├── .gitignore
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── adaptive-aggregation-networks
├── README.md
├── main.py
├── models
│ ├── modified_linear.py
│ ├── modified_resnet.py
│ ├── modified_resnet_cifar.py
│ ├── modified_resnetmtl.py
│ ├── modified_resnetmtl_cifar.py
│ └── resnet_cifar.py
├── trainer
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── base_trainer.py
│ ├── incremental_icarl.py
│ ├── incremental_lucir.py
│ ├── trainer.py
│ └── zeroth_phase.py
└── utils
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── gpu_tools.py
│ ├── imagenet
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── train_and_eval.py
│ ├── utils_dataset.py
│ └── utils_train.py
│ ├── incremental
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── compute_accuracy.py
│ ├── compute_features.py
│ └── conv2d_mtl.py
│ ├── misc.py
│ └── process_fp.py
└── mnemonics-training
├── 1_train
├── main.py
├── models
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── modified_linear.py
│ ├── modified_resnet_cifar.py
│ └── modified_resnetmtl_cifar.py
├── trainer
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── baseline.py
│ ├── incremental.py
│ └── mnemonics.py
└── utils
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── compute_accuracy.py
│ ├── compute_features.py
│ ├── conv2d_mtl.py
│ ├── gpu_tools.py
│ ├── misc.py
│ ├── process_fp.py
│ └── process_mnemonics.py
├── 2_eval
├── README.md
├── main.py
├── models
│ ├── modified_linear.py
│ ├── modified_resnet.py
│ ├── modified_resnet_cifar.py
│ ├── modified_resnetmtl.py
│ ├── modified_resnetmtl_cifar.py
│ └── resnet_cifar.py
├── process_imagenet
│ ├── generate_imagenet.py
│ └── generate_imagenet_subset.py
├── run_eval.sh
├── script
│ └── download_ckpt.sh
├── trainer
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── train.py
└── utils
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── gpu_tools.py
│ ├── imagenet
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── train_and_eval.py
│ ├── utils_dataset.py
│ └── utils_train.py
│ ├── incremental
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── compute_accuracy.py
│ ├── compute_confusion_matrix.py
│ ├── compute_features.py
│ └── conv2d_mtl.py
│ └── misc.py
└── README.md
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # File types
2 | *.pyc
3 | *.npy
4 | *.tar.gz
5 | *.sh
6 | *.out
7 |
8 | # Folders
9 | data
10 | logs
11 | runs
12 | __pycache__
13 |
14 | # File
15 | .DS_Store
16 | bashrc
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2020-2021 Yaoyao Liu
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Class-Incremental Learning
2 |
3 | [](https://github.com/yaoyao-liu/class-incremental-learning/blob/master/LICENSE)
4 | [](https://www.python.org/)
5 | [](https://pytorch.org/)
6 |
7 | ### Papers
8 |
9 | - Adaptive Aggregation Networks for Class-Incremental Learning,
10 | CVPR 2021. \[[PDF](https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/CVPR2021/papers/Liu_Adaptive_Aggregation_Networks_for_Class-Incremental_Learning_CVPR_2021_paper.pdf)\] \[[Project Page](https://class-il.mpi-inf.mpg.de/)\]
11 |
12 | - Mnemonics Training: Multi-Class Incremental Learning without Forgetting,
13 | CVPR 2020. \[[PDF](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2002.10211.pdf)\] \[[Project Page](https://class-il.mpi-inf.mpg.de/mnemonics-training/)\]
14 |
15 | ### Citations
16 |
17 | Please cite our papers if they are helpful to your work:
18 |
19 | ```bibtex
20 | @inproceedings{Liu2020AANets,
21 | author = {Liu, Yaoyao and Schiele, Bernt and Sun, Qianru},
22 | title = {Adaptive Aggregation Networks for Class-Incremental Learning},
23 | booktitle = {The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
24 | pages = {2544-2553},
25 | year = {2021}
26 | }
27 | ```
28 |
29 | ```bibtex
30 | @inproceedings{liu2020mnemonics,
31 | author = {Liu, Yaoyao and Su, Yuting and Liu, An{-}An and Schiele, Bernt and Sun, Qianru},
32 | title = {Mnemonics Training: Multi-Class Incremental Learning without Forgetting},
33 | booktitle = {The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
34 | pages = {12245--12254},
35 | year = {2020}
36 | }
37 | ```
38 |
39 | ### Acknowledgements
40 |
41 | Our implementation uses the source code from the following repositories:
42 |
43 | * [Learning a Unified Classifier Incrementally via Rebalancing](https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning)
44 |
45 | * [iCaRL: Incremental Classifier and Representation Learning](https://github.com/srebuffi/iCaRL)
46 |
47 | * [Dataset Distillation](https://github.com/SsnL/dataset-distillation)
48 |
49 | * [Generative Teaching Networks](https://github.com/uber-research/GTN)
50 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Adaptive Aggregation Networks for Class-Incremental Learning
2 |
3 | [](https://github.com/yaoyao-liu/class-incremental-learning/blob/master/LICENSE)
4 | [](https://www.python.org/)
5 | [](https://pytorch.org/)
6 |
9 |
10 | \[[PDF](https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/CVPR2021/papers/Liu_Adaptive_Aggregation_Networks_for_Class-Incremental_Learning_CVPR_2021_paper.pdf)\] \[[Project Page](https://class-il.mpi-inf.mpg.de/)\] \[[GitLab@MPI](https://gitlab.mpi-klsb.mpg.de/yaoyaoliu/adaptive-aggregation-networks)\]
11 |
12 | #### Summary
13 |
14 | * [Introduction](#introduction)
15 | * [Getting Started](#getting-started)
16 | * [Download the Datasets](#download-the-datasets)
17 | * [Running Experiments](#running-experiments)
18 | * [Citation](#citation)
19 | * [Acknowledgements](#acknowledgements)
20 |
21 | ### Introduction
22 |
23 | Class-Incremental Learning (CIL) aims to learn a classification model with the number of classes increasing phase-by-phase. The inherent problem in CIL is the stability-plasticity dilemma between the learning of old and new classes, i.e., high-plasticity models easily forget old classes but high-stability models are weak to learn new classes. We alleviate this issue by proposing a novel network architecture called Adaptive Aggregation Networks (AANets) in which we explicitly build two residual blocks at each residual level (taking ResNet as the baseline architecture): a stable block and a plastic block. We aggregate the output feature maps from these two blocks and then feed the results to the next-level blocks. We meta-learn the aggregating weights in order to dynamically optimize and balance between two types of blocks, i.e., between stability and plasticity. We conduct extensive experiments on three CIL benchmarks: CIFAR-100, ImageNet-Subset, and ImageNet, and show that many existing CIL methods can be straightforwardly incorporated on the architecture of AANets to boost their performance.
24 |
25 |
26 | 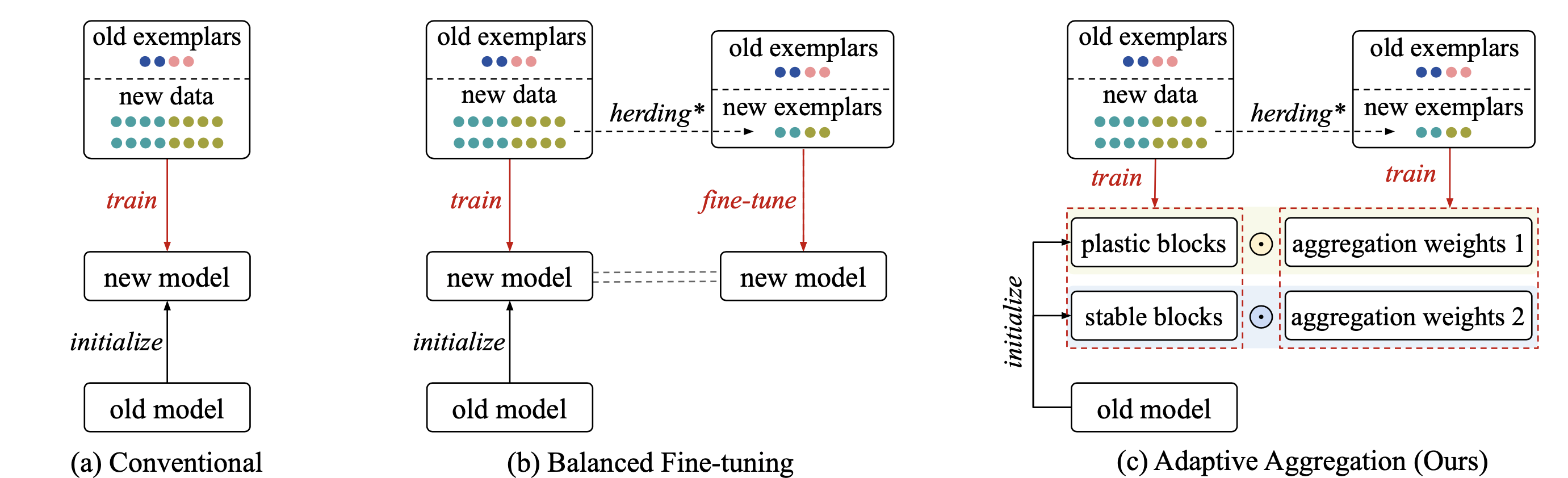 27 |
27 |
28 |
29 | > Figure: Conceptual illustrations of different CIL methods. (a) Conventional methods use all available data (imbalanced classes) to train the model (Rebuffi et al., 2017; Hou et al., 2019) (b) Castro et al. (2018), Hou et al. (2019) and Douillard et al. (2020) follow the convention but add a fine-tuning step using the balanced set of exemplars. (c) Our AANets approach uses all available data to update the plastic and stable blocks, and use the balanced set of exemplars to meta-learn the aggregating weights. We continuously update these weights such as to dynamically balance between plastic and stable blocks, i.e., between plasticity and stability
30 |
31 | ### Getting Started
32 |
33 | In order to run this repository, we advise you to install python 3.6 and PyTorch 1.2.0 with Anaconda.
34 |
35 | You may download Anaconda and read the installation instruction on their official website:
36 |
37 |
38 | Create a new environment and install PyTorch and torchvision on it:
39 |
40 | ```bash
41 | conda create --name AANets-PyTorch python=3.6
42 | conda activate AANets-PyTorch
43 | conda install pytorch=1.2.0
44 | conda install torchvision -c pytorch
45 | ```
46 |
47 | Install other requirements:
48 | ```bash
49 | pip install tqdm scipy sklearn tensorboardX Pillow==6.2.2
50 | ```
51 |
52 | Clone this repository and enter the folder `adaptive-aggregation-networks`:
53 | ```bash
54 | git clone https://github.com/yaoyao-liu/class-incremental-learning.git
55 | cd class-incremental-learning/adaptive-aggregation-networks
56 |
57 | ```
58 |
59 | ### Download the Datasets
60 | #### CIFAR-100
61 | It will be downloaded automatically by `torchvision` when running the experiments.
62 |
63 | #### ImageNet-Subset
64 | We create the ImageNet-Subset following [LUCIR](https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning).
65 | You may download the dataset using the following links:
66 | - [Download from Google Drive](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1n5Xg7Iye_wkzVKc0MTBao5adhYSUlMCL/view?usp=sharing)
67 | - [Download from 百度网盘](https://pan.baidu.com/s/1MnhITYKUI1i7aRBzsPrCSw) (提取码: 6uj5)
68 |
69 | File information:
70 | ```
71 | File name: ImageNet-Subset.tar
72 | Size: 15.37 GB
73 | MD5: ab2190e9dac15042a141561b9ba5d6e9
74 | ```
75 | You need to untar the downloaded file, and put the folder `seed_1993_subset_100_imagenet` in `class-incremental-learning/adaptive-aggregation-networks/data`.
76 |
77 | Please note that the ImageNet-Subset is created from ImageNet. ImageNet is only allowed to be downloaded by researchers for non-commercial research and educational purposes. See the terms of ImageNet [here](https://image-net.org/download.php).
78 |
79 | ### Running Experiments
80 | #### Running Experiments w/ AANets on CIFAR-100
81 |
82 | [LUCIR](https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning) w/ AANets
83 | ```bash
84 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=10 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=lucir --branch_mode=dual --branch_1=ss --branch_2=free --dataset=cifar100
85 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=5 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=lucir --branch_mode=dual --branch_1=ss --branch_2=free --dataset=cifar100
86 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=2 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=lucir --branch_mode=dual --branch_1=ss --branch_2=free --dataset=cifar100
87 | ```
88 |
89 | [iCaRL](https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning) w/ AANets
90 | ```bash
91 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=10 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=icarl --branch_mode=dual --branch_1=ss --branch_2=free --dataset=cifar100
92 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=5 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=icarl --branch_mode=dual --branch_1=ss --branch_2=free --dataset=cifar100
93 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=2 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=icarl --branch_mode=dual --branch_1=ss --branch_2=free --dataset=cifar100
94 | ```
95 |
96 | #### Running Baseline Experiments on CIFAR-100
97 |
98 | [LUCIR](https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning) w/o AANets, dual branch
99 | ```bash
100 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=10 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=lucir --branch_mode=dual --branch_1=free --branch_2=free --fusion_lr=0.0 --dataset=cifar100
101 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=5 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=lucir --branch_mode=dual --branch_1=free --branch_2=free ---fusion_lr=0.0 -dataset=cifar100
102 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=2 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=lucir --branch_mode=dual --branch_1=free --branch_2=free --fusion_lr=0.0 --dataset=cifar100
103 | ```
104 |
105 | [iCaRL](https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning) w/o AANets, dual branch
106 | ```bash
107 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=10 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=icarl --branch_mode=dual --branch_1=free --branch_2=free --fusion_lr=0.0 --dataset=cifar100
108 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=5 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=icarl --branch_mode=dual --branch_1=free --branch_2=free --fusion_lr=0.0 --dataset=cifar100
109 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=2 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=icarl --branch_mode=dual --branch_1=free --branch_2=free --fusion_lr=0.0 --dataset=cifar100
110 | ```
111 |
112 | [LUCIR](https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning) w/o AANets, single branch
113 | ```bash
114 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=10 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=lucir --branch_mode=single --branch_1=free --dataset=cifar100
115 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=5 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=lucir --branch_mode=single --branch_1=free -dataset=cifar100
116 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=2 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=lucir --branch_mode=single --branch_1=free --dataset=cifar100
117 | ```
118 |
119 | [iCaRL](https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning) w/o AANets, single branch
120 | ```bash
121 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=10 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=icarl --branch_mode=single --branch_1=free --dataset=cifar100
122 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=5 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=icarl --branch_mode=single --branch_1=free --dataset=cifar100
123 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=2 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=icarl --branch_mode=single --branch_1=free --dataset=cifar100
124 | ```
125 |
126 | #### Running Experiments on ImageNet-Subset
127 | [LUCIR](https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning) w/ AANets
128 | ```bash
129 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=10 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=lucir --branch_mode=dual --branch_1=ss --branch_2=free --dataset=imagenet_sub --test_batch_size=50 --epochs=90 --num_workers=1 --custom_weight_decay=0.0005 --the_lambda=10 --K=2 --dist=0.5 --lw_mr=1 --base_lr1=0.05 --base_lr2=0.05 --dynamic_budget
130 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=5 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=lucir --branch_mode=dual --branch_1=ss --branch_2=free --dataset=imagenet_sub --test_batch_size=50 --epochs=90 --num_workers=1 --custom_weight_decay=0.0005 --the_lambda=10 --K=2 --dist=0.5 --lw_mr=1 --base_lr1=0.05 --base_lr2=0.05 --dynamic_budget
131 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=2 --gpu=0 --random_seed=1993 --baseline=lucir --branch_mode=dual --branch_1=ss --branch_2=free --dataset=imagenet_sub --test_batch_size=50 --epochs=90 --num_workers=1 --custom_weight_decay=0.0005 --the_lambda=10 --K=2 --dist=0.5 --lw_mr=1 --base_lr1=0.05 --base_lr2=0.05 --dynamic_budget
132 | ```
133 |
134 | ### Code for [PODNet](https://github.com/arthurdouillard/incremental_learning.pytorch) w/ AANets
135 |
136 | We are still cleaning up the code for [PODNet](https://github.com/arthurdouillard/incremental_learning.pytorch) w/ AANets. So we will add it to the GitHub repository later.
137 |
138 | If you need to use it now, here is a preliminary version:
139 |
140 | Please note that you need to install the same environment as [PODNet](https://github.com/arthurdouillard/incremental_learning.pytorch) to run this code.
141 |
142 | ### Accuracy for Each Phase
143 |
144 | We provide the accuracy for each phase on CIFAR-100, ImageNet-Subset, and ImageNet-Full in different settings (*N=5, 10, 25*).
145 |
146 | You may view the results using the following link:
147 | [\[Google Sheet Link\]](https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1rSA0IH7OilDgfx2cvl86ixjVno4I15bmrDWkS4cUtBA/edit?usp=sharing)
148 |
149 | Please note that we re-run some experiments, so some results are slightly different from the paper table.
150 |
151 |
152 | ### Citation
153 |
154 | Please cite our paper if it is helpful to your work:
155 |
156 | ```bibtex
157 | @inproceedings{Liu2020AANets,
158 | author = {Liu, Yaoyao and Schiele, Bernt and Sun, Qianru},
159 | title = {Adaptive Aggregation Networks for Class-Incremental Learning},
160 | booktitle = {The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
161 | pages = {2544-2553},
162 | year = {2021}
163 | }
164 | ```
165 |
166 | ### Acknowledgements
167 |
168 | Our implementation uses the source code from the following repositories:
169 |
170 | * [Learning a Unified Classifier Incrementally via Rebalancing](https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning)
171 |
172 | * [iCaRL: Incremental Classifier and Representation Learning](https://github.com/srebuffi/iCaRL)
173 |
174 | * [PODNet: Pooled Outputs Distillation for Small-Tasks Incremental Learning](https://github.com/arthurdouillard/incremental_learning.pytorch)
175 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/main.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Created by: Yaoyao Liu
3 | ## Max Planck Institute for Informatics
4 | ## yaoyao.liu@mpi-inf.mpg.de
5 | ## Copyright (c) 2021
6 | ##
7 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
8 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
9 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
10 | """ Main function for this project. """
11 | import os
12 | import argparse
13 | import numpy as np
14 | from trainer.trainer import Trainer
15 | from utils.gpu_tools import occupy_memory
16 |
17 | if __name__ == '__main__':
18 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
19 |
20 | ### Basic parameters
21 | parser.add_argument('--gpu', default='0', help='the index of GPU')
22 | parser.add_argument('--dataset', default='cifar100', type=str, choices=['cifar100', 'imagenet_sub', 'imagenet'])
23 | parser.add_argument('--data_dir', default='data/seed_1993_subset_100_imagenet/data', type=str)
24 | parser.add_argument('--baseline', default='lucir', type=str, choices=['lucir', 'icarl'], help='baseline method')
25 | parser.add_argument('--ckpt_label', type=str, default='exp01', help='the label for the checkpoints')
26 | parser.add_argument('--ckpt_dir_fg', type=str, default='-', help='the checkpoint file for the 0-th phase')
27 | parser.add_argument('--resume_fg', action='store_true', help='resume 0-th phase model from the checkpoint')
28 | parser.add_argument('--resume', action='store_true', help='resume from the checkpoints')
29 | parser.add_argument('--num_workers', default=1, type=int, help='the number of workers for loading data')
30 | parser.add_argument('--random_seed', default=1993, type=int, help='random seed')
31 | parser.add_argument('--train_batch_size', default=128, type=int, help='the batch size for train loader')
32 | parser.add_argument('--test_batch_size', default=100, type=int, help='the batch size for test loader')
33 | parser.add_argument('--eval_batch_size', default=128, type=int, help='the batch size for validation loader')
34 | parser.add_argument('--disable_gpu_occupancy', action='store_false', help='disable GPU occupancy')
35 |
36 | ### Network architecture parameters
37 | parser.add_argument('--branch_mode', default='dual', type=str, choices=['dual', 'single'], help='the branch mode for AANets')
38 | parser.add_argument('--branch_1', default='ss', type=str, choices=['ss', 'fixed', 'free'], help='the network type for the first branch')
39 | parser.add_argument('--branch_2', default='free', type=str, choices=['ss', 'fixed', 'free'], help='the network type for the second branch')
40 | parser.add_argument('--imgnet_backbone', default='resnet18', type=str, choices=['resnet18', 'resnet34'], help='network backbone for ImageNet')
41 |
42 | ### Incremental learning parameters
43 | parser.add_argument('--num_classes', default=100, type=int, help='the total number of classes')
44 | parser.add_argument('--nb_cl_fg', default=50, type=int, help='the number of classes in the 0-th phase')
45 | parser.add_argument('--nb_cl', default=10, type=int, help='the number of classes for each phase')
46 | parser.add_argument('--nb_protos', default=20, type=int, help='the number of exemplars for each class')
47 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', default=160, type=int, help='the number of epochs')
48 | parser.add_argument('--dynamic_budget', action='store_true', help='using dynamic budget setting')
49 | parser.add_argument('--fusion_lr', default=1e-8, type=float, help='the learning rate for the aggregation weights')
50 |
51 | ### General learning parameters
52 | parser.add_argument('--lr_factor', default=0.1, type=float, help='learning rate decay factor')
53 | parser.add_argument('--custom_weight_decay', default=5e-4, type=float, help='weight decay parameter for the optimizer')
54 | parser.add_argument('--custom_momentum', default=0.9, type=float, help='momentum parameter for the optimizer')
55 | parser.add_argument('--base_lr1', default=0.1, type=float, help='learning rate for the 0-th phase')
56 | parser.add_argument('--base_lr2', default=0.1, type=float, help='learning rate for the following phases')
57 |
58 | ### LUCIR parameters
59 | parser.add_argument('--the_lambda', default=5, type=float, help='lamda for LF')
60 | parser.add_argument('--dist', default=0.5, type=float, help='dist for margin ranking losses')
61 | parser.add_argument('--K', default=2, type=int, help='K for margin ranking losses')
62 | parser.add_argument('--lw_mr', default=1, type=float, help='loss weight for margin ranking losses')
63 |
64 | ### iCaRL parameters
65 | parser.add_argument('--icarl_beta', default=0.25, type=float, help='beta for iCaRL')
66 | parser.add_argument('--icarl_T', default=2, type=int, help='T for iCaRL')
67 |
68 | the_args = parser.parse_args()
69 |
70 | # Checke the number of classes, ensure they are reasonable
71 | assert(the_args.nb_cl_fg % the_args.nb_cl == 0)
72 | assert(the_args.nb_cl_fg >= the_args.nb_cl)
73 |
74 | # Print the parameters
75 | print(the_args)
76 |
77 | # Set GPU index
78 | os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = the_args.gpu
79 | print('Using gpu:', the_args.gpu)
80 |
81 | # Occupy GPU memory in advance
82 | if the_args.disable_gpu_occupancy:
83 | occupy_memory(the_args.gpu)
84 | print('Occupy GPU memory in advance.')
