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习45之用高斯混合模型来预测.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习44之高斯混合聚类GaussianMixture.md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习48之流式k均值(Streaming kmeans).md
├── Spark中组件Mllib的学习47之隐含狄利克雷分布(Latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA)学习.md
└── Spark中组件Mllib的学习47之隐含狄利克雷分布(Latent Dirichlet allocation,LDA)学习.md
├── README.md
├── 11优化
└── Spark中组件Mllib的学习75之L-BFGS.md
└── 10PMML模型输出
└── Spark中组件Mllib的学习74之预言模型标记语言PMML.md
/Spark中组件Mllib的学习100之模版.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 | 2.代码:
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 | 3.结果:
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 | 参考
20 |
21 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
22 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
23 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
24 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
25 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/1数据类型/Spark中组件Mllib的学习12之密集向量和稀疏向量的生成.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之基础概念篇
3 | 1解释
4 | mllib生成Vector
5 |
6 | 2.代码:
7 |
8 | ```
9 | /**
10 | * @author xubo
11 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
12 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
13 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
14 | */
15 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.basic
16 |
17 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
18 |
19 | /**
20 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
21 | * Vector
22 | */
23 | object VectorLearning {
24 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
25 |
26 | val vd = Vectors.dense(2, 0, 6)
27 | println(vd(2))
28 | println(vd)
29 |
30 | //数据个数,序号,value
31 | val vs = Vectors.sparse(4, Array(0, 1, 2, 3), Array(9, 5, 2, 7))
32 | println(vs(2))
33 | println(vs)
34 |
35 | val vs2 = Vectors.sparse(4, Array(0, 2, 1, 3), Array(9, 5, 2, 7))
36 | println(vs2(2))
37 | println(vs2)
38 |
39 |
40 | }
41 | }
42 |
43 | ```
44 |
45 | 3.结果:
46 |
47 | ```
48 | 6.0
49 | [2.0,0.0,6.0]
50 | 2.0
51 | (4,[0,1,2,3],[9.0,5.0,2.0,7.0])
52 | 5.0
53 | (4,[0,2,1,3],[9.0,5.0,2.0,7.0])
54 | ```
55 |
56 | 参考
57 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
58 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
59 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/1数据类型/Spark中组件Mllib的学习13之给向量打标签.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之基础概念篇
3 | 1解释
4 | 给数据打label,用于后续监督学习等
5 |
6 | 2.代码:
7 |
8 | ```
9 | /**
10 | * @author xubo
11 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
12 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
13 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
14 | */
15 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.basic
16 |
17 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
18 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
19 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
20 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint
21 |
22 | /**
23 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
24 | * 给Vector打Label
25 | */
26 | object LabeledPointLearning {
27 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
28 |
29 | val vd = Vectors.dense(2, 0, 6)
30 | val pos = LabeledPoint(1, vd) //对密集向量建立标记点
31 | println(pos.features)
32 | println(pos.label)
33 | println(pos)
34 |
35 | val vs = Vectors.sparse(4, Array(0, 1, 2, 3), Array(9, 5, 2, 7))
36 | val neg = LabeledPoint(2, vs) //对稀疏向量建立标记点
37 | println(neg.features)
38 | println(neg.label)
39 | println(neg)
40 |
41 |
42 | }
43 | }
44 |
45 | ```
46 |
47 | 3.结果:
48 |
49 | ```
50 | [2.0,0.0,6.0]
51 | 1.0
52 | (1.0,[2.0,0.0,6.0])
53 | (4,[0,1,2,3],[9.0,5.0,2.0,7.0])
54 | 2.0
55 | (2.0,(4,[0,1,2,3],[9.0,5.0,2.0,7.0]))
56 |
57 | ```
58 |
59 | 参考
60 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
61 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
62 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
63 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/7特征提取和转换/Spark中组件Mllib的学习53之HashingTF理解和使用.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | HashingTF将文档的每行转换成(hash值(2^20),(词的id,单个字符时同ascii码一样),(词频))形式
9 |
10 |
11 | 2.代码:
12 |
13 | test("hashing tf on an RDD") {
14 | val hashingTF = new HashingTF
15 | val localDocs: Seq[Seq[String]] = Seq(
16 | "a a b b b c d".split(" "),
17 | "a b c d a b c".split(" "),
18 | "c b a c b a a".split(" "))
19 | val docs = sc.parallelize(localDocs, 2)
20 | assert(hashingTF.transform(docs).collect().toSet === localDocs.map(hashingTF.transform).toSet)
21 |
22 | println("docs:")
23 | docs.foreach(println)
24 | println("hashingTF.transform(docs).collect():")
25 | hashingTF.transform(docs).collect().foreach(println)
26 | println(" localDocs.map(hashingTF.transform):")
27 | localDocs.map(hashingTF.transform).foreach(println)
28 |
29 | }
30 |
31 |
32 | 3.结果:
33 |
34 | docs:
35 | WrappedArray(a, a, b, b, b, c, d)
36 | WrappedArray(a, b, c, d, a, b, c)
37 | WrappedArray(c, b, a, c, b, a, a)
38 | hashingTF.transform(docs).collect():
39 | (1048576,[97,98,99,100],[2.0,3.0,1.0,1.0])
40 | (1048576,[97,98,99,100],[2.0,2.0,2.0,1.0])
41 | (1048576,[97,98,99],[3.0,2.0,2.0])
42 | localDocs.map(hashingTF.transform):
43 | (1048576,[97,98,99,100],[2.0,3.0,1.0,1.0])
44 | (1048576,[97,98,99,100],[2.0,2.0,2.0,1.0])
45 | (1048576,[97,98,99],[3.0,2.0,2.0])
46 |
47 |
48 | aa的id为3104
49 |
50 |
51 |
52 | 参考
53 |
54 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
55 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
56 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
57 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
58 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/2基本统计/Spark中组件Mllib的学习20之假设检验-卡方检验.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之基础概念篇
3 | 1解释
4 | 分别对Vector和Matrix进行卡方检验
5 |
6 |
7 | 2.代码:
8 |
9 | ```
10 | /**
11 | * @author xubo
12 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
13 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
14 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
15 | */
16 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.basic
17 |
18 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.{Matrices, Vectors}
19 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.stat.Statistics
20 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
21 |
22 | /**
23 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
24 | */
25 | object ChiSqLearning {
26 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
27 | val vd = Vectors.dense(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
28 | val vdResult = Statistics.chiSqTest(vd)
29 | println(vdResult)
30 | println("-------------------------------")
31 | val mtx = Matrices.dense(3, 2, Array(1, 3, 5, 2, 4, 6))
32 | val mtxResult = Statistics.chiSqTest(mtx)
33 | println(mtxResult)
34 | //print :方法、自由度、方法的统计量、p值
35 | }
36 | }
37 |
38 | ```
39 |
40 | 3.结果:
41 |
42 | ```
43 | Chi squared test summary:
44 | method: pearson
45 | degrees of freedom = 4
46 | statistic = 3.333333333333333
47 | pValue = 0.5036682742334986
48 | No presumption against null hypothesis: observed follows the same distribution as expected..
49 | -------------------------------
50 | Chi squared test summary:
51 | method: pearson
52 | degrees of freedom = 2
53 | statistic = 0.14141414141414144
54 | pValue = 0.931734784568187
55 | No presumption against null hypothesis: the occurrence of the outcomes is statistically independent..
56 | ```
57 |
58 | 参考
59 |
60 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
61 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
62 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/8频繁项挖掘/Spark中组件Mllib的学习67之关联规则AssociationRules.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | Association Rules
9 |
10 | AssociationRules implements a parallel rule generation algorithm for constructing rules that have a single item as the consequent.
11 |
12 |
13 | 2.代码:
14 |
15 | /**
16 | * @author xubo
17 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
18 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
19 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
20 | */
21 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.FrequentPatternMining
22 |
23 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
24 |
25 | /**
26 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
27 | */
28 | class AssociationRulesFunSuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
29 | test("testFunSuite") {
30 | import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
31 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.fpm.AssociationRules
32 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.fpm.FPGrowth.FreqItemset
33 |
34 | val freqItemsets = sc.parallelize(Seq(
35 | new FreqItemset(Array("a"), 15L),
36 | new FreqItemset(Array("b"), 35L),
37 | new FreqItemset(Array("a", "b"), 12L)
38 | ));
39 |
40 | val ar = new AssociationRules()
41 | .setMinConfidence(0.8)
42 | val results = ar.run(freqItemsets)
43 |
44 | results.collect().foreach { rule =>
45 | println("[" + rule.antecedent.mkString(",")
46 | + "=>"
47 | + rule.consequent.mkString(",") + "]," + rule.confidence)
48 | }
49 | }
50 | }
51 |
52 |
53 | 3.结果:
54 |
55 | [a=>b],0.8
56 |
57 | 结果分析:12/15=0.8
58 |
59 | 参考
60 |
61 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
62 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
63 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
64 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
65 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
66 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/3分类和回归/Spark中组件Mllib的学习24之线性回归1-小数据集.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之回归分析篇
3 | 1解释
4 | 简单的对6组数据进行model的training,然后再利用model来predict具体的值
5 | 。过程中有输出model的权重
6 | 公式:f(x)=aX1+bX2
7 |
8 |
9 | 2.代码:
10 |
11 | ```
12 | /**
13 | * @author xubo
14 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
15 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
16 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
17 | */
18 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.regression
19 |
20 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
21 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.{LinearRegressionWithSGD, LabeledPoint}
22 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
23 |
24 | /**
25 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
26 | */
27 | object LinearRegression2Learning {
28 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
29 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[4]").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
30 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
31 |
32 | val data = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/ridge-data/lpsa2.data") //获取数据集路径
33 | val parsedData = data.map { line => //开始对数据集处理
34 | val parts = line.split(',') //根据逗号进行分区
35 | LabeledPoint(parts(0).toDouble, Vectors.dense(parts(1).split(' ').map(_.toDouble)))
36 | }.cache() //转化数据格式
37 | val model = LinearRegressionWithSGD.train(parsedData, 100, 0.1) //建立模型
38 | val result = model.predict(Vectors.dense(2,1)) //通过模型预测模型
39 | println("model weights:")
40 | println(model.weights)
41 | println("result:")
42 | println(result) //打印预测结果
43 | sc.stop
44 | }
45 | }
46 |
47 | ```
48 | 数据:
49 |
50 | ```
51 | 5,1 1
52 | 7,2 1
53 | 9,3 2
54 | 11,4 1
55 | 19,5 3
56 | 18,6 2
57 | ```
58 |
59 | 3.结果:
60 |
61 | ```
62 | model weights:
63 | [2.54036018771162,1.5591873026695686]
64 | result:
65 | 6.6399076780928095
66 | ```
67 |
68 | 参考
69 |
70 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
71 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
72 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
73 | 【4】Spark MlLib机器学习实战
74 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/8频繁项挖掘/Spark中组件Mllib的学习68之PrefixSpan.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | PrefixSpan 是一种序列模式挖掘算法
9 |
10 | 序列模式定义:给定一个由不同序列组成的集合,其中,每个序列由不同的元素按顺序有序排列,每个元素由不同项目组成,同时给定一个用户指定的最小支持度阈值,序列模式挖掘就是找出所有的频繁子序列,即该子序列在序列集中的出现频率不低于用户指定的最小支持度阈值
11 |
12 | Spak.mllib PrefixSpan 需要配置以下参数
13 |
14 | 1) minSupport : 满足频度序列模式的最小支持度
15 |
16 | 2) maxPatternLength: 频度序列的最大长度。凡是超过此长度的频度序列都会被乎略。
17 |
18 | 3) maxLocalProjDBSize:本地迭代处理投影数据库(projected database)之前,需要满足前缀投影数据库(prefix-projecteddatabase)中最大的物品数。
19 |
20 | 2.代码:
21 |
22 | /**
23 | * @author xubo
24 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
25 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
26 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
27 | */
28 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.FrequentPatternMining
29 |
30 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
31 |
32 | /**
33 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
34 | */
35 | class PrefixSpanFunSuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
36 | test("testFunSuite") {
37 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.fpm.PrefixSpan
38 |
39 | val sequences = sc.parallelize(Seq(
40 | Array(Array(1, 2), Array(3)),
41 | Array(Array(1), Array(3, 2), Array(1, 2)),
42 | Array(Array(1, 2), Array(5)),
43 | Array(Array(6))
44 | ), 2).cache()
45 | val prefixSpan = new PrefixSpan()
46 | .setMinSupport(0.5)
47 | .setMaxPatternLength(5)
48 | val model = prefixSpan.run(sequences)
49 | model.freqSequences.collect().foreach { freqSequence =>
50 | println(
51 | freqSequence.sequence.map(_.mkString("[", ", ", "]")).mkString("[", ", ", "]") + ", " + freqSequence.freq)
52 | }
53 | }
54 | }
55 |
56 |
57 | 3.结果:
58 |
59 | [[2]], 3
60 | [[3]], 2
61 | [[1]], 3
62 | [[2, 1]], 3
63 | [[1], [3]], 2
64 |
65 | 参考
66 |
67 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
68 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
69 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
70 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
71 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
72 | 【6】http://www.jone.tech/?p=41
73 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/7特征提取和转换/Spark中组件Mllib的学习64之元素智能乘积ElementwiseProduct.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | 元素智能乘积
9 |
10 | ElementwiseProduct对每一个输入向量乘以一个给定的“权重”向量。换句话说,就是通过一个乘子对数据集的每一列进行缩放。这个转换可以表示为如下的形式:
11 |
12 | 
13 |
14 | 2.代码:
15 |
16 | /**
17 | * @author xubo
18 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
19 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
20 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
21 | */
22 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.FeatureExtractionAndTransformation
23 |
24 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
25 |
26 | /**
27 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
28 | */
29 | class ElementwiseProductFunSuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
30 | test("testFunSuite") {
31 |
32 |
33 | import org.apache.spark.SparkContext._
34 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.feature.ElementwiseProduct
35 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
36 |
37 | // Create some vector data; also works for sparse vectors
38 | val data = sc.parallelize(Array(Vectors.dense(1.0, 2.0, 3.0), Vectors.dense(4.0, 5.0, 6.0)))
39 |
40 | val transformingVector = Vectors.dense(0.0, 1.0, 2.0)
41 | val transformer = new ElementwiseProduct(transformingVector)
42 |
43 | // Batch transform and per-row transform give the same results:
44 | val transformedData = transformer.transform(data)
45 | val transformedData2 = data.map(x => transformer.transform(x))
46 |
47 | println("data:")
48 | data.foreach(println)
49 | println("transformer:" + transformer.scalingVec)
50 |
51 | // transformer.foreach(println)
52 | println("transformedData:")
53 | transformedData.foreach(println)
54 |
55 | }
56 | }
57 |
58 |
59 | 3.结果:
60 |
61 | data:
62 | [1.0,2.0,3.0]
63 | [4.0,5.0,6.0]
64 | transformer:[0.0,1.0,2.0]
65 | transformedData:
66 | [0.0,5.0,12.0]
67 | [0.0,2.0,6.0]
68 |
69 |
70 | 参考
71 |
72 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
73 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
74 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
75 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
76 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
77 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/1数据类型/Spark中组件Mllib的学习15之创建分布式矩阵.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之基础概念篇
3 | 1解释
4 | 创建分布式矩阵
5 |
6 | 2.代码:
7 |
8 | ```
9 |
10 | /**
11 | * @author xubo
12 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
13 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
14 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
15 | */
16 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.basic
17 |
18 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Matrices
19 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
20 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkContext, SparkConf}
21 |
22 | /**
23 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
24 | * 创建分布式矩阵
25 | */
26 | object MatrixLearning {
27 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
28 | val mx = Matrices.dense(2, 3, Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)) //创建一个分布式矩阵
29 | println(mx) //打印结果
30 |
31 | val arr=(1 to 6).toArray.map(_.toDouble)
32 | val mx2 = Matrices.dense(2, 3, arr) //创建一个分布式矩阵
33 | println(mx2) //打印结果
34 |
35 | val arr3=(1 to 20).toArray.map(_.toDouble)
36 | val mx3 = Matrices.dense(4, 5, arr3) //创建一个分布式矩阵
37 | println(mx3) //打印结果
38 | println(mx3.index(0,0))
39 | println(mx3.index(1,1))
40 | println(mx3.index(2,2))
41 | println(mx3.numRows)
42 | println(mx3.numCols)
43 | }
44 | }
45 |
46 |
47 | ```
48 |
49 | 3.结果:
50 |
51 | ```
52 | 1.0 3.0 5.0
53 | 2.0 4.0 6.0
54 |
55 | 1.0 3.0 5.0
56 | 2.0 4.0 6.0
57 |
58 | 1.0 5.0 9.0 13.0 17.0
59 | 2.0 6.0 10.0 14.0 18.0
60 | 3.0 7.0 11.0 15.0 19.0
61 | 4.0 8.0 12.0 16.0 20.0
62 | 0
63 | 5
64 | 10
65 | 4
66 | 5
67 | ```
68 |
69 | 感觉index有问题:
70 | 源码:
71 |
72 | ```
73 | /** Return the index for the (i, j)-th element in the backing array. */
74 | private[mllib] def index(i: Int, j: Int): Int
75 | ```
76 |
77 | 在dense的时候:
78 |
79 | ```
80 | private[mllib] def index(i: Int, j: Int): Int = {
81 | if (!isTransposed) i + numRows * j else j + numCols * i
82 | }
83 |
84 | ```
85 | 如果按照这个源码理解没问题
86 | 将数组改为:
87 |
88 | ```
89 | val arr3=(21 to 40).toArray.map(_.toDouble)
90 | ```
91 |
92 | ```
93 | 21.0 25.0 29.0 33.0 37.0
94 | 22.0 26.0 30.0 34.0 38.0
95 | 23.0 27.0 31.0 35.0 39.0
96 | 24.0 28.0 32.0 36.0 40.0
97 | 0
98 | 5
99 | 10
100 | 4
101 | 5
102 | ```
103 |
104 | 疑问:如何按照坐标打印元素?比如(1,1)对应6
105 |
106 |
107 | 参考
108 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
109 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
110 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
111 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/9评估度量/Spark中组件Mllib的学习73之回归问题的评估.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | Regression model evaluation
9 | 
10 |
11 | 2.代码:
12 |
13 | /**
14 | * @author xubo
15 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
16 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
17 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
18 | */
19 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.EvaluationMetrics
20 |
21 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
22 |
23 | /**
24 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
25 | */
26 | class RegressionModelEvaluationFunSuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
27 | test("testFunSuite") {
28 |
29 |
30 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint
31 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LinearRegressionModel
32 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LinearRegressionWithSGD
33 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
34 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.evaluation.RegressionMetrics
35 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
36 |
37 | // Load the data
38 | val data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(sc, "file/data/mllib/input/mllibFromSpark/sample_linear_regression_data.txt").cache()
39 |
40 | // Build the model
41 | val numIterations = 100
42 | val model = LinearRegressionWithSGD.train(data, numIterations)
43 |
44 | // Get predictions
45 | val valuesAndPreds = data.map{ point =>
46 | val prediction = model.predict(point.features)
47 | (prediction, point.label)
48 | }
49 |
50 | // Instantiate metrics object
51 | val metrics = new RegressionMetrics(valuesAndPreds)
52 |
53 | // Squared error
54 | println(s"MSE = ${metrics.meanSquaredError}")
55 | println(s"RMSE = ${metrics.rootMeanSquaredError}")
56 |
57 | // R-squared
58 | println(s"R-squared = ${metrics.r2}")
59 |
60 | // Mean absolute error
61 | println(s"MAE = ${metrics.meanAbsoluteError}")
62 |
63 | // Explained variance
64 | println(s"Explained variance = ${metrics.explainedVariance}")
65 |
66 |
67 | }
68 | }
69 |
70 |
71 |
72 | 3.结果:
73 |
74 | MSE = 103.30968681818085
75 | RMSE = 10.164137288436281
76 | R-squared = 0.027639110967836777
77 | MAE = 8.148691907953307
78 | Explained variance = 2.888395201717894
79 |
80 | 参考
81 |
82 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
83 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
84 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
85 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
86 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
87 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/2基本统计/Spark中组件Mllib的学习17之colStats_以列为基础计算统计量的基本数据.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之基础概念篇
3 | 1解释
4 | colStats:以列为基础计算统计量的基本数据
5 |
6 | 2.代码:
7 |
8 | ```
9 | /**
10 | * @author xubo
11 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
12 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
13 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
14 | */
15 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.basic
16 |
17 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
18 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.stat.Statistics
19 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
20 |
21 | /**
22 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
23 | */
24 | object StatisticsColStatsLearning {
25 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
26 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[4]").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
27 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
28 | // val rdd = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/basic/MatrixRow.txt") //读取文件
29 | val rdd = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/basic/stats.txt") //读取文件
30 | .map(_.split(' ') //按“ ”分割
31 | .map(_.toDouble)) //转成Double类型
32 | .map(line => Vectors.dense(line))
33 | val summary = Statistics.colStats(rdd) //获取Statistics实例
34 |
35 | // rdd.foreach(each => print(each + " "))
36 | rdd.foreach(println)
37 | println("rdd.count:" + rdd.count())
38 | println()
39 | println(summary)
40 | println(summary.max) //最大
41 | println(summary.min) //最小
42 | println("count" + summary.count) //个数
43 | println(summary.numNonzeros) //非零
44 | println("variance:" + summary.variance) //方差
45 | println(summary.mean) //计算均值
46 | println(summary.variance) //计算标准差
47 | println(summary.normL1) //计算曼哈段距离:相加
48 | println(summary.normL2) //计算欧几里得距离:平方根
49 |
50 |
51 | // /行向量
52 | println("\n row Vector:")
53 | val vec = Vectors.dense(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
54 | println(vec)
55 | println(vec.size)
56 | println(vec.numActives)
57 | // println(vec.variance)//不存在
58 |
59 | sc.stop
60 | }
61 | }
62 |
63 | ```
64 |
65 | 3.结果:
66 |
67 | ```
68 | [1.0]
69 | [2.0]
70 | [3.0]
71 | [4.0]
72 | [5.0]
73 | rdd.count:5
74 |
75 | org.apache.spark.mllib.stat.MultivariateOnlineSummarizer@7f9de19a
76 | [5.0]
77 | [1.0]
78 | count5
79 | [5.0]
80 | variance:[2.5]
81 | [3.0]
82 | [2.5]
83 | [15.0]
84 | [7.416198487095663]
85 |
86 | row Vector:
87 | [1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0]
88 | 5
89 | 5
90 | ```
91 |
92 | 参考
93 |
94 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
95 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
96 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
97 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/3分类和回归/Spark中组件Mllib的学习35之随机森林(entropy)进行分类.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之分类篇
3 | 1解释
4 | 随机森林:RandomForest
5 | 大概思想就是生成多个决策树,都单独训练;如果来了一个数据,用各个决策树进行回归预测,如果是非连续结果,则取最多个数的值;如果连续,则取多个决策树结果的平均值。
6 |
7 | 2.代码:
8 |
9 | ```
10 | /**
11 | * @author xubo
12 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
13 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
14 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
15 | */
16 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.classification
17 |
18 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.{RandomForest, DecisionTree}
19 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
20 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
21 |
22 | /**
23 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
24 | *
25 | */
26 | object DecisionTrees3GBT {
27 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
28 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[4]").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
29 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
30 |
31 | // Load and parse the data file.
32 | val data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(sc, "file/data/mllib/input/classification/dt.txt")
33 | val numClasses = 2 //设定分类的数量
34 | val categoricalFeaturesInfo = Map[Int, Int]() //设置输入数据格式
35 | val numTrees = 3 //设置随机雨林中决策树的数目
36 | val featureSubsetStrategy = "auto" //设置属性在节点计算数
37 | val impurity = "entropy" //设定信息增益计算方式
38 | val maxDepth = 5 //设定树高度
39 | val maxBins = 3 //设定分裂数据集
40 |
41 | val model = RandomForest.trainClassifier(data, numClasses, categoricalFeaturesInfo,
42 | numTrees, featureSubsetStrategy, impurity, maxDepth, maxBins) //建立模型
43 |
44 | model.trees.foreach(println) //打印每棵树的相信信息
45 |
46 | val labelAndPreds = data.take(2).map { point =>
47 | val prediction = model.predict(point.features)
48 | (point.label, prediction)
49 | }
50 | labelAndPreds.foreach(println)
51 | println(model.toDebugString)
52 | sc.stop
53 | }
54 | }
55 |
56 | ```
57 |
58 | 3.结果:
59 |
60 | ```
61 | DecisionTreeModel classifier of depth 2 with 5 nodes
62 | DecisionTreeModel classifier of depth 1 with 3 nodes
63 | DecisionTreeModel classifier of depth 0 with 1 nodes
64 | (1.0,1.0)
65 | (0.0,0.0)
66 | TreeEnsembleModel classifier with 3 trees
67 |
68 | Tree 0:
69 | If (feature 2 <= 0.0)
70 | If (feature 0 <= 0.0)
71 | Predict: 0.0
72 | Else (feature 0 > 0.0)
73 | Predict: 1.0
74 | Else (feature 2 > 0.0)
75 | Predict: 0.0
76 | Tree 1:
77 | If (feature 2 <= 0.0)
78 | Predict: 1.0
79 | Else (feature 2 > 0.0)
80 | Predict: 0.0
81 | Tree 2:
82 | Predict: 1.0
83 | ```
84 |
85 | 参考
86 |
87 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
88 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
89 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/7特征提取和转换/Spark中组件Mllib的学习60之归一化(Normalizer)Normalization using L^Inf distance.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | 归一化
9 |
10 | Normalization using L^Inf distance
11 |
12 | 公式:分母为元素中绝对值最大值
13 |
14 |
15 | 2.代码:
16 |
17 | test("Normalization using L^Inf distance.") {
18 | val lInfNormalizer = new Normalizer(Double.PositiveInfinity)
19 |
20 | val dataInf = data.map(lInfNormalizer.transform)
21 | val dataInfRDD = lInfNormalizer.transform(dataRDD)
22 |
23 | println("dataRDD:")
24 | dataRDD.foreach(println)
25 | println("dataInf:")
26 | dataInf.foreach(println)
27 | println("dataInfRDD:")
28 | dataInfRDD.foreach(println)
29 |
30 | assert((data, dataInf, dataInfRDD.collect()).zipped.forall {
31 | case (v1: DenseVector, v2: DenseVector, v3: DenseVector) => true
32 | case (v1: SparseVector, v2: SparseVector, v3: SparseVector) => true
33 | case _ => false
34 | }, "The vector type should be preserved after normalization.")
35 |
36 | assert((dataInf, dataInfRDD.collect()).zipped.forall((v1, v2) => v1 ~== v2 absTol 1E-5))
37 |
38 | assert(dataInf(0).toArray.map(math.abs).max ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
39 | assert(dataInf(2).toArray.map(math.abs).max ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
40 | assert(dataInf(3).toArray.map(math.abs).max ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
41 | assert(dataInf(4).toArray.map(math.abs).max ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
42 |
43 | assert(dataInf(0) ~== Vectors.sparse(3, Seq((0, -0.86956522), (1, 1.0))) absTol 1E-5)
44 | assert(dataInf(1) ~== Vectors.dense(0.0, 0.0, 0.0) absTol 1E-5)
45 | assert(dataInf(2) ~== Vectors.dense(0.2, -0.36666667, -1.0) absTol 1E-5)
46 | assert(dataInf(3) ~== Vectors.sparse(3, Seq((1, 0.284375), (2, 1.0))) absTol 1E-5)
47 | assert(dataInf(4) ~== Vectors.dense(1.0, 0.12631579, 0.473684211) absTol 1E-5)
48 | assert(dataInf(5) ~== Vectors.sparse(3, Seq()) absTol 1E-5)
49 | }
50 |
51 |
52 | 3.结果:
53 |
54 | dataRDD:
55 | [0.6,-1.1,-3.0]
56 | (3,[1,2],[0.91,3.2])
57 | (3,[0,1],[-2.0,2.3])
58 | [0.0,0.0,0.0]
59 | (3,[0,1,2],[5.7,0.72,2.7])
60 | (3,[],[])
61 | dataInf:
62 | (3,[0,1],[-0.8695652173913044,1.0])
63 | [0.0,0.0,0.0]
64 | [0.19999999999999998,-0.3666666666666667,-1.0]
65 | (3,[1,2],[0.284375,1.0])
66 | (3,[0,1,2],[1.0,0.12631578947368421,0.4736842105263158])
67 | (3,[],[])
68 | dataInfRDD:
69 | [0.19999999999999998,-0.3666666666666667,-1.0]
70 | (3,[1,2],[0.284375,1.0])
71 | (3,[0,1],[-0.8695652173913044,1.0])
72 | [0.0,0.0,0.0]
73 | (3,[0,1,2],[1.0,0.12631578947368421,0.4736842105263158])
74 | (3,[],[])
75 |
76 |
77 | 结果分析:
78 |
79 |
80 | -3/3=-1
81 |
82 | 参考
83 |
84 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
85 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
86 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
87 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
88 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
89 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/7特征提取和转换/Spark中组件Mllib的学习60之归一化(Normalizer)Normalization using L^Inf distance.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | 归一化
9 |
10 | Normalization using L^Inf distance
11 |
12 | 公式:分母为元素中绝对值最大值
13 |
14 |
15 | 2.代码:
16 |
17 | test("Normalization using L^Inf distance.") {
18 | val lInfNormalizer = new Normalizer(Double.PositiveInfinity)
19 |
20 | val dataInf = data.map(lInfNormalizer.transform)
21 | val dataInfRDD = lInfNormalizer.transform(dataRDD)
22 |
23 | println("dataRDD:")
24 | dataRDD.foreach(println)
25 | println("dataInf:")
26 | dataInf.foreach(println)
27 | println("dataInfRDD:")
28 | dataInfRDD.foreach(println)
29 |
30 | assert((data, dataInf, dataInfRDD.collect()).zipped.forall {
31 | case (v1: DenseVector, v2: DenseVector, v3: DenseVector) => true
32 | case (v1: SparseVector, v2: SparseVector, v3: SparseVector) => true
33 | case _ => false
34 | }, "The vector type should be preserved after normalization.")
