├── .gitignore
├── ICPP_FORMAL.pdf
├── ICPP_Presentation.pdf
├── LICENSE.md
├── Makefile
├── README.md
├── core
├── __init__.py
├── optim
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── gradient_sgd.py
├── server.py
└── utils
│ ├── GradualWarmupScheduler.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── constant.py
│ ├── log.py
│ ├── messaging.py
│ └── serialization.py
├── example
├── ImageNet_dali_dataloader.py
├── Imagenet_dist.py
├── Imagenet_local.py
├── an4.py
├── cifar10.py
├── graph.py
├── main.py
├── models.py
├── pssh_script.py
└── tinyimagenet.py
├── notebook
├── Async-result-analyze-cifar.ipynb
├── Async-result-analyze-imagenet.ipynb
├── Async-result-analyze.ipynb
├── Untitled.ipynb
└── result_analyze.ipynb
├── requirements.txt
└── setup.py
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | data
2 | __pycache__/
3 | .pyc*
4 | train.log
5 | env/
6 | venv/
7 | .idea/
8 | .ipynb_checkpoints/*
9 | log/*
10 | build/*
11 | dist/*
12 | pytorch_distbelief.egg-info/*
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ICPP_FORMAL.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yanring/DGS/97e738995eccd771741f87af2251e929788e106e/ICPP_FORMAL.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ICPP_Presentation.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yanring/DGS/97e738995eccd771741f87af2251e929788e106e/ICPP_Presentation.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
2 | Version 3, 29 June 2007
3 |
4 | Copyright (C) 2007 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
5 | Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies
6 | of this license document, but changing it is not allowed.
7 |
8 | Preamble
9 |
10 | The GNU General Public License is a free, copyleft license for
11 | software and other kinds of works.
12 |
13 | The licenses for most software and other practical works are designed
14 | to take away your freedom to share and change the works. By contrast,
15 | the GNU General Public License is intended to guarantee your freedom to
16 | share and change all versions of a program--to make sure it remains free
17 | software for all its users. We, the Free Software Foundation, use the
18 | GNU General Public License for most of our software; it applies also to
19 | any other work released this way by its authors. You can apply it to
20 | your programs, too.
21 |
22 | When we speak of free software, we are referring to freedom, not
23 | price. Our General Public Licenses are designed to make sure that you
24 | have the freedom to distribute copies of free software (and charge for
25 | them if you wish), that you receive source code or can get it if you
26 | want it, that you can change the software or use pieces of it in new
27 | free programs, and that you know you can do these things.
28 |
29 | To protect your rights, we need to prevent others from denying you
30 | these rights or asking you to surrender the rights. Therefore, you have
31 | certain responsibilities if you distribute copies of the software, or if
32 | you modify it: responsibilities to respect the freedom of others.
33 |
34 | For example, if you distribute copies of such a program, whether
35 | gratis or for a fee, you must pass on to the recipients the same
36 | freedoms that you received. You must make sure that they, too, receive
37 | or can get the source code. And you must show them these terms so they
38 | know their rights.
39 |
40 | Developers that use the GNU GPL protect your rights with two steps:
41 | (1) assert copyright on the software, and (2) offer you this License
42 | giving you legal permission to copy, distribute and/or modify it.
43 |
44 | For the developers' and authors' protection, the GPL clearly explains
45 | that there is no warranty for this free software. For both users' and
46 | authors' sake, the GPL requires that modified versions be marked as
47 | changed, so that their problems will not be attributed erroneously to
48 | authors of previous versions.
49 |
50 | Some devices are designed to deny users access to install or run
51 | modified versions of the software inside them, although the manufacturer
52 | can do so. This is fundamentally incompatible with the aim of
53 | protecting users' freedom to change the software. The systematic
54 | pattern of such abuse occurs in the area of products for individuals to
55 | use, which is precisely where it is most unacceptable. Therefore, we
56 | have designed this version of the GPL to prohibit the practice for those
57 | products. If such problems arise substantially in other domains, we
58 | stand ready to extend this provision to those domains in future versions
59 | of the GPL, as needed to protect the freedom of users.
60 |
61 | Finally, every program is threatened constantly by software patents.
62 | States should not allow patents to restrict development and use of
63 | software on general-purpose computers, but in those that do, we wish to
64 | avoid the special danger that patents applied to a free program could
65 | make it effectively proprietary. To prevent this, the GPL assures that
66 | patents cannot be used to render the program non-free.
67 |
68 | The precise terms and conditions for copying, distribution and
69 | modification follow.
70 |
71 | TERMS AND CONDITIONS
72 |
73 | 0. Definitions.
74 |
75 | "This License" refers to version 3 of the GNU General Public License.
76 |
77 | "Copyright" also means copyright-like laws that apply to other kinds of
78 | works, such as semiconductor masks.
79 |
80 | "The Program" refers to any copyrightable work licensed under this
81 | License. Each licensee is addressed as "you". "Licensees" and
82 | "recipients" may be individuals or organizations.
83 |
84 | To "modify" a work means to copy from or adapt all or part of the work
85 | in a fashion requiring copyright permission, other than the making of an
86 | exact copy. The resulting work is called a "modified version" of the
87 | earlier work or a work "based on" the earlier work.
88 |
89 | A "covered work" means either the unmodified Program or a work based
90 | on the Program.
91 |
92 | To "propagate" a work means to do anything with it that, without
93 | permission, would make you directly or secondarily liable for
94 | infringement under applicable copyright law, except executing it on a
95 | computer or modifying a private copy. Propagation includes copying,
96 | distribution (with or without modification), making available to the
97 | public, and in some countries other activities as well.
98 |
99 | To "convey" a work means any kind of propagation that enables other
100 | parties to make or receive copies. Mere interaction with a user through
101 | a computer network, with no transfer of a copy, is not conveying.
102 |
103 | An interactive user interface displays "Appropriate Legal Notices"
104 | to the extent that it includes a convenient and prominently visible
105 | feature that (1) displays an appropriate copyright notice, and (2)
106 | tells the user that there is no warranty for the work (except to the
107 | extent that warranties are provided), that licensees may convey the
108 | work under this License, and how to view a copy of this License. If
109 | the interface presents a list of user commands or options, such as a
110 | menu, a prominent item in the list meets this criterion.
111 |
112 | 1. Source Code.
113 |
114 | The "source code" for a work means the preferred form of the work
115 | for making modifications to it. "Object code" means any non-source
116 | form of a work.
117 |
118 | A "Standard Interface" means an interface that either is an official
119 | standard defined by a recognized standards body, or, in the case of
120 | interfaces specified for a particular programming language, one that
121 | is widely used among developers working in that language.
122 |
123 | The "System Libraries" of an executable work include anything, other
124 | than the work as a whole, that (a) is included in the normal form of
125 | packaging a Major Component, but which is not part of that Major
126 | Component, and (b) serves only to enable use of the work with that
127 | Major Component, or to implement a Standard Interface for which an
128 | implementation is available to the public in source code form. A
129 | "Major Component", in this context, means a major essential component
130 | (kernel, window system, and so on) of the specific operating system
131 | (if any) on which the executable work runs, or a compiler used to
132 | produce the work, or an object code interpreter used to run it.
133 |
134 | The "Corresponding Source" for a work in object code form means all
135 | the source code needed to generate, install, and (for an executable
136 | work) run the object code and to modify the work, including scripts to
137 | control those activities. However, it does not include the work's
138 | System Libraries, or general-purpose tools or generally available free
139 | programs which are used unmodified in performing those activities but
140 | which are not part of the work. For example, Corresponding Source
141 | includes interface definition files associated with source files for
142 | the work, and the source code for shared libraries and dynamically
143 | linked subprograms that the work is specifically designed to require,
144 | such as by intimate data communication or control flow between those
145 | subprograms and other parts of the work.
146 |
147 | The Corresponding Source need not include anything that users
148 | can regenerate automatically from other parts of the Corresponding
149 | Source.
150 |
151 | The Corresponding Source for a work in source code form is that
152 | same work.
153 |
154 | 2. Basic Permissions.
155 |
156 | All rights granted under this License are granted for the term of
157 | copyright on the Program, and are irrevocable provided the stated
158 | conditions are met. This License explicitly affirms your unlimited
159 | permission to run the unmodified Program. The output from running a
160 | covered work is covered by this License only if the output, given its
161 | content, constitutes a covered work. This License acknowledges your
162 | rights of fair use or other equivalent, as provided by copyright law.
163 |
164 | You may make, run and propagate covered works that you do not
165 | convey, without conditions so long as your license otherwise remains
166 | in force. You may convey covered works to others for the sole purpose
167 | of having them make modifications exclusively for you, or provide you
168 | with facilities for running those works, provided that you comply with
169 | the terms of this License in conveying all material for which you do
170 | not control copyright. Those thus making or running the covered works
171 | for you must do so exclusively on your behalf, under your direction
172 | and control, on terms that prohibit them from making any copies of
173 | your copyrighted material outside their relationship with you.
174 |
175 | Conveying under any other circumstances is permitted solely under
176 | the conditions stated below. Sublicensing is not allowed; section 10
177 | makes it unnecessary.
178 |
179 | 3. Protecting Users' Legal Rights From Anti-Circumvention Law.
180 |
181 | No covered work shall be deemed part of an effective technological
182 | measure under any applicable law fulfilling obligations under article
183 | 11 of the WIPO copyright treaty adopted on 20 December 1996, or
184 | similar laws prohibiting or restricting circumvention of such
185 | measures.
186 |
187 | When you convey a covered work, you waive any legal power to forbid
188 | circumvention of technological measures to the extent such circumvention
189 | is effected by exercising rights under this License with respect to
190 | the covered work, and you disclaim any intention to limit operation or
191 | modification of the work as a means of enforcing, against the work's
192 | users, your or third parties' legal rights to forbid circumvention of
193 | technological measures.
194 |
195 | 4. Conveying Verbatim Copies.
196 |
197 | You may convey verbatim copies of the Program's source code as you
198 | receive it, in any medium, provided that you conspicuously and
199 | appropriately publish on each copy an appropriate copyright notice;
200 | keep intact all notices stating that this License and any
201 | non-permissive terms added in accord with section 7 apply to the code;
202 | keep intact all notices of the absence of any warranty; and give all
203 | recipients a copy of this License along with the Program.
204 |
205 | You may charge any price or no price for each copy that you convey,
206 | and you may offer support or warranty protection for a fee.
207 |
208 | 5. Conveying Modified Source Versions.
209 |
210 | You may convey a work based on the Program, or the modifications to
211 | produce it from the Program, in the form of source code under the
212 | terms of section 4, provided that you also meet all of these conditions:
213 |
214 | a) The work must carry prominent notices stating that you modified
215 | it, and giving a relevant date.
216 |
217 | b) The work must carry prominent notices stating that it is
218 | released under this License and any conditions added under section
219 | 7. This requirement modifies the requirement in section 4 to
220 | "keep intact all notices".
221 |
222 | c) You must license the entire work, as a whole, under this
223 | License to anyone who comes into possession of a copy. This
224 | License will therefore apply, along with any applicable section 7
225 | additional terms, to the whole of the work, and all its parts,
226 | regardless of how they are packaged. This License gives no
227 | permission to license the work in any other way, but it does not
228 | invalidate such permission if you have separately received it.
229 |
230 | d) If the work has interactive user interfaces, each must display
231 | Appropriate Legal Notices; however, if the Program has interactive
232 | interfaces that do not display Appropriate Legal Notices, your
233 | work need not make them do so.
234 |
235 | A compilation of a covered work with other separate and independent
236 | works, which are not by their nature extensions of the covered work,
237 | and which are not combined with it such as to form a larger program,
238 | in or on a volume of a storage or distribution medium, is called an
239 | "aggregate" if the compilation and its resulting copyright are not
240 | used to limit the access or legal rights of the compilation's users
241 | beyond what the individual works permit. Inclusion of a covered work
242 | in an aggregate does not cause this License to apply to the other
243 | parts of the aggregate.
244 |
245 | 6. Conveying Non-Source Forms.
246 |
247 | You may convey a covered work in object code form under the terms
248 | of sections 4 and 5, provided that you also convey the
249 | machine-readable Corresponding Source under the terms of this License,
250 | in one of these ways:
251 |
252 | a) Convey the object code in, or embodied in, a physical product
253 | (including a physical distribution medium), accompanied by the
254 | Corresponding Source fixed on a durable physical medium
255 | customarily used for software interchange.
256 |
257 | b) Convey the object code in, or embodied in, a physical product
258 | (including a physical distribution medium), accompanied by a
259 | written offer, valid for at least three years and valid for as
260 | long as you offer spare parts or customer support for that product
261 | model, to give anyone who possesses the object code either (1) a
262 | copy of the Corresponding Source for all the software in the
263 | product that is covered by this License, on a durable physical
264 | medium customarily used for software interchange, for a price no
265 | more than your reasonable cost of physically performing this
266 | conveying of source, or (2) access to copy the
267 | Corresponding Source from a network server at no charge.
268 |
269 | c) Convey individual copies of the object code with a copy of the
270 | written offer to provide the Corresponding Source. This
271 | alternative is allowed only occasionally and noncommercially, and
272 | only if you received the object code with such an offer, in accord
273 | with subsection 6b.
274 |
275 | d) Convey the object code by offering access from a designated
276 | place (gratis or for a charge), and offer equivalent access to the
277 | Corresponding Source in the same way through the same place at no
278 | further charge. You need not require recipients to copy the
279 | Corresponding Source along with the object code. If the place to
280 | copy the object code is a network server, the Corresponding Source
281 | may be on a different server (operated by you or a third party)
282 | that supports equivalent copying facilities, provided you maintain
283 | clear directions next to the object code saying where to find the
284 | Corresponding Source. Regardless of what server hosts the
285 | Corresponding Source, you remain obligated to ensure that it is
286 | available for as long as needed to satisfy these requirements.
287 |
288 | e) Convey the object code using peer-to-peer transmission, provided
289 | you inform other peers where the object code and Corresponding
290 | Source of the work are being offered to the general public at no
291 | charge under subsection 6d.
292 |
293 | A separable portion of the object code, whose source code is excluded
294 | from the Corresponding Source as a System Library, need not be
295 | included in conveying the object code work.
296 |
297 | A "User Product" is either (1) a "consumer product", which means any
298 | tangible personal property which is normally used for personal, family,
299 | or household purposes, or (2) anything designed or sold for incorporation
300 | into a dwelling. In determining whether a product is a consumer product,
301 | doubtful cases shall be resolved in favor of coverage. For a particular
302 | product received by a particular user, "normally used" refers to a
303 | typical or common use of that class of product, regardless of the status
304 | of the particular user or of the way in which the particular user
305 | actually uses, or expects or is expected to use, the product. A product
306 | is a consumer product regardless of whether the product has substantial
307 | commercial, industrial or non-consumer uses, unless such uses represent
308 | the only significant mode of use of the product.
309 |
310 | "Installation Information" for a User Product means any methods,
311 | procedures, authorization keys, or other information required to install
312 | and execute modified versions of a covered work in that User Product from
313 | a modified version of its Corresponding Source. The information must
314 | suffice to ensure that the continued functioning of the modified object
315 | code is in no case prevented or interfered with solely because
316 | modification has been made.
317 |
318 | If you convey an object code work under this section in, or with, or
319 | specifically for use in, a User Product, and the conveying occurs as
320 | part of a transaction in which the right of possession and use of the
321 | User Product is transferred to the recipient in perpetuity or for a
322 | fixed term (regardless of how the transaction is characterized), the
323 | Corresponding Source conveyed under this section must be accompanied
324 | by the Installation Information. But this requirement does not apply
325 | if neither you nor any third party retains the ability to install
326 | modified object code on the User Product (for example, the work has
327 | been installed in ROM).
328 |
329 | The requirement to provide Installation Information does not include a
330 | requirement to continue to provide support service, warranty, or updates
331 | for a work that has been modified or installed by the recipient, or for
332 | the User Product in which it has been modified or installed. Access to a
333 | network may be denied when the modification itself materially and
334 | adversely affects the operation of the network or violates the rules and
335 | protocols for communication across the network.
336 |
337 | Corresponding Source conveyed, and Installation Information provided,
338 | in accord with this section must be in a format that is publicly
339 | documented (and with an implementation available to the public in
340 | source code form), and must require no special password or key for
341 | unpacking, reading or copying.
342 |
343 | 7. Additional Terms.
344 |
345 | "Additional permissions" are terms that supplement the terms of this
346 | License by making exceptions from one or more of its conditions.
347 | Additional permissions that are applicable to the entire Program shall
348 | be treated as though they were included in this License, to the extent
349 | that they are valid under applicable law. If additional permissions
350 | apply only to part of the Program, that part may be used separately
351 | under those permissions, but the entire Program remains governed by
352 | this License without regard to the additional permissions.
353 |
354 | When you convey a copy of a covered work, you may at your option
355 | remove any additional permissions from that copy, or from any part of
356 | it. (Additional permissions may be written to require their own
357 | removal in certain cases when you modify the work.) You may place
358 | additional permissions on material, added by you to a covered work,
359 | for which you have or can give appropriate copyright permission.
360 |
361 | Notwithstanding any other provision of this License, for material you
362 | add to a covered work, you may (if authorized by the copyright holders of
363 | that material) supplement the terms of this License with terms:
364 |
365 | a) Disclaiming warranty or limiting liability differently from the
366 | terms of sections 15 and 16 of this License; or
367 |
368 | b) Requiring preservation of specified reasonable legal notices or
369 | author attributions in that material or in the Appropriate Legal
370 | Notices displayed by works containing it; or
371 |
372 | c) Prohibiting misrepresentation of the origin of that material, or
373 | requiring that modified versions of such material be marked in
374 | reasonable ways as different from the original version; or
375 |
376 | d) Limiting the use for publicity purposes of names of licensors or
377 | authors of the material; or
378 |
379 | e) Declining to grant rights under trademark law for use of some
380 | trade names, trademarks, or service marks; or
381 |
382 | f) Requiring indemnification of licensors and authors of that
383 | material by anyone who conveys the material (or modified versions of
384 | it) with contractual assumptions of liability to the recipient, for
385 | any liability that these contractual assumptions directly impose on
386 | those licensors and authors.
387 |
388 | All other non-permissive additional terms are considered "further
389 | restrictions" within the meaning of section 10. If the Program as you
390 | received it, or any part of it, contains a notice stating that it is
391 | governed by this License along with a term that is a further
392 | restriction, you may remove that term. If a license document contains
393 | a further restriction but permits relicensing or conveying under this
394 | License, you may add to a covered work material governed by the terms
395 | of that license document, provided that the further restriction does
396 | not survive such relicensing or conveying.
397 |
398 | If you add terms to a covered work in accord with this section, you
399 | must place, in the relevant source files, a statement of the
400 | additional terms that apply to those files, or a notice indicating
401 | where to find the applicable terms.
402 |
403 | Additional terms, permissive or non-permissive, may be stated in the
404 | form of a separately written license, or stated as exceptions;
405 | the above requirements apply either way.
406 |
407 | 8. Termination.
408 |
409 | You may not propagate or modify a covered work except as expressly
410 | provided under this License. Any attempt otherwise to propagate or
411 | modify it is void, and will automatically terminate your rights under
412 | this License (including any patent licenses granted under the third
413 | paragraph of section 11).
414 |
415 | However, if you cease all violation of this License, then your
416 | license from a particular copyright holder is reinstated (a)
417 | provisionally, unless and until the copyright holder explicitly and
418 | finally terminates your license, and (b) permanently, if the copyright
419 | holder fails to notify you of the violation by some reasonable means
420 | prior to 60 days after the cessation.
421 |
422 | Moreover, your license from a particular copyright holder is
423 | reinstated permanently if the copyright holder notifies you of the
424 | violation by some reasonable means, this is the first time you have
425 | received notice of violation of this License (for any work) from that
426 | copyright holder, and you cure the violation prior to 30 days after
427 | your receipt of the notice.
428 |
429 | Termination of your rights under this section does not terminate the
430 | licenses of parties who have received copies or rights from you under
431 | this License. If your rights have been terminated and not permanently
432 | reinstated, you do not qualify to receive new licenses for the same
433 | material under section 10.
434 |
435 | 9. Acceptance Not Required for Having Copies.
436 |
437 | You are not required to accept this License in order to receive or
438 | run a copy of the Program. Ancillary propagation of a covered work
439 | occurring solely as a consequence of using peer-to-peer transmission
440 | to receive a copy likewise does not require acceptance. However,
441 | nothing other than this License grants you permission to propagate or
442 | modify any covered work. These actions infringe copyright if you do
443 | not accept this License. Therefore, by modifying or propagating a
444 | covered work, you indicate your acceptance of this License to do so.
445 |
446 | 10. Automatic Licensing of Downstream Recipients.
447 |
448 | Each time you convey a covered work, the recipient automatically
449 | receives a license from the original licensors, to run, modify and
450 | propagate that work, subject to this License. You are not responsible
451 | for enforcing compliance by third parties with this License.
452 |
453 | An "entity transaction" is a transaction transferring control of an
454 | organization, or substantially all assets of one, or subdividing an
455 | organization, or merging organizations. If propagation of a covered
456 | work results from an entity transaction, each party to that
457 | transaction who receives a copy of the work also receives whatever
458 | licenses to the work the party's predecessor in interest had or could
459 | give under the previous paragraph, plus a right to possession of the
460 | Corresponding Source of the work from the predecessor in interest, if
461 | the predecessor has it or can get it with reasonable efforts.
462 |
463 | You may not impose any further restrictions on the exercise of the
464 | rights granted or affirmed under this License. For example, you may
465 | not impose a license fee, royalty, or other charge for exercise of
466 | rights granted under this License, and you may not initiate litigation
467 | (including a cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that
468 | any patent claim is infringed by making, using, selling, offering for
469 | sale, or importing the Program or any portion of it.
470 |
471 | 11. Patents.
472 |
473 | A "contributor" is a copyright holder who authorizes use under this
474 | License of the Program or a work on which the Program is based. The
475 | work thus licensed is called the contributor's "contributor version".
476 |
477 | A contributor's "essential patent claims" are all patent claims
478 | owned or controlled by the contributor, whether already acquired or
479 | hereafter acquired, that would be infringed by some manner, permitted
480 | by this License, of making, using, or selling its contributor version,
481 | but do not include claims that would be infringed only as a
482 | consequence of further modification of the contributor version. For
483 | purposes of this definition, "control" includes the right to grant
484 | patent sublicenses in a manner consistent with the requirements of
485 | this License.
486 |
487 | Each contributor grants you a non-exclusive, worldwide, royalty-free
488 | patent license under the contributor's essential patent claims, to
489 | make, use, sell, offer for sale, import and otherwise run, modify and
490 | propagate the contents of its contributor version.
491 |
492 | In the following three paragraphs, a "patent license" is any express
493 | agreement or commitment, however denominated, not to enforce a patent
494 | (such as an express permission to practice a patent or covenant not to
495 | sue for patent infringement). To "grant" such a patent license to a
496 | party means to make such an agreement or commitment not to enforce a
497 | patent against the party.
498 |
499 | If you convey a covered work, knowingly relying on a patent license,
500 | and the Corresponding Source of the work is not available for anyone
501 | to copy, free of charge and under the terms of this License, through a
502 | publicly available network server or other readily accessible means,
503 | then you must either (1) cause the Corresponding Source to be so
504 | available, or (2) arrange to deprive yourself of the benefit of the
505 | patent license for this particular work, or (3) arrange, in a manner
506 | consistent with the requirements of this License, to extend the patent
507 | license to downstream recipients. "Knowingly relying" means you have
508 | actual knowledge that, but for the patent license, your conveying the
509 | covered work in a country, or your recipient's use of the covered work
510 | in a country, would infringe one or more identifiable patents in that
511 | country that you have reason to believe are valid.