85 |
86 | # Set the trainer and start training
87 | trainer = Trainer(the_args)
88 | trainer.train()
89 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/models/modified_linear.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Created by: Yaoyao Liu
3 | ## Modified from: https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning
4 | ## Max Planck Institute for Informatics
5 | ## yaoyao.liu@mpi-inf.mpg.de
6 | ## Copyright (c) 2021
7 | ##
8 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
9 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
10 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
11 | import math
12 | import torch
13 | from torch.nn.parameter import Parameter
14 | from torch.nn import functional as F
15 | from torch.nn import Module
16 |
17 | class CosineLinear(Module):
18 | def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, sigma=True):
19 | super(CosineLinear, self).__init__()
20 | self.in_features = in_features
21 | self.out_features = out_features
22 | self.weight = Parameter(torch.Tensor(out_features, in_features))
23 | if sigma:
24 | self.sigma = Parameter(torch.Tensor(1))
25 | else:
26 | self.register_parameter('sigma', None)
27 | self.reset_parameters()
28 |
29 | def reset_parameters(self):
30 | stdv = 1. / math.sqrt(self.weight.size(1))
31 | self.weight.data.uniform_(-stdv, stdv)
32 | if self.sigma is not None:
33 | self.sigma.data.fill_(1)
34 |
35 | def forward(self, input):
36 | out = F.linear(F.normalize(input, p=2,dim=1), \
37 | F.normalize(self.weight, p=2, dim=1))
38 | if self.sigma is not None:
39 | out = self.sigma * out
40 | return out
41 |
42 | class SplitCosineLinear(Module):
43 | def __init__(self, in_features, out_features1, out_features2, sigma=True):
44 | super(SplitCosineLinear, self).__init__()
45 | self.in_features = in_features
46 | self.out_features = out_features1 + out_features2
47 | self.fc1 = CosineLinear(in_features, out_features1, False)
48 | self.fc2 = CosineLinear(in_features, out_features2, False)
49 | if sigma:
50 | self.sigma = Parameter(torch.Tensor(1))
51 | self.sigma.data.fill_(1)
52 | else:
53 | self.register_parameter('sigma', None)
54 |
55 | def forward(self, x):
56 | out1 = self.fc1(x)
57 | out2 = self.fc2(x)
58 | out = torch.cat((out1, out2), dim=1)
59 | if self.sigma is not None:
60 | out = self.sigma * out
61 | return out
62 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/models/modified_resnet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Created by: Yaoyao Liu
3 | ## Modified from: https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning
4 | ## Max Planck Institute for Informatics
5 | ## yaoyao.liu@mpi-inf.mpg.de
6 | ## Copyright (c) 2021
7 | ##
8 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
9 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
10 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
11 | import torch.nn as nn
12 | import math
13 | import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
14 | import models.modified_linear as modified_linear
15 |
16 | def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
17 | return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
18 | padding=1, bias=False)
19 |
20 | class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
21 | expansion = 1
22 |
23 | def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, last=False):
24 | super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
25 | self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
26 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
27 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
28 | self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
29 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
30 | self.downsample = downsample
31 | self.stride = stride
32 | self.last = last
33 |
34 | def forward(self, x):
35 | residual = x
36 |
37 | out = self.conv1(x)
38 | out = self.bn1(out)
39 | out = self.relu(out)
40 |
41 | out = self.conv2(out)
42 | out = self.bn2(out)
43 |
44 | if self.downsample is not None:
45 | residual = self.downsample(x)
46 |
47 | out += residual
48 | if not self.last:
49 | out = self.relu(out)
50 |
51 | return out
52 |
53 | class ResNet(nn.Module):
54 |
55 | def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=1000):
56 | self.inplanes = 64
57 | super(ResNet, self).__init__()
58 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3,
59 | bias=False)
60 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
61 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
62 | self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
63 | self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0])
64 | self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2)
65 | self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2)
66 | self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2, last_phase=True)
67 | self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(7, stride=1)
68 | self.fc = modified_linear.CosineLinear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
69 |
70 | for m in self.modules():
71 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
72 | nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
73 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
74 | nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
75 | nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
76 |
77 | def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, last_phase=False):
78 | downsample = None
79 | if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
80 | downsample = nn.Sequential(
81 | nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
82 | kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
83 | nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
84 | )
85 |
86 | layers = []
87 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
88 | self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
89 | if last_phase:
90 | for i in range(1, blocks-1):
91 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
92 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, last=True))
93 | else:
94 | for i in range(1, blocks):
95 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
96 |
97 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
98 |
99 | def forward(self, x):
100 | x = self.conv1(x)
101 | x = self.bn1(x)
102 | x = self.relu(x)
103 | x = self.maxpool(x)
104 |
105 | x = self.layer1(x)
106 | x = self.layer2(x)
107 | x = self.layer3(x)
108 | x = self.layer4(x)
109 |
110 | x = self.avgpool(x)
111 | x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
112 | x = self.fc(x)
113 |
114 | return x
115 |
116 | def resnet18(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
117 | model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2], **kwargs)
118 | return model
119 |
120 | def resnet34(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
121 | model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], **kwargs)
122 | return model
123 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/models/modified_resnet_cifar.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Created by: Yaoyao Liu
3 | ## Modified from: https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning
4 | ## Max Planck Institute for Informatics
5 | ## yaoyao.liu@mpi-inf.mpg.de
6 | ## Copyright (c) 2021
7 | ##
8 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
9 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
10 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
11 | import torch.nn as nn
12 | import math
13 | import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
14 | import models.modified_linear as modified_linear
15 |
16 | def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
17 | """3x3 convolution with padding"""
18 | return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
19 | padding=1, bias=False)
20 |
21 | class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
22 | expansion = 1
23 |
24 | def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, last=False):
25 | super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
26 | self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
27 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
28 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
29 | self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
30 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
31 | self.downsample = downsample
32 | self.stride = stride
33 | self.last = last
34 |
35 | def forward(self, x):
36 | residual = x
37 |
38 | out = self.conv1(x)
39 | out = self.bn1(out)
40 | out = self.relu(out)
41 |
42 | out = self.conv2(out)
43 | out = self.bn2(out)
44 |
45 | if self.downsample is not None:
46 | residual = self.downsample(x)
47 |
48 | out += residual
49 | if not self.last:
50 | out = self.relu(out)
51 |
52 | return out
53 |
54 | class ResNet(nn.Module):
55 |
56 | def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=10):
57 | self.inplanes = 16
58 | super(ResNet, self).__init__()
59 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1,
60 | bias=False)
61 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(16)
62 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
63 | self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 16, layers[0])
64 | self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 32, layers[1], stride=2)
65 | self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[2], stride=2, last_phase=True)
66 | self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(8, stride=1)
67 | self.fc = modified_linear.CosineLinear(64 * block.expansion, num_classes)
68 |
69 | for m in self.modules():
70 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
71 | nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
72 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
73 | nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
74 | nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
75 |
76 | def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, last_phase=False):
77 | downsample = None
78 | if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
79 | downsample = nn.Sequential(
80 | nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
81 | kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
82 | nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
83 | )
84 |
85 | layers = []
86 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
87 | self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
88 | if last_phase:
89 | for i in range(1, blocks-1):
90 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
91 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, last=True))
92 | else:
93 | for i in range(1, blocks):
94 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
95 |
96 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
97 |
98 | def forward(self, x):
99 | x = self.conv1(x)
100 | x = self.bn1(x)
101 | x = self.relu(x)
102 |
103 | x = self.layer1(x)
104 | x = self.layer2(x)
105 | x = self.layer3(x)
106 |
107 | x = self.avgpool(x)
108 | x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
109 | x = self.fc(x)
110 |
111 | return x
112 |
113 | def resnet20(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
114 | n = 3
115 | model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [n, n, n], **kwargs)
116 | return model
117 |
118 | def resnet32(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
119 | n = 5
120 | model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [n, n, n], **kwargs)
121 | return model
122 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/models/modified_resnetmtl.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Created by: Yaoyao Liu
3 | ## Modified from: https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning
4 | ## Max Planck Institute for Informatics
5 | ## yaoyao.liu@mpi-inf.mpg.de
6 | ## Copyright (c) 2021
7 | ##
8 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
9 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
10 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
11 | import torch.nn as nn
12 | import math
13 | import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
14 | import models.modified_linear as modified_linear
15 | from utils.incremental.conv2d_mtl import Conv2dMtl
16 |
17 | def conv3x3mtl(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
18 | """3x3 convolution with padding"""
19 | return Conv2dMtl(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
20 | padding=1, bias=False)
21 |
22 |
23 | class BasicBlockMtl(nn.Module):
24 | expansion = 1
25 |
26 | def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, last=False):
27 | super(BasicBlockMtl, self).__init__()
28 | self.conv1 = conv3x3mtl(inplanes, planes, stride)
29 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
30 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
31 | self.conv2 = conv3x3mtl(planes, planes)
32 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
33 | self.downsample = downsample
34 | self.stride = stride
35 | self.last = last
36 |
37 | def forward(self, x):
38 | residual = x
39 |
40 | out = self.conv1(x)
41 | out = self.bn1(out)
42 | out = self.relu(out)
43 |
44 | out = self.conv2(out)
45 | out = self.bn2(out)
46 |
47 | if self.downsample is not None:
48 | residual = self.downsample(x)
49 |
50 | out += residual
51 | if not self.last:
52 | out = self.relu(out)
53 |
54 | return out
55 |
56 | class ResNetMtl(nn.Module):
57 |
58 | def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=1000):
59 | self.inplanes = 64
60 | super(ResNetMtl, self).__init__()
61 | self.conv1 = Conv2dMtl(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3,
62 | bias=False)
63 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
64 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
65 | self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
66 | self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0])
67 | self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2)
68 | self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2)
69 | self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2, last_phase=True)
70 | self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(7, stride=1)
71 | self.fc = modified_linear.CosineLinear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
72 |
73 | for m in self.modules():
74 | if isinstance(m, Conv2dMtl):
75 | nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
76 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
77 | nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
78 | nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
79 |
80 | def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, last_phase=False):
81 | downsample = None
82 | if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
83 | downsample = nn.Sequential(
84 | Conv2dMtl(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
85 | kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
86 | nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
87 | )
88 |
89 | layers = []
90 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
91 | self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
92 | if last_phase:
93 | for i in range(1, blocks-1):
94 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
95 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, last=True))
96 | else:
97 | for i in range(1, blocks):
98 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
99 |
100 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
101 |
102 | def forward(self, x):
103 | x = self.conv1(x)
104 | x = self.bn1(x)
105 | x = self.relu(x)
106 | x = self.maxpool(x)
107 |
108 | x = self.layer1(x)
109 | x = self.layer2(x)
110 | x = self.layer3(x)
111 | x = self.layer4(x)
112 |
113 | x = self.avgpool(x)
114 | x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
115 | x = self.fc(x)
116 |
117 | return x
118 |
119 | def resnetmtl18(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
120 | model = ResNetMtl(BasicBlockMtl, [2, 2, 2, 2], **kwargs)
121 | return model
122 |
123 | def resnetmtl34(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
124 | model = ResNetMtl(BasicBlockMtl, [3, 4, 6, 3], **kwargs)
125 | return model
126 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/models/modified_resnetmtl_cifar.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Created by: Yaoyao Liu
3 | ## Modified from: https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning
4 | ## Max Planck Institute for Informatics
5 | ## yaoyao.liu@mpi-inf.mpg.de
6 | ## Copyright (c) 2021
7 | ##
8 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
9 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
10 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
11 | import torch.nn as nn
12 | import math
13 | import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
14 | import models.modified_linear as modified_linear
15 | from utils.incremental.conv2d_mtl import Conv2dMtl
16 |
17 | def conv3x3mtl(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
18 | return Conv2dMtl(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
19 | padding=1, bias=False)
20 |
21 | class BasicBlockMtl(nn.Module):
22 | expansion = 1
23 |
24 | def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, last=False):
25 | super(BasicBlockMtl, self).__init__()
26 | self.conv1 = conv3x3mtl(inplanes, planes, stride)
27 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
28 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
29 | self.conv2 = conv3x3mtl(planes, planes)
30 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
31 | self.downsample = downsample
32 | self.stride = stride
33 | self.last = last
34 |
35 | def forward(self, x):
36 | residual = x
37 |
38 | out = self.conv1(x)
39 | out = self.bn1(out)
40 | out = self.relu(out)
41 |
42 | out = self.conv2(out)
43 | out = self.bn2(out)
44 |
45 | if self.downsample is not None:
46 | residual = self.downsample(x)
47 |
48 | out += residual
49 | if not self.last:
50 | out = self.relu(out)
51 |
52 | return out
53 |
54 | class ResNetMtl(nn.Module):
55 |
56 | def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=10):
57 | self.inplanes = 16
58 | super(ResNetMtl, self).__init__()
59 | self.conv1 = Conv2dMtl(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1,
60 | bias=False)
61 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(16)
62 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
63 | self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 16, layers[0])
64 | self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 32, layers[1], stride=2)
65 | self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[2], stride=2, last_phase=True)
66 | self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(8, stride=1)
67 | self.fc = modified_linear.CosineLinear(64 * block.expansion, num_classes)
68 |
69 | for m in self.modules():
70 | if isinstance(m, Conv2dMtl):
71 | nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
72 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
73 | nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
74 | nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
75 |
76 | def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, last_phase=False):
77 | downsample = None
78 | if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
79 | downsample = nn.Sequential(
80 | Conv2dMtl(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
81 | kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
82 | nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
83 | )
84 |
85 | layers = []
86 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
87 | self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
88 | if last_phase:
89 | for i in range(1, blocks-1):
90 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
91 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, last=True))
92 | else:
93 | for i in range(1, blocks):
94 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
95 |
96 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
97 |
98 | def forward(self, x):
99 | x = self.conv1(x)
100 | x = self.bn1(x)
101 | x = self.relu(x)
102 |
103 | x = self.layer1(x)
104 | x = self.layer2(x)
105 | x = self.layer3(x)
106 |
107 | x = self.avgpool(x)
108 | x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
109 | x = self.fc(x)
110 |
111 | return x
112 |
113 | def resnetmtl20(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
114 | n = 3
115 | model = ResNetMtl(BasicBlockMtl, [n, n, n], **kwargs)
116 | return model
117 |
118 | def resnetmtl32(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
119 | n = 5
120 | model = ResNetMtl(BasicBlockMtl, [n, n, n], **kwargs)
121 | return model
122 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/models/resnet_cifar.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Created by: Yaoyao Liu
3 | ## Modified from: https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning
4 | ## Max Planck Institute for Informatics
5 | ## yaoyao.liu@mpi-inf.mpg.de
6 | ## Copyright (c) 2021
7 | ##
8 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
9 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
10 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
11 | import torch.nn as nn
12 | import math
13 | import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
14 | from utils.incremental.conv2d_mtl import Conv2d
15 |
16 | def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
17 | """3x3 convolution with padding"""
18 | return Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
19 | padding=1, bias=False)
20 |
21 | class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
22 | expansion = 1
23 |
24 | def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None):
25 | super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
26 | self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
27 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
28 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
29 | self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
30 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
31 | self.downsample = downsample
32 | self.stride = stride
33 |
34 | def forward(self, x):
35 | residual = x
36 | import pdb
37 | pdb.set_trace()
38 | out = self.conv1(x)
39 | out = self.bn1(out)
40 | out = self.relu(out)
41 |
42 | out = self.conv2(out)
43 | out = self.bn2(out)
44 |
45 | if self.downsample is not None:
46 | residual = self.downsample(x)
47 |
48 | out += residual
49 | out = self.relu(out)
50 |
51 | return out
52 |
53 |
54 | class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
55 | expansion = 4
56 |
57 | def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None):
58 | super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
59 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
60 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
61 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
62 | padding=1, bias=False)
63 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
64 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes * self.expansion, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
65 | self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * self.expansion)
66 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
67 | self.downsample = downsample
68 | self.stride = stride
69 |
70 | def forward(self, x):
71 | residual = x
72 |
73 | out = self.conv1(x)
74 | out = self.bn1(out)
75 | out = self.relu(out)
76 |
77 | out = self.conv2(out)
78 | out = self.bn2(out)
79 | out = self.relu(out)
80 |
81 | out = self.conv3(out)
82 | out = self.bn3(out)
83 |
84 | if self.downsample is not None:
85 | residual = self.downsample(x)
86 |
87 | out += residual
88 | out = self.relu(out)
89 |
90 | return out
91 |
92 |
93 | class ResNet(nn.Module):
94 |
95 | def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=10):
96 | self.inplanes = 16
97 | super(ResNet, self).__init__()
98 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1,
99 | bias=False)
100 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(16)
101 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
102 | self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 16, layers[0])
103 | self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 32, layers[1], stride=2)
104 | self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[2], stride=2)
105 | self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(8, stride=1)
106 | self.fc = nn.Linear(64 * block.expansion, num_classes)
107 |
108 | for m in self.modules():
109 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
110 | nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
111 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
112 | nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
113 | nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
114 |
115 | def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1):
116 | downsample = None
117 | if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
118 | downsample = nn.Sequential(
119 | nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
120 | kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
121 | nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
122 | )
123 |
124 | layers = []
125 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
126 | self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
127 | for i in range(1, blocks):
128 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
129 |
130 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
131 |
132 | def forward(self, x):
133 | x = self.conv1(x)
134 | x = self.bn1(x)
135 | x = self.relu(x)
136 |
137 | x = self.layer1(x)
138 | x = self.layer2(x)
139 | x = self.layer3(x)
140 |
141 | x = self.avgpool(x)
142 | x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
143 | x = self.fc(x)
144 |
145 | return x
146 |
147 | def resnet20(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
148 | n = 3
149 | model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [n, n, n], **kwargs)
150 | return model
151 |
152 | def resnet32(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
153 | n = 5
154 | model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [n, n, n], **kwargs)
155 | return model
156 |
157 | def resnet56(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
158 | n = 9
159 | model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [n, n, n], **kwargs)
160 | return model
161 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/trainer/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yaoyao-liu/class-incremental-learning/701af9f819f559c6ab3d3ee73bb3d7c21e924572/adaptive-aggregation-networks/trainer/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/trainer/incremental_icarl.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Created by: Yaoyao Liu
3 | ## Modified from: https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning
4 | ## Max Planck Institute for Informatics
5 | ## yaoyao.liu@mpi-inf.mpg.de
6 | ## Copyright (c) 2019
7 | ##
8 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
9 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
10 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
11 | """ Training code for iCaRL """
12 | import torch
13 | import tqdm
14 | import numpy as np
15 | import torch.nn as nn
16 | import torchvision
17 | from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
18 | from torchvision import datasets, models, transforms
19 | from utils.misc import *
20 | from utils.process_fp import process_inputs_fp
21 | import torch.nn.functional as F
22 |
23 | def incremental_train_and_eval(the_args, epochs, fusion_vars, ref_fusion_vars, b1_model, ref_model, b2_model, ref_b2_model, tg_optimizer, tg_lr_scheduler, fusion_optimizer, fusion_lr_scheduler, trainloader, testloader, iteration, start_iteration, X_protoset_cumuls, Y_protoset_cumuls, order_list,lamda, dist, K, lw_mr, balancedloader, T=None, beta=None, fix_bn=False, weight_per_class=None, device=None):
24 |
25 | # Setting up the CUDA device
26 | if device is None:
27 | device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
28 | # Set the 1st branch reference model to the evaluation mode
29 | ref_model.eval()
30 |
31 | # Get the number of old classes
32 | num_old_classes = ref_model.fc.out_features
33 |
34 | # If the 2nd branch reference is not None, set it to the evaluation mode
35 | if iteration > start_iteration+1:
36 | ref_b2_model.eval()
37 |
38 | for epoch in range(epochs):
39 | # Start training for the current phase, set the two branch models to the training mode
40 | b1_model.train()
41 | b2_model.train()
42 |
43 | # Fix the batch norm parameters according to the config
44 | if fix_bn:
45 | for m in b1_model.modules():
46 | if isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
47 | m.eval()
48 |
49 | # Set all the losses to zeros
50 | train_loss = 0
51 | train_loss1 = 0
52 | train_loss2 = 0
53 | # Set the counters to zeros
54 | correct = 0
55 | total = 0
56 |
57 | # Learning rate decay
58 | tg_lr_scheduler.step()
59 | fusion_lr_scheduler.step()
60 |
61 | # Print the information
62 | print('\nEpoch: %d, learning rate: ' % epoch, end='')
63 | print(tg_lr_scheduler.get_lr()[0])
64 |
65 | for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(trainloader):
66 |
67 | # Get a batch of training samples, transfer them to the device
68 | inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)
69 |
70 | # Clear the gradient of the paramaters for the tg_optimizer
71 | tg_optimizer.zero_grad()
72 |
73 | # Forward the samples in the deep networks
74 | outputs, _ = process_inputs_fp(the_args, fusion_vars, b1_model, b2_model, inputs)
75 |
76 | if iteration == start_iteration+1:
77 | ref_outputs = ref_model(inputs)
78 | else:
79 | ref_outputs, ref_features_new = process_inputs_fp(the_args, ref_fusion_vars, ref_model, ref_b2_model, inputs)
80 | # Loss 1: logits-level distillation loss
81 | loss1 = nn.KLDivLoss()(F.log_softmax(outputs[:,:num_old_classes]/T, dim=1), \
82 | F.softmax(ref_outputs.detach()/T, dim=1)) * T * T * beta * num_old_classes
83 | # Loss 2: classification loss
84 | loss2 = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight_per_class)(outputs, targets)
85 | # Sum up all looses
86 | loss = loss1 + loss2
87 |
88 | # Backward and update the parameters
89 | loss.backward()
90 | tg_optimizer.step()
91 |
92 | # Record the losses and the number of samples to compute the accuracy
93 | train_loss += loss.item()
94 | train_loss1 += loss1.item()
95 | train_loss2 += loss2.item()
96 | _, predicted = outputs.max(1)
97 | total += targets.size(0)
98 | correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item()
99 |
100 | # Print the training losses and accuracies
101 | print('Train set: {}, train loss1: {:.4f}, train loss2: {:.4f}, train loss: {:.4f} accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(len(trainloader), train_loss1/(batch_idx+1), train_loss2/(batch_idx+1), train_loss/(batch_idx+1), 100.*correct/total))
102 |
103 | # Update the aggregation weights
104 | b1_model.eval()
105 | b2_model.eval()
106 |
107 | for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(balancedloader):
108 | fusion_optimizer.zero_grad()
109 | inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)
110 | outputs, _ = process_inputs_fp(the_args, fusion_vars, b1_model, b2_model, inputs)
111 | loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight_per_class)(outputs, targets)
112 | loss.backward()
113 | fusion_optimizer.step()
114 |
115 | # Running the test for this epoch
116 | b1_model.eval()
117 | b2_model.eval()
118 | test_loss = 0
119 | correct = 0
120 | total = 0
121 | with torch.no_grad():
122 | for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(testloader):
123 | inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)
124 | outputs, _ = process_inputs_fp(the_args, fusion_vars, b1_model, b2_model, inputs)
125 | loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight_per_class)(outputs, targets)
126 | test_loss += loss.item()
127 | _, predicted = outputs.max(1)
128 | total += targets.size(0)
129 | correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item()
130 | print('Test set: {} test loss: {:.4f} accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(len(testloader), test_loss/(batch_idx+1), 100.*correct/total))
131 |
132 | print("Removing register forward hook")
133 | return b1_model, b2_model
134 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/trainer/incremental_lucir.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Created by: Yaoyao Liu
3 | ## Modified from: https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning
4 | ## Max Planck Institute for Informatics
5 | ## yaoyao.liu@mpi-inf.mpg.de
6 | ## Copyright (c) 2021
7 | ##
8 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
9 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
10 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
11 | """ Training code for LUCIR """
12 | import torch
13 | import tqdm
14 | import numpy as np
15 | import torch.nn as nn
16 | import torchvision
17 | from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
18 | from torchvision import datasets, models, transforms
19 | from utils.misc import *
20 | from utils.process_fp import process_inputs_fp
21 |
22 | cur_features = []
23 | ref_features = []
24 | old_scores = []
25 | new_scores = []
26 |
27 | def get_ref_features(self, inputs, outputs):
28 | global ref_features
29 | ref_features = inputs[0]
30 |
31 | def get_cur_features(self, inputs, outputs):
32 | global cur_features
33 | cur_features = inputs[0]
34 |
35 | def get_old_scores_before_scale(self, inputs, outputs):
36 | global old_scores
37 | old_scores = outputs
38 |
39 | def get_new_scores_before_scale(self, inputs, outputs):
40 | global new_scores
41 | new_scores = outputs
42 |
43 | def map_labels(order_list, Y_set):
44 | map_Y = []
45 | for idx in Y_set:
46 | map_Y.append(order_list.index(idx))
47 | map_Y = np.array(map_Y)
48 | return map_Y
49 |
50 |
51 | def incremental_train_and_eval(the_args, epochs, fusion_vars, ref_fusion_vars, b1_model, ref_model, b2_model, ref_b2_model, \
52 | tg_optimizer, tg_lr_scheduler, fusion_optimizer, fusion_lr_scheduler, trainloader, testloader, iteration, \
53 | start_iteration, X_protoset_cumuls, Y_protoset_cumuls, order_list, the_lambda, dist, \
54 | K, lw_mr, balancedloader, fix_bn=False, weight_per_class=None, device=None):
55 |
56 | # Setting up the CUDA device
57 | if device is None:
58 | device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
59 | # Set the 1st branch reference model to the evaluation mode
60 | ref_model.eval()
61 |
62 | # Get the number of old classes
63 | num_old_classes = ref_model.fc.out_features
64 |
65 | # Get the features from the current and the reference model
66 | handle_ref_features = ref_model.fc.register_forward_hook(get_ref_features)
67 | handle_cur_features = b1_model.fc.register_forward_hook(get_cur_features)
68 | handle_old_scores_bs = b1_model.fc.fc1.register_forward_hook(get_old_scores_before_scale)
69 | handle_new_scores_bs = b1_model.fc.fc2.register_forward_hook(get_new_scores_before_scale)
70 |
71 | # If the 2nd branch reference is not None, set it to the evaluation mode
72 | if iteration > start_iteration+1:
73 | ref_b2_model.eval()
74 |
75 | for epoch in range(epochs):
76 | # Start training for the current phase, set the two branch models to the training mode
77 | b1_model.train()
78 | b2_model.train()
79 |
80 | # Fix the batch norm parameters according to the config
81 | if fix_bn:
82 | for m in b1_model.modules():
83 | if isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
84 | m.eval()
85 |
86 | # Set all the losses to zeros
87 | train_loss = 0
88 | train_loss1 = 0
89 | train_loss2 = 0
90 | train_loss3 = 0
91 | # Set the counters to zeros
92 | correct = 0
93 | total = 0
94 |
95 | # Learning rate decay
96 | tg_lr_scheduler.step()
97 | fusion_lr_scheduler.step()
98 |
99 | # Print the information
100 | print('\nEpoch: %d, learning rate: ' % epoch, end='')
101 | print(tg_lr_scheduler.get_lr()[0])
102 |
103 | for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(trainloader):
104 |
105 | # Get a batch of training samples, transfer them to the device
106 | inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)
107 |
108 | # Clear the gradient of the paramaters for the tg_optimizer
109 | tg_optimizer.zero_grad()
110 |
111 | # Forward the samples in the deep networks
112 | outputs, _ = process_inputs_fp(the_args, fusion_vars, b1_model, b2_model, inputs)
113 |
114 | # Loss 1: feature-level distillation loss
115 | if iteration == start_iteration+1:
116 | ref_outputs = ref_model(inputs)
117 | loss1 = nn.CosineEmbeddingLoss()(cur_features, ref_features.detach(), torch.ones(inputs.shape[0]).to(device)) * the_lambda
118 | else:
119 | ref_outputs, ref_features_new = process_inputs_fp(the_args, ref_fusion_vars, ref_model, ref_b2_model, inputs)
120 | loss1 = nn.CosineEmbeddingLoss()(cur_features, ref_features_new.detach(), torch.ones(inputs.shape[0]).to(device)) * the_lambda
121 |
122 | # Loss 2: classification loss
123 | loss2 = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight_per_class)(outputs, targets)
124 |
125 | # Loss 3: margin ranking loss
126 | outputs_bs = torch.cat((old_scores, new_scores), dim=1)
127 | assert(outputs_bs.size()==outputs.size())
128 | gt_index = torch.zeros(outputs_bs.size()).to(device)
129 | gt_index = gt_index.scatter(1, targets.view(-1,1), 1).ge(0.5)
130 | gt_scores = outputs_bs.masked_select(gt_index)
131 | max_novel_scores = outputs_bs[:, num_old_classes:].topk(K, dim=1)[0]
132 | hard_index = targets.lt(num_old_classes)
133 | hard_num = torch.nonzero(hard_index).size(0)
134 | if hard_num > 0:
135 | gt_scores = gt_scores[hard_index].view(-1, 1).repeat(1, K)
136 | max_novel_scores = max_novel_scores[hard_index]
137 | assert(gt_scores.size() == max_novel_scores.size())
138 | assert(gt_scores.size(0) == hard_num)
139 | loss3 = nn.MarginRankingLoss(margin=dist)(gt_scores.view(-1, 1), max_novel_scores.view(-1, 1), torch.ones(hard_num*K).to(device)) * lw_mr
140 | else:
141 | loss3 = torch.zeros(1).to(device)
142 |
143 | # Sum up all looses
144 | loss = loss1 + loss2 + loss3
145 |
146 | # Backward and update the parameters
147 | loss.backward()
148 | tg_optimizer.step()
149 |
150 | # Record the losses and the number of samples to compute the accuracy
151 | train_loss += loss.item()
152 | train_loss1 += loss1.item()
153 | train_loss2 += loss2.item()
154 | train_loss3 += loss3.item()
155 | _, predicted = outputs.max(1)
156 | total += targets.size(0)
157 | correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item()
158 |
159 | # Print the training losses and accuracies
160 | print('Train set: {}, train loss1: {:.4f}, train loss2: {:.4f}, train loss3: {:.4f}, train loss: {:.4f} accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(len(trainloader), train_loss1/(batch_idx+1), train_loss2/(batch_idx+1), train_loss3/(batch_idx+1), train_loss/(batch_idx+1), 100.*correct/total))
161 |
162 | # Update the aggregation weights
163 | b1_model.eval()
164 | b2_model.eval()
165 |
166 | for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(balancedloader):
167 | if batch_idx <= 500:
168 | inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)
169 | outputs, _ = process_inputs_fp(the_args, fusion_vars, b1_model, b2_model, inputs)
170 | loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight_per_class)(outputs, targets)
171 | loss.backward()
172 | fusion_optimizer.step()
173 |
174 | # Running the test for this epoch
175 | b1_model.eval()
176 | b2_model.eval()
177 | test_loss = 0
178 | correct = 0
179 | total = 0
180 | with torch.no_grad():
181 | for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(testloader):
182 | inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)
183 | outputs, _ = process_inputs_fp(the_args, fusion_vars, b1_model, b2_model, inputs)
184 | loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight_per_class)(outputs, targets)
185 | test_loss += loss.item()
186 | _, predicted = outputs.max(1)
187 | total += targets.size(0)
188 | correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item()
189 | print('Test set: {} test loss: {:.4f} accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(len(testloader), test_loss/(batch_idx+1), 100.*correct/total))
190 |
191 | print("Removing register forward hook")
192 | handle_ref_features.remove()
193 | handle_cur_features.remove()
194 | handle_old_scores_bs.remove()
195 | handle_new_scores_bs.remove()
196 | return b1_model, b2_model
197 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/trainer/trainer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Created by: Yaoyao Liu
3 | ## Modified from: https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning
4 | ## Max Planck Institute for Informatics
5 | ## yaoyao.liu@mpi-inf.mpg.de
6 | ## Copyright (c) 2021
7 | ##
8 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
9 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
10 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
11 | """ Class-incremental learning trainer. """
12 | import torch
13 | import torch.nn as nn
14 | import torch.nn.functional as F
15 | import torch.optim as optim
16 | from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
17 | import torchvision
18 | from torchvision import datasets, models, transforms
19 | from torch.autograd import Variable
20 | from tensorboardX import SummaryWriter
21 | import numpy as np
22 | import time
23 | import os
24 | import os.path as osp
25 | import sys
26 | import copy
27 | import argparse
28 | from PIL import Image
29 | try:
30 | import cPickle as pickle
31 | except:
32 | import pickle
33 | import math
34 | import utils.misc
35 | import models.modified_resnet_cifar as modified_resnet_cifar
36 | import models.modified_resnetmtl_cifar as modified_resnetmtl_cifar
37 | import models.modified_resnet as modified_resnet
38 | import models.modified_resnetmtl as modified_resnetmtl
39 | import models.modified_linear as modified_linear
40 | from utils.imagenet.utils_dataset import split_images_labels
41 | from utils.imagenet.utils_dataset import merge_images_labels
42 | from utils.incremental.compute_accuracy import compute_accuracy
43 | from trainer.incremental_lucir import incremental_train_and_eval as incremental_train_and_eval_lucir
44 | from trainer.incremental_icarl import incremental_train_and_eval as incremental_train_and_eval_icarl
45 | from trainer.zeroth_phase import incremental_train_and_eval_zeroth_phase as incremental_train_and_eval_zeroth_phase
46 | from utils.misc import process_mnemonics
47 | from trainer.base_trainer import BaseTrainer
48 | import warnings
49 | warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
50 |
51 | class Trainer(BaseTrainer):
52 | def train(self):
53 | """The class that contains the code for the class-incremental system.