35 |
36 | assert((dataInf, dataInfRDD.collect()).zipped.forall((v1, v2) => v1 ~== v2 absTol 1E-5))
37 |
38 | assert(dataInf(0).toArray.map(math.abs).max ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
39 | assert(dataInf(2).toArray.map(math.abs).max ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
40 | assert(dataInf(3).toArray.map(math.abs).max ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
41 | assert(dataInf(4).toArray.map(math.abs).max ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
42 |
43 | assert(dataInf(0) ~== Vectors.sparse(3, Seq((0, -0.86956522), (1, 1.0))) absTol 1E-5)
44 | assert(dataInf(1) ~== Vectors.dense(0.0, 0.0, 0.0) absTol 1E-5)
45 | assert(dataInf(2) ~== Vectors.dense(0.2, -0.36666667, -1.0) absTol 1E-5)
46 | assert(dataInf(3) ~== Vectors.sparse(3, Seq((1, 0.284375), (2, 1.0))) absTol 1E-5)
47 | assert(dataInf(4) ~== Vectors.dense(1.0, 0.12631579, 0.473684211) absTol 1E-5)
48 | assert(dataInf(5) ~== Vectors.sparse(3, Seq()) absTol 1E-5)
49 | }
50 |
51 |
52 | 3.结果:
53 |
54 | dataRDD:
55 | [0.6,-1.1,-3.0]
56 | (3,[1,2],[0.91,3.2])
57 | (3,[0,1],[-2.0,2.3])
58 | [0.0,0.0,0.0]
59 | (3,[0,1,2],[5.7,0.72,2.7])
60 | (3,[],[])
61 | dataInf:
62 | (3,[0,1],[-0.8695652173913044,1.0])
63 | [0.0,0.0,0.0]
64 | [0.19999999999999998,-0.3666666666666667,-1.0]
65 | (3,[1,2],[0.284375,1.0])
66 | (3,[0,1,2],[1.0,0.12631578947368421,0.4736842105263158])
67 | (3,[],[])
68 | dataInfRDD:
69 | [0.19999999999999998,-0.3666666666666667,-1.0]
70 | (3,[1,2],[0.284375,1.0])
71 | (3,[0,1],[-0.8695652173913044,1.0])
72 | [0.0,0.0,0.0]
73 | (3,[0,1,2],[1.0,0.12631578947368421,0.4736842105263158])
74 | (3,[],[])
75 |
76 |
77 | 结果分析:
78 |
79 |
80 | -3/3=-1
81 |
82 | 参考
83 |
84 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
85 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
86 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
87 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
88 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
89 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/2基本统计/Spark中组件Mllib的学习21之随机数-RandomRDD产生.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之基础概念篇
3 | 1解释
4 | 在org.apache.spark.mllib.random下RandomRDDs对象,处理生成RandomRDD,还可以生成uniformRDD、poissonRDD、exponentialRDD、gammaRDD等
5 |
6 |
7 | 2.代码:
8 |
9 | ```
10 | /**
11 | * @author xubo
12 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
13 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
14 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
15 | */
16 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.basic
17 |
18 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.random.RandomRDDs._
19 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
20 |
21 | /**
22 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
23 | */
24 | object RandomRDDLearning {
25 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
26 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[4]").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
27 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
28 | println("normalRDD:")
29 | val randomNum = normalRDD(sc, 10)
30 | randomNum.foreach(println)
31 | println("uniformRDD:")
32 | uniformRDD(sc, 10).foreach(println)
33 | println("poissonRDD:")
34 | poissonRDD(sc, 5,10).foreach(println)
35 | println("exponentialRDD:")
36 | exponentialRDD(sc,7, 10).foreach(println)
37 | println("gammaRDD:")
38 | gammaRDD(sc, 3,3,10).foreach(println)
39 | sc.stop
40 | }
41 | }
42 |
43 | ```
44 |
45 | 3.结果:
46 |
47 | ```
48 | normalRDD:
49 | 0.19139342057444655
50 | 0.42847625833602926
51 | 0.432676150766411
52 | 2.031243580737701
53 | -1.6210366564577097
54 | -0.5736390968158938
55 | 0.5118950917391826
56 | 0.36612870444413614
57 | -0.7841387585110905
58 | 0.11439913262616007
59 | uniformRDD:
60 | 0.2438450552072624
61 | 0.7003522704053741
62 | 0.24235558263747725
63 | 0.49701950142885765
64 | 0.46652368533423283
65 | 0.980827677073354
66 | 0.6825558070196546
67 | 0.4817949839139517
68 | 0.9965017651788755
69 | 0.7568845648015728
70 | poissonRDD:
71 | 2.0
72 | 2.0
73 | 4.0
74 | 6.0
75 | 4.0
76 | 2.0
77 | 4.0
78 | 2.0
79 | 3.0
80 | 9.0
81 | exponentialRDD:
82 | 12.214082193307469
83 | 4.682554578220504
84 | 0.9758739534780947
85 | 1.0228072708547165
86 | 5.844697536923258
87 | 1.11718191688843
88 | 18.3001169404778
89 | 3.0254219574726964
90 | 1.9807047388403134
91 | 7.218371820752084
92 | gammaRDD:
93 | 15.362945490679401
94 | 12.508341430761691
95 | 6.284582685039609
96 | 2.731284321611819
97 | 19.032454731810525
98 | 14.508395124068773
99 | 8.684880785422951
100 | 3.5329956660355206
101 | 15.852625148469828
102 | 4.284198644233831
103 |
104 | ```
105 |
106 | 参考
107 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
108 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
109 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/6降维/Spark中组件Mllib的学习49之奇异值分解SVD(Singular value decomposition).md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | 具体请参考【4】,讲的比较详细
9 |
10 |
11 | 2.代码:
12 |
13 | /**
14 | * @author xubo
15 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
16 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
17 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
18 | */
19 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.DimensionalityReduction
20 |
21 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
22 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
23 |
24 | /**
25 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
26 | * book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
27 | */
28 | class SVDSuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
29 | test("testFunSuite") {
30 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Matrix
31 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.distributed.RowMatrix
32 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.SingularValueDecomposition
33 |
34 | // val mat: RowMatrix =...
35 | val rdd = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/basic/MatrixRow33.txt") //创建RDD文件路径
36 | .map(_.split(' ') //按“ ”分割
37 | .map(_.toDouble)) //转成Double类型
38 | .map(line => Vectors.dense(line)) //转成Vector格式
39 | val mat = new RowMatrix(rdd)
40 |
41 |
42 | // Compute the top 3 singular values and corresponding singular vectors.
43 | val svd: SingularValueDecomposition[RowMatrix, Matrix] = mat.computeSVD(3, computeU = true)
44 | val U: RowMatrix = svd.U // The U factor is a RowMatrix.
45 | val s = svd.s // The singular values are stored in a local dense vector.
46 | val V: Matrix = svd.V // The V factor is a local dense matrix.
47 |
48 | println("mat:")
49 | mat.rows.foreach(println)
50 | println("U:")
51 | U.rows.foreach(println)
52 | println("s:" + s)
53 | println("V:\n" + V)
54 | }
55 | }
56 |
57 |
58 |
59 | 3.结果:
60 |
61 | mat:
62 | [1.0,1.0,1.0]
63 | [1.0,1.0,1.0]
64 | [1.0,0.0,0.0]
65 | [1.0,1.0,0.0]
66 | U:
67 | [-0.6067637394094294,-0.3352266406762714,0.13950220040841022]
68 | [-0.2418162496491055,0.712015746118639,0.6592104964916438]
69 | [-0.45299054127146393,0.517957311021789,-0.7256168365450623]
70 | [-0.6067637394094294,-0.3352266406762714,0.13950220040841022]
71 | s:[2.809211800166755,0.88646771116676,0.5678944081980605]
72 | V:
73 | -0.6793130619863371 0.6311789687764828 0.37436195478307166
74 | -0.5932333119173848 -0.1720265367929079 -0.7864356987513785
75 | -0.431981482758553 -0.7563200248659911 0.49129626351156824
76 |
77 |
78 | 参考
79 |
80 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
81 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
82 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
83 | 【4】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-dimensionality-reduction.html
84 | 【5】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/3分类和回归/Spark中组件Mllib的学习25之线性回归2-较大数据集(多元).md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之回归分析篇
3 | 1解释
4 |
5 | 对多组数据进行model的training,然后再利用model来predict具体的值。过程中有输出model的权重 公式:f(x)=a1X1+a2X2+a3X3+......
6 |
7 | 2.代码:
8 |
9 | ```
10 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.regression
11 |
12 | import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
13 | import java.util.Date
14 |
15 | import org.apache.log4j.{Level, Logger}
16 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
17 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.{LabeledPoint, LinearRegressionWithSGD}
18 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
19 |
20 | import scala.Array.canBuildFrom
21 |
22 | object LinearRegression {
23 | def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
24 | // 屏蔽不必要的日志显示终端上
25 | Logger.getLogger("org.apache.spark").setLevel(Level.ERROR)
26 | Logger.getLogger("org.eclipse.jetty.server").setLevel(Level.OFF)
27 |
28 | // 设置运行环境
29 | val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$'))).setMaster("local[4]")
30 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
31 |
32 | // Load and parse the data
33 | val data = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/ridge-data/lpsa.data",1)
34 | //如果读入不加1,会产生两个文件,应该是默认生成了两个partition
35 | val parsedData = data.map { line =>
36 | val parts = line.split(',')
37 | LabeledPoint(parts(0).toDouble, Vectors.dense(parts(1).split(' ').map(_.toDouble)))
38 | }
39 |
40 | // Building the model
41 | //建立model的数据和predict的数据没有分开
42 | val numIterations = 100
43 | val model = LinearRegressionWithSGD.train(parsedData, numIterations)
44 | // for(i<-parsedData) println(i.label+":"+i.features);
45 | // Evaluate model on training examples and compute training error
46 | val valuesAndPreds = parsedData.map { point =>
47 | val prediction = model.predict(point.features)
48 | (point.label, prediction)
49 | }
50 | //print model.weights
51 | var weifhts=model.weights
52 | println("model.weights"+weifhts)
53 |
54 | //save as file
55 | val iString = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmssSSS").format(new Date())
56 | val path = "file/data/mllib/output/LinearRegression/" + iString + "/result"
57 | valuesAndPreds.saveAsTextFile(path)
58 | val MSE = valuesAndPreds.map { case (v, p) => math.pow((v - p), 2) }.reduce(_ + _) / valuesAndPreds.count
59 | println("training Mean Squared Error = " + MSE)
60 |
61 | sc.stop()
62 | }
63 | }
64 | ```
65 | 数据请见github或者spark源码
66 |
67 | 3.结果:
68 |
69 | ```
70 | model.weights[0.5808575763272221,0.18930001482946976,0.2803086929991066,0.1110834181777876,0.4010473965597895,-0.5603061626684255,-0.5804740464000981,0.8742741176970946]
71 | training Mean Squared Error = 6.207597210613579
72 | ```
73 |
74 | 参考
75 |
76 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
77 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
78 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
79 | 【4】Spark MlLib机器学习实战
80 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/7特征提取和转换/Spark中组件Mllib的学习59之归一化(Normalizer)Normalization using L2 distance.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | 归一化
9 |
10 | Normalization using L2 distance
11 |
12 | 公式:
13 |
14 | 分母为:其中本例中p为2
15 |
16 | 
17 |
18 |
19 | 2.代码:
20 |
21 | test("Normalization using L2 distance") {
22 | val l2Normalizer = new Normalizer()
23 |
24 | val data2 = data.map(l2Normalizer.transform)
25 | val data2RDD = l2Normalizer.transform(dataRDD)
26 |
27 | println("dataRDD:")
28 | dataRDD.foreach(println)
29 | println("data2RDD:")
30 | data2RDD.foreach(println)
31 |
32 | assert((data, data2, data2RDD.collect()).zipped.forall {
33 | case (v1: DenseVector, v2: DenseVector, v3: DenseVector) => true
34 | case (v1: SparseVector, v2: SparseVector, v3: SparseVector) => true
35 | case _ => false
36 | }, "The vector type should be preserved after normalization.")
37 |
38 | assert((data2, data2RDD.collect()).zipped.forall((v1, v2) => v1 ~== v2 absTol 1E-5))
39 |
40 | assert(brzNorm(data2(0).toBreeze, 2) ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
41 | assert(brzNorm(data2(2).toBreeze, 2) ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
42 | assert(brzNorm(data2(3).toBreeze, 2) ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
43 | assert(brzNorm(data2(4).toBreeze, 2) ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
44 |
45 | assert(data2(0) ~== Vectors.sparse(3, Seq((0, -0.65617871), (1, 0.75460552))) absTol 1E-5)
46 | assert(data2(1) ~== Vectors.dense(0.0, 0.0, 0.0) absTol 1E-5)
47 | assert(data2(2) ~== Vectors.dense(0.184549876, -0.3383414, -0.922749378) absTol 1E-5)
48 | assert(data2(3) ~== Vectors.sparse(3, Seq((1, 0.27352993), (2, 0.96186349))) absTol 1E-5)
49 | assert(data2(4) ~== Vectors.dense(0.897906166, 0.113419726, 0.42532397) absTol 1E-5)
50 | assert(data2(5) ~== Vectors.sparse(3, Seq()) absTol 1E-5)
51 | }
52 |
53 |
54 | 3.结果:
55 |
56 | dataRDD:
57 | [0.6,-1.1,-3.0]
58 | (3,[0,1],[-2.0,2.3])
59 | (3,[1,2],[0.91,3.2])
60 | [0.0,0.0,0.0]
61 | (3,[0,1,2],[5.7,0.72,2.7])
62 | (3,[],[])
63 | data2RDD:
64 | [0.18454987557625951,-0.3383414385564758,-0.9227493778812975]
65 | (3,[1,2],[0.2735299305180406,0.9618634919315713])
66 | (3,[0,1,2],[0.8979061661970154,0.11341972625646508,0.4253239734617441])
67 | (3,[],[])
68 | (3,[0,1],[-0.6561787149247866,0.7546055221635046])
69 | [0.0,0.0,0.0]
70 |
71 | 结果分析:
72 |
73 |
74 | scala> 0.6/Math.sqrt(0.6*0.6+1.1*1.1+3.0*3)
75 | res32: Double = 0.18454987557625951
76 |
77 | scala> -1.1/Math.sqrt(0.6*0.6+1.1*1.1+3.0*3)
78 | res33: Double = -0.3383414385564758
79 |
80 | scala> -3.0/Math.sqrt(0.6*0.6+1.1*1.1+3.0*3)
81 | res34: Double = -0.9227493778812975
82 |
83 | 参考
84 |
85 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
86 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
87 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
88 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
89 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
90 | 【6】https://github.com/endymecy/spark-ml-source-analysis/blob/master/%E7%89%B9%E5%BE%81%E6%8A%BD%E5%8F%96%E5%92%8C%E8%BD%AC%E6%8D%A2/normalizer.md
91 |
92 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/7特征提取和转换/Spark中组件Mllib的学习59之归一化(Normalizer)Normalization using L2 distance.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | 归一化
9 |
10 | Normalization using L2 distance
11 |
12 | 公式:
13 |
14 | 分母为:其中本例中p为2
15 |
16 | 
17 |
18 |
19 | 2.代码:
20 |
21 | test("Normalization using L2 distance") {
22 | val l2Normalizer = new Normalizer()
23 |
24 | val data2 = data.map(l2Normalizer.transform)
25 | val data2RDD = l2Normalizer.transform(dataRDD)
26 |
27 | println("dataRDD:")
28 | dataRDD.foreach(println)
29 | println("data2RDD:")
30 | data2RDD.foreach(println)
31 |
32 | assert((data, data2, data2RDD.collect()).zipped.forall {
33 | case (v1: DenseVector, v2: DenseVector, v3: DenseVector) => true
34 | case (v1: SparseVector, v2: SparseVector, v3: SparseVector) => true
35 | case _ => false
36 | }, "The vector type should be preserved after normalization.")
37 |
38 | assert((data2, data2RDD.collect()).zipped.forall((v1, v2) => v1 ~== v2 absTol 1E-5))
39 |
40 | assert(brzNorm(data2(0).toBreeze, 2) ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
41 | assert(brzNorm(data2(2).toBreeze, 2) ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
42 | assert(brzNorm(data2(3).toBreeze, 2) ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
43 | assert(brzNorm(data2(4).toBreeze, 2) ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
44 |
45 | assert(data2(0) ~== Vectors.sparse(3, Seq((0, -0.65617871), (1, 0.75460552))) absTol 1E-5)
46 | assert(data2(1) ~== Vectors.dense(0.0, 0.0, 0.0) absTol 1E-5)
47 | assert(data2(2) ~== Vectors.dense(0.184549876, -0.3383414, -0.922749378) absTol 1E-5)
48 | assert(data2(3) ~== Vectors.sparse(3, Seq((1, 0.27352993), (2, 0.96186349))) absTol 1E-5)
49 | assert(data2(4) ~== Vectors.dense(0.897906166, 0.113419726, 0.42532397) absTol 1E-5)
50 | assert(data2(5) ~== Vectors.sparse(3, Seq()) absTol 1E-5)
51 | }
52 |
53 |
54 | 3.结果:
55 |
56 | dataRDD:
57 | [0.6,-1.1,-3.0]
58 | (3,[0,1],[-2.0,2.3])
59 | (3,[1,2],[0.91,3.2])
60 | [0.0,0.0,0.0]
61 | (3,[0,1,2],[5.7,0.72,2.7])
62 | (3,[],[])
63 | data2RDD:
64 | [0.18454987557625951,-0.3383414385564758,-0.9227493778812975]
65 | (3,[1,2],[0.2735299305180406,0.9618634919315713])
66 | (3,[0,1,2],[0.8979061661970154,0.11341972625646508,0.4253239734617441])
67 | (3,[],[])
68 | (3,[0,1],[-0.6561787149247866,0.7546055221635046])
69 | [0.0,0.0,0.0]
70 |
71 | 结果分析:
72 |
73 |
74 | scala> 0.6/Math.sqrt(0.6*0.6+1.1*1.1+3.0*3)
75 | res32: Double = 0.18454987557625951
76 |
77 | scala> -1.1/Math.sqrt(0.6*0.6+1.1*1.1+3.0*3)
78 | res33: Double = -0.3383414385564758
79 |
80 | scala> -3.0/Math.sqrt(0.6*0.6+1.1*1.1+3.0*3)
81 | res34: Double = -0.9227493778812975
82 |
83 | 参考
84 |
85 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
86 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
87 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
88 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
89 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
90 | 【6】https://github.com/endymecy/spark-ml-source-analysis/blob/master/%E7%89%B9%E5%BE%81%E6%8A%BD%E5%8F%96%E5%92%8C%E8%BD%AC%E6%8D%A2/normalizer.md
91 |
92 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/6降维/Spark中组件Mllib的学习50之主成份分析PCA.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | Principal component analysis (PCA):主成份分析
9 |
10 | 从数据矩阵中抽取矩阵的k个主向量,代表矩阵的主要影响向量
11 |
12 | 具体请看【5】和【6】
13 |
14 | 2.代码:
15 |
16 | /**
17 | * @author xubo
18 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
19 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
20 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
21 | */
22 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.DimensionalityReduction
23 |
24 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
25 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
26 |
27 | /**
28 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
29 | */
30 | class PCASuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
31 | test("testFunSuite") {
32 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Matrix
33 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.distributed.RowMatrix
34 |
35 | // val mat: RowMatrix = ...
36 | val rdd = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/basic/MatrixRow33.txt") //创建RDD文件路径
37 | .map(_.split(' ') //按“ ”分割
38 | .map(_.toDouble)) //转成Double类型
39 | .map(line => Vectors.dense(line)) //转成Vector格式
40 | val mat = new RowMatrix(rdd)
41 |
42 | // Compute the top 10 principal components.
43 | val pc: Matrix = mat.computePrincipalComponents(3) // Principal components are stored in a local dense matrix.
44 |
45 | // Project the rows to the linear space spanned by the top 10 principal components.
46 | val projected: RowMatrix = mat.multiply(pc)
47 |
48 | println("mat:")
49 | mat.rows.foreach(println)
50 | println("pc:")
51 | println(pc)
52 | println("projected:")
53 | projected.rows.foreach(println)
54 | }
55 | }
56 |
57 |
58 | 3.结果:
59 |
60 | 主成份为2:
61 |
62 | mat:
63 | [1.0,0.0,0.0]
64 | [1.0,1.0,1.0]
65 | [1.0,1.0,0.0]
66 | [1.0,1.0,1.0]
67 | pc:
68 | 0.0 0.0
69 | -0.6154122094026357 -0.7882054380161092
70 | -0.7882054380161091 0.6154122094026356
71 | projected:
72 | [0.0,0.0]
73 | [-1.403617647418745,-0.17279322861347357]
74 | [-0.6154122094026357,-0.7882054380161092]
75 | [-1.403617647418745,-0.17279322861347357]
76 |
77 | 主成份为3:
78 |
79 | mat:
80 | [1.0,0.0,0.0]
81 | [1.0,1.0,1.0]
82 | [1.0,1.0,0.0]
83 | [1.0,1.0,1.0]
84 | pc:
85 | 0.0 0.0 1.0
86 | -0.6154122094026357 -0.7882054380161092 0.0
87 | -0.7882054380161091 0.6154122094026356 0.0
88 | projected:
89 | [0.0,0.0,1.0]
90 | [-1.403617647418745,-0.17279322861347357,1.0]
91 | [-0.6154122094026357,-0.7882054380161092,1.0]
92 | [-1.403617647418745,-0.17279322861347357,1.0]
93 |
94 | 参考
95 |
96 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
97 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
98 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
99 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
100 | 【5】Spark MlLib机器学习实战
101 | 【6】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-dimensionality-reduction.html
102 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/3分类和回归/Spark中组件Mllib的学习30之逻辑回归LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之分类篇
3 | 1解释
4 |
5 | Limited-memory BFGS (L-BFGS or LM-BFGS)
6 | Broyden–Fletcher–Goldfarb–Shanno (BFGS) algorithm
7 | =》
8 | LBFGS :Limited-memory Broyden–Fletcher–Goldfarb–Shanno
9 |
10 | 具体的概念在【4】、【5】中都有讲到,还没细看
11 |
12 |
13 | 2.代码:
14 |
15 | ```
16 | /**
17 | * @author xubo
18 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
19 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
20 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
21 | */
22 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.regression
23 |
24 | import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
25 | import java.util.Date
26 |
27 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
28 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.{LogisticRegressionModel, LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS}
29 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.evaluation.MulticlassMetrics
30 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint
31 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
32 |
33 | /**
34 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
35 | * 一元逻辑回归
36 | */
37 | object LogisticRegressionWithLDFGS {
38 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
39 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[4]").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
40 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
41 |
42 | // Load training data in LIBSVM format.
43 | val data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(sc, "file/data/mllib/input/regression/sample_libsvm_data.txt")
44 |
45 | // Split data into training (60%) and test (40%).
46 | val splits = data.randomSplit(Array(0.6, 0.4), seed = 11L)
47 | val training = splits(0).cache()
48 | val test = splits(1)
49 |
50 | // Run training algorithm to build the model
51 | val model = new LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS()
52 | .setNumClasses(10)
53 | .run(training)
54 |
55 | // Compute raw scores on the test set.
56 | val predictionAndLabels = test.map { case LabeledPoint(label, features) =>
57 | val prediction = model.predict(features)
58 | (prediction, label)
59 | }
60 |
61 | // Get evaluation metrics.
62 | val metrics = new MulticlassMetrics(predictionAndLabels)
63 | val precision = metrics.precision
64 | println("Precision = " + precision)
65 |
66 | // Save and load model
67 | val iString = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmssSSS").format(new Date())
68 | val path = "file/data/mllib/output/regression/LogisticRegressionWithLDFGS" + iString + "/result"
69 | model.save(sc, path)
70 | val sameModel = LogisticRegressionModel.load(sc, path)
71 | sc.stop
72 | }
73 | }
74 |
75 | ```
76 |
77 | 3.结果:
78 |
79 | ```
80 | Precision = 1.0
81 | ```
82 | 准确率也是1
83 |
84 |
85 | 参考
86 |
87 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
88 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
89 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
90 | 【4】http://blog.csdn.net/itplus/article/details/21897715
91 | 【5】http://blog.csdn.net/zhirom/article/details/38332111
92 | 【6】https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Broyden%E2%80%93Fletcher%E2%80%93Goldfarb%E2%80%93Shanno_algorithm
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/5聚类/Spark中组件Mllib的学习46之Power iteration clustering.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | Power iteration clustering是生成图聚类的聚类算法,翻译为幂迭代聚类
9 | 测试数据为:
10 |
11 |
12 | 0 1 1.0
13 | 0 2 1.0
14 | 0 3 1.0
15 |
16 | 其中第一列和第二列都是点的id,第三列为相似度的值。
17 |
18 | 对于图的顶点聚类(顶点相似度作为边的属性)问题,幂迭代聚类(PIC)是高效并且易扩展的算法(参考: Lin and Cohen, Power Iteration Clustering)。MLlib包含了一个使用GraphX(MLlib)为基础的实现。算法的输入是RDD[srcID, dstID, similarity],输出是每个顶点对应的聚类的模型。相似度(similarity)必须是非负值。PIC假设相似度的衡量是对称的,也就是说在输入数据中,(srcID, dstID)顺序无关(例如:<1, 2, 0.1>, <2, 1, 0.1等价),但是只能出现一次。输入中没有指定相似度的点对,相似度会置0。MLlib中的PIC实现具有下列参数:
19 |
20 | k: 聚簇的数量
21 | maxIterations: 最大迭代次数
22 | initializationMode: 初始化模式:默认值“random”,表示使用一个随机向量作为顶点的聚类属性;也可以是“degree”,表示使用归一化的相似度和(作为顶点的聚类属性)。
23 | 具体请间【4】
24 |
25 | 2.代码:
26 |
27 | /**
28 | * @author xubo
29 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
30 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
31 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
32 | */
33 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.clustering.PowerIterationClusteringLearning
34 |
35 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
36 |
37 | /**
38 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
39 | */
40 | class PICFromWebSuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
41 | test("testFunSuite") {
42 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.clustering.{PowerIterationClustering, PowerIterationClusteringModel}
43 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
44 |
45 | // Load and parse the data
46 | val data = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/mllibFromSpark/pic_data.txt")
47 | val similarities = data.map { line =>
48 | val parts = line.split(' ')
49 | (parts(0).toLong, parts(1).toLong, parts(2).toDouble)
50 | }
51 |
52 | // Cluster the data into two classes using PowerIterationClustering
53 | val pic = new PowerIterationClustering()
54 | .setK(2)
55 | .setMaxIterations(10)
56 | val model = pic.run(similarities)
57 |
58 | model.assignments.foreach { a =>
59 | println(s"${a.id} -> ${a.cluster}")
60 | }
61 | // model.pre
62 | // Save and load model
63 | // model.save(sc, "myModelPath")
64 | // val sameModel = PowerIterationClusteringModel.load(sc, "myModelPath")F
65 | }
66 | }
67 |
68 |
69 | 数据:
70 |
71 | 0 1 1.0
72 | 0 2 1.0
73 | 0 3 1.0
74 | 1 2 1.0
75 | 1 3 1.0
76 | 2 3 1.0
77 | 3 4 0.1
78 | 4 5 1.0
79 | 4 15 1.0
80 | 5 6 1.0
81 | 6 7 1.0
82 | 7 8 1.0
83 | 8 9 1.0
84 | 9 10 1.0
85 | 10 11 1.0
86 | 11 12 1.0
87 | 12 13 1.0
88 | 13 14 1.0
89 | 14 15 1.0
90 |
91 |
92 | 3.结果:
93 |
94 | 4 -> 0
95 | 14 -> 0
96 | 0 -> 1
97 | 6 -> 0
98 | 8 -> 0
99 | 12 -> 0
100 | 10 -> 0
101 | 2 -> 1
102 | 13 -> 0
103 | 15 -> 0
104 | 11 -> 0
105 | 1 -> 1
106 | 3 -> 1
107 | 7 -> 0
108 | 9 -> 0
109 | 5 -> 0
110 |
111 | 该模型中没有看到predict函数
112 |
113 | 参考
114 |
115 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
116 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
117 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
118 | 【4】http://www.fuqingchuan.com/2015/03/609.html#power-iteration-clustering-pic
119 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/7特征提取和转换/Spark中组件Mllib的学习58之归一化(Normalizer)Normalization using L1 distance.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | 规则化器缩放单个样本让其拥有单位范数。这是文本分类和聚类常用的操作。例如,两个规则化的TFIDF向量的点乘就是两个向量的cosine相似度。
9 |
10 | Normalizer实现VectorTransformer,将一个向量规则化为转换的向量,或者将一个RDD规则化为另一个RDD。下面是一个规则化的例子。
11 |
12 | Normalization using L1 distance ,来自spark mllib 的test
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 | 2.代码:
17 |
18 | val data = Array(
19 | Vectors.sparse(3, Seq((0, -2.0), (1, 2.3))),
20 | Vectors.dense(0.0, 0.0, 0.0),
21 | Vectors.dense(0.6, -1.1, -3.0),
22 | Vectors.sparse(3, Seq((1, 0.91), (2, 3.2))),
23 | Vectors.sparse(3, Seq((0, 5.7), (1, 0.72), (2, 2.7))),
24 | Vectors.sparse(3, Seq())
25 | )
26 |
27 | lazy val dataRDD = sc.parallelize(data, 3)
28 |
29 | test("Normalization using L1 distance") {
30 | val l1Normalizer = new Normalizer(1)
31 |
32 | val data1 = data.map(l1Normalizer.transform)
33 | val data1RDD = l1Normalizer.transform(dataRDD)
34 |
35 | println("dataRDD:")
36 | dataRDD.foreach(println)
37 | println("data1RDD:")
38 | data1RDD.foreach(println)
39 | assert((data, data1, data1RDD.collect()).zipped.forall {
40 | case (v1: DenseVector, v2: DenseVector, v3: DenseVector) => true
41 | case (v1: SparseVector, v2: SparseVector, v3: SparseVector) => true
42 | case _ => false
43 | }, "The vector type should be preserved after normalization.")