512 |
513 | If, pursuant to or in connection with a single transaction or
514 | arrangement, you convey, or propagate by procuring conveyance of, a
515 | covered work, and grant a patent license to some of the parties
516 | receiving the covered work authorizing them to use, propagate, modify
517 | or convey a specific copy of the covered work, then the patent license
518 | you grant is automatically extended to all recipients of the covered
519 | work and works based on it.
520 |
521 | A patent license is "discriminatory" if it does not include within
522 | the scope of its coverage, prohibits the exercise of, or is
523 | conditioned on the non-exercise of one or more of the rights that are
524 | specifically granted under this License. You may not convey a covered
525 | work if you are a party to an arrangement with a third party that is
526 | in the business of distributing software, under which you make payment
527 | to the third party based on the extent of your activity of conveying
528 | the work, and under which the third party grants, to any of the
529 | parties who would receive the covered work from you, a discriminatory
530 | patent license (a) in connection with copies of the covered work
531 | conveyed by you (or copies made from those copies), or (b) primarily
532 | for and in connection with specific products or compilations that
533 | contain the covered work, unless you entered into that arrangement,
534 | or that patent license was granted, prior to 28 March 2007.
535 |
536 | Nothing in this License shall be construed as excluding or limiting
537 | any implied license or other defenses to infringement that may
538 | otherwise be available to you under applicable patent law.
539 |
540 | 12. No Surrender of Others' Freedom.
541 |
542 | If conditions are imposed on you (whether by court order, agreement or
543 | otherwise) that contradict the conditions of this License, they do not
544 | excuse you from the conditions of this License. If you cannot convey a
545 | covered work so as to satisfy simultaneously your obligations under this
546 | License and any other pertinent obligations, then as a consequence you may
547 | not convey it at all. For example, if you agree to terms that obligate you
548 | to collect a royalty for further conveying from those to whom you convey
549 | the Program, the only way you could satisfy both those terms and this
550 | License would be to refrain entirely from conveying the Program.
551 |
552 | 13. Use with the GNU Affero General Public License.
553 |
554 | Notwithstanding any other provision of this License, you have
555 | permission to link or combine any covered work with a work licensed
556 | under version 3 of the GNU Affero General Public License into a single
557 | combined work, and to convey the resulting work. The terms of this
558 | License will continue to apply to the part which is the covered work,
559 | but the special requirements of the GNU Affero General Public License,
560 | section 13, concerning interaction through a network will apply to the
561 | combination as such.
562 |
563 | 14. Revised Versions of this License.
564 |
565 | The Free Software Foundation may publish revised and/or new versions of
566 | the GNU General Public License from time to time. Such new versions will
567 | be similar in spirit to the present version, but may differ in detail to
568 | address new problems or concerns.
569 |
570 | Each version is given a distinguishing version number. If the
571 | Program specifies that a certain numbered version of the GNU General
572 | Public License "or any later version" applies to it, you have the
573 | option of following the terms and conditions either of that numbered
574 | version or of any later version published by the Free Software
575 | Foundation. If the Program does not specify a version number of the
576 | GNU General Public License, you may choose any version ever published
577 | by the Free Software Foundation.
578 |
579 | If the Program specifies that a proxy can decide which future
580 | versions of the GNU General Public License can be used, that proxy's
581 | public statement of acceptance of a version permanently authorizes you
582 | to choose that version for the Program.
583 |
584 | Later license versions may give you additional or different
585 | permissions. However, no additional obligations are imposed on any
586 | author or copyright holder as a result of your choosing to follow a
587 | later version.
588 |
589 | 15. Disclaimer of Warranty.
590 |
591 | THERE IS NO WARRANTY FOR THE PROGRAM, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY
592 | APPLICABLE LAW. EXCEPT WHEN OTHERWISE STATED IN WRITING THE COPYRIGHT
593 | HOLDERS AND/OR OTHER PARTIES PROVIDE THE PROGRAM "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY
594 | OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
595 | THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
596 | PURPOSE. THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE OF THE PROGRAM
597 | IS WITH YOU. SHOULD THE PROGRAM PROVE DEFECTIVE, YOU ASSUME THE COST OF
598 | ALL NECESSARY SERVICING, REPAIR OR CORRECTION.
599 |
600 | 16. Limitation of Liability.
601 |
602 | IN NO EVENT UNLESS REQUIRED BY APPLICABLE LAW OR AGREED TO IN WRITING
603 | WILL ANY COPYRIGHT HOLDER, OR ANY OTHER PARTY WHO MODIFIES AND/OR CONVEYS
604 | THE PROGRAM AS PERMITTED ABOVE, BE LIABLE TO YOU FOR DAMAGES, INCLUDING ANY
605 | GENERAL, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE
606 | USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE PROGRAM (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO LOSS OF
607 | DATA OR DATA BEING RENDERED INACCURATE OR LOSSES SUSTAINED BY YOU OR THIRD
608 | PARTIES OR A FAILURE OF THE PROGRAM TO OPERATE WITH ANY OTHER PROGRAMS),
609 | EVEN IF SUCH HOLDER OR OTHER PARTY HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF
610 | SUCH DAMAGES.
611 |
612 | 17. Interpretation of Sections 15 and 16.
613 |
614 | If the disclaimer of warranty and limitation of liability provided
615 | above cannot be given local legal effect according to their terms,
616 | reviewing courts shall apply local law that most closely approximates
617 | an absolute waiver of all civil liability in connection with the
618 | Program, unless a warranty or assumption of liability accompanies a
619 | copy of the Program in return for a fee.
620 |
621 | END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
622 |
623 | How to Apply These Terms to Your New Programs
624 |
625 | If you develop a new program, and you want it to be of the greatest
626 | possible use to the public, the best way to achieve this is to make it
627 | free software which everyone can redistribute and change under these terms.
628 |
629 | To do so, attach the following notices to the program. It is safest
630 | to attach them to the start of each source file to most effectively
631 | state the exclusion of warranty; and each file should have at least
632 | the "copyright" line and a pointer to where the full notice is found.
633 |
634 |
635 | Copyright (C)
636 |
637 | This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
638 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
639 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
640 | (at your option) any later version.
641 |
642 | This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
643 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
644 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
645 | GNU General Public License for more details.
646 |
647 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
648 | along with this program. If not, see .
649 |
650 | Also add information on how to contact you by electronic and paper mail.
651 |
652 | If the program does terminal interaction, make it output a short
653 | notice like this when it starts in an interactive mode:
654 |
655 | Copyright (C)
656 | This program comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY; for details type `show w'.
657 | This is free software, and you are welcome to redistribute it
658 | under certain conditions; type `show c' for details.
659 |
660 | The hypothetical commands `show w' and `show c' should show the appropriate
661 | parts of the General Public License. Of course, your program's commands
662 | might be different; for a GUI interface, you would use an "about box".
663 |
664 | You should also get your employer (if you work as a programmer) or school,
665 | if any, to sign a "copyright disclaimer" for the program, if necessary.
666 | For more information on this, and how to apply and follow the GNU GPL, see
667 | .
668 |
669 | The GNU General Public License does not permit incorporating your program
670 | into proprietary programs. If your program is a subroutine library, you
671 | may consider it more useful to permit linking proprietary applications with
672 | the library. If this is what you want to do, use the GNU Lesser General
673 | Public License instead of this License. But first, please read
674 | .
675 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Makefile:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | setup:
2 | sudo apt-get -y virtualenv
3 | virtualenv -p python3 venv
4 | . venv/bin/activate && pip install -r requirements.txt && pip install .
5 |
6 | install:
7 | pip install .
8 |
9 | graph:
10 | python example/graph.py
11 | mv train_time.png test_time.png docs
12 |
13 | first:
14 | python example/main.py --rank 1 --world-size 3
15 |
16 | second:
17 | python example/main.py --rank 2 --world-size 3
18 |
19 | server:
20 | python example/main.py --rank 0 --world-size 3 --server
21 |
22 | single:
23 | python example/main.py --no-distributed
24 |
25 | gpu:
26 | python example/main.py --no-distributed --cuda
27 |
28 | dist:
29 | python3 setup.py sdist bdist_wheel
30 |
31 | upload: dist
32 | twine upload dist/*
33 |
34 | upload-test: dist
35 | twine upload --repository-url https://test.pypi.org/legacy/ dist/*
36 |
37 | install-test:
38 | python3 -m pip install --index-url https://test.pypi.org/simple/ pytorch-distbelief
39 |
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # DGS PyTorch
2 | []()
3 |
4 | Modern large scale machine learning applications require stochastic optimization algorithms to be implemented with distributed computational architectures. A key bottleneck is the communication overhead for exchanging information, such as stochastic gradients, among different nodes. Recently, gradient sparsification techniques have been proposed to reduce communications cost and thus alleviate the network overhead. However, most of gradient sparsification techniques consider only synchronous parallelism and cannot be applied in asynchronous distributed training.
5 |
6 | In this project, we present a dual-way gradient sparsification approach (DGS) that is suitable for asynchronous distributed training.
7 |
8 | 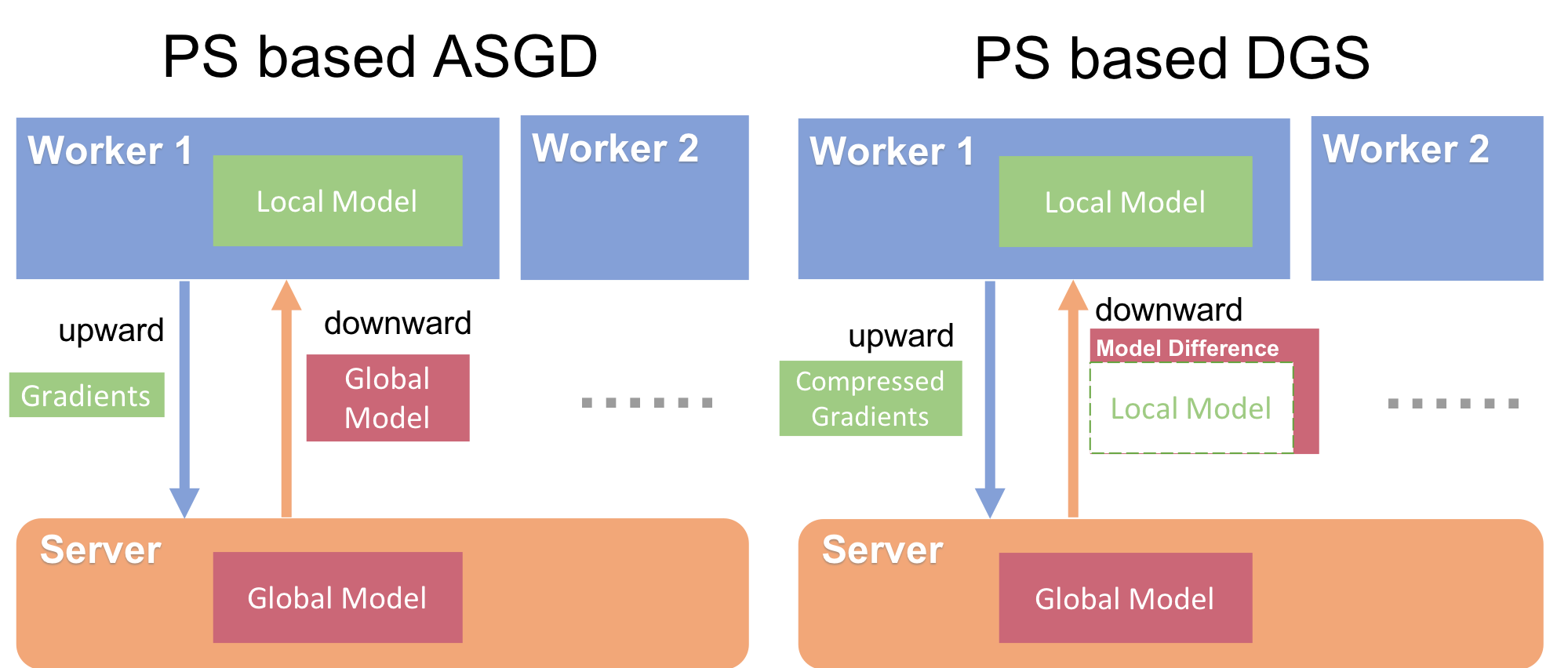
9 |
10 | We implemented a async parameter server based on PyTorch gloo backend. Our optimizer implemented 5 training methonds: DGS, ASGD, GradientDropping, DeepGradientCompression, single node momentum SGD.
11 |
12 | ## Features
13 | 1. Async parameter server on PyTorch
14 | 2. Support gradient sparsification, e.g. gradient dropping [1].
15 | 3. Sparse communication.
16 | 4. GPU training.
17 | 5. DALI dataloader for imagenet.
18 | 6. Two distributed example script: cifar10 and ImageNet.
19 |
20 | ## Performance
21 |
22 | Experiments with different scales on ImageNet and CIFAR-10 show that:
23 | (1) compared with ASGD, Gradient Dropping and Deep Gradient Compression, DGS with SAMomentum consistently achieves better performance;
24 | (2) DGS improves the scalability of asynchronous training, especially with limited networking infrastructure.
25 |
26 | 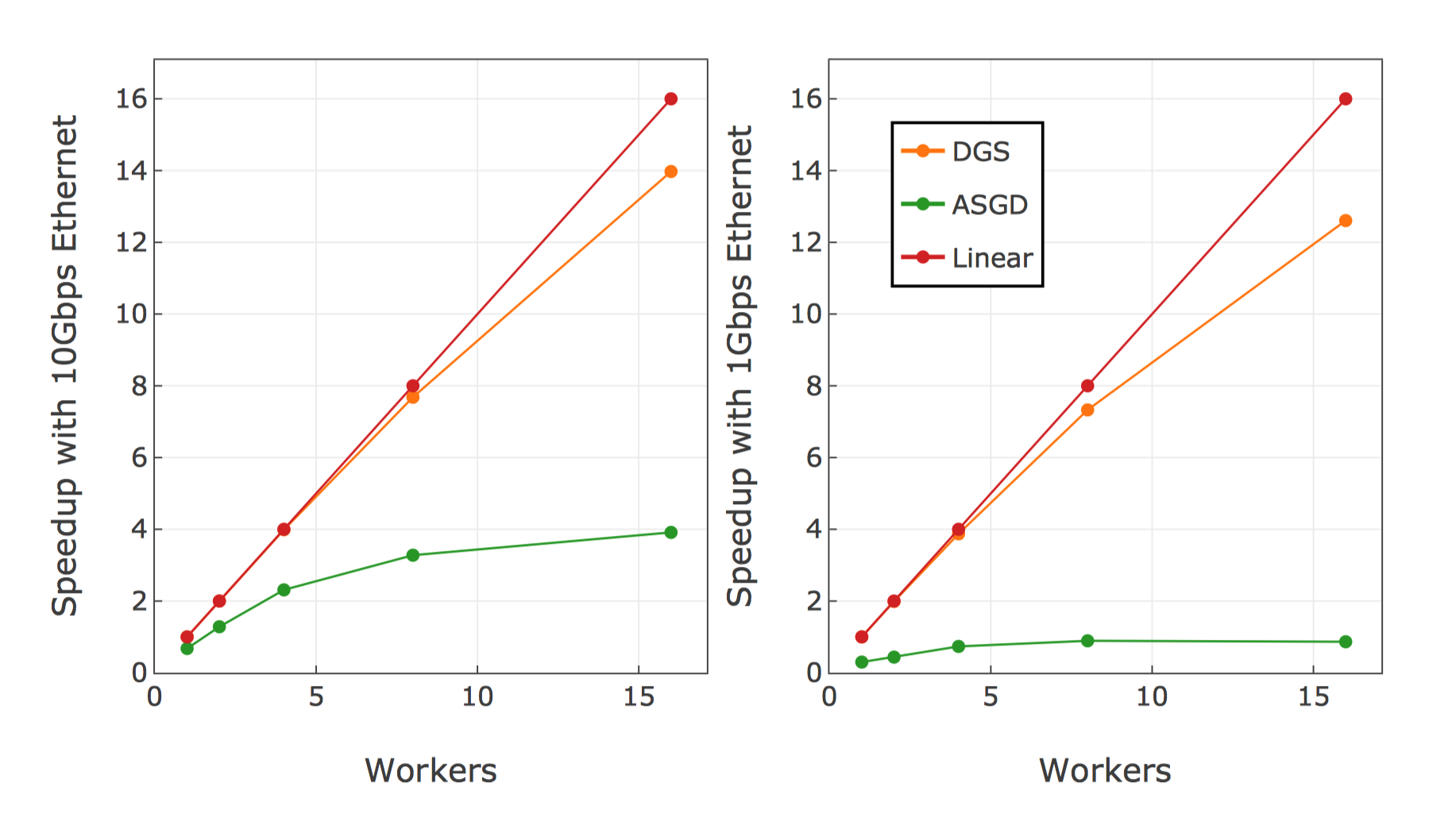
27 |
28 | Figure above shows the training speedup with different network bandwidth values.
29 | As the number of workers increases, the acceleration of ASGD decreases to nearly zero due to the bottleneck of communication. In contrast, DGS achieves nearly linear speedup with 10Gbps. With 1Gbps network, ASGD only achieves $1\times$ speedup with 16 workers, while DGS achieves $12.6\times$ speedup, which proves the the superiority of our DGS under low bandwidth.
30 |
31 |
32 | ## Quick Start
33 | ```
34 | # environ setup
35 |
36 | git clone https://github.com/yanring/GradientServer.git
37 |
38 | cd GradientServer
39 |
40 | pip install -r requirements.txt
41 | ```
42 |
43 | ```
44 | # distributed cifar-10 example
45 | # On the server (rank 0 is the server)
46 | python example/cifar10.py --world-size 3 --rank 0 --cuda
47 | # On the worker 1
48 | python example/cifar10.py --world-size 3 --rank 1 --cuda
49 | # On the worker 2
50 | python example/cifar10.py --world-size 3 --rank 2 --cuda
51 | ```
52 |
53 |
54 | ## Use DGS in Your Code
55 |
56 | First, you should start a server.
57 | ```
58 | init_server(args, net)
59 | ```
60 | Second, replace your torch.optimizer.sgd with GradientSGD.
61 | ```
62 |
63 | optimizer = GradientSGD(net.parameters(), lr=args.lr, model=net, momentum=args.momentum,weight_decay=args.weight_decay,args=args)
64 | ```
65 |
66 | ## Limitations and Future Plans
67 | TODO
68 |
69 | ## Publications
70 | Zijie Yan, Danyang Xiao, Mengqiang Chen, Jieying Zhou, Weigang Wu: Dual-Way Gradient Sparsification for Asynchronous Distributed Deep Learning. ICPP 2020: 49:1-49:10
71 |
72 | ## Refrence
73 | [1] Alham Fikri Aji and Kenneth Heafield, ‘Sparse communication for distributed gradient descent’, arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.05021, (2017).
74 | [2] Jesse Cai and Rohan Varma, Implementation of Google's DistBelief paper. https://github.com/ucla-labx/distbelief
75 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/core/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yanring/DGS/97e738995eccd771741f87af2251e929788e106e/core/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/core/optim/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .gradient_sgd import GradientSGD
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/core/optim/gradient_sgd.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import logging
2 | import os
3 | import sys
4 | import threading
5 | import time
6 | from queue import Queue
7 |
8 | import torch.distributed as dist
9 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer, required
10 |
11 | from core.utils.messaging import send_message, GSMessageCode, GradientMessageListener
12 | from core.utils.serialization import ravel_model_params, update_model_params, unravel_model_params, \
13 | ravel_sparse_gradient, unravel_sparse_gradient, worker_gradient_executor, DGC, Aji
14 |
15 | WORKPATH = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))))
16 | sys.path.append(WORKPATH)
17 | print(WORKPATH)
18 | _LOGGER = logging.getLogger(__name__)
19 | lock = threading.Lock()
20 |
21 |
22 | class GradientListener(GradientMessageListener):
23 | """DownpourListener"""
24 |
25 | def __init__(self, model, queue, args=None):
26 | super(GradientListener, self).__init__(ravel_model_params(model).numel(), source=0, args=args)
27 | self.lr = 0.05
28 | self.queue = queue
29 | self.version = 0
30 | self.model = model
31 | self.flag = False
32 |
33 | def receive(self, sender, message_code, gradient_version, lr, parameter):
34 | """receive parameter updates from the server and reflect them into the client's model."""
35 | _LOGGER.info("Processing message: {}, version: {}, lr: {}".format(message_code.name, gradient_version, self.lr))
36 | # print("Processing message: {}, version: {}, lr: {}".format(message_code.name, gradient_version, lr))
37 | self.lr = lr
38 | if message_code == GSMessageCode.GradientUpdate:
39 | update_model_params(self.model, parameter, -1)
40 | self.version = gradient_version
41 | self.queue.put(gradient_version)
42 | elif message_code == GSMessageCode.SparseGradientUpdate:
43 | parameter = unravel_sparse_gradient(parameter).cuda().to_dense()
44 | update_model_params(self.model, parameter, -1)
45 | # print('4',parameter.sum())
46 |
47 | self.version = gradient_version
48 | self.queue.put(gradient_version)
49 | elif message_code == GSMessageCode.ModelRequest:
50 | model = ravel_model_params(self.model, grads=False)
51 | send_message(GSMessageCode.ModelUpdate, model, dst=0, gradient_version=0)
52 | print('send model to server')
53 | elif message_code == GSMessageCode.ModelUpdate:
54 | # print('sync model!', gradient_version, ' ', datetime.now(), ' synced model :', parameter.sum())
55 | unravel_model_params(self.model, parameter)
56 | self.version = gradient_version
57 | self.flag = True
58 | # TODO change back
59 | if self.version > 1:
60 | self.queue.put(gradient_version)
61 | # lock.release()
62 |
63 |
64 | class GradientSGD(Optimizer):
65 | """GradientSGD"""
66 |
67 | def __init__(self, params, lr=required, model=required, momentum=None, weight_decay=0, args=None):
68 | """
69 | :param params:
70 | :param lr:
71 | :param n_push:
72 | :param n_pull:
73 | :param model:
74 | """
75 | print('in my optimizer ')
76 | if lr is not required and lr < 0.0:
77 | raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
78 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, )
79 | self.model = model
80 | self.filter_gradient = ravel_model_params(model)
81 | self.momentum = momentum
82 | self.v_kt = self.filter_gradient.clone().zero_()
83 | self.u_kt = self.filter_gradient.clone().zero_()
84 | self.idx = 0
85 | self.version = 0
86 | self.queue = Queue(maxsize=1)
87 | if args.rank > 0:
88 | time.sleep(0.1 * int(args.rank))
89 | dist.init_process_group('gloo', init_method='file://%s/sharedfile' % WORKPATH, group_name='mygroup',
90 | world_size=args.world_size, rank=args.rank)
91 | print('I am node rank:%d' % dist.get_rank())
92 | self.listener = GradientListener(model, self.queue, args=args)
93 | self.listener.start()
94 | self.tmp = 0
95 | self.compress_ratio = None
96 | self.weight_decay = weight_decay
97 | print('weight_decay', self.weight_decay, 'lr', lr, 'momentum', self.momentum)
98 | self.args = args
99 | super(GradientSGD, self).__init__(params, defaults)
100 |
101 | def step(self, closure=None):
102 | """Performs a single optimization step.
103 |
104 | Arguments:
105 | closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
106 | and returns the loss.