54 | This trianer is based on the base_trainer.py in the same folder.
55 | If you hope to find the source code of the functions used in this trainer, you may find them in base_trainer.py.
56 | """
57 |
58 | # Set tensorboard recorder
59 | self.train_writer = SummaryWriter(comment=self.save_path)
60 |
61 | # Initial the array to store the accuracies for each phase
62 | top1_acc_list_cumul = np.zeros((int(self.args.num_classes/self.args.nb_cl), 3, 1))
63 | top1_acc_list_ori = np.zeros((int(self.args.num_classes/self.args.nb_cl), 3, 1))
64 |
65 | # Load the training and test samples from the dataset
66 | X_train_total, Y_train_total, X_valid_total, Y_valid_total = self.set_dataset()
67 |
68 | # Initialize the aggregation weights
69 | self.init_fusion_vars()
70 |
71 | # Initialize the class order
72 | order, order_list = self.init_class_order()
73 | np.random.seed(None)
74 |
75 | # Set empty lists for the data
76 | X_valid_cumuls = []
77 | X_protoset_cumuls = []
78 | X_train_cumuls = []
79 | Y_valid_cumuls = []
80 | Y_protoset_cumuls = []
81 | Y_train_cumuls = []
82 |
83 | # Initialize the prototypes
84 | alpha_dr_herding, prototypes = self.init_prototypes(self.dictionary_size, order, X_train_total, Y_train_total)
85 |
86 | # Set the starting iteration
87 | # We start training the class-incremental learning system from e.g., 50 classes to provide a good initial encoder
88 | start_iter = int(self.args.nb_cl_fg/self.args.nb_cl)-1
89 |
90 | # Set the models and some parameter to None
91 | # These models and parameters will be assigned in the following phases
92 | b1_model = None
93 | ref_model = None
94 | b2_model = None
95 | ref_b2_model = None
96 | the_lambda_mult = None
97 |
98 | for iteration in range(start_iter, int(self.args.num_classes/self.args.nb_cl)):
99 | ### Initialize models for the current phase
100 | b1_model, b2_model, ref_model, ref_b2_model, lambda_mult, cur_lambda, last_iter = self.init_current_phase_model(iteration, start_iter, b1_model, b2_model)
101 |
102 | ### Initialize datasets for the current phase
103 | if iteration == start_iter:
104 | indices_train_10, X_valid_cumul, X_train_cumul, Y_valid_cumul, Y_train_cumul, \
105 | X_train_cumuls, Y_valid_cumuls, X_protoset_cumuls, Y_protoset_cumuls, X_valid_cumuls, Y_valid_cumuls, \
106 | X_train, map_Y_train, map_Y_valid_cumul, X_valid_ori, Y_valid_ori = \
107 | self.init_current_phase_dataset(iteration, \
108 | start_iter, last_iter, order, order_list, X_train_total, Y_train_total, X_valid_total, Y_valid_total, \
109 | X_train_cumuls, Y_train_cumuls, X_valid_cumuls, Y_valid_cumuls, X_protoset_cumuls, Y_protoset_cumuls)
110 | else:
111 | indices_train_10, X_valid_cumul, X_train_cumul, Y_valid_cumul, Y_train_cumul, \
112 | X_train_cumuls, Y_valid_cumuls, X_protoset_cumuls, Y_protoset_cumuls, X_valid_cumuls, Y_valid_cumuls, \
113 | X_train, map_Y_train, map_Y_valid_cumul, X_protoset, Y_protoset = \
114 | self.init_current_phase_dataset(iteration, \
115 | start_iter, last_iter, order, order_list, X_train_total, Y_train_total, X_valid_total, Y_valid_total, \
116 | X_train_cumuls, Y_train_cumuls, X_valid_cumuls, Y_valid_cumuls, X_protoset_cumuls, Y_protoset_cumuls)
117 |
118 | is_start_iteration = (iteration == start_iter)
119 |
120 | # Imprint weights
121 | if iteration > start_iter:
122 | b1_model = self.imprint_weights(b1_model, b2_model, iteration, is_start_iteration, X_train, map_Y_train, self.dictionary_size)
123 |
124 | # Update training and test dataloader
125 | trainloader, testloader = self.update_train_and_valid_loader(X_train, map_Y_train, X_valid_cumul, map_Y_valid_cumul, \
126 | iteration, start_iter)
127 |
128 | # Set the names for the checkpoints
129 | ckp_name = osp.join(self.save_path, 'iter_{}_b1.pth'.format(iteration))
130 | ckp_name_b2 = osp.join(self.save_path, 'iter_{}_b2.pth'.format(iteration))
131 | print('Check point name: ', ckp_name)
132 |
133 | if iteration==start_iter and self.args.resume_fg:
134 | # Resume the 0-th phase model according to the config
135 | b1_model = torch.load(self.args.ckpt_dir_fg)
136 | elif self.args.resume and os.path.exists(ckp_name):
137 | # Resume other models according to the config
138 | b1_model = torch.load(ckp_name)
139 | b2_model = torch.load(ckp_name_b2)
140 | else:
141 | # Start training (if we don't resume the models from the checkppoints)
142 |
143 | # Set the optimizer
144 | tg_optimizer, tg_lr_scheduler, fusion_optimizer, fusion_lr_scheduler = self.set_optimizer(iteration, \
145 | start_iter, b1_model, ref_model, b2_model, ref_b2_model)
146 |
147 | if iteration > start_iter:
148 | # Training the class-incremental learning system from the 1st phase
149 |
150 | # Set the balanced dataloader
151 | balancedloader = self.gen_balanced_loader(X_train_total, Y_train_total, indices_train_10, X_protoset, Y_protoset, order_list)
152 |
153 | # Training the model for different baselines
154 | if self.args.baseline == 'lucir':
155 | b1_model, b2_model = incremental_train_and_eval_lucir(self.args, self.args.epochs, self.fusion_vars, \
156 | self.ref_fusion_vars, b1_model, ref_model, b2_model, ref_b2_model, tg_optimizer, tg_lr_scheduler, \
157 | fusion_optimizer, fusion_lr_scheduler, trainloader, testloader, iteration, start_iter, \
158 | X_protoset_cumuls, Y_protoset_cumuls, order_list, cur_lambda, self.args.dist, self.args.K, self.args.lw_mr, balancedloader)
159 | elif self.args.baseline == 'icarl':
160 | b1_model, b2_model = incremental_train_and_eval_icarl(self.args, self.args.epochs, self.fusion_vars, \
161 | self.ref_fusion_vars, b1_model, ref_model, b2_model, ref_b2_model, tg_optimizer, tg_lr_scheduler, \
162 | fusion_optimizer, fusion_lr_scheduler, trainloader, testloader, iteration, start_iter, \
163 | X_protoset_cumuls, Y_protoset_cumuls, order_list, cur_lambda, self.args.dist, self.args.K, self.args.lw_mr, balancedloader, \
164 | self.args.icarl_T, self.args.icarl_beta)
165 | else:
166 | raise ValueError('Please set the correct baseline.')
167 | else:
168 | # Training the class-incremental learning system from the 0th phase
169 | b1_model = incremental_train_and_eval_zeroth_phase(self.args, self.args.epochs, b1_model, \
170 | ref_model, tg_optimizer, tg_lr_scheduler, trainloader, testloader, iteration, start_iter, \
171 | cur_lambda, self.args.dist, self.args.K, self.args.lw_mr)
172 |
173 | # Select the exemplars according to the current model
174 | X_protoset_cumuls, Y_protoset_cumuls, class_means, alpha_dr_herding = self.set_exemplar_set(b1_model, b2_model, \
175 | is_start_iteration, iteration, last_iter, order, alpha_dr_herding, prototypes)
176 |
177 | # Compute the accuracies for current phase
178 | top1_acc_list_ori, top1_acc_list_cumul = self.compute_acc(class_means, order, order_list, b1_model, b2_model, X_protoset_cumuls, Y_protoset_cumuls, \
179 | X_valid_ori, Y_valid_ori, X_valid_cumul, Y_valid_cumul, iteration, is_start_iteration, top1_acc_list_ori, top1_acc_list_cumul)
180 |
181 | # Compute the average accuracy
182 | num_of_testing = iteration - start_iter + 1
183 | avg_cumul_acc_fc = np.sum(top1_acc_list_cumul[start_iter:,0])/num_of_testing
184 | avg_cumul_acc_icarl = np.sum(top1_acc_list_cumul[start_iter:,1])/num_of_testing
185 | print('Computing average accuracy...')
186 | print(" Average accuracy (FC) :\t\t{:.2f} %".format(avg_cumul_acc_fc))
187 | print(" Average accuracy (Proto) :\t\t{:.2f} %".format(avg_cumul_acc_icarl))
188 |
189 | # Write the results to the tensorboard
190 | self.train_writer.add_scalar('avg_acc/fc', float(avg_cumul_acc_fc), iteration)
191 | self.train_writer.add_scalar('avg_acc/proto', float(avg_cumul_acc_icarl), iteration)
192 |
193 | # Save the results and close the tensorboard writer
194 | torch.save(top1_acc_list_ori, osp.join(self.save_path, 'acc_list_ori.pth'))
195 | torch.save(top1_acc_list_cumul, osp.join(self.save_path, 'acc_list_cumul.pth'))
196 | self.train_writer.close()
197 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/trainer/zeroth_phase.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Created by: Yaoyao Liu
3 | ## Modified from: https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning
4 | ## Max Planck Institute for Informatics
5 | ## yaoyao.liu@mpi-inf.mpg.de
6 | ## Copyright (c) 2019
7 | ##
8 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
9 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
10 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
11 | """ Training code for the 0-th phase """
12 | import torch
13 | import tqdm
14 | import numpy as np
15 | import torch.nn as nn
16 | import torchvision
17 | from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
18 | from torchvision import datasets, models, transforms
19 | from utils.misc import *
20 | from utils.process_fp import process_inputs_fp
21 | import torch.nn.functional as F
22 |
23 | def incremental_train_and_eval_zeroth_phase(the_args, epochs, b1_model, ref_model, \
24 | tg_optimizer, tg_lr_scheduler, trainloader, testloader, iteration, start_iteration, \
25 | lamda, dist, K, lw_mr, fix_bn=False, weight_per_class=None, device=None):
26 |
27 | # Setting up the CUDA device
28 | if device is None:
29 | device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
30 |
31 | for epoch in range(epochs):
32 | # Set the 1st branch model to the training mode
33 | b1_model.train()
34 |
35 | # Fix the batch norm parameters according to the config
36 | if fix_bn:
37 | for m in b1_model.modules():
38 | if isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
39 | m.eval()
40 |
41 | # Set all the losses to zeros
42 | train_loss = 0
43 | train_loss1 = 0
44 | train_loss2 = 0
45 | # Set the counters to zeros
46 | correct = 0
47 | total = 0
48 |
49 | # Learning rate decay
50 | tg_lr_scheduler.step()
51 |
52 | # Print the information
53 | print('\nEpoch: %d, learning rate: ' % epoch, end='')
54 | print(tg_lr_scheduler.get_lr()[0])
55 |
56 | for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(trainloader):
57 | # Get a batch of training samples, transfer them to the device
58 | inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)
59 | # Clear the gradient of the paramaters for the tg_optimizer
60 | tg_optimizer.zero_grad()
61 | # Forward the samples in the deep networks
62 | outputs = b1_model(inputs)
63 | # Compute classification loss
64 | loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight_per_class)(outputs, targets)
65 | # Backward and update the parameters
66 | loss.backward()
67 | tg_optimizer.step()
68 | # Record the losses and the number of samples to compute the accuracy
69 | train_loss += loss.item()
70 | _, predicted = outputs.max(1)
71 | total += targets.size(0)
72 | correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item()
73 |
74 | # Print the training losses and accuracies
75 | print('Train set: {}, train loss: {:.4f} accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(len(trainloader), train_loss/(batch_idx+1), 100.*correct/total))
76 |
77 | # Running the test for this epoch
78 | b1_model.eval()
79 | test_loss = 0
80 | correct = 0
81 | total = 0
82 | with torch.no_grad():
83 | for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(testloader):
84 | inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)
85 | outputs = b1_model(inputs)
86 | loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight_per_class)(outputs, targets)
87 | test_loss += loss.item()
88 | _, predicted = outputs.max(1)
89 | total += targets.size(0)
90 | correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item()
91 | print('Test set: {} test loss: {:.4f} accuracy: {:.4f}'.format(len(testloader), test_loss/(batch_idx+1), 100.*correct/total))
92 |
93 | return b1_model
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/utils/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yaoyao-liu/class-incremental-learning/701af9f819f559c6ab3d3ee73bb3d7c21e924572/adaptive-aggregation-networks/utils/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/utils/gpu_tools.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Created by: Yaoyao Liu
3 | ## Max Planck Institute for Informatics
4 | ## yaoyao.liu@mpi-inf.mpg.de
5 | ## Copyright (c) 2021
6 | ##
7 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
8 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
9 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
10 | """ GPU tools. """
11 | import os
12 | import torch
13 | import time
14 |
15 | def check_memory(cuda_device):
16 | """ Check the total memory and occupied memory for GPU """
17 | devices_info = os.popen('"/usr/bin/nvidia-smi" --query-gpu=memory.total,memory.used --format=csv,nounits,noheader').read().strip().split("\n")
18 | total, used = devices_info[int(cuda_device)].split(',')
19 | return total,used
20 |
21 | def occupy_memory(cuda_device):
22 | """ Create a large tensor and delete it.
23 | This operation occupies the GPU memory, so other processes cannot use the occupied memory.
24 | It is used to ensure that this process won't be stopped when it requires additional GPU memory.
25 | Be careful with this operation. It will influence other people when you are sharing GPUs with others.