44 |
45 | assert((data1, data1RDD.collect()).zipped.forall((v1, v2) => v1 ~== v2 absTol 1E-5))
46 |
47 | assert(brzNorm(data1(0).toBreeze, 1) ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
48 | assert(brzNorm(data1(2).toBreeze, 1) ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
49 | assert(brzNorm(data1(3).toBreeze, 1) ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
50 | assert(brzNorm(data1(4).toBreeze, 1) ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
51 |
52 | assert(data1(0) ~== Vectors.sparse(3, Seq((0, -0.465116279), (1, 0.53488372))) absTol 1E-5)
53 | assert(data1(1) ~== Vectors.dense(0.0, 0.0, 0.0) absTol 1E-5)
54 | assert(data1(2) ~== Vectors.dense(0.12765957, -0.23404255, -0.63829787) absTol 1E-5)
55 | assert(data1(3) ~== Vectors.sparse(3, Seq((1, 0.22141119), (2, 0.7785888))) absTol 1E-5)
56 | assert(data1(4) ~== Vectors.dense(0.625, 0.07894737, 0.29605263) absTol 1E-5)
57 | assert(data1(5) ~== Vectors.sparse(3, Seq()) absTol 1E-5)
58 | }
59 |
60 | 3.结果:
61 |
62 | dataRDD:
63 | [0.6,-1.1,-3.0]
64 | (3,[0,1],[-2.0,2.3])
65 | (3,[1,2],[0.91,3.2])
66 | [0.0,0.0,0.0]
67 | (3,[0,1,2],[5.7,0.72,2.7])
68 | (3,[],[])
69 | data1RDD:
70 | [0.1276595744680851,-0.23404255319148937,-0.6382978723404255]
71 | (3,[1,2],[0.2214111922141119,0.778588807785888])
72 | (3,[0,1],[-0.46511627906976744,0.5348837209302325])
73 | [0.0,0.0,0.0]
74 | (3,[0,1,2],[0.625,0.07894736842105261,0.29605263157894735])
75 | (3,[],[])
76 |
77 | 结果分析:
78 |
79 | -3/(0.6+1.1+3)=-0.6382978723404255
80 |
81 | scala> 3.0/4.7
82 | res16: Double = 0.6382978723404255
83 |
84 | scala> 5.7/9.12
85 | res17: Double = 0.6250000000000001
86 |
87 | 故L1来归一化是将每个值除以所有元素绝对值只和
88 |
89 | 参考
90 |
91 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
92 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
93 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
94 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
95 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
96 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/7特征提取和转换/Spark中组件Mllib的学习58之归一化(Normalizer)Normalization using L1 distance.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | 规则化器缩放单个样本让其拥有单位范数。这是文本分类和聚类常用的操作。例如,两个规则化的TFIDF向量的点乘就是两个向量的cosine相似度。
9 |
10 | Normalizer实现VectorTransformer,将一个向量规则化为转换的向量,或者将一个RDD规则化为另一个RDD。下面是一个规则化的例子。
11 |
12 | Normalization using L1 distance ,来自spark mllib 的test
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 | 2.代码:
17 |
18 | val data = Array(
19 | Vectors.sparse(3, Seq((0, -2.0), (1, 2.3))),
20 | Vectors.dense(0.0, 0.0, 0.0),
21 | Vectors.dense(0.6, -1.1, -3.0),
22 | Vectors.sparse(3, Seq((1, 0.91), (2, 3.2))),
23 | Vectors.sparse(3, Seq((0, 5.7), (1, 0.72), (2, 2.7))),
24 | Vectors.sparse(3, Seq())
25 | )
26 |
27 | lazy val dataRDD = sc.parallelize(data, 3)
28 |
29 | test("Normalization using L1 distance") {
30 | val l1Normalizer = new Normalizer(1)
31 |
32 | val data1 = data.map(l1Normalizer.transform)
33 | val data1RDD = l1Normalizer.transform(dataRDD)
34 |
35 | println("dataRDD:")
36 | dataRDD.foreach(println)
37 | println("data1RDD:")
38 | data1RDD.foreach(println)
39 | assert((data, data1, data1RDD.collect()).zipped.forall {
40 | case (v1: DenseVector, v2: DenseVector, v3: DenseVector) => true
41 | case (v1: SparseVector, v2: SparseVector, v3: SparseVector) => true
42 | case _ => false
43 | }, "The vector type should be preserved after normalization.")
44 |
45 | assert((data1, data1RDD.collect()).zipped.forall((v1, v2) => v1 ~== v2 absTol 1E-5))
46 |
47 | assert(brzNorm(data1(0).toBreeze, 1) ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
48 | assert(brzNorm(data1(2).toBreeze, 1) ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
49 | assert(brzNorm(data1(3).toBreeze, 1) ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
50 | assert(brzNorm(data1(4).toBreeze, 1) ~== 1.0 absTol 1E-5)
51 |
52 | assert(data1(0) ~== Vectors.sparse(3, Seq((0, -0.465116279), (1, 0.53488372))) absTol 1E-5)
53 | assert(data1(1) ~== Vectors.dense(0.0, 0.0, 0.0) absTol 1E-5)
54 | assert(data1(2) ~== Vectors.dense(0.12765957, -0.23404255, -0.63829787) absTol 1E-5)
55 | assert(data1(3) ~== Vectors.sparse(3, Seq((1, 0.22141119), (2, 0.7785888))) absTol 1E-5)
56 | assert(data1(4) ~== Vectors.dense(0.625, 0.07894737, 0.29605263) absTol 1E-5)
57 | assert(data1(5) ~== Vectors.sparse(3, Seq()) absTol 1E-5)
58 | }
59 |
60 | 3.结果:
61 |
62 | dataRDD:
63 | [0.6,-1.1,-3.0]
64 | (3,[0,1],[-2.0,2.3])
65 | (3,[1,2],[0.91,3.2])
66 | [0.0,0.0,0.0]
67 | (3,[0,1,2],[5.7,0.72,2.7])
68 | (3,[],[])
69 | data1RDD:
70 | [0.1276595744680851,-0.23404255319148937,-0.6382978723404255]
71 | (3,[1,2],[0.2214111922141119,0.778588807785888])
72 | (3,[0,1],[-0.46511627906976744,0.5348837209302325])
73 | [0.0,0.0,0.0]
74 | (3,[0,1,2],[0.625,0.07894736842105261,0.29605263157894735])
75 | (3,[],[])
76 |
77 | 结果分析:
78 |
79 | -3/(0.6+1.1+3)=-0.6382978723404255
80 |
81 | scala> 3.0/4.7
82 | res16: Double = 0.6382978723404255
83 |
84 | scala> 5.7/9.12
85 | res17: Double = 0.6250000000000001
86 |
87 | 故L1来归一化是将每个值除以所有元素绝对值只和
88 |
89 | 参考
90 |
91 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
92 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
93 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
94 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
95 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
96 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/2基本统计/Spark中组件Mllib的学习42之rowMatrix的QR分解.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | 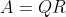
9 |
10 | 求矩阵A的Q和R分解矩阵
11 | 更多请见:【4】
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 | 2.代码:
16 |
17 | /**
18 | * @author xubo
19 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
20 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
21 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
22 | */
23 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.basic
24 |
25 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
26 | import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
27 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
28 |
29 | /**
30 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
31 | * ref:http://blog.csdn.net/openspirit/article/details/13800067
32 | * 结论:与ref一致
33 | * 有些矩阵无法QR分解,会报空指针异常
34 | */
35 | class RowMatrixSuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
36 | test("testFunSuite") {
37 | // val rdd = sc.parallelize(Array(1, 2, 3))
38 | // println("count:" + rdd.count())
39 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vector
40 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.distributed.RowMatrix
41 | val rdd = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/basic/MatrixRow33.txt") //创建RDD文件路径
42 | .map(_.split(' ') //按“ ”分割
43 | .map(_.toDouble)) //转成Double类型
44 | .map(line => Vectors.dense(line)) //转成Vector格式
45 | val mat = new RowMatrix(rdd)
46 |
47 | // Get its size.
48 | val m = mat.numRows()
49 | val n = mat.numCols()
50 | println("m:" + m)
51 | println("n:" + n)
52 | println("mat:" + mat)
53 | // QR decomposition
54 | val qrResult = mat.tallSkinnyQR(true)
55 | println()
56 | println("qrResult.R:\n" + qrResult.R)
57 | println("qrResult.Q:" + qrResult.Q)
58 | qrResult.Q.rows.foreach(println)
59 | }
60 | }
61 |
62 |
63 | 数据:
64 |
65 | 1 0 0
66 | 1 1 0
67 | 1 1 1
68 | 1 1 1
69 |
70 | 3.结果:
71 |
72 | m:4
73 | n:3
74 | mat:org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.distributed.RowMatrix@4a34ddc9
75 | 2016-06-13 16:30:55 WARN LAPACK:61 - Failed to load implementation from: com.github.fommil.netlib.NativeSystemLAPACK
76 | 2016-06-13 16:30:55 WARN LAPACK:61 - Failed to load implementation from: com.github.fommil.netlib.NativeRefLAPACK
77 |
78 | qrResult.R:
79 | 2.0000000000000004 1.4999999999999996 0.9999999999999998
80 | 0.0 -0.8660254037844386 -0.577350269189626
81 | 0.0 0.0 -0.8164965809277259
82 | qrResult.Q:org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.distributed.RowMatrix@29dbcdf9
83 | 2016-06-13 16:30:56 WARN BLAS:61 - Failed to load implementation from: com.github.fommil.netlib.NativeSystemBLAS
84 | 2016-06-13 16:30:56 WARN BLAS:61 - Failed to load implementation from: com.github.fommil.netlib.NativeRefBLAS
85 | [0.4999999999999999,-0.2886751345948133,-0.4082482904638629]
86 | [0.4999999999999999,-0.2886751345948133,-0.4082482904638629]
87 | [0.4999999999999999,0.8660254037844384,-2.719479911021037E-16]
88 | [0.4999999999999999,-0.2886751345948133,0.8164965809277263]
89 |
90 |
91 |
92 | 参考
93 |
94 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
95 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
96 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
97 | 【4】http://blog.csdn.net/openspirit/article/details/13800067
98 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/3分类和回归/Spark中组件Mllib的学习34之决策树(使用entropy)_.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之分类篇
3 | 1解释
4 |
5 | MLlib决策树支持三种不纯度的计算:gini、entropy、variance。其他的目前不支持
6 |
7 | ```
8 | def fromString(name: String): Impurity = name match {
9 | case "gini" => Gini
10 | case "entropy" => Entropy
11 | case "variance" => Variance
12 | case _ => throw new IllegalArgumentException(s"Did not recognize Impurity name: $name")
13 | }
14 | }
15 | ```
16 |
17 | 
18 | 参考【4】
19 | 官网:
20 |
21 | 
22 |
23 | 主要的决策树算法包括ID3,C4.5, CART等,参考【5】
24 |
25 | 2.代码:
26 |
27 | ```
28 | /**
29 | * @author xubo
30 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
31 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
32 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
33 | */
34 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.classification
35 |
36 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.DecisionTree
37 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
38 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
39 |
40 | /**
41 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
42 | *
43 | */
44 | object DecisionTrees2ByEntropy {
45 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
46 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[4]").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
47 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
48 |
49 | // Load and parse the data file.
50 | val data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(sc, "file/data/mllib/input/classification/dt.txt")
51 | // Split the data into training and test sets (30% held out for testing)
52 | val numClasses = 2 //设定分类数量
53 | val categoricalFeaturesInfo = Map[Int, Int]() //设定输入格式
54 | val impurity = "entropy" //设定信息增益计算方式
55 | val maxDepth = 5 //设定树高度
56 | val maxBins = 3 //设定分裂数据集
57 |
58 | val model = DecisionTree.trainClassifier(data, numClasses, categoricalFeaturesInfo,
59 | impurity, maxDepth, maxBins) //建立模型
60 | println("model.depth:" + model.depth)
61 | println("model.numNodes:" + model.numNodes)
62 | println("model.topNode:" + model.topNode)
63 |
64 | val labelAndPreds = data.take(2).map { point =>
65 | val prediction = model.predict(point.features)
66 | (point.label, prediction)
67 | }
68 | labelAndPreds.foreach(println)
69 | sc.stop
70 | }
71 | }
72 |
73 | ```
74 |
75 | ```
76 | 1 1:1 2:0 3:0 4:1
77 | 0 1:1 2:0 3:1 4:1
78 | 0 1:0 2:1 3:0 4:0
79 | 1 1:1 2:1 3:0 4:0
80 | 1 1:1 2:0 3:0 4:0
81 | 1 1:1 2:1 3:0 4:0
82 |
83 | ```
84 |
85 |
86 | 3.结果:
87 |
88 | ```
89 | model.depth:2
90 | model.numNodes:5
91 | model.topNode:id = 1, isLeaf = false, predict = 1.0 (prob = 0.6666666666666666), impurity = 0.9182958340544896, split = Some(Feature = 0, threshold = 0.0, featureType = Continuous, categories = List()), stats = Some(gain = 0.31668908831502096, impurity = 0.9182958340544896, left impurity = 0.0, right impurity = 0.7219280948873623)
92 | (1.0,1.0)
93 | (0.0,0.0)
94 |
95 | ```
96 |
97 | 参考
98 |
99 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
100 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
101 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
102 | 【4】《数据挖掘导论》
103 | 【5】http://blog.csdn.net/taigw/article/details/44840771
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/9评估度量/Spark中组件Mllib的学习71之对多标签分类进行评估.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 |
9 | 
10 | 
11 |
12 | 2.代码:
13 |
14 | /**
15 | * @author xubo
16 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
17 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
18 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
19 | */
20 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.EvaluationMetrics
21 |
22 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
23 |
24 | /**
25 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
26 | */
27 | class MultilabelClassificationFunSuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
28 | test("testFunSuite") {
29 |
30 |
31 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.evaluation.MultilabelMetrics
32 | import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD;
33 |
34 | val scoreAndLabels: RDD[(Array[Double],Array[Double])] = sc.parallelize(
35 | Seq((Array(0.0, 1.0), Array(0.0, 2.0)), (Array(0.0, 2.0), Array(0.0, 1.0)),
36 | (Array(), Array(0.0)),
37 | (Array(2.0), Array(2.0)),
38 | (Array(2.0, 0.0), Array(2.0, 0.0)),
39 | (Array(0.0, 1.0, 2.0), Array(0.0, 1.0)), (Array(1.0), Array(1.0, 2.0))), 2)
40 |
41 | // Instantiate metrics object
42 | val metrics = new MultilabelMetrics(scoreAndLabels)
43 |
44 | // Summary stats
45 | println(s"Recall = ${metrics.recall}")
46 | println(s"Precision = ${metrics.precision}")
47 | println(s"F1 measure = ${metrics.f1Measure}")
48 | println(s"Accuracy = ${metrics.accuracy}")
49 |
50 | // Individual label stats
51 | metrics.labels.foreach(label => println(s"Class $label precision = ${metrics.precision(label)}"))
52 | metrics.labels.foreach(label => println(s"Class $label recall = ${metrics.recall(label)}"))
53 | metrics.labels.foreach(label => println(s"Class $label F1-score = ${metrics.f1Measure(label)}"))
54 |
55 | // Micro stats
56 | println(s"Micro recall = ${metrics.microRecall}")
57 | println(s"Micro precision = ${metrics.microPrecision}")
58 | println(s"Micro F1 measure = ${metrics.microF1Measure}")
59 |
60 | // Hamming loss
61 | println(s"Hamming loss = ${metrics.hammingLoss}")
62 |
63 | // Subset accuracy
64 | println(s"Subset accuracy = ${metrics.subsetAccuracy}")
65 |
66 |
67 | }
68 | }
69 |
70 |
71 |
72 | 3.结果:
73 |
74 | Recall = 0.6428571428571429
75 | Precision = 0.6666666666666666
76 | F1 measure = 0.6380952380952382
77 | Accuracy = 0.5476190476190476
78 | Class 0.0 precision = 1.0
79 | Class 1.0 precision = 0.6666666666666666
80 | Class 2.0 precision = 0.5
81 | Class 0.0 recall = 0.8
82 | Class 1.0 recall = 0.6666666666666666
83 | Class 2.0 recall = 0.5
84 | Class 0.0 F1-score = 0.888888888888889
85 | Class 1.0 F1-score = 0.6666666666666666
86 | Class 2.0 F1-score = 0.5
87 | Micro recall = 0.6666666666666666
88 | Micro precision = 0.7272727272727273
89 | Micro F1 measure = 0.6956521739130435
90 | Hamming loss = 0.3333333333333333
91 | Subset accuracy = 0.2857142857142857
92 |
93 | 参考
94 |
95 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
96 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
97 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
98 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
99 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
100 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/7特征提取和转换/Spark中组件Mllib的学习53之Word2Vec简单实例.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | word2vec是NLP领域的重要算法,它的功能是将word用K维的dense vector来表达,训练集是语料库,不含标点,以空格断句。因此可以看作是种特征处理方法。
9 |
10 | 主要优点:
11 |
12 | 加法操作。
13 | 高效。单机可处理1小时2千万词。
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 | 
18 |
19 |
20 | 2.代码:
21 |
22 | /**
23 | * @author xubo
24 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
25 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
26 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
27 | */
28 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.FeatureExtractionAndTransformation
29 |
30 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
31 |
32 | /**
33 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
34 | */
35 | class word2VecSuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
36 | test("testFunSuite") {
37 |
38 | import org.apache.spark._
39 | import org.apache.spark.rdd._
40 | import org.apache.spark.SparkContext._
41 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.feature.{Word2Vec, Word2VecModel}
42 |
43 | val input = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/FeatureExtractionAndTransformation/text8").map(line => line.split(" ").toSeq)
44 | //java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
45 |
46 |
47 | // val input = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/FeatureExtractionAndTransformation/a.txt").map(line => line.split(" ").toSeq)
48 |
49 | val word2vec = new Word2Vec()
50 |
51 | val model = word2vec.fit(input)
52 |
53 | val synonyms = model.findSynonyms("china", 1)
54 | // val synonyms = model.findSynonyms("hello", 2)
55 | // val synonyms = model.findSynonyms("hell", 2)
56 | println("synonyms:" + synonyms.length)
57 | for ((synonym, cosineSimilarity) <- synonyms) {
58 | println(s"$synonym $cosineSimilarity")
59 | }
60 |
61 | // Save and load model
62 | // model.save(sc, "myModelPath")
63 | // val sameModel = Word2VecModel.load(sc, "myModelPath")
64 |
65 | }
66 |
67 | test("testFunSuite ,code From book by pk") {
68 |
69 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.feature.Word2Vec
70 |
71 | // val input = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/FeatureExtractionAndTransformation/text8").map(line => line.split(" ").toSeq)
72 | //java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
73 | val data = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/FeatureExtractionAndTransformation/aWord2vec.txt").map(line => line.split(" ").toSeq)
74 |
75 |
76 | val word2vec = new Word2Vec() //创建词向量实例
77 | val model = word2vec.fit(data) //训练模型
78 | println(model.getVectors) //打印向量模型
79 | val synonyms = model.findSynonyms("spark", 1) //寻找spar的相似词
80 | println("synonyms:" + synonyms.length)
81 | for (synonym <- synonyms) {
82 | //打印找到的内容
83 | println(synonym)
84 | }
85 | }
86 | }
87 |
88 |
89 |
90 | 3.结果:
91 |
92 | Map(hello -> [F@21cab9e, spark -> [F@28471327)
93 | synonyms:1
94 | (hello,-8.927243828523911E-4)
95 |
96 | 前面一个spark官网的test由于报内存不足,所以没有放上来。
97 |
98 | 参考
99 |
100 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
101 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
102 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
103 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
104 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
105 | 【6】http://www.cnblogs.com/aezero/p/4586605.html
106 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/3分类和回归/Spark中组件Mllib的学习26之逻辑回归-简单数据集,带预测.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之逻辑回归篇
3 | 1解释
4 | 什么是逻辑回归?
5 |
6 | Logistic回归与多重线性回归实际上有很多相同之处,最大的区别就在于它们的因变量不同,其他的基本都差不多。正是因为如此,这两种回归可以归于同一个家族,即广义线性模型(generalizedlinear model)。
7 |
8 | 这一家族中的模型形式基本上都差不多,不同的就是因变量不同。
9 | 如果是连续的,就是多重线性回归;
10 | 如果是二项分布,就是Logistic回归;
11 | 如果是Poisson分布,就是Poisson回归;
12 | 如果是负二项分布,就是负二项回归。
13 |
14 | Logistic回归的因变量可以是二分类的,也可以是多分类的,但是二分类的更为常用,也更加容易解释。所以实际中最常用的就是二分类的Logistic回归。
15 |
16 | Logistic回归的主要用途:
17 |
18 | 寻找危险因素:寻找某一疾病的危险因素等;
19 | 预测:根据模型,预测在不同的自变量情况下,发生某病或某种情况的概率有多大;
20 | 判别:实际上跟预测有些类似,也是根据模型,判断某人属于某病或属于某种情况的概率有多大,也就是看一下这个人有多大的可能性是属于某病。
21 |
22 | 更多请见参考【4】,【4】中还有推理、迭代更新和求解过程,正则化也有
23 |
24 | 逻辑回归:
25 | 
26 |
27 | 2.代码:
28 |
29 | ```
30 | /**
31 | * @author xubo
32 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
33 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
34 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
35 | */
36 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.regression
37 |
38 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.LogisticRegressionWithSGD
39 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
40 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint
41 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
42 |
43 | /**
44 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
45 | * 一元逻辑回归
46 | */
47 | object LogisticRegressionLearning {
48 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
49 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[4]").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
50 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
51 |
52 | val data = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/regression/logisticRegression1.data") //获取数据集路径
53 | val parsedData = data.map { line => //开始对数据集处理
54 | val parts = line.split('|') //根据逗号进行分区
55 | LabeledPoint(parts(0).toDouble, Vectors.dense(parts(1).split(' ').map(_.toDouble)))
56 | }.cache() //转化数据格式
57 | parsedData.foreach(println)
58 | val model = LogisticRegressionWithSGD.train(parsedData, 50) //建立模型
59 | val target = Vectors.dense(-1) //创建测试值
60 | val resulet = model.predict(target) //根据模型计算结果
61 | println("model.weights:")
62 | println(model.weights)
63 | println(resulet) //打印结果
64 | println(model.predict(Vectors.dense(10)))
65 | sc.stop
66 | }
67 | }
68 |
69 | ```
70 |
71 | 数据:
72 |
73 | ```
74 | 1|2
75 | 1|3
76 | 1|4
77 | 1|5
78 | 1|6
79 | 0|7
80 | 0|8
81 | 0|9
82 | 0|10
83 | 0|11
84 | ```
85 |
86 | 3.结果:
87 |
88 | ```
89 | 2016-05-24 21:59:06 WARN :139 - Your hostname, xubo-PC resolves to a loopback/non-reachable address: fe80:0:0:0:482:722f:5976:ce1f%20, but we couldn't find any external IP address!
90 | (0.0,[8.0])
91 | (1.0,[2.0])
92 | (0.0,[9.0])
93 | (1.0,[3.0])
94 | (0.0,[10.0])
95 | (1.0,[4.0])
96 | (0.0,[11.0])
97 | (1.0,[5.0])
98 | (1.0,[6.0])
99 | (0.0,[7.0])
100 | 2016-05-24 21:59:07 WARN BLAS:61 - Failed to load implementation from: com.github.fommil.netlib.NativeSystemBLAS
101 | 2016-05-24 21:59:07 WARN BLAS:61 - Failed to load implementation from: com.github.fommil.netlib.NativeRefBLAS
102 | model.weights:
103 | [-0.10590621151462867]
104 | 1.0
105 | 0.0
106 | ```
107 |
108 | 参考
109 |
110 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
111 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
112 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
113 | 【4】http://blog.csdn.net/pakko/article/details/37878837
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/5聚类/Spark中组件Mllib的学习45之用高斯混合模型来预测.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 | 前面主要是建立模型,这篇讲的是使用mllib中的gmm来预测,主要改自mllib test中的suite
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 | 2.代码:
12 |
13 | test("model prediction, parallel and local") {
14 | val data = sc.parallelize(GaussianTestData.data)
15 | val gmm = new GaussianMixture().setK(4).setSeed(0).run(data)
16 |
17 | val batchPredictions = gmm.predict(data)
18 | batchPredictions.zip(data).collect().foreach { case (batchPred, datum) =>
19 | print("batchPred:"+batchPred)
20 | println(" datum:"+datum)
21 | assert(batchPred === gmm.predict(datum))
22 | }
23 | /** ****************add by xubo 20160613 *************/
24 | for (i <- 0 until gmm.k) {
25 | println("weight=%f\nmu=%s\nsigma=\n%s\n" format
26 | (gmm.weights(i), gmm.gaussians(i).mu, gmm.gaussians(i).sigma))
27 | }
28 |
29 | /** ****************add by xubo 20160613 *************/
30 | }
31 |
32 | 数据:
33 |
34 | object GaussianTestData {
35 |
36 | val data = Array(
37 | Vectors.dense(-5.1971), Vectors.dense(-2.5359), Vectors.dense(-3.8220),
38 | Vectors.dense(-5.2211), Vectors.dense(-5.0602), Vectors.dense(4.7118),
39 | Vectors.dense(6.8989), Vectors.dense(3.4592), Vectors.dense(4.6322),
40 | Vectors.dense(5.7048), Vectors.dense(4.6567), Vectors.dense(5.5026),
41 | Vectors.dense(4.5605), Vectors.dense(5.2043), Vectors.dense(6.2734)
42 | )
43 |
44 | val data2: Array[Vector] = Array.tabulate(25) { i: Int =>
45 | Vectors.dense(Array.tabulate(50)(i + _.toDouble))
46 | }
47 |
48 | }
49 |
50 | 3.结果:
51 | k=2:
52 |
53 | batchPred:1 datum:[-5.1971]
54 | batchPred:1 datum:[-2.5359]
55 | batchPred:1 datum:[-3.822]
56 | batchPred:1 datum:[-5.2211]
57 | batchPred:1 datum:[-5.0602]
58 | batchPred:0 datum:[4.7118]
59 | batchPred:0 datum:[6.8989]
60 | batchPred:0 datum:[3.4592]
61 | batchPred:0 datum:[4.6322]
62 | batchPred:0 datum:[5.7048]
63 | batchPred:0 datum:[4.6567]
64 | batchPred:0 datum:[5.5026]
65 | batchPred:0 datum:[4.5605]
66 | batchPred:0 datum:[5.2043]
67 | batchPred:0 datum:[6.2734]
68 | weight=0.666667
69 | mu=[5.160440000000388]
70 | sigma=
71 | 0.8664462983997272
72 |
73 | weight=0.333333
74 | mu=[-4.367259999996172]
75 | sigma=
76 | 1.1098061864295243
77 |
78 | k=4:
79 |
80 |
81 | batchPred:0 datum:[-5.2211]
82 | batchPred:0 datum:[-5.0602]
83 | batchPred:2 datum:[4.7118]
84 | batchPred:1 datum:[6.8989]
85 | batchPred:2 datum:[3.4592]
86 | batchPred:2 datum:[4.6322]
87 | batchPred:2 datum:[5.7048]
88 | batchPred:2 datum:[4.6567]
89 | batchPred:2 datum:[5.5026]
90 | batchPred:2 datum:[4.5605]
91 | batchPred:2 datum:[5.2043]
92 | batchPred:2 datum:[6.2734]
93 | weight=0.199703
94 | mu=[-5.159541319359388]
95 | sigma=
96 | 0.005019244232416107
97 |
98 | weight=0.264231
99 | mu=[5.2562903953513125]
100 | sigma=
101 | 0.9154479492242813
102 |
103 | weight=0.402436
104 | mu=[5.09750654075634]
105 | sigma=
106 | 0.8242799738536565
107 |
108 | weight=0.133631
109 | mu=[-3.183244472524267]
110 | sigma=
111 | 0.42087592390746537
112 |
113 |
114 | 参考
115 |
116 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
117 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
118 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
119 |
120 |
121 |
122 | 完整代码路径:【3】中可以找到
123 |
124 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.clustering.GaussianMixture
125 |
126 | class GaussianMixtureFromSparkSuite
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/1数据类型/Spark中组件Mllib的学习16之分布式行矩阵的四种形式.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之基础概念篇
3 | 1解释
4 | 分布式行矩阵有:基本行矩阵、index 行矩阵、坐标行矩阵、块行矩阵
5 | 功能一次增加
6 |
7 | 2.代码:
8 |
9 | ```
10 |
11 | /**
12 | * @author xubo
13 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
14 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
15 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
16 | */
17 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.basic
18 |
19 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
20 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.distributed._
21 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
22 |
23 | /**
24 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
25 | */
26 | object MatrixRowLearning {
27 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
28 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
29 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
30 |
31 | println("First:Matrix ")
32 | val rdd = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/basic/MatrixRow.txt") //创建RDD文件路径
33 | .map(_.split(' ') //按“ ”分割
34 | .map(_.toDouble)) //转成Double类型
35 | .map(line => Vectors.dense(line)) //转成Vector格式
36 | val rm = new RowMatrix(rdd) //读入行矩阵
37 | // for(i <- rm){
38 | // println(i)
39 | // }
40 | //error
41 | //疑问:如何打印行矩阵所有值,如何定位?