107 | """
108 | loss = None
109 | if closure is not None:
110 | loss = closure()
111 | if not self.listener.flag:
112 | while not self.args.no_distributed and not self.listener.flag:
113 | print('wait for server')
114 | time.sleep(1)
115 | return loss
116 |
117 | # get the lr
118 | if self.args.rank == 1:
119 | lr = self.param_groups[0]['lr']
120 | # lr = 0.2
121 | else:
122 | if self.tmp != self.listener.lr:
123 | print('lr from %f to %f' % (self.tmp, self.listener.lr))
124 | self.tmp = self.listener.lr
125 | self.param_groups[0]['lr'] = self.tmp
126 | lr = self.param_groups[0]['lr']
127 | # print(lr)
128 | # lr = self.param_groups[0]['lr']
129 | # keep track of accumulated gradients so that we can send
130 | # ASYNC
131 | if self.args.mode == 'asgd':
132 | # print('Running asgd')
133 | for param in self.model.parameters():
134 | if self.weight_decay != 0:
135 | param.grad.data.add_(self.weight_decay, param.data)
136 | self.filter_gradient = ravel_model_params(self.model, grads=True, cuda=True).mul_(lr)
137 |
138 | send_message(GSMessageCode.GradientUpdate, self.filter_gradient, dst=0,
139 | gradient_version=self.listener.version + 1)
140 | self.version = self.queue.get()
141 | self.idx += 1
142 | return loss
143 | elif self.args.mode == 'gradient_sgd':
144 | # if self.version < 5:
145 | # print('Running gradient_sgd')
146 |
147 | raveled_gradients = worker_gradient_executor(self.model, self.filter_gradient, self.u_kt, self.v_kt,
148 | rate=0.01 * (lr / self.args.lr),
149 | lr=lr, momentum=self.momentum, weight_decay=self.weight_decay)
150 | # print(1,raveled_gradients.sum())
151 | sparse_gradient = ravel_sparse_gradient(raveled_gradients)
152 |
153 | elif self.args.mode == 'dgc':
154 | # if self.version < 5:
155 | # print('Running dgc')
156 | raveled_gradients = DGC(self.model, self.filter_gradient, self.u_kt, self.v_kt,
157 | rate=0.01,
158 | # rate=self.compress_ratio,
159 | lr=lr, momentum=self.momentum, weight_decay=self.weight_decay)
160 | sparse_gradient = ravel_sparse_gradient(raveled_gradients)
161 | elif self.args.mode == 'aji':
162 | # if self.version < 5:
163 | # print('Running aji ', self.version)
164 | raveled_gradients = Aji(self.model, self.filter_gradient, self.u_kt, self.v_kt,
165 | rate=0.01,
166 | lr=lr, weight_decay=self.weight_decay)
167 | sparse_gradient = ravel_sparse_gradient(raveled_gradients)
168 | elif self.args.mode == 'sgd':
169 | # if self.version < 5:
170 | # print('Running sgd')
171 | weight_decay = self.weight_decay
172 | momentum = self.momentum
173 | dampening = 0
174 | nesterov = 0
175 | g = ravel_model_params(self.model, grads=True)
176 | p = ravel_model_params(self.model, grads=False)
177 | g.add_(weight_decay, p)
178 | self.u_kt.mul_(momentum).add_(g)
179 | raveled_gradients = self.u_kt.mul(lr)
180 | else:
181 | raise Exception('no optimizer')
182 | # reset gradient version
183 | if self.args.no_distributed:
184 | # parameter = unravel_sparse_gradient(sparse_gradient).cuda()
185 | update_model_params(self.model, raveled_gradients, 1)
186 | # self.version = gradient_version
187 | self.queue.put(self.idx)
188 | else:
189 | send_message(GSMessageCode.SparseGradientUpdate, sparse_gradient, dst=0,
190 | gradient_version=self.listener.version + 1, lr=lr)
191 | self.version = self.queue.get()
192 | self.idx += 1
193 | return loss
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/core/server.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #
2 | """
3 | Parameter server for DGS
4 | """
5 | import logging
6 | import threading
7 |
8 | import torch
9 | import torch.optim
10 |
11 | from core.utils.messaging import MessageCode, MessageListener, send_message, GSMessageCode, \
12 | GradientMessageListener
13 | from core.utils.serialization import ravel_model_params, ravel_sparse_gradient, unravel_sparse_gradient, \
14 | server_gradient_filter
15 |
16 | _LOGGER = logging.getLogger(__name__)
17 | cond = threading.Condition()
18 |
19 |
20 | class ParameterServer(MessageListener):
21 | """ParameterServer"""
22 |
23 | def __init__(self, model):
24 | _LOGGER.info("Creating ParameterServer")
25 | print("Creating ParameterServer")
26 | self.parameter_shard = torch.rand(ravel_model_params(model).numel())
27 | self.model = model
28 | # init superclass
29 | super(ParameterServer, self).__init__(model)
30 |
31 | def receive(self, sender, message_code, parameter):
32 | print("Processing message: {} from sender {}".format(message_code.name, sender))
33 |
34 | if message_code == MessageCode.ParameterUpdate:
35 | # be sure to clone here
36 | self.parameter_shard = parameter.clone()
37 |
38 | elif message_code == MessageCode.ParameterRequest:
39 | send_message(MessageCode.ParameterUpdate, self.parameter_shard, dst=sender)
40 |
41 | elif message_code == MessageCode.GradientUpdate:
42 | self.parameter_shard.add_(parameter)
43 |
44 |
45 |
46 | un_synced_worker = set()
47 |
48 | global_lr = 0.001
49 |
50 |
51 | class GradientServer(GradientMessageListener):
52 | """GradientServer"""
53 |
54 | def __init__(self, model, rank=0, worker_num=None, global_model=None, synced_model=None, size_list=None, args=None):
55 | _LOGGER.info("Creating GradientServer")
56 | print("Creating GradientServer")
57 | # self.gradient_warehouse = gradient_warehouse
58 | # self.net = model
59 | self.max_version = 0
60 | self.worker_count = 0
61 | self.worker_num = worker_num
62 | self.global_model = global_model
63 | self.global_model.share_memory_()
64 | super(GradientServer, self).__init__(model_size=global_model.numel(), source=rank, args=args)
65 | self.synced_model = synced_model
66 | self.synced_model.share_memory_()
67 | self.synced_version = 0
68 | self.acc_send_grad = synced_model.clone().zero_()
69 | self.acc_send_grad.share_memory_()
70 | self.agg_gradient = None
71 | self.size_list = size_list
72 | self.send_grad = self.acc_send_grad.clone()
73 | self.cuda = self.synced_model.is_cuda
74 | if rank == 1:
75 | for i in range(1, self.worker_num):
76 | self.sync_worker_model(i, 1)
77 | self.node_gradient = {}
78 |
79 | def sync_worker_model(self, sender, version):
80 | send_message(GSMessageCode.ModelUpdate, self.synced_model, dst=sender, gradient_version=version, lr=global_lr)
81 |
82 | def sync_model(self):
83 | self.synced_model.copy_(self.global_model)
84 | # self.synced_version = self
85 | return self.synced_model
86 |
87 | def update(self, rank, version, gradient_update):
88 | """
89 | :param rank: rank of worker node
90 | :param version: version of gradient
91 | :param gradient_update: tensor, gradient update tensor
92 | :return:
93 | """
94 | # print("update gradient from rank%d,version%d" % (rank, version))
95 | self.global_model.add_(-1, gradient_update)
96 |
97 | self.agg_gradient = self.global_model.add(-1, self.synced_model)
98 |
99 | return self.agg_gradient, version
100 |
101 | def receive(self, sender, message_code, gradient_version, lr, parameter):
102 | global un_synced_worker, global_lr
103 | # print("rank {} Processing message: {} from sender {} gradient version {}".format(self.source, message_code.name,
104 | # sender,
105 | # gradient_version))
106 | self.max_version = max(self.max_version, gradient_version)
107 | if sender == 1:
108 | global_lr = lr
109 |
110 | if message_code == GSMessageCode.GradientUpdate:
111 | if self.cuda:
112 | self.update(sender, gradient_version, parameter.cuda().float())
113 | else:
114 | self.update(sender, gradient_version, parameter.float())
115 |
116 | send_message(GSMessageCode.ModelUpdate, self.global_model, dst=sender,
117 | gradient_version=gradient_version)
118 | elif message_code == GSMessageCode.SparseGradientUpdate:
119 | if self.cuda:
120 | send_grad = self.update(sender, gradient_version, unravel_sparse_gradient(parameter).cuda())
121 | else:
122 | send_grad = self.update(sender, gradient_version, unravel_sparse_gradient(parameter))
123 |
124 | if sender == 1 and self.max_version % 150 is 1 and gradient_version > 20:
125 | self.sync_model()
126 | un_synced_worker = set(range(1, self.worker_num))
127 | if sender in un_synced_worker:
128 | self.acc_send_grad.zero_()
129 | self.sync_worker_model(sender, gradient_version)
130 | un_synced_worker.remove(sender)
131 | else:
132 | self.send_grad = self.agg_gradient.add(-1, self.acc_send_grad)
133 | server_gradient_filter(self.size_list, self.send_grad, rate=0.01)
134 | # end = time.time()
135 |
136 | # print(abs(self.send_grad).sum())
137 | # print('server cal cost time : %f' % (end - start))
138 | send_message(GSMessageCode.SparseGradientUpdate, ravel_sparse_gradient(self.send_grad), sender,
139 | gradient_version, lr=global_lr)
140 |
141 | self.acc_send_grad.add_(self.send_grad)
142 |
143 | else:
144 | raise Exception('GSMessageCode not implemented')
145 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/core/utils/GradualWarmupScheduler.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import ReduceLROnPlateau
2 | from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import _LRScheduler
3 |
4 |
5 | class GradualWarmupScheduler(_LRScheduler):
6 | """ Gradually warm-up(increasing) learning rate in optimizer.
7 | Proposed in 'Accurate, Large Minibatch SGD: Training ImageNet in 1 Hour'.
8 | Args:
9 | optimizer (Optimizer): Wrapped optimizer.
10 | multiplier: target learning rate = base lr * multiplier
11 | total_epoch: target learning rate is reached at total_epoch, gradually
12 | after_scheduler: after target_epoch, use this scheduler(eg. ReduceLROnPlateau)
13 | """
14 |
15 | def __init__(self, optimizer, multiplier, total_epoch, after_scheduler=None):
16 | self.multiplier = multiplier
17 | print('Using warm up lr scheduler')
18 | if self.multiplier <= 1.:
19 | raise ValueError('multiplier should be greater than 1.')
20 | self.total_epoch = total_epoch
21 | self.after_scheduler = after_scheduler
22 | self.finished = False
23 | super().__init__(optimizer)
24 |
25 | def get_lr(self):
26 | if self.last_epoch > self.total_epoch:
27 | if self.after_scheduler:
28 | if not self.finished:
29 | self.after_scheduler.base_lrs = [base_lr * self.multiplier for base_lr in self.base_lrs]
30 | self.finished = True
31 | return self.after_scheduler.get_lr()
32 | return [base_lr * self.multiplier for base_lr in self.base_lrs]
33 |
34 | return [base_lr * ((self.multiplier - 1.) * self.last_epoch / self.total_epoch + 1.) for base_lr in
35 | self.base_lrs]
36 |
37 | def step_ReduceLROnPlateau(self, metrics, epoch=None):
38 | if epoch is None:
39 | epoch = self.last_epoch + 1
40 | self.last_epoch = epoch if epoch != 0 else 1 # ReduceLROnPlateau is called at the end of epoch, whereas others are called at beginning
41 | if self.last_epoch <= self.total_epoch:
42 | warmup_lr = [base_lr * ((self.multiplier - 1.) * self.last_epoch / self.total_epoch + 1.) for base_lr in
43 | self.base_lrs]
44 | for param_group, lr in zip(self.optimizer.param_groups, warmup_lr):
45 | param_group['lr'] = lr
46 | else:
47 | self.after_scheduler.step(metrics, epoch)
48 |
49 | def step(self, epoch=None, metrics=None):
50 | if type(self.after_scheduler) != ReduceLROnPlateau:
51 | if self.finished and self.after_scheduler:
52 | return self.after_scheduler.step(epoch)
53 | else:
54 | return super(GradualWarmupScheduler, self).step(epoch)
55 | else:
56 | self.step_ReduceLROnPlateau(metrics, epoch)
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/core/utils/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yanring/DGS/97e738995eccd771741f87af2251e929788e106e/core/utils/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/core/utils/constant.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MODEL_SIZE = None
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/core/utils/log.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python
2 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
3 | # Last Update: 2015/06/30 10:53:52
4 | '''Implements a simple log library.
5 |
6 | This module is a simple encapsulation of logging module to provide a more
7 | convenient interface to write log. The log will both print to stdout and
8 | write to log file. It provides a more flexible way to set the log actions,
9 | and also very simple. See examples showed below:
10 |
11 | Example 1: Use default settings
12 |
13 | import log
14 | log = log.Log(cmdlevel='info')
15 | log.debug('hello, world')
16 | log.info('hello, world')
17 | log.error('hello, world')
18 | log.critical('hello, world')
19 |
20 | Result:
21 | Print all log messages to file, and only print log whose level is greater
22 | than ERROR to stdout. The log file is located in 'xxx.log' if the module
23 | name is xxx.py. The default log file handler is size-rotated, if the log
24 | file's size is greater than 20M, then it will be rotated.
25 |
26 | Example 2: Use set_logger to change settings
27 |
28 | # Change limit size in bytes of default rotating action
29 | log.set_logger(limit = 10240) # 10M
30 |
31 | # Use time-rotated file handler, each day has a different log file, see
32 | # logging.handlers.TimedRotatingFileHandler for more help about 'when'
33 | log.set_logger(when = 'D', limit = 1)
34 |
35 | # Use normal file handler (not rotated)
36 | log.set_logger(backup_count = 0)
37 |
38 | # File log level set to INFO, and stdout log level set to DEBUG
39 | log.set_logger(cmdlevel = 'DEBUG', filelevel = 'INFO')
40 |
41 | # Change default log file name and log mode
42 | log.set_logger(filename = 'yyy.log', mode = 'w')
43 |
44 | # Change default log formatter
45 | log.set_logger(cmdfmt = '[%(levelname)s] %(message)s')
46 | '''
47 |
48 | __author__ = "Mingo "
49 | __status__ = "Development"
50 |
51 | import logging
52 | import logging.handlers
53 | import os
54 | import sys
55 | import traceback
56 |
57 |
58 | class ColoredFormatter(logging.Formatter):
59 | '''A colorful formatter.'''
60 |
61 | def __init__(self, fmt=None, datefmt=None):
62 | logging.Formatter.__init__(self, fmt, datefmt)
63 |
64 | def format(self, record):
65 | # Color escape string
66 | COLOR_RED = '\033[1;31m'
67 | COLOR_GREEN = '\033[1;32m'
68 | COLOR_YELLOW = '\033[1;33m'
69 | COLOR_BLUE = '\033[1;34m'
70 | COLOR_PURPLE = '\033[1;35m'
71 | COLOR_CYAN = '\033[1;36m'
72 | COLOR_GRAY = '\033[1;37m'
73 | COLOR_WHITE = '\033[1;38m'
74 | COLOR_RESET = '\033[1;0m'
75 | # Define log color
76 | LOG_COLORS = {
77 | 'DEBUG': '%s',
78 | 'INFO': COLOR_GREEN + '%s' + COLOR_RESET,
79 | 'WARNING': COLOR_YELLOW + '%s' + COLOR_RESET,
80 | 'ERROR': COLOR_RED + '%s' + COLOR_RESET,
81 | 'CRITICAL': COLOR_RED + '%s' + COLOR_RESET,
82 | 'EXCEPTION': COLOR_RED + '%s' + COLOR_RESET,
83 | }
84 | level_name = record.levelname
85 | msg = logging.Formatter.format(self, record)
86 | return LOG_COLORS.get(level_name, '%s') % msg
87 |
88 |
89 | class Log():
90 | def __init__(self, loggername='', filename=None, mode='a',
91 | cmdlevel='DEBUG',
92 | filelevel='INFO',
93 | cmdfmt='[%(asctime)s] %(filename)s line:%(lineno)d %(levelname)-8s%(message)s',
94 | filefmt='[%(asctime)s] %(levelname)-8s%(message)s',
95 | cmddatefmt='%H:%M:%S',
96 | filedatefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',
97 | backup_count=0, limit=20480, when=None, colorful=False):
98 | self.filename = filename
99 | self.loggername = loggername
100 | if self.filename is None:
101 | self.filename = getattr(sys.modules['__main__'], '__file__', 'log.py')
102 | self.filename = os.path.basename(self.filename.replace('.py', '.log'))
103 | # self.filename = os.path.join('/tmp', self.filename)
104 | if not os.path.exists(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(self.filename))):
105 | os.makedirs(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(self.filename)))
106 | self.mode = mode
107 | self.cmdlevel = cmdlevel
108 | self.filelevel = filelevel
109 | if isinstance(self.cmdlevel, str):
110 | self.cmdlevel = getattr(logging, self.cmdlevel.upper(), logging.DEBUG)
111 | if isinstance(self.filelevel, str):
112 | self.filelevel = getattr(logging, self.filelevel.upper(), logging.DEBUG)
113 | self.filefmt = filefmt
114 | self.cmdfmt = cmdfmt
115 | self.filedatefmt = filedatefmt
116 | self.cmddatefmt = cmddatefmt
117 | self.backup_count = backup_count
118 | self.limit = limit
119 | self.when = when
120 | self.colorful = colorful
121 | self.logger = None
122 | self.streamhandler = None
123 | self.filehandler = None
124 | if self.cmdlevel > 10:
125 | self.filefmt = '[%(asctime)s] %(levelname)-8s%(message)s'
126 | self.cmdfmt = '[%(asctime)s] %(levelname)-8s%(message)s'
127 | self.cmddatefmt = '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'
128 | self.set_logger(cmdlevel=self.cmdlevel)
129 |
130 | def init_logger(self):
131 | '''Reload the logger.'''
132 | if self.logger is None:
133 | self.logger = logging.getLogger(self.loggername)
134 | else:
135 | logging.shutdown()
136 | self.logger.handlers = []
137 | self.streamhandler = None
138 | self.filehandler = None
139 | self.logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
140 |
141 | def add_streamhandler(self):
142 | '''Add a stream handler to the logger.'''
143 | self.streamhandler = logging.StreamHandler()
144 | self.streamhandler.setLevel(self.cmdlevel)
145 | if self.colorful:
146 | formatter = ColoredFormatter(self.cmdfmt, self.cmddatefmt)
147 | else:
148 | formatter = logging.Formatter(self.cmdfmt, self.cmddatefmt, )
149 | self.streamhandler.setFormatter(formatter)
150 | self.logger.addHandler(self.streamhandler)
151 |
152 | def add_filehandler(self):
153 | '''Add a file handler to the logger.'''
154 | # Choose the filehandler based on the passed arguments
155 | if self.backup_count == 0: # Use FileHandler
156 | self.filehandler = logging.FileHandler(self.filename, self.mode)
157 | elif self.when is None: # Use RotatingFileHandler
158 | self.filehandler = logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler(self.filename,
159 | self.mode, self.limit, self.backup_count)
160 | else: # Use TimedRotatingFileHandler
161 | self.filehandler = logging.handlers.TimedRotatingFileHandler(self.filename,
162 | self.when, 1, self.backup_count)
163 | self.filehandler.setLevel(self.filelevel)
164 | formatter = logging.Formatter(self.filefmt, self.filedatefmt, )
165 | self.filehandler.setFormatter(formatter)
166 | self.logger.addHandler(self.filehandler)
167 |
168 | def set_logger(self, **kwargs):
169 | '''Configure the logger.'''
170 | keys = ['mode', 'cmdlevel', 'filelevel', 'filefmt', 'cmdfmt', \
171 | 'filedatefmt', 'cmddatefmt', 'backup_count', 'limit', \
172 | 'when', 'colorful']
173 | for (key, value) in kwargs.items():
174 | if not (key in keys):
175 | return False
176 | setattr(self, key, value)
177 | if isinstance(self.cmdlevel, str):
178 | self.cmdlevel = getattr(logging, self.cmdlevel.upper(), logging.DEBUG)
179 | if isinstance(self.filelevel, str):
180 | self.filelevel = getattr(logging, self.filelevel.upper(), logging.DEBUG)
181 | if not "cmdfmt" in kwargs:
182 | self.filefmt = '[%(asctime)s] %(filename)s line:%(lineno)d %(levelname)-8s%(message)s'
183 | self.filedatefmt = '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'
184 | self.cmdfmt = '[%(asctime)s] %(filename)s line:%(lineno)d %(levelname)-8s%(message)s'
185 | self.cmddatefmt = '%H:%M:%S'
186 | if self.cmdlevel > 10:
187 | self.filefmt = '[%(asctime)s] %(levelname)-8s%(message)s'
188 | self.cmdfmt = '[%(asctime)s] %(levelname)-8s%(message)s'
189 | self.cmddatefmt = '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'
190 | self.init_logger()
191 | self.add_streamhandler()
192 | self.add_filehandler()
193 | # Import the common log functions for convenient
194 | self.import_log_funcs()
195 | return True
196 |
197 | def addFileLog(self, log):
198 | self.logger.addHandler(log.filehandler)
199 | return self
200 |
201 | def import_log_funcs(self):
202 | '''Import the common log functions from the logger to the class'''
203 | log_funcs = ['debug', 'info', 'warning', 'error', 'critical',
204 | 'exception']
205 | for func_name in log_funcs:
206 | func = getattr(self.logger, func_name)
207 | setattr(self, func_name, func)
208 |
209 | def trace(self):
210 | info = sys.exc_info()
211 | for file, lineno, function, text in traceback.extract_tb(info[2]):
212 | self.error('%s line:%s in %s:%s' % (file, lineno, function, text))
213 | self.error('%s: %s' % info[:2])
214 |
215 |
216 | if __name__ == '__main__':
217 | log = Log(cmdlevel='info', colorful=True)
218 | err_log = Log('error', cmdlevel='info', filename='../../err.log', backup_count=1, when='D')
219 | # log = Log(cmdlevel='debug')
220 | log.set_logger(cmdlevel='debug')
221 | # log = log.addFileLog(err_log)
222 | for i in range(100000):
223 | log.debug('debug')
224 | err_log.debug('debug')
225 | log.info('debug%s' % 'haha')
226 | err_log.info('info%s' % 'haha')
227 | log.error((1, 2))
228 | log.error('debug')
229 | log.info({'a': 1, 'b': 2})
230 | os.system("pause")
231 |
232 |
233 | class A():
234 | def __init__(self, log):
235 | self.log = log
236 |
237 | def a(self, a):
238 | self.log.info(a)
239 |
240 |
241 | class B():
242 | def __init__(self, log):
243 | self.log = log
244 |
245 | def b(self, a):
246 | self.log.info(a)
247 |
248 |
249 | a = A(log)
250 | a.a("test a")
251 | b = B(log)
252 | b.b(5)
253 |
254 |
255 | def fun(a):
256 | return 10 / a
257 |
258 |
259 | try:
260 | a = fun(0)
261 | except:
262 | log.trace()
263 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/core/utils/messaging.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import logging
2 | import os
3 | import queue
4 | import socket
5 | import time
6 | from enum import Enum
7 | from multiprocessing.managers import BaseManager
8 | from threading import Thread
9 |
10 | import torch
11 | import torch.distributed as dist
12 |
13 | from core.utils.serialization import ravel_model_params
14 |
15 | _LOGGER = logging.getLogger(__name__)
16 |
17 | isCUDA = 0
18 | manager = None
19 |
20 |
21 | def tail(filename):
22 | with open(filename, 'r') as f:
23 | while True:
24 | line = f.readline()
25 | if not line:
26 | time.sleep(0.01)
27 | continue
28 | if dist.get_rank() == 0:
29 | print('delay:', time.time() - os.stat(filename).st_mtime)
30 | yield int(line)
31 |
32 |
33 | class MessageCode(Enum):
34 | """Different types of messages between client and server that we support go here."""