26 | """
27 | total, used = check_memory(cuda_device)
28 | total = int(total)
29 | used = int(used)
30 | max_mem = int(total * 0.90)
31 | print('Total memory: ' + str(total) + ', used memory: ' + str(used))
32 | block_mem = max_mem - used
33 | if block_mem > 0:
34 | x = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(256, 1024, block_mem)
35 | del x
36 |
37 | def set_gpu(x):
38 | """ Set up which GPU we use for this process """
39 | os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = x
40 | print('Using gpu:', x)
41 |
42 |
43 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/utils/imagenet/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python
2 | # coding=utf-8
3 | # for incremental-class train and eval
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/utils/imagenet/train_and_eval.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Copied from: https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning
3 | ##
4 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
5 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
6 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
7 | """ Tools for ImageNet """
8 | import argparse
9 | import os
10 | import shutil
11 | import time
12 |
13 | import torch
14 | import torch.nn as nn
15 | import torch.nn.parallel
16 | import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
17 | import torch.distributed as dist
18 | import torch.optim
19 | import torch.utils.data
20 | import torch.utils.data.distributed
21 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
22 | import torchvision.datasets as datasets
23 | import torchvision.models as models
24 |
25 | from .utils_train import *
26 |
27 | def train_and_eval(epochs, start_epoch, model, optimizer, lr_scheduler, \
28 | train_loader, val_loader, gpu=None):
29 | for epoch in range(start_epoch, epochs):
30 | lr_scheduler.step()
31 | print('\nEpoch: %d, LR: ' % epoch, end='')
32 | print(lr_scheduler.get_lr())
33 |
34 | train(train_loader, model, optimizer, epoch, gpu)
35 | validate(val_loader, model, gpu)
36 |
37 | return model
38 |
39 | def train(train_loader, model, optimizer, epoch, gpu=None):
40 | batch_time = AverageMeter()
41 | data_time = AverageMeter()
42 | losses = AverageMeter()
43 | top1 = AverageMeter()
44 | top5 = AverageMeter()
45 |
46 | model.train()
47 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda(gpu)
48 |
49 | end = time.time()
50 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
51 | data_time.update(time.time() - end)
52 |
53 | if gpu is not None:
54 | input = input.cuda(gpu, non_blocking=True)
55 | target = target.cuda(gpu, non_blocking=True)
56 |
57 | output = model(input)
58 | loss = criterion(output, target)
59 |
60 | prec1, prec5 = accuracy(output, target, topk=(1, 5))
61 | losses.update(loss.item(), input.size(0))
62 | top1.update(prec1[0], input.size(0))
63 | top5.update(prec5[0], input.size(0))
64 |
65 | optimizer.zero_grad()
66 | loss.backward()
67 | optimizer.step()
68 |
69 |
70 | batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
71 | end = time.time()
72 |
73 | if i % 10 == 0:
74 | print('Epoch: [{0}][{1}/{2}]\t'
75 | 'Time {batch_time.val:.3f} ({batch_time.avg:.3f})\t'
76 | 'Data {data_time.val:.3f} ({data_time.avg:.3f})\t'
77 | 'Loss {loss.val:.4f} ({loss.avg:.4f})\t'
78 | 'Prec@1 {top1.val:.3f} ({top1.avg:.3f})\t'
79 | 'Prec@5 {top5.val:.3f} ({top5.avg:.3f})'.format(
80 | epoch, i, len(train_loader), batch_time=batch_time,
81 | data_time=data_time, loss=losses, top1=top1, top5=top5))
82 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/utils/imagenet/utils_dataset.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Copied from: https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning
3 | ##
4 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
5 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
6 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
7 | """ Tools for ImageNet """
8 | import argparse
9 | import os
10 | import shutil
11 | import time
12 | import numpy as np
13 |
14 | def split_images_labels(imgs):
15 | images = []
16 | labels = []
17 | for item in imgs:
18 | images.append(item[0])
19 | labels.append(item[1])
20 |
21 | return np.array(images), np.array(labels)
22 |
23 | def merge_images_labels(images, labels):
24 | images = list(images)
25 | labels = list(labels)
26 | assert(len(images)==len(labels))
27 | imgs = []
28 | for i in range(len(images)):
29 | item = (images[i], labels[i])
30 | imgs.append(item)
31 |
32 | return imgs
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/utils/imagenet/utils_train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Copied from: https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning
3 | ##
4 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
5 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
6 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
7 | """ Tools for ImageNet """
8 | import argparse
9 | import os
10 | import shutil
11 | import time
12 |
13 | import torch
14 | import torch.nn as nn
15 | import torch.nn.parallel
16 | import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
17 | import torch.distributed as dist
18 | import torch.optim
19 | import torch.utils.data
20 | import torch.utils.data.distributed
21 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
22 | import torchvision.datasets as datasets
23 | import torchvision.models as models
24 |
25 | def validate(val_loader, model, gpu=None):
26 | batch_time = AverageMeter()
27 | losses = AverageMeter()
28 | top1 = AverageMeter()
29 | top5 = AverageMeter()
30 |
31 | model.eval()
32 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda(gpu)
33 |
34 | with torch.no_grad():
35 | end = time.time()
36 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(val_loader):
37 | if gpu is not None:
38 | input = input.cuda(gpu, non_blocking=True)
39 | target = target.cuda(gpu, non_blocking=True)
40 |
41 | output = model(input)
42 | loss = criterion(output, target)
43 |
44 | prec1, prec5 = accuracy(output, target, topk=(1, 5))
45 | losses.update(loss.item(), input.size(0))
46 | top1.update(prec1[0], input.size(0))
47 | top5.update(prec5[0], input.size(0))
48 |
49 | batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
50 | end = time.time()
51 |
52 | if i % 10 == 0:
53 | print('Test: [{0}/{1}]\t'
54 | 'Time {batch_time.val:.3f} ({batch_time.avg:.3f})\t'
55 | 'Loss {loss.val:.4f} ({loss.avg:.4f})\t'
56 | 'Prec@1 {top1.val:.3f} ({top1.avg:.3f})\t'
57 | 'Prec@5 {top5.val:.3f} ({top5.avg:.3f})'.format(
58 | i, len(val_loader), batch_time=batch_time, loss=losses,
59 | top1=top1, top5=top5))
60 |
61 | print(' * Prec@1 {top1.avg:.3f} Prec@5 {top5.avg:.3f}'
62 | .format(top1=top1, top5=top5))
63 |
64 | return top1.avg
65 |
66 | class AverageMeter(object):
67 | """Computes and stores the average and current value"""
68 | def __init__(self):
69 | self.reset()
70 |
71 | def reset(self):
72 | self.val = 0
73 | self.avg = 0
74 | self.sum = 0
75 | self.count = 0
76 |
77 | def update(self, val, n=1):
78 | self.val = val
79 | self.sum += val * n
80 | self.count += n
81 | self.avg = self.sum / self.count
82 |
83 | def accuracy(output, target, topk=(1,)):
84 | """Computes the precision@k for the specified values of k"""
85 | with torch.no_grad():
86 | maxk = max(topk)
87 | batch_size = target.size(0)
88 |
89 | _, pred = output.topk(maxk, 1, True, True)
90 | pred = pred.t()
91 | correct = pred.eq(target.view(1, -1).expand_as(pred))
92 |
93 | res = []
94 | for k in topk:
95 | correct_k = correct[:k].view(-1).float().sum(0, keepdim=True)
96 | res.append(correct_k.mul_(100.0 / batch_size))
97 | return res
98 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/utils/incremental/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python
2 | # coding=utf-8
3 | # for incremental train and eval
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/utils/incremental/compute_accuracy.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Created by: Yaoyao Liu
3 | ## Modified from: https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning
4 | ## Max Planck Institute for Informatics
5 | ## yaoyao.liu@mpi-inf.mpg.de
6 | ## Copyright (c) 2021
7 | ##
8 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
9 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
10 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
11 | """ The functions that compute the accuracies """
12 | import torch
13 | import torch.nn as nn
14 | import torch.nn.functional as F
15 | import torch.optim as optim
16 | from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
17 | import torchvision
18 | from torchvision import datasets, models, transforms
19 | from torch.autograd import Variable
20 | import numpy as np
21 | import time
22 | import os
23 | import copy
24 | import argparse
25 | from PIL import Image
26 | from scipy.spatial.distance import cdist
27 | from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
28 | from utils.misc import *
29 | from utils.imagenet.utils_dataset import merge_images_labels
30 | from utils.process_fp import process_inputs_fp
31 |
32 | def map_labels(order_list, Y_set):
33 | map_Y = []
34 | for idx in Y_set:
35 | map_Y.append(order_list.index(idx))
36 | map_Y = np.array(map_Y)
37 | return map_Y
38 |
39 | def compute_accuracy(the_args, fusion_vars, b1_model, b2_model, tg_feature_model, class_means, \
40 | X_protoset_cumuls, Y_protoset_cumuls, evalloader, order_list, is_start_iteration=False, \
41 | fast_fc=None, scale=None, print_info=True, device=None, cifar=True, imagenet=False, \
42 | valdir=None):
43 | if device is None:
44 | device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
45 | b1_model.eval()
46 | tg_feature_model.eval()
47 | b1_model.eval()
48 | if b2_model is not None:
49 | b2_model.eval()
50 | fast_fc = 0.0
51 | correct = 0
52 | correct_icarl = 0
53 | correct_icarl_cosine = 0
54 | correct_icarl_cosine2 = 0
55 | correct_ncm = 0
56 | correct_maml = 0
57 | total = 0
58 | with torch.no_grad():
59 | for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(evalloader):
60 | inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)
61 | total += targets.size(0)
62 |
63 | if is_start_iteration:
64 | outputs = b1_model(inputs)
65 | else:
66 | outputs, outputs_feature = process_inputs_fp(the_args, fusion_vars, b1_model, b2_model, inputs)
67 |
68 | outputs = F.softmax(outputs, dim=1)
69 | if scale is not None:
70 | assert(scale.shape[0] == 1)
71 | assert(outputs.shape[1] == scale.shape[1])
72 | outputs = outputs / scale.repeat(outputs.shape[0], 1).type(torch.FloatTensor).to(device)
73 | _, predicted = outputs.max(1)
74 | correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item()
75 |
76 | if is_start_iteration:
77 | outputs_feature = np.squeeze(tg_feature_model(inputs))
78 | sqd_icarl = cdist(class_means[:,:,0].T, outputs_feature.cpu(), 'sqeuclidean')
79 | score_icarl = torch.from_numpy((-sqd_icarl).T).to(device)
80 | _, predicted_icarl = score_icarl.max(1)
81 | correct_icarl += predicted_icarl.eq(targets).sum().item()
82 | sqd_icarl_cosine = cdist(class_means[:,:,0].T, outputs_feature.cpu(), 'cosine')
83 | score_icarl_cosine = torch.from_numpy((-sqd_icarl_cosine).T).to(device)
84 | _, predicted_icarl_cosine = score_icarl_cosine.max(1)
85 | correct_icarl_cosine += predicted_icarl_cosine.eq(targets).sum().item()
86 | fast_weights = torch.from_numpy(np.float32(class_means[:,:,0].T)).to(device)
87 | sqd_icarl_cosine2 = F.linear(F.normalize(torch.squeeze(outputs_feature), p=2,dim=1), F.normalize(fast_weights, p=2, dim=1))
88 | score_icarl_cosine2 = sqd_icarl_cosine2
89 | _, predicted_icarl_cosine2 = score_icarl_cosine2.max(1)
90 | correct_icarl_cosine2 += predicted_icarl_cosine2.eq(targets).sum().item()
91 | sqd_ncm = cdist(class_means[:,:,1].T, outputs_feature.cpu(), 'sqeuclidean')
92 | score_ncm = torch.from_numpy((-sqd_ncm).T).to(device)
93 | _, predicted_ncm = score_ncm.max(1)
94 | correct_ncm += predicted_ncm.eq(targets).sum().item()
95 | if print_info:
96 | print(" Current accuracy (FC) :\t\t{:.2f} %".format(100.*correct/total))
97 | print(" Current accuracy (Proto) :\t\t{:.2f} %".format(100.*correct_icarl/total))
98 | print(" Current accuracy (Proto-UB) :\t\t{:.2f} %".format(100.*correct_ncm/total))
99 | cnn_acc = 100.*correct/total
100 | icarl_acc = 100.*correct_icarl/total
101 | ncm_acc = 100.*correct_ncm/total
102 | return [cnn_acc, icarl_acc, ncm_acc], fast_fc
103 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/utils/incremental/compute_features.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Created by: Yaoyao Liu
3 | ## Modified from: https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning
4 | ## Max Planck Institute for Informatics
5 | ## yaoyao.liu@mpi-inf.mpg.de
6 | ## Copyright (c) 2021
7 | ##
8 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
9 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
10 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
11 | """ The functions that compute the features """
12 | import torch
13 | import torch.nn as nn
14 | import torch.nn.functional as F
15 | import torch.optim as optim
16 | from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
17 | import torchvision
18 | from torchvision import datasets, models, transforms
19 | from torch.autograd import Variable
20 | import numpy as np
21 | import time
22 | import os
23 | import copy
24 | import argparse
25 | from PIL import Image
26 | from scipy.spatial.distance import cdist
27 | from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
28 | from utils.misc import *
29 | from utils.process_fp import process_inputs_fp
30 |
31 | def compute_features(the_args, fusion_vars, tg_model, free_model, tg_feature_model, \
32 | is_start_iteration, evalloader, num_samples, num_features, device=None):
33 | if device is None:
34 | device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
35 | tg_feature_model.eval()
36 | tg_model.eval()
37 | if free_model is not None:
38 | free_model.eval()
39 |
40 | features = np.zeros([num_samples, num_features])
41 | start_idx = 0
42 | with torch.no_grad():
43 | for inputs, targets in evalloader:
44 | inputs = inputs.to(device)
45 | if is_start_iteration:
46 | the_feature = tg_feature_model(inputs)
47 | else:
48 | the_feature = process_inputs_fp(the_args, fusion_vars, tg_model, free_model, inputs, feature_mode=True)
49 | features[start_idx:start_idx+inputs.shape[0], :] = np.squeeze(the_feature.cpu())
50 | start_idx = start_idx+inputs.shape[0]
51 | assert(start_idx==num_samples)
52 | return features
53 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/utils/incremental/conv2d_mtl.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Created by: Yaoyao Liu
3 | ## Modified from: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch
4 | ## Max Planck Institute for Informatics
5 | ## yaoyao.liu@mpi-inf.mpg.de
6 | ## Copyright (c) 2021
7 | ##
8 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
9 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
10 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
11 | """ SS CONV layers.
12 | This file contains the source code for the scaling and shifting weights.
13 | If this architecture is applied, the convolution weights will be frozen, and only the channel-wise masks will be updated.
14 | """
15 | import math
16 | import torch
17 | from torch.nn.parameter import Parameter
18 | import torch.nn.functional as F
19 | from torch.nn.modules.module import Module
20 | from torch.nn.modules.utils import _single, _pair, _triple
21 |
22 | class _ConvNdMtl(Module):
23 |
24 | def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride,
25 | padding, dilation, transposed, output_padding, groups, bias):
26 | super(_ConvNdMtl, self).__init__()
27 | if in_channels % groups != 0:
28 | raise ValueError('in_channels must be divisible by groups')
29 | if out_channels % groups != 0:
30 | raise ValueError('out_channels must be divisible by groups')
31 | self.in_channels = in_channels
32 | self.out_channels = out_channels
33 | self.kernel_size = kernel_size
34 | self.stride = stride
35 | self.padding = padding
36 | self.dilation = dilation
37 | self.transposed = transposed
38 | self.output_padding = output_padding
39 | self.groups = groups
40 | if transposed:
41 | self.weight = Parameter(torch.Tensor(
42 | in_channels, out_channels // groups, *kernel_size))
43 | self.mtl_weight = Parameter(torch.ones(in_channels, out_channels // groups, 1, 1))
44 | else:
45 | self.weight = Parameter(torch.Tensor(
46 | out_channels, in_channels // groups, *kernel_size))
47 | self.mtl_weight = Parameter(torch.ones(out_channels, in_channels // groups, 1, 1))
48 | self.weight.requires_grad=False
49 | if bias:
50 | self.bias = Parameter(torch.Tensor(out_channels))
51 | self.bias.requires_grad=False
52 | self.mtl_bias = Parameter(torch.zeros(out_channels))
53 | else:
54 | self.register_parameter('bias', None)
55 | self.register_parameter('mtl_bias', None)
56 | self.reset_parameters()
57 |
58 | def reset_parameters(self):
59 | n = self.in_channels
60 | for k in self.kernel_size:
61 | n *= k
62 | stdv = 1. / math.sqrt(n)
63 | self.weight.data.uniform_(-stdv, stdv)
64 | self.mtl_weight.data.uniform_(1, 1)
65 | if self.bias is not None:
66 | self.bias.data.uniform_(-stdv, stdv)
67 | self.mtl_bias.data.uniform_(0, 0)
68 |
69 | def extra_repr(self):
70 | s = ('{in_channels}, {out_channels}, kernel_size={kernel_size}'
71 | ', stride={stride}')
72 | if self.padding != (0,) * len(self.padding):
73 | s += ', padding={padding}'
74 | if self.dilation != (1,) * len(self.dilation):
75 | s += ', dilation={dilation}'
76 | if self.output_padding != (0,) * len(self.output_padding):
77 | s += ', output_padding={output_padding}'
78 | if self.groups != 1:
79 | s += ', groups={groups}'
80 | if self.bias is None:
81 | s += ', bias=False'
82 | return s.format(**self.__dict__)
83 |
84 | class Conv2dMtl(_ConvNdMtl):
85 |
86 | def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1,
87 | padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True):
88 | kernel_size = _pair(kernel_size)
89 | stride = _pair(stride)
90 | padding = _pair(padding)
91 | dilation = _pair(dilation)
92 | super(Conv2dMtl, self).__init__(
93 | in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation,
94 | False, _pair(0), groups, bias)
95 |
96 | def forward(self, input):
97 | new_mtl_weight = self.mtl_weight.expand(self.weight.shape)
98 | new_weight = self.weight.mul(new_mtl_weight)
99 | if self.bias is not None:
100 | new_bias = self.bias + self.mtl_bias
101 | else:
102 | new_bias = None
103 | return F.conv2d(input, new_weight, new_bias, self.stride,
104 | self.padding, self.dilation, self.groups)
105 |
106 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/utils/misc.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import print_function, division
2 |
3 | import torch
4 | import torch.nn as nn
5 | import torch.nn.init as init
6 | from collections import OrderedDict
7 | import torch.optim as optim
8 | import torchvision
9 | import argparse
10 | import numpy as np
11 | import os
12 | import os.path as osp
13 | import sys
14 | import time
15 | import math
16 | import subprocess
17 | try:
18 | import cPickle as pickle
19 | except:
20 | import pickle
21 |
22 | def savepickle(data, file_path):
23 | mkdir_p(osp.dirname(file_path), delete=False)
24 | print('pickle into', file_path)
25 | with open(file_path, 'wb') as f:
26 | pickle.dump(data, f, pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)
27 |
28 | def unpickle(file_path):
29 | with open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
30 | data = pickle.load(f)
31 | return data
32 |
33 | def mkdir_p(path, delete=False, print_info=True):
34 | if path == '': return
35 |
36 | if delete:
37 | subprocess.call(('rm -r ' + path).split())
38 | if not osp.exists(path):
39 | if print_info:
40 | print('mkdir -p ' + path)
41 | subprocess.call(('mkdir -p ' + path).split())
42 |
43 | def get_mean_and_std(dataset):
44 | '''Compute the mean and std value of dataset.'''
45 | dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=1, shuffle=True, num_workers=2)
46 | mean = torch.zeros(3)
47 | std = torch.zeros(3)
48 | print('==> Computing mean and std..')
49 | for inputs, targets in dataloader:
50 | for i in range(3):
51 | mean[i] += inputs[:,i,:,:].mean()
52 | std[i] += inputs[:,i,:,:].std()
53 | mean.div_(len(dataset))
54 | std.div_(len(dataset))
55 | return mean, std
56 |
57 | def init_params(net):
58 | '''Init layer parameters.'''
59 | for m in net.modules():
60 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
61 | init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out')
62 | if m.bias:
63 | init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
64 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
65 | init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
66 | init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
67 | elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
68 | init.normal_(m.weight, std=1e-3)
69 | if m.bias is not None:
70 | init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
71 |
72 | def map_labels(order_list, Y_set):
73 | map_Y = []
74 | for idx in Y_set:
75 | map_Y.append(order_list.index(idx))
76 | map_Y = np.array(map_Y)
77 | return map_Y
78 |
79 | def format_time(seconds):
80 | days = int(seconds / 3600/24)
81 | seconds = seconds - days*3600*24
82 | hours = int(seconds / 3600)
83 | seconds = seconds - hours*3600
84 | minutes = int(seconds / 60)
85 | seconds = seconds - minutes*60
86 | secondsf = int(seconds)
87 | seconds = seconds - secondsf
88 | millis = int(seconds*1000)
89 |
90 | f = ''
91 | i = 1
92 | if days > 0:
93 | f += str(days) + 'D'
94 | i += 1
95 | if hours > 0 and i <= 2:
96 | f += str(hours) + 'h'
97 | i += 1
98 | if minutes > 0 and i <= 2:
99 | f += str(minutes) + 'm'
100 | i += 1
101 | if secondsf > 0 and i <= 2:
102 | f += str(secondsf) + 's'
103 | i += 1
104 | if millis > 0 and i <= 2:
105 | f += str(millis) + 'ms'
106 | i += 1
107 | if f == '':
108 | f = '0ms'
109 | return f
110 |
111 | def tensor2im(input_image, imtype=np.uint8):
112 | mean = [0.5071, 0.4866, 0.4409]
113 | std = [0.2009, 0.1984, 0.2023]
114 | if not isinstance(input_image, np.ndarray):
115 | if isinstance(input_image, torch.Tensor):
116 | image_tensor = input_image.data
117 | else:
118 | return input_image
119 | image_numpy = image_tensor.cpu().detach().float().numpy()
120 | if image_numpy.shape[0] == 1:
121 | image_numpy = np.tile(image_numpy, (3, 1, 1))
122 | for i in range(len(mean)):
123 | image_numpy[i] = image_numpy[i] * std[i] + mean[i]
124 | image_numpy = image_numpy * 255
125 | image_numpy = np.transpose(image_numpy, (1, 2, 0))
126 | else:
127 | image_numpy = input_image
128 | return image_numpy.astype(imtype)
129 |
130 | def process_mnemonics(X_protoset_cumuls, Y_protoset_cumuls, mnemonics, mnemonics_label, order_list):
131 | mnemonics_array_new = np.zeros(np.array(X_protoset_cumuls).shape)
132 | mnemonics_list = []
133 | mnemonics_label_list = []
134 | for idx in range(len(mnemonics)):
135 | this_mnemonics = []
136 | for sub_idx in range(len(mnemonics[idx])):
137 | processed_img = tensor2im(mnemonics[idx][sub_idx])
138 | mnemonics_array_new[idx][sub_idx] = processed_img
139 |
140 | diff = len(X_protoset_cumuls) - len(mnemonics_array_new)
141 | for idx in range(len(mnemonics_array_new)):
142 | X_protoset_cumuls[idx+diff] = mnemonics_array_new[idx]
143 |
144 | return X_protoset_cumuls
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/adaptive-aggregation-networks/utils/process_fp.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Created by: Yaoyao Liu
3 | ## Max Planck Institute for Informatics
4 | ## yaoyao.liu@mpi-inf.mpg.de
5 | ## Copyright (c) 2021
6 | ##
7 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
8 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
9 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
10 | """ Using the aggregation weights to compute the feature maps from two branches """
11 | import torch
12 | import torch.nn as nn
13 | from utils.misc import *
14 |
15 | def process_inputs_fp(the_args, fusion_vars, b1_model, b2_model, inputs, feature_mode=False):
16 |
17 | # The 1st level
18 | if the_args.dataset == 'cifar100':
19 | b1_model_group1 = [b1_model.conv1, b1_model.bn1, b1_model.relu, b1_model.layer1]
20 | b2_model_group1 = [b2_model.conv1, b2_model.bn1, b2_model.relu, b2_model.layer1]
21 | elif the_args.dataset == 'imagenet_sub' or the_args.dataset == 'imagenet':
22 | b1_model_group1 = [b1_model.conv1, b1_model.bn1, b1_model.relu, b1_model.maxpool, b1_model.layer1]
23 | b2_model_group1 = [b2_model.conv1, b2_model.bn1, b2_model.relu, b2_model.maxpool, b2_model.layer1]
24 | else:
25 | raise ValueError('Please set correct dataset.')
26 | b1_model_group1 = nn.Sequential(*b1_model_group1)
27 | b1_fp1 = b1_model_group1(inputs)
28 | b2_model_group1 = nn.Sequential(*b2_model_group1)
29 | b2_fp1 = b2_model_group1(inputs)
30 | fp1 = fusion_vars[0]*b1_fp1+(1-fusion_vars[0])*b2_fp1
31 |
32 | # The 2nd level
33 | b1_model_group2 = b1_model.layer2
34 | b1_fp2 = b1_model_group2(fp1)
35 | b2_model_group2 = b2_model.layer2
36 | b2_fp2 = b2_model_group2(fp1)
37 | fp2 = fusion_vars[1]*b1_fp2+(1-fusion_vars[1])*b2_fp2
38 |
39 | # The 3rd level
40 | if the_args.dataset == 'cifar100':
41 | b1_model_group3 = [b1_model.layer3, b1_model.avgpool]
42 | b2_model_group3 = [b2_model.layer3, b2_model.avgpool]
43 | elif the_args.dataset == 'imagenet_sub' or the_args.dataset == 'imagenet':
44 | b1_model_group3 = b1_model.layer3
45 | b2_model_group3 = b2_model.layer3
46 | else:
47 | raise ValueError('Please set correct dataset.')
48 | b1_model_group3 = nn.Sequential(*b1_model_group3)
49 | b1_fp3 = b1_model_group3(fp2)
50 | b2_model_group3 = nn.Sequential(*b2_model_group3)
51 | b2_fp3 = b2_model_group3(fp2)
52 | fp3 = fusion_vars[2]*b1_fp3+(1-fusion_vars[2])*b2_fp3
53 |
54 | if the_args.dataset == 'cifar100':
55 | fp_final = fp3.view(fp3.size(0), -1)
56 | elif the_args.dataset == 'imagenet_sub' or the_args.dataset == 'imagenet':
57 | # The 4th level
58 | b1_model_group4 = [b1_model.layer4, b1_model.avgpool]
59 | b1_model_group4 = nn.Sequential(*b1_model_group4)
60 | b1_fp4 = b1_model_group4(fp3)
61 | b2_model_group4 = [b2_model.layer4, b2_model.avgpool]
62 | b2_model_group4 = nn.Sequential(*b2_model_group4)
63 | b2_fp4 = b2_model_group4(fp3)
64 | fp4 = fusion_vars[3]*b1_fp4+(1-fusion_vars[3])*b2_fp4
65 | fp_final = fp4.view(fp4.size(0), -1)
66 | else:
67 | raise ValueError('Please set correct dataset.')