42 | println(rm.numRows()) //打印列数
43 | println(rm.numCols()) //打印行数
44 | rm.rows.foreach(println)
45 |
46 | println("Second:index Row Matrix ")
47 | val rdd2 = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/basic/MatrixRow.txt") //创建RDD文件路径
48 | .map(_.split(' ') //按“ ”分割
49 | .map(_.toDouble)) //转成Double类型
50 | .map(line => Vectors.dense(line)) //转化成向量存储
51 | .map((vd) => new IndexedRow(vd.size, vd)) //转化格式
52 | val irm = new IndexedRowMatrix(rdd2) //建立索引行矩阵实例
53 | println(irm.getClass) //打印类型
54 | irm.rows.foreach(println) //打印内容数据
55 | //如何定位?
56 |
57 | println("Third: Coordinate Row Matrix ")
58 | val rdd3 = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/basic/MatrixRow.txt") //创建RDD文件路径
59 | .map(_.split(' ') //按“ ”分割
60 | .map(_.toDouble)) //转成Double类型
61 | .map(vue => (vue(0).toLong, vue(1).toLong, vue(2))) //转化成坐标格式
62 | .map(vue2 => new MatrixEntry(vue2 _1, vue2 _2, vue2 _3)) //转化成坐标矩阵格式
63 | val crm = new CoordinateMatrix(rdd3) //实例化坐标矩阵
64 | crm.entries.foreach(println) //打印数据
65 | println(crm.numCols())
66 | println(crm.numCols())
67 | // Return approximate number of distinct elements in the RDD.
68 | println(crm.entries.countApproxDistinct())
69 |
70 |
71 | println("Fourth: Block Matrix :null")
72 | //块矩阵待完善
73 |
74 | sc.stop
75 | }
76 | }
77 |
78 | ```
79 |
80 | 3.结果:
81 |
82 | ```
83 | First:Matrix
84 | 2016-05-23 19:04:24 WARN :139 - Your hostname, xubo-PC resolves to a loopback/non-reachable address: fe80:0:0:0:482:722f:5976:ce1f%20, but we couldn't find any external IP address!
85 | 2
86 | 3
87 | [1.0,2.0,3.0]
88 | [4.0,5.0,6.0]
89 | Second:index Row Matrix
90 | class org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.distributed.IndexedRowMatrix
91 | IndexedRow(3,[1.0,2.0,3.0])
92 | IndexedRow(3,[4.0,5.0,6.0])
93 | Third: Coordinate Row Matrix
94 | MatrixEntry(1,2,3.0)
95 | MatrixEntry(4,5,6.0)
96 | 6
97 | 6
98 | 2
99 | Fourth: Block Matrix :null
100 | ```
101 |
102 | 参考
103 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
104 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
105 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
106 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/5聚类/Spark中组件Mllib的学习44之高斯混合聚类GaussianMixture.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | GaussianMixture可以理解为多个高斯函数进行混合,每个高斯函数权重不一样。
9 |
10 | 源码分析请见【4】
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 | 2.代码:
15 |
16 | /**
17 | * @author xubo
18 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
19 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
20 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
21 | */
22 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.clustering.GaussianMixture
23 |
24 | import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
25 | import java.util.Date
26 |
27 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.clustering.{GaussianMixture, GaussianMixtureModel}
28 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
29 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
30 |
31 | /**
32 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
33 | */
34 | class GaussianMixtureSuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
35 | test("testFunSuite") {
36 |
37 | // Load and parse the data
38 | val data = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/mllibFromSpark/gmm_data.txt")
39 | val parsedData = data.map(s => Vectors.dense(s.trim.split(' ').map(_.toDouble))).cache()
40 |
41 | // Cluster the data into two classes using GaussianMixture
42 | val gmm = new GaussianMixture().setK(2).run(parsedData)
43 |
44 | // Save and load model
45 | val iString = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmssSSS").format(new Date())
46 | val output = "file/data/mllib/output/mllibFromSpark/myGMMModel" + iString
47 | println("output:" + output)
48 | println("gmm.weights:" + gmm.weights)
49 | println("gmm.weights:" + gmm.weights)
50 | println("gmm.weights.length:" + gmm.weights.length)
51 |
52 | // gmm.save(sc, output)
53 | // val sameModel = GaussianMixtureModel.load(sc, output)
54 |
55 | // output parameters of max-likelihood model
56 | for (i <- 0 until gmm.k) {
57 | println("weight=%f\nmu=%s\nsigma=\n%s\n" format
58 | (gmm.weights(i), gmm.gaussians(i).mu, gmm.gaussians(i).sigma))
59 | }
60 | }
61 | }
62 |
63 |
64 |
65 | 3.结果:
66 | k=2:
67 |
68 | output:file/data/mllib/output/mllibFromSpark/myGMMModel20160613172124714
69 | gmm.weights:[D@76556aff
70 | gmm.weights.length:2
71 | weight=0.479516
72 | mu=[0.07229334132596348,0.016699872146612848]
73 | sigma=
74 | 4.787456829778775 1.8802887426093131
75 | 1.8802887426093131 0.9160786892956797
76 |
77 | weight=0.520484
78 | mu=[-0.10418516009966565,0.04279316009103921]
79 | sigma=
80 | 4.899755775046639 -2.002791396537124
81 | -2.002791396537124 1.0099533766097555
82 |
83 |
84 | k=3:
85 |
86 | output:file/data/mllib/output/mllibFromSpark/myGMMModel20160613173058582
87 | gmm.weights:[D@63f7f62
88 | gmm.weights.length:3
89 | weight=0.478456
90 | mu=[0.07294229123698849,0.016880200460870468]
91 | sigma=
92 | 4.799622783996325 1.884861638240691
93 | 1.884861638240691 0.9186484216430504
94 |
95 | weight=0.352254
96 | mu=[-0.016078882202045494,-0.09041925014095285]
97 | sigma=
98 | 4.214865453249383 -1.679616942501954
99 | -1.679616942501954 0.8180392275099243
100 |
101 | weight=0.169290
102 | mu=[-0.2882428708757841,0.31930454247949075]
103 | sigma=
104 | 6.239284901444058 -2.5886021455230255
105 | -2.5886021455230255 1.288079844267794
106 |
107 |
108 |
109 | 参考
110 |
111 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
112 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
113 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
114 | 【4】http://blog.csdn.net/notheory/article/details/50219451
115 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 系统环境:
3 | Spark-1.5.2
4 | hadoop2.6.0
5 | scala-2.10.4
6 | idea 15.0.4
7 |
8 | Spark mllib学习目录:
9 |
10 | **1.数据类型**
11 |
12 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习12之密集向量和稀疏向量的生成
13 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习13之给向量打标签
14 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习14之从文本中读取带标签的数据,生成带label的向量
15 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习15之创建分布式矩阵
16 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习16之分布式行矩阵的四种形式
17 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习43之BlockMatrix
18 |
19 | **2.基本统计**
20 |
21 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习3之用户相似度计算
22 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习17之colStats_以列为基础计算统计量的基本数据
23 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习18之corr_两组数据相关关系计算(Pearson、Spearman)
24 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习19之分层抽样
25 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习20之假设检验-卡方检验
26 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习21之随机数-RandomRDD产生
27 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习22之假设检验-卡方检验概念理解
28 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习42之rowMatrix的QR分解
29 |
30 | **3.分类和回归**
31 |
32 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习23之随机梯度下降(SGD)
33 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习24之线性回归1-小数据集
34 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习25之线性回归2-较大数据集(多元)
35 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习26之逻辑回归-简单数据集,带预测
36 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习27之逻辑回归-多元逻辑回归,较大数据集,带预测准确度计算
37 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习28之支持向量机SVM-方法1
38 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习29之支持向量机SVM-方法2
39 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习30之逻辑回归LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS
40 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习31之朴素贝叶斯分类器(多项式朴素贝叶斯)
41 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习32之朴素贝叶斯分类器(伯努利朴素贝叶斯)
42 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习33之决策树(使用Gini)
43 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习34之决策树(使用entropy)
44 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习35之随机森林(entropy)进行分类
45 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习36之决策树(使用variance)进行回归
46 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习37之随机森林(Gini)进行分类
47 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习38之随机森林(使用variance)进行回归
48 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习39之梯度提升树(GBT)用于分类
49 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习40之梯度提升树(GBT)用于回归
50 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习41之保序回归(Isotonic regression)
51 |
52 |
53 | **4.协同过滤**
54 |
55 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习2之MovieLensALS学习(集群run-eaxmples运行)
56 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习4之examples中的MovieLensALS修改本地运行
57 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习5之ALS测试(apache spark)
58 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习6之ALS测试(apache spark 含隐式转换)
59 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习7之ALS隐式转换训练的model来预测数据
60 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习8之ALS训练的model来预测数据
61 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习9之ALS训练的model来预测数据的准确率研究
62 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习10之修改MovieLens来对movieLen中的100k数据进行预测
63 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习11之使用ALS对movieLens中一百万条(1M)数据集进行训练,并对输入的新用户数据进行电影推荐
64 |
65 | **5.聚类**
66 |
67 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习1之Kmeans错误解决
68 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习44之高斯混合聚类GaussianMixture
69 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习45之用高斯混合模型来预测
70 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习46之Power iteration clustering
71 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习47之隐含狄利克雷分布(Latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA)学习
72 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习48之流式k均值(Streaming kmeans)
73 |
74 | **6.降维**
75 |
76 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习49之奇异值分解SVD(Singular value decomposition)
77 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习50之主成份分析PCA
78 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习51之使用PCA从数据集中得到主向量
79 |
80 | **7.特征提取和转换**
81 |
82 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习52之TF-IDF学习
83 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习53之HashingTF理解和使用
84 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习53之Word2Vec简单实例
85 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习54之word2Vec实例分析(text8数据集)
86 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习55之使用TfIdf来分析20news数据集
87 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习56之标准化(StandardScaler,来自SparkWeb)
88 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习57之标准化参数和公式理解(StandardScaler,来自SparkCode)
89 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习58之归一化(Normalizer)Normalization using L1 distance
90 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习59之归一化(Normalizer)Normalization using L2 distance
91 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习60之归一化(Normalizer)Normalization using L^Inf distance
92 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习61之归一化(Normalizer)SparkWeb实例分析
93 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习62之特征选择中的卡方选择器
94 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习63之特征选择中的卡方选择器实例(libsvm数据集)
95 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习64之元素智能乘积ElementwiseProduct
96 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习65之使用PCA进行特征转换
97 |
98 | **8.频繁项挖掘**
99 |
100 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习66之FP-growth
101 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习67之关联规则AssociationRules
102 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习68之PrefixSpan
103 |
104 | **9.评估度量**
105 |
106 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习69之对二分类进行评估Binary classification
107 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习70之对多类分类结果进行评估Multiclass classification
108 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习71之对多标签分类进行评估
109 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习72之RankingSystem进行评估
110 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习73之回归问题的评估
111 |
112 | **10.PMML模型输出**
113 |
114 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习74之预言模型标记语言PMML
115 |
116 | **11优化**
117 |
118 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习75之L-BFGS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/11优化/Spark中组件Mllib的学习75之L-BFGS.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | L-BFGS的概念请参考【6】
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 | 2.代码:
13 |
14 | /**
15 | * @author xubo
16 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
17 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
18 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
19 | */
20 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.Optimization
21 |
22 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
23 |
24 | /**
25 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
26 | */
27 | class LBFGSFunSuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
28 | test("testFunSuite") {
29 |
30 |
31 | import org.apache.spark.SparkContext
32 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.evaluation.BinaryClassificationMetrics
33 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
34 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
35 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.LogisticRegressionModel
36 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.optimization.{LBFGS, LogisticGradient, SquaredL2Updater}
37 |
38 | val data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(sc, "file/data/mllib/input/mllibFromSpark/sample_libsvm_data.txt")
39 | val numFeatures = data.take(1)(0).features.size
40 |
41 | // Split data into training (60%) and test (40%).
42 | val splits = data.randomSplit(Array(0.6, 0.4), seed = 11L)
43 |
44 | // Append 1 into the training data as intercept.
45 | val training = splits(0).map(x => (x.label, MLUtils.appendBias(x.features))).cache()
46 |
47 | val test = splits(1)
48 |
49 | // Run training algorithm to build the model
50 | val numCorrections = 10
51 | val convergenceTol = 1e-4
52 | val maxNumIterations = 20
53 | val regParam = 0.1
54 | val initialWeightsWithIntercept = Vectors.dense(new Array[Double](numFeatures + 1))
55 |
56 | val (weightsWithIntercept, loss) = LBFGS.runLBFGS(
57 | training,
58 | new LogisticGradient(),
59 | new SquaredL2Updater(),
60 | numCorrections,
61 | convergenceTol,
62 | maxNumIterations,
63 | regParam,
64 | initialWeightsWithIntercept)
65 |
66 | val model = new LogisticRegressionModel(
67 | Vectors.dense(weightsWithIntercept.toArray.slice(0, weightsWithIntercept.size - 1)),
68 | weightsWithIntercept(weightsWithIntercept.size - 1))
69 |
70 | // Clear the default threshold.
71 | model.clearThreshold()
72 |
73 | // Compute raw scores on the test set.
74 | val scoreAndLabels = test.map { point =>
75 | val score = model.predict(point.features)
76 | (score, point.label)
77 | }
78 |
79 | // Get evaluation metrics.
80 | val metrics = new BinaryClassificationMetrics(scoreAndLabels)
81 | val auROC = metrics.areaUnderROC()
82 |
83 | println("Loss of each step in training process")
84 | loss.foreach(println)
85 | println("Area under ROC = " + auROC)
86 |
87 |
88 | }
89 | }
90 |
91 |
92 |
93 | 3.结果:
94 |
95 | Loss of each step in training process
96 | 0.6931471805599448
97 | 0.6493820266740578
98 | 0.21500294643532605
99 | 0.0021993980987416607
100 | 5.202713917046544E-4
101 | 3.4927255641289994E-4
102 | 1.888143055954077E-4
103 | 1.2596418162046915E-4
104 | 9.190860508937821E-5
105 | 7.563586578488929E-5
106 | 6.752517240852286E-5
107 | 6.361011786413444E-5
108 | 6.141097383991715E-5
109 | 5.932972379127243E-5
110 | 5.554554457038146E-5
111 | 4.480277717224111E-5
112 | 3.240944275555446E-5
113 | 3.0444586625324565E-5
114 | Area under ROC = 1.0
115 |
116 | 参考
117 |
118 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
119 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
120 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
121 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
122 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
123 | 【6】https://github.com/endymecy/spark-ml-source-analysis/blob/master/%E6%9C%80%E4%BC%98%E5%8C%96%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95/L-BFGS/lbfgs.md
124 |
125 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/3分类和回归/Spark中组件Mllib的学习38之随机森林(使用variance)进行回归.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之分类篇
3 | 1解释
4 | 随机森林(使用variance)进行回归
5 |
6 |
7 | 2.代码:
8 |
9 | ```
10 | /**
11 | * @author xubo
12 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
13 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
14 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
15 | */
16 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.classification
17 |
18 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.RandomForest
19 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
20 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
21 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.RandomForest
22 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.model.RandomForestModel
23 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
24 |
25 | /**
26 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
27 | */
28 | object RandomForest3VarianceRegression {
29 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
30 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[4]").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
31 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
32 |
33 | // Load and parse the data file.
34 | val data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(sc, "file/data/mllib/input/classification/sample_libsvm_data.txt")
35 |
36 | // Split the data into training and test sets (30% held out for testing)
37 | val splits = data.randomSplit(Array(0.7, 0.3))
38 | val (trainingData, testData) = (splits(0), splits(1))
39 |
40 | // Train a RandomForest model.
41 | // Empty categoricalFeaturesInfo indicates all features are continuous.
42 | val numClasses = 2
43 | val categoricalFeaturesInfo = Map[Int, Int]()
44 | val numTrees = 3 // Use more in practice.
45 | val featureSubsetStrategy = "auto" // Let the algorithm choose.
46 | val impurity = "variance"
47 | val maxDepth = 4
48 | val maxBins = 32
49 |
50 | val model = RandomForest.trainRegressor(trainingData, categoricalFeaturesInfo,
51 | numTrees, featureSubsetStrategy, impurity, maxDepth, maxBins)
52 |
53 | // Evaluate model on test instances and compute test error
54 | val labelsAndPredictions = testData.map { point =>
55 | val prediction = model.predict(point.features)
56 | (point.label, prediction)
57 | }
58 | val testMSE = labelsAndPredictions.map { case (v, p) => math.pow((v - p), 2) }.mean()
59 | println("Test Mean Squared Error = " + testMSE)
60 | println("Learned regression forest model:\n" + model.toDebugString)
61 |
62 | println("data.count:" + data.count())
63 | println("trainingData.count:" + trainingData.count())
64 | println("testData.count:" + testData.count())
65 | println("model.algo:" + model.algo)
66 | println("model.trees:" + model.trees)
67 |
68 | // Save and load model
69 | // val iString = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmssSSS").format(new Date())
70 | // val path = "file/data/mllib/output/classification/RandomForestModel" + iString + "/result"
71 | // model.save(sc, path)
72 | // val sameModel = RandomForestModel.load(sc, path)
73 | // println(sameModel.algo)
74 | sc.stop
75 | }
76 | }
77 |
78 | ```
79 |
80 | 3.结果:
81 |
82 | ```
83 | Test Mean Squared Error = 0.006944444444444447
84 | Learned regression forest model:
85 | TreeEnsembleModel regressor with 3 trees
86 |
87 | Tree 0:
88 | If (feature 379 <= 23.0)
89 | Predict: 0.0
90 | Else (feature 379 > 23.0)
91 | Predict: 1.0
92 | Tree 1:
93 | If (feature 434 <= 0.0)
94 | Predict: 0.0
95 | Else (feature 434 > 0.0)
96 | Predict: 1.0
97 | Tree 2:
98 | If (feature 490 <= 31.0)
99 | Predict: 0.0
100 | Else (feature 490 > 31.0)
101 | Predict: 1.0
102 |
103 | data.count:100
104 | trainingData.count:68
105 | testData.count:32
106 | model.algo:Regression
107 | model.trees:[Lorg.apache.spark.mllib.tree.model.DecisionTreeModel;@43f17f99
108 | ```
109 |
110 | 参考
111 |
112 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
113 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
114 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/2基本统计/Spark中组件Mllib的学习22之假设检验-卡方检验概念理解.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之基础概念篇
4 | 1解释
5 | 参考【4】的博文讲的比较清楚了,只是里面有些错误。
6 | 定义
7 |
8 | 卡方检验就是统计样本的实际观测值与理论推断值之间的偏离程度,实际观测值与理论推断值之间的偏离程度就决定卡方值的大小,卡方值越大,越不符合;卡方值越小,偏差越小,越趋于符合,若两个值完全相等时,卡方值就为0,表明理论值完全符合。
9 |
10 | (1)提出原假设:
11 | H0:总体X的分布函数为F(x).
12 |
13 | 基于皮尔逊的检验统计量:
14 | 
15 |
16 | 理解:n次试验中样本值落入第i个小区间Ai的频率fi/n与概率pi应很接近,当H0不真时,则fi/n与pi相差很大。在假设成立的情况下服从自由度为k-1的卡方分布。
17 |
18 | 参考【4】中给了例子,比较好理解,下面是截图:
19 | 
20 |
21 | 说明:19,34,24,10为实际测量值,括号内为计算值,比如26.2=(53/87)*43
22 | 计算卡方检验的值:
23 | 如上图3,也可以是下图专门的计算公式:
24 | 
25 |
26 | p-value确定:具体的没理解,根据参考【4】查表可以知道大概在0.001
27 |
28 |
29 | 【4】中还给出了:“从表20-14可见,T1.2和T2.2数值都<5,且总例数大于40,故宜用校正公式(20.15)检验”,可以去看看
30 |
31 | 2.代码:
32 |
33 | ```
34 | /**
35 | * @author xubo
36 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
37 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
38 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
39 | */
40 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.basic
41 |
42 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.{Matrix, Matrices, Vectors}
43 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.stat.Statistics
44 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
45 |
46 | /**
47 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
48 | */
49 | object ChiSqLearning {
50 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
51 | val vd = Vectors.dense(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
52 | val vdResult = Statistics.chiSqTest(vd)
53 | println(vd)
54 | println(vdResult)
55 | println("-------------------------------")
56 | val mtx = Matrices.dense(3, 2, Array(1, 3, 5, 2, 4, 6))
57 | val mtxResult = Statistics.chiSqTest(mtx)
58 | println(mtx)
59 | println(mtxResult)
60 | //print :方法、自由度、方法的统计量、p值
61 | println("-------------------------------")
62 | val mtx2 = Matrices.dense(2, 2, Array(19.0, 34, 24, 10.0))
63 | printChiSqTest(mtx2)
64 | printChiSqTest( Matrices.dense(2, 2, Array(26.0, 36, 7, 2.0)))
65 | // val mtxResult2 = Statistics.chiSqTest(mtx2)
66 | // println(mtx2)
67 | // println(mtxResult2)
68 | }
69 |
70 | def printChiSqTest(matrix: Matrix): Unit = {
71 | println("-------------------------------")
72 | val mtxResult2 = Statistics.chiSqTest(matrix)
73 | println(matrix)
74 | println(mtxResult2)
75 | }
76 |
77 |
78 | }
79 |
80 | ```
81 |
82 | 3.结果:
83 |
84 | ```
85 | [1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0]
86 | Chi squared test summary:
87 | method: pearson
88 | degrees of freedom = 4
89 | statistic = 3.333333333333333
90 | pValue = 0.5036682742334986
91 | No presumption against null hypothesis: observed follows the same distribution as expected..
92 | -------------------------------
93 | 1.0 2.0
94 | 3.0 4.0
95 | 5.0 6.0
96 | Chi squared test summary:
97 | method: pearson
98 | degrees of freedom = 2
99 | statistic = 0.14141414141414144
100 | pValue = 0.931734784568187
101 | No presumption against null hypothesis: the occurrence of the outcomes is statistically independent..
102 | -------------------------------
103 | -------------------------------
104 | 19.0 24.0
105 | 34.0 10.0
106 | Chi squared test summary:
107 | method: pearson
108 | degrees of freedom = 1
109 | statistic = 9.999815802502738
110 | pValue = 0.0015655588405594223
111 | Very strong presumption against null hypothesis: the occurrence of the outcomes is statistically independent..
112 | -------------------------------
113 | 26.0 7.0
114 | 36.0 2.0
115 | Chi squared test summary:
116 | method: pearson
117 | degrees of freedom = 1
118 | statistic = 4.05869675818742
119 | pValue = 0.043944401832082036
120 | Strong presumption against null hypothesis: the occurrence of the outcomes is statistically independent..
121 |
122 | ```
123 | 第四个例子可以用【4】中的校正公式,这里代码没用。
124 |
125 | 参考
126 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
127 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
128 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
129 | 【4】http://blog.csdn.net/wermnb/article/details/6628555
130 | 【5】http://baike.baidu.com/link?url=y1Ryc0tbOLSL4zULGihtY3gXRbJO26FvHw05cfFYZ01V87h9h2gF0Bl2su2uA52TWq4FGnPAblXLX2jQhFRK3K
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/3分类和回归/Spark中组件Mllib的学习36之决策树(使用variance)进行回归.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之分类篇
3 | 1解释
4 | 决策树(使用variance)进行回归
5 |
6 | 2.代码:
7 |
8 | ```
9 | /**
10 | * @author xubo
11 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
12 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
13 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
14 | */
15 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.classification
16 |
17 | import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
18 | import java.util.Date
19 |
20 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.DecisionTree
21 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.model.DecisionTreeModel
22 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
23 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
24 |
25 | /**
26 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
27 | */
28 | object DecisionTrees4ByVarianceRegression {
29 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
30 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[4]").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
31 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
32 |
33 | // Load and parse the data file.
34 | val data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(sc, "file/data/mllib/input/classification/sample_libsvm_data.txt")
35 |
36 | // Split the data into training and test sets (30% held out for testing)
37 | val splits = data.randomSplit(Array(0.7, 0.3))
38 | val (trainingData, testData) = (splits(0), splits(1))
39 |
40 | // Train a DecisionTree model.
41 | // Empty categoricalFeaturesInfo indicates all features are continuous.