35 | ParameterRequest = 0
36 | GradientUpdate = 1
37 | ParameterUpdate = 2
38 | EvaluateParams = 3
39 |
40 |
41 | class GSMessageCode(Enum):
42 | """Different types of messages between client and server that we support go here."""
43 | GradientRequest = 0
44 | GradientUpdate = 1
45 | # ParameterUpdate = 2
46 | EvaluateParams = 3
47 | ModelRequest = 4
48 | ModelUpdate = 5
49 | SparseGradientUpdate = 6
50 |
51 |
52 | class ModelSize(Enum):
53 | """Different model size"""
54 | AlexNet = 2472266
55 | ResNet18 = 11173962
56 |
57 |
58 | class MessageListener(Thread):
59 | """MessageListener
60 |
61 | base class for message listeners, extends pythons threading Thread
62 | """
63 |
64 | def __init__(self, model):
65 | """__init__
66 |
67 | :param model: nn.Module to be defined by the user
68 | """
69 | self.running = True
70 | self.model = model
71 | _LOGGER.info("Setting m_parameter")
72 | self.m_parameter = torch.zeros(ravel_model_params(model).numel() + 2)
73 | super(MessageListener, self).__init__()
74 |
75 | def receive(self, sender, message_code, parameter):
76 | """receive
77 |
78 | :param sender: rank id of the sender
79 | :param message_code: Enum code
80 | :param parameter: the data payload
81 | """
82 | raise NotImplementedError()
83 |
84 | def run(self):
85 | _LOGGER.info("Started Running!")
86 | while self.running:
87 | _LOGGER.info("Polling for message...")
88 | dist.recv(tensor=self.m_parameter)
89 | self.receive(int(self.m_parameter[0].item()),
90 | MessageCode(self.m_parameter[1].item()),
91 | self.m_parameter[2:])
92 |
93 |
94 | a1 = queue.Queue()
95 | b1 = queue.Queue()
96 | a2 = queue.Queue()
97 | b2 = queue.Queue()
98 | a3 = queue.Queue()
99 | b3 = queue.Queue()
100 | a4 = queue.Queue()
101 | b4 = queue.Queue()
102 | a5 = queue.Queue()
103 | b5 = queue.Queue()
104 | a6 = queue.Queue()
105 | b6 = queue.Queue()
106 | a7 = queue.Queue()
107 | b7 = queue.Queue()
108 | a8 = queue.Queue()
109 | b8 = queue.Queue()
110 | a9 = queue.Queue()
111 | b9 = queue.Queue()
112 | a10 = queue.Queue()
113 | b10 = queue.Queue()
114 | a11 = queue.Queue()
115 | b11 = queue.Queue()
116 | a12 = queue.Queue()
117 | b12 = queue.Queue()
118 | a13 = queue.Queue()
119 | b13 = queue.Queue()
120 | a14 = queue.Queue()
121 | b14 = queue.Queue()
122 | a15 = queue.Queue()
123 | b15 = queue.Queue()
124 | a16 = queue.Queue()
125 | b16 = queue.Queue()
126 | a17 = queue.Queue()
127 | b17 = queue.Queue()
128 | a18 = queue.Queue()
129 | b18 = queue.Queue()
130 | a19 = queue.Queue()
131 | b19 = queue.Queue()
132 | a20 = queue.Queue()
133 | b20 = queue.Queue()
134 | a21 = queue.Queue()
135 | b21 = queue.Queue()
136 | a22 = queue.Queue()
137 | b22 = queue.Queue()
138 | a23 = queue.Queue()
139 | b23 = queue.Queue()
140 | a24 = queue.Queue()
141 | b24 = queue.Queue()
142 | a25 = queue.Queue()
143 | b25 = queue.Queue()
144 | a26 = queue.Queue()
145 | b26 = queue.Queue()
146 | a27 = queue.Queue()
147 | b27 = queue.Queue()
148 | a28 = queue.Queue()
149 | b28 = queue.Queue()
150 | a29 = queue.Queue()
151 | b29 = queue.Queue()
152 | a30 = queue.Queue()
153 | b30 = queue.Queue()
154 | a31 = queue.Queue()
155 | b31 = queue.Queue()
156 | a32 = queue.Queue()
157 | b32 = queue.Queue()
158 |
159 |
160 | def rta1():
161 | return a1
162 |
163 |
164 | def rtb1():
165 | return b1
166 |
167 |
168 | def rta2():
169 | return a2
170 |
171 |
172 | def rtb2():
173 | return b2
174 |
175 |
176 | def rta3():
177 | return a3
178 |
179 |
180 | def rtb3():
181 | return b3
182 |
183 |
184 | def rta4():
185 | return a4
186 |
187 |
188 | def rtb4():
189 | return b4
190 |
191 |
192 | def rta5():
193 | return a5
194 |
195 |
196 | def rtb5():
197 | return b5
198 |
199 |
200 | def rta6():
201 | return a6
202 |
203 |
204 | def rtb6():
205 | return b6
206 |
207 |
208 | def rta7():
209 | return a7
210 |
211 |
212 | def rtb7():
213 | return b7
214 |
215 |
216 | def rta8():
217 | return a8
218 |
219 |
220 | def rtb8():
221 | return b8
222 |
223 |
224 | def rta9():
225 | return a9
226 |
227 |
228 | def rtb9():
229 | return b9
230 |
231 |
232 | def rta10():
233 | return a10
234 |
235 |
236 | def rtb10():
237 | return b10
238 |
239 |
240 | def rta11():
241 | return a11
242 |
243 |
244 | def rtb11():
245 | return b11
246 |
247 |
248 | def rta12():
249 | return a12
250 |
251 |
252 | def rtb12():
253 | return b12
254 |
255 |
256 | def rta13():
257 | return a13
258 |
259 |
260 | def rtb13():
261 | return b13
262 |
263 |
264 | def rta14():
265 | return a14
266 |
267 |
268 | def rtb14():
269 | return b14
270 |
271 |
272 | def rta15():
273 | return a15
274 |
275 |
276 | def rtb15():
277 | return b15
278 |
279 |
280 | def rta16():
281 | return a16
282 |
283 |
284 | def rtb16():
285 | return b16
286 |
287 |
288 | def rta17():
289 | return a17
290 |
291 |
292 | def rtb17():
293 | return b17
294 |
295 |
296 | def rta18():
297 | return a18
298 |
299 |
300 | def rtb18():
301 | return b18
302 |
303 |
304 | def rta19():
305 | return a19
306 |
307 |
308 | def rtb19():
309 | return b19
310 |
311 |
312 | def rta20():
313 | return a20
314 |
315 |
316 | def rtb20():
317 | return b20
318 |
319 |
320 | def rta21():
321 | return a21
322 |
323 |
324 | def rtb21():
325 | return b21
326 |
327 |
328 | def rta22():
329 | return a22
330 |
331 |
332 | def rtb22():
333 | return b22
334 |
335 |
336 | def rta23():
337 | return a23
338 |
339 |
340 | def rtb23():
341 | return b23
342 |
343 |
344 | def rta24():
345 | return a24
346 |
347 |
348 | def rtb24():
349 | return b24
350 |
351 |
352 | def rta25():
353 | return a25
354 |
355 |
356 | def rtb25():
357 | return b25
358 |
359 |
360 | def rta26():
361 | return a26
362 |
363 |
364 | def rtb26():
365 | return b26
366 |
367 |
368 | def rta27():
369 | return a27
370 |
371 |
372 | def rtb27():
373 | return b27
374 |
375 |
376 | def rta28():
377 | return a28
378 |
379 |
380 | def rtb28():
381 | return b28
382 |
383 |
384 | def rta29():
385 | return a29
386 |
387 |
388 | def rtb29():
389 | return b29
390 |
391 |
392 | def rta30():
393 | return a30
394 |
395 |
396 | def rtb30():
397 | return b30
398 |
399 |
400 | def rta31():
401 | return a31
402 |
403 |
404 | def rtb31():
405 | return b31
406 |
407 |
408 | def rta32():
409 | return a32
410 |
411 |
412 | def rtb32():
413 | return b32
414 |
415 |
416 | class GradientMessageListener(Thread):
417 | """MessageListener
418 |
419 | base class for message listeners, extends pythons threading Thread
420 | """
421 |
422 | def __init__(self, model_size, source=0, args=None):
423 | """__init__
424 |
425 | :param model: nn.Module to be defined by the user
426 | """
427 | # self.model = model
428 | self.source = source
429 | _LOGGER.info("Setting m_parameter")
430 | self.m_parameter = torch.zeros(model_size + 4).double()
431 | self.cached_stamp = 0
432 | self.size_filename = None
433 | self.manager = None
434 | self.args = args
435 | if dist.get_rank() == 0 and self.source == 1:
436 | self.init_server_queue_manager()
437 | elif dist.get_rank() > 0:
438 | self.recv_queue, self.send_queue = self.init_worker_queue_manager()
439 | super(GradientMessageListener, self).__init__()
440 |
441 | def receive(self, sender, message_code, gradient_version, lr, parameter):
442 | """receive
443 |
444 | :param lr:
445 | :param gradient_version:
446 | :param sender: rank id of the sender
447 | :param message_code: Enum code
448 | :param parameter: the data payload
449 | """
450 | raise NotImplementedError()
451 |
452 | def run(self):
453 | # for sparse gradient transmission
454 | _LOGGER.info("Started Running!")
455 | self.running = True
456 | while self.running:
457 | _LOGGER.info("Polling for sparse message...")
458 | # for size in tail(self.size_filename):
459 | while True:
460 | size = QueueManager.get_size(self.source)
461 | # if dist.get_rank() == 0:
462 | # print('RECEIVING MESSAGE %dto%d.size:%d,' % (
463 | # self.source, dist.get_rank(), size))
464 | self.m_parameter = torch.zeros(size + 4).double()
465 | try:
466 | sender = dist.recv(tensor=self.m_parameter, src=self.source)
467 | except Exception as e:
468 | # print('Exception :', e)
469 | raise e
470 | time.sleep(0.5)
471 | continue
472 | self.m_parameter = self.m_parameter
473 | # if dist.get_rank() == 0:
474 | # print('run',self.m_parameter[int(len(self.m_parameter) / 2)-3:int(len(self.m_parameter) / 2)+2],self.m_parameter[int(len(self.m_parameter) / 2)-3:int(len(self.m_parameter) / 2)+2].long())
475 | self.receive(int(self.m_parameter[0].item()),
476 | GSMessageCode(self.m_parameter[1].item()),
477 | int(self.m_parameter[2].item()),
478 | float(self.m_parameter[3].item()),
479 | self.m_parameter[4:])
480 |
481 | def init_server_queue_manager(self):
482 |
483 | QueueManager.register('from0to1', callable=rta1)
484 | QueueManager.register('from1to0', callable=rtb1)
485 | QueueManager.register('from0to2', callable=rta2)
486 | QueueManager.register('from2to0', callable=rtb2)
487 | QueueManager.register('from0to3', callable=rta3)
488 | QueueManager.register('from3to0', callable=rtb3)
489 | QueueManager.register('from0to4', callable=rta4)
490 | QueueManager.register('from4to0', callable=rtb4)
491 | QueueManager.register('from0to5', callable=rta5)
492 | QueueManager.register('from5to0', callable=rtb5)
493 | QueueManager.register('from0to6', callable=rta6)
494 | QueueManager.register('from6to0', callable=rtb6)
495 | QueueManager.register('from0to7', callable=rta7)
496 | QueueManager.register('from7to0', callable=rtb7)
497 | QueueManager.register('from0to8', callable=rta8)
498 | QueueManager.register('from8to0', callable=rtb8)
499 | QueueManager.register('from0to9', callable=rta9)
500 | QueueManager.register('from9to0', callable=rtb9)
501 | QueueManager.register('from0to10', callable=rta10)
502 | QueueManager.register('from10to0', callable=rtb10)
503 | QueueManager.register('from0to11', callable=rta11)
504 | QueueManager.register('from11to0', callable=rtb11)
505 | QueueManager.register('from0to12', callable=rta12)
506 | QueueManager.register('from12to0', callable=rtb12)
507 | QueueManager.register('from0to13', callable=rta13)
508 | QueueManager.register('from13to0', callable=rtb13)
509 | QueueManager.register('from0to14', callable=rta14)
510 | QueueManager.register('from14to0', callable=rtb14)
511 | QueueManager.register('from0to15', callable=rta15)
512 | QueueManager.register('from15to0', callable=rtb15)
513 | QueueManager.register('from0to16', callable=rta16)
514 | QueueManager.register('from16to0', callable=rtb16)
515 | QueueManager.register('from0to17', callable=rta17)
516 | QueueManager.register('from17to0', callable=rtb17)
517 | QueueManager.register('from0to18', callable=rta18)
518 | QueueManager.register('from18to0', callable=rtb18)
519 | QueueManager.register('from0to19', callable=rta19)
520 | QueueManager.register('from19to0', callable=rtb19)
521 | QueueManager.register('from0to20', callable=rta20)
522 | QueueManager.register('from20to0', callable=rtb20)
523 | QueueManager.register('from0to21', callable=rta21)
524 | QueueManager.register('from21to0', callable=rtb21)
525 | QueueManager.register('from0to22', callable=rta22)
526 | QueueManager.register('from22to0', callable=rtb22)
527 | QueueManager.register('from0to23', callable=rta23)
528 | QueueManager.register('from23to0', callable=rtb23)
529 | QueueManager.register('from0to24', callable=rta24)
530 | QueueManager.register('from24to0', callable=rtb24)
531 | QueueManager.register('from0to25', callable=rta25)
532 | QueueManager.register('from25to0', callable=rtb25)
533 | QueueManager.register('from0to26', callable=rta26)
534 | QueueManager.register('from26to0', callable=rtb26)
535 | QueueManager.register('from0to27', callable=rta27)
536 | QueueManager.register('from27to0', callable=rtb27)
537 | QueueManager.register('from0to28', callable=rta28)
538 | QueueManager.register('from28to0', callable=rtb28)
539 | QueueManager.register('from0to29', callable=rta29)
540 | QueueManager.register('from29to0', callable=rtb29)
541 | QueueManager.register('from0to30', callable=rta30)
542 | QueueManager.register('from30to0', callable=rtb30)
543 | QueueManager.register('from0to31', callable=rta31)
544 | QueueManager.register('from31to0', callable=rtb31)
545 | QueueManager.register('from0to32', callable=rta32)
546 | QueueManager.register('from32to0', callable=rtb32)
547 |
548 | self.manager = QueueManager(address=('', 5000), authkey=b'abc')
549 | QueueManager.send_queue_list.append(0)
550 | QueueManager.recv_queue_list.append(0)
551 | QueueManager.manager = self.manager
552 | self.manager.start()
553 | for i in range(1, dist.get_world_size()):
554 | send_queue = eval('self.manager.from0to%d' % i)()
555 | QueueManager.send_queue_list.append(send_queue)
556 | recv_queue = eval('self.manager.from%dto0' % i)()
557 | QueueManager.recv_queue_list.append(recv_queue)
558 | pass
559 |
560 | def init_worker_queue_manager(self):
561 | # time.sleep(1)
562 | QueueManager.register('from0to%d' % dist.get_rank())
563 | QueueManager.register('from%dto0' % dist.get_rank())
564 | time.sleep(10)
565 | # self.manager = QueueManager(address=(socket.gethostbyname('localhost'), 5000), authkey=b'abc')
566 | if socket.gethostname() == 'yan-pc' or socket.gethostname() == 'yrx-MS-7A93' or 'ubuntu' in socket.gethostname():
567 | print('queue init in 522')
568 | # self.manager = QueueManager(address=('172.18.166.108', 5000), authkey=b'abc')
569 | self.manager = QueueManager(address=(self.args.master, 5000), authkey=b'abc')
570 | else:
571 | time.sleep(10)
572 | print('queue init in th')
573 | self.manager = QueueManager(address=(self.args.master, 5000), authkey=b'abc')
574 | try:
575 | self.manager.connect()
576 | except Exception as e:
577 | print(e)
578 | time.sleep(10)
579 | self.manager.connect()
580 | send_queue = eval('self.manager.from%dto0' % dist.get_rank())()
581 | QueueManager.send_queue_list.append(send_queue)
582 | recv_queue = eval('self.manager.from0to%d' % dist.get_rank())()
583 | QueueManager.recv_queue_list.append(recv_queue)
584 | QueueManager.manager = self.manager
585 | return recv_queue, send_queue
586 |
587 |
588 | class QueueManager(BaseManager):
589 | manager = None
590 | send_queue_list = []
591 | recv_queue_list = []
592 |
593 | @classmethod
594 | def get_manager(cls):
595 | return cls.manager
596 |
597 | @classmethod
598 | def get_size(cls, opposite):
599 | recv_queue = cls.recv_queue_list[opposite]
600 | # exec('recv_queue = cls.manager.from%dto%d()' % (source, target))
601 | res = None
602 | try:
603 | res = recv_queue.get(timeout=4000)
604 | except queue.Empty:
605 | print('task queue is empty')
606 | # print('RECV ', res, type(recv_queue), recv_queue)
607 | return int(res)
608 |
609 | @classmethod
610 | def put_size(cls, opposite, size):
611 | # send_queue = None
612 | # exec('send_queue = cls.manager.from%dto%d()' % (source, target))
613 | send_queue = cls.send_queue_list[opposite]
614 | # print('SEND ', type(send_queue), size, send_queue)
615 | send_queue.put(size)
616 |
617 |
618 | def send_message(message_code, payload, dst=0, gradient_version=None, lr=0.1):
619 | """Sends a message to a destination
620 | Concatenates both the message code and destination with the payload into a single tensor and then sends that as a tensor
621 | """
622 | # _LOGGER.info("SENDING MESSAGE: {} RANK: {}".format(message_code, dist.get_rank()))
623 | m_parameter = torch.Tensor([dist.get_rank(), message_code.value, gradient_version, lr])
624 | # print(m_parameter.size(), payload.size())
625 | if payload.is_cuda:
626 | payload = payload.cpu()
627 | size = str(payload.numel())
628 | payload = torch.cat((m_parameter.double(), payload.double()))
629 | if dist.get_rank() == 0:
630 | print('%s SENDING MESSAGE %s gradient_version %d, %dto%d.size:%d' % (
631 | str(time.time()), message_code, gradient_version, dist.get_rank(), dst, payload.numel()))
632 | # with open('%dto%d.size' % (dist.get_rank(), dst), 'a') as f:
633 | # f.write(size)
634 | QueueManager.put_size(dst, size)
635 | dist.send(tensor=payload, dst=dst)
636 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/core/utils/serialization.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import time
2 |
3 | import torch
4 |
5 | from core.utils import constant
6 |
7 | current_model_size = None
8 |
9 |
10 | def ravel_model_params(model, grads=False, cuda=False):
11 | """
12 | Squash model parameters or gradients into a single tensor.
13 | """
14 | if next(model.parameters()).is_cuda:
15 | m_parameter = torch.Tensor([0]).cuda()
16 | else:
17 | m_parameter = torch.Tensor([0])
18 | for parameter in list(model.parameters()):
19 | if grads:
20 | m_parameter = torch.cat((m_parameter, parameter.grad.view(-1)))
21 | else:
22 | m_parameter = torch.cat((m_parameter, parameter.data.view(-1)))
23 | return m_parameter[1:]
24 |
25 |
26 | def unravel_model_params(model, parameter_update):
27 | """
28 | Assigns parameter_update params to model.parameters.
29 | This is done by iterating through model.parameters() and assigning the relevant params in parameter_update.
30 | NOTE: this function manipulates model.parameters.
31 | """
32 | current_index = 0 # keep track of where to read from parameter_update
33 | for parameter in model.parameters():
34 | numel = parameter.data.numel()
35 | size = parameter.data.size()
36 | parameter.data.copy_(parameter_update[current_index:current_index + numel].view(size))
37 | current_index += numel
38 |
39 |
40 | def update_model_params(model, parameter_update, lr):
41 | """
42 | Assigns parameter_update params to model.parameters.
43 | This is done by iterating through model.parameters() and adding the gradient in parameter_update.
44 | NOTE: this function manipulates model.parameters.