68 | if feature_mode:
69 | return fp_final
70 | else:
71 | outputs = b1_model.fc(fp_final)
72 | return outputs, fp_final
73 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/1_train/main.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import argparse
3 | import numpy as np
4 | from trainer.mnemonics import Trainer as MnemonicsTrainer
5 | from trainer.baseline import Trainer as BaselineTrainer
6 |
7 | if __name__ == '__main__':
8 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
9 | parser.add_argument('--gpu', default='0')
10 | parser.add_argument('--method', default='mnemonics', type=str, choices=['mnemonics', 'baseline'])
11 | parser.add_argument('--dataset', default='cifar100', type=str, choices=['cifar100'])
12 | parser.add_argument('--data_dir', default='data/seed_1993_subset_100_imagenet/data', type=str)
13 | parser.add_argument('--num_classes', default=100, type=int)
14 | parser.add_argument('--nb_cl_fg', default=50, type=int)
15 | parser.add_argument('--nb_cl', default=10, type=int)
16 | parser.add_argument('--nb_protos', default=20, type=int)
17 | parser.add_argument('--nb_runs', default=1, type=int)
18 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', default=160, type=int)
19 | parser.add_argument('--T', default=2, type=float)
20 | parser.add_argument('--beta', default=0.25, type=float)
21 | parser.add_argument('--resume', action='store_true')
22 | parser.add_argument('--resume_fg', action='store_true')
23 | parser.add_argument('--ckpt_dir_fg', type=str, default='-')
24 | parser.add_argument('--dynamic_budget', action='store_true')
25 | parser.add_argument('--phase', type=str, default='train', choices=['train', 'eval'])
26 | parser.add_argument('--fusion_mode', default='free', type=str, choices=['std', 'free', 'mtl'])
27 | parser.add_argument('--ckpt_label', type=str, default='01')
28 | parser.add_argument('--num_workers', default=2, type=int)
29 | parser.add_argument('--load_iter', default=0, type=int)
30 | parser.add_argument('--dictionary_size', default=500, type=int)
31 | parser.add_argument('--mimic_score', action='store_true')
32 | parser.add_argument('--lw_ms', default=1, type=float)
33 | parser.add_argument('--rs_ratio', default=0, type=float)
34 | parser.add_argument('--less_forget', action='store_true')
35 | parser.add_argument('--lamda', default=5, type=float)
36 | parser.add_argument('--adapt_lamda', action='store_true')
37 | parser.add_argument('--dist', default=0.5, type=float)
38 | parser.add_argument('--K', default=2, type=int)
39 | parser.add_argument('--lw_mr', default=1, type=float)
40 | parser.add_argument('--random_seed', default=1993, type=int)
41 | parser.add_argument('--train_batch_size', default=128, type=int)
42 | parser.add_argument('--test_batch_size', default=100, type=int)
43 | parser.add_argument('--eval_batch_size', default=128, type=int)
44 | parser.add_argument('--base_lr1', default=0.1, type=float)
45 | parser.add_argument('--base_lr2', default=0.1, type=float)
46 | parser.add_argument('--lr_factor', default=0.1, type=float)
47 | parser.add_argument('--custom_weight_decay', default=5e-4, type=float)
48 | parser.add_argument('--custom_momentum', default=0.9, type=float)
49 | parser.add_argument('--load_ckpt_prefix', type=str, default='-')
50 | parser.add_argument('--load_order', type=str, default='-')
51 | parser.add_argument('--maml_lr', default=0.1, type=float)
52 | parser.add_argument('--maml_epoch', default=50, type=int)
53 | parser.add_argument('--mnemonics_images_per_class_per_step', default=1, type=int)
54 | parser.add_argument('--mnemonics_steps', default=20, type=int)
55 | parser.add_argument('--mnemonics_epochs', default=1, type=int)
56 | parser.add_argument('--mnemonics_lr', type=float, default=1e-5)
57 | parser.add_argument('--mnemonics_decay_factor', type=float, default=0.5)
58 | parser.add_argument('--mnemonics_outer_lr', type=float, default=1e-5)
59 | parser.add_argument('--mnemonics_total_epochs', type=int, default=1)
60 | parser.add_argument('--mnemonics_decay_epochs', type=int, default=1)
61 |
62 | the_args = parser.parse_args()
63 |
64 | assert(the_args.nb_cl_fg % the_args.nb_cl == 0)
65 | assert(the_args.nb_cl_fg >= the_args.nb_cl)
66 |
67 | print(the_args)
68 |
69 | os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = the_args.gpu
70 | print('Using gpu:', the_args.gpu)
71 |
72 | if the_args.method == 'mnemonics':
73 | trainer = MnemonicsTrainer(the_args)
74 | elif the_args.method == 'baseline':
75 | trainer = BaselineTrainer(the_args)
76 | else:
77 | raise ValueError('Please set the correct method.')
78 | trainer.train()
79 |
80 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/1_train/models/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yaoyao-liu/class-incremental-learning/701af9f819f559c6ab3d3ee73bb3d7c21e924572/mnemonics-training/1_train/models/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/1_train/models/modified_linear.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | import torch
3 | from torch.nn import Module
4 | from torch.nn.parameter import Parameter
5 | from torch.nn import functional as F
6 |
7 | class CosineLinear(Module):
8 | def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, sigma=True):
9 | super(CosineLinear, self).__init__()
10 | self.in_features = in_features
11 | self.out_features = out_features
12 | self.weight = Parameter(torch.Tensor(out_features, in_features))
13 | if sigma:
14 | self.sigma = Parameter(torch.Tensor(1))
15 | else:
16 | self.register_parameter('sigma', None)
17 | self.reset_parameters()
18 |
19 | def reset_parameters(self):
20 | stdv = 1. / math.sqrt(self.weight.size(1))
21 | self.weight.data.uniform_(-stdv, stdv)
22 | if self.sigma is not None:
23 | self.sigma.data.fill_(1)
24 |
25 | def forward(self, input):
26 | out = F.linear(F.normalize(input, p=2,dim=1), \
27 | F.normalize(self.weight, p=2, dim=1))
28 | if self.sigma is not None:
29 | out = self.sigma * out
30 | return out
31 |
32 | class SplitCosineLinear(Module):
33 | def __init__(self, in_features, out_features1, out_features2, sigma=True):
34 | super(SplitCosineLinear, self).__init__()
35 | self.in_features = in_features
36 | self.out_features = out_features1 + out_features2
37 | self.fc1 = CosineLinear(in_features, out_features1, False)
38 | self.fc2 = CosineLinear(in_features, out_features2, False)
39 | if sigma:
40 | self.sigma = Parameter(torch.Tensor(1))
41 | self.sigma.data.fill_(1)
42 | else:
43 | self.register_parameter('sigma', None)
44 |
45 | def forward(self, x):
46 | out1 = self.fc1(x)
47 | out2 = self.fc2(x)
48 | out = torch.cat((out1, out2), dim=1)
49 | if self.sigma is not None:
50 | out = self.sigma * out
51 | return out
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/1_train/models/modified_resnet_cifar.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
4 | import models.modified_linear as modified_linear
5 |
6 | def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
7 | return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
8 | padding=1, bias=False)
9 |
10 | class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
11 | expansion = 1
12 |
13 | def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, last=False):
14 | super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
15 | self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
16 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
17 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
18 | self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
19 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
20 | self.downsample = downsample
21 | self.stride = stride
22 | self.last = last
23 |
24 | def forward(self, x):
25 | residual = x
26 |
27 | out = self.conv1(x)
28 | out = self.bn1(out)
29 | out = self.relu(out)
30 |
31 | out = self.conv2(out)
32 | out = self.bn2(out)
33 |
34 | if self.downsample is not None:
35 | residual = self.downsample(x)
36 |
37 | out += residual
38 | if not self.last:
39 | out = self.relu(out)
40 |
41 | return out
42 |
43 | class ResNet(nn.Module):
44 |
45 | def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=10):
46 | self.inplanes = 16
47 | super(ResNet, self).__init__()
48 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1,
49 | bias=False)
50 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(16)
51 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
52 | self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 16, layers[0])
53 | self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 32, layers[1], stride=2)
54 | self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[2], stride=2, last_phase=True)
55 | self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(8, stride=1)
56 | self.fc = modified_linear.CosineLinear(64 * block.expansion, num_classes)
57 |
58 | for m in self.modules():
59 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
60 | nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
61 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
62 | nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
63 | nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
64 |
65 | def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, last_phase=False):
66 | downsample = None
67 | if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
68 | downsample = nn.Sequential(
69 | nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
70 | kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
71 | nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
72 | )
73 |
74 | layers = []
75 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
76 | self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
77 | if last_phase:
78 | for i in range(1, blocks-1):
79 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
80 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, last=True))
81 | else:
82 | for i in range(1, blocks):
83 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
84 |
85 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
86 |
87 | def forward(self, x):
88 | x = self.conv1(x)
89 | x = self.bn1(x)
90 | x = self.relu(x)
91 |
92 | x = self.layer1(x)
93 | x = self.layer2(x)
94 | x = self.layer3(x)
95 |
96 | x = self.avgpool(x)
97 | x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
98 | x = self.fc(x)
99 |
100 | return x
101 |
102 | def resnet32(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
103 | n = 5
104 | model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [n, n, n], **kwargs)
105 | return model
106 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/1_train/models/modified_resnetmtl_cifar.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
2 | ## Modified by: Yaoyao Liu
3 | ## Modified from: https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning
4 | ## MPI for Informatics
5 | ## yaoyao.liu@mpi-inf.mpg.de
6 | ## Copyright (c) 2020
7 | ##
8 | ## This source code is licensed under the MIT-style license found in the
9 | ## LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree
10 | ##+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
11 | """Modified ResNet wit transferring weights."""
12 | import math
13 | import torch.nn as nn
14 | import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
15 | import models.modified_linear as modified_linear
16 | from utils.conv2d_mtl import Conv2dMtl
17 |
18 | def conv3x3mtl(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
19 | return Conv2dMtl(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
20 | padding=1, bias=False)
21 |
22 | class BasicBlockMtl(nn.Module):
23 | expansion = 1
24 |
25 | def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, last=False):
26 | super(BasicBlockMtl, self).__init__()
27 | self.conv1 = conv3x3mtl(inplanes, planes, stride)
28 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
29 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
30 | self.conv2 = conv3x3mtl(planes, planes)
31 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
32 | self.downsample = downsample
33 | self.stride = stride
34 | self.last = last
35 |
36 | def forward(self, x):
37 | residual = x
38 |
39 | out = self.conv1(x)
40 | out = self.bn1(out)
41 | out = self.relu(out)
42 |
43 | out = self.conv2(out)
44 | out = self.bn2(out)
45 |
46 | if self.downsample is not None:
47 | residual = self.downsample(x)
48 |
49 | out += residual
50 | if not self.last:
51 | out = self.relu(out)
52 |
53 | return out
54 |
55 | class ResNetMtl(nn.Module):
56 |
57 | def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=10):
58 | self.inplanes = 16
59 | super(ResNetMtl, self).__init__()
60 | self.conv1 = Conv2dMtl(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1,
61 | bias=False)
62 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(16)
63 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
64 | self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 16, layers[0])
65 | self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 32, layers[1], stride=2)
66 | self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[2], stride=2, last_phase=True)
67 | self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(8, stride=1)
68 | self.fc = modified_linear.CosineLinear(64 * block.expansion, num_classes)
69 |
70 | for m in self.modules():
71 | if isinstance(m, Conv2dMtl):
72 | nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
73 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
74 | nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
75 | nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
76 |
77 | def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, last_phase=False):
78 | downsample = None
79 | if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
80 | downsample = nn.Sequential(
81 | Conv2dMtl(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
82 | kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
83 | nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
84 | )
85 |
86 | layers = []
87 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
88 | self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
89 | if last_phase:
90 | for i in range(1, blocks-1):
91 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
92 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, last=True))
93 | else:
94 | for i in range(1, blocks):
95 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
96 |
97 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
98 |
99 | def forward(self, x):
100 | x = self.conv1(x)
101 | x = self.bn1(x)
102 | x = self.relu(x)
103 |
104 | x = self.layer1(x)
105 | x = self.layer2(x)
106 | x = self.layer3(x)
107 |
108 | x = self.avgpool(x)
109 | x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
110 | x = self.fc(x)
111 |
112 | return x
113 |
114 | def resnetmtl32(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
115 | n = 5
116 | model = ResNetMtl(BasicBlockMtl, [n, n, n], **kwargs)
117 | return model
118 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/1_train/trainer/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yaoyao-liu/class-incremental-learning/701af9f819f559c6ab3d3ee73bb3d7c21e924572/mnemonics-training/1_train/trainer/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/1_train/trainer/incremental.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import tqdm
3 | import torch.nn as nn
4 | from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
5 | from torchvision import datasets, models, transforms
6 | from utils.misc import *
7 | from utils.process_fp import process_inputs_fp
8 | import torch.nn.functional as F
9 |
10 | def incremental_train_and_eval(epochs, tg_model, ref_model, free_model, ref_free_model, tg_optimizer, tg_lr_scheduler, trainloader, testloader, iteration, start_iteration, lamda, dist, K, lw_mr, fix_bn=False, weight_per_class=None, device=None):
11 | if device is None:
12 | device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
13 | T = 2.0
14 | beta = 0.25
15 | if iteration > start_iteration:
16 | ref_model.eval()
17 | num_old_classes = ref_model.fc.out_features
18 | for epoch in range(epochs):
19 | tg_model.train()
20 | if fix_bn:
21 | for m in tg_model.modules():
22 | if isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
23 | m.eval()
24 | train_loss = 0
25 | train_loss1 = 0
26 | train_loss2 = 0
27 | correct = 0
28 | total = 0
29 | tg_lr_scheduler.step()
30 | print('\nEpoch: %d, LR: ' % epoch, end='')
31 | print(tg_lr_scheduler.get_lr())
32 | for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(trainloader):
33 | inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)
34 | tg_optimizer.zero_grad()
35 | outputs = tg_model(inputs)
36 | if iteration == start_iteration:
37 | loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight_per_class)(outputs, targets)
38 | else:
39 | ref_outputs = ref_model(inputs)
40 | loss1 = nn.KLDivLoss()(F.log_softmax(outputs[:,:num_old_classes]/T, dim=1), \
41 | F.softmax(ref_outputs.detach()/T, dim=1)) * T * T * beta * num_old_classes
42 | loss2 = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight_per_class)(outputs, targets)
43 | loss = loss1 + loss2
44 | loss.backward()
45 | tg_optimizer.step()
46 |
47 | train_loss += loss.item()
48 | if iteration > start_iteration:
49 | train_loss1 += loss1.item()
50 | train_loss2 += loss2.item()
51 | _, predicted = outputs.max(1)
52 | total += targets.size(0)
53 | correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item()
54 | if iteration == start_iteration:
55 | print('Train set: {}, Train Loss: {:.4f} Acc: {:.4f}'.format(\
56 | len(trainloader), train_loss/(batch_idx+1), 100.*correct/total))
57 | else:
58 | print('Train set: {}, Train Loss1: {:.4f}, Train Loss2: {:.4f},\
59 | Train Loss: {:.4f} Acc: {:.4f}'.format(len(trainloader), \
60 | train_loss1/(batch_idx+1), train_loss2/(batch_idx+1),
61 | train_loss/(batch_idx+1), 100.*correct/total))
62 | tg_model.eval()
63 | test_loss = 0
64 | correct = 0
65 | total = 0
66 | with torch.no_grad():
67 | for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(testloader):
68 | inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)
69 | outputs = tg_model(inputs)
70 | loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight_per_class)(outputs, targets)
71 |
72 | test_loss += loss.item()
73 | _, predicted = outputs.max(1)
74 | total += targets.size(0)
75 | correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item()
76 | print('Test set: {} Test Loss: {:.4f} Acc: {:.4f}'.format(\
77 | len(testloader), test_loss/(batch_idx+1), 100.*correct/total))
78 | return tg_model
79 |
80 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/1_train/utils/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yaoyao-liu/class-incremental-learning/701af9f819f559c6ab3d3ee73bb3d7c21e924572/mnemonics-training/1_train/utils/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/1_train/utils/compute_accuracy.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torchvision
3 | import numpy as np
4 | import torch.nn.functional as F
5 | from torchvision import datasets, models, transforms
6 | from scipy.spatial.distance import cdist
7 | from utils.misc import *
8 | from utils.process_fp import process_inputs_fp
9 |
10 | def map_labels(order_list, Y_set):
11 | map_Y = []
12 | for idx in Y_set:
13 | map_Y.append(order_list.index(idx))
14 | map_Y = np.array(map_Y)
15 | return map_Y
16 |
17 | def compute_accuracy(tg_model, free_model, tg_feature_model, class_means, X_protoset_cumuls, Y_protoset_cumuls, evalloader, order_list, is_start_iteration=False, fast_fc=None, scale=None, print_info=True, device=None, maml_lr=0.1, maml_epoch=50):
18 | if device is None:
19 | device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
20 | tg_feature_model.eval()
21 | tg_model.eval()
22 | if free_model is not None:
23 | free_model.eval()
24 | if fast_fc is None:
25 | transform_proto = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(),transforms.Normalize((0.5071, 0.4866, 0.4409), (0.2009, 0.1984, 0.2023)),])
26 | protoset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR100(root='./data', train=False, download=False, transform=transform_proto)
27 | X_protoset_array = np.array(X_protoset_cumuls).astype('uint8')
28 | protoset.test_data = X_protoset_array.reshape(-1, X_protoset_array.shape[2], X_protoset_array.shape[3], X_protoset_array.shape[4])
29 | Y_protoset_cumuls = np.array(Y_protoset_cumuls).reshape(-1)
30 | map_Y_protoset_cumuls = map_labels(order_list, Y_protoset_cumuls)
31 | protoset.test_labels = map_Y_protoset_cumuls
32 | protoloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(protoset, batch_size=128, shuffle=True, num_workers=2)
33 |
34 | fast_fc = torch.from_numpy(np.float32(class_means[:,:,0].T)).to(device)
35 | fast_fc.requires_grad=True
36 |
37 | epoch_num = maml_epoch
38 | for epoch_idx in range(epoch_num):
39 | for the_inputs, the_targets in protoloader:
40 | the_inputs, the_targets = the_inputs.to(device), the_targets.to(device)
41 | the_features = tg_feature_model(the_inputs)
42 | the_logits = F.linear(F.normalize(torch.squeeze(the_features), p=2,dim=1), F.normalize(fast_fc, p=2, dim=1))
43 | the_loss = F.cross_entropy(the_logits, the_targets)
44 | the_grad = torch.autograd.grad(the_loss, fast_fc)
45 | fast_fc = fast_fc - maml_lr * the_grad[0]
46 | correct = 0
47 | correct_icarl = 0
48 | correct_ncm = 0
49 | correct_maml = 0
50 | total = 0
51 | with torch.no_grad():
52 | for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(evalloader):
53 | inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)
54 | total += targets.size(0)
55 | if is_start_iteration:
56 | outputs = tg_model(inputs)
57 | else:
58 | outputs, outputs_feature = process_inputs_fp(tg_model, free_model, inputs)
59 | outputs = F.softmax(outputs, dim=1)
60 | if scale is not None:
61 | assert(scale.shape[0] == 1)
62 | assert(outputs.shape[1] == scale.shape[1])
63 | outputs = outputs / scale.repeat(outputs.shape[0], 1).type(torch.FloatTensor).to(device)
64 | _, predicted = outputs.max(1)
65 | correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item()
66 |
67 | if is_start_iteration:
68 | outputs_feature = np.squeeze(tg_feature_model(inputs))
69 | sqd_icarl = cdist(class_means[:,:,0].T, outputs_feature, 'sqeuclidean')
70 | score_icarl = torch.from_numpy((-sqd_icarl).T).to(device)
71 | _, predicted_icarl = score_icarl.max(1)
72 | correct_icarl += predicted_icarl.eq(targets).sum().item()
73 | sqd_ncm = cdist(class_means[:,:,1].T, outputs_feature, 'sqeuclidean')
74 | score_ncm = torch.from_numpy((-sqd_ncm).T).to(device)
75 | _, predicted_ncm = score_ncm.max(1)
76 | correct_ncm += predicted_ncm.eq(targets).sum().item()
77 | the_logits = F.linear(F.normalize(torch.squeeze(outputs_feature), p=2,dim=1), F.normalize(fast_fc, p=2, dim=1))
78 | _, predicted_maml = the_logits.max(1)
79 | correct_maml += predicted_maml.eq(targets).sum().item()
80 | cnn_acc = 100.*correct/total
81 | icarl_acc = 100.*correct_icarl/total
82 | ncm_acc = 100.*correct_ncm/total
83 | maml_acc = 100.*correct_maml/total
84 | if print_info:
85 | print(" Accuracy for LwF :\t\t{:.2f} %".format(cnn_acc))
86 | print(" Accuracy for iCaRL :\t\t{:.2f} %".format(icarl_acc))
87 | print(" The above results are the accuracy for the current phase.")
88 | print(" For the average accuracy, you need to record the results for all phases and calculate the average value.")
89 | return [cnn_acc, icarl_acc, ncm_acc, maml_acc], fast_fc
90 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/1_train/utils/compute_features.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import numpy as np
3 | from torchvision import models
4 | from utils.misc import *
5 | from utils.process_fp import process_inputs_fp
6 |
7 | def compute_features(tg_model, free_model, tg_feature_model, is_start_iteration, evalloader, num_samples, num_features, device=None):
8 | if device is None:
9 | device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
10 | tg_feature_model.eval()
11 | tg_model.eval()
12 | if free_model is not None:
13 | free_model.eval()
14 | features = np.zeros([num_samples, num_features])
15 | start_idx = 0
16 | with torch.no_grad():
17 | for inputs, targets in evalloader:
18 | inputs = inputs.to(device)
19 | if is_start_iteration:
20 | the_feature = tg_feature_model(inputs)
21 | else:
22 | the_feature = process_inputs_fp(tg_model, free_model, inputs, feature_mode=True)
23 | features[start_idx:start_idx+inputs.shape[0], :] = np.squeeze(the_feature)
24 | start_idx = start_idx+inputs.shape[0]
25 | assert(start_idx==num_samples)
26 | return features
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/1_train/utils/conv2d_mtl.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | import torch
3 | from torch.nn.parameter import Parameter
4 | import torch.nn.functional as F
5 | from torch.nn.modules.module import Module
6 | from torch.nn.modules.utils import _single, _pair, _triple
7 |
8 | class _ConvNdMtl(Module):
9 |
10 | def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride,
11 | padding, dilation, transposed, output_padding, groups, bias):
12 | super(_ConvNdMtl, self).__init__()
13 | if in_channels % groups != 0:
14 | raise ValueError('in_channels must be divisible by groups')
15 | if out_channels % groups != 0:
16 | raise ValueError('out_channels must be divisible by groups')
17 | self.in_channels = in_channels
18 | self.out_channels = out_channels
19 | self.kernel_size = kernel_size
20 | self.stride = stride
21 | self.padding = padding
22 | self.dilation = dilation
23 | self.transposed = transposed
24 | self.output_padding = output_padding
25 | self.groups = groups
26 | if transposed:
27 | self.weight = Parameter(torch.Tensor(
28 | in_channels, out_channels // groups, *kernel_size))
29 | self.mtl_weight = Parameter(torch.ones(in_channels, out_channels // groups, 1, 1))
30 | else:
31 | self.weight = Parameter(torch.Tensor(
32 | out_channels, in_channels // groups, *kernel_size))
33 | self.mtl_weight = Parameter(torch.ones(out_channels, in_channels // groups, 1, 1))
34 | self.weight.requires_grad=False
35 | if bias:
36 | self.bias = Parameter(torch.Tensor(out_channels))
37 | self.bias.requires_grad=False
38 | self.mtl_bias = Parameter(torch.zeros(out_channels))
39 | else:
40 | self.register_parameter('bias', None)
41 | self.register_parameter('mtl_bias', None)
42 | self.reset_parameters()
43 |
44 | def reset_parameters(self):
45 | n = self.in_channels
46 | for k in self.kernel_size:
47 | n *= k
48 | stdv = 1. / math.sqrt(n)
49 | self.weight.data.uniform_(-stdv, stdv)
50 | self.mtl_weight.data.uniform_(1, 1)
51 | if self.bias is not None:
52 | self.bias.data.uniform_(-stdv, stdv)
53 | self.mtl_bias.data.uniform_(0, 0)
54 |
55 | def extra_repr(self):
56 | s = ('{in_channels}, {out_channels}, kernel_size={kernel_size}'
57 | ', stride={stride}')
58 | if self.padding != (0,) * len(self.padding):
59 | s += ', padding={padding}'
60 | if self.dilation != (1,) * len(self.dilation):
61 | s += ', dilation={dilation}'
62 | if self.output_padding != (0,) * len(self.output_padding):
63 | s += ', output_padding={output_padding}'
64 | if self.groups != 1:
65 | s += ', groups={groups}'
66 | if self.bias is None:
67 | s += ', bias=False'
68 | return s.format(**self.__dict__)
69 |
70 | class Conv2dMtl(_ConvNdMtl):
71 |
72 | def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1,
73 | padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True):
74 | kernel_size = _pair(kernel_size)
75 | stride = _pair(stride)
76 | padding = _pair(padding)
77 | dilation = _pair(dilation)
78 | super(Conv2dMtl, self).__init__(
79 | in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation,
80 | False, _pair(0), groups, bias)
81 |
82 | def forward(self, input):
83 | new_mtl_weight = self.mtl_weight.expand(self.weight.shape)
84 | new_weight = self.weight.mul(new_mtl_weight)
85 | if self.bias is not None:
86 | new_bias = self.bias + self.mtl_bias
87 | else:
88 | new_bias = None
89 | return F.conv2d(input, new_weight, new_bias, self.stride,
90 | self.padding, self.dilation, self.groups)
91 |
92 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/1_train/utils/gpu_tools.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import torch
3 | import time
4 |
5 | def check_memory(cuda_device):
6 | devices_info = os.popen('"/usr/bin/nvidia-smi" --query-gpu=memory.total,memory.used --format=csv,nounits,noheader').read().strip().split("\n")
7 | total, used = devices_info[int(cuda_device)].split(',')
8 | return total, used
9 |
10 | def occupy_memory(cuda_device):
11 | total, used = check_memory(cuda_device)
12 | total = int(total)
13 | used = int(used)
14 | max_mem = int(total * 0.90)
15 | print('Total memory: ' + str(total) + ', used memory: ' + str(used))
16 | block_mem = max_mem - used
17 | if block_mem > 0:
18 | x = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(256, 1024, block_mem)
19 | del x
20 |
21 | def set_gpu(cuda_device):
22 | os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = cuda_device
23 | print('Using gpu:', cuda_device)
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/1_train/utils/misc.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import print_function, division
2 | import os
3 | import torch
4 | import sys
5 | import time
6 | import subprocess
7 | import torch.nn as nn
8 | import torch.nn.init as init
9 | import os.path as osp
10 | try:
11 | import cPickle as pickle
12 | except:
13 | import pickle
14 |
15 | def savepickle(data, file_path):
16 | mkdir_p(osp.dirname(file_path), delete=False)
17 | print('pickle into', file_path)
18 | with open(file_path, 'wb') as f:
19 | pickle.dump(data, f, pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)
20 |
21 | def unpickle(file_path):
22 | with open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
23 | data = pickle.load(f)
24 | return data
25 |
26 | def mkdir_p(path, delete=False, print_info=True):
27 | if path == '': return
28 |
29 | if delete:
30 | subprocess.call(('rm -r ' + path).split())
31 | if not osp.exists(path):
32 | if print_info:
33 | print('mkdir -p ' + path)
34 | subprocess.call(('mkdir -p ' + path).split())
35 |
36 | def get_mean_and_std(dataset):
37 | dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=1, shuffle=True, num_workers=2)
38 | mean = torch.zeros(3)
39 | std = torch.zeros(3)
40 | print('==> Computing mean and std..')