42 | val categoricalFeaturesInfo = Map[Int, Int]()
43 | val impurity = "variance"
44 | val maxDepth = 5
45 | val maxBins = 32
46 |
47 | val model = DecisionTree.trainRegressor(trainingData, categoricalFeaturesInfo, impurity,
48 | maxDepth, maxBins)
49 |
50 | // Evaluate model on test instances and compute test error
51 | val labelsAndPredictions = testData.map { point =>
52 | val prediction = model.predict(point.features)
53 | (point.label, prediction)
54 | }
55 | // println("Learned classification tree model:\n" + model.toDebugString)
56 | println("data.count:" + data.count())
57 | println("trainingData.count:" + trainingData.count())
58 | println("testData.count:" + testData.count())
59 | println("model.depth:" + model.depth)
60 | println("model.numNodes:" + model.numNodes)
61 | println("model.topNode:" + model.topNode)
62 |
63 | println("labelAndPreds")
64 | labelsAndPredictions.take(10).foreach(println)
65 |
66 | val testMSE = labelsAndPredictions.map { case (v, p) => math.pow((v - p), 2) }.mean()
67 | println("Test Mean Squared Error = " + testMSE)
68 | println("Learned regression tree model:\n" + model.toDebugString)
69 |
70 | // Save and load model
71 | // val iString = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmssSSS").format(new Date())
72 | // val path = "file/data/mllib/output/classification/DecisionTreesLearning" + iString + "/result"
73 | // model.save(sc, path)
74 | // val sameModel = DecisionTreeModel.load(sc, path)
75 | // println(sameModel.algo)
76 | sc.stop
77 | }
78 | }
79 |
80 | ```
81 |
82 | 3.结果:
83 |
84 | ```
85 | data.count:100
86 | trainingData.count:65
87 | testData.count:35
88 | model.depth:2
89 | model.numNodes:5
90 | model.topNode:id = 1, isLeaf = false, predict = 0.6307692307692307 (prob = -1.0), impurity = 0.23289940828402367, split = Some(Feature = 434, threshold = 0.0, featureType = Continuous, categories = List()), stats = Some(gain = 0.2181301775147929, impurity = 0.23289940828402367, left impurity = 0.0384, right impurity = 0.0)
91 | labelAndPreds
92 | (1.0,1.0)
93 | (0.0,0.0)
94 | (1.0,1.0)
95 | (0.0,0.0)
96 | (0.0,0.0)
97 | (1.0,1.0)
98 | (0.0,0.0)
99 | (0.0,0.0)
100 | (1.0,1.0)
101 | (1.0,1.0)
102 | Test Mean Squared Error = 0.0
103 | Learned regression tree model:
104 | DecisionTreeModel regressor of depth 2 with 5 nodes
105 | If (feature 434 <= 0.0)
106 | If (feature 100 <= 165.0)
107 | Predict: 0.0
108 | Else (feature 100 > 165.0)
109 | Predict: 1.0
110 | Else (feature 434 > 0.0)
111 | Predict: 1.0
112 | ```
113 |
114 | 参考
115 |
116 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
117 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
118 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/1数据类型/Spark中组件Mllib的学习14之从文本中读取带标签的数据,生成带label的向量.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之基础概念篇
3 | 1解释
4 | 从文本中读取带标签的数据,生成带label的向量
5 |
6 | 2.代码:
7 |
8 | ```
9 | /**
10 | * @author xubo
11 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
12 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
13 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
14 | */
15 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.basic
16 |
17 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
18 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkContext, SparkConf}
19 |
20 | /**
21 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
22 | * 从文本中读取带标签的数据
23 | */
24 | object LabeledPointLoadlibSVMFile {
25 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
26 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
27 | // println(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
28 | //设置环境变量
29 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
30 |
31 | val mu = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(sc, "file/data/mllib/input/basic/sample_libsvm_data.txt") //读取文件
32 | mu.foreach(println) //打印内容
33 |
34 | sc.stop
35 | }
36 | }
37 |
38 | ```
39 | 数据:
40 | 一行
41 |
42 | ```
43 | 0 128:51 129:159 130:253 131:159 132:50 155:48 156:238 157:252 158:252 159:252 160:237 182:54 183:227 184:253 185:252 186:239 187:233 188:252 189:57 190:6 208:10 209:60 210:224 211:252 212:253 213:252 214:202 215:84 216:252 217:253 218:122 236:163 237:252 238:252 239:252 240:253 241:252 242:252 243:96 244:189 245:253 246:167 263:51 264:238 265:253 266:253 267:190 268:114 269:253 270:228 271:47 272:79 273:255 274:168 290:48 291:238 292:252 293:252 294:179 295:12 296:75 297:121 298:21 301:253 302:243 303:50 317:38 318:165 319:253 320:233 321:208 322:84 329:253 330:252 331:165 344:7 345:178 346:252 347:240 348:71 349:19 350:28 357:253 358:252 359:195 372:57 373:252 374:252 375:63 385:253 386:252 387:195 400:198 401:253 402:190 413:255 414:253 415:196 427:76 428:246 429:252 430:112 441:253 442:252 443:148 455:85 456:252 457:230 458:25 467:7 468:135 469:253 470:186 471:12 483:85 484:252 485:223 494:7 495:131 496:252 497:225 498:71 511:85 512:252 513:145 521:48 522:165 523:252 524:173 539:86 540:253 541:225 548:114 549:238 550:253 551:162 567:85 568:252 569:249 570:146 571:48 572:29 573:85 574:178 575:225 576:253 577:223 578:167 579:56 595:85 596:252 597:252 598:252 599:229 600:215 601:252 602:252 603:252 604:196 605:130 623:28 624:199 625:252 626:252 627:253 628:252 629:252 630:233 631:145 652:25 653:128 654:252 655:253 656:252 657:141 658:37
44 | 。。。
45 |
46 | ```
47 |
48 | 3.结果:
49 |
50 | ```
51 | (0.0,(692,[127,128,129,130,131,154,155,156,157,158,159,181,182,183,184,185,186,187,188,189,207,208,209,210,211,212,213,214,215,216,217,235,236,237,238,239,240,241,242,243,244,245,262,263,264,265,266,267,268,269,270,271,272,273,289,290,291,292,293,294,295,296,297,300,301,302,316,317,318,319,320,321,328,329,330,343,344,345,346,347,348,349,356,357,358,371,372,373,374,384,385,386,399,400,401,412,413,414,426,427,428,429,440,441,442,454,455,456,457,466,467,468,469,470,482,483,484,493,494,495,496,497,510,511,512,520,521,522,523,538,539,540,547,548,549,550,566,567,568,569,570,571,572,573,574,575,576,577,578,594,595,596,597,598,599,600,601,602,603,604,622,623,624,625,626,627,628,629,630,651,652,653,654,655,656,657],[51.0,159.0,253.0,159.0,50.0,48.0,238.0,252.0,252.0,252.0,237.0,54.0,227.0,253.0,252.0,239.0,233.0,252.0,57.0,6.0,10.0,60.0,224.0,252.0,253.0,252.0,202.0,84.0,252.0,253.0,122.0,163.0,252.0,252.0,252.0,253.0,252.0,252.0,96.0,189.0,253.0,167.0,51.0,238.0,253.0,253.0,190.0,114.0,253.0,228.0,47.0,79.0,255.0,168.0,48.0,238.0,252.0,252.0,179.0,12.0,75.0,121.0,21.0,253.0,243.0,50.0,38.0,165.0,253.0,233.0,208.0,84.0,253.0,252.0,165.0,7.0,178.0,252.0,240.0,71.0,19.0,28.0,253.0,252.0,195.0,57.0,252.0,252.0,63.0,253.0,252.0,195.0,198.0,253.0,190.0,255.0,253.0,196.0,76.0,246.0,252.0,112.0,253.0,252.0,148.0,85.0,252.0,230.0,25.0,7.0,135.0,253.0,186.0,12.0,85.0,252.0,223.0,7.0,131.0,252.0,225.0,71.0,85.0,252.0,145.0,48.0,165.0,252.0,173.0,86.0,253.0,225.0,114.0,238.0,253.0,162.0,85.0,252.0,249.0,146.0,48.0,29.0,85.0,178.0,225.0,253.0,223.0,167.0,56.0,85.0,252.0,252.0,252.0,229.0,215.0,252.0,252.0,252.0,196.0,130.0,28.0,199.0,252.0,252.0,253.0,252.0,252.0,233.0,145.0,25.0,128.0,252.0,253.0,252.0,141.0,37.0]))
52 | 。。。
53 | ```
54 |
55 | 参考
56 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
57 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
58 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/9评估度量/Spark中组件Mllib的学习70之对多类分类结果进行评估Multiclass classification.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | 对多分类结果进行评估
9 |
10 | 
11 | 
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 | 2.代码:
16 |
17 | /**
18 | * @author xubo
19 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
20 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
21 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
22 | */
23 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.EvaluationMetrics
24 |
25 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
26 |
27 | /**
28 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
29 | */
30 | class MulticlassClassificationFunSuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
31 | test("testFunSuite") {
32 |
33 |
34 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS
35 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.evaluation.MulticlassMetrics
36 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint
37 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
38 |
39 | // Load training data in LIBSVM format
40 | val data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(sc, "file/data/mllib/input/mllibFromSpark/sample_multiclass_classification_data.txt")
41 |
42 | // Split data into training (60%) and test (40%)
43 | val Array(training, test) = data.randomSplit(Array(0.6, 0.4), seed = 11L)
44 | training.cache()
45 |
46 | // Run training algorithm to build the model
47 | val model = new LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS()
48 | .setNumClasses(3)
49 | .run(training)
50 |
51 | // Compute raw scores on the test set
52 | val predictionAndLabels = test.map { case LabeledPoint(label, features) =>
53 | val prediction = model.predict(features)
54 | (prediction, label)
55 | }
56 |
57 | // Instantiate metrics object
58 | val metrics = new MulticlassMetrics(predictionAndLabels)
59 |
60 | // Confusion matrix
61 | println("Confusion matrix:")
62 | println(metrics.confusionMatrix)
63 |
64 | // Overall Statistics
65 | val precision = metrics.precision
66 | val recall = metrics.recall // same as true positive rate
67 | val f1Score = metrics.fMeasure
68 | println("Summary Statistics")
69 | println(s"Precision = $precision")
70 | println(s"Recall = $recall")
71 | println(s"F1 Score = $f1Score")
72 |
73 | // Precision by label
74 | val labels = metrics.labels
75 | labels.foreach { l =>
76 | println(s"Precision($l) = " + metrics.precision(l))
77 | }
78 |
79 | // Recall by label
80 | labels.foreach { l =>
81 | println(s"Recall($l) = " + metrics.recall(l))
82 | }
83 |
84 | // False positive rate by label
85 | labels.foreach { l =>
86 | println(s"FPR($l) = " + metrics.falsePositiveRate(l))
87 | }
88 |
89 | // F-measure by label
90 | labels.foreach { l =>
91 | println(s"F1-Score($l) = " + metrics.fMeasure(l))
92 | }
93 |
94 | // Weighted stats
95 | println(s"Weighted precision: ${metrics.weightedPrecision}")
96 | println(s"Weighted recall: ${metrics.weightedRecall}")
97 | println(s"Weighted F1 score: ${metrics.weightedFMeasure}")
98 | println(s"Weighted false positive rate: ${metrics.weightedFalsePositiveRate}")
99 |
100 |
101 | }
102 | }
103 |
104 |
105 | 3.结果:
106 |
107 | Confusion matrix:
108 | 11.0 0.0 1.0
109 | 0.0 12.0 0.0
110 | 10.0 0.0 16.0
111 | Summary Statistics
112 | Precision = 0.78
113 | Recall = 0.78
114 | F1 Score = 0.78
115 | Precision(0.0) = 0.5238095238095238
116 | Precision(1.0) = 1.0
117 | Precision(2.0) = 0.9411764705882353
118 | Recall(0.0) = 0.9166666666666666
119 | Recall(1.0) = 1.0
120 | Recall(2.0) = 0.6153846153846154
121 | FPR(0.0) = 0.2631578947368421
122 | FPR(1.0) = 0.0
123 | FPR(2.0) = 0.041666666666666664
124 | F1-Score(0.0) = 0.6666666666666667
125 | F1-Score(1.0) = 1.0
126 | F1-Score(2.0) = 0.744186046511628
127 | Weighted precision: 0.8551260504201681
128 | Weighted recall: 0.78
129 | Weighted F1 score: 0.7869767441860466
130 | Weighted false positive rate: 0.08482456140350877
131 |
132 |
133 |
134 | 参考
135 |
136 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
137 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
138 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
139 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
140 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
141 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/5聚类/Spark中组件Mllib的学习48之流式k均值(Streaming kmeans).md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | 流式K均值
9 |
10 | 当数据以流式到达,就需要动态预测分类,每当新数据到来时要更新模型。MLlib提供了流式k均值聚类,该方法使用参数来控制数据的衰减。这个算法使用mini-batch k均值更新规则的一种泛化版本。对于每一批数据,将所有点赋给最近的簇,计算新的簇中心,然后使用下面的方法更新簇:
11 | 
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 | 2.代码:
16 |
17 | test("accuracy for single center and equivalence to grand average") {
18 | // set parameters
19 | val numBatches = 10
20 | val numPoints = 50
21 | val k = 1
22 | val d = 5
23 | val r = 0.1
24 |
25 | // create model with one cluster
26 | val model = new StreamingKMeans()
27 | .setK(1)
28 | .setDecayFactor(1.0)
29 | .setInitialCenters(Array(Vectors.dense(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0)), Array(0.0))
30 |
31 | // generate random data for k-means
32 | val (input, centers) = StreamingKMeansDataGenerator(numPoints, numBatches, k, d, r, 42)
33 |
34 | // setup and run the model training
35 | ssc = setupStreams(input, (inputDStream: DStream[Vector]) => {
36 | model.trainOn(inputDStream)
37 | inputDStream.count()
38 | })
39 | runStreams(ssc, numBatches, numBatches)
40 |
41 | // estimated center should be close to true center
42 | assert(centers(0) ~== model.latestModel().clusterCenters(0) absTol 1E-1)
43 | /** ****************add by xubo 20160613 *************/
44 | println("model.latestModel().clusterCenters:")
45 | model.latestModel().clusterCenters.foreach(println)
46 | println("model.latestModel().clusterWeights:")
47 | model.latestModel().clusterWeights.foreach(println)
48 |
49 | /** ****************add by xubo 20160613 *************/
50 | // estimated center from streaming should exactly match the arithmetic mean of all data points
51 | // because the decay factor is set to 1.0
52 | val grandMean =
53 | input.flatten.map(x => x.toBreeze).reduce(_ + _) / (numBatches * numPoints).toDouble
54 | assert(model.latestModel().clusterCenters(0) ~== Vectors.dense(grandMean.toArray) absTol 1E-5)
55 | /** ****************add by xubo 20160613 *************/
56 | //println("input")
57 | //input.foreach(println)
58 | println("grandMean")
59 | grandMean.foreach(println)
60 |
61 | /** ****************add by xubo 20160613 *************/
62 | }
63 |
64 |
65 |
66 | 3.结果:
67 |
68 | model.latestModel().clusterCenters:
69 | [-0.4725511979691583,0.9644503899125422,-1.668776373542808,1.2721254429935838,0.37815209739836425]
70 | model.latestModel().clusterWeights:
71 | 500.0
72 | grandMean
73 | -0.4725511979691581
74 | 0.9644503899125427
75 | -1.6687763735428087
76 | 1.2721254429935853
77 | 0.37815209739836464
78 |
79 | input数据量有点多,就没有放上来了。
80 |
81 | 参考
82 |
83 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
84 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
85 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
86 |
87 |
88 | 附录:
89 |
90 | /**
91 | * @author xubo
92 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
93 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
94 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
95 | */
96 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.clustering.kmeans
97 |
98 | import org.apache.spark.SparkConf
99 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
100 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint
101 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.clustering.StreamingKMeans
102 | import org.apache.spark.streaming.{Seconds, StreamingContext}
103 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
104 |
105 | /**
106 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
107 | * 需要集群运行,目前没有运行测试
108 | */
109 | class StreamingKmeansFromWebSuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
110 | test("testFunSuite") {
111 | val conf = new SparkConf()
112 | .setMaster("local[4]")
113 | .setAppName("SparkLearningTest")
114 | val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf, Seconds(1))
115 | val trainingData = ssc.textFileStream("file/data/mllib/input/trainingDic").map(Vectors.parse)
116 | val testData = ssc.textFileStream("file/data/mllib/input/testingDic").map(LabeledPoint.parse)
117 | val numDimensions = 3
118 | val numClusters = 2
119 | val model = new StreamingKMeans()
120 | .setK(numClusters)
121 | .setDecayFactor(1.0)
122 | .setRandomCenters(numDimensions, 0.0)
123 | model.trainOn(trainingData)
124 | model.predictOnValues(testData.map(lp => (lp.label, lp.features))).print()
125 |
126 | ssc.start()
127 | ssc.awaitTermination()
128 | }
129 | }
130 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/3分类和回归/Spark中组件Mllib的学习33之决策树(使用Gini).md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之分类篇
3 | 1解释
4 | 决策树:Decision Trees
5 | 请见【4】【5】
6 | 数据每次是随机划分,所以准确率每次不一定
7 |
8 | 2.代码:
9 |
10 | ```
11 | /**
12 | * @author xubo
13 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
14 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
15 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
16 | */
17 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.classification
18 |
19 | import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
20 | import java.util.Date
21 |
22 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.DecisionTree
23 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.model.DecisionTreeModel
24 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
25 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
26 |
27 | /**
28 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
29 | */
30 | object DecisionTreesLearning {
31 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
32 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[4]").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
33 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
34 |
35 | // Load and parse the data file.
36 | val data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(sc, "file/data/mllib/input/classification/sample_libsvm_data.txt")
37 | // Split the data into training and test sets (30% held out for testing)
38 | val splits = data.randomSplit(Array(0.7, 0.3))
39 | val (trainingData, testData) = (splits(0), splits(1))
40 |
41 | // Train a DecisionTree model.
42 | // Empty categoricalFeaturesInfo indicates all features are continuous.
43 | val numClasses = 2
44 | val categoricalFeaturesInfo = Map[Int, Int]()
45 | val impurity = "gini"
46 | val maxDepth = 5
47 | val maxBins = 32
48 |
49 | val model = DecisionTree.trainClassifier(trainingData, numClasses, categoricalFeaturesInfo,
50 | impurity, maxDepth, maxBins)
51 |
52 | // Evaluate model on test instances and compute test error
53 | val labelAndPreds = testData.map { point =>
54 | val prediction = model.predict(point.features)
55 | (point.label, prediction)
56 | }
57 | val testErr = labelAndPreds.filter(r => r._1 != r._2).count.toDouble / testData.count()
58 | println("Test Error = " + testErr)
59 | println("Learned classification tree model:\n" + model.toDebugString)
60 | println("data.count:" + data.count())
61 | println("trainingData.count:" + trainingData.count())
62 | println("testData.count:" + testData.count())
63 | println("model.depth:"+model.depth)
64 | println("model.numNodes:"+model.numNodes)
65 | println("model.topNode:"+model.topNode)
66 |
67 | println("labelAndPreds")
68 | labelAndPreds.take(30).foreach(println)
69 | // Save and load model
70 | // val iString = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmssSSS").format(new Date())
71 | // val path = "file/data/mllib/output/classification/DecisionTreesLearning" + iString + "/result"
72 | // model.save(sc, path)
73 | // val sameModel = DecisionTreeModel.load(sc, path)
74 | // println(sameModel.algo)
75 | sc.stop
76 | }
77 | }
78 |
79 | ```
80 |
81 | 3.结果:
82 |
83 | ```
84 | Test Error = 0.0
85 | Learned classification tree model:
86 | DecisionTreeModel classifier of depth 2 with 5 nodes
87 | If (feature 434 <= 0.0)
88 | If (feature 100 <= 165.0)
89 | Predict: 0.0
90 | Else (feature 100 > 165.0)
91 | Predict: 1.0
92 | Else (feature 434 > 0.0)
93 | Predict: 1.0
94 |
95 | data.count:100
96 | trainingData.count:78
97 | testData.count:22
98 | model.depth:2
99 | model.numNodes:5
100 | model.topNode:id = 1, isLeaf = false, predict = 1.0 (prob = 0.5384615384615384), impurity = 0.49704142011834324, split = Some(Feature = 434, threshold = 0.0, featureType = Continuous, categories = List()), stats = Some(gain = 0.47209339517031834, impurity = 0.49704142011834324, left impurity = 0.05259313367421467, right impurity = 0.0)
101 | labelAndPreds
102 | (0.0,0.0)
103 | (0.0,0.0)
104 | (1.0,1.0)
105 | (1.0,1.0)
106 | (1.0,1.0)
107 | (0.0,0.0)
108 | (1.0,1.0)
109 | (0.0,0.0)
110 | (1.0,1.0)
111 | (0.0,0.0)
112 | (1.0,1.0)
113 | (1.0,1.0)
114 | (0.0,0.0)
115 | (1.0,1.0)
116 | (1.0,1.0)
117 | (1.0,1.0)
118 | (0.0,0.0)
119 | (1.0,1.0)
120 | (1.0,1.0)
121 | (1.0,1.0)
122 | (1.0,1.0)
123 | (1.0,1.0)
124 | ```
125 |
126 | 参考
127 |
128 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
129 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
130 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
131 | 【4】http://blog.csdn.net/dark_scope/article/details/13168827
132 | 【5】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-decision-tree.html
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/3分类和回归/Spark中组件Mllib的学习32之朴素贝叶斯分类器(伯努利朴素贝叶斯)_.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之分类篇
3 | 1解释
4 |
5 | (1) 朴素贝叶斯分类器种类
6 |
7 | 在把训练集中的每个文档向量化的过程中,存在两个模型。一个是统计词在文档中出现的次数(多项式模型);一个是统计词是否在文档中出现过(柏努利模型)
8 | 目前mllib只支持多项式朴素贝叶斯和伯努利贝叶斯(spark-1.5.2),不支持高斯朴素贝叶斯。
9 |
10 | 根据:
11 |
12 | ```
13 | /**
14 | * Trains a Naive Bayes model given an RDD of `(label, features)` pairs.
15 | *
16 | * This is the Multinomial NB ([[http://tinyurl.com/lsdw6p]]) which can handle all kinds of
17 | * discrete data. For example, by converting documents into TF-IDF vectors, it can be used for
18 | * document classification. By making every vector a 0-1 vector, it can also be used as
19 | * Bernoulli NB ([[http://tinyurl.com/p7c96j6]]). The input feature values must be nonnegative.
20 | */
21 | @Since("0.9.0")
22 | class NaiveBayes private (
23 | private var lambda: Double,
24 | private var modelType: String) extends Serializable with Logging {
25 |
26 | import NaiveBayes.{Bernoulli, Multinomial}
27 |
28 | @Since("1.4.0")
29 | def this(lambda: Double) = this(lambda, NaiveBayes.Multinomial)
30 |
31 | ```
32 |
33 | 三种朴素贝叶斯分类器都在【4】中有提到
34 |
35 | (2)伯努利贝叶斯分类器
36 | 
37 | 参考【5】
38 |
39 | 2.代码:
40 |
41 | ```
42 | /**
43 | * @author xubo
44 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
45 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
46 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
47 | */
48 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.classification
49 |
50 | import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
51 | import java.util.Date
52 |
53 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.NaiveBayes._
54 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.{NaiveBayes, NaiveBayesModel}
55 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
56 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint
57 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkException, SparkConf, SparkContext}
58 |
59 | /**
60 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
61 | * From:NaiveBayesSuite.scala in spark 1.5.2 sources
62 | * another examples:NaiveBayesSuite test("Naive Bayes Bernoulli")
63 | */
64 | object BernoulliNaiveBayesLearning {
65 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
66 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[4]").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
67 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
68 |
69 | val badTrain = Seq(
70 | LabeledPoint(1.0, Vectors.dense(1.0)),
71 | // LabeledPoint(0.0, Vectors.dense(2.0)),
72 | LabeledPoint(1.0, Vectors.dense(1.0)),
73 | LabeledPoint(1.0, Vectors.dense(0.0)))
74 |
75 |
76 | val model1 = NaiveBayes.train(sc.makeRDD(badTrain, 2), 1.0, Bernoulli)
77 | println("model1:")
78 | println(model1)
79 | sc.makeRDD(badTrain, 2).foreach(println)
80 |
81 | val okTrain = Seq(
82 | LabeledPoint(1.0, Vectors.dense(1.0)),
83 | LabeledPoint(0.0, Vectors.dense(0.0)),
84 | LabeledPoint(1.0, Vectors.dense(1.0)),
85 | LabeledPoint(1.0, Vectors.dense(1.0)),
86 | LabeledPoint(0.0, Vectors.dense(0.0)),
87 | LabeledPoint(1.0, Vectors.dense(1.0)),
88 | LabeledPoint(1.0, Vectors.dense(1.0))
89 | )
90 |
91 | val badPredict = Seq(
92 | Vectors.dense(1.0),
93 | // Vectors.dense(2.0),
94 | Vectors.dense(1.0),
95 | Vectors.dense(0.0))
96 |
97 | val model = NaiveBayes.train(sc.makeRDD(okTrain, 2), 1.0, Bernoulli)
98 | // intercept[SparkException] {
99 | val pre2 = model.predict(sc.makeRDD(badPredict, 2)).collect()
100 | // }
101 | println("model2:")
102 | sc.makeRDD(okTrain, 2).foreach(println)
103 | println("predict data:")
104 | sc.makeRDD(badPredict, 2).foreach(println)
105 | println(model)
106 | println("predict result:")
107 | pre2.foreach(println)
108 |
109 | sc.stop
110 | }
111 | }
112 |
113 | ```
114 |
115 | 3.结果:
116 |
117 | ```
118 | model1:
119 | org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.NaiveBayesModel@79d63340
120 | (1.0,[1.0])
121 | (1.0,[1.0])
122 | (1.0,[0.0])
123 | model2:
124 | (1.0,[1.0])
125 | (0.0,[0.0])
126 | (1.0,[1.0])
127 | (1.0,[1.0])
128 | (0.0,[0.0])
129 | (1.0,[1.0])
130 | (1.0,[1.0])
131 | predict data:
132 | [1.0]
133 | [0.0]
134 | [1.0]
135 | org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.NaiveBayesModel@3eda0bed
136 | predict result:
137 | 1.0
138 | 1.0
139 | 0.0
140 | ```
141 |
142 | 参考
143 |
144 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
145 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
146 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
147 | 【4】http://www.letiantian.me/2014-10-12-three-models-of-naive-nayes/
148 | 【5】http://blog.csdn.net/xlinsist/article/details/51264829
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/3分类和回归/Spark中组件Mllib的学习31之朴素贝叶斯分类器(多项式朴素贝叶斯).md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之分类篇
3 | 1 解释
4 | (1) 贝叶斯:
5 | 
6 |
7 | 推广:
8 | 
9 |
10 | (2)朴素贝叶斯:
11 |
12 | 为了简化计算,朴素贝叶斯算法做了一假设:“朴素的认为各个特征相互独立”。这么一来,上式的分子就简化成了:
13 |
14 | P(C)*P(F1|C)*P(F2|C)...P(Fn|C)。
15 |
16 | 这样简化过后,计算起来就方便多了。
17 |
18 | 朴素贝叶斯分类器 naive Bayes有:
19 |
20 | 多项式朴素贝叶斯( multinomial naive Bayes )和伯努利朴素贝叶斯( Bernoulli naive Bayes)
21 | 要注意的是,MultinomialNB这个分类器以出现次数作为特征值,使用的TF-IDF也能符合这类分布。
22 | 其他的朴素贝叶斯分类器如GaussianNB适用于高斯分布(正态分布)的特征,而BernoulliNB适用于伯努利分布(二值分布)的特征。
23 |
24 | 贝叶斯理论是处理不确定性信息的重要工具。作为一种不确定性推理方法,它基于概率和统计理论,具有坚实的数学基础,贝叶斯网络在处理不确定信息的智能化系统中已经得到了广泛的应用,并且成功地用于医疗诊断、统计决策、专家系统等领域。这些成功的应用,充分说明了贝叶斯技术是一种强有力的不确定性推理方法。贝叶斯分类器分为两种:一种是朴素贝叶斯分类器,另一种贝叶斯网分类器。
25 |
26 | 朴素贝叶斯分类器是一种有监督的学习方法,其假定一个属性的值对给定类的影响而独立于其他属性值,此限制条件较强,现实中往往不能满足,但是朴素贝叶斯分类器取得了较大的成功,表现出高精度和高效率,具有最小的误分类率,耗时开销小的特征。贝叶斯网分类器是一种有向无环图模型,能够表示属性集间的因果依赖。通过提供图形化的方法来表示知识,以条件概率分布表表示属性依赖关系的强弱,将先验信息和样本知识有机结合起来;通过贝叶斯概率对某一事件未来可能发生的概率进行估计,克服了基于规则的系统所具有的许多概念和计算上的困难。其优点是具有很强的学习和推理能力,能够很好地利用先验知识,缺点是对发生频率较低的事件预测效果不好,且推理与学习过程是NP—Hard的。
27 |
28 | 具体请看参考【4】【5】
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 | 2.代码:
33 |
34 | ```
35 | /**
36 | * @author xubo
37 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
38 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
39 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
40 | */
41 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.classification
42 |
43 | import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
44 | import java.util.Date
45 |
46 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.{LogisticRegressionModel, NaiveBayes, NaiveBayesModel}
47 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
48 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint
49 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
50 |
51 | /**
52 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
53 | */
54 | object NaiveBayesLearning {
55 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
56 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[4]").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
57 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
58 |
59 |
60 | val data = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/classification/sample_naive_bayes_data.txt")
61 | val parsedData = data.map { line =>
62 | val parts = line.split(',')
63 | LabeledPoint(parts(0).toDouble, Vectors.dense(parts(1).split(' ').map(_.toDouble)))
64 | }
65 | // Split data into training (60%) and test (40%).
66 | val splits = parsedData.randomSplit(Array(0.6, 0.4), seed = 11L)
67 | val training = splits(0)
68 | val test = splits(1)
69 |
70 | val model = NaiveBayes.train(training, lambda = 1.0, modelType = "multinomial")
71 |
72 | val predictionAndLabel = test.map(p => (model.predict(p.features), p.label))
73 | val accuracy = 1.0 * predictionAndLabel.filter(x => x._1 == x._2).count() / test.count()
74 |
75 |
76 | println("result:")
77 | println("training.count:" + training.count())
78 | println("test.count:" + test.count())
79 | println("model.modelType:" + model.modelType)
80 | println("accuracy:" + accuracy)
81 | predictionAndLabel.take(10).foreach(println)
82 | // model.
83 |
84 | // Save and load model
85 | val iString = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmssSSS").format(new Date())
86 | val path = "file/data/mllib/output/classification/NaiveBayesModel" + iString + "/result"
87 | model.save(sc, path)
88 | val sameModel = NaiveBayesModel.load(sc, path)
89 | println(sameModel.modelType)
90 |
91 | println("end")
92 | // model.save(sc, "myModelPath")
93 | // val sameModel = NaiveBayesModel.load(sc, "myModelPath")
94 |
95 | sc.stop
96 | }
97 | }
98 |
99 | ```
100 |
101 | 3.结果:
102 |
103 | ```
104 | result:
105 | training.count:10
106 | test.count:2
107 | model.modelType:multinomial
108 | accuracy:1.0
109 | (1.0,1.0)
110 | (2.0,2.0)
111 | SLF4J: Failed to load class "org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder".
112 | SLF4J: Defaulting to no-operation (NOP) logger implementation
113 | SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#StaticLoggerBinder for further details.
114 | 2016-05-24 23:00:45 WARN ParquetRecordReader:193 - Can not initialize counter due to context is not a instance of TaskInputOutputContext, but is org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.TaskAttemptContextImpl
115 | multinomial
116 | end
117 | ```
118 | 准确率为1
119 |
120 |
121 | 参考
122 |
123 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
124 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
125 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
126 | 【4】http://blog.csdn.net/sulliy/article/details/6629201
127 | 【5】http://blog.csdn.net/lsldd/article/details/41542107
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/3分类和回归/Spark中组件Mllib的学习37之随机森林(Gini)进行分类.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之分类篇
3 | 1解释
4 | 随机森林:RandomForest
5 | 大概思想就是生成多个决策树,都单独训练;如果来了一个数据,用各个决策树进行回归预测,如果是非连续结果,则取最多个数的值;如果连续,则取多个决策树结果的平均值。
6 |
7 |
8 | 2.代码:
9 |
10 | ```
11 | /**
12 | * @author xubo
13 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
14 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
15 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
16 | */
17 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.classification
18 |
19 | import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
20 | import java.util.Date
21 |
22 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.RandomForest
23 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.model.RandomForestModel
24 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
25 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
26 |
27 | /**
28 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
29 | */
30 | object RandomForest2Spark {
31 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
32 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[4]").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
33 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
34 |
35 | // Load and parse the data file.
36 | val data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(sc, "file/data/mllib/input/classification/sample_libsvm_data.txt")
37 |
38 | // Split the data into training and test sets (30% held out for testing)
39 | val splits = data.randomSplit(Array(0.7, 0.3))
40 | val (trainingData, testData) = (splits(0), splits(1))
41 |
42 | // Train a RandomForest model.
43 | // Empty categoricalFeaturesInfo indicates all features are continuous.
44 | val numClasses = 2
45 | val categoricalFeaturesInfo = Map[Int, Int]()
46 | val numTrees = 3 // Use more in practice.
47 | val featureSubsetStrategy = "auto" // Let the algorithm choose.