45 | """
46 | current_index = 0 # keep track of where to read from parameter_update
47 | for parameter in model.parameters():
48 | numel = parameter.data.numel()
49 | size = parameter.data.size()
50 | # print(parameter.data.device,parameter_update.device)
51 | parameter.data.add_(-lr, parameter_update[current_index:current_index + numel].view(size))
52 | current_index += numel
53 |
54 |
55 | def worker_gradient_executor(net, payload, u_kt, v_kt, rate=0.01, lr=0.1, momentum=None, weight_decay=0):
56 | """
57 | :param momentum:
58 | :param lr:
59 | :param v_kt:
60 | :param payload:
61 | :param u_kt:
62 | :param net: model
63 | :param rate: compression rate
64 | :return: gradients which lager than threshold
65 | """
66 | # start = time.time()
67 | current_index = 0
68 | u_kt.mul_(momentum)
69 | for param in net.parameters():
70 | numel = param.data.numel()
71 | layer_u_kt = u_kt[current_index:current_index + numel]
72 | if weight_decay != 0:
73 | param.grad.data.add_(weight_decay, param.data)
74 | layer_u_kt.add_(param.grad.data.view(-1).mul(lr))
75 | k = int(numel * rate) if int(numel * rate) != 0 else 1
76 | k = numel - k
77 | abs_layer_u_kt = layer_u_kt.abs()
78 | threshold = torch.kthvalue(abs_layer_u_kt, k).values
79 | mask = abs_layer_u_kt.gt(threshold).float()
80 | # print(mask.sum()-len(layer_u_kt))
81 | payload[current_index:current_index + numel].copy_(layer_u_kt.mul(mask))
82 | layer_u_kt.add_(layer_u_kt.mul(1 - mask).mul(1 / momentum - 1))
83 | # print(layer_u_kt.sum())
84 | current_index += numel
85 | # end = time.time()
86 | return payload
87 |
88 |
89 | def DGC(net, payload, u_kt, v_kt, rate=0.01, lr=0.1, momentum=None, weight_decay=None):
90 | """
91 | :param momentum:
92 | :param lr:
93 | :param v_kt:
94 | :param payload:
95 | :param u_kt:
96 | :param net: model
97 | :param rate: compression rate
98 | :return: gradients which lager than threshold
99 | """
100 | start = time.time()
101 | current_index = 0
102 | u_kt.mul_(momentum)
103 | sum = 0
104 | for param in net.parameters():
105 | numel = param.data.numel()
106 | layer_u_kt = u_kt[current_index:current_index + numel]
107 | layer_v_kt = v_kt[current_index:current_index + numel]
108 | if weight_decay != 0:
109 | param.grad.data.add_(weight_decay, param.data)
110 | layer_u_kt.add_(param.grad.data.view(-1))
111 | layer_v_kt.add_(layer_u_kt)
112 | k = int(numel * rate) if int(numel * rate) != 0 else 1
113 | topn = [[1.0]]
114 | try:
115 | topn = torch.topk(abs(layer_v_kt), k)
116 | except Exception as e:
117 | print(e)
118 | print(k, layer_v_kt.nelement())
119 | # print(layer_v_kt)
120 | threshold = float(topn[0][-1])
121 | mask = (abs(layer_v_kt) > threshold).float()
122 | payload[current_index:current_index + numel].copy_(layer_v_kt.mul(mask).mul(lr))
123 | layer_v_kt.mul_(1 - mask)
124 | layer_u_kt.mul_(1 - mask)
125 | current_index += numel
126 | return payload
127 |
128 |
129 | def Aji(net, payload, u_kt, v_kt, rate=0.01, lr=0.1, momentum=None, weight_decay=0):
130 | """
131 | :param momentum:
132 | :param lr:
133 | :param v_kt:
134 | :param payload:
135 | :param u_kt:
136 | :param net: model
137 | :param rate: compression rate
138 | :return: gradients which lager than threshold
139 | """
140 | start = time.time()
141 | current_index = 0
142 | # u_kt.mul_(momentum)
143 | for param in net.parameters():
144 | numel = param.data.numel()
145 | # layer_u_kt = u_kt[current_index:current_index + numel]
146 | layer_v_kt = v_kt[current_index:current_index + numel]
147 | # layer_u_kt.add_(param.grad.data.view(-1))
148 | if weight_decay != 0:
149 | param.grad.data.add_(weight_decay, param.data)
150 | layer_v_kt.add_(param.grad.data.view(-1).mul(lr))
151 | k = int(numel * rate) if int(numel * rate) != 0 else 1
152 | topn = [[1.0]]
153 | try:
154 | topn = torch.topk(abs(layer_v_kt), k)
155 | except Exception as e:
156 | print(e)
157 | print(k, layer_v_kt.nelement())
158 | threshold = float(topn[0][-1])
159 | mask = (abs(layer_v_kt) > threshold).float()
160 | payload[current_index:current_index + numel].copy_(layer_v_kt.mul(mask))
161 | layer_v_kt.mul_(1 - mask)
162 | # layer_u_kt.mul_(1 - mask)
163 | current_index += numel
164 | return payload
165 |
166 |
167 |
168 | def server_gradient_filter(size_list, gradients, rate=0.01):
169 | # print('gradients', gradients)
170 | current_index = 0
171 | for size in size_list:
172 | numel = size
173 | temp = gradients[current_index:current_index + numel]
174 | current_index += numel
175 | k = int(numel * rate) if int(numel * rate) != 0 else 1
176 | k = numel - k
177 | abs_temp = temp.abs()
178 | threshold = torch.kthvalue(abs_temp, k).values
179 | mask = abs_temp.gt(threshold)
180 | temp.mul_(mask)
181 | return gradients
182 |
183 |
184 | def ravel_sparse_gradient(temp_param):
185 | indices = temp_param.nonzero()
186 | values = temp_param[indices]
187 | sparse_gradient = torch.cat((indices.double(), values.double())).view(-1)
188 | return sparse_gradient
189 |
190 |
191 | def unravel_sparse_gradient(sparse_gradient):
192 | # len is 2472266 11173962 2400w
193 | split = int(len(sparse_gradient) / 2)
194 | i = sparse_gradient[:split]
195 | v = sparse_gradient[split:]
196 | size = torch.Size([constant.MODEL_SIZE])
197 | # print('3',v.sum())
198 | try:
199 | dense_gradient = torch.sparse_coo_tensor(i.reshape(1, -1).long(), v.float(), size, device=torch.device('cuda'))
200 | except Exception as e:
201 | print(i, v)
202 | print('sum indice', sum(i))
203 | raise (e)
204 | print(size, constant.MODEL_SIZE, i[-5:], v[-5:])
205 | dense_gradient = torch.FloatTensor(size).zero_()
206 |
207 | # print(dense_gradient.sum())
208 | return dense_gradient
209 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/example/ImageNet_dali_dataloader.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import time
2 |
3 | import nvidia.dali.ops as ops
4 | import nvidia.dali.types as types
5 | import torch.utils.data
6 | import torchvision.datasets as datasets
7 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
8 | from nvidia.dali.pipeline import Pipeline
9 | from nvidia.dali.plugin.pytorch import DALIClassificationIterator
10 |
11 |
12 | class HybridTrainPipe(Pipeline):
13 | def __init__(self, batch_size, num_threads, device_id, data_dir, crop, dali_cpu=False, local_rank=0, world_size=1):
14 | super(HybridTrainPipe, self).__init__(batch_size, num_threads, device_id, seed=12 + device_id)
15 | dali_device = "gpu"
16 | self.input = ops.FileReader(file_root=data_dir, shard_id=local_rank, num_shards=world_size, random_shuffle=True)
17 | self.decode = ops.ImageDecoder(device="mixed", output_type=types.RGB)
18 | self.res = ops.RandomResizedCrop(device="gpu", size=crop, random_area=[0.08, 1.25])
19 | self.cmnp = ops.CropMirrorNormalize(device="gpu",
20 | output_dtype=types.FLOAT,
21 | output_layout=types.NCHW,
22 | image_type=types.RGB,
23 | mean=[0.485 * 255, 0.456 * 255, 0.406 * 255],
24 | std=[0.229 * 255, 0.224 * 255, 0.225 * 255])
25 | self.coin = ops.CoinFlip(probability=0.5)
26 | print('DALI "{0}" variant'.format(dali_device))
27 |
28 | def define_graph(self):
29 | rng = self.coin()
30 | self.jpegs, self.labels = self.input(name="Reader")
31 | images = self.decode(self.jpegs)
32 | images = self.res(images)
33 | output = self.cmnp(images, mirror=rng)
34 | return [output, self.labels]
35 |
36 |
37 | class HybridValPipe(Pipeline):
38 | def __init__(self, batch_size, num_threads, device_id, data_dir, crop, size, local_rank=0, world_size=1):
39 | super(HybridValPipe, self).__init__(batch_size, num_threads, device_id, seed=12 + device_id)
40 | self.input = ops.FileReader(file_root=data_dir, shard_id=local_rank, num_shards=world_size,
41 | random_shuffle=False)
42 | self.decode = ops.ImageDecoder(device="mixed", output_type=types.RGB)
43 | self.res = ops.Resize(device="gpu", resize_shorter=size, interp_type=types.INTERP_TRIANGULAR)
44 | self.cmnp = ops.CropMirrorNormalize(device="gpu",
45 | output_dtype=types.FLOAT,
46 | output_layout=types.NCHW,
47 | crop=(crop, crop),
48 | image_type=types.RGB,
49 | mean=[0.485 * 255, 0.456 * 255, 0.406 * 255],
50 | std=[0.229 * 255, 0.224 * 255, 0.225 * 255])
51 |
52 | def define_graph(self):
53 | self.jpegs, self.labels = self.input(name="Reader")
54 | images = self.decode(self.jpegs)
55 | images = self.res(images)
56 | output = self.cmnp(images)
57 | return [output, self.labels]
58 |
59 |
60 | def get_imagenet_iter_dali(type, image_dir, batch_size, num_threads, device_id, num_gpus, crop, val_size=256,
61 | world_size=1,
62 | local_rank=0):
63 | if type == 'train':
64 | pip_train = HybridTrainPipe(batch_size=batch_size, num_threads=num_threads, device_id=device_id,
65 | data_dir=image_dir + '/train',
66 | crop=crop, world_size=world_size, local_rank=local_rank)
67 | pip_train.build()
68 | dali_iter_train = DALIClassificationIterator(pip_train, size=pip_train.epoch_size("Reader") // world_size)
69 | return dali_iter_train
70 | elif type == 'val':
71 | pip_val = HybridValPipe(batch_size=batch_size, num_threads=num_threads, device_id=device_id,
72 | data_dir=image_dir + '/val',
73 | crop=crop, size=val_size, world_size=world_size, local_rank=local_rank)
74 | pip_val.build()
75 | dali_iter_val = DALIClassificationIterator(pip_val, size=pip_val.epoch_size("Reader") // world_size)
76 | return dali_iter_val
77 |
78 |
79 | def get_imagenet_iter_torch(type, image_dir, batch_size, num_threads, device_id, num_gpus, crop, val_size=256,
80 | world_size=1, local_rank=0):
81 | if type == 'train':
82 | transform = transforms.Compose([
83 | transforms.RandomResizedCrop(crop, scale=(0.08, 1.25)),
84 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
85 | transforms.ToTensor(),
86 | transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),
87 | ])
88 | dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(image_dir + '/train', transform)
89 | dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=num_threads,
90 | pin_memory=True)
91 | else:
92 | transform = transforms.Compose([
93 | transforms.Resize(val_size),
94 | transforms.CenterCrop(crop),
95 | transforms.ToTensor(),
96 | transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),
97 | ])
98 | dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(image_dir + '/val', transform)
99 | dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=num_threads,
100 | pin_memory=True)
101 | return dataloader
102 |
103 |
104 | if __name__ == '__main__':
105 | train_loader = get_imagenet_iter_dali(type='train', image_dir='/userhome/memory_data/imagenet', batch_size=256,
106 | num_threads=4, crop=224, device_id=0, num_gpus=1)
107 | print('start iterate')
108 | start = time.time()
109 | for i, data in enumerate(train_loader):
110 | images = data[0]["data"].cuda(non_blocking=True)
111 | labels = data[0]["label"].squeeze().long().cuda(non_blocking=True)
112 | end = time.time()
113 | print('end iterate')
114 | print('dali iterate time: %fs' % (end - start))
115 |
116 | train_loader = get_imagenet_iter_torch(type='train', image_dir='/userhome/data/imagenet', batch_size=256,
117 | num_threads=4, crop=224, device_id=0, num_gpus=1)
118 | print('start iterate')
119 | start = time.time()
120 | for i, data in enumerate(train_loader):
121 | images = data[0].cuda(non_blocking=True)
122 | labels = data[1].cuda(non_blocking=True)
123 | end = time.time()
124 | print('end iterate')
125 | print('torch iterate time: %fs' % (end - start))
126 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/example/Imagenet_dist.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import argparse
2 | import os
3 | import random
4 | import shutil
5 | import socket
6 | import sys
7 | import time
8 | import warnings
9 | from datetime import datetime
10 |
11 | import pandas
12 | import torch
13 | import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
14 | import torch.distributed as dist
15 | import torch.multiprocessing as mp
16 | import torch.nn as nn
17 | import torch.nn.parallel
18 | import torch.optim
19 | import torch.utils.data
20 | import torch.utils.data.distributed
21 | import torchvision.datasets as datasets
22 | import torchvision.models as models
23 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
24 | from PIL import ImageFile
25 |
26 | # if 'gpu' in socket.gethostname():
27 | # print('network in th v100')
28 | # os.environ['GLOO_SOCKET_IFNAME'] = 'enp183s0f0'
29 | # else:
30 | # os.environ['GLOO_SOCKET_IFNAME'] = 'enp3s0'
31 |
32 | WORKPATH = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
33 | sys.path.append(WORKPATH)
34 | from core.utils import constant
35 | from core.utils.serialization import ravel_model_params
36 |
37 | from core.optim import GradientSGD
38 | from example.main import init_server
39 | import _pickle as pickle
40 |
41 | ImageFile.LOAD_TRUNCATED_IMAGES = True
42 | model_names = sorted(name for name in models.__dict__
43 | if name.islower() and not name.startswith("__")
44 | and callable(models.__dict__[name]))
45 |
46 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch ImageNet Training')
47 | parser.add_argument('-data', default='/home/yan/tmpfs/data/',
48 | help='path to dataset')
49 | parser.add_argument('-a', '--arch', metavar='ARCH', default='resnet18',
50 | choices=model_names,
51 | help='model architecture: ' +
52 | ' | '.join(model_names) +
53 | ' (default: mobilenet_v2/resnet18)')
54 | parser.add_argument('-j', '--workers', default=8, type=int, metavar='N',
55 | help='number of data loading workers (default: 4)')
56 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', default=90, type=int, metavar='N',
57 | help='number of total epochs to run')
58 | parser.add_argument('--start-epoch', default=0, type=int, metavar='N',
59 | help='manual epoch number (useful on restarts)')
60 | parser.add_argument('-b', '--batch-size', default=256, type=int,
61 | metavar='N',
62 | help='mini-batch size (default: 256), this is the total '
63 | 'batch size of all GPUs on the current node when '
64 | 'using Data Parallel or Distributed Data Parallel')
65 | parser.add_argument('--lr', '--learning-rate', default=0.1, type=float,
66 | metavar='LR', help='initial learning rate', dest='lr')
67 | parser.add_argument('--momentum', deNonefault=0.7, type=float, metavar='M',
68 | help='momentum')
69 | parser.add_argument('--wd', '--weight-decay', default=1e-4, type=float,
70 | metavar='W', help='weight decay (default: 1e-4)',
71 | dest='weight_decay')
72 | parser.add_argument('-p', '--print-freq', default=100, type=int,
73 | metavar='N', help='print frequency (default: 10)')
74 | parser.add_argument('--resume', default='', type=str, metavar='PATH',
75 | help='path to latest checkpoint (default: none)')
76 | parser.add_argument('-e', '--evaluate', dest='evaluate', action='store_true',
77 | help='evaluate model on validation set')
78 | parser.add_argument('--pretrained', dest='pretrained', action='store_true',
79 | help='use pre-trained model')
80 | parser.add_argument('--world-size', default=-1, type=int,
81 | help='number of nodes for distributed training')
82 | parser.add_argument('--rank', default=-1, type=int,
83 | help='node rank for distributed training')
84 | parser.add_argument('--dist-url', default='tcp://224.66.41.62:23456', type=str,
85 | help='url used to set up distributed training')
86 | parser.add_argument('--dist-backend', default='nccl', type=str,
87 | help='distributed backend')
88 | parser.add_argument('--seed', default=None, type=int,
89 | help='seed for initializing training. ')
90 | parser.add_argument('--multiprocessing-distributed', action='store_true',
91 | help='Use multi-processing distributed training to launch '
92 | 'N processes per node, which has N GPUs. This is the '
93 | 'fastest way to use PyTorch for either single node or '
94 | 'multi node data parallel training')
95 | parser.add_argument('--network-interface', type=str, default='enp3s0',
96 | help='By default, Gloo backends will try to find the right network interface to use. '
97 | 'If the automatically detected interface is not correct, you can override it ')
98 |
99 | # my settings
100 | parser.add_argument('--mode', type=str, default='gradient_sgd', help='gradient_sgd, dgc, Aji or asgd')
101 | parser.add_argument('--cuda', action='store_true', default=True, help='use CUDA for training')
102 | parser.add_argument('--no-distributed', action='store_true', default=False,
103 | help='distributed or local')
104 |
105 | logs = []
106 |
107 | best_acc1 = 0
108 |
109 |
110 | def main():
111 | args = parser.parse_args()
112 | os.environ['GLOO_SOCKET_IFNAME'] = args.network_interface
113 | if socket.gethostname() == 'yan-pc':
114 | os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '%d' % (args.rank % 1)
115 | elif 'gn' in socket.gethostname():
116 | print('init in K80')
117 | os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '%d' % (args.rank % 4)
118 | elif 'gpu' in socket.gethostname():
119 | print('init in V100')
120 | os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '%d' % (args.rank % 4)
121 | else:
122 | os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '%d' % (args.rank % 1)
123 | # os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '1'
124 | print('Using device%s, device count:%d' % (os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'], torch.cuda.device_count()))
125 | if args.seed is not None:
126 | random.seed(args.seed)
127 | torch.manual_seed(args.seed)
128 | cudnn.deterministic = True
129 | warnings.warn('You have chosen to seed training. '
130 | 'This will turn on the CUDNN deterministic setting, '
131 | 'which can slow down your training considerably! '
132 | 'You may see unexpected behavior when restarting '
133 | 'from checkpoints.')
134 |
135 | if args.rank == 0:
136 | print("=> creating server '{}'".format(args.arch))
137 | model = models.__dict__[args.arch]()
138 | init_server(args, model)
139 | exit(999)
140 |
141 |
142 | args.gpu = args.rank % torch.cuda.device_count()
143 | if args.gpu is not None:
144 | warnings.warn('You have chosen a specific GPU. This will completely '
145 | 'disable data parallelism.')
146 |
147 | if args.dist_url == "env://" and args.world_size == -1:
148 | args.world_size = int(os.environ["WORLD_SIZE"])
149 |
150 | args.distributed = False
151 | # args.distributed = args.world_size > 1 or args.multiprocessing_distributed
152 | ngpus_per_node = torch.cuda.device_count()
153 | if args.multiprocessing_distributed:
154 | # Since we have ngpus_per_node processes per node, the total world_size
155 | # needs to be adjusted accordingly
156 | args.world_size = ngpus_per_node * args.world_size
157 | # Use torch.multiprocessing.spawn to launch distributed processes: the
158 | # main_worker process function
159 | mp.spawn(main_worker, nprocs=ngpus_per_node, args=(ngpus_per_node, args))
160 | else:
161 | # Simply call main_worker function
162 | main_worker(args.gpu, ngpus_per_node, args)
163 |
164 |
165 | def main_worker(gpu, ngpus_per_node, args):
166 | global best_acc1, logs
167 | args.gpu = gpu
168 |
169 | if args.gpu is not None:
170 | print("Use GPU: {} for training".format(args.gpu))
171 |
172 | if args.distributed:
173 | if args.dist_url == "env://" and args.rank == -1:
174 | args.rank = int(os.environ["RANK"])
175 | if args.multiprocessing_distributed:
176 | # For multiprocessing distributed training, rank needs to be the
177 | # global rank among all the processes
178 | args.rank = args.rank * ngpus_per_node + gpu
179 | dist.init_process_group(backend=args.dist_backend, init_method=args.dist_url,
180 | world_size=args.world_size, rank=args.rank)
181 | # create model
182 | if args.pretrained:
183 | print("=> using pre-trained model '{}'".format(args.arch))
184 | model = models.__dict__[args.arch](pretrained=True)
185 | else:
186 | print("=> creating model '{}'".format(args.arch))
187 | model = models.__dict__[args.arch]()
188 | constant.MODEL_SIZE = ravel_model_params(model).numel()
189 |
190 | if args.distributed:
191 | # For multiprocessing distributed, DistributedDataParallel constructor
192 | # should always set the single device scope, otherwise,
193 | # DistributedDataParallel will use all available devices.
194 | if args.gpu is not None:
195 | torch.cuda.set_device(args.gpu)
196 | model.cuda(args.gpu)
197 | # When using a single GPU per process and per
198 | # DistributedDataParallel, we need to divide the batch size
199 | # ourselves based on the total number of GPUs we have
200 | args.batch_size = int(args.batch_size / ngpus_per_node)
201 | args.workers = int((args.workers + ngpus_per_node - 1) / ngpus_per_node)
202 | model = torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel(model, device_ids=[args.gpu])
203 | else:
204 | model.cuda()
205 | # DistributedDataParallel will divide and allocate batch_size to all
206 | # available GPUs if device_ids are not set
207 | model = torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel(model)
208 | elif args.gpu is not None:
209 | torch.cuda.set_device(args.gpu)
210 | model = model.cuda(args.gpu)
211 | else:
212 | # DataParallel will divide and allocate batch_size to all available GPUs
213 | if args.arch.startswith('alexnet') or args.arch.startswith('vgg'):
214 | model.features = torch.nn.DataParallel(model.features)
215 | model.cuda()
216 | else:
217 | # model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model).cuda()
218 | model = model.cuda()
219 |
220 | # define loss function (criterion) and optimizer
221 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda(args.gpu)
222 |
223 | # optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), args.lr,
224 | # momentum=args.momentum,
225 | # weight_decay=args.weight_decay)
226 | optimizer = GradientSGD(model.parameters(), lr=args.lr,
227 | model=model, momentum=args.momentum,
228 | weight_decay=args.weight_decay,
229 | args=args)
230 |
231 | # optionally resume from a checkpoint
232 | if args.resume:
233 | if os.path.isfile(args.resume):
234 | print("=> loading checkpoint '{}'".format(args.resume))
235 | if args.gpu is None:
236 | checkpoint = torch.load(args.resume)
237 | else:
238 | # Map model to be loaded to specified single gpu.