41 | for inputs, targets in dataloader:
42 | for i in range(3):
43 | mean[i] += inputs[:,i,:,:].mean()
44 | std[i] += inputs[:,i,:,:].std()
45 | mean.div_(len(dataset))
46 | std.div_(len(dataset))
47 | return mean, std
48 |
49 | def init_params(net):
50 | '''Init layer parameters.'''
51 | for m in net.modules():
52 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
53 | init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out')
54 | if m.bias:
55 | init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
56 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
57 | init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
58 | init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
59 | elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
60 | init.normal_(m.weight, std=1e-3)
61 | if m.bias is not None:
62 | init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
63 |
64 | _, term_width = os.popen('stty size', 'r').read().split()
65 | term_width = int(term_width)
66 |
67 | TOTAL_BAR_LENGTH = 65.
68 | last_time = time.time()
69 | begin_time = last_time
70 | def progress_bar(current, total, msg=None):
71 | global last_time, begin_time
72 | if current == 0:
73 | begin_time = time.time() # Reset for new bar.
74 |
75 | cur_len = int(TOTAL_BAR_LENGTH*current/total)
76 | rest_len = int(TOTAL_BAR_LENGTH - cur_len) - 1
77 |
78 | sys.stdout.write(' [')
79 | for i in range(cur_len):
80 | sys.stdout.write('=')
81 | sys.stdout.write('>')
82 | for i in range(rest_len):
83 | sys.stdout.write('.')
84 | sys.stdout.write(']')
85 |
86 | cur_time = time.time()
87 | step_time = cur_time - last_time
88 | last_time = cur_time
89 | tot_time = cur_time - begin_time
90 |
91 | L = []
92 | L.append(' Step: %s' % format_time(step_time))
93 | L.append(' | Tot: %s' % format_time(tot_time))
94 | if msg:
95 | L.append(' | ' + msg)
96 |
97 | msg = ''.join(L)
98 | sys.stdout.write(msg)
99 | for i in range(term_width-int(TOTAL_BAR_LENGTH)-len(msg)-3):
100 | sys.stdout.write(' ')
101 |
102 | for i in range(term_width-int(TOTAL_BAR_LENGTH/2)+2):
103 | sys.stdout.write('\b')
104 | sys.stdout.write(' %d/%d ' % (current+1, total))
105 |
106 | if current < total-1:
107 | sys.stdout.write('\r')
108 | else:
109 | sys.stdout.write('\n')
110 | sys.stdout.flush()
111 |
112 | def format_time(seconds):
113 | days = int(seconds / 3600/24)
114 | seconds = seconds - days*3600*24
115 | hours = int(seconds / 3600)
116 | seconds = seconds - hours*3600
117 | minutes = int(seconds / 60)
118 | seconds = seconds - minutes*60
119 | secondsf = int(seconds)
120 | seconds = seconds - secondsf
121 | millis = int(seconds*1000)
122 |
123 | f = ''
124 | i = 1
125 | if days > 0:
126 | f += str(days) + 'D'
127 | i += 1
128 | if hours > 0 and i <= 2:
129 | f += str(hours) + 'h'
130 | i += 1
131 | if minutes > 0 and i <= 2:
132 | f += str(minutes) + 'm'
133 | i += 1
134 | if secondsf > 0 and i <= 2:
135 | f += str(secondsf) + 's'
136 | i += 1
137 | if millis > 0 and i <= 2:
138 | f += str(millis) + 'ms'
139 | i += 1
140 | if f == '':
141 | f = '0ms'
142 | return f
143 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/1_train/utils/process_fp.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | from utils.misc import *
4 |
5 | def process_inputs_fp(tg_model, free_model, inputs, fusion_mode=False, feature_mode=False):
6 | tg_model_group1 = [tg_model.conv1, tg_model.bn1, tg_model.relu, tg_model.layer1]
7 | tg_model_group1 = nn.Sequential(*tg_model_group1)
8 | tg_fp1 = tg_model_group1(inputs)
9 | fp1 = tg_fp1
10 | tg_model_group2 = tg_model.layer2
11 | tg_fp2 = tg_model_group2(fp1)
12 | fp2 = tg_fp2
13 | tg_model_group3 = [tg_model.layer3, tg_model.avgpool]
14 | tg_model_group3 = nn.Sequential(*tg_model_group3)
15 | tg_fp3 = tg_model_group3(fp2)
16 | fp3 = tg_fp3
17 | fp3 = fp3.view(fp3.size(0), -1)
18 | if feature_mode:
19 | return fp3
20 | else:
21 | outputs = tg_model.fc(fp3)
22 | feature = fp3
23 | return outputs, feature
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/1_train/utils/process_mnemonics.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.optim as optim
3 | import torchvision
4 | import time
5 | import os
6 | import argparse
7 | import numpy as np
8 |
9 | def tensor2im(input_image, imtype=np.uint8):
10 | mean = [0.5071, 0.4866, 0.4409]
11 | std = [0.2009, 0.1984, 0.2023]
12 | if not isinstance(input_image, np.ndarray):
13 | if isinstance(input_image, torch.Tensor):
14 | image_tensor = input_image.data
15 | else:
16 | return input_image
17 | image_numpy = image_tensor.cpu().detach().float().numpy()
18 | if image_numpy.shape[0] == 1:
19 | image_numpy = np.tile(image_numpy, (3, 1, 1))
20 | for i in range(len(mean)):
21 | image_numpy[i] = image_numpy[i] * std[i] + mean[i]
22 | image_numpy = image_numpy * 255
23 | image_numpy = np.transpose(image_numpy, (1, 2, 0))
24 | else:
25 | image_numpy = input_image
26 | return image_numpy.astype(imtype)
27 |
28 | def process_mnemonics(X_protoset_cumuls, Y_protoset_cumuls, mnemonics_raw, mnemonics_label, order_list, nb_cl_fg, nb_cl, iteration, start_iter):
29 | mnemonics = mnemonics_raw[0]
30 | mnemonics_array_new = np.zeros((len(mnemonics), len(mnemonics[0]), 32, 32, 3))
31 | mnemonics_list = []
32 | mnemonics_label_list = []
33 | for idx in range(len(mnemonics)):
34 | this_mnemonics = []
35 | for sub_idx in range(len(mnemonics[idx])):
36 | processed_img = tensor2im(mnemonics[idx][sub_idx])
37 | mnemonics_array_new[idx][sub_idx] = processed_img
38 | diff = len(X_protoset_cumuls) - len(mnemonics_array_new)
39 | for idx in range(len(mnemonics_array_new)):
40 | X_protoset_cumuls[idx+diff] = mnemonics_array_new[idx]
41 | return X_protoset_cumuls
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Evaluation on our models
2 |
3 | ### Clone this repository
4 | ```bash
5 | cd ~
6 | git clone git@github.com:yaoyao-liu/mnemonics-training.git
7 | ```
8 |
9 | ### Processing the datasets
10 |
11 | Process ImageNet-Sub and ImageNet:
12 | ```bash
13 | cd ~/mnemonics-training/eval/process_imagenet
14 | python generate_imagenet_subset.py
15 | python generate_imagenet.py
16 | ```
17 |
18 | ### Download models
19 |
20 | Download the models for CIFAR-100, ImageNet-Sub and ImageNet:
21 | ```bash
22 | cd ~/mnemonics-training/eval
23 | sh ./script/download_ckpt.sh
24 | ```
25 | You may also download the checkpoints on [Google Drive](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1sKO2BOssWgTFBNZbM50qDzgk6wqg4_l8/view).
26 |
27 | ### Running the evaluation
28 |
29 | Run evaluation code with our models:
30 | ```bash
31 | cd ~/mnemonics-training/eval
32 | sh run_eval.sh
33 | ```
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/main.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python
2 | # coding=utf-8
3 | import os
4 | import argparse
5 | import numpy as np
6 | from trainer.train import Trainer
7 | from utils.gpu_tools import occupy_memory
8 |
9 | if __name__ == '__main__':
10 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
11 | parser.add_argument('--gpu', default='0') # GPU id
12 | parser.add_argument('--dataset', default='cifar100', type=str, choices=['cifar100', 'imagenet_sub', 'imagenet'])
13 | parser.add_argument('--data_dir', default='data/seed_1993_subset_100_imagenet/data', type=str)
14 | parser.add_argument('--num_classes', default=100, type=int)
15 | parser.add_argument('--nb_cl_fg', default=50, type=int, help='the number of classes in first group')
16 | parser.add_argument('--nb_cl', default=10, type=int, help='Classes per group')
17 | parser.add_argument('--nb_protos', default=20, type=int, help='Number of prototypes per class at the end')
18 | parser.add_argument('--nb_runs', default=1, type=int, help='Number of runs (random ordering of classes at each run)')
19 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', default=160, type=int, help='Epochs')
20 | parser.add_argument('--T', default=2, type=float, help='Temporature for distialltion')
21 | parser.add_argument('--beta', default=0.25, type=float, help='Beta for distialltion')
22 | parser.add_argument('--resume', action='store_true', help='resume from checkpoint')
23 | parser.add_argument('--resume_fg', action='store_true', help='resume first group from checkpoint')
24 | parser.add_argument('--ckpt_dir_fg', type=str, default='-')
25 | parser.add_argument('--dynamic_budget', action='store_true', help='fix budget')
26 | parser.add_argument('--phase', type=str, default='train', choices=['train', 'eval'])
27 | parser.add_argument('--ckpt_label', type=str, default='exp01')
28 | parser.add_argument('--use_mtl', action='store_true', help='using mtl weights')
29 | parser.add_argument('--num_workers', default=2, type=int, help='the number of workers for loading data')
30 | parser.add_argument('--load_iter', default=0, type=int)
31 | parser.add_argument('--mimic_score', action='store_true', help='To mimic scores for cosine embedding')
32 | parser.add_argument('--lw_ms', default=1, type=float, help='loss weight for mimicking score')
33 | parser.add_argument('--rs_ratio', default=0, type=float, help='The ratio for resample')
34 | parser.add_argument('--imprint_weights', action='store_true', help='Imprint the weights for novel classes')
35 | parser.add_argument('--less_forget', action='store_true', help='Less forgetful')
36 | parser.add_argument('--lamda', default=5, type=float, help='Lamda for LF')
37 | parser.add_argument('--adapt_lamda', action='store_true', help='Adaptively change lamda')
38 | parser.add_argument('--dist', default=0.5, type=float, help='Dist for MarginRankingLoss')
39 | parser.add_argument('--K', default=2, type=int, help='K for MarginRankingLoss')
40 | parser.add_argument('--lw_mr', default=1, type=float, help='loss weight for margin ranking loss')
41 | parser.add_argument('--random_seed', default=1993, type=int, help='random seed')
42 | parser.add_argument('--train_batch_size', default=128, type=int)
43 | parser.add_argument('--test_batch_size', default=100, type=int)
44 | parser.add_argument('--eval_batch_size', default=128, type=int)
45 | parser.add_argument('--base_lr1', default=0.1, type=float)
46 | parser.add_argument('--base_lr2', default=0.1, type=float)
47 | parser.add_argument('--lr_factor', default=0.1, type=float)
48 | parser.add_argument('--custom_weight_decay', default=5e-4, type=float)
49 | parser.add_argument('--custom_momentum', default=0.9, type=float)
50 | parser.add_argument('--load_ckpt_prefix', type=str, default='-')
51 | parser.add_argument('--load_order', type=str, default='-')
52 | parser.add_argument('--add_str', default=None, type=str)
53 |
54 | the_args = parser.parse_args()
55 | assert(the_args.nb_cl_fg % the_args.nb_cl == 0)
56 | assert(the_args.nb_cl_fg >= the_args.nb_cl)
57 |
58 | print(the_args)
59 |
60 | np.random.seed(the_args.random_seed)
61 |
62 | if not os.path.exists('./logs/cifar100_nfg50_ncls2_nproto20_mtl_exp01'):
63 | print('Download checkpoints from Google Drive.')
64 | os.system('sh ./script/download_ckpt.sh')
65 |
66 | os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = the_args.gpu
67 | print('Using gpu:', the_args.gpu)
68 |
69 | occupy_memory(the_args.gpu)
70 | print('Occupy GPU memory in advance.')
71 |
72 | trainer = Trainer(the_args)
73 | trainer.eval()
74 |
75 |
76 |
77 |
78 |
79 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/models/modified_linear.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 |
3 | import torch
4 | from torch.nn.parameter import Parameter
5 | from torch.nn import functional as F
6 | from torch.nn import Module
7 |
8 | class CosineLinear(Module):
9 | def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, sigma=True):
10 | super(CosineLinear, self).__init__()
11 | self.in_features = in_features
12 | self.out_features = out_features
13 | self.weight = Parameter(torch.Tensor(out_features, in_features))
14 | if sigma:
15 | self.sigma = Parameter(torch.Tensor(1))
16 | else:
17 | self.register_parameter('sigma', None)
18 | self.reset_parameters()
19 |
20 | def reset_parameters(self):
21 | stdv = 1. / math.sqrt(self.weight.size(1))
22 | self.weight.data.uniform_(-stdv, stdv)
23 | if self.sigma is not None:
24 | self.sigma.data.fill_(1) #for initializaiton of sigma
25 |
26 | def forward(self, input):
27 | #w_norm = self.weight.data.norm(dim=1, keepdim=True)
28 | #w_norm = w_norm.expand_as(self.weight).add_(self.epsilon)
29 | #x_norm = input.data.norm(dim=1, keepdim=True)
30 | #x_norm = x_norm.expand_as(input).add_(self.epsilon)
31 | #w = self.weight.div(w_norm)
32 | #x = input.div(x_norm)
33 | out = F.linear(F.normalize(input, p=2,dim=1), \
34 | F.normalize(self.weight, p=2, dim=1))
35 | if self.sigma is not None:
36 | out = self.sigma * out
37 | return out
38 |
39 | class SplitCosineLinear(Module):
40 | #consists of two fc layers and concatenate their outputs
41 | def __init__(self, in_features, out_features1, out_features2, sigma=True):
42 | super(SplitCosineLinear, self).__init__()
43 | self.in_features = in_features
44 | self.out_features = out_features1 + out_features2
45 | self.fc1 = CosineLinear(in_features, out_features1, False)
46 | self.fc2 = CosineLinear(in_features, out_features2, False)
47 | if sigma:
48 | self.sigma = Parameter(torch.Tensor(1))
49 | self.sigma.data.fill_(1)
50 | else:
51 | self.register_parameter('sigma', None)
52 |
53 | def forward(self, x):
54 | out1 = self.fc1(x)
55 | out2 = self.fc2(x)
56 | out = torch.cat((out1, out2), dim=1) #concatenate along the channel
57 | if self.sigma is not None:
58 | out = self.sigma * out
59 | return out
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/models/modified_resnet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | import math
3 | import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
4 | import models.modified_linear as modified_linear
5 |
6 | def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
7 | """3x3 convolution with padding"""
8 | return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
9 | padding=1, bias=False)
10 |
11 |
12 | class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
13 | expansion = 1
14 |
15 | def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, last=False):
16 | super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
17 | self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
18 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
19 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
20 | self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
21 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
22 | self.downsample = downsample
23 | self.stride = stride
24 | self.last = last
25 |
26 | def forward(self, x):
27 | residual = x
28 |
29 | out = self.conv1(x)
30 | out = self.bn1(out)
31 | out = self.relu(out)
32 |
33 | out = self.conv2(out)
34 | out = self.bn2(out)
35 |
36 | if self.downsample is not None:
37 | residual = self.downsample(x)
38 |
39 | out += residual
40 | if not self.last: #remove ReLU in the last layer
41 | out = self.relu(out)
42 |
43 | return out
44 |
45 | class ResNet(nn.Module):
46 |
47 | def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=1000):
48 | self.inplanes = 64
49 | super(ResNet, self).__init__()
50 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3,
51 | bias=False)
52 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
53 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
54 | self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
55 | self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0])
56 | self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2)
57 | self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2)
58 | self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2, last_phase=True)
59 | self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(7, stride=1)
60 | self.fc = modified_linear.CosineLinear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
61 |
62 | for m in self.modules():
63 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
64 | nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
65 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
66 | nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
67 | nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
68 |
69 | def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, last_phase=False):
70 | downsample = None
71 | if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
72 | downsample = nn.Sequential(
73 | nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
74 | kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
75 | nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
76 | )
77 |
78 | layers = []
79 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
80 | self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
81 | if last_phase:
82 | for i in range(1, blocks-1):
83 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
84 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, last=True))
85 | else:
86 | for i in range(1, blocks):
87 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
88 |
89 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
90 |
91 | def forward(self, x):
92 | x = self.conv1(x)
93 | x = self.bn1(x)
94 | x = self.relu(x)
95 | x = self.maxpool(x)
96 |
97 | x = self.layer1(x)
98 | x = self.layer2(x)
99 | x = self.layer3(x)
100 | x = self.layer4(x)
101 |
102 | x = self.avgpool(x)
103 | x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
104 | x = self.fc(x)
105 |
106 | return x
107 |
108 |
109 | def resnet18(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
110 | """Constructs a ResNet-18 model.
111 |
112 | Args:
113 | pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
114 | """
115 | model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2], **kwargs)
116 | return model
117 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/models/modified_resnet_cifar.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #remove ReLU in the last layer, and use cosine layer to replace nn.Linear
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | import math
4 | import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
5 | import models.modified_linear as modified_linear
6 |
7 | def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
8 | """3x3 convolution with padding"""
9 | return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
10 | padding=1, bias=False)
11 |
12 | class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
13 | expansion = 1
14 |
15 | def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, last=False):
16 | super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
17 | self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
18 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
19 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
20 | self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
21 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
22 | self.downsample = downsample
23 | self.stride = stride
24 | self.last = last
25 |
26 | def forward(self, x):
27 | residual = x
28 |
29 | out = self.conv1(x)
30 | out = self.bn1(out)
31 | out = self.relu(out)
32 |
33 | out = self.conv2(out)
34 | out = self.bn2(out)
35 |
36 | if self.downsample is not None:
37 | residual = self.downsample(x)
38 |
39 | out += residual
40 | if not self.last: #remove ReLU in the last layer
41 | out = self.relu(out)
42 |
43 | return out
44 |
45 | class ResNet(nn.Module):
46 |
47 | def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=10):
48 | self.inplanes = 16
49 | super(ResNet, self).__init__()
50 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1,
51 | bias=False)
52 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(16)
53 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
54 | self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 16, layers[0])
55 | self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 32, layers[1], stride=2)
56 | self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[2], stride=2, last_phase=True)
57 | self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(8, stride=1)
58 | self.fc = modified_linear.CosineLinear(64 * block.expansion, num_classes)
59 |
60 | for m in self.modules():
61 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
62 | nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
63 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
64 | nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
65 | nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
66 |
67 | def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, last_phase=False):
68 | downsample = None
69 | if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
70 | downsample = nn.Sequential(
71 | nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
72 | kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
73 | nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
74 | )
75 |
76 | layers = []
77 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
78 | self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
79 | if last_phase:
80 | for i in range(1, blocks-1):
81 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
82 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, last=True))
83 | else:
84 | for i in range(1, blocks):
85 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
86 |
87 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
88 |
89 | def forward(self, x):
90 | x = self.conv1(x)
91 | x = self.bn1(x)
92 | x = self.relu(x)
93 |
94 | x = self.layer1(x)
95 | x = self.layer2(x)
96 | x = self.layer3(x)
97 |
98 | x = self.avgpool(x)
99 | x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
100 | x = self.fc(x)
101 |
102 | return x
103 |
104 | def resnet20(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
105 | n = 3
106 | model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [n, n, n], **kwargs)
107 | return model
108 |
109 | def resnet32(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
110 | n = 5
111 | model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [n, n, n], **kwargs)
112 | return model
113 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/models/modified_resnetmtl.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | import math
3 | import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
4 | import models.modified_linear as modified_linear
5 | from utils.incremental.conv2d_mtl import Conv2dMtl
6 |
7 | def conv3x3mtl(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
8 | """3x3 convolution with padding"""
9 | return Conv2dMtl(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
10 | padding=1, bias=False)
11 |
12 |
13 | class BasicBlockMtl(nn.Module):
14 | expansion = 1
15 |
16 | def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, last=False):
17 | super(BasicBlockMtl, self).__init__()
18 | self.conv1 = conv3x3mtl(inplanes, planes, stride)
19 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
20 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
21 | self.conv2 = conv3x3mtl(planes, planes)
22 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
23 | self.downsample = downsample
24 | self.stride = stride
25 | self.last = last
26 |
27 | def forward(self, x):
28 | residual = x
29 |
30 | out = self.conv1(x)
31 | out = self.bn1(out)
32 | out = self.relu(out)
33 |
34 | out = self.conv2(out)
35 | out = self.bn2(out)
36 |
37 | if self.downsample is not None:
38 | residual = self.downsample(x)
39 |
40 | out += residual
41 | if not self.last: #remove ReLU in the last layer
42 | out = self.relu(out)
43 |
44 | return out
45 |
46 | class ResNetMtl(nn.Module):
47 |
48 | def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=1000):
49 | self.inplanes = 64
50 | super(ResNetMtl, self).__init__()
51 | self.conv1 = Conv2dMtl(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3,
52 | bias=False)
53 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
54 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
55 | self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
56 | self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0])
57 | self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2)
58 | self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2)
59 | self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2, last_phase=True)
60 | self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(7, stride=1)
61 | self.fc = modified_linear.CosineLinear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
62 |
63 | for m in self.modules():
64 | if isinstance(m, Conv2dMtl):
65 | nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
66 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
67 | nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
68 | nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
69 |
70 | def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, last_phase=False):
71 | downsample = None
72 | if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
73 | downsample = nn.Sequential(
74 | Conv2dMtl(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
75 | kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
76 | nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
77 | )
78 |
79 | layers = []
80 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
81 | self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
82 | if last_phase:
83 | for i in range(1, blocks-1):
84 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
85 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, last=True))
86 | else:
87 | for i in range(1, blocks):
88 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
89 |
90 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
91 |
92 | def forward(self, x):
93 | x = self.conv1(x)
94 | x = self.bn1(x)
95 | x = self.relu(x)
96 | x = self.maxpool(x)
97 |
98 | x = self.layer1(x)
99 | x = self.layer2(x)
100 | x = self.layer3(x)
101 | x = self.layer4(x)
102 |
103 | x = self.avgpool(x)
104 | x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
105 | x = self.fc(x)
106 |
107 | return x
108 |
109 |
110 | def resnetmtl18(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
111 | """Constructs a ResNet-18 model.