48 | val impurity = "gini"
49 | val maxDepth = 4
50 | val maxBins = 32
51 |
52 | val model = RandomForest.trainClassifier(trainingData, numClasses, categoricalFeaturesInfo,
53 | numTrees, featureSubsetStrategy, impurity, maxDepth, maxBins)
54 |
55 | // Evaluate model on test instances and compute test error
56 | val labelAndPreds = testData.map { point =>
57 | val prediction = model.predict(point.features)
58 | (point.label, prediction)
59 | }
60 | val testErr = labelAndPreds.filter(r => r._1 != r._2).count.toDouble / testData.count()
61 | println("Test Error = " + testErr)
62 | println("Learned classification forest model:\n" + model.toDebugString)
63 |
64 |
65 | // println("Learned classification tree model:\n" + model.toDebugString)
66 | println("data.count:" + data.count())
67 | println("trainingData.count:" + trainingData.count())
68 | println("testData.count:" + testData.count())
69 | println("model.algo:" + model.algo)
70 | println("model.trees:" + model.trees)
71 |
72 | println("labelAndPreds")
73 | labelAndPreds.take(10).foreach(println)
74 |
75 | // Save and load model
76 | // val iString = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmssSSS").format(new Date())
77 | // val path = "file/data/mllib/output/classification/RandomForestModel" + iString + "/result"
78 | // model.save(sc, path)
79 | // val sameModel = RandomForestModel.load(sc, path)
80 | // println(sameModel.algo)
81 | sc.stop
82 | }
83 | }
84 |
85 | ```
86 |
87 | 3.结果:
88 |
89 | ```
90 | Test Error = 0.04
91 | Learned classification forest model:
92 | TreeEnsembleModel classifier with 3 trees
93 |
94 | Tree 0:
95 | If (feature 511 <= 0.0)
96 | If (feature 434 <= 0.0)
97 | Predict: 0.0
98 | Else (feature 434 > 0.0)
99 | Predict: 1.0
100 | Else (feature 511 > 0.0)
101 | Predict: 0.0
102 | Tree 1:
103 | If (feature 490 <= 31.0)
104 | Predict: 0.0
105 | Else (feature 490 > 31.0)
106 | Predict: 1.0
107 | Tree 2:
108 | If (feature 302 <= 0.0)
109 | If (feature 461 <= 0.0)
110 | If (feature 208 <= 107.0)
111 | Predict: 1.0
112 | Else (feature 208 > 107.0)
113 | Predict: 0.0
114 | Else (feature 461 > 0.0)
115 | Predict: 1.0
116 | Else (feature 302 > 0.0)
117 | Predict: 0.0
118 |
119 | data.count:100
120 | trainingData.count:75
121 | testData.count:25
122 | model.algo:Classification
123 | model.trees:[Lorg.apache.spark.mllib.tree.model.DecisionTreeModel;@753c93d5
124 | labelAndPreds
125 | (1.0,1.0)
126 | (1.0,0.0)
127 | (0.0,0.0)
128 | (0.0,0.0)
129 | (1.0,1.0)
130 | (0.0,0.0)
131 | (1.0,1.0)
132 | (1.0,1.0)
133 | (1.0,1.0)
134 | (0.0,0.0)
135 | ```
136 |
137 | 参考
138 |
139 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
140 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
141 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/3分类和回归/Spark中组件Mllib的学习23之随机梯度下降(SGD).md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之回归分析篇
3 | 1解释
4 | SGD(Stochastic Gradient Descent-随机梯度下降)
5 |
6 | 
7 |
8 | sgd解决了梯度下降的两个问题: 收敛速度慢和陷入局部最优。 具体的介绍请见【4】、【5】和【6】
9 |
10 | 背景:
11 |
12 | 梯度下降法的缺点是:
13 | 靠近极小值时速度减慢。
14 | 直线搜索可能会产生一些问题。
15 | 可能会'之字型'地下降。
16 |
17 | ```
18 | 随机梯度下降法stochastic gradient descent,也叫增量梯度下降
19 | 由于梯度下降法收敛速度慢,而随机梯度下降法会快很多
20 |
21 | –根据某个单独样例的误差增量计算权值更新,得到近似的梯度下降搜索(随机取一个样例)
22 |
23 | –可以看作为每个单独的训练样例定义不同的误差函数
24 |
25 | –在迭代所有训练样例时,这些权值更新的序列给出了对于原来误差函数的梯度下降的一个合理近似
26 |
27 | –通过使下降速率的值足够小,可以使随机梯度下降以任意程度接近于真实梯度下降
28 |
29 | •标准梯度下降和随机梯度下降之间的关键区别
30 |
31 | –标准梯度下降是在权值更新前对所有样例汇总误差,而随机梯度下降的权值是通过考查某个训练样例来更新的
32 |
33 | –在标准梯度下降中,权值更新的每一步对多个样例求和,需要更多的计算
34 |
35 | –标准梯度下降,由于使用真正的梯度,标准梯度下降对于每一次权值更新经常使用比随机梯度下降大的步长
36 |
37 | –如果标准误差曲面有多个局部极小值,随机梯度下降有时可能避免陷入这些局部极小值中
38 | ```
39 |
40 | 2.代码:
41 |
42 | ```
43 | /**
44 | * @author xubo
45 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
46 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
47 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
48 | */
49 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.regression
50 |
51 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
52 |
53 | import scala.collection.mutable.HashMap
54 |
55 | /**
56 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
57 | */
58 | object SGDLearning {
59 | val data = HashMap[Int, Int]()
60 |
61 | //创建数据集
62 | def getData(): HashMap[Int, Int] = {
63 | //生成数据集内容
64 | for (i <- 1 to 50) {
65 | //创建50个数据
66 | data += (i -> (20 * i)) //写入公式y=2x
67 | }
68 | data //返回数据集
69 | }
70 |
71 | var θ: Double = 0
72 | //第一步假设θ为0
73 | var α: Double = 0.1 //设置步进系数
74 |
75 | def sgd(x: Double, y: Double) = {
76 | //设置迭代公式
77 | θ = θ - α * ((θ * x) - y) //迭代公式
78 | }
79 |
80 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
81 | val dataSource = getData() //获取数据集
82 | println("data:")
83 | dataSource.foreach(each => print(each + " "))
84 | println("\nresult:")
85 | var num = 1;
86 | dataSource.foreach(myMap => {
87 | //开始迭代
88 | println(num + ":" + θ+" ("+myMap._1+","+myMap._2+")")
89 | sgd(myMap._1, myMap._2) //输入数据
90 | num = num + 1;
91 | })
92 | println("最终结果θ值为 " + θ) //显示结果
93 | }
94 | }
95 |
96 | ```
97 |
98 | 3.结果:
99 |
100 | ```
101 | data:
102 | (23,460) (50,1000) (32,640) (41,820) (17,340) (8,160) (35,700) (44,880) (26,520) (11,220) (29,580) (38,760) (47,940) (20,400) (2,40) (5,100) (14,280) (46,920) (40,800) (49,980) (4,80) (13,260) (22,440) (31,620) (16,320) (7,140) (43,860) (25,500) (34,680) (10,200) (37,740) (1,20) (19,380) (28,560) (45,900) (27,540) (36,720) (18,360) (9,180) (21,420) (48,960) (3,60) (12,240) (30,600) (39,780) (15,300) (42,840) (24,480) (6,120) (33,660)
103 | result:
104 | 1:0.0 (23,460)
105 | 2:46.0 (50,1000)
106 | 3:-84.0 (32,640)
107 | 4:248.8 (41,820)
108 | 5:-689.2800000000002 (17,340)
109 | 6:516.4960000000003 (8,160)
110 | 7:119.29920000000004 (35,700)
111 | 8:-228.24800000000016 (44,880)
112 | 9:864.0432000000006 (26,520)
113 | 10:-1330.469120000001 (11,220)
114 | 11:155.04691200000025 (29,580)
115 | 12:-236.58913280000047 (38,760)
116 | 13:738.4495718400013 (47,940)
117 | 14:-2638.263415808005 (20,400)
118 | 15:2678.263415808006 (2,40)
119 | 16:2146.610732646405 (5,100)
120 | 17:1083.3053663232024 (14,280)
121 | 18:-405.3221465292811 (46,920)
122 | 19:1551.159727505412 (40,800)
123 | 20:-4573.4791825162365 (49,980)
124 | 21:17934.568811813326 (4,80)
125 | 22:10768.741287087996 (13,260)
126 | 23:-3204.6223861264007 (22,440)
127 | 24:3889.546863351681 (31,620)
128 | 25:-8106.04841303853 (16,320)
129 | 26:4895.6290478231185 (7,140)
130 | 27:1482.6887143469353 (43,860)
131 | 28:-4806.872757344887 (25,500)
132 | 29:7260.309136017331 (34,680)
133 | 30:-17356.741926441595 (10,200)
134 | 31:20.0 (37,740)
135 | 32:20.0 (1,20)
136 | 33:20.0 (19,380)
137 | 34:20.0 (28,560)
138 | 35:20.0 (45,900)
139 | 36:20.0 (27,540)
140 | 37:20.0 (36,720)
141 | 38:20.0 (18,360)
142 | 39:20.0 (9,180)
143 | 40:20.0 (21,420)
144 | 41:20.0 (48,960)
145 | 42:20.0 (3,60)
146 | 43:20.0 (12,240)
147 | 44:20.0 (30,600)
148 | 45:20.0 (39,780)
149 | 46:20.0 (15,300)
150 | 47:20.0 (42,840)
151 | 48:20.0 (24,480)
152 | 49:20.0 (6,120)
153 | 50:20.0 (33,660)
154 | 最终结果θ值为 20.0
155 | ```
156 |
157 | 分析:
158 | 当α为0.1的时候,一般30次计算就计算出来了;如果是0.5,一般15次计算就有正确结果 。如果是1,则50次都没有结果
159 |
160 | 参考
161 |
162 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
163 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
164 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
165 | 【4】Spark MlLib机器学习实战
166 | 【5】http://blog.csdn.net/zbc1090549839/article/details/38149561
167 | 【6】http://blog.csdn.net/woxincd/article/details/7040944
168 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/8频繁项挖掘/Spark中组件Mllib的学习66之FP-growth.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | FP-growth是数据挖掘里面很常见的一个算法
9 |
10 |
11 | 2.代码:
12 |
13 | /**
14 | * @author xubo
15 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
16 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
17 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
18 | */
19 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.FrequentPatternMining
20 |
21 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
22 |
23 | /**
24 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
25 | */
26 | class FPgroupFunSuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
27 | test("testFunSuite") {
28 | import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
29 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.fpm.FPGrowth
30 |
31 | val data = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/mllibFromSpark/sample_fpgrowth.txt")
32 |
33 | val transactions: RDD[Array[String]] = data.map(s => s.trim.split(' '))
34 |
35 | val fpg = new FPGrowth()
36 | .setMinSupport(0.2)
37 | .setNumPartitions(10)
38 | val model = fpg.run(transactions)
39 |
40 | model.freqItemsets.collect().foreach { itemset =>
41 | println(itemset.items.mkString("[", ",", "]") + ", " + itemset.freq)
42 | }
43 |
44 | val minConfidence = 0.8
45 | model.generateAssociationRules(minConfidence).collect().foreach { rule =>
46 | println(
47 | rule.antecedent.mkString("[", ",", "]")
48 | + " => " + rule.consequent.mkString("[", ",", "]")
49 | + ", " + rule.confidence)
50 | }
51 | }
52 | }
53 |
54 |
55 | 3.结果:
56 |
57 | [z], 5
58 | [x], 4
59 | [x,z], 3
60 | [y], 3
61 | [y,x], 3
62 | [y,x,z], 3
63 | [y,z], 3
64 | [r], 3
65 | [r,x], 2
66 | [r,z], 2
67 | [s], 3
68 | [s,y], 2
69 | [s,y,x], 2
70 | [s,y,x,z], 2
71 | [s,y,z], 2
72 | [s,x], 3
73 | [s,x,z], 2
74 | [s,z], 2
75 | [t], 3
76 | [t,y], 3
77 | [t,y,x], 3
78 | [t,y,x,z], 3
79 | [t,y,z], 3
80 | [t,s], 2
81 | [t,s,y], 2
82 | [t,s,y,x], 2
83 | [t,s,y,x,z], 2
84 | [t,s,y,z], 2
85 | [t,s,x], 2
86 | [t,s,x,z], 2
87 | [t,s,z], 2
88 | [t,x], 3
89 | [t,x,z], 3
90 | [t,z], 3
91 | [p], 2
92 | [p,r], 2
93 | [p,r,z], 2
94 | [p,z], 2
95 | [q], 2
96 | [q,y], 2
97 | [q,y,x], 2
98 | [q,y,x,z], 2
99 | [q,y,z], 2
100 | [q,t], 2
101 | [q,t,y], 2
102 | [q,t,y,x], 2
103 | [q,t,y,x,z], 2
104 | [q,t,y,z], 2
105 | [q,t,x], 2
106 | [q,t,x,z], 2
107 | [q,t,z], 2
108 | [q,x], 2
109 | [q,x,z], 2
110 | [q,z], 2
111 | [t,s,y] => [x], 1.0
112 | [t,s,y] => [z], 1.0
113 | [y,x,z] => [t], 1.0
114 | [y] => [x], 1.0
115 | [y] => [z], 1.0
116 | [y] => [t], 1.0
117 | [p] => [r], 1.0
118 | [p] => [z], 1.0
119 | [q,t,z] => [y], 1.0
120 | [q,t,z] => [x], 1.0
121 | [q,y] => [x], 1.0
122 | [q,y] => [z], 1.0
123 | [q,y] => [t], 1.0
124 | [t,s,x] => [y], 1.0
125 | [t,s,x] => [z], 1.0
126 | [q,t,y,z] => [x], 1.0
127 | [q,t,x,z] => [y], 1.0
128 | [q,x] => [y], 1.0
129 | [q,x] => [t], 1.0
130 | [q,x] => [z], 1.0
131 | [t,x,z] => [y], 1.0
132 | [x,z] => [y], 1.0
133 | [x,z] => [t], 1.0
134 | [p,z] => [r], 1.0
135 | [t] => [y], 1.0
136 | [t] => [x], 1.0
137 | [t] => [z], 1.0
138 | [y,z] => [x], 1.0
139 | [y,z] => [t], 1.0
140 | [p,r] => [z], 1.0
141 | [t,s] => [y], 1.0
142 | [t,s] => [x], 1.0
143 | [t,s] => [z], 1.0
144 | [q,z] => [y], 1.0
145 | [q,z] => [t], 1.0
146 | [q,z] => [x], 1.0
147 | [q,y,z] => [x], 1.0
148 | [q,y,z] => [t], 1.0
149 | [y,x] => [z], 1.0
150 | [y,x] => [t], 1.0
151 | [q,x,z] => [y], 1.0
152 | [q,x,z] => [t], 1.0
153 | [t,y,z] => [x], 1.0
154 | [q,y,x] => [z], 1.0
155 | [q,y,x] => [t], 1.0
156 | [q,t,y,x] => [z], 1.0
157 | [t,s,x,z] => [y], 1.0
158 | [s,y,x] => [z], 1.0
159 | [s,y,x] => [t], 1.0
160 | [s,x,z] => [y], 1.0
161 | [s,x,z] => [t], 1.0
162 | [q,y,x,z] => [t], 1.0
163 | [s,y] => [x], 1.0
164 | [s,y] => [z], 1.0
165 | [s,y] => [t], 1.0
166 | [q,t,y] => [x], 1.0
167 | [q,t,y] => [z], 1.0
168 | [t,y] => [x], 1.0
169 | [t,y] => [z], 1.0
170 | [t,z] => [y], 1.0
171 | [t,z] => [x], 1.0
172 | [t,s,y,x] => [z], 1.0
173 | [t,y,x] => [z], 1.0
174 | [q,t] => [y], 1.0
175 | [q,t] => [x], 1.0
176 | [q,t] => [z], 1.0
177 | [q] => [y], 1.0
178 | [q] => [t], 1.0
179 | [q] => [x], 1.0
180 | [q] => [z], 1.0
181 | [t,s,z] => [y], 1.0
182 | [t,s,z] => [x], 1.0
183 | [t,x] => [y], 1.0
184 | [t,x] => [z], 1.0
185 | [s,z] => [y], 1.0
186 | [s,z] => [x], 1.0
187 | [s,z] => [t], 1.0
188 | [s,y,x,z] => [t], 1.0
189 | [s] => [x], 1.0
190 | [t,s,y,z] => [x], 1.0
191 | [s,y,z] => [x], 1.0
192 | [s,y,z] => [t], 1.0
193 | [q,t,x] => [y], 1.0
194 | [q,t,x] => [z], 1.0
195 | [r,z] => [p], 1.0
196 |
197 |
198 |
199 | 参考
200 |
201 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
202 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
203 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
204 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
205 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
206 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/2基本统计/Spark中组件Mllib的学习19之分层抽样.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之基础概念篇
3 | 1解释
4 | 分层抽样的概念就不讲了,具体的操作:
5 | RDD有个操作可以直接进行抽样:sampleByKey和sample等,这里主要介绍这两个
6 | (1)将字符串长度为2划分为层1和层2,对层1和层2按不同的概率进行抽样
7 | 数据
8 |
9 | ```
10 | aa
11 | bb
12 | cc
13 | dd
14 | ee
15 | aaa
16 | bbb
17 | ccc
18 | ddd
19 | eee
20 | ```
21 | 比如:
22 | val fractions: Map[Int, Double] = (List((1, 0.2), (2, 0.8))).toMap //设定抽样格式
23 | sampleByKey(withReplacement = false, fractions, 0)
24 | fractions表示在层1抽0.2,在层2中抽0.8
25 | withReplacement false表示不重复抽样
26 | 0表示随机的seed
27 |
28 | 源码:
29 |
30 | ```
31 | /**
32 | * Return a subset of this RDD sampled by key (via stratified sampling).
33 | *
34 | * Create a sample of this RDD using variable sampling rates for different keys as specified by
35 | * `fractions`, a key to sampling rate map, via simple random sampling with one pass over the
36 | * RDD, to produce a sample of size that's approximately equal to the sum of
37 | * math.ceil(numItems * samplingRate) over all key values.
38 | *
39 | * @param withReplacement whether to sample with or without replacement
40 | * @param fractions map of specific keys to sampling rates
41 | * @param seed seed for the random number generator
42 | * @return RDD containing the sampled subset
43 | */
44 | def sampleByKey(withReplacement: Boolean,
45 | fractions: Map[K, Double],
46 | seed: Long = Utils.random.nextLong): RDD[(K, V)] = self.withScope {
47 |
48 | require(fractions.values.forall(v => v >= 0.0), "Negative sampling rates.")
49 |
50 | val samplingFunc = if (withReplacement) {
51 | StratifiedSamplingUtils.getPoissonSamplingFunction(self, fractions, false, seed)
52 | } else {
53 | StratifiedSamplingUtils.getBernoulliSamplingFunction(self, fractions, false, seed)
54 | }
55 | self.mapPartitionsWithIndex(samplingFunc, preservesPartitioning = true)
56 | }
57 | ```
58 |
59 | (2)和(3)类似,请看代码
60 |
61 |
62 | 2.代码:
63 |
64 | ```
65 | /**
66 | * @author xubo
67 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
68 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
69 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
70 | */
71 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.basic
72 |
73 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
74 |
75 | /**
76 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
77 | */
78 | object StratifiedSamplingLearning {
79 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
80 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[4]").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
81 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
82 | println("First:")
83 | val data = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/basic/StratifiedSampling.txt") //读取数
84 | .map(row => {
85 | //开始处理
86 | if (row.length == 3) //判断字符数
87 | (row, 1) //建立对应map
88 | else (row, 2) //建立对应map
89 | }).map(each => (each._2, each._1))
90 | data.foreach(println)
91 | println("sampleByKey:")
92 | val fractions: Map[Int, Double] = (List((1, 0.2), (2, 0.8))).toMap //设定抽样格式
93 | val approxSample = data.sampleByKey(withReplacement = false, fractions, 0) //计算抽样样本
94 | approxSample.foreach(println)
95 |
96 | println("Second:")
97 | //http://homepage.cs.latrobe.edu.au/zhe/ZhenHeSparkRDDAPIExamples.html#sampleByKey
98 | val randRDD = sc.parallelize(List((7, "cat"), (6, "mouse"), (7, "cup"), (6, "book"), (7, "tv"), (6, "screen"), (7, "heater")))
99 | val sampleMap = List((7, 0.4), (6, 0.8)).toMap
100 | val sample2 = randRDD.sampleByKey(false, sampleMap, 42).collect
101 | sample2.foreach(println)
102 |
103 | println("Third:")
104 | //http://bbs.csdn.net/topics/390953396
105 | val a = sc.parallelize(1 to 20, 3)
106 | val b = a.sample(true, 0.8, 0)
107 | val c = a.sample(false, 0.8, 0)
108 | println("RDD a : " + a.collect().mkString(" , "))
109 | println("RDD b : " + b.collect().mkString(" , "))
110 | println("RDD c : " + c.collect().mkString(" , "))
111 | sc.stop
112 | }
113 | }
114 |
115 | ```
116 |
117 | 3.结果:
118 |
119 | ```
120 | First:
121 | 2016-05-23 22:37:34 WARN :139 - Your hostname, xubo-PC resolves to a loopback/non-reachable address: fe80:0:0:0:482:722f:5976:ce1f%20, but we couldn't find any external IP address!
122 | (2,aa)
123 | (1,bbb)
124 | (2,bb)
125 | (1,ccc)
126 | (2,cc)
127 | (1,ddd)
128 | (2,dd)
129 | (1,eee)
130 | (2,ee)
131 | (1,aaa)
132 | sampleByKey:
133 | (2,aa)
134 | (2,bb)
135 | (2,cc)
136 | (2,ee)
137 | Second:
138 | (7,cat)
139 | (6,mouse)
140 | (6,book)
141 | (6,screen)
142 | (7,heater)
143 | Third:
144 | RDD a : 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20
145 | RDD b : 2 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 10 , 14 , 19 , 20
146 | RDD c : 1 , 2 , 4 , 5 , 8 , 10 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20
147 | ```
148 |
149 | 参考
150 |
151 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
152 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
153 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/3分类和回归/Spark中组件Mllib的学习40之梯度提升树(GBT)用于回归_.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之分类篇
3 | 1解释
4 | GBRT(Gradient Boost Regression Tree)渐进梯度回归树
5 | 同样的setCategoricalFeaturesInfo有问题。注释掉了。
6 |
7 | 2.代码:
8 |
9 | ```
10 | /**
11 | * @author xubo
12 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
13 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
14 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
15 | */
16 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.classification
17 |
18 | import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
19 | import java.util.Date
20 |
21 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.DecisionTree
22 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
23 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
24 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.GradientBoostedTrees
25 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.configuration.BoostingStrategy
26 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.model.{DecisionTreeModel, GradientBoostedTreesModel}
27 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
28 | import java.util.Map
29 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.GradientBoostedTrees
30 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.configuration.BoostingStrategy
31 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.model.GradientBoostedTreesModel
32 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
33 |
34 | /**
35 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
36 | */
37 | object GBTs2Regression {
38 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
39 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[4]").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
40 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
41 |
42 | // Load and parse the data file.
43 | val data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(sc, "file/data/mllib/input/classification/sample_libsvm_data.txt")
44 |
45 | // Split the data into training and test sets (30% held out for testing)
46 | val splits = data.randomSplit(Array(0.7, 0.3))
47 | val (trainingData, testData) = (splits(0), splits(1))
48 |
49 | // Train a GradientBoostedTrees model.
50 | // The defaultParams for Classification use LogLoss by default.
51 | val boostingStrategy = BoostingStrategy.defaultParams("Regression")
52 | boostingStrategy.setNumIterations(3)
53 | boostingStrategy.treeStrategy.setMaxDepth(5)
54 | // boostingStrategy.treeStrategy.setCategoricalFeaturesInfo(Map[Int, Int]())
55 |
56 | // Train a GradientBoostedTrees model.
57 | // The defaultParams for Regression use SquaredError by default.
58 | // val boostingStrategy = BoostingStrategy.defaultParams("Regression")
59 | // boostingStrategy.numIterations = 3 // Note: Use more iterations in practice.
60 | // boostingStrategy.treeStrategy.maxDepth = 5
61 | // // Empty categoricalFeaturesInfo indicates all features are continuous.
62 | // boostingStrategy.treeStrategy.categoricalFeaturesInfo = Map[Int, Int]()
63 |
64 | val model = GradientBoostedTrees.train(trainingData, boostingStrategy)
65 |
66 | // Evaluate model on test instances and compute test error
67 | val labelsAndPredictions = testData.map { point =>
68 | val prediction = model.predict(point.features)
69 | (point.label, prediction)
70 | }
71 | val testMSE = labelsAndPredictions.map { case (v, p) => math.pow((v - p), 2) }.mean()
72 | println("Test Mean Squared Error = " + testMSE)
73 | println("Learned regression GBT model:\n" + model.toDebugString)
74 |
75 |
76 |
77 | println("data.count:" + data.count())
78 | println("trainingData.count:" + trainingData.count())
79 | println("testData.count:" + testData.count())
80 | println("model.algo:" + model.algo)
81 | println("model.trees:" + model.trees)
82 | println("model.treeWeights:" + model.treeWeights)
83 |
84 |
85 |
86 | // Save and load model
87 | // val iString = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmssSSS").format(new Date())
88 | // val path = "file/data/mllib/output/classification/GradientBoostedTreesModel" + iString + "/result"
89 | // model.save(sc, path)
90 | // val sameModel = DecisionTreeModel.load(sc, path)
91 | // println(sameModel.algo)
92 | sc.stop
93 | }
94 | }
95 |
96 | ```
97 |
98 | 3.结果:
99 |
100 | ```
101 | Test Mean Squared Error = 0.06896551724137932
102 | Learned regression GBT model:
103 | TreeEnsembleModel regressor with 3 trees
104 |
105 | Tree 0:
106 | If (feature 406 <= 72.0)
107 | If (feature 99 <= 0.0)
108 | Predict: 0.0
109 | Else (feature 99 > 0.0)
110 | Predict: 1.0
111 | Else (feature 406 > 72.0)
112 | Predict: 1.0
113 | Tree 1:
114 | Predict: 0.0
115 | Tree 2:
116 | Predict: 0.0
117 |
118 | data.count:100
119 | trainingData.count:71
120 | testData.count:29
121 | model.algo:Regression
122 | model.trees:[Lorg.apache.spark.mllib.tree.model.DecisionTreeModel;@5e9a7c29
123 | model.treeWeights:[D@78bf694d
124 | ```
125 |
126 | 参考
127 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
128 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
129 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/9评估度量/Spark中组件Mllib的学习72之RankingSystem进行评估.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | 主要用于推荐系统
9 |
10 | 
11 |
12 |
13 | 2.代码:
14 |
15 | /**
16 | * @author xubo
17 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
18 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
19 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
20 | */
21 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.EvaluationMetrics
22 |
23 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
24 |
25 | /**
26 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
27 | */
28 | class RankingSystemsFunSuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
29 | test("testFunSuite") {
30 |
31 |
32 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.evaluation.{RegressionMetrics, RankingMetrics}
33 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.recommendation.{ALS, Rating}
34 |
35 | // Read in the ratings data
36 | val ratings = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/mllibFromSpark/sample_movielens_data.txt").map { line =>
37 | val fields = line.split("::")
38 | Rating(fields(0).toInt, fields(1).toInt, fields(2).toDouble - 2.5)
39 | }.cache()
40 |
41 | // Map ratings to 1 or 0, 1 indicating a movie that should be recommended
42 | val binarizedRatings = ratings.map(r => Rating(r.user, r.product, if (r.rating > 0) 1.0 else 0.0)).cache()
43 |
44 | // Summarize ratings
45 | val numRatings = ratings.count()
46 | val numUsers = ratings.map(_.user).distinct().count()
47 | val numMovies = ratings.map(_.product).distinct().count()
48 | println(s"Got $numRatings ratings from $numUsers users on $numMovies movies.")
49 |
50 | // Build the model
51 | val numIterations = 10
52 | val rank = 10
53 | val lambda = 0.01
54 | val model = ALS.train(ratings, rank, numIterations, lambda)
55 |
56 | // Define a function to scale ratings from 0 to 1
57 | def scaledRating(r: Rating): Rating = {
58 | val scaledRating = math.max(math.min(r.rating, 1.0), 0.0)
59 | Rating(r.user, r.product, scaledRating)
60 | }
61 |
62 | // Get sorted top ten predictions for each user and then scale from [0, 1]
63 | val userRecommended = model.recommendProductsForUsers(10).map { case (user, recs) =>
64 | (user, recs.map(scaledRating))
65 | }
66 |
67 | // Assume that any movie a user rated 3 or higher (which maps to a 1) is a relevant document
68 | // Compare with top ten most relevant documents
69 | val userMovies = binarizedRatings.groupBy(_.user)
70 | val relevantDocuments = userMovies.join(userRecommended).map { case (user, (actual, predictions)) =>
71 | (predictions.map(_.product), actual.filter(_.rating > 0.0).map(_.product).toArray)
72 | }
73 |
74 | // Instantiate metrics object
75 | val metrics = new RankingMetrics(relevantDocuments)
76 |
77 | // Precision at K
78 | Array(1, 3, 5).foreach { k =>
79 | println(s"Precision at $k = ${metrics.precisionAt(k)}")
80 | }
81 |
82 | // Mean average precision
83 | println(s"Mean average precision = ${metrics.meanAveragePrecision}")
84 |
85 | // Normalized discounted cumulative gain
86 | Array(1, 3, 5).foreach { k =>
87 | println(s"NDCG at $k = ${metrics.ndcgAt(k)}")
88 | }
89 |
90 | // Get predictions for each data point
91 | val allPredictions = model.predict(ratings.map(r => (r.user, r.product))).map(r => ((r.user, r.product), r.rating))
92 | val allRatings = ratings.map(r => ((r.user, r.product), r.rating))
93 | val predictionsAndLabels = allPredictions.join(allRatings).map { case ((user, product), (predicted, actual)) =>
94 | (predicted, actual)
95 | }
96 |
97 | // Get the RMSE using regression metrics
98 | val regressionMetrics = new RegressionMetrics(predictionsAndLabels)
99 | println(s"RMSE = ${regressionMetrics.rootMeanSquaredError}")
100 |
101 | // R-squared
102 | println(s"R-squared = ${regressionMetrics.r2}")
103 |
104 |
105 | }
106 | }
107 |
108 |
109 |
110 | 3.结果:
111 |
112 | Got 1501 ratings from 30 users on 100 movies.