239 | loc = 'cuda:{}'.format(args.gpu)
240 | checkpoint = torch.load(args.resume, map_location=loc)
241 | args.start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch']
242 | best_acc1 = checkpoint['best_acc1']
243 | logs = checkpoint['logs']
244 | if args.gpu is not None:
245 | # best_acc1 may be from a checkpoint from a different GPU
246 | best_acc1 = best_acc1.to(args.gpu)
247 | model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
248 | optimizer.load_state_dict(checkpoint['optimizer'])
249 | print("=> loaded checkpoint '{}' (epoch {})"
250 | .format(args.resume, checkpoint['epoch']))
251 | else:
252 | print("=> no checkpoint found at '{}'".format(args.resume))
253 |
254 | cudnn.benchmark = True
255 |
256 | # Data loading code
257 | traindir = os.path.join(args.data, 'train')
258 | valdir = os.path.join(args.data, 'val')
259 | normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
260 | std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
261 |
262 | train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(
263 | traindir,
264 | transforms.Compose([
265 | transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
266 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
267 | transforms.ToTensor(),
268 | normalize,
269 | ]))
270 | val_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(valdir, transforms.Compose([
271 | transforms.Resize(256),
272 | transforms.CenterCrop(224),
273 | transforms.ToTensor(),
274 | normalize,
275 | ]))
276 |
277 | if args.distributed:
278 | train_sampler = torch.utils.data.distributed.DistributedSampler(train_dataset)
279 | else:
280 | # train_sampler = None
281 | train_sampler = torch.utils.data.distributed.DistributedSampler(train_dataset, args.world_size - 1,
282 | args.rank - 1)
283 |
284 | train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
285 | train_dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=(train_sampler is None),
286 | num_workers=args.workers, pin_memory=True, sampler=train_sampler)
287 | val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
288 | val_dataset,
289 | batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=False,
290 | num_workers=args.workers, pin_memory=True)
291 | if 'gpu' in socket.gethostname():
292 | print('Init Dataloader in V100 cluster, using memory dataloader')
293 | # train_loader = MemoryDataLoader(args, train_loader,'train').load()
294 | val_loader = MemoryDataLoader(args, val_loader, 'val').load()
295 |
296 | if args.evaluate:
297 | validate(val_loader, model, criterion, args)
298 | return
299 |
300 | for epoch in range(args.start_epoch, args.epochs):
301 | if args.distributed:
302 | train_sampler.set_epoch(epoch)
303 | adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch, args)
304 |
305 | # train for one epoch
306 | train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch, args)
307 |
308 | # evaluate on validation set
309 | acc1 = validate(val_loader, model, criterion, args)
310 |
311 | # remember best acc@1 and save checkpoint
312 | is_best = acc1 > best_acc1
313 | best_acc1 = max(acc1, best_acc1)
314 |
315 | # if not args.multiprocessing_distributed or (args.multiprocessing_distributed
316 | # and args.rank % ngpus_per_node == 0):
317 | # save_checkpoint({
318 | # 'epoch': epoch + 1,
319 | # 'arch': args.arch,
320 | # 'state_dict': model.state_dict(),
321 | # 'best_acc1': best_acc1,
322 | # 'optimizer': optimizer.state_dict(),
323 | # 'logs': logs
324 | # }, is_best)
325 |
326 | # running log
327 |
328 | with open(WORKPATH + '/running.log', 'a+') as f:
329 | running_log = '{},node{}_{}_{}_m{}_e{}_{}.csv'.format(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime()),
330 | args.rank - 1, args.mode,
331 | args.arch, args.momentum,
332 | epoch,
333 | logs[-1]['test_accuracy'])
334 | f.write(running_log + '\n')
335 |
336 | df = pandas.DataFrame(logs)
337 | df.to_csv(WORKPATH + '/log/node{}_{}_{}_m{}_e{}_b{}_{}worker.csv'.format(args.rank - 1, args.mode,
338 | args.arch, args.momentum,
339 | args.epochs,
340 | args.batch_size,
341 | args.world_size - 1, ),
342 | index_label='index')
343 |
344 |
345 | def train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch, args):
346 | batch_time = AverageMeter('Time', ':6.3f')
347 | data_time = AverageMeter('Data', ':6.3f')
348 | losses = AverageMeter('Loss', ':.4e')
349 | top1 = AverageMeter('Acc@1', ':6.2f')
350 | top5 = AverageMeter('Acc@5', ':6.2f')
351 | progress = ProgressMeter(
352 | len(train_loader),
353 | [batch_time, data_time, losses, top1, top5],
354 | prefix="Epoch: [{}]".format(epoch))
355 |
356 | # switch to train mode
357 | model.train()
358 |
359 | end = time.time()
360 | for i, (images, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
361 | # measure data loading time
362 | data_time.update(time.time() - end)
363 |
364 | if args.gpu is not None:
365 | images = images.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
366 | target = target.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
367 |
368 | # compute output
369 | output = model(images)
370 | loss = criterion(output, target)
371 |
372 | # measure accuracy and record loss
373 | acc1, acc5 = accuracy(output, target, topk=(1, 5))
374 | losses.update(loss.item(), images.size(0))
375 | top1.update(acc1[0], images.size(0))
376 | top5.update(acc5[0], images.size(0))
377 | log_obj = {
378 | 'timestamp': datetime.now(),
379 | 'iteration': i,
380 | 'training_loss': loss.item(),
381 | 'training_accuracy': acc1.tolist()[0],
382 | 'training_accuracy5': acc5.tolist()[0],
383 | }
384 | logs.append(log_obj)
385 | # compute gradient and do SGD step
386 | optimizer.zero_grad()
387 | loss.backward()
388 | optimizer.step()
389 |
390 | # measure elapsed time
391 | batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
392 | end = time.time()
393 |
394 | if i % args.print_freq == 0:
395 | progress.display(i)
396 |
397 |
398 | def validate(val_loader, model, criterion, args):
399 | batch_time = AverageMeter('Time', ':6.3f')
400 | losses = AverageMeter('Loss', ':.4e')
401 | top1 = AverageMeter('Acc@1', ':6.2f')
402 | top5 = AverageMeter('Acc@5', ':6.2f')
403 | progress = ProgressMeter(
404 | len(val_loader),
405 | [batch_time, losses, top1, top5],
406 | prefix='Test: ')
407 |
408 | # switch to evaluate mode
409 | model.eval()
410 | if 'gpu' not in socket.gethostname():
411 | val_loader = enumerate(val_loader)
412 | with torch.no_grad():
413 | end = time.time()
414 | # check
415 | for i, (images, target) in val_loader:
416 | if args.gpu is not None:
417 | images = images.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
418 | target = target.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
419 |
420 | # compute output
421 | output = model(images)
422 | loss = criterion(output, target)
423 |
424 | # measure accuracy and record loss
425 | acc1, acc5 = accuracy(output, target, topk=(1, 5))
426 | losses.update(loss.item(), images.size(0))
427 | top1.update(acc1[0], images.size(0))
428 | top5.update(acc5[0], images.size(0))
429 |
430 | # measure elapsed time
431 | batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
432 | end = time.time()
433 |
434 | if i % args.print_freq == 0:
435 | progress.display(i)
436 |
437 | # TODO: this should also be done with the ProgressMeter
438 | print(' * Acc@1 {top1.avg:.3f} Acc@5 {top5.avg:.3f}'
439 | .format(top1=top1, top5=top5))
440 | logs[-1]['test_loss'], logs[-1]['test_accuracy'], logs[-1]['test_accuracy5'] = (
441 | loss.item(), top1.avg.item(), top5.avg.item())
442 |
443 | return top1.avg
444 |
445 |
446 | def save_checkpoint(state, is_best, filename='checkpoint.pth.tar'):
447 | torch.save(state, filename)
448 | if is_best:
449 | shutil.copyfile(filename, 'model_best.pth.tar')
450 |
451 |
452 | class AverageMeter(object):
453 | """Computes and stores the average and current value"""
454 |
455 | def __init__(self, name, fmt=':f'):
456 | self.name = name
457 | self.fmt = fmt
458 | self.reset()
459 |
460 | def reset(self):
461 | self.val = 0
462 | self.avg = 0
463 | self.sum = 0
464 | self.count = 0
465 |
466 | def update(self, val, n=1):
467 | self.val = val
468 | self.sum += val * n
469 | self.count += n
470 | self.avg = self.sum / self.count
471 |
472 | def __str__(self):
473 | fmtstr = '{name} {val' + self.fmt + '} ({avg' + self.fmt + '})'
474 | return fmtstr.format(**self.__dict__)
475 |
476 |
477 | class ProgressMeter(object):
478 | def __init__(self, num_batches, meters, prefix=""):
479 | self.batch_fmtstr = self._get_batch_fmtstr(num_batches)
480 | self.meters = meters
481 | self.prefix = prefix
482 |
483 | def display(self, batch):
484 | entries = [self.prefix + self.batch_fmtstr.format(batch)]
485 | entries += [str(meter) for meter in self.meters]
486 | print('\t'.join(entries))
487 |
488 | def _get_batch_fmtstr(self, num_batches):
489 | num_digits = len(str(num_batches // 1))
490 | fmt = '{:' + str(num_digits) + 'd}'
491 | return '[' + fmt + '/' + fmt.format(num_batches) + ']'
492 |
493 |
494 | def adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch, args):
495 | """Sets the learning rate to the initial LR decayed by 10 every 30 epochs"""
496 | lr = args.lr * (0.1 ** (epoch // 30))
497 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
498 | param_group['lr'] = lr
499 |
500 |
501 | def accuracy(output, target, topk=(1,)):
502 | """Computes the accuracy over the k top predictions for the specified values of k"""
503 | with torch.no_grad():
504 | maxk = max(topk)
505 | batch_size = target.size(0)
506 |
507 | _, pred = output.topk(maxk, 1, True, True)
508 | pred = pred.t()
509 | correct = pred.eq(target.view(1, -1).expand_as(pred))
510 |
511 | res = []
512 | for k in topk:
513 | correct_k = correct[:k].view(-1).float().sum(0, keepdim=True)
514 | res.append(correct_k.mul_(100.0 / batch_size))
515 | return res
516 |
517 |
518 | class MemoryDataLoader(object):
519 |
520 | def __init__(self, args, dataloader, type, path='.', dataset='imagenet'):
521 | self.pickle_name = '_'.join([dataset, str(args.batch_size), type])
522 | self.path = os.path.join(path, self.pickle_name)
523 | if not os.path.exists(self.path):
524 | self.save(dataloader)
525 |
526 | def load(self):
527 | print('Loading pickle to memory')
528 | with open(self.path, 'rb') as file:
529 | data_loader_list = pickle.load(file)
530 | return data_loader_list
531 |
532 | def save(self, dataloader):
533 | loader_list = []
534 | for i, (images, target) in enumerate(dataloader):
535 | print(self.pickle_name, ' Processing dataloader: ', str(i) + '/' + str(len(dataloader)))
536 | t = (i, (images, target))
537 | loader_list.append(t)
538 |
539 | with open(self.path, 'wb') as file:
540 | print('Saving dataloader to pickle')
541 | pickle.dump(loader_list, file)
542 | print('Saving dataloader Success')
543 |
544 |
545 | if __name__ == '__main__':
546 | main()
547 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/example/Imagenet_local.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import argparse
2 | import os
3 | import random
4 | import shutil
5 | import time
6 | import warnings
7 | from datetime import datetime
8 |
9 | import pandas
10 | import torch
11 | import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
12 | import torch.distributed as dist
13 | import torch.multiprocessing as mp
14 | import torch.nn as nn
15 | import torch.nn.parallel
16 | import torch.optim
17 | import torch.utils.data
18 | import torch.utils.data.distributed
19 | import torchvision.datasets as datasets
20 | import torchvision.models as models
21 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
22 |
23 | WORKPATH = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
24 | model_names = sorted(name for name in models.__dict__
25 | if name.islower() and not name.startswith("__")
26 | and callable(models.__dict__[name]))
27 | from PIL import ImageFile
28 |
29 | ImageFile.LOAD_TRUNCATED_IMAGES = True
30 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch ImageNet Training')
31 | parser.add_argument('data', metavar='DIR',
32 | help='path to dataset')
33 | parser.add_argument('-a', '--arch', metavar='ARCH', default='resnet18',
34 | choices=model_names,
35 | help='model architecture: ' +
36 | ' | '.join(model_names) +
37 | ' (default: resnet18)')
38 | parser.add_argument('-j', '--workers', default=8, type=int, metavar='N',
39 | help='number of data loading workers (default: 4)')
40 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', default=90, type=int, metavar='N',
41 | help='number of total epochs to run')
42 | parser.add_argument('--start-epoch', default=0, type=int, metavar='N',
43 | help='manual epoch number (useful on restarts)')
44 | parser.add_argument('-b', '--batch-size', default=256, type=int,
45 | metavar='N',
46 | help='mini-batch size (default: 256), this is the total '
47 | 'batch size of all GPUs on the current node when '
48 | 'using Data Parallel or Distributed Data Parallel')
49 | parser.add_argument('--lr', '--learning-rate', default=0.1, type=float,
50 | metavar='LR', help='initial learning rate', dest='lr')
51 | parser.add_argument('--momentum', default=0.7, type=float, metavar='M',
52 | help='momentum')
53 | parser.add_argument('--wd', '--weight-decay', default=1e-4, type=float,
54 | metavar='W', help='weight decay (default: 1e-4)',
55 | dest='weight_decay')
56 | parser.add_argument('-p', '--print-freq', default=10, type=int,
57 | metavar='N', help='print frequency (default: 10)')
58 | parser.add_argument('--resume', default='', type=str, metavar='PATH',
59 | help='path to latest checkpoint (default: none)')
60 | parser.add_argument('-e', '--evaluate', dest='evaluate', action='store_true',
61 | help='evaluate model on validation set')
62 | parser.add_argument('--pretrained', dest='pretrained', action='store_true',
63 | help='use pre-trained model')
64 | parser.add_argument('--world-size', default=-1, type=int,
65 | help='number of nodes for distributed training')
66 | parser.add_argument('--rank', default=-1, type=int,
67 | help='node rank for distributed training')
68 | parser.add_argument('--dist-url', default='tcp://224.66.41.62:23456', type=str,
69 | help='url used to set up distributed training')
70 | parser.add_argument('--dist-backend', default='nccl', type=str,
71 | help='distributed backend')
72 | parser.add_argument('--seed', default=None, type=int,
73 | help='seed for initializing training. ')
74 | parser.add_argument('--gpu', default=None, type=int,
75 | help='GPU id to use.')
76 | parser.add_argument('--multiprocessing-distributed', action='store_true',
77 | help='Use multi-processing distributed training to launch '
78 | 'N processes per node, which has N GPUs. This is the '
79 | 'fastest way to use PyTorch for either single node or '
80 | 'multi node data parallel training')
81 | logs = []
82 | best_acc1 = 0
83 |
84 |
85 | def main():
86 | args = parser.parse_args()
87 |
88 | if args.seed is not None:
89 | random.seed(args.seed)
90 | torch.manual_seed(args.seed)
91 | cudnn.deterministic = True
92 | warnings.warn('You have chosen to seed training. '
93 | 'This will turn on the CUDNN deterministic setting, '
94 | 'which can slow down your training considerably! '
95 | 'You may see unexpected behavior when restarting '
96 | 'from checkpoints.')
97 |
98 | if args.gpu is not None:
99 | warnings.warn('You have chosen a specific GPU. This will completely '
100 | 'disable data parallelism.')
101 |
102 | if args.dist_url == "env://" and args.world_size == -1:
103 | args.world_size = int(os.environ["WORLD_SIZE"])
104 |
105 | args.distributed = args.world_size > 1 or args.multiprocessing_distributed
106 |
107 | ngpus_per_node = torch.cuda.device_count()
108 | if args.multiprocessing_distributed:
109 | # Since we have ngpus_per_node processes per node, the total world_size
110 | # needs to be adjusted accordingly
111 | args.world_size = ngpus_per_node * args.world_size
112 | # Use torch.multiprocessing.spawn to launch distributed processes: the
113 | # main_worker process function
114 | mp.spawn(main_worker, nprocs=ngpus_per_node, args=(ngpus_per_node, args))
115 | else:
116 | # Simply call main_worker function
117 | main_worker(args.gpu, ngpus_per_node, args)
118 |
119 |
120 | def main_worker(gpu, ngpus_per_node, args):
121 | global best_acc1, logs
122 | args.gpu = gpu
123 |
124 | if args.gpu is not None:
125 | print("Use GPU: {} for training".format(args.gpu))
126 |
127 | if args.distributed:
128 | if args.dist_url == "env://" and args.rank == -1:
129 | args.rank = int(os.environ["RANK"])
130 | if args.multiprocessing_distributed:
131 | # For multiprocessing distributed training, rank needs to be the
132 | # global rank among all the processes
133 | args.rank = args.rank * ngpus_per_node + gpu
134 | dist.init_process_group(backend=args.dist_backend, init_method=args.dist_url,
135 | world_size=args.world_size, rank=args.rank)
136 | # create model
137 | if args.pretrained:
138 | print("=> using pre-trained model '{}'".format(args.arch))
139 | model = models.__dict__[args.arch](pretrained=True)
140 | else:
141 | print("=> creating model '{}'".format(args.arch))
142 | model = models.__dict__[args.arch]()
143 |
144 | if args.distributed:
145 | # For multiprocessing distributed, DistributedDataParallel constructor
146 | # should always set the single device scope, otherwise,
147 | # DistributedDataParallel will use all available devices.
148 | if args.gpu is not None:
149 | torch.cuda.set_device(args.gpu)
150 | model.cuda(args.gpu)
151 | # When using a single GPU per process and per
152 | # DistributedDataParallel, we need to divide the batch size
153 | # ourselves based on the total number of GPUs we have
154 | args.batch_size = int(args.batch_size / ngpus_per_node)
155 | args.workers = int((args.workers + ngpus_per_node - 1) / ngpus_per_node)
156 | model = torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel(model, device_ids=[args.gpu])
157 | else:
158 | model.cuda()
159 | # DistributedDataParallel will divide and allocate batch_size to all
160 | # available GPUs if device_ids are not set
161 | model = torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel(model)
162 | elif args.gpu is not None:
163 | torch.cuda.set_device(args.gpu)
164 | model = model.cuda(args.gpu)
165 | else:
166 | # DataParallel will divide and allocate batch_size to all available GPUs
167 | if args.arch.startswith('alexnet') or args.arch.startswith('vgg'):
168 | model.features = torch.nn.DataParallel(model.features)
169 | model.cuda()
170 | else:
171 | model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model).cuda()
172 |
173 | # define loss function (criterion) and optimizer
174 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda(args.gpu)
175 |
176 | optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), args.lr,
177 | momentum=args.momentum,
178 | weight_decay=args.weight_decay)
179 |
180 | # optionally resume from a checkpoint
181 | if args.resume:
182 | if os.path.isfile(args.resume):
183 | print("=> loading checkpoint '{}'".format(args.resume))
184 | if args.gpu is None:
185 | checkpoint = torch.load(args.resume)
186 | else:
187 | # Map model to be loaded to specified single gpu.
188 | loc = 'cuda:{}'.format(args.gpu)
189 | checkpoint = torch.load(args.resume, map_location=loc)
190 | args.start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch']
191 | best_acc1 = checkpoint['best_acc1']
192 | if args.gpu is not None:
193 | # best_acc1 may be from a checkpoint from a different GPU
194 | best_acc1 = best_acc1.to(args.gpu)
195 | model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
196 | optimizer.load_state_dict(checkpoint['optimizer'])
197 | print("=> loaded checkpoint '{}' (epoch {})"
198 | .format(args.resume, checkpoint['epoch']))
199 | else:
200 | print("=> no checkpoint found at '{}'".format(args.resume))
201 |
202 | cudnn.benchmark = True
203 |
204 | # Data loading code
205 | traindir = os.path.join(args.data, 'train')
206 | valdir = os.path.join(args.data, 'val')
207 | normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
208 | std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
209 |
210 | train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(
211 | traindir,
212 | transforms.Compose([
213 | transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
214 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
215 | transforms.ToTensor(),
216 | normalize,
217 | ]))
218 |
219 | if args.distributed:
220 | train_sampler = torch.utils.data.distributed.DistributedSampler(train_dataset)
221 | else:
222 | train_sampler = None
223 |
224 | train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
225 | train_dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=(train_sampler is None),
226 | num_workers=args.workers, pin_memory=True, sampler=train_sampler)
227 |
228 | val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
229 | datasets.ImageFolder(valdir, transforms.Compose([
230 | transforms.Resize(256),
231 | transforms.CenterCrop(224),
232 | transforms.ToTensor(),
233 | normalize,
234 | ])),
235 | batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=False,
236 | num_workers=args.workers, pin_memory=True)
237 |
238 | if args.evaluate:
239 | validate(val_loader, model, criterion, args)
240 | return
241 |
242 | for epoch in range(args.start_epoch, args.epochs):
243 | if args.distributed:
244 | train_sampler.set_epoch(epoch)
245 | adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch, args)
246 |
247 | # train for one epoch
248 | train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch, args)
249 |
250 | # evaluate on validation set
251 | acc1 = validate(val_loader, model, criterion, args)
252 |
253 | # remember best acc@1 and save checkpoint
254 | is_best = acc1 > best_acc1
255 | best_acc1 = max(acc1, best_acc1)
256 |
257 | if not args.multiprocessing_distributed or (args.multiprocessing_distributed
258 | and args.rank % ngpus_per_node == 0):
259 | save_checkpoint({
260 | 'epoch': epoch + 1,
261 | 'arch': args.arch,
262 | 'state_dict': model.state_dict(),
263 | 'best_acc1': best_acc1,
264 | 'optimizer': optimizer.state_dict(),
265 | }, is_best)
266 |
267 | with open(WORKPATH + '/running.log', 'a+') as f:
268 | running_log = '{},node{}_{}_{}_m{}_e{}_{}.csv'.format(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime()),
269 | args.rank - 1, 'single',
270 | args.arch, args.momentum,
271 | epoch,
272 | logs[-1]['test_accuracy'])
273 | f.write(running_log + '\n')
274 |
275 | df = pandas.DataFrame(logs)
276 | df.to_csv(WORKPATH + '/log/node{}_{}_{}_m{}_e{}_b{}_{}worker.csv'.format(args.rank - 1, 'single',
277 | args.arch, args.momentum,
278 | args.epochs,
279 | args.batch_size,
280 | args.world_size - 1, ),
281 | index_label='index')
282 |
283 |
284 | def train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch, args):
285 | batch_time = AverageMeter('Time', ':6.3f')
286 | data_time = AverageMeter('Data', ':6.3f')
287 | losses = AverageMeter('Loss', ':.4e')
288 | top1 = AverageMeter('Acc@1', ':6.2f')
289 | top5 = AverageMeter('Acc@5', ':6.2f')
290 | progress = ProgressMeter(
291 | len(train_loader),
292 | [batch_time, data_time, losses, top1, top5],
293 | prefix="Epoch: [{}]".format(epoch))
294 |
295 | # switch to train mode
296 | model.train()
297 |
298 | end = time.time()
299 | for i, (images, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
300 | # measure data loading time
301 | data_time.update(time.time() - end)
302 |
303 | if args.gpu is not None:
304 | images = images.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
305 | target = target.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
306 |
307 | # compute output
308 | output = model(images)
309 | loss = criterion(output, target)
310 |
311 | # measure accuracy and record loss
312 | acc1, acc5 = accuracy(output, target, topk=(1, 5))
313 | losses.update(loss.item(), images.size(0))
314 | top1.update(acc1[0], images.size(0))
315 | top5.update(acc5[0], images.size(0))
316 | log_obj = {
317 | 'timestamp': datetime.now(),
318 | 'iteration': i,
319 | 'training_loss': loss.item(),
320 | 'training_accuracy': acc1.tolist()[0],
321 | 'training_accuracy5': acc5.tolist()[0],
322 | }
323 | logs.append(log_obj)
324 |
325 | # compute gradient and do SGD step
326 | optimizer.zero_grad()
327 | loss.backward()
328 | optimizer.step()
329 |
330 | # measure elapsed time
331 | batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
332 | end = time.time()
333 |
334 | if i % args.print_freq == 0:
335 | progress.display(i)
336 |
337 |
338 | def validate(val_loader, model, criterion, args):
339 | batch_time = AverageMeter('Time', ':6.3f')
340 | losses = AverageMeter('Loss', ':.4e')
341 | top1 = AverageMeter('Acc@1', ':6.2f')
342 | top5 = AverageMeter('Acc@5', ':6.2f')
343 | progress = ProgressMeter(
344 | len(val_loader),
345 | [batch_time, losses, top1, top5],
346 | prefix='Test: ')
347 |
348 | # switch to evaluate mode
349 | model.eval()
350 |
351 | with torch.no_grad():
352 | end = time.time()
353 | for i, (images, target) in enumerate(val_loader):
354 | if args.gpu is not None:
355 | images = images.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
356 | target = target.cuda(args.gpu, non_blocking=True)
357 |
358 | # compute output
359 | output = model(images)
360 | loss = criterion(output, target)
361 |
362 | # measure accuracy and record loss
363 | acc1, acc5 = accuracy(output, target, topk=(1, 5))
364 | losses.update(loss.item(), images.size(0))
365 | top1.update(acc1[0], images.size(0))
366 | top5.update(acc5[0], images.size(0))
367 |
368 | # measure elapsed time
369 | batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
370 | end = time.time()
371 |
372 | if i % args.print_freq == 0:
373 | progress.display(i)
374 |
375 | # TODO: this should also be done with the ProgressMeter
376 | logs[-1]['test_loss'], logs[-1]['test_accuracy'], logs[-1]['test_accuracy5'] = (
377 | loss.item(), top1.avg.item(), top5.avg.item())
378 | print(' * Acc@1 {top1.avg:.3f} Acc@5 {top5.avg:.3f}'
379 | .format(top1=top1, top5=top5))
380 |
381 | return top1.avg
382 |
383 |
384 | def save_checkpoint(state, is_best, filename='checkpoint.pth.tar'):
385 | torch.save(state, filename)
386 | if is_best:
387 | shutil.copyfile(filename, 'model_best.pth.tar')
388 |
389 |
390 | class AverageMeter(object):
391 | """Computes and stores the average and current value"""
392 |
393 | def __init__(self, name, fmt=':f'):
394 | self.name = name
395 | self.fmt = fmt
396 | self.reset()
397 |
398 | def reset(self):
399 | self.val = 0
400 | self.avg = 0
401 | self.sum = 0
402 | self.count = 0
403 |
404 | def update(self, val, n=1):
405 | self.val = val
406 | self.sum += val * n
407 | self.count += n
408 | self.avg = self.sum / self.count
409 |
410 | def __str__(self):
411 | fmtstr = '{name} {val' + self.fmt + '} ({avg' + self.fmt + '})'
412 | return fmtstr.format(**self.__dict__)
413 |
414 |
415 | class ProgressMeter(object):
416 | def __init__(self, num_batches, meters, prefix=""):
417 | self.batch_fmtstr = self._get_batch_fmtstr(num_batches)
418 | self.meters = meters
419 | self.prefix = prefix
420 |
421 | def display(self, batch):
422 | entries = [self.prefix + self.batch_fmtstr.format(batch)]
423 | entries += [str(meter) for meter in self.meters]
424 | print('\t'.join(entries))
425 |
426 | def _get_batch_fmtstr(self, num_batches):
427 | num_digits = len(str(num_batches // 1))
428 | fmt = '{:' + str(num_digits) + 'd}'
429 | return '[' + fmt + '/' + fmt.format(num_batches) + ']'
430 |
431 |
432 | def adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch, args):
433 | """Sets the learning rate to the initial LR decayed by 10 every 30 epochs"""
434 | lr = args.lr * (0.1 ** (epoch // 30))
435 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
436 | param_group['lr'] = lr
437 |
438 |
439 | def accuracy(output, target, topk=(1,)):
440 | """Computes the accuracy over the k top predictions for the specified values of k"""
441 | with torch.no_grad():
442 | maxk = max(topk)
443 | batch_size = target.size(0)
444 |
445 | _, pred = output.topk(maxk, 1, True, True)
446 | pred = pred.t()
447 | correct = pred.eq(target.view(1, -1).expand_as(pred))
448 |
449 | res = []
450 | for k in topk:
451 | correct_k = correct[:k].view(-1).float().sum(0, keepdim=True)
452 | res.append(correct_k.mul_(100.0 / batch_size))
453 | return res
454 |
455 |
456 | if __name__ == '__main__':
457 | main()
458 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/example/an4.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import json
2 | import os
3 | import sys
4 | import time
5 |
6 | import torch.optim as optim
7 | import torch.utils.data.distributed
8 | from torch_baidu_ctc import CTCLoss
9 | from tqdm import tqdm
10 |
11 | WORKPATH = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
12 | print(WORKPATH)
13 | sys.path.append(WORKPATH + '/deepspeech')
14 |
15 | from data.data_loader import AudioDataLoader, SpectrogramDataset, DistributedBucketingSampler
16 | from decoder import GreedyDecoder
17 | from model import DeepSpeech, supported_rnns
18 | from datetime import datetime
19 | import pandas as pd
20 |
21 | torch.manual_seed(123456)
22 | torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(123456)
23 | device = torch.device("cuda")
24 |
25 |
26 | def to_np(x):
27 | return x.data.cpu().numpy()
28 |
29 |
30 | class AverageMeter(object):
31 | """Computes and stores the average and current value"""
32 |
33 | def __init__(self):
34 | self.reset()
35 |
36 | def reset(self):
37 | self.val = 0
38 | self.avg = 0
39 | self.sum = 0
40 | self.count = 0
41 |
42 | def update(self, val, n=1):
43 | self.val = val
44 | self.sum += val * n
45 | self.count += n
46 | self.avg = self.sum / self.count
47 |
48 |
49 | Total_param_num = 0
50 | Sparse_param_num = 0
51 | criterion = CTCLoss()
52 | best_wer = None
53 | decoder = None
54 | audio_conf = None
55 | labels = None
56 |
57 |
58 | # 获取数据
59 |
60 |
61 | def init_net(args):
62 | # Model
63 | global decoder, audio_conf, labels
64 | with open(args.labels_path) as label_file:
65 | labels = str(''.join(json.load(label_file)))
66 | audio_conf = dict(sample_rate=args.sample_rate,
67 | window_size=args.window_size,
68 | window_stride=args.window_stride,
69 | window=args.window,
70 | noise_dir=args.noise_dir,
71 | noise_prob=args.noise_prob,
72 | noise_levels=(args.noise_min, args.noise_max))
73 |
74 | rnn_type = args.rnn_type.lower()
75 | decoder = GreedyDecoder(labels)
76 | assert rnn_type in supported_rnns, "rnn_type should be either lstm, rnn or gru"
77 | net = DeepSpeech(rnn_hidden_size=args.hidden_size,
78 | nb_layers=args.hidden_layers,
79 | labels=labels,
80 | rnn_type=supported_rnns[rnn_type],
81 | audio_conf=audio_conf,
82 | bidirectional=args.bidirectional)
83 | net = net.cuda()
84 | return net
85 |
86 |
87 | def an4(args, optimizer, net):
88 | avg_loss, start_epoch, start_iter = 0, 0, 0
89 |
90 | # Training Data
91 | train_dataset = SpectrogramDataset(audio_conf=audio_conf, manifest_filepath=args.train_manifest, labels=labels,
92 | normalize=True, augment=True)
93 | train_sampler = DistributedBucketingSampler(train_dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size,
94 | num_replicas=args.world_size - 1, rank=args.rank - 1)
95 | train_loader = AudioDataLoader(train_dataset, num_workers=args.num_workers, batch_sampler=train_sampler)
96 |
97 | # Testing Data
98 | test_dataset = SpectrogramDataset(audio_conf=audio_conf, manifest_filepath=args.val_manifest, labels=labels,
99 | normalize=True, augment=False)
100 | test_loader = AudioDataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size, num_workers=args.num_workers)
101 |
102 | # Optimizer and scheduler of Training
103 | # optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=args.lr, momentum=args.momentum, nesterov=True)
104 | scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, patience=2, verbose=True, factor=args.learning_anneal)
105 |
106 | logs = []
107 | print("Training Start")
108 | losses = AverageMeter()
109 |
110 | for epoch in range(args.epochs):
111 |
112 | print("Training for epoch {}".format(epoch))
113 | net.train()
114 |
115 | for i, (data) in enumerate(train_loader):
116 | batch_start_time = time.time()
117 |
118 | inputs, targets, input_percentages, target_sizes = data
119 | input_sizes = input_percentages.mul_(int(inputs.size(3))).int()
120 |
121 | inputs = inputs.to(device)
122 |
123 | optimizer.zero_grad()
124 |
125 | out, output_sizes = net(inputs, input_sizes)
126 | out = out.transpose(0, 1) # TxNxH
127 |
128 | # Loss Operation
129 | loss = criterion(out, targets, output_sizes, target_sizes).to(device)
130 | loss = loss / inputs.size(0) # average the loss by minibatch
131 |
132 | inf = float("inf")
133 |
134 | loss_value = loss.item()
135 |
136 | if loss_value == inf or loss_value == -inf:
137 | print("WARNING: received an inf loss, setting loss value to 0")
138 | loss_value = 0
139 |
140 | avg_loss += loss_value
141 | losses.update(loss_value, inputs.size(0))
142 |
143 | # compute gradient
144 | loss.backward()
145 |
146 | # Gradient Clip
147 | torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(net.parameters(), args.max_norm)
148 |
149 | # paralist = gradient_execute(net)
150 |
151 | # SGD step
152 | optimizer.step()
153 |
154 | # for para1, para2 in zip(paralist, net.parameters()):
155 | # para2.grad.data = para1
156 |
157 | log_obj = {
158 | 'timestamp': datetime.now(),
159 | 'iteration': i,
160 | 'training_loss': losses.avg,
161 | 'total_param': Total_param_num,
162 | 'sparse_param': Sparse_param_num,
163 | 'mini_batch_time': (time.time() - batch_start_time)
164 | }
165 | logs.append(log_obj)
166 |
167 |
168 | if i % 5 == 0:
169 | print("Timestamp: {timestamp} | "
170 | "Iteration: {iteration:6} | "
171 | "Loss: {training_loss:6.4f} | "
172 | "Total_param: {total_param:6} | "
173 | "Sparse_param: {sparse_param:6} | "
174 | "Mini_Batch_Time: {mini_batch_time:6.4f} | ".format(**log_obj))
175 |
176 |
177 | # if True:
178 | test_wer, test_cer = evaluate(net, test_loader)
179 | logs[-1]['test_wer'], logs[-1]['test_cer'] = test_wer, test_cer
180 |
181 | print("Timestamp: {timestamp} | "
182 | "Iteration: {iteration:6} | "
183 | "Loss: {training_loss:6.4f} | "
184 | "Total_param: {total_param:6} | "
185 | "Sparse_param: {sparse_param:6} | "
186 | "Mini_Batch_Time: {mini_batch_time:6.4f} | "
187 | "Test Wer: {test_wer:6.4f} | "
188 | "Test Cer: {test_cer:6.4f}".format(**logs[-1]))
189 |
190 | # sche_wer, sche_cer = evaluate(net, test_loader)
191 | scheduler.step(test_wer)
192 |
193 | df = pd.DataFrame(logs)
194 | df.to_csv(WORKPATH + '/log/node{}_{}_{}_m{}_e{}_b{}_{}worker_{}.csv'.format(args.rank - 1, args.mode,
195 | 'an4', args.momentum,
196 | args.epochs,
197 | args.batch_size,
198 | args.world_size - 1,
199 | test_wer))
200 | # df.to_csv('./log/{}_Node{}_{}.csv'.format(args.file_name, args.dist_rank, datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")), index_label='index')
201 | print("Finished Training")
202 |
203 |
204 | def evaluate(net, test_loader):
205 | total_cer, total_wer = 0, 0
206 | net.eval()
207 | with torch.no_grad():
208 | for i, (data) in tqdm(enumerate(test_loader), total=len(test_loader)):
209 | inputs, targets, input_percentages, target_sizes = data
210 | input_sizes = input_percentages.mul_(int(inputs.size(3))).int()
211 | inputs = inputs.to(device)
212 |
213 | # unflatten targets
214 | split_targets = []
215 | offset = 0
216 | for size in target_sizes:
217 | split_targets.append(targets[offset:offset + size])
218 | offset += size
219 |
220 | out, output_sizes = net(inputs, input_sizes)
221 |
222 | decoded_output, _ = decoder.decode(out, output_sizes)
223 | target_strings = decoder.convert_to_strings(split_targets)
224 | wer, cer = 0, 0
225 | for x in range(len(target_strings)):
226 | transcript, reference = decoded_output[x][0], target_strings[x][0]
227 | wer += decoder.wer(transcript, reference) / float(len(reference.split()))
228 | cer += decoder.cer(transcript, reference) / float(len(reference))
229 | total_cer += cer
230 | total_wer += wer
231 | del out
232 | wer = total_wer / len(test_loader.dataset)
233 | cer = total_cer / len(test_loader.dataset)
234 | wer *= 100
235 | cer *= 100
236 | print('Validation Summary Epoch: [{0}]\t'
237 | 'Average WER {wer:.3f}\t'
238 | 'Average CER {cer:.3f}\t'.format(-1, wer=wer, cer=cer))
239 | return wer, cer
240 |
241 |
242 | if __name__ == "__main__":
243 | pass
244 | # dist.init_process_group(backend='nccl', init_method=args.init_method, rank=args.dist_rank,world_size=args.world_size)
245 | # dist.init_process_group(backend='nccl', init_method=args.init_method, world_size=args.world_size,group_name='mygroup')
246 | # an4(args2,None)
247 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/example/cifar10.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import argparse
2 | import os
3 | import socket
4 | import sys
5 | import time
6 |
7 | WORKPATH = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))))
8 | sys.path.append(WORKPATH)
9 | from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import MultiStepLR
10 |
11 | from core.optim import GradientSGD
12 | from core.utils import constant
13 | from core.utils.GradualWarmupScheduler import GradualWarmupScheduler
14 | from core.utils.serialization import ravel_model_params
15 | from example.main import init_server
16 |
17 | import torchvision
18 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
19 | from torch.utils.data.distributed import DistributedSampler
20 |
21 | from datetime import datetime
22 | from example.models import *
23 | from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, accuracy_score
24 | import pandas as pd
25 |
26 |
27 | def get_dataset(args, transform_train, transform_test):
28 | """
29 | :param args:
30 | :param transform:
31 | :return:
32 | """
33 | if args.dataset == 'MNIST':
34 | trainset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='%s/data' % WORKPATH, train=True, download=True,
35 | transform=transform_train)
36 | testset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='%s/data' % WORKPATH, train=False, download=True,
37 | transform=transform_test)
38 | elif args.dataset == 'cifar10':
39 | trainset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='%s/data' % WORKPATH, train=True, download=True,
40 | transform=transform_train)
41 | testset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='%s/data' % WORKPATH, train=False, download=True,
42 | transform=transform_test)
43 |
44 | sampler = DistributedSampler(trainset, args.world_size - 1, args.rank - 1)
45 | # sampler = DistributedSampler(trainset, 1, 0)
46 | trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=1,
47 | sampler=sampler)
48 | testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testset, batch_size=args.test_batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=1)
49 | return trainloader, testloader
50 |
51 |
52 | def init_net(args):
53 | if args.model == 'AlexNet':
54 | net = AlexNet()
55 | elif args.model == 'ResNet18':
56 | net = ResNet18()
57 | args.test_batch_size = 1000
58 | elif args.model == 'ResNet50':
59 | net = ResNet50()
60 | args.test_batch_size = 1000
61 | elif args.model == 'ResNet101':
62 | net = ResNet101()
63 | args.test_batch_size = 500
64 | if args.cuda:
65 | net = net.cuda()
66 | if args.no_distributed and args.half:
67 | net = net.half()
68 | return net
69 |
70 |
71 | def cifar10(args, optimizer, net):
72 | logs = []
73 | transform_train = transforms.Compose([
74 | transforms.RandomCrop(32, padding=4),
75 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
76 | transforms.ToTensor(),
77 | transforms.Normalize((0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465), (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010)),
78 | ])
79 |
80 | transform_test = transforms.Compose([
81 | transforms.ToTensor(),
82 | transforms.Normalize((0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465), (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010)),
83 | ])
84 | trainloader, testloader = get_dataset(args, transform_train, transform_test)
85 |
86 | if args.warmup:
87 | args.lr = args.lr / 10
88 |
89 | # optimizer = DownpourSGD(net.parameters(), lr=args.lr, n_push=args.num_push, n_pull=args.num_pull, model=net)
90 | # scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, patience=3, cooldown=1, verbose=True, factor=0.25)
91 | scheduler = MultiStepLR(optimizer, milestones=[30, 40], gamma=0.1)
92 | if args.warmup:
93 | scheduler = GradualWarmupScheduler(optimizer, multiplier=10, total_epoch=4,
94 | after_scheduler=scheduler)
95 | compress_ratio = [0.01] * (args.epochs + 10)
96 | compress_ratio[1:4] = [0.25, 0.0625, 0.0625 * 0.25, 0.01]
97 | # train
98 | net.train()
99 |
100 | for epoch in range(1, args.epochs + 1): # loop over the dataset multiple times
101 | # scheduler.step()
102 |
103 | if not args.no_distributed:
104 | optimizer.compress_ratio = compress_ratio[epoch]
105 | print("Training for epoch {}, lr={}".format(epoch, scheduler.optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr']))
106 | net.train()
107 | # set distributed_sampler.epoch to shuffle data.
108 | trainloader.sampler.set_epoch(epoch)
109 | start = time.time()
110 | for i, data in enumerate(trainloader, 0):
111 | # get the inputs
112 | inputs, labels = data
113 |
114 | if args.cuda:
115 | inputs, labels = inputs.cuda(), labels.cuda()
116 | if args.no_distributed and args.half:
117 | inputs = inputs.half()
118 |
119 | # zero the parameter gradients
120 | optimizer.zero_grad()
121 | # forward + backward + optimize
122 | outputs = net(inputs)
123 | loss = F.cross_entropy(outputs, labels)
124 | loss.backward()
125 | optimizer.step()
126 | _, predicted = torch.max(outputs, 1)
127 | accuracy = accuracy_score(predicted.cpu(), labels.cpu())
128 |
129 | log_obj = {
130 | 'timestamp': datetime.now(),
131 | 'iteration': i,
132 | 'training_loss': loss.item(),
133 | 'training_accuracy': accuracy,
134 | }
135 | if i % 80 == 0:
136 | print("Timestamp: {timestamp} | "
137 | "Iteration: {iteration:6} | "
138 | "Loss: {training_loss:6.4f} | "
139 | "Accuracy : {training_accuracy:6.4f} | ".format(**log_obj))
140 |
141 | logs.append(log_obj)
142 | if args.no_distributed or args.rank == 1:
143 | # scheduler.step(logs[-1]['test_loss'])
144 | scheduler.step(epoch)
145 | if True: # print every n mini-batches
146 | end = time.time()
147 | print('minibatch cost :%f, time cost: %f' % ((end - start) / (781 / (args.world_size - 1)), (end - start)))
148 | logs[-1]['test_loss'], logs[-1]['test_accuracy'] = evaluate(net, testloader, args)
149 | print("Timestamp: {timestamp} | "
150 | "Iteration: {iteration:6} | "
151 | "Loss: {training_loss:6.4f} | "
152 | "Accuracy : {training_accuracy:6.4f} | "
153 | "Test Loss: {test_loss:6.4f} | "
154 | "Test Accuracy: {test_accuracy:6.4f}".format(**logs[-1])
155 | )
156 | # val_loss, val_accuracy = evaluate(net, testloader, args, verbose=True)
157 |
158 | df = pd.DataFrame(logs)
159 | with open(WORKPATH + '/running.log', 'a+') as f:
160 | running_log = '{},node{}_{}_{}_m{}_e{}_{}.csv'.format(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime()),
161 | args.rank - 1, args.mode,
162 | args.model, args.momentum,
163 | epoch,
164 | logs[-1]['test_accuracy'])
165 | f.write(running_log + '\n')
166 |
167 | print(df)
168 | if args.no_distributed:
169 | if args.cuda:
170 | df.to_csv(
171 | WORKPATH + '/log/gpu_{}_{}_m{}_e{}_b{}_{}.csv'.format(args.mode, args.model, args.momentum, args.epochs,
172 | args.batch_size, logs[-1]['test_accuracy']),
173 | index_label='index')
174 | else:
175 | df.to_csv(WORKPATH + '/log/single.csv', index_label='index')
176 | else:
177 | df.to_csv(WORKPATH + '/log/node{}_{}_{}_m{}_e{}_b{}_{}worker_dual_{}.csv'.format(args.rank - 1, args.mode,
178 | args.model, args.momentum,
179 | args.epochs,
180 | args.batch_size,
181 | args.world_size - 1,
182 | logs[-1]['test_accuracy']),
183 | index_label='index')
184 | print('Finished Training')
185 |
186 |
187 | def evaluate(net, testloader, args, verbose=False):
188 | if args.dataset == 'MNIST':
189 | classes = [str(i) for i in range(10)]
190 | else:
191 | classes = ('plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck')
192 | net.eval()
193 | total = 0
194 | correct = 0
195 | test_loss = 0
196 | with torch.no_grad():
197 | for data in testloader:
198 | images, labels = data
199 | if args.cuda:
200 | images, labels = images.cuda(), labels.cuda()
201 | if args.no_distributed and args.half:
202 | images = images.half()
203 | outputs = net(images)
204 | _, predicted = torch.max(outputs, 1)
205 | test_loss += F.cross_entropy(outputs, labels).item()
206 | total += labels.size(0)
207 | correct += (predicted == labels).sum()
208 |
209 | fake_test_accuracy = accuracy_score(predicted.cpu(), labels.cpu())
210 | test_accuracy = correct.item() / total
211 | print('%f,%f,%f|%f,%s' % (
212 | test_accuracy, correct.item(), total, fake_test_accuracy, str((predicted == labels).sum())))
213 | if verbose:
214 | print('Loss: {:.3f}'.format(test_loss))
215 | print('Accuracy: {:.3f}'.format(test_accuracy))
216 | print(classification_report(predicted, labels, target_names=classes))
217 |
218 | return test_loss, test_accuracy
219 |
220 |
221 | if __name__ == "__main__":
222 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Distbelief training example')
223 |
224 | parser.add_argument('--test-batch-size', type=int, default=20000, metavar='N',
225 | help='input batch size for testing (default: 10000)')
226 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=50, metavar='N', help='number of epochs to train (default: 20)')
227 | parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=64, metavar='N',
228 | help='input batch size for training (default: 64)')
229 | parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=0.1, metavar='LR', help='learning rate (default: 0.1)')
230 | parser.add_argument('--momentum', type=float, default=0.9, metavar='momentum', help='momentum (default: 0.9')
231 | parser.add_argument('--wd', '--weight-decay', default=5e-4, type=float,
232 | metavar='W', help='weight decay (default: 5e-4)',
233 | dest='weight_decay')
234 | parser.add_argument('--cuda', action='store_true', default=True, help='use CUDA for training')
235 | parser.add_argument('--warmup', action='store_true', default=False, help='use warmup or not')
236 | parser.add_argument('--log-interval', type=int, default=10, metavar='N', help='how often to evaluate and print out')
237 | parser.add_argument('--no-distributed', action='store_true', default=False,
238 | help='whether to use DownpourSGD or normal SGD')
239 | parser.add_argument('--rank', type=int, default=0, metavar='N',
240 | help='rank of current process (0 is server, 1+ is training node)')
241 | parser.add_argument('--world-size', type=int, default=3, metavar='N', help='size of the world')
242 | # parser.add_argument('--server', action='store_true', default=False, help='server node?')