112 |
113 | Args:
114 | pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
115 | """
116 | model = ResNetMtl(BasicBlockMtl, [2, 2, 2, 2], **kwargs)
117 | return model
118 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/models/modified_resnetmtl_cifar.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #remove ReLU in the last layer, and use cosine layer to replace nn.Linear
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | import math
4 | import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
5 | import models.modified_linear as modified_linear
6 | from utils.incremental.conv2d_mtl import Conv2dMtl
7 |
8 | def conv3x3mtl(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
9 | """3x3 convolution with padding"""
10 | return Conv2dMtl(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
11 | padding=1, bias=False)
12 |
13 | class BasicBlockMtl(nn.Module):
14 | expansion = 1
15 |
16 | def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, last=False):
17 | super(BasicBlockMtl, self).__init__()
18 | self.conv1 = conv3x3mtl(inplanes, planes, stride)
19 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
20 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
21 | self.conv2 = conv3x3mtl(planes, planes)
22 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
23 | self.downsample = downsample
24 | self.stride = stride
25 | self.last = last
26 |
27 | def forward(self, x):
28 | residual = x
29 |
30 | out = self.conv1(x)
31 | out = self.bn1(out)
32 | out = self.relu(out)
33 |
34 | out = self.conv2(out)
35 | out = self.bn2(out)
36 |
37 | if self.downsample is not None:
38 | residual = self.downsample(x)
39 |
40 | out += residual
41 | if not self.last: #remove ReLU in the last layer
42 | out = self.relu(out)
43 |
44 | return out
45 |
46 | class ResNetMtl(nn.Module):
47 |
48 | def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=10):
49 | self.inplanes = 16
50 | super(ResNetMtl, self).__init__()
51 | self.conv1 = Conv2dMtl(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1,
52 | bias=False)
53 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(16)
54 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
55 | self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 16, layers[0])
56 | self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 32, layers[1], stride=2)
57 | self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[2], stride=2, last_phase=True)
58 | self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(8, stride=1)
59 | self.fc = modified_linear.CosineLinear(64 * block.expansion, num_classes)
60 |
61 | for m in self.modules():
62 | if isinstance(m, Conv2dMtl):
63 | nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
64 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
65 | nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
66 | nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
67 |
68 | def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, last_phase=False):
69 | downsample = None
70 | if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
71 | downsample = nn.Sequential(
72 | Conv2dMtl(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
73 | kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
74 | nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
75 | )
76 |
77 | layers = []
78 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
79 | self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
80 | if last_phase:
81 | for i in range(1, blocks-1):
82 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
83 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, last=True))
84 | else:
85 | for i in range(1, blocks):
86 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
87 |
88 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
89 |
90 | def forward(self, x):
91 | x = self.conv1(x)
92 | x = self.bn1(x)
93 | x = self.relu(x)
94 |
95 | x = self.layer1(x)
96 | x = self.layer2(x)
97 | x = self.layer3(x)
98 |
99 | x = self.avgpool(x)
100 | x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
101 | x = self.fc(x)
102 |
103 | return x
104 |
105 | def resnetmtl20(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
106 | n = 3
107 | model = ResNetMtl(BasicBlockMtl, [n, n, n], **kwargs)
108 | return model
109 |
110 | def resnetmtl32(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
111 | n = 5
112 | model = ResNetMtl(BasicBlockMtl, [n, n, n], **kwargs)
113 | return model
114 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/models/resnet_cifar.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | import math
3 | import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
4 | from utils.incremental.conv2d_mtl import Conv2d
5 |
6 | def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
7 | """3x3 convolution with padding"""
8 | return Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
9 | padding=1, bias=False)
10 |
11 | class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
12 | expansion = 1
13 |
14 | def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None):
15 | super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
16 | self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
17 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
18 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
19 | self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
20 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
21 | self.downsample = downsample
22 | self.stride = stride
23 |
24 | def forward(self, x):
25 | residual = x
26 | import pdb
27 | pdb.set_trace()
28 | out = self.conv1(x)
29 | out = self.bn1(out)
30 | out = self.relu(out)
31 |
32 | out = self.conv2(out)
33 | out = self.bn2(out)
34 |
35 | if self.downsample is not None:
36 | residual = self.downsample(x)
37 |
38 | out += residual
39 | out = self.relu(out)
40 |
41 | return out
42 |
43 |
44 | class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
45 | expansion = 4
46 |
47 | def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None):
48 | super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
49 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
50 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
51 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
52 | padding=1, bias=False)
53 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
54 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes * self.expansion, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
55 | self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * self.expansion)
56 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
57 | self.downsample = downsample
58 | self.stride = stride
59 |
60 | def forward(self, x):
61 | residual = x
62 |
63 | out = self.conv1(x)
64 | out = self.bn1(out)
65 | out = self.relu(out)
66 |
67 | out = self.conv2(out)
68 | out = self.bn2(out)
69 | out = self.relu(out)
70 |
71 | out = self.conv3(out)
72 | out = self.bn3(out)
73 |
74 | if self.downsample is not None:
75 | residual = self.downsample(x)
76 |
77 | out += residual
78 | out = self.relu(out)
79 |
80 | return out
81 |
82 |
83 | class ResNet(nn.Module):
84 |
85 | def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=10):
86 | self.inplanes = 16
87 | super(ResNet, self).__init__()
88 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1,
89 | bias=False)
90 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(16)
91 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
92 | self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 16, layers[0])
93 | self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 32, layers[1], stride=2)
94 | self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[2], stride=2)
95 | self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(8, stride=1)
96 | self.fc = nn.Linear(64 * block.expansion, num_classes)
97 |
98 | for m in self.modules():
99 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
100 | nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
101 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
102 | nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
103 | nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
104 |
105 | def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1):
106 | downsample = None
107 | if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
108 | downsample = nn.Sequential(
109 | nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
110 | kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
111 | nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
112 | )
113 |
114 | layers = []
115 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
116 | self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
117 | for i in range(1, blocks):
118 | layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
119 |
120 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
121 |
122 | def forward(self, x):
123 | x = self.conv1(x)
124 | x = self.bn1(x)
125 | x = self.relu(x)
126 |
127 | x = self.layer1(x)
128 | x = self.layer2(x)
129 | x = self.layer3(x)
130 |
131 | x = self.avgpool(x)
132 | x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
133 | x = self.fc(x)
134 |
135 | return x
136 |
137 | def resnet20(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
138 | n = 3
139 | model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [n, n, n], **kwargs)
140 | return model
141 |
142 | def resnet32(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
143 | n = 5
144 | model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [n, n, n], **kwargs)
145 | return model
146 |
147 | def resnet56(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
148 | n = 9
149 | model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [n, n, n], **kwargs)
150 | return model
151 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/process_imagenet/generate_imagenet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python
2 | # coding=utf-8
3 | import argparse
4 | import os
5 | import random
6 | import shutil
7 | import time
8 | import warnings
9 | import numpy as np
10 |
11 | import torch
12 | import torch.nn as nn
13 | import torch.nn.parallel
14 | import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
15 | import torch.distributed as dist
16 | import torch.optim
17 | import torch.utils.data
18 | import torch.utils.data.distributed
19 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
20 | import torchvision.datasets as datasets
21 | import torchvision.models as models
22 | from PIL import Image
23 |
24 | src_root_dir = 'data/imagenet/data/'
25 | des_root_dir = 'data/imagenet_resized_256/data/'
26 | if not os.path.exists(des_root_dir):
27 | os.makedirs(des_root_dir)
28 |
29 | phase_list = ['train', 'val']
30 | for phase in phase_list:
31 | if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(des_root_dir, phase)):
32 | os.mkdir(os.path.join(des_root_dir, phase))
33 | data_dir = os.path.join(src_root_dir, phase)
34 | tg_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(data_dir)
35 | for cls_name in tg_dataset.classes:
36 | if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(des_root_dir, phase, cls_name)):
37 | os.mkdir(os.path.join(des_root_dir, phase, cls_name))
38 | cnt = 0
39 | for item in tg_dataset.imgs:
40 | img_path = item[0]
41 | img = Image.open(img_path)
42 | img = img.convert('RGB')
43 | save_path = img_path.replace('imagenet', 'imagenet_resized_256')
44 | resized_img = img.resize((256,256), Image.BILINEAR)
45 | resized_img.save(save_path)
46 | cnt = cnt+1
47 | if cnt % 1000 == 0:
48 | print(cnt, save_path)
49 |
50 | print("Generation finished.")
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/process_imagenet/generate_imagenet_subset.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python
2 | # coding=utf-8
3 | import argparse
4 | import os
5 | import random
6 | import shutil
7 | import time
8 | import warnings
9 | import numpy as np
10 |
11 | import torch
12 | import torch.nn as nn
13 | import torch.nn.parallel
14 | import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
15 | import torch.distributed as dist
16 | import torch.optim
17 | import torch.utils.data
18 | import torch.utils.data.distributed
19 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
20 | import torchvision.datasets as datasets
21 | import torchvision.models as models
22 |
23 | data_dir = 'data/imagenet/data/'
24 |
25 | # Data loading code
26 | traindir = os.path.join(data_dir, 'train')
27 | train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(traindir, None)
28 | classes = train_dataset.classes
29 | print("the number of total classes: {}".format(len(classes)))
30 |
31 | seed = 1993
32 | np.random.seed(seed)
33 | subset_num = 100
34 | subset_classes = np.random.choice(classes, subset_num, replace=False)
35 | print("the number of subset classes: {}".format(len(subset_classes)))
36 | print(subset_classes)
37 |
38 | des_root_dir = 'data/seed_{}_subset_{}_imagenet/data/'.format(seed, subset_num)
39 | if not os.path.exists(des_root_dir):
40 | os.makedirs(des_root_dir)
41 | phase_list = ['train', 'val']
42 | for phase in phase_list:
43 | if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(des_root_dir, phase)):
44 | os.mkdir(os.path.join(des_root_dir, phase))
45 | for sc in subset_classes:
46 | src_dir = os.path.join(data_dir, phase, sc)
47 | des_dir = os.path.join(des_root_dir, phase, sc)
48 | cmd = "cp -r {} {}".format(src_dir, des_dir)
49 | print(cmd)
50 | os.system(cmd)
51 |
52 | print("Generation finished.")
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/run_eval.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=2 --nb_protos=20 --epochs=160 --gpu=0 --dataset=cifar100 --random_seed=1993 --use_mtl
2 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=50 --nb_cl=2 --nb_protos=20 --epochs=90 --gpu=0 --dataset=imagenet_sub --data_dir=./data/seed_1993_subset_100_imagenet/data --num_workers=16 --test_batch_size=50 --use_mtl
3 | python main.py --nb_cl_fg=500 --nb_cl=20 --nb_protos=20 --epochs=90 --gpu=0 --dataset=imagenet --data_dir=./data/imagenet/data --num_workers=16 --test_batch_size=50 --num_classes=1000 --use_mtl
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/script/download_ckpt.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | wget --load-cookies /tmp/cookies.txt "https://docs.google.com/uc?export=download&confirm=$(wget --quiet --save-cookies /tmp/cookies.txt --keep-session-cookies --no-check-certificate 'https://docs.google.com/uc?export=download&id=1sKO2BOssWgTFBNZbM50qDzgk6wqg4_l8' -O- | sed -rn 's/.*confirm=([0-9A-Za-z_]+).*/\1\n/p')&id=1sKO2BOssWgTFBNZbM50qDzgk6wqg4_l8" -O logs.tar.gz && rm -rf /tmp/cookies.txt
2 | tar zxvf logs.tar.gz
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/trainer/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yaoyao-liu/class-incremental-learning/701af9f819f559c6ab3d3ee73bb3d7c21e924572/mnemonics-training/2_eval/trainer/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/trainer/train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python
2 | # coding=utf-8
3 | import torch
4 | import torch.nn as nn
5 | import torch.nn.functional as F
6 | import torch.optim as optim
7 | from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
8 | import torchvision
9 | from torchvision import datasets, models, transforms
10 | from torch.autograd import Variable
11 | from tensorboardX import SummaryWriter
12 | import numpy as np
13 | import time
14 | import os
15 | import os.path as osp
16 | import sys
17 | import copy
18 | import argparse
19 | from PIL import Image
20 | try:
21 | import cPickle as pickle
22 | except:
23 | import pickle
24 | import math
25 | import utils.misc
26 | import models.modified_resnet_cifar as modified_resnet_cifar
27 | import models.modified_resnetmtl_cifar as modified_resnetmtl_cifar
28 | import models.modified_resnet as modified_resnet
29 | import models.modified_resnetmtl as modified_resnetmtl
30 | import models.modified_linear as modified_linear
31 | from utils.imagenet.utils_dataset import split_images_labels
32 | from utils.imagenet.utils_dataset import merge_images_labels
33 | from utils.incremental.compute_features import compute_features
34 | from utils.incremental.compute_accuracy import compute_accuracy
35 | from utils.incremental.compute_confusion_matrix import compute_confusion_matrix
36 | import warnings
37 | warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
38 |
39 | class Trainer(object):
40 | def __init__(self, the_args):
41 | self.args = the_args
42 | self.log_dir = './logs/'
43 | if not osp.exists(self.log_dir):
44 | os.mkdir(self.log_dir)
45 | self.save_path = self.log_dir + self.args.dataset + '_nfg' + str(self.args.nb_cl_fg) + '_ncls' + str(self.args.nb_cl) + \
46 | '_nproto' + str(self.args.nb_protos)
47 | if self.args.use_mtl:
48 | self.save_path += '_mtl'
49 | if self.args.add_str is not None:
50 | self.save_path += self.args.add_str
51 | self.save_path += '_' + str(self.args.ckpt_label)
52 | if not osp.exists(self.save_path):
53 | os.mkdir(self.save_path)
54 |
55 | self.device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
56 |
57 | if self.args.dataset == 'cifar100':
58 | self.transform_train = transforms.Compose([ \
59 | transforms.RandomCrop(32, padding=4), \
60 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), \
61 | transforms.ToTensor(), \
62 | transforms.Normalize((0.5071, 0.4866, 0.4409), (0.2009, 0.1984, 0.2023)),])
63 | self.transform_test = transforms.Compose([ \
64 | transforms.ToTensor(), \
65 | transforms.Normalize((0.5071, 0.4866, 0.4409), (0.2009, 0.1984, 0.2023)),])
66 | self.trainset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR100(root='./data', train=True, download=True, transform=self.transform_train)
67 | self.testset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR100(root='./data', train=False, download=True, transform=self.transform_test)
68 | self.evalset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR100(root='./data', train=False, download=False, transform=self.transform_test)
69 |
70 | self.network = modified_resnet_cifar.resnet32
71 | self.network_mtl = modified_resnetmtl_cifar.resnetmtl32
72 | self.lr_strat = [int(self.args.epochs*0.5), int(self.args.epochs*0.75)]
73 | self.dictionary_size = 500
74 |
75 | elif self.args.dataset == 'imagenet_sub' or self.args.dataset == 'imagenet':
76 | traindir = os.path.join(self.args.data_dir, 'train')
77 | valdir = os.path.join(self.args.data_dir, 'val')
78 | normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
79 | self.trainset = datasets.ImageFolder(traindir, \
80 | transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224), \
81 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), \
82 | transforms.ToTensor(), normalize,]))
83 | self.testset = datasets.ImageFolder(valdir, \
84 | transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize(256), \
85 | transforms.CenterCrop(224), \
86 | transforms.ToTensor(), normalize, ]))
87 | self.evalset = datasets.ImageFolder(valdir, \
88 | transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize(256), \
89 | transforms.CenterCrop(224), \
90 | transforms.ToTensor(), normalize,]))
91 |
92 | self.network = modified_resnet.resnet18
93 | self.network_mtl = modified_resnetmtl.resnetmtl18
94 | self.lr_strat = [30, 60]
95 | self.dictionary_size = 1500
96 |
97 | else:
98 | raise ValueError('Please set correct dataset.')
99 |
100 |
101 | def eval(self):
102 | self.train_writer = SummaryWriter(comment=self.save_path)
103 | dictionary_size = self.dictionary_size
104 | top1_acc_list_cumul = np.zeros((int(self.args.num_classes/self.args.nb_cl), 4, self.args.nb_runs))
105 | top1_acc_list_ori = np.zeros((int(self.args.num_classes/self.args.nb_cl), 4, self.args.nb_runs))
106 |
107 | if self.args.dataset == 'cifar100':
108 | X_train_total = np.array(self.trainset.train_data)
109 | Y_train_total = np.array(self.trainset.train_labels)
110 | X_valid_total = np.array(self.testset.test_data)
111 | Y_valid_total = np.array(self.testset.test_labels)
112 | elif self.args.dataset == 'imagenet_sub' or self.args.dataset == 'imagenet':
113 | X_train_total, Y_train_total = split_images_labels(self.trainset.imgs)
114 | X_valid_total, Y_valid_total = split_images_labels(self.testset.imgs)
115 | else:
116 | raise ValueError('Please set correct dataset.')
117 |
118 | for iteration_total in range(self.args.nb_runs):
119 | order_name = osp.join(self.save_path, \
120 | "seed_{}_{}_order_run_{}.pkl".format(self.args.random_seed, self.args.dataset, iteration_total))
121 | print("Order name:{}".format(order_name))
122 |
123 | if osp.exists(order_name):
124 | print("Loading orders")
125 | order = utils.misc.unpickle(order_name)
126 | else:
127 | print("Generating orders")
128 | order = np.arange(self.args.num_classes)
129 | np.random.shuffle(order)
130 | utils.misc.savepickle(order, order_name)
131 | order_list = list(order)
132 | print(order_list)
133 |
134 | X_valid_cumuls = []
135 | X_protoset_cumuls = []
136 | Y_valid_cumuls = []
137 | Y_protoset_cumuls = []
138 |
139 | start_iter = int(self.args.nb_cl_fg/self.args.nb_cl)-1
140 |
141 | for iteration in range(start_iter, int(self.args.num_classes/self.args.nb_cl)):
142 | if iteration == start_iter:
143 | last_iter = 0
144 | tg_model = self.network(num_classes=self.args.nb_cl_fg)
145 | in_features = tg_model.fc.in_features
146 | out_features = tg_model.fc.out_features
147 | print("in_features:", in_features, "out_features:", out_features)
148 | ref_model = None
149 | elif iteration == start_iter+1:
150 | last_iter = iteration
151 | ref_model = copy.deepcopy(tg_model)
152 | if self.args.use_mtl:
153 | tg_model = self.network_mtl(num_classes=self.args.nb_cl_fg)
154 | else:
155 | tg_model = self.network(num_classes=self.args.nb_cl_fg)
156 | ref_dict = ref_model.state_dict()
157 | tg_dict = tg_model.state_dict()
158 | tg_dict.update(ref_dict)
159 | tg_model.load_state_dict(tg_dict)
160 | tg_model.to(self.device)
161 | in_features = tg_model.fc.in_features
162 | out_features = tg_model.fc.out_features
163 | print("in_features:", in_features, "out_features:", out_features)
164 | new_fc = modified_linear.SplitCosineLinear(in_features, out_features, self.args.nb_cl)
165 | new_fc.fc1.weight.data = tg_model.fc.weight.data
166 | new_fc.sigma.data = tg_model.fc.sigma.data
167 | tg_model.fc = new_fc
168 | lamda_mult = out_features*1.0 / self.args.nb_cl
169 | else:
170 | last_iter = iteration
171 | ref_model = copy.deepcopy(tg_model)
172 | in_features = tg_model.fc.in_features
173 | out_features1 = tg_model.fc.fc1.out_features
174 | out_features2 = tg_model.fc.fc2.out_features
175 | print("in_features:", in_features, "out_features1:", out_features1, "out_features2:", out_features2)
176 | new_fc = modified_linear.SplitCosineLinear(in_features, out_features1+out_features2, self.args.nb_cl)
177 | new_fc.fc1.weight.data[:out_features1] = tg_model.fc.fc1.weight.data
178 | new_fc.fc1.weight.data[out_features1:] = tg_model.fc.fc2.weight.data
179 | new_fc.sigma.data = tg_model.fc.sigma.data
180 | tg_model.fc = new_fc
181 | lamda_mult = (out_features1+out_features2)*1.0 / (self.args.nb_cl)
182 |
183 | actual_cl = order[range(last_iter*self.args.nb_cl,(iteration+1)*self.args.nb_cl)]
184 | indices_train_10 = np.array([i in order[range(last_iter*self.args.nb_cl,(iteration+1)*self.args.nb_cl)] for i in Y_train_total])
185 | indices_test_10 = np.array([i in order[range(last_iter*self.args.nb_cl,(iteration+1)*self.args.nb_cl)] for i in Y_valid_total])
186 |
187 | X_valid = X_valid_total[indices_test_10]
188 | X_valid_cumuls.append(X_valid)
189 | X_valid_cumul = np.concatenate(X_valid_cumuls)
190 |
191 | Y_valid = Y_valid_total[indices_test_10]
192 | Y_valid_cumuls.append(Y_valid)
193 | Y_valid_cumul = np.concatenate(Y_valid_cumuls)
194 |
195 | if iteration == start_iter:
196 | X_valid_ori = X_valid
197 | Y_valid_ori = Y_valid
198 |
199 | ckp_name = osp.join(self.save_path, 'run_{}_iteration_{}_model.pth'.format(iteration_total, iteration))
200 |
201 | print('ckp_name', ckp_name)
202 | print("[*] Loading models from checkpoint")
203 | tg_model = torch.load(ckp_name)
204 | tg_feature_model = nn.Sequential(*list(tg_model.children())[:-1])
205 |
206 | if self.args.dataset == 'cifar100':
207 | map_Y_valid_ori = np.array([order_list.index(i) for i in Y_valid_ori])
208 | print('Computing accuracy on the original batch of classes...')
209 | self.evalset.test_data = X_valid_ori.astype('uint8')
210 | self.evalset.test_labels = map_Y_valid_ori
211 | evalloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(self.evalset, batch_size=self.args.eval_batch_size,
212 | shuffle=False, num_workers=self.args.num_workers)
213 | ori_acc = compute_accuracy(tg_model, tg_feature_model, evalloader)
214 | top1_acc_list_ori[iteration, :, iteration_total] = np.array(ori_acc).T
215 | self.train_writer.add_scalar('ori_acc/cnn', float(ori_acc), iteration)
216 | map_Y_valid_cumul = np.array([order_list.index(i) for i in Y_valid_cumul])
217 | print('Computing cumulative accuracy...')
218 | self.evalset.test_data = X_valid_cumul.astype('uint8')
219 | self.evalset.test_labels = map_Y_valid_cumul
220 | evalloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(self.evalset, batch_size=self.args.eval_batch_size,
221 | shuffle=False, num_workers=self.args.num_workers)
222 | cumul_acc = compute_accuracy(tg_model, tg_feature_model, evalloader)
223 | top1_acc_list_cumul[iteration, :, iteration_total] = np.array(cumul_acc).T
224 | self.train_writer.add_scalar('cumul_acc/cnn', float(cumul_acc), iteration)
225 | elif self.args.dataset == 'imagenet_sub' or self.args.dataset == 'imagenet':
226 | map_Y_valid_ori = np.array([order_list.index(i) for i in Y_valid_ori])
227 | print('Computing accuracy on the original batch of classes...')
228 | current_eval_set = merge_images_labels(X_valid_ori, map_Y_valid_ori)
229 | self.evalset.imgs = self.evalset.samples = current_eval_set
230 | evalloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(self.evalset, batch_size=self.args.eval_batch_size,
231 | shuffle=False, num_workers=self.args.num_workers, pin_memory=True)
232 | ori_acc = compute_accuracy(tg_model, tg_feature_model, evalloader)
233 | top1_acc_list_ori[iteration, :, iteration_total] = np.array(ori_acc).T
234 | self.train_writer.add_scalar('ori_acc/cnn', float(ori_acc), iteration)
235 | map_Y_valid_cumul = np.array([order_list.index(i) for i in Y_valid_cumul])
236 | print('Computing cumulative accuracy...')
237 | current_eval_set = merge_images_labels(X_valid_cumul, map_Y_valid_cumul)
238 | self.evalset.imgs = self.evalset.samples = current_eval_set
239 | evalloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(self.evalset, batch_size=self.args.eval_batch_size,
240 | shuffle=False, num_workers=self.args.num_workers, pin_memory=True)
241 | cumul_acc = compute_accuracy(tg_model, tg_feature_model, evalloader)
242 | top1_acc_list_cumul[iteration, :, iteration_total] = np.array(cumul_acc).T
243 | self.train_writer.add_scalar('cumul_acc/cnn', float(cumul_acc), iteration)
244 | else:
245 | raise ValueError('Please set correct dataset.')