113 | 2016-06-14 21:05:44 WARN BLAS:61 - Failed to load implementation from: com.github.fommil.netlib.NativeSystemBLAS
114 | 2016-06-14 21:05:44 WARN BLAS:61 - Failed to load implementation from: com.github.fommil.netlib.NativeRefBLAS
115 | 2016-06-14 21:05:45 WARN LAPACK:61 - Failed to load implementation from: com.github.fommil.netlib.NativeSystemLAPACK
116 | 2016-06-14 21:05:45 WARN LAPACK:61 - Failed to load implementation from: com.github.fommil.netlib.NativeRefLAPACK
117 | Precision at 1 = 0.3
118 | Precision at 3 = 0.3888888888888889
119 | Precision at 5 = 0.4800000000000001
120 | Mean average precision = 0.26666169370152676
121 | NDCG at 1 = 0.3
122 | NDCG at 3 = 0.3687147515984829
123 | NDCG at 5 = 0.43771295011419203
124 | RMSE = 0.2403021781310338
125 | R-squared = 0.9590077885328022
126 |
127 | 参考
128 |
129 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
130 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
131 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
132 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
133 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
134 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/7特征提取和转换/Spark中组件Mllib的学习62之特征选择中的卡方选择器.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | 特征选择试图识别相关的特征用于模型构建。它改变特征空间的大小,它可以提高速度以及统计学习行为。ChiSqSelector实现卡方特征选择,它操作于带有类别特征的标注数据。 ChiSqSelector根据独立的卡方测试对特征进行排序,然后选择排序最高的特征。
9 |
10 | 卡方选择(ChiSqSelector)
11 |
12 | ChiSqSelector是指使用卡方(Chi-Squared)做特征选择。该方法操作的是有标签的类别型数据。ChiSqSelector基于卡方检验来排序数据,然后选出卡方值较大(也就是跟标签最相关)的特征(topk)。
13 | 模型拟合
14 |
15 | ChiSqSelector 的构造函数有如下特征:
16 |
17 | numTopFeatures 保留的卡方较大的特征的数量。
18 |
19 | ChiSqSelector.fit() 方法以具有类别特征的RDD[LabeledPoint]为输入,计算汇总统计信息,然后返回ChiSqSelectorModel,这个类将输入数据转化到降维的特征空间。
20 |
21 | 模型实现了 VectorTransformer,这个类可以在Vector和RDD[Vector]上做卡方特征选择。
22 |
23 | 注意:也可以手工构造一个ChiSqSelectorModel,需要提供升序排列的特征索引。
24 |
25 | 2.代码:
26 |
27 | /*
28 | * Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
29 | * contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
30 | * this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
31 | * The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
32 | * (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
33 | * the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
34 | *
35 | * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
36 | *
37 | * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
38 | * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
39 | * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
40 | * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
41 | * limitations under the License.
42 | */
43 |
44 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.FeatureExtractionAndTransformation
45 |
46 | import org.apache.spark.SparkFunSuite
47 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.feature.ChiSqSelector
48 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
49 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint
50 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLlibTestSparkContext
51 |
52 | class ChiSqSelectorSuite extends SparkFunSuite with MLlibTestSparkContext {
53 |
54 | /*
55 | * Contingency tables
56 | * feature0 = {8.0, 0.0}
57 | * class 0 1 2
58 | * 8.0||1|0|1|
59 | * 0.0||0|2|0|
60 | *
61 | * feature1 = {7.0, 9.0}
62 | * class 0 1 2
63 | * 7.0||1|0|0|
64 | * 9.0||0|2|1|
65 | *
66 | * feature2 = {0.0, 6.0, 8.0, 5.0}
67 | * class 0 1 2
68 | * 0.0||1|0|0|
69 | * 6.0||0|1|0|
70 | * 8.0||0|1|0|
71 | * 5.0||0|0|1|
72 | *
73 | * Use chi-squared calculator from Internet
74 | */
75 |
76 | test("ChiSqSelector transform test (sparse & dense vector)") {
77 | val labeledDiscreteData = sc.parallelize(
78 | Seq(LabeledPoint(0.0, Vectors.sparse(3, Array((0, 8.0), (1, 7.0)))),
79 | LabeledPoint(1.0, Vectors.sparse(3, Array((1, 9.0), (2, 6.0)))),
80 | LabeledPoint(1.0, Vectors.dense(Array(0.0, 9.0, 8.0))),
81 | LabeledPoint(2.0, Vectors.dense(Array(8.0, 9.0, 5.0)))), 2)
82 | val preFilteredData =
83 | Set(LabeledPoint(0.0, Vectors.dense(Array(0.0))),
84 | LabeledPoint(1.0, Vectors.dense(Array(6.0))),
85 | LabeledPoint(1.0, Vectors.dense(Array(8.0))),
86 | LabeledPoint(2.0, Vectors.dense(Array(5.0))))
87 | val model = new ChiSqSelector(2).fit(labeledDiscreteData)
88 | val filteredData = labeledDiscreteData.map { lp =>
89 | LabeledPoint(lp.label, model.transform(lp.features))
90 | }.collect().toSet
91 | // assert(filteredData == preFilteredData)
92 |
93 | println("labeledDiscreteData:")
94 | labeledDiscreteData.foreach(println)
95 | println("model:")
96 | model.selectedFeatures.foreach(println)
97 | // model.selectedFeatures.
98 | println("filteredData:")
99 | filteredData.foreach(println)
100 | println("preFilteredData:")
101 | preFilteredData.foreach(println)
102 | }
103 | }
104 |
105 |
106 | 3.结果:
107 |
108 | (1)new ChiSqSelector(1)
109 |
110 | labeledDiscreteData:
111 | (0.0,(3,[0,1],[8.0,7.0]))
112 | (1.0,(3,[1,2],[9.0,6.0]))
113 | (1.0,[0.0,9.0,8.0])
114 | (2.0,[8.0,9.0,5.0])
115 | model:
116 | 2
117 | filteredData:
118 | (0.0,(1,[],[]))
119 | (1.0,(1,[0],[6.0]))
120 | (1.0,[8.0])
121 | (2.0,[5.0])
122 | preFilteredData:
123 | (0.0,[0.0])
124 | (1.0,[6.0])
125 | (1.0,[8.0])
126 | (2.0,[5.0])
127 |
128 | (2)new ChiSqSelector(2)
129 |
130 | labeledDiscreteData:
131 | (1.0,[0.0,9.0,8.0])
132 | (2.0,[8.0,9.0,5.0])
133 | (0.0,(3,[0,1],[8.0,7.0]))
134 | (1.0,(3,[1,2],[9.0,6.0]))
135 | model:
136 | 0
137 | 2
138 | filteredData:
139 | (0.0,(2,[0],[8.0]))
140 | (1.0,(2,[1],[6.0]))
141 | (1.0,[0.0,8.0])
142 | (2.0,[8.0,5.0])
143 | preFilteredData:
144 | (0.0,[0.0])
145 | (1.0,[6.0])
146 | (1.0,[8.0])
147 | (2.0,[5.0])
148 |
149 |
150 |
151 | 参考
152 |
153 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
154 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
155 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
156 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
157 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
158 | 【6】https://github.com/endymecy/spark-ml-source-analysis/blob/master/%E7%89%B9%E5%BE%81%E6%8A%BD%E5%8F%96%E5%92%8C%E8%BD%AC%E6%8D%A2/chi-square-selector.md
159 | 【7】http://www.fuqingchuan.com/2015/03/643.html#standardscaler
160 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/5聚类/Spark中组件Mllib的学习47之隐含狄利克雷分布(Latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA)学习.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | 隐含狄利克雷分布(Latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA)
9 |
10 | 隐含狄利克雷分布(LDA) 是一个主题模型,它能够推理出一个文本文档集合的主体。LDA可以认为是一个聚类算法,原因如下:
11 |
12 | 主题对应聚类中心,文档对应数据集中的样本(数据行)
13 | 主题和文档都在一个特征空间中,其特征向量是词频向量。
14 | 跟使用传统的距离来评估聚类不一样的是,LDA使用评估方式是一个函数,该函数基于文档如何生成的统计模型。
15 |
16 | LDA以词频向量表示的文档集合作为输入。然后在最大似然函数上使用期望最大(EM)算法 来学习聚类。完成文档拟合之后,LDA提供:
17 |
18 | Topics: 推断出的主题,每个主体是单词上的概率分布。
19 | Topic distributions for documents: 对训练集中的每个文档,LDA给了一个在主题上的概率分布。
20 |
21 | LDA参数如下:
22 |
23 | k: 主题数量(或者说聚簇中心数量)
24 | maxIterations: EM算法的最大迭代次数。
25 | docConcentration: 文档在主题上分布的先验参数。当前必须大于1,值越大,推断出的分布越平滑。
26 | topicConcentration: 主题在单词上的先验分布参数。当前必须大于1,值越大,推断出的分布越平滑。
27 | checkpointInterval: 检查点间隔。maxIterations很大的时候,检查点可以帮助减少shuffle文件大小并且可以帮助故障恢复。
28 |
29 | 参考【4】
30 |
31 | 2.代码:
32 |
33 | /**
34 | * @author xubo
35 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
36 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
37 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
38 | */
39 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.clustering.LDALearning
40 |
41 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.clustering.LDA
42 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
43 |
44 | /**
45 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
46 | */
47 | class LDAFromWebSuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
48 | test("testFunSuite") {
49 |
50 |
51 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
52 |
53 | // Load and parse the data
54 | val data = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/mllibFromSpark/sample_lda_data.txt")
55 | val parsedData = data.map(s => Vectors.dense(s.trim.split(' ').map(_.toDouble)))
56 | // Index documents with unique IDs
57 | val corpus = parsedData.zipWithIndex.map(_.swap).cache()
58 |
59 | // Cluster the documents into three topics using LDA
60 | val ldaModel = new LDA().setK(3).run(corpus)
61 |
62 | //input data
63 | println("parsedData:")
64 | parsedData.foreach(println)
65 | println("corpus:")
66 | corpus.foreach(println)
67 |
68 | // Output topics. Each is a distribution over words (matching word count vectors)
69 | println("Learned topics (as distributions over vocab of " + ldaModel.vocabSize + " words):")
70 | val topics = ldaModel.topicsMatrix
71 | for (topic <- Range(0, 3)) {
72 | print("Topic " + topic + ":")
73 | for (word <- Range(0, ldaModel.vocabSize)) {
74 | print(" " + topics(word, topic));
75 | }
76 | println()
77 | }
78 |
79 | // Save and load model.
80 | // ldaModel.save(sc, "myLDAModel")
81 | // val sameModel = DistributedLDAModel.load(sc, "myLDAModel")
82 |
83 |
84 | }
85 | }
86 |
87 | 数据:
88 |
89 | 1 2 6 0 2 3 1 1 0 0 3
90 | 1 3 0 1 3 0 0 2 0 0 1
91 | 1 4 1 0 0 4 9 0 1 2 0
92 | 2 1 0 3 0 0 5 0 2 3 9
93 | 3 1 1 9 3 0 2 0 0 1 3
94 | 4 2 0 3 4 5 1 1 1 4 0
95 | 2 1 0 3 0 0 5 0 2 2 9
96 | 1 1 1 9 2 1 2 0 0 1 3
97 | 4 4 0 3 4 2 1 3 0 0 0
98 | 2 8 2 0 3 0 2 0 2 7 2
99 | 1 1 1 9 0 2 2 0 0 3 3
100 | 4 1 0 0 4 5 1 3 0 1 0
101 |
102 |
103 | 3.结果:
104 |
105 | parsedData:
106 | [1.0,1.0,1.0,9.0,2.0,1.0,2.0,0.0,0.0,1.0,3.0]
107 | [1.0,2.0,6.0,0.0,2.0,3.0,1.0,1.0,0.0,0.0,3.0]
108 | [4.0,4.0,0.0,3.0,4.0,2.0,1.0,3.0,0.0,0.0,0.0]
109 | [1.0,3.0,0.0,1.0,3.0,0.0,0.0,2.0,0.0,0.0,1.0]
110 | [2.0,8.0,2.0,0.0,3.0,0.0,2.0,0.0,2.0,7.0,2.0]
111 | [1.0,4.0,1.0,0.0,0.0,4.0,9.0,0.0,1.0,2.0,0.0]
112 | [1.0,1.0,1.0,9.0,0.0,2.0,2.0,0.0,0.0,3.0,3.0]
113 | [2.0,1.0,0.0,3.0,0.0,0.0,5.0,0.0,2.0,3.0,9.0]
114 | [4.0,1.0,0.0,0.0,4.0,5.0,1.0,3.0,0.0,1.0,0.0]
115 | [3.0,1.0,1.0,9.0,3.0,0.0,2.0,0.0,0.0,1.0,3.0]
116 | [4.0,2.0,0.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,4.0,0.0]
117 | [2.0,1.0,0.0,3.0,0.0,0.0,5.0,0.0,2.0,2.0,9.0]
118 | corpus:
119 | (7,[1.0,1.0,1.0,9.0,2.0,1.0,2.0,0.0,0.0,1.0,3.0])
120 | (8,[4.0,4.0,0.0,3.0,4.0,2.0,1.0,3.0,0.0,0.0,0.0])
121 | (9,[2.0,8.0,2.0,0.0,3.0,0.0,2.0,0.0,2.0,7.0,2.0])
122 | (0,[1.0,2.0,6.0,0.0,2.0,3.0,1.0,1.0,0.0,0.0,3.0])
123 | (10,[1.0,1.0,1.0,9.0,0.0,2.0,2.0,0.0,0.0,3.0,3.0])
124 | (1,[1.0,3.0,0.0,1.0,3.0,0.0,0.0,2.0,0.0,0.0,1.0])
125 | (11,[4.0,1.0,0.0,0.0,4.0,5.0,1.0,3.0,0.0,1.0,0.0])
126 | (2,[1.0,4.0,1.0,0.0,0.0,4.0,9.0,0.0,1.0,2.0,0.0])
127 | (3,[2.0,1.0,0.0,3.0,0.0,0.0,5.0,0.0,2.0,3.0,9.0])
128 | (4,[3.0,1.0,1.0,9.0,3.0,0.0,2.0,0.0,0.0,1.0,3.0])
129 | (5,[4.0,2.0,0.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,4.0,0.0])
130 | (6,[2.0,1.0,0.0,3.0,0.0,0.0,5.0,0.0,2.0,2.0,9.0])
131 | Learned topics (as distributions over vocab of 11 words):
132 | Topic 0: 10.452679685126427 10.181668875779492 2.558644879228586 3.851438041310386 9.929534544713832 11.940154625598604 14.086100675895626 4.8961707413781115 2.2995952755592106 7.381361487130488 8.981150231959049
133 | Topic 1: 10.279220142758316 5.956661018866242 4.910211518699095 30.538789151743963 5.928882165794898 5.447495432535608 6.549479250479619 3.011959583638183 1.0753194351327675 3.217481558556803 9.62611924184504
134 | Topic 2: 5.268100172115256 12.861670105354264 4.531143602072319 5.6097728069456565 9.141583289491269 4.612349941865787 10.364420073624755 2.0918696749837067 4.625085289308021 13.40115695431271 14.392730526195912
135 |
136 |
137 |
138 | 参考
139 |
140 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
141 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
142 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
143 | 【4】http://www.fuqingchuan.com/2015/03/609.html#latent-dirichlet-allocation-lda
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/5聚类/Spark中组件Mllib的学习47之隐含狄利克雷分布(Latent Dirichlet allocation,LDA)学习.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | 隐含狄利克雷分布(Latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA)
9 |
10 | 隐含狄利克雷分布(LDA) 是一个主题模型,它能够推理出一个文本文档集合的主体。LDA可以认为是一个聚类算法,原因如下:
11 |
12 | 主题对应聚类中心,文档对应数据集中的样本(数据行)
13 | 主题和文档都在一个特征空间中,其特征向量是词频向量。
14 | 跟使用传统的距离来评估聚类不一样的是,LDA使用评估方式是一个函数,该函数基于文档如何生成的统计模型。
15 |
16 | LDA以词频向量表示的文档集合作为输入。然后在最大似然函数上使用期望最大(EM)算法 来学习聚类。完成文档拟合之后,LDA提供:
17 |
18 | Topics: 推断出的主题,每个主体是单词上的概率分布。
19 | Topic distributions for documents: 对训练集中的每个文档,LDA给了一个在主题上的概率分布。
20 |
21 | LDA参数如下:
22 |
23 | k: 主题数量(或者说聚簇中心数量)
24 | maxIterations: EM算法的最大迭代次数。
25 | docConcentration: 文档在主题上分布的先验参数。当前必须大于1,值越大,推断出的分布越平滑。
26 | topicConcentration: 主题在单词上的先验分布参数。当前必须大于1,值越大,推断出的分布越平滑。
27 | checkpointInterval: 检查点间隔。maxIterations很大的时候,检查点可以帮助减少shuffle文件大小并且可以帮助故障恢复。
28 |
29 | 参考【4】
30 |
31 | 2.代码:
32 |
33 | /**
34 | * @author xubo
35 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
36 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
37 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
38 | */
39 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.clustering.LDALearning
40 |
41 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.clustering.LDA
42 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
43 |
44 | /**
45 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
46 | */
47 | class LDAFromWebSuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
48 | test("testFunSuite") {
49 |
50 |
51 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
52 |
53 | // Load and parse the data
54 | val data = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/mllibFromSpark/sample_lda_data.txt")
55 | val parsedData = data.map(s => Vectors.dense(s.trim.split(' ').map(_.toDouble)))
56 | // Index documents with unique IDs
57 | val corpus = parsedData.zipWithIndex.map(_.swap).cache()
58 |
59 | // Cluster the documents into three topics using LDA
60 | val ldaModel = new LDA().setK(3).run(corpus)
61 |
62 | //input data
63 | println("parsedData:")
64 | parsedData.foreach(println)
65 | println("corpus:")
66 | corpus.foreach(println)
67 |
68 | // Output topics. Each is a distribution over words (matching word count vectors)
69 | println("Learned topics (as distributions over vocab of " + ldaModel.vocabSize + " words):")
70 | val topics = ldaModel.topicsMatrix
71 | for (topic <- Range(0, 3)) {
72 | print("Topic " + topic + ":")
73 | for (word <- Range(0, ldaModel.vocabSize)) {
74 | print(" " + topics(word, topic));
75 | }
76 | println()
77 | }
78 |
79 | // Save and load model.
80 | // ldaModel.save(sc, "myLDAModel")
81 | // val sameModel = DistributedLDAModel.load(sc, "myLDAModel")
82 |
83 |
84 | }
85 | }
86 |
87 | 数据:
88 |
89 | 1 2 6 0 2 3 1 1 0 0 3
90 | 1 3 0 1 3 0 0 2 0 0 1
91 | 1 4 1 0 0 4 9 0 1 2 0
92 | 2 1 0 3 0 0 5 0 2 3 9
93 | 3 1 1 9 3 0 2 0 0 1 3
94 | 4 2 0 3 4 5 1 1 1 4 0
95 | 2 1 0 3 0 0 5 0 2 2 9
96 | 1 1 1 9 2 1 2 0 0 1 3
97 | 4 4 0 3 4 2 1 3 0 0 0
98 | 2 8 2 0 3 0 2 0 2 7 2
99 | 1 1 1 9 0 2 2 0 0 3 3
100 | 4 1 0 0 4 5 1 3 0 1 0
101 |
102 |
103 | 3.结果:
104 |
105 | parsedData:
106 | [1.0,1.0,1.0,9.0,2.0,1.0,2.0,0.0,0.0,1.0,3.0]
107 | [1.0,2.0,6.0,0.0,2.0,3.0,1.0,1.0,0.0,0.0,3.0]
108 | [4.0,4.0,0.0,3.0,4.0,2.0,1.0,3.0,0.0,0.0,0.0]
109 | [1.0,3.0,0.0,1.0,3.0,0.0,0.0,2.0,0.0,0.0,1.0]
110 | [2.0,8.0,2.0,0.0,3.0,0.0,2.0,0.0,2.0,7.0,2.0]
111 | [1.0,4.0,1.0,0.0,0.0,4.0,9.0,0.0,1.0,2.0,0.0]
112 | [1.0,1.0,1.0,9.0,0.0,2.0,2.0,0.0,0.0,3.0,3.0]
113 | [2.0,1.0,0.0,3.0,0.0,0.0,5.0,0.0,2.0,3.0,9.0]
114 | [4.0,1.0,0.0,0.0,4.0,5.0,1.0,3.0,0.0,1.0,0.0]
115 | [3.0,1.0,1.0,9.0,3.0,0.0,2.0,0.0,0.0,1.0,3.0]
116 | [4.0,2.0,0.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,4.0,0.0]
117 | [2.0,1.0,0.0,3.0,0.0,0.0,5.0,0.0,2.0,2.0,9.0]
118 | corpus:
119 | (7,[1.0,1.0,1.0,9.0,2.0,1.0,2.0,0.0,0.0,1.0,3.0])
120 | (8,[4.0,4.0,0.0,3.0,4.0,2.0,1.0,3.0,0.0,0.0,0.0])
121 | (9,[2.0,8.0,2.0,0.0,3.0,0.0,2.0,0.0,2.0,7.0,2.0])
122 | (0,[1.0,2.0,6.0,0.0,2.0,3.0,1.0,1.0,0.0,0.0,3.0])
123 | (10,[1.0,1.0,1.0,9.0,0.0,2.0,2.0,0.0,0.0,3.0,3.0])
124 | (1,[1.0,3.0,0.0,1.0,3.0,0.0,0.0,2.0,0.0,0.0,1.0])
125 | (11,[4.0,1.0,0.0,0.0,4.0,5.0,1.0,3.0,0.0,1.0,0.0])
126 | (2,[1.0,4.0,1.0,0.0,0.0,4.0,9.0,0.0,1.0,2.0,0.0])
127 | (3,[2.0,1.0,0.0,3.0,0.0,0.0,5.0,0.0,2.0,3.0,9.0])
128 | (4,[3.0,1.0,1.0,9.0,3.0,0.0,2.0,0.0,0.0,1.0,3.0])
129 | (5,[4.0,2.0,0.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,4.0,0.0])
130 | (6,[2.0,1.0,0.0,3.0,0.0,0.0,5.0,0.0,2.0,2.0,9.0])
131 | Learned topics (as distributions over vocab of 11 words):
132 | Topic 0: 10.452679685126427 10.181668875779492 2.558644879228586 3.851438041310386 9.929534544713832 11.940154625598604 14.086100675895626 4.8961707413781115 2.2995952755592106 7.381361487130488 8.981150231959049
133 | Topic 1: 10.279220142758316 5.956661018866242 4.910211518699095 30.538789151743963 5.928882165794898 5.447495432535608 6.549479250479619 3.011959583638183 1.0753194351327675 3.217481558556803 9.62611924184504
134 | Topic 2: 5.268100172115256 12.861670105354264 4.531143602072319 5.6097728069456565 9.141583289491269 4.612349941865787 10.364420073624755 2.0918696749837067 4.625085289308021 13.40115695431271 14.392730526195912
135 |
136 |
137 |
138 | 参考
139 |
140 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
141 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
142 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
143 | 【4】http://www.fuqingchuan.com/2015/03/609.html#latent-dirichlet-allocation-lda
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/7特征提取和转换/Spark中组件Mllib的学习52之TF-IDF学习.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | TF-IDF(Term frequency-inverse document frequency ) 是文本挖掘中一种广泛使用的特征向量化方法。TF-IDF反映了语料中单词对文档的重要程度。假设单词用t表示,文档用d表示,语料用D表示,那么文档频度DF(t, D)是包含单词t的文档数。如果我们只是使用词频度量重要性,就会很容易过分强调重负次数多但携带信息少的单词,例如:”a”, “the”以及”of”。如果某个单词在整个语料库中高频出现,意味着它没有携带专门针对某特殊文档的信息。逆文档频度(IDF)是单词携带信息量的数值度量。
9 |
10 | TF-IDF的概念参考【4】中也讲的很详细,例子也很详细。
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 | 2.代码:
16 |
17 | /**
18 | * @author xubo
19 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
20 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
21 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
22 | */
23 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.FeatureExtractionAndTransformation
24 |
25 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
26 |
27 | /**
28 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
29 | */
30 | class TFIDFSuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
31 | test("testFunSuite") {
32 | import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
33 | import org.apache.spark.SparkContext
34 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.feature.HashingTF
35 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vector
36 |
37 | // val sc: SparkContext = ...
38 |
39 | // Load documents (one per line).
40 | val documents: RDD[Seq[String]] = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/FeatureExtractionAndTransformation/a.txt").map(_.split(" ").toSeq)
41 |
42 | val hashingTF = new HashingTF()
43 | val tf: RDD[Vector] = hashingTF.transform(documents)
44 | println("tf:" + tf)
45 | tf.foreach(println)
46 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.feature.IDF
47 |
48 | // ... continue from the previous example
49 | tf.cache()
50 | val idf = new IDF().fit(tf)
51 | val tfidf: RDD[Vector] = idf.transform(tf)
52 | // println("idf:" + idf.idf)
53 | // idf.idf
54 | println("tfidf:" + tfidf)
55 | tfidf.foreach(println)
56 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.feature.IDF
57 |
58 | // ... continue from the previous example
59 | // tf.cache()
60 | val idf2 = new IDF(minDocFreq = 2).fit(tf)
61 | val tfidf2: RDD[Vector] = idf2.transform(tf)
62 | // println("idf2:" + idf2.idf)
63 | // tf.foreach(println)
64 | println("tfidf2:" + tfidf2)
65 | tfidf2.foreach(println)
66 | }
67 | }
68 |
69 | 第一次数据:
70 |
71 | hello scala
72 | goodbyr spark
73 | hello spark
74 | hello mllib
75 | spark
76 | goodbyr spark
77 |
78 | 第二次数据:
79 |
80 | hello scala hello scala hello scala hello
81 | goodbyr spark
82 | hello spark
83 | hello mllib
84 | spark
85 | goodbyr spark
86 |
87 |
88 | 3.结果:
89 |
90 | 第一次:
91 |
92 | tf:MapPartitionsRDD[3] at map at HashingTF.scala:78
93 | 2016-06-13 21:40:33 WARN :139 - Your hostname, xubo-PC resolves to a loopback/non-reachable address: fe80:0:0:0:482:722f:5976:ce1f%39, but we couldn't find any external IP address!
94 | (1048576,[179334,596178],[1.0,1.0])
95 | (1048576,[198982,596178],[1.0,1.0])
96 | (1048576,[586461],[1.0])
97 | (1048576,[452894,586461],[1.0,1.0])
98 | (1048576,[452894,586461],[1.0,1.0])
99 | (1048576,[586461,596178],[1.0,1.0])
100 | tfidf:MapPartitionsRDD[5] at mapPartitions at IDF.scala:182
101 | (1048576,[198982,596178],[1.252762968495368,0.5596157879354227])
102 | (1048576,[452894,586461],[0.8472978603872037,0.3364722366212129])
103 | (1048576,[586461,596178],[0.3364722366212129,0.5596157879354227])
104 | (1048576,[179334,596178],[1.252762968495368,0.5596157879354227])
105 | (1048576,[586461],[0.3364722366212129])
106 | (1048576,[452894,586461],[0.8472978603872037,0.3364722366212129])
107 | tfidf2:MapPartitionsRDD[7] at mapPartitions at IDF.scala:182
108 | (1048576,[198982,596178],[0.0,0.5596157879354227])
109 | (1048576,[452894,586461],[0.8472978603872037,0.3364722366212129])
110 | (1048576,[586461,596178],[0.3364722366212129,0.5596157879354227])
111 | (1048576,[179334,596178],[0.0,0.5596157879354227])
112 | (1048576,[586461],[0.3364722366212129])
113 | (1048576,[452894,586461],[0.8472978603872037,0.3364722366212129])
114 |
115 | 第二次:
116 |
117 | tf:MapPartitionsRDD[3] at map at HashingTF.scala:78
118 | 2016-06-13 21:51:20 WARN :139 - Your hostname, xubo-PC resolves to a loopback/non-reachable address: fe80:0:0:0:482:722f:5976:ce1f%39, but we couldn't find any external IP address!
119 | (1048576,[198982,596178],[3.0,4.0])
120 | (1048576,[586461,596178],[1.0,1.0])
121 | (1048576,[452894,586461],[1.0,1.0])
122 | (1048576,[179334,596178],[1.0,1.0])
123 | (1048576,[586461],[1.0])
124 | (1048576,[452894,586461],[1.0,1.0])
125 | idf:1048576
126 | tfidf:MapPartitionsRDD[5] at mapPartitions at IDF.scala:182
127 | (1048576,[198982,596178],[3.758288905486104,2.2384631517416906])
128 | (1048576,[452894,586461],[0.8472978603872037,0.3364722366212129])
129 | (1048576,[586461,596178],[0.3364722366212129,0.5596157879354227])
130 | (1048576,[179334,596178],[1.252762968495368,0.5596157879354227])
131 | (1048576,[586461],[0.3364722366212129])
132 | (1048576,[452894,586461],[0.8472978603872037,0.3364722366212129])
133 | idf2:1048576
134 | tfidf2:MapPartitionsRDD[7] at mapPartitions at IDF.scala:182
135 | (1048576,[198982,596178],[0.0,2.2384631517416906])
136 | (1048576,[452894,586461],[0.8472978603872037,0.3364722366212129])
137 | (1048576,[586461,596178],[0.3364722366212129,0.5596157879354227])
138 | (1048576,[179334,596178],[0.0,0.5596157879354227])
139 | (1048576,[586461],[0.3364722366212129])
140 | (1048576,[452894,586461],[0.8472978603872037,0.3364722366212129])
141 |
142 | 参考
143 |
144 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
145 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
146 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
147 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
148 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
149 | 【6】http://www.fuqingchuan.com/2015/03/643.html#tf-idf
150 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/3分类和回归/Spark中组件Mllib的学习41之保序回归(Isotonic regression).md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
2 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习之分类篇
3 | 1解释
4 |
5 | 问题描述:给定一个无序数字序列,要求不改变每个元素的位置,但可以修改每个元素的值,修改后得到一个非递减序列,问如何使误差(该处取平方差)最小?
6 | 保序回归法:从该序列的首元素往后观察,一旦出现乱序现象停止该轮观察,从该乱序元素开始逐个吸收元素组成一个序列,直到该序列所有元素的平均值小于或等于下一个待吸收的元素。
7 | 举例:
8 | 原始序列:<9, 10, 14>
9 | 结果序列:<9, 10, 14>
10 | 分析:从9往后观察,到最后的元素14都未发现乱序情况,不用处理。
11 | 原始序列:<9, 14, 10>
12 | 结果序列:<9, 12, 12>
13 | 参考【4】
14 |
15 | 2.代码:
16 |
17 | ```
18 | /**
19 | * @author xubo
20 | * ref:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
21 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
22 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
23 | */
24 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.classification
25 |
26 | import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
27 | import java.util.Date
28 |
29 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.DecisionTree
30 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
31 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
32 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.GradientBoostedTrees
33 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.configuration.BoostingStrategy
34 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.model.{DecisionTreeModel, GradientBoostedTreesModel}
35 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
36 | import java.util.Map
37 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.{IsotonicRegression, IsotonicRegressionModel}
38 |
39 | /**
40 | * Created by xubo on 2016/5/23.