243 | parser.add_argument('--dataset', type=str, default='cifar10', help='which dataset to train on')
244 | parser.add_argument('--master', type=str, default='localhost', help='ip address of the master (server) node')
245 | parser.add_argument('--port', type=str, default='29500', help='port on master node to communicate with')
246 | parser.add_argument('--mode', type=str, default='gradient_sgd', help='gradient_sgd, dgc, Aji or asgd')
247 | parser.add_argument('--model', type=str, default='ResNet18', help='AlexNet, ResNet18, ResNet50')
248 | parser.add_argument('--network-interface', type=str, default='enp3s0',
249 | help='By default, Gloo backends will try to find the right network interface to use. '
250 | 'If the automatically detected interface is not correct, you can override it ')
251 | args = parser.parse_args()
252 | if args.network_interface:
253 | os.environ['GLOO_SOCKET_IFNAME'] = args.network_interface
254 | if args.cuda:
255 | if socket.gethostname() == 'yan-pc':
256 | os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '%d' % (args.rank % 1)
257 | elif 'gn' in socket.gethostname():
258 | print('init in th')
259 | os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '%d' % (args.rank % 4)
260 | else:
261 | os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '%d' % (args.rank % 2)
262 | # os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '1'
263 | print('Using device%s, device count:%d' % (os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'], torch.cuda.device_count()))
264 |
265 | net = None
266 |
267 | if args.dataset == 'cifar10':
268 | args.warmup = False
269 | net = init_net(args)
270 | print('MODEL:%s, momentum:%f' % (args.model, args.momentum))
271 | assert net is not None
272 | constant.MODEL_SIZE = ravel_model_params(net).numel()
273 | if args.rank == 0 and not args.no_distributed:
274 | if args.cuda is False:
275 | print('server init in cpu')
276 | init_server(args, net)
277 | else:
278 | optimizer = GradientSGD(net.parameters(), lr=args.lr, model=net, momentum=args.momentum,
279 | weight_decay=args.weight_decay,
280 | args=args)
281 | cifar10(args, optimizer, net)
282 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/example/graph.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | plots accuracy (test and train) vs. time
3 | """
4 | import matplotlib as mpl
5 | mpl.use('TkAgg')
6 |
7 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
8 | import pandas as pd
9 |
10 | colors = ['blue', 'green', 'red', 'orange', 'magenta']
11 | files_to_read = ['log/single.csv', 'log/gpu.csv', 'log/node1.csv', 'log/node2.csv', 'log/node3.csv']
12 | log_dataframes = list(map(pd.read_csv, files_to_read))
13 |
14 | for df in log_dataframes:
15 | df['timestamp'] = pd.to_datetime(df['timestamp'])
16 | df['timestamp'] -= df['timestamp'].min()
17 |
18 |
19 | def plot_train(df, label, color):
20 | plt.plot(df['timestamp'].dt.seconds / 3600.0,
21 | df['training_accuracy'].rolling(50).mean(),
22 | label=label,
23 | color=color)
24 |
25 | def plot_test(df, label, color):
26 | plt.plot(df.dropna()['timestamp'].dt.seconds / 3600.0,
27 | df.dropna()['test_accuracy'].rolling(5).mean(),
28 | label=label,
29 | color=color)
30 |
31 |
32 | fig1 = plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10))
33 |
34 | for color, filename, df in zip(colors, files_to_read, log_dataframes):
35 | plot_train(df, filename, color)
36 |
37 | plt.ylabel('Training Accuracy')
38 | plt.xlabel('Time (hours)')
39 | plt.legend()
40 | plt.title("Training Accuracy vs. Time (50 iteration rolling average, freq: 3, lr: 0.1)")
41 | plt.savefig('train_time.png')
42 |
43 | fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10))
44 |
45 | for color, filename, df in zip(colors, files_to_read, log_dataframes):
46 | plot_test(df, filename, color)
47 |
48 | plt.ylabel('Test Accuracy')
49 | plt.xlabel('Time (hours)')
50 | plt.legend()
51 | plt.title("Test Accuracy vs. Time (5 iteration rolling average, freq: 3, lr: 0.1)")
52 | plt.savefig('test_time.png')
53 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/example/main.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import sys
3 |
4 | WORKPATH = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
5 | print(WORKPATH)
6 | sys.path.append(WORKPATH)
7 |
8 | from core.utils.serialization import ravel_model_params
9 |
10 | from core.utils import constant
11 | import torch.distributed as dist
12 | from core.server import GradientServer
13 |
14 |
15 | def init_server(args, net):
16 | print('init server')
17 | dist.init_process_group('gloo', init_method='file://%s/sharedfile' % WORKPATH, group_name='mygroup',
18 | world_size=args.world_size, rank=args.rank)
19 |
20 | if args.cuda:
21 | model = net.cuda()
22 | else:
23 | model = net
24 | size_list = [i.data.numel() for i in net.parameters()]
25 | threads_num = dist.get_world_size() - 1
26 | threads = []
27 | global_model = ravel_model_params(model)
28 | constant.MODEL_SIZE = global_model.numel()
29 | synced_model = global_model.clone()
30 | for i in range(1, threads_num + 1):
31 | th = GradientServer(model=model, rank=i, worker_num=args.world_size, global_model=global_model,
32 | synced_model=synced_model, size_list=size_list, args=args)
33 | threads.append(th)
34 | th.start()
35 | for t in threads:
36 | t.join()
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/example/models.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 |
3 |
4 | class LeNet(nn.Module):
5 | def __init__(self):
6 | super(LeNet, self).__init__()
7 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 6, kernel_size=5)
8 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=5)
9 | self.conv2_drop = nn.Dropout2d()
10 | self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120)
11 | self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
12 | self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
13 |
14 | def forward(self, x):
15 | x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv1(x), 2))
16 | x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv2_drop(self.conv2(x)), 2))
17 | x = x.view(-1, 16 * 5 * 5)
18 | x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
19 | x = F.dropout(x, training=self.training)
20 | x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
21 | x = self.fc3(x)
22 | return x
23 |
24 |
25 | class ConvBN(nn.Module):
26 | def __init__(self, c_in, c_out, bn_weight_init=1.0):
27 | super().__init__()
28 | self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c_in, c_out, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
29 | self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c_out)
30 | self.bn.weight.data.fill_(bn_weight_init)
31 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(True)
32 |
33 | def forward(self, inputs):
34 | return self.relu(self.bn(self.conv(inputs)))
35 |
36 |
37 | class ResBlk(nn.Module):
38 | def __init__(self, c_in, c_out, pool, res=False):
39 | super().__init__()
40 | self.conv_bn = ConvBN(c_in, c_out)
41 | self.pool = pool
42 | self.res = res
43 | if self.res:
44 | self.res1 = ConvBN(c_out, c_out)
45 | self.res2 = ConvBN(c_out, c_out)
46 |
47 | def forward(self, inputs):
48 | h = self.pool(self.conv_bn(inputs))
49 | if self.res:
50 | h = h + self.res2(self.res1(h))
51 | return h
52 |
53 |
54 | class DavidNet(nn.Module):
55 | def __init__(self, c=64, weight=0.125):
56 | super().__init__()
57 | pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
58 | self.init_conv_bn = ConvBN(3, c)
59 | self.blk1 = ResBlk(c, c * 2, pool, res=True)
60 | # self.blk1 = ResBlk(c, c*2, pool)
61 | self.blk2 = ResBlk(c * 2, c * 4, pool)
62 | self.blk3 = ResBlk(c * 4, c * 8, pool, res=True)
63 | # self.blk3 = ResBlk(c*4, c*8, pool)
64 | self.pool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d((1, 1))
65 | self.linear = nn.Linear(c * 8, 10, bias=False)
66 |
67 | self.weight = weight
68 | self.loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='sum')
69 |
70 | def to_dev(self, device):
71 | self.to(device)
72 | self.blk1.to(device)
73 | self.blk2.to(device)
74 | self.blk3.to(device)
75 | return self
76 |
77 | def forward(self, x):
78 | h = self.pool(self.blk3(self.blk2(self.blk1(self.init_conv_bn(x)))))
79 | h = h.view(h.size(0), h.size(1))
80 | h = self.linear(h) * self.weight
81 | # loss = self.loss(h, y)
82 | # correct = (h.max(dim = 1)[1] == y).sum()
83 | return h
84 |
85 | # class AlexNet(nn.Module):
86 | # def __init__(self, num_classes=10):
87 | # super(AlexNet, self).__init__()
88 | # self.features = nn.Sequential(
89 | # nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
90 | # nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
91 | # nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2),
92 | # nn.Conv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
93 | # nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
94 | # nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2),
95 | # nn.Conv2d(192, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
96 | # nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
97 | # nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
98 | # nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
99 | # nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
100 | # nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
101 | # nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2),
102 | # )
103 | # self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
104 | # nn.Dropout(),
105 | # nn.Linear(256 * 2 * 2, 4096),
106 | # nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
107 | # nn.Dropout(),
108 | # nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
109 | # nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
110 | # nn.Linear(4096, num_classes),
111 | # )
112 | #
113 | # def forward(self, x):
114 | # x = self.features(x)
115 | # x = x.view(x.size(0), 256 * 2 * 2)
116 | # x = self.classifier(x)
117 | # return x
118 | class AlexNet(nn.Module):
119 | def __init__(self, num_classes=10):
120 | super(AlexNet, self).__init__()
121 | self.features = nn.Sequential(
122 | nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=5),
123 | nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
124 | nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
125 | nn.Conv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
126 | nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
127 | nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
128 | nn.Conv2d(192, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
129 | nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
130 | nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
131 | nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
132 | nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
133 | nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
134 | nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
135 | )
136 | self.classifier = nn.Linear(256, num_classes)
137 |
138 | def forward(self, x):
139 | x = self.features(x)
140 | x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
141 | x = self.classifier(x)
142 | return x
143 |
144 | import torch
145 | import torch.nn as nn
146 | import torch.nn.functional as F
147 |
148 |
149 | class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
150 | expansion = 1
151 |
152 | def __init__(self, in_planes, planes, stride=1):
153 | super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
154 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
155 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
156 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
157 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
158 |
159 | self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
160 | if stride != 1 or in_planes != self.expansion * planes:
161 | self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
162 | nn.Conv2d(in_planes, self.expansion * planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
163 | nn.BatchNorm2d(self.expansion * planes)
164 | )
165 |
166 | def forward(self, x):
167 | out = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
168 | out = self.bn2(self.conv2(out))
169 | out += self.shortcut(x)
170 | out = F.relu(out)
171 | return out
172 |
173 |
174 | class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
175 | expansion = 4
176 |
177 | def __init__(self, in_planes, planes, stride=1):
178 | super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
179 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
180 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
181 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
182 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
183 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(planes, self.expansion * planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
184 | self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.expansion * planes)
185 |
186 | self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
187 | if stride != 1 or in_planes != self.expansion * planes:
188 | self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
189 | nn.Conv2d(in_planes, self.expansion * planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
190 | nn.BatchNorm2d(self.expansion * planes)
191 | )
192 |
193 | def forward(self, x):
194 | out = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
195 | out = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(out)))
196 | out = self.bn3(self.conv3(out))
197 | out += self.shortcut(x)
198 | out = F.relu(out)
199 | return out
200 |
201 |
202 | class ResNet(nn.Module):
203 | def __init__(self, block, num_blocks, num_classes=10):
204 | super(ResNet, self).__init__()
205 | self.in_planes = 64
206 |
207 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
208 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
209 | self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, num_blocks[0], stride=1)
210 | self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, num_blocks[1], stride=2)
211 | self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, num_blocks[2], stride=2)
212 | self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, num_blocks[3], stride=2)
213 | self.linear = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
214 |
215 | def _make_layer(self, block, planes, num_blocks, stride):
216 | strides = [stride] + [1] * (num_blocks - 1)
217 | layers = []
218 | for stride in strides:
219 | layers.append(block(self.in_planes, planes, stride))
220 | self.in_planes = planes * block.expansion
221 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
222 |
223 | def forward(self, x):
224 | out = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
225 | out = self.layer1(out)
226 | out = self.layer2(out)
227 | out = self.layer3(out)
228 | out = self.layer4(out)
229 | out = F.avg_pool2d(out, 4)
230 | out = out.view(out.size(0), -1)
231 | out = self.linear(out)
232 | return out
233 |
234 |
235 | def ResNet18():
236 | return ResNet(BasicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2])
237 |
238 |
239 | def ResNet34():
240 | return ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3])
241 |
242 |
243 | def ResNet50():
244 | return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3])
245 |
246 |
247 | def ResNet101():
248 | return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3])
249 |
250 |
251 | def ResNet152():
252 | return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 8, 36, 3])
253 |
254 |
255 | def test():
256 | net = ResNet18()
257 | y = net(torch.randn(1, 3, 32, 32))
258 | print(y.size())
259 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/example/pssh_script.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # from __future__ import print_function
2 | import argparse
3 | import threading
4 |
5 | from pssh.clients import ParallelSSHClient
6 | from pssh.utils import enable_host_logger
7 |
8 | enable_host_logger()
9 |
10 | stdout = []
11 |
12 |
13 | def Print(host, host_out):
14 | for line in host_out.stdout:
15 | try:
16 | stdout.append(line)
17 | except Exception as e:
18 | print(e)
19 |
20 |
21 | if __name__ == '__main__':
22 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Distbelief training example')
23 | parser.add_argument('--where', type=str, default='522', help='522 or th')
24 | args = parser.parse_args()
25 | # where = '522'
26 | print(args)
27 | if args.where == '522':
28 | threads = []
29 | server = ['192.168.3.100']
30 | worker = ['192.168.3.101', '192.168.3.102', '192.168.3.103', '192.168.3.104']
31 | process_per_worker = 1
32 |
33 | # server
34 | host_args = ['--rank %d' % 0]
35 | client = ParallelSSHClient(server, timeout=10000, proxy_host='172.18.233.41', proxy_user='yan',
36 | proxy_port=10000, )
37 | command = '/home/yan/anaconda3/envs/torch1.3/bin/python /share/DGS/example/cifar10.py --network-interface enp3s0 --world-size ' + str(
38 | len(worker) * process_per_worker + 1) + ' %s'
39 | output = client.run_command(command, host_args=host_args, use_pty=True, timeout=10000)
40 | for host, host_out in output.items():
41 | t = threading.Thread(target=Print, args=(host, host_out))
42 | t.start()
43 | threads.append(t)
44 | # worker
45 | for i in range(process_per_worker):
46 | host_args = ['--rank %d' % (j * process_per_worker - i) for j in range(1, len(worker) + 1)]
47 | print(host_args)
48 | client = ParallelSSHClient(worker, timeout=10000, proxy_host='172.18.233.41', proxy_user='yan',
49 | proxy_port=10000, )
50 | command = '/home/yan/anaconda3/envs/torch1.3/bin/python /share/DGS/example/cifar10.py --network-interface enp3s0 --mode aji --world-size ' + str(
51 | len(worker) * process_per_worker + 1) + ' %s'
52 | output = client.run_command(command, host_args=host_args, use_pty=True, timeout=10000)
53 | for host, host_out in output.items():
54 | t = threading.Thread(target=Print, args=(host, host_out))
55 | t.start()
56 | threads.append(t)
57 | for thread in threads:
58 | thread.join()
59 | exit(12580)
60 | elif args.where == 'th':
61 | pass
62 | elif args.where == 'v100':
63 | threads = []
64 | server = ['gpu2']
65 | worker = ['gpu9', 'gpu15', 'gpu18', 'gpu26']
66 | process_per_worker = 4
67 | # server
68 | host_args = ['--rank %d' % 0]
69 | client = ParallelSSHClient(server, timeout=10000)
70 | command = '/GPUFS/app_GPU/application/anaconda3/5.3.1/envs/pytorch-py36/bin/python /GPUFS/sysu_wgwu_8/GradientServer/DGS/example/Imagenet_dist.py -data /GPUFS/sysu_wgwu_8/ImageNet --world-size ' + str(
71 | len(worker) * process_per_worker + 1) + ' %s'
72 | output = client.run_command(command, host_args=host_args, use_pty=True, timeout=10000)
73 | for host, host_out in output.items():
74 | t = threading.Thread(target=Print, args=(host, host_out))
75 | t.start()
76 | threads.append(t)
77 | # worker
78 | for i in range(1, process_per_worker + 1):
79 | host_args = ['--rank %d' % j for j in range(i, i + len(worker) * process_per_worker, process_per_worker)]
80 | print(host_args)
81 | client = ParallelSSHClient(worker, timeout=10000)
82 | command = '/GPUFS/app_GPU/application/anaconda3/5.3.1/envs/pytorch-py36/bin/python /GPUFS/sysu_wgwu_8/GradientServer/DGS/example/Imagenet_dist.py -data /GPUFS/sysu_wgwu_8/ImageNet --mode aji --epoch 90 --momentum 0.45 --world-size ' + str(
83 | len(worker) * process_per_worker + 1) + ' %s'
84 | output = client.run_command(command, host_args=host_args, use_pty=True, timeout=10000)
85 | for host, host_out in output.items():
86 | t = threading.Thread(target=Print, args=(host, host_out))
87 | t.start()
88 | threads.append(t)
89 | for thread in threads:
90 | thread.join()
91 | exit(12580)
92 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/example/tinyimagenet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import argparse
2 | import os
3 | from datetime import datetime
4 |
5 | import torch
6 | import torch.nn as nn
7 | import torch.nn.parallel
8 | import torch.optim
9 | import torch.utils.data
10 | import torch.utils.data.distributed
11 | import torchvision.datasets as datasets
12 | import torchvision.models as models
13 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
14 |
15 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch ImageNet Training')
16 | # parser.add_argument('data', metavar='DIR',
17 | # help='path to dataset')
18 | parser.add_argument('--gpu', default=None, type=int,
19 | help='GPU id to use.')
20 |
21 |
22 | def adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch):
23 | """Sets the learning rate to the initial LR decayed by 10 every 30 epochs"""
24 | lr = 0.01 * (0.1 ** (epoch // 30))
25 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
26 | param_group['lr'] = lr
27 |
28 |
29 | def accuracy(output, target, topk=(1,)):
30 | """Computes the accuracy over the k top predictions for the specified values of k"""
31 | with torch.no_grad():
32 | maxk = max(topk)
33 | batch_size = target.size(0)
34 |
35 | _, pred = output.topk(maxk, 1, True, True)
36 | pred = pred.t()
37 | correct = pred.eq(target.view(1, -1).expand_as(pred))
38 |
39 | res = []
40 | for k in topk:
41 | correct_k = correct[:k].view(-1).float().sum(0, keepdim=True)
42 | res.append(correct_k.mul_(100.0 / batch_size))
43 | return res
44 |
45 |
46 | def train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch):
47 | # switch to train mode
48 | model.train()
49 | losses = list()
50 | top1 = list()
51 | top5 = list()
52 |
53 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
54 |
55 | # compute output
56 | input, target = input.cuda(), target.cuda()
57 | output = model(input)
58 | loss = criterion(output, target)
59 |
60 | losses.append(loss.item())
61 | acc1, acc5 = accuracy(output, target, topk=(1, 5))
62 | top1.append(acc1[0].item())
63 | top5.append(acc5[0].item())
64 |
65 | optimizer.zero_grad()
66 | loss.backward()
67 | optimizer.step()
68 |
69 | if i % 1 == 0:
70 | print(str(datetime.now()) + ' Epoch: [{0}][{1}/{2}]\t'
71 | 'Loss {loss:.4f} ({loss_avg:.4f})\t'
72 | 'Acc@1 {top1:.3f} ({top1_avg:.3f})\t'
73 | 'Acc@5 {top5:.3f} ({top5_avg:.3f})'.format(
74 | epoch, i, len(train_loader), loss=loss.item(), loss_avg=sum(losses) / float(len(losses)),
75 | top1=acc1[0].item(), top1_avg=sum(top1) / float(len(top1)),
76 | top5=acc5[0].item(), top5_avg=sum(top5) / float(len(top5))))
77 |
78 |
79 | def validate(test_loader, model, criterion):
80 | # switch to train mode
81 | model.eval()
82 | losses = list()
83 | top1 = list()
84 | top5 = list()
85 |
86 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(test_loader):
87 |
88 | # compute output
89 | input, target = input.cuda(), target.cuda()
90 | output = model(input)
91 | loss = criterion(output, target)
92 |
93 | losses.append(loss.item())
94 | acc1, acc5 = accuracy(output, target, topk=(1, 5))
95 | top1.append(acc1[0].item())
96 | top5.append(acc5[0].item())
97 |
98 | if i % 10 == 0:
99 | print('[{0}/{1}]\t'
100 | 'Loss {loss:.4f} ({loss_avg:.4f})\t'
101 | 'Acc@1 {top1:.3f} ({top1_avg:.3f})\t'
102 | 'Acc@5 {top5:.3f} ({top5_avg:.3f})'.format(
103 | i, len(test_loader), loss=loss.item(), loss_avg=sum(losses) / float(len(losses)),
104 | top1=acc1[0].item(), top1_avg=sum(top1) / float(len(top1)),
105 | top5=acc5[0].item(), top5_avg=sum(top5) / float(len(top5))))
106 |
107 | print(' * Acc@1 {top1_avg:.3f} Acc@5 {top5_avg:.3f}'
108 | .format(top1_avg=sum(top1) / float(len(top1)), top5_avg=sum(top5) / float(len(top5))))
109 |
110 |
111 | def main():
112 | args = parser.parse_args()
113 | args.gpu = 0
114 | # args.data = '/share/DGS/data/tiny-imagenet-200/'
115 | args.data = '/home/yan/data/'
116 | traindir = os.path.join(args.data, 'train') # /train/ を指定されたパスに追加
117 | testdir = os.path.join(args.data, 'val')
118 | normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
119 | std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # 正規化定数
120 |
121 | train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(
122 | traindir,
123 | transforms.Compose([
124 | transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224), # 画像をサイズ224に切り出しもしくはリサイズ
125 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), # ランダムに画像をフリップ(水増し)
126 | transforms.ToTensor(),
127 | normalize,
128 | ]))
129 |
130 | train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
131 | train_dataset, batch_size=256, shuffle=True,
132 | num_workers=4, pin_memory=True)
133 |
134 | test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
135 | datasets.ImageFolder(testdir, transforms.Compose([
136 | transforms.Resize(256),
137 | transforms.CenterCrop(224),
138 | transforms.ToTensor(),
139 | normalize,
140 | ])),
141 | batch_size=64, shuffle=False,
142 | num_workers=4, pin_memory=True)
143 |
144 | model = models.resnet18(num_classes=1000)
145 | # model = EfficientNet.from_name('efficientnet-b0')
146 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda(args.gpu)
147 | optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), 0.01,
148 | momentum=0.9,
149 | weight_decay=1e-4)
150 |
151 | if args.gpu is not None:
152 | model = model.cuda(args.gpu)
153 |
154 | for epoch in range(0, 100):
155 | adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch)
156 |
157 | # train for one epoch
158 | train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch)
159 |
160 | # evaluate on validation set
161 | acc1 = validate(test_loader, model, criterion)
162 |
163 |
164 | main()
165 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/notebook/Untitled.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "code",
5 | "execution_count": 6,
6 | "metadata": {},
7 | "outputs": [
8 | {
9 | "data": {
10 | "text/html": [
11 | ""
12 | ],
13 | "text/vnd.plotly.v1+html": [
14 | ""
15 | ]
16 | },
17 | "metadata": {},
18 | "output_type": "display_data"
19 | },
20 | {
21 | "data": {
22 | "application/vnd.plotly.v1+json": {
23 | "data": [
24 | {
25 | "type": "scatter",
26 | "uid": "a27bdfe2-f472-11e8-84d1-7d4a4274f24f",
27 | "x": [
28 | 1,
29 | 2,
30 | 3,
31 | 4
32 | ],
33 | "y": [
34 | 4,
35 | 3,
36 | 2,
37 | 1
38 | ]
39 | }
40 | ],
41 | "layout": {
42 | "title": "hello world"
43 | }
44 | },
45 | "text/html": [
46 | ""
47 | ],
48 | "text/vnd.plotly.v1+html": [
49 | ""
50 | ]
51 | },
52 | "metadata": {},
53 | "output_type": "display_data"
54 | }
55 | ],
56 | "source": [
57 | "import plotly\n",
58 | "import plotly.graph_objs as go\n",
59 | "\n",
60 | "plotly.offline.init_notebook_mode(connected=True)\n",
61 | "\n",
62 | "plotly.offline.iplot({\n",
63 | " \"data\": [go.Scatter(x=[1, 2, 3, 4], y=[4, 3, 2, 1])],\n",
64 | " \"layout\": go.Layout(title=\"hello world\")\n",
65 | "})"
66 | ]
67 | },
68 | {
69 | "cell_type": "code",
70 | "execution_count": null,
71 | "metadata": {},
72 | "outputs": [],
73 | "source": []
74 | }
75 | ],
76 | "metadata": {
77 | "kernelspec": {
78 | "display_name": "Python 3",
79 | "language": "python",
80 | "name": "python3"
81 | },
82 | "language_info": {
83 | "codemirror_mode": {
84 | "name": "ipython",
85 | "version": 3
86 | },
87 | "file_extension": ".py",
88 | "mimetype": "text/x-python",
89 | "name": "python",
90 | "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
91 | "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
92 | "version": "3.7.0"
93 | }
94 | },
95 | "nbformat": 4,
96 | "nbformat_minor": 2
97 | }
98 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/requirements.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | bcrypt==3.1.7
2 | certifi==2019.9.11
3 | cffi==1.13.0
4 | cryptography==3.2
5 | future==0.18.2
6 | gevent==1.4.0
7 | greenlet==0.4.15
8 | joblib==0.13.2
9 | numpy==1.17.2
10 | olefile==0.46
11 | pandas==0.25.2
12 | parallel-ssh==1.9.1
13 | paramiko==2.6.0
14 | Pillow==7.1.0
15 | pycparser==2.19
16 | PyNaCl==1.3.0
17 | python-dateutil==2.8.0
18 | pytz==2019.3
19 | scikit-learn==0.21.3
20 | scipy==1.3.1
21 | six==1.12.0
22 | ssh2-python==0.18.0.post1
23 | torch==1.3.0
24 | torchvision==0.4.1a0+d94043a
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import setuptools
2 |
3 | with open("README.md", "r") as fh:
4 | long_description = fh.read()
5 |
6 | setuptools.setup(
7 | name="pytorch-DGS",
8 | version="0.1.0",
9 | author="Jesse Cai",
10 | author_email="jcjessecai@gmail.com",
11 | description="Distributed training for pytorch",
12 | long_description=long_description,
13 | long_description_content_type="text/markdown",
14 | url="https://github.com/ucla-labx/DGS",
15 | packages=setuptools.find_packages(),
16 | classifiers=(
17 | "Programming Language :: Python :: 3",
18 | "License :: OSI Approved :: MIT License",
19 | "Operating System :: OS Independent",
20 | ),
21 | )
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------