246 |
247 | self.train_writer.close()
248 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/utils/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yaoyao-liu/class-incremental-learning/701af9f819f559c6ab3d3ee73bb3d7c21e924572/mnemonics-training/2_eval/utils/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/utils/gpu_tools.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import torch
3 | import time
4 |
5 | def check_memory(cuda_device):
6 | devices_info = os.popen('"/usr/bin/nvidia-smi" --query-gpu=memory.total,memory.used --format=csv,nounits,noheader').read().strip().split("\n")
7 | total, used = devices_info[int(cuda_device)].split(',')
8 | return total,used
9 |
10 | def occupy_memory(cuda_device):
11 | total, used = check_memory(cuda_device)
12 | total = int(total)
13 | used = int(used)
14 | max_mem = int(total * 0.90)
15 | print('Total memory: ' + str(total) + ', used memory: ' + str(used))
16 | block_mem = max_mem - used
17 | if block_mem > 0:
18 | x = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(256, 1024, block_mem)
19 | del x
20 |
21 | def set_gpu(x):
22 | os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = x
23 | print('Using gpu:', x)
24 |
25 |
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/utils/imagenet/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python
2 | # coding=utf-8
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/utils/imagenet/train_and_eval.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import argparse
2 | import os
3 | import shutil
4 | import time
5 |
6 | import torch
7 | import torch.nn as nn
8 | import torch.nn.parallel
9 | import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
10 | import torch.distributed as dist
11 | import torch.optim
12 | import torch.utils.data
13 | import torch.utils.data.distributed
14 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
15 | import torchvision.datasets as datasets
16 | import torchvision.models as models
17 |
18 | from .utils_train import *
19 |
20 | def train_and_eval(epochs, start_epoch, model, optimizer, lr_scheduler, \
21 | train_loader, val_loader, gpu=None):
22 | for epoch in range(start_epoch, epochs):
23 | #adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch)
24 | lr_scheduler.step()
25 | print('\nEpoch: %d, LR: ' % epoch, end='')
26 | print(lr_scheduler.get_lr())
27 |
28 | # train for one epoch
29 | train(train_loader, model, optimizer, epoch, gpu)
30 |
31 | # evaluate on validation set
32 | validate(val_loader, model, gpu)
33 |
34 | return model
35 |
36 | def train(train_loader, model, optimizer, epoch, gpu=None):
37 | batch_time = AverageMeter()
38 | data_time = AverageMeter()
39 | losses = AverageMeter()
40 | top1 = AverageMeter()
41 | top5 = AverageMeter()
42 | model.train()
43 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda(gpu)
44 | end = time.time()
45 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
46 | data_time.update(time.time() - end)
47 | if gpu is not None:
48 | input = input.cuda(gpu, non_blocking=True)
49 | target = target.cuda(gpu, non_blocking=True)
50 | output = model(input)
51 | loss = criterion(output, target)
52 | prec1, prec5 = accuracy(output, target, topk=(1, 5))
53 | losses.update(loss.item(), input.size(0))
54 | top1.update(prec1[0], input.size(0))
55 | top5.update(prec5[0], input.size(0))
56 | optimizer.zero_grad()
57 | loss.backward()
58 | optimizer.step()
59 | batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
60 | end = time.time()
61 |
62 | if i % 10 == 0:
63 | print('Epoch: [{0}][{1}/{2}]\t'
64 | 'Time {batch_time.val:.3f} ({batch_time.avg:.3f})\t'
65 | 'Data {data_time.val:.3f} ({data_time.avg:.3f})\t'
66 | 'Loss {loss.val:.4f} ({loss.avg:.4f})\t'
67 | 'Prec@1 {top1.val:.3f} ({top1.avg:.3f})\t'
68 | 'Prec@5 {top5.val:.3f} ({top5.avg:.3f})'.format(
69 | epoch, i, len(train_loader), batch_time=batch_time,
70 | data_time=data_time, loss=losses, top1=top1, top5=top5))
71 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/utils/imagenet/utils_dataset.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import argparse
2 | import os
3 | import shutil
4 | import time
5 | import numpy as np
6 |
7 | def split_images_labels(imgs):
8 | images = []
9 | labels = []
10 | for item in imgs:
11 | images.append(item[0])
12 | labels.append(item[1])
13 | return np.array(images), np.array(labels)
14 |
15 | def merge_images_labels(images, labels):
16 | images = list(images)
17 | labels = list(labels)
18 | assert(len(images)==len(labels))
19 | imgs = []
20 | for i in range(len(images)):
21 | item = (images[i], labels[i])
22 | imgs.append(item)
23 | return imgs
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/utils/imagenet/utils_train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import argparse
2 | import os
3 | import shutil
4 | import time
5 |
6 | import torch
7 | import torch.nn as nn
8 | import torch.nn.parallel
9 | import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
10 | import torch.distributed as dist
11 | import torch.optim
12 | import torch.utils.data
13 | import torch.utils.data.distributed
14 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
15 | import torchvision.datasets as datasets
16 | import torchvision.models as models
17 |
18 | def validate(val_loader, model, gpu=None):
19 | batch_time = AverageMeter()
20 | losses = AverageMeter()
21 | top1 = AverageMeter()
22 | top5 = AverageMeter()
23 |
24 | model.eval()
25 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda(gpu)
26 |
27 | with torch.no_grad():
28 | end = time.time()
29 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(val_loader):
30 | if gpu is not None:
31 | input = input.cuda(gpu, non_blocking=True)
32 | target = target.cuda(gpu, non_blocking=True)
33 |
34 | output = model(input)
35 | loss = criterion(output, target)
36 |
37 | prec1, prec5 = accuracy(output, target, topk=(1, 5))
38 | losses.update(loss.item(), input.size(0))
39 | top1.update(prec1[0], input.size(0))
40 | top5.update(prec5[0], input.size(0))
41 |
42 | batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
43 | end = time.time()
44 |
45 | if i % 10 == 0:
46 | print('Test: [{0}/{1}]\t'
47 | 'Time {batch_time.val:.3f} ({batch_time.avg:.3f})\t'
48 | 'Loss {loss.val:.4f} ({loss.avg:.4f})\t'
49 | 'Prec@1 {top1.val:.3f} ({top1.avg:.3f})\t'
50 | 'Prec@5 {top5.val:.3f} ({top5.avg:.3f})'.format(
51 | i, len(val_loader), batch_time=batch_time, loss=losses,
52 | top1=top1, top5=top5))
53 |
54 | print(' * Prec@1 {top1.avg:.3f} Prec@5 {top5.avg:.3f}'
55 | .format(top1=top1, top5=top5))
56 |
57 | return top1.avg
58 |
59 | class AverageMeter(object):
60 | """Computes and stores the average and current value"""
61 | def __init__(self):
62 | self.reset()
63 |
64 | def reset(self):
65 | self.val = 0
66 | self.avg = 0
67 | self.sum = 0
68 | self.count = 0
69 |
70 | def update(self, val, n=1):
71 | self.val = val
72 | self.sum += val * n
73 | self.count += n
74 | self.avg = self.sum / self.count
75 |
76 | def accuracy(output, target, topk=(1,)):
77 | with torch.no_grad():
78 | maxk = max(topk)
79 | batch_size = target.size(0)
80 |
81 | _, pred = output.topk(maxk, 1, True, True)
82 | pred = pred.t()
83 | correct = pred.eq(target.view(1, -1).expand_as(pred))
84 |
85 | res = []
86 | for k in topk:
87 | correct_k = correct[:k].view(-1).float().sum(0, keepdim=True)
88 | res.append(correct_k.mul_(100.0 / batch_size))
89 | return res
90 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/utils/incremental/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python
2 | # coding=utf-8
3 | # for incremental train and eval
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/utils/incremental/compute_accuracy.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python
2 | # coding=utf-8
3 | import torch
4 | import torch.nn as nn
5 | import torch.nn.functional as F
6 | import torch.optim as optim
7 | from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
8 | import torchvision
9 | from torchvision import datasets, models, transforms
10 | from torch.autograd import Variable
11 | import numpy as np
12 | import time
13 | import os
14 | import copy
15 | import argparse
16 | from PIL import Image
17 | from scipy.spatial.distance import cdist
18 | from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
19 | from utils.misc import *
20 | from utils.imagenet.utils_dataset import merge_images_labels
21 |
22 | def compute_accuracy(tg_model, tg_feature_model, evalloader, scale=None, print_info=True, device=None, cifar=True, imagenet=False, valdir=None):
23 | if device is None:
24 | device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
25 | tg_model.eval()
26 | tg_feature_model.eval()
27 |
28 | correct = 0
29 | correct_icarl = 0
30 | correct_icarl_cosine = 0
31 | correct_icarl_cosine2 = 0
32 | correct_ncm = 0
33 | correct_maml = 0
34 | total = 0
35 | with torch.no_grad():
36 | for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(evalloader):
37 | inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)
38 | total += targets.size(0)
39 | outputs = tg_model(inputs)
40 | outputs = F.softmax(outputs, dim=1)
41 | if scale is not None:
42 | assert(scale.shape[0] == 1)
43 | assert(outputs.shape[1] == scale.shape[1])
44 | outputs = outputs / scale.repeat(outputs.shape[0], 1).type(torch.FloatTensor).to(device)
45 | _, predicted = outputs.max(1)
46 | correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item()
47 |
48 | if print_info:
49 | print(" top 1 accuracy :\t\t{:.2f} %".format(100.*correct/total))
50 | acc = 100.*correct/total
51 | return acc
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/utils/incremental/compute_confusion_matrix.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python
2 | # coding=utf-8
3 | import torch
4 | import torch.nn as nn
5 | import torch.nn.functional as F
6 | import torch.optim as optim
7 | from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
8 | import torchvision
9 | from torchvision import datasets, models, transforms
10 | from torch.autograd import Variable
11 | import numpy as np
12 | import time
13 | import os
14 | import copy
15 | import argparse
16 | from PIL import Image
17 | from scipy.spatial.distance import cdist
18 | from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
19 | from utils.misc import *
20 |
21 | def compute_confusion_matrix(tg_model, tg_feature_model, class_means, evalloader, print_info=False, device=None):
22 | if device is None:
23 | device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
24 | tg_model.eval()
25 | tg_feature_model.eval()
26 |
27 | #evalset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR100(root='./data', train=False,
28 | # download=False, transform=transform_test)
29 | #evalset.test_data = input_data.astype('uint8')
30 | #evalset.test_labels = input_labels
31 | #evalloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(evalset, batch_size=128,
32 | # shuffle=False, num_workers=2)
33 |
34 | correct = 0
35 | correct_icarl = 0
36 | correct_ncm = 0
37 | total = 0
38 | num_classes = tg_model.fc.out_features
39 | cm = np.zeros((3, num_classes, num_classes))
40 | all_targets = []
41 | all_predicted = []
42 | all_predicted_icarl = []
43 | all_predicted_ncm = []
44 | with torch.no_grad():
45 | for batch_idx, (inputs, targets) in enumerate(evalloader):
46 | inputs, targets = inputs.to(device), targets.to(device)
47 | total += targets.size(0)
48 | all_targets.append(targets)
49 |
50 | outputs = tg_model(inputs)
51 | _, predicted = outputs.max(1)
52 | correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item()
53 | all_predicted.append(predicted)
54 |
55 |
56 |
57 | cm[0, :, :] = confusion_matrix(np.concatenate(all_targets), np.concatenate(all_predicted))
58 |
59 | if print_info:
60 | print(" top 1 accuracy :\t\t{:.2f} %".format( 100.*correct/total ))
61 | return cm
62 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/utils/incremental/compute_features.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python
2 | # coding=utf-8
3 | #!/usr/bin/env python
4 | # coding=utf-8
5 | import torch
6 | import torch.nn as nn
7 | import torch.nn.functional as F
8 | import torch.optim as optim
9 | from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
10 | import torchvision
11 | from torchvision import datasets, models, transforms
12 | from torch.autograd import Variable
13 | import numpy as np
14 | import time
15 | import os
16 | import copy
17 | import argparse
18 | from PIL import Image
19 | from scipy.spatial.distance import cdist
20 | from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
21 | from utils.misc import *
22 |
23 | def compute_features(tg_feature_model, evalloader, num_samples, num_features, device=None):
24 | if device is None:
25 | device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
26 | tg_feature_model.eval()
27 | features = np.zeros([num_samples, num_features])
28 | start_idx = 0
29 | with torch.no_grad():
30 | for inputs, targets in evalloader:
31 | inputs = inputs.to(device)
32 | features[start_idx:start_idx+inputs.shape[0], :] = np.squeeze(tg_feature_model(inputs))
33 | start_idx = start_idx+inputs.shape[0]
34 | assert(start_idx==num_samples)
35 | return features
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/utils/incremental/conv2d_mtl.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | import torch
3 | from torch.nn.parameter import Parameter
4 | import torch.nn.functional as F
5 | from torch.nn.modules.module import Module
6 | from torch.nn.modules.utils import _single, _pair, _triple
7 |
8 |
9 | class _ConvNdMtl(Module):
10 |
11 | def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride,
12 | padding, dilation, transposed, output_padding, groups, bias):
13 | super(_ConvNdMtl, self).__init__()
14 | if in_channels % groups != 0:
15 | raise ValueError('in_channels must be divisible by groups')
16 | if out_channels % groups != 0:
17 | raise ValueError('out_channels must be divisible by groups')
18 | self.in_channels = in_channels
19 | self.out_channels = out_channels
20 | self.kernel_size = kernel_size
21 | self.stride = stride
22 | self.padding = padding
23 | self.dilation = dilation
24 | self.transposed = transposed
25 | self.output_padding = output_padding
26 | self.groups = groups
27 | if transposed:
28 | self.weight = Parameter(torch.Tensor(
29 | in_channels, out_channels // groups, *kernel_size))
30 | self.mtl_weight = Parameter(torch.ones(in_channels, out_channels // groups, 1, 1))
31 | else:
32 | self.weight = Parameter(torch.Tensor(
33 | out_channels, in_channels // groups, *kernel_size))
34 | self.mtl_weight = Parameter(torch.ones(out_channels, in_channels // groups, 1, 1))
35 | self.weight.requires_grad=False
36 | if bias:
37 | self.bias = Parameter(torch.Tensor(out_channels))
38 | self.bias.requires_grad=False
39 | self.mtl_bias = Parameter(torch.zeros(out_channels))
40 | else:
41 | self.register_parameter('bias', None)
42 | self.register_parameter('mtl_bias', None)
43 | self.reset_parameters()
44 |
45 | def reset_parameters(self):
46 | n = self.in_channels
47 | for k in self.kernel_size:
48 | n *= k
49 | stdv = 1. / math.sqrt(n)
50 | self.weight.data.uniform_(-stdv, stdv)
51 | self.mtl_weight.data.uniform_(1, 1)
52 | if self.bias is not None:
53 | self.bias.data.uniform_(-stdv, stdv)
54 | self.mtl_bias.data.uniform_(0, 0)
55 |
56 | def extra_repr(self):
57 | s = ('{in_channels}, {out_channels}, kernel_size={kernel_size}'
58 | ', stride={stride}')
59 | if self.padding != (0,) * len(self.padding):
60 | s += ', padding={padding}'
61 | if self.dilation != (1,) * len(self.dilation):
62 | s += ', dilation={dilation}'
63 | if self.output_padding != (0,) * len(self.output_padding):
64 | s += ', output_padding={output_padding}'
65 | if self.groups != 1:
66 | s += ', groups={groups}'
67 | if self.bias is None:
68 | s += ', bias=False'
69 | return s.format(**self.__dict__)
70 |
71 | class Conv2dMtl(_ConvNdMtl):
72 |
73 | def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1,
74 | padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True):
75 | kernel_size = _pair(kernel_size)
76 | stride = _pair(stride)
77 | padding = _pair(padding)
78 | dilation = _pair(dilation)
79 | super(Conv2dMtl, self).__init__(
80 | in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation,
81 | False, _pair(0), groups, bias)
82 |
83 | def forward(self, input):
84 | new_mtl_weight = self.mtl_weight.expand(self.weight.shape)
85 | new_weight = self.weight.mul(new_mtl_weight)
86 | if self.bias is not None:
87 | new_bias = self.bias + self.mtl_bias
88 | else:
89 | new_bias = None
90 | return F.conv2d(input, new_weight, new_bias, self.stride,
91 | self.padding, self.dilation, self.groups)
92 |
93 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/2_eval/utils/misc.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python
2 | # coding=utf-8
3 | from __future__ import print_function, division
4 |
5 | import torch
6 | import torch.nn as nn
7 | import torch.nn.init as init
8 | from collections import OrderedDict
9 |
10 | import numpy as np
11 | import os
12 | import os.path as osp
13 | import sys
14 | import time
15 | import math
16 | import subprocess
17 | try:
18 | import cPickle as pickle
19 | except:
20 | import pickle
21 |
22 | def savepickle(data, file_path):
23 | mkdir_p(osp.dirname(file_path), delete=False)
24 | print('pickle into', file_path)
25 | with open(file_path, 'wb') as f:
26 | pickle.dump(data, f, pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)
27 |
28 | def unpickle(file_path):
29 | with open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
30 | data = pickle.load(f)
31 | return data
32 |
33 | def mkdir_p(path, delete=False, print_info=True):
34 | if path == '': return
35 |
36 | if delete:
37 | subprocess.call(('rm -r ' + path).split())
38 | if not osp.exists(path):
39 | if print_info:
40 | print('mkdir -p ' + path)
41 | subprocess.call(('mkdir -p ' + path).split())
42 |
43 | def get_mean_and_std(dataset):
44 | dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=1, shuffle=True, num_workers=2)
45 | mean = torch.zeros(3)
46 | std = torch.zeros(3)
47 | print('==> Computing mean and std..')
48 | for inputs, targets in dataloader:
49 | for i in range(3):
50 | mean[i] += inputs[:,i,:,:].mean()
51 | std[i] += inputs[:,i,:,:].std()
52 | mean.div_(len(dataset))
53 | std.div_(len(dataset))
54 | return mean, std
55 |
56 | def init_params(net):
57 | for m in net.modules():
58 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
59 | init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out')
60 | if m.bias:
61 | init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
62 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
63 | init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
64 | init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
65 | elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
66 | init.normal_(m.weight, std=1e-3)
67 | if m.bias is not None:
68 | init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
69 |
70 | _, term_width = os.popen('stty size', 'r').read().split()
71 | term_width = int(term_width)
72 |
73 | TOTAL_BAR_LENGTH = 65.
74 | last_time = time.time()
75 | begin_time = last_time
76 | def progress_bar(current, total, msg=None):
77 | global last_time, begin_time
78 | if current == 0:
79 | begin_time = time.time() # Reset for new bar.
80 |
81 | cur_len = int(TOTAL_BAR_LENGTH*current/total)
82 | rest_len = int(TOTAL_BAR_LENGTH - cur_len) - 1
83 |
84 | sys.stdout.write(' [')
85 | for i in range(cur_len):
86 | sys.stdout.write('=')
87 | sys.stdout.write('>')
88 | for i in range(rest_len):
89 | sys.stdout.write('.')
90 | sys.stdout.write(']')
91 |
92 | cur_time = time.time()
93 | step_time = cur_time - last_time
94 | last_time = cur_time
95 | tot_time = cur_time - begin_time
96 |
97 | L = []
98 | L.append(' Step: %s' % format_time(step_time))
99 | L.append(' | Tot: %s' % format_time(tot_time))
100 | if msg:
101 | L.append(' | ' + msg)
102 |
103 | msg = ''.join(L)
104 | sys.stdout.write(msg)
105 | for i in range(term_width-int(TOTAL_BAR_LENGTH)-len(msg)-3):
106 | sys.stdout.write(' ')
107 |
108 | for i in range(term_width-int(TOTAL_BAR_LENGTH/2)+2):
109 | sys.stdout.write('\b')
110 | sys.stdout.write(' %d/%d ' % (current+1, total))
111 |
112 | if current < total-1:
113 | sys.stdout.write('\r')
114 | else:
115 | sys.stdout.write('\n')
116 | sys.stdout.flush()
117 |
118 | def format_time(seconds):
119 | days = int(seconds / 3600/24)
120 | seconds = seconds - days*3600*24
121 | hours = int(seconds / 3600)
122 | seconds = seconds - hours*3600
123 | minutes = int(seconds / 60)
124 | seconds = seconds - minutes*60
125 | secondsf = int(seconds)
126 | seconds = seconds - secondsf
127 | millis = int(seconds*1000)
128 |
129 | f = ''
130 | i = 1
131 | if days > 0:
132 | f += str(days) + 'D'
133 | i += 1
134 | if hours > 0 and i <= 2:
135 | f += str(hours) + 'h'
136 | i += 1
137 | if minutes > 0 and i <= 2:
138 | f += str(minutes) + 'm'
139 | i += 1
140 | if secondsf > 0 and i <= 2:
141 | f += str(secondsf) + 's'
142 | i += 1
143 | if millis > 0 and i <= 2:
144 | f += str(millis) + 'ms'
145 | i += 1
146 | if f == '':
147 | f = '0ms'
148 | return f
149 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mnemonics-training/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Mnemonics Training
2 |
3 | [](https://github.com/yaoyao-liu/class-incremental-learning/blob/master/LICENSE)
4 | [](https://www.python.org/)
5 | [](https://pytorch.org/)
6 | [](https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=Qi2PSmEAAAAJ&citation_for_view=Qi2PSmEAAAAJ:UeHWp8X0CEIC)
7 |
8 | \[[PDF](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2002.10211.pdf)\] \[[Project Page](https://class-il.mpi-inf.mpg.de/mnemonics-training/)\]
9 |
10 | ## Requirements
11 |
12 | See the versions for the requirements [here](https://yyliu.net/files/mnemonics_packages.txt).
13 |
14 | ## Download the Datasest
15 |
16 | See the details [here](https://github.com/yaoyao-liu/class-incremental-learning/tree/main/adaptive-aggregation-networks#download-the-datasets).
17 |
18 |
19 | ## Running Experiments
20 |
21 | ### Running experiments for baselines
22 |
23 | ```bash
24 | cd ./mnemonics-training/1_train
25 | python main.py --method=baseline --nb_cl=10
26 | python main.py --method=baseline --nb_cl=5
27 | python main.py --method=baseline --nb_cl=2
28 | ```
29 |
30 | ### Running experiments for our method
31 |
32 | ```bash
33 | cd ./mnemonics-training/1_train
34 | python main.py --method=mnemonics --nb_cl=10
35 | python main.py --method=mnemonics --nb_cl=5
36 | python main.py --method=mnemonics --nb_cl=2
37 | ```
38 |
39 | ### Performance
40 |
41 | #### Average accuracy (%)
42 |
43 | | Method | Dataset | 5-phase | 10-phase | 25-phase |
44 | | ---------- | --------- | ---------- | ---------- |------------ |
45 | | [LwF](https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.09282) | CIFAR-100 | 52.44 | 48.47 | 45.75 |
46 | | [LwF](https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.09282) w/ ours | CIFAR-100 | 54.21 | 52.72 | 51.59 |
47 | | [iCaRL](https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.07725) | CIFAR-100 | 58.03 | 53.01 | 48.47 |
48 | | [iCaRL](https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.07725) w/ ours | CIFAR-100 | 60.01 | 57.37 | 54.13 |
49 |
50 | #### Forgetting rate (%, lower is better)
51 |
52 | | Method | Dataset | 5-phase | 10-phase | 25-phase |
53 | | ---------- | --------- | ---------- | ---------- |------------ |
54 | | [LwF](https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.09282) | CIFAR-100 | 45.02 | 42.50 | 39.86 |
55 | | [LwF](https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.09282) w/ ours | CIFAR-100 | 40.00 | 36.50 | 34.25 |
56 | | [iCaRL](https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.07725) | CIFAR-100 | 32.87 | 32.98 | 36.32 |
57 | | [iCaRL](https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.07725) w/ ours | CIFAR-100 | 25.93 | 26.92 | 28.92 |
58 |
59 | ## Citation
60 |
61 | Please cite our paper if it is helpful to your work:
62 |
63 | ```bibtex
64 | @inproceedings{liu2020mnemonics,
65 | author = {Liu, Yaoyao and Su, Yuting and Liu, An{-}An and Schiele, Bernt and Sun, Qianru},
66 | title = {Mnemonics Training: Multi-Class Incremental Learning without Forgetting},
67 | booktitle = {The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
68 | pages = {12245--12254},
69 | year = {2020}
70 | }
71 | ```
72 |
73 | ### Acknowledgements
74 |
75 | Our implementation uses the source code from the following repositories:
76 |
77 | * [Learning a Unified Classifier Incrementally via Rebalancing](https://github.com/hshustc/CVPR19_Incremental_Learning)
78 |
79 | * [iCaRL: Incremental Classifier and Representation Learning](https://github.com/srebuffi/iCaRL)
80 |
81 | * [Dataset Distillation](https://github.com/SsnL/dataset-distillation)
82 |
83 | * [Generative Teaching Networks](https://github.com/uber-research/GTN)
84 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 27 |
27 |  27 |
27 |