41 | */
42 | object IsotonicRegression1 {
43 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
44 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[4]").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
45 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
46 |
47 | // Load and parse the data file.
48 | // val data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(sc, "file/data/mllib/input/classification/dt.txt")
49 |
50 | val data = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/classification/sample_isotonic_regression_data.txt")
51 |
52 | // Create label, feature, weight tuples from input data with weight set to default value 1.0.
53 | val parsedData = data.map { line =>
54 | val parts = line.split(',').map(_.toDouble)
55 | (parts(0), parts(1), 1.0)
56 | }
57 |
58 | // Split data into training (60%) and test (40%) sets.
59 | val splits = parsedData.randomSplit(Array(0.6, 0.4), seed = 11L)
60 | val training = splits(0)
61 | val test = splits(1)
62 |
63 | // Create isotonic regression model from training data.
64 | // Isotonic parameter defaults to true so it is only shown for demonstration
65 | val model = new IsotonicRegression().setIsotonic(true).run(training)
66 |
67 | // Create tuples of predicted and real labels.
68 | val predictionAndLabel = test.map { point =>
69 | val predictedLabel = model.predict(point._2)
70 | (predictedLabel, point._1)
71 | }
72 |
73 | // Calculate mean squared error between predicted and real labels.
74 | val meanSquaredError = predictionAndLabel.map { case (p, l) => math.pow((p - l), 2) }.mean()
75 | println("Mean Squared Error = " + meanSquaredError)
76 | println("data.count:" + data.count())
77 | println("trainingData.count:" + training.count())
78 | println("testData.count:" + test.count())
79 | println(model.boundaries)
80 | println(model.isotonic)
81 | model.predictions.take(10).foreach(println)
82 | println("predictionAndLabel")
83 | predictionAndLabel.take(10).foreach(println)
84 |
85 |
86 | // Save and load model
87 | val iString = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmssSSS").format(new Date())
88 | val path = "file/data/mllib/output/classification/IsotonicRegressionModel" + iString + "/result"
89 | model.save(sc, path)
90 | val sameModel = IsotonicRegressionModel.load(sc, path)
91 | println(sameModel.isotonic)
92 |
93 | sc.stop
94 | }
95 | }
96 |
97 | ```
98 |
99 | 3.结果:
100 |
101 | ```
102 | Mean Squared Error = 0.004883368896285485
103 | data.count:100
104 | trainingData.count:64
105 | testData.count:36
106 | [D@7dd9d603
107 | true
108 | 0.1739693246153848
109 | 0.1739693246153848
110 | 0.196430394
111 | 0.196430394
112 | 0.20040796
113 | 0.29576747
114 | 0.51300357
115 | 0.51300357
116 | 0.5566037736363637
117 | 0.5566037736363637
118 | predictionAndLabel
119 | (0.1739693246153848,0.03926568)
120 | (0.1739693246153848,0.12952575)
121 | (0.1739693246153848,0.08873024)
122 | (0.18519985930769242,0.15247323)
123 | (0.196430394,0.19581846)
124 | (0.196430394,0.13717491)
125 | (0.196430394,0.19020908)
126 | (0.196430394,0.2009179)
127 | (0.198419177,0.18510964)
128 | (0.40438552,0.43396226)
129 | SLF4J: Failed to load class "org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder".
130 | SLF4J: Defaulting to no-operation (NOP) logger implementation
131 | SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#StaticLoggerBinder for further details.
132 | 2016-05-25 16:58:04 WARN ParquetRecordReader:193 - Can not initialize counter due to context is not a instance of TaskInputOutputContext, but is org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.TaskAttemptContextImpl
133 | 2016-05-25 16:58:04 WARN ParquetRecordReader:193 - Can not initialize counter due to context is not a instance of TaskInputOutputContext, but is org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.TaskAttemptContextImpl
134 | 2016-05-25 16:58:04 WARN ParquetRecordReader:193 - Can not initialize counter due to context is not a instance of TaskInputOutputContext, but is org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.TaskAttemptContextImpl
135 | 2016-05-25 16:58:04 WARN ParquetRecordReader:193 - Can not initialize counter due to context is not a instance of TaskInputOutputContext, but is org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.TaskAttemptContextImpl
136 | true
137 | ```
138 |
139 | 参考
140 |
141 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
142 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
143 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
144 | 【4】http://blog.csdn.net/fsz521/article/details/7706250
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/7特征提取和转换/Spark中组件Mllib的学习54之word2Vec实例分析(text8数据集).md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | text8数据集下载:http://mattmahoney.net/dc/text8.zip,没有上传到github,主要是由于大于50M,上传不了。
9 |
10 | 需要解压上传到hdfs
11 |
12 | 对text8数据集进行训练,然后查找与china相关的40个单词和相似度
13 |
14 | 使用的是余弦相似度
15 |
16 |
17 | 2.代码:
18 |
19 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.FeatureExtractionAndTransformation
20 |
21 | /**
22 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
23 | */
24 | object Word2VecSparkWeb {
25 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
26 | import org.apache.spark._
27 | import org.apache.spark.rdd._
28 | import org.apache.spark.SparkContext._
29 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.feature.{Word2Vec, Word2VecModel}
30 | val conf = new SparkConf()
31 | .setAppName("Word2VecSparkWeb")
32 | // println("start sc")
33 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
34 | // "file/data/mllib/input/FeatureExtractionAndTransformation/text8"
35 | val input = sc.textFile(args(0)).map(line => line.split(" ").toSeq)
36 | //java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
37 |
38 |
39 | // val input = sc.textFile("file/data/mllib/input/FeatureExtractionAndTransformation/a.txt").map(line => line.split(" ").toSeq)
40 |
41 | val word2vec = new Word2Vec()
42 |
43 | val model = word2vec.fit(input)
44 |
45 | val synonyms = model.findSynonyms("china", 40)
46 | // val synonyms = model.findSynonyms("hello", 2)
47 | // val synonyms = model.findSynonyms("hell", 2)
48 | println("synonyms:" + synonyms.length)
49 | for ((synonym, cosineSimilarity) <- synonyms) {
50 | println(s"$synonym $cosineSimilarity")
51 | }
52 | }
53 | }
54 |
55 | 脚本:
56 |
57 | hadoop@Master:~/xubo/project/sparkLearning/Word2VecSparkWeb$ cat run.sh
58 | #!/usr/bin/env bash
59 | spark-submit \
60 | --class org.apache.spark.mllib.FeatureExtractionAndTransformation.Word2VecSparkWeb \
61 | --master spark://Master:7077 \
62 | --executor-memory 4096M \
63 | --total-executor-cores 20 SparkLearning.jar /xubo/project/sparkLearning/text8
64 |
65 |
66 |
67 | 3.结果:
68 | 第一次运行
69 |
70 | synonyms:40
71 | taiwan 2.0250848910722588
72 | korea 1.8783838604188001
73 | japan 1.8418373325670603
74 | mongolia 1.6881217861875888
75 | thailand 1.6622166551684234
76 | republic 1.6286308610644606
77 | manchuria 1.6185821262551892
78 | kyrgyzstan 1.6155559907230572
79 | taiwan 2.0250848910722588
80 | korea 1.8783838604188001
81 | japan 1.8418373325670603
82 | mongolia 1.6881217861875888
83 | thailand 1.6622166551684234
84 | republic 1.6286308610644606
85 | manchuria 1.6185821262551892
86 | kyrgyzstan 1.6155559907230572
87 | laos 1.6103165736195577
88 | tibet 1.5989105922525122
89 | kazakhstan 1.5744151601314242
90 | singapore 1.5616986094026124
91 | macau 1.5499675794102241
92 | mainland 1.5375663678873703
93 | malaysia 1.5285559184299211
94 | tajikistan 1.5243343371990146
95 | india 1.5165506076453936
96 | nepal 1.5119063076061532
97 | pakistan 1.5024014083777038
98 | macedonia 1.5019503598037696
99 | russia 1.4935935877285467
100 | manchukuo 1.4881581055559592
101 | myanmar 1.4821476909912992
102 | indonesia 1.4793831566122821
103 | liberia 1.463797338924459
104 | xinjiang 1.4609436920718337
105 | philippines 1.4547708371463373
106 | shanghai 1.4503251746969463
107 | latvia 1.4386811130949109
108 | shenzhen 1.4199746865615956
109 | vietnam 1.418931441623602
110 | changsha 1.418418516788373
111 |
112 | 第二次运行:
113 |
114 | hadoop@Master:~/xubo/project/sparkLearning/Word2VecSparkWeb$ ./run.sh
115 | synonyms:40
116 | taiwan 1.9833786891085838
117 | korea 1.8726567347414271
118 | japan 1.7783736448331358
119 | republic 1.7004898528298036
120 | thailand 1.6917626667336083
121 | tibet 1.6878122461434133
122 | mongolia 1.652209839095614
123 | kyrgyzstan 1.645476213591011
124 | manchuria 1.6096494198211908
125 | nepal 1.6029630877195205
126 | singapore 1.5831389923108918
127 | xinjiang 1.5792116676867995
128 | guangdong 1.578964448792793
129 | laos 1.5787364724446695
130 | macau 1.5749300509413349
131 | indonesia 1.5711485054771392
132 | india 1.5706135472342697
133 | malaysia 1.5674786938684857
134 | shanghai 1.5370738084879059
135 | malaya 1.5315005636344519
136 | philippines 1.5288921196216254
137 | yuan 1.5130452356753659
138 | pakistan 1.498783617851528
139 | mainland 1.4975791691563867
140 | kazakhstan 1.4828377324602193
141 | guangzhou 1.479015936080569
142 | cambodia 1.4727652499197696
143 | tajikistan 1.469555846355169
144 | russia 1.4676529059005547
145 | uzbekistan 1.4619275437713692
146 |
147 | 第三次运行:
148 |
149 | hadoop@Master:~/xubo/project/sparkLearning/Word2VecSparkWeb$ ./run.sh
150 | synonyms:40
151 | taiwan 1.9153186898933967
152 | japan 1.79181381373875
153 | korea 1.775808989075448
154 | mongolia 1.7218100800986855
155 | thailand 1.7082852803611082
156 | indonesia 1.679178757980267
157 | malaysia 1.6728186293077718
158 | pakistan 1.6419833973021383
159 | india 1.6394439184980092
160 | laos 1.632823427649131
161 | kazakhstan 1.6233583074612854
162 | manchuria 1.6154866307442364
163 | republic 1.605084908540867
164 | nepal 1.5889757766337764
165 | tibet 1.5553698521689054
166 | mainland 1.5422192430156836
167 | cambodia 1.5393252900985754
168 | myanmar 1.5363584360594595
169 | kyrgyzstan 1.531264076283158
170 | singapore 1.5305132940994244
171 | philippines 1.523034664556905
172 | macau 1.5160013609117333
173 | xinjiang 1.4825373292002604
174 | latvia 1.471622519733523
175 | kenya 1.4696299318908457
176 | changsha 1.4664040946553276
177 | shanghai 1.455466110605061
178 | malaya 1.4548293900077052
179 | burma 1.4509943221704922
180 | ingushetia 1.4487999900318091
181 |
182 |
183 | 参考
184 |
185 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
186 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
187 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
188 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
189 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
190 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/10PMML模型输出/Spark中组件Mllib的学习74之预言模型标记语言PMML.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 更多代码请见:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
3 |
4 | Spark中组件Mllib的学习
5 |
6 | 1.解释
7 |
8 | 全称预言模型标记语言(Predictive Model Markup Language),利用XML描述和存储数据挖掘模型,是一个已经被W3C所接受的标准。MML是一种基于XML的语言,用来定义预言模型。
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 | 2.代码:
13 |
14 | /**
15 | * @author xubo
16 | * ref:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
17 | * more code:https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
18 | * more blog:http://blog.csdn.net/xubo245
19 | */
20 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.EvaluationMetrics
21 |
22 | import org.apache.spark.util.SparkLearningFunSuite
23 |
24 | /**
25 | * Created by xubo on 2016/6/13.
26 | */
27 | class RegressionModelEvaluationFunSuite extends SparkLearningFunSuite {
28 | test("testFunSuite") {
29 |
30 |
31 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint
32 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LinearRegressionModel
33 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LinearRegressionWithSGD
34 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
35 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.evaluation.RegressionMetrics
36 | import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils
37 |
38 | // Load the data
39 | val data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(sc, "file/data/mllib/input/mllibFromSpark/sample_linear_regression_data.txt").cache()
40 |
41 | // Build the model
42 | val numIterations = 100
43 | val model = LinearRegressionWithSGD.train(data, numIterations)
44 |
45 | // Get predictions
46 | val valuesAndPreds = data.map{ point =>
47 | val prediction = model.predict(point.features)
48 | (prediction, point.label)
49 | }
50 |
51 | // Instantiate metrics object
52 | val metrics = new RegressionMetrics(valuesAndPreds)
53 |
54 | // Squared error
55 | println(s"MSE = ${metrics.meanSquaredError}")
56 | println(s"RMSE = ${metrics.rootMeanSquaredError}")
57 |
58 | // R-squared
59 | println(s"R-squared = ${metrics.r2}")
60 |
61 | // Mean absolute error
62 | println(s"MAE = ${metrics.meanAbsoluteError}")
63 |
64 | // Explained variance
65 | println(s"Explained variance = ${metrics.explainedVariance}")
66 |
67 |
68 | }
69 | }
70 |
71 |
72 |
73 | 3.结果:
74 |
75 | PMML Model:
76 |
77 |
78 |
79 |
80 | 2016-06-14T21:20:36
81 |
82 |
83 |
84 |
85 |
86 |
87 |
88 |
89 |
90 |
91 |
92 |
93 |
94 |
95 |
96 |
97 |
98 |
99 |
100 | 9.099999999999998 9.099999999999998 9.099999999999998
101 |
102 |
103 | 0.1 0.1 0.1
104 |
105 |
106 |
107 |
108 |
109 |
110 |
111 |
112 | 2016-06-14T21:20:40
113 |
114 |
115 |
116 |
117 |
118 |
119 |
120 |
121 |
122 |
123 |
124 |
125 |
126 |
127 |
128 |
129 |
130 |
131 |
132 | 9.099999999999998 9.099999999999998 9.099999999999998
133 |
134 |
135 | 0.1 0.1 0.1
136 |
137 |
138 |
139 |
140 | analysis:
141 |
142 | clusters.clusterCenters.foreach(println)
143 |
144 | [9.099999999999998,9.099999999999998,9.099999999999998]
145 | [0.1,0.1,0.1]
146 |
147 | 参考
148 |
149 | 【1】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/mllib-guide.html
150 | 【2】http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.5.2/programming-guide.html
151 | 【3】https://github.com/xubo245/SparkLearning
152 | 【4】book:Machine Learning with Spark ,Nick Pertreach
153 | 【5】book:Spark MlLib机器学习实战
154 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/1数据类型/Spark中组件Mllib的学习3之用户相似度计算.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 代码:
2 |
3 | ```
4 | /**
5 | * @author xubo
6 | * time 2016.516
7 | * ref 《Spark MlLib 机器学习实战》P64
8 | */
9 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.recommend
10 |
11 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
12 |
13 | import scala.collection.mutable.Map
14 |
15 | object CollaborativeFilteringSpark {
16 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
17 | println(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
18 | //设置环境变量
19 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
20 | //实例化环境
21 | val users = sc.parallelize(Array("aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd", "eee"))
22 | //设置用户
23 | val films = sc.parallelize(Array("smzdm", "ylxb", "znh", "nhsc", "fcwr")) //设置电影名
24 |
25 | val source = Map[String, Map[String, Int]]()
26 | //使用一个source嵌套map作为姓名电影名和分值的存储
27 | val filmSource = Map[String, Int]()
28 |
29 | //设置一个用以存放电影分的map
30 | def getSource(): Map[String, Map[String, Int]] = {
31 | //设置电影评分
32 | val user1FilmSource = Map("smzdm" -> 2, "ylxb" -> 3, "znh" -> 1, "nhsc" -> 0, "fcwr" -> 1)
33 | val user2FilmSource = Map("smzdm" -> 1, "ylxb" -> 2, "znh" -> 2, "nhsc" -> 1, "fcwr" -> 4)
34 | val user3FilmSource = Map("smzdm" -> 2, "ylxb" -> 1, "znh" -> 0, "nhsc" -> 1, "fcwr" -> 4)
35 | val user4FilmSource = Map("smzdm" -> 3, "ylxb" -> 2, "znh" -> 0, "nhsc" -> 5, "fcwr" -> 3)
36 | val user5FilmSource = Map("smzdm" -> 5, "ylxb" -> 3, "znh" -> 1, "nhsc" -> 1, "fcwr" -> 2)
37 | source += ("aaa" -> user1FilmSource) //对人名进行存储
38 | source += ("bbb" -> user2FilmSource) //对人名进行存储
39 | source += ("ccc" -> user3FilmSource) //对人名进行存储
40 | source += ("ddd" -> user4FilmSource) //对人名进行存储
41 | source += ("eee" -> user5FilmSource) //对人名进行存储
42 | source //返回嵌套map
43 | }
44 |
45 | //两两计算分值,采用余弦相似性
46 | def getCollaborateSource(user1: String, user2: String): Double = {
47 | val user1FilmSource = source.get(user1).get.values.toVector //获得第1个用户的评分
48 | val user2FilmSource = source.get(user2).get.values.toVector //获得第2个用户的评分
49 | val member = user1FilmSource.zip(user2FilmSource).map(d => d._1 * d._2).reduce(_ + _).toDouble //对公式分子部分进行计算
50 | val temp1 = math.sqrt(user1FilmSource.map(num => {
51 | //求出分母第1个变量值
52 | math.pow(num, 2) //数学计算
53 | }).reduce(_ + _)) //进行叠加
54 | val temp2 = math.sqrt(user2FilmSource.map(num => {
55 | ////求出分母第2个变量值
56 | math.pow(num, 2) //数学计算
57 | }).reduce(_ + _)) //进行叠加
58 | val denominator = temp1 * temp2 //求出分母
59 | member / denominator //进行计算
60 | }
61 |
62 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
63 | getSource() //初始化分数
64 | var name = "bbb" //设定目标对象
65 | users.foreach(user => {
66 | //迭代进行计算
67 | println(name + " 相对于 " + user + "的相似性分数是:" + getCollaborateSource(name, user))
68 | })
69 | println()
70 | name = "aaa"
71 | users.foreach(user => {
72 | //迭代进行计算
73 | println(name + " 相对于 " + user + "的相似性分数是:" + getCollaborateSource(name, user))
74 | })
75 | }
76 | }
77 |
78 | ```
79 |
80 |
81 | 结果:
82 |
83 | ```
84 | D:\1win7\java\jdk\bin\java -Didea.launcher.port=7534 "-Didea.launcher.bin.path=D:\1win7\idea\IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition 15.0.4\bin" -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath "D:\all\idea\SparkLearning\bin;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\charsets.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\deploy.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\ext\access-bridge-64.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\ext\dnsns.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\ext\jaccess.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\ext\localedata.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\ext\sunec.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\ext\sunjce_provider.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\ext\sunmscapi.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\ext\zipfs.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\javaws.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\jce.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\jfr.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\jfxrt.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\jsse.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\management-agent.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\plugin.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\resources.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\rt.jar;D:\1win7\scala;D:\1win7\scala\lib;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\spark-assembly-1.5.2-hadoop2.6.0.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\adam-apis_2.10-0.18.3-SNAPSHOT.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\adam-cli_2.10-0.18.3-SNAPSHOT.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\adam-core_2.10-0.18.3-SNAPSHOT.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\SparkCSV\com.databricks_spark-csv_2.10-1.4.0.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\SparkCSV\com.univocity_univocity-parsers-1.5.1.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\SparkCSV\org.apache.commons_commons-csv-1.1.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\SparkAvro\spark-avro_2.10-2.0.1.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\SparkAvro\spark-avro_2.10-2.0.1-javadoc.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\SparkAvro\spark-avro_2.10-2.0.1-sources.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\avro\spark-avro_2.10-2.0.2-SNAPSHOT.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\tachyon\tachyon-assemblies-0.7.1-jar-with-dependencies.jar;D:\1win7\scala\lib\scala-actors-migration.jar;D:\1win7\scala\lib\scala-actors.jar;D:\1win7\scala\lib\scala-library.jar;D:\1win7\scala\lib\scala-reflect.jar;D:\1win7\scala\lib\scala-swing.jar;D:\1win7\idea\IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition 15.0.4\lib\idea_rt.jar" com.intellij.rt.execution.application.AppMain org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.recommend.CollaborativeFilteringSpark
85 | CollaborativeFilteringSpark
86 | SLF4J: Class path contains multiple SLF4J bindings.
87 | SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/D:/1win7/java/otherJar/spark-assembly-1.5.2-hadoop2.6.0.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]
88 | SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/D:/1win7/java/otherJar/adam-cli_2.10-0.18.3-SNAPSHOT.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]
89 | SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/D:/1win7/java/otherJar/tachyon/tachyon-assemblies-0.7.1-jar-with-dependencies.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]
90 | SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#multiple_bindings for an explanation.
91 | SLF4J: Actual binding is of type [org.slf4j.impl.Log4jLoggerFactory]
92 | 2016-05-16 20:57:50 WARN NativeCodeLoader:62 - Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
93 | 2016-05-16 20:57:52 WARN MetricsSystem:71 - Using default name DAGScheduler for source because spark.app.id is not set.
94 | bbb 相对于 aaa的相似性分数是:0.7089175569585667
95 | bbb 相对于 bbb的相似性分数是:1.0000000000000002
96 | bbb 相对于 ccc的相似性分数是:0.8780541105074453
97 | bbb 相对于 ddd的相似性分数是:0.6865554812287477
98 | bbb 相对于 eee的相似性分数是:0.6821910402406466
99 |
100 | aaa 相对于 aaa的相似性分数是:0.9999999999999999
101 | aaa 相对于 bbb的相似性分数是:0.7089175569585667
102 | aaa 相对于 ccc的相似性分数是:0.6055300708194983
103 | aaa 相对于 ddd的相似性分数是:0.564932682866032
104 | aaa 相对于 eee的相似性分数是:0.8981462390204985
105 |
106 | Process finished with exit code 0
107 |
108 | ```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/2基本统计/Spark中组件Mllib的学习3之用户相似度计算.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 代码:
2 |
3 | ```
4 | /**
5 | * @author xubo
6 | * time 2016.516
7 | * ref 《Spark MlLib 机器学习实战》P64
8 | */
9 | package org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.recommend
10 |
11 | import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
12 |
13 | import scala.collection.mutable.Map
14 |
15 | object CollaborativeFilteringSpark {
16 | val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
17 | println(this.getClass().getSimpleName().filter(!_.equals('$')))
18 | //设置环境变量
19 | val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
20 | //实例化环境
21 | val users = sc.parallelize(Array("aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "ddd", "eee"))
22 | //设置用户
23 | val films = sc.parallelize(Array("smzdm", "ylxb", "znh", "nhsc", "fcwr")) //设置电影名
24 |
25 | val source = Map[String, Map[String, Int]]()
26 | //使用一个source嵌套map作为姓名电影名和分值的存储
27 | val filmSource = Map[String, Int]()
28 |
29 | //设置一个用以存放电影分的map
30 | def getSource(): Map[String, Map[String, Int]] = {
31 | //设置电影评分
32 | val user1FilmSource = Map("smzdm" -> 2, "ylxb" -> 3, "znh" -> 1, "nhsc" -> 0, "fcwr" -> 1)
33 | val user2FilmSource = Map("smzdm" -> 1, "ylxb" -> 2, "znh" -> 2, "nhsc" -> 1, "fcwr" -> 4)
34 | val user3FilmSource = Map("smzdm" -> 2, "ylxb" -> 1, "znh" -> 0, "nhsc" -> 1, "fcwr" -> 4)
35 | val user4FilmSource = Map("smzdm" -> 3, "ylxb" -> 2, "znh" -> 0, "nhsc" -> 5, "fcwr" -> 3)
36 | val user5FilmSource = Map("smzdm" -> 5, "ylxb" -> 3, "znh" -> 1, "nhsc" -> 1, "fcwr" -> 2)
37 | source += ("aaa" -> user1FilmSource) //对人名进行存储
38 | source += ("bbb" -> user2FilmSource) //对人名进行存储
39 | source += ("ccc" -> user3FilmSource) //对人名进行存储
40 | source += ("ddd" -> user4FilmSource) //对人名进行存储
41 | source += ("eee" -> user5FilmSource) //对人名进行存储
42 | source //返回嵌套map
43 | }
44 |
45 | //两两计算分值,采用余弦相似性
46 | def getCollaborateSource(user1: String, user2: String): Double = {
47 | val user1FilmSource = source.get(user1).get.values.toVector //获得第1个用户的评分
48 | val user2FilmSource = source.get(user2).get.values.toVector //获得第2个用户的评分
49 | val member = user1FilmSource.zip(user2FilmSource).map(d => d._1 * d._2).reduce(_ + _).toDouble //对公式分子部分进行计算
50 | val temp1 = math.sqrt(user1FilmSource.map(num => {
51 | //求出分母第1个变量值
52 | math.pow(num, 2) //数学计算
53 | }).reduce(_ + _)) //进行叠加
54 | val temp2 = math.sqrt(user2FilmSource.map(num => {
55 | ////求出分母第2个变量值
56 | math.pow(num, 2) //数学计算
57 | }).reduce(_ + _)) //进行叠加
58 | val denominator = temp1 * temp2 //求出分母
59 | member / denominator //进行计算
60 | }
61 |
62 | def main(args: Array[String]) {
63 | getSource() //初始化分数
64 | var name = "bbb" //设定目标对象
65 | users.foreach(user => {
66 | //迭代进行计算
67 | println(name + " 相对于 " + user + "的相似性分数是:" + getCollaborateSource(name, user))
68 | })
69 | println()
70 | name = "aaa"
71 | users.foreach(user => {
72 | //迭代进行计算
73 | println(name + " 相对于 " + user + "的相似性分数是:" + getCollaborateSource(name, user))
74 | })
75 | }
76 | }
77 |
78 | ```
79 |
80 |
81 | 结果:
82 |
83 | ```
84 | D:\1win7\java\jdk\bin\java -Didea.launcher.port=7534 "-Didea.launcher.bin.path=D:\1win7\idea\IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition 15.0.4\bin" -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath "D:\all\idea\SparkLearning\bin;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\charsets.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\deploy.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\ext\access-bridge-64.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\ext\dnsns.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\ext\jaccess.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\ext\localedata.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\ext\sunec.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\ext\sunjce_provider.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\ext\sunmscapi.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\ext\zipfs.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\javaws.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\jce.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\jfr.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\jfxrt.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\jsse.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\management-agent.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\plugin.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\resources.jar;D:\1win7\java\jdk\jre\lib\rt.jar;D:\1win7\scala;D:\1win7\scala\lib;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\spark-assembly-1.5.2-hadoop2.6.0.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\adam-apis_2.10-0.18.3-SNAPSHOT.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\adam-cli_2.10-0.18.3-SNAPSHOT.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\adam-core_2.10-0.18.3-SNAPSHOT.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\SparkCSV\com.databricks_spark-csv_2.10-1.4.0.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\SparkCSV\com.univocity_univocity-parsers-1.5.1.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\SparkCSV\org.apache.commons_commons-csv-1.1.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\SparkAvro\spark-avro_2.10-2.0.1.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\SparkAvro\spark-avro_2.10-2.0.1-javadoc.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\SparkAvro\spark-avro_2.10-2.0.1-sources.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\avro\spark-avro_2.10-2.0.2-SNAPSHOT.jar;D:\1win7\java\otherJar\tachyon\tachyon-assemblies-0.7.1-jar-with-dependencies.jar;D:\1win7\scala\lib\scala-actors-migration.jar;D:\1win7\scala\lib\scala-actors.jar;D:\1win7\scala\lib\scala-library.jar;D:\1win7\scala\lib\scala-reflect.jar;D:\1win7\scala\lib\scala-swing.jar;D:\1win7\idea\IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition 15.0.4\lib\idea_rt.jar" com.intellij.rt.execution.application.AppMain org.apache.spark.mllib.learning.recommend.CollaborativeFilteringSpark
85 | CollaborativeFilteringSpark
86 | SLF4J: Class path contains multiple SLF4J bindings.
87 | SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/D:/1win7/java/otherJar/spark-assembly-1.5.2-hadoop2.6.0.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]
88 | SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/D:/1win7/java/otherJar/adam-cli_2.10-0.18.3-SNAPSHOT.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]
89 | SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/D:/1win7/java/otherJar/tachyon/tachyon-assemblies-0.7.1-jar-with-dependencies.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]
90 | SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#multiple_bindings for an explanation.
91 | SLF4J: Actual binding is of type [org.slf4j.impl.Log4jLoggerFactory]
92 | 2016-05-16 20:57:50 WARN NativeCodeLoader:62 - Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
93 | 2016-05-16 20:57:52 WARN MetricsSystem:71 - Using default name DAGScheduler for source because spark.app.id is not set.
94 | bbb 相对于 aaa的相似性分数是:0.7089175569585667
95 | bbb 相对于 bbb的相似性分数是:1.0000000000000002
96 | bbb 相对于 ccc的相似性分数是:0.8780541105074453
97 | bbb 相对于 ddd的相似性分数是:0.6865554812287477
98 | bbb 相对于 eee的相似性分数是:0.6821910402406466
99 |
100 | aaa 相对于 aaa的相似性分数是:0.9999999999999999
101 | aaa 相对于 bbb的相似性分数是:0.7089175569585667
102 | aaa 相对于 ccc的相似性分数是:0.6055300708194983
103 | aaa 相对于 ddd的相似性分数是:0.564932682866032
104 | aaa 相对于 eee的相似性分数是:0.8981462390204985
105 |
106 | Process finished with exit code 0
107 |
108 | ```
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------